[Contents]
The Sunday Story
When Englishmen and Englishwomen are little boys and girls, they
listen with open ears to the tales of Golden-hair and the three Bears,
of Cinderella and the Prince, and of the Wolf and Little Red Riding
Hood. As the boys and girls grow up, the stories fade gradually from
their minds. But a time comes when they have children of their own. And
then, to amuse the children, they can find no tales more thrilling than
those which fascinated them in their own childhood. Thus the old
nursery tales are handed down for centuries from generation to
generation. Exactly the same process goes on in India, There, too, when
little Indian boys and girls grow up and have little boys and girls of
their own, they too tell to wide-eyed audiences the tales which they
[2]themselves found so thrilling in their own
childhood. Indian nursery tales, it is true, have a more religious
tinge than those of Europe, but they are none the less appreciated on
that account. The first six stories in this little book purport to
explain the connexion between the heavenly bodies and the days of the
week. So each day of the week has its separate tale. And all through
Shravan or August, probably because it is the wettest month in the
year, Deccan mothers tell afresh every week-day that day’s story.
And little Deccan children listen to the tales as they fall due with
the same unvarying attention. For in nurseries, Indian as well as
English, tales are loved the better when no longer new, and where the
end is well known to, and therefore the better understood by, the tiny
round-eyed listeners.
Now this is the tale which is told every Sunday1 in Shravan:
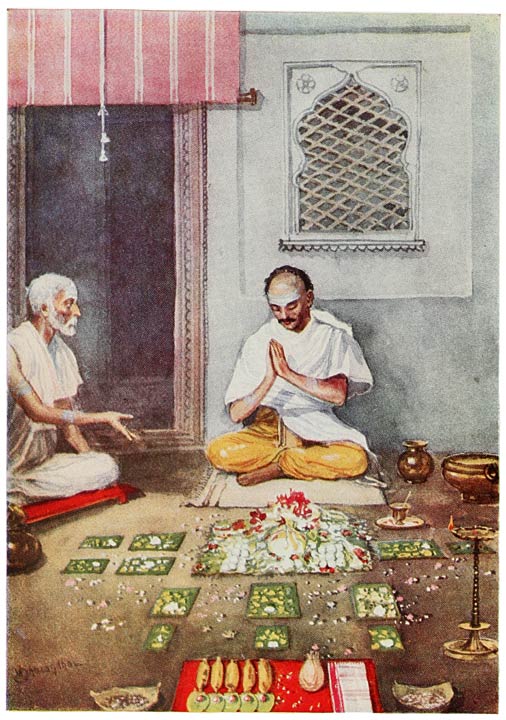
Once upon a time there [3]was a town called Atpat, and
in it there lived a poor Brahman. Every day he used to go into the
woods to fetch sticks and to cut grass. One day he met there some
nymphs and wood-fairies, who said that they were performing holy rites
in honour of the sun. He asked, “What are these rites?”
They replied, “If we tell you, you will become proud and vain and
you will not perform them properly.” But the Brahman promised,
“No, I shall not become proud or vain and I shall observe the
rites you tell me.” They then told him that the month of Shravan
was coming, and that on the first Sunday of Shravan he was to draw a
picture of the sun with red sandal paste, that he was to offer to the
drawing flowers and fruit, and that he should continue doing this for
six months. Thereafter he should in various ways, which they told him,
entertain guests and give alms to the poor.
The Brahman went home and performed the rites to the letter, so that
the sun-god was very pleased. Wealth came to the Brahman and he grew
richer and richer, and at last the queen of the land sent for him. The
poor Brahman began to tremble and shake all over, [4]but the queen said, “Do not shake or
tremble, but give your daughters in marriage to our house.” The
Brahman said, “My daughters are poor; you will make them slaves
or maid-servants.” “No,” said the queen, “I
shall not make them slaves or maid-servants; I shall marry one to a
king, and one to a minister.” The Brahman agreed, and when the
month of Margashish, or December, came he gave his two daughters in
marriage, one to the king and one to the minister. Immediately after
the marriage the Brahman said good-bye to his daughters, and did not
see them again for twelve years. Then he visited the elder one, who had
married the king. She gave him a wooden stand on which to sit while
eating, and water in which to wash his feet, and then said,
“Papa, papa, there is pudding to eat, there is water to
drink.” But the Brahman said, “Before I eat or drink, I
must tell you my story.” But his daughter said, “Papa, I
have no time to listen to your story; the king is going a-hunting, and
I must not keep him waiting for his dinner.” The Brahman thought
this very disrespectful and went off in a great rage to [5]the house of his other daughter, who had
married a minister. She welcomed her father and gave him a wooden stand
on which to eat, and water to wash his feet, and said, “Papa,
papa, here is pudding to eat and here is water to drink.” But the
Brahman said, “Before I eat or drink I must tell you my
story.” His daughter said, “Of course, papa, tell it to me,
and I shall listen as long as you like.” Then she went into an
inner room and she fetched six pearls. She took three herself and three
she put in her father’s hand. And he told her how he had met the
nymphs and wood-fairies, who had told him to worship the sun-god, and
she listened to it all without missing a syllable. Then the Brahman ate
and drank and went back to his own house. His wife asked him about
their two daughters. He told her everything and said, “The elder
one who would not listen to my story will come to grief.”
And so she did. For the king, her husband, took an army into a far
country and never came back. But the daughter who had listened to the
story lived well and happy. As time went on the undutiful daughter
[6]became poorer and poorer, until one day she
said to her eldest son, “Go to your aunt’s house and beg of
her to give you a present, and bring back whatever she gives
you.” Next Sunday the boy started and went to the village where
his aunt lived. Standing by the village tank he called out, “O
maids, O slave-girls, whose maids and slave-girls are ye?” They
answered, “We are the maids and the slave-girls of the
minister.” The boy said, “Go and tell the minister’s
wife that her sister’s son is here. Tell her that he is standing
by the village tank, that his coat is tattered and that his garments
are torn, and ask her to let him come into her house through the back
door.” The slave-girls took him in through the back door. His
aunt had him bathed, and gave him clothes to wear, and food to eat, and
drink, and a pumpkin hollowed out and filled with gold coins. As he
left, she called to him, “Do not drop it, do not forget it, but
take it carefully home.” But as the boy went home, the sun-god
came disguised as a gardener and stole the pumpkin filled with gold.
When the boy reached his mother’s house she asked, “Well,
my son, what did your aunt give you?” [7]He said, “Fortune gave, but
Karma2 took away; I lost everything my aunt bestowed on
me.” Next Sunday the second son went and stood by the village
tank and called out, “O slave-girls and maid-servants, who is
your master?” They said, “Our master is the
minister.” “Then tell the minister’s wife that her
nephew is here.” He was taken in by the back door. He was bathed
and clothed and given food and drink. As he was going, his aunt gave
him a hollow stick full of gold coins and said, “Do not drop it,
do not forget it, mind it carefully and take it home.” On the way
the sun-god came in the guise of a cowherd and stole the stick. When
the boy got home his mother asked him what he had brought. He said,
“Fortune gave, but Karma took away.” On the third Sunday a
third son went and stood by the village tank. His aunt received him
like the others and had him bathed, clothed, and fed. As he was going
away, she gave him a hollow cocoa-nut stuffed with gold coins and said,
“Do not drop it, do not forget it, but mind it carefully and take
it home.” On the way back he put down the [8]cocoa-nut on the edge of a well, and it toppled
over and fell into the water with a great splash. When he reached his
mother’s house she asked him what his aunt’s present was.
He said, “I have lost everything which fortune brought me.”
On the fourth Sunday the fourth son went. His aunt welcomed him like
the others, and had him bathed and fed. When he left she gave him an
earthen pot full of gold coins. But the sun-god came in the guise of a
kite and snatched the pot away. When the boy reached home his mother
asked him whether his aunt had given him anything. He said, “I
have lost everything which my aunt gave me.” On the fifth Sunday
the mother herself got up and went to her sister’s village and
stood by the tank. The minister’s wife took her in through her
back door and had her clothed and fed. Then the minister’s wife
told her that all her trouble had come through not listening to her
father’s story, and the minister’s wife repeated it to her.
The king’s wife listened to it, and stayed with her sister until
the following month of Shravan, or August, when she did fitting worship
to the sun. [9]
Instantly good fortune came to her. After years of weary fighting,
her husband, the king, at last overcame his enemies, and after taking
great wealth from them turned homewards with his army. As he went
towards his capital, he passed the village where the minister’s
wife lived. There he learnt that his queen was with her sister, so he
sent for her with a befitting escort. “O auntie, auntie,”
cried all the queen’s little nephews and nieces, “umbrellas
have come for you, and horse-tails and guards and foot-soldiers.”
Every one rushed out to see, and the king and queen greeted each other
after years of separation. The sisters gave each other gifts of
clothes, and the king and his queen went away together. At the first
halting-place the servants cooked the food. The queen filled the
king’s plate and then her own, and then she thought of the story
which her sister had told her. She ordered her servants to go through
the neighbouring village and bring in any one who was hungry and too
poor to buy food. They found none such in the village, but on the way
back they met a starving wood-cutter, and, bringing him to the queen,
told him to [10]listen to the tale which she would tell
him. The queen brought six pearls. Three she gave to the wood-cutter,
and three she kept herself. Then she told him the story of her father
and the wood-fairies. The wood-cutter listened with all attention, and
as he listened his faggot of wood became all of gold. He went away
delighted, promising to worship the sun in the way the wood-fairies had
shown to the Brahman.
Next day the cavalcade reached the second halting-place. Food was
cooked; the queen filled the king’s plate and then her own plate,
and again she told her, servants to bring from the neighbouring village
any one who was hungry and too poor to buy food. They came upon a petty
farmer, whose well had dried up and whose crops had withered. He was
sitting sadly by his field when they called him to go with them and
listen to the queen’s tale. He went with them to the camp. There
the queen brought six pearls and gave three of them to the farmer and
kept three of them herself. Then she told the story of her father and
the wood-fairies. And as the farmer listened, all attention, the water
began to pour [11]into the well, and the crop began to look
fresh and green. He went away delighted, and promised to worship the
sun in the way the wood-fairies had told the Brahman. Next day the
cavalcade reached the third halting-place. Food was cooked, and the
queen filled the king’s plate and then her own plate. Then she
told the servants to search in the neighbouring village for any one who
was hungry and too poor to buy food. They met an old woman. Her eldest
son had been lost in the forest. Her second son had been drowned in a
pond. Her third son had died of snake-bite. They told her to come and
listen to the queen’s story. She went with them, and as she
listened, all attention, first the son who had been lost in the forest
walked into the camp, next the son who had been drowned in the pond,
and last of all the son who had died of a snake-bite. The old woman
went away crying with joy, and promising to worship the sun in the way
the wood-fairies had instructed the Brahman. Next day the cavalcade
reached the fourth halting-place. Food was cooked, and the queen first
filled the king’s plate and then her own. After dinner she sent
her [12]servants as before to bring in some poor and
hungry man from the neighbouring village. They found a man whose eyes
were so crooked that he could hardly see, who had no arms or legs, and
who had not even a name. For he was only known as “Lump of
flesh.” He was lying on his face, but when they brought him into
camp, the queen had him placed on his back and had a jug of water
poured over him. Then she took six pearls. Three she kept herself, and
three she placed on the stomach of “Lump of flesh.” Then
she told him the tale of her father and the wood-fairies. He listened,
all attention, and as he listened his arms and legs grew out of his
body, and hands and feet appeared at the ends of them. He too went away
delighted, and he promised to worship the sun in the way the
wood-fairies had told the Brahman.
At the end of the next day’s march the king and queen reached
their home. Food was cooked, and as they sat down to dinner the sun-god
himself appeared and joined them at their meal. The king had all the
doors flung wide open, and ordered a fresh and far more splendid dinner
to be prepared, with any [13]number of dishes, each dish
having six separate flavours. When it was served the sun-god and the
king began to eat, but in the first mouthful the sun-god found a hair.
He got very very angry, and called out, “To what sinful woman
does this hair belong?” Then the poor queen remembered that
during her twelve years of poverty she had always sat under the eaves
combing her hair, and knew that it must have been one of her hairs
which had got into the sun-god’s food. She begged for mercy, but
the sun-god would not forgive her until she had clothed herself in a
black blanket, plucked a stick out of the eaves, and had gone outside
the town and there thrown the stick and the hair over her left
shoulder. Then the sun-god recovered his good-humour, and finished his
dinner. And the Brahman, the king and queen, and the wood-cutter and
the farmer whose well had dried up, and the old woman who had lost her
children, and “Lump of flesh” with the cross eyes, they all
remained in the favour of the sun-god and lived happily ever
afterwards. [14]
[Contents]
The Monday Story
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
very saintly king. One day he formed the wish to fill the shrine of
Shiva, the moon-god, with milk up to the ceiling. He consulted his
chief minister, and the latter sent a crier through Atpat ordering,
under terrible penalties, all the townspeople to bring every Monday all
the milk in their houses and offer it to the god Shiva. The townspeople
were frightened at the threatened punishments, and the next Monday they
brought all the milk in Atpat to Shiva’s shrine, not keeping a
drop for their calves or even for their children. But although all the
milk in Atpat was every Monday poured into Shiva’s shrine, it yet
did not become full to the ceiling. But one day an old woman came to
the shrine. [15]She had done all her housework. She had
fed all the children and had bathed all her little daughters-in-law.
Then she took a few drops of milk, a little sandal-wood paste, and a
few flowers, and half-a-dozen grains of rice and went to worship at
Shiva’s shrine. She prayed to Shiva, “The little milk that
I can offer is not likely to fill your shrine, seeing that all the milk
offered by the king could not. Nevertheless I offer the milk with all
my heart.” She then got up and went back to her house. Then a
strange thing happened. Directly the old woman turned her back, the
shrine filled with milk right up to the ceiling. The priests ran and
told the king, but none of them could say how it happened. The
following Monday the king placed a soldier by the door; and again the
old woman came and worshipped, and again the shrine filled with milk to
the ceiling. The soldier ran and told the king, but could not explain
the cause. The third Monday the king himself went and watched by the
shrine. From his hiding-place he saw the old woman come up and noticed
that the shrine filled with milk immediately after she had worshipped.
He ran after her [16]and caught her. The old woman
begged the king to spare her life, and this he promised to do if she
told the truth. She said, “O King! you ordered all the milk in
Atpat to be brought to Shiva’s shrine. But what was the result?
All the calves began lowing and all the children began crying, because
they could get no milk. And all the grown-up people were so worried by
the noise that they did not know what to do. Shiva was displeased at
this, so He would not let the shrine fill. This, therefore, is what you
should do. Let the children and the calves have their milk. Then take
whatever is over to the shrine, and it will at once fill up to the
ceiling.” The king let the old woman go, and had it proclaimed by
beat of drum that the townspeople were to bring to the shrine on the
following Monday only the milk remaining after the children and the
calves had been fed. The townspeople were delighted. The children
stopped crying and the calves stopped lowing, and all the milk left by
them was brought to Shiva’s shrine. The king prayed long and
earnestly, and when he looked up he saw that the shrine was full right
up to the ceiling. He gave [17]the old woman a handsome
present. And she went back to her home, and she did her housework, and
then she bathed all her little daughters and all her little
daughters-in-law. [18]
[Contents]
The Tuesday Story
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat.1 In it there
lived a bania who had no son. Every day a religious mendicant used to
come to his house and call out, “Alms! Alms! In the name of God,
give me alms.” But when the bania’s wife offered him alms
he refused them, because she had no children. She told her husband, who
advised her to play a trick on the mendicant. She hid behind her door,
and as he called out “Alms! alms!” she slipped a gold piece
into his wallet. But the mendicant caught her and became very angry. He
cursed her and told her that she would always remain without any
children. [19]She was terrified and fell at his feet
and begged for forgiveness. Then he pitied her and said, “Tell
your husband to put on blue clothes, mount a blue horse, and ride into
the jungle. He should ride on until he meets a horse. He should then
dismount and dig in the ground. He will in the end come to a temple to
Parwati. He must pray to her and she will bestow a child on him.”
When her husband came back she told him what had happened. So he at
once put on blue clothes, mounted a blue horse, and rode into the
forest. He met the horse, dismounted, and began digging. At last he
discovered a temple to Parwati, all of gold, with diamond pillars and a
spire made of rubies. Inside was a statue of the goddess, and to it he
prayed, saying, “I have houses and cottages, cattle and horses,
money and goods of all kinds, but I am very sad because I have no
son.” The goddess pitied him and asked, “Which will you
have, a son who will be good but will die young, or a son who will live
long but will be born blind?” The poor bania became greatly
perplexed, but at last said, “I choose a son who will be good but
will die young,” The goddess said, “Very well. [20]Step behind me. There you will find an image
of Ganpati. Behind it is a mango tree. Climb upon Ganpati’s
stomach and pick one mango. Go home and give it to your wife to eat,
and your wish will be gratified.” Parwati then disappeared. The
bania climbed upon Ganpati’s stomach and ate as many mangoes as
he could. He next filled a large bundle full of mangoes and stepped
down. But when he reached the ground he found that there was only one
mango in the bundle. He climbed up again and refilled his bundle, but
when he stepped down he again found only one mango. This happened three
or four times. At last Ganpati got very sore and angry with having his
stomach trampled on. So he shouted out, “One mango is all
you’ll get. So be off home!” The bania was frightened out
of his wits and galloped home with his one mango. His wife ate it, and
in nine months she presented her husband with a son. When the little
boy was eight years old his sacred thread was put on, and his mother
said, “It is time to think of his marriage.” But the bania
said, “I dare not marry him unless he first makes a pilgrimage to
Benares.” His [21]maternal uncle agreed to take
the little boy to Benares.
So off they started together, and some days later the uncle and
nephew halted at a village where some little girls were playing. One of
the little girls said to the other, “You are nothing but a
wretched little widow.” But the other little girl said, “Oh
no! there are never any widows in our family. Mother worships Parwati
and so I can never be a widow.” The uncle heard this, and thought
that if his nephew could only marry a little girl who could not become
a widow, he would not die young. So he began to think how he could
bring about the marriage. Now it so happened that the little girl was
to be married that day. But in the morning the boy to whom she was
betrothed fell ill. Her parents were in great trouble, but at last they
thought that, rather than postpone the wedding and disappoint all the
guests, it would be better to marry their little daughter to the first
traveller who passed through the village. So they went to the
rest-house to inquire if any one was there. There they found the uncle
and nephew, and they married their [22]little girl
to the latter that very evening when the cows were homing. They drew on
the wall a picture of Shiva and Parwati, and they put the children to
bed beneath it. Parwati appeared to the little girl in her sleep. The
goddess said, “My child, a snake will come to bite your husband:
give it milk to drink. Then put near it a new earthen jar. When the
snake has finished drinking, it will enter the earthen jar. Then at
once pull off your bodice and stuff it into the jar’s mouth. Next
morning give the jar to your mother.” Next evening everything
happened as Parwati had said. The snake came to bite her husband as he
slept. But the little girl offered it milk, which it drank. After
drinking, it curled itself up inside the earthen jar, and, the moment
it did so, the little girl slipped off her bodice and stuffed it into
the mouth of the jar. Next morning her husband gave her a ring, and she
in exchange gave him a sweet-dish, and he and his uncle continued their
journey to Benares. When they had gone, the little girl gave the
earthen jar with the snake inside it to her mother. The mother took out
the bodice, but instead of a snake a garland lay inside, and
[23]the mother put it round her little
daughter’s neck. Some weeks passed, but neither uncle nor nephew
returned. So the little girl’s parents grew anxious. The sick boy
who was to have been her husband recovered, but she could no longer
marry him, and the boy whom she had married had gone away and might
never return. In despair the parents built a house, in which they
entertained every traveller who passed by, hoping that sooner or later
one of the travellers would prove to be their daughter’s husband.
To all of them the mother gave water; the daughter washed their feet;
her brother gave them sandal-wood paste; and her father gave them
betel-nut. But it was all in vain; none of the travellers’
fingers fitted the ring given to the little girl by her husband, nor
could any of them produce the sweet-dish which she had given him in
exchange.
In the meantime the uncle and nephew had reached Benares and had
given large sums in charity, and had visited all the holy places and
had received the blessings of all the Brahmans. One day the little boy,
fainted. And in a dream he saw the messenger of Yama, the god
[24]of death, come close to him as if to carry him
off. Next he saw the goddess Parwati come to his rescue and, after a
struggle, drive away Yama’s messenger. When the boy woke up he
told the dream to his uncle. The latter was overjoyed because he felt
certain that now the boy would no longer die young. He told his nephew
to get ready, and next day they left Benares. On their way home they
passed by the village where the nephew had been married. As they were
having breakfast near the village tank, a maid-servant invited them to
come to the house which the girl’s parents had built for the
reception of travellers. At first the uncle declined, but when a palki
was sent for them, he and his nephew entered it. When the little girl
began to wash her husband’s feet, she recognised him. She tried
on the ring, which fitted his finger, and he in turn showed her the
sweet-dish which she had given him. The parents were as pleased as
possible, and they sent a messenger to invite the boy’s parents.
They came, and the boy’s mother threw herself at her
daughter-in-law’s feet and thanked her for saving her son. Then
there was a great feast and everybody [25]was very
happy indeed, and at the end they all worshipped Parwati,2 so
she became as pleased as everybody else. [26]
[Contents]
The Wednesday and Thursday Story
There was once upon a time a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
prince who had seven sons and seven daughters-in-law. Every day there
used to come to the prince’s house two Brahmans, an uncle and a
nephew. But when they asked for alms the daughters-in-law sent word
that they were too busy to give them any. Some time afterwards the
prince lost all his riches and became very poor. The two Brahmans again
came to beg, but the elder daughter-in-law said to them, “We are
no longer busy, but we have nothing to give you. If we had, we should
give it to you.” The youngest daughter-in-law, however, was a
clever little girl, and she thought to herself, “The Brahmans
will get very angry with us. [27]When we had money, we
gave them nothing; and now we give them nothing because we have nothing
to give.” So she fell at the elder Brahman’s feet and said,
“We have been very wicked and have deserved to become poor. But
please forgive us and tell me how we may become rich as we were
before.” The elder Brahman said, “Every Wednesday and every
Thursday you must invite a Brahman to dinner. And if you have no money
to pay for the dinner, draw a pair of cow’s feet on your
money-box. If you want grain for the dinner, draw a pair of cow’s
feet on your corn-bin. Then worship the feet and welcome the Brahmans.
For you will find that you will have money in your box and grain in
your corn-bin. And in time you will all get as rich as you were
before.” The little girl did what the Brahman told her. And
whenever she invited Brahmans to dinner, she drew the cow’s feet
on the cash-box and on the corn-bin, and there was always money and
grain sufficient for the meal.
But some days later she fell asleep and dreamt that Budh1
and Brahaspati came to her [28]bedside and said,
“Little girl, little girl, your husband has been made king over a
great country. Go to him, and, when you have found him, do not forget
to worship us and to give feast to the Brahmans.” Then the little
girl woke up and she told the other six daughters-in-law. But they were
jealous of her, and they became very angry; and they kicked her so
often and boxed her ears so hard that she forgot all about drawing the
cow’s feet on her money-box and on the corn-bin. So she never
found any money in the box or any corn in the bin. And every day they
became poorer and poorer. First all the men servants ran away, then the
male members of the family left, and at last the seven daughters-in-law
were left alone in the house. They were starving, but they did not know
how to get any food. One day they heard that a king in a neighbouring
country wished to construct a tank and was calling for labourers. So
they decided to go to the tank and work there just like common coolie
women. Now who do you think the king was? He was the youngest son of
the prince of Atpat and the husband of the youngest daughter-in-law.
When the [29]prince had lost all his money, his youngest
son left the house and set off on a journey. As he travelled he came to
a city, the king of which had just died without leaving any children or
relatives. His subjects did not know how to choose a successor. At last
they gave a garland of flowers to a she-elephant and turned it loose.
The elephant walked straight to the prince’s son and put the
garland round his neck. The townspeople were very angry. They snatched
away the garland and drove away the prince’s son. They again gave
the garland to the elephant, but the elephant again put the garland
round the neck of the prince’s son. The townspeople again
snatched away the garland. But when the elephant put it round the young
man’s neck for the third time, they lifted him high in the air
and declared him to be their king. At first he was so pleased at being
king that he forgot all about his poor little wife. But one night Budh
and Brahaspati appeared to him in a dream and reminded him of her and
told him how poor she was. But he could not leave his kingdom to go and
look for her. So he thought that he would dig a tank and call
[30]together labourers from every quarter. And
every day he used to go to the tank and search among the labourers to
see if his wife was there. One day he recognised his wife and called
her to him. Then they told each other how Budh and Brahaspati had
appeared to each of them in a dream. And the king was so delighted at
finding his wife that he at once proclaimed her queen of the
country.
So the little daughter-in-law was crowned queen, but she did not let
the other daughters-in-law who were also working at the tank know of
her good fortune. As queen, she gave a great feast to all the workers
on the tank. But in her own palace she took some wheat flour, and she
kneaded it into shapes resembling human feet and human fists. And when
the other daughters-in-law were with the crowd of workers eating at the
feast, she went up to them, and to each daughter-in-law who had kicked
her she gave a flour foot, and to each daughter-in-law who had struck
her with her hands she gave a flour fist. Then the daughters-in-law
recognised who the little queen was, and they fell at her feet
[31]and begged for her forgiveness. So the little
queen forgave them and took them back with her into her husband’s
palace. And they all lived together happily ever afterwards.
[32]
[Contents]
The Friday Story
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
miserably poor Brahman. He had a wife who was as poor as he was. One
day she felt her poverty so much that she went to a gossip of hers who
lived close by and told her all about her troubles. The neighbour could
suggest nothing better than that the poor woman should worship the
goddess Shukra or Venus. So she told the Brahman woman to fast every
Friday through the month of Shravan. Every Friday evening she should
invite a married lady friend to her house. She should bathe her
friend’s feet. She should give her sweetened milk to drink and
fill her lap with wheat cakes and bits of cocoa-nut. She should
continue to worship Shukra in this way every Friday for a whole year,
and in the end the goddess would certainly [33]do something for her. The Brahman woman
thought the advice good, and every Friday she worshipped Shukra and had
a married friend to dine with her just as her neighbour had advised
her.
Now the Brahman woman had a rich brother living in the same town,
who one day invited one thousand Brahmans to dine. At the same time he
invited all the townspeople with the single exception of his sister.
The poor lady thought that she must have been left out by accident, and
that there would be no harm in going, even although uninvited. She put
on her silk dining-clothes, and, taking her children with her, went off
to the dinner. She seated herself close to her children, and was eating
away when her brother came round serving ghee. When he saw his sister
he shouted at her, “You have neither nice clothes nor nice
jewelry. You have made me a laughing-stock by coming as you have come.
I shall not turn you out, but do not come to-morrow.”
Next day she did not want to go, but her children, who had enjoyed
the previous day’s feast, persuaded their mother to take them
again to her brother’s house. Once more [34]she went and sat down with her children among
the rows of feasters. Her brother saw her as before when he came round
serving the ghee. He shouted at her, “A beggar woman must, I
suppose, act like a village sow, and will not go away although told to.
But do not come to-morrow. If you do, I’ll have you turned
out.” Next day, however, she again went with her children to her
brother’s house. But near the entrance his servants caught her
and turned her out before she could eat anything. She went home sad and
hungry and prayed to Shukra. Now the goddess had been pleased with her
devotion and so took pity on her. She helped the poor woman’s
husband so that he rapidly acquired great wealth. When her husband had
become very rich she asked her brother to dinner. But the brother
remembered how he had treated her and was ashamed to accept. He pressed
her to dine with him first, and begged so hard that she at last
consented. Next day she put on all her jewels and her finest clothes.
Her brother gave her a wooden platform to sit on and plates made out of
leaves from which to eat her dinner. Before she sat down she took off
her gold-embroidered [35]shawl and put it close to her
plate. Her brother saw her, but thought she did it because she felt the
room hot. She then placed her jewelry on the wooden platform. Her
brother thought that she did it because she felt the jewelry heavy. She
took a portion of rice and placed it on her necklace. She put a portion
of vegetables on her pendant, and a sweet ball she placed on her
jewelled star.
Her brother at last asked her, “What are you doing?” She
said, “I am giving to the guests whom you really invited.”
But he did not understand, and asked, “Why do you not begin to
eat?” She said, “I have not been invited to this dinner. It
was given in honour of my finery and not of me. I had my dinner the day
when you gave the feast to the one thousand Brahmans.”
The brother felt thoroughly ashamed of himself. He threw himself at
his sister’s feet and begged for her forgiveness. So she forgave
him and sat down to dinner. And the brother in turn went to her house
and dined with her. And Shukra was pleased with both sister and
brother, and they all lived happily ever afterwards. May I and my
readers do the same. [36]
[Contents]
The Saturday Story
Once upon a time there was a town-called Atpat. In it there lived a
poor Brahman who had three daughters-in-law. He rose early even during
the rainy season, and every day immediately after his morning meal he
used to go to his field with his children and his daughters-in-law. One
first Saturday in Shravan he got up as usual and said to the youngest
of his daughters-in-law, “To-day is Saturday; you had better stay
at home, and although there is very little in the house, you must try
to get some sort of a dinner ready. Go upstairs and scrape together all
the grain there is in the grain-jars and make bread with it. For
vegetables you had better gather grass and make some chutney out of
clover leaves.” When the Brahman had left, his [37]little daughter-in-law followed his orders as
best she could. There was in the jar upstairs only grain for half an
ordinary loaf. So she made tiny, tiny loaves and prepared some
vegetables out of grass and made some clover chutney. Then she sat down
to wait for the family’s return from the field. As she did so,
Saturn came disguised as a beggar all covered with sores, and cried,
“O Lady! I am aching all over: give me hot water to bathe in and
oil to rub myself with, and then give me something to eat.” The
little daughter-in-law felt very sorry for the poor beggar. She went
inside and got him a few drops of oil and warmed some water for his
bath, and then gave him one of the tiny loaves to eat. The beggar ate
it, and then gave her his blessing, saying, “You will never want
for anything.” He then folded up the leaves from which he had
eaten, stuck them into a corner of the eaves, and disappeared.
Shortly afterwards the family came home and found a splendid dinner
waiting for them. They said to themselves, “Where did this all
come from? There was practically nothing in the house.” Next
Saturday another daughter-in-law stayed at home. Again [38]Saturn in the guise of a beggar covered with
sores came to the house. He asked as before for hot water, oil, and
food. But his daughter-in-law said, “I have nothing to give
you.” The god pressed her, saying, “Give me a little of
anything that you have.” But the daughter-in-law repeated,
“I have nothing.” The god replied, “Very well, you
will lose that little you have.” With this threat he disappeared.
But, when the daughter-in-law went upstairs to fetch grain for dinner,
she could find nothing in any of the jars. Shortly afterwards the
family came home, but there was no dinner for them. So they all got
angry with the daughter-in-law, and, although she told them about the
beggar, they scolded her harder than ever. A third Saturday came round,
and a third daughter-in-law remained at home. Again Saturn came, and
the third daughter-in-law behaved just as the second had done. She gave
the god neither hot water, oil, nor food. And the god told her that she
should lose the little she had. When the family came home there was no
dinner for them, and they scolded the third daughter-in-law just as
hard as they had scolded the second one.
[39]
The fourth Saturday it was once more the turn of the youngest
daughter-in-law. Again Saturn came in the guise of a beggar covered
with sores and asked for hot water, oil, and food. The little
daughter-in-law gave them as she had done before, and the god blessed
her, saying, “God will make you rich and happy.” Then he
folded up the leaves from which he had eaten and stuck them into a
corner of the eaves. When the little daughter-in-law went upstairs, she
saw any amount of grain in the jars, and she prepared a splendid
dinner. So when the family came home they were delighted. They could no
longer restrain their curiosity, and exclaimed, “Where did all
this food come from?” The little daughter-in-law told them about
the beggar covered with sores and about his blessing. To test her
story, they looked for the folded leaves which he had stuck into a
corner of the roof. They found them, but when they pulled them out they
were full of pearls and diamonds. Then the old Brahman guessed that the
beggar was Saturn in disguise, and he also understood why, when the
other two daughters-in-law gave him nothing and were cursed by him,
there was [40]nothing for dinner. So they all knelt
down and prayed to Saturn, and the god forgave the two-daughters-in-law
who had given him nothing. And he was more pleased than ever with the
little daughter-in-law who had befriended him. And so they all lived
happily ever afterwards. And may Saturn be pleased with us all as he
was with the little daughter-in-law. [41]
[Contents]
Mahalaxmi and the Two Queens
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
king who had two queens. Of one of them he was very fond, but the other
one he did not care for. The name of the favoured one was
Patmadhavrani, and the name of the unloved one was Chimadevrani. Now
the king had an enemy called Nandanbaneshwar. Such a terrible enemy he
was too! He could jump into the clouds or dive into the bottom of the
ocean. At one moment he would shoot up into heaven. At another he would
sink down into hell, and through fear of his enemy, the king had become
as dry and as thin as an old bit of stick. One day the king, in
despair, assembled all his subjects and ordered them to seek out and
kill Nandanbaneshwar. All the subjects said, [42]“Certainly, certainly, O King,”
and began to search everywhere for Nandanbaneshwar. Now in Atpat there
lived a poor woman who had one son. On hearing the orders of the king,
he said to her, “Mother, Mother, give me some bread, for I am
going out to kill the king’s enemy.” The old woman said,
“Do not be silly; you are only a poor boy, and people will laugh
at you. Here, take this bit of bread and go and eat it behind a
tree.” The boy said, “Very well,” and took the bread.
But, after taking it, he joined the other villagers and went at their
head to seek out and kill Nandanbaneshwar. But when evening fell they
had not yet met Nandanbaneshwar, so all the villagers returned home.
And when the king heard of their ill-success he was greatly grieved.
But the old woman’s son stayed in a wood outside the village. And
lo and behold! just about midnight the serpent-maidens from
Patâla1 and the wood-nymphs came close to where he was and
began to worship Mahalaxmi. The boy was at first terribly frightened,
but at last he plucked up courage enough to ask, “Ladies, ladies,
what [43]does one gain by worshipping Mahalaxmi?”
“Whatever you lose you will find,” said the serpent-maidens
from Patala; “and whatever you want you will get.” The boy
resolved that he too would worship Mahalaxmi. And he joined the
serpent-maidens from Patâla and the wood-nymphs, and all night
long they blew on earthen pots to do the goddess honour; and the woods
echoed and re-echoed with the deep-booming noise which they
made.2
At dawn Mahalaxmi revealed herself, and all of them, the boy
included, prostrated themselves before her and asked for her blessing.
She first blessed the serpent--maidens from Patâla and then the
wood-nymphs. And then she blessed the poor old woman’s son and
said, “You will get half the kingdom of Atpat and half the
king’s treasure. He will build you a house as high as his own,
and he will give you the name of ‘Navalvat’ or
‘Wonderways.’ For this very morning the king’s mighty
enemy will break his neck and be found lying dead in the king’s
courtyard,” With these words [44]the goddess
vanished and flew to Kolhapur,3 and the old woman’s son went
home. Now at dawn Queen Patmadhavrani got up and went into the
king’s courtyard, and there she saw Nandanbaneshwar lying dead
from a broken neck. She was overjoyed, and ran back into the palace to
tell the king. The king inquired who had killed Nandanbaneshwar. Every
one said that the old woman’s son must have killed him, because
he stayed behind when the others went home. The king sent for the old
woman’s son. He was very frightened, and when he reached the
royal hall he called out, “I have made no false charge against
any one. I have done no one any harm. Why, therefore, O King, have you
sent for me?” “Do not be afraid,” said the king.
“My enemy Nandanbaneshwar is dead, and every one says that it is
you who killed him. Tell me if this is true.” “No, O
King,” said the boy, “he was killed by the arts of
Mahalaxmi.” “Where did you meet her?” asked the king.
The boy said, “I stayed when the other villagers returned home,
and during the night there came the serpent-maidens from [45]Patâla and the wood-nymphs. They taught
me how to worship Mahalaxmi. In the morning she revealed herself and
promised me that Nandanbaneshwar would be found lying dead, that you
would give me half your kingdom and half your treasure, that you would
build me a palace as high as your own, and that you would call me
Navalvat or Wonderways.” The king did as the goddess had
foretold. He handed half his provinces and half his treasuries to
Wonderways, and built him a palace of which the roof was exactly on the
same level as that of his own palace.
When Queen Patmadhavrani heard what had happened, she sent for
Wonderways and asked him how to worship Mahalaxmi. And he told her all
that he had seen the serpent-maidens of Patâla do, and he also
told her on the eighth day of the month of Ashwin4 to tie on her
wrist a thread with sixteen strands in it, and to wear it continually
for the rest of the month. When the 8th of Ashwin came, Queen
Patmadhavrani dutifully tied round her wrist a thread of sixteen
strands, and resolved to wear it every [46]day for the
rest of the month. But a day or two later the king came to Queen
Patmadhavrani’s apartments and began to play saripat5
with her. As they played he noticed the thread on her wrist and asked
what it was. She told him how Wonderways had instructed her to tie it
on. But the king got very angry and roared out, “I have in my
palace garlands and twine, bracelets, and hobbling-ropes. So throw away
that wretched piece of thread. I will not let you wear it.” The
queen did as she was bid, and, pulling off the thread bracelet, threw
it on the floor. Next morning the maids and the slave-girls began to
sweep the palace, and among the sweepings one of them noticed the
queen’s thread bracelet. She picked it up and showed it to
Wonderways, and he grew very wroth with Queen Patmadhavrani. He took
the thread and at once went with it to the palace of the unloved Queen
Chimadevrani. He told her what had happened, and she begged him to give
the thread to her and to tell her how to worship Mahalaxmi. But he
said, “You will grow vain and get so conceited that you will not
do what I tell you [47]to do.” But she
promised that she would obey him in everything. So just as he had told
the Queen Patmadhavrani, he told Queen Chimadevrani all the rites which
he had seen the serpent-maidens from Patala and the wood-nymphs
perform. Everything went on just the same for a whole year. But the
next year on the 8th of Ashwin a very strange thing happened. The
goddess Mahalaxmi disguised herself as an old beggar-woman and came to
Atpat. First she went to the part of the palace where Queen
Patmadhavrani lived. But no one there was paying the least honour to
the goddess Mahalaxmi, although it was the 8th of Ashwin, and therefore
specially sacred to her. Mahalaxmi was dreadfully put out at this, and
when she saw Queen Patmadhavrani she said, “Lady, lady,
Patmadhavrani, mother of sons, what have you in your house
to-day?” The queen replied, “I have nothing in my house
to-day.” The old woman went on, “Lady, lady, Patmadhavrani,
mother of sons, if you give this beggar-woman a little water, you will
acquire merit sufficient for all your kingdom.” But the queen
replied, “Even if I were to give you a copper cauldron
[48]of water it would not suffice for all my
kingdom.” The old woman then said, “Lady, lady,
Patmadhavrani, mother of sons, if you give this old beggar-woman a
little rice and curds, you will gain enough merit for all your
kingdom.” The queen replied, “Even if I were to give you a
big dinner of nothing but rice and curds, I should not gain enough
merit for all my kingdom.” Then the old woman got very angry and
cursed the queen, saying, “You will become half a frog and half a
human being, and you will stand outside your co-wife’s bath-room
and croak like a frog.” But the queen did not mind her the least
little bit, and she laughed so loud at the old woman that the noise was
like two chains rattling together. Mahalaxmi went off in a great rage
and entered Queen Chimadevrani’s part of the palace. There she
saw all the accessories of worship ready, and there was a beautiful
image of Mahalaxmi leaning against the wall; The old woman cried,
“Lady, lady, Chimadevrani, mother of sons, what have you in your
house to-day?” “To-day,” said the queen, “we
are worshipping Mahalaxmi.” Then the old beggar-woman said,
“I am Mahalaxmi.” But [49]the queen
doubted and asked her, “By what sign shall I know you?” The
goddess replied, “In the morning I shall take the shape of a
little girl. In the afternoon I shall take that of a young married
woman. In the evening I shall become an old hag.” After the
goddess had taken all three shapes, Queen Chimadevrani called her into
the palace and bathed and anointed her. She gave her a silk skirt and a
platform to sit upon. Then she sent for Wonderways, and both of them
worshipped the old beggar-woman and blew on earthen pots in her honour.
The king heard the blowing on the pots and told a sepoy to find out why
there was such a noise in Queen Chimadevrani’s quarters. The
sepoy went there, and when he saw what was happening joined also in the
worship. After a little while he went back and told the king. The king
said that he would go there too. He followed the sepoy, and Queen
Chimadevrani came to the steps and met him and took him upstairs, where
both played at saripat until dawn. And all the time Mahalaxmi sat by
and watched them. At dawn Queen Chimadevrani asked Mahalaxmi for her
blessing. She blessed the [50]queen and said, “The
king will take you back with him to the palace, and your co-wife will
become half frog, half human being, and will have to croak outside your
bath-room while you bathe.” But Queen Chimadevrani begged the
goddess not to place such a terrible curse on Patmadhavrani. The
goddess relented a little, but said, “The king will drive her
into the jungle for twelve years.” At these words she vanished
and flew to Kolhapur. When the sun rose the king placed Queen
Chimadevrani in his chariot and drove her to his own part of the
palace. He then sent a message to Queen Patmadhavrani asking her to
join them. Shortly afterwards Queen Patmadhavrani appeared, dressed all
in rags with a skirt round her legs and her hair all
unfastened. On her head was a pot full of burning coal, and she began
to shout and scream at the top of her voice. The king became very angry
and roared out, “Who is this that is shouting and screaming? Is
it a ghost or a she-devil or what?” The sepoys replied, “O
King, it is neither a ghost nor a she-devil, it is your Queen
Patmadhavrani.” “Take her into the jungle,” roared
the king, “and kill her there.” [51]Then he went back into the palace and began to
live in great happiness with Queen Chimadevrani. But the sepoys took
Patmadhavrani into the jungle and told her that they had been ordered
to kill her. She began to weep. The sepoys were kind-hearted men and
they felt very sorry for her. They said, “Lady, lady, do not
weep. We have eaten bread and drunk water at your hands so we cannot
kill you. We will leave you here, but you must never come back into the
kingdom again.” The sepoys left her and returned to Atpat. But
the poor queen wandered on until she came to a distant town, where she
entered a coppersmith’s lane. Therein a coppersmith was making
bangles for a beautiful young princess who had just been crowned queen
of the city. But suddenly none of the bangles would join. He began to
search for the cause, and asked his workmen whether any stranger had
come near his house. The workmen looked about and found Queen
Patmadhavrani in hiding close by. They told the coppersmith, and he and
his men beat her soundly and drove her away. She ran into the lane of
some weavers who were weaving a sari for the new queen. [52]Suddenly none of the looms would work. They
began looking about to see if any stranger had come. After a little
while they found the queen. So they beat her soundly and drove her
away. Then she ran out of the town back into the jungle. There she
wandered about until she came to the cave of a rishi or sage. The rishi
was sitting lost in meditation. But she bided her time, and, when he
went to bathe, she slipped into the cave and swept it and neaped it and
tidied up all the utensils used by him for worship. Then she slipped
out of the cave and ran back into the jungle. This went on every day
for twelve years without the rishi showing that he was aware of what
she was doing. But in his heart he was really pleased with her. And one
day he called out in a loud voice, “Who is it who sweeps and
neaps my cave? Whoever she is, let her step forward.” The queen
stepped into the presence of the rishi and threw herself at his feet
and said, “If you promise not to punish me, I shall tell
you.” The rishi promised, and she told him her story. The rishi
took out his magic books and, consulting them, learned that Mahalaxmi
[53]had cursed her. So he taught her how to
worship Mahalaxmi, and all night long they blew on earthen pots and
performed rites in her honour. At dawn she revealed herself and the
queen asked her for her blessing. But the goddess was still very angry
with the queen. Then the rishi joined her in begging the
goddess’s pardon, and at last she relented. She said to the
queen, “Put under that tree a foot-bath full of water,
sandal-wood ointment, plates full of fruit, a stick of camphor, fans
made of odorous grasses; and handle them all so that they retain the
fragrance of some scent which the king will remember you used.
To-morrow the king will come. He will be thirsty. He will send his
sepoys to look for water. They will see all your things ready. And when
they go back and tell him, he will come himself.” Next morning,
as the goddess had foretold, the king came. He saw the cool shade of
the tree. He was tired with hunting, so he sat down and rested. He
washed his feet in the foot-bath. He ate up all the fruit, drank the
cold water, and sucked the stick of camphor. When he had rested to his
heart’s content, he asked the sepoy, “How is it that
[54]in the water I drank, in the fruit I took, in
the camphor I ate, I noticed a scent which Patmadhavrani always
used?” The sepoys replied, “If the king promises to pardon
us, we will tell him.” The king promised. The sepoys then told
him how they had not killed the queen, because they had eaten bread and
had drunk water at her hands, but had let her go. The king told them to
look and see if she was anywhere about. They searched and searched
until they came to the rishi’s cave. Then they ran back and told
the king. The king rose, and going to the cave did homage to the rishi.
The rishi accepted the homage and lectured him at great length. At last
he ordered the king to prostrate himself before the queen. The king
obeyed, and the rishi handed Patmadhavrani back to his care and blessed
both her and her husband. The king put her in his chariot and took her
to Atpat. Outside the town the king stopped his chariot and sent for
Queen Chimadevrani Chimadevrani bathed and anointed herself, and put on
all her silk clothes, her shawls, her embroideries, and her jewels. In
front of her she placed all the horn-blowers of Atpat. And as she went
[55]to meet the king they blew their very loudest
on their horns. The king was amazed when he heard the noise, and roared
out, “Who is coming with such pomp and splendour? Is it the
serpent-maidens of Patâla or is it the wood-nymphs who live in
the heart of the forest?” The sepoys said, “O King, it is
neither the serpent-maidens of Patâla nor is it the wood-nymphs
who live in the heart of the forest. It is Queen Chimadevrani, who is
coming to meet you as you ordered.” The king turned to
Patmadhavrani and said, “If you had come in this guise to meet
me, instead of coming like a mad woman, you would never have suffered
as you did.” Queen Patmadhavrani said nothing, but sat still in
the chariot, and the king lifted Queen Chimadevrani into the chariot,
and all three entered the city. And as they entered, the horn-blowers
blew so loud that every one was quite deafened. And the king lived from
that time forth in perfect happiness with both his wives. And because
of his happiness, he ruled so well that his subjects thought that King
Ramchandra of Ayodhya had come back to rule over them. [56]
[Contents]
The Island Palace
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
Brahman. He had a disciple who used every day to go to the village pond
and bathe and worship the god Shiva. On the way he had to walk through
the sandy island in the dry bed of the river. And, as he went home
across the island, he used to hear a voice cry, “Shall I come?
Shall I come? Shall I come?”; but when he looked round he could
see no one. The Brahman’s disciple at last got so frightened that
he withered up until he became as dry and as thin as a bone. At last
the Brahman said, “You have no wish to eat or drink; yet you are
so thin. What is the reason?” The boy replied, “I neither
wish to eat, nor want to eat, nor crave to eat. But I am frightened
[57]out of my wits. For whenever I come back from
my bath I hear a voice behind me call out, ‘Shall I come? Shall I
come? Shall I come?’; but when I look round there is no one
there.” The Brahman said, “Do not be afraid, and when you
next hear the voice, do not look behind you, but call out as boldly as
you can, ‘Come along, come along, come along.’” Next
day the disciple went as usual to his bath in the village pond. He
worshipped the god Shiva, and as he came home he heard the cry behind
him, “Shall I come? Shall I come? Shall I come?” The boy
was very frightened, but he did not look behind him. In a short time he
mastered his fears, and then in a voice like a bull roaring he cried
out, “Come along, come along, come along.” At last he
reached home, calling all the time and without once looking behind
him.
The Brahman looked up as the disciple came in, and he saw that just
behind was walking a young girl. He at once married the girl to his
disciple and gave them a house to live in close by his own. Now, on the
first Monday in the month of Shravan, or August, [58]the disciple got up and said to his wife,
“I am going out to worship the god Shiva. But do not wait for me.
Just eat your breakfast directly you feel hungry.” He went out,
and in a little time his wife began to feel hungry. Nevertheless, she
knew that, in spite of what her husband had said, she ought not to eat
anything while he was worshipping Shiva. So she waited for a little
time, but at last she got so terribly hungry that she could not wait
any more. So she sat down and cooked her breakfast, and had just put
one mouthful into her mouth when her husband came to the outer door.
“Wife, wife,” he called, “open the door!” Then
the little wife got very frightened. She pushed the uneaten breakfast
under the bed, got up, washed her hands, and opened the door. She then
told her husband that she had waited for him, and she cooked a fresh
breakfast, which both ate one after the other. Next Monday exactly the
same thing happened. The little wife cooked her breakfast and was just
beginning it when her husband came. She then hid her uneaten breakfast
under her bed and pretended that she had waited for his return. And on
the [59]two following Mondays the naughty little wife
deceived her husband in just the same way.
Now on the last Sunday in Shravan, when husband and wife went to lie
down, the former noticed a light shining under the bed. He looked to
see what it was, and saw several platefuls of jewels. He asked his wife
whence they had come. Now they were really the uneaten breakfasts,
which the god Shiva had turned into gold and jewels. But the naughty
little wife got very frightened and told her husband a bigger story
than ever. “They are presents,” she said, “from my
mother and father and their family.” “But where is your
father’s house?” asked the husband. “It is in the
sandy island,” said the little wife, “which lies in the dry
bed of the river.” “You must take me there,” said her
husband. Next morning they started off together. And the naughty little
wife could hardly walk, she was so frightened. For she knew quite well
that her father had no house in the sandy island. But on the way she
prayed to Shiva, “Please, please, god Shiva, create a house for
my father in the sandy island which lies in the dry bed of the river,
even if it be only for half an hour.” [60]
At last the husband and wife came to the sandy island. And there, lo
and behold! they saw a great big palace, and a splendidly dressed young
man came forward and greeted the disciple as his brother-in-law. And a
handsome old knight came forward and greeted the disciple as his
son-in-law. And a beautiful young woman greeted the naughty little wife
as the sister of her husband. And a lovely little girl ran up and
embraced her and called her “sister.” And slave girls and
maid-servants ran forward to offer her their service. A guard of
soldiers kept watch by the palace, and at the door there were sentries,
who made way for them as they passed. Inside the house the little wife
and her husband were given platforms to sit upon, and a splendid feast
was all ready prepared for them to eat. After they had feasted, they
got up and said good-bye to the little wife’s father and mother,
and garlands of flowers were placed round their necks, and they started
for their home. When they had gone half-way, the naughty little wife
remembered that she had hung her garland on a peg and had forgotten to
bring it with her. So she and her husband went back to the [61]sandy island. But when they got there, there
was no palace, there were no soldiers to guard it, there were no
sentries at the door, there were no maid-servants nor slave girls.
There was nothing there but just a sandy island in the middle of a dry
river-bed. And on the sand lay the garland which the naughty little
wife had forgotten. She took it up and put it round her neck.
But her husband asked her, “What has happened to your
father’s house?” The naughty little wife replied, all in
tears, “As it came, so it went. But if you promise to forgive me,
I shall tell you.” The husband promised. So she told him how
every Monday she had felt so hungry and how she had cooked her
breakfast, and then, on hearing her husband’s voice, had pushed
it under their bed. She also told him that the god Shiva had turned the
food into gold and jewels. “Then when you asked me,” she
went on, “I felt so frightened that I said they were presents
from my father and mother and the rest of my family. And when you made
me take you to my father’s house, I prayed the god Shiva to
create, if only for half an hour, a house for my [62]father on the sandy island in the dry
river-bed. And he graciously granted my request.” Then the
husband forgave the naughty little wife. And she became quite good and
never told him any more stories. And they both went home and lived
happily ever afterwards. [63]
[Contents]
Nagoba, the Snake-King
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
Brahman who had seven little daughters-in-law. In the fulness of time
the month of Shravan came and with it Nagpanchmi Day1. In honour
of the festival, one little daughter-in-law went to her
grandpapa’s house, another went to her great grandpapa’s
house, another went to her father’s house, until at last only the
youngest daughter-in-law remained behind. Her father and mother were
dead, and she had no uncles and no aunts and no little brothers or
sisters. So the poor little daughter-in-law felt very sad and sat down
and cried in a corner. Then she remembered that it was Nagpanchmi Day,
and [64]that it was a festival in honour of Nagoba,
the great snake-king. So she prayed under her breath, “Please,
please, snake-king, come and pretend that you have been sent to fetch
me to my father’s house!” And the great snake-king heard
the prayer and felt quite sorry for the poor little daughter-in-law who
was crying in the corner. He assumed the guise of a Brahman and came to
the house where the little daughter-in-law was, and said that he had
been sent to fetch her to her father’s house. Her father-in-law
was very much astonished. For he wondered why, if the new-comer really
was a relative of the little daughter-in-law, he had never paid him a
visit before. At last he asked the little daughter-in-law who the
new-comer was. She did not know in the least. But she was so overjoyed
that some one should have come for her that she at once answered,
“He is my mother’s brother.” Her father-in-law
believed her and sent her off in the care of Nagoba, the snake-king.
Still disguised as a Brahman, he took her to the entrance of his
underground palace and there he told her who he was. He then reassumed
his true appearance, and, expanding the mighty [65]hood behind his head, he seated the little
girl on it and took her down to his splendid dwelling-house beneath the
earth. In the central hall he presented her to the snake-queen and to
all the snake-princes, and told them that in no circumstances whatever
were they to bite the little daughter-in-law.
One day the snake-queen was about to be confined. So she asked the
little daughter-in-law to sit by her side with the lamp in her hand.
The little daughter-in-law did so, and a little time afterwards the
snake-queen gave birth to a fresh litter of little snake-princes. When
the little daughter-in-law saw them all wriggling about, she was
frightened out of her wits. She let the lamp slip out of her hands. It
fell on the ground and burnt all the little snakes’ tails off.
The snake-queen did her best to comfort them, but the stumps of the
little princes’ tails ached so dreadfully that it was ever so
long before the snake-queen could put them off to sleep. When the
snake-king came home that evening, she told him what had happened. And
she was so cross with the little daughter-in-law, that the snake-king
had to promise that she should go back to her [66]father-in-law’s house. A few days later,
the snake-king assumed once again the guise of a Brahman, and, loading
the little daughter-in-law with presents, took her back to her
husband’s home. In the course of time the little snake-princes
grew up, but their tails never grew again. So their father, the
snake-king, called one little prince, No-tail; and the second little
prince, Cut-tail; and the third little prince, Dock-tail. And one day
they asked the snake-queen how it was that their tails had been broken
off. She told them how the little daughter-in-law had burnt them off by
dropping the lamp on them.
The snake-princes, when they heard their mother’s answer, were
terribly cross with the little daughter-in-law, and they vowed that
they would be revenged on her. So they found out where she lived, and
they sent a message to her house, saying that they were coming to pay
her a visit. But they really meant to bite her to death directly they
saw her. The little daughter-in-law was overjoyed when she heard that
the snake-princes were coming to visit her. For ever since the
snake-king had pretended to be her uncle, she always thought
[67]of little No-tail and little Cut-tail and
little Dock-tail as if they had been her own cousins. Now it so
happened that the very day on which they were expected at the little
daughter-in-law’s house was Nagpanchmi Day. The little
daughter-in-law was sitting in the house all alone waiting for little
Prince No-tail, little Prince Cut-tail, and little Prince Dock-tail.
They were late in coming, so to pass the time she drew pictures of
Nagoba, the snake-king, on her dining-platform and on the wall. When
she had finished the pictures, she worshipped them and offered them
milk and food. Then she prayed to the great snake-king, “Please
please, King Nagoba, guard from all hurt, wherever they may be, my
little cousins No-tail and Cut-tail and Dock-tail.” And last of
all she prostrated herself at full length before the pictures which she
had drawn on the wall and on her dining-platform.
In the meantime little Prince No-tail and little Prince Cut-tail and
little Prince Dock-tail had come up without the little daughter-in-law
noticing them. But when they saw the honour which she was paying their
father, King Nagoba, and heard the prayer which [68]she had offered on their behalf, they no
longer wished to kill or bite the little daughter-in-law. On the
contrary, they made themselves known to her and stayed all that day in
the house and were as good and as nice as possible. When night fell,
they drank the milk which she had offered to the snake-king. And in its
place they put a necklace with nine beautiful jewels in it. Before day
broke they went away quietly and returned to their father’s
palace under the ground. Next morning when the little daughter-in-law
woke up she saw the lovely necklace lying where the milk had been. She
gave a shout of delight, and putting it round her neck, she ran all
over the house showing it to everybody. And every one was perfectly
charmed with it. And the snake-princes never again came to bite any one
in that household. And the little daughter-in-law and her husband and
her father-in-law and little Prince No-tail and little Prince Cut-tail
and little Prince Dock-tail, they all lived happily for ever so long
afterwards. [69]
[Contents]
Parwati and the Beggar-Man
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In It there lived a
Brahman. He had seven daughters, and when they had reached a
marriageable age he asked them who would arrange their marriages and
bring them handsome husbands and make their fortunes. The six eldest
daughters said, “Papa, Papa, you of course. You will arrange our
marriages and bring us handsome husbands and make our fortunes for
us.” But the youngest daughter was a naughty little girl. She got
into a temper all about nothing, and she stamped her foot, and she
turned her back on her father and said, “I will arrange my own
marriage, and I will get a handsome husband for myself, and I will make
my fortune myself.” The Brahman was very angry with her, and so
how do you [70]think he punished her? He first searched
about and found six rich and handsome boys. Then he married them with
great pomp and display to his six eldest daughters. But the youngest
girl he gave in marriage to a miserable beggar-man. You never saw such
a beggar-man as he was! There was not a spot on his skin that was not
black with leprosy, and his feet and hands had rotted right off. If you
had seen him you would have said, “If that beggar-man does not
die to-day he will certainly die to-morrow. For he cannot possibly live
any longer!” When the marriage was celebrated, the little
girl’s mother filled her lap with pulse and then handed her over
to the beggar-man to see what sort of fortune would be hers. But in a
few days the beggar-man died. His corpse was taken to the
burning-ground, and his little widow followed it. But when his
relatives wanted to burn the body, she forbade them and told them to go
away. For she said, “My fortune is still to come, whatever it may
be.” They all got round her and tried to persuade her that there
was no use in her staying by the corpse, but she would not mind what
they said. At last they were [71]quite tired out and went
home, leaving her in the burning-ground. When they had gone she took
her husband’s corpse on to her lap. Then she prayed to the god
Shiva and said:
“My parents disown me. O why was I born
Both as orphan and widow to live all
forlorn?”
As she prayed, she put the pulse which her mother had put into her
lap grain by grain in the dead man’s mouth. Then she sat there
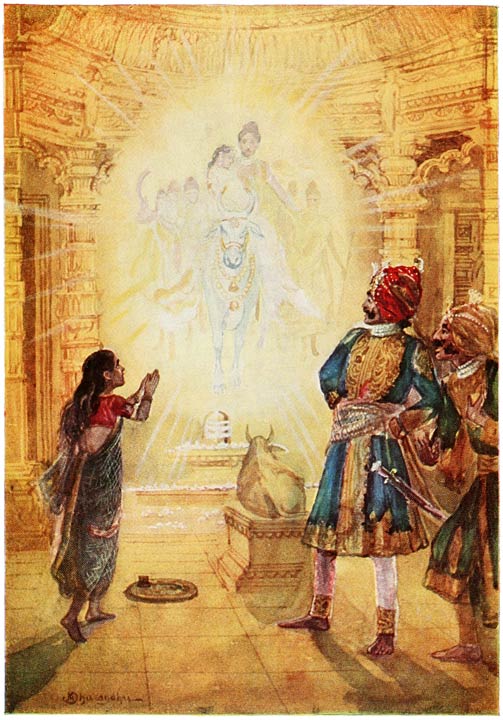
crying until midnight. Now it happened that on that very night Shiva
and Parwati were in their chariot driving through the air over that
very place. Parwati said suddenly to her husband, “I hear a woman
crying, let us go and see what it is.” The god Shiva drove his
chariot down to earth. He and Parwati got out and saw the
Brahman’s youngest daughter crying. They asked her what the
reason was, and she told them. Then Parwati pitied her and said,
“Your aunt has acquired great merit by her piety and devotions.
You go to her and get her to give you all her merit and so you will
bring your husband back to life.” The god Shiva and Parwati then
mounted on their [72]chariot and disappeared. Next
morning the little widow left her husband’s body, went to her
aunt’s house and begged her to give her all the merit which she
had acquired, and told her the cause of the request. The aunt was very
good and gave her all her own merit. The little widow then went back to
the burning-ground and with its aid brought her husband back to life.
But this time he was no longer a beggar-man black with leprosy and with
feet and hands that had rotted away. He was a beautiful young man with
well-shaped feet and a beautiful fair skin, and the little widow took
her husband back to her father’s house. “Papa, Papa,”
she said, “you turned me out, but the gods have brought me back,
and good fortune came to me without your bringing it.” The father
was too frightened of Parwati to say anything, so he held his peace.
And the little girl and her husband, the beggar-man, lived happily ever
afterwards. [73]
[Contents]
Parwati and the Brahman
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
poor Brahman. When the month of Bhadrapad came round, every household
bought little images of Parwati, and the women began to walk about the
streets and sound gongs. When the poor Brahman’s children saw
this they went home and said to their mother, “Mummy, Mummy,
please buy us little images of Parwati like the other little boys and
girls have.” But their mother said, “What is the use of my
buying images of Parwati? If I do we shall have to make offerings, and
there is absolutely nothing in the house. You run to papa and tell him
to go into the bazaar and buy grain. If he buys grain I’ll buy
you images of Parwati.” The children got up and ran to their
father and cried out, “Papa, Papa, [74]Mama says
that she will buy us images of Parwati if you will go into the bazaar
and get food to offer to them.” Their father at first searched
all over the house but could find no grain. And then he looked in his
purse but he could find no money with which to go to the bazaar and buy
grain. But although he tried to explain this to his children, they
would not listen to him. They screamed at him and shouted, “Papa,
Papa, Mummy says that she will buy us images of Parwati if you will get
food to offer to them.” “Papa, Papa, why should we not have
images of Parwati like the other little boys and girls.” At last
they bothered the poor Brahman so much that he felt worried to death.
“I love,” he said, “my children as if they were made
of gold, but they will not mind what I say. They will not understand
that it is nothing but poverty which prevents my buying food and
offering it to Parwati. I might go out and beg, but when I do, no one
ever gives me anything. Death is better than a life like this.”
With these words he got up and walked to the edge of the village pond
and determined to drown himself. It was dark when he started, and
half-way [75]he met an old woman. She heard him coming and
asked him who he was. He told her all his trouble, and said that he
meant to jump into the pond to escape from his children. The woman
comforted him and prevailed on him to turn home again. He took her
home. His wife came to the door with a lamp and asked who she was. The
husband did not like to say that he had only just met her on the road,
so he said to his wife, “She is my grandmother.” The wife
thereupon welcomed her and invited her to come in and stay to supper.
But her heart felt as heavy as lead, for she knew that there was
nothing to eat inside the house. When the old woman had seated herself
inside the house, the Brahman’s wife got up and, in despair, went
to look inside the grain-pots. She knew they were empty, but she
thought that she would first look into them once again. But, lo and
behold! when she looked this time she found the grain-pots brimming
over with grain. She called her husband, and they were both perfectly
delighted. And the wife prepared bowls full of rice-gruel, and every
one, children and all, ate the rice-gruel till the skins on their
[76]stomachs felt quite tight. And they went to
bed as happy as possible. Next morning the old woman called to the
Brahman, “My son, my son, get me water for my bath and cook me a
nice hot dinner, and please be quick about it, and do not start making
objections.” The Brahman got up and called his wife, and they got
water for the old woman’s bath, and then the Brahman went out to
beg. When he had gone out before, no one had ever given him anything.
But to-day every one ran out and gave him food and molasses and copper
coins. Then he went back home in splendid spirits. His wife prepared a
glorious dinner, and the children ate so much that the skin on their
stomachs felt as tight as a kettle-drum. After breakfast the old woman
said to the Brahman, “To-morrow I want a milk-pudding for
dinner.” “But, Grandmamma,” said the Brahman,
“where shall I get the milk from?” The old woman said,
“Don’t worry about that. Just get up and hammer down as
many pegs as you can in your courtyard. Then this evening, when the
cattle come home, call to the village cows and buffaloes by name, and
they will come to you, and if you milk them [77]you will get enough milk for my pudding
to-morrow.” The Brahman did as the old woman ordered him, and
that evening he called to the cows and buffaloes by name to come to his
courtyard. And from every direction the cows and buffaloes came running
up. And behind them galloped all the little calves with their heels in
the air and their tails stuck out straight behind them. At last the
Brahman’s courtyard was filled so full that no more cows or
buffaloes could enter. And he milked them all, and next day his wife
cooked a milk-pudding such as one would not see again if one lived a
thousand years. And the children ate until they were so tired of eating
that they just rolled over and went fast asleep. But that evening the
old woman said, “My son, my son, I want you to take me
home.” “But, Grandmamma, Grandmamma,” said the
Brahman, “how can I take you home, for I have had all this good
luck only because of you. Directly you go away my good luck will
vanish.” “Do not be afraid,” said the old woman,
“for I am Parwati. If I bless you your good luck will never
vanish. Therefore you must come with me and see me home.”
[78]But the Brahman said, “I do not want my
good luck only to continue. I want it to increase.” The old woman
said, “If you come with me I shall give you some sand. When you
go back home, scatter it all over the house and over your jars and your
pots, and put it inside your boxes and your cupboards, and scatter it
all over your courtyard too, and you will find that your good luck will
never be any less than it is now.” The Brahman was satisfied with
this. He worshipped the old woman and went with her towards the tank
until she suddenly disappeared. He returned home and scattered sand all
over his house and over his jars and his pots and inside his boxes and
his cupboards, and from that day on, his good luck never left him. And
his wealth increased, and his children increased. And they all lived
happily ever afterwards. [79]
[Contents]
Soma, the Washerwoman
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
poor Brahman who had seven sons and seven daughters-in-law. He had also
one daughter called Gunvanti and a wife called Dhanvanti. Whenever a
mendicant Brahman came to this house, it was the custom of all the
ladies to give him alms and then prostrate themselves in front of him.
One day a Brahman came, tall as a tree and shining like the sun. The
seven daughters-in-law ran out as usual and gave him alms and then
threw themselves at full length at his feet. The Brahman blessed them
and said, “Increase of children be yours; increase of wealth be
yours; may your husbands cherish you all your lives.” But the
Brahman’s daughter Gunvanti was a lazy little girl, and
[80]when the mendicant came she was still in bed.
Her mother, Dhanvanti, rushed into her room and cried, “Daughter,
daughter, get up and give the Brahman alms,” The little girl
jumped up in a fright and ran out and put alms before him and
prostrated herself at his feet. The mendicant blessed her and said,
“Observe the precepts of religion.”
The little girl ran back to her mother. “Mother,
Mother,” she cried, “Bhatji1 did not give me
the same blessing as he gave to my sisters-in-law,” Her mother
said, “Go back again and give him some more alms and see what he
does,” The little girl ran back, put some more alms before the
mendicant, and again prostrating herself asked for his blessing. Once
more he said, “Observe the precepts of religion,” Then
Dhanvanti asked him why he gave her daughter such a strange blessing.
The mendicant replied, “Because widowhood will come upon her
immediately after her marriage,” Dhanvanti threw herself before
the Brahman and grasped his feet and cried, weeping, “Tell me how
I may escape this evil; what shall I do to save my one little
[81]girl from becoming a widow?” The Brahman
pitied her and said, “Lady, lady, do not weep; I shall give you a
remedy by which to cure this evil. Across the seven seas there is an
island. In it there lives a washerwoman called Soma. If you can fetch
her to your daughter’s wedding, she will escape the evil that
threatens her. When the wedding is over, you must send Soma back with
all honour to her house.” With these words the mendicant took up
his wallet and went to collect alms elsewhere. When her husband
returned home Dhanvanti told him what had happened. “Some
one,” she added, “must go across the seven seas, to fetch
Soma, the washerwoman.” The father and mother called up their
sons and said, “Those of you who honour your parents will take
your sister and cross the seven seas to bring Soma here.” But all
the sons turned to their mother and said, “All you care about is
your daughter. You do not love us the least little bit. So we shall not
cross the seven seas and bring Soma here just on her account.”
The mother began to cry, and the father got very cross. He turned to
his wife and said, “From henceforth you [82]have no sons. To me our seven sons are as if
they had never been born. But do not get frightened about our little
girl I myself shall cross the seven seas and fetch Soma, the
washerwoman.” Then the youngest of the seven sons said to his
father, “Daddy, Daddy, you must not say that you have no sons
when here we are, all seven of us. I shall take my sister Gunvanti with
me, and we shall go and fetch Soma, the washerwoman.” A few days
later the two children prostrated themselves before their parents and
began their voyage.
In course of time they came to the seashore. But the wind was
blowing, the waves were rolling in, and the foam was splashing over the
rocks. The brother and sister could not imagine how they were to
continue their journey. There was no one near to give them food, there
was no one near to give them drink, and they could think of nothing
better than to lie down and die. But they first resolved to pray to the
god Shiva, “Please, please, God Shiva,” prayed the two
children, “get us out of this terrible trouble.” After
praying they went and sat under a banian tree, [83]and all day long they had nothing to eat or
drink. Now on the very top of the banian tree was an eagle’s
nest, and in it there were several little eagles. When evening came,
father eagle and mother eagle came home and began to feed their young.
But the little eagles would not eat anything at all. Mother eagle said,
“Children, children, what is the matter?” “O Mummy,
Mummy,” cried the little eagles, “two strangers have come
to our house, and they are sitting under our tree, and they have had
nothing to eat all day!” Father eagle and mother eagle flew to
the ground and began to ask the boy what his trouble was. “Do not
be frightened,” said father eagle; “whatever your business,
I’ll help you to get it done. Do not go to bed without supper.
I’ll bring you some fruit. Eat some of it yourself and give the
rest to your little sister.”
The boy told father eagle what had happened, and how it was that
they had to cross the seven seas. Father eagle said, “I shall
carry you both across directly you wake up to-morrow, and I shall put
you down at Soma the washerwoman’s door.” Then the two
children felt very happy and thanked the god [84]Shiva. And after eating father eagle’s
fruit, they lay down under the tree and fell fast asleep in no time.
Next morning father eagle and mother eagle came down the tree, and
father eagle took the boy on his back, and mother eagle took the girl
on her back, and off they flew across the seven seas. The wind blew,
and the waves rolled mountains high, and the foam splashed over the
rocks. But father eagle and mother eagle flew straight on until they
came to the door of Soma, the washerwoman. There they left the boy and
girl and went back to the tree where the little eagles were waiting for
them. The boy and girl were too frightened to walk into Soma’s
house, so they hid all that day, and next morning they got up at dawn
and they swept the courtyard and neaped the floor with cow-dung. And
then, before any one could see them, they ran away and hid. And this
they did every day for a whole year.
At last Soma one day called all her children and all her little
daughters-in-law and said, “Who among you gets up so early? Who
sweeps my courtyard? Who clears my floor?” All the children and
all the little [85]daughters-in-law said, “It is not
I,” “It is not I,” “It is not I.” Then
Soma became very curious to know who it was. So the following night she
did not go to bed. She sat up, but nothing happened until just after
dawn. Then she saw the little Brahman girl sweeping the courtyard and
her brother cleaning the floor. Soma got up and said, “Children,
who are you?” They replied, “We are Brahmans.”
“But I am only a washerwoman,” said Soma; “I am a
low-caste woman, why do you sweep my courtyard and neap my floor? It
will be reckoned unto me as a sin If I accept the service of
Brahmans.” The boy said, “This is my sister, and a Brahman
has told us that unless you come to her wedding she will be widowed
shortly after marriage. Our father and mother told us to go and bring
you back with us. So, in order to make you pleased with us, we have
been working as your servants.” “Do not work for me any
more,” said Soma, “I shall gladly go to your
wedding,” She then called to her daughters-in-law and said,
“I am going to this child’s wedding. But if any one of our
relations dies when I am away, do not burn his [86]body until I come back.” She went with
the two Brahman children to the seashore. The wind was blowing, and the
great waves were rolling in, and the foam was splashing over the rocks.
But Soma took the boy under one arm and the girl under the other. She
jumped far up into the sky and right over the seven seas, and when she
got to the opposite shore she put the children down again. They led her
to their father’s house. Their mother Dhanvanti welcomed the
washerwoman and fell at her feet to thank her for her coming. The
youngest brother then went to Ujjain, and after making inquiries
brought back a boy of suitable caste and age to be a husband for his
sister. On an auspicious day the wedding was celebrated. But as the
bridegroom and bride were throwing rice2 over each
other, the bridegroom fainted. He fell on the ground and lay there
motionless. The little bride did not know what to do, she was so
frightened. And all the grown-up people were almost as frightened as
she was. But Soma, the washerwoman, stepped forward and said, “It
is nothing, do not be afraid.” She took some [87]water in her hand and sprinkled it over
herself. Now the secret of Soma’s power was this:--
She had acquired great merit by observing every Monday the following
practices: She would get up early, bathe, dress in silence, make
various gifts to Brahmans, and then walk one hundred and eight times
round a peepul tree. But now by sprinkling water over herself she had
transferred the whole of her merit to Gunvanti. By this means the
little bride had been able to restore her husband to life, and the
wedding ceremony finished amidst the happiness of all. Soma then took
leave to go, and started on her homeward journey. When she reached the
seashore, the wind was blowing, and the great waves came rolling in,
and the spray was splashing over the rocks. But now that she had given
away all her merit to Gunvanti, she had none left by means of which she
could jump across the seven seas. She sat down forlorn by the bank of a
river. Then she got up, bathed in the water, and prayed to the god
Vishnu. Next she took one hundred and eight sand-grains in her hand,
and then walked one hundred and eight times [88]round a peepul tree by the river’s edge.
Instantly her powers returned to her, and going back to the shore, she
sprang into the heavens and over the seven seas and alighted close to
her own door. There all her little daughters-in-law ran out to meet her
and cried, “O Mother-in-law, Mother-in-law, we have been watching
for you. For while you were away your sons, your husband, and all your
sons-in-law died. But just as you told us to do, we did not burn their
corpses, but kept them in the house. And now they have all suddenly
come back to life.” Soma questioned the little daughters-in-law
and learnt that her sons and husband and sons-in-law had all died at
the very moment when she gave her merit to Gunvanti, and that they had
come back to life precisely when she finished her
one-hundred-and-eighth turn round the peepul tree. And they were all so
glad to have Soma back with them again, and for ever such a long time
afterwards she and her family lived happily together. And the Brahman
in his joy at his son-in-law’s recovery forgave his disobedient
sons, and they too all lived happily together ever afterwards.
[89]
[Contents]
Vasishta and the Four Queens
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there ruled a
king who had four wives. They were always quarrelling over the
housework; so, in order to get some peace at home, the king himself
divided the work between them. To the first queen he gave all the dairy
work, to the second queen he gave all the cooking, to the third he gave
the nursery, and he ordered the fourth to look after the royal
wardrobe. At first all went well. But in a little while the first queen
said to the third queen, “Why should you have charge of the
nursery? Why should you not work in the dairy?” The second queen
said to the fourth queen, “Why should I have to do all the
cooking?” The third queen asked, “Why should I have always
to look after the children?” [90]And the
fourth queen stamped her foot and said, “I won’t
look after the king’s clothes.” And all day long they
quarrelled and screamed at each other, and the poor king was more
uncomfortable than ever. His face grew sad and careworn, and, from the
time he got up to the time he went to bed, he could think of nothing
but the way that his four queens were squabbling with each other.
One day the rishi, or sage, Vasishta1 paid the king a
visit. The king prostrated himself before the great sage and gave him a
throne to sit upon. Vasishta looked at the king’s face and saw
how sad and careworn it was. He asked the cause, and the king told him.
Then the rishi rose, and the king went with him to the palace of the
four queens. When they reached it, they called to the queens to come
out. The rishi then asked them why they quarrelled. The first queen
cried out, “Why should I have to do the dairy work?” And
the second queen cried out, “Why should I be only a
cook-woman?” And the third cried [91]out,
“Why should I have all the children to look after?” And the
fourth cried out, “Why should I have all the bother of sorting
out all the king’s clothes?” The king said, “You must
do these things because I ordered you to.” But the queens did not
mind a word that he said, and they all screamed together so loud that
the king and the rishi had to put their fingers in their ears to save
themselves from being deafened. For a while the rishi became absorbed
in thought, and then he turned to the first queen and said, “You
have been placed in charge of the dairy, have you not?” The first
queen assented. “Then listen to me,” said Vasishta.
“In a former life you were a cow, and near the spot in the jungle
where you used to graze was an altar to Shiva. And every day at noon
you used to come and stand near it and let milk drop upon it. And,
because in this way you honoured the god Shiva, you have in this life
become one of the queens of the king of Atpat. But you did not in your
former life attain to full merit. So the god Shiva directed the king to
place you in charge of his dairy, and the king conveyed the god’s
directions to you. [92]You should therefore obey
them, and you should honour the king as if he were Shiva himself. In
this way you will attain to full merit and ascend to Shiva’s
heaven, Kailas.” Vasishta then blessed the first queen. She
prostrated herself before him, and, giving up all thought of
quarrelling, went away and busied herself with her dairy work.
Then Vasishta turned to the second queen and asked, “What are
you quarrelling about?” She replied, “Why should I be just
a cook-woman?” The rishi thought for a while and said,
“Lady, in a former life you were the wife of a poor Brahman, and
you used to beg your food from door to door. But every Monday you used
to fast, and whatever grain you begged that day you used to cook and
offer to the god Shiva. And he was pleased with your devotion.
Therefore in this life he made you one of the queens of Atpat. And
because you cooked for the god Shiva, he directed the king to put you
in charge of his kitchen. Therefore, obey the god’s directions
and give a great feast to all in Atpat. In this way you will gain the
favour of Shiva, and he will take you with him to Kailas.” Then
he blessed the second [93]queen, and she prostrated
herself and went off quite cheerfully to cook the king’s
dinner.
The sage next turned to the third queen and asked, “What are
you quarrelling about?” The queen answered, “Why should I
do nothing but fiddle about the nursery?” Vasishta thought for a
while and said, “In a former life, O Queen, you were a maid of a
jungle tribe. Every Monday you used to fast yourself and offer the
choicest fruits that you picked to the god Shiva. In return for them he
has made you a queen, and he has entrusted the king’s children to
you. Therefore look after them and be kind to them, and in the end he
will take you to live with him in Kailas.” The rishi then blessed
the third queen, and she prostrated herself before him. Then she ran
off, her face all smiles, to play with the king’s children.
Vasishta last of all turned to the fourth queen and said,
“What are you quarrelling about?” She answered, “Why
should I do nothing but look after the king’s clothes?” The
rishi said, “In a former life, O Queen, you were a kite that flew
high up in the heavens. Beneath where you used to fly was an altar to
[94]Shiva, and every day at noon you would spread
your wings over it and shade it from the sun’s heat. So the god
was pleased with you and in this life made you one of the queens of
Atpat. As you spread your wings over Shiva’s altar, so now a
canopy hangs over your bed. And just as you served Shiva, now do
service to the king, your husband. And you will thereby gain full merit
and in the end reach Kailas.” Then the rishi blessed her, and she
went off quite gaily to attend to the king’s clothes.
And the four queens never quarrelled any more, but lived happily
ever afterwards with the king. And all little girls who hear this story
should try to be as good as the queens were after Vasishta had cured
them of their squabbling. [95]
[Contents]
The Lamps and the King’s Daughter-in-Law
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
king who had one little daughter-in-law. Now she was a very greedy
little girl, and one day when some sweetmeats were got ready for all
the family she went quietly and ate them all up herself. Then she got
very frightened, for she knew that, if the king knew what she had done,
he would order her to be well slapped. So, when the family began asking
where the sweetmeats were she said that the mice had eaten them. And
then every one began abusing the mice, saying what horrid little
wretches they were, and what a good thing it would be if the cat caught
and ate them up. But, when the mice heard all this, they were very
angry with the little daughter-in-law for [96]bringing a
false charge against them, and they all met together and vowed that
they would be revenged on her. Some days later the king invited a guest
to his house, and the same night the mice went into the little
daughter-in-law’s room and dragged out one of her bodices and put
it across the guest’s bed. Next morning the bodice was discovered
in the stranger’s bed, and the little daughter-in-law was utterly
disgraced. Her father-in-law and all her brothers-in-law scolded her
dreadfully, and at last the king drove her out of the house. Now it so
happened that it had till then always been the work of the little
daughter-in-law to look after the lamps in the king’s palace.
Every morning she used to rub them well and trim the wicks. She used to
light them herself and neap the burners with sugar-candy, and on
Divali1 Day she used to worship them and make them suitable
offerings. But, directly the little daughter-in-law was driven away,
none of the lamps were any longer cared for. On the next Divali Day the
king was returning from a hunt, and he camped under a tree. Suddenly he
saw all the lamps [97]in his town of Atpat come and
settle on its branches. One lamp after another told what was happening
in its house--when there had been a dinner party, what there had been
to eat, who had been invited, how they themselves had been cared for,
and what honours they had received on Divali Day. After all the other
lamps had told their story, the big lamp from the king’s palace
began, “Brother lamps, I do not know how to tell you. For none
among you is so wretched as I am. In former years I was the most
fortunate of all the lamps in Atpat. No other lamp had such honours
paid it as I had, and this year I have to drag out my days In
unspeakable misery.” All the other lamps tried to comfort it, and
asked it how it was that ill-fortune had overtaken it. “O brother
lamps, how can I tell you?” repeated the big lamp. “I am
the chief among the lamps that shine In the palace of the King of
Atpat. One day the king’s little daughter-in-law ate some
sweetmeats and to save herself blamed the mice. To revenge themselves,
they in turn brought a false charge against her by putting her bodice
on the bed of one of the king’s guests. So she was disgraced and
[98]driven out of the house. And after she left
ill-fortune came upon me. For every year it was she who worshipped me
and paid me honour; and wherever she is I wish her well, and I give her
my blessing.” The king listened attentively to the talk between
the lamps, and thus he learnt that his daughter-in-law was innocent. He
went home and asked whether there was any other evidence against her
besides her bodice. And when he learnt that there was none, and that no
one had seen anything happen between her and the king’s guest, he
sent a messenger for her and had her brought home. And he begged her
pardon for the past, and gave her full authority over all his
household; and the king lived and ruled ever afterwards as wisely and
as well as King Ramchandra of Ayodhya. And if any one brings a false
charge against any of us, may the lamps save us as they did the
king’s little daughter-in-law. [99]
[Contents]
Parwati and the Priest
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there was a
temple to the god Shiva. One day when Shiva and his wife Parwati were
walking about they happened to come to this temple. They sat down there
and began to play saripat.1 After some time Parwati seeing a
priest close by asked him who had won, she or Shiva.
“Shiva,” the priest replied. Parwati became very angry and
cursed him, so that he became a leper, and the pains which overtook him
were absolutely unendurable. One day a band of Apsaras2
came down from heaven to the temple. They saw that the priest who lived
in it was a leper, and they asked him the reason. He told them
[100]how Parwati had cursed him. They replied,
“Do not be afraid; do as we tell you and you will get rid of your
leprosy. Fast all next Monday, bathe that evening, worship the god
Shiva, and then get half a pound of flour and mix it with treacle and
ghee and eat it for dinner. But whatever you do, eat no salt all day.
Do this for sixteen Mondays in succession, and on the seventeenth
Monday get five pounds of flour, mix with it ghee and treacle, and
offer it to Shiva inside this temple. Then divide it into three parts;
leave one for the god, distribute a second among the Brahmans or give
it to your cows, and take the third home to be eaten by you and your
family.” The Apsaras disappeared, and the priest followed their
instructions and became quite well. Some time afterwards Shiva and
Parwati came again to the temple. Parwati saw the priest cured of his
leprosy and asked him how he had got rid of it. He told her exactly
what he had done. She was very much surprised, and thought that if she
did the same she might win back her son Kartakswami,3 who had
quarrelled with her and had run off in a rage. [101]On the seventeenth Monday Kartakswami
suddenly appeared, and both of them were reconciled. Later on,
Kartakswami asked Parwati how she had brought him back, and Parwati
told him. Now Kartakswami had a Brahman friend who had gone into a
far-off country, and Kartakswami met him by accident shortly
afterwards. He told the Brahman how the priest had cured himself of
leprosy, and how he and Parwati had become reconciled. So the Brahman
also practised the same rites for seventeen Mondays. He then set out
for a distant country. As he travelled he came to a town. Now it
happened that in that town arrangements were being made for the
marriage of the king’s daughter. Several princes had come from
far-off countries to compete for her hand, and the king had erected a
splendid pavilion for the royal betrothal. But he would not himself
choose a prince to be his daughter’s husband. He ordered that a
garland should be placed on a she-elephant’s trunk, and that the
prince round whose neck the she-elephant threw the garland should be
chosen to marry the king’s daughter. But the she-elephant passed
by all the princes in turn, until she came [102]to where the Brahman stood. For he had come
with the crowds of people to see the royal betrothal. Then the
she-elephant stopped and put the garland round the Brahman’s
neck. The king ordered the Brahman to step forward, and he married him
to his daughter. Some years later when the princess grew up, and she
and the Brahman began to live together, she asked her husband by what
merit he had succeeded in winning her for his wife, and he told her.
And she in turn practised the same rites for seventeen Mondays. Nine
months later a beautiful baby boy was born to her; and when he in turn
grew up she told him the rites which she had practised to obtain him.
And he in turn began to perform them. On the sixteenth Monday he set
out for a journey. As he travelled in a distant country he came to a
town over which ruled a king who had no son and only one daughter. The
king had for a long time past been searching for a beautiful and
virtuous young man, resolved when he found him to hand over to him his
kingdom and marry him to his daughter. As the Brahman’s son
entered the town the king saw him and noticed on him [103]all the marks of royal origin. So he summoned
him to his house and married him to his daughter and seated him on his
own throne. Now the next Monday was the seventeenth Monday since the
Brahman’s son had begun the rites which the Apsaras had told to
the priest. That morning he got up and went to the temple and sent a
message home to his wife that she should send him five sers of flour
mixed with ghee and treacle. But the queen was too proud to do this.
For she feared that the people in the street would laugh at her if she
sent her husband five sers of flour mixed with ghee and treacle. So
instead she sent him five hundred rupees in a plate. But because the
flour and ghee and treacle were not sent, the king was unable to
complete his ceremonial, and it was all spoilt. And the god Shiva
instead of being pleased became very angry indeed. And he told the king
that, if he kept the queen as his wife, he would lose his kingdom and
die a beggar. Next day the king sent for his chief minister and told
him what had happened. At first the minister said, “The kingdom
belongs to the queen’s father. If you drive her out your
[104]subjects will hate you.” But the king
replied, “Yes, but not to obey the god’s command is a worse
thing still.” At last the minister agreed with the king, and the
order went forth that the queen should be driven out of the city. So
the queen was driven out and became quite poor and wandered along the
road. At last she came to a distant town and lodged there with an old
woman, who gave her food and drink. One day the old woman sent the
queen out to sell fruit puddings. As she went into the bazaar a great
wind came and carried off the fruit puddings. When she returned to the
old woman’s house, the queen told her what had happened, and the
old woman drove her out of the house. Then she went and lodged with an
oilman, who had great jars full of oil. But one day she went and looked
inside the jars, and all the oil disappeared. So the oilman drove her
off out of the house. The queen left the town and walked along until
she came to a river with abundant water in it. But directly her eyes
fell on the water, it all flowed away and left the water-bed quite dry.
She then journeyed on until she came to a beautiful lake, but when her
glance rested [105]on the lake, it became full of worms,
and the water began to stink. And, when the cowherds came as usual to
water their cattle, the cattle would not drink the stinking water, and
they had to go home thirsty. By chance a Gosavi, or holy man, came that
way and saw the queen, and she told him her story. The holy man took
her to his house and treated her as his own daughter, and she did her
best to serve him faithfully. But, at whatever thing she looked, it
would either disappear or become full of worms and maggots. At last the
holy man searched for the cause of this by means of his inner
knowledge. And thus he learnt that she had incurred the sin of spoiling
the worship of Shiva, which the Apsaras had first taught the priest.
Unless that sin were atoned for, her evil glance would never be
purified. So the holy man prayed to the god Shiva, and the god was
pleased with him; and when the holy man interceded with him on the
queen’s behalf, the god said that he would forgive her if she
began and completed properly the rites which she had spoiled when her
husband was performing them. The queen did so, and the god’s
anger vanished. Suddenly there rose in [106]the heart of
her husband, the king, a wish to see his queen, and he sent out
messengers on every side to look for her. At last one of the messengers
saw the queen in the holy man’s hermitage and went back and told
the king. The king was overjoyed, and, taking his chief minister with
him, he journeyed to the hermitage. He threw himself at the holy
man’s feet and then loaded him with presents. And the holy man
was pleased and said, “O King, I have treated your wife exactly
as if she had been my own daughter. She has lived here just as if she
had been in her father’s house. Now take her with you back again
and once more go through the marriage ceremony with her.” The
king consented, and both he and the queen prostrated themselves before
the holy man, and then they both returned to Atpat. And they celebrated
their home-coming with the greatest splendour. And the rest of the
king’s reign was as happy as possible. And we shall be just as
happy if we honour Shiva like the King of Atpat did.
[107]
[Contents]
The Rishi and the Brahman
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
Brahman. For many years he lived happily and cultivated his fields of
rice and grain. But one day his wife gave up the observances imposed on
her, and, as a result, the whole house was stained by her conduct, and
pollution hung like a black cloud over it. Her husband should have
driven her out, but he had not the heart to do so. So he, too, incurred
the blame of his wife’s sin. In course of time they died, and, as
a punishment for their wickedness, the husband became in his next life
a bullock, and the wife became a dog. But the gods so far relented as
to find them a home in the house of their only son.
Now the son was a very pious man, who never failed in his religious
rites. He worshipped [108]the gods, gave memorial
honours to his dead father, and welcomed to his house every Brahman who
passed by. One year, on the anniversary of his father’s death, he
told his wife to prepare a milk-pudding in honour of the dead, and
announced that he would invite Brahmans to partake of it. The wife was
as pious as her husband and never failed to obey his commands. So she
made a big milk-pudding, and she boiled vegetables and stewed fruits.
But just as she had finished and was about to invite her husband and
his Brahman guests to begin their feast, the dog saw that a snake had
entered the grain-jar, which had not been properly shut, and that it
had left its poisonous trail all over the grain from which the
milk-pudding had been prepared. The dog at once realised that, if the
Brahmans who had been invited to the memorial feast ate the poisoned
grain, they would die, and that the sin of Brahman murder would be
incurred by the host, her son. So she suddenly rushed up and put her
foot right into the middle of the milk-pudding. The son’s wife
was very angry. She threw a red-hot coal at the dog with such skill
that it dropped on to the [109]middle of her back and burnt
a big hole in it. Then the son’s wife cooked a fresh milk-pudding
and fed the Brahmans. But she was so cross with the dog that she would
not give her the smallest possible scrap. So the poor dog remained
hungry all day. When night fell she went to the bullock who had been
her husband and began to howl as loudly as she could. The bullock asked
her what the matter was. She told him how she had seen that a snake had
poisoned the grain, and how, to prevent the Brahmans dying and her son
incurring the sin of their death, she had put her paw into the middle
of the milk-pudding; how her daughter-in-law had been angry and had
burnt a hole in her back with a live coal, and how her back hurt so
that she did not know what to do. The bullock answered, “You are
suffering for the pollution with which you darkened our house in a
former life, and, because I let you remain in the house and touched
you, I too am suffering, and I have become a bullock. Only to-day my
son fastened me to his plough, tied up my mouth, and beat me, I too
have, like you, had nothing to eat all day. Thus all my son’s
memorial [110]services are useless.” Now the son
happened to be passing by the stable and heard this conversation. He at
once fetched the bullock some grass and the dog some food, and he
brought them both water to drink; and then he went to bed very sad at
heart. Next morning he got up early and went into a dark forest until
at last he came to the hermitage of a rishi. He prostrated himself
before the rishi, who asked him why he was so sad. The Brahman’s
son said, “I am sad because my father has been born again as a
bullock and my mother as a dog. Pray tell me how I can get their
release,” The rishi said, “There is only one way to help
them. You must worship the seven sages who have their home in the Great
Bear.”1 And he told the Brahman’s son the ceremonies
which he should observe, and how he should worship the seven sages
continually every month of Bhadrapad, or September, for seven years.
The Brahman’s son obeyed the rishi, and at the end of the seven
years a fiery [111]chariot came down from heaven. The
bullock suddenly became a handsome man, and the dog became a handsome
woman. They both seated themselves in the chariot and were carried off
to live with the sages who have their home for ever in the Great Bear.
[112]
[Contents]
The King and the Water-Goddesses
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. Over it there ruled
a king. One day he founded a new village, and close by he built a
village tank. But no matter how hard he tried he could not get it
filled with water. So he prayed to the water-goddesses to help him, and
the water-goddesses were pleased and said, “O King, O King,
sacrifice to us the eldest son of your daughter-in-law, and the tank
will fill with water.” The king heard it and went home very
troubled. He was ready to sacrifice his grandson; for though he loved
the boy, yet he knew that the life of one was less than the welfare of
many. But he knew that his daughter-in-law would never agree. At last
he thought of a trick. He went up to her and said,
“Daughter-in-law, it is a long time since you went to see your
parents. You had [113]better go and pay them a
visit and leave your eldest boy behind. I shall look after him
here.” The daughter-in-law consented and went to visit her
parents, leaving her son behind. The king waited for a favourable day
and then bathed and anointed his grandson. He gave a feast in his
honour and covered his body with costly jewelry. He then took him into
the middle of the pond and made him lie down on a bed and told him not
to stir. The water-goddesses were pleased, and a great mass of water
suddenly rushed into the tank, and it was filled right up to the brink.
After a time the daughter-in-law came back from her father’s
house and brought her brother with her. They asked where her son was,
but they could get no information. Whenever they asked the king, he did
nothing but say how the water had come into the tank, and what a
beautiful tank it was, and how happy it would make all the villagers.
At last the daughter-in-law guessed what had happened, and when the
seventh day of the bright half of the month of Shravan, or August, came
round, she and her brother went to the edge of the tank and began to
worship the water-goddesses. She took a [114]cucumber
leaf, and on it she placed some curds and rice. Next she mixed with
them some butter and a farthing’s worth of betel-nut. Then she
told her brother to pray, “O Goddess, Mother of All, if any one
of our family is drowned in the tank please give him back to us.”
He did so and then threw the offering into the lake. Then they both
turned to go home. But as she was turning homewards, she felt some one
pull her by the legs. She looked down and saw that it was her missing
son. When she saw him she dragged him with all her might to the bank,
and then she and her brother walked home with him. When the king heard
that she was coming, together with her missing son, he wondered
greatly, and going to her he fell at her feet and said, “O my
daughter, I offered your son to the water-goddesses; how has he come
back again?” She said, “I worshipped the water-goddesses
and made offerings to them. Then my son came out of the water, and I
lifted him up and drew him to the shore.” The king was overjoyed
and showed the greatest favour to his daughter-in-law. And she and her
little son lived happily ever afterwards. [115]
[Contents]
The Lid of the Sacred Casket
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
Brahman who had two twin sons. While they were still quite young, the
twins’ parents died, and their relatives stole from them all
their property and then turned them out of the house. The twins
wandered along until they came to a town. It was then noon, and the
boys were weary with walking and were tortured with hunger and thirst.
As they entered the town, a Brahman came out of his door to throw food
to the crows. He saw the two boys and called them in, fed them, and
then made them tell him their story. When he heard it he resolved to
provide for them, and he lodged them in his house and taught them to
recite [116]the Vedas. On Lalita Panchmi Day the Brahman
began to perform certain ceremonies. His pupils asked him why he did
so. The sage replied that by doing so one could attain to wealth,
knowledge, and to the wish of one’s heart. The boys begged him to
instruct them, and they quickly learnt how to worship the goddess
Parwati. Not long afterwards the Brahman provided them with wives, and
they returned to their own city, acquired wealth, and were very happy.
A year or two later the twins separated. But the elder was a wise boy
and never forgot to worship the goddess Parwati on Lalita Panchmi Day.
So he retained the riches which he had gained. But the younger was
foolish and forgot all about it, so the goddess began to dislike him,
and he lost all his money. And at last he became so poor that he and
his wife had to give up their house and go and live on the charity of
his elder brother. One day the elder brother’s wife spoke so
crossly and said such nasty things to the younger twin, that he felt
that he could not stay in the house any longer. And he remembered then
that of recent years he had entirely forgotten to [117]worship Parwati. He felt very penitent, and
he decided that somehow or other he would win back the goddess’s
favour. Taking his wife with him, he left his brother’s house and
journeyed to a distant country. At last he came near a town, and,
meeting a cowherd, the younger twin asked him what its name was. The
cowherd said, “The town is called Upang.” “Who is the
king?” asked the younger twin. The cowherd replied, “He
also is called Upang.” The wanderer then asked whether there was
any place where he and his wife could lodge. The cowherd told him that
in the town there was a temple of Parwati, and close to it was a
rest-house where the wanderer and his wife could lodge. The cowherd
directed them to the rest-house. And before lying down the younger twin
worshipped Parwati in the temple and begged her pardon for his previous
neglect. Parwati felt sorry for him, and that night she appeared to him
in a dream. She told him to go to King Upang’s palace and to beg
from him the lid of the sacred casket in which the accessories of
worship were kept. He should, thereafter, always pray to it, and in the
end he would come [118]by his heart’s desire.
The younger twin woke up, and the same morning he went to King
Upang’s palace and begged from him the lid of the sacred casket
in which were kept the accessories of worship. The king at first
refused, but when the younger twin told the king of his dream the king
consented. The Brahman took the lid home, worshipped it, and, just as
the goddess had foretold, he came by his heart’s desire. Property
and happiness returned, and a year later his wife bore him a daughter.
As the years passed the little girl grew up. One day she took the lid
of the sacred casket and went with some playmates to play and bathe by
the bank of a river. Suddenly the corpse of a Brahman came floating by.
Seeing it, the little girl took the lid of the casket and for fun began
to splash water on it. Such was the power of the sacred lid, that the
corpse instantly became alive again and became a Brahman, tall as a
tree and beautiful as the sun. The little girl fell in love with him on
the spot and told him that he must become her husband.
“But,” said the Brahman, “how shall I manage
it?” The little girl said, “Come home with me at
[119]dinner-time, take as usual water1 in
your hand, but do not sip it. Then my daddy will ask you,
‘Bhatji, Bhatji, why do you not sip the water in your
hand?’ You must reply, ‘I am ready to dine if you marry me
to your daughter. If you will not, I shall get up and go away.’
Then he will consent to our marriage.” The Brahman agreed, and he
went home with the little girl, and everything happened as she had
planned. To prevent the Brahman from getting up without any food, the
little girl’s father agreed to their marriage. When a favourable
day came they were married, and when she was old enough the little girl
went to her husband’s house. As she went she carried off the lid
of the sacred casket of King Upang. But, because it had gone, her
father lost all his wealth and fell once more into the greatest
poverty. His wife went to her daughter’s house and asked for it
back, but she refused to give it up. The wife was very angry and every
day began to hate her son-in-law more and more. But for him, as she
thought, the little girl would [120]never have married and
would not have stolen the lid of the sacred casket. One day the wife
met her son-in-law on the road, and she gave him such a fearful slap in
the face that he instantly fell on the ground and became a corpse
again. His mother-in-law then-snatched from him the lid of the casket,
which he happened to have in his hand, and ran away home. There he lay
until the little girl, his wife, began to search for him. When she
found him she prayed to the goddess, and by her aid and by means of the
merit which she had acquired by worshipping the lid of the casket while
she had it, she restored her husband to life. But the twin and his wife
went on becoming poorer and poorer. And at last they went back to his
brother’s house and asked him why it was that the younger twin
was always losing his wealth as fast as he gained it. The elder brother
listened to the whole story and then he said, “I do not wonder at
it. First you lost the lid of the casket, then, in order to get it
back, your wife killed a Brahman. Your only chance now is to worship
Parwati harder than ever, and perhaps in the end you may recover your
good estate.” So [121]the younger brother went
home and worshipped Parwati with greater vigour than ever. And at last
she relented and gave him her blessing. He recovered his wealth and
came by all that his heart desired. And he and his wife lived happily
ever afterwards. [122]
[Contents]
The Brahman Wife and Her Seven Sons
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there lived a
poor Brahman who used always to perform Shradh or memorial ceremonies
to his father on the last day of the month of Shravan. When performing
these ceremonies he always invited other Brahmans to dine. But it so
happened that on every last day of the month of Shravan,1
from the day of his father’s death onwards, his daughter-in-law
gave birth to a little boy. And just as the Brahmans had begun to enjoy
their dinner, the child would die. So all the Shradh ceremonies had to
cease, and the poor Brahmans [123]had to be sent away
feeling most dreadfully hungry. This happened regularly for six years.
But, when the seventh little boy was born only to die just as his
guests were beginning to enjoy their dinner, the poor Brahman lost all
patience. He took the newly-born child and placed it in his
daughter-in-law’s lap and then drove her out of the house and
into the jungle. The poor woman walked along until she came to a great,
dark forest. In it she met the wife of a hobgoblin,2 who asked,
“Lady, Lady, whose wife are you, and why do you come here? Run
away as quickly as you can. For, if my husband the hobgoblin sees you,
he will tear you to pieces and gobble you up.” The poor woman
said she was the daughter-in-law of a Brahman, and explained how every
year she had given birth to a son on the last day of Shravan, how it
had died in the middle of the Shradh feast, and how at last her
father-in-law had put the child in her lap and had driven her from home
and into the forest. The hobgoblin’s wife repeated, “If you
value your life at all, go away.” The [124]Brahman woman began to cry, until at last the
hobgoblin’s wife had pity on her and said, “Do not be
afraid; walk a little way until you come to an altar to the god Shiva,
Close by is a bel3 tree; climb into it and hide among the
branches. To-night the serpent-maidens from Patâla and the
wood-nymphs, together with a train of seven demon Asuras,4
will come and worship at the altar. After making their offerings to the
god, they will call out, ‘Is there any uninvited guest present to
whom we can make a gift?’ You must then call out in reply,
‘Yes, I am here.’ They will see you and question you, and
you must tell them all your story.” The poor Brahman woman
agreed. She walked on until she came to the god Shiva’s altar.
She climbed into the branches of the bel tree. She remained there until
midnight came. Suddenly the serpent-maidens from Patâla and the
wood-nymphs, accompanied by a [125]train of seven demon
Asuras, came and worshipped at the altar. After making offerings to the
god they called out, “Is there any uninvited guest present to
whom we can make a gift?” The Brahman woman at once climbed down
the bel tree and called out in answer, “Yes, I am here,”
The serpent-maidens from Pâtala and the wood-nymphs, greatly
surprised, asked her who she was, and she told them all her story. Then
the serpent-maidens of Pâtala and the wood-nymphs ordered their
train of demon Asuras to go and search for the seven sons of the
Brahman woman. The seven demon Asuras spurred their horses and rode off
in all directions. In a little time the giant captain of the demon
guards rode up carrying in his arms the body of a little boy of six.
Then another rode up carrying the body of a little boy of five. And
four others rode up carrying a little boy of four, a little boy of
three, a little boy of two, and a little boy only one year old. Last of
all the seventh demon Asura rode up with a newly-born baby boy. The
demons placed the bodies in front of the serpent-maidens from
Patâla and of the wood-nymphs. And first of [126]all the little boy of six came to life and
got up and ran to his mother. Next the little boy of five, and then the
little boy of four, and then the little boy of three came to life and
ran to their mother. Then the little boy of two came to life and got
up, but he could only walk to his mother. Next the little one-year-old
boy came to life, but he could not get up, so he lay on his back and
kicked up his legs. And last of all the newly-born baby came to life,
but he could not even kick up his legs. And they were all delighted to
see their mother, and she was overjoyed to have all her sons again. But
the serpent-maidens from Patâla and the wood-nymphs warned her
that she must pray to the sixty-four Yoginis, the attendants who wait
on Durga, the Goddess of Death, or else her children would be snatched
from her again. And they told her to pray her hardest, for her prayer
had to travel down to the depths of Hell. So the Brahman woman prayed
her hardest to the sixty-four Yoginis, and then she prostrated herself
before the serpent-maidens from Patâla, and the wood-nymphs, and
their train of demon Asuras. And then she took the little one-year-old
boy [127]on her hip, and the newly-born baby boy in
her arms, and she walked with her other five sons to the village. When
the villagers saw her coming they ran and said to the Brahman,
“Bhatji, Bhatji, your daughter-in-law is coming back home.”
And the Brahman became very angry and vowed that he would drive her
away again. So he watched for her coming. But first of all he saw
walking towards his house a little boy of six, and then a little boy of
five, and then a little boy of four, and then two other little boys of
three and two. Last of all he saw his daughter-in-law with a
one-year-old boy on her hip and a newly-born baby in her arms. He rose
and fetched a cauldron of water and two handfuls of rice from his
house. And he waved his hands filled with rice round the heads of his
daughter-in-law and of all her children, and last of all he washed
their feet. In this way he welcomed back to his house his grandchildren
and their mother. And he made her tell him all her story; and she, and
her children, and the Brahman spent the rest of their lives in great
peace and perfect happiness. [128]
[Contents]
The Golden Temple
Once upon a time there was a town called Atpat. In it there reigned
a king who had four daughters-in-law. He loved three of them very
dearly, but the fourth, who was an ugly little girl, he did not like at
all. To the three daughters-in-law he gave nice food and fine clothes.
But to the ugly little daughter-in-law he gave nothing but scraps from
his table and thick, coarse clothes to wear. He would not even let her
sleep inside the house, but made her sleep in the stable and look after
the cows. The poor ugly daughter-in-law grew so unhappy that, when the
first Monday in Shravan1 came, she ran out of the palace,
and out of the town, and then away as fast as her fat little legs would
carry her. At last she [129]went and hid herself in the
woods. Now it so happened that that very day a band of
serpent-maidens2 had come up from Patala. After wandering through the
forest and bathing in the running streams, they had joined a bevy of
wood-nymphs and were coming in her direction. At first she was too
terrified to say a single word. But at last she asked, “Ladies,
ladies, where are you going?” “To the temple of
Shiva,” they replied, “to worship the god. For by doing
that, one wins the love of one’s husband, one obtains children,
and one comes by the wish of one’s heart.” When the ugly
daughter-in-law heard that by doing what the serpent-maidens and the
wood-nymphs were about to do she could win love for herself, she at
once thought that in this way she, too, might win the love of her
father-in-law. So she told the serpent-maidens of Patala and the
wood-nymphs that she would go with them. They went deeper and deeper
into the forest until at last they came to a temple of the god Shiva.
There the serpent-maidens [130]and the wood-nymphs
offered to the god rice, betel-nut, incense, flowers, and the leaves of
the bel tree. The ugly little daughter-in-law did just as they did. And
when she had finished she cried out, “O God Shiva, please, please
vouchsafe my prayer also, and make my father-in-law and my
mother-in-law, my brothers-in-law and my sisters-in-law like me as much
as they now dislike me.” That evening she went home and fasted,
and all the scraps which they threw to her from the king’s table
she gave to her favourite cow. And then she sat by herself and prayed
to the god Shiva. The following Monday she once more ran out of the
palace and out of the town and into the woods as fast as her fat little
legs would carry her. There she met again the serpent-maidens of
Patâla and the bevy of wood-nymphs and went with them to the
temple of Shiva in the distant heart of the forest. The first time the
serpent-maidens and the wood-nymphs had given her the incense and the
flowers, the rice and the betel-nut, and the leaves of the bel tree,
with which to perform her worship. But they had told her that the next
time she must bring [131]them herself. So when she
ran away on the second Monday in Shravan she brought with her incense
and flowers, rice and betel-nut and bel-tree leaves, and after offering
them and some sesamums to the god she once more prayed, “O God
Shiva, please, please grant my prayer and make my father-in-law and my
mother-in-law, my brothers-in-law and my sisters-in-law like me as much
as they now dislike me.” Then she went home and fasted, and
giving all her dinner to her favourite cow she sat by herself and
prayed to Shiva. That evening the king asked her who the god was whom
she was honouring, and where he lived. The ugly little daughter-in-law
replied, “Afar off my god lives, and the roads to him are hard,
and the paths to him are full of thorns. Where snakes abound and where
tigers lie in wait, there is his temple.” The third Monday in
Shravan, the ugly little daughter-in-law again started from the palace
with her flowers and incense, her betel-nut and bel leaves, her rice
and sesamum, in order to meet the serpent-maidens of Patâla and
the bevy of wood-nymphs, and with them to worship the god in the hidden
depths of the forest. This time the king and [132]her other male relatives followed her and
said to her, “Ugly little daughter-in-law, take us with you and
show us your god.” But the temple of Shiva was ever so far from
the king’s palace. The ugly daughter-in-law did not mind, for she
was used to cruel treatment. She had also walked to the temple twice
before, and her feet had got as hard as two little stones. But the king
and his relatives were tired to death; and their feet swelled up to the
size of an elephant’s, and they became as full of thorns as the
back of a porcupine. And they muttered to each other, “How on
earth does that ugly little daughter-in-law manage to walk as she does
through the heart of the forest?” The ugly daughter-in-law at
last felt sorry for them. She prayed to the god Shiva to build a temple
near at hand. The god consented, and, with the help of the
serpent-maidens of Patâla and of the wood-nymphs, he created
suddenly a beautiful temple all of pure, yellow gold. Its pillars were
studded with jewels, and the jars in it were all of crystal. In the
middle there rose from the ground an altar to the god Shiva. And last
of all the god revealed himself to the [133]king and
his companions in all his glory and splendour. For a moment only they
saw him; and then he vanished. The king and his companions stared, too
astonished to move or speak. But the ugly little daughter-in-law
prostrated herself and offered to the god flowers and incense. Then she
cried out, “O God Shiva, please, please vouchsafe my prayer and
make my father-in-law and my mother-in-law, my brothers-in-law and my
sisters-in-law like me as much as they now dislike me.” When the
king heard her prayer his heart softened to her, and he spoke kindly to
her and gave her jewelry and trinkets. In a little while he took off
his turban and, placing it on a peg, walked out to look at a lovely
lake which, unnoticed by any one before, now stretched out close by the
temple. And behind him strolled out his companions. But when they had
gone out of sight, the beautiful golden temple by the lake vanished for
ever. After looking at the lake the king came back to fetch his turban
which he had left in the temple. But he could not find the beautiful
temple all of pure, yellow gold, with its jewel-studded pillars and its
crystal jars. [134]The king asked the little
daughter-in-law the cause. She said nothing, but straightway walked
deeper into the forest. And the king and his companions, although weary
to death, followed her. At last they came to the temple where she had
worshipped, together with the serpent-maidens from Patâla and the
bevy of wood-nymphs. It was a tiny temple, and inside it there was a
rough altar. At the foot of the altar lay the flowers which the ugly
daughter-in-law had offered to the god, and close by on a peg hung the
turban left by the king. Again the king asked his daughter-in-law the
meaning of what had happened. She replied, “This temple that you
see is my own poor little temple. But, because of my prayers, the god
Shiva showed himself to you in the beautiful temple, all of pure,
yellow gold, with its jewel-studded pillars and its crystal
jars.” When the king heard her reply, he grew more pleased than
ever with the daughter-in-law whom formerly he had so disliked. And
because the god had revealed himself at her prayer, the king, to do her
honour, sent for his royal palanquin and had her carried home in state.
And the ugly little daughter-in-law [135]became
out of the four the king’s favourite. And he was so much nicer to
her than he was to his other three daughters-in-law that they became as
jealous as cats. But the king and the ugly little daughter-in-law did
not mind them the least little bit. And they both lived happily ever
afterwards.
The End