BIRDS
A MONTHLY SERIAL
ILLUSTRATED BY COLOR PHOTOGRAPHY
DESIGNED TO PROMOTE
KNOWLEDGE OF BIRD-LIFE
VOLUME II.
CHICAGO.
NATURE STUDY PUBLISHING COMPANY.
copyright, 1897
by
Nature Study Publishing Co.
chicago.
BIRDS.
Illustrated by COLOR PHOTOGRAPHY.
JOHN JAMES AUDUBON.
OHN JAMES AUDUBON has always been a favorite with the writer, for the invincibleness of his love of Nature and of birds is only equalled by the spontaneous freshness of his style, springing from an affectionate and joyous nature. Recently there was found by accident, in an old calf-skin bound volume, an autobiography of the naturalist. It is entitled “Audubon’s Story of his Youth,” and would make a very pretty book. As introductory to the diaries and ornithological biographies of the birds, it would be very useful.
Two or three incidents in the life of this fascinating character are interesting as showing the influence of the accidental in ultimate achievement.
“One incident,” he says, “which is as perfect in my memory as if it had occurred this very day, I have thought thousands of times since, and will now put on paper as one of the curious things which perhaps did lead me in after times to love birds, and to finally study them with pleasure infinite. My mother had several beautiful parrots, and some monkeys; one of the latter was a full-grown male of a very large species. One morning, while the servants were engaged in arranging the room I was in, ‘Pretty Polly’ asking for her breakfast as usual, ‘Du pain au lait pour le perroquet Mignonne,’ (bread and milk for the parrot Mignonne,) the man of the woods probably thought the bird presuming upon his rights in the scale of nature; be this as it may, he certainly showed his supremacy in strength over the denizen of the air, for, walking deliberately and uprightly toward the poor bird, he at once killed it, with unnatural composure. The sensations of my infant heart at this cruel sight were agony to me. I prayed the servant to beat the monkey, but he, who for some reason, preferred the monkey to the parrot, refused. I uttered long and piercing cries, my mother rushed into the room; I was tranquilized; the monkey was forever afterward chained, and Mignonne buried with all the pomp of a cherished lost one. This made, as I have said, a very deep impression on my youthful mind.”
In consequence of the long absences of his father, who was an admiral in the French navy, the young naturalist’s education was neglected, his mother suffering him to do much as he pleased, and it was not to be wondered at, as he says, that instead of applying closely to his studies, he preferred associating with boys of his own age and disposition, who were more fond of going in search of bird’s nests, fishing, or shooting, than of better studies. Thus almost every day, instead of going to school, he usually made for the fields where he spent the day, returning with his little basket filled with what he called curiosities, such as birds’ nests, birds’ [Pg 162] eggs, curious lichens, flowers of all sorts, and even pebbles gathered along the shore of some rivulet. Nevertheless, he did study drawing and music, for which he had some talent. His subsequent study of drawing under the celebrated David, richly equipped him for a work which he did not know was ever to be his, and enabled him to commence a series of drawings of birds of France, which he continued until he had upwards of two hundred completed. “All bad enough,” he says, “yet they were representations of birds, and I felt pleased with them.” Before sailing for France, he had begun a series of drawings of the birds of America, and had also begun a study of their habits. His efforts were commended by one of his friends, who assured him the time might come when he should be a great American naturalist, which had such weight with him that he felt a certain degree of pride in the words, even then, when he was about eighteen years of age.
“The store at Louisville went on prosperously, when I attended to it; but birds were birds then as now, and my thoughts were ever and anon turning toward them as the objects of my greatest delight. I shot, I drew, I looked on nature only; my days were happy beyond human conception, and beyond this I really cared not.” [How like Agassiz, who said he had not time to make money.] As he could not bear to give the attention required by his business, his business abandoned him. “Indeed, I never thought of business beyond the ever-engaging journeys which I was in the habit of taking to Philadelphia or New York, to purchase goods; those journeys I greatly enjoyed, as they afforded me ample means to study birds and their habits as I traveled through the beautiful, the darling forests of Ohio, Kentucky, and Pennsylvania.” Poor fellow, how many ups and downs he had! He lost everything and became burdened with debt. But he did not despair for had he not a talent for drawing? He at once undertook to take portraits of the human head divine in black chalk, and thanks to his master, David, succeeded admirably. He established a large drawing school at Cincinnati, and formed an engagement to stuff birds for the museum there at a large salary.
“One of the most extraordinary things among all these adverse circumstances” he adds, “was, that I never for a day give up listening to the songs of our birds, or watching their peculiar habits, or delineating them in the best way I could; nay, during my deepest troubles, I frequently would wrench myself from the persons around me and retire to some secluded part of our noble forests; and many a time, at the sound of the wood-thrushes’ melodies, have I fallen on my knees and there prayed earnestly to our God. This never failed to bring me the most valuable of thoughts, and always comfort, and it was often necessary for me to exert my will and compel myself to return to my fellow-beings.”
Do you not fancy that Audubon was himself a rara avis and worthy of admiration and study?
Such a man, in the language of a contemporary, should have a monument in the old Creole country in which he was born, and whose birds inspired his childish visions. It should be the most beautiful work possible to the sculptor’s art, portraying Audubon in the garb he wore when he was proud and happy to be called the “American Woodman,” and at his feet should stand the Eagle which he named the “Bird of Washington,” and near should perch the Mocking Bird, as once, in his description, it flew and fluttered and sang to the mind’s eye and ear from the pages of the old reading book.
C. C. Marble.
 summer tanager
summer tanagerFrom col. F. M. Woodruff. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE SUMMER TANAGER.

HE TANAGERS are birds of such uncommon beauty that when we have taken the pictures of the entire family the group will be a notable one and will add attractiveness to the portfolio. [See Vol. I, pp. 31 and 216.] This specimen is also called the Summer Red-bird or Rose Tanager, and is found pretty generally distributed over the United States during the summer months, wintering in Cuba, Central America, and northern South America. As will be seen, the adult male is a plain vermilion red. The plumage of the female is less attractive. In habits this species resembles the Scarlet Tanager, perhaps the most brilliant of the group, but is not so retiring, frequenting open groves and often visiting towns and cities.
The nesting season of this charming bird extends to the latter part of July, but varies with the latitude and season. Bark strips and leaves interwoven with various vegetable substances compose the nest, which is usually built on a horizontal or drooping branch, near its extremity and situated at the edge of a grove near the roadside. Davie says: “All the nests of this species which I have seen collected in Ohio are very thin and frail structures; so thin that the eggs may often be seen from beneath. A nest sent me from Lee county, Texas, is compactly built of a cottony weed, a few stems of Spanish moss, and lined with fine grass stems.” Mr. L. O. Pindar states that nests found in Kentucky are compactly built, but not very thickly lined. The eggs are beautiful, being a bright, light emerald green, spotted, dotted, and blotched with various shades of lilac, brownish-purple, and dark brown.
Chapman says the Summer Tanager may be easily identified, not alone by its color but by its unique call-note, a clearly enunciated chicky, tucky, tuck. Its song bears a general resemblance to that of the Scarlet, but to some ears is much sweeter, better sustained, and more musical. It equals in strength, according to one authority, that of the Robin, but is uttered more hurriedly, is more “wiry,” and much more continued.
The Summer Tanager is to a greater or less extent known to farmers as the Red Bee-Bird. Its food consists largely of hornets, wasps, and bees.
The male of this species requires several years to attain the full plumage. Immature individuals, it is said, show a mixture of red and yellow in relative proportions according to age. The female has more red than the male, but the tint is peculiar, a dull Chinese orange, instead of a pure rosy vermilion, as in the male.
An interesting study for many of our readers during the summer months when the Tanagers are gay in their full plumage, would be to seek out, with Birds in hand, the most attractive denizens of the groves, identifying and observing them in their haunts until the entire group, of which five species are represented in the United States, is made familiar. When we remember that there are about three hundred and eighty known species of Tanagers in Tropical America, it would seem a light task to acquaint oneself with the small family at home.
THE AMERICAN WHITE-FRONTED GOOSE.
“As stupid as a Goose!”
Yes, I know that is the way our family is usually spoken of. But then I’m not a tame Goose, you know. We wild fellows think we know a little more than the one which waddles about the duck-pond in your back yard.
He sticks to one old place all the time. Waddles and talks and looks the same year after year. We migratory birds, on the other hand, fly from place to place. Our summers are passed here, our winters there; so that we pick up a thing or two the common Goose never dreams of.
“The laughing Goose!”
Yes, some people call me that. I don’t know why, unless my Honk, honk, honk! sounds like a laugh. Perhaps, though, it is because the look about my mouth is so pleasant.
Did you ever see a flock of us in motion, in October or November, going to our winter home?
Ah, that is a sight! When the time comes for us to start, we form ourselves into a figure like this >· a big gander taking the lead where the dot is. Such a honk, honk, honking you never heard. People who have heard us, and seen us, say it sounds like a great army overhead.
Where do we live in summer, and what do we eat?
You will find us throughout the whole of North America, but in greater numbers on the Pacific coast. The fresh-water lakes are our favorite resorts. We visit the wheat fields and corn fields, nibbling the young, tender blades and feeding on the scattered grain. The farmers don’t like it a bit, but we don’t care. That is the reason our flesh tastes so sweet.
And tough!
My, how you talk! It is only we old fellows that are tough, we fellows over a year old. But of course a great many people don’t know that, or don’t care.
Why, I once heard of a gander that had waddled around a barnyard for five long years. Thanksgiving Day arrived, and they roasted him for dinner.
Think of eating an old, old friend like that!
Where do we build our nests?
Away up north, in Alaska, and on the islands of the Arctic Sea. We make them of hay, feathers, and down, building them in hollow places on the ground.
How many eggs?
Six. I am very good to my mate, and an affectionate father.
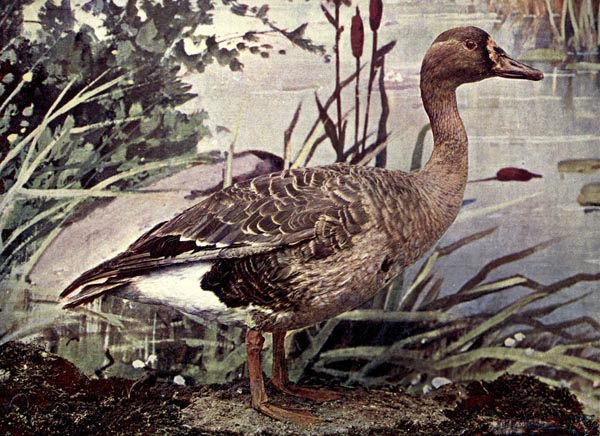 white-fronted goose.
white-fronted goose.From col. Chi. Acad. Sciences. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE AMERICAN WHITE-FRONTED GOOSE.

HITE-FRONTED or Laughing Geese are found in considerable numbers on the prairies of the Mississippi Valley. They are called Prairie Brant by market-men and gunners. Though not abundant on the Atlantic seaboard, vast flocks may be seen in the autumn months on the Pacific Slope. In Oregon and northern California some remain all winter, though the greater number go farther south. They appear to prefer the grassy patches along streams flowing into the ocean, or the tide-water flats so abundant in Oregon and Washington, where the Speckle-bellies, as they are called, feed in company with the Snow Geese. The nesting place of this favorite species is in the wooded districts of Alaska and along the Yukon river. No nest is formed, from seven to ten eggs being laid in a depression in the sand.
It is said that notwithstanding all references to their ungainly movement and doltish intellect, the Wild Goose, of which the White-fronted is one of the most interesting, is held in high estimation by the sportsman, and even he, if keen of observation, will learn from it many things that will entitle the species to advancement in the mental grade, and prove the truth of a very old adage, that you cannot judge of things by outward appearance. A goose, waddling around the barnyard, may not present a very graceful appearance, nor seem endowed with much intelligence, yet the ungainly creature, when in its natural state, has an ease of motion in flight which will compare with that of any of the feathered tribe, and shows a knowledge of the means of defense, and of escaping the attacks of its enemies, that few possess. There is probably no bird more cautious, vigilant, and fearful at danger than this. Should their suspicion be aroused, they rise upward slowly in a dense cloud of white, and sound their alarm notes, but they may not go over fifty yards before they alight again, so that the amusement of watching them may be continued without much toil or inconvenience.
The White-fronted Goose visits Illinois only during its migrations, coming some time in October or early in November, and returning in March or April. During its sojourn there it frequents chiefly open prairies, or wheat fields, where it nibbles the young and tender blades, and cornfields, where it feeds upon the scattered grains. In California, Ridgway says, it is so numerous in winter as to be very destructive of the growing wheat crop, and it is said that in the Sacramento and San Joaquin valleys, farmers often find it necessary to employ men by the month to hunt and drive them from the fields. This is most successfully accomplished by means of brush hiding places, or “blinds,” or by approaching the flocks on horseback by the side of an ox which has been trained for the purpose.
The White-fronted Goose is greatly esteemed for the excellent quality of its flesh, which, by those who have learned to appreciate it, is generally considered superior to that of any other species. While the cruel pursuit of the bird, merely for purpose of sport ought not to be continued, appreciation of its value as food may well be encouraged.
THE TURNSTONE.

HIS small plover-like bird is found on the sea-coasts of nearly all countries; in America, from Greenland and Alaska to Chili and Brazil; more or less common in the interior along the shores of the Great Lakes and larger rivers.
It is generally found in company with flocks of the smaller species of Sandpipers, its boldly marked plumage contrasting with surroundings, while the Sandpipers mingle with the sands and unless revealed by some abrupt movement can hardly be seen at a little distance.
The name Turnstone has been applied to this bird on account of its curious habit of dexterously inserting its bill beneath stones and pebbles along the shore in quest of food, overturning them in search of the insects or prey of any kind which may be lurking beneath. It is found on smooth, sandy beaches, though more commonly about the base of rocky cliffs and cones. The eggs of horseshoe crabs are its particular delight.
In the nesting season the Turnstone is widely distributed throughout the northern portions of both continents, and wanders southward along the sea-coasts of all countries. In America it breeds commonly in the Barren Lands of the Arctic coasts and the Anderson River districts, on the Islands of Franklin and Liverpool bays, nesting in July. In the Hudson’s Bay country the eggs are laid in June. The nest is a hollow scratched in the earth, and is lined with bits of grass.
The Turnstone is known by various names: “Brant Bird,” “Bead-bird,” “Horse-foot-Snipe,” “Sand-runner,” “Calico-back,” “Chicaric” and “Chickling.” The two latter names have reference to its rasping notes, “Calico-back,” to the variegated plumage of the upper parts.
In summer the adults are oddly pied above with black, white, brown, and chestnut-red, but the red is totally wanting in winter. They differ from the true Plovers in the well developed hind-toe, and the strong claws, but chiefly in the more robust feet, without trace of web between the toes.
The eggs are greenish-drab in color, spotted, blotched, and dotted irregularly and thickly with yellowish and umber brown. The eggs are two or four, abruptly pyriform in shape.
SNOWBIRDS.
Along the narrow sandy height
I watch them swiftly come and go,
Or round the leafless wood,
Like flurries of wind-driven snow,
Revolving in perpetual flight,
A changing multitude.
Nearer and nearer still they sway,
And, scattering in a circled sweep,
Rush down without a sound;
And now I see them peer and peep,
Across yon level bleak and gray,
Searching the frozen ground,—
Until a little wind upheaves,
And makes a sudden rustling there,
And then they drop their play,
Flash up into the sunless air,
And like a flight of silver leaves
Swirl round and sweep away.
Archibald Lampman.
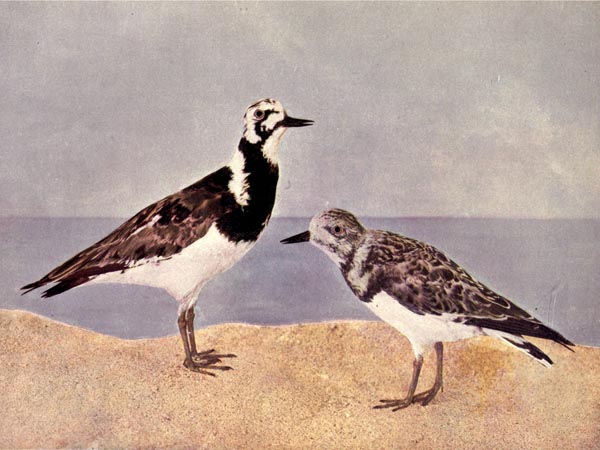 turnstone.
turnstone.From col. F. M. Woodruff. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
BIRDS OF PASSAGE.
Black shadows fall
From the lindens tall,
That lift aloft their massive wall
Against the southern sky;
And from the realms
Of the shadowy elms,
A tide-like darkness overwhelms
The fields that round us lie.
But the night is fair
And everywhere
A warm, soft vapor fills the air
And distant sounds seem near;
And above, in the light
Of the star-lit night,
Swift birds of passage wing their flight
Through the dewy atmosphere.
I hear the beat
Of their pinions fleet,
As from the land of snow and sleet
They seek a southern lea.
I hear the cry
Of their voices high
Falling dreamily through the sky,
But their forms I cannot see.
—Longfellow.
THE BELTED PIPING PLOVER.
N the Missouri river region and in contiguous parts of the interior of the United States, the Belted Piping Plover is a common summer resident, and is found along the shores of the great lakes, breeding on the flat, pebbly beach between the sand dunes and shore. It is the second of the ring-necked Plovers, and arrives in April in scattering flocks, which separate into pairs a month later. It strays at times into the interior, and has been known to breed on the borders of ponds many miles from the coast. In New England, however, it seldom wanders far from the shore, and prefers sand islands near the main land for its nesting haunts. Nelson says, that some thirty pairs, which were breeding along the beach at Waukegan, within a space of two miles, successfully concealed their nests, for which he made diligent search, although the birds were continually circling about or standing at a short distance, uttering an occasional note of alarm.
These birds have a soft, low, piping note, which they utter not only upon the wing, but occasionally as they run about upon the ground, and, during the early nesting season, a peculiar, loud, prolonged, musical call, that readily attracts attention. In other respects, their habits are not noticeably differed from the Semi-palmated. (See July Birds, p. 8.)
Their nests are without lining, a mere depression in the sand. The eggs are usually four, light gray to creamy buff, finely and rather sparsely speckled or dotted with blackish brown and purplish gray.
The female Belted Piping Plover is similar to the male, but with the dark colors lighter and less in extent. The young have no black band in front, while the collar around the neck is ashy brown.
These interesting and valuable game birds are found associated with various beach birds and Sandpipers, and they become exceedingly fat during the latter part of the summer.
All the Plovers have a singular habit when alighting on the ground in the nesting time; they drop their wings, stand with their legs half bent, and tremble as if unable to support their bodies. In this absurd position they will stand, according to a well-known observer, for several minutes, uttering a curious sound, and then seem to balance themselves with great difficulty. This singular manœuvre is no doubt intended to produce a belief that they may be easily caught, and thus turn the attention of the egg-gatherer from the pursuit of the eggs to themselves, their eggs being recognized the world over, as a great delicacy.
The Plover utters a piping sound
While on the wing or on the ground;
All a tremble it drops its wings,
And, with legs half bent, it sings:
“My nest is near, come take the eggs,
And take me too,—I’m off my legs.”
In vain men search with eager eyes,
No nest is found, the Plover flies!
—C. C. M
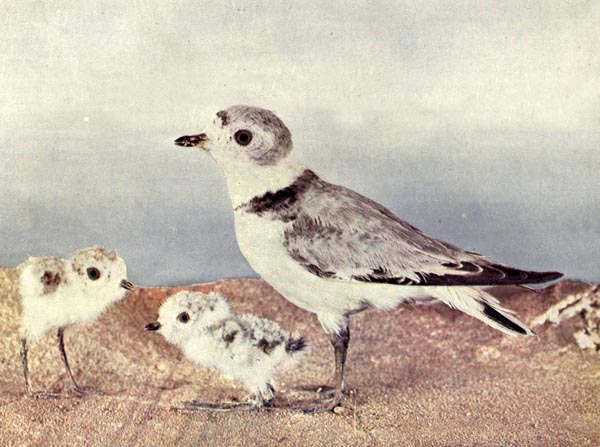 belted piping plover.
belted piping plover.From col. F. M. Woodruff. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
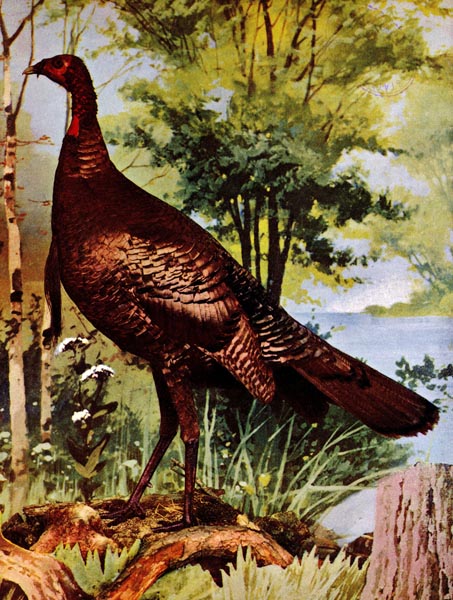
THE WILD TURKEY.
T has been observed that when the Turkey makes its appearance on table all conversation should for the moment be suspended. That it is eaten in silence on some occasions may be inferred from the following anecdote: A certain judge of Avignon, famous for his love of the glorious bird, which the American people have wisely selected for the celebration of Thanksgiving Day, said to a friend: “We have just been dining on a superb Turkey. It was excellent. Stuffed with truffles to the very throat—tender, delicate, filled with perfume! We left nothing but the bones!” “How many were there of you?” asked his friend. “Two,” replied the judge, “the Turkey—and myself!” The reason, no doubt, why this brilliant bird, which so much resembles the domestic Turkey, is now almost extinct. It was formerly a resident of New England, and is still found to some extent as far north-west as the Missouri River and south-west as Texas. In Ohio it was formerly an abundant resident. Dr. Kirtland (1850) mentions the time when Wild Turkeys were more common than tame ones are now.
The nests of this bird are very difficult to discover, as they are made on the ground, midst tall, thick weeds or tangled briars. The female will not leave the nest until almost trodden upon. It is stated that when the eggs are once touched, she will abandon her nest.
The Turkey became known to Europeans almost immediately upon the discovery of America by the Spaniards in 1518, and it is probable that it is distinctively an American bird. In its wild state, its plumage, as in the case of the Honduras Turkey, grows more lustrous and magnificent as the family extends southward.
The “Gobblers,” as the males are called, associate in parties of ten to one hundred, seeking their food apart from the females, which wander singly with their young or in troops with other hens and their families, sometimes to the number of seventy or eighty. They travel on foot, unless disturbed by the hunter or a river compels them to take wing. It is said that when about to cross a river, they select a high eminence from which to start, that their flight may be more sure, and in such a position they sometimes remain for a day or more, as if in consultation. On such occasions the males gobble vociferously, strutting about pompously as if to animate their companions. At the signal note of their leader, they wing their way to the opposite shore.
The Wild Turkey feeds on many kinds of berries, fruits, and grasses. Beetles, tadpoles, young frogs, and lizards are sometimes found in its crop. When the Turkeys reach their destination, they disperse in flocks, devouring the mast as they proceed.
Pairing time begins in March. The sexes roost apart, but at no great distance, so that when the female utters a call, every male within hearing responds, rolling note after note in rapid succession, in a voice resembling that of the tame Turkey when he hears any unusual noise. Where the Turkeys are numerous, the woods from one end to the other, sometimes for many miles, resound with these voices of wooing.
The specimen of the Wild Turkey presented in this number of Birds is of extraordinary size and beauty, and has been much admired. The day is not far distant when a living specimen of this noble bird will be sought for in vain in the United States.
THE CERULEAN WARBLER.

HIS beautiful little sky-blue feathered creature is well named Azure Warbler, or again White-throated Blue Warbler, and is the most abundant of the genus here.
It is a bird of the wood, everywhere associated with the beautiful tall forests of the more northern counties of western New York, sometimes found in the open woods of pasture-lands, and quite partial to hardwood trees. In its flitting motion in search of insect-prey, and in the jerking curves of its more prolonged flight, as also in its structure, it is a genuine Wood Warbler and keeps for the most part to what Thoreau calls the “upper story” of its sylvan domain.
All Warblers, it has been said, depend upon their markings rather than song for their identity, which renders the majority of the tribe of greater interest to the scientist than to the novice. Until you have named four or five of the commonest species as landmarks, you will be considerably confused.
Audubon described the song of the Cerulean Warbler as “extremely sweet and mellow,” whereas it is a modest little strain, says Chapman, or trill, divided into syllables like zee, zee, zee, ze-ee-ee-eep, or according to another observer, rheet, rheet, rheet, rheet, ridi, idi, e-e-e-e-ee; beginning with several soft warbling notes and ending in a rather prolonged but quite musical squeak. The latter and more rapid part of the strain, which is given in the upward slide, approaches an insect quality of tone which is more or less peculiar to all true Warblers, a song so common as to be a universal characteristic of our tall forests.
It is not strange that the nest of this species has been so seldom discovered, even where the bird is very abundant during the breeding season. It is built in the higher horizontal branches of forest trees, always out some distance from the trunk, and ranging from twenty to fifty feet above the ground. One described by Dr. Brewer, found in Ontario, near Niagara Falls, was built in a large oak tree at the height of fifty or more feet from the ground. It was placed horizontally on the upper surface of a slender limb between two small twigs; and the branch on which it was thus saddled was only an inch and a half in thickness, being nine feet from the trunk of the tree. The abandoned home was secured with great difficulty.
The nest is a rather slender fabric, somewhat similar to the nest of the Redstart, and quite small for the bird, consisting chiefly of a strong rim firmly woven of strips of fine bark, stems of grasses, and pine needles, bound round with flaxen fibres of plants and wool. Around the base a few bits of hornets’ nests, mosses, and lichens are loosely fastened. The nest within is furnished with fine stems and needles, the flooring very thin and slight.
The bird is shy when started from the nest, and has a sharp chipping alarm-note common to the family.
The Cerulean Warbler is found in the Eastern States, but is more numerous west of the Allegheny mountains, and throughout the heavily wooded districts of the Mississippi valley. In winter it migrates to Central America and Cuba. The Warblers are of unfailing interest to the lover of bird life. Apart from the beauty of the birds themselves, with their perpetually contrasting colors among the green leaves, their pretty ways furnish to the silent watcher an ever changing spectacle of the innocent life in the tree-tops.
 wild turkey.
wild turkey.From col. Fred. Kaempfer. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
 cerulean warbler.
cerulean warbler.From col. F. M. Woodruff. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE WILD TURKEY.
I thought my picture would appear in this number of Birds. What would Thanksgiving be without a Turkey, I’d like to know.
The editor says that I am a bird of ex-tra-or-di-na-ry size and beauty. That word is as big as I am, but by spelling it, I guess you will understand.
I look as proud as a peacock, don’t I? Well, I am just as proud. You ought to see me strut, and hear me talk when the hen-turkeys are around. Why, sometimes when there is a large troop of us in the woods you can hear us gobble, gobble, gobble, for many miles. We are so fond of talking to each other.
That is when we are about to set up housekeeping, you think.
Yes, in March and April. After the nests are made, and the little turkeys hatched out, we big, handsome fellows go off by ourselves. The hen-turkeys, with their young broods, do the same.
Sometimes there are as many as a hundred in our troop and seventy or eighty in theirs. We travel on foot, picking up food as we go, till we meet a man with a gun, or come to a wide river.
Then we have to fly.
In a flock? Oh, yes. We choose some high place from which to get a good start. There we all stay, sometimes a day or two, strutting about and talking big. It is gobble, gobble gobble, from morning till night. Just like one of your conventions, you know. After awhile our leader gives the signal and off we all fly to the opposite shore.
Did you ever see one of our nests? No? Well, they are not easily seen, though they are made on the ground. You see, we are cunning and build them among tall, thick weeds and tangled briars.
I hope, if you ever come across one, you will not touch it, because my mate would never return to it again, if you did.
What do we eat?
Berries, fruit and grasses, beetles, tadpoles, frogs and lizards. In fact anything we consider good.
THE YELLOW-BILLED TROPIC BIRD.
N appearance this bird resembles a large Tern (see Vol. I, page 103), and its habits are similar to those of the Terns. Inter-tropical, it is of a wandering disposition, breeding on the islands of mid-ocean thousands of miles apart. It is noted for its elegant, airy, and long-protracted flight. Davie says that on Bourbon, Mauritius and other islands east and south of Madagascar it breeds in the crevices of the rocks of inaccessible cliffs, and in hollow trees. In the Bermuda Islands it nests about the first of May in holes in high rocky places along the shores. Here its favorite resorts are the small islands of Great Sound, Castle Harbor, and Harrington Sound. The Phaeton, as it is felicitously called, nests in the Bahamas in holes in the perpendicular faces of cliffs and on the flat surfaces of rocks. A single egg is laid, which has a ground-color of purplish brownish white, covered in some specimens almost over the entire surface with fine reddish chocolate-colored spots.
These species compose the small but distinct family of tropic birds and are found throughout the tropical and sub-tropical regions of the world. Long journeys are made by them across the open sea, their flight when emigrating being strong, rapid, and direct, and immense distances are covered by them as they course undismayed by wind or storm. In feeding, Chapman says, they course over the water, beating back and forth at a height of about forty feet, and their long willowy tail-feathers add greatly to the grace and beauty of their appearance when on the wing. They are of rare and probably accidental occurrence on our coasts.
The Songs of Nature never cease,
Her players sue not for release
In nearer fields, on hills afar,
Attendant her musicians are:
From water brook or forest tree,
For aye comes gentle melody,
The very air is music blent—
An universal instrument.
—John Vance Cheney.
 yellow-billed tropic bird.
yellow-billed tropic bird.From col. F. M. Woodruff. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE YELLOW-BILLED TROPIC BIRD.
The people who make a study of birds say that I look like a large Tern, and that my habits are like his.
I don’t know whether that is so, I am sure, for I have no acquaintance with that bird, but you little folks can turn to your March number of Birds and see for yourselves if it is true.
For my part, I think I am the prettier of the two on account of my long, willowy tail-feathers. They add greatly, it is said, to the grace and beauty of my appearance when on the wing. Then, the color of my coat is much more beautiful than his, I think, don’t you think so, too?
We are not so common as the Terns, either, for they are very numerous. There are only three species of our family, so we consider ourselves quite distinct.
What are we noted for?
Well, principally for our long distance flights across the sea, elegant and airy, as the writers say of us. Maybe that is the reason they call us the Phaeton sometimes.
Do we go north in the summer as so many other birds do?
Ugh! You make me shudder. No, indeed! We never go farther north than Florida. Our home, or where we build our nests, is in the tropical and sub-tropical regions, where the weather is very warm, you know.
We are great wanderers and build our nests on islands, way out in the ocean many thousands of miles apart.
In trees?
Oh, no, but in any hole we see in the face of a great rock or cliff, and sometimes right on the top of a rock.
How many eggs?
Only one. That is the reason, you see, that our family remains small.
Sing?
Oh, my, no! We are not singing birds. We have a call-note, though harsh and guttural, which sounds like tip, tip, tip.
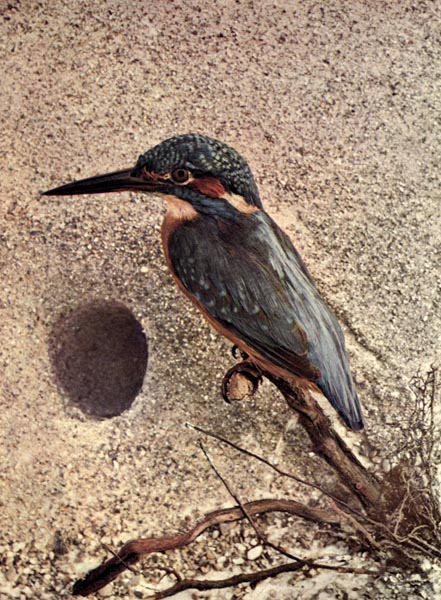
THE EUROPEAN KINGFISHER.

ARELY indeed is this charming bird now found in England, where formerly it could be seen darting hither and thither in most frequented places. Of late years, according to Dixon, he has been persecuted so greatly, partly by the collector, who never fails to secure the brilliant creature for his cabinet at every opportunity, and partly by those who have an inherent love for destroying every living object around them. Gamekeepers, too, are up in arms against him, because of his inordinate love of preying on the finny tribe. Where the Kingfisher now is seen is in the most secluded places, the author adds, where the trout streams murmur through the silent woods, but seldom trod by the foot of man; or in the wooded gullies down which the stream from the mountains far above rushes and tumbles over the huge rocks, or lies in pools smooth as the finest mirror.
The Kingfisher is comparatively a silent bird, though he sometimes utters a few harsh notes as he flies swift as a meteor through the wooded glades. You not unfrequently flush the Kingfisher from the holes in the banks, and amongst the brambles skirting the stream. He roosts at night in holes, usually the nesting cavity. Sometimes he will alight on stumps and branches projecting from the water, and sit quiet and motionless, but on your approach he darts quickly away, often uttering a feeble seep, seep, as he goes.
The habits of the English Kingfisher are identical with those of the American, though the former is the more brilliant bird in plumage. (See Birds, Vol. I, p. 61.) The ancients had a very absurd idea as to its nesting habits. They believed that the bird built a floating nest, and whenever the old bird and her charge were drifted by the winds, as they floated over the briny deep, the sea remained calm. He was, therefore, to the ancient mariner, a bird held sacred in the extreme. Even now these absurd superstitions have not wholly disappeared. For instance, the nest is said to be made of the fish bones ejected by the bird, while the real facts are, that they not only nest but roost in holes, and it must follow that vast quantities of rejected fish bones accumulate, and on these the eggs are of necessity laid.
These eggs are very beautiful objects, being of a deep pinkish hue, usually six in number.
The food of the Kingfisher is not composed entirely of fish, the remains of fresh-water shrimps being found in their stomachs, and doubtless other animals inhabiting the waters are from time to time devoured.
The English Kingfisher, says Dixon, remains throughout the year, but numbers perish when the native streams are frozen. There is, perhaps, not a bird in all the ranks of the feathered gems of equatorial regions, be it ever so fair, the Humming-bird excepted, that can boast a garb so lovely as this little creature of the northland. Naturalists assert that the sun has something to do with the brilliant colors of the birds and insects of the tropics, but certainly, the Kingfisher is an exception of the highest kind. Alas, that he has no song to inspire the muse of some English bard!
 european kingfisher.
european kingfisher.From col. Chi. Acad. Sciences. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE EUROPEAN KINGFISHER.
Little Folks:
I shouldn’t have liked it one bit if my picture had been left out of this beautiful book. My cousin, the American Kingfisher, had his in the February number, and I find he had a good deal to say about himself in his letter, too.
Fine feathers make fine birds, they say. Well, if that is true, I must be a very fine bird, for surely my feathers are gay enough to please anybody—I think.
To see me in all my beauty, you must seek me in my native wood. I look perfectly gorgeous there, flitting from tree to tree. Or maybe you would rather see me sitting on a stump, gazing down into the clear pool which looks like a mirror.
“Oh, what a vain bird!” you would say; “see him looking at himself in the water;” when all the time I had my eye on a fine trout which I intended to catch for my dinner.
Well, though I wear a brighter dress than my American cousin, our habits are pretty much alike. I am sure he catches fish the same way I do—when he is hungry.
With a hook and line, as you do?
Oh, no; with my bill, which is long, you observe, and made for that very purpose. You should just see me catch a fish! Down I fly to a stump near the brook, or to a limb of a tree which overhangs the water, and there I sit as quiet as a mouse for quite a while.
Everything being so quiet, a fine speckled trout, or a school of troutlets, play near the surface. Now is my chance! Down I swoop, and up I come with a fish crosswise in my bill.
Back I go to my perch, toss the minnow into the air, and as it falls catch it head first and swallow it whole. I tell you this because you ought to know why I am called Kingfisher.
Do we swallow bones and all?
Yes, but we afterwards eject the bones, when we are resting or roosting in our holes in the banks of the stream. That must be the reason people who write about us say we build our nests of fish bones.
Sing?
Oh, no, we are not singing birds; but sometimes, when flying swiftly through the air, we give a harsh cry that nobody but a bird understands.
Your friend,
The English Kingfisher.
THE VERMILION FLY-CATCHER.

HICKETS along water courses are favorite resorts of this beautiful Fly-catcher, which may be seen only on the southern border of the United States, south through Mexico to Guatemala, where it is a common species. Mr. W. E. D. Scott notes it as a common species about Riverside, Tucson, and Florence, Arizona. Its habits are quite similar to those of other Fly-catchers, though it has not been so carefully observed as its many cousins in other parts of the country. During the nesting season, the male frequently utters a twittering song while poised in the air, in the manner of the Sparrow Hawk, and during the song it snaps its bill as if catching insects.
The Vermilion’s nest is usually placed in horizontal forks of ratana trees, and often in mesquites, not more than six feet from the ground; they are composed of small twigs and soft materials felted together, with the rims covered with lichens, and the shallow cavity lined with a few horse or cow hairs. Dr. Merrill states that they bear considerable resemblance to nests of the Wood Pewee in appearance and the manner in which they are saddled to the limb. Nests have been found, however, which lacked the exterior coating of lichens.
Three eggs are laid of a rich creamy-white with a ring of large brown and lilac blotches at the larger end.
A WINTER NEST.
Pallid, wan-faced clouds
Press close to the frozen pines,
And follow the jagged lines
Of fence, that the sleet enshrouds.
Sharp in the face of the sky,
Gaunt, thin-ribbed leaves are blown;
They rise with a shuddering moan,
Then sink in the snow and die.
At the edge of the wood a vine
Still clings to the sleeping beech,
While its stiffened tendrils reach
A nest, and around it twine.
A little gray nest all alone,
With its feathery lining of snow,
Where bleak winds, piping low,
Croon a sweet minor tone.
—Nora A. Piper.
 vermilion fly-catcher.
vermilion fly-catcher.From col. George F. Breninger. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
BIRD MISCELLANY.
Red and yellow, green and brown,
Leaves are whirling, rustling down;
Acorn babes in their cradles lie,
Through the bare trees the brown birds fly;
The Robin chirps as he flutters past—
November days have come at last.
—Clara Louise Strong.
“I have watched birds at their singing under many and widely differing circumstances, and I am sure that they express joyous anticipation, present content, and pleasant recollection, each as the mood moves, and with equal ease.”
—M. Thompson.
“The act of singing is evidently a pleasurable one; and it probably serves as an outlet for superabundant nervous energy and excitement, just as dancing, singing, and field sports do with us.”
—A. R. Wallace.
“The bird upon the tree utters the meaning of the wind—a voice of the grass and wild flower, words of the green leaf; they speak through that slender tone. Sweetness of dew and rifts of sunshine, the dark hawthorn touched with breadths of open bud, the odor of the air, the color of the daffodil—all that is delicious and beloved of spring-time are expressed in his song.”
—Richard Jefferies.
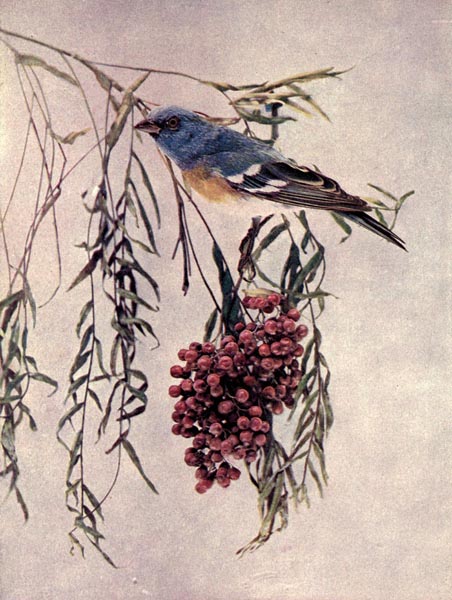
THE LAZULI BUNTING.
The joy is great of him who strays
In shady woods on summer days.
—Maurice Thompson.
N Colorado and Arizona the Lazuli Painted Finch, as it is called, is common, while in California it is very abundant, being, in fact, generally distributed throughout the west, and along the Pacific Coast it is found as far north as Puget Sound, during the summer. Davie says it replaces the Indigo Bunting, (See Birds, Vol. I, page 174,) from the Plains to the Pacific, being found in all suitable localities. The nest is usually built in a bush or in the lower limbs of trees, a few feet from the ground. Fine strips of bark, small twigs, grasses, and hair are used in preparing it for the four tiny, light bluish-green eggs, which readily fade when exposed to light. The eggs so closely resemble those of the Bluebird as not to be distinguishable with certainty. The nest is an inartistic one for a bird of gay plumage.
From Florence A. Merriam’s charming book, “A-Birding on a Bronco,” we select a description of the pretty manners of this attractive bird. She says:
“While waiting for the Woodpeckers, one day, I saw a small brownish bird flying busily back and forth to some green weeds. She was joined by her mate, a handsome blue Lazuli Bunting, even more beautiful than our lovely Indigo, and he flew beside her full of life and joy. He lit on the side of a cockle stem, and on the instant caught sight of me. Alas! he seemed suddenly turned to stone. He held onto that stalk as if his little legs had been bars of iron and I a devouring monster. When he had collected his wits enough to fly off, instead of the careless gay flight with which he had come out through the open air, he timidly kept low within the cockle field, making a circuitous way through the high stalks. He could be afraid of me if he liked, I thought, for after a certain amount of suspicion, an innocent person gets resentful; at any rate I was going to see that nest. Creeping up cautiously when the mother bird was away, so as not to scare her, and carefully parting the mallows, I looked in. Yes, there it was, a beautiful little sage-green nest of old grass laid in a coil. I felt as pleased as if having a right to share the family happiness. After that I watched the small worker gather material with new interest, knowing where she was going to put it. She worked fast, but did not take the first thing she found, by any means. With a flit of the wing she went in nervous haste from cockle to cockle, looking eagerly about her. Jumping down to the ground, she picked up a bit of grass, threw it down dissatisfied, and turned away like a person looking for something. At last she lit on the side of a thistle, and tweaking out a fibre, flew with it to the nest.
“A month after the first encounter with the father Lazuli, I found him looking at me around the corner of a cockle stalk, and in passing back again, caught him singing full tilt, though his bill was full of insects! After we had turned our backs I looked over my shoulder and had the satisfaction of seeing him take his beakful to the nest. You couldn’t help admiring him, for though not a warrior who would snap his bill over the head of an enemy of his home, he had a gallant holiday air with his blue coat and merry song, and you felt sure his little brown mate would get cheer and courage enough from his presence to make family dangers appear less frightful.”
 lazuli bunting.
lazuli bunting.From col. John F. Ferry. Copyrighted by
Nature Study Pub. Co., 1897, Chicago.
THE LAZULI BUNTING.
You think you have seen me before? Well, I must admit my relative, the Indigo Bunting, and I do look alike. They say though, I am the prettier bird of the two. Turn to your May number, page 174, and decide for yourselves.
I live farther west than he does. You find him in the eastern and middle states. Then he disappears and I take his place, all the way from the Great Plains to the Pacific Ocean.
Some people call me the Lazuli Painted Finch. That’s funny, for I never painted anything in my life—not even my cheeks. Would you like to know how my mate and I go to housekeeping? A lady who visits California, where I live, will tell you all about it. She rides a horse called Mountain Billy. He will stand still under a tree so that she can peep into nests and count the eggs, when the mother bird is away.
She can travel a good many miles in that way, and meet lots of birds. She says in her book, that she has got acquainted with seventy-five families, without robbing one nest, or doing the little creatures any harm.
Well, one day this lady saw a brownish bird flying busily back and forth to some tall green weeds. After a while a handsome blue Bunting flew along side of her, full of life and joy.
That was my mate and I. How frightened I was! for our nest was in those green weeds and not very far from the ground. I flew away as soon as I could pluck up courage, but not far, so that I could watch the lady and the nest. How my heart jumped when I saw her creep up, part the weeds and look in. All she saw was a few twigs and a sage-green nest of old grass laid in a coil. My mate hadn’t put in the lining yet; you see it takes her quite a while to get the thistle down and the hair and strips of bark for the inside. The next time the lady passed, the house was done and my mate was sitting on the nest. She just looked down at us from the back of Mountain Billy and passed on.
Four weeks after, she came again, and there I was, flying about and singing “like a bird,” my mouth full of insects, too. I waited ’till she had turned away before I flew to the nest to feed our little ones. I didn’t know, you see, that she was such a good friend of ours, or I wouldn’t have been so afraid.
SUMMARY
Page 163.
SUMMER TANAGER.—Piranga rubra. Other names: “Summer Red-bird,” “Rose Tanager.”
Range—Eastern United States west to the edge of the Plains; north regularly to about 40°—New Jersey, central Ohio, Illinois, casually north to Connecticut and Ontario, accidentally to Nova Scotia, wintering in Cuba, Central America, and northern South America. (Davie.)
Nest—Of bark strips and leaves interwoven with various vegetable substances, on drooping branch of tree.
Eggs—Three or four, bluish-white or greenish-blue, with cinnamon or olive-brown markings.
Page 168.
AMERICAN WHITE-FRONTED GOOSE—Anser albifrons gambeli. Other names: “Laughing Goose,” “Speckle Belly.”
Range—North America, breeding far northward; in winter south to Mexico and Cuba, rare on the Atlantic coast.
Nest—On the ground, of grasses lined with down.
Eggs—Six or seven, dull greenish-yellow with obscure darker tints.
Page 171.
TURNSTONE.—Arenaria interpres. Other names: “Brant Bird,” “Calico-back,” “Bead-bird,” “Sand-runner,” “Chickling,” “Horse-foot Snipe.”
Range—Nearly cosmopolitan; nests in the Arctic regions, and in America migrates southward to Patagonia. (Chapman.)
Nest—A slight depression on the ground.
Eggs—Two or four, greenish-drab, spotted all over with brown.
Page 175.
THE BELTED PIPING PLOVER.—Aegialitis meloda circumcincta.
Range—Missouri river region; occasionally eastward to the Atlantic coast.
Nest—Depression in the sand without lining.
Eggs—Four, light gray to creamy buff, finely speckled with blackish brown and purplish gray.
Page 180.
WILD TURKEY—Meleagris gallopava.
Range—Eastern United States from Pennsylvania southward to Florida, west to Wisconsin, the Indian Territory and Texas.
Nest—On the ground, at the base of a bush or tree.
Eggs—Ten to fourteen, pale cream buff, finely and evenly speckled with grayish brown.
Page 181.
CERULEAN WARBLER—Dendræca caerulea. Other names: “Azure Warbler;” “White-throated Blue Warbler.”
Range—Mississippi valley as far north as Minnesota, and eastward as far as Lockport, N. Y. (Davison.) Winters in the tropics.
Nest—Of fine grasses bound with spider’s silk, lined with strips of bark and with a few lichens attached to its upper surface, in a tree, twenty-five to fifty feet from the ground. (Chapman.)
Eggs—Four, creamy-white, thickly covered with rather heavy blotches of reddish brown.
Page 186.
YELLOW-BILLED TROPIC BIRD.—Phaethon flavirostris. Other names: “Phaeton.”
Range.—Tropical coasts; Atlantic coasts of tropical America, West Indies, Bahamas, Bermudas; casual in Florida and accidental in Western New York and Nova Scotia. (Chapman.)
Nest—In holes in the perpendicular faces of cliffs, also on the flat surfaces of rocks.
Eggs—One, ground color of purplish brownish white, covered with fine reddish chocolate-colored spots. (Davie.)
Page 190.
EUROPEAN KINGFISHER.—Alcedo ispida.
Range—England and portions of Europe.
Nest—In holes of the banks of streams.
Eggs—Usually six, of a deep pinkish hue.
Page 193.
VERMILION FLY-CATCHER.—Pyocephalus rubineus mexicanus.
Range—Southern Border of the United States south through Mexico and Guatemala.
Nest—In forks of ratana trees, not more than six feet up, of small twigs and soft materials felted together, the rims covered with lichens; the cavity is shallow.
Eggs—Usually three, the ground color a rich creamy-white, with a ring of large brown and lilac blotches at the larger end.
Page 198.
LAZULI BUNTING.—Passerina amoena. Other name: “Lazuli Painted Finch.”
Range—Western United States from the Great Plains to the Pacific; south in winter to Western Mexico.
Nest—In a bush or the lower limbs of trees, a few feet from the ground, of fine strips of bark, small twigs, grasses, and is lined with hair.
Eggs—Usually four, light bluish-green.