Museum of Natural History
in Northeastern Kansas
University Of Kansas
Lawrence
1953
University of Kansas Publications, Museum of Natural History
Editors: E. Raymond Hall, Chairman, A. Byron Leonard, Robert W. Wilson
Published August 24, 1953
Lawrence, Kansas
FERD VOILAND, JR., STATE PRINTER
TOPEKA, KANSAS
1953
24-7812
in Northeastern Kansas
On the 590-acre University of Kansas Natural History Reservation where our study was made, the opossum, Didelphis marsupialis virginiana Kerr, is the largest predatory animal having a permanently resident population. The coyote, racoon and red fox also occur on the area but each ranges widely, beyond the Reservation boundaries. With the passing nearly a century ago of the larger animals of the original fauna, the buffalo, elk, deer, antelope, wild turkey, gray wolf and others, lesser herbivores and carnivores including the opossum and animals of similar size fell heir to their key positions of predominance at the peak of the food pyramid. These smaller animals, however, exert less powerful effects in controlling the general aspect of the biotic community, and affect it in different directions. The over-all ecology is greatly altered. The flora and fauna both are undergoing successional changes which will continue for a long time and probably will culminate in a biotic community much different from the original climax.
The opossum plays an important part in this process of change; being relatively large, numerous, and of omnivorous habits, it variously influences, directly and indirectly, the populations of its plant and animal associates, through a complex web of interrelationships. Several excellent field- and laboratory-studies of the opossum have been published (Hartman, 1928, 1952; Lay, 1942; Reynolds, 1945; Wiseman and Hendrickson, 1950) and the life history of this remarkable marsupial is already well known. The purpose of our study, therefore, was to gain a better understanding of the ecological relationships of the opossum in the particular region represented by the study area. To accomplish this, we gathered data concerning the animal's responses to climate and varying weather conditions; its annual cycle of breeding, growth and activity, movements, principal food sources, numbers, population turnover, and natural enemies. Although we did gain a somewhat better understanding of the opossum's ecology, results are remarkably meager in proportion to the large amount of time expended. The hours of work daily in setting and tending a line of live-traps ordinarily were rewarded with only a few records, sometimes none. Comparable time and effort [Pg 310] directed to the study of smaller and more abundant kinds of animals has been far more productive of data. Field work was carried on in parts of 1949, 1950, 1951 and 1952.
Because opossums are nocturnal and rarely seen in the course of their regular activities, the present study is based mainly on information gained by live-trapping them. Several different sizes of traps of the type described by Fitch (1951) were used. The most successful were 2' × 8" × 8" in dimensions although many of the larger ones were also used. They were constructed of hardware cloth having a half-inch mesh. Live-trapping was begun in October 1949 by Fitch with a line of about a dozen traps. In the following month Sandidge joined in the field work. The trapping was continued throughout the winter and spring of 1949-1950 and was resumed the [Pg 311] following fall and more traps were added from time to time until a maximum line of approximately 60 was attained. Sandidge's participation ended in December, 1950. The live-trapping was continued on a reduced scale by Fitch through the winter and spring of 1951 and some was done sporadically in the fall, winter and spring of 1951 to 1952.
Traps were baited with a variety of foods such as carcasses of small vertebrates, meat scraps, canned dog food, ground horse meat and bacon grease. At each capture, sex, weight, and individual formula of the opossum, based on toe-clipping and ear-clipping (Fitch, 1952), were recorded. Also recorded was the exact site of capture as located in one of 84 divisions of the Reservation and estimated in feet from some named landmark. Notes on breeding condition, pelage, injuries, parasites and general appearance were also taken at the time of capture. For opossums caught in 1951 and 1952, the hind foot measurement was recorded.
Often, attempt was made to follow the released opossum to determine the direction and distance of its homeward travel but this was difficult because of brushy terrain and secretive habits of the animal. An opossum being followed would almost invariably take refuge in a tree if it caught sight of the observer. Other information regarding the animal's habits was obtained from tracks in snow or soft soil and from the distribution and contents of scats. Carcasses of opossums which had fallen victim to predators were found on a few occasions and in some instances clues as to the identity of the predator were obtained. One hundred and seventeen opossums were live-trapped and handled a total of 276 times. Six of these were dead when first found in the traps. The remaining 111 were marked and released. In addition, 207 pouch-young carried by adult females were recorded and 115 of these were individually marked by toe-clipping. Some of the opossums that were marked while in the mother's pouch were subsequently recaptured when they were well-grown, independent young, or adults, affording information on growth and dispersal.
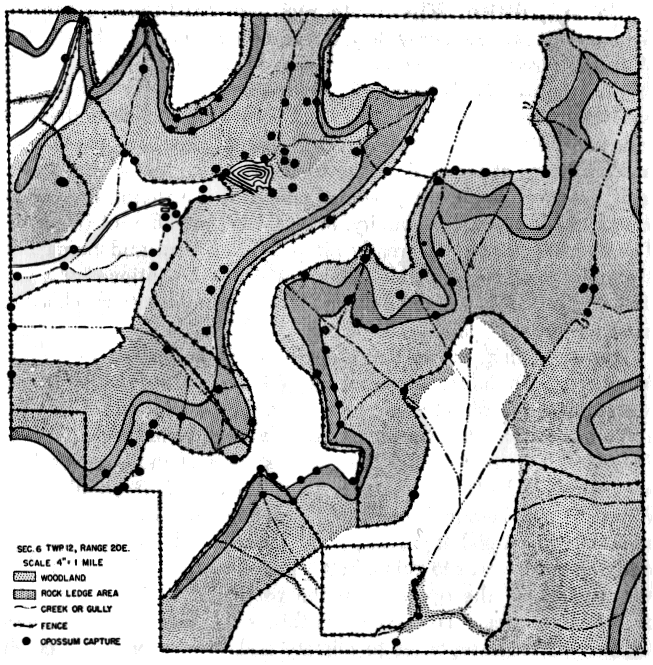
The habitats of the Reservation have been described briefly by Fitch (1952) and by Leonard and Goble (1952). More than half the area consists of steep wooded slopes with mixed second growth forest, consisting of elm, hickory, oak, walnut, ash, honey locust, hackberry and osage orange, in about that order of abundance, with thickets of blackberry, crabapple, wild plum and grape. Fallow [Pg 312] fields and pastures of the upland and valley floors alternate with the woodland. The varied habitat provides numerous different food sources. Along the edges of the hilltops there is a nearly continuous limestone outcrop with a lower outcrop paralleling it. These rock ledges, well distributed throughout the area, provide an abundance of den sites and most of the opossums definitely trailed to a home base were found to be utilizing dens in the rock ledges. Two small creeks on the area have some water for most of the year. As compared with wooded bottomland of larger stream courses in Douglas County and those counties adjoining it, the Reservation area probably supports a relatively low population density of opossums. "Sign" has been found in much greater abundance in near-by areas supporting a heavier woodland.
Every part of the Reservation is used by opossums, but their activity is concentrated in the woodland, and all dens found were in woodland. Most parts of the fields are within 100 yards of the edge of the woodland and no point is more than 700 feet from the edge. Most of the opossums' foraging in fields was concentrated along the edge; otherwise they tended to follow creeks and gullies and they follow well worn trails more often than they do in the woods. Within the woodland, activity tended to be concentrated along the small streams, and along the rock ledges where den sites were plentiful. Throughout the annual cycle, and from year to year, there were minor shifts in areas of concentrated activity depending on seasonal changes in food sources such as thickets of wild plum, crabapple, blackberry and grape, with fruits ripening at slightly different times of year. The areas adjoining the Reservation offer somewhat similar habitat conditions, part woodland, part pasture land and some cultivated fields with corn or other crops which provide food sources for the opossum.
Under original conditions the area that is now the Reservation probably was marginal habitat for opossums, consisting mainly of open grassland with trees in small and scattered clumps, if indeed they were present at all. There has been steady encroachment of shrubs and trees, originally chiefly confined to near-by bottomlands such as those of the Kaw and Wakarusa valleys. Concurrently, the original hardwood forest of the bottomlands has mostly disappeared, and the land has been taken over for intensive agricultural use. The new upland forest provides a habitat different in many respects from the original bottomland forest. The species composition, in trees and other plants, is somewhat different, with more xeric types, [Pg 313] especially on steep south slopes. Logs and large old hollow trees are scarce. The lack of such potential den sites is compensated for by the abundance of holes and crevices along hilltop rock ledges.
Undisturbed opossums were seen in the course of their normal activities on only a few occasions, and behavior is known to us mainly from the sign and from observations made on those that were live-trapped. Ordinarily those taken in live-traps were found curled up in deep sleep from which they did not arouse until touched or until the trap was moved or jarred. Reactions to humans varied greatly in individuals and was not necessarily correlated with age or sex. Adult males were uniformly hostile to the trapper and reacted with harsh, low growls, with back arched and hair bristling. Although many adult females and young of both sexes were similarly hostile in behavior, others were not. Some cowered silently in the trap. Others showed hardly any uneasiness. A small proportion of them feigned death when handled or even before they were touched. Feigning was especially frequent in response to clipping of toes and ears when the animal was marked. In some that were handled, the feigning reaction was weak or incomplete, the animal arising almost immediately after collapsing or beginning to collapse in the feint.
Those that feigned death usually maintained the deception for not more than two or three minutes after a person had moved away out of sight. The opossum first raised its head and sniffed, listened, and looked about cautiously for a short time, with body and limbs still relaxed in the feigning posture. Failing to detect any sign of danger, it gradually shifted to a sitting position, and then to a standing one, from which it began moving away with many short pauses at first, and then more rapidly.
Upon being released, some opossums scrambled for shelter immediately; others stood their ground defiantly with back arched, hair bristling and fangs bared. One that was put on the defensive would usually maintain its stance for less than a minute if not further disturbed by movements of the trapper. It would then slowly turn its head and begin walking away with deliberate gliding movements, often pausing abruptly in the middle of its stride with one or two feet off the ground in a pose reminiscent of that of a bird dog making its "point." After moving away a few yards, it would gradually accelerate its pace in a scramble for shelter, but an occasional individual moved away unhurriedly, even foraging as it went.

On the few occasions when opossums were seen at night, their relative alertness and speed of movement contrasted with the sluggishness and seeming stupidity of those observed in daylight. Several were seen on roads in the beam of automobile headlights. These were quick to escape, running into thick roadside vegetation or woods to elude pursuit. Others were found in woodland, with the aid of a powerful flashlight as the investigator moved about on foot. They did not permit close approach, and escaped by running. One hid in a blackberry thicket. Several that were chased climbed trees when hard pressed. One that was overtaken, and others that were shaken out of trees and caught, showed fight, standing on the defensive, and slashing at the pursuer with a rapidity and vigor never encountered in those removed from traps in the daytime.

Nocturnal tendencies of the opossum were emphasized by the infrequency with which undisturbed individuals were seen in the daytime. In more than a thousand days of field work on the Reservation, opossums were found out on only four occasions. These occasional daytime forays seem to occur almost always in animals driven by hunger on winter days, when the temperature has suddenly risen after periods of severely cold weather that have imposed inactivity and fasting.
Earlier field studies of the opossum have produced somewhat conflicting evidence and conclusions regarding the extent and manner of the opossum's travels. Lay (1942:158) live-trapped and marked 117 opossums on an 86-acre study area in eastern Texas over a two-year period and caught 29 of them at three or more different [Pg 316] trapping stations. He found that "The average minimum area between the stations in these 29 home ranges was 11.5 acres. The mean of the greatest distances traveled between stations was 1460 feet, which would form a theoretical circle of 38.4 acres.... Separate individual territories are not important to opossums as home ranges overlapped in every instance." Reynolds, in central Missouri, concluded that: "The subsequent recovery of only 5 of 68 released animals, the reported capture of one individual 7 miles from the point of release nine months later, and the rapid repopulation of an area devoid of opossums at the close of the hunting season indicate that most opossums are nomadic." In southeastern Iowa, Wisemann and Hendrickson (1950:336) found that: "Recaptures, in 1942, of three opossums tagged in 1941 indicated a yearly mobility of one-fourth mile; four tagged in 1942 were recaptured within one-half mile from sites of tagging."
Opossums, like other animals, obviously make various types of movements. Ordinarily one tends to keep within a relatively small area that is familiar to it and that satisfies all its ecological requirements. This constitutes its home range. Many other animals, including various mammals, are characterized by territoriality; individuals, pairs or groups occupy definite areas, defended as territories, to the exclusion of other members of their species. Like Lay (loc. cit.) we found no evidence of territoriality in the opossum. In general, opossums are unsocial but not intolerant in their behavior. In the present study numerous individuals of both sexes and various sizes and ages were found to be occupying the same area simultaneously, with overlapping but no exact correspondence in home ranges. Occasionally two or more opossums may use the same den, but each goes its own way on its foraging and it seems that no sociability is involved.
On many occasions opossums were tracked in soft snow or mud which retained footprints. Under conditions prevailing locally, it was difficult to follow such a trail for any great distance but trailing did divulge information concerning the type of route followed and the method of foraging. Opossums were found to have little inclination to follow beaten trails, either their own or those of other animals. A foraging opossum moved about in an extremely circuitous and erratic route, seldom taking more than a few steps without a change of direction, and frequently crossing its own course in a series of loops, some only a few feet or a few inches in diameter. In moving about, it is guided partly by the tactile and olfactory [Pg 317] stimuli of objects on or beneath the ground surface which are potential food sources. Foraging consists of a succession of tests of such objects, as the animal moves from one to another. Opossums may habitually follow intermittent creeks or gullies or even roads when these provide better foraging than does the adjoining habitat. Metamorphosing amphibians may provide such a food source along a creek and the supply of crushed insects or other small animals along a road attracts the opossum. Food is found by turning chips and leaves, and by poking and probing in chinks and crevices with its snout and paws. On a few occasions short, well worn trails made [Pg 318] by opossums were found, from dens to near-by feeding areas where grape tangles provided an abundant and readily available food source over periods of weeks. More often, an opossum follows no trail in its search for food, but seems to wander at random within its home range.

Evidence of the existence and extent of home range was obtained for those opossums that were trapped on several or many occasions. Records of each were usually well scattered over an area hundreds of feet in diameter. Limits of home ranges are not sharply defined and at any time the opossum may extend its range into new areas. It may shift to a new den from which areas beyond its original home range are readily accessible, and may then occupy a new home range overlapping part of the old one. Or, it may make a relatively long shift, to an area entirely distinct from the original home range and well separated from it. That such shifts are frequent was indicated by the brief span of records for most of the opossums live-trapped on the Reservation. After the first capture and marking an individual was often caught consistently over periods of weeks, only to drop out suddenly either having been eliminated or having moved elsewhere. Of the 111 opossums marked and released, 62 were caught only once and 25 others were recaptured only within a period of one or two months. Relatively few, only 24 (14 males and 10 females), had records extending over more than two months. Many of the opossums trapped were probably at or near the edges of their home ranges which barely overlapped the study area; consequently the chances of recapturing them were poor. Those caught well within the trapping area were much more likely to be recaptured.
Tracking of opossums suggested that having once left the home den, an animal ordinarily did not return until it had finished its nightly foraging, and wandered more or less at random over its home range. Successive capture sites for any one opossum might be near together or far apart with respect to its over-all range, but on the average, they would be separated by approximately half the breadth of the home range assuming the animal's activity to be evenly distributed over the whole area. Each of twenty-two opossums was caught at only two different trapping stations. For this group, the average distance between stations was 761 feet (657 feet for seven males and 810 feet for 15 females) indicating home ranges of approximately 42 acres in extent. Each of ten opossums was caught at three different stations; for these the distances between the first and second stations, between the first and third and between the second and third comprise three distinct movement [Pg 319] records, and the average of all three probably affords a more reliable figure for the radius of the home range than does the single movement available for each of the 22 animals captured at only two stations. For these average individual movements the mean of this whole group of 10 was 841.5 feet. Each of five opossums was taken at 4 different trapping stations, and for each of these a record of six different movements was available. The average was 1016 feet. For the 37 opossums caught at two, three or four different trapping stations, the mean distance was 817 feet; this is an indication of home ranges of approximately 48 acres in extent. Each of thirteen opossums was caught at five or more trapping stations. The distribution of these stations affords a crude idea of the extent and position of each animal's home range, but ordinarily it might be expected that the area included between capture sites would be less than the animal's actual home range, because relatively few of the sites of capture would be on the margin of the home range. For this group, maximum distances between trapping stations averaged 1954 feet suggesting a home range of nearly 70 acres, larger than that computed for the opossums caught at only two, three, or four stations. However, for those caught at five or more stations, the time involved averaged longer and probably some had altered their ranges to invade new areas. Ranges may have been broadly oval rather than circular so that the maximum diameter measured between stations exceeded somewhat the average range diameter for each animal.
The opossums having home ranges entirely within the study area were those most likely to be caught repeatedly and at different locations, while those with ranges centering near the edge of the area, or outside of it tended to be caught at fewer locations and less frequently. For those animals with ranges partly outside the study area, the captures recorded would represent only one sector of the home range and would tend to be near together, so that many of the radii computed for individual home ranges are too small. Each average figure for home range is perhaps erroneously low for this reason. The error tends to be greatest for those taken at only two locations, and least for those trapped at the greatest number of different locations.
Approximate size of the usual home range is apparent from the several figures although various unknown or unmeasurable factors distort the data. The usual home range of the opossum in the area of the study is in the neighborhood of 50 acres or a little less. With the data available no significant differences in sizes of home ranges are [Pg 320] discernible between males and females nor between adults and young of the year. Shifts occur frequently, contributing to population turnover, which may result in almost complete replacement of individuals in the course of a year's time, on an area of less than a square mile.
One hundred and fifteen small young of 14 different litters were marked while still attached to the mother's teats in the pouches. A fairly high rate of mortality probably is normal in the small dependent young and further mortality probably resulted from the deleterious effects of examining and handling them and the females that carried them. At any rate, 47 of 208 young recorded, were missing at subsequent recaptures of the females, before the young were old enough to become independent. It is almost certain that the actual losses were much higher, because the records for each female cover only part of the period during which young are carried in the pouch.
Fifteen of these marked young of seven different litters were recaptured after periods of months, when they were well grown or adult and the locations of these recaptures afford information concerning the animals' dispersal. Their records are summarized below. Opossums that wandered much more than half a mile or at most three-fourths of a mile from the place of original capture were unlikely to be recaptured, and some originally recorded at sites near the edge of the study area might have moved beyond its boundary with much shorter shifts.
| Sex | Date of capture and marking as pouch young |
Date of recapture |
Distance in feet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | April 14, 1951 | September 22, 1951 | 1870 |
| Female | May 6, 1950 | February 28, 1952 | 1800 |
| Female | May 14, 1950 | December 31, 1950 | 1750 |
| Female | March 28, 1951 | January 23, 1952 | 1700 |
| Female | May 11, 1951 | November 9, 1951 | 1700 |
| Female | May 11, 1951 | March 2, 1952 | 1450 |
| Female | April 2, 1950 | October 7, 1950 | 1160 |
| Female | April 14, 1951 | May 19, 1952 | 1100 |
| Male | May 11, 1951 | February 3, 1952 | 800 |
| Female | May 11, 1951 | January 9, 1952 | 700 |
| Female | April 2, 1950 | October 3, 1950 | 700 |
| Female | May 6, 1950 | April 3, 1951 | 650 |
| Female | March 28, 1951 | February 2, 1952 | 500 |
| Male | April 18, 1952 | July 6, 1952 | 120 |
| Female | April 2, 1950 | April 14, 1951 | 10 |
Most of these opossums were recaptured within a year of the time they were marked as small young in the females' pouches, and on the average they had moved a little less than 400 yards. While the [Pg 321] sex ratio was equal in the pouch young that were marked, it is noteworthy that all but two of the recaptured opossums were females; and of the two males, one was recaptured early, before it could have had time to wander far. The young males, after becoming independent must tend to wander much more widely, and to settle in new areas far removed from the mother's home range. It is unlikely that this dispersal of the young males is motivated either by rivalry and intolerance of larger males or by sexual drive. The dispersal occurs in late summer when there is no breeding activity, and when food is present in greatest abundance and variety.
The feeding habits of the opossum in Douglas County, northeastern Kansas, have been discussed by Sandidge (1953). His data were obtained from stomach analysis of specimens caught in steel traps. In the present study no stomachs were available for analysis as the opossums on the Reservation were not sacrificed for this purpose and effort was made to avoid mortality in those that were live-trapped. Information concerning their feeding habits was obtained mainly by examination of scats in the field. On this 590-acre tract maintained as a Natural Area with human disturbance kept to a minimum, the available food sources differed somewhat from those of other woodland areas and especially from those of cultivated or suburban areas as reported upon by Sandidge.
The feces or "scats" of the opossum are not liable to be confused with those of other mammals except possibly with those of the striped skunk or raccoon, both relatively uncommon on the Reservation. Favorite sites for deposition of opossum scats were at the bases of large trees, usually honey locusts or elms, near the animal's den. Accumulations of several dozen scats may collect in such situations. Often the opossums live-trapped were found to have deposited scats and many of these were saved for examination, although they were usually trampled, broken and mixed with earth and hair. Few scats were seen in the field throughout the summer. Their disintegration is rapid at that time of year because of the high temperature, frequent heavy rains, and abundance of dung-feeding insects. Scats were seen in greatest abundance in the fall, partly because the opossum population was then at its annual high point. During fall, wild fruits made up the greater part of the diet and were represented in almost every scat that was seen. Wild grape (Vitis vulpina) is an abundant woodland vine on the area and often forms dense tangles both in deep woods and in edge situations. [Pg 322] Grape was the most abundant single item, and a large number of scats consisted exclusively of grape seeds and skins. In November and December opossums could be trapped most effectively by making sets in or near grapevine tangles where the animals were attracted by the abundant ripe fruits. The crops of wild grapes were especially heavy in 1948 (before live-trapping was begun) and in 1949, and scats containing them were noticed in those years especially. Opossums, too, were more numerous on the Reservation in 1948 and 1949 than they were in 1950, 1951, and 1952.
Hackberry fruit (Celtis occidentalis) was second to grape in importance and large numbers of scats were found to be composed mainly or entirely of the skins and seeds of this fruit. In the fall of 1951, these fruits were especially important and were the principal food source.
Wild plum (Prunus americanus) and wild crabapple (Pyrus ioensis) also are important in fall and winter and are present in many scats. In summer, blackberry, abundant on some parts of the Reservation, is an important food. Other wild fruits noticed in scats include those of cherry (Prunus virginiana) and climbing bittersweet (Celastrus scandens), and mast (acorn ?). In the fall of 1948, corn made up a large part of the contents of scats noticed. Crops of corn were grown on two fields of the Reservation in that year. In following years, corn was noticed less frequently in scats but still continued to be one of the important food items. Several cornfields adjoined the Reservation, and the scats containing the grain were observed mainly along the borders of these fields.
The crayfish is evidently the most important animal food, at least during the cooler half of the year when scats are seen in greatest numbers. Remains of crayfish were far more conspicuous than those of other invertebrates, and often made up the greater part of the scat. The sample of scats examined in the field, as noted below, are thought to be representative of the much larger number noticed but not examined in detail.
August 19, 1951, 16 scats. Food items in their approximate order of importance were: blackberry in six (100% in 5, 95% in 1); grape in five (100% in 2, 97% in 1, 95% in 1, 50% in 1); crayfish in three (100% in 1, 60% in 1, 40% in 1); wild plum in two (85% in 1, 5% in 1); wild crabapple in two (100% in both); insects in three (scarabaeid beetle 10% in 1, cicada 2% in 1, unidentified insect fragments in 5); fox squirrel in one (15%); unidentified plant fibers in one (40%).
September, 1951, 16 scats. Grape in seven (all or most of 5 scats and small percentages of 2 others); cherry in seven (all or most of 5 scats and small percentages of 2 others); crayfish in seven (all or most of 5 and small percentages [Pg 323] of 2 others); rabbit in two, making up most of both; insects (grasshopper, and large black beetle) in two making up small percentages.
October, 1951, 8 scats. Hackberry in three, making up nearly all of them; grape in two (all of 1 and most of the other); wild plum in one (100%); mast (acorn?) in one, making up 100%; crayfish in one making up about half; fox squirrel in one making up the remainder of the scat containing crayfish; rabbit in one making up a small percentage.
November, 1951, 12 scats. Hackberry in five, making up all or most of four and a small part of the fifth; grape in five, making up all or most of four and a small part of the fifth; wild crabapple in three, making up all of two and most of the third; and cottontail in one, making up all of it.
January, 1952, 3 scats. Hackberry in all, making up all of two and most of the third; copperhead (scales of medium-sized adult) making up a fraction of the third scat. Pile of more than a dozen scats not individually separable, nearly all consisted mainly or entirely of hackberry fruits estimated at 2000; other contents chiefly crabapple and corn.
September, 1952, 8 scats. Grape in all, making up all of six and 90% of the seventh, and about 20% of the eighth; wild plum seeds in one making up 40%; blue feathers, evidently of a jay, in one, making up a trace; carabid beetles in one making up a trace.
October, 1952, about 14 scats, two separate (both consisting exclusively of grape) and the remainder mixed in two approximately equal piles, one pile consisting of grape, except for small quantity of fine fur; second pile consisting mainly of grape (about 90%) with small percentages of yellowjackets (Vespula, about 6 individuals, all in one scat), toe bones and fur of cottontail rabbit; a few scales of immature copperhead; and a snail.
November, 1952, 2 scats. Grape in both, making up all of one and about 90% of the other.
Sandidge (loc. cit.) found remains of cottontail rabbit in some of the stomachs he examined, but followed Reynolds (1945) in regarding these as carrion since the opossum was considered to be too inefficient a predator to catch and kill cottontails—prey approximating its own size and much superior in speed. Adult cottontails seem to be secure from opossum predation under ordinary circumstances. However, the opossum obtains some of its food by raiding the nests of small animals, including those of rabbits. At the Reservation, on May 21, 1951, at 9:00 P. M., distressed squealing of a rabbit was heard in high brome grass. Investigation revealed that a large male opossum had killed a young cottontail, weighing approximately 150 grams, and had started to eat it. This young rabbit, about the minimum size of young wandering outside the nest, evidently was pounced upon as it hid beneath the high grass.
Live-traps for mice, in lines or grids of 100 or more, often were set on the Reservation, and predators, including opossums, disturbed them on many occasions. Attacks sometimes resulted in release and escape of the trapped animal, and in other instances resulted in its [Pg 324] being caught and eaten. In many instances identity of the predator could not be determined, but it is believed that such attacks by the opossum were relatively infrequent and inefficient. Steel traps set beside the mouse traps after consistent raids, to catch or discourage the predator, caught opossums on several occasions. These opossums usually had overturned mouse traps without opening them and when the trapped mouse was missing from the trap no evidence of its having been eaten was obtained. On other occasions raccoons were caught in the steel traps, and their raids were characterized by systematic and dextrous opening of the mouse traps and, frequently, by predation on the small mammals inside them.
Wire funnel traps set for reptiles along rock ledges also were often disturbed by predators, mainly skunks and opossums, both of which were caught on several occasions, when steel traps were used as a protective measure. The opossums often were attracted to the funnel traps by large insects such as camel crickets, grasshoppers and beetles, but also by trapped lizards including the skinks (Eumeces fasciatus and E. obsoletus) and the racerunner (Cnemidophorus sexlineatus). Both Sandidge (1953) and Reynolds (1945) recorded the five-lined skink (E. fasciatus) in opossum stomachs. On the Reservation this common lizard probably is one of the most frequent items of vertebrate prey of the opossum. Flat rocks a few inches in diameter frequently have been found flipped over; larger flat rocks and those solidly anchored in the ground often have been found partly undermined by opossums scratching away the loose dirt at their edges. Flat rocks similar to those found disturbed by opossums are the favorite resting places of the skinks, which, in cold or wet weather, are sluggish when beneath such shelters; this is especially true of female skinks that are nesting. The shape and size of some of the excavations suggested predation on skink nests. Other possible food sources in the same situation, in loose soil beneath flat rocks, include narrow-mouthed toads, lycosid spiders, beetles (mainly carabids such as Pasimachus and Brachinus) and occasionally, snails, centipedes and millipedes.
A pond, a little more than an acre in size, was a focal area for opossums and more were caught there than on any other part of the Reservation. Opossums that were trapped and marked on other parts of the Reservation were likely to be caught here sooner or later. Tracks in the mud showed that the edge was patrolled almost nightly by one or more opossums and this activity was especially noticeable when the pond was drying. Frogs were obviously the chief attraction inducing the opossums to forage there. [Pg 325] Of the 8 kinds of frogs and toads breeding at the pond, the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana), leopard frog (Rana pipiens) and cricket frog (Acris gryllus) were most abundant, throughout the season and especially when drying occurred. All three probably are important foods of the opossum locally.
Opossums were weighed in the field, with small spring scales of 2000-gram capacity, graduated in 25-gram intervals. Weights recorded were accurate within a margin of about 10 grams. After other data were recorded, the opossum was offered the hook at the base of the scale, and usually bit and held fast. Then it could be suspended off the ground and a reading taken.
When the same opossum was trapped two or more times within a few days, weight was usually found to fluctuate sometimes more than 200 grams, or more than 10 per cent of the animal's body weight. Opossums recaptured soon after their original capture and toe-clipping were generally found to have lost weight, reflecting the deleterious effect of marking by this method. The temporary laming of the animals prevented them from traveling as far or as fast as they normally would have; consequently they probably obtained correspondingly less food. They were also handicapped in digging, grasping and climbing. Nineteen such animals taken within a month of the original capture and marking, averaged 94 per cent of their original weights. The minimum was 82 per cent. Only 2 of the 19 had gained.
The stumps of amputated toes did not heal rapidly in opossums—contrary to experiences with many other kinds of mammals, reptiles, and amphibians also marked by toe-clipping. For many weeks the toes remained unhealed, sore and swollen. In several instances after periods of months the clipped toe stumps were unhealed. This was observed even in some of the opossums that were marked as pouch young and recaptured when grown to nearly adult size.
Some adult opossums trapped were heavier than the 2000-gram capacity of the spring scale usually used in the field, and no definite weights were recorded for most of these animals. Some of them that were caught near the laboratory were brought there for weighing.
Even within the same age- and sex-group at any one time, opossums varied widely in general condition and in weight. Some were emaciated and sickly in appearance with sparse, ragged pelage, while others were in excellent condition, fat and with thick, glossy [Pg 326] pelage. Seasonal trends are partly obscured by these differences in individuals, by the tendency to lose weight in those recently marked, and by the irregular fluctuations that occur in each animal.

The few opossums caught in summer were thin and appeared to be suffering from infestations of ectoparasites, especially chiggers (Eutrombicula alfreddugesi) and ticks (Dermacentor variabilis). Those trapped in October and November were mostly fat and in good condition. For individuals caught at different seasons, maximum weights were generally recorded in these two months. The maximum weight record of the study was one of an adult male weighing 5000 grams on December 23, 1950. The weight records of this individual were more complete than most and are recorded below to illustrate seasonal trends for adults. May 10, 1950, 1925 grams; May 14, 1830 grams; May 17, 1940 grams; November 5, 4540 grams; November 28, 4540 grams; December 23, 5000 grams; February 18, 1951, 3300 grams; March 6, 3080 grams; March 28, 3080 grams; May 28, 3080 grams; June 18, 2620 grams.
[Pg 327] Of opossums that were trapped alive, the weight ranged from the maximum of 5000 grams to a minimum of 126 grams. The maximum in males was higher than in females. In fall, three rather poorly defined age-size groups were discernible in each sex: adults more than a year old and including all the largest individuals; large young born late the preceding winter and approaching small adult size; smaller young born in early summer and still less than half-grown. After November, young cease to gain, or gain slowly and irregularly through the winter and spring and adults tend to decline in weight, as food becomes scarce and frequent fasting is enforced by cold or stormy weather. The smaller young probably are subject to drastic reduction in numbers as a result, directly or indirectly, of severe winter weather. Many of these smaller young, weighing considerably less than 1000 grams, did not survive overnight when caught in live-traps in cool autumn weather, whereas adults and well-grown young generally survived exposure even for several successive nights in various extremes of weather conditions.
Hartman (1928:154) stated that there were at least two litters of young per year in the southern states with a small percentage of unusually fecund females producing a third litter. Lay, in eastern Texas, concluded (1942:155) that "The present investigation substantiates Hartman's deduction of two litters being normal, but fails to disclose any evidence of a third litter." He found females carrying young in the pouch only within the seven-months period January to July with definite peaks in February and June, and stated that second litters appear in the pouch from early April to as late as May 20 to 23. Reynolds (1945:362) found that the breeding season in central Missouri in 1941 and 1942 began about the first of February, with known or calculated birth dates of 42 litters rather evenly distributed throughout the periods February 12 to April 2, and May 16 to June 4. Eight of these females had given birth to young between March 16 and April 2, approximately six to nine weeks after the beginning of the breeding season. Reynolds assumed that these were individuals that had failed to find mates during the first oestrus of the season and that after completing the regular dioestrus of about 28 days they had then mated and borne young. Wiseman and Hendrickson (1950:333) in southeastern Iowa recorded a female with a litter no more than two days old on February 23, and several other females with young were estimated to have borne litters at approximately this same date, while still [Pg 328] others bore litters as late as early March. Two lots of small young found in early June may have been second litters.
For the region represented by the present study, the data indicate a breeding season with later onset and sharply circumscribed limits as compared with an earlier onset and less circumscribed limits in Texas, central Missouri, and even southeastern Iowa, which is a little farther north. The available data indicate that there are two distinct and well-defined breeding seasons in the course of the annual cycle on the University of Kansas Natural History area. The whole population, including young of the preceding year, some still far below average adult size, breeds from about the middle of February into early March, and first litters are born mainly in early March. Individual females may vary as much as two to three weeks in the time of breeding, and varying weather conditions from year to year may hasten or delay onset of the breeding season. Data are recorded below for all females caught in March that were carrying litters.
| Date | Weight of female in grams |
Number of young | Development of young |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 1, 1952 | 2000 | 9 | Newborn |
| March 2, 1952 | 1450 | 6 | Newborn |
| March 2, 1952 | 1230 | 7 | Newborn |
| March 5, 1950 | 1200 | 10 | About 16 mm. snout to vent |
| March 5, 1950 | 1300 | 1 | About 14 mm. snout to vent |
| March 6, 1951 | 1110 | 4 | Newborn |
| March 18, 1952 | 1930 | 8 | Not present when female was trapped on March 1 |
| March 18, 1952 | 1520 | 6 | |
| March 18, 1952 | 1230 | 12 | About 40 mm. snout to vent |
| March 19, 1951 | 1000 | 8 | Estimated 1 week old |
| March 22, 1950 | 1040 | 9 | About 34 mm. snout to vent |
| March 24, 1950 | 1280 | 10 | 74 mm. snout to vent |
| March 24, 1950 | 1480 | 8 | |
| March 27, 1950 | 965 | 8 | Total length 26 mm., weight .8 g. |
| March 28, 1951 | 820 | 7 | 20 mm. crown to rump; born since previous capture of female on March 7 |
| March 30, 1950 | 1325 | 9 | Total length 33 mm. |
| March 31, 1952 | 1930 | 8 | |
| March 31, 1952 | 1630 | 5 | Total length 73 mm. |
None of the females trapped in February was carrying young in the pouch, but probably some early litters are born in the last week of February or even earlier. By late March most of the females are carrying young in their pouches, and those which do not have young, have their pouches enlarged and vascularized for accommodation of the young. Presumably such females have already borne young and then lost them. Nearly all the litters seen in the latter half of March had young that were much larger than at birth.
[Pg 329] Of 13 females examined in April, 12 were carrying young, and the remaining one was known to have been carrying a single young on March 1, but had lost it. Eleven females were examined in May, four of which were the same ones examined in April. Eight of the eleven females were carrying young; of the remaining three, one had lost the litter of young that it had been carrying when trapped in April. Two had empty pouches on May 19 and 20, but probably had successfully reared the litters of young which they had been carrying when trapped in April. The young of all those females trapped on different dates in April and May were in stages of growth indicative of birth about the first week in March. The latest date on which a female was recorded with first-litter young in the pouch was May 22, 1951, and these were the largest pouch young observed. Their eyes were recently opened, they were estimated to weigh 60 grams each with hind feet 20 mm. long. Young continue to grow rapidly after leaving the female's pouch. A young female caught on June 16, 1949, weighed 126 grams. For seven young caught on July 5 and 6, 1952, weights and hind-foot measurements were, for males: 660 grams, 52 mm.; 560 grams, 46 mm.; 550 grams, 48 mm.; 450 grams, 44 mm.; 370 grams, 44 mm.; 330 grams, 37 mm.; and for the one female: 430 grams, 46 mm.
The wide variation in size in this small group of young of nearly the same age is noteworthy. Size and condition of the females carrying them, number of competing litter mates, and early success or handicap in independent life causes so much divergence in size that at the age of four months some young are twice as large as others.
By late fall the young grow to small-adult size. For example, the female that weighed 126 grams when first caught on June 16, 1949, was recaptured on November 29, 1949, and on that date weighed 1710 grams.
A second breeding season ensues soon after the young of the first litter leave the pouch, and these young probably soon learn to shift for themselves. Second litters are usually born in early June. On June 14, 1952, a female was taken with young only a few days old in her pouch. On July 5, 1952, two females last taken on May 19 and May 20, with their pouches recently vacated by first litters, were found to have young the size of half-grown mice, evidently two to three weeks old. In the months of October, November, December and January, a total of 11 young, thought to represent second litters, [Pg 330] were taken. Dates of capture, weights in grams and sexes were as follows:
| Oct. 3, 1950 | 400 grams | male |
| Oct. 6, 1950 | 510 grams | female |
| Oct. 8, 1950 | 260 grams | female |
| Oct. 8, 1950 | 350 grams | female |
| Oct. 18, 1950 | 350 grams[A] | female |
| Dec. 5, 1951 | 630 grams | female |
| Dec. 30, 1950 | 710 grams | female |
| Jan. 1, 1951 | 660 grams | female |
| Jan. 1, 1950 | 700 grams[A] | male |
| Jan. 9, 1950 | 550 grams | male |
| Jan. 11, 1950 | 550 grams | male |
The hind foot measured 48 mm. and 51 mm., respectively, in the young weighing 630 grams and 660 grams. These young, born in early summer have grown, by October, to a size comparable with that attained in July by young of the early spring litters. The variation in size is also similar but with a little wider range. The summer breeding season may be somewhat more protracted than the breeding season in early spring.
Too few females were caught in summer to compare the summer breeding season with the early spring breeding season, with respect to size of litters, percentage of non-breeders, and other factors which might affect the size of the crop of young produced. It is not clear why, among opossums trapped in winter, the young born in early spring outnumber those born in early summer by about four to one. Some females are eliminated after rearing the first litter, and others, exhausted by rearing large first litters may fail to participate in the second breeding season. However, it seems that the young of the summer litters must be subject to other unusual and selective mortality factors which eliminate most of them by fall. That such factors vary from year to year is indicated by the changing ratio of summer-born young to other opossums in each of the three winter seasons when trapping was carried on.
Hartman (1952) has summarized his own findings and those of other authors regarding the embryology, birth, and early development of the opossum, and has corrected numerous popular misconceptions. He states that an average litter consists of about 21 eggs, but mentions much larger litters of up to as many as 56. However, many of these may fail to develop. The female normally has 13 functional nipples in her pouch and each one accommodates a single young. Excess young beyond this number are doomed, and soon perish from starvation if they reach the pouch after all the nipples are occupied. None of the females examined in the present study had a full complement of 13 young. Under unfavorable conditions, [Pg 331] most or all of the young may fail to make the trip from the vaginal orifice to the pouch. Also, the pouch young are subject to heavy mortality, but observations concerning the time and cause of mortality are lacking.
Lay (loc. cit.) found an average of 6.8 pouch young in 65 litters examined in eastern Texas; Reynolds found an average of 8.9 (5 to 13) in 42 litters from Boone County, central Missouri; Wiseman and Hendrickson found an average of 9 (6 to 12) in southeastern Iowa. In the present study, 28 of the female opossums examined were carrying litters in their pouches, and all these females were caught in the months of March, April, May, June and July. The number of young varied from one to 12. Seven females each had seven young, six each had eight, three had six, three had five, and there were two each with nine, 10, and 12 young, and one each with one, four and 11 young. The average was 7.4 per litter. On several occasions females captured with young in their pouches and recaptured one or more times within a few weeks, were found to have lost some or all of the young. Some of the females examined probably had already lost parts of their litters. For instance, the female recorded with just one small young on March 1, probably had lost most of her litter and when recaptured a month later she did not have any young.
Nineteen yearling opossums were taken in the fall-winter-spring season of 1951-52; 42 per cent of the total, and 67 per cent of the females were individuals marked as pouch young the preceding spring. In the course of live-trapping, that spring, some first litters may have been missed. No second litters were marked because trapping was not continued into June and July when second litters are being carried by females. These figures suggest that the breeding population of females on an area consists chiefly of those born there the preceding spring.
Sex ratio of opossums trapped was approximately 1:1; 59 males to 58 females. Age groups for opossums caught in the three seasons are shown in the following tabular fashion. For a few individuals age status was doubtful.
| 1949-1950 | 1950-1951 | 1951-1952 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old adults | 11(25%) | 9(26.4%) | 11(39.2%) | 31(29.2%) |
| Yearlings: | ||||
| Born in late winter | 29(66%) | 18(53.0%) | 13(46.5%) | 60(56.6%) |
| Born in late spring | 4(9.1%) | 7(20.6%) | 4(14.3%) | 15(14.2%) |
| Total | 44 | 34 | 28 | 106 |
[Pg 332] In the 1950-51 season, small young of the summer brood seemed unusually numerous. In the 1951-52 period, young of both age classes were relatively scarce and old adults made up an unusually high proportion of the population. Excluding the 14 marked pouch young that were later recaptured, there were only four of the total of 106 that were trapped in each of two seasons. One young less than a quarter grown, that was accidentally caught in a live-trap set for woodrats, was recaptured as a breeding adult the following winter. An adult male and two adult females each caught in the 1949-50 season were each recaptured repeatedly in the 1950-51 season. Ninety-five per cent replacement of the breeding population by the following breeding season is indicated by our figures. Only 3 (or 5 per cent) of the individuals of the population trapped and marked in the season of 1949-50, were recaptured among the 62 opossums recorded in the two subsequent seasons. Various mortality factors including predation, disease, and accidents account for some 70 per cent. These are replaced by first-year young which make up the greater part of the breeding population. The remaining 25 per cent presumably shift their ranges sufficiently in the course of a year to have moved beyond the limits of an area of the size encompassed by the present study.
No precise measurement of the population density on the study area was obtained. It was not practical to capture every individual present there, and rapid population turnover, due to mortality and wandering, obscured the trends. The information obtained concerning movements of opossums suggest that one may habitually forage as much as 900 feet from its home base. Assuming that 900 feet is the typical cruising radius, the areas drawn upon by the trap lines in the three different seasons were approximately as follows: 1949-50—400 acres; 1950-51—350 acres; 1951-52—220 acres. In these same three seasons the numbers of opossums caught were, respectively, 46, 37, and 30. If these figures represent the numbers actually present, densities of one to 8.7 acres, one to 9.5 acres, and one to 7.3 acres are indicated. However, some opossums using the area probably were missed; and on the other hand, not all those caught in the course of a season were present there simultaneously. Many of those present early in the season would have moved away a few months later, and others would have moved in, replacing them. The number present at any one time could scarcely have been more than half the number caught in the entire season.
| Sampling period | Number of individuals taken in period |
Number of individuals taken in following period |
Number of recatures in following period |
Computed population for sampling period |
| Early November 1949 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 21 |
| Late November 1949 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 18.7 |
| Early December 1949 | 8 | 11 | 3 | 29.3 |
| Late December 1949 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 19.2 |
| Early January 1950 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 21 |
| Early March 1950 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 20 |
| Late March 1950 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 16 |
| Early April 1950 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 18 |
| Late April 1950 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 9 |
| Early May 1950 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 9 |
| Early November 1950 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Late December 1950 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 18 |
| Early February 1951 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 17.3 |
| Late February 1951 | 13 | 6 | 3 | 26 |
| Early March 1951 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 8 |
| Late March 1951 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 10 |
| Early April 1951 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Late April 1951 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| Early May 1951 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 7.5 |
| Early February 1952 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 18 |
| Late February 1952 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 36 |
| Early March 1952 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 27 |
| Late March 1952 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 15 |
| Sampling period | Number of individuals taken in period |
Number of individuals taken in following period |
Number of recatures in following period |
Computed population for sampling period |
| November 1949 | 9 | 16 | 7 | 21 |
| December 1949 | 16 | 9 | 3 | 48 |
| March 1950 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 33 |
| April 1950 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 32 |
| October 1950 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| November 1950 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 9 |
| December 1950 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 7 |
| January 1951 | 7 | 14 | 3 | 33 |
| February 1951 | 14 | 7 | 4 | 25 |
| March 1951 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 12 |
| April 1951 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 10 |
| November 1951 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 18 |
| December 1951 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 30 |
| January 1952 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 18 |
| February 1952 | 11 | 13 | 4 | 36 |
| March 1952 | 13 | 9 | 5 | 23 |
| April 1952 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 27 |
Crude census-figures were obtained by utilizing the Lincoln Index and computing the total on the basis of the ratio of marked (and recognizable) individuals to others caught in a sampling period. A large number of census figures were obtained over the three-year period of the study. Each separate census, however, was based on an inadequate sample as the number of marked individuals taken [Pg 334] at each sampling, as recaptures from the previous sampling period, varied from one to five. While little confidence can be placed in any one census computation, the trends of figures from series of such computations reveal the approximate number of opossums on the area if due allowance is made for certain distorting factors. Presumably the differences in figures obtained at different samplings result chiefly from the margin of error in the data, although it is true that there is rapid change in the actual number of opossums.
The number of active opossums in the region of the study reaches a peak in late summer and early fall, when second litters of young have grown large enough to become independent. At this season the population contains a high proportion of young of the year. During the ensuing months of fall and winter there is a steady decrease in numbers, through various mortality factors, with no replacement until young are born about the first week of March. These young do not become independent until late May or early June, and during the intervening months there is a further reduction of the adults and yearlings, so that the active population reaches its annual low point in late spring. At that time of year most opossums are in poor physical condition.
The area represented by the opossums trapped totaled more than 500 acres, but not more than 400 acres were within the area drawn upon by the trap line at any one time. Usually the area represented at any one time by the trap line was less—100 to 350 acres, with from 25 to 45 traps. Traps were moved from time to time depending on the distribution of opossum sign and food sources, the weather, and the time available for this study. As a result, successive samples are not strictly comparable and a major source of error is introduced into the census computations. Lack of exact correspondence in the area represented by successive samples would result in a disproportionally small number of recaptures, and an erroneously high census computation. While adequate adjustment cannot be made, examination of the data suggests that census figures are too high, by as much as 50 per cent in many instances as a result of this factor, while in some other instances when there was little or no alteration of a trap line from one period to another, the census figure was not affected. In the winter of 1949-50, the area covered was most extensive, from 350 to 400 acres, and the numbers of opossums taken were correspondingly larger. In the 1950-51 season the area involved was approximately 220 acres, and in the 1951-52 season it was a little less than 200 acres. In view of the census figures obtained and the probable errors, it appears that the opossum [Pg 335] population in early autumn is about one to 20 acres, and that by late spring it is reduced to not much more than half that number.
Many of the opossums trapped were suffering from injury, disease, or parasite infestation, and some were in critical conditions. A large adult male trapped on April 2, 1952, seemed to be dying from disease. It was much emaciated and the pelage was sparse and ragged, as if the animal had been sick for a long time. The skin had numerous light-colored pustules 1 to 2 mm. in diameter, and these were especially prominent on the ears, lips, and penis. When released, the opossum was too weak to move away. It was excited by movements of the trapper, and stood erect with violent involuntary rocking movements. After a few seconds it gradually slumped to the ground and subsided into quiescence. On the next day no trace of it could be found.
Most of the opossums caught in summer and early fall had eye infections, and all of them were infested with ticks (Dermacentor variabilis). Sometimes ticks were attached in dense clusters of several dozen on the animal's ears and scattered over other parts of the body.
In March and April, 1950, seven adult opossums were found dead in the traps. None of these showed any evidence of disease or injury and they were normal in appearance except that they were thin. It was concluded that death had resulted from exposure and starvation in the traps in these animals already in critical condition as a result of winter food scarcity and frequent fasting. Up to this time the procedure had been to check the trap line only on alternate days and no mortality had resulted, even in the coldest part of the winter. The implication is that by spring, opossums are in a condition so critical that they are unable to withstand exposure or fasting and die whenever weather conditions are unusually severe.
After these losses in the spring of 1950, trap lines were checked daily. However, in October, 1950, further mortality in traps resulted in the loss of three or more opossums. All three of these were rat-sized young of second litters. These young lacked the abundant supply of fat characteristic of larger opossums in fall, and seemingly were unable to withstand exposure to chilly nights. Such susceptibility to cold might result in heavy mortality in retarded second-litter young when cold weather of autumn is unseasonably early or is unusually severe.
Natural enemies of the opossum on the area include the red-tailed [Pg 336] hawk, horned owl and coyote. Because of the opossum's nocturnal habits it is rarely exposed to hawk predation. Food habits of the coyote on the area have not yet been investigated. Numerous instances of horned owl predation on opossums have been recorded in the literature. On January 15, 1950, an owl attacked an opossum caught in a live-trap. The trap was found overturned, and a few feet away were entrails and a quantity of opossum hair where the animal was eaten. Low vegetation in the vicinity had many fine down feathers of the owl clinging to it. On December 24, 1950, the carcass of a small adult opossum was found in a pasture near the edge of the woods. The head and tail were intact, but otherwise little more remained than the spinal column, girdles and larger limb bones. White excreta of a large bird beside the carcass indicated predation by a raptor, probably a horned owl.
On a natural area, the University of Kansas Natural History Reservation, in Douglas County, northeastern Kansas, the population of opossums was studied, chiefly by live-trapping, in the fall-winter-spring seasons of 1949-50, 1950-51 and 1951-52. The study area provided a varied habitat of elm-oak-hickory woodland, pastureland, and fallow fields. Opossums use all parts of it, but concentrate their activities in the woodland.
Opossums being mainly nocturnal were rarely seen in the daytime, except when caught in traps. Reactions to humans varied; some were indifferent, some feigned death, others merely tried to escape, and some defended themselves vigorously, snarling and snapping.
No evidence of territorial behavior was found in the opossum. Many individuals of both sexes and various sizes, occurred together on the same area. Successive captures of individuals revealed the usual extent of home ranges, which averaged approximately 50 acres, and tended to a circular or broadly oval shape. No significant difference in size of home ranges between males and females, or between adults and well-grown young, was found. Of 115 young marked by toe-clipping while still in the females' pouches, 15 were recaptured after periods of months. All but two of these recaptured young were females which had settled down within a few hundred feet of the locations where they were born. The young males seem to wander much more extensively than do the females.
Feeding habits were investigated by field examination of scats found mainly in fall and winter. These consisted mainly of wild fruits, especially grape, blackberry, wild crabapple, wild plum, and [Pg 337] hackberry. Crayfish was the most important animal food. No comparable data for spring or summer were obtained because scats deteriorate rapidly in warm weather and were seldom found then. Clues as to the summer food were gained from sign. On many occasions opossums disturbed live-traps set for small animals, to obtain the voles, mice, skinks, or insects caught in them. Evidence of opossum activity such as digging and scratching was frequently noticed at the edges of rocks and in crevices, where such prey as skinks, narrow-mouthed toads, beetles, spiders and centipedes seek shelter. One opossum was observed to catch and kill a young cottontail.
The opossums trapped ranged in weight from 126 grams to 5000 grams but most weighed between 1000 and 2000 grams. After being trapped and marked by toe-clipping, animals usually lost weight, up to as much as 18 per cent of the original weight. Food scarcity and enforced fasting in cold weather caused a weight loss from November until the arrival of warm spring weather. By late April and May some opossums were emaciated and in critical condition.
The entire population of opossums, including the majority less than a year old, breeds in February, and litters are born mainly in the first half of March. The young develop rapidly in the female's pouch, and become independent in late May, and there is a second breeding season with young born mainly in the first half of June. By the onset of cool fall weather, young born in early spring have grown so that most are as large as small adults. The young born in early summer are still less than half-grown. The young of the second litter are less successful than those of the first litter and make up only a small part of the breeding population the following year. In 28 litters of young the average was 7.4, but probably some of these litters had already sustained losses.
In each of three different winters, the largest age group in the population of opossums was that of the newly matured young born in early spring. The old adults were the next most numerous group, and the second-litter young born in early summer were the least numerous. The figures obtained from live-trapping indicate an annual population turnover of approximately 95 per cent, with some 70 per cent eliminated by various mortality factors and replaced by young, the remaining 25 per cent shifting to new areas, with compensatory shifts of individuals replacing them.
The various mortality factors which regulate the numbers of opossums are not well known, and even less is known regarding the relative importance of the factors. Food supply and weather are obviously of major importance and closely interrelated in their effect on [Pg 338] the population. One large adult opossum that was trapped seemed to be dying from disease and was scarcely able to stand; but others caught near-by before and after were unaffected. The horned owl is perhaps the most important natural enemy of the opossum on the Reservation, and instances of owl predation on opossums were noted.
Fitch, H. S.
Hall, E. R., and Kelson, K. R.
Hartman, C. G.
Report 1921:347-363.
Lay, D. W.
Leonard, A. B., and Goble, R. C.
Reynolds, H. C.
Sandidge, L. L.
Wiseman, G. L., and Hendrickson, G. O.
Transmitted May 4, 1953.
Other than two possible typographical errors listed below, the title and verso (second) page specifies the pages are 305-338; but the first numbered page (the third one) is numbered "309". The content provider examined the text at page breaks and looked for evidence of a missing leaf; but found none. So, this appears to be a printer's error in the pagination as the numbering sequence otherwise follows the normal format for these scientific texts. Therefore, the numbering was changed in the descriptions to read "... pp. 307-338, ..."
| Page | Correction |
| 316 | Occasionaly => Occasionally |
| 338 | Possible typo: Didelphis Virginiana => Didelphis virginiana |