 CHARLES LEWIS COCKE
CHARLES LEWIS COCKE
Project Gutenberg's Charles Lewis Cocke, by William Robert Lee Smith
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Charles Lewis Cocke
Founder of Hollins College
Author: William Robert Lee Smith
Release Date: October 6, 2011 [EBook #37636]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK CHARLES LEWIS COCKE ***
Produced by Julia Neufeld, Roberta Staehlin, David Garcia
and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at
http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images
generously made available by The Internet Archive/American
Libraries.)
It will be obvious that this biography has been written in a passion of admiration and loyal love. Conscious of the eminent worthiness of its subject, the writer has felt no temptation to exceed the just limits of praise, or to violate the demands of a true sincerity. The effort has been to hold the record to a faithful presentation of the facts in a long and distinguished career. The singular unity of his life-work, localized on one spot of earth, has made the gathering of materials an easy task. An intimate and affectionate friendship of twenty-three years, is one of the author's invaluable sources. Then, abundant information was found in the minutes of the trustee meetings, the yearly catalogues, the college magazines, the occasional reminiscent speeches to students and the annual commencement address.
One makes bold to say that he fears not the verdict of the older Hollins girls on this memoir. If it shall awaken hallowed memories and unseal the fount of tears; if it shall tighten the clasp of their heartstrings to dear old Hollins, its purpose will have been largely accomplished.
| page | |
| CHAPTER I | |
| The Early Years | 21 |
| CHAPTER II | |
| Call of the Southwest | 34 |
| CHAPTER III | |
| Hollins Institute in Struggle and Growth | 49 |
| CHAPTER IV | |
| The Clearing Skies | 63 |
| CHAPTER V | |
| Expansion and Achievement | 75 |
| CHAPTER VI | |
| The President and his Girls | 91 |
| CHAPTER VII | |
| Commencements and Addresses | 105 |
| CHAPTER VIII | |
| Religious Enthusiasms and Activities | 123 |
| CHAPTER IX | |
| Characteristics | 132 |
| CHAPTER X | |
| His Comrades and Co-Workers | 142 |
| CHAPTER XI | |
| His Monument | 159 |
| Charles Lewis Cocke | Frontispiece |
| facing page | |
| Charles Lewis Cocke and Susanna Virginia Pleasants, About 1840 | 30 |
| The Valley Union Seminary, 1842-1852 | 36 |
| The Female Seminary at Botetourt Springs, 1852-1855 | 46 |
| Hollins Institute | 60 |
| Mrs. Charles L. Cocke | 70 |
| "Good Morning, 'Gyrls'" | 92 |
| Charles L. Cocke | 132 |
| Mrs. Charles L. Cocke | 142 |
| Mrs. Anne Hollins | 150 |
| John Hollins | 154 |
| Hollins College | 160 |
This biographical sketch of Charles L. Cocke has been written with fine appreciation and sympathy. It brings before us an exceptionally strong man, who after years of struggle against discouragements realized, in large measure, the ideals of his early years. It is a story of heroic achievement that can not be read without emotion.
Hollins College stands today as a fitting and permanent memorial of its founder's indomitable will and noble aims. But there was something still finer connected with his years of struggle and toil. Long before the end came, he had made the noblest achievement of human life, bringing from its disappointments and conflicts, not a cynical distrust of his fellow men, but a courageous, hopeful and invincible character of righteousness and love. He learned to look upon the tumultuous world with a serene and benignant spirit.
It was my privilege for many years to serve as one of the chaplains of Hollins College. The hours spent in Mr. Cocke's office after the evening service are among my cherished memories.[10] Our talk, often protracted till nearly midnight, turned chiefly on educational, religious, and social subjects, which always made a strong appeal to his vigorous mind and earnest nature. He loved the truth; but in the expression of his opinions there was sometimes a delightful touch of exaggeration that lent a peculiar charm to his conversation.
Beyond any man I have ever known he possessed the power to call forth noble sentiment and stimulate intellectual activity. This quality explains, in part at least, the loyal devotion of his co-workers and the grateful affection of his students. It made him a great teacher. It endowed him with a sort of divine right to leadership; it crowned him with the glory of perennial, unconscious beneficence.
In the quality of his intellect he was distinctly Roman. By the law of resemblance he easily conjures up before our minds the dignified and sturdy personality of a Cato. Without the gifts of Attic versatility, his strong intellect and sound judgment set him apart for substantial practical achievement. We are fully warranted in believing that he would have won in any industrial or political field the same distinguished success that he achieved in education.
The religion of the New Testament was a vital element in his character. Its dominant feature[11] was not emotion but conscience. To him the call of duty was imperative and final. It was in obedience to this call that he entered upon his work at Hollins. The materialistic science of the latter half of the nineteenth century left him untouched. He recognized the Divine agency in the lives of men no less than in the destiny of nations. This profound and dominant faith habitually filled the future with hope, and imparted to him, as to all who cherish it, unfailing courage and strength.
A massive intellect, supported by a deep sense of religious duty, made him an independent and fearless thinker. He had the force to break the trammels of tradition. With the vision of a true pioneer he saw the need of a better intellectual training for American women, and with the resourcefulness of a strong nature he led the way in its attainment. His aims and efforts were manifestations of real greatness. It is men of like vision and resourcefulness who are raised up from time to time to lead the forward movements of our race. It is no reproach to say that Mr. Cocke would hardly have been in full sympathy with the feminist movement of recent years. No man can live too far ahead of his time. But he helped to prepare the way for it by his pioneer insistence on a richer culture and larger opportunities for women; and it may justly be said that[12] no other man in Virginia or the South has a higher claim on their recognition and gratitude.
He was fortunate to recognize in his early manhood his vocation as a pioneer educator. The call was clear, and his consecration complete. Few men have ever labored with greater singleness of purpose. As Tennyson dedicated his life to poetry and Darwin to science, so Mr. Cocke gave himself to the work of a nobler culture for the women of Virginia and later of our whole country. Without this singleness of aim, which gave unity to his efforts for more than fifty years, he could not have brought his great life-task to a triumphant conclusion.
But his great mind and heart were not so utterly absorbed in this work as to exclude from his thought and effort other important interests. Before the present movement for social betterment had been inaugurated, he labored unselfishly for the material and moral improvement of his community and State. He was interested in the establishment of schools for boys. He was a recognized leader in the extension of the Baptist Church in Southwestern Virginia, and his foresight and wise counsel contributed in no small measure to the vigorous life and growth of that denomination.
Yet he was not narrowly sectarian. His broad outlook on life welcomed every agency that contributed[13] to moral and religious advancement. To his mind denominational differences of creed were of secondary importance as compared with the great fundamental agreement in the work of establishing the kingdom of God in the world. He cultivated friendly relations with all branches of the Christian Church, and invited their ministers from time to time to conduct services in the Hollins Chapel. His chief requirement was a helpful message supported by an upright life.
He delighted, it seems to me, in what we might call intellectual athletics. He welcomed a disagreement of view, and enjoyed measuring strength in an argument. The enjoyment, I think, was independent of the outcome of the discussion; it was found in the pleasurable exercise of a vigorous brain. Defeat in argument yielded him scarcely less pleasure than did victory. The warmest discussion never ruffled in the slightest degree his self-possession and friendly courtesy.
In the massiveness of his character he was exempt from the foibles of smaller natures. In his striving after truth he was unswayed in his judgment by petty prejudices. His broad benevolence and warm interest in the welfare of others shielded him from envy and jealousy. While sternly intolerant of wrong-doing, he was gently patient with the wrong-doer, being less anxious to punish than to reclaim. Though he was doubtless[14] conscious of his strength, as are all truly great men, he was too sensible and honest to feel the inflation of egotism. His natural stately dignity forbade familiarity; but to those in need he was uniformly kind and helpful. It is the memory of his kindness and helpfulness that has enshrined his image in many hearts.
The life of so rare a character deserves to be recorded in permanent form. It will thus stand as an inspiration and guide to others. As biographer Dr. Smith has performed his task worthily; and I esteem it a privilege to write this introduction and pay this tribute of admiration and affection to one of the greatest men I have known.
Salem, Va.,
September 2, 1920.
February 21 Charles L. Cocke was born at Edgehill, King William County, Va.
He entered Richmond College.
He entered Columbian College at Washington, D. C.
Graduated from Columbian College, and accepted a position at Richmond College.
On December 31 married Susanna Virginia Pleasants, of Henrico County.
Connected with Richmond College.
Called to take charge of "Valley Union Seminary," a co-educational school, Roanoke County, Va., at Botetourt Springs.[16]
June 23 arrived at Botetourt Springs to take charge of the school.
July 1 the first session under Mr. Cocke's superintendence opened with 36 boys and 27 girls.
Board of Trustees discontinued the department for boys.
July 20 the session 1852-'53 opened for girls only, under the name The Female Seminary at Botetourt Springs, Va., Mr. Cocke, Principal, Registration 81 girls.
September 4 the session of 1853-'54 opened with increased faculty and registration of 150 girls.
Mr. and Mrs. John Hollins of Lynchburg, Va., donated funds to the institution, and in their Honor the name was changed to Hollins Institute.
Average attendance 106.[17]
Doors not closed during this period. Average attendance 134.
Average attendance 73.
Buildings, enlarged to accommodate 225 students.
I think I would rather have written a great biography than a great book of any other sort, as I would have rather painted a great portrait than any other kind of picture.
In the library at Hollins College is a life-size portrait of a great Virginian. In its presence, you instantly feel the spell of a commanding personality. The figure is tall, graceful, well proportioned, and in the right hand is a diploma, the proper symbol of the vocation of a College President. The attitude exactly fits the supreme moment on Commencement day. In the face, the artist has cunningly gathered the insignia of fine mental quality, and pictured the forces of achieving manhood. The ample brow looks the home of ideality and enterprise, the aquiline nose hints endurance and tireless energy. Napoleon selected as his marshals men marked by the prominence of this feature. That jaw and chin and those thin lips speak virility and determination. In the glance of those blue, eagle eyes, are intimations[22] of keen intensity and lightning force, yet subduable to all the moods of tenderness and love. Truly, this is a notably fine presentation in art of one of the noblest Virginians of the 19th century.
This man was marked for high performance, and would have won distinction in any sphere of honorable endeavor. "Excelsior" was the divine imprimatur stamped on his nature. His call was to leadership, and his response enrolled him among the pioneers in the cause of the higher education of women in the South. The educational ideals of Thomas Jefferson became the inspiration of his youth, and with astonishing tenacity and unity of purpose he pursued them until he worked out Hollins College, making it one of the rare gems of American culture. His work stimulated the founding of other like institutions in Virginia and the South. Thus he builded wiser than he knew. He wrought well in his generation, and a multitude of splendid women throughout the whole nation will revere his name forever. It was a brilliant battle he fought against hostile conditions and appalling odds. He was cast in heroic mold. In fancy we can see him bearing his banner up the heights, his eyes flashing strange fires, and every energy of soul and body exerted to its utmost. The name of this remarkable man is Charles Lewis Cocke, and[23] there stands the faithful, impressive likeness of him in the library building at Hollins College.
It is the story of this man that we want to know, and to that end the following pages are written. It is the right of every child to be born of honorable parentage. The life of Charles L. Cocke began with a good heredity. He was born February 21, 1820, at Edgehill, the home of his father, James Cocke, in King William County, Virginia. Elizabeth Fox was the maiden name of his mother. Both family names run back a number of generations, the old English ancestors having come to Virginia in the 17th century. Richard Cocke bought a home with three thousand acres, and from 1644 to 1654 represented Henrico in the House of Burgesses. John Fox located in York County and then in Gloucester, in the years 1660 to 1680. From this worthy stock descended the subject of this biography. Charles Lewis was the oldest son of the family at Edgehill. Religious reverence and intelligence dwelt in the home, and correct views of conduct were expressed in parental example. The Baptist faith was an important part of his inheritance, and at Beulah Church near by his childhood received its first impressions of divine worship. By singular good fortune, the benign influence of the eloquent pastor and friend, the Rev. Dr. Andrew Broaddus, fell on the family and the growing lad.[24] In the atmosphere of this happy home, and in the moral securities and privileges of a good country community, the early years were passed. The boy's mind was alert, and both on the farm and in the local schools, gave hints of latent powers. The growing youth demonstrated his managerial capacity one year by taking charge of a kinsman's farm and raising, as he said, "the finest crop it had ever borne." Self-reliance and the power of bringing things to pass early became distinguishing qualities. The father was proud of the promise of his son, and when the boy was about fifteen years of age, gave him his choice of a career on the farm or in some professional calling. The father could hardly have been surprised at the prompt decision in favor of a profession.
Richmond College was then new, and under the presidency of the Rev. Dr. Robert Ryland, was prosecuting its work in the suburbs of the Capital City. The College was only twenty miles distant from Edgehill and soon our ambitious youth was diligently pursuing his studies within its walls. No special genius betrayed itself, but there was the same bent of assiduous application which was on display when the abundant crop was raised. Dr. Ryland was not slow in discovering the promising traits in the new student, and a mutual interest sprang up between them. The[25] astute President saw in the boy the prophecy of stalwart young manhood, just such a factor as might some day be of value to himself in the labors of the Institution. The interest grew into intimacy, and there were occasional confidential interchanges respecting the boy's hopes and aspirations. The time of attendance on the College classes was drawing to a close, when one day the Doctor suggested to him a further course at Columbian College, a Baptist institution of higher learning in Washington City. The thought enlisted the youth's enthusiasm, but he urged the lack of funds needful for such a scheme. Then the generous friend replied: "I will furnish that, and you can repay me at your convenience."
Here was a compliment from a wise educator which, though it tended to no inflation of conceit, put a glowing stimulus in a young man's soul. No true man or woman ever fails to give gratitude and honor to those who quickened and encouraged aspiration in the days of youth. Impressed deeply by the kindly offer, and stirred by leaping ambition, Charles Lewis Cocke left the College and returned to his home. At once he communicated to his father the new visions and hopes. The father, pleased at the hunger of the son for larger knowledge, said: "You shall go to Columbian College; but we will not draw[26] on the generosity of Dr. Ryland. I will supply the means." Charles was then about eighteen years of age.
The boy Daniel Webster was riding one day in a buggy with his father, when at a certain point of the conversation the father said: "Son, I have decided to send you to Dartmouth College." The announcement fell like music on the aspiring soul, and the only response the delighted son could make was to lean his head on his father's bosom and burst into tears. Edgehill knew an emotion like that in the summer of 1838. Pursuant to plans for early departure to Washington, James Cocke and his son drove to Richmond in a buggy. While the reins were in the father's hands, the horse went at a sluggish gait. Presently they were passed to the son, when instantly the drudging steed pricked up his ears and struck a new stride.
"You have been whipping this horse," exclaimed the surprised father.
"No," was the reply, "I have never whipped him, but he knows what I want him to do."
Long years afterward, this little incident was told by the President of Hollins Institute to his graduating class, with the reflection, that he had learned that the best movements in horses and in people can be secured without whipping.
The new student was welcomed into Columbian[27] College and there pursued the courses of study with unabating enthusiasm. Naturally the environment of the national Capital served as a wholesome stimulus to all his faculties. The good habits of his life suffered no deterioration and the fine qualities of his mind went on maturing rapidly. It was during this period that deepening religious impressions resulted in an open confession of faith, and in union with a Baptist church in the city. He was baptized in the Potomac river. Closely following his twentieth birthday came his graduation with the degree of M.A. It is to be regretted that no letters written to his parents during this season have been preserved. Fortunately, two written to his friends do survive. One, sent to his college chum, Mr. A. B. Clark, of Richmond, Virginia, bears date of May 22, 1839:
"I walk at the usual times alone, spending the moments mostly in meditation on serious subjects. My thoughts are more apt to turn this way than formerly. I write two lessons per day in Greek and read but little in other books."
Something far more significant appears in the second letter which was addressed to a kinswoman in the neighborhood of Edgehill. In that he declared a settled purpose, "To devote my life to the higher education of women in the South, which I consider one of our greatest needs. In[28] this decision, my promised wife concurs." What special influences led the college boy to such a majestic consecration, we have no means of discovering. That it is a mark of uncommon maturity and breadth of intelligent conception, there can be no question.
The benignant spirit of Democracy was becoming atmospheric and the intellectual emancipation of woman steadily and slowly pressed to the fore. Ancient prejudices and stupidities were beginning reluctantly to yield. Not one of the elder ages had ever grasped the thought of woman's mental, social and political equality with her brothers. Here and there a lone voice had been lifted in her behalf to fall on deaf ears and unresponsive hearts. The world habit of thought laughed the innovation out of court and the bondage of general ignorance remained unbroken. But the imperial idea of the dignity and worth of the human individual could not be forever submerged. Its persistent pressure loosened the bonds of tradition and began to breach the walls of custom. Modern freedom wrought itself into the minds of men, and thinkers announced the harbinger of a new era. Practice, as usual, lagged behind theory, and one hundred years ago when Charles L. Cocke was born, advantages for the culture of daughters were inferior to those afforded the sons. That this[29] inequality should have impressed the mind of a young collegian, shows uncommon susceptibility to social needs and sacred human rights. A rare young manhood came to expression when he dedicated himself to the new ideal. He did not originate the ideal. It was borne to him in the expansive thought of the time. His shining merit is in the fact that he made the early resolve to be an agent in bringing in the better day for the liberal education of young women.
It was in the Spring of 1840 that his college work closed and he received the degree of Master of Arts. Before the Finals of that session, there was some important correspondence between himself and Doctor Ryland. The good President had startled Charles with the flattering proposition that he should become a member of the Faculty of Richmond College, as assistant teacher in Mathematics and as manager of the dining hall. The college was then trying to combine training in agriculture with the usual curriculum, an experiment that was soon abandoned. The young man was too genuinely modest to fancy himself equipped for so responsible a position. He faced the issue frankly, however, and much influenced by confidence in the judgment of Doctor Ryland, decided to accept. Leaving Columbian College he hastened to witness the closing exercises at Richmond College.
[30]It must have seemed almost comical to see a practically beardless youngster put in charge of some of the vitally important duties of the Institution. There he was, without a touch of egotism of self-consciousness, quiet of manner, and yet with something about him that looked resourceful, unapologetic, and unafraid. You may be sure that the boys looked at him curiously, and asked themselves, "Can he do it?" Of course there were cautious conservatives who doubted the competency of the new incumbent. This tribe is always with us. However, there was ground of assurance in the known confidence of Doctor Ryland, and nothing remained but to wait and see its vindication. No misgivings troubled the Doctor himself. Without bluster or consequential airs, the assistant professor made prompt acquaintance with his tasks, and discharged them with an efficiency that left nothing to be desired. He was on his mettle, conscious of the questioning curiosity centered upon himself. For the first time in his life he stood before the footlights of public observation and expectation. Leadership had thrust its burdens on him early and had imposed its first critical test.
 CHARLES LEWIS COCKE AND SUSANNA VIRGINIA PLEASANTS
ABOUT 1840
CHARLES LEWIS COCKE AND SUSANNA VIRGINIA PLEASANTS
ABOUT 1840
A survey of the affairs of the dining hall convinced him that a change of methods was necessary, and with pure audacity he introduced them. At the opening of the fall session of 1840 he presented[31] the boys with a new bill of fare. To their astonishment he gave them oysters, finding them as cheap as other meats. He gave them raisins and plum pudding for dessert. He scored instant success, and the boys' heartstrings were in his hands. Without incurring increased expense, the new manager secured a new satisfaction with the dining hall. Noiselessly other needed changes were made and the voice of the growler ceased to be heard. At the helm was an officer who knew college boys, and the college spirit was noticeably improved. Like competency appeared in the duties of the class room. He could teach mathematics and he did. Before the Commencement in 1841, Charles L. Cocke was recognized as a distinct contribution to the life of the Institution. Here is a young professor who does not propose to rest content with inadequate facilities and outworn methods. His whole nature cries for improvement and for better ways of doing things. What a boon to many a school and college would such a man be. Good Doctor Ryland's face wore a smile which plainly said, "I told you so." His judgment of capacity and character was sufficiently justified. The young comrade was to him an object of ever-deepening interest and their relations steadily ripened into sincere and loving friendship.
Now, the President knew that his assistant was[32] romantically entangled with an affair of the heart. He also knew the fair young woman who was responsible for that state of things. Miss Susanna V. Pleasants lived five miles north of Richmond in a lovely old Virginia home which bore the Indian name of "Picquenocque." Knowing that a matrimonial alliance was imminent, the Doctor, one day, ventured to ask Charles about the date of the coming event. He warmly approved the match and was exuberant in congratulations. As a matter of fact he was hoping that the marriage would tend to fix his assistant more firmly in Richmond College. This genial intrusion into sacred privacy was not resented, but Charles found it inconvenient to confide. The question was asked in November, and at that very moment the issue to be decided between the sweethearts was whether the ceremony should come off on the last day of December, or the first of January following. That problem enabled the young gentleman to make a complete but truthful evasion. His honest reply was: "I know neither the day, nor the month, nor the year." There the matter ended, and the mystified Doctor relapsed into silence. Later the mighty problem was solved and the marriage was solemnized on the last day of 1840. Doctor Ryland, officiating, beamed on the happy pair and found great merriment in the perfectly true, but dextrously[33] non-committal answer, made just six weeks before. The bride and groom had not quite reached their twenty-first birthdays when they began that remarkable human pilgrimage which was to endure a little more than sixty years. The angels of domestic peace and joy sang benediction all the way. That home life is a glorious memory now, but its lesson is more precious than gold. An astronomer discerned a luminous star. On closer inspection he found it, not single but binary. The twin stars joined their radiance, which came streaming down in one glorious pencil of light. Such a star beams forever in the Hollins firmament.
The attraction of the Blue Ridge and Alleghany mountains was a fact freely confessed by eastern Virginians. Even before the Revolutionary War the section, now known as the Tazewell country, became an Eldorado, and thitherward set the streams of migration. Along the beautiful valleys and in the hearts of the hills lay the possibilities of fabulous wealth. Through the early decades of the nineteenth century this fascination continued, population increased, centers of culture were formed, and men of enterprise began to think of a railroad from Lynchburg, Virginia, to East Tennessee. Christian evangelism was active, but education lagged. There were fine brains in the Southwest, but the means of culture were deficient. The land called for the school teacher. Slowly the providential workings were preparing a place for a young professor in Richmond College, who as yet had no dream of it.
[35]Seven miles north of the City of Roanoke, Carvin's creek pours down out of the mountains into the wonderful Roanoke Valley. Right in the aperture of the hills where it emerges, was discovered a little sulphur spring whose properties suggested the establishment of a watering place. Accordingly, Mr. Johnston, a man of wealth from Richmond, bought a hundred acres and built a commodious brick hotel near the two springs, one limestone, the other sulphur. This was somewhere near the year 1815. A race course was made one of the additional attractions. The place took the name of "Botetourt Springs," and at once leaped into fame as a health resort. The turnpike from the west passed immediately in front of the hotel and between the springs, which are one hundred yards apart. General Andrew Jackson stopped here for entertainment on his way to and from Washington City. General Lafayette, on his last visit to the United States, was an honored guest. Touring south, he came out of his way to pay respect to his old friend, Mr. Johnston.
Interesting legends from the old pioneer days gathered round the spot. One bold adventurer, named Carvin, was said to have built a rock castle on a crag near the springs and to have had many hair-breadth escapes from Indians and wild beasts. All that is certainly known is, that[36] he left his name on the little creek that passes nearby. A huge, isolated mountain, in the shape of an elephant, rises just one mile to the north, and tradition says that cowardly slackers of the Revolutionary period made it a hiding place. They mended pots, plates and pans, and so were called "tinkers." Thus it comes that the beautiful mountain wears a homely name and perpetuates an unworthy memory.
Botetourt Springs was popular and well patronized by seekers for health and pleasure, but the death of Mr. Johnston brought a crisis, and in 1840 the property was on the market. The administrator, Col. George P. Tayloe, offered it to the highest bidder. Just at this time a Baptist minister, the Rev. Mr. Bradley, from New York State, had come into the neighborhood, seeking a home and work. Being an intelligent man and especially interested in education, he saw that this property was capable of being converted to the uses of a school. His zeal and industry soon materialized in the organization of the "Valley Union Education Society," and that body purchased Botetourt Springs with promises to pay.
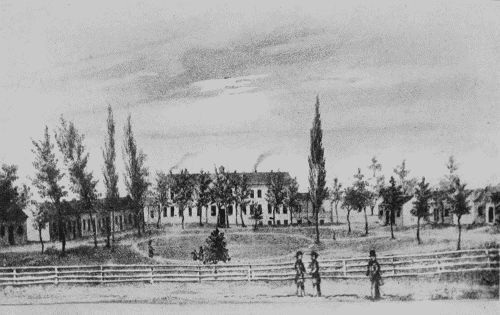 THE VALLEY UNION SEMINARY, 1842-1852
THE VALLEY UNION SEMINARY, 1842-1852
The buildings were easily adaptable to the purposes in hand. The old hotel, consisting of a basement and two stories, provided a dining hall, a chapel, and thirty-one rooms. Then, there were seven smaller buildings with two to four[37] rooms each. These latter were ranged on opposite sides of the front yard, at right angles to the main building. In the fall of 1842 the "Valley Union Seminary" was launched, under encouraging conditions, with Mr. Bradley at the head. The patronage was large and the prospects alluring at the outset, but soon the relations of the Principal with his faculty and students became unhappy. He was a worthy, irreproachable man, and intellectually competent, but it seemed impossible for him to make tactful adjustments with the young Virginians. The management was changed, attendance was large, and the only cloud on the enterprise was the unpaid notes. The affairs of Mr. Johnston's estate must be wound up. The young Seminary in its third year was in the breakers, and looked disaster in the face. It was now in the spring of 1845. Deliverance must come speedily, or another dead school would pass into the abyss. In this critical hour, two or three students just returned from Richmond College said to members of the society: "We know a man who can handle your Seminary and make it go." Any remark that hinted at relief was more than welcomed by the trustees, who asked whom the students had in mind.
"It is Professor Charles L. Cocke of Richmond College. He is only twenty-five years old but he has had five years' experience in teaching. He[38] knows how to bring things to pass, and if your school can be pulled out of a hole, he is the man you want."
Such was the homely but emphatic tribute of the college boys, and it did not pass unheeded. Propositions from the Society went promptly to Richmond, and the Professor was induced to come to the mountains to look the situation over. The Society was pleased with him, and he was impressed with the possibilities of the Seminary. The call of the great Southwest sounded in his ears and the visions of the things that may be, beckoned him on. The call was made in the spring of 1845. He would ponder it devoutly.
Shall he break all the tender ties that bind him to his Tidewater home? Shall he sunder relations with Richmond College and bring grief to the heart of his devoted friend, Dr. Ryland? Shall he take his young wife and three little children into a rugged land, remote and destitute of the comforts they have known? Such questions voiced the negative, self-regarding view, and he asked himself: "Is not this Southwest a land of great promise and educational need? May not this be the providential arena for the realization of my fond dream of mental liberation for the daughters of Virginia and the South?" This noble speculation, still working, was hid away in his soul, vague and undefined. It would grow.[39] This was the positive and unselfish view, and he knew it. "Yes, I will go," was the final settlement of the painful controversy. Like Abraham, he would go forth all unknowing, yet believing in the guidance of a divine wisdom. No, this young man was not the football of impulse. His decisions were the outcome of long deliberate thought. This was the most vital step of his life. He heard the voice of duty, that "stern daughter of God," and obeyed. He had an imaginative power which went, not to the uses of poetry, but to the practical problems of life. It was his habit to project his thought thirty years forward, deploying before him the reasonable developments of a growing civilization. In these forecasts, imagination did him a fine service. Here was the spring of those ceaseless demands for enlargement and improvement of facilities, which later marked his work as college president.
The spring of 1846 is come; the six years of work in Richmond College are closed; the farewells are spoken; and Mr. Cocke journeys toward the sunset. It is a weary overland drive of five days in a carriage from Richmond to Botetourt Springs. Lofty "Tinker" salutes the pilgrims as they move up the highway, and now the vehicle stops in front of the old hotel, whose front yard is a wilderness of weeds. Mrs. Cocke's heart sinks within her as she looks on the inhospitable[40] desolation. Ghosts of dilapidation and decay stretch out hands of welcome in sheer, grim mockery. The anguish in the young wife's heart is momentary. With a sublime courage, equal to that of her husband's, from that awful moment she goes smilingly with him to the task of preparing for the coming session. Unwittingly, they are laying the foundations of the noble Institution which, today, is a pride and joy to the state and nation. Little do they dream that before the closing of their toil, they will see girls from thirty states parading and singing on that outlandish front yard.
"I'd rather walk with God in the night
Than go alone by day."
By a business arrangement with the trustees, Mr. Cocke had put into the treasury of the Society $1,500.00 of his own and his wife's money, to stay off the creditors. On the 23rd day of June, 1846, the session opened with the new Principal in charge. It was a new dignity, truly, but how precarious and involving what weight of responsibility! The young soldier is on the firing line with an independent command. He can hardly anticipate the leagued masses of trouble, disappointment and despair that lurk in the mountains, plotting his destruction. For the next twenty-five years we shall see the storms of battle break upon[41] him, and we shall see his banner waving in victory to the shoutings of a multitude. The Principal is a born leader. He is resolute and confident without egotism; resourceful and wise without display. The Richmond College boys were right. Here is the man. However, the burden-bearing years must develop the fact. The first nine years will carry us through seasons of struggle and painful progress. With the outstanding facts of this period, it is the purpose of this chapter to deal.
He was now the head of a co-educational Seminary, which from its inception was designed to be strictly benevolent in character. In ample proof is the fact that $45.00 paid the student's bill for tuition and board for five months. The school never made money, nor was that ever its end. The purpose of the founders was to put education in the reach of all who thirsted for it. Such was the generous basis of the enterprise. The small revenues thus realized, yielded the teachers pitifully inadequate reward, and made improvements practically impossible.
You may be sure that good order was maintained and good lessons were required. From the start, Mr. Cocke's administration won popular confidence and approval. Soon after his coming he was announced to speak in the Baptist church in Big Lick (now the City of Roanoke),[42] and a large audience was there to greet him. In the address he said, among other things, "I have come to Southwest Virginia to give my life to the cause of education, to spend and be spent in that work." A fine impression was made on the citizens, and on dismission a gentleman said to a lady: "That is the man to send your son to." Fifteen years later that boy was a Colonel in the Confederate army. This boy's older brother had told Mr. Cocke that Thomas was a bad boy, and had added, "If he does not behave, I hope you will thrash him." For two whole sessions the youth found himself seated at the table next to Mr. Cocke and the coffee pot. He was entrusted with messages here and there, and finally the boys began to say that Tom Lewis was Mr. Cocke's pet. Not so: that was his ingenious discipline. He could control horses and boys without whipping. In the long after years the Principal had no more faithful and devoted friend than Colonel Lewis. Once a group of older boys made some of the younger ones drunk. The offenders were promptly expelled, and nothing was done to the innocent victims. Other young men made angry threats, and their expulsion followed. Rebellion grew; a large body of the boys defiantly paraded the campus, making the situation ominous. The school was called to the chapel, the boys on one side and the girls on the[43] other. The Principal fronted the boys and said: "I am the head of this school and I am going to run it. I have sent some disorderly students away, and if necessary I will send more. I will send every one of you home and start a new school, and if I can't run it I will give it up and go at some other business." The audience understood the tone of that voice and took warning from the gleam in the blue eyes. After that the incident was closed.
His skill in dealing with mischievous boys is exhibited in another episode. Some of them felt that school life was dull without a little spice of adventure, so in pure fun they sallied forth at night to visit the neighbors' orchards, and even to take unwarranted liberties with their chicken roosts. Complaints came to the Principal, who at once sought a private interview with the culprits. He talked to them kindly, yet with earnest protestations against such pranks. He knew they were not thieves, far from it, but they should not take people's property that had cost labor and care. After duly moralizing on the case, he closed the interview with the following burst of magnanimity: "Now boys, if hereafter some irresistible impulse is on you to prowl, spare the neighbors and plunder my poultry yard." What human heart but a school boy's could resist an appeal like that? One night not long thereafter,[44] Mrs. Cocke heard curious noises on the back premises. Mr. Cocke slipped out in the darkness and readily took in the situation. The following night he stood at the window of one of the boys' cottages and saw the preliminaries looking to a midnight carnival on roast duck. Just as the feast was ready to begin, there was a tap at the door. Hospitality invited entrance, when in stepped Mr. Cocke! To his friendly inquiries they responded that they were about to dispose of a savory meal and coolly invited the visitor to share it, which he as coolly proceeded to do. The party was jolly, and though all knew that nobody was deceived, the fact was not betrayed by one look or word. Mr. Cocke bowed himself out with a pleasant good night, and the mystified marauders went to bed. Depredations ceased, and the boys' admiration of that midnight diplomacy was unconcealed.
When a boy was guilty of some offense, not mean, but mischievous, his case was stated in the presence of the school, and the roaring laughter that followed was sufficient correction. There was not a case of disobedience among the girls in the years 1846-'52, but they would keep their windows open. The boys lifted hats in passing, and were rewarded with pleased and winning glances. Often while sitting by the open window, a thoughtful look covered one side of a girl's face,[45] while on the other side, looking window-ward, played a bewitching smile. In those days was established the yearly October visit to the top of Tinker. The day of the excursion was a "secret between Charles and the Lord," as Mrs. Cocke once humorously said to the inquiring girls. Arriving on the summit, and viewing the landscape over, suddenly an apple would fall in the midst, as from the sky. Where did it come from? The girls knew, and the boys knew. The boys had gone before and hidden behind the rocks and brush. Then the mountain scenery lost its charm, and a romantic search for flowers began.
The halls of the Seminary filled to their capacity and the Principal pleaded for more room. Alas, the Trustees had no money, and the school's revenue was a sacrifice to the benevolent principle of minimum rates. The Institution he wanted could come only through increased equipment and accommodations. There the young Principal was, the sport of harsh conditions. One balm came to his heart in the timely sensible praise of the Trustees. In their meeting, January 10, 1851, they said in formal resolution: "We cannot speak in terms too high of the untiring diligence of the Principal and his assistants in maintaining judicious discipline, and in the prosecution of their responsible duties."
His efforts for notable success had a double[46] motive. First, he quite properly wanted to convince all of his capacity for educational work. Second, by the overcrowded conditions, he wanted to force an issue on the Trustees respecting the future policy of the school. The accommodations were palpably insufficient, and as there was no possibility of increasing them, what should be done? The Principal knew what to do. He boldly advised a radical change: dismiss the male department and convert the Seminary into a school for girls. To his immense delight, the proposition was accepted. The new order looked like the opening of an approach to the goal of ambitions born in his college days. His loyal interest in the education of young men was not abated, but the dream of the higher education of women became a passion. This important decision was made in the spring of 1852, and thus a ten years co-educational school, in which Mr. Cocke had labored for six prosperous years, came to a close. With mingled feelings of grateful hope and keen anxiety, he now faced a golden opportunity. He enjoyed the distinction of being the head of the first chartered school for girls in Virginia. The fall session of 1852 opened with eighty-one pupils. That of the fall of 1853, with one hundred and fifty. The wisdom of the radical change was fully justified. It was a time of radiant satisfaction and jubilant hope.
 THE FEMALE SEMINARY AT BOTETOURT SPRINGS, 1852-1855
THE FEMALE SEMINARY AT BOTETOURT SPRINGS, 1852-1855
But it was now that the battle with austere conditions and scant equipment became the torment of his mind. The Trustees could give no material aid, and popular interest in education was too feeble to proffer financial help. It is simple truth to say that on this vestibule of his great enterprise, the gravest doubts and trepidations of his whole career assailed him. In moods of depression the heroic man feared that he had attempted the impossible. Was he unnerved or unstrung? Not for one minute. In these black days he fronted his task with the resourcefulness of an uncommon manhood. The stamina of his nature came to expression in a way that surprised even himself. He made imploring appeals to friends who were well to do in this world's goods. A good providence put him in touch with two noble spirits, Mr. John Hollins and his wife, of Lynchburg, Virginia, members of his own denomination. Mr. Hollins presented the Seminary with a gift of $5,000 cash, and then the daylight began to break. The good man proposed as a condition of his gift that the old management by an Education Society and its appointed Trustees must give way to a board of self-perpetuating Trustees. To all concerned the proposition seemed wise and just, and it was so ordered. It was then generously agreed that the name of the Institution should be changed, and that henceforth it should[48] be known as "Hollins Institute." To Mr. Cocke and the dissolving Society, this appeared to be a compliment well deserved by the man and his wife who had saved the life of the school.
The transfer of all the property of the Valley Union Education Society to the Trustees of Hollins Institute was made in March, 1855. Thus in the first nine years of his incumbency, Mr. Cocke saw two revisions of the original charter granted in January, 1844. By the first revision in 1852, the Seminary was made a school for girls. By the second, in December, 1855, the name of the Institution was changed, the old management was abolished, and its functions put into the hands of a self-perpetuating Board of Trustees. No friction arose; all was harmony. The old régime passed, but its personnel remained steadfast.
In all the stress and tribulation of the past years, Mr. Cocke had been the central bolt that held the structure intact. Around his single heroic personality gathered all the forces that made possible the perpetuity of the Institution. His reward had now come, and a blessed assurance threw its foregleams on the future. He was now in his thirty-sixth year and athrill with that full health and masculine energy that was his blessing to the end of his life.
That was a high day, in the summer of 1855, when Hollins Institute flung its banner to the breeze. A munificent gift, a new régime and a new name put fresh enthusiasm into the Institution, and the gladness of hope into the hearts of all its friends. You have noticed how these joyous effects always flow from new deals and revisions of plans. A better day has dawned, bright visions float in the brain of Mr. Cocke, and the blue mountains seem to hail him with congratulation. The human heart would famish but for these fountains that break out in the midst of weary, toiling years. Economic conditions are improving in the Southwest. The Kanawha Canal now connects Richmond with Buchanan, a village just twenty miles away. The Virginia and Tennessee Railroad has been built (1852), supplying quick communication with the outside world; and the macadamized turnpike[50] has been built from Buchanan to the west, passing within a few hundred yards of the School. The general conditions were never so cheering, nor was the outlook ever so bright.
Some necessary changes have been made by the Trustees in internal affairs. The rates of board and tuition are moderately increased, and Mr. Cocke is put in charge of all departments, with authority to select his teachers and to fix their salaries. The new Board of Trustees knows the qualities and capacities of the Principal, and from this time forth they give him confidence and almost unlimited powers. Charles L. Cocke, not yet thirty-six years of age, had attained enviable distinction in the educational ranks of his native State. He will justify the faith of his friends.
The Hollins gift of $5,000 was put to work. The East Building with thirty-eight rooms, was projected, and by January, 1857, completed at a cost of $12,000. Alas, calamity crashed upon the school. In the fall of 1856 typhoid fever broke out and forced a temporary suspension. With cruel suddenness the epidemic worked a loss of public confidence, and once more the heart of the Principal was harrowed with discouraging thoughts. It was given out that bad sanitary conditions had invited the scourge, but rigid investigation exploded the theory. The fact was that the disease had been brought to the Institute by[51] one of the pupils. Slowly the panic yielded and confidence returned, but the experience was shocking. Quickly the Principal regained his tone of courageous hope and its wholesome contagion spread far and near. In July, 1857, in a report to the Trustees, he made this important and assuring statement: "By affording these superior inducements the school has realized a degree of prosperity beyond that of any boarding school in the state, and has given an impulse to female education heretofore unknown. The plan and policy of our school must be considered the true one. This plan recognizes the principle that in the present state of society in our country, young ladies require the same thorough mental training as that afforded to young men, and accordingly, in the arrangement of the course of studies, and the selection of teachers, and the conferment of distinctions, we have kept this principle steadily in view. This feature of the Institution has given to it its prominence and past success, and other Institutions, originating since our plan was made public, have almost uniformly adopted it."
During the year 1858, the activity of the Trustees secured a good many subscriptions, and the[52] generous Mrs. Anne Hollins rallied with her own gift of $2,500. The dark days of 1857 began to be a memory, and the revival of public confidence and patronage smoothed the brow of care.
It must not be supposed that Mr. Cocke lost interest in the education of boys when the co-educational system was abandoned in 1852. No man in Virginia was more enlisted in the education of all the people than he. There must be a school for the boys in the Virginia Mountains, and in the later fifties, though sufficiently burdened with local cares, he turns his attention to this interest. With the valuable assistance of Dr. George B. Taylor, later an eminent Baptist missionary to Italy, he was the chief factor in establishing Alleghany College, in Greenbrier County, one hundred miles northwest of Hollins Institute. This county was included in the new state of West Virginia, organized in 1861. The school opened with one hundred young men and ran well for a brief season, but was suspended at the beginning of the Civil War. The buildings were occupied by Federal soldiers, and shortly afterwards were destroyed by fire. All subsequent efforts to revive the college were unavailing. With characteristic loyalty, Mr. Cocke matriculated his son, Joseph James Cocke, at the opening of the first session. The brave boy laid down his books at the first alarm of war and entered the Confederate[53] army, and in the terrible battles in Northern Virginia, he was twice dangerously wounded. That boy is now a venerable and honored citizen of the State of Texas.
Long years after, Mr. Cocke bent his efforts towards the erection of Alleghany Institute at Roanoke, and had great satisfaction in its commodious buildings and its promising attendance of boys. In the course of varying fortunes this enterprise fainted by the way and ceased to be. One can but fancy that if Mr. Cocke himself could have held the helm in these two adventures, the story would have been different. The storms beat and the floods came, but Hollins Institute stands. Her standards are stirring thought currents and stimulating like enterprises in Virginia and the nation. For our pioneer in the Southwest, this is compensation and a crown of glory. Without one thrill of jealousy does he see the spread of his views and the certainty of large competition. To stand in his own place and make good, is the one guiding and all-controlling purpose of his life.
In 1860, Mrs. Hollins, now a lonely widow, signalized her profound interest in a new gift of $10,000. This generous and timely act pushed up the contributions of the Hollins family to the handsome sum of $17,500. The growing popularity of Hollins sprung the problem of enlarged[54] facilities and to solve it was the design of this latest benevolence. It was greeted with boundless gratitude, and the Trustees deputed one of their members, Mr. Wm. A. Miller, to bear to her their most cordial thanks. Accompanying this message was an urgent request for the oil portraits of the two benefactors. In due time the portraits came, and to this day they adorn the walls of the Main Building, whose erection was made possible by the recent gift. An architect was employed, and work was begun on this building in the spring of 1861, on the very day that Virginia seceded from the Union. The tempest and blight of the Civil War came down to threaten the life of the Institution and to almost break the heart of the founder. Expectant hope had looked for early occupancy, but it was not to be. In one year the walls were upreared, the roof was on, and then the work stopped. The contractor quit his job because the war had disorganized labor and the situation was simply helpless. There stands the unfinished structure, and there it will stand, a ghastly skeleton for eight long years.
At this beginning of horrors, Mr. Cocke's reputation as a strong man was established, and the fair name of his school was extended beyond the limits of the State. Seasoned in old battles and richly schooled in experience, he stands in his place[55] unterrified. He dares, even amid the clouds and disasters of war, to send out his adventurous thought, thirty years to the fore. What ought to be, what may be, the facilities and achievements of this Institution a generation hence? He is now too well fortified in his convictions of educational theory and practice, and of their fitness to the needs of the time, to be affrighted by the spectres and goblins of ultimate failure.
In 1862, he speaks to his girls and the public in this fashion: "The organization of this school is unlike all others in Virginia. To some extent it is denominational, but decidedly anti-sectarian. Its Trustees perpetuate their own existence. Its funds cannot revert to any other object. It is responsible to no religious body and its success depends solely on its merits. It looks to permanent existence and to the good of the whole commonwealth. Its successes have exceeded the most sanguine expectations of its friends. It was first to adopt a high standard of classical education for young women in Virginia; first to place the English Department under a regular professor; and first in the nation to adopt the elective system of studies. With the prestige of a history of twenty years, it may properly and confidently appeal to the general public to make it an addition to the permanent wealth and moral elevation of the country. I believe its reputation will[56] spread until it draws pupils from all over the South." Under the distressful conditions, is there not something morally grand in this utterance? It was a prophetic speech, and the daring prediction was more than realized in the thirty years that followed.
In 1863, one hundred girls filled every room, and seventy-five applicants were turned away. Oh, for the forty-six student-rooms in that unfinished hulk! Sequestered snugly in the mountains, no Institution in the country suffered less from the demoralization of the war. Families driven from the areas of invasion sent their daughters to the haven of its seclusion. The faculty of four gentlemen and three ladies had ample occupation. It was at this juncture that the President dropped the wise remark that the success of an Institution demands a capable manager as much as qualified instructors, and that he is harder to find. Of course, during this period, the depreciated currency and the correspondingly high cost of living required advance in the rates of the tuition and board. In 1864, one hundred and twenty-eight students were crowded into the rooms, and an equal number were turned away. In these days of inevitable stringency, the fare was far from luxurious, but it was accepted by teacher and pupil with that cheerfulness which becomes sensible and considerate people.
[57]That year the school was not immune to the alarms of war. A Federal raid, led by General Hunter, rushed into the town of Salem, nine miles distant, and the news spread consternation at Hollins, but without panic. The President had prepared a paper, stating the defenseless condition of the college and entreating protection by the General of any invading force. This paper he kept in his pocket, ready to be sent by messenger, if from any cause he himself should be prevented from going to make an oral request. Happily, Hunter came no nearer than Salem, and the awful suspense was relieved. On that very day, George Newman, the faithful colored driver, went to Salem with his omnibus, and was waiting at the depot, when the horsemen in blue came thundering down the street. He cracked his whip over his trusty four and dashed southward across the river, amid a shower of bullets. He was going in a course directly opposite from Hollins, but that was the only avenue of escape. When he was not heard from for the best part of two days, he was given up for lost. But late on the second day, who should drive in but this same George Newman, with an air of triumph and an ecstasy of smiles on his face! He came bare-headed, having lost his hat in the impetuosity of that patriotic retreat. The girls hailed him with a storm of acclamation and instantly took[58] up a collection with which they crowned the hero with a new straw hat!
Mrs. Cocke, in these times of nervous excitement, was perfectly sure of her own demeanor in case of irruption by the enemy. She would stand defiant in the doorway and forbid all entrance. The family tell a story which the dear mother never denied. One day her son Charley, a lad of ten years, with some of the servants, was coming back to the stables with the horses which had been hidden in the woods of Carvin's creek, to escape the hands of the enemy. The youngsters came galloping down the road, when some excitable person imagining it a charge of Yankee cavalry, raised the alarm, and then followed the worst panic Hollins ever knew. Mrs. Cocke, quietly busy in the pantry, hearing the shrieks, following an irresistible impulse, left the pantry door wide open and vanished to some place, she was never quite sure where.
It was Mr. Cocke's custom in those days to send a group of girls in the omnibus to the Sunday morning service of one of the churches in Salem. Such was the economic stress of the period that a handsome new hat in the school produced a sensation. Fortune crowned one of the students with a beautiful headgear. She wore it to church, and generously, on the following Sunday put the treasure on the head of a comrade[59] who was going up to worship. So the ornament became a regular attendant at the Salem services. Gathered at the church doors were the Salem boys, of course, and they soon became merrily interested in the new hat. One day after service, the girls found in the omnibus a note, inquiring: "Who does that hat belong to?" The owner lives, today, in Blacksburg, Va. Those trips to Salem ceased long ago, and now in the Hollins Chapel, regular Sunday evening services are conducted by chaplain pastors from the various denominations.
In the spring of 1865, pneumonia became epidemic in the school, taking off six of the pupils and two more in their homes. This disaster caused a suspension one month before the close of the regular term.
With the fall of the Confederacy, Mr. Cocke had again to face a condition that seemed the mockery of his hopes. Everywhere were economic prostration, social disorganization, and pinching poverty. Shall Hollins keep up the fight? Will the sun of Austerlitz ever rise on her long and varying battles? What young Institution ever threaded its way through a wilderness so gloomy or by pits and precipices so dangerous? Hollins will go on, walking by faith, and its doors shall not be closed, even for the part of a session. That is the mind of the President. He and his[60] faculty, though exhausted in means, will face the destitution and never give up the ship. The session of 1865-6 ran on with forty-five students. Rates had to be increased, and even with that, the college would have been compelled to close but for a timely loan from Colonel Tayloe to buy food. This noble friend and President of the Board of Trustees had been a comfort to Mr. Cocke from the beginning, and will continue so for thirty years more. Our great leader did not talk about his troubles, being always master of himself. Once he made this brief pathetic admission to his Trustees: "I am so burdened that I do not feel fit for my work." What can move us to tears like a strong man's grief? And there stands the ghastly figure of the unfinished Main Building, mocking his struggles and dreams. For five years now, pine boards have been nailed up to cover the windows, and not even a porch relieves the monotony of its ugliness. Two alternatives were before him: first, reduce the faculty, which is a most deplorable thing to do; second, go on as we are, but that is bankruptcy and ruin. Hear him: "I will go on; I will trust in God and the people." He insisted to his Trustees: "We must not descend to the character of a neighborhood school." Their sympathies were with him, but they felt unable to cope with the iron stringencies of the time. He did go on, never lowering[61] a standard or abating the passionate cry for more room and better equipment. How he ever pulled through this slough of despond, he himself could not possibly tell. Of one thing he was in no doubt and it was this, that in the long night of anguish, there was a precious mystery of heavenly aid.
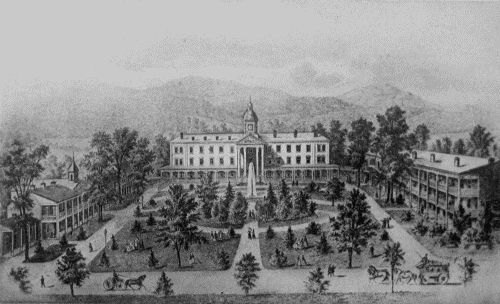 HOLLINS INSTITUTE
HOLLINS INSTITUTEOne of the encouraging incidents of this season, was the fact that one of the finest young scholars in Virginia accepted a call to the Institute. When Professor Joseph A. Turner, in 1866, consented to become a member of the faculty, it meant that a finely accomplished man had confidence in the character and destiny of the College, and that certified confidence was a tonic to the President's soul. But Hollins is still in the depths. There is no bracing of firm rock under her feet. All the officials know that the whole property is in peril of a public sale. How did the School go on? You must find answer in the resourcefulness and adamantine will of one great man. Hollins did go on, and complimentary testimonials from leading scholars in the State began to be written and spoken. Mr. Cocke was cheered at the generous recognition and said: "We must lift our standards a little higher than ever before. Our school should be second to none in the State and we must reach out for more distant patrons." The tide begins[62] to rise, and on the horizon there are gleaming hints of a better day. In 1868, Mr. Cocke secured a loan of $10,000, and by the end of 1869, that nightmare of the Main Building was transformed into a handsome and completed edifice. The passing of this melancholy incubus made a new epoch in his life. It was the cutting of chains from his feet, and the addition of wings wherewith to fly. The new structure greatly increased the accommodations, and now begins active propaganda in the South, acquainting the people with Hollins Institute. Newly risen, like a star above tempest and cloud, she will shed benignant light on the homes and daughters of the land. May she go on shining forever!
The torturing issues of the past are now settled. Mr. Cocke will let them pass to practical oblivion while he presses on to larger realizations. Of course annoying problems will continue to dog his steps, but they will not wear the malignant aspect so familiar in the strenuous years. His ideal is a flying goal, and he will never see his loved college free from growing pains. The happiest decade of work that he has yet known is before him. He stands on its threshold with hope assured, and his face is lit with thanksgiving as he beholds the clouds receding, and the sunshine flooding all the sky. It is a time to grasp his hand and shower him with congratulations. He has now completed twenty-four years of toilsome labor beside the little sulphur spring. Into the holy enterprise he has grandly flung himself, his property and his family. Never had a man a more tactful and sympathetic co-worker than he found in his wife. Without[64] one murmur of complaint she has shared all his burdens and cares. Her feminine quietness and grace have matched his masculine push and executive force. In him is a certain rugged virility which is delightfully supplemented by her charm of patient gentleness. With a noiseless and tireless efficiency, she has managed the domestic details, while he has handled the administrative affairs of the school. In the apportionment of praise, he would resent a bestowal that made her unequal to himself; nor would he fail to recognize the services of his children. Since the wedding bells rang, thirty years ago, nine have come into the home [Joseph J., Leila V. (Mrs. Joseph A. Turner), Sallie Lewis, Mary Susan (Mrs. C. W. Hayward), Rosa Pleasants (Mrs. W. R. L. Smith), Charles Henry, Matty L., Lucian H., and Bessie (Mrs. J. P. Barbee)]. Brought up in an atmosphere of service, all of them have, for longer or shorter periods, loyally served the institution.
The new session of 1870-'71 began with the registration of eighty girls. The Trustees at this juncture stepped to the front with a cheering note, announcing that the Institute was "Getting on a firm basis," and expressing their intense gratification at its increasing popularity and patronage. They emphasized their high appreciation of the[65] system of instruction, and the thoroughgoing diligence of the President and his faculty. All honor to these men who were sensitive to merit, and who had the grace to crown it with praise. These men also had learned that human progress is not much accelerated by whips of fault-finding and rebuke. In all their official records there is not an instance of clash between them and the President, nor even a hint of cross-purpose or loss of good understanding. When we think of the rough road they had travelled together, and the bewildering tangle of issues with which they had grappled, this concord is as surprising as it is honorable. An obstinate and wrangling Board could have crippled him cruelly. These harmonies were due to two facts: first, the absolute confidence of these gentlemen in the judgment and business capacity of Mr. Cocke; second, his reciprocal confidence in them, accompanied by the most cordial respect and courtesy. At the Board meetings through this decade they will not forget the value of commendatory resolutions, and it is pleasing to mention now, that this congenial partnership never knew a jar in all the after years.
Never was sunshine more grateful to the flowers, or music more cheering to a tired spirit, than were the tokens of the spreading fame of Hollins[66] to the soul of Mr. Cocke. Golden appreciations by distinguished men began to be spoken and written. Here is a tribute from Professor Edward S. Joynes, of Washington College, Lexington, Virginia: "I am intimately acquainted with the history of Hollins. It is an Institution of the very highest character, certainly second to none of its kind in this State. It has existed for upward of twenty-five years and been conducted upon the very highest standards of moral and intellectual education. Its success and permanence have been due to its merits alone. It is an unendowed Institution, founded originally by benevolence and supported by public patronage, and by the energy and economy of its administration. The President is a man of ability and of the highest personal character, and no Institution in this State has a higher claim on the public confidence." Dr. John A. Broaddus, of the Baptist Theological Seminary, Greenville, South Carolina, wrote his estimate: "I know of no better female school in the whole country, and very few, that for a moment, can be compared with Hollins. The instruction takes an ample range, and is able, skillful and honest." The Rev. Dr. J. L. Burrows, pastor of the First Baptist Church, Richmond, Virginia, stated his view: "In beauty and healthfulness of location; in attractiveness and adaptableness of its buildings; in tasteful adornment[67] of grounds; in the wild grandeur of surrounding scenery, Hollins Institute occupies one of the most charming and sequestered nooks among the far-famed mineral springs of Virginia. In the comprehensiveness and thoroughness of its course of study; in the ability and devotion of its instructors; in the carefulness and homefulness of its domestic economy; in its seclusion from the distractions of fashion and social disquietude, I regard this Institution as one of the very best for girls on this continent."
Many such heartening notes by University professors, ministers, editors and heads of colleges for girls, began to sound forth as early as 1868. Golden opinions, rightly deserved and rapidly spreading, brought the natural result. The session of 1869-'70 opened with twenty-one girls from nine Southern States, not including Virginia. The year following, the number grew to twenty-eight from the nine states. The session of 1873-'74 reported thirty-nine girls from thirteen states outside of Virginia, and that of 1875-'76 enrolled fifty-three from fourteen states. The session of 1877-'78 registered a total of one hundred and seventeen students, seventy of them coming from other states. This noticeable decline in the percentage of Virginia girls is easily accounted for by the increasing competition of the new and excellent schools for girls, now arisen in the Old[68] Dominion. During this decade, the fair fame of Hollins spread swiftly, and from this time on, a gradually increasing and uninterrupted stream of pupils, from all points of the compass, poured smilingly through her doors. Nor did her native commonwealth fail in admiration and generous support.
You can imagine the emotions of the founder in this happy emergence from the dilemmas and horrible incertitudes of the past twenty-five years. His bearing was calm and undemonstrative, while in his bosom the peans of thanksgiving go up to the great White Throne. But on the gladness of these days, a blight of bereavement was about to fall. In 1871, the brilliant and able Professor Turner had married Miss Leila Virginia Cocke, an accomplished daughter of the President. He was a shining light in the faculty, and on him great hopes centered. For two years his health declined, and on May 5th, 1878, gloom settled on Hollins. Great was the grief at the going of the beloved scholar and teacher. His twelve years of service began in the dark days of 1866, and closed in the full tide of victory. The memory of him will never perish from the hearts of pupils and friends who almost idolized him.
An event in 1874 meant much relief and comfort to our veteran educator, amid his manifold labors and cares. Charles H. Cocke, his son,[69] now in early manhood, capable, courageous and completely responsive to the father's wish, took on himself the duties of business manager of the Institution. Here was a much needed and most grateful division of responsibilities, and the competent new official magnified his calling to the uttermost. The thoroughness and courtesy with which he handled affairs, won for him the confidence and affection of the girls.
Have we ever found Mr. Cocke in a state of perfect satisfaction with things as they are? Never. He is a stranger to that experience, and will ever remain so. When we met him forty years ago as an assistant professor in Richmond College, his slogan was, "Betterment, enlargement, progress." The urgencies of an early ideal are still upon him, and he will never count himself to have attained. This fact touches him pathetically, now that he is nearing his sixtieth year. Unrealized aims add somber hues to every earnest life.
The equipment of growing Hollins is far from complete; much remains to be done. The spirit of advance gives him no rest. He has a vision, and "forward" is ever his imperious challenge to things as they are. Absolutely sure is he that[70] his beloved College, with its reasonably low rates, and its high standards, is on the sure road to greatness in human service.
 MRS. CHARLES L. COCKE
MRS. CHARLES L. COCKE
All through this decade his brain had been active with schemes of improvements. In the early seventies, the Baptists of Virginia were freshly aroused on the subject of education, and made large plans for strengthening Richmond College. Taking cue from this new denominational interest, the Trustees of Hollins Institute determined to go before the public and ask for a contribution of $100,000. A financial agent went among the people with argument and appeal. The result was disappointing and the agent was withdrawn. The failure was depressing, but by no means unnerving. From the beginning of the "Seminary" in 1842, the intermittent calls on public benevolence had never met with notable response. Nor is this fact any real ground for reproach. The mood of the general public had never been toned and cultivated in the interests of liberal education. From first to last the benevolent gifts to Hollins amounted to but $35,000, exactly half of which had come from Mrs. Ann Hollins and her husband. In the light of the recent failure Mr. Cocke saw that there was no further ground of hope from this source of supply. The school's expanding reputation and growing patronage gratified him exceedingly, but the financial situation[71] excited disquieting apprehensions. The Trustees had no funds in the treasury; the Institution was making no money, and their debt was growing every year. The mind of the President was filled with foreboding and grave anxiety.
Let it now be said that not one dollar had ever been added to the debt by any form of extravagance. No head of an Institution ever practiced a more rigid economy in projecting improvements. Not even a fancy catalogue was ever sent out from Hollins. His severe frugality, and the constantly demanded investment of his personal means in improvements, actually limited the reasonable privileges and gratifications of his family. Never did a family bear restrictions more cheerfully and uncomplainingly. It was not in Mr. Cocke to rebel against the law of sacrifice, but once, in his annual report to the Trustees in 1879, he permitted himself to say: "It is a hard case, however, that a man should have all his means so wound up in an Institution, conducted for the public, that he cannot command enough money to give his family anything at all, except hard work and self-denial."
In 1846, by express contract with the Trustees, Mr. Cocke became Principal and Steward of the Seminary without stipulated salary. Neither he nor any one of his sons and daughters, who worked so loyally with him, ever received a salary[72] from the Board. That initial agreement illustrates the unbargaining generosity of the man. He pressed on the attention of the Trustees the certainty of continuous demand for enlarged facilities. To provide for this, it was agreed that the revenue from the boarding department should go to the Trustees, who would devote it to that purpose. How ridiculously small that revenue was likely to be, may be gathered from the fact that a student was boarded at the rate of $5.00 a month! Through all the subsequent years this principle of benevolent rates had never been abandoned. The figures were necessarily increased, but only with the view of keeping out of debt. Now what possible promise was there in this arrangement for increasing facilities? Absolutely none. So the long issue of events proved. By the same agreement, Mr. Cocke was to pay his teachers' salaries and maintain himself and family out of the tuition funds. What remained in the treasury after the teachers were paid was his. Out of that residue, it soon became evident, must come much of the means for repairs and improvements. There was no other source from which to draw. Improvements were made, and self-denial paid the bills.
Now, while this involved inconveniences, it did not, of course, mean the making of gifts to the Trustees. In just business fashion, they recorded[73] each outlay of this kind as a loan to themselves. As a consequence they went steadily in debt to Mr. Cocke, until by 1864 they owed him $7,785. This included the $1,500 which he lent to them in 1846. This curious financial arrangement continued, unavoidable and regretted by all concerned. In 1868, the debt of the Trustees ran up to $17,473, and in 1876 it reached the sum of $22,094. Why had not these claims been settled? We have seen the source of the Trustees' revenue; how could they pay? The $35,000 raised by public gift had been given to the Trustees, who invested every cent of it in new buildings and accommodations. Not a dollar of it ever touched the hand of Mr. Cocke. On the contrary, as noted above, the growing plant had commandeered much of his own slow, hard earnings. Either this undesirable order of things had to go on, or Mr. Cocke had to abandon his dear ambition. But the time had come for better adjustments. He felt that the multiplying years required that he think of the interests of his family. With these views and wishes, the Trustees were in their usual cordial sympathy. The Institution was their property. They were in debt to Mr. Cocke in a large and yearly increasing sum. They had no possible way of liquidating that debt. What could they do? What ought they to have done? They solved the question by[74] offering to give Mr. Cocke a deed to their Institution in satisfaction of their debt. The proposition was declined. He did not want to own the College. Such had never been his aim. He saw that the move would be a relief to the Trustees, but a disadvantage to the school. He deprecated the idea of the College going into private ownership. The associated wisdom and responsibility of a good Board of Trustees he regarded as one of its best assets. Moreover, what could such a deal effect in the way of relieving his financial embarrassments? He could not see, and so the troublesome question was left unsolved. The school was prosperous, his heart was serenely grateful; and this personal matter could wait.
The projection, building, and safe establishment of Cornell University, in the State of New York, was essentially the work of that remarkable man, Andrew D. White. In the face of many obstacles and antagonisms he founded it, named it in honor of its chief benefactor, was its first President and led its fortunes until he saw it take rank among the famous Institutions of the United States. Another famous man performed the same kind of service for his people in the South. The founder and builder of Hollins Institute was long a voice in the wilderness. You have seen the stern, invincible purpose of this man in the face of an apathetic public, painfully straitened finances, epidemics, and the desolations of war. Several times his enterprise trembled on the verge of ruin. But in him was that iron quality that never knew when it was beaten. Forty years of toil in the educational field sat lightly on him, thanks to the natural vigor of a[76] well knit body and the resilient tone of a well endowed mind. We come now to the last lap of the journey, which most gratefully takes the form of a triumphal progress. In the good providence of God, the next twenty-one years were to be filled with expansion and achievement. His years multiplied, but there was no slowing down of energy and contriving strategy. Destiny put him benignantly into a life-long association with the young, and he could not grow old. To thousands of us still, no figure on the Hollins quadrangle ever stands out so statuesque as his large form, becomingly clad in a Prince Albert suit, and surmounted with a favorite tall beaver hat. As he walked in unconscious majesty, one could hear that resonant voice, issuing orders or bestowing courtly greetings. The grace and evenness of the old Virginia gentleman sat on him like a crown, making him ever accessible to student and friend. He was a worker, and he hated idleness as sin. Unrelentingly he demanded work. Never a student was allowed to escape that imperious law. For this his girls gave him honor. Well did they understand that Hollins was not for fashionable finish, or for money-squandering, but for downright honest study and true adornment of womanhood. He requested parents not to encourage extravagance in their daughters by putting in their hands undue sums of money to spend.
[77]The sessions in the early eighties showed a rising volume of patronage from the Southern states, a condition that was to go from more to more. His chief resulting gratification was in the obvious awakening of Southern people to better appreciation of the higher culture of women. Along with this pleasing discovery, however, he began to realize a serious barrier to the task at Hollins, created by the defective preparatory training in the primary and secondary schools of the country. In later years the difficulty began to disappear. To him, education consisted in the acquisition of knowledge, the training of faculty, and more especially, the broadening and multiplication of powers. His students must think, reason, and understand. That is the top of culture. Did he show any disposition to remain satisfied with the standards already erected? Not by any means. This is a growing world where nothing is stationary but a cemetery. The developing impulse in the mind of the Founder would never subside while the perfect was unattained. Even in this good summertime of 1920, nineteen years after his going, the mighty momentum he gave to the College operates with undiminished force. One does not expect spectacular variety in the life of an educator, particularly in one whose labors for fifty years were focalized on one spot. The[78] philosopher Kant never went away from the place of his birth, nor figured once in the publicities of his time, and yet the patient thinker has won undying fame among the intellectuals of the world. So we shall not find abundant incident at Hollins, but we shall know that its organizing genius is ever active and sounding the note of progress.
On the 15th of June, 1882, was adopted a new adjustment with the Trustees. Mr. Cocke was still unwilling to take over the property in payment of the Trustees' debt, but he had come to the conclusion that it might be wise to take a lease on it for fifteen years. To this the Trustees agreed, and the lease was duly written in favor of Charles L. Cocke and his son, Charles H. Cocke. At this time the debt due Mr. Cocke was $42,212, and by the terms of the contract, that sum might be increased to $50,000. An annual rental of $3,500 was to be due the Trustees, which was offset by the interest due on their $50,000 debt. In this arrangement the only right reserved by the Trustees was that of sanction of all improvements that might be undertaken during the period of the lease. On the very day when this agreement was written, Mr. Cocke submitted a plan for a Chapel. This was promptly approved by the Trustees. The work began, and soon the sacred edifice was an accomplished[79] fact. A little later the open grates and hot air furnaces in the buildings were abolished in favor of steam heat. The limestone spring and the pump in the yard were abandoned to give place to a reservoir on the side of Tinker Mountain, which supplied running water on every floor. Needed philosophical and chemical apparatus were forthcoming, and a beautiful Art and Music hall was built on the site of Carvin's rock castle. Then followed a new and enlarged dining room with all its appurtenances. The Trustees acquiesced cheerfully in all these betterments, but they looked on the vast increase of their debt in a sort of helpless wonderment. How should they ever meet the huge obligation? While they forbore to put a check on this advance, they were sure that there could be only one way of ultimate settlement.
In July, 1882, came the first great heartbreak his own household had ever known. His daughter, Rosa Pleasants Cocke, wife of the Rev. W. R. L. Smith, pastor of the First Baptist Church, Lynchburg, Virginia, passed to her dreamless sleep. She was young, beautiful, universally loved,—the fairest bloom of queenly womanhood. She left a little Edith, who, twenty months later, went to rest with her mother on the green hill near Hollins.
The enrollment of one hundred and seventy-six[80] girls in the session of 1888-'89, was the largest in the history of the school. At this date the President found, by careful comparison, that during the past forty-seven years, the average attendance had been greater than that of any other school for girls in the State. The session of 1889-'90 registered two hundred and nine students, and for the first time since 1864 applications had to be declined. The only minor chord that marred the general joy sounded in the troubled minds of the Trustees. In his own private reflections, Mr. Cocke had to confess that the solution offered by the Trustees looked like the obstinate, unavoidable necessity. About this time he made known to the Trustees and friends, a compliment to the Institution, recently paid by the National Bureau of Education at Washington. In a report of that body concerning schools for girls in Virginia, Hollins was named the foremost Institution for girls, the best known and the most effective in the State. The report continues: "There is an admirable foundation already laid at Hollins Institute ... for a woman's college of the type of Vassar, Smith, Wellesley and Bryn Mawr ... in a beautiful and healthful region with ample buildings for a great beginning.... An investment of a million would place here a great school of the highest type, and perpetuate the well-earned reputation[81] of this well-known Institute,—for the past forty years one of the most notable of Southern schools." This fine appraisement, coming from an independent and impartial source, was unspeakably pleasing to the man around whom this school had grown, and he could but cherish the hope that some large-minded man of wealth would arise to follow the suggestion of endowment made in the quotation.
A rare sensation was sprung on the Hollins community in the celebration of Mr. and Mrs. Cocke's Golden Wedding, December 31, 1890. All unknown to them, a group of loving hearts and hands had prepared an elaborate and impressive program. But some days before the brilliant event, mysterious hints, furtive interviews and beaming expectancy gave away the secret. Mr. Cocke himself began the jubilee in the early dawn, by slipping on the finger of his sleeping wife a handsome plain gold ring. All day, by letter and telegram, came happy congratulations and "bridal presents" from former pupils and friends. In the evening, Hollins took on unprecedented splendor with illuminations everywhere. Chandeliers, windows and doors were hung with ivy, and over the door of the main parlor, in large green figures, were placed the dates, 1840-1890. At 7:30 p.m. Mr. and Mrs. Cocke took their stand in the large parlor,[82] thronged by loved ones and friends. Prayer was made by Rev. Dr. G. W. Beale, pastor of Enon Baptist Church and chaplain of the college. Then, the Rev. Dr. E. C. Dargan of Charleston, S. C., a former pastor of Enon and college chaplain, made an affectionate address. Among the appropriate remarks is the following quotation: "This great school, the love and labor of your life, speaks for itself, both in glad presence and widely extended absence. From over all the land, and indeed from far distant lands, the pupils of Hollins send their love and congratulations. Through the willing service of one who has labored long at your side,[1] they present to you this book, containing the signatures of hundreds, who came to learn of you. Their affection also presents to you this portrait, intending that it shall be a perpetual heirloom, at once a splendid souvenir of this day and a monument of their lasting gratitude."
As these words were spoken, two of his little granddaughters, Thalia Hayward and Leila Turner, touched a wire, and the veil dropped, revealing the fine life-size portrait of Mr. Cocke, described in the first chapter of this book. It was the work of his accomplished daughter-in-law, Mrs. Lucian H. Cocke of Roanoke, Va. Mr. Cocke made brief and tender acknowledgment[83] of the honor done him, and then his son, Mr. Lucian H. Cocke, expressed in few words the same sentiment. Professor Wm. H. Pleasants read a poem, written for the occasion by a former pupil and teacher of Hollins. Two other short speeches were made by admiring friends and Dr. Dargan pronounced the benediction.
In every particular, this program was beautifully conceived and gracefully executed, making one of the most felicitous and memorable events ever known in the life of the Institution.
On the occasion of their meeting in July, 1896, the Trustees signalized the completion of a half century of service by renewed expressions of admiration and love for Mr. Cocke. One year later they returned to the theme and took action which gave the most general delight. They passed two resolutions: "First, that in honor of President Cocke, while living, and after his death, in memory of his great achievements in education, the 21st of February, his birthday, be set apart as a legal holiday in Hollins Institute. Second, that the young ladies be permitted to celebrate the day in such manner as may be deemed by the officers of the school appropriate to the occasion." Such was the origin of Founder's Day, only three happy celebrations of which the beloved President was destined to see.
The eventide drew gently on, and that good,[84] gray head was crowned with glory and honor. His own health was still fine, but his dear family was drawing near to a land of shadows. Three times in a very short period the billows of bereavement went over him. An avalanche of grief fell on his stout heart in the sudden loss of three of his children. Mrs. Leila Virginia Turner, on October 21st, 1899, laid her burden down and was put to rest beside her husband on the green hill. On the 3rd of May, 1900, the noble Manager, Charles H. Cocke, passed away, and was gathered to the loved ones gone before. Miss Sallie Lewis Cocke died on July 29th, 1900, and was added to the silent company of brothers and sisters.
"Though He slay me, yet will I trust Him." With chastened tenderness and submissive resignation, Mr. Cocke held his course as one who gets support from an invisible world. The concerns of the Institute pressed on him, and he must still take hold on life's affairs. The lease, in 1897, had been extended for a new period of ten years. But, obviously, it was now full time that his business relations to the Trustees be brought to a definite and final settlement. The issue, pending through many years, could be deferred no longer, and on June 2nd, 1900, a radical change in the old order was made. The Trustees found themselves in debt to Mr. Cocke $101,253, in addition[85] to the $50,000 in bonds already executed. Not yet had they been able even to pay the $1,500 loaned by him in 1846. He gave up his notes and bonds to the Trustees, and they in turn gave over the Institution. Thus the Board of Trustees, after a period of forty-five years, went out of existence, and Hollins became the property of Mr. Cocke. It was not the consummation that he wished, but there was no other alternative.
The venerable man, now in his 81st year, had on his hands the great Institution he had so laboriously builded. If he could have called back forty years, the responsibility would have rested on strong shoulders and a confident brain. But the competencies of the earlier years were spent, and age could only plan for the activities in which it should not share. He stood a noble, picturesque figure on the peak of life's work, looking backward with thankful satisfaction, and then wistfully forward into those years when other hands, hearts and brains should shape and guide the Institution. Not with one touch of gloomy foreboding did he make this provision. He believed that his children and grandchildren would loyally cherish his ideals and aspirations. They would hold the legacy sacred, maintain its standards, and keep it true to its aims. In the mellowing days of life's late afternoon this confidence gave him comfort and peace. Human affection[86] played around him soft and tender as summer sunset on the mountains, but it could not be doubted that among the deepest satisfactions of his soul was the conviction that his successors would do him the real homage of preserving the fruitage of his long, unselfish labors.
His form was unbent and his physical force gave him hope of ten more years of life. It was not to be. In the summer of 1898 a violent carbuncle brought him perilously near the brink of the great mystery. Two years later, warning symptoms came upon him suddenly. They did not yield to careful treatment, and with premonitions of the end, he decided in January, 1901, to go to the home of his son, Lucian H. Cocke, in Roanoke. This arrangement was his own device. He thought thereby to save Hollins from the anxiety which his illness would create, and from the shock of its probable end. What could be lovelier than the two letters that follow?
"Our Dear Mr. Cocke:—
"We, the members of your Faculty,—or rather of your great household here at Hollins,—deeply touched by your never-ceasing thought of us, and your intense interest in the work of our classes which prompted you even in the hour of great bodily distress to send us from your bed of sickness a message of comfort and encouragement,[87] feel that we can not suffer this, your birthday, to pass by without some expression of our gratitude and sympathy.
"We can never cease to be grateful for the kindly wisdom of your counsel which has directed us always unerringly to what is true and right, and for the firm guidance of your hand which has unfalteringly led us through the dark places of doubt and despair. Though we miss your wise head and guiding hand, we shall ever feel the inspiration of your spirit and the silent influence of your example; and trusting in that Divine Providence which has so long directed and prospered the labors of your brain and hand, we will endeavor to carry out, along your own lines, the work which you have so nobly planned and which you are now forced to lay aside.
"In this time of your physical weakness and bodily suffering, our thoughts are often with you, and we send you this message assuring you of our sympathy, both as a body and as individuals. May our Heavenly Father take you in His keeping and give to you unwavering faith and comfort and peace.
"With the expression of our affectionate regard.
"On behalf of your fellow laborers, the Faculty of Hollins Institute."
"To The Faculty and Pupils of Hollins Institute:
"It is now nearly two months since I have been with you. During this time I have been prostrated by great infirmities of body, and my weakness still is extreme. During my illness, however, there has been no time when I have ceased to have the welfare of each of you upon my mind and heart. Of all the expressions of sympathy that have come to me, none have been so comforting and gratifying as those that have come from my faculty and pupils. I wish to extend to each one of you my sincere appreciation of your earnest solicitude on my account. From every source the information comes to me of the orderly conduct of affairs at Hollins—teachers and pupils in their accustomed places, performing in a faithful and conscientious manner each duty that the occasion demands. It would be difficult indeed to adequately express to you the gratification that this information brings to me. For many years it has been my earnest desire to so conduct the affairs of the Institution, that whether I was present or absent there should be no abatement in the earnest purpose and devotion to duty which I have sought to make a part of the atmosphere of Hollins. I can not express to you a proper idea of what a pleasure it has been to me to know that this ideal is being exemplified[89] in your conduct, and I feel that in my declining years I am greatly blessed in having your sympathy and co-operation in the proper conduct of the work which has been on my heart for these many years.
"I trust that under the care of a favoring Providence, I may yet be able to be with you, and exchange once more the kindly greetings that have been a delight to me; but should it be otherwise, I always feel well assured that I can rely with confidence upon you to give to the Institution and the work with which I have been connected, the same devotion and loyalty which you have, without stint, accorded to me.
"May our Father in Heaven preserve each one of you in His holy keeping.
"March 10th, 1901."
It was on May 4th, 1901, that the end came. In the early morning of May 6th, the body was brought to Hollins and placed in the Chapel. Mr. Cocke had planned the two funeral services of the day. The first was held in the Chapel, for the family, faculty and students, who crowded the room. It was conducted by the Rev. Dr. F. H. Martin, Baptist pastor at Salem, assisted by ministers[90] of the Presbyterian, Lutheran and Episcopal churches. At the beginning and close of the service were sung his favorite hymns: "How Firm a Foundation," and "My Hope is Built on Nothing Less."
At 4 p.m., the second service was held at Enon Church, which was thronged by neighbors and friends. The pastor, the Rev. J. M. Luck, presided, and after the singing of "There is a Fountain Filled With Blood," remarks followed by the pastor, the Rev. Dr. W. E. Hatcher, and Mr. William Ellyson of Richmond, and the Rev. Dr. P. T. Hale of Roanoke. The service closed with "My Jesus, as Thou Wilt," and then the procession moved up the hill in a sudden shower of rain. As the casket was lowered, the great assemblage sang softly, "There's a Land That is Fairer Than Day," and the Rev. T. J. Shipman offered the closing prayer. Two impressive incidents followed. A procession of Hollins girls, dressed in white and bearing white carnations, came up the slope and covered the grave with flowers. In the same moment the setting sun broke through the clouds and bathed the scene in a radiance of glory. Dr. Hatcher, with felicitous tact, called attention to the shining symbol of heaven's benediction on the proceedings of that solemn day.
A careful examination of the catalogues and school registers of the early years leads us to believe that by June, 1896, when Mr. Cocke delivered his semi-centennial address, he had seen under training at Hollins not fewer than 5,000 young women. To the privileges of the school he had welcomed the children and grandchildren of his first pupils. As terms of study closed, what did this host of girls think of the Head of the Institution? Today in thousands of homes throughout the nation, the name of Hollins unseals, as by magic, a well-spring of precious and tender reminiscence. With unanimous devotion, the girls who knew him, honored and loved the name of Charles L. Cocke. Hardly did Tinker and Dead Man Mountain loom so large to them as the form of the venerable man. They honored him because he was strict and absolutely just; because he held high standards of school decorum and culture, and insisted on hard work. He was too honorable to take the daughters of[92] patrons, and allow waste of time and opportunity. His stringent demands may sometimes have caused irritation, but the good sense of the student was certain to react to grateful recognition of his wisdom. The after years never fail to evoke loving acknowledgment in the heart of a girl whose teacher requires her to make good in her studies. The Hollins girls loved Mr. Cocke because he was uniformly considerate and kind. The fatherly interest in his heart, not one was allowed to doubt. Daily he met them at the evening worship. Often has the visiting "old girl" spoken of those unforgotten prayers. He welcomed them in his office, listened to their requests, responding with sound advice and encouragement. Arbitrariness and severity were foreign to his nature, but all knew that the standards of conduct and study must be maintained.
How proud he was of the distinctions won by his girls! In the early eighties five of them, in the English literature classes, took the Shakespeare prize offered in London.
 "GOOD MORNING, 'GYRLS'"
"GOOD MORNING, 'GYRLS'"
The class room work was ever the major interest, but beyond this was a large range of activity and diversion. In 1855 the Euzelian (Love of Wisdom) Society was organized for debate, recitations and essays. Increasing numbers in 1874 required the formation of the Euepian (Pure Diction) Society. Still memorable [93]are those exciting joint debates, held occasionally by the Societies, along the years. In these latter days, they have given place to other disciplines more in harmony with the practical spirit of the age. Class organizations, Sororities, Clubs, Student Government, the College "Spinster" and Magazine, monopolize the spare hours. The Young Women's Christian Association maintains its prominence and usefulness.
But the old-time diversions do not pass. Those glorious romping trips up Carvin's Creek to the Falls, and the annual holiday climb to the top of Tinker in October, together with the strenuous games and sports on the campus, will continue to furnish happy memories.
The democratic spirit of the Institution Mr. Cocke constantly cultivated, and with profound satisfaction he welcomed students from the homes of rich and poor. All entered on terms of equality in privilege and opportunity. The rich girl of common sense and industry won popularity and honor; and by the same token the poor girl gained the love of classmates and the medals of distinction. At no institution was there more contempt for snobbery or for the spirit of favoritism. Moral and intellectual worth were the sole tests of credit and high standing.
His interest followed the students, and he smiled at the tidings of their usefulness. He[94] counted on their private and public values in society. Some, he was fond of saying, had become the wives of ministers, of lawyers and judges, of officers of the Army and of the Navy, of political leaders and of distinguished men in all ranks and professions. With pride, he spoke of those who were teaching in the schools and colleges, and of those who had gone into the far mission fields of the world. In his heart the grand old man felt: "They are all my daughters, and the sweetest benedictions be on every one." You will never meet the daughters of Hollins, old or young, whose faces do not light up at the mention of his name, or that of the dear place where many of life's holiest memories were stored. When old Hollins girls meet—whether as bosom cronies, after years of separation, or as strangers at some Exposition, gazing through tears at a portrait—a listener need but catch fragments of their reminiscences to know how Mr. Cocke's personality glows in the memory of his "gyrls."
"Could we ever forget how he used to read the hymns at evening worship? Nobody else could, or can, read them as he did:
This last always with an unconscious lifting of the head in his vision of the glory one day to be revealed. It meant much to look, once a day, on a colossal faith like his. Was it due to those unbroken, silent trysts with his Savior in the chapel, in the early morning?"
"Latin and mathematics were always second to the Bible with Mr. Cocke," testifies another. "He was certainly never afraid of the 'hard-grained muses' for us. I once heard him say, with a touch of regret, 'The next generation in our country will produce many more readers, but fewer scholars.' He revered true learning and made us revere it, however little some of us possessed it. Scholarship with him was no musty work, smelling of the midnight oil. He never laughed at it as odd or pedantic. It was, in his mind, never dissociated from service; but scholarship was a high thing, and he flung out the work as a challenge to the best within us.
"One now laughs to recall her own mental protests, as a new girl, when Mr. Cocke would so earnestly tell her fellow-students that they would be leaders in their communities, in their states. 'How mistaken Mr. Cocke is about this,' I would say to myself. 'He doesn't know this year's girls. He is thinking about those women who shone out so brilliantly here two, four, ten, thirty years ago—those stars in the crown of Hollins.[96] But these girls are just ordinary people. The best of them don't even know their lessons every time—not to mention the rest of us. They could never lead communities. Great women would be necessary for that.' But those girls have been real leaders, just as Mr. Cocke said. They were nothing but girls, just like other girls, but they did, many of them, go forth to lead and to lead straight. It may be that they had from him some touch of his power; it may be that he opened their eyes to the fact that there is, after all, nobody else to do most of these things except just plain humanity. There really is nobody else, you know.
"And Mr. Cocke's dignity withal—how cheap have many other men looked to my eyes when set beside my image of him! It is like that fabled measuring rod which made inflated pride shrink to its true stature. Mr. Cocke was the only man I ever saw who really seemed equal to wearing a high hat. I have watched the throng of the genteel coming down Broadway in their Sunday best and have thought, 'Not a man of you looks right in it—looks wholly free from affectation.' To him it was as natural as the crown of white hair beneath it.
"Imperious sometimes? Yes. I recall once, certainly. That new invention, the telephone, had been installed at Hollins. It was wonderful,[97] enabling one to talk to the depot agent at Cloverdale, three miles away. For the first few days of the new 'fixture,' Miss Matty had attended to all the preliminaries, so Mr. Cocke had not realized just what these preliminaries were, or that any were necessary. I saw him walk up to the transmitter and speak into it, without ringing the bell, asking a question of the agent. No response, of course. He spoke again. The same dead silence. Then he right royally tapped the transmitter as with a rod of office and commanded, 'Here, answer me!' Although I knew that the ringing of the bell was essential, I had the feeling that some response must come when Mr. Cocke spoke like that.
"By means of credit and otherwise, he helped me and helped other girls from my section of Virginia who had less ready money than craving for an education. The work of one of these, as Foreign Missionary, has been so good and so big that I love to think that in her, Hollins may have its reward for what it did for the rest of us. But so utterly did Mr. Cocke ignore all such benefits conferred by himself that I used to think he surely must not know about these things, that they must have all been transacted in the privacy of Mr. Charley's business office. The President looked so far above any money considerations; and still he must have been a wonderful financier.[98] Who else could have found the means of building and maintaining that great Institution without aid of church or state or millionaire? I never know what to say when asked by school men how Hollins was financed in the old days. The means must have been brought down by prayer from Heaven somehow.
"We talk much of the prudence that keeps at a safe distance from the plague of influenza. That is right, often. But when LaGrippe came from Russia in 1889 and invaded Hollins, I saw how the suffering was, to some of the girls, far outweighed by the honor and joy of having Mr. Cocke himself make the rounds to visit them as if he cared. Cared? I have looked out into the semi-darkness of the campus and seen that stately figure, with bowed head, walking up and down beneath the window of the infirmary, where some girl lay extremely ill, moving to and fro, far into the night, in a vigil, which, let me say it with reverence, has made it easier to believe that close to all earth's pains,
Such was the inner life of Hollins. It was and is the loving fellowship and co-operative industry of a big family, consecrated to true culture, good[99] citizenship and human progress. It was the life-work of the Good President, to cheer and help his girls onward to the realization of these noble ideals.
One day in May, 1901, the sad tidings of Mr. Cocke's death reached them. Out of the multitude of letters that came to Hollins, all bearing the same message of sympathetic grief, only a few can be subjoined.
"It is sad, and almost unbearable, to think of
Hollins without Mr. Cocke. And yet, our grief
at his death has, mingled with it, a spirit of
thanksgiving for his life. We are so glad that
we came under the influence of that life. I was
so young when I first went to Hollins, and Hollins
was my home for so long, that its influence, the
life-example of Mr. Cocke, all, indeed, that made
up the strength and beauty of those days, are
woven into every fibre of my being, have become
a part of my very life, so that I know I am better
for having known Hollins, and Mr. Cocke."
"For a long time I have realized that I owe more to the influence of my teachers and friends at Hollins than to all the text-books I have ever opened, and today I count it one of the greatest blessings of my life that it was in the pure, elevating[100] atmosphere of Hollins that I grew into womanhood. To dear Mr. Cocke, the Founder, the Head, the Life of Hollins, I do now and ever shall feel the deepest gratitude, and shall ever think of him with reverence, so high has always been my regard for him. Hundreds of women all over the land are sorrowing that they will see his noble face no more; for we, his old pupils, have lost a benefactor, a teacher, a friend."
"Indeed, a course so nobly run can be as fitly congratulated on its close—a close pertaining not merely to the finite conditions which fetter it here, but which, freeing it from these, ushers its powers, refined, magnified, glorified, into the blessed sphere of attainment awaiting those who have steadily followed the steps of the Master in ceaseless effort for the good of man. It is not the note of lamentation that accords with this grand freeing and glorious entrance of a friend of man, a soldier of the Cross, into the kingdom he has won: we rather shout our acclamations for the triumph of our friend, and drop the tear only that we are for a moment shut from the comfort of his countenance. We all, in fullest degree, offer our love and attachment, founded on unspeakable memories of early and lasting life."
"I am only one of the hundreds of girls who loved Mr. Cocke dearly, and honored him beyond the power of words to express. I feel that I loved him particularly well, more than others did; but perhaps many others feel the same way. I never knew any other man whose religion showed so plainly in his daily life. It always seemed to me that he walked with God. Hollins will never be the same again to the old girls."
"I feel sure that all you dear Hollins people know how fully my heart is with you at this time; but I feel that I must give some outward expression to the love and sympathy that I feel. Along with thousands of other old Hollins girls, I know what a great loss the world has sustained, and what a great and lasting grief has come to all of us who knew and loved and revered Mr. Cocke. To think of the thousands of minds and souls he has helped to strengthen and fit out for life's work! His opportunity was great, and he made the most of it,—and what higher praise can be given to any man?"
"I have been more distressed than I can tell you to hear of dear Mr. Cocke's increasing feebleness and dangerous illness, and I have[102] opened each letter from Hollins with a feeling of dread, always fearing the worst. But although the sad news, now that it has come, does not find me unprepared, my grief is no less acute. I know so well what this loss means not only to the thousands of girls who, like me, loved him as a father, but to the cause of education and religion, in which he stood ever as a beacon light. My heart is very sad when I think of how much goodness and greatness and strength went out of the world when he was taken. I have not the power to express in words the grief I feel! I shall always thank God for the priceless boon of being for a time under the influence of that consecrated life, and it is my earnest prayer that I may never lose sight of that blessed example of 'pure religion and undefiled before God and the Father.'"
"A friend writes me that Mr. Cocke's work is done, and that today he is laid to rest, I suppose on the beautiful hill that looks down on the field of his labors, that field that has borne such beautiful fruit. We are all distressed, as will be a great many others throughout the South who have felt the importance in life of a character like that of Mr. Cocke. If there were more men with like quality of character and mind, the[103] world would speedily become a better place. He did what he could to better it, and there are many left to honor him who have not the strength to do likewise."
"As one of the many thousands who owe to him unestimated, because inestimable, blessings, treasures of thought and influence and inspiration that time can not touch any more than it can dim his priceless memory, I sorrow today for Hollins' great 'creator, builder, guide.'"
"The news of dear Mr. Cocke's death has filled me with sorrow, for I realize what an inestimable loss the church, the school, his friends, and his family have sustained. I never knew any one like him! No one ever laid down a life more filled with good works, and he has indeed earned the blessed rest which he is now enjoying."
"The knowledge of such a life is invaluable. We should, we will, cherish the remembrance of it and hold this among the greatest object lessons taught us by God. The treasure of his memory would not be so priceless had his life been one smooth journey. It is the knowledge of the[104] struggle, the knowledge that a man has fought and gloriously won in life's severest conflicts, that furnishes us the incentive, that lends us the inspiration."
The fine portrait of Mr. Cocke in the Hollins Library, executed by his daughter-in-law, Mrs. Lucian H. Cocke of Roanoke, was formally presented at the Golden Wedding celebration in 1890. Death claimed the brilliant artist in 1899. With keen insight she portrayed her subject at the culminating moment of the final exercises of the Institution. The diploma in his hand is the one which he handed to his daughter, Miss Matty L. Cocke, on the day of her graduation. The artist wanted a real diploma, and by felicitous chance, this was the one supplied. At the time, the owner little dreamed of being her father's successor as President of Hollins Institute.
As now, so during the lifetime of Mr. Cocke, Maytime at Hollins stirred a flutter of excitement in the student's mind. The session's close was drawing near, with its terrors of examinations; its flourish of music, oratory and white dresses; its orderly pomp and splendor. The season brought a new flush of animation and[106] gaiety. There were happy greetings of fathers and mothers. The old girls came, eager for the raptures of re-union. The bright stars shone on dear old Hollins; the blue mountains stood guard round their jewel; and the sky dropped down benediction. Nature and the human heart held high festival on Commencement Day.
Services began with an interesting dramatic presentation, and the Reception to the Senior Class. The Sunday services were conducted by invited ministers. In the days following, came the jollities of Class Day, the joint celebration of the Societies, the Musical Concert, and lastly, the annual address by the President, with the conferring of Diplomas. Of course the programs of the earlier years were not so elaborate as the one just indicated, but the exercises were as vitally interesting and popular. On these occasions many distinguished men delivered strong and eloquent addresses. Woe to the man who ventured to stand before a Hollins audience without honest preparation. Declamatory rhetoric never deceived this group of intellectually alert students. Mr. Cocke drew his ministers for Commencement from the various Protestant denominations, as the students came from all these bodies. Sectarian narrowness never guided his choice, and that spirit never thrived in his school. Christian truth and character were to him the[107] eternal verities, and among all communions he made devoted friends. One of his preachers disappointed him cruelly. That good man made a calamitous mistake. He had fancied that he was to appear before a mountain school, and that almost any sort of a sermon would answer. Lazy unpreparedness meets retribution. Arriving at Hollins, his disillusion was instantaneous, and all that Saturday night he tossed in mental misery. The next morning he appeared in the pulpit with an irrelevant theme, and a profitless sermon. College girls are never profoundly impressed by unctuous platitudes, or by theological combat.
One of the surprises about these years is the small number of Full Diplomas that were given. From 1855 to 1900, Mr. Cocke bestowed this honor on one hundred and twenty-five girls. To secure it the student had to graduate in at least seven of the departments of study. The standards were high, so that to win the Full Diploma, demanded native ability and long, hard work. In the operation of the school's elective system, each girl chose the classes she preferred, and received certificates of graduation as the work in each subject was accomplished. Though, as we have said, Full Diplomas were rare, many girls won these minor distinctions, which also bore the name of Diploma. Many were the students who, coming for one year's course, were stirred by[108] these Commencement occasions to larger views and longer attendance. This imposing pageant of the Finals was apt to awaken in the ambitious, first-year girl, a sense of her intellectual poverty, and to inspire noble resolution for ampler education.
At the close of the session of 1899-1900, Mr. Cocke delivered his 52nd annual address. Sad to say, it was his last. It is a notable and probably an unparalleled fact, that he should, through fifty-two consecutive years, have made the graduation address and have delivered the Diplomas. In these messages he dealt with the many problems of educational theory and practice, never failing to appeal for high and noble standards of living. He counted on his girls as the finest advertisement, and as the most eloquent testimonial of the merits of Hollins. It was no vain reckoning. As a matter of fact, it became no unusual thing for him to hear patrons confess that they had seen Hollins girls and had been deeply impressed by their intelligence, cultured manners and social grace.
Now we yield the platform to the President. There can be no more fitting close of this chapter than a few paragraphs, taken from his annual addresses. The captions are not his, but they indicate the special thought of the passage.[109]
"I have aimed to implant deep in the hearts of my pupils the principles and precepts of our holy religion, as taught in the Word of God. As to those externals of religion which divide the Christian world into parties and sects innumerable, I have nothing to say; for our great Law-Giver and High Priest has said, 'The Kingdom of God is within you,' and unless we are subject to this law, all rites and ordinances and organizations put together and scrupulously practiced, cannot save the soul."
"Our trouble has been all during these fifty years, to secure equipment. Had this been furnished, the history of the school would have been far more satisfactory. The success of the school in 1852 and years following, gave a wonderful impetus to girls' schools in Virginia. Many chartered schools came into existence during that decade. Some of course proved failures, and others exist to this day.
"The annual registers of pupils during the entire existence of the school, aggregate 6,689. It[110] has been almost exclusively a boarding school, and as such has led in numbers all the schools of Virginia. Its contributions to the teaching profession have been most valuable and probably more numerous than that of any other Virginia school. It has educated many daughters of ministers of different communions, free of charge for tuition. It has aided large numbers of indigent girls. Its graduates are in all parts of this country, North, East and West as well as in the South, where they are numerous. Some six or eight are in foreign mission fields. The school has far surpassed my own expectations and has been a surprise to the general public.
"As soon as we took charge in 1846, and became acquainted with the surroundings and prospects, we saw clearly that the school could not live with a merely local patronage. It was almost wholly a boarding school, and it must draw its pupils from a broad area. The necessary steps were taken to make its advantages known in all parts of Virginia, and that patronage was sufficient for our limited accommodations until the close of 'the war.' We often declined applicants for want of proper accommodations. But after Virginia had been devastated by two contending armies within her borders for four years, we had to look to still broader fields for pupils. It was about the year 1870 that we first[111] made known the advantages of the school in other states, and now a majority of our pupils come from other sections beyond our state lines. This patronage, with more ample equipment, might be greatly increased, and with broader and more ample facilities, it might be made the most prominent school for girls in all the South. Its country location, its invigorating atmosphere, its mineral waters, its glorious mountain scenery, all combine to bring to it increasing numbers from different and distinct sections. The great boarding schools for girls in the North, in which millions are invested, are in the country.
"My life has been one of unceasing work and energy, of constant cares and anxieties, and of a deep sense of responsibility. I have only laid a foundation on which the next generation may build. Will Virginia, the most desirable State in the Union for institutions of learning of every grade and class, seize the opportunity and again advance, through educational channels, to the leadership of States, and inaugurate an era of greater glory and higher destinies for this great American people? Oh, that she may be wise to discern the ominous signs of these times and seek through great schools for young men and young ladies, a power and progress which shall far eclipse her pristine glories!
"And now, at the close of fifty years' connection[112] with this school, I can, without reservation or modification, say I have done all I could to conduct and perpetuate an Institution which might prove a blessing to the people without distinction of sect or class, and an honor to my native State. And this, too, on the very basis I found it standing when I took charge."
"These graduates are not confined to a single Christian denomination; they have come from all denominations. And this is, in my judgment, the true ideal of a Christian school. I have often said that the associations of a school for young ladies, properly conducted, are worth more to them than any single department of study. They learn so much from contact and association with each other.
"Certainly a school for young ladies should not aim to send forth all its pupils of exactly the same type. Its facilities and associations should be such as to give ample scope for individuality of development, and that genuine sympathetic contact and impress, which lifts the less cultured to higher walks and ways, and impresses the more fortunate with their duty to the needy and dependent, often the most deserving, and often[113] reaching, under such influence, the highest stations of life.
"The school from its beginning has maintained and made prominent one feature so culpably neglected, and even opposed by most schools for girls. It has maintained a broad and elevated course of study and fixed high standards of graduation. This has been done with special reference to the demands of that class of girls who propose to make teaching their profession or business in life. And most abundantly has it been rewarded in this effort. Its graduates are in great demand and many of them hold elevated positions as teachers. But there are other courses in addition to that required for full graduation. These are intended to meet the varied wants of other classes of students, who, from feeble health, inadequate means or mere preference, decline to pursue the full course.
"The school has accomplished far more than its early founders aimed at or even dreamed of. They looked to local demands and a limited sphere. But its influence has been felt not only through Virginia, but throughout the South and West, and even from the great North, pupils have sought and enjoyed its advantages. Graduation from school does not imply full and complete knowledge on any subject or in any department[114] of learning. The object of true scholastic training is, first, to discipline the powers, and, second, to open to pupils the sources of knowledge. In these processes, of course, much information is imparted; but to stop here and read and study no more, would be fatal to a high and commanding success in life. You must read and read systematically and continuously. You must keep up with the progress of the times, and times are in quick movement in this day...."
"If you would have your minds well disciplined and well stored with useful information, you must be willing to retire, for a time at least, from the enticing and distracting scenes of the busy world, and in the quietude of academic life, devote your powers to those labors which alone can secure the desired boon. Here the work must be done, here the foundation must be laid, upon which your future attainments and your future eminence must rest. Neglect this preparation, and you can have no well grounded hope of rising to distinction in society, or of exerting an influence which shall leave a record of your name and your deeds upon the hearts and memories of those who shall come after you....
[115]"The secret of success is the ability to fix the attention on one subject at a time...."
"I urge you to cultivate a taste not only for literature, but for making literature. The literature of a country determines its institutions, its social conditions, and its destiny. It is really its inner life whence its external manifestations spring."
"Many a wise man has said repeatedly: 'Let me go into a young lady's parlor and examine the literature which lies on her table, and the books which fill the shelves of her library, and I will tell you all about her; the secret thoughts which habitually haunt her imagination, the purposes, the ambitions, the affections, good or bad, which agitate and fill her heart; the scenes, the sights, the objects, the aims which thrill her soul—all this I know from the companionship amid which she delights to linger and live, and with which she delights to commune.' Young ladies, when you reach home and unpack your trunks, will you take out the text books you have studied[116] in this school, one by one, and place them on the highest shelf of your library and in the far corner, and with a scowl on your face say to them, 'Now, you go and stay where I put you; you have cost me weeks and months and years of toil, of anxieties, of troubles, vexations and tears, but you have at last given me my full diploma and I want nothing more to do with you'! Are you going to speak thus to your best friends, who have done more for you than father and mother?
"Are you going to turn your back upon, and quit the company of, the only true aristocracy of all the ages and all countries, and seek lower associations? These people are not upstarts; they have lived and still live in all ages and countries; they have been the intimate and loving companions of kings and queens; of emperors and statesmen; divines and poets, scientists and linguists, and all the great of all the earth and every clime and kindred.
"Again, the Good Book says, 'Where there is no vision the people perish.' This was spoken most probably in regard to the ancient prophets and seers who received the divine light from the great original source, and reflected it from their own hearts and minds on a benighted race.
"But has not the great Inspirer of light and knowledge, since that remote past, raised up other prophets and seers and imparted other[117] visions that the people might not perish? These great men are among us; they do not compel, but they invite companionship; they say, 'Come, go with us, talk with us, commune with our spirit, drink with us of the clear, cool springs of nature; the journey is pleasant and the scenery is grand; come, go with us and we will do thee good.'
"Will you reject the invitation and decline the association? So, young ladies, as I said in the beginning, from a literary standpoint, from a social standpoint, from a business standpoint, and from the standpoint of philanthropic and Christian usefulness, your future position and success in life depend upon the company you keep. Under the great principle of the freedom of the press, the newspaper has become a universal institution in America,—omnipresent, and almost omnipotent. The result is that the vast constituency of our great government are better informed on current events all over the land and all over the world, than any people on the earth.
"But the curse of the land is this: We spend too much time on this and kindred literature; this habit enfeebles the mind, contracts the vision, and suppresses high ambitions in the fields, the vast and elevated fields of broader, more solid, more useful and more permanent knowledge. Our people are making the most marvelous progress on all lines of human thought and effort, but on[118] none more rapid than that of science and literature. The spirit of the nation seems to be a consuming ambition to lead the world in thought, in intellectual development, and in products of the brain of men. To keep in harmony with this spirit, you, young ladies, must rise above the plane on which so much of our literature moves and study the works of great minds."
"The great mistake which so many make and which satisfactorily accounts for their want of success, is that they regard the mere accumulation of facts as the sole object of scholastic study;—that knowledge may be stored in the mind as we gather grain into a garner, and this, too, without regard to its character or quality, or the order in which the deposits are made. We have aimed, young ladies, to give you a better theory of education, and a more enduring foundation of scholarship....
"The great object of that culture and training which courses of scholastic study afford, is to assist the mind in the processes of its own development; to give to its searchings after truth and its toils in the fields of literature, direction and system; to enable it to think, to reason, to solve; to give it scope and expansion that it may successfully[119] grasp both the theoretical and the practical of life and advance to those objects and destinies which its very structure implies and foreshadows...."
"I would remind you, young ladies, that you go forth into life at a time when society is advancing on all lines of progress. In breadth, variety and thoroughness of literary and scientific knowledge, we are no less a marvel to ourselves than the wonder and admiration of the oldest civilizations of the world. This American people proposes to hold no inferior rank in the world-wide race for the greatest and grandest results in material development and production. This the most casual observer beholds all around him in every-day life. But when we come to review, critically and comparatively, the rise and progress of American learning, we see one determined and steady advance towards the highest standards the world has ever known. In the production and giving forth of all kinds of literature, this people aspires to the highest place; to the most advanced achievements that bless society and adorn life.
"And shall our own section and people continue heedless and oblivious of this throbbing, restless, inspiring energy to rise to the very acme[120] of literary fame and glory? We blush to own that, thus far, we have made but a feeble response to the high and honorable calling. When the poison diffused through the channels of a false and envenomed literature during the last generation, South as well as North, shall have spent its force, and the prejudices and passions that literature engendered and fostered shall have given place to just and generous award, then, and not until then, will the whole people and the outside world be prepared to receive and appreciate a truthful revelation, and do mental honor to all, of every section, who from their standpoint and environment, and with the light that shone upon their pathway, lived and labored for great ends, and the same ends. That record will show that not only under Southern skies, but throughout the nation, in national Senate, in Northern cities, even in Western wilds, Southern counsel has contributed in full proportion to the great results which today astonish the world. And furthermore, it will show that Northern energy, foresight and enterprise have made their deep and ineffaceable mark on the whole country in its educational and religious work, its business, political and social life, and its institutions. The gigantic struggle which occurred on this continent just before your eyes opened on the light of day[121] was the result of a misunderstanding; a family quarrel on a grand scale, such as more than once has occurred in the land of our forefathers. But even when the conflict rose to its most fearful height, deep down in the heart, this people were one. They are now one, and may the high council of Heaven ordain that they shall never be other than one.
"Young ladies, suffer no sectional jealousies or narrow prejudices to find a resting place in your bosoms. They dwarf your souls, they contract your minds. Love your country in all its sections and broad limits and constituent elements, and contribute your best energies, in appropriate spheres, to its high and grand mission."
"You go forth at a dark and threatening hour.... When the great plans of His far-reaching and comprehensive providence shall have been accomplished, in the stupendous conflict which you now behold, He will speak peace to the troubled waters, and there will be peace. Till then let us wait with calm resignation and abiding confidence in His designs of mercy.... This providence, however complicated and strange, leads only to some good and grand result, opening up new[122] channels of usefulness to the virtuous and the good, and saying to the faithful—nations as well as individuals: 'This is the way, walk ye in it.'"
"For many years it has been my earnest desire to so conduct the affairs of the institution that whether I was present or absent, there should be no abatement in the earnest purpose and devotion to duty which I have sought to make a part of the atmosphere of Hollins."
All the activities of a good man's life are religious. Intelligent Christian thought has long since abolished the distinctions, "sacred" and "secular." The minister is not the only man with a divine calling. It is the right of every true man to regard his tasks, of whatever kind, as sacred, and the vigorous discharge of them as religious fidelity. The apostle, making tents, was serving God as truly as when preaching to the philosophers of Athens. All the vocations are spheres in which men serve their generation, increasing the sum of human comfort, and securing the moral order of the world. The man who serves his fellowmen is the anointed servant of the Lord.
Mr. Cocke's life was an uninterrupted consecration to the cause of the education of women, permeated and energized by spiritual motive. No man understood better than he the living unity between intellectual and moral culture. He[124] knew that cultivated faculties without corresponding nurture of the spiritual nature may prove a curse rather than a blessing. Along with growing mental power, must go a development of religious character. The two are inseparable in any right conception of human life. So, while he wrought with a wonderfully sustained enthusiasm in the sphere of education, he kept always in mind the transcendent claims of religion. There he recognized the fundamental interest of humanity. Teaching was his vocation, but the honor of God was his comprehensive guiding principle. To him the Bible was the word of Life, and the worship of the Holy One of Israel the supreme privilege and duty. Such was his view and, without intermission, his practice.
From the beginning of his work at Botetourt Springs in 1846, daily the assembled students heard the reading of Scripture and united with the President in ascriptions of praise. Nor were Mr. Cocke's religious services given only to the school. His Christian interest ran out to the whole community. He recognized an obligation to his neighbors, and was soon meeting them here and there, instructing them in the Scriptures, and leading them in their worship. In 1855 the little Enon Baptist Church was organized and located within a quarter of a mile of the Springs. Into membership in this church he and his family went,[125] to be a strong nucleus around which has since grown the excellent congregation and the beautiful building of today. The pastors of Enon never had a more loving and loyal member of their church. By all odds the strongest force in the body, he could have ruled as he pleased, but the humble man never dreamed of domination, or of the assertion of any kind of superior right. He wanted harmony and growth, and sought it by preferring his brethren in honor. His wise counsel and influence were potent, of course, but not another member of the church was farther from the assumption of authority. He was a model church member in attendance and gifts; hence all the people gave him honor and love.
But Enon set no limits on his religious activity. The neighboring towns and communities felt the force of his spirit of evangelism. The Christian religion must have free course in the regions round about. There was not a village within twenty miles of his school that failed to catch something of his spirit. The impulses he gave in that early day lie at the foundation of much of the present religious strength and prosperity in the regions he touched.
Did this young school teacher overlook the needs of the colored people? Would it look strange to see him conducting a Sunday School[126] for the slaves on Sunday afternoons at Big Lick? That is what he did. "Inasmuch as ye have done it to the least of these, ye have done it unto me." The negroes, in the days of slavery, learned to love him as a friend, and when freedom came, his service among them did not cease. Their struggling pastors and congregations sought his counsel and were not disappointed. They looked on him as their big white brother, wise and good, and to this day he is remembered among them with affection. Here is a tribute written by a negro teacher on the occasion of Mr. Cocke's death. No more tender or significant praise has been accorded him.
"My race in this section of the State would be guilty of the rankest ingratitude did they not pay a humble tribute to the memory of their friend and benefactor, Professor Charles L. Cocke. Any tribute to his memory must needs be incomplete without a touching reminder of his devotion to the cause of Christianity among my people in the days of slavery. To him my people looked for religious instruction in those dark days. Through his zeal and untiring efforts the slaves of this section of the State were allowed to attend services at the white Baptist church Sunday evenings where they could hear the word of God preached to them by the white ministers of the gospel, Professor Cocke himself frequently leading[127] the meetings. He taught the slaves sound lessons in morality and honesty, and it is a well known fact that the slaves of this county were among the most upright, honest and trustworthy to be found anywhere in the South. Upon every plantation were to be found Christian men and women of our race whose lives were honest and true, and whose characters were spotless, and they enjoyed the confidence, respect, and sometimes a devotion, from their masters, that was touching and beautiful. Upon every plantation were to be found colored preachers who 'exhorted' to their people and explained to them the lessons that had been taught them by Professor Cocke. Whilst laboring faithfully amongst the whites, he did not forget the poor African slave.
"At the close of the war, when freedom came to our people, he gave them the best advice and encouragement in the organization of their own churches. He was full of the milk of human kindness. He was ever ready, willing, yea, anxious to give advice and instruction to our preachers who sought his aid. His purse was open to any colored minister who appealed to him for help. No colored church was ever built in this county that did not receive substantial aid at his hands. Thousands of our people with bowed heads mourn his loss and revere his memory. My mother and father received religious instruction[128] at his hands, and it is with a heart full of untold gratitude that I pen this tribute. Professor Cocke was a white man in all that word implied, but he was a Christian and not afraid to labor among men of 'low estate.'
"Such men are the negro's best friends on earth. We have nothing to fear at their hands. To them we have ever been true and devoted, and shall forever remain so. Such men are the salt of the earth, and the negro believes in such salt.
"We, too, drop a tear upon his bier and shall ever hold in grateful remembrance his many acts of kindness to a benighted race. Sweet be his rest."
With the increase of Baptist churches in the Southwest, the Valley Association was organized, and Enon became a member. Not a pastor brought into that body more interest and zeal than did Mr. Cocke. He was not of those whose Christian liberality slackens and enfeebles devotion to their own communion. While broadly charitable, he was firmly Baptist. The influence he carried into these conferences with his people arose from his personal worth, not from his official prominence in education. Not one of the denominational causes failed to receive his cordial support. They appealed to him in the degree[129] of their relative importance, but in the roundness and balance of his benevolence nothing was slighted. He spoke in advocacy of each and all. Of course many gatherings wished to hear Mr. Cocke speak on the subject of Education. In such addresses the fire of his soul was apt to burst into flame. He did not quote much. Being the impersonation of the educational spirit, he did not need to borrow thoughts. The man who does things has power with an audience. Your theoretical orator has no thrills. After one of his powerful utterances, many fathers and mothers said in their hearts: "I want to send my daughter to that man." His motive was not the cunning calculation of a man with a school, but rather the pure devotion of a large-minded servant of the Master.
In the State assemblies of his brethren, where he was regularly found, he was equally a man of recognized distinction. Likewise in the meetings of the Southern Baptist Convention, he was greeted with the honor due to one who had advanced the credit of the denomination. He knew that fact himself, but no man could have been more innocent of self-important airs. While the higher education of young women was the goal of his daily thought and labor, the Kingdom of God was central to all his aims.
Religious controversy never interested him.[130] Through the years ministers of the various churches were invited to Hollins to lead its services and receive its hospitalities. Many were the interviews with them in his office and on the verandas in which conversation drifted into animated discussions of things political, educational and religious. Views differed, thoughts clashed, but the best of humor prevailed. In every denomination he had devoted friends.
In vacation periods it was his frequent custom to make tours through the Southwest in a large vehicle, capable of carrying six or eight persons. His trusty colored driver, Prince Smith, held the reins, and commonly there was in the party a goodly number of Baptist ministers from middle or eastern Virginia. From one District Association to another, the caravan went, adding zest and interest to the meetings. It was a genuinely delightful religious progress. The Baptists in all this region considered him as their greatest layman and their unordained Bishop. Everywhere he and his fellow-travelers were welcome guests. Sometimes they lodged in homes presided over by women who had been Hollins girls. Then the hospitality was overflowing. These summer visits did much to stimulate the hope and courage of many small and slowly growing churches. And what charmingly exhilarating experiences they brought to the caravan! The men who[131] shared these progresses with the "Bishop" of the Southwest considered themselves the favorites of fortune.
It was never his habit to go off for a summer's rest. It might have been well if he had done so, but such was not his bent. When the pressure ceased at the close of the session, he began to plan another visit to his brethren in the mountains. To go about doing good was the call of his heart in those long past summertimes.
Religion and Education were the watchwords, written on the tablets of his heart. "This one thing I do, ever pressing on to the mark of the prize of the high calling of God." Here is the rare spectacle of a long life, full of religious activity, supported by unfailing enthusiasm, by fixed, high purpose, and by that ardor of achievement which are the marks of a great soul. Unselfish human service magnified him and gave his name to grateful remembrance.
There was nothing angular or disproportionate in the structure of Mr. Cocke's mind. The photograph of it may be said to have been reflected in his face, with its fine assemblage of strong and well-balanced features. The intellect was clear, the will robust, and the feeling intense. One never saw him when he did not know what he wanted to do; never found him irresolute or languid of purpose; and never knew him indifferent or unresponsive. Along every line of enterprise that summoned him, these powers were joined in unity and concert of action. He was not in the smallest degree visionary or quixotic. Illusions, phantasms, Utopian dreams, perished in the light of his large common sense. Yet this man was a true idealist. In his youth he saw a vision. At first he saw it dimly, but as time passed it grew in clarity, until it materialized in a better system for the higher education of young women. Had he failed, we might have called him a dreamer; but as he succeeded gloriously,[133] we rank him with the adventurous thinkers who have blessed the world. He followed the gleam and domesticated it in society. In his early days Hollins Institute was to him what the Holy Grail was to the Knights of King Arthur, or what the Golden Fleece was to the ancient Argonauts. The thing that makes a man great, is a great idea seized and brought into beneficent application. He is greatest that is servant of all. When Mr. Cocke said that his habit was to think thirty years ahead, he was hardly conscious that it was a fine feat of imagination. Yet this is his title to the crown of the Legion of Honor. Intellectual and moral heroism must have its reward.
 CHARLES L. COCKE
CHARLES L. COCKE
He would not have us say that his scholarship was broad. Too honest was he to make pretense of much learning. Broadly intelligent and well informed he was, and an efficient teacher of mathematics, but he made no claim to extended acquaintance with literature, science or philosophy. It is interesting to know that he was fond of Milton's "Paradise Lost" and Pollock's "Course of Time," and could quote long passages from each. He deplored inability to devote himself more assiduously to wide reading and deep study. The scholarly instinct and craving was in him, but the engrossing cares of his Institution absolutely monopolized his attention. Pathetic necessity barred him from the fuller measures of[134] intellectual culture. On administrative burden bearing depended the life and growth of the school, and with perfect intelligence of the personal sacrifice involved, the responsibility was accepted. However, he was keen to discover scholarship, and quick, with the wisdom of a master, to add it to his Faculty.
It was sometimes said that he was autocratic, and he himself admitted that there was some ground for the charge. How could it be otherwise? He was the informing soul and energy of the Institution, and in that fact was the sole guaranty of its development and perpetuity. He knew his plans and hopes, he had bold confidence in his own judgment, and he possessed an indomitable will. He had to speak with decision and authority. All confessed his right to command and understood the certain penalties of faulty service or of disobedience. The harassments of interminable worries and of defeated hopes may at times have resulted in a look of sternness, or have given his manner a touch of unpleasing abruptness; but, withal, it was far from him to inflict intentional pain. Austerity of manner, incidentally of expression, was balanced by as kind a heart as ever beat. He was a superb gentleman, and in his prevailing gentler moods, had pleasant greetings for all. He was at the helm, and the necessity was on him to guide and direct,[135] but behind the flash of those keen blue eyes lay a wealth of human kindness and affection. All Hollins knew it. Tyrant he could not be, but master he was. Never did it pass from his thought that he was a servant of God and that the mind of the Master was the goal of his life. He had the bearing of a lord, but the child in his heart never died. Then, if ruggedness appeared, it was but a surface exhibition, the fatherly feeling being the deep inextinguishable fact within. For this, his pupils and friends gave him a life-long devotion, and his children loved him, almost to adoration. This man was no autocrat.
He was conspicuous for his liberality. Owing to the fact that his earnings and that of his family were constantly swallowed up by improvements in the Institution, he was never a wealthy man. Yet that fact did not close the door of his compassions and generosities. Gifts went to the poor, contributions unstinted went to his church and to the benevolences of his denomination. Once, when attending the Baptist State Association at Petersburg, Virginia, after several speeches had been made on missions, he arose and said: "Now let us do something. I wish right here to subscribe $100." The suggestion struck the body and a handsome subscription was taken. Mrs. Cocke said, some time after the event: "Charles came home and sold a horse to pay that[136] subscription." At an educational gathering in Enon Church, when the inevitable subscription was taken, his young son, Lucian, signalized his immature and reckless enthusiasm by saying: "Put me down for $100." The cautious collector called out to the father what the boy had done. "All right," said the acquiescent father; "he has a pony." In dismay the youth saw the meaning, and the pony went to education.
Not often did he relate jokes and anecdotes, but he enjoyed them at the hands of his friends. He had a saving sense of humor and could relish a flash of it even at his own expense. This incident he told on himself. At one of the Valley meetings of ministers and laymen, he made a stirring speech. His oratory was of the spontaneous, practical type, often impassioned and tremendously moving. When he closed an admiring brother arose and paid compliment to the speaker for his "exhaustive" address. The modest orator meekly protested the extravagant language. Then a wit of a preacher stood up to explain to Mr. Cocke that the brother did not mean that the speaker had "exhausted" the subject, but that he had "exhausted" himself! The house was instantly in a roar of laughter, in which the orator himself as heartily joined. His brethren knew they could take innocent liberties with him, because they loved him so. At Walnut Grove Baptist[137] Church in Bedford County, Virginia, a meeting was in progress in the fall of 1881. The house was crowded when Mr. Cocke arose. The good genius of speech was upon him and that address on education was memorable for power. Later, in the church yard, a good mother was talking to a minister about the speech. A flush was on her face and tears glistened in her eyes as she said, "Oh, I wish I was able to send my daughter to Hollins." Now he had not said one word about Hollins, his effort being to magnify the importance of the education of young women, and to fasten conviction on parental hearts. At another time, while he was attending a Baptist meeting in Southern Virginia, he spoke before the body. A college professor in the audience inquired as to the personality of the speaker. On being told, he said: "I want to meet him, for he said more forcible things in five minutes than all the speakers before him in fifteen." An interview followed, with the result that the distinguished Professor Kusian spent twenty-eight years in teaching at Hollins.
Self-conceit Mr. Cocke regarded as a sort of vulgarity. With all sincerity, his soul responded to the sentiment of him who asked: "Why should the spirit of mortal be proud?" His friends thought that in some instances his humility was overdone. Richmond College gave him the[138] degree of LL.D., but he declined it, silently and unostentatiously. His frank reverence for truth disallowed acceptance. The degree, in his view, stood for a measure of learning which he regarded himself as lacking. His modesty wronged him. The compliment has come to be bestowed on high civic merit and achievement as well as on broad scholarship. In the former virtues, Mr. Cocke stood pre-eminent. His standard, if applied, would strip a multitude of names of this honorary title.
Interest in making money seems never to have touched him. Not once did he venture on an investment. The material prosperity of men gratified him. He knew that most men ought to make money, but he had no time for it. "This one thing I do." On one thing, the gifts, plans and powers of his long life were literally and undividedly centered.
He loathed the feeling of jealousy. He would have despised himself if he had been unable to hear the praise of other college presidents and of their institutions without inward pangs. Eulogize his brethren, and you smote on no chord of envy. He was a large man. He bore no grudges and carried no enmities, the common luggage of proud and envious minds.
What a good and generous neighbor this man was! The successes and sorrows of the countryside[139] round about Hollins touched him sensibly. He was their counsellor in times of perplexity; their comforter in seasons of grief. Frequent were the times when a minister not being accessible, he conducted funerals and buried the dead. He loved the people as do all who really love God. The religion that attempts to terminate on God, ignoring human beings, is as sounding brass and a clanging cymbal. Of such worship this man knew nothing. He expressed love to the divine in even-handed justice and in benevolent sympathy among men. Perhaps the finest tribute paid at his funeral was spoken by the Lutheran minister, Dr. F. V. N. Painter, a part of which is as follows:
"Dr. Cocke was a great educator. He was great both in theory and practice. He had not made, I think, an elaborate study of the science and history of education, as they are presented in text-books. His knowledge was deeper than the knowledge acquired in that way. In the educational work of more than fifty years, his strong intellect worked out independent views of educational principles and methods. In no small degree he helped to make the educational history of Virginia and of the South.
"Dr. Cocke always impressed me as a large man. His stalwart frame was but the counterpart of a vigorous intellect. There was nothing[140] petty, narrow, cynical, in his views or aims or methods. He loved to deal with fundamental principles and great facts; and in his discussion of any subject, there was always a breadth of view and a vigor of utterance that commanded attention. In his great, absorbing concern for truth, he cared but little for that delicacy of diction and that refinement of phrasing which so often, in the hands of smaller men, become an end in themselves. He was a strong earnest man, wrapped about with invincible integrity, reminding us of Carlyle's words on Luther, 'Great, not as a hewn obelisk, but as an Alpine mountain, yet in the clefts of it beautiful valleys with flowers'.
"Dr. Cocke was a man of sterling integrity of character. A brief acquaintance was sufficient to elicit our highest confidence. He was straightforward and honest in his aims and methods of work. He attempted to deceive neither himself nor others; and it is impossible now to associate an insincere or crafty diplomacy with his character. His native integrity of soul, which must have come as a rich inheritance from worthy ancestors, was strengthened by his deep religious life. He recognized his supreme obligations to God; and he took the life of Jesus Christ as his model. Thus he stood before us as a beautiful example of Christian manhood. In character and[141] in life he reflected credit on our common humanity."
It is the divine way to do mighty works through consecrated men and women. Christian faith so identifies one with the life of God that the eternal energies can flow onward to great consummations, even to the casting of mountains of difficulty into the sea. Nothing evil was ever charged against Mr. Cocke. The absolute open purity of the man shamed all envy, and paralyzed misrepresentation. Misunderstood and unappreciated at times he doubtless was, but this he accepted as one of the inevitable assets of an ongoing, achieving career. He was not perfect, but he pressed far up the heights of resplendent manhood. The signature of a divine call was upon him, and he honored it to the end. His long labor fell far short of his dreams, but it was crowned with the blessings of Heaven.
Hollins College is his monument. There it stands, a thing of beauty, by the little Sulphur Spring. There may it stand forever!
The building of Hollins Institute was not the achievement of one man. It was the outcome of associated work. There was a leader, gifted with vision, judgment and iron will, but without abundant and able co-operation, there would have been no realization of his scheme. No man would be more prompt than Mr. Cocke in acknowledgment of this fact. He was accurate in measurements of the qualities of men and women, and not often in his selection of teachers was his judgment at fault. It was a compliment to be invited into his Faculty, and its members always found Hollins one big family. In one dining hall, students and teachers met three times a day, and the warmth of home feeling fused all generous natures into one delightful fellowship. Mr. Cocke did not look on his comrades as hired people. He took them into his confidence and high regard as honorable and worthy associates in his sacred work of education. He was no dictator; he issued no commands. He trusted his[143] teachers, invited their freedom of initiative, and complimented them with the expectation of efficient service. He asked for good team work. It is no surprise that in such an atmosphere and under such genial conditions, he always had a loyal and harmonious Faculty. Rarely did one of its members go away without happy memories and loving attachments. Many fine men and women, through the long years, made invaluable contributions to the upbuilding of the Institution. Their work was worthy of all praise, and it is a matter of regret that most of their names have to be omitted from this brief record.
 MRS. CHARLES L. COCKE
MRS. CHARLES L. COCKE
In the presentation of Mr. Cocke's fellow-workers in the building up of Hollins Institute, no one will deny the first place to his wife. Her pre-eminent worth has already been indicated in the foregoing chapters. Longer than others, she bore him company and demonstrated a sturdiness of character, quite as marked as his own. She did not want to come to the mountains with her three little children. In 1845, she listened with loving interest to the enthusiastic recitals of her husband, just returned from the Southwest, but kept hidden in her heart an invincible preference for her old home. Yet, in the summer of 1846, she went with him, loyally and cheerfully. His[144] optimism she could not share, but the path of duty she trod as willingly as he. In the far after years she confided to her children that she had never loved the mountains, and then added, "But I never told Charles!" The fact would not have helped him, hence it was shut up in her heart. That confession is full of great meanings, pathetic, unselfish and honorable. Such was her faith in him, such her love and hearty comradeship in toil and sacrifice, that he most likely never suspected the secret feeling.
The shock of that first view of her new home we have seen. A little later, the primitive rawness of it was accentuated to her as she saw a wild bear leisurely passing through the premises! Bravely she plied the domestic tasks, and smiled sympathetically on her husband's plans. In truth, without such a wife he could not have won. In the strong cord that held him to his work, she was the golden strand. Though loaded with the cares of the household and of her little ones, this wonderful woman gave herself to numberless ministries among the girls. One feels astonishment at her physical endurance. Her energies and womanly loveliness were elemental in the making of Hollins. Six years after her arrival, it was her joy to see her brother, Professor William H. Pleasants, added to the Faculty. In the long, dark struggles that were to follow, there[145] was no breaking down of her faith and courage. Through two generations, the girls loved her with a genuine affection, and made no distinction between her and Mr. Cocke in the bestowal of honors.
It was truly said, that if Mr. Cocke was the head of Hollins, Mrs. Cocke was its heart. That splendid patriarchal Trustee, Mr. Wm. A. Miller, says: "It is common to speak of the wife as the better half. In my view, Mrs. Cocke was the better two-thirds." She watched the health of the girls, and entered into their amusements, sometimes even lending her own wardrobe for a histrionic performance. She could never endure harsh criticism, and if conversation drifted in that direction, she invariably withdrew. No unkind speech ever escaped her lips. To most mortals this will seem unbelievable, but ample testimony supports it. If ever compelled to express disapproval, it was in fashion so gentle that no sting was left. In the latter years, all the graces and beatitudes seemed to cluster on that feminine face, framed in with silver locks and the little white cap. She had a delightful gift of humor and many times the unconscious play of it surprised her by its mirthful effects. Enon Church and its worship always enlisted her active sympathy and gave her spiritual comfort. Often in quiet seclusion, she was found reading her Bible.
[146]The eventide came slowly on, with the relaxation of cares long borne. Then came the desolation of sorrow, and a deepening of life's lonesomeness. There was no decay of mental power, no encroachment of disease. At last the mortal part went down without pain, and on January 5th, 1906, the Mother of Hollins went away. Just three weeks more, and she would have rounded out her eighty-sixth year. The last services revived memories of those solemn scenes of May 6th, 1901. She was laid beside him on the hill, and weeping college girls strewed the grave with flowers.
Here is a great looking man, scholarly, courtly, popular, and in his maturer years, affectionately called, "Uncle Billy." He was born at the "Picquenocque" homestead, five miles north of Richmond, January 29th, 1831, the youngest in a family of nine children. The family was reared under the quiet influence of the Quaker faith. At about eighteen years of age, the young man graduated at Richmond College, and entered into business relations with a foreign tobacco firm, in which was the promise of promotion and wealth. Turning from this inviting prospect, he went to the University of Virginia, and by diligence in study, bore off its honors. Mr. Cocke invited[147] him to Hollins in 1852, just as the "Female Seminary" began its work. Soon thereafter, he married Miss Minta Smoot, of Washington City. After a few years, the young wife passed away, leaving him with a little daughter and son, who became the sole objects of his devotion. It was his joy to see the daughter, Mary, achieve distinction as a teacher of Music at Hollins.
He was a lover of Latin and Greek; and literature, ancient and modern, was his passion. Latin was his special department of instruction, but so versatile was his culture that he often taught the classes in Natural Science and Philosophy. He was a magnetic teacher, accurate, clear and inspiring. He won reputation as a polished writer and speaker, and had a natural fondness for music and flowers. In association with congenial friends, he was the center of courtesy and charm. Masonry was his pleasing avocation, and he was twice honored with the office of Grand Master of Masons of Virginia.
Here are a few of the many fine sayings which reflect his quality:
"Find out things for yourself, and you will know them better than if I were to tell you beforehand."
"I am afraid that the average teacher of the present day prepares the students for examinations, not for life."
[148]"All higher education is essentially self-education."
"Can anyone who himself neither intelligently observes, reflects, nor reasons, aid others in so doing?"
Washington and Lee University gave him the degree of LL.D. in 1907. He gave up his work as teacher in 1912, having spent sixty years in the service. On November 26th, 1914, he passed away, lacking only two months of fulfilling his eighty-fourth year. He sleeps with his kindred in the little cemetery on the hill.
Professor Turner was born in Greenville County, Virginia, August 6th, 1839; was a B.A. of Richmond College in 1858, and an M.A. of the University of Virginia, in 1860. He served in Mahone's Brigade, Army of Northern Virginia, during the entire war, and in 1866 accepted the chair of English and Modern Languages at Hollins Institute, which position he held to the time of his death, May 5th, 1878. Hollins has had many able and popular teachers, but it is simple truth to say that none ever stirred more enthusiastic admiration and devotion than he. Indeed, after hearing and reading his eulogies, one is almost forced to the conclusion that he was one of the most remarkable teachers the Institution[149] has ever known. Of high character, broad scholarly sympathies, and passion for teaching, he made his classroom electric with literary contagions and enthusiasms. Not only did he teach, but he magnetized and inspired the student. His teaching was largely by lecture, punctuated with pointed questions. Intellectually honest, accurate, painstaking, he cultivated the same qualities in the student. He published a valuable treatise on Punctuation and left several works in manuscript on his special subjects of English literature and philosophy. He contributed occasionally to Appleton's Journal and The Atlantic Monthly, and regularly to the editorial columns of The Nation.
Mr. Cocke honored and loved him, and the tribute he paid to the lost teacher in his annual report to the Trustees in 1878, is probably the finest ever given by him:
"Mr. Turner was a man of no ordinary type. When a boy, he was a mark among boys; when he became a man, he was a man among men. He hesitated long between law and teaching, and when the question was settled, he gave all the energies of his soul to his chosen calling. Prompt, able, faithful and enthusiastic, he carried his pupils to the highest standards of improvement of which they were capable, opening the fields of Literature, where they might wander, explore[150] and gather the richest fruits in after years. Not only did he give them knowledge and culture, but he inspired a zest for knowledge which would carry them beyond the ordinary confines of female acquirements. As an officer in a school for girls, his eminent literary attainments, his temperament, manners and very person, inspired respect and affection. His purpose was to make this a prominent Institution for young ladies, and accordingly he was engaged in preparation of textbooks adapted to that end. Among literary men, Mr. Turner was regarded as a scholar of mark, and destined to become a figure in the literary world."
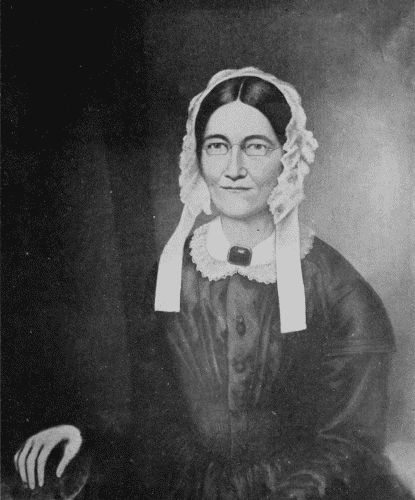 MRS. ANNE HOLLINS
MRS. ANNE HOLLINS
Mrs. Turner, Mr. Cocke's oldest daughter, was born in Richmond, Virginia, February 5th, 1844. She was educated at Hollins and taught twenty-one years in the Institution. Brightly gifted, ardent, magnetic, witty and companionable, she had peculiar power to win and hold the hearts of students and friends. She was happily married to Professor Joseph A. Turner in 1871, and was consigned to early widowhood in 1878. Two little children were left to her care. The daughter, now Mrs. Erich Rath, teaches in the College, and the son, Mr. Joseph A. Turner, is its Business Manager.
This gentle and accomplished daughter was born in Richmond, Virginia, May 25th, 1845. She was a graduate of Hollins, and taught many years in the college. Though frail in body, she was alert in mind, and lovingly responsive to all those tasks wherein she could do her father service. Gentleness and spiritual refinement were eminent qualities. Friendliness and social grace seemed native to her character. Her teaching was in the department of Literature and Languages, and to this day her pupils speak in praise of her taste and skill in the teaching art. She was a model of feminine culture, and filled her mission well. On the 29th of July, 1900, the lovable life faded away, at Hollins.
This nobly useful man was born at Hollins, May 21st, 1853. He took a course at Richmond College and in early manhood became an invaluable helper to his father in the business affairs at Hollins. The growth of the Institution, with the multiplying years and cares of the President, made assistance imperative. No more timely relief could have been given than that which came when young Charles H. Cocke threw his fresh energies and enthusiasm into this work. On the new manager a multitudinous and bewildering[152] mass of incessant duties descended. He discharged them with surprising swiftness and ability. A friendlier manner or a kinder heart could not be. He had patience even with the trivial and senseless interruptions that arose. Everybody leaned on him and everybody loved him. His work at Hollins was one of the finest contributions given by any one to the success and stability of the Institution. All honor to his name. His health began to fail before the end of twenty-five years of service, and, too late, he began to recruit his spent vitalities. On May 3rd, 1900, his labors closed in death. All Hollins wept and mourned his loss. Mr. Cocke said: "He was the right arm of my strength. Without him the school would never have reached the commanding position it now holds." With the precious company on the hill he rests in peace. One is glad to see his son, M. Estes Cocke, a prominent member of the Faculty.
This noble woman was one of the distinguished factors in the evolution of beautiful Hollins. Rich and varied are the contributions which she made to the school. She was born in Washington City, July 26th, 1829. Her father, William Speiden, was a U. S. Naval officer, and rose to the rank of Commodore. Her mother was an[153] English lady. Eliza was the oldest of seven children. She was educated at Mrs. Kingsford's School in Washington, and in that environment of elegant culture, her young womanhood was nourished. By the strange vicissitudes of human life, she was, before middle age, twice a widow, with two little children in her care. In the year 1873, by good fortune both to herself and Mr. Cocke, she came to Hollins as Associate Principal, a position she was to fill for twenty-five years. After resignation, she was made "Emeritus." Mr. Cocke said of her: "Mrs. Childs' gifts and qualifications were of inestimable value to the Institution, and without them and her untiring service, it could not have reached the excellence it has."
There was about her a captivating nameless grace of womanly finish, delicacy and comeliness. Her unaffected goodness blended smoothly with her emphasis of authority, and a perfect taste joined itself to charm of manner and flowing sympathy. It was social culture to be in her company. Her influence went out over all the South and will abide. Her daughter, Miss Marian Bayne, is Librarian at Hollins today. Mrs. Childs resigned at Hollins in 1898, and on August 11, 1901, she passed away, at Marshall, Virginia. Her body was laid to rest at Alexandria, Virginia, near the scenes of her childhood.[154]
 JOHN HOLLINS
JOHN HOLLINS
Here is one of the most picturesque and delightful of scholars. His history is dramatic and his experience of the world is rich. He was born in France and educated in Germany. During the Civil War his sympathies were with the South, and he bought supplies for the Confederacy in France and Italy. He came to the United States while still young, and took out naturalization papers in Kentucky. He married a Virginia lady, and taught a number of years in the Baptist College at Danville, Virginia. From there he was called to Hollins in 1890. After more than twenty-five years of work in the department of Modern Languages, he retired as Professor Emeritus. He was a man of remarkable memory, never forgetting a fact or a face. He was one of the most competent, courteous and obliging of teachers and friends, and for Mr. Cocke he had the most sincere admiration and attachment. Honored and revered by all, he fell asleep March 24th, 1920, at his home in Accomac County, Virginia.
Two of the original Trustees of Hollins stand out particularly as notable for long service and devotion.
This venerable and delightful gentleman was born in Pittsylvania County, Virginia, in March, 1824, and is now in his ninety-seventh year. This summer of 1920, he is in fair health, and goes daily to his place of business in Lynchburg, where most of his life has been spent. His whole career has been one of stainless virtue and lofty Christian character. His first meeting with the Trustees of Hollins was on July 5th, 1855; his last was in February, 1900, making a term of forty-five years. He was always high in the esteem of Mr. Cocke. He recently explained in humorous way, that his long term of life was due to long teaching in Baptist Sunday Schools. This got into the papers, and he has received letters from all over the country, and some from people in other countries, asking his methods of teaching the lessons. A halo of honor is on his head, and thousands of friends wish him long life.
On the 18th of April, 1897, this splendid citizen of Roanoke, Virginia, this strong and invaluable friend of Hollins Institute, passed away, in the ninety-third year of his age. He was the first-named Trustee on the Board of the Valley Union Seminary, in 1842. That position he held[156] until the school took the name of Hollins Institute. In 1857 he became President of the Board of Trustees, and as long as he lived, he held this office with distinction. In 1896 some members thought it expedient to elect another President, owing to Colonel Tayloe's frequent, enforced absence on account of sickness. Mr. Cocke objected, however, and the grand old man was re-elected. Before the next annual meeting he was no more.
Mr. William A. Miller has this to say of his comrade: "Colonel Tayloe was a gentleman in every sense of the word, and was often consulted by Mr. Cocke. He seemed to feel himself a part of Hollins and was almost like the right arm of the President."
Mr. Cocke himself, in giving a brief history of the Institution, in 1896, said, "I cannot close this sketch without a tribute to one who well deserves to be mentioned on this occasion. The Hon. George P. Tayloe, of this County, a gentleman of wealth and exalted social station, was the administrator of the estate which held possession of the property at the time the purchase was made for educational purposes. He not only heartily approved of the establishment of the school and gave liberally to its funds, but he gave his personal influence and more than all, he indulged the Trustees in the payments due the estate, to the utmost[157] limits of the law, refusing to accept offers made by others, until he finally secured the property to its present owners, thus enabling the school to continue its high mission. For nearly the entire period of fifty years, he has held the Presidency of the Board of Trustees, and seldom has he been absent. When at any time during the history of the school, money had to be raised for any emergency, he was the first to subscribe and prompt to pay. His influence has contributed largely to its successful career."
The Institution never had a more loyal friend, or a more generous and intelligent Trustee. Hollins and its community ought to wipe the opprobrious name of "Tinker" off the beautiful mountain, and replace it with the honorable and cherished name of "Tayloe."
Mr. and Mrs. Hollins lived at Lynchburg, Virginia, prosperous, highly respected and influential. Mr. Hollins was a man of superior worth and always responsive to the generous impulses of his intelligent wife. Her ancestors, the Halseys, came from England in 1623. One of these kinsmen was a member of the English Parliament, and another went to the United States Congress from New Jersey. She was a member of the First Baptist Church of Lynchburg, but her husband,[158] on account of self-distrust, never joined. Mr. Hollins' gift of $5,000 in 1855 was by her inspiration. Her own later gifts, amounting to $12,500, assured the life of the Institution. But for the Civil War, which destroyed most of her wealth, she would have given much more. They had no children. Mr. Hollins was born February 11th, 1786, and died April 7th, 1859. Mrs. Hollins was born in 1792 and died July 3rd, 1864. Both were buried in Spring Hill cemetery, at Lynchburg.
The perpetual, unsatisfied longings of the Founder of Hollins projected plans and schemes whose completion had to be left to other hands. In his wise view, an Institution completed was an Institution already on the downward grade. The large, expansive life of the age requires continuous modifications and enlargements to meet the ever-springing exigencies of society. In his eighty-first year, amid the desolations of a triple bereavement, the aged hero sounded this note: "I will devote my energies to putting the Institution on a permanent, broad basis, with facilities of all kinds to meet the advancing demands for such schools; for education of every kind throughout the South is on rising grade, and Virginia, like New England, may yet have a reputation for school facilities with scholarly men and women equal to those of any section of this broad and progressive land." This is the same clarion voice so familiar through two generations. Thus came from his lips the[160] general program, committed to his successors for the following thirty years. With no consciousness of the fact, he was providing his own monument which lives in the noble Hollins College of today.
 HOLLINS COLLEGE
HOLLINS COLLEGE
When the Institution passed from the Trustees to Mr. Cocke, it became the charge of a Board of Governors, selected from the members of his own family. From that day, they have regarded as their precious inheritance the plans of his mind and the wishes of his heart. His principle of progress has been the guiding light of the Board of Governors and not for a moment have they forgotten that the passionate desire of the Founder of the College was to make Hollins, in an ever increasing degree, a leader in the cause of the education of women.
What has been done during the nineteen years of the Board's control? It is impossible to visit Hollins without feeling that the memory of Mr. Cocke and his influence equally abide. He, being dead, yet speaketh. At his death the Presidency of the college went to his daughter, Matty L. Cocke, and the Chairmanship of the Board of Governors to his son, Lucian H. Cocke. The business affairs, so long and heroically managed by Charles Henry Cocke, are now entrusted to two of the Founder's grandsons: Marion Estes [161]Cocke as Secretary and Treasurer, and Joseph Augustine Turner as General Manager.
The improvements on the grounds and buildings, and on the farm, have been many. A beautiful Library building, made possible by the Alumnæ, was erected in 1908, as a memorial to Mr. Cocke. The Susanna Infirmary was built in 1911, as a memorial to Mrs. Cocke. In 1914, the Science Hall was built. Meanwhile important changes were being made in the courses of study. The curriculum was gradually enlarged, and eight years after the Founder's death, the institution was standardized on the basis of a four years college course. When this change was recognized in a new charter from the legislature of Virginia, the name "Hollins Institute" gave place to that of "Hollins College."
The realization of the Founder's dream is an endless process, and the motto will ever be, "Forward and Upward." In the very atmosphere of the place, the sensitive soul feels a brooding presence. The trees on the campus, nearly all of which he planted, seem to whisper the revered name. His Ideal lives, and his Spirit interfuses all. His monument is building still. Let it go shining down the centuries!
End of Project Gutenberg's Charles Lewis Cocke, by William Robert Lee Smith
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK CHARLES LEWIS COCKE ***
***** This file should be named 37636-h.htm or 37636-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/3/7/6/3/37636/
Produced by Julia Neufeld, Roberta Staehlin, David Garcia
and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at
http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images
generously made available by The Internet Archive/American
Libraries.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.