 THE RUE DU CHAUME IN 1866 (TO-DAY, THE RUE DES ARCHIVES)
THE RUE DU CHAUME IN 1866 (TO-DAY, THE RUE DES ARCHIVES)SOUBISE MANSION—CLISSON TOWER
Drawing by A. Maignan
 THE RUE DU CHAUME IN 1866 (TO-DAY, THE RUE DES ARCHIVES)
THE RUE DU CHAUME IN 1866 (TO-DAY, THE RUE DES ARCHIVES)
G. C.
December 1905.
| PREFACE |
| INTRODUCTION |
| THE OLD CITY |
| THE ISLE OF SAINT-LOUIS |
| THE LEFT BANK OF THE SEINE |
| THE RIGHT BANK OF THE RIVER |
 Drawn by Saffrey
Drawn by Saffrey
Grandson and son of two rare and justly-renowned artists, P. J. Mène and Auguste Cain, my excellent friend, Georges Cain, has abundantly shown that he is the worthy inheritor of their talent. To-day, he wishes to prove that he knows how "to handle the pen as well as the pencil" as our Ancients used to say, and that the Carnavalet Museum has in him, not only the active and enthusiastic Curator that we constantly see at his task, but also the most enlightened guide possible in matters of Parisian lore; and so he has written this bewitching book which conjures up before me the Paris of my childhood and youth—the Paris of times gone by, which, in the course of centuries, has[Pg xiv] undergone many transformations, but not one so rapid and so complete as that which I have witnessed. The change, indeed, is such that, in certain quarters, I have difficulty in recognising, in the city of Napoleon III., that of Louis-Philippe. The latter would have been uninhabitable now, owing to the requirements of modern life, but it answered to the needs and customs of its time. People put up then with difficulties and defects that were judged unavoidable, no Capital being without them. And, in fact, in spite of its drawbacks and blemishes, the Paris of that period had its own charms.
Most of its streets were very narrow and had no sidewalks. Pedestrians were obliged to take refuge, from passing carriages, on shop thresholds, under entrance gates, or else beside posts erected here and there for that purpose. Still, even in the densest traffic, one ran fewer risks walking along the road than one runs at present crossing the boulevards.... On these boulevards, where a single omnibus plied between the Madeleine and the Bastille every quarter of an hour, and where there was practically no danger of being knocked down by a horse, I have seen a crowd watching a fencing-bout on the spot[Pg xv] to-day occupied by a refuge-pavement; and, on the Bastille Square, I used to play quietly, trundling my hoop round the Elephant and the July Pillar. There was little else to dread, throughout Paris, save splashes from the gutters, whose waters flowed in the middle of the streets ... when they flowed at all; for, during the hot summer days, there was nothing but stagnant household slops, which lay in the gutters until the next storm of rain. In winter, as the snow was never swept away, and the employment of salt for melting it was unknown, the thaws were something terrible! Every corner—and the houses being hardly ever in line, there were many—was used as a rubbish-heap, or for the committing of nuisances excusable only through lack of modern conveniences. Moreover, the streets, by very reason of their narrowness, were more noisy than ours. The rolling of heavy waggons over big, round paving-stones badly set, with jolts that shook both windows and houses; the constant cries of men and women selling fruit, vegetables, fish and flowers, &c. ... and pushing their handcarts, not to speak of dealers in clothes, umbrellas, and hand-brushes, of glaziers and of chimney-sweeps; the din of watermen blowing[Pg xvi] into their taps; the calls of water-bearers as they loudly clinked their bucket-handles; the clarionets and tambourines of strolling singers that went from one courtyard to another; all this composed the gaiety of the street. What was less tolerable was the incessant noise of barrel-organs beneath your windows from morning till evenings and inflicting on you a torture that it makes me angry to think of even now.
To crown all, the lighting of the streets was wretched. In most, it was
the ancient lamp whose illumination was an affair that stopped traffic
while the operation lasted. On the other hand, however, the city was
better guarded at night than it is at present, owing to the rounds of
the "grey patrols" which, with their Indian files of cloak-muffled,
slow-walking figures, crept along the walls and crossed one another's
beats so as to be within helping distance, at the least alarm. Happy
time, when, at one o'clock in the morning, in my lonely quarter, I was
sure to come across one of them, and when one could stay out late
without a revolver in one's pocket. This, it will be said, was because
Paris was smaller, less populus, and the task of the police easier.
But[Pg xvii]
[Pg xviii] it is the duty of the police to proportion the protection to the
danger, and the numbers of its officers to those of the evil-doers that
infest our streets, for whom, formerly, little of the regard was felt
that is lavished on them to-day.
As a set-off to its narrow, badly-paved, badly-kept, and badly-lighted[Pg xix] streets, Paris then had an attraction which it no longer possesses—its gardens.
The idea formed of the old city is, generally, that of a heap of ancient houses with neither light, fresh air, nor verdure. In reality, the houses of the time, whether recent or old, existed only as a border to the street. Behind them, in the whole of the space that extended from one road to another, there were vast enclosures affording the sun, silence and verdure that did not exist in front. Many dwellings had fashioned, out of the grounds of mansions and convents parcelled up during the last century or two, large courtyards and private gardens which, separated merely by low fences, mingled their foliage and shade. This was so everywhere throughout the city, except in the part of it properly so called, and in the central portion near the Town Hall and the markets. A glance at the old plans of Paris will[Pg xx] suffice to show that these unbuilt-on spaces comprised, under Louis XVI., the half, and, under Louis-Philippe, a third of the city's present area. In the Marais and Arsenal quarters, in the Saint-Antoine, Temple, and Popincourt faubourgs, in the Courtille, the Chaussée d'Antin, the Porcherons, the Roule quarters, in the Saint-Honoré faubourg, and along all the left bank of the river, which last was privileged in this respect, there were only scattered dwellings amidst orchards, kitchen-gardens, trellis-vineyards, farmyards, groves, and parks planted with century-old trees. The little that remains of this past is being rapidly destroyed; and, from the health and pleasure point of view, it is a great pity.
From my window in the Rue d'Enfer, Estrapade Square, close to the blind alley of the Feuillantines, I used to cast my eyes, as far as I could see in every direction, over a wealth of foliage. In the Rue Neuve-Saint-Étienne, from the place where Bernardin de Saint-Pierre once lived, I beheld the towers of Notre Dame, beyond avenues of trimmed trees; and I could say, like the good Monsieur Rollin, in the distich engraved on his door a few yards away:[Pg xxi] Ruris et urbis incola, that I was "an inhabitant both of the town and of the country." Through these gardens, through these silent streets so propitious to quiet labour, and scenting of lilacs and blossoming with pink and white chestnuts, new roads have been cut; the Saint-Germain and Saint-Michel Boulevards, the Rues de Rennes and Gay-Lussac, the Rue Monge which caused the demolition of the rustic cottage where Pascal died in the Rue Saint-Étienne itself; and the Rue Claude-Bernard which did away with the Feuillantines, where Victor Hugo, as a child, used to chase butterflies. Soon, the last of the monastic enclosures of the Saint-Jacques quarter, that of the Ursulines, will disappear to make room for three new streets!
The use of such small gardens, belonging mostly to private houses, was
keenly appreciated by Parisians of the lower middle-classes who have
always been of a stay-at-home disposition. This characteristic of theirs
was satirised, during last century, in a well-known pamphlet: "A Journey
from Paris to Saint-Cloud by Sea and by Land." Their curiosity with
regard to far-off countries was not awakened as it is nowadays by
stories of travel, and by engravings,[Pg xxii] photographs, or coloured
advertisements. And getting from one place to another was very
expensive. Railways had not yet made it easy for every one to go long
distances by means of reduced fares and cheap circular tickets. An
ordinary working man, in these modern times, will travel more easily
to Biarritz, Switzerland, or Monte-Carlo, than an independent gentleman
of the Marais could then have done. During the midsummer heat, Paris
was as full as in winter's cold; and the theatres reaped their most
abundant harvest, especially popular ones like the Ambigu, the
Porte-Saint-Martin, the Gaieti, the Cirque, the Folies-Dramatiques, the
Petit Lazary, Madame Saqui's, the Théâtre Historique, &c., which were
situated near together about the Temple Boulevard. The fine weather
allowed people living at long distances to come on foot to this dramatic
fair, saving the price of a carriage both ways, and to make tail at the
doors, without having to fear rain or cold; for the good-tempered public
of those days, loving a play for its own sake, had no objection to be
penned up so, between two barriers, while waiting for the opening of the
ticket-offices, which then used to take place[Pg xxiii]
[Pg xxiv] between five and six in
the evening; it was one of the conditions, one of the stimulants of
their pleasure, something to whet their appetite before the
performance.
Even the holidays did not empty Paris very perceptibly, except on the left bank of the Seine. From May to October, the majority of the middle-class—small shopkeepers, functionaries, retired people, as well as employees, clerks, and workers of every kind—contented themselves,[Pg xxv] like Paul de Kock's heroes, with excursions and picnics in the various Parisian suburbs—Vincennes, Montmorency, Saint-Cloud, Romainville, &c. In Paris, shopkeepers laid the cloth for a meal out in the open air, in the yard or garden, or, failing that, in the street. When I returned from my Sunday walk, at the dinner-hour, between four and five in the afternoon, I used to see, everywhere in the busiest streets, nothing but families at table before their doors, while boys and girls played about the road at shuttlecock, hot cockles, or blindman's buff. Occasionally, I was caught as I passed by some little girl with bandaged eyes, who, in order to recognise me, would feel my face, amid shouts of laughter from all the diners. And if,[Pg xxvi] during the long summer evenings, I went with my companions to play at prisoners' base in the Rues de Vaugirard, or d'Enfer, or on the small Saint-Michel Square, the good folk, enjoying the fresh air on their doorsteps, paid no attention to us boys galloping all over the street.
In a word, Paris was no different from the country-town!
These "bourgeois" customs, which one might distinguish briefly by
saying that they were "eighteen-hundred-and-thirty customs" survived
till the 1848 Revolution, and persisted even into the Second Empire,
when railway extension, the influx of strangers, great industrial and[Pg xxvii]
commercial enterprises, an increasing prosperity, the desire for comfort
and luxury, a more active public life, keener competition, and the
intenser struggle for life brought into existence our present customs
and manners. It was a surprising transformation, one which was no little
fostered by the creation of a new Paris on the ruins of the old. How
often have I congratulated myself on having, from the time when I was
fifteen years of age, devoted my holiday rambles to ferreting out, in
the old quarters of the city now cut through,[Pg xxviii]
[Pg xxix] parcelled up and
destroyed, the slightest vestiges of the past, as if I had foreseen
that, within a brief delay, they would be reduced to dust by the
demolisher's pick-axe.
The Paris of Louis-Philippe was very nearly that of the Great Revolution and the First Empire. Each step in it awoke souvenirs that people thought but little of in my childhood, romanticism being more interested in the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, and more inquisitive about the massacre of Saint-Barthelemy than about those of September. It looked with tenderness at the old corner turret of the Grève Square, but gave no glance at the sign-post on the same Square, where the unfortunate Foulon was hanged. It deplored the disappearance of the Barbette Gate which marked the site where Charles d'Orléans was murdered, but did not suggest going to see, a few steps further, in the Rue des Ballets, the post where Madame de Lamballe's corpse was beheaded. Artists, novelists, poets, historians disdained these localities still warm from the Revolutionary drama, some episodes of which they claimed to relate. Ary Scheffer purports to show us the arrest of Charlotte Corday; but does not care to[Pg xxx] consult documents of the greatest exactitude that would have brought her before his eyes and ours with just her face, her attitude, and her dress. He does not even think to go to the Rue des Cordeliers and visit Marat's dwelling, still remaining as it was, including his bell rope. And he offers us a Charlotte of his own invention, cleverly painted, who looks like a chambermaid arrested by the porter, just as she is going off with her mistress's gown on her back!
In his "Stello," Alfred de Vigny is quite as indifferent to local colouring as he is to facts. He places André Chénier's scaffold "on the Revolution Square" after taking him thither in a cart laden with more than "eighty victims, among them being some women with children sucking at the breast"!!!
It is the same with the rest!
Being more careful, I did not disdain the old stones that were humble
witnesses of deeds so great; and, thanks to them, I was able to live
through the Revolution again on the spot. They were fated to disappear.
A new city cannot be built except on the remains of the old; and it is
hard to reconcile the requirements of the present with the worship[Pg xxxi]
[Pg xxxii]
[Pg xxxiii] of
the past. Indeed most of the old things, even those that might be saved,
would have a sorry air amid the splendours of our modern City. What
grieves me is to find that they have often been replaced in such a way
as to cause one to regret their disappearance.
As for the City, so called, it may be granted that the pulling down of its old buildings, its dark alleys, could only give pain to those whose passion is the picturesque, or to the admirers of the Mysteries of Paris. Yet one must confess that, framed in its old close, Notre-Dame looked nobler than now at the end of a vast, desert space, where it seems to be stupidly posing before a photographer's camera, between the emptiness of the river and the frightful Town Hall, that might be taken for a slaughter-house.
Nor was it necessary, when displacing the flower-market, to forbid the sellers' continuing the habit of improvising those pretty bowers of foliage and flowers, and to impose on them those zinc roofs that should shelter only artificial blooms,—not at all necessary, simply to complete the charm of the present administrative arbour.
It might have also been possible to avoid cutting through the Dauphine Square, which I have seen in my time as charming as the Place Royale, with its pink bricks, since all we have in return is the funereal-looking structure forming the entrance of the Palais de Justice and the horrible balustrade of its staircase.
Since my chance stroll has brought me to the Pont-Neuf I may just as well pursue in this direction my retrospective way.
The Pont-Neuf which is newer than ever, may be congratulated on the loss of its high foot-pavements, its shoeblacks, dog shearers, and cat doctors squatting among its pillars, and its haberdashers, stationers,[Pg xxxv] perfumers, fried-potato men and matchsellers, whose stalls, set up in the semi-circular projections of the bridge, have been pulled down, together with the old sentry-boxes that sheltered them, to make room for the benches of the present day. But what vandalism—the whitewashing of the two brick houses that face Henry IV.'s statue! They were built for the site they occupy. They are an integral part of the bridge, and contribute greatly to its adornment. If the owners, who have already whitewashed them, take[Pg xxxvi] it into their heads to replace them by so-so sort of constructions, it will mean the spoiling of one of the prettiest sights of Old Paris.
Saint-Germain-l'Auxerrois, too, might have been spared the proximity of the tower which pretends to be Gothic, and of the Mairie which believes[Pg xxxvii] itself Renaissance. In their company, the church loses all its grace, and the group is ridiculous.
At least, when turning one's back, one has the satisfaction no longer to see in front of the Colonnade a waste ground surrounded with rotten palings. Only crosses were lacking to give the place the appearance of a cemetery.
And, as a matter of fact, it was one!
In the Restoration period, where now the equestrian statue of Velasquez stands, Egyptian mummies had been buried—mummies that had become decomposed, through too long sojourning in the damp ground-floor rooms of the Louvre. In 1830, in the same spot, the corpses of the assailants killed in the attack on the Louvre were hastily cast into a common grave. Ten years later, when it was desired to give these brave fellows a nobler sepulture, patriots and mummies were dug up pell-mell; and[Pg xxxviii] now contemporaries of the Pharaohs lie piously buried beneath the column of the Bastille, side by side with the July heroes.
I knew the courtyard of the Louvre when it had a statue of the Duke of Orléans, put away after 1848, one of Francis I. by Clésinger succeeding it. Some fool or other having nicknamed it the "Sire de Framboisy," the joke was too idiotic not to have the greatest success. And to the nickname is partly due the disappearance of a work of art that deserved a better fate.
No description can give any idea of what the Carrousel Square was then,
in the intermediate state to which it was condemned, after the First
Empire, by the joining of the Louvre to the Tuileries, which joining was
still unachieved, though always being planned and replanned. It was[Pg xxxix]
nothing but a medley of half-destroyed streets, isolated houses half
pulled-down and shored up with beams. The unpaved, uneven, broken ground
was a veritable bog in rainy weather. The great gallery of the Louvre
was flanked with an ugly wooden corridor, for ever ready to flare up!
For, as tradition has it, there is always some permanent risk of fire
in[Pg xl]
[Pg xli] the vicinity of the Museum! On the same side, the Civil Service
had run up temporary buildings which, from the small courtyard of the
Sphinx to the gate facing the Saints-Pères bridge, enclosed the ruins of
the ancient church of Saint-Thomas-du-Louvre and its dependencies, such
as the Priory where Théophile Gautier, Gérard de Nerval, Nanteuil,
Arsène Houssaye, and others, had established their "Bohème galante."
These buildings, in favour of which extenuating circumstances might be
pleaded, were hired out to colour, engraving, picture, and
curiosity-dealers of all kinds. I still see a large shop of knick-knacks
where, among a most amusing collection of ostriches' eggs, stuffed
crocodiles, and Red-Skins' heads of hair, the amateur used to come
across wonderful bargains. And what riches also in the cases exposed by
engraving-dealers in front of their doors to the curiosity of those
interested in such things! Besides the engravings, there were lots of
drawings, sketches, red crayon designs, water-colours by Cochin, Moreau,
Boucher, Lawrence, Fragonard, Saint-Aubin, Proudhon, Boilly, Isabey, &c.
I have passed there delightful hours, looking through such cases, the
contents of which, alas! I could only[Pg xlii] admire, being unable to afford to
buy masterpieces which I felt would have a future value, and which were
then sold for a mere song, the pedants of David's school despising the
French art of the eighteenth century, it being too amiable and witty for
their taste. "Sir," said one of these dealers later to me, "I have
rolled up before now engravings of Poussin, for which I would not pay
two francs to-day, in other engravings of Debucourt that I would not
sell to-day for a thousand francs!"
All this was swept away by the amalgamation of the two Palaces and the prolonging of the Rue de Rivoli, which has, moreover, endowed us with a very fine Square in front of the Palais Royal, in lieu of the old one, so mean, with its fountain of water, decorative enough but all blackened with dirt and slime.
As for the Palais Royal, which the Duke d'Orléans seemed to have had
built, so that it might be the Forum of the Revolution, if it was no
longer the rendezvous of politicians, clubmen, gazetteers, open-air
orators, and stock-jobbers, the battlefield of 1793 Republicans and
fops, of Royalists and half-pay soldiers, the official promenade for
the[Pg xliii]
[Pg xliv]
[Pg xlv] Merveilleuses, and courtesans of all degrees, if it no longer had
its wooden galleries, its Tartar camp, its Dutch grotto, its gambling
hells, it was still the headquarters of the nymphs of the neighbourhood;
and, thanks to its two theatres, its eating-houses, its renowned
coffee-houses, its rich shops, especially those of the jewellers, it was
still the central point of attraction in Paris for newcomers from the
country and abroad. With the least shower, it was impossible to walk
about beneath its porticoes; and, in all weathers, especially on
Sunday—the day of meeting par excellence—there were crowds in the
glass-covered arcade where, quite recently, I found myself
alone—absolutely alone!
What shall I say of the Tuileries Palace, except that it once was and is no more? How I regret the magnificent shades of its grand avenue, unrivalled even at Versailles, and its clumps of chestnuts that braved the ardent sun rays! Nature alone is to blame for their disappearance, but they might have been replaced by trees less pitiable than the inevitable plane and acacia, which latter, without its flowers, is really the silliest and ugliest of trees. It promises a fine foliage for the future, if[Pg xlvi] the future of this unfortunate garden is not to be totally suppressed, or at least to be broken up into lots!
Time was when I have seen the Place de la Concorde without its fountains and its statues, save the four horses of Marly—those of Coysevox at the gate of the Tuileries, those of Coustou at the entrance to the Champs-Elysées. When I was a boy, the socles of the future towns of France were being restored. Since the days of Louis XV., they had[Pg xlvii] been decked with plaster caps, like saucepan lids, and were despised so much that the one bearing the town of Strasburg was flanked with a base stove-pipe. Anyway, it was the only one that shocked one's eyes. Count those at present that crown the monuments of Gabriel! Round the Square the ditches still remained, which on fête days had already made so many victims through the hindrance they offered to the crowd's getting away. One evenings when some fireworks were being let off on the Concorde bridge in honour of the King's birthday, I had only just time enough to take refuge on one of their balustrades, whence I was nearly thrown down into the moat by those that followed my example.
The obelisk had just been erected in the centre of the Square, where its only justification was the fact of its having extricated the July Monarchy from an embarrassing position. The authorities did not know where to put it so as to conciliate everybody's opinion. The old stone monument, indifferent to all parties, was a fitting symbol of their[Pg xlix] Concord.
The Champs-Elysées are unrecognisable now by any one who saw them under Louis-Philippe! The avenue was not then, like the Boulevard des Italiens, the meeting-place for what was called, in foolish Anglomania, "Fashion." Ices were not drunk there as on Tortoni's steps. Society dames and gentlemen passed along it only on horseback or in a carriage, contemptuously abandoning the side-ways to the more modest walkers, the small folk, who elbowed each other in the dust, to strollers, idlers, strangers, convalescents, scholars, nurses, soldiers, players at ball or prisoners' base on the Marigny Square, and to the innumerable urchins that disputed with each other the goat-carts and shouted for joy in front of the Punch-and-Judy shows!
In the way of coffee-houses, there were only three pavilions, all unworthy of the name, little ambulating[Pg l] drinking-stalls on trestles, with decanters of lemonade and barley-water, and the cocoanut-beverage sellers shaking their bell; the only eating-houses were two wretched wine-shops, and the places where Nanterre cakes, gingerbread, and wafers could be bought from dealers that stood and sold their wares while springing their rattle. For concerts, there were the fiddlers, guitarists, and harpists, the singers of popular songs and the man who was a band in himself; in the way of entertainments, before the opening of the Mabille Garden, there were Franconi's summer circus, Colonel Langlois' panorama, the swings, merry-go-rounds, and archery galleries, the Dutch top, and the game from Siam. As illumination, there were a few gas-lamps, the candles used by stall-keepers, and the red lanterns exhibited by orange-women. And with all this, not a bit of lawn, not a clump of trees, not a bed of flowers!—nothing, absolutely nothing, of what to-day constitutes this exquisite promenade.
Paris ended at the Rond-Point!
Beyond, it was only a sort of faubourg, with a fine mansion here and there belonging to the previous century, a large garden, land unbuilt on to be sold,[Pg li] tenant houses, sorry-enough-looking, furniture repositories, coach-houses, riding-schools, and carriage-builders' premises—particularly carriage-builders'! Near the Rue Chaillot, the Avenue was bordered, on the left, with a broad turf embankment. I have seen, in the fine-weather season, diners cutting up their melon and leg-of-mutton on it, with the naïve joy of city folk enjoying the purer field air.
 PATROL ROAD LEADING FROM THE BARRIER OF THE ETOILE IN 1854
PATROL ROAD LEADING FROM THE BARRIER OF THE ETOILE IN 1854In the vicinity of the Arc de Triomphe, the Avenue was lonelier and ill-inhabited, and, as soon as one crossed the barrier of the Etoile, it was no longer the faubourg but the suburbs. Instead of the fine avenues of the Bois and of Victor Hugo, only waste grounds were to be seen, market-gardeners' patches, quarries and uncanny-looking, tumble-down buildings. As for the Bois de Boulogne itself, it was so ugly by day and so dangerous by night that the less there is said about it the better.
On the right, the Roule quarter was more civilised; but beyond, towards Mousseaux, such was not the case. One evening, out of curiosity, I went to see the house that Balzac had just had built in the street bearing his name. Afterwards, by chance, I strolled into this Ternes quarter, which[Pg lii] was unknown to me. Night came on and I soon lost my way. On my left, I had a big, rascally wall which seemed endless, and, in the light of the pale gas-lamps, separated by long distances, I saw on my right nothing but stables, workyards, dairy outhouses, exhaling odours of poultry and dung, and red-curtained, low-character eating-houses which reminded me that, at the same hour, a professor whom I knew had been collared by a big blackguard that exclaimed to him: "Your money, you scamp!" My friend was smoking a cigar. Being sly, like the wise Ulysses, he pretended to comply by putting his left hand into his waistcoat[Pg liii] pocket, while, with his right, he took the cigar from his mouth, knocked off the ashes with his little finger, and stuck it right in the eye of the footpad, who loosed him with a howl that Polyphemus might have uttered! This souvenir haunted me; and, after traversing a wretched hamlet, in which I was guided only by the slope of the ground, I at last breathed freely again in the neighbourhood of the Pépinière, promising myself that I would never again venture into such a cut-throat locality.
And yet I live in it now!
This cut-throat locality is to-day the Monceau quarter, the Avenue Hoche, the Avenue de Messine, the Courcelles, Malesherbes and Haussmann Boulevards; what was once called "Poland" where General Lagrange used to[Pg lv] tell me he had shot partridges in his youth.
And the conclusion of this chat—for I must conclude—is that I regret the old Paris, but that I am fond of the new.
VICTORIEN SARDOU.
Paris! What visions this magic word calls up—historic Paris, with its palaces, churches, monuments, streets, and squares; the Paris of literature and its admirable procession of writers, poets, thinkers, dramatists, philosophers, and humourists; the Paris of society, its fêtes, receptions, fashions, elegancies, and snobbism; the Paris of politicians, the Paris of journalists, religious Paris, the Paris of the police, bohemian Paris, industrial Paris. And how many others still!
So many passions, events, and interests clash, mingle, and unravel again in it that a study on this admirable and complex city is no sooner finished than it is almost needful to write it over again, the truth of the day before being no longer that of the morrow, the accurate document of yesterday being found incorrect this morning.
Our ambition is more modest, and our title indicates a programme—"Nooks and Corners of Paris."
Deliberately neglecting that which is too well known, already too much described—having neither the desire nor the pretension to compose a "Guide-book for the Foreigner in Paris"; seeking only the rare, if not the never-yet-brought-to-light—we would simply give to those who, like us, adore our old City a little of the joy[Pg lviii] we have each day in "strolling" about this incomparable Town. Our object is to continue, by means of walks through what remains to us of the dear old Paris, the series of documents painted, pencilled, or engraved which are contained in the Carnavalet Museum.
The house that Madame de Sévigné loved so much has, in fact, become the museum of the historical collections of the French Capital.
It is a delightful nook in which still throbs a little of the old soul
of the great City! Our predecessors and we ourselves have striven to
gather together the documents of every kind that bear traces of Paris
life. Charters, plans, engravings, pictures, autographs, faded placards,
and commemorative stones; sign-boards in wrought-iron that guided
drinkers of the sixteenth century to the various public-houses;
shot-silk costumes worn by pretty Parisian women of the time of Louis
XV.; red caps of the age of Terror; girdles that girls adorned
themselves with around the funeral car of Voltaire; tricolour-bowed
shoes that trod the soil of the Champ de Mars at the moment of the
Federation Feast; the light, black tulle kerchief worn by
Marie-Antoinette when going to sit for her portrait to Dumont the
miniaturist; the woman-citizen's pike or sabre of honour; the
commemorative stone of the Bastille; Grisettes' caps of the year 1830 or
buskins worn by the Merveilleuses; the warrant for the appearance of
"Widow Capet" before the Revolutionary Tribunal; a play-bill of the
King's great dancers, and convocations to the sittings of the
Convention; the great periods of the Kings,[Pg lix]
[Pg lx]
[Pg lxi] the glorious days of the
Revolution, the tragedies of the Terror, the proclamations of the
Empire; announcements of victories, requiem masses, joys, griefs, the
life in fine of the most impressionable, most nervous, most enthusiastic
people that has ever existed—all is found at Carnavalet; and the same
case or folio, gathering together, with terrible eclecticism, the
lightning succession of events that took place on the same spot, shows
us, for a lapse of scarcely twenty years and in the same Tuileries, for
instance, the arrival of Louis XVI., the capture of the castle on the
10th of August, the execution of the King, then of the Queen, the Feast
of the Supreme Being, Thermidor, Prairial and the invasion of the
Convention, the sections annihilated at Saint-Roch by Bonaparte, the
Carrousel reviews, the apotheosis of the King of Rome, the departure of
the Emperor, the arrival of Louis XVIII., his flight, the return of
Napoleon, the coming back of Louis XVIII., &c.
That, I fancy, is a serious lesson of history—and of philosophy.
Our aim, I repeat, is therefore simply to continue in a few walks, which we will try to render as attractive as possible, the search for documents which, alas! are disappearing more and more every day.
We will divide Paris into three great sections—the old City and the Isle of St. Louis; the left bank of the Seine; the right bank of the same river.
After the document written or pencilled, the living document, or at least what remains of it.
This volume "Nooks and Corners of Paris" is, in great part, the re-edition of a work entitled, "Sketches of Old Paris," printed only in a very small number of copies and published in 1904 with equal elegance and taste by Conard.
Since then, the volume has been not only revised and added to, but new illustrations were chosen. An artist of great talent, Monsieur Tony Beltrand—too soon, alas! taken away from us by death—had adorned the "Sketches of Old Paris" with a number of admirable compositions, of which, moreover, he had been the clever engraver. We have been compelled to replace these illustrations by a series of reproductions of pictures, designs, etchings, and lithographs borrowed from private collections, museums, libraries—and our very pleasant duty is to remark on the exceeding good grace with which every one has helped us. May our gratitude be allowed to mention the names of Messieurs Sardou, Claretie, Detaille, Lavedan, Lenôtre, Bouchot, H. Martin, Funck-Brentano, A. Meignan, Massenet, Pigoreau, Ch. Drouet, de Rochegude, Beaurepaire, Ch. Sellier, J. Robiquet, our masters or our friends, not forgetting many, besides, who have lent us most precious aid. Indeed, when Paris is in question, all doors open and all hearts beat.
Our task was an easy one, and, if we have not been able to discharge it better, the fault is ours alone. A suitable termination, therefore, to this introduction will be the old formula—more than ever apropos—"Excuse the faults of the author."
 THE PONT-ROYAL, THE TUILERIES, AND THE LOUVRE (18th CENTURY)
THE PONT-ROYAL, THE TUILERIES, AND THE LOUVRE (18th CENTURY)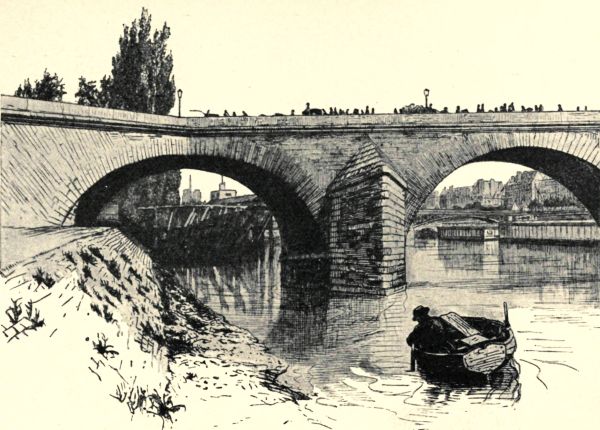 Etching by Martial
Etching by Martial
 VIEW OF THE PONT-NEUF, TAKEN FROM AN OVAL WINDOW IN THE COLONNADE OF THE LOUVRE
VIEW OF THE PONT-NEUF, TAKEN FROM AN OVAL WINDOW IN THE COLONNADE OF THE LOUVREParis was born in the Isle of the Seine, whose shape is that of a cradle, and of which Sauval speaks so picturesquely: "The isle of the City is fashioned like a great ship sunk in the slime and stranded at the surface of the water, in the middle of the Seine."
This particularity must certainly have struck the heraldists of every age, and from it comes the vessel that is blazoned on the old escutcheon of Paris.
So the City presents itself with its prow to the west and its poop to the east.
The poop is Notre-Dame, and the prow, joined to the two banks by two ropes of stone, is the old Pont-Neuf, raised on the extreme end of what was formerly the islet of the Cow-Ferryman, where, on the 11th of March 1314, were burnt Jacques de Molay, Grand-Master of the Templars, and Guy, Prior of Normandy,—the Pont-Neuf, the foundation of which was laid by Henri III. on the 31st of May 1578, and was decorated with the coats-of-arms of the King, the Queen-Mother, and the Town of Paris. When the first pile emerged from the water, on the side of the Quay of the Augustines, the King betook himself thither from the Louvre in a magnificent barque, accompanied by the Queen-Mother, Catherine de Medici, and by Queen Louise de Vaudemont, his wife. Henri III. looked melancholy; on the same morning, he had interred, in the Church of St. Paul Quélus, the dearest of his favourites, who had died from wounds received, some weeks before, in the famous duel of the Minions.
The irreverent Parisians did not hesitate to declare that, out of
respect for the Royal sadness, the new bridge ought to be called "the
Bridge of Tears." But this opinion did not last; and, as soon as Henri
IV. had inaugurated it, in June 1603, "still unsafe" and unachieved, the
Pont-Neuf became the gayest place in Paris. Mondor sold his balsam
there, and Tabarin spouted his idle talk; there it was that the ape
of[Pg 67]
[Pg 68]
[Pg 69] Brioché amused the passers-by; there that the Mazarinades were
hummed; there that duellists unsheathed their swords, and the bands of
Cartouche and Mandrin gallantly relieved pedestrians of their purses. On
the merry Pont-Neuf all Paris took their airings, enjoyed themselves,
made appointments; Loret went there to gather information for the
Rhyming Gazette:—
"If I this week had been the man
To visit the Samaritan,
From Jack and Tom I should have heard
Everything that has occurred...."
 WORKSHOPS AND FOUNDATIONS OF THE CITY BARRACKS IN 1864-1865
WORKSHOPS AND FOUNDATIONS OF THE CITY BARRACKS IN 1864-1865From the seventeenth century, it was asserted to be impossible to cross the twelve arches of the popular bridge without meeting a monk, a white horse, and two obliging women. It was the official route for Royal processions proceeding to the Parliament; and, at the Pont-Neuf, rioters assembled when going to burn in effigy, on the Dauphine Square, such Presidents as were suspected of rendering more services than judicial decisions. Here also, in 1789, the people compelled those who were in carriages to stop and bow low to the effigy of good King Henri, whose statue, supported at the four angles by the four figures of slaves that Richelieu had had placed there, stood in the middle of the raised space where, in 1792, were signed the voluntary enlistments, and where the cannon resounded, calling to arms, at tragical moments of the Revolution. The whole history of Paris has to do with the wonderful old Pont-Neuf, celebrated throughout the world, the[Pg 70] masterpiece of Androuet du Cerceau and of Germain Pilon—the Pont-Neuf which was the main thoroughfare of ancient Paris.
It is therefore by the Old City that our walks should commence. We shall come across some rare vestiges of the primitive Lutecia. On several occasions, behind the apse of Notre-Dame, fragments of ramparts have been found, and some of the stones forming these antique defences are discovered to have been taken from the arenas constructed by the Romans. The benches of the circus had contributed to check the Norman invasion; does not the wall of Pericles on the Acropolis contain broken fragments of antique marble statues?...
But the glory of the City is Notre-Dame! Let us follow the winding, picturesque Rue Chanoinesse, where the great Balzac lodged Madame de la Chanterie, and, at No. 18, let us climb the tottering staircase of the Dagobert Tower, an old and precious débris of the canonical buildings that once enclosed the Cathedral of Paris. A few dozen worn-down steps will bring us to a narrow platform whence we shall behold an admirable sight.
Notre-Dame, radiantly beautiful, rises, like a large stone flower, from
a mass of flat roofs, grey or blue, and the majestic outlines of its
towers stand out in their immensity against the horizon. Beneath every
caprice of the hour or light, whether the sun gilds this splendour or
its carvings are mantled in snow, while a carpet of[Pg 71]
[Pg 72]
[Pg 73] spotless flakes
stretches below, whether the flaming sky frames its violet bulk in
melting gold or the storm wraps it in its copper clouds, ever the noble
Cathedral appears in its shining beauty and unsurpassed grandeur. The
elegant spire that completes it shoots clearly and proudly into the air,
and flights of crows whirl, with shrill cawings, round the blossoming
roofs of the Paris Basilica. Over there, above a dazzling view of
carvings, chimneys, gables, bridges, steeples, and streets, the far-off
azures melt into soft tints, and finally mingle, on the horizon, in a
vague colouring; the beasts of the Apocalypse, which the talented
artists of times gone by poised on the tower balustrades, bend
grimacingly and jeeringly over the vast Paris that feverishly lives and
moves below! It is one of the noblest sights of the Tower that our
enchanted eyes have just gazed upon.
On the other side, it is the Seine, a silver streak furrowed with boats and barges; then, further on, the noble outlines of the old Paris, and, marking its profiles on the low clouds, in the foreground, Saint-Gervais and Saint-Protais, an antique and precious sanctuary of the sixteenth century, one of the few remaining that preserve the secret charm of those country churches in which the soul feels itself, within the demi-obscurity of their chapels, more devout, more touched, and closer to the infinite, beneath the painted windows darkened by the dust of centuries and the smoke of incense.
In the prolongation of Notre Dame and behind the Hôtel-Dieu, before reaching the Palais de Justice, one[Pg 74] formerly came across a labyrinth of winding, narrow, evil-smelling streets—the Rue de la Juiverie, the Rue aux Fèves, the Rue de la Calandre, the Rue des Marmousets; for centuries this quarter had been the haunt of the lowest prostitution; there, too, dyers had established their many-coloured tubs; and blue, red, or green streams flowed down these streets with their old Parisian names. Humble chapels nestled under the eaves of Notre-Dame,—Sainte-Marine, Saint-Pierre-aux-Bœufs, and Saint-Jean-le-Rond, in which last d'Alembert was buried. The Hôtel-Dieu opened on the right of the Cathedral, and formed, with the close of Notre-Dame, a really imposing setting for it. On this site, the Second Empire built the new Hôtel-Dieu and the Prefecture of Police; and these two ugly structures, without taste or originality, seem to be the natural foils of France's national glory, Notre-Dame-de-Paris.
In the Rue Massillon, at the back of a stone porch which time has
covered with moss, a tiny courtyard opens, at No. 6, over whose damp
pavement occasionally passes a Sister of Charity in her white cap; an
old, monumental, wooden staircase, dating back to Henri IV., leads there
to some poor dwellings in a building up this courtyard. Within this
humble, provincial-looking house, half monastic in appearance, who would
believe himself in the heart of Paris, a few yards away from the Town
Hall and the Prefecture of Police? Gone the "Cloister," whose gardens at
the bottom were still in existence seven years ago. A huge, hideous[Pg 75]
[Pg 76]
[Pg 77]
structure, resembling a barracks, to-day hides all the apse of
Notre-Dame, and the antique "Motte-aux-Papelards," the ordinary
meeting-place for the staff of the Metropolis, is replaced by a square,
a sort of open-roofed museum, where the bits of carving are arranged
that time, or regrettable though necessary restorations, have detached
from the Cathedral.
Along the Rue de la Colombe passed the Gallo-Roman belt of the City, near the house inhabited by Fulbert, the uncle who employed such cruel arguments with the unfortunate Héloïse, Abelard's friend. In the Rue des Ursins, at No. 19, may still be perceived the remains of a chapel of the twelfth century, by name Saint-Aignan; St. Bernard is said to have preached in it. It was one of the numerous sanctuaries in which, during the Terror, refractory priests, under the most singular disguises—water-carriers, national guards, waggoners, masons—came, as they passed through the town, to say mass almost regularly to the faithful, who were frightened neither by the guillotine, nor Fouquier's trackers, nor the Revolutionary Committees' order-bearers. It is an astonishing thing that not for a single day or hour was religious ministration wanting to those who called for it, not even in the Terror's most terrible period. At this time, the Bishop of Agde, disguised as a costermonger, with a long beard, and carrying the sacrament under his carmagnole, scoured Paris, officiating, and confessing people in lofts, outhouses, and back-shops. In the Rue Neuve-des-Capucins, mass was said[Pg 78] in a chamber above the very dwelling occupied by the terrible Conventional Babœuf.
Did not the Abbé Emery, the Superior of Saint-Sulpice, from the depths of his dungeon, where he strengthened the courage of the prisoners ("he prevents them from crying out," said Fouquier-Tinville), organise throughout the Paris prisons a ministry of monks that visited all the sinister gaols, disguised as porters, old clothes-dealers, laundrymen, wine-sellers? Even on the way to the scaffold, the unfortunates that were being led to execution received the aid of religion: as the death-carts passed by, from certain windows indicated beforehand, priests, placed there, wafted to the condemned the absolution pronounced over the dying.
Let us go to the other side of the close of Notre-Dame, where the Hôtel-Dieu and its dependencies used to stand. There, once was the Tower of the Foundlings, and the Cagnards, that old den of debauch of which Meryon has left us such powerful etchings, and before which, as a child, we were accustomed to stop with dread, while we watched the huge rats that hid and roamed there, appearing in broad daylight and eating the heaps of offal.
Between Notre-Dame and the Palais de Justice, there once existed a
network of small streets round the Sainte-Chapelle and the Prefecture of
Police, with gardens that ran nearly down to the water's edge. At the
Pont Saint-Michel, some old houses still remain which witnessed the
riots of 1793, 1830, and 1848;[Pg 79]
[Pg 80]
[Pg 81] another is to be found on the Quai des
Orfèvres, where the celebrated Sabra worked; he was a popular dentist
who modestly called himself the "people's tooth-drawer." To-day it is
one of the spots dear to lovers of old books, with its open-air
book-stalls, and also to anglers, who, in the sun and out of the way of
the river passenger-boats, can practise their tranquil sport.
Before describing the Conciergerie, let us cross the Cour du Mai; there it was, in front of the steps leading to the Palais de Justice, on the right, that every day the death-carts came during the Terror, and took, at 4 o'clock, their dismal batch of those doomed to death, while, from his office-window, Fouquier-Tinville coldly counted, as he picked his teeth, the number of the victims who were going over there.
From this courtyard of blood, on a foggy day of November 1793, poor Madame Roland, with hair cut and hands tied, started for the scaffold. Her joyous childhood had been spent in[Pg 82] a red-and-white brick house which stood at the angle of the Quai de l'Horloge and the platform of the Pont-Neuf, a few yards from the Conciergerie!
The charming landscape in which she had dreamed so fondly of glory and liberty, she saw once more as she was being led to the guillotine amid the shouts of infuriated men and women. Sanson had taken his ghastly procession along the usual road—the Pont-au-Change, the Quai de la Mégisserie, the Trois-Marie Square; and so, turning her eyes to the further bank of the Seine, the poor woman, before she died, was able to give a last look at the scenery she had been familiar with in happier years, scenery over which rose the massive walls of the French Panthéon—it was the new name of Sainte-Geneviève's Church which the Convention had just re-baptized and devoted to the worship of our national glories.
The Conciergerie was entered by a large arched door, containing a triple wicket as protection, at the further side of a gloomy, narrow courtyard, with mouldy paving-stones, which now is found on the right of the large staircase of the Palais de Justice.
The nine steps that put it on a level with the Cour du Mai were mounted
by all the condemned victims of the Revolution. The Queen and Charlotte
Corday, Madame Elizabeth and Hubért's widow, the virtuous Bailly and
Madame du Bailly, Fouquier-Tinville and Monsieur de Malesherbes, Danton,
Robespierre, Camille Desmoulins, the Abbess of Montmartre, Madame
de[Pg 83]
[Pg 84]
[Pg 85]
[Pg 86]
[Pg 87] Monaco and Anacharsis Clootz: princesses and Conventional, dukes
and Hébertists, generals of the Republic and "Fouquiers sheep," the
noblest, purest, bravest, the maddest and most miserable crossed this
fateful threshold.
Sanson, with his death-lists in hand, waited at the top of the staircase, in front of the carts.
The guillotine "tricoteuses" and criers thronged the top-steps of the Palace and leaned forward, with shouts and abuse, and often with hand that cast filth, over the unhappy prisoners. The melancholy toilet of the condemned had been effected in the rotunda where the concierge had his quarters, near the small whitewashed room in which the clerk registered the arrival of the newcomers, and to which Sanson came to give his receipt for the successive deliveries of those that he conveyed to execution.
The clerk's arm-chair, and his table laden with registers, took up about half of the narrow room. Sorts of desks placed along the wall sufficed to receive the things which prisoners left behind, their sad relics, the hair that had been cut off. A wooden railing separated the clerk's office, properly so called, from a back portion of it, where these prisoners spent the weary hours that intervened before the fatal summons, so that those entering could talk with them. Fierce dogs came smelling round to recognise a master, mistress, or acquaintance, and friends or relatives could try to obtain from the gaoler's pity bits of news concerning dear ones still shut up in the dark prison.
"On the day of my arrival," wrote Beugnot in his Memoirs, "two men were waiting for the coming of the headsman. They were stripped of their garments, and already had their hair thinned out and their neck prepared. Their features were not changed. Either by accident or with design, they held their hands in the position ready to be tied, and were essaying attitudes of firmness and disdain. Mattresses down on the floor revealed that they had spent their night in the place, had already undergone this long punishment. By their side, were seen the remains of the meal they had eaten. Their clothes were flung here and there; and two candles that they had forgotten to extinguish cast back the daylight and seemed to be the sole funereal illumination of the scene."
In the hundreds of "Prison Souvenirs" which were published immediately after the fall of Robespierre, one may gain an idea of what sort of existence prisoners led, deprived of every necessity, devoured by vermin, brutally treated by drunken or cruel keepers; and one should see the gloomy courtyard where they came to get a breath of fresh air, a narrow triangular space of ground between the walls of the prison and the women's yard. This arrangement had one compensation; a simple iron railing separated the two enclosures, so that friends could exchange looks and language, and even the last kiss and embrace.
This railing still exists, black, rusty, and ill-looking, creaking as of
yore; and it is not difficult to conjure[Pg 89]
[Pg 90]
[Pg 91] up the images of those that
bent over it. Madame Elizabeth, Madame Roland, Cécile Renaud, Lucile
Desmoulins, Madame de Montmorency, and Charlotte Corday touched it with
their dresses; and Du Barry, one of the few women who trembled at the
prospect of death—"A minute longer, headsman"—also clung to it!
This railing, the so-called chapel of the Girondins, the passage called the "Rue de Paris," the small infirmary, and the Queen's dungeon are, together with the barred cell in which women awaited execution, the sole vestiges of the ancient prison. Farther on, a big wall, newly raised, shuts off the dismal route along which the condemned passed, and closes up the former entrance to the registrar's office in the Conciergerie.
Let us take a hasty walk round the Prison, alas! modified and rearranged. Let us pause, however, before the door of the dungeon in which Marie Antoinette was confined during the last thirty-five days of her life.
The Restoration, which assumed the task of sweeping away many things, began with this melancholy place. Abominable coloured panes have been put in the more than half-blocked up and carefully barred window from behind which the Queen, whose eyes had suffered from the damp prison and want of care, tried to obtain a little air and light.
Only the flooring of this room, three yards by five, is intact. A low screen once divided it off from the chamber where two prison gendarmes were continually on guard. There, the unfortunate woman pined, in lack[Pg 92] of everything, a prey to anxiety, without news of her family, reduced to borrow the linen she required from the kindness of Richard, the porter. Her last tire-woman was the humble servant Rosalie Lamorlière, who, "not daring to make her a single curtsey for fear of compromising or afflicting her," threw over her shoulders a white linen handkerchief, an hour before her departure to the scaffold.
In striking contrast, this dungeon is separated only by a thin partition from the apothecary's room, whither Robespierre—with fractured, hanging jaw, his stockings down over his ankles on account of his varicose sores, still clad in the fine, blue suit that, a few weeks previously, at the Fête of the Supreme Being, had made so many jealous—was hustled, all over blood and mud, like a hideous bundle.
Sinister-looking, silent, showing no signs of life save by the twinges of pain he was suffering, impassible in presence of the insults of the cowards who had acclaimed him the day before, the "Incorruptible one" waited for them to come and tie him, panting, to the top of the cart that should convey him, amid the cries of a whole population, to the foot of the guillotine.
Above these dungeons, and connected with them by a narrow, winding staircase, sat the terrible Revolutionary Tribunal in public audience. Strangely enough, there is an almost total lack of documents as to this most interesting corner of the Palace, where such great dramas were played.
A picture by Boilly—The Triumph of Marat—which figures in the Lille Museum, shows us, however, the entrance to the Revolutionary Tribunal.
The popular tribune, after his acquittal, issues in triumph from the hall, frantically cheered by his habitual escort of criers and adherents!
At the back, between two pillars, and underneath a bass-relief representing the Law, a sort of forepart in boards opens, with an inscription on it, "Revolutionary Tribunal!" That is the place.
The hall in which the Queen, the Girondins, and Madame Roland were tried, was called The Hall of Liberty. In another, called The Hall of Equality, appeared Danton, Camille Desmoulins, Westermann, Hubert, and Charlotte Corday. The windows overlooked the Quai de l'Horloge; and tradition relates that the echoes of Danton's powerful voice, when he was on trial, penetrated through the open casements to the anxious crowd massed on the other side of the Seine.
The last alterations carried out in this part of the Palais de Justice have, alas! disturbed and changed everything; so that, of the registrar's office, occupied by Richard and de Bault, which ought to have remained sacred for ever, and of the unique exit from the Prison, where such heartrending adieux were witnessed, and of the antechamber of death, whose pavement was trodden by the condemned of all parties, nothing is left to-day!
Administrative vandals have turned it into the Palace restaurant; and cold meat, beer, and lemonade are sold[Pg 96] in it. A telephone has been installed, and a "coffee filter"! Gaunt spindle-trees struggle in vain to thrive in the sombre, narrow courtyard illustrious for its past scenes of agony! As Paul-Louis Courier used to repeat: Immane nefas.
At the rear of the Palais de Justice was formerly the delightful
Dauphine Square, where the first "Public Exhibitions of Youth" were
held, the exhibits being works of artists not belonging to the official
Academies. The Carnavalet Museum possesses a most amusing pencil
drawing, signed "Duché de Vancy," and dated May 1783, which bears this
manuscript inscription: "Picturesque view of the Exhibition of paintings
and drawings, on the Dauphine Square, the day of the lesser Corpus
Christi feast." As a matter of fact, on the Sunday of the Corpus
Christi, "when it did not rain," artists had the authorisation—in the
morning—to submit their works to the public; if it did rain—and this
was the case in 1783—the fête was adjourned to the following Thursday.
The pictures were exposed in the northern corner of the Square, on white
hangings fixed by the shopkeepers in front of their shops; and the
Exhibition extended on to the bridge as far as opposite the good Henri's
statue. Oudry, Restout, de Troy, Grimoud, Boucher, Nattier, Louis
Tocqué, and, last of all, Chardin showed their works there. In an
excellent study devoted to these Exhibitions of Youth, Monsieur Prosper
Dorbec details the works that Chardin took to this ephemeral Salon of
the Dauphine Square. In 1728, when he was[Pg 97]
[Pg 98]
[Pg 99] twenty-nine, he presented
there two masterpieces, The Ray-fish and The Side-board, which
to-day are two of the glories of the French School at the Louvre Museum.
Up to the time of the Revolution, this little artistic manifestation
roused Parisian enthusiasm; and what a pretty sight must have been
offered by the Dauphine Square, and the pink fronts of the two corner
houses and the old Pont-Neuf—an exquisite, picturesque setting—with
the throng of amateurs, saunterers, critics, fine ladies, artists,
amiable models in light-coloured costume, full of mirth and busy talk,
eagerly gazing, on a mild May morning, at the freshly-hung canvases of
the Minor Exhibitors of the Dauphine Square.
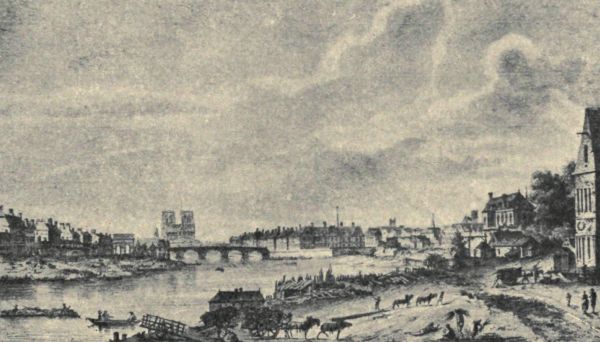
The Isle of Saint-Louis is, in some sort, the continuation of the old City. It is a kind of provincial town in Paris. The streets are silent and deserted; there are no shops, no promenaders, no business; a few old aristocratic mansions, with their tall façades, their emblazoned pediments and their severe architecture, alone tell the glorious past of this noble quarter.
The finely carved spire of Saint-Louis' Church confers an elegance on the somewhat melancholy whole. The quays of Orléans and Bethune contain vast buildings of grand style. In the Rue Saint-Louis, is the admirable Lambert mansion, that masterpiece of the architect Le Vau, which was lost at the gaming-table in one night by Monsieur Dupin de Chenonceaux, the ungrateful pupil[Pg 102] of Jean-Jacques Rousseau. Le Brun painted the gallery of the Fêtes in it, and Le Sueur the saloon of the Muses.
At that time, it was the rendezvous of all the wits. Madame du Châtelet throned there, Voltaire lived in it, and the Lambert mansion radiated over the length and breadth of dazzled Paris.
Then came darker days. The masterpieces of Le Sueur were sold—most of them found their way to the Louvre—and nothing survives of this great painter's work in the Lambert mansion except a grey camaïeu placed under a staircase, and a few panels scattered here and there.
Last of all—as if to mark its definitive decadence;—the mansion was occupied by some military-bed purveyors. The fine carvings, sumptuous paintings and gilded arabesques disappeared beneath a thick white dust from cards of wool. In the great gallery, so magnificently decorated by Le Brun and Van Opstaël, mattress-women set up their trestles and seamstresses began to sew sacking.
Later, Prince Czartorisky bought this noble dwelling and thus saved it from ruin.
Below the Lambert Hotel, along the river, is the Marie Bridge, at the
foot of which used to moor the famous water-diligence from whose deck
disembarked for the first time in Paris, on the 19th of October 1784, a
pale-complexioned youth of resolute brow, with eyes that gazed from
their depths on the horizons of the immense[Pg 103]
[Pg 104]
[Pg 105] town. It was Bonaparte, a
pupil from the Brienne School, who had come to continue his studies at
the École Militaire; and the first glimpse the future Cæsar had of the
great Paris which was ultimately to acclaim him was the apse of
Notre-Dame, the old and venerable Notre-Dame in which he was to be
crowned, and round which, in preparation for the coronation day, the 2nd
of December 1804, eighteen houses were pulled down, so that the pomp of
the ceremony might be celebrated without obstacle and in all its
magnificence!
Finally, on the Anjou Quay, we meet with one of the handsomest mansions of old Paris, that bearing the name of Lauzun, which the generous initiative of the Municipal Council has saved from destruction, the Lauzun mansion with its inimitable wainscoting, its ancient gildings, its glorious past, which is destined to become the museum of all belonging to the seventeenth century: a fine frame for a fine project.
In this old quarter of the Isle of Saint-Louis, at the confluence of the Seine's two arms, painters, writers and poets have always dwelt: George Sand, Baudelaire, Théophile Gautier, Gérard de Nerval, Méry, Daubigny, Corot, Barye, Daumier, all lived there for a long time. In the Lauzun mansion, were held the sittings of the hashish smokers' club; and the chipped Virgin that looks from her niche at the corner of the Rue Le-Regrattier—formerly known as the street of the Headless Woman—and saw the passage of the whole Romantic Pleiad, will long continue to receive visits from lovers of old Paris.
It is from the Bourbon Quay that one of the most beautiful sights imaginable may best be obtained: a sunset over Paris.
The violet-tinted mass of Notre-Dame stands out with its superbly imposing silhouette against the purpled gold of the fiery sky. All the town dies away in a pink dust of light, whilst the broad roofs of the Louvre, the spire of the Sainte-Chapelle, the pepper-box turrets of the Conciergerie, the Saint-Jacques Tower, and the campaniles of the Town Hall, all this landscape alive with history glows in the last rays of the sinking sun. The Seine flows with a surface of liquid gold.
The spectacle is sublime.
No less than the old part of the City, the left bank of the river is rich in souvenirs. There the Roman occupation left the deepest traces. We find the arenas of Lutecia, and, above all, the Thermae of Julian, saved from destruction by the taste and initiative of Du Sommerard at the moment when these grandiose ruins, which were being used as coopers' store-rooms, were about to be pulled down, involving in their fall that jewel of the fifteenth century, the marvellous Hôtel de Cluny. Quite recently, remains of Roman substructures have been discovered near the College de France, in the Rue Saint-Jacques and the[Pg 110] Saint-Michel Boulevard; but the glory of the left bank of the river was, in particular, the University and the Sorbonne.
Little to-day is left of these old walls; but, ten years ago, the hill of Sainte-Geneviève still preserved much of its whilom picturesqueness.
There was the Rue Saint-Jacques, with its old book-sellers and seventeenth-century houses, and especially—what dread reminiscences!—the heavy-leaved gate of the Louis-le-Grand Lycée, where Robespierre, Camille Desmoulins, and the future Marshal Brune had studied under the mastership of the good Abbé Berardier. I confess that the Louis-le-Grand of our boyhood was black, and gloomy enough also, with its moss-grown playgrounds, its smoky rooms, its punishment chambers up under the roof, where one was frozen in winter and stifled in summer, its punishment chambers in which tradition relates that Saint-Huruge was confined; quite near to the Saint-Jacques blind alley where Auvergne dealers sold such fine trinkets, and to the little Rue Cujas, noisy with the noise of rowdy students—but which rendered us pensive.
There was the Sorbonne, with its paved courtyard, where we used to wait,
pale, feverish and anxious, for the posting of the small white notice
bearing the names of those candidates for the Baccalaureat that were
admitted to the vivâ voce; and we were half-dead with fear at the idea
of appearing before the terrible Monsieur Bernès, while we blessed the
gods to have given us as examiner[Pg 111]
[Pg 112]
[Pg 113] the witty and indulgent Monsieur
Mézières, who, at least for his part, has not grown old.
Further on, in the rear of Sainte-Barbe, we come to the Rue de la Montagne-Sainte-Geneviève, alive and teeming with its old mansions converted into dispensaries or business premises, its petty trades, its popular dancing-rooms, and, last but not least, its celebrated École Polytechnique, dear to all Parisians, which adds its note of cheerfulness to this somewhat sombre quarter.
Quite near there is the Rue Clovis, where formerly stood the Abbey of Sainte-Geneviève, whose square tower still remains and makes us regret the part that has disappeared. In this Rue Clovis may be seen, crumbling to decay and half-buried under climbing plants—lichens, ivy, sage and moss—a big side of a primitive-looking wall, a fragment[Pg 114] of the fortifications of Philippe-Auguste, the belt of stone and lofty strong towers behind which for centuries were heaped houses, palaces, colleges, churches and abbeys, huddling against one another. The church of Saint-Etienne-du-Mont opens its elegant portal a few yards away from the Rue Clovis. Illustrious dead were buried there: Pascal, Racine, Boileau.
A crime was also committed in it.
On the 3rd of January 1858, the first day of the novena of Sainte-Geneviève, whose relics repose in one of the side-chapels of the church, dreadful cries were heard: "They have just murdered Monseigneur," and soon a man of haggard looks, clad in black, with blood-red hands, was seen on the Square in the grasp of some policemen who had just arrested him. It was Verger, a half-mad, interdicted priest, who had stabbed to the heart Monseigneur Sibour, Archbishop of Paris!
This charming church should be seen in the early days of January.
A sort of small religious fair is then held in front of the porch. A
veritable liturgical library is there for sale, under umbrellas
resembling those that used to shelter the orange-dealers: "Mary's
Rose-trees," "Miracles at Lourdes," "Synopses of Novenas," "Acts of
Faith," "Acts of Contrition," "Lives of the Saints," "Glorifications of
the Blessed." Chaplets are sold, holy images, devotional post-cards,
orthodox rituals, medals, scapularies—and unfortunately these objects
have less artistic value than sentiment about them. It is a[Pg 115]
[Pg 116]
[Pg 117]
delightful Parisian tableau in one of the prettiest settings of the
great town.
At the end of the Rue Clovis, is the Rue du Cardinal-Lemoine, where the painter Lebrun possessed a lovely house, still standing at No. 49, over-run with ivy and honeysuckle, two or three yards distant from the Scotch college—at present the "Institution Chevallier,"—converted into a prison during the Terror, like most educational institutions. Saint-Just was conveyed thither, after being outlawed on the 9th of Thermidor; and his friends came there to fetch him at eight o'clock in the evening, as well as his colleague Couthon, who was confined in the Port-Libre (the old religious house of Port-Royal). It is easy to imagine the gendarmes, on the steep slopes of the Rue Saint-Jacques, running round the mechanical seat which the impotent Couthon feverishly worked and propelled with handles levered to the wheels, and which travelled rapidly over the hard stones, amid shouts and frightened "sectionnaires,"—easy to conjure up before one's senses the call to arms, the sound of the tocsin, under the downpour of the storm that dispersed the Robespierrian bands camped about the Town Hall, and enabled the troops of the Convention to invade the "Maison Commune" without resistance.
An hour later, Robespierre had his jaw smashed by Merda's bullet; his brother sprang through the window; Le Bas committed suicide; Saint-Just, haughty and impassible, allowed himself to be arrested in silence;[Pg 118] Couthon, with his paralysed legs, was flung on to a rubbish heap, and then, bleeding and motionless, was dragged by the feet to the parapet of the quay. He pretended to be dead. "Let us cast him into the water," howled a multitude of fierce voices. "Excuse me, citizens," murmured Couthon, "but I am still alive." So he was reserved for the scaffold.
Behind Saint-Etienne-du-Mont, there is a nook almost unknown to Parisians: a little cloister close to the apse of the church, and containing some admirable painted glass windows by Pinaigrier, the great artist, who, in 1568, charged for the "Parable of the Guests," a three-compartment window painting, which masterpiece now adorns the chapel of the Crucifix, "92 livres 10 sols, including the leading and iron trellis."
It is one of the retreats for poetry and devotion so common in Paris, and yet ofttimes so unsuspected amid the city's noise; and one never forgets the impression produced when leaving the Latin Quarter, with its laughter and songs, and plunging suddenly into this deserted cloister full of dream and melancholy, though so close to the sunny, busy square of the Panthéon, where, on the 27th of July 1830, to the shouts of the people and the army, an actor at the Odéon Theatre, Eric Besnard, replaced once more the inscription: "To her great men the grateful mother country" on the fine temple built by Soufflot, which the Restoration had consecrated to the worship of Sainte-Geneviève.
The Panthéon is certainly the one Parisian building[Pg 119]
[Pg 120]
[Pg 121] which has been
most often baptized and re-baptized. Constructed in consequence of a vow
made by Louis XV. when ill at Metz, on the gardens belonging to the
original Abbey of Sainte-Geneviève, the money that paid for it was
derived from a portion of the funds raised by three lotteries drawn
every month in Paris.
Soufflot, whose grandiose plans had been accepted, set to work in 1755. Towards 1764, the edifice began to[Pg 122] assume shape, and the Parisians in enthusiasm admired the magnificent forms that modified the ancient outlines of their city. But cracks and fissures and sinkings-in occurred; a mad terror succeeded to the wonder: "The building will tumble, and its fall will involve a part of the old quarter of the Sorbonne," people said. Works of shoring up, embanking and strengthening were carried out. Paris breathed again; but poor Soufflot, in despair, could not survive so many tragic emotions. He died in 1781 without finishing his undertaking.
In 1791, the constituent Assembly set apart for the "Honouring of Great Men" the church primitively dedicated to Sainte-Geneviève; and Mirabeau's body was conveyed thither in triumph "to the sounds of trombone and gong, whose notes, by the intensity with which they were produced, tore the bowels and harrowed the heart," says a chronicle of the time.
The great tribune was destined to make but a short stay in the
Panthéon,—this was the name given to the secularised church—for on the
27th of November 1793, at the instigation of Joseph Chénier, and after
study of the documents found in the iron safe, documents that left no
doubt as to "the great treason of the Count de Mirabeau," the
Convention, "considering that a man cannot be great without virtue,
decreed that Mirabeau's ashes should be removed from the Panthéon, and
that those of Marat should be buried there." The sentence was carried
out by night, and the "virtuous" Marat took the place of Mirabeau; not
for long, however, since, some[Pg 123]
[Pg 124]
[Pg 125] months later, Marat's body,
"depantheonised" in its turn, was cast into the common grave of the
small graveyard belonging to Saint-Etienne-du-Mont. Voltaire and
Rousseau were, in their turn, triumphantly interred. Voltaire's body,
after remaining all night in the ruins of the Bastille, had been brought
to the Panthéon on a triumphal car, escorted by fifty girls dressed in
antique style through David's care, and by the actors and actresses of
the Théâtre Français in their stage dresses. The widow and daughters of
the unfortunate Calas walked behind, close to the torn flag of the
Bastille. In order to make this interment a never-to-be-forgotten fête,
its organisers had provided for everything except for the weather. A
dreadful storm descended on the heads of those composing the procession:
Mérope, Lusignan, the Virgins, Brutus, and the delegates sent in the
names of Politics, the Arts, and Agriculture, were wet to the skin; and,
covered with mud and in wretched plight, were compelled to huddle into
cabs or shelter themselves under umbrellas.
And thus it was that, on the 12th of July 1791, Voltaire made his entry into the Panthéon.
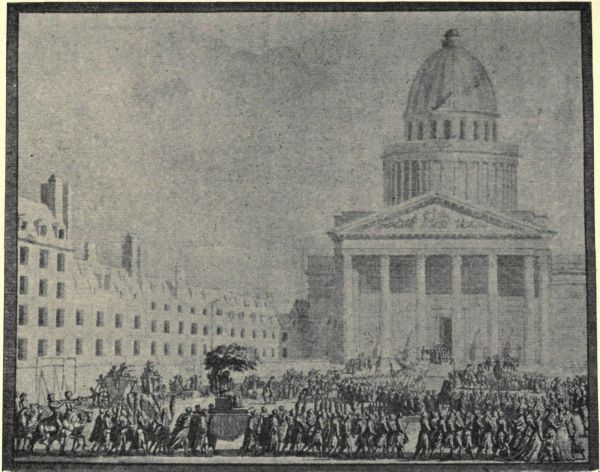 THE APOTHEOSIS OF JEAN-JACQUES ROUSSEAU
THE APOTHEOSIS OF JEAN-JACQUES ROUSSEAUJean-Jacques Rousseau followed him there on the 11th of October 1794; his body brought back from Ermenonville, beneath a bower of flowering shrubs, to the agreeable sounds of the "Village Seer," had passed the preceding night on the basin of the Tuileries, transformed for the occasion into an "Isle of Poplars." While yet not so popular as that of Voltaire, his triumph was[Pg 126] "one of sensitive souls," and "the man of nature" was interred according to the rites he had himself prescribed. Later, Napoleon peopled the Panthéon with the shades of obscure senators and some few artists, admirals, and generals. Subsequently, the Second Republic made a definitive assignment of the edifice to the cult of great men; and there, on a sunny day, the 3rd of May 1885, Victor Hugo's body was brought in the humble hearse of the poor, amid the acclamations of an immense concourse of people, after spending a night of apotheosis under the Arc de Triomphe, which he had so nobly sung. Since then, Baudin, President Carnot, La Tour d'Auvergne have been buried there; and an admirable decoration, the work of our best contemporary artists, covers the vast walls of this necropolis. Puvis de Chavannes, Humbert, Henri-Lévy, Cabanel, Jean-Paul Laurens are finely represented in it; and, last of all, Edouard Detaille, surpassing himself, has, in an admirable soaring of art, created on the canvas—in Homeric proportions—a mad rush of horses and riders, the old cavaliers of the Republic and the Empire, towards the radiant image of the Motherland, with standards conquered from the enemy by their dauntless heroism.
Around the Panthéon, there used to be, and still is, a labyrinth of little streets, poor and crowded together, once inhabited by those that attended the schools, so numerous in that quarter of the Sorbonne.
The Rue des Carmes remains to us as a perfect specimen of the past, with
its houses whose shaking[Pg 127]
[Pg 128]
[Pg 129] walls support each other, its crumbling
façades, its dilapidated staircases; and then, here and there, the
relics of a vanished splendour, the entrance to two important colleges,
to-day dwindled down into dens of misery, into lodgings of the poor.
Narrow and uneven, the Rue des Carmes ascends toilingly between shops
whose paint has been streaked by storms, faded by dust and wind; and yet
it continues to be full of charm and poetry, this sorry-looking street,
crowned at the top by the august proportions of the Panthéon, and
framing at the bottom, with its two lines of dingy houses, mean hotels,
and dancing-rooms, the delicate and elegant spire of Notre-Dame aloft on
the horizon of the clear sky.
It was at the corner of this Rue des Carmes and the Rue des Sept-Voies, not far from Sainte-Geneviève's church, that, at seven o'clock in the evening of the 9th of March 1804, George Cadoudal sprang into the cab that was to take him to the fresh hiding-place which his friends had prepared for him in the house of Caron, the royalist perfumer of the Rue du Four-Saint-Germain. George was narrowly watched, all the Paris police being on the alert. He was recognised, and pursued by the Inspectors of the Prefecture, two of whom pounced on him at the corner of the Rue Monsieur-le-Prince and the Rue de l'Observance. The one he killed with a pistol bullet in his forehead, the second he wounded. Meanwhile, the assembled crowd hindered his flight; and a hatter of the neighbourhood seized the outlaw[Pg 130] and dragged him to the Police Station. His calmness and dignity and the wit of his replies disconcerted his adversaries. Reproached with having killed a married detective, the father of a family: "Next time have me arrested by bachelors," he retorted. After he had owned to the dagger found upon him, he was asked if the engraving on the handle were not the English hall-mark. "I cannot say," he replied, "but I can assure you that I have not had it[1] hall-marked in France."
Quite near, is the Luxembourg, both palace and prison, the Luxembourg,
where Marie de Medici gave such magnificent fêtes, where Gaston
d'Orléans yawned so much, and where the Grande Mademoiselle sulked,
sighing for the handsome Lauzun; where also the Count de Provence so
cleverly prepared, with Monsieur d'Avaray, his escape from France, on
the same evening that Louis XVI. and Marie-Antoinette made such bad
arrangements for the lugubrious journey that was to lead them to
Varennes; the Luxembourg, whose courtyard was used as a promenade by
such prisoners as the Terror crowded there; the Luxembourg, whence
Camille Desmoulins wrote to his Lucile those heartrending letters that
still bear the traces of tears; the Luxembourg whither, a few weeks
later, Robespierre was brought as a prisoner, and where, "for want of
room," Hally, the porter, refused to receive him; the Luxembourg where,
after Thermidor, the artist David painted, from, his dungeon, the shady
walk in which he could[Pg 131]
[Pg 132]
[Pg 133] see his children playing at ball; the
Luxembourg of Barras, of Bonaparte, of the Directory fêtes; the
Luxembourg, too, of Nodier, of Saint-Beuve, of Murger, of Michelet, of
the students, of the workers of Bohemia, of the songs of the worthy
Nadaud and Mimi Pinson, near to Bullier's and the Lilac Closerie and
also to the Observatory and the ill-omened wall "scored with bullets"
where Marshal Ney fell. Everywhere, the same mingling of mirth and
sorrow, of laughter and blood. The reason is that each street, each
cross-road, almost each house has seen some dark procession pass by or
some victorious fête celebrated.
 FRATERNAL SUPPERS IN THE SECTIONS OF PARIS
FRATERNAL SUPPERS IN THE SECTIONS OF PARISOn all these dingy walls of Paris, hands of women or of artists have contrived to put flowers or bird-cages; and no alley is so dismal that it does not harbour a little poetry and dreaming, some gillyflowers and songs.
Not far away is the Carmes prison, in the Rue de Vaugirard, at the corner of the Rue d'Assas; and there all the externals are the same as they were at the moment of the terrible massacre of 1792. At the foot of the staircase one sees still the tiled floor of the small room where, between two corridors, Maillard placed the chair and table that formed the bloody tribunal of the September slaughter; the balcony covered with climbing plants through which issued the unfortunates that were felled, stabbed with pikes, or shot in the large garden; and, at the top of the first story, on the wall bearing even now the red marks of the blood-dripping sabres used by the slayers, may be read the signatures of the[Pg 134] fair prisoners who, day after day, in terrified anxiety, waited, each evening, for the fatal order to appear before the Tribunal: Mesdames d'Aiguillon, Terezia Cabarrus-Tallien, Joséphine de Beauharnais. At this date, Tallien, himself suspected and followed by a band of spies, prowled from eve till morn round the sinister prison in which the woman he loved was confined. One day, on his table, 17 Rue de la Perle, he found a poniard that he recognised, a gem of Spain with which Terezia's hands were familiar. It was an imperative order; and on the 7th of Thermidor this note was transmitted to him from "La Force." "The head of the police has just gone from here. He came to tell me that to-morrow I shall ascend to the Tribunal, that is, to the scaffold. It is different from the dream I had in the night: Robespierre dead and the prisons opened.... But, thanks to your signal cowardice, there will soon be no one in France capable of realising it!"
As a matter of fact, the fair Terezia, being more especially aimed at by
the Committee, had been mysteriously transferred from the Carmes prison
to La Force; and it was from this latter place that she sent her will
and testament of vengeance and death. Then, Tallien swore to save his
country; the mother country for him was the woman he worshipped. Mad
with love and rage, rousing against Robespierre every rancour, terror,
and hatred, he spent the night and the day of the 8th in preparing the
dreadful and tragical sitting of the 9th of Thermidor, which was a
merciless[Pg 135]
[Pg 136]
[Pg 137] duel between the two sides. He appealed to Fouché, to
Collot d'Herbois as to Durand-Maillane and Louchet, to Cambon as to
Vadier, to Thuriot as to Legendre, to the few remaining Dantonists as to
the eternal tremblers of the Marais; then, springing to the rostrum with
a dagger in his hand, he threatened Robespierre, who was nervous,
uneasy, distraught, from the presentiment that his power was escaping
him; and, at length, after a fearful five hours' struggle, obtained the
dread decree outlawing and condemning to the guillotine those who
themselves for two years had been mowing down the members of the
Convention.
 FÊTE GIVEN AT THE LUXEMBOURG ON THE 20TH OF FRIMAIRE, ANNO VII.
FÊTE GIVEN AT THE LUXEMBOURG ON THE 20TH OF FRIMAIRE, ANNO VII.Opposite the Luxembourg, is the Rue de Tournon, where Théroigne de Méricourt and Mademoiselle Lenormand lived; the Countess d'Houdetot dwelt at No. 12, the appearance of which has hardly changed since. If he were to come back and wander about these parts, Jean-Jacques Rousseau would again find almost intact the home of her he chiefly loved, quite near to the Rue Servandoni, a dark, damp lane lurking beneath the walls of Saint-Sulpice, where Condorcet, during the Terror, succeeded in safely hiding himself at the house of Madame Vernet, No. 15. There he terminated—under what sorry conditions!—his Tableau of the Progress of the Human Mind. His wife was living at Auteuil and there painted pastels. No industry prospered under the Terror. "Every one," says Michelet, "was in a hurry to fix on the canvas a shadow of this uncertain life." On the 6th of April, his work being[Pg 138] finished, Condorcet dressed himself as a workman, with long beard and cap down over his eyes, a "Horace" in his hand, and in his pocket some poison, for a case of need, prepared him by Cabanis; and escaped from Madame Vernet's. All day, he roamed about the country, in the vicinity of Fontenay-aux-Roses, hoping to find with some friends, Monsieur and Madame Suard, a shelter that they refused him. He spent the night in the woods; then, on the morrow, haggard and starved, he entered a Clamart public-house. There, he made a ravenous meal, while reading his dear Horace. Being questioned and suspected, he was carried off to the district, put on an old horse and thus conducted to the prison at Bourg-la-Reine. At dawn, the gaolers, on going into his cell, stumbled over his corpse. Poison had made an end of this noble life of work, glory, and misery.
Aloft in the same quiet quarter, Saint-Sulpice rears its two unequal
towers, on which Chappe planted the great arms of his aërial telegraph.
It was in the fine vestry of this imposing church, which has preserved
its admirable wood-carvings, that Camille Desmoulins signed the marriage
register, when, on the 29th of December 1790, he married his adored
Lucile Duplessis. The marriage was a veritable romance; and all Paris
crowded to the gates of Saint-Sulpice to see the procession go by. The
bride and bridegroom were congratulated; and cheers were given for the
witnesses, whose names had already become popular; Sillery,[Pg 139]
[Pg 140]
[Pg 141] Pétion,
Mercier, and Robespierre. Then, the wedding party ascended the Rue de
Condé to go and breakfast at Camille's home, No. 1 Rue du Théâtre
François (to-day, No. 38 Rue de l'Odéon), on the third floor. There, on
the 20th of March 1794, the day of his mother's death, he was arrested,
bound like a malefactor, and thence was taken to the Luxembourg hard by.
On the 5th of April, Camille was executed amid the shouts of the people
who had so flattered him. Lucile followed him to the scaffold a week
later! They had sworn to love each other in life and death.... The idyll
finished in blood.
Round about Saint-Sulpice, one comes across the Rue Férou, the Rue Cassette, the Rue Garancière, the Rue Monsieur-le-Prince, the Rue Madame, with their ancient names and provincial aspect, devout and silent quarters of monastic and semi-mysterious life, and, for this reason, full of infinite charm.
There, on all sides, are heard convent bells and liturgic sounds. The few shops that exist are austere in air and devoted to religious purposes: chasuble makers', holy image dealers', church book and jewellery sellers'. Behind long, sombre walls, shoots of verdure, the plumes of a tree joyously bursting forth remind one of large, unkempt gardens, where all grows wild, full of flowers and birds, inhabited by pious persons and old people who pray as they walk and regretfully dream of the times that are no more.
In the huge Paris, noisy and flippant, mad with[Pg 142] sound and movement, tramways and underground railways, it is the refuge of the past, the quarter for prayer, silence, and oblivion; there still seem to live "a few dolent voices of yearnings for the past, which ring the curfew," says Chateaubriand in his Memoirs from beyond the Grave.
Old mansions are numerous.
In the Rue de Varenne alone, each portal awakes a remembrance of the most illustrious names of France's nobility: Broglie, Bourbon, Condé, Villeroy, Castries, Rohan-Chabot, Tessé, Béthune-Sully, Montmorency, Rougé, Ségur, Aubeterre, Narbonne-Pelet, &c., and some of the hosts of these aristocratic dwellings were certainly found disguised, dressed up as horse-dealers, drovers, peasants, workmen, in the Golden Cup hostelry at the corner of the Rue de Varenne, which was celebrated in the history of the Chouannerie: the heroes of Tournebut, my dear friend Lenôtre's interesting work, put up there, says the author, who, himself filled with enthusiasm, knows how to inspire his reader with the same. It was one of the meeting-places used by the sworn companions of George Cadoudal, who hid there several times; and there, too, the royalist conspirators met to complete, for Vendémiaire, Anno IV., their arrangements relative to the abduction of the Convention.
At some little distance, in the Rue Canettes, another rendezvous
existed, for emigrants and chouans, in the house of the perfumer, Caron,
where a famous hiding-place was used. Hyde de Neuville tells us, in his
picturesque[Pg 143]
[Pg 144]
[Pg 145] memoirs, that one needed only to slip behind the picture,
serving as signboard to the perfumery—a picture overhanging the
street—then to draw over one the shutter of the neighbouring chamber,
for all the police Fouché employed to be tricked, in spite of searching,
as they frequently did, the house through and through.
Next, we come upon the Odéon—the old Odéon—still standing on its base, in spite of the countless jests levelled at it, with its famous galleries, where, for many a long year, saunterers have gone to have a look at the last productions of contemporary literature. How often have we lingered in front of the old books or new ones, turning over the leaves, or reading between two pages yet uncut?
It was in 1873 that, under three arcades of the Odéon galleries, the most amiable of publishers, Ernest Flammarion, installed himself in partnership with Ch. Marpon; both of them indefatigable workers, benevolent and witty, they spent treasures of contrivance to get into too narrow a space all the nice, fine books they loved so well, and understood so well how to make others love.
But soon the three arcades were really inadequate; and, progressively, the untiring Flammarion spread round two sides of the big building, before starting out to conquer Paris, and to establish in the city so many bookshops. He had his faithful readers: an old book-lover of narrow purse owned to him that he had read the whole of Darwin's Origin of Species (450 pages) while standing in front of the stall!
Other customers less scrupulous have sometimes carried off the volume they had begun; but the good Flammarion is infinitely indulgent to such "absent-minded" individuals. "The desire to instruct themselves is too strong for their feelings," he murmurs by way of excuse, and, philosophically, he smiles and passes these petty larcenies to his profit and loss account.
Along the Rue de l'École-de-Médecine, passing by the Dupuytren Museum,
which was formerly the refectory of the Franciscan monastery, we reach
the Boulevard Saint-Germain, the cutting of which did away with so many
precious relics; among others, the abode where Marat was assassinated,
the Mignon College, and the Saint-Germain Abbey, the front of which
opened opposite the row of old, curiously gabled houses which so far
have been left alone by architects and builders. These latter heard the
cries of the victims that were massacred in the[Pg 147]
[Pg 148]
[Pg 149] September slaughters.
They were lighted by the reflection of eighty-four fire-pots supplied by
a certain Bourgain, the candle-maker of the quarter, in order that the
families of the slaughterers and the amateurs of fine spectacles might
come and contemplate the work; the shopkeepers of the quarter, who were
complaisant witnesses, supplied details. These houses also saw
Billaud-Varennes congratulate the "workers" and distribute wine tickets
to them; and Maillard, surnamed Strike Hard, they saw leave, when his
work was done, with his hands crossed behind the skirts of his long grey
overcoat, and walk quietly back to his home, like a worthy clerk
quitting his office, coughing the while, for he had a delicate chest.
Together with the present presbytery, they form the sole extant witnesses of that dreadful butchery.
Within a stone's throw, once there was the Passage du Commerce, where resounded the butt-ends of the guns of the sectionaries who, on the 31st of March 1794, came at daybreak to arrest Danton and conduct him to the Luxembourg; and it is easy to fancy what must have been that hour of fright and stupefaction. Arrest Danton! the Titan of the Revolution, him whose formidable eloquence had raised fourteen armies from the soil! the Danton of the 10th of August, Danton till then untouchable! It was only a few days after the arrest of Camille with his cruel wit; the Camille of the Palais-Royal, of the Lanterne, the Revolutions of France and Brabant, the Brissot unmasked; the Camille of the "Vieux Cordelier," that masterpiece of wit and courage,[Pg 150] in which he dared to speak of clemency to Robespierre and of respect for his fellows to the ignoble Hébert! On the site of Danton's house, the tribune's statue stands to-day; we regret the house.
The Rohan courtyard (the word ought to be written Rouen, for, in the fifteenth century, the yard depended on the old mansion possessed by the Cardinal de Rouen) joins the Passage du Commerce, a few steps from the bookshop where the philanthropic Doctor Guillotin tried on a sheep the knife of his "beheading machine"; it is picturesque and curious, this Rohan courtyard, where you can still see the well of the house once inhabited by Coictier, the doctor of Louis XI.; where, too, the "mule's step" may be found, that Sorbonne doctors, who frequented this quarter, used in order to get off their steeds, and which preserved a very old wall round a garden planted with lilac and turf—alas! destroyed last year. The wall, like that of the Rue Clovis, was a fragment of Philippe-Auguste's fortification, the base of one of whose towers is still to be made out in the Passage du Commerce, No. 4, at the house of a locksmith, who has set up his forge upon it!
The houses there are old, dilapidated, and sordid, but perfect in their picturesqueness; the strangest industries flourish in them, and quite recently one might read there this characteristically Parisian advertisement, "Small hands required for flowers and feathers," beside a plate pointing out the address of the newspaper, Heaven, on the fourth floor, door to the left!
The Rue de l'Ancienne Comédie is on one side; it is the ancient Rue des Fossés-Saint-Germain, where Marat set up his press and printing-machine in a cellar. At No. 14, in the courtyard of an old mansion occupied by a wall-paper merchant, once stood the premises of the Théâtre-Français. The large entrance door, the staircases leading to the actors' private rooms, the slanting pit of the hall, and even the friezes are still in existence. The King's Comedians played there, on April 18th, 1689, Phèdre and the Médecin malgré lui, and performed in the same building until 1770.
The encyclopædists, d'Alembert, Diderot and his friends, used to meet opposite at the Procope coffee-house, the handsome iron balcony of which is yet subsisting, from where it was so agreeable to hobnob with the balcony of the Comedy. The Procope coffee-house, celebrated in the eighteenth century, was even more so under the Second Empire. In 1867, on the eve of the Baudin trial, Gambetta poured forth in it, to the students of the various University schools, the thunder and lightning bursts of his admirable eloquence. The great orator in 1859 lived at No. 7 Rue de Tournon, in the hotel of the Senate and the Nations, at present to be found there. His small room afforded a fine view over the roofs of Paris, and also remains as it was then.
Near the spot, at No. 1 Rue Bourbon-le-Château, on the 23rd of December 1850, two poor women were assassinated. One of them, Mademoiselle Ribault, a designer on the staff of the Petit Courrier des Dames,[Pg 154] edited by Monsieur Thiéry, had the strength to write on a screen with a finger dipped in her own blood: "The assassin is the clerk of M. Thi...." This clerk, Laforcade, was arrested the next day.
How many delightful nooks besides, hardly known by Parisians, are to be met with on the left bank of the river!
Not all have disappeared for ever of those vast melancholy gardens, those hoary mansions buried in streets where the grass grows, and whose noble but gloomy façades would never cause one to suspect the riches they contain. Many are in the vicinity of the Hôtel des Invalides. Others are in the Rue Vanneau, the Rue Bellechasse, the Rue de Varenne, the Rue Saint-Guillaume, the Rue Bonaparte; some also in the Rue Visconti, which dark narrow lane possesses illustrious souvenirs. The famous Champmeslé, Clairon, and Adrienne Lecouvreur lived in the Ranes mansion, built on the site of the Petit-Pré-aux-Clercs, and J. Racine died there in 1697. This house, which bears the number 21, is to-day a girls' boarding-school! And last of all, at No. 17 the great Balzac established the printing-press that ruined him, and that later became the studio of Paul Delaroche. There, was played the sentimental and commercial drama whose poignant phases have been related to us so eloquently by Messieurs Hanoteaux and Vicaire.
All these houses, so pregnant with history, are still visible; yet how few Parisians are acquainted with them!
On the Voltaire Quay lived Vivant, Denon, Ingres, Alfred de Musset, Judge Perrault, Chamillard, Gluck, and Voltaire himself who died there, and whose corpse, wrapped in a dressing-gown and held up by straps, like a traveller asleep, started by night in a travelling-coach, on the 30th of May 1778, from the courtyard of Monsieur de Villette's mansion, with its entrance still in the Rue de Beaune, to be buried outside Paris at the Abbey of Scellières in Champagne.
The flat in which Voltaire passed away has not been altered, and its decoration has remained almost intact, with its wall mirrors, its painted ceilings, and its small mirrored salons contrived in the thick walls.
 THE FAÇADE OF THE INSTITUTE
THE FAÇADE OF THE INSTITUTEThe Institute is not far, but for the ancient College of the Four[Pg 158] Nations to produce its best impression, it needs a special day—an extraordinary sitting, a sensational reception, when the prettiest costumes of the most elegant Parisian dames contrast with the Academicians' green uniforms. On one side, are beauty, charm, and grace; on the other, some of the noblest intelligences, the most illustrious names in Literature, Art, and Science. It is the great intellectual banquet of France in one of the fairest sights of the Capital.
If, however, we wish for something to amuse us, something original, we must mount the endless staircases of the Institute and seek it in the attic portion of the palace, visiting the tiny chambers where formerly it was the custom to put candidates for the Prix de Rome in the competitive music examination.
Inside these closets, at which the sumptuously lodged prisoners of
Fresnes-les-Rungis would grumble, on these decrepit walls, the finest
talents of our modern school have left traces of their whilom
presence—bars of music, verses, drawings, writings of varied nature. I
confess I should not dare to reproduce, even expurgated,[Pg 159]
[Pg 160]
[Pg 161]
[Pg 162]
[Pg 163] the
inscriptions which confinement and absence from Paris streets and
acquaintance have suggested to many an admirable composer of to-day.
Saint-Saëns would certainly blush, Bizet's great shade would be
troubled, our great and witty Massenet would surely refuse to accept the
paternity of his vigorous apostrophes, and—I will be discreet; never
mind—it's something very enjoyable, very funny, and quite in the
character of the language.
Between the Mint and the lion-poodle of the Institute (from the shelter of which, if we are to believe his delightful Memoirs, Alexandre Dumas contributed so valiantly to the triumph of the 1830 Revolution) nestles a small, provincial-looking Square; Madame Permon, mother of the future Madame Junot, Duchess of Abrantès, lived there until the Revolution. In a small garret of the same house, at the left corner, on the third floor, Bonaparte used to lodge during his rare holidays from the École Militaire. The fine, carved wainscotings are still round the walls of the drawing-room on the ground floor, overlooking the Seine, which the Cæsar that-was-to-be used to enter and there speak of his hopes, and the marble chimney-piece is in its old place; at it he would come and dry his big patched boots that "smoked again," the talkative Madame d'Abrantès tells us. So, while dreaming, the little sub-lieutenant might, from the window, see opposite him the palace whence, for a number of years, he was to conqueringly dispose of the destinies of the dazzled world.
In front of the Institute is the Pont des Arts. There the sight is an enchanting one; the Seine—the gayest, most lively of rivers—crowded with passenger-boats, tugs, barges, and barques. The grey or blue sky is reflected in the water, and the river flows majestically between two verdure-clad quays, surmounted by book-sellers' cases, and inhabited by the most picturesque of populations.
What strange trades there are on the river sides!—watermen's barbers, dog shearers, dockmen, and sand-carters, tollmen and mattress-carders, anglers, bathmen, washerwomen; it is a separate population with its own customs, habits, and peculiar language. And what a splendid frame is round this odd little world seen from the Pont des Arts!
On the one bank, the Louvre, the green foliage of the Tuileries, and the Champs-Elysées, with the minarets of the Trocadero and the heights of Chaillot on the horizon; on the other, all old Paris, a series of monuments haloed with souvenirs—the Palais de Justice, the Conciergerie, the Sainte-Chapelle, Notre-Dame; the churches of Saint-Germain-l'Auxerrois, Saint-Gervais, Saint-Paul; the Pointe de la Cité.
At night, these noble, suggestive silhouettes assume a still more imposing majesty—modern blemishes, glaring colourings, shameless advertisements are blotted out.
The moon spreads its delicate white light over the old walls, and a
silvern Paris rears itself in the darkness. At times, too, underneath a
storm-red sky, an entirely[Pg 165]
[Pg 166]
[Pg 167] sombre town arises, made known only as a
tragic vision in successive flashes of lightning.
Either we have a Paris of sunny mirth or a Paris bathed in night's gloom.
Descending once again towards the Seine, through the picturesque streets that surround the Institute—the Rue Dauphine, the Rue de Nesles, the Rue Mazarine—we discover in the Rue Contrescarpe-Dauphine—at present the Rue Mazet—the remains of the old White Horse Inn. The stables, with their ancient mangers and quaint eaves, still exist. They date back to Louis XIV. In that time, every week the huge inn-yard was filled with travellers going to Orléans and Blois; and the unwieldy coach started in a cloud of dust, amidst crackings of whip, trumpetings, adieus, and shakings of handkerchiefs; horses pranced, women wept, dogs barked, postilions swore. To-day the animation has disappeared, but the scene has remained, age-stricken, impressive, still charming, so much so that Massenet, moved by it, murmured one morning: "It must be here that Manon[2] alighted from the diligence!"
The neighbouring house was once the Magny restaurant, at which those celebrated dinners were given that Goncourt speaks of so often in his Memoirs, dinners shared by Renan, Sainte-Beuve, Georges Sand, Flaubert, Théophile Gautier, Gavarni, and many others.
Not far away, and connecting the Rue Mazarine—where Molière and his company played—with the Rue de[Pg 168] Seine, let us go through the Passage du Pont-Neuf, occupying the site of the ancient entrance to the theatre, and being the scene of Zola's terrible novel Thérèse Raquin.
It is a typical nook—sordid, dingy, and malodorous, but strangely attractive, with its fried-potato sellers and Italian modellers. The shops in it seem to belong to another century; some months back, one only was frequented by customers, that of a drawing-paper dealer. The artist, Bonnat, told us he had bought his "Ingres paper" there, when he was a pupil at the School of Fine Arts, of which to-day he is the eminent head. The shop had not altered for sixty years, and the saleswoman asserted that the "stomping-rags she sold were exactly similar to those used by Monsieur Flandrin." In front of us is the Institute, and it is impossible to walk along the interminable black-looking wall enclosing it, on the side of the Rue Mazarine, without thinking of the painful paragraph in the preface of the Fils Naturel, wherein the younger Dumas, speaking of his childhood, recalls the souvenir of the return from the first performance, at the Odéon, of Charles VI. chez ses grands vassaux, on the 20th of October 1831.
The evening had been a stormy one, and the success of the play was
doubtful. Consequently, a continuation of their poverty was to be
expected. Alexandre Dumas had heavy burdens to support—his mother, a
household, a child. He had to live himself and to keep his family on the
meagre salary his situation under the Duke[Pg 169]
[Pg 170]
[Pg 171] d'Orléans procured him. It
was not of his talents but of his star that he doubted; and the younger
Dumas always remembered his father's broad shadow cast by the moon on
the dark, gloomy wall of the Institute, and himself timidly guessing at
his father's anxieties and endeavouring, with his little eight-year-old
legs, to follow and keep up with the studies of the good-natured giant.
It was in the Rue Guénégaud, in the Hôtel Britannique, that Madame Roland took up her quarters in 1791. There, joyous and confident in the future, she opened her political salon. What a pleasure for the little Manon to show to all the Pont-Neuf neighbourhood, where her childhood had been spent, that she had become a lady and received people of mark. Brissot, Buzot, Pétion, Robespierre, Danton himself, were pleased to come, between two sittings, and talk at this amiable woman's house; and I fancy what attracted them was far more the pretty Parisian's qualities than the virtues of the austere husband, who must have been a great bore! On the 26th of March 1792, Dumouriez came to Roland's door and rang to tell him that he was appointed Minister. On the morrow, the little Manon of the Quai des Lunettes settled in triumph at the Calonne mansion. It was the way to the scaffold.
Skirting the quays, we reach the Saint-Michel Square, then the Rue Galande. In spite of recent demolitions, this old street still contains some ancient abodes; but it has lost the singular house called the Red Castle, or more prosaically, "the Guillotine."
In what was, during the seventeenth century, a sumptuous dwelling—the mansion, 'tis said, of Gabrielle d'Estrées—behind the huge, tall front steps at the back of the courtyard, was the dingy, smoky habitation, stinking of wine, dirt, debauch, and vice.
One had to step over the bodies of male and female drunkards to get inside the dens where such poor wretches came seeking some sort of lodging and an hour of forgetfulness. It was at once hideous and lugubrious. Amateurs of ugly sights might continue their studies hard by, on the premises of "Gaffer" Lunette, in the Rue des Anglais. The inhabitants were similar; a prison population—"bestiality in all its horror," as Mephistopheles sings in the Damnation of Faust. Recent building and sanitary improvements have done away with the "Red Castle."
The Rue Saint-Séverin is a picturesque medley of old houses round the ancient Gothic church—"that flora of stone"—one of the most curious perhaps in Paris; one of those that best preserve the traces of a past of art, devotion, and prayer.
The sublime artists who, in several centuries, knew how to create the
forest of fine carvings with which the apse is adorned, have, alas! left
but sorry successors. By the side of old painted glass windows, brought
from the church of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, other cold, modern stained
windows of loud colour have taken from Saint-Séverin's the religious,
poetical mysteriousness, the inviting half-obscurity that appeal to the
soul of the[Pg 173]
[Pg 174]
[Pg 175] believer; and their crude light renders only too visible
the marks of successive mutilations inflicted on this fine church. In
the next street, the present clergy-house is built on the old graveyard,
where, in 1641—as the erudite Monsieur de Rochegude informs us—the
first operation for gravel was publicly performed on a criminal
condemned to death, who, happy man, was cured, and pardoned by Louis XI.
The whole of the quarter is one of the busiest in Paris. It would seem
as if the vagabonds, the lewd and their lemans, the tatterdemalions of
bygone centuries, had left there a direct line of descendants. People
live in the street, eat scraps in low drink-shops; a smell of spirits
floats in the air at the corners of the various cross-roads; bars and
petty restaurants are thronged with customers. Part of the money begged
or stolen in Paris is spent there.
Saint-Médard's church is quite close, with its small, dusty, quaint Square, and its round tower at the end of the Rue Monge and the corner of the Rue Mouffetard. It is a gloomy, rat-gnawed, poverty-stricken church, looking as if worn-out with age; and is blocked in by old houses covered with gaudy-coloured advertisements. It has left, far behind in the past, the days when the tomb of the Deacon Pâris in it performed its miracles, when the townsfolk and courtfolk crowded in the small graveyard, a door of which still exists, the one perhaps whereon was written the famous couplet:—
"In the King's name, forbid is God
To work a wonder on this sod."
The Rue Mouffetard passes in front of the church porch, overflowing with
life and activity. A hundred petty trades are exercised in it; the house
doors themselves—old eighteenth-century doors—shelter women-sellers of
flowers, milk, fried potatoes, cooked mussels; children play about the
middle of the road; carriage traffic is rare. Housewives gossip on their
doorsteps, people live together—and in the street. The Passage[Pg 177]
[Pg 178]
[Pg 179] des
Patriarches, which opens at No. 99, was famous in days of yore. The
Calvinists, who used to preach there, had bloody quarrels with the
Catholics of Saint-Médard's. To-day, it is nothing but a dank, dirty,
melancholy alley, inhabited by bric-à-brac dealers, old-iron sellers,
and petty hucksters; and smells of rags, old lead, and cauliflower!
Maubert Square is the converging centre of these strange streets. At present, modernised and rearranged—adorned,[Pg 180] if I may say so, with a wretched statue of Etienne Dolet, who was burnt there in 1546—the Square only vaguely resembles the "Plac' Maub'," still visible six or seven years ago, ill-famed, narrow, bordered with old steep-roofed houses, a den of vagabonds, full of suspicious lurking-corners where the police might be sure of making good hauls. Near at hand, in the Maubert Blind Alley, Sainte-Croix used to dwell; and it was in the same mysterious retreat that Madame de Brinvilliers, the sorry heroine of the Poisons drama so well told by our witty friend, F. Funck-Brentano, used to meet her accomplice and with him prepare the terrible "succession powder," composed, according to her avowal, of "vitriol, toad's venom, and rarefied arsenic," which she made use of to poison her father, her two brothers, and to try to make away with her sisters and husband.
In 1304, Dante attended, hard by, one of the numerous schools of the Rue du Fouarre; and, at the corner of the Colbert-Mansion Street, the Faculty of Medicine had its amphitheatre. This curious building is still almost intact with its ancient cupola, and would supply an admirable piece of decoration to some retrospective museum of surgery.
Not far from this spot, the Rue Maître-Albert—which up to 1844 was
called the Rue Perdue—owes its present name to the Dominican Maître
Albert who, in the thirteenth century, taught in the open air in Maubert
Square. It contains curious houses, to-day dens for[Pg 181]
[Pg 182]
[Pg 183]
[Pg 184]
[Pg 185] tramps, who
spend the night in them. In 1819, an old negro of miserable appearance
and strange manners used to go down this dark street every evening,
trying his best to escape observation, and used to seek food and shelter
in one of its sorry eating-houses. People pointed him out as he went,
whispering that he was formerly Dubarry's black servant, Zamore, whom
Louis XV. had played with; Zamore who became a power, petted and courted
by noble lords, fine ladies, and princes of the Church that emulously
strove to gain the favourite's good graces. Later, having been appointed
a municipal officer under the Terror, he vilely, ungratefully, and in a
cowardly way, betrayed his benefactress, gave her up, and cast her
beneath the knife of the guillotine. At length, sinking lower and lower,
Zamore came and hid himself at No. 13, on the second courtyard floor of
this gloomy Rue Perdue, and died there on the 7th of February 1820.
 THE CHURCH OF SAINT-NICOLAS-DU-CHARDONNERET, AND THE RUE SAINT-VICTOR
THE CHURCH OF SAINT-NICOLAS-DU-CHARDONNERET, AND THE RUE SAINT-VICTORThe two churches nearest the spot are those of Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonneret and Saint-Julien-le-Pauvre. Connected with the former is a dismal little seminary, in which, under the guidance of the Abbé Dupanloup, the eminent philosopher Ernest Renan went through part of his theological studies. Every one should read in the Souvenirs of my Childhood and Youth the admirable pages this marvellous writer has devoted to his stay in this studious home. "The parish, which derived its name from the field of thistles well known of the students at the Paris University in the Middle[Pg 186] Ages, was then the centre of a rich quarter inhabited chiefly by the legal profession. The boarding-school régime weighed heavily upon me. My best friend, a young man from Coutances, I think, like myself, full of enthusiasm, and of excellent heart, held himself aloof, refused to reconcile himself, and died. The Savoy students showed themselves still less acclimatisable. One of them, older than I, owned to me that, each evening, he measured with his eye the height of the three-storey dormitory above the pavement of the Rue Saint-Victor. I fell ill; apparently I was doomed. My Breton soul lost itself in an infinite melancholy. The last angelus of evening I had heard resound over our dear hills, and the last sunset I had watched over the tranquil landscape came back to my memory like sharp arrows. In the ordinary course of things I ought to have died. Perhaps it would have been better if I had...."
The artist Le Brun's mother is buried in the Saint-Charles chapel of the church of Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonneret, and also Pierre de Chamousset, the inventor of the petty Postal service. Parisian ladies, bless his memory!
The church of Saint-Julien-le-Pauvre is set apart for the Greek ritual. Enclosed on its sides and rear by the ancient buildings of the Hôtel-Dieu, this melancholy-looking chapel is falling to ruin; a stopped-up well with meagre weeds growing from its border-stones seems to guard the door, which opens on a dirty, rubbish-strewn courtyard where a few half-starved fowls peck their scanty meal. It is a nook of poverty and suffering. The walls are damp and dingy; in these sombre yards, where a few sickly trees barely exist, all is solitude and abandon. Only three years ago, stretchers or ambulance carriages still stopped from time to time in it, and from them were taken victims of crime, disease, or accident, that had fallen in the street. Through the vast Paris, busy and indifferent, monopolised by its pleasures or its cares, one or another human wreck was brought to the Assistance Publique in this dismal Rue Saint-Julien-le-Pauvre with its suggestive name.
 THE JARDIN DES PLANTES—THE CEDAR OF LEBANON AND THE LABYRINTH
THE JARDIN DES PLANTES—THE CEDAR OF LEBANON AND THE LABYRINTHTo refresh ourselves after so painful a spectacle, let us come back to the lovely Parisian quays, and walk along the fair river, quivering in the daylight or in the moon's nightly rays; let us pass by the beautiful mansions of the Miramionnes, of Nesmond, of Judge Rolland, in front of the wine market—"catacombs of[Pg 190] thirst," and pause at the old Jardin des Plantes, dear to Buffon. A touch of the charm of things past, but not entirely vanished, lingers yet!
The trees are centuries old, the ornamental hornbeams have not been altered; there are aviaries and goat-pens which are the same as when Daubigny and Charles Jacques sketched them in 1843, to illustrate the handsome work published by Curmer.
The reptiles are better housed than in our childhood; but the hippopotamus wallows in the same basin; the giraffe stretches his neck over the same enclosures, and the elephant holds through the same railings his gluttonous trunk in search of rolls.
The bear-pit has not changed; and the crowd of idlers continue to tempt the eternal "Martin" to climb up the same tree. Still to the noisy children the delightful labyrinth offers its capricious meandering; and the cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus Libani) [Linnæus], which tradition tells us Monsieur Jussieu brought back in his hat, has not ceased to wave its ample branches over dreamers, loungers, workers, or grisette—the grisette that comes and sits beneath its venerable shade to read the exciting magazine story which fills with sweet emotion her heart athirst for the ideal!
And, in fine, is there anything nattier than the tiny rooms of the Louis XVI. buildings? which once formed Buffon's natural history cabinet, and whose delicate grey wood carvings made such a suitable framework for the admirable butterfly collections brought from every country.
Within these finely decorated and cosy rooms there was, so to speak, an ideal assemblage of blossoms, a fairy scene of exquisite colours, an enchantment wrought by a brilliant palette.
There they were, all of them, beautiful butterflies, with their metallic lustres from India and Brazil, French butterflies of a thousand tints, both the great death's-head sphynx and the little blue creature of the meadows.
Perhaps time had powdered and somewhat dimmed the marvellous brightness of their first colouring; but it was better so. Their pristine lustre would have been too great a contrast in the quaint surroundings, and it was an extra charm to see such gems of the air thus lightly decked with the dust of the past! To-day, alas! these rooms, flowering with sculpture, are closed and forsaken; a part of their wainscoting has disappeared.... Where have decorations so pleasing gone?... Why these everlasting, culpable mutilations, which I know are a grief to Monsieur Périer, the eminent Director of the Museum? The collections of butterflies are now transferred to the vast and sumptuous central hall of the new pavilion devoted to natural history. I liked them better in the charming rooms which once contained them and suited them so well!
The water-flowers bloom, as of yore, in the same low, stifling hot-houses, near the bizarre-shaped orchids; and it was in the old amphitheatre, where so many illustrious scholars taught, that the noble artist Madame Madeleine Lemaire,—the only "woman professor" that has ever held[Pg 194] a post at the Museum,—initiated her attentive, spell-bound audience into the divine beauty of flowers!
In all periods, artists have come and installed their light easel or their modelling-stands in front of the lions' cages, or in the Garden itself, on the grass, opposite the antelopes, hinds, walla-birds, or the goats of Thibet.
We remember, my brother and I, having, as little boys, accompanied our father, who was modelling from life the tigers and lions in the wild beasts' corridor. The odour was pungently alkaline, the heat sultry; we heard the hissing of polecats in the entrance and exit rotundas; sometimes a terrible roar, a complaint of anger, pain, or ennui, arose and shook the panes.
Most of these unfortunate animals, deprived of air and light, shut up in the horrible, narrow, stinking cages, died a lingering death of consumption. Indeed, they quickly grew familiar with those who spent whole weeks studying them; and their huge heads rubbed caressingly against the thick cage-bars, while their eyes became soft and almost tender.
Often we went, inquisitive, ferreting school-boys, to the reptiles' menagerie, an old building crumbling with age, and passed long hours peeping at the chameleons, gazing at the boa-constrictors, trying to rouse the sleepy crocodiles, which seemed to be already stuffed! What reminiscences and souvenirs in the dear old Jardin des Plantes, one of the few "Nooks and Corners of Paris" that have remained almost untouched!
On the side, the ancient house Cuvier lived in does[Pg 195]
[Pg 196]
[Pg 197] not look very
stable, and perhaps would go to pieces but for the network of plants
round it: ivy, birthwort honeysuckle, lianes of all kinds caparisoned it
with verdure. They are carpets, cascades of glossy green, shining
together: a nosegay of leaves in a garden.
Behind the Jardin des Plantes is Salpêtrière with its walls of evil memory, the Salpêtrière of the September massacres, the Salpêtrière whence Madame de Lamotte so easily escaped after her condemnation; with its broad gardens and its ugly covered-yards surrounded by railings, where, as De Goncourt said, "Women madder than their fellows" are confined. The dome, visible from everywhere, commands, like a lighthouse of misery, all this quarter infected by the Bièvre, the poor, sacrificed river, which is now in part walled over; the oily Bièvre, streaked with tannery acids, reddened by skins of sheep recently flayed that steep in it; the Bièvre which flows miserably and sordidly, but yet so picturesquely, amidst starch factories, fellmongers' stores and other works, after traversing the tiny gardens of Gentilly and creating the illusion of a landscape in the quarter of the Fontaine-à-Mulard.
Gone is the time when this ill-starred river washed the banks of smiling meadows and reflected the willows in its clear waters. Tamed, domesticated, adapted to tasks of every sort, unceasingly used by tanners, curriers, tawers, dyers, it flows dirty and putrid! To follow it in its windings, the Rue du Moulin-des-Prés must be ascended, and entrance made into the Rue de Tolbiac.[Pg 198] There, through a gate, it enters a dark, dismal passage, whence it will issue only to glide in a kind of sinister-looking canal between black, repulsive manufactories. Here and there, along the scanty banks, a few washerwomen have fixed their tubs on a level with the water, and sing as they dolly their linen; elsewhere, wretched urchins endeavour to catch a stray fish that might have lost its way in the mephitic stream. Then the Bièvre disappears once again and this time underground, coming to view afresh in the Rue des Gobelins. At this spot, some rare traces of a glorious past are discovered. The ancient houses have many of them remained. But how often transformed! The owners of works and of shops, after enslaving the river, have taken possession of the houses bordering it.
Offices, warehouses, leather stores have invaded the noble mansions of the sixteenth century, and the Bièvre winds, as if ashamed, through poor gardens, like it, fallen from their antique splendour.
Further on, there are more works and tanneries, black corners mean and malodorous, where thousands of rabbit-skins, hanging in mid-air, hard and dry, clash together with a noise of wood. To the very end, the unlucky river, harassed and exploited, cleans blood-stained skins, moves heavy wheels, or washes ghastly offal, amidst a smell as of barege. Finally, it runs to earth once more beneath the Hospital Boulevard, within evil-smelling, dark holes.
But before the last fall, the Bièvre passes through[Pg 199]
[Pg 200]
[Pg 201] an astonishingly
strange lane, one of the oddest in this odd quarter: the Ruelle des
Gobelins. It flows as a stream of red, green, and yellow tints, between
patched-up, mouldy, tumble-down houses, in an odour of ammonia. And yet,
near these hovels, among the heaps of tan, beside pits in which are
macerating skins of flayed animals, a gem of carving rises as it were an
appeal of beauty, a vestige of past splendour. It is the sculptured
remains of an adorable Louis XV. pavilion of which Monsieur de Julienne
had made a hunting-box; and this lovely paradox, this blossom of stone
cast among such a mass of ugliness, is not one of the least surprises of
the quarter so fertile in matters for astonishment. Moreover, a few
yards from this sewer, the artists of the Gobelins Manufactory have laid
out their work-and-study-gardens, in which shine the purple, gold and
azure of the prettiest flowers in France. These, cleverly distributed,
arrange a carpet of exquisite and radiant colours athwart the
surrounding district of sombre sadness.
On the confines of the town, is the Butte-aux-Cailles, a vast piece of waste land, cheerless and without charm, which, until 1863, was a sort of fresh country spot, with mills and farms on it. To-day, it is a quarter of hard labour, where numbers of rag-pickers classify the refuse of Paris. At the corner of the Ruelle des Peupliers, faggot-dealers have set up their huts; and hovels line strange streets made with the clearings of other streets.
Once, these spacious grounds were one stretch of[Pg 202] flower gardens and market gardens watered by the Bièvre.
In a most interesting book, somewhat forgotten now, Alfred Delvau tells us much of the former history, under Louis-Philippe, of the Saint-Marceau faubourg, the Butte-aux-Cailles, the Rue Croulebarde, and also the Rue du Champ-de-l'Alouette, in which last street the "Shepherdess of Ivry" was murdered, the crime by its bizarre character producing a deep impression in the Capital in 1827. It was a public-house waiter, Honoré Ulbach, who had stabbed a girl, Aimée Millot by name; she, as a keeper of goats, was popular at Ivry. Every day, she was to be seen, with a large straw hat on her head and a book in her hand, tending her mistress's goats. The "Shepherdess of Ivry" she was called in the neighbourhood; in 1827, there were still shepherdesses in Paris!
The trial that followed excited the whole town; the crime was one of love and jealousy; the victim was nineteen; she was virtuous and a shepherdess; women "cursed the murderer, even while pitying him perhaps," wrote the newspapers of the time; and even the giraffe but recently arrived at the King's Garden was neglected for the Ivry drama.
On the 27th of July, Ulbach, who seems to have been half-mad, was condemned to death; and, at four o'clock in the evening on the 10th of September, he was executed on the Grève Square.
A Municipal Crèche, in the Rue des Gobelins,[Pg 203]
[Pg 204]
[Pg 205] occupies, at No. 3, a
fine Louis XIII. mansion, once inhabited by the Marquis of Saint-Mesme,
a lieutenant-general and the husband of Elizabeth Gobelin, close to a
handsome lordly-looking building which in the quarter bears the name of
Queen Blanche's Mansion.
The legend attaching to the latter is false, affirms Monsieur Beaurepaire, the learned and amiable librarian of the City of Paris. "It was," he says, "simply Catherine d'Hausserville's home, where Charles VI. was nearly burnt alive during the performance of a ballet, his fancy dress having caught fire." The edifice, with its noble appearance, forms a strange contrast in this poor yet picturesque district.
Another fine mansion, in the Rue Scipio, is the one built by Scipio Sardini, in the reign of Henri III., with terra-cotta medallions, rare Parisian specimens of the exceedingly pretty decoration that pleases us so much at Florence, Pisa, and Verona. This Scipio Sardini was a peculiar man, and his story deserves to be told. Of Tuscan origin, he came to France after the death of Henri II., just when Catherine de Medici seized the reins of power. Amiable, witty, ingratiating, a great financier, clever in his enterprises, and unscrupulous, he quickly gained a preponderant position in the frivolous, dissolute, mirth-loving Court. He excelled in combining business and pleasure. An illustrious marriage seemed to him essential to people's forgetting his low origin and the rapid rise of his fortunes. He married the "fair Limeuil," one of the most seductive beauties of the[Pg 206] Queen's flying squadron—"All of them capable of setting the whole world on fire," said Brantôme. This attractive person had been successively courted by the most noble lords of the Court before effecting the conquest of Condé, by whom she had a child. At Dijon, during one of the Queen's receptions, Mademoiselle de Limeuil was taken ill and was delivered of a boy. "It is inexplicable," writes Mézeray, "that such a prudent woman should have so miscalculated." There was a scandal; the Queen Mother was indignant; the fair Isabella was imprisoned; but Condé who was still amorous, succeeded in effecting her escape. The Protestants, however, were on the watch, and induced their leader to give up his too compromising mistress. Then it was that Scipio Sardini came forward, the richest man of the period, the King's banker, as also the nobles' and clergy's. He managed to get himself accepted; the marriage took place; and he settled in this pretty mansion that we still admire, and that is mentioned by Sauval as one of the most beautiful in Paris, amidst vineyards, orchards, and fields bordering on the Bièvre. There he lived, surrounded by luxury, works of art, books and flowers, and died there about 1609. As early as 1636, the mansion was converted into a hospital, which in 1742 was once more transformed, this time into a bakery. To-day, it is the Bakery of the City of Paris Hospitals.
Let us keep along by the Wine Market, and, before crossing to the right
bank of the river, respectfully pause on the Stockade Bridge, close to
the small monument[Pg 207]
[Pg 208]
[Pg 209] erected to the famous sculptor Barye by his
admirers,—to the great Barye who, misunderstood and mocked, sold up by
his creditors, often came in the evening, after leaving his modest
studio on the Célestins Quay, to forget his sufferings and muse in this
same place before the splendid panorama of Paris crowned by the grand
silhouette of the Panthéon. Here, too, is one of the City's best views.
Nothing is more relative than an impression felt. To certain minds in love with the Past, this or that ruin is much more affecting than the most modern palace; it is the same with streets, houses, and pavements.
An exquisite hour to call up the soul of old Paris is at twilight.
The colour peculiar to each object has melted into the general shades and tints spread by the day which is departing and the night which comes.
Delicate lace-work outlines stand out against the sky, while huge violet, black, and blue masses of atmosphere bathe whole streets in fathomless mystery. Then thought awakens, souvenirs revive and grow clear; scenes are lived through again of which these streets and houses were the silent witnesses. One hears cries of fury or of joy; drums beat, bells ring, groups pass singing 'mid these dream visions that rise again!
In order to enjoy such an experience no better spot could be chosen than the Stockade Bridge, which, with[Pg 210] its barrier of black beams, as it were shuts off to the east Paris of the olden days.
The City slumbers in the calm of evening, the smoke curls lazily up. Afar sound bells; swallows sweep crying in the air embalmed by falling night; noises ascend vague and weird, interpreted according to the fancy of one's musings. All life seems to sleep; the soul of the past awakes. It is the hour desired.
The Arsenal quarter, built over the site of the two Royal Palaces—the Saint-Paul mansion, the Tournelles palace—and the soil of the Louviers Isle, joined to the river bank in 1843, serve as a natural transition from the old to modern Paris.
Notwithstanding its warlike name, the Arsenal quarter is one of the most peaceful parts of the Capital. Centuries ago, the palaces disappeared that brought it its wealth, life and movement. On their ruins and their huge gardens, humble, tranquil streets have been made: the Rue de la Cerisaie, where Marshal Villeroy received Peter the Great in the sumptuous Zamet mansion; the Rue Charles V., where once was the elegant home of the Marchioness de Brinvilliers, now at No. 12, premises in which a white-capped sister-of-charity distributes cod-liver oil and woollen socks to poor, suffering children; the Rue des Lions-Saint-Paul;[Pg 214] the Rue Beautreillis, where Victorien Sardou was born; near there the great Balzac dwelt. "I was then living," he says in his admirable Facino Cane, "in a small street you probably don't know, the Rue de Lesdiguières. It commences at the Rue Saint-Antoine, opposite a fountain near the Place de la Bastille, and issues in the Rue de la Cerisaie. Love of knowledge had driven me into a garret, where I worked during the night, and spent the day in a neighbouring library, that of Monsieur. When it was fine, I took rare walks on the Bourdon Boulevard." This modest Rue de Lesdiguières still exists in part; on the site occupied by Nos. 8 and 10, could be seen, a few years ago, one of the containing walls of the Bastille; narrow houses have been stuck against it; and, at No. 10, it is the very wall of the old Parisian fortress which constitutes the back of the porter's lodge! What a destiny for a prison wall!
Of what was once the Arsenal only the mansion of the Grand Master is left; it is, at present, the Arsenal Library—formerly called, as Balzac says, the Library of Monsieur. It used to be a fine dwelling, the home of Sully, and possesses priceless books and autographs, and most valuable writings. In a coffer, covered with flower-de-luces, may be admired Saint Louis's book of hours, side by side with a fragment of his royal mantle, the blue silk of it, worn with time, being strewn with golden flower-de-luces; the old book bears this venerable inscription: "It is the psalter of Monseigneur Loys,[Pg 215] once his mother's;" and was taken from the scattered treasures of the Sainte-Chapelle. Then there is Charles the Fifth's Bible with the King's writing on it: "This book (belongs) to me, the King of France;" and a missal, each leaf of which is framed with an incomparable garland due to the brush of the "master of flowers," a great artist whose name is unknown to us. Besides,[Pg 216] there are rare manuscripts, marvellous bindings, unique editions, romances of chivalry, classics, poets of every age, complete in this fine palace; together with Latude's letters, the box that served for his ridiculous attempt against Madame de Pompadour; and, near them, the cross-examination of the Marchioness de Brinvilliers, and the death-certificate of the Man in the Iron Mask; Henri IV.'s love-letters too, with his kisses sent to the Marchioness de Verneuil, and the documents relating to the affair of the Necklace. How many more things in addition...!
Let us add that the curators—Henri Martin, so learned and obliging, Funck-Brentano, the exquisite historian of the Bastille, the picturesque relater of all its dramas. Sheffer and Eugène Muller are not only scholars needing no praise but most courteous and genial men—and you will quite understand why the Arsenal is one of the few corners in Paris where it is delightful to go and work or to saunter about. Indeed, it is a tradition of the house. Nodier, good old Nodier, who was one of Monsieur de Bornier's predecessors and a predecessor also of J. M. de Heredia, the master who has so recently gone from us, Nodier, the admirable author of the Trophées, had succeeded in making the Arsenal the centre of literary and artistic Paris. Hugo, Lamartine, de Musset, Balzac, Méry, de Vigny, and Fr. Soulié used to meet there; and fine verses were said while regarding the sun glow with red flame behind the towers of Notre Dame.
"The towers of Notre Dame his name's great H composed!"
wrote Vacquerie.
Of the Bastille nothing remains except a few stones which formed the substructure of one of the old towers; and these have been carefully removed to the Célestins Quay, along the Seine, where they are visible to-day. In vain, therefore, would any one now seek for a vestige of the sombre fortress over which so many legends hovered. Latude's great shade itself would hardly locate the spot; and yet how full Paris history is of this traditional Bastille, which the people, amazed with their easy victory, could not tire of visiting after the 15th of July 1789. Such was their curiosity and such their eagerness that Soulès, the governor appointed by the Parisian municipality, was compelled to stop the visits, on the curious ground "that such damage had already been done to the fortress by visitors that more than 200,000 livres would be required to repair it." Repair the Bastille! The souvenir manuscripts of Paré tell us the fury excited by this strange pretension in Danton, sergeant of a section of the National Guard, who, with his company, was turned back by the order.
Danton had himself admitted into the presence of the unfortunate Soulès, seized him by the collar and dragged him to the Town Hall; the prohibition was removed; and Citizen Palloy was thenceforth allowed to exploit the celebrated State prison. The stones were "hewn and cut into images of the fortress and dedicated to the various departments and assemblies," or into "commemorative slabs intended to rouse people's courage." Palloy cut up the leads into medals, and made rings with the iron[Pg 220] chains; out of the marble he manufactured games of dominoes, and had the delicate thought to offer one of these games to the young Dauphin to inspire him with "the horror of tyranny."
 COMMEMORATIVE BALL ON THE RUINS OF THE BASTILLE
COMMEMORATIVE BALL ON THE RUINS OF THE BASTILLEBalls were held on the site of the Bastille. Wine flowed, fiddles were scraped, and printed calicoes of that period show us the ruins of the old Parisian citadel surmounted with this inscription: "Dancing here."
The huge space left vacant by the demolition had to be filled up. Napoleon I., whose artistic conceptions were sometimes disconcerting, had constructed there, in 1811, by Alavoine, a strange sort of fountain of bizarre appearance: it was a colossal elephant, twenty-four metres high, which spouted water from its trunk. Built temporarily in plaster and mud, the elephant quickly crumbled away under the action of weather and rain; and soon became a lamentable débris surrounded with disjointed planks. The urchins of the district made it the scene of Homeric struggles; but the real familiars were the rats that had made their home inside the structure, so that, when the demolition began, regular battues had to be organised with men and dogs; and, for months, these dreaded rodents infested the terrorised quarter. In 1840, the present column was erected; since then, the genius of Liberty has poised over Paris his airy foot, and Barye's fine lion watches over the repose of the victims of 1830 that are interred within the crypt of the monument.
The Rue Saint-Antoine contains certain handsome[Pg 221]
[Pg 222]
[Pg 223] mansions: the Cossé
mansion, where Quélus died; the Mayenne and Ormesson mansion, built by
du Cerceau on the remains of the Saint-Paul mansion and Germain Pilon's
studio; the Sully mansion, whose noble front was not long ago mutilated.
Hard by, at the corner of the Rue du Figuier and the picturesque Rue de
l'Hôtel de Ville, which latter used to be the Rue de la Mortellerie,
stands what is left of the Sens mansion, the only specimen, together
with the Cluny Museum, of what private architecture was in the fifteenth
century. After being inhabited by Princes of the Church, Bishops,
Cardinals, and also by Marguerite de Valois (Queen Margot), the Sens
mansion fell on evil days. It became the "Diligence Office"; and from
its courtyard is said to have started the famous courier whose murder
was attributed to Lesurques, the unfortunate Lesurques popularised by
the well-known drama performed at the Ambigu, which caused so many tears
to flow.
In more recent times, the Hôtel de Sens derogated further still. It became a manufactory of sweets!
At No. 5 of the Rue du Figuier, we meet with a draw-well, the top of which is finely sculptured; the spot brings back the memory of Rabelais, the admirable Rabelais, who died quite near, in the Rue des Jardins. At No. 15, opened the sixteenth-century door through which the actors of the illustrious theatre established on the ancient site of the Jeu de Paume de la Croix-Noire, proceeded to their private stage-room. It was before this door that Molière was arrested and taken to the[Pg 224] Châtelet, because he owed "142 livres to Antoine Fausseur, master-chandler, his purveyor of light."
Let us cross the Place de la Bastille and go down the Rue du Faubourg-Saint-Antoine. There, at No. 115, in front of an old eighteenth-century house, the Deputy Baudin was killed against a barricade, on the 3rd of December 1851. At No. 303, in the reign of Napoleon I., stood Dr. Dubuisson's private hospital, where General Malet was confined. There he hatched the prodigious plot the disconcerting history of which we intend shortly to relate. Farther on, near the Rue de Montreuil, we pass by the remains of Réveillon's wall-paper stores, pillaged on the 17th of April 1789; it was one of the preludes of the Revolution.
Last of all, at No. 70, in the Rue de Charonne, Dr. Belhomme's private hospital stood, which was used as a special prison under the Revolution. Only those were admitted who could pay and pay well. The irrefutable memoirs of Monsieur de Saint-Aulaine reveal to us a Belhomme familiar, cynical, exacting his fees and thouing Duchesses short of money who haggled with him on the question of their life. The most amiable of historians, my excellent friend G. Lenôtre, whom it is always necessary to quote when facts of the Revolutionary epoch are in question, has reconstituted the terrible and surprising story of the Belhomme institution where they laughed, danced, or even flirted under the dread eye of Fouquier-Tinville; and has related, with his habitual documentation, the bizarre liaison of the Duchess of[Pg 225] Orléans, widow of Louis-Philippe Egalité, with Rouzet, the Conventional, buried later at Dreux under the name of the "Count de Folmon" in the Orléans family vault.
Pursuing our way and passing by the Church of Sainte Marguerite, in which Louis XVIII. was interred ... or his double, we reach the barrier of the Throne (the Throne overthrown, people said in 1793). The scaffold, which had temporarily quitted the Revolution Square, was put up here during the most terrible period of the Terror, and the "great batches" were executed upon it. In six weeks, 1300 victims perished, among them, André Chénier, the Baron de Trenck, the Abbess of Montmorency, Cécile Renaud, Madame de Sainte-Amaranthe, the poet Roucher, and many others. The bodies of these unfortunate people, stripped of their clothing, were loaded each evening on covered waggons, with their severed heads between their legs; and the horrible vehicle, dripping with blood along the road, was tipped into some pit dug at the bottom of the Picpus Convent Gardens, where still exists the cemetery of those that were executed during the Revolution.
Retracing our steps, we arrive at No. 9 of the Rue de Reuilly; here was once the Hortensia Tavern, kept in 1789 by the famous Santerre, a major in the National Guard. The house has not much changed; at present, however, it is a girls' boarding-school which occupies the large rooms where the thundering General organised those terrible descents on Paris and launched those[Pg 226] dreadful battalions of the faubourg that terrorised even the Convention itself.
 THE PROVOST HUGUES AUBRYOT'S MANSION
THE PROVOST HUGUES AUBRYOT'S MANSIONOn the other side of the Place de la Bastille, in the Rue Saint-Antoine, near Saint Paul's Church, is the Charlemagne Passage, most picturesque by reason of the old souvenirs it contains and the strange population it harbours: chair-menders, mattress-carders, milk-women, open-air flower-women gather round the ruin of the charming mansion which, under Charles V., was the sumptuous abode of the provost, Hugues Aubryot.
The front, which is still remarkable and fine-looking, is an astonishing contrast to the poor, low houses that huddle round it. Fowls peck at the foot of the fifteenth-century turrets, which enclose a handsome staircase; and patched linen dries on iron wire stretched between the caryatide windows of the seventeenth century, replacing those behind which once mused the Duke d'Orléans and the Duke de Berri, as also, in 1409, Jean de Montaigu, beheaded for sorcery! who were formerly illustrious guests in this elegant dwelling.
And now, let us stop at the Vosges Square on the other side of the
Bastille. It is another rare nook of our old City, which, through the
centuries, has preserved its ancient character very nearly intact. The
houses there, in Louis XIII. style, have not changed. The scenery has
remained the same. The Précieuses could take their favourite walks
there; and those punctilious in honour might draw their sword, as in the
time of Richelieu and the Edict-malcontents; only the public[Pg 227]
[Pg 228]
[Pg 229] of
spectators would be quite different. The fine ladies of the country
hight Tender, the Cydalises and Aramynthas, the lords once living in
those noble dwellings, they who, on the 16th of March 1612, were present
at the tournament given by the Queen Regent, Marie de Médici, in honour
of the peace concluded with Spain, or they who proceeded in grand
coaches to the fair Marion de Lorme's or to Madame de Sévigné's, are
to-day replaced by petty annuitants, modest shopkeepers retired from
business and pensioned-off officers. Humble charwomen work at their
tasks in the spots where Mazarin's nieces paused in their sedan-chairs;
and the numerous Jews that live in the quarter meet there on Saturdays.
It is a curious spectacle to see these men and women of strongly marked
type betaking themselves to the Synagogue, which is near a partially
subsisting eighteenth-century mansion still bearing delicate
decorations, but at present occupied by a butcher, in the Rue du
Pas-de-la-Mule. Not a few old men wear the long gaberdine, their hair in
corkscrew curls, and earrings in their ears. Velvet-eyed girls coifed
with bands, wonderfully handsome and peculiarly dressed, assemble there
on certain religious feast-days. It is a strange evocation; 'twould seem
that in these peaceful quarters biblical traditions have been preserved
in some Jewish families.
The old-time animation, however, is an exception. The Vosges Square, once the Place Royale, where Richelieu lived and Fronsac, Chabannes, Marshal de[Pg 230] Chaulnes, Rohan-Chabot, Rotrou, Dangeau, Canillac, the Prince de Talmont and Mademoiselle du Châtelet, where Madame de Sévigné was born, where the tragic actress Rachel dwelt, and Théophile Gautier and Victor Hugo, is to-day completely neglected; and this delightful Paris nook, where so much wit was spent, such fine ladies rivalled in grace and elegance and so many exquisites drew their swords, is now nothing but a large, lonely garden, provincial and melancholy, frequented almost exclusively by the pupils of neighbouring boarding-schools, who play there at prisoners' base, and leap-frog, beneath the debonair shadow of Louis XIII.'s statue, with its philosophic frame of a Punch-and-Judy show and a chair-woman's stall.
In the ancient Rue Culture-Sainte-Catherine (at present called the Rue
de Sévigné) on the site now occupied by No. 11, formerly stood the
Marais theatre, built with money provided by Beaumarchais. In 1792, the
Guilty Mother was performed there, for the benefit, said the
play-bill, "of the first soldier who shall send citizen Beaumarchais an
Austrian's ear." The modern building is a modest private-bath
establishment, with a small garden in front in which grow some
spindle-trees—in boxes, and which is adorned with silvered balls. The
huge wall, all grim and grey, backing the slightly-built bath
establishment, is the old wall of the Force Prison, where, on a post at
the corner of the Rue des Balais, Madame de Lamballe was executed, where
also Madame de Tallien was transferred, and Princess de Tarente was[Pg 231]
[Pg 232]
[Pg 233]
confined, the latter, the grandmother of the kind, courteous and learned
Duke de la Trémoïlle, who had only to dip into his incomparable family
archives to give us the most precious documents of French history, and
to whom we are indebted for those picturesque and exciting "Souvenirs of
Madame de Tarente," one of the most valuable narrations by an
eye-witness of the Revolutionary period.
The Carnavalet mansion, Madame de Sévigné's "dear Carnavalette," is close by, as also the ancient Le Peletier-Saint-Fargeau mansion, to-day the City of Paris Library. It is a fine, large building of noble appearance, which contains wonderful books, maps, plans and manuscripts. The written history of Paris is there; and all workers know the pretty, sculpture-ornamented room of Monsieur le Vayer, the erudite, obliging Curator of these fine collections. Messieurs Poète, Beaurepaire, Jacob, Jarach and Wilhem, in the Library; Messieurs Pètre and Stirling in the History room are the wise and welcoming hosts of this admirable Parisian Library.
All this Marais quarter, indeed, contains sumptuous mansions, not one of which, alas! has been respected. All are given over to business and manufacturing. The Lamoignon mansion is occupied by glass-polishers and garden-seatmakers; the Albret mansion by a bronze lamp-dealer; those of Tallard, Maulevrier, Sauvigny, Brevannes, Epernon, &c., are still standing, but in what a state! The Rue des Nonnains-d'Hyères offers us its curious bass-relief, in painted stone, representing a knife-grinder[Pg 234] in eighteenth-century costume. In 1748, a Madame de Pannelier kept a "wit-office" in this same street; Lalande, Sautereau, Guichard, Leclerc de Merry used to attend meetings there. They were held on Wednesdays, and were preceded by an excellent dinner. The tradition has happily been preserved in Paris.
In the Rue François-Miron, one sees a spacious, handsome mansion with circular pediment, escutcheons and garlands. It is the Beauvais mansion, built by Le Pautre in 1658.
To look at it now, old and in a dull street, one would hardly think that the coaches of Louis XIV.—King Sun—had passed under the dark vault of the entrance gate and that, from the top of the central pavilion balcony, Queen Anne of Austria, in company with the Queen of England, Cardinal Mazarin, Marshal de Turenne and other illustrious nobles, had watched her son Louis XIV. and her daughter-in-law, the new Queen Marie-Thérèse of Austria, go by as they made, through Saint-Antoine's Gate, their solemn entry into Paris on the 26th of August 1660![3]
On account of its picturesque aspect and the fine mansions it contains, the Rue Geoffroy-l'Asnier is one of the most curious in Paris. At No. 26 stands the Châlons-Luxembourg mansion, with its monumental door and wonderful knocker. At the bottom of the courtyard is an exceedingly elegant Louis XIII. pavilion in brick and stone, and of delicate proportions. The[Pg 235] mansion was built for the second Constable of Montmorency, and though it is quite lost in this gloomy quarter, it maintains its proud bearing.
After the Revolution, this street, whence nearly all the owners of houses had emigrated, if they had not been guillotined, was completely stripped of its former splendour. Petty annuitants, small clerks, and poor people took up their abode in the abandoned buildings. Grass grew in the streets; many of the dwellings had been sold as national property; and the Rue Geoffroy-l'Asnier underwent the common fate; it became democratic.
Between this street and the neighbouring Rue des Barres, one is surprised to see a sort of fissure so narrow that two persons would find it difficult to walk abreast through it, a sort of corridor along which the wind[Pg 236] sweeps past dilapidated, leaning houses on either side. It is the Rue Grenier-sur-l'Eau, wretched and dirty enough, but quaint, with the glorious tower of Saint-Gervais-Saint-Protais in the background, rising and standing out against the sky.
The proper moment to take a look at the sinister little Rue des Barres is on a stormy night, behind the church of Saint-Gervais. It is then easy to imagine what this quiet quarter must have been like when, on the 9th of Thermidor, about eleven in the evening, 'mid torch-lights, calls to arms, the noise of the tocsin and shouts of the multitude, the dead body of Lebas was brought thither, and, on a chair, Augustin Robespierre, who had broken his thighs in leaping from one of the Town Hall windows. The dead man and the dying man were dragged to the Barres mansion transformed into a Sectional Committee Tribunal. On the morrow Lebas was buried, and Robespierre was carried before the Committee of Public Safety, who sent him to the scaffold.
The Rue des Barres descends to the Seine, near the old Town Hall Quay, where the big, flat boats laden with apples, stones, or sand take their moorings. Into it opens one of the exits of the charming Church of Saint-Gervais, whose fine painted windows, masterpieces of Pinaigrier and Jean Cousin, were almost totally destroyed twenty years ago by an explosion of dynamite. Against the church walls, in the laicised ruins of an ancient chapel, a sweet manufacturer has[Pg 237] installed his alembics and copper pans; and it is a curious sight to see the lighted fires of this strange kitchen beneath these antique Gothic arches, between these blackened pillars still bearing traces of the candles that once burned in front of the holy images, on a ground formerly used for burying and even now concealing bones. The out-offices of the old church still remain, wonderfully picturesque, and open into the[Pg 238] Rue François-Miron, No. 2, on the left of the entrance portal of the church, between a laundress's establishment and a furniture-remover's premises!
 THE BARBETT MANSION
THE BARBETT MANSIONOn one side, the little Rue de l'Hôtel-de-Ville brings us to the Rue Vieille-du-Temple, where we can admire, at No. 47, what is left of the quaint mansion of the Dutch Ambassadors, where "Monsieur Caron de Beaumarchais and Madame his spouse," as an almanac of 1787 called them, established in 1784 a Provident Institution for poor nursing mothers. Indeed, it was for the benefit of this undertaking that the fiftieth performance of the Mariage de Figaro was given. Farther on, to the right, at the corner of the Rue des Francs-Bourgeois, stands the pretty turret built about 1500 for Jean Hérouet; and, last of all, the[Pg 239] fine Rohan palace, which to-day is the National Printing House. This last is a noble and spacious building which the elegant Cardinal that once lived in it took pleasure in sumptuously decorating. A masterpiece may be seen there, "the Horses of Apollo," in a wonderful bass-relief by Pierre Le Lorrain. The saloon of the Apes, by Huet, is charming, and the private room of Monsieur Christian, the witty and learned Director of the National Printing House, contains a beautiful Caffieri time-piece. Why must, alas! this fine palace be condemned soon to disappear? The Rohan mansion is to be demolished, and the State will commit the sacrilege! May the endeavours of lovers of Paris succeed in preserving for us this precious vestige of a past that each day removes farther from us!
A cabman whose astonishment must have been great was a certain George who, on the 22nd of October 1812, at half-past eleven in the evening, amid a driving rain that turned the miry soil of Saint-Peter's pudding-bag (now the Villehardouin blind alley) into a veritable bog, saw get out of his cab, near the Rue Saint-Gilles, a completely naked man, with his uniform under his arm—a soldier whom, twenty minutes before, he had picked up in the Louvre Square. This strange passenger was Corporal Rateau, proceeding to the appointment made with him by General Malet, inside Dr. Dubuisson's private hospital and asylum, 303 Faubourg-Saint-Antoine, where the latter was[Pg 240] confined by the authorities. In his haste to put on the fine uniform of an orderly officer, which was ready for him in exchange for his own, Rateau had undressed in the cab; and up the dark staircase of the gloomy house in the gloomy street he rushed with absolutely nothing on.
The little house still exists, wretched and dingy-looking, where Malet appointed to meet his accomplices, on the third floor in the abode of the Abbé Cajamanos, an old bewildered Spanish priest who had quitted the Bicêtre asylum.
This adventure of General Malet's is both prodigious and disconcerting. For, in 1812, at the moment when Napoleon seemed to be at the summit of his power, Malet, in a sort of dungeon, with the help of five or six obscure assistants, an old priest with hardly any knowledge of French, a half-pay officer, an almost illiterate sergeant and a few other hare-brained people, had been able, even while confined, watched and suspected, to combine everything, prepare everything, so that the report of the Emperor's death might be believed—the Emperor being absent in the icy steppes of Russia, and no news arriving from him. And his calculations were justified. All the Imperial functionaries, from Savary, the head of the police, down to Frochot, the Prefect of the Seine, accepted General Malet's allegations, without testing or discussing them. Especially, all believed his fine promises; and it is hard to say where the hoaxer would have stopped if[Pg 241] an officer, simply obeying his orders, had not refused to be gained over with fine words, and asked for proofs. Malet, being taken aback, grew impatient, and replied with a pistol-shot. Major Doucet forthwith arrested him, and the comedy ended in a tragedy.
All the more haste was made to get rid of the organisers of this plot, which had so nearly succeeded, as it was necessary to suppress as quickly as possible their awkward testimony to such cowardice, lying, and compromise.
The poor dwelling in the Villehardouin blind alley was searched by all the Paris police; papers, uniforms, cocked hats, and swords were fished out of the little well, still existing, into which they had been wildly thrown. In a few hours, Malet, Lahorie, Rateau, and Guidal were tried, condemned, and executed. The replies of the General to the Tribunal that so summarily judged him were home-thrusts. Asked (somewhat late) who were his accomplices: "All of you," he said, "if I had succeeded!"
Taken to the wall of evil memory in the plain of Grenelle, he insisted on giving the firing-order to the execution-platoon; and, as if he had been on the drill-ground, made the soldiers repeat the aiming movement, which had not been carried out with military precision. Rateau, who, as a matter of fact, had understood nothing of this strange drama, in which he had been one of the most picturesque confederates, is said to have died in crying: "Long live the Emperor!"
Between the Archives and the Rue Sainte-Croix-de-la-Bretonnerie, there was once a large monastery, which, in 1631, became the property of the Carmelite Billettes,—the name being derived from an ornament worn by these monks on their gowns. The Revolution suppressed the monastery; but the small cloister has come down to us with its charming proportions and its monastic cosiness. To-day, it is a Town School, and the neighbouring church is devoted to Protestant worship.
The Rue de Venise, one of the most ancient Paris streets, is not far away. It is now a low, bad-smelling lane inhabited by vagabonds of both sexes. Women, whose age it is impossible to tell, trail and traipse in front of alleys within which loom greasy, black staircases. Mended linen hangs from the windows; acrid smoke issues from between thick bars protecting old mansions now degenerated into mere dens, defended, however, by heavy doors studded with rusty nails.
It is hideous, yet quaint, as indeed all this quarter, which is made up besides of the Rue Pierre-au-Lard, the Rue Brise-Miche, and the Rue Taille-Pain; not forgetting Saint-Merri's cloister, the name being that of the old church whose tocsin so often sounded the alarm during the riots in the reign of Louis-Philippe.
At the least popular excitement, this inextricable labyrinth of small
streets used to bristle with barricades. At the crossing of the Rue
Saint-Martin and the Rue Aubry-le-Boucher was raised the terrible[Pg 243]
[Pg 244]
[Pg 245]
barricade defended by Jeanne and his intrepid companions. Following on
the burial of General Lamarque, who died while pressing to his lips the
sword offered to him by the Bonapartist officers of the Hundred Days, an
immense revolutionary movement had galvanized Paris. The old soldiers of
the Empire, the survivors of the Terror and those of 1830, allied in
their common hatred of Louis-Philippe's government, had joined the
malcontents of all parties and the members of the then numerous secret
societies. In the evening of the 5th of June 1832, the centre of Paris
was covered with barricades; and both troops and National Guard had been
obliged to reconquer, one by one, the positions that had been lost.
Slaughter had been going on the whole night. When the dawn of the 6th of
June tinged the house-roofs with pink, the large Saint-Merri barricade
was seen to be holding out; its defenders, a handful of heroic men, had
sworn to bury themselves under its ruins. Already they had repulsed ten
furious assaults; now they were awaiting death; and the loud tones of
the Saint-Merri tocsin, unceasingly sounding above their heads, seemed
to be tolling their funeral knell! Part of the Paris army had to be
utilised to vanquish these dauntless insurgents. Firing went on from
windows, cellars, the pavement. Round the barricades, dead bodies of
National Guards and soldiers, riddled with balls, crushed beneath blocks
of stone hurled from roof-tops, testified to the frightful savagery of
this intestine struggle. For long afterwards,[Pg 246] the ground was red with
blood! What numbers of balls and bullets, what quantities of grapeshot
all these old house-fronts have received in the haphazard of riots,
frequent during the reign of Louis-Philippe.
The drums no sooner beat than the citizens armed and hurried to defend order ... or to attack it; anxious women, cowering behind closed shutters, watched for the biers.
Things resumed their ordinary course immediately the disorder was over; the insurgent hobnobbed with the honest National Guard whom he had aimed his gun at on the day before. Sometimes, however, grudges remained.
My parents knew an old woman, living in the Rue Saint-Merri, who, for
forty years after 1836, never passed without trembling by the door of
the tenant underneath her flat. As people were surprised at this
persistent apprehension, she said: "If you only knew what happened to
me!" and she related that, one evening when there was a riot and her
husband had been absent all day firing in the ranks of the National
Guard, she was in the house alone, mad with anxiety; suddenly, at the
corner of the street, she saw a stretcher appear, covered with sacking,
which the bearers deposited at her door. Was it her husband that they
were bringing home dead? She rushed out, raised the edge of the cover
and recognised in the person lying with smashed jaw, haggard eyes,
bleeding from a ball in the cheek, the tenant underneath:[Pg 247]
[Pg 248]
[Pg 249] "Ah, what a
good thing!" she cried; "it's you, Monsieur Vitry!"
Since that day Monsieur Vitry had given her the cold shoulder.
In the reign of Charles VI., under pretext of purifying the quarter—the pretext and the Vicar of Saint-Merri's complaint being only too well grounded—these "hot streets" were cleared of the majority of low, lewd people who had taken up their domicile in them. But, if morality had its claims, business also had its interests; and the worthy shopkeepers of the neighbourhood, deeming these of more importance than decency, energetically protested against the measure so prejudicial to their petty commerce. They gained the day, and, on the 21st of January 1388, Parliament reversed the Provost's decision, the result being that the merry band returned in triumph to their old haunts, celebrating the event with feasting and banqueting.
 THE RUE DES PROUVAIRES AND THE RUE SAINT-EUSTACHE ABOUT 1850
THE RUE DES PROUVAIRES AND THE RUE SAINT-EUSTACHE ABOUT 1850In his Chronicle of the Streets, our learned friend, Beaurepaire, librarian of the City of Paris, asserts that the Rue Pirouette, near Saint-Eustace's Church, owes its singular name to the "Market Stocks that stood at this spot. It was an octagonal tower with lofty ogival windows, in the centre of which was an iron wheel pierced with holes for the head and arms of vagabonds, murderers, panders, and blasphemers, who were exposed thus to public derision. On three consecutive market-days, for two hours each day, they were fastened in the stocks and turned every half-hour in a[Pg 250] different direction. In other words, they were forced to 'pirouette,' whence the name of the street."
After doing penance there, in the olden times, malefactors betake
themselves thither to-day to sup. The "Guardian Angel," a thieves'
restaurant, exhibits its signboard almost at the corner of the street:
in it[Pg 251]
[Pg 252]
[Pg 253] rogues laugh, drink and sing, and hatch their morrow's
exploits. The Staff of the army of vice make it their meeting-place. It
is the fashionable resort, a sort of burglars' "Maxim-restaurant," where
Paris hooligans deem it elegant to appear. Casque-d'or and his pals
reign there, and the scoundrel who has just committed an evil deed is
certain to secure good lodging within, and all else he requires. But it
is not only knights of the blood-letting industry who inhabit this noble
dwelling; other lords come there to eat snails and drink champagne:
suspicious-looking young men with plastered hair, who noisily spend
their money gained by blackmailing or some other reprehensible action.
The place is a disgrace to the Capital. The landlord affirms that there
are honest folk among his customers. The thing is possible—anyway, they
must find themselves in very bad company.
Quite close, almost next door, at No. 5, is the "Helmet Courtyard," which gives us a striking impression of what ancient dwellings were. It was, in fact, once a sumptuous fourteenth-century mansion; to-day, it is only a hand-cart repository, where shafts point up to the old ceilings with their projecting beams, shafts shiny with use, and a fishmonger's warehouse, in which Burgundy snails, and cooked or raw lobsters are sold. The nook is a quaint one, and the quarter also, with its remains of the Rue de la Grande-Truanderie, where, on the 10th of May 1797, one of the ancestors of Communism, Babœuf, was arrested.
Not far away used to be the Rue de la Tonnellerie, where Molière lived. This street disappeared when the Rue Turbigo was cut.
In the Central Market quarter, where every one works, where each shop offers to Paris gourmands the best victuals, the freshest vegetables, the daintiest fruits, where, every night, long files of market gardeners' carts bring in loads of provisions of all sorts, each street has, so to speak, its speciality. Housewives know where to find their poultry, crayfish, cheese, or oranges. All the little streets, skirting the Halles, are full of astonishing shops contrived in[Pg 255] door-corners, or cellar-corners, all of which for generations have been kept by worthy husbandmen, petty dealers, hucksters, or basket-hawkers, having their own line, their own customers. In the curious Rue Montorgueil, old abodes that amaze one are still to be found; for instance, between Nos. 64 and 72, the ancient Golden Compass Inn, which was the calling place for so many generations of carriers. Its double entrance, blocked up with small butchers', tripe-dealers', and poulterers' stalls, opens on a huge yard, where fowls peck on heaps of golden dung, where ducks quack, and goats bleat under the eyes of some thirty[Pg 256] horses, peaceful tenants of the ground floor, with their inquisitive heads thrust over the half-doors, through the low windows or open air-holes. At the back, beneath the spacious shed, the carriages and carts are put up, 'midst a healthy country smell of verdure and hay; and it really is a curious sight to see such a silent nook, with its farmyard, at the back of the noisy, populous, crowded street, full of workmen, pedlars, and shouts or cries of bubbling life and movement.
What is left of the Rue Quincampoix, behind the old Tower of
Saint-Jacques-la-Boucherie, emphasises the strangeness of this
neighbourhood, in which the exterior, though renewed, has been partly
preserved, but which has been more modified and transformed as regards
inhabitants and customs than perhaps any other quarter. It was, in fact,
in the Rue Quincampoix that the famous Law established his offices of
the Mississippi Bank. There, all Paris suffered the fever of
speculation. The madness was general. For months nothing but folly and
ruin reigned. All gambled—duchess, priest, philosopher and courtier,
shopkeeper and ballet-actress, peer and lackey, excise-farmer and his
clerk. In order to profit by proximity to the celebrated stock-jobber,
each shop, room and cellar even, rented at foolishly high prices, was
turned into a gaming establishment; and the case is quoted of a cobbler
who hired for a hundred livres a day his stall stinking with wax and old
leather; the gold mania had[Pg 257]
[Pg 258]
[Pg 259]
[Pg 260]
[Pg 261] broken down all distinctions. And then
the fatal crisis came, the panic, the crash. In the Rue Quincampoix one
saw none but despairing faces. Every day there was a series of murders,
suicides, attacks of lunacy. On one single occasion, twenty-seven bodies
of suicides or murdered people were fished out of the river at the nets
of Saint-Cloud. To speculate still, money at any price was needed.
Highway robbery was practised, and the footpads were of all classes of
society. One of these, the young Count de Horn, a relative of the
Regent, and already notorious through his follies, hired two rascals of
his own kind, enticed a rich young stock-jobber into an inn of the Rue
de Venise, stabbed him and took his money. The scandal was enormous!
Both Court and City lost their heads. Would justice at last act and
severity be shown? There was a good deal of intriguing and excitement;
but, finally, the Lieutenant for criminal affairs, acting on the orders
of the Regent, arrested the Count de Horn, on the 22nd of March 1720;
and, four days after, the latter was broken on the wheel and executed in
the centre of the Grève Square, amidst the applause of all Paris.
The Rue Quincampoix likewise contains some few old mansions now inhabited by certain "medical specialists," cheese-dealers, eau-de-seltz makers, &c. At Nos. 58, 28, 14, 15, and, notably, at No. 10, are seen remnants of forged iron, broken balconies, chipped grotesque masks of stone.... But the whole[Pg 262] is tumbling to pieces, and to ruin, and only by a strong effort of the imagination can one reconstitute, out of these wretched fragments, the life of luxury, fever and stock-jobbing that once filled this old street, now foul with chemical smells and rancid odours of fried potatoes.
Collé's prophecy has been fulfilled: "One no longer belongs to Paris when one belongs to the Marais!"
Trade has laid hold of the fine mansions of yore; druggists have set up their distilleries in them, toy-makers sell their puppets in them, and the hawker with his Paris article is the monarch that governs them.
The population at present is poor, laborious, yet intelligent and active; and the contrast between it and the transformed dwellings wherein it dwells is not without interest and grace. A visit to the Archives, Marais and Saint-Merri quarters is certainly something no one should omit.
The picturesque line of central boulevards extends from the Bastille to the Madeleine Church. There Paris life may be studied under the most varied aspects, as well as the most elegant.
To speak of there being a general characterisation of the boulevards would be hardly correct, inasmuch as each of them has its special physiognomy.
The Beaumarchais Boulevard has an atmosphere of middle-class
tranquillity about it. Nothing has survived of the fine mansion,
surmounted with a feather-shaped[Pg 263]
[Pg 264]
[Pg 265] weather-cock and flag, which was
built there by the author of the Mariage de Figaro, nor yet of the
famous gardens, once the wonder of Paris, which could only be visited
with a special card signed by Beaumarchais himself and given but to few.
Yet some one of our own generation has known them, and penetrated into
what for a while remained of the gorgeous abode; and that some one is
Victorien Sardou. Did he have a presentiment that, in talent and wit, he
would one day be the successor of the Beaumarchais whose property he
thus intruded on? Anyway, in 1839, Victorien Sardou, aged seven, was
living with his parents in the Place de la Bastille. With his little
companions he used to play at ball or with hoop round the elephant and
the canal banks. At the entrance to the Beaumarchais Boulevard of to-day
some long, worm-eaten palisades bordered a piece of waste ground. On the
palisades were hung halfpenny pictures of actors, actresses, and
soldiers; and no one was fonder of looking at them than the little
Sardou.
One day, while enjoying his open-air picture-gallery, he caught a glimpse of a huge garden through the interstice between two of the palings. "What was this garden?" "Suppose he entered!" So he and another urchin of his own age wrenched away a paling with the sticks of their hoops, and in a delight of terror slipped into the unknown domain. What an amazement! They found themselves in a Sleeping Beauty's[Pg 266] realm. Weeds, lianes, branches, trees had grown over everything. It was a flora and fauna of the virgin forests; rabbits, birds and butterflies were its denizens; and Robinson Crusoe was not more surprised in exploring his island than these two youngsters in wandering about this jungle.
Sardou vaguely remembers there being a ruined pavilion and some tumble-down old walls; what he recollects better are the banks, ditches, and slopes where he and his companion had such delightful escapades; and nothing is more interesting than to hear this witty and charming talker relate his stories of the bygone Paris which he regrets so much and remembers so well.
The old dwellings have disappeared. A single one still exists at the corner of the Rue Saint-Claude, No. 1. It is the celebrated abode in which the talented charlatan, Cagliostro, installed his furnaces, his crucibles, his alembics, his transformation machines, all the weird utensils that served for his magic sittings.
The house has not been much altered. It remains, as always, strange,
enigmatical, mysterious, with its staircases constructed in the body of
the walls, its secret corridors, its mechanical ceilings, its cellars of
many exits. The greatest lords, the noblest dames frequented this abode.
Cardinal de Rohan was a familiar guest. The report ran that gold was
made there, and that Cagliostro, the great Copht, had discovered the
secret of the philosopher's stone! He offered,[Pg 267]
[Pg 268]
[Pg 269] continued the legend,
repasts of thirteen covers at which the guests were enabled to call up
the dead, which was why Montesquieu, Choiseul, Voltaire and Diderot had
taken part at Cagliostro's last supper.
All that made a stir; there were murmurs; the thing was proclaimed a scandal. Louis XVI. shrugged his shoulders and Marie Antoinette forbade any one to "speak to her of this charlatan." But every one tried to obtain entrance into the "divine sorcerer's house," and Lorenza, his wife, was obliged to open a class of magic for the benefit of the ladies of the upper circles.
Then came the affair of the necklace. Cagliostro, being compromised with Cardinal de Rohan and Madame de Lamotte, was arrested and thrown into the Bastille; and it was not until ten months later, on the 1st of June 1787, that he was able to return to the house in the Rue Saint-Claude, escorted by a crowd of eight to ten thousand persons, blocking the Boulevard, the courtyard of the house and the staircases. He was cheered, embraced, carried in triumph. This grand day was a climax. A few hours after it, a King's order banished him from France, and the house was shut up. Only in 1805 were its doors reopened for the sale of the furniture; and the sight must have been a curious one! In 1855, the building was repaired; the leaves of the entrance gate were changed; those to-day opening into the Rue Saint-Claude came from the ancient buildings of the Temple;[Pg 270] so that the gates of Louis XVI.'s prison give access now to the mansion where Cagliostro once performed his marvels.
In the Filles-du-Calvaire Boulevard stands the Winter Circus, still unchanged, with its Icarian Games and its equilibrists, its smiling horse-women who for so many years have leaped through the same paper-filled hoops and made the same pleased bow to the worshipping crowd. But, if the spectacle is not much varied, the public of youngsters is constantly renewed, and the laughs we heard in our childhood still welcome the same clowns' grimaces. Only Monsieur Loyal is no longer there, the admirable, imposing Monsieur Loyal, tight-buttoned in his fine blue coat, who, with such noble gesture and slashing whip, restrained the mocking clown's quips and quirks or the shyings of the mare Rigolette exhibited at liberty.
Would any one now believe that for more than a century the Temple
Boulevard was the centre of Paris gaiety? A charming engraving by
Saint-Aubin shows us it joyous, smart, and full of life. Coaches, cabs,
and other vehicles pass and repass; grand ladies and fashionably dressed
women rival with each other in grace, manners and toilet, the latter of
the strangest names; and the draughtsman Briou can write below a fashion
engraving of the period: "The provoking Julia reposing on the Boulevard,
while awaiting a stroke of good fortune; she is in morning gown with a
Diana hat that flying hearts adorn." At[Pg 271]
[Pg 272]
[Pg 273] Alexander's Cafè Royal, there
is supper and dancing; people crowd to listen to Nicolet's patter; and a
circle of hearers surround Fanchon, the hurdy-gurdy player. On the same
Boulevard, Curtius sets up his luxuriously arranged wax-work saloons;
and, later, the parades of Bobèche and Galimafré will be the joy of
Paris; for a long time, the fair will continue.
The Ambigu, the Historic Theatre, the Gaiety, the Funambules, the Olympic Circus, the Little-Lazari, the Délassements Comiques,—ten theatres or so will add to the excitement with their strange, nervous, grandiloquent, noisy companies of actors. The gay apprentices, at all times fond of plays, will cheer[Pg 274] as they go by the heroes of all these dramas and melodramas, so numerous that popular slang had nicknamed as Crime Boulevard the thoroughfare where, at twelve each evening, so much blood flowed on the boards of these theatres. There were Madame Dorval, Mademoiselle George, Mademoiselle Déjazet, Messieurs Bocage, Mélingue, Bouffé, Dumaine, Saint-Ernest, Boutin, Colbrun, Lesueur, Deburau—the ideal Pierrot—and also Gobert, so like Napoleon I., as was Taillade, who, thin and nervous, was incarnating Bonaparte. It was the period when the Bonapartist epopee turned people's heads to such an extent that the poor comedian Briand, who, in one of the many Napoleon plays, was acting the ungrateful part of Sir Hudson Lowe, said: "I shall never have a similar success. Yesterday, I was waited for at the theatre door and thrown into the Château-d'Eau canal basin!"
All the quarter waxed enthusiastic about its favourite actors, espoused their quarrels, repeated their witticisms or their adventures: Frédéric Lemaitre especially, a tragic, dare-devil, drinking, extravagant yet talented artist, decking himself in private life, as well as on the stage, in the frayed-out plumes of Don Cæsar de Bazan, had his own story. People went into ecstasies over his amours with Clarisse Miroy, interwoven with thrashings and fond tenderness. On the day after one of these noisy quarrels, Frédéric is said to have rung at his lady-love's door, which was opened by Clarisse's mother. The good dame, frightened at the[Pg 275] brutal actor's appearance, raised her arm instinctively as if to ward off a blow.... "I beat you, I!" thundered Frédéric in Richard d'Arlington's tones, "I beat you! Why?... Do I love you?"
The Historic Theatre subsequently became the Lyric Theatre, and the wonderful Madame Miolan-Carvalho, the queen of song, was there to create, with her magnificent art, Faust, Mireille, Jeannette's Wedding, Queen Topaz, &c. About 1861, the celebrated composer Massenet, yet a pupil at the Conservatory and on the point of obtaining his Rome prize, discharged in the theatre orchestra the duties of kettle-drummer, for the modest salary of forty-five francs a month.
Others to perform there were the Davenport brothers and the conjurer Robin, with their amusing séances of hypnotism and white magic. On this always-to-be-remembered Temple Boulevard were to be met the various fashionable authors: Dennery, Théodore Barrière, Victor Séjour, Paul Féval, Gounod, Berlioz, A. Adam, Clapisson, Saint-Georges, the Cogniard brothers, Clairville; and the great Dumas used to pass in triumph, shaking hands with everybody as he went. The coffee-houses had to turn customers away; orange-sellers made fortunes, while boys sold checks, conveyed nosegays to pretty actresses, and hailed cabs. People called to each other, shouted, disputed, laughed above all, under the indulgent eye of the police and to the noise of liquorice-water-seller's bell: it was the golden age!
In 1862, a regrettable decision of Baron Haussmann, the Prefect of the Seine, suppressed this bit of Paris, so lively and gay; and, on the ruins of all these theatres, which brought money and mirth to the quarter, were built Prince Eugène's barracks, the ugly Hôtel Moderne, and the wretched monument of the Republic Square. Of all this fine, artistic past nothing is left except the tiny Déjazet Theatre, at the corner of the Vendôme Passage, and the Turkish Coffee-house; the latter different far from what it was when Bailly depicted it under the Directory. Elegant dames, the Merveilleuses, the Incroyables used to frequent it for the purpose of nibbling an ice or sipping little pots of cream, while listening to cithern concerts. Young Savoyards made their marmots dance in presence of "sensitive souls," and thrifty burgesses of the quarter took their family to get an idea of the high Parisian life which made the Turkish Coffee-house one of its favourite meeting-places.
Restaurants were numerous, being souvenirs of coffee-houses formerly
renowned, like the Godet and Yon cafés. There one found singing and
dancing, and, now and again, plotting. It was at the Burgundy Vintage
Restaurant in the Temple faubourg, the ordinary rendezvous of Paris
wedding-breakfasts or National Guard love-feasts, that—on the 9th of
May 1831, at the end of a banquet given to celebrate the acquittal of
Guinard, Cavaignac, and the Garnier brothers, charged with plotting
against the State—Évariste[Pg 277]
[Pg 278]
[Pg 279] Gallois, with a knife in his hand,
proposed in three words this threatening toast: "To Louis-Philippe!"
The great Flaubert lived on the Temple Boulevard at No. 42. There, on Sundays, he gathered his disciples at noisy lunches—Zola, Goncourt, Daudet, de Maupassant, Huysmans, Céard, George Pouchet—a few yards away from a building of tragic fame. No. 50, in fact, was the wretched house whose third-story Venetian blinds concealed Fieschi and the twenty-five pistol barrels loaded with bullets which constituted his infernal machine. A train of powder passed over twenty-five lights. The discharge of grapeshot to be vomited by this dreadful instrument of death was terrible. The grocer Morey, who had helped to prepare the monstrous crime, had even taken the useful precaution to damage four of the gun-barrels, whose explosion was to suppress Fieschi himself.
Pépin, another accomplice, had been careful to walk his horse several times past the fatal window; and from behind the Venetian blinds, Fieschi, who was an excellent shot, had been able at his ease to regulate the aim of his horrible slaughtering-machine. It was intended that Louis-Philippe, who had ten times escaped the assassin's hand, should, on this occasion, be struck by it. The conspirators, however, had not calculated that the King, when reviewing the National Guard, would avoid the middle of the Boulevard, which sloped down towards the sides for draining purposes, and would keep to the lower portions, along which the[Pg 280] troops were stationed. The rain of bullets therefore passed over the King's head, touching only the top of his cocked-hat, and mowed down women, children, officers and other spectators that were on the King's left. It was a frightful butchery; the Boulevard streamed with blood. More than forty victims lay on the road, among them being the glorious Marshal Mortier, who expired on one of the marble tables in the Turkish Coffee-house, whither the dead and wounded had been transported. Fieschi, who was wounded, was arrested in the backyard of the next house, while trying to fly through the Rue des Fossés-du-Temple. On the 19th of February 1836, he ascended the scaffold with his accomplices, Pépin and Morey.
At the corner of the Temple Boulevard, to the right, in front of the first house in the Voltaire Boulevard, the barricade was raised where Delescluze was killed in May 1871. At this spot, formerly stood the Gaiety Theatre; while the Lyric Theatre opened its doors on the present site of the Metropolitan railway station in the Republic Square.
The Saint-Martin Boulevard, where Paul de Kock took up his abode, in
order to study from his windows, which were on the first story, near the
Porte Saint-Martin, the seething life of the Capital, now has no
animation except in the evening. Four theatres—the Folies-Dramatiques,
the Ambigu, the Porte Saint-Martin, and the Renaissance—add life and
movement[Pg 281]
[Pg 282]
[Pg 283] to it then; and nothing is more amusing than the hour
following the end of the performances. The coffee-houses fill with
visitors, cigarettes are lighted, newspaper-vendors shout the latest
news; people hustle, and touts run after carriages, in which one sees a
rapidly passing vision of pretty women in light-coloured dresses and
opera-cloaks. Afterwards issue the actors, with blue chins and turned-up
collars, and often looking cross. Last of all, come the handsome
actresses, who quickly step into their brougham, inside which may
frequently be seen, dimly outlined behind the red point of a cigarette,
the form of an expectant friend.
Near the Porte Saint-Denis, at the entrance to the narrow Rue de Cléry, there was formerly a rise in the road, which was the scene of a tragic occurrence. There, on the 21st of January 1793, the intrepid De Batz had appointed to meet a few companions. It was determined that a forlorn hope should be led with a view to snatch Louis XVI. from the shame of the guillotine. The plan was to force the line of soldiers, to overpower the escort surrounding the carriage, and to carry off the King.
But, already, on the day before, the Committee of Public Safety had been warned "by a well-known private individual," say the police reports, of the mad plot that was in preparation, and every necessary precaution was taken. During the night all the persons denounced in the warning as suspicious were placed under arrest. De Batz, who thought to find a[Pg 284] hundred and fifty confederates at the meeting-place, only found seven. Notwithstanding their small number, they did not hesitate, and rushed at the horses' heads. The Guards cut them down. Three were killed. De Batz managed to escape.
This strange, winding Rue de Cléry, whose thin edge stands out so
curiously against the sky, was the scene of another drama. The father of
André and Marie-Joseph Chénier lived at No. 97. There, on the 7th of
Thermidor, he was anxiously waiting for the liberation of his son André,
who for long months had been a prisoner at Saint-Lazare. The poor man
had foolishly taken it into his head to appeal to Collot d'Herbois'
heart(!) and to ask him to free his son. Collot d'Herbois had once been
an actor; and now, on another sort[Pg 285]
[Pg 286]
[Pg 287] of stage, revenged himself for
having been hissed. He had not forgotten the lines in which André
Chénier had satirised him in such masterly fashion, but he did not know
in what prison his enemy was confined. Marie-Joseph, the brother,
himself an object of suspicion, had been able to lengthen out the
proceedings and to keep as a secret the place where André was confined.
At this supreme hour of the Terror, it was the only possible chance
Collot d'Herbois had to satisfy his vengeance; and the information thus
unadvisedly but innocently given by the prisoner's father was utilised
by the revengeful actor. "To-morrow," Collot assured the unhappy father,
"your son shall quit Saint-Lazare." He kept his word; and, on the 7th of
Thermidor, just at the hour when the guest was so impatiently expected,
André got into the cart to go to the scaffold, erected that day at the
barrier of the Throne Square.
Round about the picturesque Rue de Cléry, the quarter is an odd medley of little streets, lanes, and alleys: the Rue Notre-Dame-de-Recouvrance, the Rue Sainte-Foy, the Rue des Petits-Carreaux, the Rue de la Lune, in which last Balzac lodged his Lucien de Rubempré watching over Coralie's dead body, and composing libertine songs, in order to gain the money required for his mistress's funeral.
In these tortuous, sombre, narrow streets it is easy to reconstitute the physiognomy of the older Paris; ancient dwellings are still numerous enough; but, as[Pg 288] in the Marais, are given over to petty trade and industry. After the Egyptian campaign, the Consulate cut a certain number of new streets bearing the names of victories: the Rues de Damiette, d'Aboukir, du Nil. On the site of the Cairo Square, once stood the mansion of the Temple Knights, or Knights Templars. A portion of an old Gothic Chapel, in which were preserved the helmet and armour of Jacques Molay, founder and Grand Master of the Order, was used in 1835 as a meeting-place by surviving adepts of this rite; and Rosa Bonheur's father, who was a Knight Templar, had his daughter baptized there beneath an "arch of steel" made by the crossed swords of the Order, clad in white tunics, with a red cross embroidered on their breasts, booted in deer-skin, and coifed with a white cloth square cap surmounted by three feathers—one yellow, one black, and one white!
A delightful picture by Dagnan, which is now in the Carnavalet Museum,
shows us the Poissonnière Boulevard in 1834. Most of the houses remain
to-day; but, alas! the tall, thick-foliaged trees that made the
Boulevard a sort of park avenue have long since disappeared. That lover
of Paris, Victorien Sardou, who was born in it, and who is cheered,
loved, and honoured in it, very well remembers seeing the trees as they
used to be, and his long saunterings in front of the Gymnase Theatre.
Did he foresee the successes he was to gain with les Ganaches, les
Vieux Garçons,[Pg 289]
[Pg 290]
[Pg 291] les Bons Villageois, Andréa, Féréol,
Séraphine, Fernande, &c.?
Further on, we come across the ancient Variety Theatre, whose antique front speaks of a glorious past; Duvert, Lauzanne, Bayard, Scribe, Meilhac, Ludovic Halévy, and, above all, Offenbach, whose haunting music bewitched Paris for twenty years.
Ludovic Halévy, who was a charming chronicler of Paris life, has left us an interesting sketch of the Montmartre Boulevard towards 1810: "The Variety actors had been obliged to quit the Montansier hall; their vaudevilles had more success than the tragedies at the Théâtre Français. The Emperor made a decree depriving them of the Palais-Royal premises; but they were allowed to move to new premises on the Montmartre Boulevard!... A frightful quarter for a theatre!... It was almost in the country; not one of the large houses existed which you see there! Nothing but little single-story shops, wretched wooden stalls, and the two small panoramas of Monsieur Boulogne.... No foot-pavements, a road simply of beaten earth between two rows of tall trees.... A few old cabs and carriages passed now and again.... In fine, the country.... It was the country!!.."
With the Variety Theatre began what was called, without epithet, The
Boulevard. For idlers, saunterers, wits, clubmen, writers, journalists,
under the second Empire, it was a sort of sacred ground.
Grammont-Caderousse, the Prince of Orange, Khalil-Bey, Paul[Pg 292] Demidoff,
Aurélien Scholl, Roqueplan, Aubryet, Jules Lecomte, Auguste Villemot
were kings there. The Café Anglais, the Maison Dorée, Tortoni's were
frequented by the fashionables of society and literature. The gas
flared, champagne corks flew, and one had only to open pianos for them
to play automatically the Evohe of Orpheus in Hades! An apropos
witticism stopped a quarrel. The princes of intelligence held their own
with princes of the blood or of money; as, for instance, on the day
when, at Tortoni's, the[Pg 293]
[Pg 294]
[Pg 295] Duke de Grammont-Caderousse flung a packet of
goose-quills in the face of Paul Mahalin, who, the day before, in a
small newspaper had severely animadverted on the diva S——, she being
under the Duke's protection.
"From Mademoiselle S——," said the Duke.
Making his grandest bow, Mahalin retorted: "I was aware, Monsieur, that Mademoiselle S—— feathered her lovers, but I did not dare hope it was for my benefit."
 THE BOULEVARDS, THE HOTEL DE SALM, AND WINDMILLS OF MONTMARTRE
THE BOULEVARDS, THE HOTEL DE SALM, AND WINDMILLS OF MONTMARTRESince the dark days of 1870, the elegant Boulevard has become more democratic. The old dwellings themselves have changed their uses; and electro-plate is sold in the beautiful pavilion built by Marshal de Saxe—after the Hanoverian wars—at the corner of the Boulevard and the Rue Louis-le-Grand. In the eighteenth century, some one took it into his head to decorate with flowers the roofs of the houses in the vicinity of this fine mansion; so that it was possible to dine merrily—under the shade of hornbeams—while watching the windmills of Montmartre turn in the distance. The example has been imitated in our own times—people cried that it was an innovation; this is only another error; there is nothing new under the sun. What is done is merely a modification, and generally the alteration is for the worse! Tortoni's flight of steps has disappeared. Taverns, with their onion soup and their sourcrout and sausage, replace the aristocratic restaurants of yore. The features are[Pg 296] different; but still it is a Paris nook, really gay, amusing, and original. A walk in it is delightful, though nothing, alas! can be said to vividly recall the past, since the terrible fire of 1887 destroyed the Comic Opera of our fathers; the Opera of Grétry, Dalayrac, Méhul, Boïeldieu, and Hérold; the Opera whose façade does not open on the boulevard, according to the desire formally expressed in 1782 to Heurtier, the architect, by the King's Comedians refusing to be confused with the "Boulevard Comedians"; the Opéra-Comique where, every evening, in the spacious foyer adorned with busts of dead musical celebrities and composers that had contributed to the theatre's fame, the habitués met whose attendance was a protest against modern music: Auber, Adam, Clapisson, Bazin, Maillard; later, and with another æsthetic doctrine, G. Bizet, Léo Delibes, V. Massé, J. Massenet, Carvalho, Meilhac, Halévy, and old Dupin, the last an astonishing centenarian who, one evening, with rancorous eye looked at Hérold's bust and grumbled: "How that urchin used to rile me!" In presence of the general bewilderment he explained: "I was his school companion, in 1806, at Saint-Louis' College!" we were then in May 1885! This was the obstinately reactionary Dupin who once drew from a contradictor the threatening retort: "We missed you in '93. When the next Revolution comes, we'll take good care not to!"
The amiable chats, the agreeable meetings which brought together so many
witty people, clever talkers,[Pg 297]
[Pg 298]
[Pg 299] artists, men of the world, those of the
Comic Opera foyer, of the Grand Opera, or the Comédie Française are
now hardly anything but a memory. Not that the practice itself is
abolished. Art gatherings are quite as frequent and as well attended;
but they have emigrated,—many of them to Montmartre, to the "Butte
Sacrée," the holy mound, "the teat of the world," yelled the astonishing
Salis in his Chat Noir patter; and truly the spot is one of the
Capital's curiosities.
Gay, industrious, cynical, flippant, and yet religious, this composite quarter offers the most singular mingling of poets, painters, sculptors, lemonade-makers and pilgrims. On the Clichy and Batignolles Boulevards, the revolving[Pg 300] lights of the Moulin Rouge illuminate a population of rakes, dandies, artists, lemans and bullies. Each wine-shop—and there are many—harbours one or several poets, more or less comic, but always railers and rosses,[4] as the witty Fursy says, one of the best performers in these "music-boxes." In these latter the great ones of the earth, politicians, ministers, are unmercifully berhymed, as also the events of the day; a minister's latest speech, Pelletan's elegance, Le Bargy's cravats, Santos-Dumont's ascent, the Pope's latest Encyclical letter, the automobile tax, the divorce of the moment, the King of Spain's recent visit, or that of the Prince of Bulgaria, all put into couplets.
Montmartre is the Capital's pot-house; it is all good-humoured laughter and chaff. People enjoy themselves at night and work in the day, for it has always been a favourite abode for artists of every kind: Henri Monnier, the Duchess d'Abrantès, Madame Haudebourg-Lescot, Mademoiselle Mars, Horace Vernet, Berlioz, Ch. Jacque, Reyer, Victor Massé, Vollon, Manet, André Gill, Steinlen, Guillemet, Willette, Jules Jouy, Mac-Nab, Xanrof, Maurice Donnay. Their memory there is alive and respected, the legend of their prowess is preserved. It is Montmartre's Iliad.
A few yards from these noisy streets, the "Butte" begins, on which, at
the close of the 1871 siege, the Parisians had hoisted the National
Guards' cannons. In vain the Government tried to regain possession of[Pg 301]
[Pg 302]
[Pg 303]
them; and the rest is known:—the resistance, the troops disbanded,
Generals Clement Thomas and Lecomte arrested, dragged into a small house
in the Rue des Rosiers and shot against a garden wall.
Part of the wall still stands; and though the house has disappeared in which this tragedy of the 18th of March was played, a little of the garden itself remains, behind the modern buildings of the Abri Saint-Joseph, vast sheds used as refectories by the crowds of pilgrims attracted to the basilica of the Sacré-Cœur.
Indeed, all this quarter is melancholy-looking, silent, quaint, and monastic. Chaplet, scapulary, candle, missal, and pious picture-dealers have their shops in it. The spot is a sort of religious fair; even the streets have liturgical names: Saint-Eleuthère, Saint-Rustique, near the Rue Girardon, and the Calvary cemetery, overlooked by the awkward outlines of the old Galette Windmill, the ordinary rendezvous for idlers, boulevard inquisitives, artists' models, lemans and bullies of the neighbourhood. The ancient Montmartre, with its[Pg 304] picturesqueness, is again met with in the Rue Saint-Vincent, in the Rue des Saules containing the "Lively Rabbit" tavern, and in the Rue de la Fontaine-du-But, sordid streets, bordered with sorry habitations whose windows are hung with linen drying, and which seem at each story to harbour a different poverty; strange streets, running for the most part between a crumbling old house and a hoarding mossy with rain and covered with inscriptions. As a matter of fact, these palisades serve as an outlet for the confidences of the "pals" and their "gals" of the quarter. Amorous effusions may be read side by side with threats, and the great ones of the earth are sometimes severely dealt with. The epithet is always a bitter one. It savours of debauch, vice and crime.
And yet, in this corner of Paris, which modern embellishments will soon have made unrecognisable, bits of admirable scenery are to be met with, exquisite lanes of verdure, birds, tame pigeons, whistling blackbirds; and one might fancy one's self far away in some peaceful country-place, if, at the end of all these streets, were not seen the huge violet-coloured mass of the Capital, in fairy panorama, an ocean of stone, whence heave, like masts, the bell-towers of palaces, the turrets, belfries and steeples of churches, with domes, roofs and gardens—an incomparable vision of art, grandeur and beauty.
The great Balzac informs us that César Birotteau was ruined by
speculations he engaged in on the "waste ground round about the
Madeleine church."[Pg 305]
[Pg 306]
[Pg 307]
[Pg 308]
[Pg 309] He lost in them the profits realised by his "Eau
Carminative" and by the "Double Pâte des Sultanes." His "Rose Queen"
perfumery was swallowed up in them....
And, however, César Birotteau was right in his reasoning. To-day, the Madeleine building ground is the highest quoted in Paris.
In 1802, the surface was occupied by foundation works and scaffolding, showing the pillars of the church so long since commenced and still in the building.
There took place the charming episode depicted by Duplessis-Bertaux, under the pleasing title: "Ingenuous[Pg 310] Benevolence" (an historic fact of the 5th Messidor, anno X.). A long notice, beneath the picture, tells us that Pradère, Persuis, Elleviou and "his spouse," walking one evening along the Magdalene Boulevard, met a blind street-singer, who "by the strains of his piano was soliciting public charity." The receipts were wretched; so our kind artists improvised a little open-air concert and remedied the ill-fortune of the poor fellow. After delightfully singing, Madame Elleviou, her husband and Pradère made a collection, and poured the proceeds, thirty-six francs, into the blind man's hands trembling with emotion!
Along the Rue Royale, we reach the Champs-Elysées, after stopping for a moment at the "Cité Berryer," a strange alley in which once stood the hotel of the King's Musketeers. It is a sort of poor market lost in this rich quarter.
 THE ENTRANCE TO THE TUILERIES, OVER THE SWING-BRIDGE, IN 1788
THE ENTRANCE TO THE TUILERIES, OVER THE SWING-BRIDGE, IN 1788Then comes the Place de la Concorde, the finest Square in the world,
with its unrivalled perspectives of the Champs Elysées, the Seine, the
Tuileries, the Garde-Meuble, the Crillon mansion, and the charming house
of Grimod de la Reynière, to-day the Cercle de l'Union artistique, at
the corner of the Rue de "la Bonne Morue"—at present the Rue Boissy
d'Anglas—in front of which still stood, until the second Empire, one of
the corner pavilions erected by Gabriel. What souvenirs! the raising of
Louis the Fifteenth's statue; the festivities in honour of the Dauphin's
marriage to Marie Antoinette, so tragically[Pg 311]
[Pg 312]
[Pg 313] terminated by a
catastrophe—the crowd that had come to witness the fireworks being
crushed in the moat—which was the beginning of the hatred against the
"Austrian woman"; the reviews of the Swiss Guards; the military charges
of Lambesc; the people's storming of the swing-bridge, the gates forced,
the ditches crossed, and then the sinister scaffold, smoking in front of
the statue to Liberty, and the Conventionals terrified, stopping before
they entered their hall and taking a close look at the death which, each
day, hovered over them. "Yesterday, as I was proceeding to the Assembly
with Pénières," writes Dulaure in his[Pg 314] Memoirs, "we perceived, as we
passed through the Revolution Square, preparations being made for an
execution. 'Let us pause,' my colleague said to me; 'let us accustom
ourselves to the sight. Perhaps we shall soon need to make proof of our
courage by calmly ascending this scaffold. Let us familiarise ourselves
with the punishment.'"
 CORNER PAVILION OF THE LOUIS XV. SQUARE
CORNER PAVILION OF THE LOUIS XV. SQUARESevered heads were exhibited by the executioner at the four corners of the huge Square: Danton, Camille Desmoulins, Hérault de Séchelles, Charlotte Corday, Madame Roland, Louis XVI., Marie Antoinette, and Robespierre. A dreadful pell-mell, a disastrous butchery; the ground was red with blood. Then followed the soldiers of the Empire, singing as they defiled, on entering the Tuileries to cheer their triumphant Emperor at his return from some victorious campaign.
A white head, big golden epaulets, a blue ribbon: such was the appearance of Louis XVIII., impotent, with paralysed legs, who, in his carriage surrounded with body-guards, galloped through the Square at full speed.
It was at the corner of this Place de la Concorde that, on the 28th of February 1848, Louis-Philippe, broken and vanquished, got into the humble cab that proved to be the hearse of the Monarchy.
Napoleon III., with his blue dreamy eyes, used to cross it nearly every
day, driving his phaeton; and the boy, whom the Parisians of that time
called "the little Prince," would show his pretty fair head of hair at
the[Pg 315]
[Pg 316]
[Pg 317] window of the "berline" escorted by the household troops.
The gates of the Tuileries were again to open, on the 4th of September 1870, under the pressure of the invaders; and, during the siege of Paris, artillery were to camp in the vast ruined garden. Finally, the palace of the kings of France was to disappear in a cloud of fire, 'midst the last convulsions of the expiring Commune; and, to-day, a poor fellow, in a shabby sun-faded cloak and wearing an old felt hat, spends his time distributing bread and grain to the Paris pigeons and sparrows, on the very spot where once stood the rostrum of the Convention, some yards from the place where the four hoofs of the Emperor Napoleon's white horse pranced, as his rider reviewed the Guard, before flying his victorious eagles towards Moscow, Madrid, Rome, Vienna, or Berlin!
The Champs Elysées are of almost modern creation. A decade ago, the fine avenues surrounding the Arc de l'Etoile—the Avenue Kléber, the Avenue Wagram, the Avenue Niel, the Avenue de l'Alma—offered most picturesque contrasts; beside a sumptuous mansion, subsisted wretched little houses, remains of old hovels that once were scattered all over this luxurious quarter, where now nothing recalls the waste pieces of land, dangerous even to cross, of sixty years ago. Under the Directory, Madame Tallien's cottage (Notre Dame de Thermidor, she was called) to which the Incroyables and the Merveilleuses dared not go without escort, was[Pg 318] situated as far up as the Avenue Montaigne. Dancing-gardens and open-air bars occupied the space now filled by restaurants and cafés-concerts. An engraving by Carle Vernet shows us a Cossack encampment round a humble, country-looking inn. Now the Le Doyen restaurant stands there!
Under Louis-Philippe, the Champs-Elysées were at length altered: side
avenues were laid out, the main avenue was widened; and Emile Augier
used to relate that, in the hollow of one of the trees numbered for
trimming (No. 116, I believe), the ticket porter belonging to the
Gymnase Theatre deposited the one intended for Balzac at the time of the
rehearsals of Mercadet. The great novelist, in order to escape from
his numerous creditors, was lodging at this period in the Rue Beaujon,
under the name of Madame Dupont, widow. Gozlan, who ultimately
discovered his illustrious[Pg 319]
[Pg 320]
[Pg 321] friend's address, added on the envelopes
he sent to him—"née Balzac."
The curious Memoirs of the Abbé de Salamon, a Papal internuncio, give us a striking picture of the Bois de Boulogne under the Revolution: a sort of forest, or jungle, in which those took refuge who, being suspected, were tracked by the Committees and the police, and to whom the precious citizens' card had been refused. "I continually remained in the thickest part of the Bois de Boulogne," he says. "It seemed to me that each person I met read on my face that I was outlawed and was hastening to deliver me to the headsman. I took up my abode in the loneliest place of the wood. I lit a fire with a tinder-box and some twigs, and cooked my vegetables; my soup was excellent.... Later I discovered another fairly convenient spot, on the side of the Bagatelle Villa, quite near to the Pyramid and not far from Madrid.
"One night, I was wakened in the middle of my dreams by the piercing cries of two women, who drew back terrified on beholding me through the darkness of night.
"It was a mother and her daughter, who also were flying from an arrest-warrant. I called to them: 'Keep silence, whoever you are! You have nothing to fear.' They asked me what I was doing in the wood so late: 'The same thing as you no doubt are doing yourselves,' I answered."
Subsequently it became the ordinary meeting-place[Pg 322] for duellists. Already, in the time of Louis XV., some ladies, the Marchioness de Nesles and the Countess de Polignac, had exchanged pistol shots in it on account of the Duke de Richelieu. Under the Revolution, in 1790, Cazalès and Barnave went there to settle a political quarrel: "I should be sorry to kill you," exclaimed Cazalès; "but you annoy us considerably, and I want to keep you away from the rostrum for a while." "I am more generous," retorted Barnave; "I wish merely to touch you; for you are the only orator on your side, whereas on mine my absence would not even be perceived." Afterwards it was Elleviou and Monsieur de Bieville;[Pg 323] General Foy and Monsieur de Corday; Marshal Soult and Colonel Briqueville; Benjamin Constant and Forbin des Essarts; with this peculiarity in the last duel that the two adversaries fought at ten yards' distance, sitting in two armchairs, which were not even grazed! And how many others!...
Under Louis-Philippe, the Duke d'Orléans, the Duke de Nemours, Lord Seymour, the Duke de Fitz-James, Ernest Le Roy—the Jockey Club at its formation—organised races there. The stakes were modest; most often, a few bottles of champagne were gained and lost. Then fashion took hold of the thing. More importance was attached to racing; and, to-day, it is the great Parisian event—in festivities. As early as[Pg 324] 1850, the Hippodrome of the Eylau Square revived the souvenir of Antiquity's favourite chariot-races.
The Bois de Boulogne became the rendezvous of society. There, was displayed the luxury of the Second Empire. Its trees and avenues formed an exquisite framework to elegance and worldly show. In the Curèe, Emile Zola was able to write: "It was four o'clock and the Bois awoke from its afternoon sultriness. Along the Empress' Avenue, clouds of dust were flying; and, afar, lawns of verdure could be seen, with the hills of Saint-Cloud and Suresnes beyond, crowned with the grey of Mont Valerien. The sun, aloft on the horizon, sailed in an effulgence of golden light that filled the depths of the foliage, flamed the top branches, and transformed this ocean of leaves into an ocean of luminousness.... The varnished panels of the carriages, the flashing of the copper and steel mountings, the bright colours of the dresses streamed together with the horses' regular trot, and cast on the background of the Bois a broad, moving band, a beam from the welkin, lengthening as it followed the curves of the road. The waved roundness of the sunshades radiated like metal moons."
The sight has not changed. It is the same triumphal defile, which each day gathers within these select surroundings the most elegant women in Paris, fashionable horsemen, vibrating autocars with their chauffeurs, clubmen as well as artists and workmen, who come to enjoy the fair spectacle, this feast of the eyes, this[Pg 325] unique scenery: the Bois de Boulogne, the Avenue du Bois, the Champs Elysées.
From the top of the Arc de Triomphe, 'mid the twilight of May, the vision is a magic one; it is from the terraces of the portico erected to the glory of the Grand Army that a view is obtained of the sumptuous quarters of modern Paris.
Some sixty years ago, Balzac showed his hero dreaming on the hill of Père-Lachaise, and contemplating, as it lay in the valley, the Monster he intended to tame. To-day Rastignac would have to mount the Arc de Triomphe, if he wished to threaten Paris. Thence, he might launch his famous defiance: "It is a[Pg 326] struggle between us now!" for, if the aspect of things has altered, the impression made by the immense City is still and ever the same: an impression of weight, of imperious conflict, of hard victory. In verity, no one disembarks without a sort of anguish in this great Paris,—Paris, so redoubtable to the valiant that attempt its conquest and so prodigal to the fortunate ones that have known how to win its favour.
GEORGES CAIN.
| History of and Researches into the Antiquities of the City of Paris. By H. Sauval (1724). |
| History of the City and Diocese of Paris. By the Abbé Lebeuf (1883). |
| Tableau of Paris. By Mercier (1782). |
| History of Paris. By Dulaure (1825). |
| Tableau of Paris. By Texier (1850). |
| Paris Demolished. By E. Fournier (1855). |
| Enigma of the Streets of Paris. By E. Fournier (1860). |
| Chronicle of the Streets of Paris. By E. Fournier (1864). |
| Paris throughout the Ages. By E. Fournier (1875). |
| My Old Paris. By E. Drumont (1879). |
| Paris. By Auguste Vitu (1889). |
| Paris (History of the Twenty Arrondissements or Quarters). By Labédollière. |
| Revolutionary Paris. By Lenôtre (1895). |
| Old Papers, Old Houses. (1900). |
| The Bièvre and Saint-Séverin. By Huysmans (1898). |
| The Chronicle of the Streets. By Beaurepaire (1900). |
| Paris-Atlas. By F. Bournon. |
| New Itinerary Guide to Paris. By Ch. Normand. |
| Through Old Paris. By the Marquis de Rochegrude (1903). |
| Minutes of the Municipal Commission of Old Paris (from 1898). |
[1] There is a pun here in the French impossible to render in English.
[2] Manon Lescaut.
[3] Successive landlords have more or less spoilt this fine dwelling. The grand staircase is almost the only part intact, and it is a marvel. The carving is by Martin Desjardins, and the oval courtyard retains some of its ancient grace.
[4] A word here meaning ultra-naturalistic, broadly satirical.