
Project Gutenberg's Famous Singers of To-day and Yesterday, by Henry C. Lahee This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org Title: Famous Singers of To-day and Yesterday Author: Henry C. Lahee Release Date: July 15, 2010 [EBook #33168] Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FAMOUS SINGERS *** Produced by Chuck Greif and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images available by The Internet Archive.)
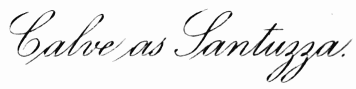
ILLUSTRATED

Boston
L. C. Page and Company
(Incorporated)
1898
Copyright, 1898
By L. C. Page and Company
(INCORPORATED)
Colonial Press:
Electrotyped and Printed by C. H. Simonds & Co.
Boston, U. S. A.
| CHAPTER | PAGE | |
| Preface | vii | |
| I. | From 1600 To 1800 A.D. | 11 |
| II. | Pasta To Mario | 41 |
| III. | Mario To Tietiens | 77 |
| IV. | Prima Donnas of the Fifties | 110 |
| V. | Prima Donnas of the Sixties | 143 |
| VI. | Prima Donnas of the Seventies | 186 |
| VII. | Prima Donnas of the Eighties | 220 |
| VIII. | Tenors and Baritones | 260 |
| IX. | Contraltos and Bassos | 296 |
| Chronological Table of Famous Singers | 325 | |
| Index | 333 |
| PAGE | |
| Calvé As Santuzza | Frontispiece |
| Jenny Lind | 84 |
| Jean de Reszke As Romeo | 98 |
| Adelina Patti | 128 |
| Nilsson As Valentine | 162 |
| Lillian Nordica | 220 |
| Melba As Ophelia | 244 |
| Emma Eames | 258 |
| Edouard de Reszke As Mephistopheles | 272 |
| Alvary in Rigoletto | 280 |
| Sofia Scalchi | 300 |
| Plançon As Ramfis in Aida | 318 |
It has been the desire of the author to give, in a book of modest dimensions, as complete a record as possible of the "Famous Singers" from the establishment of Italian Opera down to the present day. The majority are opera singers, but in a few cases oratorio and concert singers of exceptional celebrity have been mentioned also.
To give complete biographical sketches of all singers of renown would require a work of several large volumes, and all that can be attempted here is to give a mere "bird's-eye view" of those whose names exist as singers of international repute.
For much information concerning the{8} earlier celebrities the author is indebted to Clayton's "Queens of Song," "Great Singers" by Ferris, and "The Prima Donna" by Sutherland Edwards, in which interesting volumes much will be found at length which is greatly condensed in this little volume. To Maurice Strakosch's "Souvenirs d'un Impresario," and to "Mapleson's Memoirs," the writer owes something also in the way of anecdote and fact concerning many singers of the latter half of this century.
As it is impossible to give biographical sketches of more than a comparatively small number of singers who have achieved renown, the work is supplemented by a chronological table which is more comprehensive. No such table can, however, be perfect. For singers of the past the following authorities have been used: "Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians," C. Egerton Lowe's "Chronological Cyclopædia{9} of Musicians and Musical Events," James D. Brown's "Biographical Dictionary of Musicians," and "A Hundred Years of Music in America."
Concerning singers of later times, who have risen to fame since those works were compiled, such items have been used as could be found in the newspapers and magazines of their day, and the information is of necessity imperfect. It is nevertheless hoped that the table may be of some use as carrying the history of famous singers some years beyond anything hitherto published in book form, and it has been the desire of the author to make the book interesting alike to student and amateur.
The year 1600 marked the beginning of a new era in musical history, for in that year the first public performance of regular opera took place in Florence, when the "Eurydice" of Rinuccini and Peri was given in honor of the wedding of Marie de' Medici and Henry IV. of France. The growth and ever-increasing popularity of the opera, the development of civilization, the increase of wealth and the population of new countries, have led not only to the highest{12} cultivation of the human voice, wherein music exerts its greatest power of fascination, but have brought forward hundreds of competitors for the artistic laurels which are the reward of those who reach the highest state of musical perfection.
For nearly a century opera was confined to the continent of Europe, but in 1691 Margarita de L'Epine, a native of Tuscany, appeared in London. She was remarkable for her plainness of speech and of features, her rough manners and swarthy appearance, and she must indeed have been possessed of a fine voice to have been able to retain her hold on public favor. In 1692 she announced her last appearance, but it was so successful that she kept on giving last appearances and did not leave England for several years, thus inaugurating a custom which is observed to the present day. Margarita married the celebrated Doctor Pepusch.{13}
Contemporary with her was Katharine Tofts, an English woman, for an account of whom we are indebted to Colley Cibber, the great critic and playwright. She was a very beautiful woman with an exquisitely clear, sweet voice. Her career was short, for, after having achieved a tremendous success in one of her parts, she became demented, and, though eventually cured, she never returned to the stage. There was a lively rivalry between the two singers, which furnished gossip for the town.
Anastasia Robinson, mild and pleasing in manners, with great sweetness of expression and large blue eyes, was engaged to sing by George Frederick Händel, who at that time was the impresario of the London opera. Other singers he engaged in Dresden, of whom Margherita Durastanti was the soprano. Large, coarse, and masculine, she is said to have been distinguished as much for the high respectability of her character{14} as for her musical talent. Senesino was considered the leading tenor singer of his day. He was a man of imposing figure and majestic carriage, with a clear, powerful, equal, and fluent voice. The basso was Boschi, who was chiefly remarkable for a voice of immense volume and a very vigorous style of acting.
Anastasia Robinson was eclipsed, after a career of twelve years, by Francesca Cuzzoni, and married the Earl of Peterborough. She left a reputation for integrity and goodness seldom enjoyed by even the highest celebrities. Cuzzoni made an immediate and immense success, and Händel took great pains to compose airs adapted to display her exquisite voice. She, in return, treated him with insolence and caprice, so that he looked about for another singer. His choice fell upon Faustina Bordoni, a Venetian lady who had risen to fame in Italy. She was elegant in figure, agreeable in manners, and{15} had a handsome face. Cuzzoni, on the other hand, was ill made and homely, and her temper was turbulent and obstinate. A bitter rivalry at once sprang up, Händel fanning the flame by composing for Bordoni as diligently as he had previously done for Cuzzoni.
The public was soon divided, and the rivalry was carried to an absurd point. At length the singers actually came to blows, and so fierce was the conflict that the bystanders were unable to separate them until each combatant bore substantial marks of the other's esteem. Cuzzoni was then dispensed with, and went to Vienna. She was reckless and extravagant, and was at several times imprisoned for debt, finally dying in frightful indigence after subsisting by button making,—a sad termination of a brilliant career. Bordoni led a prosperous life, married Adolfo Hasse, the director of the orchestra in Dresden, sang before{16} Frederick the Great, and passed a comfortable old age. Both she and her husband died in 1783, she at the age of eighty-three and he at eighty-four.
Other singers of this period were Lavinia Fenton, who became the Duchess of Bolton, and who is chiefly remarkable for having been the original Polly in Gay's "Beggar's Opera;" Marthe le Rochois, who sang many of Lulli's operas,—a woman of ordinary appearance but wonderful magnetism; Madame La Maupin, one of the wildest, most adventurous and reckless women ever on the stage; and Caterina Mingotti, a faultless singer, of respectable habits. Mingotti was seized with the fatal ambition to manage opera, and soon reached the verge of bankruptcy. She contrived, however, to earn enough by singing during the succeeding five years to support her respectably in her old age.
To this period also belongs Farinelli, or{17} Broschi, who was the greatest tenor of his age, perhaps the greatest who ever lived, for we are told that there was no branch of his art which he did not carry to the highest pitch of perfection. His career of three years in London was a continuous triumph, and he is said to have made £5,000 each year,—a very large sum in those days. His singing also restored to health Philip V. of Spain, who was a prey to depression, and neglected all the affairs of his kingdom. At the court of Spain his influence became immense until Charles III. ascended the throne, when Farinelli quitted Spain, "at the royal suggestion," and retired to Bologna.
Of the long list of men who have distinguished themselves as singers in opera, it is curious to note that almost, if not quite, the first were a Mario and a Nicolini, names which are familiar to us as belonging to well-known tenors of this (nineteenth) century.{18} Of Mario but little is recorded; but Nicolini, whose full name was Nicolino Grimaldi Nicolini, and who was born in 1673, is known to have sung at Rome in 1694. He remained on the stage until 1726, but the date of his death is unknown. Nicolini sang in England in 1708, and at several subsequent times, and was well received. Addison wrote of him, concerning his acting, that "he gave new majesty to kings, resolution to heroes, and softness to lovers."
Caterina Gabrielli was the daughter of a cook of the celebrated Cardinal Gabrielli, and was born at Rome, November 12, 1730. She possessed an unusual share of beauty, a fine voice, and an accurate ear. She made her first appearance when seventeen years old at the theatre of Lucca, in Galuppi's opera, "Sofonisba." She was intelligent and witty, full of liveliness and grace, and an excellent actress. Her voice, though not powerful, was of exquisite quality and wonderful{19} extent, its compass being nearly two octaves and a half, and perfectly equable throughout, while her facility of vocalization was extraordinary. Her fame was immediately established, and soon she had all mankind at her feet; but she proved to be coquettish, deceitful, and extravagant. No matter with whom she came in contact, she compelled them to give way to her whims. On one occasion she refused to sing for the viceroy of Sicily, and was therefore committed to prison for twelve days, where she gave costly entertainments, paid the debts of her fellow prisoners, and distributed large sums amongst the indigent. Besides this, she sang all her best songs in her finest style every day, until the term of her imprisonment expired, when she came forth amid the shouts of the grateful poor whom she had benefited while in jail. Despite her extravagance Gabrielli had a good heart. She gave largely in charity, and never forgot her parents. Having by{20} degrees lost both voice and beauty, Gabrielli retired finally to Bologna in 1780, and died there in April, 1796, at the age of sixty-six.
In the room in Paris in which the unfortunate Admiral Coligny had been murdered, was born on February 14, 1744, the beautiful, witty, but dissipated Sophie Arnould. At the age of twelve her voice, which was remarkable for power and purity, attracted the attention of the Princess de Modena, through whose influence she was engaged to sing in the king's chapel. In 1757 she made her first appearance in opera, when her beauty and her acting enabled her to carry everything before her.
The opera was besieged whenever her name was announced, and all the gentlemen of Paris contested for the honor of throwing bouquets at her feet. At length she eloped with Count Lauraguais, a handsome, dashing young fellow, full of wit and daring. Her home resembled a little court, of which she{21} was the reigning sovereign, and her salon was always crowded by men of the highest distinction. When Benjamin Franklin arrived in Paris, he confessed that nowhere did he find such pleasure, such wit, such brilliancy, as in the salon of Mlle. Arnould. She remained faithful to her lover for four years, when he bestowed on her a life-pension of 2,000 crowns. While she never spared any one in the exercise of her wit, she was occasionally the subject of ridicule herself, as, for instance, when the Abbé Galiani was asked his opinion of her singing, and replied, "It is the finest asthma I ever heard."
Sophie Arnould appeared in several of Gluck's operas, and acquitted herself to the satisfaction of the composer. Her voice had not apparently fulfilled early expectations, but her beauty and her acting made her a success. When Voltaire one day said to her, "Ah, mademoiselle, I am eighty-four years old, and I have committed eighty-four{22} follies," she replied, "A mere trifle; I am not yet forty, and I have committed more than a thousand."
In 1792 she purchased the presbytère of Clignancourt, Luzarches (Seine-et-Oise). She had a fortune of 30,000 livres and innumerable friends, but in less than two years she had lost her fortune, and her friends being dispersed by exile, imprisonment, and the scaffold during the Revolution, she was reduced to the lowest stage of poverty. She went to Paris and sought an interview with Fouché, now a great man, who had been one of her most ardent admirers. He awarded her a pension of 2,400 livres, and ordered that apartments should be given her in the Hôtel d'Angevilliers. In 1803 she died in obscurity.
Among the celebrated male singers of this period were Gasparo Pacchierotti, and Giovanni Battista Rubinelli. The former of these was considered to have been the finest{23} singer of the latter part of the eighteenth century. Endowed with a vivid imagination, uncommon intelligence, and profound sensibility, a tall and lean figure, a voice which was often uncertain and nasal, he required much determination and strength of character to overcome the defects and take advantage of the good qualities which nature had bestowed upon him. Yet he is described by Lord Mt. Edgecumbe as "decidedly the most perfect singer it ever fell to his lot to hear."
Rubinelli, on the other hand, from his fullness of voice and simplicity of style pleased a greater number than Pacchierotti, though none perhaps so exquisitely as that singer. Rubinelli's articulation was so pure and well accented that in his recitatives no one conversant with the Italian language ever had occasion to look at a libretto while he was singing. His style was true cantabile, in which he was unexcelled.
Upon the retirement of Sophie Arnould{24} a new star appeared in the person of Antoinette Cecile Clavel St. Huberty, the daughter of a brave old soldier who was also a musician. Her first appearances in opera were made in Warsaw, where her father, M. Clavel, was engaged as repetitor to a French company. From Warsaw she went to Berlin, where she married a certain Chevalier de Croisy, after which she sang for three years at Strasbourg. At last she went to Paris, where she appeared in 1777 in Gluck's "Armida." Madame St. Huberty did not rush meteor-like into public favor. Her success was gained after years of patient labor, during which she endured bitter poverty, and sang only minor parts. In person she was small, thin, and fair; her features were not finely formed, and her mouth was of unusual size, but her countenance was expressive. In 1783 she reached the summit of her success, when she appeared in the title rôle of Piccini's opera, "Dodon." Louis XVI., who{25} did not much care for opera, had it performed twice, and was so much pleased that he granted Madame St. Huberty a pension of 1,500 livres, to which he added one of five hundred more from his privy purse. Concerning her performance of this part we are told by Grimm, "Never has there been united acting more captivating, a sensibility more perfect, singing more exquisite, happier byplay, and more noble abandon."
In 1790 Madame St. Huberty retired from the operatic stage and married Count d'Entraigues. After a political career in Spain and Russia, during which the count and his wife passed through some trying vicissitudes, they settled in England, but on the 22d of July, 1812, both the count and countess were assassinated by a servant, who had been bribed by an agent of Fouché to obtain certain papers in their possession.
Gertrude Elizabeth Mara was the daughter of Johann Schmaling, a respectable musician{26} of Hesse Cassel. Her mother died shortly after her birth in 1749, but her father out of his limited means gave her the best education he could. As she was considered a prodigy her father took her from town to town till they reached Holland, where, after performing for some time, they went to England. Thence, after earning some money by giving concerts, they travelled to Germany, arriving at Leipzig in 1766, where the young singer obtained an engagement at the theatre as first singer, at a salary of six hundred dollars. From this time she continued to prosper, and she quite captivated that opinionated monarch, Frederick the Great.
In 1773 she fell in love with, and married, a handsome violoncellist named Jean Mara. He was a showy, extravagant man, and fell into dissipated habits, but through all Madame Mara was devoted to him.
Her personal appearance was far from striking. She was short and insignificant,{27} with an agreeable, good-natured countenance. Her manner, however, was prepossessing, though she was an indifferent actress. But her voice atoned for everything. Its compass was from G to E in altissimo, which she ran with the greatest ease and force, the tones being at once powerful and sweet. Her success she owed to her untiring industry. Nothing taxed her powers, her execution was easy and neat, her shake was true, open, and liquid, and though she preferred brilliant pieces, her refined taste was well known.
In England she gathered many laurels, as well as in Germany and other countries which she visited, but she came into collision with the authorities at Oxford, on account of her ignorance of the English language and of Oxford customs.
On leaving England she sang at a farewell concert which netted seven hundred pounds, and her rival, Mrs. Billington, generously gave{28} her services. Madame Mara passed the last years of her life at Revel, where she died, January, 1833, at the age of eighty-five. On the celebration of her eighty-third birthday she was offered a poetical tribute by no less a person than Goethe.
Of Madame Mara's contemporary male singers Luigi Marchesi is entitled to mention, for he had, within three years of his début, the reputation of being the best singer in Italy. He visited all Europe, even penetrating to St. Petersburg, in company with Sarti and Todi. Besides his wonderful vocal powers, which enabled him to execute the most marvellous embellishments, he was noted for great beauty of person, and for the grace and propriety of his gestures.
Crescentini, too, who was considered the last great singer of his school, sang at all the chief cities of Europe, and was given by Napoleon the Iron Cross, an honor{29} which aroused many jealousies. "Nothing could exceed," says Fétis, "the suavity of his tones, the force of his expression, the perfect taste of his ornaments, or the large style of his phrasing." For several years after his retirement he was a professor at the Royal College of Music at Naples.
Mrs. Elizabeth Billington was considered to be the finest singer ever born in England. Her father was a member of the Italian Opera orchestra named Weichsel, and her mother, a pupil of John Christian Bach, was a leading vocalist at Vauxhall, whose voice was noted for a certain reediness of tone, caused, it is said, by her having practised with the oboe,—her husband's instrument.
Elizabeth Weichsel was born in 1770, and began to compose pieces for the pianoforte when eleven years of age. At fourteen, she appeared at a concert at Oxford. She continued her study of the piano under Thomas Billington, one of the band of Drury Lane,{30} to whom she was married in 1785, in opposition to the wishes of her parents. They were very poor, and went to Dublin to seek engagements, and here Mrs. Billington appeared at a theatre in Smock Alley, singing with the celebrated Tenduccini. Her early efforts were not crowned with the greatest success, but she did better at Waterford, and later on, when she returned to London, she was still more successful.
Her voice was a pure soprano, sweet rather than powerful, of extraordinary extent and quality in its upper notes, in which it had somewhat the tone color of a flute or flageolet. In her manner she was peculiarly bewitching. Her face and figure were beautiful, and her countenance full of good humor, but she had comparatively little talent as an actress. In 1786 she first appeared at Covent Garden, in the presence of the king and queen, and her success was beyond her most sanguine anticipations. She sang in a{31} resplendently brilliant style, and brilliancy was an innovation in English singing.
Mrs. Billington one day received a great compliment from Haydn, the composer. Reynolds, the painter, was finishing her portrait, and Haydn, on seeing it, said: "You have made a mistake. You have represented Mrs. Billington listening to the angels; you should have made the angels listening to her."
In 1796, while in Italy, Mr. Billington died in a sudden and mysterious manner. Soon afterwards his widow went to Milan, where she fell in love with a Frenchman, the son of a banker in Lyons, named Felican. He was a remarkably handsome man, but no sooner were they married (in 1799) than he commenced to treat her most brutally, and eventually she was obliged to run away from him. She returned to London under the care of her brother.
On reaching London, a lively competition{32} for her services began between Harris and Sheridan, the theatrical managers. She gave the preference to Harris, and received £3,000 to sing three times a week, also a free benefit was ensured at £500, and a place for her brother as leader of the band. Eventually, however, the dispute was ended by arbitration, and it was decided that she should sing alternately at each house. At the height of her popularity Mrs. Billington is said to have averaged an income of £14,000 a year.
She retired from the stage on March 30, 1806, on which occasion she was the first to introduce Mozart's music into England, giving the opera, "Clemenza di Tito," of which there was only one manuscript copy in England. That belonged to the Prince of Wales, who lent it for the occasion. After a separation of fifteen years, Mrs. Billington was reunited to her second husband, but he at once resumed his brutal treatment, and her{33} death, in 1818, was caused by a blow from his hand.
One of the most popular and charming singers at La Scala, in the Carnival of 1794, was Giuseppa Grassini, the daughter of a farmer of Varese in Lombardy, where she was born in 1775. She received decided advantages by making her début with some of the greatest artists of her time,—Marchesi, Crescentini, and Lazzarini.
Grassini was an exquisite vocalist in spite of her ignorance, and albeit fickle and capricious, a most beautiful and fascinating woman,—luxurious, prodigal, and generous, but heavy and dull in conversation. Her voice was originally a soprano, but changed to a deep contralto. It was rich, round, and full, though of limited compass, being confined within about one octave of good natural notes. Her style was rich and finished, and though she had not much execution, what she did was elegant and perfect. She never attempted{34} anything beyond her powers, her dramatic instincts were always true, and in the expression of the subdued and softer passions she has never been excelled. Her figure was tall and commanding, and her carriage and attitudes had a classic beauty combined with a grace peculiarly her own. Her head was noble, her features were symmetrical, her hair and eyes of the deepest black, and her entire appearance had an air of singular majesty.
Napoleon invited her to Paris, where she soon became an object of inveterate dislike to the Empress Josephine. In 1804, returning to Paris after a visit to Berlin, Napoleon made her directress of the Opera. In the same year she visited London, singing alternately with Mrs. Billington. In London she did not make a great success, and when her benefit took place she asked the good-natured Mrs. Billington to sing, fearing that she would not succeed alone. In succeeding{35} seasons, however, Grassini grew in public favor, and on reappearing in England, in 1812, she was rapturously received, but her powers were now on the wane, and at the end of the season she departed unregretted. For some years longer she sang in Italy, Holland, and Austria, retiring about 1823.
She married Colonel Ragani, afterwards director of the Opera in Paris, and resided for many years in that city. She died in Milan in 1850, at the mature age of eighty-five.
Charles Benjamin Incledon and John Braham were two English singers of renown who came into prominence about the same time. Incledon began as a choir boy in Exeter Cathedral, after which he went into the navy, where his voice developed into a fine tenor. Leaving the sea, he studied singing, and soon became popular. His natural voice was full and open, and was sent forth without the slightest artifice, and when he sang pianissimo{36} his voice retained its original quality. His style of singing was bold and manly, mixed with considerable feeling, and he excelled in ballads. In 1817 he visited America, where he was well received.
The career of John Braham is of interest to all who love the traditions of English music. In his early days he was so poor that he was obliged to sell pencils for a living, but his musical talent being discovered by Leoni, a teacher of repute, who took him under his tutelage, he appeared at the age of thirteen at Covent Garden. At the age of about twenty he was fitted for the Italian stage, and at once made his mark. Even Crescentini, who was placed in the background, acknowledged Braham's talent, and when he sang in Italy his name was freely quoted as being one of the greatest living singers. As he grew older he attained a prodigious reputation, never before equalled in England, and whether singing a simple{37} ballad, in oratorio, or in the grandest dramatic music, the largeness and nobility of his style were matched by a voice which in its prime was almost peerless. Braham amassed a large fortune, and then aspired to be a manager, an experiment which quickly reduced him to poverty. In 1840 he visited America, and made a grand operatic and concert tour. In private life he was much admired, and was always found in the most conservative and fastidious circles, where as a man of culture, a humorist, and a raconteur, he was the life of society.
Braham was frequently associated in opera with Madame Angelica Catalani, the last of the great singers who came before the public in the eighteenth century. She was a woman of tall and majestic presence, a dazzling complexion, large, beautiful blue eyes, and features of ideal symmetry,—a woman to entrance the eye as well as the ear. Her voice was a soprano of the purest{38} quality, embracing a compass of nearly three octaves, and so powerful that no band could overwhelm its tones. The greatest defect of her singing was that, while the ear was bewildered with the beauty and tremendous power of her voice, the feelings were untouched,—she never appealed to the heart. She could not thrill like Mara, nor captivate her hearers by a birdlike softness and brilliancy, like Billington. She simply astonished her audiences.
Her private life was as exemplary as her public career was dazzling. She was married, after a most romantic courtship, to a M. de Vallebregue, a French captain of Hussars, who turned out to be an ignorant, stupid man, but a driver of hard bargains for his wife's talents. His musical knowledge is illustrated by an anecdote to the effect that on one occasion, when his wife complained at a rehearsal that the piano was too high, he had the defect remedied by sending for a{39} carpenter and making him cut off six inches from the legs of the instrument. In spite of the reputation for avarice which her husband helped to create, Madame Catalani won golden opinions by her sweet temper, liberality, and benevolence.
Towards the end of her career Catalani drew down on her head the severest reprobation of all good judges by singing the most extravagant and bizarre show pieces, such as variations, composed for the violin, on "Rule Britannia," "God Save the King," etc. The public in general, however, listened to her wonderful execution with unbounded delight and astonishment.
In 1831 Madame Catalani retired from the stage. Young and brilliant rivals, such as Pasta and Sontag, were rising to contest her sovereignty, and for several years the critics had been dropping pretty plain hints that it would be the most judicious and dignified course. She settled with her family on an{40} estate near Lake Como; but in 1848 she went to Paris to escape the cholera, which was then raging, and in a few months, notwithstanding her precaution, she fell a victim to that dread disease.{41}
It is impossible in these chapters to make more than a passing sketch of many famous singers, and we must therefore be content with the mere mention of such as Fodor, Camporese, Pisaroni, and Damoreau, who all, in their day, attained high renown.
We now come to Giuditta Pasta, who must be placed in the very front rank, as an artist who could transform natural faults into the rarest beauties, who could make the world forgive the presence of many deficiencies, and who engraved deeper impressions on the memory of her hearers than any other, even in an age of great singers. Her voice at first{42} was limited, husky, and weak, without charm, without flexibility. Though her countenance spoke, its features were cast in a coarse mould. Her figure was ungraceful, her movements were awkward, and, at the end of her first season, she found herself a dire failure. She suddenly withdrew from the operatic world and betook herself to study, and when she reappeared she made a great impression. By sheer industry she had increased the range of her voice to two octaves and a half. Her tones had become rich and sweet, her shake was most beautiful, but her genius as a tragedienne surpassed her talent as a singer.
Poetical and enthusiastic by temperament, the crowning excellence of her art was a grand simplicity. There was a sublimity in her expression of vehement passion which was the result of measured force, energy which was never wasted, exalted pathos that never overshot the limits of art. Vigorous{43} without violence, graceful without artifice, she was always greatest when the greatest emergency taxed her powers.
No one could ever sing "Tancredi" like Pasta; "Desdemona" furnished the theme for the most lavish praises of the critics; "Medea" is said to have been the grandest lyric interpretation in the records of art. She had literally worked her way up to eminence, and, having attained the height, she stood on it firm and secure.
Madame Pasta was associated in many of her successes with the tenor Garcia, more celebrated as the father of Malibran and Viardot, and as one of the greatest vocal teachers of the century; with the baritone Bordogni, and the basso Levasseur.
Honors were showered upon her in all parts of Europe, and it is said that her operatic salary of £14,000 was nearly doubled by her income from other sources; but she lost nearly her entire fortune by the{44} failure of a banker in Vienna, and, in the endeavor to retrieve her fortunes, she remained on the stage long after her vocal powers were on the wane.
Rossini, the celebrated composer, married an opera singer, Isabella Angela Colbran. She was born at Madrid, her father being court musician to the King of Spain. Among her teachers was the celebrated Crescentini, and her style and voice being formed by him, she was, from 1806 to 1815, considered one of the best singers in Europe. After that time her voice began to depart; but, as she was a great favorite with the King of Naples, she remained at that city till 1821, and all good, loyal Neapolitans were expected to enjoy her singing, which was sometimes excruciatingly out of tune. She was born in 1785, but it was not until 1822 that she married Rossini, who was seven years her junior. In 1824 she went with her husband to London, and they made a great pecuniary{45} success, besides being greatly admired for artistic taste in private concerts.
Some four years after the appearance of Madame Pasta another star of the first magnitude appeared,—Henrietta Sontag, a beautiful and fascinating woman, and, as some say, the greatest German singer of the century. Nature gave her a pure soprano voice of rare and delicate quality, united with incomparable sweetness. Essentially a singer and not a declamatory artist, the sentiment of grace was carried to such a height in her art that it became equivalent to the more robust passion and force which distinguished some of her great contemporaries.
She began singing minor parts at the theatre at the early age of eight, and her regular début in opera took place when she was only fifteen. "She appeared to sing," we are told, "with the volubility of a bird, and to experience the pleasure she imparted." Her great art lay in rendering pleasing whatever{46} she did. The ear was never disturbed by a harsh note.
The most romantic stories circulated about the adoration lavished upon her by men of rank and wealth, and it was reported that no singer ever had so many offers of marriage from people of exalted station. But she had met in Berlin a Piedmontese nobleman, Count Rossi, to whom she became affianced, and Mlle. Sontag refused all the flattering overtures made by her admirers. One of her most ardent lovers was De Beriot, the great violinist, who, on his rejection, fell into a deep state of despondency, from which the fascinations of the beautiful Malibran at length roused him. Sontag's union with Rossi was for a long time kept secret on account of the objections of his family, but she retired from the stage and lived nearly twenty years of happy life in the various capitals of Europe, to which her husband, attached to the Sardinian legation, was accredited.{47} At length, in 1848, her fortune was swept away in the political revolution, and she announced her intention of returning to the stage. She was at once offered £17,000 for the season at Her Majesty's Theatre in London, and on her first appearance it was evident that time had but developed the artist. What little her voice had lost was more than compensated for by the deeper passion and feeling which permeated her efforts, and she was rapturously greeted. In 1852 she made a tour of the large cities of the United States, where she quickly established herself as one of the greatest favorites, in spite of the fact that Malibran and Jenny Lind had preceded her, and that the country had hardly recovered from the Lind mania. In New Orleans she entered into an engagement to sing in the City of Mexico; but while her agent was absent in Europe, gathering together an operatic company, she was seized with cholera and died in a few hours.{48}
Joseph Staudigl, who was born in 1807, at Wollersdorf, Austria, was one of the most distinguished and accomplished bassos of the first half of this century. He was a man of varied gifts and ardent temperament, frank, open, and amiable. In 1825 he entered upon his novitiate in the Benedictine monastery at Melk, but two years later he went to Vienna to study surgery. Here his funds gave out, and he was glad to sing in the chorus at the Kärnthnerthor Theatre. In due course the opportunity offered for him to take leading parts, and he soon gained a great reputation. He was also a great singer of church music and oratorio, for which branches of music he had an inborn love.
Staudigl's last appearance took place in 1856, on Palm Sunday, for a few days later he became a victim to insanity, from which he never recovered. He made repeated tours abroad, and was much admired wherever he went. As a singer of Schubert's Lieder he{49} was without a rival, and his performances of the "Erlkönig," the "Wanderer," and "Aufenthalt" were considered wonderful. His death occurred in 1861, and his funeral was the occasion of a great demonstration.
Manuel Garcia, the tenor, had two daughters who both achieved the highest distinction on the operatic stage. The eldest, Maria Felicien, became Madame Malibran, and she is mentioned to-day as one of the most wonderful operatic singers that the world has produced. Daring originality stamped her life as a woman and her career as an artist, and the brightness with which her star shone through a brief and stormy history had something akin in it to the dazzling but capricious passage of a meteor.
As a child she was delicate, sensitive, and self-willed, and she had a prodigious instinct for art. Nevertheless, her voice was peculiarly intractable, being thin in the upper notes, veiled in the middle tones, and her{50} intonation very imperfect. On leaving school she was taken in hand by her father, who was more pitiless to her than to his other pupils. He understood her disposition thoroughly, and said that she could never become great except at the price of much suffering, for her proud and stubborn spirit required an iron hand to control it.
Soon after making her début she went with her father to America, for he had conceived a project for establishing opera in the United States. His company consisted of himself, Madame Garcia, a son, and his daughter. Maria's charming voice and personal fascination held the public spellbound, and raised the delight of opera-goers to a wild pitch of enthusiasm. While in New York, a French merchant, M. François Eugene Malibran, fell passionately in love with her, and she, being sick of her father's brutality, and the supposed great fortune of Malibran dazzling her imagination, married{51} him, though in opposition to her father's will. A few weeks after the marriage M. Malibran was a bankrupt, and imprisoned for debt, and his bride discovered that she had been cheated by a cunning scoundrel, who had calculated on saving himself from poverty by dependence on the stage earnings of his wife. Garcia and the rest of his family went to Mexico, where he succeeded in losing his fortune. Madame Malibran remained in New York with her husband; but at the end of five months she wearied of her hard fate, and, leaving him, returned to Paris. Here she soon had the world at her feet, for the novelty and richness of her style of execution set her apart from all other singers as a woman of splendid and inventive genius.
Her voice was a mezzo-soprano, naturally full of defects, and, to the very last, she was obliged to go through her exercises every day to keep it flexible; but by the tremendously{52} severe discipline to which her father's teaching subjected her, its range extended so that it finally reached a compass of three octaves. Her high notes had an indescribable brilliancy, and her low tones were so soft, sweet, and heart-searching that they thrilled with every varying phase of her sensibilities.
Mr. Chorley writes: "She may not have been beautiful, but she was better than beautiful, insomuch as a speaking, Spanish, human countenance is ten times more fascinating than many a faultless angel face, such as Guido could paint. There was a health of tint, with but a slight touch of the yellow rose in her complexion, a great mobility of expression in her features, an honest, direct brightness of the eye, a refinement in the form of her head, and the set of it on her shoulders."
Malibran could speak and write in five languages, and sing in any school. She had the characteristic of being able to fire all her{53} fellow artists with her genius, and she was a tremendous worker. She was also very fond of outdoor exercises, being a daring horse-woman and swimmer.
On the death of her husband she married De Beriot, the violinist, to whom she had been passionately attached for some time, but shortly afterwards she was thrown from her horse, while attending a hunt in England. She sustained severe internal injury which eventually proved fatal, though not until she had made heroic efforts to continue her career, and fill all her engagements. Her death produced a painful shock throughout all Europe, for she had been as much admired and beloved as a woman, as she was worshipped as an artist.
The genius of the Garcia family shone not less in Madame Malibran's younger sister, Pauline, than in herself. Pauline was thirteen years the junior of Maria, and did not become celebrated until after the death of{54} her sister. In the meantime, Grisi and other great singers had appeared.
Pauline was the favorite child of Garcia. "Pauline," he would say, "can be guided by a thread of silk, but Maria needs a hand of iron."
At the age of six she could speak fluently in French, Spanish, Italian, and English, and to these she afterwards added German. She also learned to play the organ and piano as if by instinct. In her early days she went with her father to Mexico, where they met with many strange adventures, notably on one occasion, when they were seized by bandits, who plundered Garcia of his savings, bound him to a tree, and made him sing for his life.
Pauline was seven years old on her return to Europe, and three years later she became one of the pupils of Franz Liszt. When she was eleven her father died, and she began to study voice with Adolph Nourrit, the tenor,{55} who had been one of her father's favorite pupils.
Her first public appearance was made in Brussels, at the age of sixteen, and it was the first occasion on which De Beriot appeared after the death of Madame Malibran, his wife.
Pauline Garcia's voice was like that of her sister in quality. It combined the two registers of contralto and soprano, from low F to C above the lines, but the upper part of an originally limited mezzo-soprano had been literally fabricated by an iron discipline, conducted by the girl herself with all the science of a master. Her singing was expressive, descriptive, thrilling, full, equal and just, brilliant and vibrating, especially in the medium and lower notes. Capable of every style of art, it was adapted to all the feelings of nature, but particularly to outbursts of grief, joy, or despair.
M. Viardot, the director of the Paris Opera,{56} went to London to hear her, and was so delighted that he offered her the position of prima donna for the next season. She was then only eighteen, and by this engagement she was fairly embarked upon a brilliant career. M. Viardot fell deeply in love with her shortly after his introduction to her, and in 1840 they were married. Returning to the stage after a short retirement, Madame Viardot visited most of the great cities, and invariably received the most enthusiastic welcome. On some occasions the audience could scarcely be induced to leave the house at the end of the performance. Once she played, on account of the illness of another singer, the two parts of "Alice" and "Isabella" in "Robert le Diable," changing her costume with each change of scene, and representing in one opera the opposite rôles of princess and peasant.
After Madame Viardot's retirement in 1862, she held for many years a professional{57} chair at the Paris Conservatoire. In private life she has been always loved and admired, and she is to this day recognized as one of the great vocal teachers of Paris.
Adolf Nourrit, of whom the French stage is deservedly proud, was a pupil of Garcia, and for ten years was principal tenor at the Académie, creating all the leading tenor rôles produced during that time. He was idolized by the public, and was a man of much influence in musical circles. He gave a distinct stamp and flavor to all his parts, and was as refined and pleasing in comedy as he was pathetic and commanding in tragedy. It was he who popularized the songs of Schubert, and otherwise softened the French prejudice against the German music of his time. In private life he was witty, genial, and refined, and was, therefore, a favorite guest at the most distinguished and exclusive "salons." Nourrit was subject to alternate fits of excitement and depression, and was{58} affected to such a degree by some articles praising his rival, Duprez, at his expense, that his friends feared for his sanity. Eventually, while filling an engagement in Italy, he threw himself out of his bedroom window and was instantly killed on the paved courtyard below.
Duprez, like Nourrit, was a student at the Paris Conservatoire, and for many years a leading figure at the Académie. At first he was not a success in opera, but, by dint of study and hard work, he achieved a high reputation. In person he was insignificant, but his tragic passion and splendid intelligence gave him a deserved prominence. He composed much music, including two masses and eight operas, and was the writer of a highly esteemed musical method. After finishing his operatic career he became a professor of singing at the Conservatoire.
Madame Grisi, who made her début in 1823, and held her place as one of the greatest{59} singers for many years, was the daughter of an Italian officer of engineers, and her mother's sister was the once celebrated Grassini, a contemporary of Mrs. Billington and Madame Mara.
Giulietta Grisi, as a child, was too delicate to receive any musical training; but her ambition caused her to learn the pianoforte by her own efforts, and her imitation of her sister Giuditta's vocal exercises indicated to her family the bent of her tastes.
In due course she entered the conservatoire in her native town, and was later sent to her Uncle Ragani at Bologna, where, for three years, she was under the instruction of Giacomo Guglielmi. Gradually the beautiful quality of her voice began to manifest itself. She was remarkably apt and receptive, and profited by her masters to an extraordinary degree.
For three months she studied under Filippo Celli, and in 1828 she made her début{60} in Rossini's "Elmira." Rossini was delighted with her, and the director of the theatre immediately engaged her for the carnival season.
The career thus auspiciously commenced, continued for more than a quarter of a century, during which time Grisi delighted audiences throughout the whole of Europe, and made a tour, with Mario, of the United States.
The production of Bellini's last opera, "I Puritani," in 1834, was one of the greatest musical events of the age, not solely on account of the work, but because of the very remarkable quartet which embodied the principal characters,—Grisi, Rubini, Tamburini, and Lablache. This quartet continued in its perfection for several years, with the substitution later of Mario for Rubini, and was one of the most notable and interesting in the history of operatic music.
Giulietta Grisi's womanly fascinations made{61} havoc among that large class who become easily enamored of the goddesses of the theatre, and she was the object of many passionate addresses. She married in 1836 a French gentleman of fortune, M. Auguste Gerard de Melcy, but she did not retire. This marriage was unhappy, and after her release from it by divorce she became the wife of Mario, the great tenor.
Grisi united much of the nobleness and tragic inspiration of Pasta, with something of the fire and energy of Malibran; but, in the minds of the most capable judges, she lacked the creative originality which stamped each of the former two artists. Her dramatic instincts were strong and vehement, lending something of her own personality to the copy of another's creation, and her voice as nearly reached perfection as any ever bestowed on a singer.
Madame Grisi continued before the public until 1866, although her powers were failing{62} rapidly. In 1869 she died of inflammation of the lungs.
From the year 1834, when she made her début at the King's Theatre, London, until 1861, when she retired from the Royal Italian Opera, Grisi missed only one season in London, that of 1842. It was a rare thing indeed that illness or any other cause prevented her from fulfilling her engagements. She seldom disappointed the public by her absence, and never by her singing. Altogether her artistic life lasted about thirty-five years. During sixteen successive years she sang, during the season, at the Théâtre des Italiens in Paris, her engagements there beginning in 1832 with her appearance as Semiramide.
Both Grisi and her husband, Mario, were much admired by the Czar Nicholas of Russia, and it is said that the Czar, meeting Grisi one day walking with her children, stopped and said facetiously, "I see, these{63} are the pretty Grisettes." "No," replied Grisi, "these are my Marionettes." Mario, too, is said to have been asked by the Czar to cut his beard in order to the better look one of his parts. This he declined to do, even when the Czarina, fearing that he might become a victim of the Czar's displeasure, added her request. But Mario declared that it was better to incur the displeasure of the Czar than to lose his voice, saying that if they did not like him with his beard, upon which he relied for the protection of his voice, they surely would not like him without his voice.
During the height of their prosperity, Grisi and Mario lived in princely extravagance. Their family consisted of six daughters, of whom three died quite young, and they were enthusiastically devoted to one another.
Giambattista Rubini, who was for years associated with Grisi, was a native of Bergamo,{64} where he made his début at the age of twelve in a woman's part, sitting afterwards at the door of the theatre between two candles, and holding a plate into which the public deposited their offerings. During his early life he belonged to several wandering companies, in which he filled the position of second tenor; but in 1814, at the age of nineteen years, he was singing in Pavia for a salary of about nine dollars a month. Before the end of his career he was paid £20,000 a year for his services at the St. Petersburg Imperial Opera.
Rubini's countenance was mean, his figure awkward, and he had no conception of taste, character, or picturesque effect; but his voice was so incomparable in range and quality, his musical equipment and skill so great, that his memory is one of the greatest traditions of lyric art. Like so many of the great singers of his time, Rubini first gained his reputation in the operas of Bellini and{65} Donizetti, and many of the tenor parts of these works were composed expressly for him. The immense power, purity, and sweetness of his voice have probably never been surpassed, and its compass was of two octaves, from C in the bass clef. He could also sing in falsetto as high as treble F, and with such skill that no one could detect the change into the falsetto.
Rubini died in 1852, leaving one of the largest fortunes ever amassed on the stage.
Another member of the celebrated "Puritani" quartet was Antonio Tamburini, a native of Faenze. Without any single commanding trait of genius, he seems, with the exception of Lablache, to have combined more attractive qualities than any male singer who ever appeared. He was handsome and graceful, and a master of the art of stage costume. His voice, a baritone of over two octaves in extent, was full, round, sonorous, and perfectly equal throughout.{66} His execution was unsurpassed and unsurpassable, of a kind which at the present day is well-nigh obsolete, and is associated in the public mind with sopranos and tenors only.
An amusing instance of Tamburini's versatility was shown at Palermo during the carnival season of 1822, when the audience attended the theatre armed with drums, trumpets, shovels, and anything that would make a noise. Tamburini, being unable to make his basso heard, sang his music in falsetto, an accomplishment which so delighted the audience that they laid aside their instruments of torture, and applauded enthusiastically. The prima donna, however, was so enraged and frightened by the rough behavior of the audience that she fled from the theatre, and the manager was at his wit's end. Tamburini donned the fugitive's satin dress, clapped her bonnet over his wig, and appeared on the stage with a mincing step.{67} He sang the soprano score so admirably, burlesquing the action of the prima donna, but showing far greater powers of execution than she possessed, that his hearers were captivated. He did not shirk even the duets, but sang the woman's part in falsetto, and his own in his natural voice.
He retired in 1859, and died at Nice in 1876.
Luigi Lablache, the basso of the "Puritani" quartet, is considered by many authorities to have been the greatest artist among men that ever appeared in opera. In stature he was a giant, and we are told that one of his boots would make a good portmanteau or one of his gloves would clothe an infant. His strength was enormous, and his voice magnificent; the vibration thereof was so tremendous that it was dangerous for him to sing in a greenhouse, though why this particular danger is noted must be left to conjecture, for there is no record in history to{68} show that it was customary or essential to sing in greenhouses.
Anecdotes of Lablache's generosity and noble character are plentiful, and there are some also which show that he was a lover of good jokes. Of these, perhaps the following is the most amusing. Once when the "Puritani" quartet was in Paris, Lablache was quartered at the same hotel as General Tom Thumb, who was delighting audiences at a vaudeville. An English tourist, who was making strenuous efforts to meet Tom Thumb, burst into the great basso's apartment, but seeing such a giant, hesitated, and apologized, saying that he was looking for Tom Thumb. "I am he," said Lablache, in his deepest tones. The Englishman, taken flat aback, exclaimed: "But you were much smaller when I saw you on the stage yesterday." "Yes," replied Lablache; "that is how I have to appear, but when I get home to my own rooms I let myself out and{69} enjoy myself," and he proceeded to entertain his visitor.
In his student days Lablache was so dominated by the desire to appear on the stage that he ran away from the conservatorium no less than five times, each time being caught and brought back in disgrace. On one occasion he engaged himself to sing at Salerno for fifteen ducats a month, and received a month's pay in advance. He lingered two days in Naples and spent his money, apparently also disposing of most of his clothes. As he could not well appear at Salerno without luggage, he filled his portmanteau with sand, and set forth. A couple of days later he was captured by the vice-president of the conservatorium, and taken back to Naples. The impresario hastened to make good his loss by seizing the portmanteau, which, however, proved to be very disappointing.
After Lablache made his first appearance{70} in opera his fame grew rapidly, and in a few years had reached colossal proportions. Among the honors which fell to his lot was that of being music teacher to Queen Victoria. His death, which occurred in 1858, drew forth expressions of regret from all parts of Europe, for it was felt that in Lablache the world of song had lost one of its brightest lights.
Mario, who followed Rubini as tenor in the celebrated "Puritani" quartet, was more closely connected with the career of Madame Grisi than any other singer, for he became her husband. His proper title was Mario, Cavaliere di Candia; but, in order to soothe the family pride, he was known on the stage by his Christian name only. When he first went to Paris, in 1836, he held a commission in a Piedmontese regiment. The fascinating young Italian officer was welcomed in the highest circles, for his splendid physical beauty, and his art-talents as an amateur{71} in music, painting, and sculpture, separated him from all others, even in a throng of brilliant and accomplished men. In Paris he fell into debt, and, having a beautiful voice, he accepted the proposition of Duponchel, the manager of the opera, and entered upon stage life. Though his singing was very imperfect and amateurish, his princely beauty and delicious, fresh voice took the musical public by storm.
Mario will live in the world's memory as the best opera-lover ever seen. In such scenes as the fourth act of "Les Huguenots," and the last act of "Favorita," Mario's singing and acting were never to be forgotten by those that witnessed them. Intense passion and highly finished vocal delicacy combined to make these pictures of melodious suffering indelible. As a singer of romances he has never been equalled; in those songs where music tells the story of passion, in broad, intelligible,{72} ardent phrases, and presents itself primarily as the vehicle of violent emotion, Mario stood ahead of all others of his age. For a quarter of a century he remained before the public of Paris, London, and St. Petersburg, but he did not finally retire until 1867.
The story of Mario's life reads like a romance. At times he was steeped in the depths of poverty; at others, he enjoyed great wealth and lived in princely style. Shortly after his first arrival in Paris, he found himself deeply in debt, and so poor that he was obliged to sleep in a very cheap lodging-house where several people occupied one room. One night he awoke and found a man kneeling over him, to rob him. "What do you want?" asked Mario. "Your money," was the reply. "Take all you can find, my friend," answered Mario, "but please let me continue my dreams and my sleep."
Mario was as careless in regard to time as to money. It is related that once upon a{73} time he arrived half an hour early, to keep an appointment. Nobody was more surprised than Mario himself, and, after investigation, he discovered that he had mistaken eleven o'clock for five minutes to twelve, and would have been the customary half hour late if his calculations had been correct.
Mario had a particular aversion to writing letters, and when he received an invitation from some person of high degree he would frequently say, "Oh, I will write to-morrow," and Mario's to-morrow was the proverbial one which never came. He was nevertheless kind and thoughtful for every one, and to his personal graces and charms he owes his reputation as much as to his art, for he was always more or less of an amateur. His wonderful gifts were not developed by study, like the equally wonderful voice of Rubini, who surpassed in this respect every tenor before or after.{74}
As an instance of the admiration in which Mario was held by the fair sex, we are told that a certain lady followed him wherever he sang. She never spoke to him, never tried to press herself upon him, but never missed a performance in any part of the world in which he sang, except on three occasions when she was prevented by sickness. This continued for a period of forty years.
Like all men of similar disposition, Mario was subject to fits of wild, unreasoning jealousy, and his domestic life with Grisi was not always of the smoothest nature, though there was absolutely no cause for jealousy on either side. On one occasion, Mario is said to have worked himself up into such a state of excitement that he smashed everything in the room. Grisi, too, once reached so great a depth of despair that she rushed out to drown herself. A fleet-footed friend followed her, and reached her just as{75} she was preparing to make the final plunge. All kinds of arguments were used to turn her from her purpose, but in vain, until her rescuer pictured to her how dirty and muddy she would look when taken out of the river. This argument prevailed, and the prima donna deferred her demise.
In spite of the large amount of money earned by Mario, he retired from the stage a poor man. His improvidence was magnificent. Twice the public subscribed for his needs, and once, the old unthriftiness about him still, he flung away his capital and was royally penniless again.
At Rome, in which city he spent his last days, he was given the post of curator of the Museum; but the glory of his past still adhered to him, and he was surrounded by a host of admirers, who enjoyed hearing the old man talk about his adventures. He died, in 1883, in the arms of Signor Augusto Rotoli. His life had been triumphant beyond{76} the lot of all but the most fortunate, and the memory he left was singularly kind and beautiful.
A memorandum, published at the time of Mario's retirement, states that during his career he gave, in London alone, 935 performances, of which 225 were in operas of Donizetti, 170 Meyerbeer, 143 Rossini, 112 Verdi, 82 Bellini, 70 Gounod, and 68 Mozart, the remaining 65 performances being operas of seven other composers.{77}
Contemporary with Sontag, Malibran, and Grisi, was Madame Schröder-Devrient, who was one of the earliest and greatest interpreters of German opera. Though others have surpassed her in vocal resources, she stands high in the list of operatic tragediennes, and for a long time reigned supreme in her art. Her deep sensibilities and dramatic instincts, her noble elocution and stately beauty, fitted her admirably for tragedy, in which she was unrivalled except by Pasta. Her voice was a mellow soprano, which, though not specially flexible, united softness with volume and compass. Her stage career began at the age of six, but she{78} was seventeen when she made her début in opera. Her highest triumph was achieved as Leonora in the "Fidelio."
Her marriage with M. Devrient, a tenor singer whom she met in Dresden, did not turn out happily. Madame Devrient retired in 1849, having amassed a considerable fortune by her professional efforts. Her retirement occasioned much regret throughout Germany, and the Emperor Francis I. paid her the unusual compliment of having her portrait painted in all her principal characters, and placed in the Imperial Museum. She died in 1860 at Cologne, and the following year a marble bust was placed in the opera house at Berlin.
Madame Devrient must be classed with that group of dramatic singers who were the interpreters of the school of music which arose in Germany after the death of Mozart, and which found its characteristic type in Carl Maria Von Weber, for Beethoven, who{79} on one side belongs to this school, rather belongs to the world, than to a single nationality.
Fanny Persiani, who was contemporary with Grisi and Viardot, was the daughter of Tacchinardi, a tenor singer of no small reputation. Tacchinardi was a dwarf, hunchbacked and repulsive in appearance, yet he had one of the purest tenor voices ever given by nature and refined by art, which, together with extraordinary intelligence and admirable method of singing, and great facility of execution, elicited for him the admiration of the public.
His daughter Fanny showed a passion for music almost as an infant, and was carefully trained by her father. At eleven years of age she took part in an opera as prima donna at a little theatre which Tacchinardi had built near his country-place just out of Florence. She had a voice of immense compass, to which sweetness and flexibility were added by study{80} and practice. She married Joseph Persiani, an operatic composer, at the age of twelve, for her father did not wish her to go on the stage, and thought that an early marriage would change her tastes. For several years she lived in seclusion at her husband's house; but at last an opportunity offered to sing in opera, and she was unable to resist it. Madame Persiani belonged to the same style as Sontag, not only in character of voice but in all her sympathies and affinities. Moscheles, in his diary, speaks of the incredible technical difficulties which she overcame, and compares her performance with that of a violinist, for she could execute the most florid, rapid, and difficult music with such ease as to excite the wonder of her hearers. Aside from her wonderful executive art in singing, Madame Persiani will be remembered as having contributed, perhaps, more than any other singer to making the music of Donizetti popular. Her death occurred in 1867.{81}
The name of Jenny Lind will be remembered when Malibran, Grisi, and many of the greatest singers have sunk into oblivion, because of her good works. Besides being one of the few perfect singers of the century, her life was characterized by deep religious principles and innumerable charitable works, of which not the least was the use of the fortune of over $100,000, which she made during her American tour, in founding art scholarships and other charities in Sweden, her native land.
Jenny Lind was born in 1820 at Stockholm, and was the daughter of poor but educated parents, her father being a teacher of languages and her mother a schoolmistress.
From her cradle she showed the greatest delight in music, and at the age of three she could sing with accuracy any song that she had heard. Her musical education began at the age of nine; but, notwithstanding the brilliant career predicted for her by her{82} friends, her life for many years was a history of patient hard work and crushing disappointments.
When she was presented by her singing teacher to Count Pücke, the director of the court theatre at Stockholm, with a view to getting her admitted to the school of music connected with it, she made no impression on him, and it was only by great persuasion that he could be induced to accept her.
In this theatre she appeared in child's parts while scarcely in her teens, but when she was about thirteen years old her voice suddenly failed. She continued patiently with her other musical studies, and in four or five years her voice returned as suddenly as it had left her.
Shortly after this, she sang at a concert the part of Alice, in the fourth act of "Roberto," and made such a favorable impression that she was immediately given the part of Agatha, in "Der Freischütz," and made her{83} first appearance in opera. She soon became a great favorite in Stockholm, where she remained for nearly two years.
Filled with ambition, she now went to Paris and sought the celebrated teacher, Manuel Garcia, whose first advice to her was not to sing a note for three months. Garcia never expected great things of her, although he was pleased with her diligence and her musical intelligence. Meyerbeer, on the contrary, who heard her about a year later, at once recognized in her voice "one of the finest pearls in the world's chaplet of song," and through his influence she obtained a hearing in the salon of the Grand Opera. This did not result in an engagement, and Jenny Lind was so mortified that years afterwards, when her reputation was established, and she was offered an engagement in Paris, she declined it without giving any reason.
She now returned to Stockholm, where she was received with the greatest enthusiasm;{84} but soon afterwards she appeared at Copenhagen, and then, through Meyerbeer again, she procured an engagement at Berlin, where, in the part of Alice in "Roberto," she made a profound impression. She next sang in Vienna, where she made a veritable triumph. On the last night of her engagement her carriage was escorted home by thousands. Thirty times she was obliged to appear at the window of her hotel, and the crowd scrambled for the flowers which she threw them in acknowledgment of their applause, and carried them home as treasures.
She became the talk of musical circles throughout Europe, and prices rose enormously whenever she was to sing.
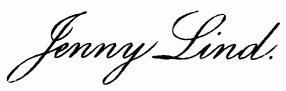
She sang in London for the first time in 1847, and, through judicious advertising, the public were worked up to a great state of expectation. Tickets were held at fabulous prices, and since the days of Mrs. Siddons's seventh farewell, nothing like the excitement{85} had been known. Many ladies sat on the stairs of the opera house, unable to penetrate to the auditorium.
Her operatic career in London was short as it was brilliant, for she sang for the last time on the operatic stage in the season of 1849, after which she appeared only in concerts and oratorio. Concerning the charm of her singing, one may judge from a sentence written by Chorley, the well-known critic, who least of all men was likely to be carried away by emotion. "It was a curious experience," he says, "to sit and wait for what should come next, and to wonder whether it was really the case that music had never been heard till the year 1847." On the other hand, Mr. Chorley wrote later on to the effect that she invariably sang somewhat sharp, and that he could not consider any prima donna to be a great artist who was only positively successful in four operas,—"Roberto," "La Sonnambula,"{86} "La Figlia del Reggimento," and "Le Nozze di Figaro." In Norma she was a failure.
But again Chorley may well be quoted: "Of all the singers whom I have ever heard, Mlle. Lind was perhaps the most assiduous. Her resolution to offer the very best of her best to the public seemed part and parcel of her nature, and of her conscience. Not a note was neglected by her, not a phrase slurred over. Her execution was great, and, as is always the case with voices originally reluctant, seemed greater than it really was. Her shake was true and brilliant, her taste in ornament was altogether original. She used her pianissimo tones so as to make them resemble an effect of ventriloquism."
Jenny Lind's tour in America was eventful. It began with a serenade by a band of one hundred and thirty musicians, preceded by seven hundred of the firemen of New York. The demonstration occurred at one{87} o'clock in the morning, and was witnessed by a crowd of thirty thousand people. The tickets for the concerts were sold by auction, and the highest price paid was $225,—by an enterprising business man. During her stay in America, Jenny Lind was followed by crowds eager to see her; receptions were arranged, and everything was done to keep up the excitement. She was under the management of Mr. P. T. Barnum, from whom she later obtained her release on payment of a forfeit of $30,000.
In 1851 Mlle. Lind put herself under the management of Mr. Otto Goldschmidt, a pianist of considerable ability, whom she married in Boston. In 1852 she returned to Europe with her husband and settled in Dresden, but eight years later they came to England and resided in London, whence they moved after several years to Malvern Wells. In 1887 Madame Lind Goldschmidt died. She is remembered as one of the{88} sweetest singers and most charming women of her time.
A singer who replaced Fanny Persiani and surpassed her in popularity, who sang in the same rôles and in the same theatres as Grisi, and who, according to Chorley, was the most ladylike person he had seen on the stage of the Italian opera, except Madame Sontag, was Angiolina Bosio. Born at Turin in 1830, and belonging to a family of artists, both musical and dramatic, she made her first appearance at the age of sixteen, and scored a decided triumph. In 1848 she sang at Paris, but without her customary success, and she immediately made a tour of the West, visiting Havana, New York, Philadelphia, and Boston, in all of which places she was greatly admired. In 1851 she returned to Europe, and married a Greek gentleman named Xindavelonis.
She returned to the stage, but was not favorably received until, at the end of the{89} season of 1852, she sang in "I Puritani," in the place of Grisi. This was the turning-point in her fortune, and her popularity increased rapidly, until she died suddenly in St. Petersburg, where the rigorous climate was too severe for her delicate constitution. At St. Petersburg she was nominated première cantatrice, an honor never previously bestowed.
Madame Bosio was possessed of much taste in the matter of dress, together with a graceful condescension of manner. Her features were irregular, and yet she was extremely pleasing, so much so, in fact, that the critics wrote of "her gay, handsome face." Her most remarkable performance was in "La Traviata," in which she sang with the tenor Gardoni and the bass Ronconi, both singers of great renown.
The greatest contralto of the middle of the century was undoubtedly Marietta Alboni, the daughter of a custom-house officer of Casena,{90} Romagna. She was born in 1822, and, like most of the great singers, showed her talent early. She was placed under good teachers, and attracted the attention of Rossini by her beautiful voice. He took so much interest in her that he gave her instruction in some of her parts. Thus she had the honor of being Rossini's only pupil.
In 1842 she made her first appearance in opera, and was soon after engaged at La Scala, Milan, where she remained for four years. After this she appeared at Vienna, and then she travelled through Europe, creating a general furore.
Alboni was not an actress,—she was a singer simply and absolutely, and her singing was such as to carry everything before it. The tones of her voice were rich, full, mellow, and liquid,—sumptuous, they have been called,—and of a pure and sympathetic quality. It was not even, for the upper register was thin. Her articulation was{91} perfectly clear and fluent, even in the most difficult passages, and her style and method were considered models. Her figure, though large, was graceful and commanding, and her disposition was amiable. She was both independent and dignified. While in Germany, and comparatively unknown, she declined to seek the favor of the press, preferring to trust to the judgment of the public.
Once upon a time, when Madame Alboni was at Trieste, she was informed of the existence of a plot to hiss her off the stage. Having ascertained the names of her detractors and where they were to be found, she donned male attire, in which her short hair and robust figure helped to complete her disguise, and went to the café at which the conspirators met. Here she found them in full consultation, and, taking a seat at a table, she listened to their conversation for a time. After awhile she addressed the leader, saying: "I hear that you intend to play a trick{92} upon some one. I am very fond of a little practical joke myself, and should be glad if you would allow me to join you on this occasion."
"With pleasure," was the reply; "we intend to hiss an opera singer off the stage this evening."
"Indeed, and of what is she guilty?"
"Oh, nothing except that, being an Italian, she has sung in Munich and Vienna to German audiences, and we think she ought to receive some castigation for her unpatriotic conduct."
"I agree with you,—and now please tell me what I am to do."
"Take this whistle," said the leader. "At a signal to be given at the conclusion of the air sung by Rosina, the noise will begin, and you will have to join in."
"I shall be very glad to do so," replied the singer, and put the whistle in her pocket.
In the evening the house was packed,{93} every seat was occupied, and the audience warmly applauded the opening numbers of the opera. In due course Madame Alboni appeared, and at the point at which she was about to address her tutor, a few of the conspirators began to make a disturbance, not waiting for the signal.
Without showing any concern, Madame Alboni walked down to the footlights, and holding up the whistle, which was hung to her neck by a ribbon, she exclaimed: "Gentlemen, are you not a little before your time? I thought we were not to commence whistling until after I had sung the air."
For a moment a deathlike stillness prevailed. Then, suddenly, the house broke into thunders of applause, which was led by the conspirators themselves.
Alboni visited the United States in 1852, just after the visit of Jenny Lind, and received what was considered a cordial welcome. Nevertheless she is said to have{94} expressed some disappointment. In 1853 she married the Count of Pepoli, and soon after retired. She did not again sing in public, except in 1871, when she sang the contralto part in Rossini's Mass, a part which the composer had desired, before his death, that she would take when it was produced.
In social life the Countess of Pepoli was as much the idol of her friends as she had previously been of the public. In 1877 she married a second time, taking Major Zieger for her husband. Her death took place at the Ville d'Avray, Paris, in 1894.
For several years the favorite tenor on the French stage was Gustave Hyppolite Roger, a man of amiable and benevolent disposition, who was educated for the legal profession. He was born in 1815, at La Chapelle St. Denis, Paris, and entered the Conservatoire in 1836, carrying off, the following year, the first prizes for singing and comic opera. His{95} début was made in February, 1838, and he remained at the Opera Comique for ten years, after which he went to the Académie, and created a great sensation with Madame Viardot, in "Le Prophète." His acting was good both in tragic and comic parts, and he created many new rôles.
In 1859 he met with an unfortunate accident, and lost his right arm by the bursting of a gun, and this put an end to his operatic career in Paris. He continued, however, to sing in provincial towns and in Germany, until 1861, when he reappeared at the Opera Comique. But it was evident that the time for his retirement had come, and he took pupils, becoming a professor of singing at the Conservatoire in 1868, and holding the position until his death in 1879.
The mantle of Braham, the greatest English tenor of his day, descended to John Sims Reeves, the son of a musician, who was born at Shooter's Hill, Kent, in 1822.{96} Reeves, we are told, received the traditions of Braham, and refined them.
He obtained his early musical instruction from his father, and at fourteen held the position of organist at North Gray Church. Upon gaining his mature voice he determined to be a singer, and at first sang baritone and second tenor parts, making his début in opera, at Newcastle-on-Tyne, as Count Rudolpho in "La Sonnambula." Before long his voice developed into a tenor of an exceptionally beautiful quality, and, in 1847, when he appeared at Drury Lane, he at once took a position as a singer of the first rank. His acting, too, was natural and easy, manly, and to the purpose, exhibiting both passion and power without exaggeration.
His greatest triumph, however, was achieved in oratorio, and his performance of "The Enemy Said," in "Israel in Egypt," at the Crystal Palace, in 1857, was of such a nature as to electrify his hearers.{97}
In England the name of Sims Reeves was for many years sufficient to draw an audience large enough to fill any auditorium to overflowing, although he frequently disappointed the public by non-appearance. It was known that he considered it wiser to disappoint the public than to risk losing his voice, and, as a result, people soon realized that to hear him once was sufficient to atone for several disappointments. To the general public Sims Reeves endeared himself chiefly by his exquisite ballad singing; and, just as Patti is associated with "Home, Sweet Home," his name is coupled with "Come into the Garden, Maud."
Up to the age of seventy, Sims Reeves appeared occasionally in concerts, and even at the present day he can secure an audience, although his powers have long since passed away.
Enrico Tamberlik, who flourished during the middle of the century, was a tenor of{98} high rank. He belonged to the class of "tenore di forza," and used to make a tremendous effect with his high C, which he produced with immense power. His voice was one of great richness of tone and volume, but his singing was marred by the persistent use of the vibrato, a fault all too common.
Tamberlik, like Sims Reeves and Jean de Reszke, sang originally as a baritone, and developed later into a tenor. His delivery was grand and noble, his phrasing perfect, and he sang with a great depth of expression. His elocution was so fine that every word was delivered with full effect, and his dramatic power was unusually great. He was seen to best advantage in heroic parts, in which his fine figure and majestic bearing, together with the power and resonance of his voice, were displayed.
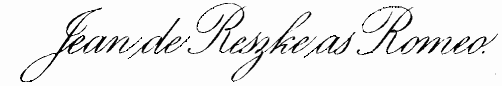
Tamberlik was born at Rome in 1820, made his début at Naples in 1841, and soon{99} built up a great reputation. In 1850 he appeared in London, and became so great a favorite that he was engaged there every season until 1864. In 1874 he made a tour of the United States, and he is said to have been the first tenor of importance who visited South America, singing at Rio Janeiro, Buenos Ayres, and Montevideo.
One of his most notable performances was in 1871, when he took the part of Otello, in Rossini's opera of that name, with Faure as Iago, and Nilsson as Desdemona.
Tamberlik was a shrewd man of business, but an excellent companion. His conversational powers were immense, and as he had come in contact with, and known intimately, many men and women famous in the world of fashion, art, and literature, he had an endless fund of interesting anecdotes. In 1877 he retired from the stage, having the good sense to seek private life before his powers had faded. He settled in Madrid, and{100} became a manufacturer of arms. While in retirement he had the rare experience of reading his own obituary notices, for, in 1882, a rumor of his death went forth into Italy and France. Though it was entirely without foundation, the press at once teemed with eulogistic biographies of the great tenor, which were copied throughout Europe. As they were highly complimentary, the subject was much pleased, and made a collection of them which he pasted into an album and enjoyed for seven years. He died in 1889.
During the same period there flourished Karl Formes, one of the most remarkable bassos of his time, who was popular in spite of the fact that he frequently offended by false intonation.
Formes was the son of a sexton of Muhlheim on the Rhine, and was born in 1810. He gained the greater part of his musical education by singing in the choir of the church. He grew up with a strong love for{101} the drama, as well as for music, and at the age of sixteen his enthusiasm was such that when Essler, the actor, visited Cologne, young Formes, not having sufficient money to pay both for the ferry and his ticket, tied his clothes around his neck, and swam the Rhine, rather than miss the performance. When Staudigl, the bass singer, visited the same city, Formes listened to his singing with awe, and the next season he begged to be allowed to sing the part of Bertram at the opera. This was one of Staudigl's favorite rôles. Staudigl, who heard the performance, was so pleased that he introduced Formes as his successor.
Formes, however, first came into notice by singing at some concerts given for the benefit of the Cathedral fund, at Cologne, in 1841. In the following year he made his operatic début, his success leading to an engagement for three years. He then sang in Vienna, and in 1849 appeared in London with{102} a German company, taking the part of Zarastro in the "Zauberflöte," at Drury Lane Theatre. The next year he was engaged for Italian opera, at Covent Garden, and sang there every season for some fifteen years.
He had a voice which, for volume, compass, and quality, was one of the most magnificent ever heard, a stage presence handsome and attractive, and exceptional dramatic ability.
Formes was a man of unsettled, roving disposition, and spent much of his time in Russia and in Spain, but in 1857 he visited the United States, and eventually began a wandering life in this country, going wherever fancy took him, and singing in almost all the larger cities.
In 1882 he, being then seventy-two years of age, married a Miss Pauline Greenwood, who had been one of his pupils in Philadelphia. Shortly afterwards the happy couple settled in San Francisco, where he frequently{103} sang in concerts, and where he had a number of pupils. His voice was wonderfully well preserved, and he was strong and active, giving some fifteen lessons daily, until his death in 1889.
Niemann is authority for a story about Formes. Once when he was in Germany, Formes was very anxious to sing at court, and Niemann succeeded in securing for him the opportunity. According to Niemann's ideas of art, Formes sang atrociously, bellowing and shouting in stentorian tones. Niemann was in an agony throughout the performance, thinking of his responsibility; but, to his surprise, when the song was over, the old Emperor William I. applauded loudly, and seemed highly delighted, and demanded an encore. He probably thought what a fine dragoon officer Formes would have made, shouting commands with his great voice.
At about the same time there flourished{104} another tenor of high rank, whose career was confined almost entirely to Germany, Joseph Alois Tichatschek. He was born in 1807, at Ober Weckelsdorf, in Bohemia, and became a chorus singer in 1830, rising in his profession until, in 1837, he made his début as a soloist at Dresden. In 1841 he sang for a few nights in London, at Drury Lane, during a season of German opera; also at Liverpool and Manchester, and was described as "young, prepossessing, and a good actor; his voice is excellent, and his style, though not wanting in cultivation, is more indebted to nature than to art." He was also said to have proved himself "the hit of the season." Tichatschek died in 1886.
A singer who was much more widely known, and who belonged to the time of Grisi, Mario, Lablache, and the great operatic representations of those days, was Georgio Ronconi, the baritone. He had a{105} reputation extending throughout Europe and into America, and he owes his celebrity rather to histrionic powers than to his voice, for we are told by Chorley that "there are few instances of a voice so limited in compass (hardly exceeding an octave), so inferior in quality, so weak, so habitually out of tune. The low stature, the features unmarked and commonplace, when silent, promising nothing to an audience, yet which could express a dignity of bearing, a tragic passion not to be exceeded, or an exuberance of the wildest, quaintest, most whimsical, most spontaneous comedy. These things we have seen, and have forgotten personal insignificance, vocal power beyond mediocrity, every disqualification, in the spell of strong, real sensibility." It was one of the many cases in which dramatic talent has made up for lack of voice.
Ronconi sang for many years in London, in all the great comic operas. He retired in{106} 1874, and became a teacher of singing. He died in 1890.
In 1849 two stars of importance appeared on the operatic horizon,—Madame Marie Caroline Félix Miolan Carvalho, and Mlle. Theresa Carolin Johanna Tietiens.
Madame Carvalho became the foremost lyric artist on the French stage, and was engaged for many years at the Opera Comique and at the Grand Opera in Paris, but she also sang frequently in London, Berlin, St. Petersburg, and other cities of Europe. Her first public appearance was made at a performance for the benefit of Duprez, her teacher, and she sang in the first act of "Lucia," and in the trio in the second act of "La Juive." Her last appearance, which took place in 1887, two years after her retirement from the stage, was also at a benefit,—a concert in aid of the sufferers by the fire at the Opera Comique. On this occasion she sang with Faure.{107}
Madame Carvalho was the daughter of an oboe player named Félix Miolan, who educated her musically until she entered the Paris Conservatoire, and studied with Duprez, gaining, in 1847, the first prize for singing. Her voice was high and thin, but was used with consummate skill and delicacy, and her interpretation of the rôle of Marguerite, in "Faust," was considered a most complete and delightful personation.
She was a native of Marseilles, born in 1827. In 1853 she married Leon Carvaillé, more generally known as Carvalho, who became director of the Opera Comique. He held this position at the time of the fire; and, as the accident was judged to have been due to the carelessness of the management, Carvalho was fined and imprisoned. Madame Carvalho died in 1895, at Puys, near Dieppe.
Tietiens has been called the last of the great race of dramatic singers made splendid by such as Pasta, Malibran, Grisi, and Viardot{108}-Garcia. Never was so mighty a voice so sweet and luscious in its tone. It had none of the soprano shrillness, but was more of a mezzo-soprano quality throughout, and softer than velvet. Her style of singing was noble and pure, her acting was earnest, animated, and forcible, her stage presence was imposing. Such parts as Norma and Lucretia Borgia are said to have died with her, so grand was her interpretation of them, and she sang the part of Ortrud in "Lohengrin" so finely that, in all probability, she would have become noted as a Wagnerian singer had not death snatched her away in her prime. No singer ever became more popular in England, where she lived for many years, and where her death was considered as a national loss. Mlle. Tietiens was born in Hamburg, in 1831, of Hungarian parents, and first appeared in opera in that city at the age of eighteen. She sang in London every season from 1859 till 1877, the year{109} of her death, and was as great an oratorio singer as she was operatic artist. Mlle. Tietiens was tall, massive, and dignified, and dominated the stage with her presence. In 1876 she visited the United States, and made a concert tour, but none could have a full conception of her power who did not see her in one of her great parts. Like other singers who have for years maintained their popularity in England, her private life was most admirable, and her kind and charitable nature endeared her to the nation.{110}
The years immediately following 1850 were rather barren of stars of the first magnitude in the line of sopranos, although Stockhausen, Faure, Wachtel, and Nicolini all belong to that period, besides Adelaide Phillips, the contralto.
The chief soprano of the year 1851 was Madame Nantier-Didier, a native of the Isle of Bourbon, who had a somewhat successful career in the chief cities of Europe, but who was considered "a first-rate singer of the second class." She had a gay, handsome face, a winning mezzo-soprano voice, and neat execution.
In the following year appeared two singers{111} of high rank, Maria Piccolomini, and Euphrosine Parepa, more generally known as Madame Parepa-Rosa.
Piccolomini owed her success chiefly to her clever acting, and her charming little figure. Her voice was weak and limited, and she was not sure in her intonation, nor did she excel in execution. She visited the United States in 1858, and was well received. Her stage career was not very long, for she retired in 1863, and married the Marchese Gaetani.
Parepa-Rosa was born in Scotland, at Edinburgh. Her father was a Wallachian boyard, and her mother (Elizabeth Seguin) a singer of some repute. Parepa's full name was Euphrosine Parepa de Boyesku. She was a well-educated woman, speaking and writing several languages correctly, and she had a voice of great power and sweetness, with a range of two and a half octaves. She was, also, a woman of fine figure and{112} imposing stage presence. Her reputation was gained, however, more in concert and oratorio than in opera, but her memory will remain in America as that of one who did much towards the cultivation of the public taste for opera.
In 1865 she came to America on a tour with Mr. Carl Rosa, whom she married in 1867, her first husband, Captain De Wolfe Carvell, having died in 1865. After this they remained for four years, during which time they organized the Carl Rosa Opera Company, for the performance of English and Italian opera. Madame Parepa-Rosa was the principal singer, and the company met with great success, singing not only in opera, but also in oratorio and concerts. In 1871 they went to Cairo, Egypt, on account of Carl Rosa's health, but they returned to America before winter, bringing with them Wachtel, the German tenor, and Santley, the English baritone.{113}
In 1873 they again returned to Europe, but Madame Rosa was soon afterwards seized with an illness which terminated in her death in January, 1874. The Carl Rosa Opera Company, which was thus established, remained in existence until recently, and has been a successful company, always employing several singers of high rank. In 1898, owing to a declining business, it was decided to wind the company up, or reorganize it, and meetings were held to decide the matter.
The star of 1856 was Madame Peschka-Leutner, who sang in 1872 at the Jubilee festival in Boston. Although she had appeared in London, she was but little known outside of her own country, where she was very popular. She died at Wiesbaden in 1890.
Before 1860 the French stage also produced two singers of high rank. In 1858 Madame Artôt made her début at the Paris{114} Opera, though she had already been heard in concerts in Belgium, Holland, and England. She was the daughter of the horn professor at the Brussels Conservatoire, and was taught singing by Madame Viardot-Garcia. Her engagement at Paris was due to Meyerbeer, and her success was such as to draw praise even from the extremely critical Berlioz. In the following year she took to Italian opera, and for many years was well known throughout Europe.
Marguérite Josephine Désirée Montaigny Artôt, for such was her name in full, was born in 1835, and in 1869 she married a well-known Spanish tenor, Padilla-y-Ramos. Together they sang in most of the great European cities until their retirement. As late as 1887 they sang in Berlin, in which city Madame Artôt settled as a teacher of singing.
Madame Galli-Marié, whose celebrity as Mignon and Carmen is world-wide, was the daughter of an opera singer, Mécène Marié{115} de l'Isle. She made her début at Strasburg in 1859, and about the same time married a sculptor named Galli, who died in 1861. Madame Galli-Marié's dramatic talent was great, and she has succeeded in characters of entirely opposite nature. Her voice was not remarkable; but, like many of the most renowned artists of the century, her originality and artistic temperament were sufficient to place her in the first rank.
When "Carmen" was produced, and Madame Galli-Marié was chosen for the title rôle, Bizet re-wrote the part to suit her voice, which was of limited range, having neither the low notes of a contralto nor the high ones of the soprano. She was, however, owing to her dramatic capabilities, not only the first but one of the best Carmens seen until the time of Calvé.
In 1859 there arose from the opposite ends of the earth, two stars of the first magnitude, whose brilliancy was sufficient to silence the{116} complaints of those who declared that the art of singing was a lost art. Such wails have arisen from time to time ever since opera was established, and possibly they may have existed in some form previous to that time, but up to the present date there is good evidence that the art of singing flourishes. It is human nature to declare that things of the past were superior to those of the present, and in their day Cuzzoni, Gabrielli, Catalani, Pasta, Grisi, and Jenny Lind, besides a number of others, were all such singers "as had never before been heard."
Between Pauline Lucca and Adelina Patti there was a wide difference, and yet both singers triumphed in the same parts.
Lucca made her début at Olmutz as Elvira in "Ernani," Patti first appeared in New York as Lucia. Both Lucca and Patti made their début at the age of sixteen, though some authorities state that Lucca was born in 1841; and both singers followed in matrimony{117} the conventional course of the prima donna, and married twice.
Pauline Lucca was born in Vienna, her father being an Italian merchant in comfortable circumstances. Pauline's high musical gifts attracted attention early, but her father objected to the idea of educating her for the stage. When she was about thirteen years old business reverses caused him to change his mind, and Pauline was placed under the best available teachers.
In due course an engagement was secured for her at Olmutz, and she at once became a favorite. For four months she sang at a salary of sixty florins a month, and then she was engaged at Prague at five hundred florins a month. Her next engagement was at Berlin at one thousand thalers a month.
Her popularity at Olmutz was so great that before she left that place she was honored by the inhabitants with a musical serenade and torchlight procession.{118}
It happened that about this time Meyerbeer, the composer, was casting his eye over the operatic world for a singer to whom he felt that he could entrust the creation of the part of Selika in his yet unpublished "L'Africaine." He heard of Lucca, and when she was singing at Prague he came over from Berlin on purpose to hear her. So pleased was he with her performance that after the opera he desired to be presented to her, and on being taken to her room, he rushed up to her and kissed her vehemently on both cheeks, much to the surprise and embarrassment of the young lady, who had no idea as to his identity. A modern prima donna, not long ago, experienced a similar burst of enthusiasm from an unknown elderly gentleman who also shed tears. After he had gone, and she had recovered from her surprise, she missed a very valuable piece of jewelry. It is only proper, therefore, for all composers intending to make a demonstration to send word before-hand.{119} On the following day Meyerbeer called at her hotel and offered Mlle. Lucca an engagement at Berlin, which she accepted, and which took effect at the end of her Prague engagement, eight months later.
During these eight months Lucca received a proposal of marriage from the young Prince Lobkowitz, who had fallen desperately in love with her; but she did not listen to his appeals, and the unfortunate prince was rejected. Some time after this event, which was so mortifying as to probably affect his disposition, he sought and found death on the field of honor, becoming involved in a duel.
Lucca now went to Berlin. Meyerbeer took her under his own immediate charge, and she appeared in three of his greatest characters, Alice in "Roberto," Bertha in "Il Prophete," and Vielka in the "Camp of Silesia." She was in her eighteenth year, and her beauty both of person and voice{120} excited the greatest admiration and drove the Berlin public wild with rapture. Under Meyerbeer's supervision she gained splendid triumphs and was appointed court singer for life.
During this time of triumph in Berlin she was visited by Adelina Patti, whose fame was also spreading over Europe; in fact, if one may judge by financial results, Patti's star was much higher in the heavens than that of Lucca, for whereas Lucca was receiving one thousand thalers a month, Patti was being paid one thousand francs a night. Lucca was living in apartments on a fourth floor, in quite an unconventional style, and was in bed when Patti called. Nevertheless, she received her visitor, and Strakosch, her manager, with many signs of unaffected pleasure, and they became firm friends, their rivalry being confined to the stage.
Lucca's progress to fame was now very rapid. She appeared in London in 1863 and{121} 1864, making a remarkable impression. In 1865 Meyerbeer's "L'Africaine" was to be produced in Paris, and he was anxious that Lucca should sing the part of Selika, but this was impossible without the consent of the King of Prussia, and as he was opposed to her singing in Paris at that time, he would not give the necessary consent. Meyerbeer felt so strongly on the subject that he added a codicil to his will stating that, if Pauline Lucca was engaged to sing Selika at the Opera House in Berlin, the work might be sung there in German,—otherwise, he forbade its production. "L'Africaine" was produced in Paris on April 28, 1865; but Meyerbeer never witnessed its performance in public, for he was seized with illness on April 23d of that year, and died on May 2d.
In London this opera was produced on July 22d, and Lucca sang the part for which Meyerbeer had selected her, as she also did at Berlin. Her performance in London is{122} on record as one of the very highest achievements in the lyrical drama. In Berlin she created a perfect furore, singing in a company which introduced Wachtel and Betz. While the performance was in progress, the house and even the carriage of the young prima donna were decorated with the rarest and most beautiful flowers, and with such profusion that she was hardly able to recognize her home.
The Czar of Russia now wished to hear this incomparable singer, so he sent a polite message to the King of Prussia, requesting that she be allowed to sing at St. Petersburg, and offering her a salary of eighty thousand rubles for the season of four months. The King of Prussia had not the same scruples concerning Russia that he had about France, so his gracious consent was given, as it was, also, on the following season.
Lucca made an immense impression at St. Petersburg, where at the end of the season{123} she was serenaded by the band of the Imperial Guards. The streets were illuminated from the theatre to her house at the orders of the Crown Princess Dagmar, the Empress gave her a priceless and beautiful pair of diamond earrings, the public, through the leader of the orchestra, presented her with a splendid diadem covered with precious stones, and the members of the orchestra subscribed and made her a present of a laurel wreath in gold. But the greatest demonstration in her honor occurred when she organized a concert for the benefit of indigent students, the receipts of which exceeded ten thousand rubles. Then she was called forward thirty times, and the students unharnessed her horses and dragged her carriage home. They seized her shawl and tore it into fragments for mementos, and she also had to give up her gloves and handkerchief for the same purpose.
Similar demonstrations have taken place{124} at different times, and in other cities, in honor of other singers. It is quite an ordinary matter in Russia for a singer to be called forward ten or twenty times, and even thirty times is not by any means so extraordinary as it would be in London or New York, or, more particularly, in Boston.
Jenny Lind lost a shawl in New York through the enthusiasm of the public, and in 1881 Patti enjoyed the experience in Brooklyn of being dragged home by a crowd of enthusiasts.
Perhaps Patti had the most curious demonstration in London, just before she sailed for New York under Mapleson's management, and Mapleson is the authority for the anecdote.
After the last performance of the season, Patti was escorted from the theatre to the train en route for Liverpool by a procession of theatrical people in costume, with a brass band. This was at one o'clock in the morning.{125} Full accounts of it were, of course, obtained somehow by the American papers.
In 1865 Pauline Lucca had married a German military officer, Baron von Rahden, who, when the Franco-German war broke out, went to the front, and was severely wounded in the celebrated charge of Mars-La-Tour. Lucca, hearing of his misfortune, made her way to the scene of the conflict, and sought him out in the military hospital, where she tenderly nursed him until he could be taken home. Her devotion to him was admirable; but, unfortunately, a change in her feelings seems to have occurred before very long, for when in 1872 she was in New York she brought suit for divorce against the Baron, and he, being unaware of the proceedings, made no defence, so that rightly or otherwise Madame Lucca secured her divorce. Later on, when von Rahden forwarded papers which were supposed to establish his innocence of the charges made{126} against him by his irate and jealous spouse, the case was closed, and no notice was taken of the defence. Matters seem, however, to have arranged themselves to the satisfaction of all concerned, for the Baron married the young lady who had been the cause of Lucca's jealousy, and Lucca married Baron von Wallhofen, an intimate friend of Von Rahden, who, also, had been wounded at Mars-La-Tour, and who had followed her to America.
Pauline Lucca was one of the few singers gifted with original genius, and she imparted specific individuality to each of her characters, even the most colorless. Her versatility was very great, and she had a repertoire of fifty-six rôles. Her voice was a full soprano of sympathetic quality, and with a range of two and a half octaves, extending to C in alt, and capable of expressing every kind of emotion. Like Patti she was of slender figure, and at one time she played{127} Marguerite in "Faust" on alternate nights with her. Lucca was essentially a lyric actress rather than a singer pure and simple, and had the power of realizing the highest dramatic conception both of poet and composer; she was able to draw inspiration from the abstract idea, and she has been called "transcendentally human."
After her memorable tour in the United States, in 1872, Madame Lucca continued before the public in Europe until 1884, since which time she has lived in Vienna, and devoted herself chiefly to teaching.
While Lucca was thus rising to the highest pinnacles of fame, Patti also was scoring great successes. In London she had become a permanent favorite, and from the year 1861, in which she made her European début, for more than twenty years she was engaged every season at Covent Garden.
In spite of all rivalry, she held her position there as the most popular opera singer{128} of modern times. She has enjoyed the same popularity on the continent, and in America also she has been immensely popular.
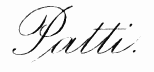
Adelina Patti's voice was one of moderate power, but great range and of wonderful flexibility. Her production was faultless, and she was, and is, undoubtedly, one of the greatest mistresses of vocalization of the century. As an actress, she could not compare with many other singers, and her greatest successes were gained in such operas as made the least demand upon the histrionic capabilities of the performer. Her repertoire included about thirty operas, mostly of the Italian school, though she also sang in the operas of Meyerbeer and Gounod, and others. She was one of the many "Carmens;" but while her interpretation vocally was excellent, she was by no means equal dramatically to Mlle. Hauk, and much less so to Calvé, the latest and by far the greatest interpreter of that rôle.{129}
One of the most notable events of Madame Patti's career occurred when, in 1868, at the funeral of Rossini, the composer, she sang with Madame Alboni the beautiful duet, "Quis est Homo," from Rossini's "Stabat Mater." On that occasion such an assembly of noted musicians and singers was gathered together to honor the great composer as probably never before met under the same roof. To hear that beautiful music, rendered by two such artists over the grave of the composer, was to feel in the truest sense the genius of Rossini, and the part that he played in the music of the nineteenth century.
The name of Patti has always been associated with high prices, and not without cause; for, although other singers have received larger sums for isolated engagements, none have ever succeeded in maintaining such a uniformly high rate.
When she returned to America in 1881,{130} after an absence of some twenty years, Patti held mistaken notions about the American people, and her early concerts were a bitter disappointment. High prices and hackneyed songs did not suit the public, and in order to make a success of the tour Madame Patti was obliged to throw over her French manager, and employ an American (Henry E. Abbey) who knew the public, and who immediately cut the prices down to one-half. Eventually the season was successful, both artistically and financially, her voice showing but little sign of wear, and her execution being as brilliant as ever. At Brooklyn the people took the horses out of her carriage, and dragged her home,—one facetious writer remarking that he saw no reason for taking away her horses, and substituting asses. The following clever rhyme, at the expense of her manager, taken from "Puck," voices the opinion of the public very neatly, in regard to Patti's tour, in 1881-2:{131}
| Patti cake, Patti cake, Franchi man! |
| "So I do, messieurs, comme vite as I can." |
| "Roulez et tournez et marquez 'with care,' |
| Et posez au publique à ten dollars a chair." |
Farinelli is said to have made $30,000 per annum, a very large sum for the times in which he lived. Catalani's profits ran almost to $100,000 a season. Malibran received $95,000 for eighty-five performances at La Scala. Jenny Lind, for ninety-five concerts, under Barnum's management, received $208,675, all good figures. But Rubini is said to have made $11,500 at one concert, and Tamagno is the highest-priced tenor of the present day.
Patti at one time made a contract for a series of performances at $4,400 a night, and later on her fee was $5,000 a night, paid in advance, but when she came to Boston in 1882, and sang in three performances given in a week, her share of the receipts was $20,895. The attendance at the Saturday{132} matinée was 9,142 people, and her share of the receipts for that performance alone was $8,395.
Madame Patti always had the advantage of excellent management. Until her marriage with the Marquis de Caux she was under the management of her brother-in-law, Maurice Strakosch, and so assiduous was he in his protection of his young star from unnecessary wear and tear that he became the subject of many jokes. It is said that he occasionally took her place at rehearsals, that when visitors called on her they saw him instead, and some people, with vivid imagination, declared that Strakosch sat for Patti's photograph, and that he once offered to receive a declaration of love for her.
One is apt to doubt the necessity of all this management, for Patti seems to have been admirably adapted for self-defence, and even for aggression in financial matters. An amusing anecdote is told of her by Max{133} Maretzek, who, one day, when she was a small child, in a moment of generosity promised her a doll, or, as some accounts have it, some bon-bons as a reward for singing in a concert. It was to be her very first appearance. Patti did not forget the promise, and when it was nearly time for her to sing she asked for her doll. Maretzek had forgotten it, and promised that she should have it after the concert, or the next day. But no, she must have it first, or she would not go on and sing. The poor man was in despair. It was late and stores were all closed, but by some means he succeeded in getting the bribe, whether dolls or bon-bons, and, rushing back in breathless haste, he handed it to her. Then she became cheerful at once, and giving it to her mother to be taken care of, she went on and performed her part in the concert.
One of the most amusing of these anecdotes was told by Colonel Mapleson, the{134} well-known impresario, who says that no one ever approached Madame Patti in the art of obtaining from a manager the greatest possible sum that he could contrive by any possibility to pay. In 1882, owing to the competition of Henry Abbey, the American impresario, Mapleson was obliged to raise Patti's salary from $1,000 per night to $4,000, and, finally, to $5,000 per night, a sum previously unheard-of in the annals of opera. The price, moreover, was to be paid at two o'clock of the day on which Patti was to sing.
On the second night of the engagement at Boston, Madame Patti was billed to sing in "Traviata." Expenses had been heavy and the funds were low, so that when Signor Franchi, Patti's agent, called at the theatre promptly at two o'clock, only $4,000 could be scraped together. Signor Franchi was indignant, and declared that the contract was broken, and that Madame Patti would{135} not sing. He refused to take the $4,000, and went off to report the matter to the prima donna. At four o'clock, Signor Franchi returned to the theatre, and congratulated Colonel Mapleson on his facility for managing Madame Patti, saying that she would do for the colonel that which she would do for no other impresario. In short, Patti would take the $4,000 and dress for her part, all except her shoes. She would arrive at the theatre at the regular time, and when the remaining paltry $1,000 was forthcoming she would put on her shoes and be ready to go on the stage.
Everything happened as Patti had promised. She arrived at the theatre costumed as Violetta, but minus her shoes. Franchi called at the box-office, but only $800 was on hand. The genial Signor took the money and returned to Patti's room. He soon appeared again to say that Madame Patti was{136} all ready except one shoe, which she could not put on until the remaining $200 was paid. It was already time for the performance to begin, but people were still coming in, and after some slight delay Signor Franchi was able to go in triumph to Madame Patti with the balance of the amount. Patti put on her other shoe and proceeded to the stage. She made her entrance at the proper time, her face radiant with smiles, and no one in the audience had any idea of the stirring events which had just taken place.
In later years, when Madame Patti invested some of her fortune in the beautiful castle at Craig-y-Nos, in Wales, the people employed to put the place into repair, knowing of her reputed wealth and extravagance, sent in enormous bills. But Madame Patti was not to be imposed upon, and the result was that the amounts melted down considerably under the gentle influence of the law.{137} The unkindest cut of all was, however, when a Belgian gentleman, who had amused himself at Craig-y-Nos, who had fished, shot, and been entertained, but who always managed to be present during discussions on business, sent in a bill of £3,000 for his services as agent.
Under the management of Colonel Mapleson, Patti travelled in most luxurious style. She had a special car which is said to have cost $65,000, and a whole retinue of servants. At Cheyenne, the legislature and assembly adjourned and chartered a special car to meet the operatic train. A military band was at the station, and nearly the whole population turned out to witness the arrival. Tickets to the opera were ten dollars each, and there was an audience of 3,000 people.
California seems to have been considered doubtful territory, for Patti left the question undecided as to whether she would go so far.{138} When she did arrive it was merely as a visitor, but her delight with the "heavenly place" was so great that she declared she must sing there. The necessary delay incurred by sending to Chicago for numerous trunks containing her wardrobe, gave sufficient time for the excitement in San Francisco to work up to fever heat. Tickets sold at unheard-of prices, and more or less damage to property was done in the scramble.
Adelina Patti made her first matrimonial venture in 1868, when she was united to the Marquis de Caux, an event which did not interfere with her operatic career, for she filled an engagement of six weeks at Paris, and then went on to St. Petersburg, where the town opened a subscription which amounted to 100,000 rubles, and presented her with a diamond necklace.
In 1885 Madame Patti obtained a divorce from the Marquis de Caux, from whom she had separated in 1877, and the following{139} year married Ernest Nicolini, the tenor singer. Nicolini was a man of fine stage presence, and, for a time, after the retirement of Mario, was considered the best tenor on the stage. His voice was of moderate power and of pleasing quality, but his tremolo was, to say the least, extensive. For some years Madame Patti declined every engagement in which Nicolini was not included, until the public indignation found vent in many protests. Signor Nicolini seems to have been a devoted and admiring husband, and to have entered heartily into the pleasures of the luxurious life of Craig-y-Nos. He died in January, 1898.
After some years of retirement from the operatic stage, during which she sang only in concerts, Patti made a reappearance at Covent Garden in 1895, and showed that her voice, notwithstanding nearly forty years of use, was wonderfully well preserved. Nevertheless it was a disappointment to those{140} who had heard her in her prime. As a reason for its preservation she says that she never sings when she is tired, and never strains for high notes. Sir Morell Mackenzie, the great throat specialist, said that she had the most wonderful throat he ever saw. It was the only one in which the vocal cords were in absolutely perfect condition after many years of use. They were not strained, warped, or roughened in the slightest degree, but absolutely perfect, and there was no reason why they should not remain so for ten or even twenty years longer. It was by her voice alone that she charmed and delighted her audiences, and she will doubtless be recorded as the possessor of the most perfect voice of the nineteenth century. She witnessed the rise of many rivals, but none ever equalled her in popularity, though many excelled her in dramatic powers. Lucca, Sembrich, Nilsson, were all greater as actresses, but of all the rivals of her prime{141} only Sembrich and Albani remain, and several years must elapse before their careers will equal the length of Patti's.
Probably no other singer has succeeded in amassing so great a fortune as Madame Patti. Her earnings enabled her to purchase, in 1878, the beautiful estate in Wales, which she remodelled to suit her own ideas. Here she has lived in regal style and entertained lavishly many of the most noted people of the civilized world.
Her wealth is by no means confined to real estate, for she has a rare collection of jewels, said to be the largest and most brilliant owned by any of the modern actresses and opera singers. One of her gowns, worn in the third act of "La Traviata," was covered with precious stones to the value of $500,000.
Madame Patti's most popular rôles were Juliet and Aida, and though she created no new parts of importance, she has amply fulfilled{142} the traditional rôle of prima donna in matters of caprice and exaction, and has even created some new precedents. In 1898 she was still before the public, singing in concerts in London and elsewhere.{143}
At the middle of the century critics began to cry out about the decadence of the vocal art, much as they have done at intervals during the past two centuries, and with as little real cause. The great singers of recent years had departed, and apparently none had arisen to take their place, and yet the latter half of the century has been adorned by stars who, as far as we are able to judge, are not inferior to those who have gone before. It is probable that other stars also will arise who will delight as large audiences and create as great excitement as Grisi, Lind, and Malibran.
While it is undoubtedly true that declamation{144} holds a more important place in modern opera than it did in the operas of bygone days, and some declare that the art of vocalization is extinct, yet singers who can charm by pure vocalization are still as welcome as ever, though more is expected of them in the dramatic branch of their art.
It is doubtful whether a greater trio of singers has been before the public at any time than Patti, Lucca, and Nilsson, and yet they appeared at a time when it was claimed that vocal art was dead.
During the first half of the century we have seen that some of the great singers visited the United States. Garcia brought his daughter to America, where she created a great sensation and found her first husband. Sontag crossed the ocean, Grisi, Alboni, and Jenny Lind had found appreciative audiences in America. Among the men, Incledon was the first singer of importance to cross the water.{145}
We now arrive at a period when not only many great singers, and some of less repute, crossed the wild Atlantic for American dollars, but America began to supply singers to the European market. When Colonel Mapleson was interviewed in San Francisco during Patti's tour, he declared that there were more than 2,000 American vocal students in Europe, and he mentioned fifteen who had appeared under his management up to 1883. This number included Patti, who could hardly be claimed as American, for she was born in Madrid, of Italian parents. But between 1860 and 1870, Clara Louise Kellogg, Minnie Hauk, and Annie Louise Gary were genuine Americans, as was also Adelaide Phillips, who made her début in 1854. In later years the number increased till, at the present day, at least two of the greatest artists among the prima donnas are of American origin, while a large number have reached a high position{146} and may be destined for the greatest honors.
The star of the year 1860 was born in Vienna, made her début there, and remained there for some years. Marie Gabrielle Krauss was one of those singers, who, with a voice far from perfect, was able by her style, her phrasing, and her musical delivery, to which must be added the incontestable power of dramatic accent, to be classed among the greatest singers of her time. In 1867 she was engaged in Paris and sung there for many years, except during the Franco-Prussian war.
In 1861, Carlotta Patti made her début, but she was obliged to abandon the operatic stage on account of lameness. She was an elder sister of Adelina Patti, and for many years was very popular on the concert stage, sharing with her sister wonderful facility of execution and beautiful quality of voice. Probably no singer of her time travelled so{147} extensively as Carlotta Patti, who is said to have visited every part of the world in which a concert could be successfully given. In 1879 she married Mr. Ernst de Munck, of Weimar, a violoncellist, but ten years later she died.
Clara Louise Kellogg was one of the early American singers, who, though her great musical gifts enabled her to win triumphs in opera in the great musical centres of the world, devoted the prime of her life to giving English opera in her native land.
Miss Kellogg was born in Sumterville, S. C., in 1842, but in 1856 she went, with her mother, who had considerable musical ability, to New York, in order to continue the musical education which her mother had begun. In 1861, before she had completed her nineteenth year, she made her début at the Academy of Music, in "Rigoletto" as Gilda, and sang during the season about a dozen times.{148}
In 1867 she appeared at Her Majesty's Theatre in London as Margherita, and was reëngaged for the following year. She then returned to the United States and made a concert tour which lasted for four years. In 1872 she was back again in London at Her Majesty's.
In 1874 she organized an English Opera company in America, translating the words, training the chorus, and doing most of the hard work of the enterprise herself. Such was her ardor and enthusiasm that she sang in the winter of 1874-5 no less than one hundred and twenty-five times. From that time until 1882, she was constantly before the public in opera or concert, and in addition to her musical talents she was remarkable for business ability. Her voice was of large compass and great purity, and when she retired she left a memory of a good, exemplary life, full of benevolent actions.
It is said that in her youth she was engaged{149} to be married to a schoolmate, but the marriage was necessarily to wait until they had sufficient means. She went on the stage, was successful, and wrote to him saying that she had sufficient money and was ready. He, however, felt it incumbent upon him to provide at least a capital equal to hers, and desired a further postponement. This annoyed her, and her enthusiasm cooled off. Money-making was a slow process with him, and before he had satisfied his conscience she had announced her engagement to another man. Miss Kellogg retired in 1882, and married Mr. Strakosch, a son of the celebrated impresario.
During Miss Kellogg's travels in the United States she visited with her company a great many towns which have since become music-loving cities, and she met with many highly amusing experiences, besides some which were less amusing than instructive. She has exerted an educational influence{150} throughout the country which it would be difficult to over-estimate; indeed, it can be claimed that the ambition of many young Americans to study music owes its origin to the efforts of those who, like Miss Kellogg, visited the smaller towns, and made it possible for a large number of people to enjoy music of a high order.
The year 1862 produced a singer of great ability, Ilma di Murska, a native of Croatia, one of the most brilliant sopranos, and one of the most eccentric women of her time. There seems to be considerable uncertainty about her early life, both as to birth and marriage. By some authorities it is stated that she was born in 1843, the year in which Patti, Nilsson, and (some say) Lucca were born. On the other hand, the date of her birth is placed both in 1836 and 1837, and there are many reasons for supposing that one of these earlier dates is the right one.{151}
Concerning her first marriage, one authority states that her first husband was Count Nugent, a descendant of a renowned Irish officer of that name, by whom she had a son and a daughter, and that the son committed suicide in 1876. Another account is that in early life she married General Eider, from whom she separated on account of her eccentricities, which made it impossible for him to live happily with her. This account speaks of her daughter, and it is tolerably well established that she did have a daughter, for that young lady played an important and not particularly creditable part in the history of the talented singer. It is not impossible that she may have married both Count Nugent and General Eider, for she certainly married frequently, and in that respect holds a unique place, even in the list of much-married prima donnas.
Madame di Murska was tall and slender in figure, of striking appearance, and with features{152} not specially attractive, but her vigor and originality were remarkable. Her impersonations were full of life, and, while she occasionally exaggerated in gesture or expression, she invariably held the attention of her audience. She sang the most difficult passages, and gave the most florid ornamentation, with ease and certainty.
As Lucia, Astrofiammante, and Dinorah, she made a great sensation, even at a time when Adelina Patti was considered to be perfection in those parts. The writer remembers her in "Roberto" at Drury Lane, when her impassioned acting resulted in a very funny incident. While she sang the beautiful aria, "Robert, toi que j'aime," the object of her adoration reposed in oblivion on a red plush sofa. In her abandon she let her face rest for a moment on the head of the sofa, where, when she arose, there remained a large, white patch, which aroused the audience to laughter, in spite{153} of themselves. Truly, the step from the sublime to the ridiculous is very small.
Ilma di Murska made her début at Florence, after which she sang at Pesth, Vienna, Berlin, Hamburg, and London. Her memory is said to have been remarkable, and her facility in learning equally so, for she could learn her part by merely reading it, sometimes in bed, from the score. In 1873 she made a tour in the United States, an account of which was once given by Mr. de Vivo,[1] who was her manager. During this tour her eccentricities caused her manager much anxiety, for at times when he needed money, and, having paid large sums to her, felt confident that she was able to furnish funds, she had always sent her earnings to her daughter, who seems to have kept her in a chronic state of poverty. The company{154} travelled across this continent, and went to Australia and New Zealand. During the Australian tour Madame di Murska became very much interested in Alfred Anderson, a young musician belonging to the company. He fell into bad health, and, when confined to his room by sickness, the eccentric singer insisted upon nursing him. Soon afterwards they were quietly married. They were then in Sidney, and the marriage took place in December, 1875. Mr. Anderson continued so ill that he was obliged to return to Melbourne, his native city, where he went to his father's house. It seems that the family were opposed to the marriage, for Madame di Murska was refused admission, and was obliged to stay at a hotel. There seem also to have been some peculiar financial transactions, for, according to accounts, when Mr. Anderson died, which was some three or four months after the marriage, Madame di Murska lost a large sum of money. This{155} experience, however, did not by any means crush her, for in May, 1876, five months after her marriage to Anderson, she fearlessly embarked on another matrimonial venture, this time taking as her partner for life Mr. John T. Hill. This union does not seem to have been permanent, for nothing more is heard of Mr. Hill in connection with Madame di Murska.
[1] Mr. Diego de Vivo died in New York, on August 11, 1898, at the age of seventy-six. He was instrumental in introducing to the American public many artists who have become well-known.
In Australia, di Murska never attained the same popularity that attended her efforts in Europe, her peculiarities were so marked. She is said to have always refused to be interviewed, or to see any one at her hotel, and she used to spend her time in training a lot of parrots, magpies, cockatoos, monkeys, and other creatures, to sing. She had a wagon-load of pets, which were taken from town to town, wherever she sang, and were an unmitigated nuisance. She also had a big Newfoundland dog, named Pluto, for whom a cover was always laid at the dinner table.{156} Pluto dined on capon and other dainties, and was a model in regard to table manners. Her parrots cost her a great deal of money, for they had a decided antipathy to silk or damask upholstery, particularly to flowered patterns, but Madame di Murska always seemed pleased when the bills for the depredations of her pets were presented to her.
Once while the company was at Glasgow, one of the members fed a parrot with parsley till it died. Di Murska called in two learned Scotch professors to hold a post-mortem examination, and they decided that the bird had died of wall-paper, and charged three guineas for their opinion.
Some few years later Madame di Murska was induced to return to the United States, where a position was secured for her in New York as a vocal teacher, but although possessed of undoubted talent, she completely failed to impart it to her pupils, nor was{157} she any longer successful in concerts. Her money, which had been sent to her daughter as fast as she earned it, had all been squandered, and she fell into the direst poverty. The musicians of New York interested themselves in her behalf, and sufficient money was raised to send her home. She survived but a short time, and, in 1889, on January 4, her troubled life ended. It was an extremely sad termination to a brilliant career, and its sadness was emphasized by the fact that her daughter, whose happiness had seemed her greatest solicitude, committed suicide over her grave. It is said that General Eider, hearing of the tragic event, caused a stone to be erected at the graves of his eccentric wife and daughter.
One of the most important and brilliant rivals of Adelina Patti was Christine Nilsson, a Swede.
Miss Nilsson was the only daughter of a poor farmer at Sjöabal, near Wexio. She{158} was born in 1843, the same year in which Patti was born, and was seven years younger than her youngest brother, who was the third son of his parents, and who, being of a musical nature, had studied the violin in the best way that he could without a teacher. He turned his talent to account by playing at balls in the neighboring villages.
When Christine was nine years old she was wont to sing the native melodies of her country, and she, too, learned to play her brother's violin in order to accompany her voice.
When she reached her twelfth year, her mother used to take her to the neighboring fairs, where, her golden hair tied simply under a handkerchief, she played and sang to admiring rustics, who would contribute their small donations to her brother, who passed his hat around.
At the age of thirteen came a turning-point in her career. She was at a fair in{159} Llungby, when a ventriloquist, who had set up his booth near where she was singing, finding that all the trade passed him and went to her, came over and made a bargain, offering her twenty francs to sing at his booth during the remaining eight days of the fair. While singing for her new employer, she attracted the attention of Judge Toernerheljm, who was touched by her beauty, her grace, and the delightful tones of her voice. He resolved to rescue her from the career of a vagrant musician, and asking about her father and mother, said that he would take her and place her with a lady who would be kind to her. The simple little maid replied that she could not break her contract with the ventriloquist, but the judge agreed to satisfy him. So she sent her brother home to tell the story and ask advice. He returned with a message from her parents saying that she was to go, but not to come home first, as they{160} could not bear to part with her if she did.
Accordingly Christine went with Judge Toernerheljm, who placed her with the Baroness Leuhusen, formerly a vocal teacher, from whom the young singer received her first lessons, and, at the same time, attended school in Halmstadt. In due time she went to Stockholm, where she took lessons under Franz Berwald, and in six months' time she sang at Court.
The young singer now went to Paris accompanied by Baroness Leuhusen, and began a course of lessons under Wartel. She so profited by his instruction, that she made her début at the Théâtre Lyrique on October 27, 1864, as Violetta in "La Traviata," and afterwards appeared as Lady Henrietta, Astrofiammante, Elvira ("Don Giovanni"), etc. She remained at the Théâtre Lyrique nearly three years, after which she went to England and sang at Her Majesty's,{161} making her first appearance as Violetta, on June 8, 1867. Notwithstanding that Patti had the world at her feet, the success of Nilsson was extremely brilliant, her impersonation of Marguerite in "Faust" calling forth unstinted praise, and it is the opinion of many that in that part she has never been excelled. Her representation of Marguerite was that of a quiet, simple girl, full of maidenly reserve during the first three acts, a deep-natured young girl, restrained from the full expression of her feelings by every instinct of her better nature, and every rule of her daily life. This very forbearance of style made her final surrender a thousand times more impressive than is usual. It was accomplished in one wild, unlooked-for rush of sudden emotion, caused by the unexpected return of her lover. The picture which Nilsson gave of this tender, gentle girl, in the pensive, anxious joy of her first love, and in the despair and misery of her darkened life,{162} was one over which painters and poets might well go wild with enthusiasm.
Nilsson had a voice of wonderful sweetness and beauty, and possessed the most thorough skill in vocalization. She could reach with ease F in alt, and showed to advantage in such operas as "Zauberflöte." Her singing was cold, clever, and shrewd, and she calculated her effects so well, that her audience was impressed by the semblance of her being deeply moved. The eulogies of London and Paris dwelt more upon her acting than upon her singing, more upon her infusion of her own individuality into Marguerite, Lucia, and Ophelia than upon any merely vocal achievement. She was considered a dramatic artist of the finest intuitions, the most magnetic presence, and the rarest expressive powers. There was, too, a refinement, a completeness, and an imaginative quality in her acting, which was altogether unique.{163}
From 1870 to the spring of 1872 Miss Nilsson was in America, where she met with a perfect ovation. In 1872 she returned to London, and in July was married by Dean Stanley, in Westminster Abbey, to M. Auguste Rouzeaud, of Paris. She visited America again in the season of 1873-4. In 1881, Nilsson sang in opera for the last time, but continued to sing in oratorio and concerts until 1888, since which time she has remained in the seclusion of private life.
According to Maurice Strakosch, Miss Nilsson once visited a celebrated palmist, Desbarolles, who examined her hand, and told her that she would encounter many troubles, of which most would be caused by madness or by fire. This prophecy proved to be true, for several times during her American tour she was annoyed by insane lovers. In New York, she was obliged to seek the protection of the court from a man who pestered her with attentions, and{164} again in Chicago she had a very unpleasant experience, both of which affairs caused some sensation at the time. But more serious than these incidents was the loss of a great part of her savings through the Boston fire, and this was followed in 1882 by the death of her husband, M. Rouzeaud, from insanity, caused by mental worry over business reverses.
The events which led up to Nilsson's retirement from the operatic stage are told by Colonel Mapleson, but it must be remembered that he was a man much harassed by the peculiarities of prima donnas, and his experiences with Madame Nilsson were not the least of his trials.
In 1868 Nilsson was so successful that she revived the drooping fortunes of Her Majesty's Theatre, which had recently been burnt down. At the same time Patti was singing at Covent Garden. Nilsson felt that her achievements were equal to those{165} of Patti, and justified her in regarding herself as Patti's successful rival. Thus, whenever Patti secured a large sum for her services, Nilsson demanded as much. When competition became keen between Mapleson and Abbey, the American impresario, Mapleson made overtures to Nilsson, as Abbey was outbidding him for Patti, but the Swedish singer would accept no engagement at less than Patti's figures. Feeling that Patti was the strongest drawing card, Mapleson gave up the idea of playing Nilsson against her, and determined to outbid Abbey for Patti. This competition resulted in the establishment of Patti's price of $5,000 a performance, and Nilsson was left without an engagement.
In 1884 she made a concert tour in the United States, when Brignoli sang with her. He once caused some merriment, which went the round of the papers, when he came forward, in a Missouri town, to apologize{166} for Nilsson's slight indisposition. "Madame Nilsson ees a leetle horse," he said. Noticing a ripple of laughter amongst the audience, he repeated the statement that Nilsson "was a leetle horse," when a facetious occupant of the gallery brought down the house by remarking, "Well, then, why don't you trot her out?" Brignoli was a very useful tenor, and toured the country many times with various prima donnas. He was as full of oddities as of music, and a very amusing story is told of him in connection with an Havana engagement. It appears that he was displeased at his reception, so he decided that on the next night he would punish the people by having a sore throat. He sent notice at the proper time to the manager, who, according to the laws of the country, was obliged to report the fact to the government. A doctor was sent by the authorities to ascertain the state of his health, and finding no sign of indisposition{167} looked very serious, and told the tenor that it was a case of yellow fever. This so frightened the capricious singer that he declared himself perfectly able to sing, and he took his revenge by singing so finely that he outshone his previous reputation, and electrified his audience.
Nilsson's first care, when she began to accrue wealth, was to purchase farms for her parents and her brother. When she returned to Sweden in her prime she met with such a reception as had not been known since the time of Jenny Lind. She entered enthusiastically into the life of her compatriots, played dances for them on the violin, as she had done in the days of her childhood, and sang the songs of her country.
In 1887 Madame Nilsson married a second time, choosing for her husband Count Casa di Miranda, and after her farewell concerts, given in 1888, retired permanently.
During her stage career Nilsson gave to{168} the world new and refined interpretations of many well-known rôles, but her only creation was the part of Edith in Balfe's "Talismano," though when Boito's "Méphistophele" was first produced in England, in 1880, she sang the part of Margaret. She also gave a remarkable dramatic and poetical interpretation of the part of Elsa in "Lohengrin."
Of all the singers of German opera, by which we now mean Wagner, none has attained so great a reputation as Frau Amalie Materna. With a soprano voice of unusual volume, compass, and sustaining power, a fine stage presence, and great musical and dramatic intelligence Frau Materna left nothing to be desired in certain rules.
Amalie Materna was born in Styria at a place named St. Georgen, where her father was a schoolmaster. This was in 1847, and when she was twelve years of age her father died, leaving his family penniless.{169}
Amalie and an older brother found means to go to Vienna where a music teacher tried her voice, and though he saw great promise in it he declined to undertake her musical education on such terms as she could offer. Sadly disappointed, Amalie joined her mother and another brother at St. Peter in Upper Styria, and lived there for the three following years, when the family migrated to Gratz.
It is related that Suppé, the composer, sometimes spent his summer holiday at Gratz with some old friends. Every evening the party would gather in the garden to play skittles. When ready to begin they would call to the woman next door to send the "lad" to set up the skittles. The "lad" was a sprightly, black-eyed girl named "Maly" Materna.
One day Suppé happened to hear her sing, and struck by the beauty of her voice, called the attention of Kapellmeister Zaitz, also a visitor at Gratz. Soon after this "Maly"{170} became a member of the chorus at the Landes theatre, and by Suppé's advice Treumann engaged her for Vienna. She had meanwhile developed her voice.
Materna's first salary was forty gulden a month, but her first appearance was so successful that this was raised to one hundred gulden. For two years she sang in Offenbachian rôles, and it was at the termination of her second season that she became engaged at the Karl Theatre in Vienna, at a yearly salary of five thousand gulden, with an extra honorarium of five gulden for each performance.
While appearing nightly in the light works of the French and German composers of the time, Fraulein Materna studied diligently during the day at the more exacting rôles of heavy opera with Professor Proch, and in 1868 sang, in the presence of Hoffkapellmeister Esser, Donna Elvira's grand air from "Don Giovanni."{171}
Esser was delighted with her, and insisted that Hofrath Dingelstedt should give the young singer a hearing, and the result was that she was engaged for the Imperial Opera House.
Shortly after her engagement at the theatre in Gratz she married an actor named Friedrich, who was engaged with her when she went to the Karl Theatre, Vienna.
In 1869 she made her début at the Imperial Opera House in the rôle of Selika, in the "Africaine," in which part she was able to demonstrate her capabilities, for she won a signal success, and was at once placed in a high position among opera singers of the German school.
Still higher honors were in store for her. In 1876, twenty-eight years after its first conception, "Der Ring des Nibelungen" of Wagner was performed entire at Bayreuth, on which occasion the part of Brunhilde was entrusted to Frau Materna. The really{172} magnificent impersonation which she gave earned for her a world-wide reputation. It was a part for which she was exceptionally well qualified, and in which she never had an equal. It is stated that Wagner, hearing Materna sing at Vienna while she was at the Imperial Opera House, and while the production of the Nibelungen Trilogy was uppermost in his mind, exclaimed: "Now I have found my Brunhilde. I take her with thanks. I am glad to have found her in Vienna."
During the Wagner festival, which was held in London in 1877, Materna confirmed the high reputation which she had gained in Germany, and when "Parsifal" was produced in 1882 at Bayreuth, Materna created the part of Kundry.
In 1882 she visited the United States, singing in New York, Cincinnati, and Chicago, and again in 1884 she crossed the Atlantic and sang in the Wagner festival of{173} that year with Scaria and Winkelmann, all of whom made good impressions and helped to pave the way for the production of the operas entire.
Frau Materna retired from the stage in 1897, on which occasion she sang in a concert given in the hall of the Musical Union in Vienna. A remarkable gathering of musicians and celebrities was there. Materna's first number was the entrance aria of Elizabeth from "Tannhäuser," which was given with such dramatic force that one could not fail to ask, "Is this the singer who is about to retire?" Her great triumph came, however, in the last number, which was "Isolden's Liebestod," and as her wonderful voice, full of passion and dramatic power, rang through the hall, the enthusiasm of the audience knew no bounds. After being recalled many times Frau Materna was obliged to make a speech of thanks, in which she touchingly referred to the many years which{174} she had passed at Vienna, and to the fact that Wagner had found her there and entrusted her with the creation of his greatest parts.
In private life Materna is simple and unaffected. She is as unpretentious in her personality as she is great in her talent. She has the unassuming manners which so endeared Parepa-Rosa to the hearts of the people.
As an artist she may best be called a vocal musician. She was not a vocal technician of the school of Jenny Lind, Nilsson, Patti, or Gerster. Her voice, though unable to give phenomenal runs, trills, or cadenzas, was adequately trained, and was of remarkable richness and breadth. The work of the poet rather than of the singing teacher was apparent in her interpretations, and the dramatic intensity and passionate force of her delivery were effective even upon the concert stage. It is doubtful whether any{175} singer will ever combine more of the qualities which are essential to the perfect interpretation of Wagner's operas, and Materna may, therefore, be set down as the greatest singer of her school.
Materna's original contract for three years at the Imperial Opera House was many times renewed, and she scarcely ever left Vienna during the season. Occasionally she was heard in Frankfort, Berlin, Hamburg, and Leipzig. She also sang in London in the Wagner concerts, and she visited the United States several times. Since her retirement, she has left Vienna to take up her permanent abode in the Château St. Johann, near Gratz, which she has purchased.
When Bizet wrote "Carmen" he intended it for Marie Roze, a versatile artist of the French stage. She, however, had made an engagement in England which prevented her from creating the rôle as intended, and it was re-written for Madame Galli-Marié, but although{176} she at first had made some objections to the character which Carmen was supposed to represent, she afterwards became famous in that part.
Marie Roze was born in Paris in 1846, and in 1865 gained first prizes at the Paris Conservatoire in singing and comic opera. In the same year she made her début at the Opera Comique, and was engaged for the following four years, during which she appeared in many rôles. Her operatic career was uniformly successful; she made several tours of Europe, and came to America in 1877, after which she became a member of the Carl Rosa Opera Company.
At the outbreak of the Franco-German war, she left the opera and joined the army, serving with the greatest zeal in the ambulance department. For her services during that struggle and during the siege of Paris, she received the Geneva Cross and a diploma from M. Thiers.{177}
Mlle. Roze married Mr. Perkins, a promising American bass singer, but his career was cut short by death in 1875. She afterwards became the wife of Colonel Henry Mapleson, the impresario, but the marriage did not prove to be a happy one, and they separated some years later. One cannot help wondering that Mapleson, whose experience with prima donnas had been so harassing, should have allied himself matrimonially to one of that ilk, but it is probable that his experiences had warped his nature, for in the scandal which the separation caused, public sympathy was with the wife. Madame Roze was the possessor of great personal attractions, and in her early days was once so pestered by an admirer that she sought the protection of the police. The aggressive youth, a French gentleman who had threatened to destroy her beauty with vitriol unless she favored his suit, attempted one night to scale the wall and{178} enter her window. The guard fired and the misguided young man dropped dead.
Madame Roze has of late taken up her residence again in Paris, where she teaches, and occasionally sings at concerts.
The year 1868 brought forth another great exponent of Wagnerian characters to whom has been accorded by many good critics a very high rank among dramatic sopranos. Lilli Lehmann was born in 1848 at Wurzburg, and was taught singing by her mother, who was formerly a harp player and prima donna at Cassel under Spohr, and the original heroine of several operas written by that master.
Fraulein Lehmann's position in the operatic world was not won suddenly. She made her first appearance in Prague as the First Boy in "Zauberflöte," after which she filled engagements in Dantzig (1868) and Leipzig (1870). In the latter year she appeared at Berlin as Vielka, and was so successful that{179} she received a further engagement. In 1876 she was appointed Imperial Chamber singer.
She now began to sing in Wagner's operas, taking the parts of Woglinde and Helmwige, and she sang the "Bird" music in Wagner's trilogy at Bayreuth. In 1880 she made a successful appearance in England as Violetta, and again as Philine in "Mignon." She also sang at Her Majesty's Theatre for two seasons, and in 1884 she went to Covent Garden and made a substantial success as Isolde. The following year she visited the United States, and for several years was frequently heard in German opera, acquiring a great reputation, but in 1892 she was taken ill and returned to Germany. At that time the condition of her health was such that it was feared she would never sing again; but in 1896 she reappeared and was engaged to sing at Bayreuth, where she electrified the world by her magnificent performance. One of the critics wrote regarding{180} the event: "Lehmann is the greatest dramatic singer alive, despite the fact that her voice is no longer fresh; but her art is consummate, her tact so delicate, and her appreciation of the dramatic situation so accurate, that to see her simply in repose is keen pleasure."
Like all the greatest Wagnerian singers, her reputation was made in work of a very different nature. It was, indeed, because of her ability to sing music of the Italian school that she was so highly successful in the Wagner rôles, and it may be stated that her long career, and Materna's, are sufficient refutation of the oft-repeated assertion, that Wagner opera wears out a singer's voice rapidly.
In 1888 Lilli Lehmann married Paul Kalisch, of Berlin, a tenor singer of good repute. The marriage took place after an engagement of several years, and was carried out, in a most informal manner, in New York.{181} Herr Kalisch telegraphed one afternoon to a clergyman to the effect that he was coming at five o'clock to be married. The clergyman held himself in readiness, the couple arrived promptly, and the knot was tied. During the few years of retirement, Frau Lehmann-Kalisch resided in Berlin, where she devoted her time to teaching the vocal art, but since her Bayreuth appearance of 1896, she has revisited America, and renewed her former triumphs.
Minnie Hauk will be remembered as the creator (in London) of "Carmen," in Bizet's opera of that name. The opera had not been very successful in Paris, but when it was produced at Her Majesty's, in London, Miss Hauk demonstrated that she was not only a singer of more than ordinary ability, but possessed also considerable dramatic power.
Miss Hauk was born in New York, in 1852. Her father was a German, and a{182} scholar of high reputation, who, having taken part in the revolutionary movement of 1848, went to New York, where he married an American lady. On account of her health he was obliged to take her, and the child, Minnie, to the West, and they settled at Leavenworth, Kan., where Mr. Hauk acquired some property. At this time Kansas was still peopled by Indians, and life was rough and unsettled. Amidst wars, inundations, hurricanes, and attacks from Indians, Minnie Hauk spent her early childhood.
Her mother's health did not improve even under these stimulating conditions, and the family moved to New Orleans, taking passage in a steamer owned by Mr. Hauk. This vessel was lost during the voyage, but the family arrived safely in New Orleans, in time to witness the siege of that city during the War of the Rebellion,—the burning of the cotton presses and ships, the battle,{183} and the occupation by Northern troops, all form most interesting and striking recollections. Yet amidst the scene of strife, the young girl was singing from morning till night, roaming about the plantations surrounding the city, climbing trees, imitating the songs of birds. The negroes on the plantations taught her their songs, she learned to play the banjo, and she organized theatrical performances amongst her playmates. All her inclinations pointed to a stage career, and when a concert was arranged for the benefit of the widows and orphans of the war, she was invited to sing, though not more than twelve years old.
This was her first appearance in public, and the pieces which she sang were "Casta Diva," and a selection from Auber's "Crown Diamonds." Her success in this concert was so great, that when the family returned to New York, she was placed under Signor Errani to begin her operatic education.{184} She made rapid progress, and after several essays at the private theatre of Mr. Leonard Jones, she made a successful début at the Academy of Music, singing the part of Amina in "La Sonnambula," and becoming at once a popular singer. This was in 1868, and later in the same year she made her début in London.
Under the management of Maurice Strakosch she made a tour through Holland and Russia, and was also well received in Vienna, in 1870, at the Imperial Opera House. In 1874, she was invited to join the Royal Opera House at Berlin, as leading prima donna, by the express desire of Emperor William and the Empress Augusta. Here she remained four years.
In 1877 she appeared at the Théâtre de la Monnaie, Brussels, and in 1878 she returned to America. During the spring seasons of 1878 to 1880, she sang on alternate nights with Nilsson, at Her Majesty's in London.{185} She made a brilliant record both in Europe and America, as a leading star of Her Majesty's Opera Company during the seasons of 1881-2-3-4-5-6, but of late years has not been heard in opera.
Mapleson gives Miss Hauk credit for being one of the most capricious of prima donnas, and declares that he generally received three or four notes a day from her containing complaints or requests. She married in 1876 Chevalier Hesse von Wartegg, who has written some interesting books on Tunis and Algiers.{186}
The decade beginning with the year 1860 was remarkably prolific in singers, producing not only the prima donnas whose careers we have reviewed in the previous chapters, but also some of the finest contralto, tenor, and baritone singers of the latter part of the century. With each decade we find the American singer more in evidence. We have had Clara Louise Kellogg and Minnie Hauk, the sopranos, Adelaide Phillips, contralto, and Annie Louise Cary, and the number increases as we proceed, until we find American singers standing on an artistic equality with the best that the world can produce.{187}
The decade of 1870 opens with a prima donna from the American continent,—a singer who has held her place in public estimation for nearly thirty years, Madame Albani. While she was not such a marvellous colorature singer as Patti or Gerster, she combined so many excellent qualities that she is justly entitled to a position among the great singers of the century. As one critic expressed his opinion, she was "beautiful, tuneful, birdlike, innocent, and ladylike," to which might be added, "always reliable."
Madame Albani's family name was Marie Louise Cecilia Emma Lajeunesse, and she was born, in 1850, of French-Canadian parents at Chambly, near Montreal. Her father was a professor of the harp, so she began life in a musical atmosphere. When she was five years of age the family moved to Montreal, and she was placed in the convent of the Sacre Cœur, where she received her{188} education, and such musical instruction as the convent could provide. In 1864 the family again moved, this time to Albany, N. Y., and when Mlle. Lajeunesse entered upon her professional career, she adopted the name of this city, because it was here that she decided upon becoming a professional singer.
While singing in the choir of the Catholic Cathedral she attracted the attention of the bishop by her beautiful voice, and he strongly urged her father to take her to Europe, and place her under proper masters for the development of her remarkable talent. To provide the necessary funds, a concert was given in Albany, after which Mlle. Lajeunesse and her father proceeded to Paris, where she commenced her studies with Duprez. After some months she went on to Milan, where she became a pupil of Lamperti, who thought so highly of her that he dedicated to her a treatise on "the shake."{189} In 1870 she made her début at Messina, in the Sonnambula, after which she sang for a time at Florence.
In 1872 she obtained an engagement in London, and on April 2d appeared at the Royal Italian Opera, Covent Garden. The beautiful qualities of her voice and the charm of her appearance were at once appreciated, and before the end of the season she was firmly established in the favor of the public. Later in the season she appeared in Paris, and then returned to Milan for further study, but so favorable an impression had she made, that she was engaged for the season of 1873 in London. She then went to St. Petersburg, after which she revisited America, and sang again in the Cathedral at Albany.
In 1878 Albani married Mr. Ernest Gye, the lessee of Covent Garden Theatre, and for many years was one of the permanent attractions at that house. She has visited America several times, and has also sung in{190} most of the large cities of Europe, where her reputation has been steadily maintained.
Madame Albani's honors have not all been won in opera, though she has an immense repertoire, including Italian, French, and German operas. She is also one of the foremost concert and oratorio singers, and has had the honor of creating numerous soprano parts at the great festivals. At the request of Sir Arthur Sullivan, she travelled from Brussels to Berlin expressly to sing the part of "Elsie" in the "Golden Legend," at its second performance in that city. She had created the part when it was produced in 1886.
In England, where Madame Albani has made her home for so many years, she is as popular and as highly respected on account of her domestic life, as on account of her artistic career, and her friends are not only numerous but include many of the most intellectual people of the day.{191}
Notwithstanding the success which Madame Albani made in England, France, Russia, and other countries, she had her trials and disappointments. At one time, when she was singing at La Scala, in Milan, she was suffering from a slight hoarseness. Most audiences would have been indulgent, but not so the Milanese, who are particularly cruel to singers who have made their reputation in other places. The Milanese hissed and groaned. Huskiness in a singer was, to them, a crime. The tenor, seeing how matters stood, was taken with a sudden indisposition, and left Albani to carry on the performance alone. The opera was "Lucia," and it proceeded no farther than the mad scene, for Madame Albani, indignant at the treatment accorded her, turned her back on the audience, and in a most dignified manner, marched off the stage, leaving the curtain to fall on a scene of confusion. No entreaties or arguments on the part of the{192} impresario would induce her to finish the opera, or even to continue her engagement at La Scala.
Colonel Mapleson tells this story concerning Albani's first London engagement. He heard of her singing at a small theatre at Malta, and, thinking that she would be successful, he made her an offer, through an agent, of a contract to sing at Her Majesty's Theatre. She agreed to it, and went to London, but, on arriving there, she told the cabman to drive her to the "Italian Opera House." He, instead of going to Her Majesty's, took her to Covent Garden, which was also devoted to Italian opera. She was shown up to the manager's office, and stated that she had come to sign the contract which Mr. Mapleson had offered her. Mr. Gye, thinking to play a joke on his rival, Mapleson, made out a contract, and Albani signed it. Mr. Gye then told her that he was not Colonel Mapleson, but that he could do much{193} better for her. He offered to tear up the contract if she liked, but told her that Nilsson was singing at Her Majesty's and would brook no rival. Albani decided to let the contract stand, and thus became one of the stars of Covent Garden, eventually marrying the son of Mr. Gye.
Concerning Albani's singing in Berlin, the Berliner Tageblatt said: "The lady possesses an exceedingly peculiar organ, trained in a remarkable manner, and no one else has a voice which can be compared to it. It is not extensive in its range; the lower chest notes of the one-line octave might be fuller and more powerful, but the upper register is distinguished for enchanting sweetness, unfailing correctness, and, what is especially worthy of notice, a softness enabling the lady to breathe forth the gentlest pianissimo in passages which others can reach only with the greatest effort. Runs, staccatos, and shakes are not merely{194} certain and pleasing, but, as regards form, so graceful that we listen to them with delight."
An interesting anecdote concerning Madame Albani, and one which may tend to confirm the faith of those who doubt theorists, is to the effect that, when she was young and unknown, she paid a visit to a throat specialist, who had a theory that, by examination, it is possible for an expert to tell whether the possessor has an organ susceptible of producing a fine singer, even if he does not know music, and never sang a note.
After examining Albani, without knowing her particular reason for consulting him, he exclaimed: "My dear young lady, Nature has given you a wonderful organ. You can, if you will, become one of the greatest of singers. If you possess dramatic ability equal to the endowment of your throat, you can become a famous lyric artist, and I advise{195} you to devote your energies to the cultivation of your powers."
The young singer thanked him, and disappeared. Some years after, he went West, and one day in Chicago, a handsomely dressed lady entered his office. "Don't you know me?" she said. But he was unable to recall her last visit, until she revealed her name, and related the whole incident, when he seemed very much surprised at the proof of his own wisdom.
In 1898 Madame Albani paid a visit to South Africa, where she had a grand reception. After a career of nearly thirty years, she is still as popular as ever.
The history of Emma Abbott is one which will be read with interest by all struggling and ambitious young people, for it is a story of brave battling against innumerable difficulties. Miss Abbott was the daughter of a poor music teacher, of Peoria, Illinois. Her early years gave her an acquaintance{196} with hardship which, perhaps, enabled her to keep up her courage in the face of all obstacles. Imbued with the desire to help the family finances, she got the idea of giving a concert on her own account, for even as a small child she had a beautiful voice. At the age of thirteen, when she went to Mount Pulaski, on a visit to some friends, she put her idea into execution. She was trusted by the printer for her programmes and handbills. She posted her notices with her own hand, and secured a good audience. Her proceeds amounted to ten dollars, of which three dollars went to settle her bills, and with the remaining seven dollars she returned in triumph to her mother. After this, she gave guitar lessons to pay her schooling. At the age of sixteen, she heard of a vacancy for a school-teacher, and walked nine miles to see the school committee, with the result that, in recognition of her pluck, the place was given to her. Four months later{197} she gave her first large concert in Peoria, and made one hundred dollars. She now travelled to various places giving concerts and fell in with an opera company from Chicago, the manager of which induced her to join the company. In due course the company broke up, and Miss Abbott found herself without money, but a kind-hearted railroad man advised her to go to New York, and present herself to Parepa-Rosa. He gave her a pass to Detroit, and then she was to go through Canada, and so to New York. Her journey was managed in the face of tremendous obstacles. She gave concerts, but found little response to her efforts. She frequently had to walk from one town to another. Once she had her feet frozen and many times she suffered from hunger. At last she reached New York, but, in spite of all her efforts, failed to reach Parepa-Rosa, and with her last fifteen dollars, she set out for the West again.{198} While in Toledo she heard that Miss Kellogg was in town, and she called at her hotel and asked to see her. She sang for Miss Kellogg, who received her kindly, and who was so pleased with her that she gave her a letter to Errani, New York, and enough money to enable her to study for two years.
Thus ended her bitterest struggles. After studying some time she secured the position of soprano in the choir of the Fifth Avenue Church, with a salary of $1,500, and on May 20, 1872, she set off for Europe with a large sum of money subscribed by the wealthy people of the church, whose admiration she had gained by her voice and her character.
She soon made her début in Paris, and made a sensation. In Paris she married Eugene Wetherell, a young druggist of New York.
If Miss Abbott is not enrolled among the great opera singers, it is because her ambition{199} led her away from the beaten track, for, having made a reputation, she established an opera company of her own, which existed in America for several years, and enabled her to make a fortune estimated at half a million dollars. Her husband died in 1889, and his loss was a blow from which she never fully recovered. She was herself taken away in her prime in 1891.
In 1873 a young singer made her début at Dresden, who was destined to achieve a high reputation as an interpreter of Wagner, and to rival the greatest stars of her school. Thérèse Malten, who was born at Insterburg, Eastern Prussia, appeared in Dresden as Pamina, and as Agatha. For nearly ten years she sang only in Dresden, taking many of the soprano rôles in Italian opera. In 1882 she sang at Bayreuth, as Kundry, at the desire of Wagner, who had a very high opinion of her ability, which was amply justified by the results.{200}
In London she appeared in May, 1882, when she made a great impression, and the critics declared that, though her art in singing was not so perfect as Materna's, her voice was fresh, magnificent, powerful, and that she had great personal beauty. Besides possessing a voice of extraordinary compass, with deep and powerful notes in the lower register, she was considered an admirable actress. In 1883 she was chosen by Wagner to sing the part of Isolde at Bayreuth, when she was described, amidst all the praise that was bestowed upon her, as a young singer who was never known out of Dresden until she sang in London the previous year.
Madame Katharina Lohse-Klafsky, who was born in the same year as Malten, and was for several years prima donna at the Hamburg Opera, visited America in 1895, and died unexpectedly at Hamburg the following year as the result of an operation.{201} She was a native of Hungary, and began her career in Italian opera, though she was best known as a Wagnerian singer. She had a large repertoire, and created the part, in German, in "La Navarraise." She met with great success in London in 1892 and 1894. She had a full, rich-toned voice and a handsome stage presence.
A career of exceptional brilliance, but all too brief, was that of Etelka Gerster, who was born at Koschau, in Hungary, in 1856. Her father was a merchant, and brought up his family to refined tastes. All his children were fond of music, but none seemed to think of special musical study until a visiting friend from Vienna spoke of the promise which he thought lay in Etelka's voice.
This gentleman asked permission to bring his friend Hellmesberger to hear her, and some time later the visit took place. Doctor Hellmesberger endorsed the opinion already given, but said that there was only one judge{202} of such matters in Vienna,—Madame Marchesi A visit was therefore made to Vienna, with the result that Mlle. Gerster became a pupil of Marchesi, and after a year of hard study won first prize at the Conservatoire.
About this time "Aida" was brought out at Vienna, and the composer Verdi came to superintend its production. He visited the Conservatoire, and a little soirée musicale was given in his honor. On this occasion Gerster sang several pieces, and Verdi was so pleased that he advised her to go on the stage.
Soon after this Gerster got an engagement to sing at Venice under the management of Signor Gardini. She spent two seasons singing in Italian and Spanish towns, but in 1877 she appeared in Berlin at Kroll's Theatre. This engagement was the turning-point of her career, for by the magic of her voice she turned the second-class theatre into a resort to which the nobility flocked{203} every night, and the venerable emperor and his court always held the front row of seats.
For three weeks the company, composed of singers unknown to fame, sang to empty houses. Then, whispers of the fact that Kroll's Theatre had a singer of extraordinary ability resulted in increasing audiences. The emperor came and was delighted, and an invitation to sing at court was the result. After this triumphant engagement, Gerster married her manager, Signor Gardini, while they were in Pesth.
Compared with many prima donnas, Madame Gerster's life has been uneventful. Her position as a singer was as a representative of the old art of beautiful singing. She charmed with gracefulness, smoothness, and exquisite finish of execution, and the most perfect musical taste, which every phrase, even in the most florid passages, revealed. She could not awe, like Pasta, but she could fascinate and charm. She{204} was not a great actress, but she was graceful and pleasing on the stage.
Madame Gerster visited the United States several times, but at the end of the season of 1881 she declared that she would never sing again under the management of Colonel Mapleson. He had hurt her feelings by neglect. He had called on other members of the company, and showed various little attentions to them, but he never called on her nor inquired about her health when she was not feeling well, and finally went off to Europe without saying "Good-by." This hurt the feelings of Signor Gardini, as well as those of his talented spouse, but she nevertheless returned as a member of his company in 1883-84, when there was great rivalry between Gerster and Patti. On approaching Cheyenne, Patti insisted on having her car detached from the train and making a separate entry, as she could not bear to share the admiration of the multitude with Gerster.{205} During this tour there was one occasion on which, Patti and Gerster appearing together, Patti received so many flowers that the audience were weary with the delay caused by handing them over the footlights. When this ceremony was over, one small basket of flowers was handed for Gerster, but the audience arose and gave her a tremendous ovation. Henceforth Patti refused to sing with Gerster, and open war was declared, Patti declaring that Gerster had "the evil eye," and Gerster saying pointed things about Patti, as, for instance, when the aged governor of Missouri, in a burst of enthusiasm, kissed Patti, and Gerster, on being asked her opinion about this frivolity, said that she saw no harm in a man kissing a woman old enough to be his mother.
In 1885 Gerster came again to America on a concert tour, but her beautiful voice had gone. She sang twice in New York, and made a most dismal failure, so she gave{206} up the tour and went home, much to the regret of Americans who remembered the days when her singing gave the most exquisite delight.
Signor and Signora Gardini had a beautiful estate in the Campagna of Italy, to which they retired between seasons, and where they enjoyed entertaining their guests. Signora Gardini was devoted to the cares of her household, and proved herself to be an excellent housekeeper and an accomplished cook.
In this home nothing was wanting to make it a most delightful place of residence for even such a spoiled child as a prima donna. But alas! this happy life was destined to end very soon. Colonel Mapleson in his memoirs declared that Gerster was a most difficult person to get along with, and now Signor Gardini was forced to the same conclusion, for it was reported that the beautiful prima donna was in the habit of{207} giving way to frightful outbursts of temper. To this cause is attributed the loss of her voice, as well as the loss of her husband. The "Villa Mezzana" was closed, and portions of the estate let to various small farmers. Madame Gerster went with her children to Paris, but soon after moved to Berlin and became a vocal teacher. She was only twenty-eight years of age when at the height of her fame, and at thirty her career was over. Referring to Mapleson once more, who was never inclined to mince matters when he was annoyed by a prima donna, we get the following anecdote. While travelling between Louisville and Chicago, the sleeping-car in which Gerster was travelling broke down and had to be side-tracked. Madame Gerster was requested to change into another car, as it was impossible to continue in the one which she was occupying, but she positively refused to move. She had paid to ride in that car, and{208} in that car would she go and in no other. No arguments could induce her to change her mind. At last an expedient was discovered,—the station agent at the nearest place was a remarkably fine-looking man. He was dressed up and introduced to her as the president of the road. He flattered her till she began to soften, and then told her that the company would be under great obligations to her if she would consent to use another car. He had a Brussels carpet laid from the door of her car to that which she was to occupy, and the lady, pleased at the deference shown to her by so high an official, at last consented to make the change.
Some of the press criticisms of Gerster's performances during her tour in 1881 were highly amusing. The following were selected from a paper published in a large Southern city: "Mrs. Gerster's Lucia is the Lucia of our youth, and our first ecstasies{209} arose as from a nest of flowers as fresh and adorable as ever," whatever that may mean. What it ordinarily described as a walk was pictured in the following mysterious sentence: "Her light tread as of a restless and frightened bird." Some of her trills were described as "aflame with passionate intoxication," while others were "white and wet with the tears of grief." All this excellence was manifested with "never a scream to mar her singing." Such admirable descriptions must have gone far towards reconciling those who were unable to see and hear the great songstress.
There is and has been much fault to find with American musical criticism. Excellent musicians have been subjected to the vulgar abuse of self-sufficient ignoramuses. A movement was recently put on foot to establish a school of musical journalism, and possibly the following selection, which was written concerning a lady of excellent musical{210} ability and of world-wide reputation, may be allowed here as an argument in favor of a proper training for critics. For absolute vulgarity it may be awarded a first prize. It was written in 1882 in a city which lays claim to civilization, and the only excuse for its introduction is the hope that it may serve a good end.
"The divine —— was as resolute as usual, which, by the way, she ought to be, being well seasoned. The editor of this paper makes no great pretensions in the way of musical criticism, but when a genuine six hundred dollar grand spiral subsand twist, back-action, self-adjusting, chronometer-balanced, full-jewelled, fourth-proof, ripsnorting conglomeration comes to town, he proposes to hump himself. Her diaphragm has evidently not, like wine, improved with old age. Her upper register is up-stairs near the skylight, while her lower register is closed for repairs. The aforesaid —— performed her triple act of singing, rolling her eyes, and speaking to some one at the wings, at the same time. Her smiles at the feller behind the scenes were divine. Her singing, when she condescended to pay attention to the audience, to my critical ear (the other ear being{211} folded up) seemed to be a blending of fortissimo, crescendo, damfino or care either. Her costume was the harmonious blending of the circus tent and balloon style, and was very gorgeous, barring a tendency to spill some of its contents out at the top. The Italian part of the business was as fidgety and furious as usual, and demonstrated what early associations with hand-organ and monkey will accomplish.
"The venerable and obese freak of nature,——, was as usual, his appearance very nearly resembling a stove in a corner grocery, or water-tank on a narrow-gauge railroad. He was not fully appreciated until he turned to go off the stage. Then he appeared to the best advantage, and seemed to take an interest in getting out of sight as quickly as possible, an effort in which he had the hearty approval of the audience."
Maurice Strakosch, on behalf of Christine Nilsson, brought suit against a paper published in a large town in New York State for printing an article under the head of "Nilsson Swindle," in which the bucolic editor declared that Nilsson was no singer and could not be compared with Jenny Lind;{212} therefore she had no right to charge Lind prices.
Marcella Sembrich, who made her début in 1877 as an opera singer, is one of the most talented musicians of the century. She was born in Galicia, at Lemberg, in 1858, and was taught music by her father, while very young. She appeared in a concert at the age of twelve, playing both the pianoforte and the violin. She continued her studies on these instruments under Stengel and Bruckmann, professors at Lemberg, and then went to Vienna to complete her studies under Franz Liszt. Here, however, she was found to be the possessor of an unusually fine voice, which she began to cultivate under Lamperti the younger, and she decided to become an opera singer.
Her engagement in Athens, where her début took place, was highly successful, and she next appeared at Dresden in October, 1878, where she remained until the spring{213} of 1880, acquiring a high reputation. In June of that year she made her first appearance in London, under the management of Mr. Ernest Gye, and was so successful that she was engaged for the two following seasons.
Of the impression made by her in London, one of the critics wrote: "Her voice has been so carefully tutored that we cannot think of any part in any opera, where a genuine soprano is essential, that could present difficulties to its possessor not easily got over per saltum." Sembrich was included with Patti, Gerster, Di Murska, and Albani, as one of "the great lights of the day," in 1880.
In St. Petersburg Mlle. Sembrich once gave a concert which drew an immense audience, all the tickets being sold. The receipts, which amounted to over nine thousand rubles, were handed over to the poor students' fund. At this concert, the audience{214} had the opportunity to admire her in the capacities of singer, violinist, and pianist. As a violinist she could be listened to with pleasure; as a pianist she was considered worthy of a place in the front rank, particularly as an excellent interpreter of Chopin, while as a singer she was one of the "great lights of the day."
Mlle. Sembrich married her former teacher, Stengel, and has for many years made her home in Dresden.
She is an ardent horse-woman, and is said to have called forth a somewhat doubtful compliment from the Emperor of Germany, when her horse became frightened during a military review, and she succeeded in managing the animal with great skill. "Madame," said he, "if you were not the greatest singer in the world, you would be empress of the circus."
In 1897 Mlle. Sembrich made a tour of the United States, singing in concerts in{215} most of the large cities, and fully maintaining her high reputation.
In 1879, at Turin, another young American singer made her début, at the age of eighteen. Marie Van Zandt came of a New York family of Dutch extraction. Her mother was a singer of some renown, and had been a member of the Carl Rosa company. Marie was taught singing by Lamperti, and after her début in Turin she went to London, and appeared at Her Majesty's Theatre, where she was well received on account of the freshness of her voice and her unaffected style. The following year she appeared in Paris at the Opera Comique as Mignon, and made such a success that she was immediately engaged for a term of years.
Although her voice was extremely light, it was of sweet quality, and marvellously flexible. Her success in Paris was instantaneous, and she became the pet of society, besides which she was, strange to say, well{216} liked by her fellow artists, and admired by her impresario. Ambroise Thomas, the composer, declared her to be the very impersonation of Mignon, and she sang in that rôle sixty-one nights to crowded houses. It is doubtful whether any singer ever won more rapid fame. At the end of her season she had impresarios from Sweden, Russia, England, and America offering her engagements. It is said, too, that no less than six composers wrote operas for her, and that Delibes's "Lakmé" was one of these.
In November, 1884, Rossini's "Barbiere" was revived, and Miss Van Zandt was cast for the leading part. She was, however, so overcome by nervousness that she lost her voice, and was, in consequence, treated most shamefully by the press and public of fickle Paris. She therefore obtained leave of absence, and played in Copenhagen and other places, appearing in St. Petersburg on December 17th. In 1885,{217} when she returned to Paris, the hostile attacks upon her were renewed, and M. Carvalho agreed to break the contract. Notwithstanding a riot, which was carried on chiefly by a mob of about a thousand persons, who surrounded the Opera House, Miss Van Zandt made a great success. The people in the house, with a few exceptions, gave her a double recall, men waved their hats, women their handkerchiefs, and there was an immense burst of applause. The rioters kept at the back of the boxes.
She now went to London and created a great impression in "Lakmé," at the Gaiety Theatre.
An incident of her early career in Paris carried with it a certain amount of romance. A young Frenchman bribed her cabman to take her to a certain restaurant after the opera, where he and his friends were waiting to invite her to supper. Through the vigilance of her mother the plan was frustrated,{218} but the story of the incident reached America, and came to the ears of a young man who had been an early playmate of the prima donna, and whose affection had grown stronger as time passed on. He went over to Paris, and challenged the young Frenchman to mortal combat. The Frenchman acknowledged the irreproachable character of Mlle. Van Zandt, but expressed himself as being quite at the service of the gentleman for any amount of fighting. Details of the fight are not on file.
Miss Van Zandt was born in Texas, where her father owned a ranch, and her childhood was spent in the enjoyment of the free life of the plains. Her family later removed to New York, and then to London. She met Adelina Patti, who was so pleased with her voice that she gave her every encouragement, and is said to have called her her successor. But there have been so many successors of Patti!{219}
A few years after Miss Van Zandt's début, an amusing rivalry sprang up between her and another young American soprano, Emma Nevada. So bitter was the hostility, that one evening, when Miss Van Zandt was taken ill suddenly during the performance, her friends went so far as to declare that she had been drugged by the adherents of Miss Nevada. Such little quarrels are frequent among prima donnas, and are doubtless largely engineered by the newspapers, whose appetite for the sensational is enormous.
On April 27, 1898, at the mayoralty of the Champs Elysées district in Paris, Marie Van Zandt was married to Petrovitch de Tcherinoff, a Russian state councillor, and professor at the Imperial Academy of Moscow, after which it was announced that she would retire from the stage.{220}
To every opera-goer of the past ten years the name of Nordica has become almost as familiar as that of Patti was during the last generation. Nordica, or rather, Giglia Nordica, was the name assumed by Lillian Norton when she made her début on the operatic stage. She was born in Farmington, Me., and at the age of fifteen, giving great promise as a singer, she entered the New England Conservatory in Boston, Mass., where she studied voice under John O'Neil. Three years later she graduated from the Conservatory with honors. She was remarkable for her beauty and amiability as much as for her voice, which was a soprano of the{221} purest kind. During her years of study at the Conservatory she gained much experience by singing in church and in concerts, and for a time she accompanied Samuel R. Kelley's Tableaux d'Art Company, receiving for her services as vocalist the modest compensation of five dollars an evening.
On leaving the Conservatory, she was invited to sing in concerts in Philadelphia, Baltimore, Cleveland, St. Louis, and New York, where she took leading parts in the oratorios of "Elijah," "Creation," "Messiah," etc. In 1873 she was engaged for a concert tour in England, Scotland, Ireland, Belgium, Holland, and France, during which her repertoire consisted of classical music only. During this tour she sang at the Crystal Palace, near London, and at the Trocadero in Paris. She then went to Milan, where she studied opera under Signor Sangiovanni, and made her operatic début at Brescia, in "Traviata."{222}
In October, 1880, she was engaged at Genoa for fifteen performances of "Faust," in which she took the part of Marguerite. She next sang at Novara, where she took the part of Alice in "Roberto," and was afterwards engaged for thirty-five performances at Aquila in "Faust," "Rigoletto," and "Lucia."
Her next engagement was in St. Petersburg, where she sang in "L'Africaine," taking the rôle of Inez, in "The Marriage of Figaro" as Cherubino, in "Mignon" as Filina, in "Ugonotti" as Queen Marguerite, in "Don Giovanni" as Zerlina, and in "Il Propheto" as Berta, besides other operas. Thus she acquired in a comparatively short time, and by dint of extremely hard work, quite an extensive repertoire.
In 1882 she endured the crucial test of the Grand Opera House in Paris, where, in spite of the "Claque," which is so frequently organized to kill off new singers, she made{223} a grand success, and an engagement for three years ensued. Some years later, however, in spite of the renown which she had gained, fickle Paris grew cold, and critics were laconic. At this time Nordica did not need the approval of Paris, for she was well established among the great singers of the period, and it is recognized that, while a success in Paris is considered an important conquest, a failure counts for little. The firm establishment of the "Claque," which is so well described by Mr. Sutherland Edwards, and the proverbial caprice of Parisian audiences, are sufficient to take the edge off of defeat. At the termination of her engagement in Paris, in 1883, Nordica married Mr. Frederick A. Gower, who shortly afterwards was supposed to have lost his life while attempting to cross the English Channel in a balloon. This matter remained a mystery for many years, for, while there was no doubt that he started on the perilous{224} journey, nothing was ever after seen or heard of him or of the balloon. The question of his death, therefore, remained in doubt, and when, after a lapse of more than a dozen years, it was announced that Madame Nordica was about to enter the bonds of matrimony a second time, she suffered much annoyance from the rumors which were spread about to the effect that Mr. Gower was in various parts of the world. These rumors never proved to have any foundation, and, except for the annoyance, must have been somewhat flattering as evidence of the interest taken in the prima donna by the public.
In 1887 Nordica sang in Berlin, and made a complete capture of the Berlinese, a most unusual achievement for an American prima donna. She also appeared in London at Drury Lane, and by the sweetness and freshness of her voice, and by the alternating charm and intensity of her style as an{225} actress, she won a firm and lasting hold on the British public. She now enjoyed the most marked social attentions, and sang at a state concert at Buckingham Palace before an audience composed of princes, princesses, dukes, Indian royalties, etc. The Princess of Wales came forward and thanked her, the prince added his word, and her triumph was complete. The climax was reached, however, when she was commanded by the queen to sing in Westminster Abbey. She sang "Let the bright Seraphim," which selection has for years been the standard for state occasions. Indeed, it may be said that when a prima donna has been commanded to sing "Let the bright Seraphim," in Westminster Abbey, she has achieved the highest honor possible in England. Madame Albani has exceeded this in having had the honor of lunching with the queen, but this latter was more a tribute to her worth as a woman than as an artist.{226}
One of Nordica's greatest assumptions has been that of the rôle of Elsa in "Lohengrin." She has the feeling, the artistic understanding, which, combined with beautiful vocal gifts, brings out the most delicate shading of the part. It is doubtful whether any greater representations of "Lohengrin" have been given than when Nordica sang Elsa, and Jean de Reszke the title rôle.
Her success in such parts led her to devote her attention more particularly to Wagnerian rôles, and in 1894 she sang with great success at Bayreuth.
Nordica has for several seasons visited the United States as a member of the Abbey and Grau Opera Company, which contained such singers as Emma Eames, Melba, Calvé, Scalchi, the De Reszkes, Plançon, and Lassalle. In 1897, when Abbey and Grau failed, Madame Nordica was a creditor to the extent of $5,000. When the affairs of the company were arranged, an agreement{227} was reached with Madame Nordica, by which she was to receive $1,000 a night. To her surprise, she afterwards discovered that Melba was to receive $1,200, Calvé $1,400, Jean de Reszke $1,200, with an additional percentage of the receipts. To add to her humiliation, the part of Brunhilde was given to Madame Melba, whose health, by the way, collapsed suddenly after her first performance of that part, and necessitated a speedy departure for Paris. Nordica left the company, and in doing so had the moral support of the public, for, while there were many complaints about the excessive salaries demanded by opera singers, there seemed to be no reason why Madame Nordica should not insist upon her share. Statements were also made to the effect that Jean de Reszke would never again sing with Nordica.
The years 1896 and 1897 were years of much financial depression in the United States, a fact which does not seem to have{228} been fully appreciated by opera singers, for the collapse of the season seems to have given rise to considerable bitterness of feeling.
Madame Nordica took unto herself Madame Scalchi, the contralto, and Barron Berthald, a young tenor, who in a night achieved fame, and toured the country giving concerts, but with little success. Whatever truth there may have been in the reported coolness between Madame Nordica and Jean de Reszke, either diplomacy or the exigencies of the opera singer's hard lot brought about an ostensible reconciliation; for in London, during the opera season of 1898, Jean de Reszke sang Tristan with Madame Nordica as Isolde, when a critic wrote, "We have so often been told that this music cannot be sung, and we have so often heard it shouted and declaimed by Tristans who could not sing, and by Isoldes without a voice, that it was a double joy, not only to hear it sung, but to hear it superbly sung,{229} with all the confidence and apparent ease one is accustomed to in a Schubert song, or a Massenet romance."
Madame Nordica is now in her prime. What new honors she may win we cannot foresee, but she now stands high in the front rank of the great singers of the day. In 1896 she married Mr. Zoltan Doehme. The engagement, which had been once broken off, came to a sudden climax while Nordica was in Indianapolis. Mr. Doehme suddenly appeared, having travelled from Germany, and in a few hours they were married without any display or previous announcement.
Madame Nordica wins many friends by frank, engaging cordiality of manner, while her impulsive nature and enthusiasm help her over many difficulties. One may imagine the consternation caused in the Boston Symphony Orchestra by her startling declaration, at a rehearsal, that they were like a Kalamazoo band. Perhaps the sore is still{230} open, but her winning manners will close it the next time that she comes among them.
One of the most brilliant singers among the number of Americans who have, during the latter half of this century, won distinction on the operatic stage, is Emma Nevada. She is the daughter of a physician named William Wallace Wixom, of Nevada City, Cal.
As a child she was so musical that she sang in public when only three years old. Her mother died when she was quite young, and she received her education at a seminary in Oakland, California. She was now consumed by a desire to go to Europe and make a study of voice, and she became one of a party of girls under the care of a Doctor Eberl, who was to escort them and keep them under his protection in Berlin. When the vessel anchored in the Elbe, the passengers were transferred to a smaller steamer to be landed. Dr. Eberl went on board the little steamer with the rest, walked into the{231} cabin and died. This was a terrible calamity for the party under his care, but Emma Wixom succeeded in finding her way to Berlin, where she sought advice with regard to her voice, and was recommended to go to Marchesi at Vienna.
It is said that on reaching Vienna she found her funds exhausted, but she sought Madame Marchesi and told her her circumstances. Marchesi was so much captivated by her voice and manners that she offered her a home and took care of her until her début.
Through Marchesi's influence an engagement was secured for her in London, where she made her début in "Sonnambula" in 1880. On making her appearance in public, Miss Wixom followed the custom of assuming the name of her native place, and so became Emma Nevada. Concerning her début a critic of the time wrote: "Mapleson has brought a new prima donna, Mlle. Nevada, who is gifted with a very light{232} voice, which is, however, extremely flexible, and is used very effectively in the upper registers. The great merits of her voice lie in her staccato effects, chromatic runs,—which she gives with great purity,—and notes in altissimo. The defects are excessive lightness of tone, lack of good lower notes, and a rather imperfect trill. She won many friends by her refined manners and culture, and if not a great singer she is certainly an agreeable one."
Another admirer tells us about a performance of "Lucia." In the roulade duet between the flute and the voice, after the competition was ended and her full, firm shake, as effortless as the simplest strain, was about half over, she ran off the stage, the shake continuing just as perfect all the way, and as she disappeared left a final note away up among the clouds. But with all this brilliant execution she delighted as much by her sustained notes, which were{233} of beautiful, flutelike quality. She also won the affection and respect of all her associates, by her kindly ways.
A staccato polka was written for Mlle. Nevada, with a view to exhibiting her voice, and her rendering of it was considered a marvellous exhibition of vocal technique.
Although her voice was criticised as being too light for grand opera, Mlle. Nevada was engaged at once to sing in Italy, after which she sang in 1883 at the Opera Comique in Paris, and has had an exceptionally successful career, both in Europe and America, where, in 1885, she was warmly welcomed. In April, 1898, Emma Nevada sang in Paris after a tour through Holland, showing no diminution of her artistic powers.
A little anecdote was told concerning a performance of "Lucia" in Paris, which tends to show the kindly disposition, of the young prima donna. She was, in the mad scene, accompanied in a most delicious manner{234} by the flutist in the orchestra. One was often puzzled during the celebrated duet to determine which were the notes of the flute and which were those of the singer. Now and then a pathetic vibration would reveal the human voice and cause it to rise triumphant above the instrument. She taxed the skill of the musician to the uttermost to follow her through the intricate mazes of sound. When, through nervousness, she for a moment forgot the words of her song, the humble musician came to her rescue and improvised a few sparkling variations to enable her to regain her breath and recollect the lost phrases. At the end of the duet, two powdered footmen advanced from the wings with a gigantic basket of flowers which had been sent to her from Rome by some friends. She selected the finest rose, and, advancing to the footlights, handed it to the leader of the orchestra to be passed on to the flute player. The action was taken{235} with much grace and spontaneity, and brought down a storm of applause, while the poor flutist, unaccustomed to the recognition of his talent, was overcome with joy at such a graceful acknowledgment.
One of her trials took place when the Edgardo (Gayarré), who more than simulated jealous rage, knocked her about in good earnest. His violence made her forget everything but her part, and she had no chance to think of the public while trying to keep her wrists out of his reach.
In 1884 Mlle. Nevada had a disagreement with M. Carvalho about a costume. He offered to cancel her contract, and she joyfully accepted the offer, after which they both had ample time to repent of their hasty action. The following year she married Doctor Raymond Palmer, a surgeon practising in the west of England, a big, bluff, handsome Englishman. She was small, slight, and graceful.{236}
The marriage, which took place in Paris, in October, 1885, was a great social event in the American colony in Paris. Speeches were made by Consul-General Walker and others. Ambroise Thomas, the composer, was there, and called her "Mignon, my dear interpreter," on which she rose from her seat, went to him, put her arms around his neck, and kissed him. The wedding presents were many and valuable, and the descriptions thereof filled many columns of the newspapers. Never before had an American prima donna been the centre of so much excitement.
After a short honeymoon, a concert tour in the United States was undertaken. Madame Nevada did not retire from the stage, but after fifteen years she is still as popular as ever, though her voice is too light to be effective in any of the grand operas of modern times.
Unquestionably the greatest artist of her{237} school on the opera stage at the present day is Emma Calvé, whose proper name is Emma Roquer. She was born in 1866, at Décazeville in the Aveyron, her father being a civil engineer, and a member of a good Spanish family. He unfortunately died when his daughter Emma was sixteen years of age, and left his family in poor circumstances. Emma, who was the eldest child, was brought up in a convent, the quiet life of which was very attractive to her, but she was prevented from taking the veil because her mother needed her help at home.
A gentleman from Paris, who heard her sing one day in the convent chapel, urged her mother to send her to Paris for musical training, and much against her own wishes the young singer began the course of training which led to her appearance on the operatic stage.
Life has not been all sunshine for Emma Calvé. She has acquired her art in the{238} school of adversity. Her early stage experiences were not highly successful, though she was reëngaged. Her début was made at Brussels at the Theatre de Monnaie, as Marguerite in "Faust," in 1881. During this season she received a salary of a hundred and forty dollars a month, which was increased the next year to two hundred and forty. In 1884 she went to Paris, where she created the leading part in "Aben Hamet," by Dubois, at the Theatre Italien, and was decidedly successful.
Her teachers up to this time had been a tenor named Puget, and Laborde, but she now began to study under Madame Marchesi, and then followed a successful tour in Italy, during which she gained much by association with the Italian people, and cultivated her dramatic instincts. Here she saw Eleanora Duse, the great actress, whose impersonations made a great impression on the young singer. Calvé's impassioned acting,{239} her magnetic personality, and beautiful voice, won for her the greatest success at La Scala. In 1889 she returned to Paris, and continued her career of hard work and success, but the day of her greatness had not yet come.
In 1891 she created the part of Suzel in "L'Amico Fritz," at Rome, an event which added greatly to her renown, and when "Cavalleria Rusticana" was given in Paris for the first time in 1892, Calvé was selected as the most fitting interpreter of the part of Santuzza. Her success in this part was something phenomenal, and was gained after much study of the story, the close intercourse she had made with the Italian people, and by the aid of some suggestions from Mascagni, the composer.
Her success as Santuzza was repeated in London, and, after ten years of unremitting labor, Calvé found herself acknowledged as a great artist. Notwithstanding the excellent{240} quality of her voice, and her mastery of technique, her victories have been gained by her dramatic impulses.
Her next triumph was achieved in the character of Carmen. In order to study for this part she went to Spain, where she learned the Spanish dances, associated with the Spanish people, and learned as much as possible of the character of the Spanish peasant.
In 1894 she appeared at the Opera Comique in Paris, as Carmen. Her triumph has become a matter of history. It was one of the greatest events in the annals of the lyric stage. Patti had played Carmen, Minnie Hauk had played Carmen, Madame Galli-Marié had played Carmen, and all had achieved success in the part; but Calvé was Carmen. Her conception of the character was a revelation. Her fascinating gestures, her complete abandon, the grace of her dances, her dazzling beauty, all combined{241} to make her Carmen one of the most wonderful impersonations ever given in opera. She has been criticised as uncertain, as giving different interpretations at different times, but the fact remains that Calvé stands pre-eminent in the world of operatic art. Her swinging, graceful walk, her fascinating half Oriental dances, her gestures, her infectious, reckless mirth, all help to make up the dazzling impersonation with which her name is associated.
Of Calvé's voice little has been said, because, in the perfection of her art, the voice is not obtrusive. It is light and sympathetic, rich in quality, and she never forces it. She frequently misses what many singers would seize as a vocal opportunity, for the sake of dramatic effect, and yet her singing has a marvellous charm. The "Havanaise," as sung by Calvé, is something to remember for a lifetime.
Calvé has a superb, lithe form, and her{242} large, dark eyes and delicately modelled features give her a charming appearance. She is frank, cordial, young-spirited, easy-going, and is intensely admired, both by her associates at the theatre, and in the drawing-room. She is a curious combination of the developed woman and the simple girl. No one can prevent her from saying and doing as she pleases, but her impulses are seldom unkind. She believes thoroughly in spiritualism, theosophy, and astrology. Whenever she sings, she carries with her an amulet from Hindostan, and nothing can induce her to appear without it.
Her first visit to America was in the season of 1893-94, during which she appeared as Mignon, in Boston, for the first time in any part of the world. Her reception during that tour was splendid. She did not again visit America until the season of 1895-96, but she returned the following season, when her appearance as Marguerite in "Faust"{243} was one of the leading events of the season. During her absence she had improved wonderfully in vocal form and appearance, and the critics gave her unstinted praise. Her impersonation of Carmen again created a furore, and, notwithstanding the superb array of talent exhibited during those seasons, "Calvé" was, above all, the subject of interest to opera-goers.
She makes her home in Paris, but her vacations are spent at a picturesque little place called Château Cambrières, situated in the shadow of the Pyrenees. Calvé is not yet at her prime, and with genius such as she possesses it is likely that she will eclipse the achievements of the greatest dramatic singers of the past.
Of the numerous successors of Patti, Madame Melba seems to have more fully met the requirements than any other. In many respects she has exceeded them, for her voice is fuller and more powerful than{244} Patti's ever was, but she has the same easy vocalization and marvellous spontaneity that constituted the great charm in Patti's singing.
Melba is the daughter of a wealthy citizen of Melbourne in Australia, and in that city, from which she takes her stage name, Nellie Mitchell was born in 1865. There was much musical talent in the family, but it was exercised for their own enjoyment only, for they were of Scotch Presbyterian descent, and the idea of the stage was objectionable to them. For this reason, while their daughter was given every advantage in the study of the pianoforte, violin, and harp, her voice was not cultivated. Singing was nevertheless her chief delight, and her great desire was to take lessons.
In 1883 Miss Mitchell married a Captain Armstrong, but the marriage was not a happy one, and when her father, shortly afterwards, was appointed commissioner from Australia to the Colonial exhibition in London,{245} she went there with him, and soon found herself able to enter upon study for a musical career.
She went to Paris, where at one of Marchesi's receptions she sang and was heard by the manager of the Brussels opera house, who offered her an engagement, and, after only nine months' training, she made her début. She had been previously offered a five years' engagement by Maurice Strakosch, but his death prevented the carrying out of the contract.
It was in 1887 that she made her first appearance in Brussels, and the following year her Parisian début was successfully accomplished. She was rapturously received, and at once found herself classed among the great singers of the century. Her career in Europe and in America was a succession of triumphs. Her voice is rich, sympathetic, and powerful. In flexibility it may be compared with that of Patti, and her trills and{246} cadenzas are accomplished with the ease and brilliancy that belong to naturally gifted singers.
Perhaps the most severe ordeal through which she ever had to pass was in 1893, when she made her début in Milan. The Milanese are very jealous of their independence of opinion, and while they will accept leniently a beginner, the artist whose reputation has been gained out of Italy is likely to fare badly at their hands. When it was announced that Melba was to sing at Milan, a feeling hostile to her at once made itself manifest. When Melba arrived, the musicians and critics did their best to keep out of the way and avoid an introduction. Stories went forth, when rehearsals began, that her voice was like a steam whistle, and everything that could contribute towards a failure was done. Madame Melba's friends endeavored to keep all this from her, and for a time they succeeded, but now she began to be{247} pestered with anonymous letters making threats of various kinds. This so unnerved the prima donna that it was found advisable to acquaint the prefect of the police with the details of the matter, and the intrigue was stopped. On the eventful evening the house was packed, and there was an air of hostile expectancy. The opera was "Lucia." The singer appeared amidst silence which was interrupted now and then by hissing sounds. Hardly had her first notes been heard when it was evident that a change of opinion had taken place in the audience, and the ovation which she received after the mad scene was tremendous. The press extolled her incomparable singing, and her victory was complete.
Melba is not a great actress; she holds her audience entranced with her marvellous vocalization, and her greatest triumphs have always been in those operas which make the smallest demands upon the dramatic powers{248} of the singer. Adelina Patti could not sing in Wagnerian opera, and was too wise to make the attempt. Melba, advised by her friends, once appeared as Brunhilde and was not a success, and she must rest content with being considered the greatest vocalist of the day.
Madame Melba has visited America several times, and during the seasons of 1895-96 and 1896-97 was under the management of Abbey and Grau. After the collapse of that company she became the star of a small opera company travelling as far as the Pacific coast. She makes her home in Paris, where she spends a portion of each year with her son. She is simple and frank in manner, generous by nature, and not given to malice or jealousy.
California added a star to the operatic firmament in Sybil Sanderson, who made her début in 1888, under an assumed name, at The Hague, in "Manon." She was successful,{249} and in a few months came out at the Opera Comique in Paris, creating the rôle of Esclarmonde, which Massenet had written for her, and in which she had the advantage of the composer's instruction.
Probably no opera singer has ever had greater advantages in the preparation for the stage than those which Miss Sanderson enjoyed. She is the daughter of a lawyer of high repute, who became judge of the Supreme Bench, and later chief counsellor of the Union Pacific Railroad. She was taken by her mother, at an early age, to Paris, where she and her sisters received the best education possible. She desired to become a prima donna, and had every assistance that the wealth of her parents could provide.
Her voice is of the kind for which American prima donnas have become celebrated, light, pure, and flexible. Its surpassing excellence lies in the upper register, her G{250} in alt being in itself a phenomenal production. Miss Sanderson is a finished actress, having received the most careful training at the hands of Massenet, who wrote also "Thais" for her. Saint-Saëns entrusted to her the creation of the title rôle of "Phryne," and, in token of his delight at her performance, presented her with a valuable necklace.
Miss Sanderson became very popular in Paris and in St. Petersburg, but met with less favor in London and New York. Once when she sang in London, Van Dyck was the tenor. At the rehearsal he sang sotto voce in order to save himself, and he supposed that she was doing likewise. In the evening, at the performance,—the opera was "Manon," which Miss Sanderson sang in Europe two hundred and fifty times,—she was overwhelmed by the power of his voice. Van Dyck, hearing her small, clear tones, and thinking that she was nervous, came near to offer encouragement, and urged her{251} to "let out your voice." "This is all the voice I have," she replied, and he, still thinking she needed encouragement, sang all the louder. Her great personal charm makes itself felt across the footlights, and while she was heavily handicapped in having to sing with such a tremendous tenor, she was yet able to captivate the audience by her sincerity.
Ella Russell, who made her début in Provo, Italy, is a native of Cleveland, Ohio. Her voice is large, rich, and even, she has an imposing stage presence and much beauty and dignity. She travelled in Europe with success, and finally made her appearance at Covent Garden in 1885.
Another American débutante of 1885 was Marie Engle, a native of Chicago, who at present is one of the opera company at Covent Garden. She has a light voice, high and flexible. Her first appearance was at the Academy of Music in New York, in{252} a concert given by pupils, assisted by members of the Mapleson Opera Company. Colonel Mapleson made her an offer which was accepted, and she went with his company to San Francisco, where she made her début, and afterwards to London, where she has appeared for several seasons.
She has so far followed the conventional domestic life of the prima donna as to marry and secure a divorce. Her husband was Gustav Amburg, a theatrical manager, whom she married in 1889. Her life with him was not happy, and he continually ill-treated her. At last she found that he had a wife living in Germany, and she secured her divorce in 1896.
In the Abbey and Grau opera company of 1894 a singer who attracted considerable attention was Madame Sigrid Arnoldson. She was the daughter of a Swedish tenor and was born in Stockholm. She made her début in grand opera in London, in 1887, but{253} had already become well known at Stockholm, where, in 1885, so great was the desire to hear her that 2,000 people stood in line all night in order to buy tickets. No singer had been so popular since the days of Jenny Lind and Nilsson. She sang "Mignon," and at the conclusion of the performance she was presented by King Oscar with a decoration exactly like those given to Lind and Nilsson. Madame Arnoldson is petite, piquant and picturesque on the stage, and has dark hair and eyes. She is an excellent linguist, speaking four languages.
When she was a small child she would sing like a bird while alone, but could never be induced to sing before strangers. Her father taught her until she was old enough to determine whether she would really have a fine voice. Then she became a pupil of Maurice Strakosch, whose nephew, Robert Fischoff, she married.
The appearance of a new singer from{254} America is now looked upon as nothing unusual, for the list of those who have acquired distinction is already long. Clara Louise Kellogg, Annie Louise Cary, Adelaide Phillips, Marie Litta, Minnie Hauk, Marie Van Zandt, Alwina Valleria, Emma Nevada, Marie Engle, Sybil Sanderson, Lillian Nordica,—yes, the list might easily be increased even without enumerating the large number of tenors and basses. The year 1890 witnessed the début of one who is already acknowledged as a great artist, and who adds to her laurels each season. One who, to a glorious voice and attractive personality, adds dramatic power and intelligence of a high order.
Emma Eames was born in China, but at a very early age was brought by her mother to Boston, where she received her education. Mrs. Eames was a highly accomplished musician, and was her daughter's earliest music teacher. As her voice developed, she began{255} to sing in church choirs and in concerts, where the beauty of her singing attracted a good deal of attention. After she went to Paris, she experienced considerable difficulty in obtaining an engagement. The road to the opera is full of intrigue and machination. Miss Eames made her way to the front by sheer talent. She was first engaged to sing at the Opera Comique, but, for some reason best known to itself, the management repented of having opened its doors to an unknown singer, and gave her no part. She therefore asked that her contract might be annulled, and her request was granted.
A pure, fresh voice, flexible and expressive, remarkably good intonation, and an attractive personality, were the qualities with which Miss Eames ruled the stage. Her fault at first was a degree of calmness in the more vehement scenes. This was noticed particularly in "Faust," and yet her{256} interpretation of the rôle of Marguerite is considered exceptionally fine.
In 1891 she accomplished the difficult feat of singing the part of Elsa in "Lohengrin," after only one rehearsal, but her greatest assumption is that of Elizabeth in "Tannhäuser," in which she appeared in 1895, and gained a reputation for originality of conception which the greatest Wagnerian singers had never developed.
During the season of 1898 in London she gained new laurels. In 1891 Miss Eames caused a sensation by marrying Mr. Julian Wetmore Story, a young artist of much promise. The circumstances of the marriage were rather romantic, and gave rise at the time to a good deal of newspaper comment. Miss Eames, whose mother was somewhat opposed to her marriage, eluded the vigilance of her natural protector, and was quietly married in the old church at Bray, which dates back 1,000 years. This{257} marriage has turned out very happily. Mr. Story has acquired a high reputation as an artist, and by no means occupies the conventional position of "prima donna's husband," but has an individuality of his own. Their home in Paris is the centre of musical and artistic society, and Madame Eames-Story has become a kind of deity amongst American students in Paris.
Only once have there been reports circulated attributing to Madame Eames the feelings of jealousy which seem to permeate the prima donna sisterhood. In Boston there was supposed to have been a coolness between Madame Eames and Calvé, and the latter lady, under the rack of the newspaper reporter, made some disagreeable remarks. Whatever cause there may have been, Madame Eames met Madame Calvé afterwards in Paris, and offered her hand frankly, as if nothing had happened, and it was accepted in the same generous manner.{258}
Madame Eames has several times been obliged in her own interests to maintain an independent position in dealing with managers, and when, after her great American successes, the Abbey, Schoeffel, and Grau Company would not offer her what she considered just terms, she would not retreat from the stand which she had taken, and the company decided to punish her by letting her alone. The result was, that Madame Eames reaped a golden harvest in Europe, and built up a reputation so great that her name is now mentioned as one of the four great sopranos,—Melba, Calvé, Nordica, and Eames.
With this slight sketch of an interesting career we must be content, for a word must be added about Mlle. Zelie de Lussan, who made herself popular to Americans during her connection with the Boston Ideal Opera Company, from 1885-88, when she secured an engagement in London, and is rapidly{259} building a great reputation. Her great part is Carmen, and in this and Mignon she has delighted the Parisians. She is piquant and brilliant, and has the faculty of charming the audience by her grace and personal magnetism. Mlle. de Lussan was born in New York of French parents, and received her musical education from her mother, who was once a well-known singer.{260}
The operatic tenor is frequently as much of a trial to the impresario as the soprano. Brignoli would feel hurt unless he received what he considered the proper amount of applause, and then he would have a sore throat, and be unable to sing. Ravelli had a mortal hatred of Minnie Hauk, because she once choked his high B flat with a too comprehensive embrace, and his expression of rage, being understood by the audience as a tremendous burst of dramatic enthusiasm, was, in consequence, loudly applauded. Nicolini, in behalf of Patti, once went out and measured the letters on a poster. It had been agreed that Patti's name was to{261} be in letters half as big again as those used for any other singer. It was discovered that the name of Nevada, who was also a member of the company, was a fraction over the stipulated size, and all the posters had to be cut in such a way that a strip was taken out of Nevada's name, and the middle dash of the E and of the A's was amputated.
Some tenors have travelled with numerous retainers, who always occupied seats at the theatre for the purpose of directing the applause, but nothing of the kind has ever been heard of with a contralto or basso.
Ernest Nicolini, who made his début in 1855, was for some time considered the best French tenor on the stage, but he is better known as Madame Patti's husband than as a singer. Nicolini died in January, 1898.
Fancelli and Masini were tenors of merit, with beautiful voices; also Brignoli, who for twenty years lived in America. Fancelli was a very ignorant man, scarcely able to read{262} or write. According to Mapleson, he once attempted to write his name in the album of the Liverpool Philharmonic Society, with deplorable results. He wished to write "Fancelli, Primo Tenore Assoluto," but after great efforts, which resulted in overturning the ink-bottle, the signature appeared thus: "Faneli Primo Tenore Ass—"
Masini's voice was more sensuously beautiful than Fancelli's, and he was more full of conceit. He travelled with a retinue of ten people, including cook, barber, doctor, and lawyer. He also distinguished himself in London by sending word to Sir Michael Costa, the conductor of the orchestra, to come around to his apartments, and run through the music of his part, as he did not care to attend the rehearsal. Costa did not go, and Masini returned to Italy in great wrath.
Joseph Victor Amédée Capoul, who made his début in 1861, was for many years considered{263} one of the best tenors on the French stage. He was born in 1839, at Toulouse, and entered the Paris Conservatoire in 1859, gaining the first prize in comic opera in 1861. He was good-looking, and had a pleasant voice, somewhat marred by vibrato, and he was an excellent actor in both light and serious parts. He visited America first in 1873, as a member of Strakosch's company, which included Nilsson, Miss Cary, Campanini, Maurel, Del Puente, and others not so well known, and to which were afterwards added Pauline Lucca and Ilma di Murska. He was also chief tenor of a French Opera Bouffe Company, which visited America in 1879-80. During the past few years M. Capoul has lived in New York, where he has become a teacher of singing.
Theodore Wachtel was for a long time one of the leading German tenors. He was the son of a stable keeper in Hamburg, and began life by driving his father's cabs.{264} He was born in 1823, and obtained his first operatic engagements in 1854, singing in several German cities. His first appearance in London was in 1862, when he sang the part of Edgardo in "Lucia," and made a complete failure. His later appearances brought better results, and yet his popularity was gained more on account of the fine quality and great power of his voice than from any artistic use of it. His high C was his chief attraction, and this note he produced from the chest with tremendous power.
Wachtel sang in America during several seasons. He died in Berlin in 1893.
The greatest German tenor, however, for many years was Albert Niemann, who was blessed with a magnificent voice and a fine appearance, suitable for the impersonation of Wagner's heroes, in which he excelled. He was born in 1831, at Erxleben, Magdeburg, and went on the stage in 1849. At{265} first he sang only small parts, or else in the chorus, but, as he improved with study, he attracted the attention of Herr von Hülsen, General Intendant of the Royal German Theatres, who took him to Berlin. He enjoyed a great reputation for a quarter of a century in Germany, and was selected by Wagner to sing Siegmund at Bayreuth, in 1876. Until he came to America in 1886, and 1887, when his voice had long since departed, his only appearances out of Germany were in the unsuccessful production of "Tannhäuser" at Paris, in 1861, and he sang in London in '82. In 1887 he formally retired from the stage.
Heinrich Vogl won distinction as an interpreter of Wagner rôles. He was born in 1845, at Au, near Munich, and was instructed in singing by Lachner, and in acting by Jenk, the stage manager of the Royal Theatre, Munich. At this theatre he made his début in 1865 as Max in "Der Freischütz.{266}" He was engaged at the same theatre almost permanently after his début and was always immensely popular. In 1868 he married Theresa Thoma, also a singer of renown, and from that time they generally appeared together.
Vogl played Loge, in the "Rheingold," and Siegmund, in "Walkyrie," when they were produced in 1869 and 1870, and his greatest triumphs have been gained in Wagner's operas. When the Trilogy was produced at Bayreuth, in 1876, he played the part of Loge, and was highly praised for his admirable declamation and fine acting.
Theresa Vogl was the original Sieglinde, at Munich, and was very successful in Wagner opera. She was born in 1846, at Tutzing, Bavaria, and studied singing at the Munich conservatory, appearing first in opera at Carlsruhe in 1865.
As Mario's powers began to wane, people wondered who would succeed him, and many{267} based their hopes on Antonio Giuglini, a native of Fano, Italy. Giuglini was born in 1827, but did not appear in England until 1857, when he sang at Her Majesty's Theatre. He possessed a sweet, high tenor voice and an elegance of style which some critics complained of as cold, languid, and drawn out. His singing was without variety and his acting colorless and tame. Notwithstanding all this, he was called by one eminent critic "the best that has been heard since the arrival of Tamberlik," seven years previously.
Giuglini's career was, however, of short duration, for he became insane in 1862, and died at Pesaro three years later.
In 1872 a tenor appeared who at first seemed to be a worthy successor to Mario,—Italo Campanini, who was born at Parma in 1846. He first attracted public attention by singing the part of Lohengrin when that opera was produced at Bologna, in 1871, and beginning with 1872, he was engaged every{268} season for ten years in London. His first engagement in America was in 1873, when he was a member of a company organized by Mapleson, which included Nilsson, Annie Louise Cary, Capoul, and Maurel. In America he became very popular, although he was considered in Europe to have disappointed the high expectations which his early career had justified. He had a pure tenor voice of richest quality, but owing to some fault in his method of production it decayed rapidly, and his declining days were a succession of unfortunate and unsuccessful attempts to regain his lost powers. As an actor he was melodramatic rather than powerful, and he was looked upon as a hard working and extremely zealous artist.
Campanini had a varied and highly interesting experience of the triumphs and vicissitudes of life. He was the son of a blacksmith, and was brought up to his father's trade, which he first left to go{269} soldiering with Garibaldi. He returned after the war, and his vocal powers were soon discovered by a musician who happened to hear him sing, and secured for him a course of free tuition in the Parma conservatory. At the age of twenty-one he commenced his career as an opera singer. He met with some success, and was engaged to travel in Russia for twenty-four dollars a month. On his return to Italy, Campanini went to Milan and took lessons for a year with Lamperti, when he appeared at La Scala in "Faust."
His repertoire was remarkable, consisting of over eighty operas. Beginning his career with a salary of eighty cents a night, he rose until he received, under Mapleson's management, $1,000 a night, and in one season with Henry E. Abbey he was paid $56,000,—yet he died poor as well as voiceless. He was simple and unaffected in his manners, and, like many of his fraternity, careless and improvident, but he had many friends and{270} with the public was very popular on ample grounds.
Mapleson relates that when he first engaged Campanini to appear in London, he was one day sitting in his office when a rough-looking individual in a colored flannel shirt, with no collar, a beard of three or four days' growth, and a small pot hat, entered and announced that Campanini had arrived in London. "Are you sure?" exclaimed the impresario, wondering how it could interest the individual before him. The strange-looking being burst out laughing, and declared that he was quite sure, as he was himself Campanini. It was a terrible crusher for Mapleson to find that his great star was such a rough-looking customer, but Campanini more than justified the reports about his singing as soon as he made his first appearance on the stage.
An American who had the honor of being for three years first tenor at the Royal Opera{271} House, Berlin, and nine years first tenor at the Vienna opera house, is Charles R. Adams. He was born in Charlestown, Mass., in 1834, and after some study with Boston teachers went abroad, where he became a pupil of Barbière in Vienna. After acquiring a high reputation in Europe, he came to America as a member of the Strakosch opera company in 1878, being associated with Miss Kellogg, Miss Cary, Miss Litta, and others. In the following year he decided to remain in Boston, and has since devoted his time chiefly to teaching.
The latter half of the nineteenth century has witnessed the growth of the Wagner opera. In several ways has the doctrine of Wagner made itself felt in musical art. Operas no longer consist of a series of solos, duets, and concerted numbers, with an opening and closing chorus, all strung together in such a manner as to give the greatest opportunities to the soloist. An opera at the{272} present day must be a drama set to music. The action of the play must not be interrupted by applause, encores, and the presentation of flowers. This continuity of action is noticeable in every opera of modern times, whether German, Italian, or French, and in itself marks a decided forward movement in the annals of lyric art.
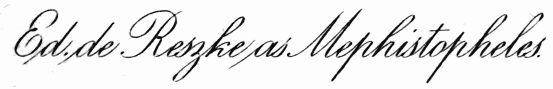
There have been many complaints that the singing of Wagner opera ruins the voice, but to contradict this statement we have only to look at the careers of the greatest Wagnerian singers,—Materna, Lehmann, Brandt, Niemann, Winkelmann, Vogl, the De Reszkes, Nordica, Brema, and others who have sung the music of Wagner for years without any unlooked-for deterioration. The fact is that they learned the art of vocalization, while many who have come before the public as Wagnerian singers have been practically ignorant of the first principles of voice production. To shout and declaim{273} does not by any means constitute the Wagnerian idea. The music is as singable as the most mellifluous Italian opera of the old school, although it does not call for the flexibility and execution which were considered the great charm of singing in the time of Malibran, Jenny Lind, and Grisi. An eminent London critic writes: "We were tired to death of German coughing, barking, choking, and gargling, when suddenly Jean de Reszke sang Tristan beautifully."
Jean de Reszke is a native of Poland, having been born at Warsaw in 1852. His father was a councillor of state and his mother an excellent amateur musician. Their home was the centre of attraction for many notable artists and musicians, so that the children were brought up in an atmosphere of art. Jean was taught singing by his mother, and at the age of twelve sang the solos in the cathedral at Warsaw. He was educated for the profession of the law, but his love of{274} music was such that he decided to prepare himself for the operatic stage, and began to study with Ciaffei, and later on with Cotogni. He made his début in 1874 at Venice as a baritone, and for some years sang baritone parts, until he found the strain telling upon his health. He phrased artistically and possessed sensibility, and his voice was of excellent quality; but feeling that he was not fully prepared, he retired from the stage for a time and studied with Sbriglia in Paris. In 1879 he appeared again, but as a tenor, in "Roberto," at Madrid, when he made a great success, and from that time he was regarded as one of the greatest tenors of the age. Of recent years his successes have been chiefly in Wagnerian rôles. He is an ideal Lohengrin, and has added to his laurels as Tristan and as Siegfried.
Probably no tenor since the days of Mario has awakened such widespread public interest. His estates in Poland, which in 1896{275} were extensively improved for the reception of his bride, the Countess Mailly-Nesle, his love of horses and of sport in general, as well as the jealousies of the numerous ladies who vied with one another for his smiles, all in their turn formed themes for newspaper and magazine comment. The personal appearance, as well as the geniality of the great tenor, helped to make him an object of interest, for he is a man of great physical beauty and grace.
Jean de Reszke created a furore in America, and has visited the country several times under the management of Abbey and Grau. When that company failed in 1896, De Reszke attempted to form an opera company to finish the season, and in so doing he incurred a great deal of popular indignation by his treatment of Madame Nordica, who felt obliged to leave the company, and by inducing Madame Melba to assume Wagnerian rôles, in which she proved to be a failure.{276} He became the object of newspaper attack on account of the large price which he demanded for his services, but much of this indignation is unmerited, for the simple reason that the remedy lies with the public rather than with the singer. An opera singer is justified in getting as much money as his services will bring, and as long as he finds people, whether managers or public, who are willing to pay that price, he will ask it. When the price is refused, it lies with him to determine whether he will sing for less money or withdraw, and it seldom happens that it is necessary for a thoroughly popular artist to withdraw, except at the end of his career. Patti received her highest prices when she was past her prime, and the same may be said of almost every great artist. The reason may be found in the fact that their greatness does not dawn upon the general public until years after their position is earned.{277}
In 1896 Jean de Reszke married the Countess Mailly-Nesle, to whom he had been engaged for several years. She is an amateur musician of exceptional ability, and a lady of much personal beauty.
One of the more recent stars in the operatic firmament, and which is at its height, is Ernest Marie Hubert Van Dyck, born in Antwerp, 1861. He at first intended to become a lawyer, and for a time studied jurisprudence at Louvain and Brussels. His musical gifts and love of art could not be repressed or hidden, and whenever he sang his voice created so great a sensation that, in spite of family opposition, he went to Paris to study. As a means of helping himself he was for a time assistant editor of a Parisian paper, La Patrie.
In 1883 Massenet heard him sing at a private party at which they were both guests, and was so much struck by his voice and style of singing that he asked him then and{278} there to act as substitute for a tenor who was ill, and could not fill his engagement. The occasion was the performance, under Massenet's management, of a cantata, "Le Gladiateur," by Paul Vidal, at the Institut de France.
Within two hours Van Dyck studied and sang the tenor solos with such an effect that he immediately became the topic of conversation among musical Parisians.
He was now engaged by Lamoureux, the champion of Wagner in Paris, for a term of four years, during which he sang the rôles of Tristan, Siegmund, etc. In 1887 he sang Lohengrin, but its production caused a great deal of excitement, owing to political causes. Nevertheless, the performance formed a golden epoch in the history of Wagnerian art.
Van Dyck was now induced by Levy and Goo, of Bayreuth, to take part in the production of "Parsifal," in 1888. For this he was{279} drilled by Felix Mottl, and he made so great a success that he was at once engaged for the following year.
He has proved himself the finest representative of the character of Parsifal that has yet been heard, even Winkelmann not being excepted. Since 1888 Van Dyck has been engaged at Vienna.
Mr. Van Dyck married, in 1886, the daughter of Servais, the great violoncellist and composer. He is a knight of Baden of the order of the Lion of Zahringen, and an officer of the Academy of France.
Of Wagnerian tenors, Anton Schott and Hermann Winkelmann gained a high reputation. The former made his début in 1870, but his career was interrupted by the outbreak of the Franco-German war, through which he served, as he had also served through the war of 1866 against Austria. Although his reputation was high in Germany, he made a comparatively small impression{280} in England. Winkelmann took the part of Parsifal at Bayreuth, when, in 1882, sixteen performances of that work were given under Wagner's supervision. He also came to America with Materna and Scaria, making a good impression.
Max Alvary also was well known in the United States as a Wagnerian singer. He made his operatic début in 1881, and appeared in the Metropolitan Opera House, New York, in 1885, since which time he has been heard in America during several seasons. His best parts were Siegfried, Tristan, and Tannhäuser, and he was for many years leading tenor at the Opera in Hamburg. His death, in November, 1898, at the age of forty-one, was the result of an accident.
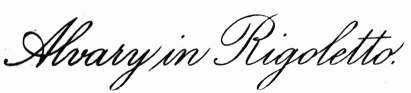
Of the Italian school, Francisco Tamagno holds a high position in the operatic world of to-day as a robust tenor. He excels in dramatic rôles, such as Otello and Arnoldo, and he made a great success in "Cavalleria{281} Rusticana." In heroic rôles he sings and acts with a simplicity, power, and authority not surpassed by any other tenor of this generation. He was born at Turin, and began his musical education at the age of eighteen. His début was made in Palermo, at the age of twenty-three, his studies having meanwhile been interrupted by military duties. In Venice he sang with Josephine de Reszke, the sister of Jean and Edouard, who had a short but brilliant career. For many years he remained at La Scala, where he was immensely popular. He is tall, big-chested, and erect, always imposing, and, unlike most Italians, he has fair hair and blue eyes. An American critic wrote of him as "hurling forth his tones without reserve, and with a vocal exuberance not reached by any living tenor. He quells and moves by overwhelming strength and splendor."
Tamagno was once the defendant in a lawsuit brought against him by the manager of{282} the opera in Buenos Ayres. It appears that in 1890 the tenor was engaged for a season of forty performances, for which he was to receive $130,000. Of this sum $31,000 was paid in advance before he would leave Italy. When he arrived at Buenos Ayres a revolution broke out, and only four performances of opera were given. The manager endeavored to recover his money. An interesting feature of the trial was that it brought out the fact that Tamagno always travels with a claque of eight, and that it is stipulated in all his contracts that he shall have eight tickets for their use. This, however, has been denied, and it is stated that Tamagno has not read a criticism of his singing for years, knows nothing about the critical opinion of him, cares less; also that the eight tickets are intended for his family. He is said to be the highest-priced tenor of the age.
Before leaving the tenors a word should be said concerning Edward Lloyd, who in{283} England seems to have inherited the mantle of Sims Reeves. He was born in 1845, and was educated as a chorister in the choir of Westminster Abbey. He has devoted himself entirely to concert and oratorio singing, and possesses a voice of the purest quality, with a style noted for its excellence and finish.
Henry Guillaume Ibos, also, a French tenor formerly a cavalry officer, who made his début in 1885, is a singer whose voice possesses much beauty. He was born at Toulouse in 1862, and has appeared with much success in France, Russia, and England. He also made a tour in 1897-98 in America.
There are tenors coming to the surface continually. Some will sink into obscurity, while others will ascend the ladder of fame; but we must leave them to the future and pay a little attention to the baritones, of whom Van Rooy has recently made his mark{284} as Wotan. He has a tremendous voice, sings with ease, and gets a pleasing softness into his tones. He is likely to be well known in the future.
Charles Santley, who is known in England as the greatest baritone of the Victorian era, was born in Liverpool in 1834. Having a voice of fine quality, extensive compass, and great power, he left England to study in Milan in 1855. Returning in 1857, he took lessons of Manuel Garcia. In the same year he appeared in oratorio, singing the part of Adam in the "Creation." His first appearance in opera in England was in 1859, as Hoel in "Dinorah" at Covent Garden.
Although Mr. Santley sang almost all the baritone rôles in opera, he was not noted for histrionic powers, but rather for his vocal abilities, and his power of seizing on the exact sentiment and significance of his part.
In 1871 he visited the United States as a{285} member of the Carl Rosa opera company, during which time he reaped substantial honors. In 1889 he made a concert tour in Australia.
In 1892 Joseph Bennett, the eminent critic, wrote: "The foremost baritone of the day is still with us, and though his physical means have suffered changes which no skill can avoid, he is a greater artist than ever, and retains plenty of vitality for his work."
Mr. Santley married, in 1859, Miss Gertrude Kemble, the granddaughter of the celebrated actor, and his daughter, Miss Edith Santley, had a short but exceedingly brilliant career as a concert singer, previous to her marriage, in 1884, to the Hon. R. H. Lyttelton.
Jean Baptiste Faure, a French singer, will be remembered as the creator of the part of Mephistopheles in Gounod's "Faust." He was a good musician and a fine actor, and he owed more to his genius as a comedian than{286} to his voice, which was of great compass, though not of a brilliant quality. In the winter of 1861 he made his first appearance at the Grand Opera in Paris, though he had made his operatic début nine years before at the Opera Comique. For many years he remained at the Grand Opera, during which time he was a prominent figure in operatic history. Faure was born in 1830, and was the son of a singer at the church of Moulins. His father died when he was but seven years old. At the age of thirteen he entered the solfeggio class at the Conservatoire in Paris, to which city his family had moved when he was three years old. At the breaking of his boy's voice he took up piano and double bass, and was for some time a member of the band at the Odéon theatre. After his voice was settled he joined the chorus at the Théâtre Italien, and in 1850 again entered the Conservatoire, where he gained, in 1852, the first prizes for{287} singing and for opera comique. He is a man of refined tastes and great culture, and an enthusiastic collector of pictures. In 1859 he married Mlle. Lefebre, an actress at the Opera Comique. Of Faure's Mephistopheles, in "Faust," a critic of 1876 writes, "No impersonation of this character at all approaching the general excellence of his could be named." What Faure respected most was the intention of the composer. It is impossible for any one to penetrate more deeply into a part, to adorn it with more delicate gradations of light and shade, to hit upon more felicitous contrasts and juster intonations, to identify himself more thoroughly with a character or an epoch. He proceeded by degrees, led his audience to sublimest heights of enthusiasm by cleverly calculated stages,—he fascinated them.
Of French baritones, Victor Maurel is the one who has succeeded Faure. His creation{288} of the part of Iago, in Verdi's "Otello," was considered a masterpiece of lyric acting, and Iago is at the present day his greatest rôle.
Maurel was born in 1848 at Marseilles, and, having a penchant for acting and singing, began to play in comedy and light opera in his native town. His ambition soon led him to Paris, where he entered the Conservatoire and studied singing with Vauthrot, and opera with Duvernoy. He gained the first prizes in both subjects in 1867.
In 1869 he made his début in "Les Huguenots," but he was not considered sufficiently successful to secure a permanent engagement, so he went for a series of tours in Italy, Spain, and America. His first London appearance was made in 1873, when he took the part of Renato at the Royal Italian Opera, and was engaged there, as a result of his success, every year until 1879, playing the parts of Don Giovanni, Tell, Almaviva,{289} Hoel, Peter the Great, Valentine, Hamlet, and the Cacique. He also played Wolfram and the Flying Dutchman, and in 1878 appeared as Domingo in Massé's "Paul and Virginia."
In 1879 he once more appeared in Paris, taking the part of Hamlet. His name had become established since his previous appearance in that city, and he was now a most decided success.
About this time M. Maurel undertook the management of Italian opera at the Théâtre des Nations. His enterprise was hailed with joy by the Parisians, who were desirous of having Italian opera.
Maurel surrounded himself with a company of the finest artists, including Mesdames Marimon, Adler-Dévriès, Nevada, and Tremelli, and Gayarré, the brothers De Reszke, and Maurel himself.
Notwithstanding the attractions offered, the outlay exceeded the income, and M.{290} Maurel relieved himself of a large amount of money in a remarkably short time. His financial disasters in no way interfered with his artistic successes, and his production of Massenet's "Herodiade," on February 1, 1884, was a great triumph.
Victor Maurel combines a good voice with a most attractive personality and a great love of his art. He is undoubtedly to be considered one of the greatest baritones of the present day. As an actor M. Maurel is magnificent, as a singer he has never had a marvellous organ, but he has used it with exquisite art. If he ceased to sing he would still be one of the greatest of Shakespearean actors. As Iago he is insidiously great, as Rigoletto overwhelming and thrilling.
He first visited the United States in 1874, and he was at once accepted as a great artist.
Amongst operatic baritones of the past{291} twenty years Señor Guiseppe Del Puente, a Spaniard, descended from an old and noble family, must be mentioned. He was born in 1845, and studied at the conservatory at Naples. Being a true artist in his instincts, and having a fine voice, he speedily excelled. He became connected with the best operatic enterprises, and was always popular on account of his handsome stage presence, dramatic capability, and fine, rotund, musical baritone voice. He was equally valuable in the comedy parts of light opera, or the heavier ones of serious opera.
He was well known in America in the eighties, when he belonged to the Mapleson company, and sang with Gerster, Valleria, Scalchi, Ravelli, and Galassi.
The greatest English baritone of the present day is Ffrançon Davies, whose voice was declared by Sims Reeves to be the purest baritone he had ever heard. Besides having this beautifully pure tone, he has perfect control{292} of the breath, and remarkable breadth and intelligence.
His first appearance took place at Free-trade Hall, Manchester, at Mr. de Jong's concerts in January, 1890.
Mr. Davies was born at Bethesda, Carnarvonshire, North Wales, and, after receiving his early education at Friar's Grammar School, at Bangor, he obtained an exhibition at Jesus College, Oxford. He gained his B.A. and M.A. degrees, but was not devoted to studies only, for he stood well in the athletic world of his University, playing football in his college team, and rowing in the Varsity trial eights.
After leaving Oxford he began to study music seriously, and entered the Guildhall School, taking lessons later with Shakespeare. He has a large repertoire of baritone operatic parts, in which he has sung with great success, and he is one of the best oratorio and concert baritones of the day.{293} He visited America in 1896, and confirmed the good accounts which had preceded him.
In the list of famous baritones of the present day, America is admirably represented by David Bispham, who has gained his greatest reputation in the part of Falstaff in Verdi's opera of that name.
Mr. Bispham was born in Philadelphia, in 1857, his father being a Quaker. Like many of the singers of to-day, he was intended for a commercial career, but, being more interested in music, he eventually allowed his love for art to overcome his desire for business, or, as he has himself said, he went the way of least resistance. His father's musical proclivities manifested themselves on the flute, which instrument he played beautifully, and young Bispham solaced the leisure hours of his youth with the guitar and zither, but never learned much of any other instrument. On every possible occasion he sang. He was a member of{294} several choral societies and church choirs, and had the advantage of many musical friends. He took parts also in amateur dramatic performances, and thus made some progress in his art.
In 1885 he gave up business and went to London, where he has since resided. He studied with Vannucini, Shakespeare, and Lamperti, and in 1891 made his début in London in "La Basoche," scoring an instantaneous success. He also made a provincial tour with Sims Reeves.
Mr. Bispham has a repertoire of nearly fifty rôles, and can sing entire parts in German, Italian, French, and English. There are few artists who work as conscientiously for the general good of art, and there are few who have made so general a success in such a wide variety of rôles, among the best of which are Wotan, Wolfram, and Beckmesser. He is also without a peer on the concert platform as an interpreter of Wagner.{295} He was seen in opera in America in 1896, and his artistic efforts made a deep impression, for he is one of the few artists who combine with unusual vocal accomplishments great dramatic powers.{296}
The contralto in an opera company has a somewhat thankless task. Her fate is to be either a boy, or else a nurse, duenna, or some character which implies age. She frequently is obliged to stand mute while the prima donna warbles and trills and receives the applause of the house, and yet the musical demands upon the contralto are equal to those made upon the soprano.
A contralto who was deservedly popular for many years during the middle of this century was Adelaide Phillips. She was born in Stratford-on-Avon in 1833, and in 1840 went with her family to Canada, afterwards settling in Boston, where, in 1843, she appeared as an infant prodigy at the Boston{297} Museum. In 1850, her voice having attracted attention, she was introduced to Jenny Lind, who advised her to study music. A subscription soon raised the necessary funds, and she was sent to Manuel Garcia in London, after which another fund was raised to enable her to go to Italy, where she made her début in 1854 at Milan. She sang with success in many cities of both hemispheres, and her repertoire consisted of all the contralto parts in the operas that held their places on the Italian stage during the twenty-five years that she was known as an opera singer. In 1879, when the Boston Ideal Opera Company was formed, Adelaide Phillips was the chief contralto. She made her last appearance, in Cincinnati, in December, 1881.
In 1882 the state of her health was such that she was obliged to go to Carlsbad, and she died there on October 3d of the same year.{298}
In private life Miss Phillips was highly esteemed, for she was not only an artist of sterling abilities, but a woman of grand character and a most devoted friend. She was buried at Marshfield, Mass., where the family had lived for some years on an estate which her success had enabled her to buy. Her life was one of hard and unceasing labor, but she had the satisfaction of being able to care for the necessities of her family, who were thrown upon her in early life.
A mezzo-soprano who took the public by storm in the early sixties was Zelia Trebelli, or, as she was more widely known, after her marriage, Madame Trebelli-Bettini. No member of Merelli's Italian troupe was gifted with so brilliant a voice and so much executive power. Her appearances in the opera houses in Germany were a series of triumphs, public and critics alike being carried away by her voice, with its brilliancy and flexibility, and her control over it.{299}
Her early triumph was the result of long preparation, for her musical education began when she was six years old, and her vocal training ten years later. It was not until after five years of close application to study that she made her début in Madrid, playing Rosina in "Il Barbiere," with Mario as Count Almaviva.
For many years Trebelli-Bettini remained one of the best of the galaxy of opera singers which the operatic stage has displayed during the last half of the century. In 1884 she made a tour in the United States with Mr. Abbey's troupe. She was born in Paris in 1838, and died in 1892. Her proper name was Zelia Gilbert, which expanded and Frenchified into Gillebert and reversed gives Trebelli(g), the Italian name which has for some years appeared to be necessary for all those who wish to succeed in opera.
When Gounod's "Faust" received its first performance in England, in 1863, the cast{300} included Tietiens, as Marguerite; Trebelli, as Siebel; Giuglini, as Faust; Gassier, as Mephistopheles; and Charles Santley, as Valentine.
Since the days of Alboni there has been no contralto singer to whom the adjective "great" could be so fitly applied as to Sofia Scalchi. She was born in Turin, and her parents were both singers. She made her début in 1866 at Mantua, in the part of Ulrica (Un Ballo in Maschera), when she was only sixteen years of age. Her first appearance in London took place two years later, and from that time she remained a favorite in England, where she sang in the memorable season of "Cenerentola," and every season afterwards for more than twenty-five years. Madame Scalchi is well known in America, where she first appeared under Mapleson's management in 1882. She had been singing in Rio Janeiro, and reached New York after a stormy voyage of twenty{301} two days, which left her in such an exhausted condition that she was incapacitated for a month, and her illness played havoc with Mapleson's managements.
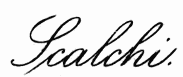
Scalchi was the possessor of a voice of delicious quality and unusual range, every note in its compass of two and a half octaves being of a wonderfully soft yet penetrating tone, and of great power. Her popularity was such that Patti and other prima donnas feared her as a rival, and regarded with jealousy the applause which attended her performances. Scalchi was imbued with the prima donna temperament, and had the regulation parrots and other pets during her travels. Concerning this portion of her equipage, Mapleson tells an anecdote to the effect that Scalchi's parrot died the night before the company reached Salt Lake City, in 1884, a bereavement which caused that lady to go into hysterics and take to a bed of sickness. Notwithstanding every art of{302} persuasion and such threats as could be used, Scalchi refused to appear, and her part had to be taken by a substitute.
In 1876 Signora Scalchi married Count Luigi Alberto Lolli, and her home is at the Villa Sofia, Turin, Italy.
Marianne Brandt is one of those singers who have made their reputation as exponents of Wagner opera. She is the daughter of a gentleman of Vienna, named Bischoff, and it is related that she assumed the name of Brandt upon beginning her stage career on account of her parents, who strongly objected to her going upon the stage, and threw in her way every possible obstacle. Marianne, however, was determined to persevere, and she went through a period of patient, hard work, in order to gain her education. It is said that at one time she supported herself, and paid for her lessons by sewing.
Her first teacher was Frau Marschner, at{303} the Conservatorium in Vienna, but later on she took lessons of Madame Pauline Viardot-Garcia.
In 1867 she received an engagement at Gratz, where she made her début as Rachel, in "La Juive." Her parents had expected failure, hence their unwillingness to allow the use of the family name.
In 1868 she sang at Hamburg, when she played Fides with such success that she was immediately offered a permanent engagement, which was accepted, and lasted for many years. During her leaves of absence she appeared in London as Fidelio, but did not make a remarkable success, though ten years later, when she sang in "Tristan and Isolde," her artistic efforts were heartily appreciated.
Fraulein Brandt sang the part of Kundry at the second representation of "Parsifal" at Bayreuth, and it is said that she generously gave her services on that occasion. She has visited the United States several{304} times, taking part in some of the earlier representations of Wagner opera in New York and other cities.
The next contralto singer to appear in opera was Annie Louise Cary, a native of the State of Maine, where she was born in 1846, at Wayne. Her family were all musical, and she was the youngest of six musical children. By the time she was sixteen her voice had developed wonderful qualities, and she was able to sing from C in the bass clef to F in alt, a range of three octaves and a half. At the age of eighteen she went to Boston, and secured a position in a church choir, while she studied music. Her career in Boston was much the same as that of many young aspirants for artistic honors,—"church choir and chores," it has been facetiously called. By this it may be understood that she earned her board by assisting in the household duties, while her church choir position enabled her to pay for{305} her vocal lessons. Her splendid voice and musical intelligence soon enabled her to obtain concert engagements, and before she went abroad she sang in many festivals and at the Handel and Haydn Society concerts, on one of which occasions she was associated with Parepa-Rosa.
Being possessed of much ambition, and with the energy which characterizes the natives of the State of Maine, Miss Cary organized and gave a concert in Music Hall, which brought her enough funds for a year's study abroad. Her Puritan training forbade the idea of opera, and it was her intention to study for concert and oratorio. At the end of her year she was discouraged, and declared that she sang no better than when she arrived. To this her teacher, Giovanni Conti, made no dissent, for his one idea of singing was opera. Miss Cary flung down her music, and left the room in disgust. And now came a curious mental revolution:{306} having refused to consider the possibility of singing in opera, and having on that account left her teacher, she shortly afterwards met an impresario named Lorini, for whom she sang. He offered her an engagement to sing in Italian opera, and she accepted it. For two years she was in Lorini's company, taking all kinds of parts. In 1869 she went to Paris for further study, and while there met Maurice Strakosch, who was at that time forming the Nilsson concert company, for a tour in America. Miss Cary accepted the engagement which he offered her. The company consisted of Miss Nilsson, soprano; Miss Cary, contralto; Brignoli, tenor; Verger, baritone, and Vieuxtemps, violinist. This tour lasted two years, and in 1873 Miss Cary again appeared in opera, creating the part of Amneris, with Italo Campanini as Rhadames, when "Aida" was produced at the Academy of Music in New York. The{307} following year Miss Cary sang Ortrud in "Lohengrin."
In 1879 and 1880 Miss Cary was a member of the Kellogg Concert Company. During the last years of her career, 1879 to 1881, she sang again in opera, adding to her repertoire the contralto part in "Favorita." Campanini and Gerster were the tenor and soprano. In 1881 she made her last appearance in opera in Philadelphia, and in 1882 she sang for the last time at the Cincinnati festival, having taken part in each one given from 1873. So well was she known at these festivals that when, in 1884, she attended as a member of the audience, she was at once recognized and received an ovation on taking her seat. On retiring from the stage in 1882, Miss Cary married Dr. C. H. Raymond, putting an end to her public career when she was at the height of her popularity. All young singers may take her early career as a model, for it should give{308} hope and courage to the many who are to-day making a similar struggle.
One of the members of Mapleson's company which visited the United States in 1884, and which included Patti and Gerster, was Anna de Belocca, a contralto of much merit. Her first appearance in this country, however, was made under the auspices of Maurice Strakosch, in 1876, when she was a new star on the operatic horizon. Mlle. de Belocca was unusually attractive in person, with brown hair, large black eyes, dead-white complexion, and symmetrical form. She was the daughter of M. de Bellokh, a scholar of St. Petersburg and acting Imperial Councillor of State. Mlle. de Belocca spoke five languages, and because of her aristocratic birth was sought after by the highest circles of society.
Mapleson seems to have been well aware of her ideas on social matters, for on one occasion he made use of his knowledge to help himself out of a dilemma. His company{309} was in Dublin, and the one suite of rooms at the hotel was claimed by both Mlle. Salla, the prima donna, and Mlle. Belocca, the contralto. Neither would give way until a happy thought struck Mapleson, and, after taking the landlord aside for a short conference, he asked whether there were actually no other rooms in the house equal to the disputed ones. "There is a suite above this," was the reply, "but they are reserved specially for Lady Spencer (wife of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland at that time), and it would be impossible for me to let any one else use them." "Well, can't we look at them?" suggested Mapleson. The landlord assented, and showed Mapleson up, Mlle. Belocca following. As soon as she entered the rooms she declared that they were delightful, and she should insist on remaining there. Of course the landlord and Mapleson gave a reluctant but delighted consent, and Lady Spencer made no requisition.{310}
The principal contralto at the festival at Cincinnati in 1896 was Marie Brema, who is to-day considered one of the greatest interpreters of Wagner. Miss Brema was born in Scotland, and made her first appearance in concert at St. James's Hall, London. She was introduced to Frau Wagner, who was so well pleased with her that she offered her an engagement to sing the part of Ortrud in "Lohengrin" and gave her personal instruction.
In 1888 a London theatrical manager saw her play in some amateur theatricals, and was so struck by her talent that he wanted to star her as an actress. She declined his proposition, feeling that the operatic stage was better suited to her capabilities. When she appeared at the Bayreuth festival, in 1894, as Kundry and Ortrud, she made an immense triumph. She sang with no apparent effort, naturally and gracefully, as all true singers do. Her voice was full, round, and well placed, and her coloring perfect.{311}
Since that time she has fully maintained her reputation, and has been heard in America with the Damrosch company, in 1894-5-9, and with Abbey and Grau the following year. During the opera season in London in 1898 her work elicited the highest praise of the critics. Miss Brema is still young, and is likely to hold a high rank among singers for many years to come.
The singer in an opera company who shares with the contralto the hard work, but seldom reaps much of the glory, is the bass, while the tenor is always an object of adoration, or should be, if he is a good singer, and the baritone has many good parts. The basso not only has thankless parts allotted to him, but, from precedent, one generally expects him to be wobbly and to sing frequently out of tune. Some bassos have broken through the law of precedent, and then they have been delightful. An operatic king or duke, who is usually a bass, is very seldom heard to sing in tune,{312} nor is the heavy villain of the opera, who is always a bass, able to keep within half a note of the path laid down for him by the composer. Two bassos who made their appearance at about the same time were Signor Foli (1862) and Signor Agnesi (1864), and for many years they were associated with Italian opera and oratorio throughout Europe. Signor Foli was an Irishman whose real name was Allan James Foley. He was born at Cahir, Tipperary, and went to America when very young. His voice was a rich, powerful bass of more than two octaves, from E below the line to F, and he had a repertoire of over sixty operas.
Of late years several singers of English and American origin have achieved distinction without the necessity of Italianizing their name,—Bispham, for instance, being a striking example. There are various reasons assigned for the necessity of a change. One is that the name must be possible of pronunciation{313} by the Italians, in whose country the opera singer germinates, and the other is that Americans and English have not yet learned to appreciate a singer by his merits, but rather by his name. One of the most ridiculous instances of Italianizing was in the case of Mr. John Clarke, of Brooklyn, who became Signor Giovanni Chiari di Broccolini. On the other hand, Santley never found it necessary to become Italian, nor did Sims Reeves. Myron Whitney is a name needing no Italianization. Emma Eames has found her name no bar to renown, and a score of singers who are now climbing the ladder of fame are not ashamed of their Anglo-Saxon origin. Louis Ferdinand Leopold Agnesi (Agniez) was a native of Namur, Belgium, and in his early days essayed to be a composer. He brought out an opera, "Harold le Normand," which met with indifferent success, and then he became a singer, receiving instruction from Duprez. His career was{314} not long, for he died in 1875, but he was a most popular singer.
Emil Fischer, who for many years has been associated with Wagner opera, was the son of musicians, his father having been a well-known basso and his mother also a singer of renown. He first appeared at Gratz at the age of seventeen. In 1862 he took the management of the theatre at Dantzig and held it for eight years. In 1882 he became a member of the Royal Opera at Dresden, and remained there until, in 1885, he went to New York and joined the German opera. Since that time he has become well known in America, having appeared in most of the representations of Wagner's operas.
Emil Scaria was for many years known as a versatile singer and actor, more particularly in German opera. He made his début in 1862 at Dessau, after having studied in the conservatoire at Vienna and with Garcia in London. From 1865 to 1872 he was at{315} Dresden, and then at Vienna for several years. Later on he visited America, and was one of the celebrated Wagner trio, consisting of Materna, Winkelmann, and Scaria, who in 1884 sang in the Wagner festivals. Scaria was born in 1838 at Gratz. He created the part of Gurnemanz in "Parsifal," at Bayreuth. In 1885 he became a victim to insanity, and died the following year.
In 1876 Edouard de Reszke made his début at Paris in "Aida," and entered on a career of renown. He is the younger brother of Jean de Reszke, the tenor, and it was at the instigation of Jean that he abandoned his proposed occupation and took to the stage. Edouard had undergone a course of study at the Agricultural College at Prikao, with a view to developing the resources of the great estates in Poland belonging to the De Reszke family. He accordingly proceeded to Milan, and studied with Stella and Alba, and later on with Coletti. At the end{316} of four years he went to Paris for further study, and to make his début.
His voice is a full, rich, resonant bass, capable of sending forth notes of immense volume, or those of the most tender quality. His appearance is that of a great, tall, broad-shouldered giant, with fair skin and blue eyes, and his stage presence is imposing.
Four years after his début in Paris he created the part of Il Re, in Catalani's "Elda," and Massenet entrusted to him the creation of "Le Roi de Lahore" when it was produced at La Scala in Milan. He has also created the parts of Carlo V., in Marchetti's "Don Giovanni d'Austria," and Don Diegue, in "Le Cid." He was engaged in London during the seasons from 1880-84, and became immensely popular. He has many friends in England, for he has a weakness for everything connected with sport, in the best sense.
Notwithstanding the many parts in which{317} he has made the greatest success, his assumption of the rôle of Mephistopheles, in "Faust," more than any other, established his reputation as a great lyric artist, and he is generally conceded to be one of the greatest bassos of the century.
Of late years a French basso has arisen to share the popularity of Edouard de Reszke,—Pol Plançon, who for more than a decade has been one of the permanent stars of the Paris Opera House. M. Plançon was intended for a mercantile career, but having been an enthusiastic singer from the age of four, he rebelled against the decision of his parents. He was nevertheless sent to Paris, and entered a large and fashionable store to learn the business. One day Theodore Ritter, the pianist, heard him sing, for he sang upon every possible occasion, and was so pleased with his voice that he advised him to turn his attention to music. Through the influence of Ritter he was admitted to{318} the École Duprez, and thereby incurred the severe displeasure of his family.
M. Plançon made his first appearance at Lyons as St. Bris, in "Les Huguenots," and remained there for two seasons. In 1883 he returned to Paris, and made his Parisian début at the Grand Opera House as Mephisto, in "Faust," a part in which he excels. Since that time he has sung all the chief bass rôles at the Grand Opera House, and has created the parts of François I., in Saint-Saëns's "Ascanio," Don Gomez, in Massenet's "Le Cid," and Pittacus, in Gounod's "Sapho," when that work was revived in 1893.
M. Plançon was born in the Ardennes, but since his position as a singer was assured he has resided in Paris, where also his parents, whose objections were disarmed by his success, have joined him.
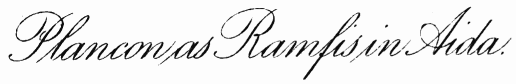
Before closing this chapter of bassos a few words should be said concerning three eminent singers whose reputation was made{319} in oratorio and concert singing,—Stockhausen, Henschel, and Myron W. Whitney.
Julius Stockhausen was one of the most remarkable singers of the century. He was born at Paris in 1826. His early career was of a varied nature, for he took part in concerts as singer, violinist, accompanist, and even drummer. He did not finally decide on music as a profession until 1848, when he took the part of Elijah in a performance of that oratorio at Basle, and his success decided his future career.
Stockhausen's singing in his best days must have been wonderful. Even to those who heard him only after he had passed his prime, it was something never to be forgotten. His delivery of opera and oratorio music was superb in taste, feeling, and execution, but it was the Lieder of Schubert and Schumann that most peculiarly suited him, and these he delivered in a truly remarkable way. The rich beauty of the{320} voice, the nobility of style, the perfect phrasing, the intimate sympathy, and the intelligible way in which the words were given, all combined to make his singing wonderful. His highest achievement is said to have been his delivery of the part of Doctor Marianus, in the third part of Schumann's "Faust."
For many years Stockhausen has been one of the chief vocal teachers of Germany, and has recently celebrated his golden wedding to the musical profession, which he formally entered in 1848.
Although not an opera singer, but rather a broad musician, the name of Georg Henschel will be remembered from the fact that for a few years he was considered one of the most excellent oratorio and concert singers before the public. He was born at Breslau in 1850, and at the age of eleven commenced his studies under Doctor Schaeffer. A year later he made his début as a pianist at{321} Berlin, where he played Weber's Concerto. He had already composed a good deal of music and shown much talent in that direction. In 1867 he entered the conservatory at Leipzig, and studied under Moscheles, Richter, Reinecke, and Goetze. After spending some time in Weimar, he settled in Berlin. One of his most marked successes was in 1874, at the Cologne festival. In 1877 he went to London, where he soon acquired a great reputation as a bass singer, and in 1879 he produced the Triumphal Hymn of Brahms.
In 1880 he visited America on a concert tour, and while in Boston became the conductor of the Boston Symphony Orchestra, which was organized and established during the three years of his conductorship. In 1881 he married Miss Lillian Bailey, a Boston lady, who was a concert singer of marked ability. In 1884 he returned to London, where he has since organized the London{322} Symphony concerts, and won an enviable position in the musical world.
Myron W. Whitney, who was born in 1836 at Ashbury, Mass., decided at an early age on following a musical career. For ten years he sang in concerts, and then went to Italy, where he studied under Vannucini, and later in London under Randegger. He now made a tour of Great Britain, and at the Birmingham festival sang the rôle of Elijah in such a manner as to make an immediate reputation for himself. He has a superb bass voice, which under long and careful training became flexible and even, and which extended for nearly three octaves. After achieving a reputation in England he returned to America, and from 1876 he has sung only in his native land, where his reputation is unexcelled.
For many years Mr. Whitney sang in light opera, but he also gave an interpretation of the King in "Lohengrin," under{323} the baton of Theodore Thomas, when the American Opera Company was floated, which is said to have been finer than any heard in this country. Of late years Mr. Whitney has retired from the stage and settled in Boston, where he teaches singing.
To give an account of all the singers who have appeared in grand opera would require several volumes. Of American singers alone there are many more who have achieved fame than can be placed in this little book. Alwina Valleria, of Baltimore, was well known, and is now married and settled in England. Emma Juch, Helene Hastreiter, Marie Litta, Emma Abbott, Louise Dotti are all of American origin and became well known. Margaret Reed, Suzanne Adams, Susan Strong are singers whose stars are in the ascendent.
As time passes on, the number of singers whose names are handed down as "famous" is very small in proportion to the number of{324} singers who come before the public, and it is possible that even some of those mentioned in this book may become dim in the distance of years.{325}
The dates in italic are not authenticated.
| Name | Birth | Début | Retired | Death |
| Ferri, Baldassare | 1610 | 1621 | 1680 | |
| Abell, John | 1660 | 1682 | 1716 | |
| Nicolini, Nicolo Grimaldi | 1673 | 1694 | 1726 | ? |
| Leveridge, Richard | 1670 | 1695 | 1730 | 1758 |
| Tofts, Mrs. Katharine | ? | 1703 | 1709 | 1740 |
| Epine, Francesca Margherita | ? | 1704 | 1718 | ? |
| Valentini, Valentino Urbani | ? | 1707 | 1714 | ? |
| Boschi, Giuseppe | ? | 1711 | 1728 | ? |
| Bernacchi, Antonio | 1690 | 1712 | 1730 | 1756 |
| Galeratti, Catherina | ? | 1714 | 1721 | ? |
| Robinson, Anastasia | ? | 1715 | 1722 | 1750 |
| Bordoni, Faustina (Hasse) | 1700 | 1716 | 1756 | 1783 |
| Cuzzoni, Francesca (Sandoni) | 1700 | 1719 | 1750 | 1770 |
| Senesino, Francesco Bernardi | 1680 | 1719 | 1735 | 1750 |
| Tesi, Tramentini Vittoria | 1690 | 1719 | 1749 | 1775 |
| Durastanti, Margherita | 1695 | 1720 | 1734 | ? |
| Carestini, Giovanni | 1705 | 1721 | 1758 | 1758 |
| Farinelli (Carlo Broschi) | 1705 | 1722 | 1762 | 1782 |
| Borosini, Francesco | 1695 | 1723 | ? | ? |
| Caffarelli, Gaetano Majorano | 1703 | 1724 | 1750 | 1783 |
| Fenton, Lavinia (Duchess of Bolton) | ? | 1726 | 1731 | 1760 |
| Fabri, Annibale | 1697 | 1729 | ? | 1760 |
| Gizziello, Gioacchino Conti | 1714 | 1729 | 1753 | 1761 |
| Monticelli, Angelo Maria | 1710 | 1730 | ? | 1764{326} |
| Beard, John | 1717 | 1736 | 1767 | 1791 |
| Raff, Anton | 1714 | 1738 | 1779 | 1797 |
| Amorevoli, Angelo | 1716 | 1741 | ? | 1798 |
| Guarducci, Tommasso Toscano | 1720 | 1745 | 1771 | ? |
| Guadagni, Gaetano | 1725 | 1747 | 1784 | 1797 |
| Gabrielli, Caterina | 1730 | 1747 | 1780 | 1796 |
| Mingotti, Regina | 1728 | 1748 | 1787 | 1807 |
| Ciprandi, Ercole | 1738 | 1754 | 1763 | 1790 |
| Arnould, Madeleine Sophie | 1744 | 1757 | 1778 | 1803 |
| Calori, Angiola | 1732 | 1758 | 1783 | 1790 |
| Tenducci, Giusto Fernandino | 1736 | 1758 | 1791 | 1800 |
| Catley, Anne | 1745 | 1762 | 1784 | 1789 |
| Amici, Anna Lucia de | 1740 | 1763 | 1789 | ? |
| Manzuoli, Giovanni | 1725 | 1764 | 1771 | ? |
| Ranzzini, Venanzio | 1747 | 1765 | 1810 | |
| Pacchierotti, Gasparo | 1744 | 1769 | 1796 | 1821 |
| Ansani, Giovanni | 1750 | 1770 | 1800 | 1815 |
| Allegranti, Madalena | ? | 1771 | 1799 | ? |
| Rubinelli, Giovanni Battista | 1753 | 1771 | 1800 | 1829 |
| Mara, Gertrude Elizabeth | 1749 | 1771 | 1800 | 1833 |
| Lebrun, Francesca | 1756 | 1771 | 1790 | 1791 |
| Davies, Cecilia | 1752 | 1773 | 1791 | 1836 |
| Marchesi, Luigi | 1755 | 1774 | 1806 | 1829 |
| Cavalieri, Katharina | 1761 | 1775 | 1793 | 1801 |
| Saint Huberty, Antoinette Cécile | 1756 | 1777 | 1789 | 1812 |
| Solié, Jean Pierre | 1755 | 1778 | 1812 | |
| Kelly, Michael | 1764 | 1779 | 1826 | 1826 |
| Banti, Brigitta Giorgi | 1759 | 1779 | ? | 1806 |
| Adamberger, Valentin | 1743 | 1780 | ? | 1804 |
| Babbini, Matteo | 1754 | 1780 | 1802 | 1816 |
| Crouch, Mrs. Anna Maria | 1763 | 1780 | 1800 | 1805 |
| Garat, Pierre Jean | 1764 | ? | 1814 | 1823 |
| Storace, Ann Selina | 1766 | 1780 | 1808 | 1817 |
| Sestini, Giovanna | ? | 1783 | 1791 | ? |
| Crescentini, Girolamo | 1766 | 1783 | 1812 | 1846 |
| Incledon, Charles Benjamin | 1763 | 1784 | 1826 | 1826 |
| Bassi, Luigi | 1766 | 1784 | 1815 | 1825 |
| Vogl, Johann Michael | 1768 | ? | ? | 1840{327} |
| Schröder-Devrient, Wilhelmine | 1804 | 1821 | 1847 | 1860 |
| Billington, Mrs. Elizabeth (née Weichsel) | 1768 | 1784 | 1809 | 1818 |
| Saint Aubin, Jeanne Charlotte Schroeder | 1764 | 1786 | 1818 | 1850 |
| Dickons, Mrs. (née Poole) | 1770 | 1787 | 1822 | 1833 |
| Braham, John | 1774 | 1787 | 1852 | 1856 |
| Bertinotti, Teresa | 1776 | 1788 | 1823 | 1854 |
| Lazzarini, Gustavo | 1765 | 1789 | 1802 | ? |
| Crivelli, Gaetano | 1774 | 1793 | 1829 | 1836 |
| Grassini, Josephine | 1773 | 1794 | 1817 | 1850 |
| Pellegrini, Felice | 1774 | 1795 | 1829 | 1832 |
| Catalani, Angelica | 1779 | 1795 | 1828 | 1849 |
| Campenhout, François van | 1780 | 1797 | 1827 | 1848 |
| Siboni, Giuseppe | 1780 | 1797 | 1818 | 1839 |
| Velluti, Giovanni Battista | 1781 | 1800 | 1829 | 1861 |
| Tacchinardi, Niccolo | 1776 | 1804 | 1831 | 1850 |
| Galli, Filippo | 1783 | 1804 | 1830 | 1853 |
| Colbran (Rossini), Isabella Angela | 1785 | 1806 | 1824 | 1845 |
| Forti, Anton | 1790 | 1807 | ? | 1859 |
| Rubini, Giovanni Battista | 1795 | 1807 | 1844 | 1854 |
| Garcia, Manuel del Popolo Vicente | 1775 | 1808 | 1828 | 1832 |
| Davide, Giovanni | 1789 | 1810 | 1841 | 1851 |
| Fodor-Mainvielle, Josephine | 1793 | 1810 | 1833 | ? |
| Pisaroni, Benedetta Rosamunda | 1793 | 1811 | 1829 | 1872 |
| Stephens, Catherine | 1794 | 1812 | 1835 | 1882 |
| Lablache, Luigi | 1794 | 1812 | 1856 | 1856 |
| Begnis, Giuseppe de | 1793 | 1813 | ? | 1849 |
| Begnis, Signora Claudine Ronzi de | 1800 | 1819 | ? | 1853 |
| Brighenti, Mme. Maria | 1792 | 1814 | 1836 | ? |
| Camporese, Violanti | 1785 | 1816 | 1829 | ? |
| Pasta, Giuditta | 1798 | 1816 | 1850 | 1865 |
| Donzelli, Domenico | 1790 | 1816 | 1841 | 1873 |
| Boccabadati, Luigia | ? | 1817 | ? | 1850 |
| Tamburini, Antonio | 1800 | 1818 | 1859 | 1876 |
| Damoreau, Laure Cinthie Montalant | 1801 | 1819 | 1846 | 1863 |
| Sontag, Henriette (Countess Rossi) | 1805 | 1820 | 1854 | 1854 |
| Curioni, Alberico | 1790 | 1815 | ? | ? |
| Nourrit, Adolphe | 1802 | 1821 | 1839 | 1839{328} |
| Schröder-Devrient, Wilhelmine | 1804 | 1821 | 1847 | 1860 |
| Frischer-Achten, Frau | 1805 | 1821 | 1856 | 1896 |
| Unger, Caroline | 1805 | 1821 | 1840 | 1877 |
| Caradori-Allan, Maria Caterina Rosalbina | 1800 | 1822 | 1846 | 1865 |
| Paton, Mary Anne | 1802 | 1822 | 1844 | 1863 |
| Duprez, Gilbert | 1806 | 1825 | 1842 | 1896 |
| Gras, Mme. Julie Aimèe Dorus | 1807 | 1825 | 1851 | 1896 |
| Malibran, Maria Felicita | 1808 | 1825 | 1836 | 1836 |
| Badiale, Cesare | 1800 | 1827 | 1865 | 1865 |
| Brambilla, Marietta | 1807 | 1827 | ? | ? |
| Templeton, John | 1802 | 1828 | 1852 | |
| Staudigl, Joseph | 1807 | 1827 | 1856 | 1861 |
| Grisi, Giulia | 1812 | 1829 | 1861 | 1869 |
| Albertazzi, Emma | 1814 | 1830 | 1846 | 1847 |
| Seguin, Arthur Edward Shelden | 1809 | 1831 | ? | 1852 |
| Ronconi, Giorgio | 1810 | 1831 | 1874 | 1890 |
| Bishop, Mme. Anna | 1814 | 1831 | ? | 1884 |
| Persiani, Fanny | 1812 | 1832 | 1858 | 1867 |
| Stoltz, Rosina | 1815 | 1832 | 1849 | ? |
| Loewe, Johanna Sophie | 1815 | 1832 | 1848 | 1866 |
| Frege, Mme. (Livia Gerhard) | 1818 | 1832 | ? | 1847 |
| Moriani, Napoleone | 1806 | 1833 | 1847 | 1878 |
| Novello, Clara Anastasia | 1818 | 1833 | 1860 | |
| Shaw, Mary (Mrs. Alfred Shaw) | 1814 | 1834 | 1843 | 1876 |
| Poole, Elizabeth | 1820 | 1834 | 1870 | |
| Pischek, Johann Baptist | 1814 | 1835 | 1863 | 1873 |
| Nau, Maria Dolores Benedicta Josephina | 1818 | 1836 | 1856 | |
| Sequin, Mrs. (Ann Childe) | 1818 | 1836 | 1889 | |
| Castellan, Jeanne Anaïs | 1819 | 1836 | 1859 | |
| Tichatschek, Joseph Alois | 1807 | 1837 | 1870 | 1885 |
| Fraschini, Gaetano | 1815 | 1837 | 1870 | |
| Viardot-Garcia, Pauline | 1821 | 1837 | 1870 | |
| Mario, Chevaliere di Candia | 1812 | 1838 | 1867 | 1883 |
| Belletti, Giovanni | 1813 | 1838 | 1863 | |
| Roger, Gustave Hyppolite | 1815 | 1838 | 1859 | 1879 |
| Frezzolini, Erminia | 1818 | 1838 | 1853 | 1884{329} |
| Thillon, Anna | 1819 | 1838 | 1856 | |
| Lind-Goldschimidt, Jenny | 1820 | 1838 | 1870 | 1887 |
| Harrison, William | 1813 | 1839 | ? | 1868 |
| Reeves, John Sims | 1822 | 1839 | 1891 | |
| Gardoni, Enrico | 1821 | 1840 | 1874 | 1882 |
| Rudersdorff, Mme. Herminie | 1822 | 1840 | 1872 | 1882 |
| Tamberlik, Enrico | 1820 | 1841 | 1877 | 1889 |
| Saiuton-Dolby, Charlotte Helen | 1821 | 1841 | 1870 | 1885 |
| Formes, Karl | 1810 | 1842 | ? | 1889 |
| Weiss, Willoughby Hunter | 1820 | 1842 | 1867 | |
| Alboni, Marietta | 1823 | 1843 | 1871 | 1894 |
| Reichardt, Alexander | 1825 | 1843 | 1857 | |
| Wagner, Johanna | 1828 | 1844 | 1861 | 1894 |
| Ander, Aloys | 1821 | 1845 | 1864 | 1864 |
| Gassier, Edouard | 1822 | 1845 | 1871 | |
| Hayes, Catharine | 1825 | 1845 | 1857 | 1861 |
| Formes, Theodora | 1826 | 1846 | 1864 | |
| Borghi, Adelaide | 1829 | 1846 | 1870 | |
| Bosio, Angiolina | 1830 | 1846 | 1859 | 1859 |
| Cruvelli, Jeanne Sophie Charlotte | 1826 | 1847 | 1855 | |
| Burde-Ney, Jenny | 1826 | 1847 | 1886 | |
| Pyne, Louisa Fanny | 1832 | 1847 | 1868 | ? |
| Cabel, Marie Josephe (née Dreulette) | 1827 | 1849 | 1877 | 1885 |
| Carvalho, Mme. Marie Caroline Félix | 1827 | 1849 | 1882 | 1895 |
| Niemann, Albert | 1831 | 1849 | 1887 | |
| Tietiens, Therese Caroline Johanna | 1831 | 1849 | 1877 | 1877 |
| Nantier-Didier, Constance Betsy Rosabelle | 1831 | 1850 | 1867 | |
| Stockhausen, Julius | 1826 | 1848 | 1870 | |
| Faure, Jean Baptiste | 1830 | 1852 | ||
| Piccolomini, Maria | 1836 | 1852 | 1863 | |
| Parepa-Rosa, Euphrosine de Boyesku | 1836 | 1852 | 1873 | 1874 |
| Bettini, Alessandro | 1830 | 1853 | ||
| Wachtel, Theodor | 1823 | 1854 | 1893 | |
| Sedie, Enrico Delle | 1826 | 1854 | 1870 | {330} |
| Phillips, Adelaide | 1833 | 1854 | 1881 | 1882 |
| Wilt, Marie | 1834 | 1857 | 1878 | 1891 |
| Nicolini, Ernest Nicolas | 1834 | 1855 | 1878 | 1898 |
| Betz, Franz | 1835 | 1856 | ||
| Rokitansky, Victor F. von | 1836 | 1856 | 1871 | |
| Peschka-Leutner, Mme. Minna | 1839 | 1856 | 1890 | |
| Giuglini, Antonio | 1826 | 1857 | 1862 | 1865 |
| Fancelli, Giuseppe | 1836 | ? | ? | 1889 |
| Santley, Charles | 1834 | 1857 | ||
| Marimon, Marie | 1839 | 1857 | 1884 | |
| Artôt, Mme. Marguerite Josephine D. M. | 1835 | 1857 | 1887 | |
| Naudin, Emilio | 1823 | 1858 | 1880 | |
| Whitney, Myron W. | 1836 | 1858 | 1897 | |
| Galli-Marié, Mme. Celestine | 1840 | 1859 | ||
| Lucca, Pauline | 1841 | 1859 | 1884 | |
| Patti-Nicolini, Mme. Adelina | 1843 | 1859 | ||
| Trebelli-Bettini, Mme. Zelia | 1838 | 1859 | 1892 | |
| Sherrington, Mme. Lemmens | 1834 | 1860 | ||
| Scaria, Emil | 1838 | 1860 | 1884 | 1886 |
| Krauss, Marie Gabrielle | 1842 | 1860 | ? | |
| Foli, Allan James (Foley) | 1841 | 1861 | ||
| Agnesi, Louis Ferdinand Leopold | 1833 | 1861 | 1871 | |
| Capoul, Joseph Victor Amédée | 1839 | 1861 | 1895 | |
| Patti, Carlotta | 1840 | 1861 | 1880 | 1889 |
| Kellogg, Clara Louise | 1842 | 1861 | 1882 | |
| Murska, Ilma di | 1836 | 1862 | 1878 | 1889 |
| Kraus, Dr. Emil | 1840 | 1889 | ||
| Henschel, Georg | 1850 | 1862 | ||
| Nilsson, Christine | 1843 | 1864 | 1888 | |
| Materna, Amalie (Frau Friedrich) | 1847 | 1864 | 1894 | |
| Patey, Janet Monach | 1842 | 1865 | 1894 | |
| Vogl, Heinrich | 1845 | 1865 | ||
| Vogl, Theresa Thoma | 1846 | 1865 | ||
| Roze, Marie | 1846 | 1865 | ||
| Nachbaur, Franz | 1835 | 1865 | ||
| Lloyd, Edward | 1845 | 1866 | ||
| Adams, Charles R. | 1848 | 1866 | 1879 | {331} |
| Scalchi, Sophia | 1850 | 1866 | ||
| Brandt, Marianne | 1842 | 1867 | 1893 | |
| Cary, Annie Louise | 1846 | 1867 | 1882 | |
| Lehmann, Lilli | 1848 | 1868 | ||
| Hauck, Minnie | 1852 | 1868 | 1886 | |
| Vaucorbeil, Anna Sternberg | 1845 | 1869 | 1873 | 1898 |
| Heilbron, Marie | 1849 | 1869 | 1886 | |
| Karl, Thomas | 1847 | 1870 | 1890 | |
| Maurel, Victor | 1845 | 1869 | ||
| Gayarre, Giuliano | 1848 | 1873 | 1890 | |
| Del Puente, Parquale | ? | 1870 | ||
| Schott, Anton | 1846 | 1870 | ||
| Sucher, Rose (Hasselbeck) | 1850 | 1870 | ||
| Albani, Marie L. C. E. Lajeunnesse(Mrs. Ernest Gye) | 1850 | 1870 | ||
| Sterling, Antoinette | 1851 | 1871 | ||
| Campanini, Italo | 1846 | 1871 | 1890 | 1896 |
| Valleria, Alwina Lohmann | 1848 | 1871 | ||
| Pappenheim, Mme. Eugenie | ? | 1872 | ||
| Abbott, Emma (Mrs. Wetherell) | 1850 | 1872 | 1891 | |
| Malten, Thérèse | 1855 | 1873 | ||
| McGuckin, Barton | 1852 | 1874 | ||
| Belocca, Anna di | 1854 | 1874 | ||
| Reicher, Hedwig | 1853 | 1874 | 1883 | |
| Shakespeare, William | 1849 | 1875 | ||
| Thursby, Emma | 1857 | 1875 | ||
| Gaylord, Mrs. Julia | 1852 | 1875 | 1894 | |
| Reszke, Josephine de | 1855 | 1875 | 1884 | 1890 |
| Litta, Marie | 1856 | 1876 | 1883 | 1883 |
| De Reszke, Jean | 1852 | 1874 | ||
| De Reszke, Edouard | 1855 | 1876 | ||
| Klafsky, Katharina | 1855 | 1896 | ||
| Gerster, Etelka | 1856 | 1876 | 1887 | |
| Fursch-Madi, Mme | ? | 1876 | 1894 | |
| Sembrich, Marcella | 1858 | 1877 | ||
| Van Zandt, Marie | 1861 | 1879 | 1898 | |
| Bispham, David Scull | 1857 | 1880 | ||
| Nordica, Giglia (Lillian Norton) | 1856 | 1880 | {332} | |
| L'Allemand, Pauline | 1862 | 1880 | ||
| Nevada, Emma (Wixom) | 1862 | 1880 | ||
| Plançon, Pol | 1860 | 1881 | ||
| Juch, Emma | 1863 | 1881 | ||
| Calvé, Emma (Roquer) | 1866 | 1882 | ||
| Russell, Ella | 1862 | 1882 | ||
| Van Dyk, Ernest Marie Hubert | 1861 | 1883 | ||
| Engel, Marie | ? | 1887 | ||
| Melba, Nellie (Mitchell) | 1864 | 1887 | ||
| Ternina, Milka | ? | 1888 | ||
| Eames, Emma | 1867 | 1888 | ||
| Sanderson, Sybil | 1865 | 1889 | ||
| Davies, Ffrançon | ? | 1890 | ||
| Delna, Marie | 1875 | 1892 | ||
| Brema, Marie | ? | 1892 |
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Famous Singers of To-day and Yesterday, by
Henry C. Lahee
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FAMOUS SINGERS ***
***** This file should be named 33168-h.htm or 33168-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/3/3/1/6/33168/
Produced by Chuck Greif and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images available by The Internet Archive.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.