|
PAPERS AND WRITINGS, VOLS I. TO VII. ## VOLUME ONE ## VOLUME TWO ## VOLUME THREE ## VOLUME FOUR ## VOLUME FIVE ## VOLUME SIX ## VOLUME SEVEN OTHER PG EBOOKS ## Lincoln's Yarns and Stories ## Lincoln Letters (with facsimiles) ## Abraham Lincoln, Vol. 1, By Herndon ## Abraham Lincoln, Vol. 2, By Herndon ## The Life Of Abraham Lincoln, By Lamon Anecdotes and Stories |
CONTENTS
ABRAHAM LINCOLN: AN ESSAY BY CARL SHURZ
ABRAHAM LINCOLN, BY JOSEPH H. CHOATE
THE WRITINGS OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN, 1832-1843
ADDRESS TO THE PEOPLE OF SANGAMON COUNTY.
RESPONSE TO REQUEST FOR POSTAGE RECEIPT
ANNOUNCEMENT OF POLITICAL VIEWS.
SPEECH IN ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
PROTEST IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE ON THE SUBJECT OF SLAVERY.
LEGAL SUIT OF WIDOW v.s. Gen. ADAMS
LINCOLN AND TALBOTT IN REPLY TO GEN. ADAMS.
Gen. ADAMS CONTROVERSY—CONTINUED
TO Mrs. O. H. BROWNING—A FARCE
REMARKS ON SALE OF PUBLIC LANDS
RESOLUTION IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
RESOLUTION IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
REMARKS IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
REMARKS IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
TO JOHN T. STUART—ON DEPRESSION
REMARKS IN THE ILLINOIS LEGISLATURE.
AGAINST THE REORGANIZATION OF THE JUDICIARY.
TO JOSHUA F. SPEED—MURDER CASE
TO MISS MARY SPEED—PRACTICAL SLAVERY
TO JOSHUA F. SPEED—ON MARRIAGE
TO JOSHUA F. SPEED—ON DEPRESSION
TO GEORGE E. PICKETT—ADVICE TO YOUTH
ADDRESS BEFORE THE SPRINGFIELD WASHINGTONIAN TEMPERANCE SOCIETY,
TO JOSHUA F. SPEED—ON MARRIAGE CONCERNS
A LETTER FROM THE LOST TOWNSHIPS
CORRESPONDENCE ABOUT THE LINCOLN-SHIELDS DUEL.
TO A. LINCOLN FROM JAS. SHIELDS
MEMORANDUM OF INSTRUCTIONS TO E. H. MERRYMAN,
RESOLUTIONS AT A WHIG MEETING AT SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, MARCH 1, 1843.
CONTENTS
SELECTION OF CONGRESSIONAL CANDIDATES
VERSES WRITTEN BY LINCOLN AFTER A VISIT TO HIS OLD HOME IN INDIANA
RESOLUTIONS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REMARKS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
DESIRE FOR SECOND TERM IN CONGRESS
SPEECH ON DECLARATION OF WAR ON MEXICO
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, JANUARY 19, 1848.
TO WILLIAM H. HERNDON—LEGAL WORK
REGARDING SPEECH ON MEXICAN WAR
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REMARKS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, MARCH 29, 1848.
REMARKS IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
DEFENSE OF MEXICAN WAR POSITION
SPEECH IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
OPPORTUNITIES FOR YOUNG POLITICIANS
SALARY OF JUDGE IN WESTERN VIRGINIA
YOUNG v.s. OLD—POLITICAL JEALOUSY
SPEECH DELIVERED AT WORCESTER, MASS., ON SEPT. 12, 1848.
HIS FATHER'S REQUEST FOR MONEY
BILL GRANTING LANDS TO THE STATES TO MAKE RAILWAYS AND CANALS
ON FEDERAL POLITICAL APPOINTMENTS
MORE POLITICAL PATRONAGE REQUESTS
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
REQUEST FOR GENERAL LAND-OFFICE APPPOINTMENT
RESOLUTIONS OF SYMPATHY WITH THE CAUSE OF HUNGARIAN FREEDOM,
RESOLUTIONS ON THE DEATH OF JUDGE NATHANIEL POPE.
PETITION ON BEHALF OF ONE JOSHUA GIPSON
REPLY TO SENATOR DOUGLAS—PEORIA SPEECH
RESPONSE TO A PRO-SLAVERY FRIEND
SPEECH DELIVERED BEFORE THE FIRST REPUBLICAN STATE CONVENTION
ON THE DANGER OF THIRD-PARTIES
TO HENRY O'CONNER, MUSCATINE, IOWA.
AFTER THE DEMOCRATIC VICTORY OF BUCHANAN
ARGUMENT IN THE ROCK ISLAND BRIDGE CASE.
ANOTHER POLITICAL PATRONAGE REFERENCE
SPEECH AT CHICAGO, JULY 10, 1858.
SPEECH AT SPRINGFIELD, JULY 17, 1858.
CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN LINCOLN AND DOUGLAS
FIRST JOINT DEBATE, AT OTTAWA,
SECOND JOINT DEBATE, AT FREEPORT,
THIRD JOINT DEBATE, AT JONESBORO,
THE LINCOLN-DOUGLAS DEBATES II
LINCOLN AND DOUGLAS FOURTH DEBATE, AT CHARLESTON, SEPTEMBER 18, 1858.
FIFTH JOINT DEBATE, AT GALESBURGH, OCTOBER 7, 1858
SIXTH JOINT DEBATE, AT QUINCY, OCTOBER 13, 1858.
LAST DEBATE, AT ALTON, OCTOBER 15, 1858
THE WRITINGS OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN, Volume Five, 1858-1862
TO SYDNEY SPRING, GRAYVILLE, ILL.
TO JOHN MATHERS, JACKSONVILLE, ILL.
TO DR. WILLIAM FITHIAN, DANVILLE, ILL.
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT PARIS, ILL.,
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT EDWARDSVILLE, ILL.,
SENATORIAL ELECTION LOST AND OUT OF MONEY
REALIZATION THAT DEBATES MUST BE SAVED
A LEGAL OPINION BY ABRAHAM LINCOLN.
TO THE GOVERNOR, AUDITOR, AND TREASURER OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS.
FIRST SUGGESTION OF A PRESIDENTIAL OFFER.
SPEECH AT CINCINNATI OHIO, SEPTEMBER 17, 1859
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT LEAVENWORTH, KANSAS,
TO G. W. DOLE, G. S. HUBBARD, AND W. H. BROWN.
ON NOMINATION TO THE NATIONAL TICKET
SPEECH AT NEW HAVEN, CONNECTICUT, MARCH 6, 1860
RESPONSE TO AN ELECTOR'S REQUEST FOR MONEY
ACCUSATION OF HAVING BEEN PAID FOR A POLITICAL SPEECH
TELEGRAM TO A MEMBER OF THE ILLINOIS DELEGATION
REPLY TO THE COMMITTEE SENT BY THE CHICAGO CONVENTION TO INFORM
ACCEPTANCE OF NOMINATION AS REPUBLICAN CANDIDATE FOR PRESIDENT
FORM OF REPLY PREPARED BY MR. LINCOLN,
SLOW TO LISTEN TO CRIMINATIONS
EARLY INFORMATION ON ARMY DEFECTION IN SOUTH
BLOCKING "COMPROMISE" ON SLAVERY ISSUE
SOME FORTS SURRENDERED TO THE SOUTH
SUPPORT OF THE FUGITIVE SLAVE CLAUSE
ATTEMPT TO FORM A COALITION CABINET
FAREWELL ADDRESS AT SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS,
REMARKS AT TOLONO, ILLINOIS, FEBRUARY 11, 1861
REPLY TO ADDRESS OF WELCOME, INDIANAPOLIS,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF INDIANA, AT INDIANAPOLIS,
ADDRESS TO THE GERMAN CLUB OF CINCINNATI, OHIO,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF OHIO AT COLUMBUS
ADDRESS AT STEUBENVILLE, OHIO,
ADDRESS AT PITTSBURGH, PENNSYLVANIA
ADDRESS AT ROCHESTER, NEW YORK,
ADDRESS AT SYRACUSE, NEW YORK,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF ALBANY, NEW YORK
REPLY TO GOVERNOR MORGAN OF NEW YORK, AT ALBANY,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF NEW YORK, AT ALBANY,
ADDRESS AT POUGHKEEPSIE, NEW YORK,
ADDRESS AT PEEKSKILL, NEW YORK,
REMARKS AT THE ASTOR HOUSE, NEW YORK CITY, FEBRUARY 19, 1861
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF NEW YORK CITY,
ADDRESS AT JERSEY CITY, NEW JERSEY
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF NEWARK, NEW JERSEY,
ADDRESS IN TRENTON AT THE TRENTON HOUSE,
ADDRESS TO THE SENATE OF NEW JERSEY
ADDRESS TO THE ASSEMBLY OF NEW JERSEY,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA,
ADDRESS IN THE HALL OF INDEPENDENCE, PHILADELPHIA,
REPLY TO THE WILMINGTON DELEGATION,
ADDRESS AT LANCASTER, PENNSYLVANIA,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF PENNSYLVANIA, AT HARRISBURG,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF WASHINGTON, D.C.,
REPLY TO A SERENADE AT WASHINGTON, D.C.,
WASHINGTON, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 1861
FIRST INAUGURAL ADDRESS, MARCH 4, 1861
REPLY TO THE PENNSYLVANIA DELEGATION,
REPLY TO THE MASSACHUSETTS DELEGATION,
NOTE ASKING CABINET OPINIONS ON FORT SUMTER.
ON ROYAL ARBITRATION OF AMERICAN BOUNDARY LINE
RESPONSE TO SENATE INQUIRY RE. FORT SUMTER
PREPARATION OF FIRST NAVAL ACTION
TO THE COMMANDANT OF THE NEW YORK NAVY-YARD.
RELIEF EXPEDITION FOR FORT SUMTER
ORDER TO CAPTAIN SAMUEL MERCER.
SECRETARY SEWARD'S BID FOR POWER
REPLY TO SECRETARY SEWARD'S MEMORANDUM
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE FROM THE VIRGINIA CONVENTION, APRIL 13, 1861
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR 75,000 MILITIA,
PROCLAMATION OF BLOCKADE, APRIL 19, 1861
TO GOVERNOR HICKS AND MAYOR BROWN.
ORDER TO DEFEND FROM A MARYLAND INSURRECTION
PROCLAMATION OF BLOCKADE, APRIL 27, 1861
REMARKS TO A MILITARY COMPANY, WASHINGTON, APRIL 27, 1861
LOCALIZED REPEAL OF WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS
MILITARY ENROLLMENT OF ST. LOUIS CITIZENS
CONDOLENCE OVER FAILURE OF FT. SUMTER RELIEF
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR 42,034 VOLUNTEERS,
COMMUNICATION WITH VICE-PRESIDENT
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS IN FLORIDA,
PRESIDENT LINCOLN'S CORRECTIONS OF A DIPLOMATIC DESPATCH
LETTER OF CONDOLENCE TO ONE OF FIRST CASUALTIES
MEMORANDUM ABOUT INDIANA REGIMENTS.
ORDER AUTHORIZING GENERAL SCOTT TO SUSPEND THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS, JULY
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS IN SPECIAL SESSION,
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MEMORANDA OF MILITARY POLICY SUGGESTED BY THE BULL RUN DEFEAT. JULY 23,
TO THE GOVERNOR OF NEW JERSEY.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
ORDER TO UNITED STATES MARSHALS.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
PROCLAMATION OF A NATIONAL FAST-DAY, AUGUST 12, 1861.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR O. P. MORTON.
PROCLAMATION FORBIDDING INTERCOURSE WITH REBEL STATES, AUGUST 16, 1861.
MEMORANDUM FOR A PLAN OF CAMPAIGN
ORDER AUTHORIZING SUSPENSION OF THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS.
TO GENERAL CURTIS, WITH INCLOSURES.
ORDER RETIRING GENERAL SCOTT AND APPOINTING
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON.
ORDER APPROVING THE PLAN OF GOVERNOR GAMBLE OF MISSOURI.
REPLY TO THE MINISTER FROM SWEDEN.
INDORSEMENT AUTHORIZING MARTIAL LAW IN SAINT LOUIS.
OFFER TO COOPERATE AND GIVE SPECIAL LINE OF INFORMATION TO HORACE GREELEY
ORDER AUTHORIZING GENERAL HALLECK TO SUSPEND THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
LETTER OF REPRIMAND TO GENERAL HUNTER
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. C. BUELL.
MESSAGES OF DISAPPOINTMENT WITH HIS GENERALS
INDORSEMENT ON LETTER FROM GENERAL HALLECK,
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO. 1
PRESIDENT'S SPECIAL WAR ORDER NO. 1.
OPPOSITION TO McCLELLAN'S PLANS
TO GENERALS D. HUNTER AND J. H. LANE.
EXECUTIVE ORDER NO. 1, RELATING TO POLITICAL PRISONERS.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. WASHINGTON CITY, February 15, 1862
EXECUTIVE ORDER NO. 2.—IN RELATION TO STATE PRISONERS.
ORDER RELATING TO COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE.
SPEECH TO THE PERUVIAN MINISTER,
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS RECOMMENDING COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION.
INDORSEMENT ON LETTER FROM GOVERNOR YATES.
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO.2.
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO.3.
INTERVIEW BETWEEN THE PRESIDENT AND SOME BORDER SLAVE STATE
PRESIDENT'S SPECIAL WAR ORDER NO.3.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL MCCLELLAN.
SPEECH TO A PARTY OF MASSACHUSETTS GENTLEMAN
INSTRUCTION TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
PROCLAMATION RECOMMENDING THANKSGIVING FOR VICTORIES,
ABOLISHING SLAVERY IN WASHINGTON, D.C.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE, MAY 1, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
RESPONSE TO EVANGELICAL LUTHERANS, MAY 6, 1862
TELEGRAM TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH.
FURTHER REPRIMAND OF McCLELLAN
TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH,
PROCLAMATION RAISING THE BLOCKADE OF CERTAIN PORTS.
THE WRITINGS OF A. LINCOLN, Volume Six, 1862-1863
RECOMMENDATION OF NAVAL OFFICERS
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
SPEECH TO THE 12TH INDIANA REGIMENT, MAY [15?] 1862
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
MEMORANDUM OF PROPOSED ADDITIONS TO INSTRUCTIONS OF ABOVE DATE
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
PROCLAMATION REVOKING GENERAL HUNTER'S ORDER OF MILITARY EMANCIPATION,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. E. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL RUFUS SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL D. S. MILES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. W. GEARY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER TAKING MILITARY POSSESSION OF RAILROADS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
HISTORY OF CONSPIRACY OF REBELLION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GOVERNOR ANDREW.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT. WASHINGTON, June 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
SPEECH AT JERSEY CITY, JUNE 24, 1862.
ORDER CONSTITUTING THE ARMY OF VIRGINIA.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAMS TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
WAR DEPARTMENT, June, 28, 1862
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD. WAR DEPARTMENT, June 30, 1862.
CALL FOR TROOPS. NEW YORK, June 30, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAMS TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
WASHINGTON, D.C., June 30, 1862.
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, JULY 1, 1862.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July 1, 1862
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING TAXES IN REBELLIOUS STATES, JULY 1, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, JULY 1, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
CIRCULAR LETTER TO THE GOVERNORS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MEMORANDUM OF AN INTERVIEW BETWEEN THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL McCLELLAN
ORDER MAKING HALLECK GENERAL-IN-CHIEF.
ORDER CONCERNING THE SOUTHWEST BRANCH OF THE PACIFIC RAILROAD.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. WAR DEPARTMENT, July 11, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK. WAR DEPARTMENT, July 11, 1862.
APPEAL TO BORDER-STATES IN FAVOR OF COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
ACT OF COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. July 17, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. July 17, 1862.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER IN REGARD TO BEHAVIOR OF ALIENS
ORDER AUTHORIZING EMPLOYMENT OF "CONTRABANDS."
HOLD MY HAND WHILST THE ENEMY STABS ME
SPEECH AT A WAR MEETING, WASHINGTON, AUGUST 6, 1862
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR ANDREW. August 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR CURTIN. August 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. R. CURTIS. August 12, 1862.
ADDRESS ON COLONIZATION TO A DEPUTATION OF COLORED MEN.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER AT CAMP CHASE, OHIO.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BURNSIDE OR GENERAL PARKE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
ORDER TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. E. WOOL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B, McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. C. BUELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TO GOVERNOR CURTIN. September 11, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL C. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
REPLY TO REQUEST THE PRESIDENT ISSUE A PROCLAMATION OF EMANCIPATION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO J. K. DUBOIS. WASHINGTON, D.C.,
PRELIMINARY EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION, SEPTEMBER 22, 1862.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
REPLY TO SERENADE, SEPTEMBER 24, 1862.
RECORD EXPLAINING THE DISMISSAL OF MAJOR JOHN J. KEY
REMARKS TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC AT FREDERICK, MARYLAND,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PIERPOINT.
EXECUTIVE ORDER ESTABLISHING A PROVISIONAL COURT IN LOUISIANA.
GENERAL McCLELLAN'S TIRED HORSES
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER RELIEVING GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN
ORDER CONCERNING THE CONFISCATION ACT.
GENERAL ORDER RESPECTING THE OBSERVANCE OF THE SABBATH DAY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
ORDER PROHIBITING THE EXPORT OF ARMS AND MUNITIONS OF WAR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
ANNUAL MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, DECEMBER 1, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. December 8, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. H. SIBLEY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TO SECRETARIES SEWARD AND CHASE.
CONGRATULATIONS TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION, JANUARY 1, 1863.
TO CALEB RUSSELL AND SALLIE A. FENTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
CORRESPONDENCE WITH GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE, JANUARY 8, 1863.
HEADQUARTERS OF THE ARMY, WASHINGTON, January 7, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. R. CURTIS.
INSTRUCTION TO THE JUDGE-ADVOCATE-GENERAL.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES. JANUARY 14, 1863.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF MANCHESTER, ENGLAND.
FITZ-JOHN PORTER COURT-MARTIAL.
FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
ORDER RELIEVING GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE AND MAKING OTHER CHANGES.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF LONDON, ENGLAND.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHENCK. [Cipher.] WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C.,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
PROCLAMATION CONVENING THE SENATE, FEBRUARY 28, 1863
PROCLAMATION RECALLING SOLDIERS TO THEIR REGIMENTS, MARCH 10, 1863
GRANT'S EXCLUSION OF A NEWSPAPER REPORTER
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. A. HURLBUT.
QUESTION OF RAISING NEGRO TROOPS
PROCLAMATION APPOINTING A NATIONAL FAST-DAY.
LICENSE OF COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE.
PROCLAMATION ABOUT COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE, APRIL 2, 1863
TELEGRAM TO THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT NASHVILLE.
TELEGRAM TO ADMIRAL S. P. DUPONT.
TO GENERAL D. HUNTER AND ADMIRAL S. F. DUPONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. HOOKER.
STATEHOOD FOR WEST VIRGINIA, APRIL 20, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. BUTTERFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL R. INGALLS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTTERFIELD.
ORDERS SENDING C. L. VALLANDIGHAM BEYOND MILITARY LINES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. A. HURLBUT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BUCKINGHAM.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER. [Cipher.] EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTTERFIELD.
TO ERASTUS CORNING AND OTHERS.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
RESPONSE TO A "BESIEGED" GENERAL
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
NEEDS NEW TIRES ON HIS CARRIAGE
CALL FOR 100,000 MILITIA TO SERVE FOR SIX MONTHS, JUNE 15, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO P. KAPP AND OTHERS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
FURTHER DEMOCRATIC PARTY CRITICISM
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL COUCH. [Cipher] WASHINGTON CITY, June 30, 1863. 3.23
ANNOUNCEMENT OF NEWS FROM GETTYSBURG.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL FRENCH. [Cipher] WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C.,
CONTINUED FAILURE TO PURSUE ENEMY
SURRENDER OF VICKSBURG TO GENERAL GRANT
TELEGRAM FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL G. C. MEADE.
NEWS OF GRANT'S CAPTURE OF VICKSBURG
TELEGRAM TO L. SWETT AND P. F. LOWE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
SON IN COLLEGE DOES NOT WRITE HIS PARENTS
INTIMATION OF ARMISTICE PROPOSALS
PROCLAMATION FOR THANKSGIVING, JULY 15, 1863
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD
To GENERAL G. G. MEADE. (Private.)
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. B. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM FROM GOVERNOR SEYMOUR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
TELEGRAM TO F. C. SHERMAN AND J. S. HAYES.
POLITICAL MOTIVATED MISQUOTATION IN NEWSPAPER
ORDER CONCERNING COMMERCIAL REGULATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO F. C. SHERMAN AND J. S. HAYES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS, SEPTEMBER 15, 1863.
REQUEST TO SUGGEST NAME FOR A BABY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO O. M. HATCH AND J. K. DUBOIS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
PROCLAMATION OPENING THE PORT OF ALEXANDRIA, VIRGINIA,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
MRS. LINCOLN'S REBEL BROTHER-IN-LAW KILLED
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. M. SCHOFIELD.
PROCLAMATION FOR THANKSGIVING, OCTOBER 3, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
THE CASE OF DR. DAVID M. WRIGHT
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
AID TO MRS. HELM, MRS. LINCOLN'S SISTER
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, OCTOBER 17, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO J. WILLIAMS AND N. G. TAYLOR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
THE WRITINGS OF A. LINCOLN, Volume Seven, 1863-1865
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 3, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, November
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
ORDER CONCERNING THE EXPORT OF TOBACCO PURCHASED BY FOREIGN NATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM to E. H. AND E. JAMESON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
ANNOUNCEMENT OF UNION SUCCESS IN EAST TENNESSEE.
PROCLAMATION OF AMNESTY AND RECONSTRUCTION. DECEMBER 8, 1863.
ANNUAL MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, DECEMBER 8, 1863.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. WASHINGTON D. C., December 8, 1863.
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE. WASHINGTON, D. C., December 8, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING DISCRIMINATING DUTIES, DECEMBER 16, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO MILITARY COMMANDER AT POINT LOOKOUT.
TELEGRAM TO MILITARY COMMANDER AT POINT LOOKOUT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PIERPOINT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BROUGH. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January 15,
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, JANUARY 20, 1864
ORDER APPROVING TRADE REGULATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE.
ORDER FOR A DRAFT OF FIVE HUNDRED THOUSAND MEN.
THE STORY OF THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING BLOCKADE, FEBRUARY 18, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
DESERTERS DEATH SENTENCES REMITTED
ORDER IN REGARD TO THE EXPORTATION OF TOBACCO BELONGING TO THE FRENCH
TELEGRAM TO UNITED STATES MARSHAL, LOUISVILLE.
ORDER ASSIGNING U. S. GRANT COMMAND OF THE ARMIES OF THE UNITED STATES.
CALL FOR TWO HUNDRED THOUSAND MEN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PASS FOR GENERAL D. E. SICKLES.
REMARKS AT A FAIR IN THE PATENT OFFICE,
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE FROM THE WORKINGMEN'S ASSOCIATION OF NEW YORK,
CORRESPONDENCE WITH GENERAL C. SCHURZ.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER COMMANDING AT FORT WARREN.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER COMMANDING AT FORT WARREN.
INDORSEMENT ON OFFER OF TROOPS, APRIL 23, 1864.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, APRIL 28, 1864.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
RECOMMENDATION OF THANKSGIVING.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL LEW WALLACE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS,
RESPONSE TO A METHODIST DELEGATION, MAY 14, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR YATES. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 18, 1864.
ARREST AND IMPRISONMENT OF IRRESPONSIBLE NEWSPAPER REPORTERS AND EDITORS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. P. BUTLER.
ORDER CONCERNING THE EXEMPTION OF AMERICAN CONSULS FROM MILITARY SERVICE
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR MORTON AND OTHERS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, May 21, 1864
TELEGRAM TO CHRISTIANA A. SACK. WAR DEPARTMENT WASHINGTON, D. C., May 21,
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BROUGH. WASHINGTON CITY, May 24, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 25,1864.
MEMORANDUM CONCERNING THE TRANSPORTATION OF THE NEW YORK NAVAL BRIGADE.
INDORSEMENT ON A LETTER TOUCHING THE REPUBLICAN NATIONAL CONVENTION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 6, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS. WASHINGTON, June 8, 1864.
REPLY TO THE COMMITTEE NOTIFYING PRESIDENT LINCOLN OF HIS RENOMINATION,
PLATFORM OF THE UNION NATIONAL CONVENTION HELD IN BALTIMORE, MD., JUNE 7
REPLY TO A DELEGATION FROM THE NATIONAL UNION LEAGUE,
REPLY TO A DELEGATION FROM OHIO,
ADDRESS TO THE ENVOY FROM THE HAWAIIAN ISLANDS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL L. THOMAS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 13,
TELEGRAM TO THOMAS WEBSTER. WASHINGTON, D. C., June 13, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, June 15, 1864. 7 A.M.
ADDRESS AT A SANITARY FAIR IN PHILADELPHIA,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS. WASHINGTON, June 24, 1864.
LETTER ACCEPTING THE NOMINATION FOR PRESIDENT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL GRANT. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 29, 1864.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GOVERNOR SEYMOUR.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
PROCLAMATION FOR A DAY OF PRAYER, JULY 7, 1864.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING A BILL "TO GUARANTEE TO CERTAIN STATES,
TELEGRAM TO J. W. GARRETT. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 9, 1864
TELEGRAM FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL WALLACE.
TELEGRAM TO T. SWAN AND OTHERS. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 10, 1864. 9.20
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON CITY, July TO, 1864.2 P.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, July 11, 1864. 8 A.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 12, 1864. 11.30
TELEGRAM AND LETTER TO HORACE GREELEY. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, JULY 15, 1864.
SAFE CONDUCT FOR CLEMENT C. CLAY AND OTHERS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. [WASHINGTON] July 17. 1864. 11.25 A.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. HUNTER WASHINGTON JULY 17, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
ANNOUNCEMENT CONCERNING TERMS OF PEACE.
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR FIVE HUNDRED THOUSAND VOLUNTEERS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. HUNTER. (Cipher.)
TO GOVERNOR CURTIN, ENCLOSING A LETTER TO WILLIAM O. SNIDER.
FROM JOHN HAY TO J. C. WELLING.
TO COLONEL, FIRST N. Y. VETERAN CAVALRY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. WASHINGTON, July 27, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U, S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
ENDORSEMENT OF APPLICATION FOR EMPLOYMENT, AUGUST 15, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING COMMERCIAL REGULATIONS, AUGUST 18, 1864.
INDORSEMENT CONCERNING AN EXCHANGE OF PRISONERS, AUGUST 18, 1864.
ADDRESS TO THE 164TH OHIO REGIMENT,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTLER. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., August
ADDRESS TO THE 166TH OHIO REGIMENT,
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, August 26,
TELEGRAM TO B. H. BREWSTER. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., August
ORDERS OF GRATITUDE AND REJOICING.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, September 3, 1864.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, September 3, 1864.
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE OF COLORED PEOPLE FROM BALTIMORE
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PICKERING.
ORDER OF THANKS TO HUNDRED-DAY TROOPS FROM OHIO.
TELEGRAM TO JAMES G. BLAINE. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., September
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN. WASHINGTON, D. C., September 17,1864.
INDORSEMENT CONCERNING AN EXCHANGE OF PRISONERS, SEPTEMBER 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL P. SHERIDAN. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, September
ORDER CONCERNING THE PURCHASE OF PRODUCTS IN INSURRECTIONARY STATES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN. WASHINGTON, D. C., September 27, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D.C., September 29,1864.
ORDER RETURNING THANKS TO THE VOLUNTEERS FOR ONE HUNDRED DAYS
INDORSEMENT ON A MEMORANDUM BY GENERAL McDOWELL, OCTOBER 7, 1864
TELEGRAM TO ROBERT T. LINCOLN, Cambridge, Mass.:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 12, 1864.
PROCLAMATION OF THANKSGIVING, OCTOBER 20, 1864.
TELEGRAM To J. G. NICOLAY. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 21, 1864. 9.45 P.M.
TO WILLIAM B. CAMPBELL AND OTHERS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. H. THOMAS. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 23, 1864 5
TELEGRAM TO T. T. DAVIS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D.C., October 31,
PROCLAMATION ADMITTING NEVADA INTO THE UNION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BURBRIDGE.
TELEGRAM TO NAVAL OFFICER AT MOBILE BAY.
TELEGRAM TO SAILORS' FAIR, BOSTON, MASSACHUSETTS.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD. WASHINGTON, November 8, 1864.
RESPONSE TO A SERENADE, NOVEMBER 9, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO H. W. HOFFMAN. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C. November 10,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. O. BURBRIDGE. WASHINGTON, D.C., November 10, 1864.
WASHINGTON, D.C., November 10, 1864. GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE, Frankfort, Ky.:
REPLY TO MARYLAND UNION COMMITTEE, NOVEMBER 17, 1864.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING BLOCKADE, NOVEMBER 19, 1864
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE. WASHINGTON, D. C. NOVEMBER 22, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR CURTIN, WASHINGTON, D.C., NOVEMBER 25, 1864
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON D.C., NOV.
ORDER CONCERNING THE STEAMER "FUNAYMA SOLACE."
RESPONSE TO A SERENADE, DECEMBER 6, 1864.
ORDER APPOINTING COMMISSIONERS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G, H. THOMAS. WASHINGTON, D.C., December 16, 1864.
ORIGIN OF THE "GREENBACK" CURRENCY
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT CHATTANOOGA. EXECUTIVE MANSION,
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, DECEMBER 19, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT LEXINGTON.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT NASHVILLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING COMMERCE, JANUARY 10, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. F. BUTLER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. F. BUTLER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. M. DODGE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January
FIRST OVERTURES FOR SURRENDER FROM DAVIS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. M. DODGE.
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE, JANUARY 24, 1865.
EARLY CONSULTATIONS WITH REBELS
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY OF WAR TO GENERAL ORD.
INDORSEMENT ON A LETTER FROM J. M. ASHLEY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
INSTRUCTIONS TO SECRETARY SEWARD.
CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT FOR THE ABOLISHING OF SLAVERY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, February 1, 1865
TELEGRAM TO MAJOR ECKERT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 1, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865.
ORDER TO MAKE CORRECTIONS IN THE DRAFT.
TELEGRAM TO LIEUTENANT-COLONEL GLENN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, February
CHRONOLOGIC REVIEW OF PEACE PROPOSALS
Afterwards Mr. Blair dictated for and authorized me to make an entry on
Afterwards the Secretary of War placed in my hands the following telegram,
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE. WASHINGTON, February 10, 1865
TO THE COMMANDING OFFICERS IN WEST TENNESSEE
PROCLAMATION CONVENING THE SENATE IN EXTRA SESSION,
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT HARPER'S FERRY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, February 25, 1865
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 27, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., March 2, 1865.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL GRANT.
SECOND INAUGURAL ADDRESS, MARCH 4, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL JOHN POPE.
TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., March 8, 1865.
PROCLAMATION OFFERING PARDON TO DESERTERS,
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL ROUGH AND OTHERS.
ADDRESS TO AN INDIANA REGIMENT,
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING INDIANS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. HANCOCK.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. CITY POINT, April 1, 1865.
TELEGRAMS TO SECRETARY STANTON. CITY POINT, VIRGINIA, April 2, 1865. 8.30
TELEGRAM TO MRS. LINCOLN. CITY POINT, VA., April 1, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
NOTE ON A CARD TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. H. GORDON.
PROCLAMATION CLOSING CERTAIN PORTS, APRIL 11, 1865.
PROCLAMATION OPENING THE PORT OF KEY WEST,
PROCLAMATION CLAIMING EQUALITY OF RIGHTS WITH ALL MARITIME NATIONS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL. WASHINGTON, D.C., April 12, 1865.
INTERVIEW WITH SCHUYLER COLFAX ON THE MORNING OF APRIL 14, 1865.
CONTENTS OF YARNS AND STORIES
LINCOLN’S NAME AROUSES AN AUDIENCE
“ABE” LINCOLN’S YARNS AND STORIES.
HIS KNOWLEDGE OF HUMAN NATURE.
LINCOLN’S STORY TO PEACE COMMISSIONERS.
IT DEPENDED UPON HIS CONDITION.
“HONEST ABE” SWALLOWS HIS ENEMIES.
A JOB FOR THE NEW CABINETMAKER.
WANTED TO BURN HIM DOWN TO THE STUMP.
THE CASE OF BETSY ANN DOUGHERTY.
“ABE” STIRRING THE “BLACK” COALS.
LOST HIS CERTIFICATE OF CHARACTER.
JEFF DAVIS AND CHARLES THE FIRST.
REMINDED HIM OF “A LITTLE STORY.”
MAKE SOMETHING OUT OF IT, ANYWAY.
VICIOUS OXEN HAVE SHORT HORNS.
LINCOLN’S NAME FOR “WEEPING WATER.”
PETER CARTWRIGHT’S DESCRIPTION OF LINCOLN.
“DON’T KILL HIM WITH YOUR FIST.”
LINCOLN ADOPTED THE SUGGESTION.
GREELEY CARRIES LINCOLN TO THE LUNATIC ASYLUM.
SAFE AS LONG AS THEY WERE GOOD.
“SMELT NO ROYALTY IN OUR CARRIAGE.”
HELL A MILE FROM THE WHITE HOUSE.
ORIGIN OF THE “INFLUENCE” STORY.
PAT WAS “FORNINST THE GOVERNMENT.”
HARDTACK BETTER THAN GENERALS.
MR. BULL DIDN’T GET HIS COTTON.
“AND YOU DON’T WEAR HOOPSKIRTS.”
LIEUTENANT TAD LINCOLN’S SENTINELS.
“ABE, YOU CAN’T PLAY THAT ON ME.”
LINCOLN CALLS MEDILL A COWARD.
“MRS. NORTH AND HER ATTORNEY.”
“WEBSTER COULDN’T HAVE DONE MORE.”
REMINDED “ABE” OF A LITTLE JOKE.
LINCOLN PROTECTED CURRENCY ISSUES.
“THE BAD BIRD AND THE MUDSILL.”
PRESIDENT LINCOLN’S LAST PUBLIC ADDRESS.
MOST VALUABLE POLITICAL ATTRIBUTE.
OFFICE SEEKERS WORSE THAN WAR.
DIDN’T KNOW GRANT’S PREFERENCE.
HOW “FIGHTING JOE” WAS APPOINTED.
A FORTUNE-TELLER’S PREDICTION.
SHOULD HAVE FOUGHT ANOTHER BATTLE.
WHEN LINCOLN AND GRANT CLASHED.
WON JAMES GORDON BENNETT’S SUPPORT.
DIDN’T WANT A MILITARY REPUTATION.
LINCOLN’S REJECTED MANUSCRIPT.
LINCOLN’S IDEAS ON CROSSING A RIVER WHEN HE GOT TO IT.
“CONSIDER THE SYMPATHY OF LINCOLN.”
HIS PASSES TO RICHMOND NOT HONORED.
“PUBLIC HANGMAN” FOR THE UNITED STATES.
LINCOLN A MAN OF SIMPLE HABITS.
FORGOT EVERYTHING HE KNEW BEFORE.
LINCOLN BELIEVED IN EDUCATION.
LINCOLN ON THE DRED SCOTT DECISION.
LINCOLN MADE MANY NOTABLE SPEECHES.
CALLED BLESSINGS ON THE AMERICAN WOMEN.
TALKED TO THE NEGROES OF RICHMOND.
ANGELS COULDN’T SWEAR IT RIGHT.
LINCOLN WASN’T BUYING NOMINATIONS.
HE ENVIED THE SOLDIER AT THE FRONT.
THE PRESIDENT HAD KNOWLEDGE OF HIM.
HOW STANTON GOT INTO THE CABINET.
WHY HE WAS CALLED “HONEST ABE.”
“ABE’S” NAME REMAINED ON THE SIGN.
HE PROPOSED TO SAVE THE UNION.
WOULD NOT RECALL A SINGLE WORD.
WOULDN’T HOLD TITLE AGAINST HIM.
COULDN’T LOCATE HIS BIRTHPLACE.
“ABE” OFFERS A SPEECH FOR SOMETHING TO EAT.
“BUTCHER-KNIFE BOYS” AT THE POLLS.
NO “SECOND COMING” FOR SPRINGFIELD.
GAVE THE SOLDIER THE PREFERENCE.
JEFF. DAVIS’ REPLY TO LINCOLN.
DESERTER’S SINS WASHED OUT IN BLOOD.
LINCOLN DEFENDS FIFTEEN MRS. NATIONS.
AVOIDED EVEN APPEARANCE OF EVIL
LINCOLN PAID HOMAGE TO WASHINGTON.
ETERNAL FIDELITY TO THE CAUSE OF LIBERTY.
WROTE “PIECES” WHEN VERY YOUNG.
“THE ‘RAIL-SPUTTER’ REPAIRING THE UNION.”
“GOVERNMENT RESTS IN PUBLIC OPINION.”
LINCOLN WOULD HAVE PREFERRED DEATH.
“PUNCH” AND HIS LITTLE PICTURE.
THE FIVE POINTS SUNDAY SCHOOL.
THOUGHT GOD WOULD HAVE TOLD HIM.
NAUGHTY BOY HAD TO TAKE HIS MEDICINE.
LINCOLN’S MEN WERE “HUSTLERS.”
DODGING “BROWSING PRESIDENTS.”
SCALPING IN THE BLACK HAWK WAR.
HOW THE TOWN OF LINCOLN, ILL., WAS NAMED.
PRESIDENT AND CABINET JOINED IN PRAYER.
LINCOLN WISHED TO SEE RICHMOND.
“LINCOLN GOES IN WHEN THE QUAKERS ARE OUT”
“ABE WANTED NO SNEAKIN’ ‘ROUND.”
“HOW DO YOU GET OUT OF THIS PLACE?”
“TAD” INTRODUCES “OUR FRIENDS.”
“LONG ABE’S” FEET “PROTRUDED OVER.”
COULD LICK ANY MAN IN THE CROWD.
“LEFT IT THE WOMEN TO HOWL ABOUT ME.”
HE’D RUIN ALL THE OTHER CONVICTS.
“FIXED UP” A BIT FOR THE “CITY FOLKS.”
EVEN REBELS OUGHT TO BE SAVED.
“HOLDING A CANDLE TO THE CZAR.”
NASHVILLE WAS NOT SURRENDERED.
HE COULDN’T WAIT FOR THE COLONEL.
LINCOLN PRONOUNCED THIS STORY FUNNY.
“I’D A BEEN MISSED BY MYSE’F.”
IT ALL “DEPENDED” UPON THE EFFECT.
TOO SWIFT TO STAY IN THE ARMY.
WISHED THE ARMY CHARGED LIKE THAT.
“UNCLE ABRAHAM” HAD EVERYTHING READY.
“NEVER REGRET WHAT YOU DON’T WRITE.”
ASSISTANT PILOT ON A STEAMBOAT.
“CAPTAIN LINCOLN” PLEASED HIM.
SURVEYOR WITH NO STRINGS ON HIM.
DEFEATS PETER CARTWRIGHT FOR CONGRESS.
MAKES SPEECHES FOR “OLD ZACH.”
TELLING STORIES ON THE CIRCUIT.
THE LION IS AROUSED TO ACTION.
HELPS TO ORGANIZE THE REPUBLICAN PARTY.
THE RAIL-SPLITTER vs. THE LITTLE GIANT.
FIRST NOMINATION FOR PRESIDENT.
FORMATION OF THE SOUTHERN CONFEDERACY.
THE “SECRET PASSAGE” TO WASHINGTON.
HIS ELOQUENT INAUGURAL ADDRESS.
FOLLOWS PRECEDENT OF WASHINGTON.
REASONS FOB FREEING THE SLAVES.
A FUN-LOVING AND HUMOR-LOVING MAN.
BOOTH BRANDISHES HIS DAGGER AND ESCAPES.
BOOTH SHOT BY “BOSTON” CORBETT.
LINCOLN MONUMENT AT SPRINGFIELD.
FACSIMILES
ABRAHAM LINCOLN, VOL. 1, BY HERNDON
INDEX FOR HERNDON TWO
ABRAHAM LINCOLN, VOL. 1, BY HERNDON
THE TRUCE WITH DOUGLAS.—TESTIMONY OF IRWIN.
AN OFFICE DISCUSSION—LINCOLN'S IDEA OF WAR.
LINCOLN AND THE KNOW-NOTHINGS.
LINCOLN'S VIEWS ON THE RIGHTS OF SUFFRAGE.
THE BURIAL OF THE ASSASSIN BOOTH.
A TRIBUTE TO LINCOLN BY A COLLEAGUE AT THE BAR.
INDEX FOR "LAM"
THE LIFE OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN BY LAMON
ILLUSTRATIONS
Mrs. Sarah Lincoln, Mother of the President
Immediately after Lincoln's re-election to the Presidency, in an off-hand speech, delivered in response to a serenade by some of his admirers on the evening of November 10, 1864, he spoke as follows:
"It has long been a grave question whether any government not too strong for the liberties of its people can be strong enough to maintain its existence in great emergencies. On this point, the present rebellion brought our republic to a severe test, and the Presidential election, occurring in regular course during the rebellion, added not a little to the strain.... The strife of the election is but human nature practically applied to the facts in the case. What has occurred in this case must ever occur in similar cases. Human nature will not change. In any future great national trial, compared with the men of this, we shall have as weak and as strong, as silly and as wise, as bad and as good. Let us therefore study the incidents in this as philosophy to learn wisdom from and none of them as wrongs to be avenged.... Now that the election is over, may not all having a common interest reunite in a common fort to save our common country? For my own part, I have striven and shall strive to avoid placing any obstacle in the way. So long as I have been here, I have not willingly planted a thorn in any man's bosom. While I am deeply sensible to the high compliment of a re-election and duly grateful, as I trust, to Almighty God for having directed my countrymen to a right conclusion, as I think for their own good, it adds nothing to my satisfaction that any other man may be disappointed or pained by the result."
This speech has not attracted much general attention, yet it is in a peculiar degree both illustrative and typical of the great statesman who made it, alike in its strong common-sense and in its lofty standard of morality. Lincoln's life, Lincoln's deeds and words, are not only of consuming interest to the historian, but should be intimately known to every man engaged in the hard practical work of American political life. It is difficult to overstate how much it means to a nation to have as the two foremost figures in its history men like Washington and Lincoln. It is good for every man in any way concerned in public life to feel that the highest ambition any American can possibly have will be gratified just in proportion as he raises himself toward the standards set by these two men.
It is a very poor thing, whether for nations or individuals, to advance the history of great deeds done in the past as an excuse for doing poorly in the present; but it is an excellent thing to study the history of the great deeds of the past, and of the great men who did them, with an earnest desire to profit thereby so as to render better service in the present. In their essentials, the men of the present day are much like the men of the past, and the live issues of the present can be faced to better advantage by men who have in good faith studied how the leaders of the nation faced the dead issues of the past. Such a study of Lincoln's life will enable us to avoid the twin gulfs of immorality and inefficiency—the gulfs which always lie one on each side of the careers alike of man and of nation. It helps nothing to have avoided one if shipwreck is encountered in the other. The fanatic, the well-meaning moralist of unbalanced mind, the parlor critic who condemns others but has no power himself to do good and but little power to do ill—all these were as alien to Lincoln as the vicious and unpatriotic themselves. His life teaches our people that they must act with wisdom, because otherwise adherence to right will be mere sound and fury without substance; and that they must also act high-mindedly, or else what seems to be wisdom will in the end turn out to be the most destructive kind of folly.
Throughout his entire life, and especially after he rose to leadership in his party, Lincoln was stirred to his depths by the sense of fealty to a lofty ideal; but throughout his entire life, he also accepted human nature as it is, and worked with keen, practical good sense to achieve results with the instruments at hand. It is impossible to conceive of a man farther removed from baseness, farther removed from corruption, from mere self-seeking; but it is also impossible to conceive of a man of more sane and healthy mind—a man less under the influence of that fantastic and diseased morality (so fantastic and diseased as to be in reality profoundly immoral) which makes a man in this work-a-day world refuse to do what is possible because he cannot accomplish the impossible.
In the fifth volume of Lecky's History of England, the historian draws an interesting distinction between the qualities needed for a successful political career in modern society and those which lead to eminence in the spheres of pure intellect or pure moral effort. He says:
"....the moral qualities that are required in the higher spheres of statesmanship [are not] those of a hero or a saint. Passionate earnestness and self-devotion, complete concentration of every faculty on an unselfish aim, uncalculating daring, a delicacy of conscience and a loftiness of aim far exceeding those of the average of men, are here likely to prove rather a hindrance than an assistance. The politician deals very largely with the superficial and the commonplace; his art is in a great measure that of skilful compromise, and in the conditions of modern life, the statesman is likely to succeed best who possesses secondary qualities to an unusual degree, who is in the closest intellectual and moral sympathy with the average of the intelligent men of his time, and who pursues common ideals with more than common ability.... Tact, business talent, knowledge of men, resolution, promptitude and sagacity in dealing with immediate emergencies, a character which lends itself easily to conciliation, diminishes friction and inspires confidence, are especially needed, and they are more likely to be found among shrewd and enlightened men of the world than among men of great original genius or of an heroic type of character."
The American people should feel profoundly grateful that the greatest American statesman since Washington, the statesman who in this absolutely democratic republic succeeded best, was the very man who actually combined the two sets of qualities which the historian thus puts in antithesis. Abraham Lincoln, the rail-splitter, the Western country lawyer, was one of the shrewdest and most enlightened men of the world, and he had all the practical qualities which enable such a man to guide his countrymen; and yet he was also a genius of the heroic type, a leader who rose level to the greatest crisis through which this nation or any other nation had to pass in the nineteenth century.
THEODORE ROOSEVELT
SAGAMORE HILL, OYSTER BAY, N. Y., September 22, 1905.
"I have endured," wrote Lincoln not long before his death, "a great deal of ridicule without much malice, and have received a great deal of kindness not quite free from ridicule." On Easter Day, 1865, the world knew how little this ridicule, how much this kindness, had really signified. Thereafter, Lincoln the man became Lincoln the hero, year by year more heroic, until to-day, with the swift passing of those who knew him, his figure grows ever dimmer, less real. This should not be. For Lincoln the man, patient, wise, set in a high resolve, is worth far more than Lincoln the hero, vaguely glorious. Invaluable is the example of the man, intangible that of the hero.
And, though it is not for us, as for those who in awed stillness listened at Gettysburg with inspired perception, to know Abraham Lincoln, yet there is for us another way whereby we may attain such knowledge—through his words—uttered in all sincerity to those who loved or hated him. Cold, unsatisfying they may seem, these printed words, while we can yet speak with those who knew him, and look into eyes that once looked into his. But in truth it is here that we find his simple greatness, his great simplicity, and though no man tried less so to show his power, no man has so shown it more clearly.
Thus these writings of Abraham Lincoln are associated with those of Washington, Hamilton, Franklin, and of the other "Founders of the Republic," not that Lincoln should become still more of the past, but, rather, that he with them should become still more of the present. However faint and mythical may grow the story of that Great Struggle, the leader, Lincoln, at least should remain a real, living American. No matter how clearly, how directly, Lincoln has shown himself in his writings, we yet should not forget those men whose minds, from their various view-points, have illumined for us his character. As this nation owes a great debt to Lincoln, so, also, Lincoln's memory owes a great debt to a nation which, as no other nation could have done, has been able to appreciate his full worth. Among the many who have brought about this appreciation, those only whose estimates have been placed in these volumes may be mentioned here. To President Roosevelt, to Mr. Schurz and to Mr. Choate, the editor, for himself, for the publishers, and on behalf of the readers, wishes to offer his sincere acknowledgments.
Thanks are also due, for valuable and sympathetic assistance rendered in the preparation of this work, to Mr. Gilbert A. Tracy, of Putnam, Conn., Major William H. Lambert, of Philadelphia, and Mr. C. F. Gunther, of Chicago, to the Chicago Historical Association and personally to its capable Secretary, Miss McIlvaine, to Major Henry S. Burrage, of Portland, Me., and to General Thomas J. Henderson, of Illinois.
For various courtesies received, the editor is furthermore indebted to the Librarian of the Library of Congress; to Messrs. McClure, Phillips & Co., D. Appleton & Co., Macmillan & Co., Dodd, Mead & Co., and Harper Brothers, of New York; to Houghton, Mifflin & Co., Dana, Estes & Co., and L. C. Page & Co., of Boston; to A. C. McClure & Co., of Chicago; to The Robert Clarke Co., of Cincinnati, and to the J. B. Lippincott Co., of Philadelphia.
It is hardly necessary to add that every effort has been made by the editor to bring into these volumes whatever material may there properly belong, material much of which is widely scattered in public libraries and in private collections. He has been fortunate in securing certain interesting correspondence and papers which had not before come into print in book form. Information concerning some of these papers had reached him too late to enable the papers to find place in their proper chronological order in the set. Rather, however, than not to present these papers to the readers they have been included in the seventh volume of the set, which concludes the "Writings."
[These later papers are, in this etext, re-arranged into chronologic
order. D.W.]
October, 1905, A. B. L.
No American can study the character and career of Abraham Lincoln without being carried away by sentimental emotions. We are always inclined to idealize that which we love,—a state of mind very unfavorable to the exercise of sober critical judgment. It is therefore not surprising that most of those who have written or spoken on that extraordinary man, even while conscientiously endeavoring to draw a lifelike portraiture of his being, and to form a just estimate of his public conduct, should have drifted into more or less indiscriminating eulogy, painting his great features in the most glowing colors, and covering with tender shadings whatever might look like a blemish.
But his standing before posterity will not be exalted by mere praise of his virtues and abilities, nor by any concealment of his limitations and faults. The stature of the great man, one of whose peculiar charms consisted in his being so unlike all other great men, will rather lose than gain by the idealization which so easily runs into the commonplace. For it was distinctly the weird mixture of qualities and forces in him, of the lofty with the common, the ideal with the uncouth, of that which he had become with that which he had not ceased to be, that made him so fascinating a character among his fellow-men, gave him his singular power over their minds and hearts, and fitted him to be the greatest leader in the greatest crisis of our national life.
His was indeed a marvellous growth. The statesman or the military hero born and reared in a log cabin is a familiar figure in American history; but we may search in vain among our celebrities for one whose origin and early life equalled Abraham Lincoln's in wretchedness. He first saw the light in a miserable hovel in Kentucky, on a farm consisting of a few barren acres in a dreary neighborhood; his father a typical "poor Southern white," shiftless and without ambition for himself or his children, constantly looking for a new piece of land on which he might make a living without much work; his mother, in her youth handsome and bright, grown prematurely coarse in feature and soured in mind by daily toil and care; the whole household squalid, cheerless, and utterly void of elevating inspirations... Only when the family had "moved" into the malarious backwoods of Indiana, the mother had died, and a stepmother, a woman of thrift and energy, had taken charge of the children, the shaggy-headed, ragged, barefooted, forlorn boy, then seven years old, "began to feel like a human being." Hard work was his early lot. When a mere boy he had to help in supporting the family, either on his father's clearing, or hired out to other farmers to plough, or dig ditches, or chop wood, or drive ox teams; occasionally also to "tend the baby," when the farmer's wife was otherwise engaged. He could regard it as an advancement to a higher sphere of activity when he obtained work in a "crossroads store," where he amused the customers by his talk over the counter; for he soon distinguished himself among the backwoods folk as one who had something to say worth listening to. To win that distinction, he had to draw mainly upon his wits; for, while his thirst for knowledge was great, his opportunities for satisfying that thirst were wofully slender.
In the log schoolhouse, which he could visit but little, he was taught only reading, writing, and elementary arithmetic. Among the people of the settlement, bush farmers and small tradesmen, he found none of uncommon intelligence or education; but some of them had a few books, which he borrowed eagerly. Thus he read and reread, AEsop's Fables, learning to tell stories with a point and to argue by parables; he read Robinson Crusoe, The Pilgrim's Progress, a short history of the United States, and Weems's Life of Washington. To the town constable's he went to read the Revised Statutes of Indiana. Every printed page that fell into his hands he would greedily devour, and his family and friends watched him with wonder, as the uncouth boy, after his daily work, crouched in a corner of the log cabin or outside under a tree, absorbed in a book while munching his supper of corn bread. In this manner he began to gather some knowledge, and sometimes he would astonish the girls with such startling remarks as that the earth was moving around the sun, and not the sun around the earth, and they marvelled where "Abe" could have got such queer notions. Soon he also felt the impulse to write; not only making extracts from books he wished to remember, but also composing little essays of his own. First he sketched these with charcoal on a wooden shovel scraped white with a drawing-knife, or on basswood shingles. Then he transferred them to paper, which was a scarce commodity in the Lincoln household; taking care to cut his expressions close, so that they might not cover too much space,—a style-forming method greatly to be commended. Seeing boys put a burning coal on the back of a wood turtle, he was moved to write on cruelty to animals. Seeing men intoxicated with whiskey, he wrote on temperance. In verse-making, too, he tried himself, and in satire on persons offensive to him or others,—satire the rustic wit of which was not always fit for ears polite. Also political thoughts he put upon paper, and some of his pieces were even deemed good enough for publication in the county weekly.
Thus he won a neighborhood reputation as a clever young man, which he increased by his performances as a speaker, not seldom drawing upon himself the dissatisfaction of his employers by mounting a stump in the field, and keeping the farm hands from their work by little speeches in a jocose and sometimes also a serious vein. At the rude social frolics of the settlement he became an important person, telling funny, stories, mimicking the itinerant preachers who had happened to pass by, and making his mark at wrestling matches, too; for at the age of seventeen he had attained his full height, six feet four inches in his stockings, if he had any, and a terribly muscular clodhopper he was. But he was known never to use his extraordinary strength to the injury or humiliation of others; rather to do them a kindly turn, or to enforce justice and fair dealing between them. All this made him a favorite in backwoods society, although in some things he appeared a little odd, to his friends. Far more than any of them, he was given not only to reading, but to fits of abstraction, to quiet musing with himself, and also to strange spells of melancholy, from which he often would pass in a moment to rollicking outbursts of droll humor. But on the whole he was one of the people among whom he lived; in appearance perhaps even a little more uncouth than most of them,—a very tall, rawboned youth, with large features, dark, shrivelled skin, and rebellious hair; his arms and legs long, out of proportion; clad in deerskin trousers, which from frequent exposure to the rain had shrunk so as to sit tightly on his limbs, leaving several inches of bluish shin exposed between their lower end and the heavy tan-colored shoes; the nether garment held usually by only one suspender, that was strung over a coarse homemade shirt; the head covered in winter with a coonskin cap, in summer with a rough straw hat of uncertain shape, without a band.
It is doubtful whether he felt himself much superior to his surroundings, although he confessed to a yearning for some knowledge of the world outside of the circle in which he lived. This wish was gratified; but how? At the age of nineteen he went down the Mississippi to New Orleans as a flatboat hand, temporarily joining a trade many members of which at that time still took pride in being called "half horse and half alligator." After his return he worked and lived in the old way until the spring of 1830, when his father "moved again," this time to Illinois; and on the journey of fifteen days "Abe" had to drive the ox wagon which carried the household goods. Another log cabin was built, and then, fencing a field, Abraham Lincoln split those historic rails which were destined to play so picturesque a part in the Presidential campaign twenty-eight years later.
Having come of age, Lincoln left the family, and "struck out for himself." He had to "take jobs whenever he could get them." The first of these carried him again as a flatboat hand to New Orleans. There something happened that made a lasting impression upon his soul: he witnessed a slave auction. "His heart bled," wrote one of his companions; "said nothing much; was silent; looked bad. I can say, knowing it, that it was on this trip that he formed his opinion on slavery. It run its iron in him then and there, May, 1831. I have heard him say so often." Then he lived several years at New Salem, in Illinois, a small mushroom village, with a mill, some "stores" and whiskey shops, that rose quickly, and soon disappeared again. It was a desolate, disjointed, half-working and half-loitering life, without any other aim than to gain food and shelter from day to day. He served as pilot on a steamboat trip, then as clerk in a store and a mill; business failing, he was adrift for some time. Being compelled to measure his strength with the chief bully of the neighborhood, and overcoming him, he became a noted person in that muscular community, and won the esteem and friendship of the ruling gang of ruffians to such a degree that, when the Black Hawk war broke out, they elected him, a young man of twenty-three, captain of a volunteer company, composed mainly of roughs of their kind. He took the field, and his most noteworthy deed of valor consisted, not in killing an Indian, but in protecting against his own men, at the peril of his own life, the life of an old savage who had strayed into his camp.
The Black Hawk war over, he turned to politics. The step from the captaincy of a volunteer company to a candidacy for a seat in the Legislature seemed a natural one. But his popularity, although great in New Salem, had not spread far enough over the district, and he was defeated. Then the wretched hand-to-mouth struggle began again. He "set up in store-business" with a dissolute partner, who drank whiskey while Lincoln was reading books. The result was a disastrous failure and a load of debt. Thereupon he became a deputy surveyor, and was appointed postmaster of New Salem, the business of the post-office being so small that he could carry the incoming and outgoing mail in his hat. All this could not lift him from poverty, and his surveying instruments and horse and saddle were sold by the sheriff for debt.
But while all this misery was upon him his ambition rose to higher aims. He walked many miles to borrow from a schoolmaster a grammar with which to improve his language. A lawyer lent him a copy of Blackstone, and he began to study law.
People would look wonderingly at the grotesque figure lying in the grass, "with his feet up a tree," or sitting on a fence, as, absorbed in a book, he learned to construct correct sentences and made himself a jurist. At once he gained a little practice, pettifogging before a justice of the peace for friends, without expecting a fee. Judicial functions, too, were thrust upon him, but only at horse-races or wrestling matches, where his acknowledged honesty and fairness gave his verdicts undisputed authority. His popularity grew apace, and soon he could be a candidate for the Legislature again. Although he called himself a Whig, an ardent admirer of Henry Clay, his clever stump speeches won him the election in the strongly Democratic district. Then for the first time, perhaps, he thought seriously of his outward appearance. So far he had been content with a garb of "Kentucky jeans," not seldom ragged, usually patched, and always shabby. Now, he borrowed some money from a friend to buy a new suit of clothes—"store clothes" fit for a Sangamon County statesman; and thus adorned he set out for the state capital, Vandalia, to take his seat among the lawmakers.
His legislative career, which stretched over several sessions—for he was thrice re-elected, in 1836, 1838, and 1840—was not remarkably brilliant. He did, indeed, not lack ambition. He dreamed even of making himself "the De Witt Clinton of Illinois," and he actually distinguished himself by zealous and effective work in those "log-rolling" operations by which the young State received "a general system of internal improvements" in the shape of railroads, canals, and banks,—a reckless policy, burdening the State with debt, and producing the usual crop of political demoralization, but a policy characteristic of the time and the impatiently enterprising spirit of the Western people. Lincoln, no doubt with the best intentions, but with little knowledge of the subject, simply followed the popular current. The achievement in which, perhaps, he gloried most was the removal of the State government from Vandalia to Springfield; one of those triumphs of political management which are apt to be the pride of the small politician's statesmanship. One thing, however, he did in which his true nature asserted itself, and which gave distinct promise of the future pursuit of high aims. Against an overwhelming preponderance of sentiment in the Legislature, followed by only one other member, he recorded his protest against a proslavery resolution,—that protest declaring "the institution of slavery to be founded on both injustice and bad policy." This was not only the irrepressible voice of his conscience; it was true moral valor, too; for at that time, in many parts of the West, an abolitionist was regarded as little better than a horse-thief, and even "Abe Lincoln" would hardly have been forgiven his antislavery principles, had he not been known as such an "uncommon good fellow." But here, in obedience to the great conviction of his life, he manifested his courage to stand alone, that courage which is the first requisite of leadership in a great cause.
Together with his reputation and influence as a politician grew his law practice, especially after he had removed from New Salem to Springfield, and associated himself with a practitioner of good standing. He had now at last won a fixed position in society. He became a successful lawyer, less, indeed, by his learning as a jurist than by his effectiveness as an advocate and by the striking uprightness of his character; and it may truly be said that his vivid sense of truth and justice had much to do with his effectiveness as an advocate. He would refuse to act as the attorney even of personal friends when he saw the right on the other side. He would abandon cases, even during trial, when the testimony convinced him that his client was in the wrong. He would dissuade those who sought his service from pursuing an obtainable advantage when their claims seemed to him unfair. Presenting his very first case in the United States Circuit Court, the only question being one of authority, he declared that, upon careful examination, he found all the authorities on the other side, and none on his. Persons accused of crime, when he thought them guilty, he would not defend at all, or, attempting their defence, he was unable to put forth his powers. One notable exception is on record, when his personal sympathies had been strongly aroused. But when he felt himself to be the protector of innocence, the defender of justice, or the prosecutor of wrong, he frequently disclosed such unexpected resources of reasoning, such depth of feeling, and rose to such fervor of appeal as to astonish and overwhelm his hearers, and make him fairly irresistible. Even an ordinary law argument, coming from him, seldom failed to produce the impression that he was profoundly convinced of the soundness of his position. It is not surprising that the mere appearance of so conscientious an attorney in any case should have carried, not only to juries, but even to judges, almost a presumption of right on his side, and that the people began to call him, sincerely meaning it, "honest Abe Lincoln."
In the meantime he had private sorrows and trials of a painfully afflicting nature. He had loved and been loved by a fair and estimable girl, Ann Rutledge, who died in the flower of her youth and beauty, and he mourned her loss with such intensity of grief that his friends feared for his reason. Recovering from his morbid depression, he bestowed what he thought a new affection upon another lady, who refused him. And finally, moderately prosperous in his worldly affairs, and having prospects of political distinction before him, he paid his addresses to Mary Todd, of Kentucky, and was accepted. But then tormenting doubts of the genuineness of his own affection for her, of the compatibility of their characters, and of their future happiness came upon him. His distress was so great that he felt himself in danger of suicide, and feared to carry a pocket-knife with him; and he gave mortal offence to his bride by not appearing on the appointed wedding day. Now the torturing consciousness of the wrong he had done her grew unendurable. He won back her affection, ended the agony by marrying her, and became a faithful and patient husband and a good father. But it was no secret to those who knew the family well that his domestic life was full of trials. The erratic temper of his wife not seldom put the gentleness of his nature to the severest tests; and these troubles and struggles, which accompanied him through all the vicissitudes of his life from the modest home in Springfield to the White House at Washington, adding untold private heart-burnings to his public cares, and sometimes precipitating upon him incredible embarrassments in the discharge of his public duties, form one of the most pathetic features of his career.
He continued to "ride the circuit," read books while travelling in his buggy, told funny stories to his fellow-lawyers in the tavern, chatted familiarly with his neighbors around the stove in the store and at the post-office, had his hours of melancholy brooding as of old, and became more and more widely known and trusted and beloved among the people of his State for his ability as a lawyer and politician, for the uprightness of his character and the overflowing spring of sympathetic kindness in his heart. His main ambition was confessedly that of political distinction; but hardly any one would at that time have seen in him the man destined to lead the nation through the greatest crisis of the century.
His time had not yet come when, in 1846, he was elected to Congress. In a clever speech in the House of Representatives he denounced President Polk for having unjustly forced war upon Mexico, and he amused the Committee of the Whole by a witty attack upon General Cass. More important was the expression he gave to his antislavery impulses by offering a bill looking to the emancipation of the slaves in the District of Columbia, and by his repeated votes for the famous Wilmot Proviso, intended to exclude slavery from the Territories acquired from Mexico. But when, at the expiration of his term, in March, 1849, he left his seat, he gloomily despaired of ever seeing the day when the cause nearest to his heart would be rightly grasped by the people, and when he would be able to render any service to his country in solving the great problem. Nor had his career as a member of Congress in any sense been such as to gratify his ambition. Indeed, if he ever had any belief in a great destiny for himself, it must have been weak at that period; for he actually sought to obtain from the new Whig President, General Taylor, the place of Commissioner of the General Land Office; willing to bury himself in one of the administrative bureaus of the government. Fortunately for the country, he failed; and no less fortunately, when, later, the territorial governorship of Oregon was offered to him, Mrs. Lincoln's protest induced him to decline it. Returning to Springfield, he gave himself with renewed zest to his law practice, acquiesced in the Compromise of 1850 with reluctance and a mental reservation, supported in the Presidential campaign of 1852 the Whig candidate in some spiritless speeches, and took but a languid interest in the politics of the day. But just then his time was drawing near.
The peace promised, and apparently inaugurated, by the Compromise of 1850 was rudely broken by the introduction of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill in 1854. The repeal of the Missouri Compromise, opening the Territories of the United States, the heritage of coming generations, to the invasion of slavery, suddenly revealed the whole significance of the slavery question to the people of the free States, and thrust itself into the politics of the country as the paramount issue. Something like an electric shock flashed through the North. Men who but a short time before had been absorbed by their business pursuits, and deprecated all political agitation, were startled out of their security by a sudden alarm, and excitedly took sides. That restless trouble of conscience about slavery, which even in times of apparent repose had secretly disturbed the souls of Northern people, broke forth in an utterance louder than ever. The bonds of accustomed party allegiance gave way. Antislavery Democrats and antislavery Whigs felt themselves drawn together by a common overpowering sentiment, and soon they began to rally in a new organization. The Republican party sprang into being to meet the overruling call of the hour. Then Abraham Lincoln's time was come. He rapidly advanced to a position of conspicuous championship in the struggle. This, however, was not owing to his virtues and abilities alone. Indeed, the slavery question stirred his soul in its profoundest depths; it was, as one of his intimate friends said, "the only one on which he would become excited"; it called forth all his faculties and energies. Yet there were many others who, having long and arduously fought the antislavery battle in the popular assembly, or in the press, or in the halls of Congress, far surpassed him in prestige, and compared with whom he was still an obscure and untried man. His reputation, although highly honorable and well earned, had so far been essentially local. As a stump-speaker in Whig canvasses outside of his State he had attracted comparatively little attention; but in Illinois he had been recognized as one of the foremost men of the Whig party. Among the opponents of the Nebraska Bill he occupied in his State so important a position, that in 1856 he was the choice of a large majority of the "Anti-Nebraska men" in the Legislature for a seat in the Senate of the United States which then became vacant; and when he, an old Whig, could not obtain the votes of the Anti-Nebraska Democrats necessary to make a majority, he generously urged his friends to transfer their votes to Lyman Trumbull, who was then elected. Two years later, in the first national convention of the Republican party, the delegation from Illinois brought him forward as a candidate for the vice-presidency, and he received respectable support. Still, the name of Abraham Lincoln was not widely known beyond the boundaries of his own State. But now it was this local prominence in Illinois that put him in a position of peculiar advantage on the battlefield of national politics. In the assault on the Missouri Compromise which broke down all legal barriers to the spread of slavery Stephen Arnold Douglas was the ostensible leader and central figure; and Douglas was a Senator from Illinois, Lincoln's State. Douglas's national theatre of action was the Senate, but in his constituency in Illinois were the roots of his official position and power. What he did in the Senate he had to justify before the people of Illinois, in order to maintain himself in place; and in Illinois all eyes turned to Lincoln as Douglas's natural antagonist.
As very young men they had come to Illinois, Lincoln from Indiana, Douglas from Vermont, and had grown up together in public life, Douglas as a Democrat, Lincoln as a Whig. They had met first in Vandalia, in 1834, when Lincoln was in the Legislature and Douglas in the lobby; and again in 1836, both as members of the Legislature. Douglas, a very able politician, of the agile, combative, audacious, "pushing" sort, rose in political distinction with remarkable rapidity. In quick succession he became a member of the Legislature, a State's attorney, secretary of state, a judge on the supreme bench of Illinois, three times a Representative in Congress, and a Senator of the United States when only thirty-nine years old. In the National Democratic convention of 1852 he appeared even as an aspirant to the nomination for the Presidency, as the favorite of "young America," and received a respectable vote. He had far outstripped Lincoln in what is commonly called political success and in reputation. But it had frequently happened that in political campaigns Lincoln felt himself impelled, or was selected by his Whig friends, to answer Douglas's speeches; and thus the two were looked upon, in a large part of the State at least, as the representative combatants of their respective parties in the debates before popular meetings. As soon, therefore, as, after the passage of his Kansas-Nebraska Bill, Douglas returned to Illinois to defend his cause before his constituents, Lincoln, obeying not only his own impulse, but also general expectation, stepped forward as his principal opponent. Thus the struggle about the principles involved in the Kansas-Nebraska Bill, or, in a broader sense, the struggle between freedom and slavery, assumed in Illinois the outward form of a personal contest between Lincoln and Douglas; and, as it continued and became more animated, that personal contest in Illinois was watched with constantly increasing interest by the whole country. When, in 1858, Douglas's senatorial term being about to expire, Lincoln was formally designated by the Republican convention of Illinois as their candidate for the Senate, to take Douglas's place, and the two contestants agreed to debate the questions at issue face to face in a series of public meetings, the eyes of the whole American people were turned eagerly to that one point: and the spectacle reminded one of those lays of ancient times telling of two armies, in battle array, standing still to see their two principal champions fight out the contested cause between the lines in single combat.
Lincoln had then reached the full maturity of his powers. His equipment as a statesman did not embrace a comprehensive knowledge of public affairs. What he had studied he had indeed made his own, with the eager craving and that zealous tenacity characteristic of superior minds learning under difficulties. But his narrow opportunities and the unsteady life he had led during his younger years had not permitted the accumulation of large stores in his mind. It is true, in political campaigns he had occasionally spoken on the ostensible issues between the Whigs and the Democrats, the tariff, internal improvements, banks, and so on, but only in a perfunctory manner. Had he ever given much serious thought and study to these subjects, it is safe to assume that a mind so prolific of original conceits as his would certainly have produced some utterance upon them worth remembering. His soul had evidently never been deeply stirred by such topics. But when his moral nature was aroused, his brain developed an untiring activity until it had mastered all the knowledge within reach. As soon as the repeal of the Missouri Compromise had thrust the slavery question into politics as the paramount issue, Lincoln plunged into an arduous study of all its legal, historical, and moral aspects, and then his mind became a complete arsenal of argument. His rich natural gifts, trained by long and varied practice, had made him an orator of rare persuasiveness. In his immature days, he had pleased himself for a short period with that inflated, high-flown style which, among the uncultivated, passes for "beautiful speaking." His inborn truthfulness and his artistic instinct soon overcame that aberration and revealed to him the noble beauty and strength of simplicity. He possessed an uncommon power of clear and compact statement, which might have reminded those who knew the story of his early youth of the efforts of the poor boy, when he copied his compositions from the scraped wooden shovel, carefully to trim his expressions in order to save paper. His language had the energy of honest directness and he was a master of logical lucidity. He loved to point and enliven his reasoning by humorous illustrations, usually anecdotes of Western life, of which he had an inexhaustible store at his command. These anecdotes had not seldom a flavor of rustic robustness about them, but he used them with great effect, while amusing the audience, to give life to an abstraction, to explode an absurdity, to clinch an argument, to drive home an admonition. The natural kindliness of his tone, softening prejudice and disarming partisan rancor, would often open to his reasoning a way into minds most unwilling to receive it.
Yet his greatest power consisted in the charm of his individuality. That charm did not, in the ordinary way, appeal to the ear or to the eye. His voice was not melodious; rather shrill and piercing, especially when it rose to its high treble in moments of great animation. His figure was unhandsome, and the action of his unwieldy limbs awkward. He commanded none of the outward graces of oratory as they are commonly understood. His charm was of a different kind. It flowed from the rare depth and genuineness of his convictions and his sympathetic feelings. Sympathy was the strongest element in his nature. One of his biographers, who knew him before he became President, says: "Lincoln's compassion might be stirred deeply by an object present, but never by an object absent and unseen. In the former case he would most likely extend relief, with little inquiry into the merits of the case, because, as he expressed it himself, it `took a pain out of his own heart.'" Only half of this is correct. It is certainly true that he could not witness any individual distress or oppression, or any kind of suffering, without feeling a pang of pain himself, and that by relieving as much as he could the suffering of others he put an end to his own. This compassionate impulse to help he felt not only for human beings, but for every living creature. As in his boyhood he angrily reproved the boys who tormented a wood turtle by putting a burning coal on its back, so, we are told, he would, when a mature man, on a journey, dismount from his buggy and wade waist-deep in mire to rescue a pig struggling in a swamp. Indeed, appeals to his compassion were so irresistible to him, and he felt it so difficult to refuse anything when his refusal could give pain, that he himself sometimes spoke of his inability to say "no" as a positive weakness. But that certainly does not prove that his compassionate feeling was confined to individual cases of suffering witnessed with his own eyes. As the boy was moved by the aspect of the tortured wood turtle to compose an essay against cruelty to animals in general, so the aspect of other cases of suffering and wrong wrought up his moral nature, and set his mind to work against cruelty, injustice, and oppression in general.
As his sympathy went forth to others, it attracted others to him. Especially those whom he called the "plain people" felt themselves drawn to him by the instinctive feeling that he understood, esteemed, and appreciated them. He had grown up among the poor, the lowly, the ignorant. He never ceased to remember the good souls he had met among them, and the many kindnesses they had done him. Although in his mental development he had risen far above them, he never looked down upon them. How they felt and how they reasoned he knew, for so he had once felt and reasoned himself. How they could be moved he knew, for so he had once been moved himself and practised moving others. His mind was much larger than theirs, but it thoroughly comprehended theirs; and while he thought much farther than they, their thoughts were ever present to him. Nor had the visible distance between them grown as wide as his rise in the world would seem to have warranted. Much of his backwoods speech and manners still clung to him. Although he had become "Mr. Lincoln" to his later acquaintances, he was still "Abe" to the "Nats" and "Billys" and "Daves" of his youth; and their familiarity neither appeared unnatural to them, nor was it in the least awkward to him. He still told and enjoyed stories similar to those he had told and enjoyed in the Indiana settlement and at New Salem. His wants remained as modest as they had ever been; his domestic habits had by no means completely accommodated themselves to those of his more highborn wife; and though the "Kentucky jeans" apparel had long been dropped, his clothes of better material and better make would sit ill sorted on his gigantic limbs. His cotton umbrella, without a handle, and tied together with a coarse string to keep it from flapping, which he carried on his circuit rides, is said to be remembered still by some of his surviving neighbors. This rusticity of habit was utterly free from that affected contempt of refinement and comfort which self-made men sometimes carry into their more affluent circumstances. To Abraham Lincoln it was entirely natural, and all those who came into contact with him knew it to be so. In his ways of thinking and feeling he had become a gentleman in the highest sense, but the refining process had polished but little the outward form. The plain people, therefore, still considered "honest Abe Lincoln" one of themselves; and when they felt, which they no doubt frequently did, that his thoughts and aspirations moved in a sphere above their own, they were all the more proud of him, without any diminution of fellow-feeling. It was this relation of mutual sympathy and understanding between Lincoln and the plain people that gave him his peculiar power as a public man, and singularly fitted him, as we shall see, for that leadership which was preeminently required in the great crisis then coming on,—the leadership which indeed thinks and moves ahead of the masses, but always remains within sight and sympathetic touch of them.
He entered upon the campaign of 1858 better equipped than he had ever been before. He not only instinctively felt, but he had convinced himself by arduous study, that in this struggle against the spread of slavery he had right, justice, philosophy, the enlightened opinion of mankind, history, the Constitution, and good policy on his side. It was observed that after he began to discuss the slavery question his speeches were pitched in a much loftier key than his former oratorical efforts. While he remained fond of telling funny stories in private conversation, they disappeared more and more from his public discourse. He would still now and then point his argument with expressions of inimitable quaintness, and flash out rays of kindly humor and witty irony; but his general tone was serious, and rose sometimes to genuine solemnity. His masterly skill in dialectical thrust and parry, his wealth of knowledge, his power of reasoning and elevation of sentiment, disclosed in language of rare precision, strength, and beauty, not seldom astonished his old friends.
Neither of the two champions could have found a more formidable antagonist than each now met in the other. Douglas was by far the most conspicuous member of his party. His admirers had dubbed him "the Little Giant," contrasting in that nickname the greatness of his mind with the smallness of his body. But though of low stature, his broad-shouldered figure appeared uncommonly sturdy, and there was something lion-like in the squareness of his brow and jaw, and in the defiant shake of his long hair. His loud and persistent advocacy of territorial expansion, in the name of patriotism and "manifest destiny," had given him an enthusiastic following among the young and ardent. Great natural parts, a highly combative temperament, and long training had made him a debater unsurpassed in a Senate filled with able men. He could be as forceful in his appeals to patriotic feelings as he was fierce in denunciation and thoroughly skilled in all the baser tricks of parliamentary pugilism. While genial and rollicking in his social intercourse—the idol of the "boys" he felt himself one of the most renowned statesmen of his time, and would frequently meet his opponents with an overbearing haughtiness, as persons more to be pitied than to be feared. In his speech opening the campaign of 1858, he spoke of Lincoln, whom the Republicans had dared to advance as their candidate for "his" place in the Senate, with an air of patronizing if not contemptuous condescension, as "a kind, amiable, and intelligent gentleman and a good citizen." The Little Giant would have been pleased to pass off his antagonist as a tall dwarf. He knew Lincoln too well, however, to indulge himself seriously in such a delusion. But the political situation was at that moment in a curious tangle, and Douglas could expect to derive from the confusion great advantage over his opponent.
By the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, opening the Territories to the ingress of slavery, Douglas had pleased the South, but greatly alarmed the North. He had sought to conciliate Northern sentiment by appending to his Kansas-Nebraska Bill the declaration that its intent was "not to legislate slavery into any State or Territory, nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States." This he called "the great principle of popular sovereignty." When asked whether, under this act, the people of a Territory, before its admission as a State, would have the right to exclude slavery, he answered, "That is a question for the courts to decide." Then came the famous "Dred Scott decision," in which the Supreme Court held substantially that the right to hold slaves as property existed in the Territories by virtue of the Federal Constitution, and that this right could not be denied by any act of a territorial government. This, of course, denied the right of the people of any Territory to exclude slavery while they were in a territorial condition, and it alarmed the Northern people still more. Douglas recognized the binding force of the decision of the Supreme Court, at the same time maintaining, most illogically, that his great principle of popular sovereignty remained in force nevertheless. Meanwhile, the proslavery people of western Missouri, the so-called "border ruffians," had invaded Kansas, set up a constitutional convention, made a constitution of an extreme pro-slavery type, the "Lecompton Constitution," refused to submit it fairly to a vote of the people of Kansas, and then referred it to Congress for acceptance,—seeking thus to accomplish the admission of Kansas as a slave State. Had Douglas supported such a scheme, he would have lost all foothold in the North. In the name of popular sovereignty he loudly declared his opposition to the acceptance of any constitution not sanctioned by a formal popular vote. He "did not care," he said, "whether slavery be voted up or down," but there must be a fair vote of the people. Thus he drew upon himself the hostility of the Buchanan administration, which was controlled by the proslavery interest, but he saved his Northern following. More than this, not only did his Democratic admirers now call him "the true champion of freedom," but even some Republicans of large influence, prominent among them Horace Greeley, sympathizing with Douglas in his fight against the Lecompton Constitution, and hoping to detach him permanently from the proslavery interest and to force a lasting breach in the Democratic party, seriously advised the Republicans of Illinois to give up their opposition to Douglas, and to help re-elect him to the Senate. Lincoln was not of that opinion. He believed that great popular movements can succeed only when guided by their faithful friends, and that the antislavery cause could not safely be entrusted to the keeping of one who "did not care whether slavery be voted up or down." This opinion prevailed in Illinois; but the influences within the Republican party over which it prevailed yielded only a reluctant acquiescence, if they acquiesced at all, after having materially strengthened Douglas's position. Such was the situation of things when the campaign of 1858 between Lincoln and Douglas began.
Lincoln opened the campaign on his side at the convention which nominated him as the Republican candidate for the senatorship, with a memorable saying which sounded like a shout from the watchtower of history: "A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved. I do not expect the house to fall, but I expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward, till it shall become alike lawful in all the States,—old as well as new, North as well as South." Then he proceeded to point out that the Nebraska doctrine combined with the Dred Scott decision worked in the direction of making the nation "all slave." Here was the "irrepressible conflict" spoken of by Seward a short time later, in a speech made famous mainly by that phrase. If there was any new discovery in it, the right of priority was Lincoln's. This utterance proved not only his statesmanlike conception of the issue, but also, in his situation as a candidate, the firmness of his moral courage. The friends to whom he had read the draught of this speech before he delivered it warned him anxiously that its delivery might be fatal to his success in the election. This was shrewd advice, in the ordinary sense. While a slaveholder could threaten disunion with impunity, the mere suggestion that the existence of slavery was incompatible with freedom in the Union would hazard the political chances of any public man in the North. But Lincoln was inflexible. "It is true," said he, "and I will deliver it as written.... I would rather be defeated with these expressions in my speech held up and discussed before the people than be victorious without them." The statesman was right in his far-seeing judgment and his conscientious statement of the truth, but the practical politicians were also right in their prediction of the immediate effect. Douglas instantly seized upon the declaration that a house divided against itself cannot stand as the main objective point of his attack, interpreting it as an incitement to a "relentless sectional war," and there is no doubt that the persistent reiteration of this charge served to frighten not a few timid souls.
Lincoln constantly endeavored to bring the moral and philosophical side of the subject to the foreground. "Slavery is wrong" was the keynote of all his speeches. To Douglas's glittering sophism that the right of the people of a Territory to have slavery or not, as they might desire, was in accordance with the principle of true popular sovereignty, he made the pointed answer: "Then true popular sovereignty, according to Senator Douglas, means that, when one man makes another man his slave, no third man shall be allowed to object." To Douglas's argument that the principle which demanded that the people of a Territory should be permitted to choose whether they would have slavery or not "originated when God made man, and placed good and evil before him, allowing him to choose upon his own responsibility," Lincoln solemnly replied: "No; God—did not place good and evil before man, telling him to make his choice. On the contrary, God did tell him there was one tree of the fruit of which he should not eat, upon pain of death." He did not, however, place himself on the most advanced ground taken by the radical anti-slavery men. He admitted that, under the Constitution, "the Southern people were entitled to a Congressional fugitive slave law," although he did not approve the fugitive slave law then existing. He declared also that, if slavery were kept out of the Territories during their territorial existence, as it should be, and if then the people of any Territory, having a fair chance and a clear field, should do such an extraordinary thing as to adopt a slave constitution, uninfluenced by the actual presence of the institution among them, he saw no alternative but to admit such a Territory into the Union. He declared further that, while he should be exceedingly glad to see slavery abolished in the District of Columbia, he would, as a member of Congress, with his present views, not endeavor to bring on that abolition except on condition that emancipation be gradual, that it be approved by the decision of a majority of voters in the District, and that compensation be made to unwilling owners. On every available occasion, he pronounced himself in favor of the deportation and colonization of the blacks, of course with their consent. He repeatedly disavowed any wish on his part to have social and political equality established between whites and blacks. On this point he summed up his views in a reply to Douglas's assertion that the Declaration of Independence, in speaking of all men as being created equal, did not include the negroes, saying: "I do not understand the Declaration of Independence to mean that all men were created equal in all respects. They are not equal in color. But I believe that it does mean to declare that all men are equal in some respects; they are equal in their right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness."
With regard to some of these subjects Lincoln modified his position at a later period, and it has been suggested that he would have professed more advanced principles in his debates with Douglas, had he not feared thereby to lose votes. This view can hardly be sustained. Lincoln had the courage of his opinions, but he was not a radical. The man who risked his election by delivering, against the urgent protest of his friends, the speech about "the house divided against itself" would not have shrunk from the expression of more extreme views, had he really entertained them. It is only fair to assume that he said what at the time he really thought, and that if, subsequently, his opinions changed, it was owing to new conceptions of good policy and of duty brought forth by an entirely new set of circumstances and exigencies. It is characteristic that he continued to adhere to the impracticable colonization plan even after the Emancipation Proclamation had already been issued.
But in this contest Lincoln proved himself not only a debater, but also a political strategist of the first order. The "kind, amiable, and intelligent gentleman," as Douglas had been pleased to call him, was by no means as harmless as a dove. He possessed an uncommon share of that worldly shrewdness which not seldom goes with genuine simplicity of character; and the political experience gathered in the Legislature and in Congress, and in many election campaigns, added to his keen intuitions, had made him as far-sighted a judge of the probable effects of a public man's sayings or doings upon the popular mind, and as accurate a calculator in estimating political chances and forecasting results, as could be found among the party managers in Illinois. And now he perceived keenly the ugly dilemma in which Douglas found himself, between the Dred Scott decision, which declared the right to hold slaves to exist in the Territories by virtue of the Federal Constitution, and his "great principle of popular sovereignty," according to which the people of a Territory, if they saw fit, were to have the right to exclude slavery therefrom. Douglas was twisting and squirming to the best of his ability to avoid the admission that the two were incompatible. The question then presented itself if it would be good policy for Lincoln to force Douglas to a clear expression of his opinion as to whether, the Dred Scott decision notwithstanding, "the people of a Territory could in any lawful way exclude slavery from its limits prior to the formation of a State constitution." Lincoln foresaw and predicted what Douglas would answer: that slavery could not exist in a Territory unless the people desired it and gave it protection by territorial legislation. In an improvised caucus the policy of pressing the interrogatory on Douglas was discussed. Lincoln's friends unanimously advised against it, because the answer foreseen would sufficiently commend Douglas to the people of Illinois to insure his re-election to the Senate. But Lincoln persisted. "I am after larger game," said he. "If Douglas so answers, he can never be President, and the battle of 1860 is worth a hundred of this." The interrogatory was pressed upon Douglas, and Douglas did answer that, no matter what the decision of the Supreme Court might be on the abstract question, the people of a Territory had the lawful means to introduce or exclude slavery by territorial legislation friendly or unfriendly to the institution. Lincoln found it easy to show the absurdity of the proposition that, if slavery were admitted to exist of right in the Territories by virtue of the supreme law, the Federal Constitution, it could be kept out or expelled by an inferior law, one made by a territorial Legislature. Again the judgment of the politicians, having only the nearest object in view, proved correct: Douglas was reelected to the Senate. But Lincoln's judgment proved correct also: Douglas, by resorting to the expedient of his "unfriendly legislation doctrine," forfeited his last chance of becoming President of the United States. He might have hoped to win, by sufficient atonement, his pardon from the South for his opposition to the Lecompton Constitution; but that he taught the people of the Territories a trick by which they could defeat what the proslavery men considered a constitutional right, and that he called that trick lawful, this the slave power would never forgive. The breach between the Southern and the Northern Democracy was thenceforth irremediable and fatal.
The Presidential election of 1860 approached. The struggle in Kansas, and the debates in Congress which accompanied it, and which not unfrequently provoked violent outbursts, continually stirred the popular excitement. Within the Democratic party raged the war of factions. The national Democratic convention met at Charleston on the 23d of April, 1860. After a struggle of ten days between the adherents and the opponents of Douglas, during which the delegates from the cotton States had withdrawn, the convention adjourned without having nominated any candidates, to meet again in Baltimore on the 18th of June. There was no prospect, however, of reconciling the hostile elements. It appeared very probable that the Baltimore convention would nominate Douglas, while the seceding Southern Democrats would set up a candidate of their own, representing extreme proslavery principles.
Meanwhile, the national Republican convention assembled at Chicago on the 16th of May, full of enthusiasm and hope. The situation was easily understood. The Democrats would have the South. In order to succeed in the election, the Republicans had to win, in addition to the States carried by Fremont in 1856, those that were classed as "doubtful,"—New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Indiana, or Illinois in the place of either New Jersey or Indiana. The most eminent Republican statesmen and leaders of the time thought of for the Presidency were Seward and Chase, both regarded as belonging to the more advanced order of antislavery men. Of the two, Seward had the largest following, mainly from New York, New England, and the Northwest. Cautious politicians doubted seriously whether Seward, to whom some phrases in his speeches had undeservedly given the reputation of a reckless radical, would be able to command the whole Republican vote in the doubtful States. Besides, during his long public career he had made enemies. It was evident that those who thought Seward's nomination too hazardous an experiment would consider Chase unavailable for the same reason. They would then look round for an "available" man; and among the "available" men Abraham Lincoln was easily discovered to stand foremost. His great debate with Douglas had given him a national reputation. The people of the East being eager to see the hero of so dramatic a contest, he had been induced to visit several Eastern cities, and had astonished and delighted large and distinguished audiences with speeches of singular power and originality. An address delivered by him in the Cooper Institute in New York, before an audience containing a large number of important persons, was then, and has ever since been, especially praised as one of the most logical and convincing political speeches ever made in this country. The people of the West had grown proud of him as a distinctively Western great man, and his popularity at home had some peculiar features which could be expected to exercise a potent charm. Nor was Lincoln's name as that of an available candidate left to the chance of accidental discovery. It is indeed not probable that he thought of himself as a Presidential possibility, during his contest with Douglas for the senatorship. As late as April, 1859, he had written to a friend who had approached him on the subject that he did not think himself fit for the Presidency. The Vice-Presidency was then the limit of his ambition. But some of his friends in Illinois took the matter seriously in hand, and Lincoln, after some hesitation, then formally authorized "the use of his name." The matter was managed with such energy and excellent judgment that, in the convention, he had not only the whole vote of Illinois to start with, but won votes on all sides without offending any rival. A large majority of the opponents of Seward went over to Abraham Lincoln, and gave him the nomination on the third ballot. As had been foreseen, Douglas was nominated by one wing of the Democratic party at Baltimore, while the extreme proslavery wing put Breckinridge into the field as its candidate. After a campaign conducted with the energy of genuine enthusiasm on the antislavery side the united Republicans defeated the divided Democrats, and Lincoln was elected President by a majority of fifty-seven votes in the electoral colleges.
The result of the election had hardly been declared when the disunion movement in the South, long threatened and carefully planned and prepared, broke out in the shape of open revolt, and nearly a month before Lincoln could be inaugurated as President of the United States seven Southern States had adopted ordinances of secession, formed an independent confederacy, framed a constitution for it, and elected Jefferson Davis its president, expecting the other slaveholding States soon to join them. On the 11th of February, 1861, Lincoln left Springfield for Washington; having, with characteristic simplicity, asked his law partner not to change the sign of the firm "Lincoln and Herndon" during the four years unavoidable absence of the senior partner, and having taken an affectionate and touching leave of his neighbors.
The situation which confronted the new President was appalling: the larger part of the South in open rebellion, the rest of the slaveholding States wavering preparing to follow; the revolt guided by determined, daring, and skillful leaders; the Southern people, apparently full of enthusiasm and military spirit, rushing to arms, some of the forts and arsenals already in their possession; the government of the Union, before the accession of the new President, in the hands of men some of whom actively sympathized with the revolt, while others were hampered by their traditional doctrines in dealing with it, and really gave it aid and comfort by their irresolute attitude; all the departments full of "Southern sympathizers" and honeycombed with disloyalty; the treasury empty, and the public credit at the lowest ebb; the arsenals ill supplied with arms, if not emptied by treacherous practices; the regular army of insignificant strength, dispersed over an immense surface, and deprived of some of its best officers by defection; the navy small and antiquated. But that was not all. The threat of disunion had so often been resorted to by the slave power in years gone by that most Northern people had ceased to believe in its seriousness. But, when disunion actually appeared as a stern reality, something like a chill swept through the whole Northern country. A cry for union and peace at any price rose on all sides. Democratic partisanship reiterated this cry with vociferous vehemence, and even many Republicans grew afraid of the victory they had just achieved at the ballot-box, and spoke of compromise. The country fairly resounded with the noise of "anticoercion meetings." Expressions of firm resolution from determined antislavery men were indeed not wanting, but they were for a while almost drowned by a bewildering confusion of discordant voices. Even this was not all. Potent influences in Europe, with an ill-concealed desire for the permanent disruption of the American Union, eagerly espoused the cause of the Southern seceders, and the two principal maritime powers of the Old World seemed only to be waiting for a favorable opportunity to lend them a helping hand.
This was the state of things to be mastered by "honest Abe Lincoln" when he took his seat in the Presidential chair,—"honest Abe Lincoln," who was so good-natured that he could not say "no"; the greatest achievement in whose life had been a debate on the slavery question; who had never been in any position of power; who was without the slightest experience of high executive duties, and who had only a speaking acquaintance with the men upon whose counsel and cooperation he was to depend. Nor was his accession to power under such circumstances greeted with general confidence even by the members of his party. While he had indeed won much popularity, many Republicans, especially among those who had advocated Seward's nomination for the Presidency, saw the simple "Illinois lawyer" take the reins of government with a feeling little short of dismay. The orators and journals of the opposition were ridiculing and lampooning him without measure. Many people actually wondered how such a man could dare to undertake a task which, as he himself had said to his neighbors in his parting speech, was "more difficult than that of Washington himself had been."
But Lincoln brought to that task, aside from other uncommon qualities, the first requisite,—an intuitive comprehension of its nature. While he did not indulge in the delusion that the Union could be maintained or restored without a conflict of arms, he could indeed not foresee all the problems he would have to solve. He instinctively understood, however, by what means that conflict would have to be conducted by the government of a democracy. He knew that the impending war, whether great or small, would not be like a foreign war, exciting a united national enthusiasm, but a civil war, likely to fan to uncommon heat the animosities of party even in the localities controlled by the government; that this war would have to be carried on not by means of a ready-made machinery, ruled by an undisputed, absolute will, but by means to be furnished by the voluntary action of the people:—armies to be formed by voluntary enlistments; large sums of money to be raised by the people, through representatives, voluntarily taxing themselves; trust of extraordinary power to be voluntarily granted; and war measures, not seldom restricting the rights and liberties to which the citizen was accustomed, to be voluntarily accepted and submitted to by the people, or at least a large majority of them; and that this would have to be kept up not merely during a short period of enthusiastic excitement; but possibly through weary years of alternating success and disaster, hope and despondency. He knew that in order to steer this government by public opinion successfully through all the confusion created by the prejudices and doubts and differences of sentiment distracting the popular mind, and so to propitiate, inspire, mould, organize, unite, and guide the popular will that it might give forth all the means required for the performance of his great task, he would have to take into account all the influences strongly affecting the current of popular thought and feeling, and to direct while appearing to obey.
This was the kind of leadership he intuitively conceived to be needed when a free people were to be led forward en masse to overcome a great common danger under circumstances of appalling difficulty, the leadership which does not dash ahead with brilliant daring, no matter who follows, but which is intent upon rallying all the available forces, gathering in the stragglers, closing up the column, so that the front may advance well supported. For this leadership Abraham Lincoln was admirably fitted, better than any other American statesman of his day; for he understood the plain people, with all their loves and hates, their prejudices and their noble impulses, their weaknesses and their strength, as he understood himself, and his sympathetic nature was apt to draw their sympathy to him.
His inaugural address foreshadowed his official course in characteristic manner. Although yielding nothing in point of principle, it was by no means a flaming antislavery manifesto, such as would have pleased the more ardent Republicans. It was rather the entreaty of a sorrowing father speaking to his wayward children. In the kindliest language he pointed out to the secessionists how ill advised their attempt at disunion was, and why, for their own sakes, they should desist. Almost plaintively, he told them that, while it was not their duty to destroy the Union, it was his sworn duty to preserve it; that the least he could do, under the obligations of his oath, was to possess and hold the property of the United States; that he hoped to do this peaceably; that he abhorred war for any purpose, and that they would have none unless they themselves were the aggressors. It was a masterpiece of persuasiveness, and while Lincoln had accepted many valuable amendments suggested by Seward, it was essentially his own. Probably Lincoln himself did not expect his inaugural address to have any effect upon the secessionists, for he must have known them to be resolved upon disunion at any cost. But it was an appeal to the wavering minds in the North, and upon them it made a profound impression. Every candid man, however timid and halting, had to admit that the President was bound by his oath to do his duty; that under that oath he could do no less than he said he would do; that if the secessionists resisted such an appeal as the President had made, they were bent upon mischief, and that the government must be supported against them. The partisan sympathy with the Southern insurrection which still existed in the North did indeed not disappear, but it diminished perceptibly under the influence of such reasoning. Those who still resisted it did so at the risk of appearing unpatriotic.
It must not be supposed, however, that Lincoln at once succeeded in pleasing everybody, even among his friends,—even among those nearest to him. In selecting his cabinet, which he did substantially before he left Springfield for Washington, he thought it wise to call to his assistance the strong men of his party, especially those who had given evidence of the support they commanded as his competitors in the Chicago convention. In them he found at the same time representatives of the different shades of opinion within the party, and of the different elements—former Whigs and former Democrats—from which the party had recruited itself. This was sound policy under the circumstances. It might indeed have been foreseen that among the members of a cabinet so composed, troublesome disagreements and rivalries would break out. But it was better for the President to have these strong and ambitious men near him as his co-operators than to have them as his critics in Congress, where their differences might have been composed in a common opposition to him. As members of his cabinet he could hope to control them, and to keep them busily employed in the service of a common purpose, if he had the strength to do so. Whether he did possess this strength was soon tested by a singularly rude trial.
There can be no doubt that the foremost members of his cabinet, Seward and Chase, the most eminent Republican statesmen, had felt themselves wronged by their party when in its national convention it preferred to them for the Presidency a man whom, not unnaturally, they thought greatly their inferior in ability and experience as well as in service. The soreness of that disappointment was intensified when they saw this Western man in the White House, with so much of rustic manner and speech as still clung to him, meeting his fellow-citizens, high and low, on a footing of equality, with the simplicity of his good nature unburdened by any conventional dignity of deportment, and dealing with the great business of state in an easy-going, unmethodical, and apparently somewhat irreverent way. They did not understand such a man. Especially Seward, who, as Secretary of State, considered himself next to the Chief Executive, and who quickly accustomed himself to giving orders and making arrangements upon his own motion, thought it necessary that he should rescue the direction of public affairs from hands so unskilled, and take full charge of them himself. At the end of the first month of the administration he submitted a "memorandum" to President Lincoln, which has been first brought to light by Nicolay and Hay, and is one of their most valuable contributions to the history of those days. In that paper Seward actually told the President that at the end of a month's administration the government was still without a policy, either domestic or foreign; that the slavery question should be eliminated from the struggle about the Union; that the matter of the maintenance of the forts and other possessions in the South should be decided with that view; that explanations should be demanded categorically from the governments of Spain and France, which were then preparing, one for the annexation of San Domingo, and both for the invasion of Mexico; that if no satisfactory explanations were received war should be declared against Spain and France by the United States; that explanations should also be sought from Russia and Great Britain, and a vigorous continental spirit of independence against European intervention be aroused all over the American continent; that this policy should be incessantly pursued and directed by somebody; that either the President should devote himself entirely to it, or devolve the direction on some member of his cabinet, whereupon all debate on this policy must end.
This could be understood only as a formal demand that the President should acknowledge his own incompetency to perform his duties, content himself with the amusement of distributing post-offices, and resign his power as to all important affairs into the hands of his Secretary of State. It seems to-day incomprehensible how a statesman of Seward's calibre could at that period conceive a plan of policy in which the slavery question had no place; a policy which rested upon the utterly delusive assumption that the secessionists, who had already formed their Southern Confederacy and were with stern resolution preparing to fight for its independence, could be hoodwinked back into the Union by some sentimental demonstration against European interference; a policy which, at that critical moment, would have involved the Union in a foreign war, thus inviting foreign intervention in favor of the Southern Confederacy, and increasing tenfold its chances in the struggle for independence. But it is equally incomprehensible how Seward could fail to see that this demand of an unconditional surrender was a mortal insult to the head of the government, and that by putting his proposition on paper he delivered himself into the hands of the very man he had insulted; for, had Lincoln, as most Presidents would have done, instantly dismissed Seward, and published the true reason for that dismissal, it would inevitably have been the end of Seward's career. But Lincoln did what not many of the noblest and greatest men in history would have been noble and great enough to do. He considered that Seward was still capable of rendering great service to his country in the place in which he was, if rightly controlled. He ignored the insult, but firmly established his superiority. In his reply, which he forthwith despatched, he told Seward that the administration had a domestic policy as laid down in the inaugural address with Seward's approval; that it had a foreign policy as traced in Seward's despatches with the President's approval; that if any policy was to be maintained or changed, he, the President, was to direct that on his responsibility; and that in performing that duty the President had a right to the advice of his secretaries. Seward's fantastic schemes of foreign war and continental policies Lincoln brushed aside by passing them over in silence. Nothing more was said. Seward must have felt that he was at the mercy of a superior man; that his offensive proposition had been generously pardoned as a temporary aberration of a great mind, and that he could atone for it only by devoted personal loyalty. This he did. He was thoroughly subdued, and thenceforth submitted to Lincoln his despatches for revision and amendment without a murmur. The war with European nations was no longer thought of; the slavery question found in due time its proper place in the struggle for the Union; and when, at a later period, the dismissal of Seward was demanded by dissatisfied senators, who attributed to him the shortcomings of the administration, Lincoln stood stoutly by his faithful Secretary of State.
Chase, the Secretary of the Treasury, a man of superb presence, of eminent ability and ardent patriotism, of great natural dignity and a certain outward coldness of manner, which made him appear more difficult of approach than he really was, did not permit his disappointment to burst out in such extravagant demonstrations. But Lincoln's ways were so essentially different from his that they never became quite intelligible, and certainly not congenial to him. It might, perhaps, have been better had there been, at the beginning of the administration, some decided clash between Lincoln and Chase, as there was between Lincoln and Seward, to bring on a full mutual explanation, and to make Chase appreciate the real seriousness of Lincoln's nature. But, as it was, their relations always remained somewhat formal, and Chase never felt quite at ease under a chief whom he could not understand, and whose character and powers he never learned to esteem at their true value. At the same time, he devoted himself zealously to the duties of his department, and did the country arduous service under circumstances of extreme difficulty. Nobody recognized this more heartily than Lincoln himself, and they managed to work together until near the end of Lincoln's first Presidential term, when Chase, after some disagreements concerning appointments to office, resigned from the treasury; and, after Taney's death, the President made him Chief Justice.
The rest of the cabinet consisted of men of less eminence, who subordinated themselves more easily. In January, 1862, Lincoln found it necessary to bow Cameron out of the war office, and to put in his place Edwin M. Stanton, a man of intensely practical mind, vehement impulses, fierce positiveness, ruthless energy, immense working power, lofty patriotism, and severest devotion to duty. He accepted the war office not as a partisan, for he had never been a Republican, but only to do all he could in "helping to save the country." The manner in which Lincoln succeeded in taming this lion to his will, by frankly recognizing his great qualities, by giving him the most generous confidence, by aiding him in his work to the full of his power, by kindly concession or affectionate persuasiveness in cases of differing opinions, or, when it was necessary, by firm assertions of superior authority, bears the highest testimony to his skill in the management of men. Stanton, who had entered the service with rather a mean opinion of Lincoln's character and capacity, became one of his warmest, most devoted, and most admiring friends, and with none of his secretaries was Lincoln's intercourse more intimate. To take advice with candid readiness, and to weigh it without any pride of his own opinion, was one of Lincoln's preeminent virtues; but he had not long presided over his cabinet council when his was felt by all its members to be the ruling mind.
The cautious policy foreshadowed in his inaugural address, and pursued during the first period of the civil war, was far from satisfying all his party friends. The ardent spirits among the Union men thought that the whole North should at once be called to arms, to crush the rebellion by one powerful blow. The ardent spirits among the antislavery men insisted that, slavery having brought forth the rebellion, this powerful blow should at once be aimed at slavery. Both complained that the administration was spiritless, undecided, and lamentably slow in its proceedings. Lincoln reasoned otherwise. The ways of thinking and feeling of the masses, of the plain people, were constantly present to his mind. The masses, the plain people, had to furnish the men for the fighting, if fighting was to be done. He believed that the plain people would be ready to fight when it clearly appeared necessary, and that they would feel that necessity when they felt themselves attacked. He therefore waited until the enemies of the Union struck the first blow. As soon as, on the 12th of April, 1861, the first gun was fired in Charleston harbor on the Union flag upon Fort Sumter, the call was sounded, and the Northern people rushed to arms.
Lincoln knew that the plain people were now indeed ready to fight in defence of the Union, but not yet ready to fight for the destruction of slavery. He declared openly that he had a right to summon the people to fight for the Union, but not to summon them to fight for the abolition of slavery as a primary object; and this declaration gave him numberless soldiers for the Union who at that period would have hesitated to do battle against the institution of slavery. For a time he succeeded in rendering harmless the cry of the partisan opposition that the Republican administration were perverting the war for the Union into an "abolition war." But when he went so far as to countermand the acts of some generals in the field, looking to the emancipation of the slaves in the districts covered by their commands, loud complaints arose from earnest antislavery men, who accused the President of turning his back upon the antislavery cause. Many of these antislavery men will now, after a calm retrospect, be willing to admit that it would have been a hazardous policy to endanger, by precipitating a demonstrative fight against slavery, the success of the struggle for the Union.
Lincoln's views and feelings concerning slavery had not changed. Those who conversed with him intimately upon the subject at that period know that he did not expect slavery long to survive the triumph of the Union, even if it were not immediately destroyed by the war. In this he was right. Had the Union armies achieved a decisive victory in an early period of the conflict, and had the seceded States been received back with slavery, the "slave power" would then have been a defeated power, defeated in an attempt to carry out its most effective threat. It would have lost its prestige. Its menaces would have been hollow sound, and ceased to make any one afraid. It could no longer have hoped to expand, to maintain an equilibrium in any branch of Congress, and to control the government. The victorious free States would have largely overbalanced it. It would no longer have been able to withstand the onset of a hostile age. It could no longer have ruled,—and slavery had to rule in order to live. It would have lingered for a while, but it would surely have been "in the course of ultimate extinction." A prolonged war precipitated the destruction of slavery; a short war might only have prolonged its death struggle. Lincoln saw this clearly; but he saw also that, in a protracted death struggle, it might still have kept disloyal sentiments alive, bred distracting commotions, and caused great mischief to the country. He therefore hoped that slavery would not survive the war.
But the question how he could rightfully employ his power to bring on its speedy destruction was to him not a question of mere sentiment. He himself set forth his reasoning upon it, at a later period, in one of his inimitable letters. "I am naturally antislavery," said he. "If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong. I cannot remember the time when I did not so think and feel. And yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act upon that judgment and feeling. It was in the oath I took that I would, to the best of my ability, preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution of the United States. I could not take the office without taking the oath. Nor was it my view that I might take an oath to get power, and break the oath in using that power. I understood, too, that, in ordinary civil administration, this oath even forbade me practically to indulge my private abstract judgment on the moral question of slavery. I did understand, however, also, that my oath imposed upon me the duty of preserving, to the best of my ability, by every indispensable means, that government, that nation, of which the Constitution was the organic law. I could not feel that, to the best of my ability, I had even tied to preserve the Constitution—if, to save slavery, or any minor matter, I should permit the wreck of government, country, and Constitution all together." In other words, if the salvation of the government, the Constitution, and the Union demanded the destruction of slavery, he felt it to be not only his right, but his sworn duty to destroy it. Its destruction became a necessity of the war for the Union.
As the war dragged on and disaster followed disaster, the sense of that necessity steadily grew upon him. Early in 1862, as some of his friends well remember, he saw, what Seward seemed not to see, that to give the war for the Union an antislavery character was the surest means to prevent the recognition of the Southern Confederacy as an independent nation by European powers; that, slavery being abhorred by the moral sense of civilized mankind, no European government would dare to offer so gross an insult to the public opinion of its people as openly to favor the creation of a state founded upon slavery to the prejudice of an existing nation fighting against slavery. He saw also that slavery untouched was to the rebellion an element of power, and that in order to overcome that power it was necessary to turn it into an element of weakness. Still, he felt no assurance that the plain people were prepared for so radical a measure as the emancipation of the slaves by act of the government, and he anxiously considered that, if they were not, this great step might, by exciting dissension at the North, injure the cause of the Union in one quarter more than it would help it in another. He heartily welcomed an effort made in New York to mould and stimulate public sentiment on the slavery question by public meetings boldly pronouncing for emancipation. At the same time he himself cautiously advanced with a recommendation, expressed in a special message to Congress, that the United States should co-operate with any State which might adopt the gradual abolishment of slavery, giving such State pecuniary aid to compensate the former owners of emancipated slaves. The discussion was started, and spread rapidly. Congress adopted the resolution recommended, and soon went a step farther in passing a bill to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia. The plain people began to look at emancipation on a larger scale as a thing to be considered seriously by patriotic citizens; and soon Lincoln thought that the time was ripe, and that the edict of freedom could be ventured upon without danger of serious confusion in the Union ranks.
The failure of McClellan's movement upon Richmond increased immensely the prestige of the enemy. The need of some great act to stimulate the vitality of the Union cause seemed to grow daily more pressing. On July 21, 1862, Lincoln surprised his cabinet with the draught of a proclamation declaring free the slaves in all the States that should be still in rebellion against the United States on the 1st of January,1863. As to the matter itself he announced that he had fully made up his mind; he invited advice only concerning the form and the time of publication. Seward suggested that the proclamation, if then brought out, amidst disaster and distress, would sound like the last shriek of a perishing cause. Lincoln accepted the suggestion, and the proclamation was postponed. Another defeat followed, the second at Bull Run. But when, after that battle, the Confederate army, under Lee, crossed the Potomac and invaded Maryland, Lincoln vowed in his heart that, if the Union army were now blessed with success, the decree of freedom should surely be issued. The victory of Antietam was won on September 17, and the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation came forth on the a 22d. It was Lincoln's own resolution and act; but practically it bound the nation, and permitted no step backward. In spite of its limitations, it was the actual abolition of slavery. Thus he wrote his name upon the books of history with the title dearest to his heart, the liberator of the slave.
It is true, the great proclamation, which stamped the war as one for "union and freedom," did not at once mark the turning of the tide on the field of military operations. There were more disasters, Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville. But with Gettysburg and Vicksburg the whole aspect of the war changed. Step by step, now more slowly, then more rapidly, but with increasing steadiness, the flag of the Union advanced from field to field toward the final consummation. The decree of emancipation was naturally followed by the enlistment of emancipated negroes in the Union armies. This measure had a anther reaching effect than merely giving the Union armies an increased supply of men. The laboring force of the rebellion was hopelessly disorganized. The war became like a problem of arithmetic. As the Union armies pushed forward, the area from which the Southern Confederacy could draw recruits and supplies constantly grew smaller, while the area from which the Union recruited its strength constantly grew larger; and everywhere, even within the Southern lines, the Union had its allies. The fate of the rebellion was then virtually decided; but it still required much bloody work to convince the brave warriors who fought for it that they were really beaten.
Neither did the Emancipation Proclamation forthwith command universal assent among the people who were loyal to the Union. There were even signs of a reaction against the administration in the fall elections of 1862, seemingly justifying the opinion, entertained by many, that the President had really anticipated the development of popular feeling. The cry that the war for the Union had been turned into an "abolition war" was raised again by the opposition, and more loudly than ever. But the good sense and patriotic instincts of the plain people gradually marshalled themselves on Lincoln's side, and he lost no opportunity to help on this process by personal argument and admonition. There never has been a President in such constant and active contact with the public opinion of the country, as there never has been a President who, while at the head of the government, remained so near to the people. Beyond the circle of those who had long known him the feeling steadily grew that the man in the White House was "honest Abe Lincoln" still, and that every citizen might approach him with complaint, expostulation, or advice, without danger of meeting a rebuff from power-proud authority, or humiliating condescension; and this privilege was used by so many and with such unsparing freedom that only superhuman patience could have endured it all. There are men now living who would to-day read with amazement, if not regret, what they ventured to say or write to him. But Lincoln repelled no one whom he believed to speak to him in good faith and with patriotic purpose. No good advice would go unheeded. No candid criticism would offend him. No honest opposition, while it might pain him, would produce a lasting alienation of feeling between him and the opponent. It may truly be said that few men in power have ever been exposed to more daring attempts to direct their course, to severer censure of their acts, and to more cruel misrepresentation of their motives: And all this he met with that good-natured humor peculiarly his own, and with untiring effort to see the right and to impress it upon those who differed from him. The conversations he had and the correspondence he carried on upon matters of public interest, not only with men in official position, but with private citizens, were almost unceasing, and in a large number of public letters, written ostensibly to meetings, or committees, or persons of importance, he addressed himself directly to the popular mind. Most of these letters stand among the finest monuments of our political literature. Thus he presented the singular spectacle of a President who, in the midst of a great civil war, with unprecedented duties weighing upon him, was constantly in person debating the great features of his policy with the people.
While in this manner he exercised an ever-increasing influence upon the popular understanding, his sympathetic nature endeared him more and more to the popular heart. In vain did journals and speakers of the opposition represent him as a lightminded trifler, who amused himself with frivolous story-telling and coarse jokes, while the blood of the people was flowing in streams. The people knew that the man at the head of affairs, on whose haggard face the twinkle of humor so frequently changed into an expression of profoundest sadness, was more than any other deeply distressed by the suffering he witnessed; that he felt the pain of every wound that was inflicted on the battlefield, and the anguish of every woman or child who had lost husband or father; that whenever he could he was eager to alleviate sorrow, and that his mercy was never implored in vain. They looked to him as one who was with them and of them in all their hopes and fears, their joys and sorrows, who laughed with them and wept with them; and as his heart was theirs; so their hearts turned to him. His popularity was far different from that of Washington, who was revered with awe, or that of Jackson, the unconquerable hero, for whom party enthusiasm never grew weary of shouting. To Abraham Lincoln the people became bound by a genuine sentimental attachment. It was not a matter of respect, or confidence, or party pride, for this feeling spread far beyond the boundary lines of his party; it was an affair of the heart, independent of mere reasoning. When the soldiers in the field or their folks at home spoke of "Father Abraham," there was no cant in it. They felt that their President was really caring for them as a father would, and that they could go to him, every one of them, as they would go to a father, and talk to him of what troubled them, sure to find a willing ear and tender sympathy. Thus, their President, and his cause, and his endeavors, and his success gradually became to them almost matters of family concern. And this popularity carried him triumphantly through the Presidential election of 1864, in spite of an opposition within his own party which at first seemed very formidable.
Many of the radical antislavery men were never quite satisfied with Lincoln's ways of meeting the problems of the time. They were very earnest and mostly very able men, who had positive ideas as to "how this rebellion should be put down." They would not recognize the necessity of measuring the steps of the government according to the progress of opinion among the plain people. They criticised Lincoln's cautious management as irresolute, halting, lacking in definite purpose and in energy; he should not have delayed emancipation so long; he should not have confided important commands to men of doubtful views as to slavery; he should have authorized military commanders to set the slaves free as they went on; he dealt too leniently with unsuccessful generals; he should have put down all factious opposition with a strong hand instead of trying to pacify it; he should have given the people accomplished facts instead of arguing with them, and so on. It is true, these criticisms were not always entirely unfounded. Lincoln's policy had, with the virtues of democratic government, some of its weaknesses, which in the presence of pressing exigencies were apt to deprive governmental action of the necessary vigor; and his kindness of heart, his disposition always to respect the feelings of others, frequently made him recoil from anything like severity, even when severity was urgently called for. But many of his radical critics have since then revised their judgment sufficiently to admit that Lincoln's policy was, on the whole, the wisest and safest; that a policy of heroic methods, while it has sometimes accomplished great results, could in a democracy like ours be maintained only by constant success; that it would have quickly broken down under the weight of disaster; that it might have been successful from the start, had the Union, at the beginning of the conflict, had its Grants and Shermans and Sheridans, its Farraguts and Porters, fully matured at the head of its forces; but that, as the great commanders had to be evolved slowly from the developments of the war, constant success could not be counted upon, and it was best to follow a policy which was in friendly contact with the popular force, and therefore more fit to stand trial of misfortune on the battlefield. But at that period they thought differently, and their dissatisfaction with Lincoln's doings was greatly increased by the steps he took toward the reconstruction of rebel States then partially in possession of the Union forces.
In December, 1863, Lincoln issued an amnesty proclamation, offering pardon to all implicated in the rebellion, with certain specified exceptions, on condition of their taking and maintaining an oath to support the Constitution and obey the laws of the United States and the proclamations of the President with regard to slaves; and also promising that when, in any of the rebel States, a number of citizens equal to one tenth of the voters in 1860 should re-establish a state government in conformity with the oath above mentioned, such should be recognized by the Executive as the true government of the State. The proclamation seemed at first to be received with general favor. But soon another scheme of reconstruction, much more stringent in its provisions, was put forward in the House of Representatives by Henry Winter Davis. Benjamin Wade championed it in the Senate. It passed in the closing moments of the session in July, 1864, and Lincoln, instead of making it a law by his signature, embodied the text of it in a proclamation as a plan of reconstruction worthy of being earnestly considered. The differences of opinion concerning this subject had only intensified the feeling against Lincoln which had long been nursed among the radicals, and some of them openly declared their purpose of resisting his re-election to the Presidency. Similar sentiments were manifested by the advanced antislavery men of Missouri, who, in their hot faction-fight with the "conservatives" of that State, had not received from Lincoln the active support they demanded. Still another class of Union men, mainly in the East, gravely shook their heads when considering the question whether Lincoln should be re-elected. They were those who cherished in their minds an ideal of statesmanship and of personal bearing in high office with which, in their opinion, Lincoln's individuality was much out of accord. They were shocked when they heard him cap an argument upon grave affairs of state with a story about "a man out in Sangamon County,"—a story, to be sure, strikingly clinching his point, but sadly lacking in dignity. They could not understand the man who was capable, in opening a cabinet meeting, of reading to his secretaries a funny chapter from a recent book of Artemus Ward, with which in an unoccupied moment he had relieved his care-burdened mind, and who then solemnly informed the executive council that he had vowed in his heart to issue a proclamation emancipating the slaves as soon as God blessed the Union arms with another victory. They were alarmed at the weakness of a President who would indeed resist the urgent remonstrances of statesmen against his policy, but could not resist the prayer of an old woman for the pardon of a soldier who was sentenced to be shot for desertion. Such men, mostly sincere and ardent patriots, not only wished, but earnestly set to work, to prevent Lincoln's renomination. Not a few of them actually believed, in 1863, that, if the national convention of the Union party were held then, Lincoln would not be supported by the delegation of a single State. But when the convention met at Baltimore, in June, 1864, the voice of the people was heard. On the first ballot Lincoln received the votes of the delegations from all the States except Missouri; and even the Missourians turned over their votes to him before the result of the ballot was declared.
But even after his renomination the opposition to Lincoln within the ranks of the Union party did not subside. A convention, called by the dissatisfied radicals in Missouri, and favored by men of a similar way of thinking in other States, had been held already in May, and had nominated as its candidate for the Presidency General Fremont. He, indeed, did not attract a strong following, but opposition movements from different quarters appeared more formidable. Henry Winter Davis and Benjamin Wade assailed Lincoln in a flaming manifesto. Other Union men, of undoubted patriotism and high standing, persuaded themselves, and sought to persuade the people, that Lincoln's renomination was ill advised and dangerous to the Union cause. As the Democrats had put off their convention until the 29th of August, the Union party had, during the larger part of the summer, no opposing candidate and platform to attack, and the political campaign languished. Neither were the tidings from the theatre of war of a cheering character. The terrible losses suffered by Grant's army in the battles of the Wilderness spread general gloom. Sherman seemed for a while to be in a precarious position before Atlanta. The opposition to Lincoln within the Union party grew louder in its complaints and discouraging predictions. Earnest demands were heard that his candidacy should be withdrawn. Lincoln himself, not knowing how strongly the masses were attached to him, was haunted by dark forebodings of defeat. Then the scene suddenly changed as if by magic.
The Democrats, in their national convention, declared the war a failure, demanded, substantially, peace at any price, and nominated on such a platform General McClellan as their candidate. Their convention had hardly adjourned when the capture of Atlanta gave a new aspect to the military situation. It was like a sun-ray bursting through a dark cloud. The rank and file of the Union party rose with rapidly growing enthusiasm. The song "We are coming, Father Abraham, three hundred thousand strong," resounded all over the land. Long before the decisive day arrived, the result was beyond doubt, and Lincoln was re-elected President by overwhelming majorities. The election over even his severest critics found themselves forced to admit that Lincoln was the only possible candidate for the Union party in 1864, and that neither political combinations nor campaign speeches, nor even victories in the field, were needed to insure his success. The plain people had all the while been satisfied with Abraham Lincoln: they confided in him; they loved him; they felt themselves near to him; they saw personified in him the cause of Union and freedom; and they went to the ballot-box for him in their strength.
The hour of triumph called out the characteristic impulses of his nature. The opposition within the Union party had stung him to the quick. Now he had his opponents before him, baffled and humiliated. Not a moment did he lose to stretch out the hand of friendship to all. "Now that the election is over," he said, in response to a serenade, "may not all, having a common interest, reunite in a common effort to save our common country? For my own part, I have striven, and will strive, to place no obstacle in the way. So long as I have been here I have not willingly planted a thorn in any man's bosom. While I am deeply sensible to the high compliment of a re-election, it adds nothing to my satisfaction that any other man may be pained or disappointed by the result. May I ask those who were with me to join with me in the same spirit toward those who were against me?" This was Abraham Lincoln's character as tested in the furnace of prosperity.
The war was virtually decided, but not yet ended. Sherman was irresistibly carrying the Union flag through the South. Grant had his iron hand upon the ramparts of Richmond. The days of the Confederacy were evidently numbered. Only the last blow remained to be struck. Then Lincoln's second inauguration came, and with it his second inaugural address. Lincoln's famous "Gettysburg speech" has been much and justly admired. But far greater, as well as far more characteristic, was that inaugural in which he poured out the whole devotion and tenderness of his great soul. It had all the solemnity of a father's last admonition and blessing to his children before he lay down to die. These were its closing words: "Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled up by the bondman's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said, `The judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.' With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow and his orphan; to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations."
This was like a sacred poem. No American President had ever spoken words like these to the American people. America never had a President who found such words in the depth of his heart.
Now followed the closing scenes of the war. The Southern armies fought bravely to the last, but all in vain. Richmond fell. Lincoln himself entered the city on foot, accompanied only by a few officers and a squad of sailors who had rowed him ashore from the flotilla in the James River, a negro picked up on the way serving as a guide. Never had the world seen a more modest conqueror and a more characteristic triumphal procession, no army with banners and drums, only a throng of those who had been slaves, hastily run together, escorting the victorious chief into the capital of the vanquished foe. We are told that they pressed around him, kissed his hands and his garments, and shouted and danced for joy, while tears ran down the President's care-furrowed cheeks.
A few days more brought the surrender of Lee's army, and peace was assured. The people of the North were wild with joy. Everywhere festive guns were booming, bells pealing, the churches ringing with thanksgivings, and jubilant multitudes thronging the thoroughfares, when suddenly the news flashed over the land that Abraham Lincoln had been murdered. The people were stunned by the blow. Then a wail of sorrow went up such as America had never heard before. Thousands of Northern households grieved as if they had lost their dearest member. Many a Southern man cried out in his heart that his people had been robbed of their best friend in their humiliation and distress, when Abraham Lincoln was struck down. It was as if the tender affection which his countrymen bore him had inspired all nations with a common sentiment. All civilized mankind stood mourning around the coffin of the dead President. Many of those, here and abroad, who not long before had ridiculed and reviled him were among the first to hasten on with their flowers of eulogy, and in that universal chorus of lamentation and praise there was not a voice that did not tremble with genuine emotion. Never since Washington's death had there been such unanimity of judgment as to a man's virtues and greatness; and even Washington's death, although his name was held in greater reverence, did not touch so sympathetic a chord in the people's hearts.
Nor can it be said that this was owing to the tragic character of Lincoln's end. It is true, the death of this gentlest and most merciful of rulers by the hand of a mad fanatic was well apt to exalt him beyond his merits in the estimation of those who loved him, and to make his renown the object of peculiarly tender solicitude. But it is also true that the verdict pronounced upon him in those days has been affected little by time, and that historical inquiry has served rather to increase than to lessen the appreciation of his virtues, his abilities, his services. Giving the fullest measure of credit to his great ministers,—to Seward for his conduct of foreign affairs, to Chase for the management of the finances under terrible difficulties, to Stanton for the performance of his tremendous task as war secretary,—and readily acknowledging that without the skill and fortitude of the great commanders, and the heroism of the soldiers and sailors under them, success could not have been achieved, the historian still finds that Lincoln's judgment and will were by no means governed by those around him; that the most important steps were owing to his initiative; that his was the deciding and directing mind; and that it was pre-eminently he whose sagacity and whose character enlisted for the administration in its struggles the countenance, the sympathy, and the support of the people. It is found, even, that his judgment on military matters was astonishingly acute, and that the advice and instructions he gave to the generals commanding in the field would not seldom have done honor to the ablest of them. History, therefore, without overlooking, or palliating, or excusing any of his shortcomings or mistakes, continues to place him foremost among the saviours of the Union and the liberators of the slave. More than that, it awards to him the merit of having accomplished what but few political philosophers would have recognized as possible,—of leading the republic through four years of furious civil conflict without any serious detriment to its free institutions.
He was, indeed, while President, violently denounced by the opposition as a tyrant and a usurper, for having gone beyond his constitutional powers in authorizing or permitting the temporary suppression of newspapers, and in wantonly suspending the writ of habeas corpus and resorting to arbitrary arrests. Nobody should be blamed who, when such things are done, in good faith and from patriotic motives protests against them. In a republic, arbitrary stretches of power, even when demanded by necessity, should never be permitted to pass without a protest on the one hand, and without an apology on the other. It is well they did not so pass during our civil war. That arbitrary measures were resorted to is true. That they were resorted to most sparingly, and only when the government thought them absolutely required by the safety of the republic, will now hardly be denied. But certain it is that the history of the world does not furnish a single example of a government passing through so tremendous a crisis as our civil war was with so small a record of arbitrary acts, and so little interference with the ordinary course of law outside the field of military operations. No American President ever wielded such power as that which was thrust into Lincoln's hands. It is to be hoped that no American President ever will have to be entrusted with such power again. But no man was ever entrusted with it to whom its seductions were less dangerous than they proved to be to Abraham Lincoln. With scrupulous care he endeavored, even under the most trying circumstances, to remain strictly within the constitutional limitations of his authority; and whenever the boundary became indistinct, or when the dangers of the situation forced him to cross it, he was equally careful to mark his acts as exceptional measures, justifiable only by the imperative necessities of the civil war, so that they might not pass into history as precedents for similar acts in time of peace. It is an unquestionable fact that during the reconstruction period which followed the war, more things were done capable of serving as dangerous precedents than during the war itself. Thus it may truly be said of him not only that under his guidance the republic was saved from disruption and the country was purified of the blot of slavery, but that, during the stormiest and most perilous crisis in our history, he so conducted the government and so wielded his almost dictatorial power as to leave essentially intact our free institutions in all things that concern the rights and liberties of the citizens. He understood well the nature of the problem. In his first message to Congress he defined it in admirably pointed language: "Must a government be of necessity too strong for the liberties of its own people, or too weak to maintain its own existence? Is there in all republics this inherent weakness?" This question he answered in the name of the great American republic, as no man could have answered it better, with a triumphant "No...."
It has been said that Abraham Lincoln died at the right moment for his fame. However that may be, he had, at the time of his death, certainly not exhausted his usefulness to his country. He was probably the only man who could have guided the nation through the perplexities of the reconstruction period in such a manner as to prevent in the work of peace the revival of the passions of the war. He would indeed not have escaped serious controversy as to details of policy; but he could have weathered it far better than any other statesman of his time, for his prestige with the active politicians had been immensely strengthened by his triumphant re-election; and, what is more important, he would have been supported by the confidence of the victorious Northern people that he would do all to secure the safety of the Union and the rights of the emancipated negro, and at the same time by the confidence of the defeated Southern people that nothing would be done by him from motives of vindictiveness, or of unreasoning fanaticism, or of a selfish party spirit. "With malice toward none, with charity for all," the foremost of the victors would have personified in himself the genius of reconciliation.
He might have rendered the country a great service in another direction. A few days after the fall of Richmond, he pointed out to a friend the crowd of office-seekers besieging his door. "Look at that," said he. "Now we have conquered the rebellion, but here you see something that may become more dangerous to this republic than the rebellion itself." It is true, Lincoln as President did not profess what we now call civil service reform principles. He used the patronage of the government in many cases avowedly to reward party work, in many others to form combinations and to produce political effects advantageous to the Union cause, and in still others simply to put the right man into the right place. But in his endeavors to strengthen the Union cause, and in his search for able and useful men for public duties, he frequently went beyond the limits of his party, and gradually accustomed himself to the thought that, while party service had its value, considerations of the public interest were, as to appointments to office, of far greater consequence. Moreover, there had been such a mingling of different political elements in support of the Union during the civil war that Lincoln, standing at the head of that temporarily united motley mass, hardly felt himself, in the narrow sense of the term, a party man. And as he became strongly impressed with the dangers brought upon the republic by the use of public offices as party spoils, it is by no means improbable that, had he survived the all-absorbing crisis and found time to turn to other objects, one of the most important reforms of later days would have been pioneered by his powerful authority. This was not to be. But the measure of his achievements was full enough for immortality.
To the younger generation Abraham Lincoln has already become a half-mythical figure, which, in the haze of historic distance, grows to more and more heroic proportions, but also loses in distinctness of outline and feature. This is indeed the common lot of popular heroes; but the Lincoln legend will be more than ordinarily apt to become fanciful, as his individuality, assembling seemingly incongruous qualities and forces in a character at the same time grand and most lovable, was so unique, and his career so abounding in startling contrasts. As the state of society in which Abraham Lincoln grew up passes away, the world will read with increasing wonder of the man who, not only of the humblest origin, but remaining the simplest and most unpretending of citizens, was raised to a position of power unprecedented in our history; who was the gentlest and most peace-loving of mortals, unable to see any creature suffer without a pang in his own breast, and suddenly found himself called to conduct the greatest and bloodiest of our wars; who wielded the power of government when stern resolution and relentless force were the order of the day and then won and ruled the popular mind and heart by the tender sympathies of his nature; who was a cautious conservative by temperament and mental habit, and led the most sudden and sweeping social revolution of our time; who, preserving his homely speech and rustic manner even in the most conspicuous position of that period, drew upon himself the scoffs of polite society, and then thrilled the soul of mankind with utterances of wonderful beauty and grandeur; who, in his heart the best friend of the defeated South, was murdered because a crazy fanatic took him for its most cruel enemy; who, while in power, was beyond measure lampooned and maligned by sectional passion and an excited party spirit, and around whose bier friend and foe gathered to praise him which they have since never ceased to do—as one of the greatest of Americans and the best of men.
[This Address was delivered before the Edinburgh Philosophical Institution, November 13, 1900. It is included in this set with the courteous permission of the author and of Messrs. Thomas Y. Crowell & Company.]
ABRAHAM LINCOLN.
When you asked me to deliver the Inaugural Address on this occasion, I recognized that I owed this compliment to the fact that I was the official representative of America, and in selecting a subject I ventured to think that I might interest you for an hour in a brief study in popular government, as illustrated by the life of the most American of all Americans. I therefore offer no apology for asking your attention to Abraham Lincoln—to his unique character and the part he bore in two important achievements of modern history: the preservation of the integrity of the American Union and the emancipation of the colored race.
During his brief term of power he was probably the object of more abuse, vilification, and ridicule than any other man in the world; but when he fell by the hand of an assassin, at the very moment of his stupendous victory, all the nations of the earth vied with one another in paying homage to his character, and the thirty-five years that have since elapsed have established his place in history as one of the great benefactors not of his own country alone, but of the human race.
One of many noble utterances upon the occasion of his death was that in which 'Punch' made its magnanimous recantation of the spirit with which it had pursued him:
"Beside this corpse that bears for winding sheet
The stars and stripes he lived to rear anew,
Between the mourners at his head and feet,
Say, scurrile jester, is there room for you?
...................
"Yes, he had lived to shame me from my sneer,
To lame my pencil, and confute my pen
To make me own this hind—of princes peer,
This rail-splitter—a true born king of men."
Fiction can furnish no match for the romance of his life, and biography will be searched in vain for such startling vicissitudes of fortune, so great power and glory won out of such humble beginnings and adverse circumstances.
Doubtless you are all familiar with the salient points of his extraordinary career. In the zenith of his fame he was the wise, patient, courageous, successful ruler of men; exercising more power than any monarch of his time, not for himself, but for the good of the people who had placed it in his hands; commander-in-chief of a vast military power, which waged with ultimate success the greatest war of the century; the triumphant champion of popular government, the deliverer of four millions of his fellowmen from bondage; honored by mankind as Statesman, President, and Liberator.
Let us glance now at the first half of the brief life of which this was the glorious and happy consummation. Nothing could be more squalid and miserable than the home in which Abraham Lincoln was born—a one-roomed cabin without floor or window in what was then the wilderness of Kentucky, in the heart of that frontier life which swiftly moved westward from the Alleghanies to the Mississippi, always in advance of schools and churches, of books and money, of railroads and newspapers, of all things which are generally regarded as the comforts and even necessaries of life. His father, ignorant, needy, and thriftless, content if he could keep soul and body together for himself and his family, was ever seeking, without success, to better his unhappy condition by moving on from one such scene of dreary desolation to another. The rude society which surrounded them was not much better. The struggle for existence was hard, and absorbed all their energies. They were fighting the forest, the wild beast, and the retreating savage. From the time when he could barely handle tools until he attained his majority, Lincoln's life was that of a simple farm laborer, poorly clad, housed, and fed, at work either on his father's wretched farm or hired out to neighboring farmers. But in spite, or perhaps by means, of this rude environment, he grew to be a stalwart giant, reaching six feet four at nineteen, and fabulous stories are told of his feats of strength. With the growth of this mighty frame began that strange education which in his ripening years was to qualify him for the great destiny that awaited him, and the development of those mental faculties and moral endowments which, by the time he reached middle life, were to make him the sagacious, patient, and triumphant leader of a great nation in the crisis of its fate. His whole schooling, obtained during such odd times as could be spared from grinding labor, did not amount in all to as much as one year, and the quality of the teaching was of the lowest possible grade, including only the elements of reading, writing, and ciphering. But out of these simple elements, when rightly used by the right man, education is achieved, and Lincoln knew how to use them. As so often happens, he seemed to take warning from his father's unfortunate example. Untiring industry, an insatiable thirst for knowledge, and an ever-growing desire to rise above his surroundings, were early manifestations of his character.
Books were almost unknown in that community, but the Bible was in every house, and somehow or other Pilgrim's Progress, AEsop's Fables, a History of the United States, and a Life of Washington fell into his hands. He trudged on foot many miles through the wilderness to borrow an English Grammar, and is said to have devoured greedily the contents of the Statutes of Indiana that fell in his way. These few volumes he read and reread—and his power of assimilation was great. To be shut in with a few books and to master them thoroughly sometimes does more for the development of character than freedom to range at large, in a cursory and indiscriminate way, through wide domains of literature. This youth's mind, at any rate, was thoroughly saturated with Biblical knowledge and Biblical language, which, in after life, he used with great readiness and effect. But it was the constant use of the little knowledge which he had that developed and exercised his mental powers. After the hard day's work was done, while others slept, he toiled on, always reading or writing. From an early age he did his own thinking and made up his own mind—invaluable traits in the future President. Paper was such a scarce commodity that, by the evening firelight, he would write and cipher on the back of a wooden shovel, and then shave it off to make room for more. By and by, as he approached manhood, he began speaking in the rude gatherings of the neighborhood, and so laid the foundation of that art of persuading his fellow-men which was one rich result of his education, and one great secret of his subsequent success.
Accustomed as we are in these days of steam and telegraphs to have every intelligent boy survey the whole world each morning before breakfast, and inform himself as to what is going on in every nation, it is hardly possible to conceive how benighted and isolated was the condition of the community at Pigeon Creek in Indiana, of which the family of Lincoln's father formed a part, or how eagerly an ambitious and high-spirited boy, such as he, must have yearned to escape. The first glimpse that he ever got of any world beyond the narrow confines of his home was in 1828, at the age of nineteen, when a neighbor employed him to accompany his son down the river to New Orleans to dispose of a flatboat of produce—a commission which he discharged with great success.
Shortly after his return from this his first excursion into the outer world, his father, tired of failure in Indiana, packed his family and all his worldly goods into a single wagon drawn by two yoke of oxen, and after a fourteen days' tramp through the wilderness, pitched his camp once more, in Illinois. Here Abraham, having come of age and being now his own master, rendered the last service of his minority by ploughing the fifteen-acre lot and splitting from the tall walnut trees of the primeval forest enough rails to surround the little clearing with a fence. Such was the meagre outfit of this coming leader of men, at the age when the future British Prime Minister or statesman emerges from the university as a double first or senior wrangler, with every advantage that high training and broad culture and association with the wisest and the best of men and women can give, and enters upon some form of public service on the road to usefulness and honor, the University course being only the first stage of the public training. So Lincoln, at twenty-one, had just begun his preparation for the public life to which he soon began to aspire. For some years yet he must continue to earn his daily bread by the sweat of his brow, having absolutely no means, no home, no friend to consult. More farm work as a hired hand, a clerkship in a village store, the running of a mill, another trip to New Orleans on a flatboat of his own contriving, a pilot's berth on the river—these were the means by which he subsisted until, in the summer of 1832, when he was twenty-three years of age, an event occurred which gave him public recognition.
The Black Hawk war broke out, and, the Governor of Illinois calling for volunteers to repel the band of savages whose leader bore that name, Lincoln enlisted and was elected captain by his comrades, among whom he had already established his supremacy by signal feats of strength and more than one successful single combat. During the brief hostilities he was engaged in no battle and won no military glory, but his local leadership was established. The same year he offered himself as a candidate for the Legislature of Illinois, but failed at the polls. Yet his vast popularity with those who knew him was manifest. The district consisted of several counties, but the unanimous vote of the people of his own county was for Lincoln. Another unsuccessful attempt at store-keeping was followed by better luck at surveying, until his horse and instruments were levied upon under execution for the debts of his business adventure.
I have been thus detailed in sketching his early years because upon these strange foundations the structure of his great fame and service was built. In the place of a school and university training fortune substituted these trials, hardships, and struggles as a preparation for the great work which he had to do. It turned out to be exactly what the emergency required. Ten years instead at the public school and the university certainly never could have fitted this man for the unique work which was to be thrown upon him. Some other Moses would have had to lead us to our Jordan, to the sight of our promised land of liberty.
At the age of twenty-five he became a member of the Legislature of Illinois, and so continued for eight years, and, in the meantime, qualified himself by reading such law books as he could borrow at random—for he was too poor to buy any to be called to the Bar. For his second quarter of a century—during which a single term in Congress introduced him into the arena of national questions—he gave himself up to law and politics. In spite of his soaring ambition, his two years in Congress gave him no premonition of the great destiny that awaited him,—and at its close, in 1849, we find him an unsuccessful applicant to the President for appointment as Commissioner of the General Land Office—a purely administrative bureau; a fortunate escape for himself and for his country. Year by year his knowledge and power, his experience and reputation extended, and his mental faculties seemed to grow by what they fed on. His power of persuasion, which had always been marked, was developed to an extraordinary degree, now that he became engaged in congenial questions and subjects. Little by little he rose to prominence at the Bar, and became the most effective public speaker in the West. Not that he possessed any of the graces of the orator; but his logic was invincible, and his clearness and force of statement impressed upon his hearers the convictions of his honest mind, while his broad sympathies and sparkling and genial humor made him a universal favorite as far and as fast as his acquaintance extended.
These twenty years that elapsed from the time of his establishment as a lawyer and legislator in Springfield, the new capital of Illinois, furnished a fitting theatre for the development and display of his great faculties, and, with his new and enlarged opportunities, he obviously grew in mental stature in this second period of his career, as if to compensate for the absolute lack of advantages under which he had suffered in youth. As his powers enlarged, his reputation extended, for he was always before the people, felt a warm sympathy with all that concerned them, took a zealous part in the discussion of every public question, and made his personal influence ever more widely and deeply felt.
My brethren of the legal profession will naturally ask me, how could this rough backwoodsman, whose youth had been spent in the forest or on the farm and the flatboat, without culture or training, education or study, by the random reading, on the wing, of a few miscellaneous law books, become a learned and accomplished lawyer? Well, he never did. He never would have earned his salt as a 'Writer' for the 'Signet', nor have won a place as advocate in the Court of Session, where the technique of the profession has reached its highest perfection, and centuries of learning and precedent are involved in the equipment of a lawyer. Dr. Holmes, when asked by an anxious young mother, "When should the education of a child begin?" replied, "Madam, at least two centuries before it is born!" and so I am sure it is with the Scots lawyer.
But not so in Illinois in 1840. Between 1830 and 1880 its population increased twenty-fold, and when Lincoln began practising law in Springfield in 1837, life in Illinois was very crude and simple, and so were the courts and the administration of justice. Books and libraries were scarce. But the people loved justice, upheld the law, and followed the courts, and soon found their favorites among the advocates. The fundamental principles of the common law, as set forth by Blackstone and Chitty, were not so difficult to acquire; and brains, common sense, force of character, tenacity of purpose, ready wit and power of speech did the rest, and supplied all the deficiencies of learning.
The lawsuits of those days were extremely simple, and the principles of natural justice were mainly relied on to dispose of them at the Bar and on the Bench, without resort to technical learning. Railroads, corporations absorbing the chief business of the community, combined and inherited wealth, with all the subtle and intricate questions they breed, had not yet come in—and so the professional agents and the equipment which they require were not needed. But there were many highly educated and powerful men at the Bar of Illinois, even in those early days, whom the spirit of enterprise had carried there in search of fame and fortune. It was by constant contact and conflict with these that Lincoln acquired professional strength and skill. Every community and every age creates its own Bar, entirely adequate for its present uses and necessities. So in Illinois, as the population and wealth of the State kept on doubling and quadrupling, its Bar presented a growing abundance of learning and science and technical skill. The early practitioners grew with its growth and mastered the requisite knowledge. Chicago soon grew to be one of the largest and richest and certainly the most intensely active city on the continent, and if any of my professional friends here had gone there in Lincoln's later years, to try or argue a cause, or transact other business, with any idea that Edinburgh or London had a monopoly of legal learning, science, or subtlety, they would certainly have found their mistake.
In those early days in the West, every lawyer, especially every court lawyer, was necessarily a politician, constantly engaged in the public discussion of the many questions evolved from the rapid development of town, county, State, and Federal affairs. Then and there, in this regard, public discussion supplied the place which the universal activity of the press has since monopolized, and the public speaker who, by clearness, force, earnestness, and wit; could make himself felt on the questions of the day would rapidly come to the front. In the absence of that immense variety of popular entertainments which now feed the public taste and appetite, the people found their chief amusement in frequenting the courts and public and political assemblies. In either place, he who impressed, entertained, and amused them most was the hero of the hour. They did not discriminate very carefully between the eloquence of the forum and the eloquence of the hustings. Human nature ruled in both alike, and he who was the most effective speaker in a political harangue was often retained as most likely to win in a cause to be tried or argued. And I have no doubt in this way many retainers came to Lincoln. Fees, money in any form, had no charms for him—in his eager pursuit of fame he could not afford to make money. He was ambitious to distinguish himself by some great service to mankind, and this ambition for fame and real public service left no room for avarice in his composition. However much he earned, he seems to have ended every year hardly richer than he began it, and yet, as the years passed, fees came to him freely. One of L 1,000 is recorded—a very large professional fee at that time, even in any part of America, the paradise of lawyers. I lay great stress on Lincoln's career as a lawyer—much more than his biographers do because in America a state of things exists wholly different from that which prevails in Great Britain. The profession of the law always has been and is to this day the principal avenue to public life; and I am sure that his training and experience in the courts had much to do with the development of those forces of intellect and character which he soon displayed on a broader arena.
It was in political controversy, of course, that he acquired his wide reputation, and made his deep and lasting impression upon the people of what had now become the powerful State of Illinois, and upon the people of the Great West, to whom the political power and control of the United States were already surely and swiftly passing from the older Eastern States. It was this reputation and this impression, and the familiar knowledge of his character which had come to them from his local leadership, that happily inspired the people of the West to present him as their candidate, and to press him upon the Republican convention of 1860 as the fit and necessary leader in the struggle for life which was before the nation.
That struggle, as you all know, arose out of the terrible question of slavery—and I must trust to your general knowledge of the history of that question to make intelligible the attitude and leadership of Lincoln as the champion of the hosts of freedom in the final contest. Negro slavery had been firmly established in the Southern States from an early period of their history. In 1619, the year before the Mayflower landed our Pilgrim Fathers upon Plymouth Rock, a Dutch ship had discharged a cargo of African slaves at Jamestown in Virginia: All through the colonial period their importation had continued. A few had found their way into the Northern States, but none of them in sufficient numbers to constitute danger or to afford a basis for political power. At the time of the adoption of the Federal Constitution, there is no doubt that the principal members of the convention not only condemned slavery as a moral, social, and political evil, but believed that by the suppression of the slave trade it was in the course of gradual extinction in the South, as it certainly was in the North. Washington, in his will, provided for the emancipation of his own slaves, and said to Jefferson that it "was among his first wishes to see some plan adopted by which slavery in his country might be abolished." Jefferson said, referring to the institution: "I tremble for my country when I think that God is just; that His justice cannot sleep forever,"—and Franklin, Adams, Hamilton, and Patrick Henry were all utterly opposed to it. But it was made the subject of a fatal compromise in the Federal Constitution, whereby its existence was recognized in the States as a basis of representation, the prohibition of the importation of slaves was postponed for twenty years, and the return of fugitive slaves provided for. But no imminent danger was apprehended from it till, by the invention of the cotton gin in 1792, cotton culture by negro labor became at once and forever the leading industry of the South, and gave a new impetus to the importation of slaves, so that in 1808, when the constitutional prohibition took effect, their numbers had vastly increased. From that time forward slavery became the basis of a great political power, and the Southern States, under all circumstances and at every opportunity, carried on a brave and unrelenting struggle for its maintenance and extension.
The conscience of the North was slow to rise against it, though bitter controversies from time to time took place. The Southern leaders threatened disunion if their demands were not complied with. To save the Union, compromise after compromise was made, but each one in the end was broken. The Missouri Compromise, made in 1820 upon the occasion of the admission of Missouri into the Union as a slave State, whereby, in consideration of such admission, slavery was forever excluded from the Northwest Territory, was ruthlessly repealed in 1854, by a Congress elected in the interests of the slave power, the intent being to force slavery into that vast territory which had so long been dedicated to freedom. This challenge at last aroused the slumbering conscience and passion of the North, and led to the formation of the Republican party for the avowed purpose of preventing, by constitutional methods, the further extension of slavery.
In its first campaign, in 1856, though it failed to elect its candidates; it received a surprising vote and carried many of the States. No one could any longer doubt that the North had made up its mind that no threats of disunion should deter it from pressing its cherished purpose and performing its long neglected duty. From the outset, Lincoln was one of the most active and effective leaders and speakers of the new party, and the great debates between Lincoln and Douglas in 1858, as the respective champions of the restriction and extension of slavery, attracted the attention of the whole country. Lincoln's powerful arguments carried conviction everywhere. His moral nature was thoroughly aroused his conscience was stirred to the quick. Unless slavery was wrong, nothing was wrong. Was each man, of whatever color, entitled to the fruits of his own labor, or could one man live in idle luxury by the sweat of another's brow, whose skin was darker? He was an implicit believer in that principle of the Declaration of Independence that all men are vested with certain inalienable rights the equal rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. On this doctrine he staked his case and carried it. We have time only for one or two sentences in which he struck the keynote of the contest.
"The real issue in this country is the eternal struggle between these two principles—right and wrong—throughout the world. They are the two principles that have stood face to face from the beginning of time, and will ever continue to struggle. The one is the common right of humanity, and the other the divine right of kings. It is the same principle in whatever shape it develops itself. It is the same spirit that says, 'You work and toil and earn bread and I'll eat it.'"
He foresaw with unerring vision that the conflict was inevitable and irrepressible—that one or the other, the right or the wrong, freedom or slavery, must ultimately prevail and wholly prevail, throughout the country; and this was the principle that carried the war, once begun, to a finish.
One sentence of his is immortal:
"Under the operation of the policy of compromise, the slavery agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented. In my opinion it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. 'A house divided against itself cannot stand.' I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved. I do not expect the house to fall, but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other; either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South."
During the entire decade from 1850 to 1860 the agitation of the slavery question was at the boiling point, and events which have become historical continually indicated the near approach of the overwhelming storm. No sooner had the Compromise Acts of 1850 resulted in a temporary peace, which everybody said must be final and perpetual, than new outbreaks came. The forcible carrying away of fugitive slaves by Federal troops from Boston agitated that ancient stronghold of freedom to its foundations. The publication of Uncle Tom's Cabin, which truly exposed the frightful possibilities of the slave system; the reckless attempts by force and fraud to establish it in Kansas against the will of the vast majority of the settlers; the beating of Summer in the Senate Chamber for words spoken in debate; the Dred Scott decision in the Supreme Court, which made the nation realize that the slave power had at last reached the fountain of Federal justice; and finally the execution of John Brown, for his wild raid into Virginia, to invite the slaves to rally to the standard of freedom which he unfurled:—all these events tend to illustrate and confirm Lincoln's contention that the nation could not permanently continue half slave and half free, but must become all one thing or all the other. When John Brown lay under sentence of death he declared that now he was sure that slavery must be wiped out in blood; but neither he nor his executioners dreamt that within four years a million soldiers would be marching across the country for its final extirpation, to the music of the war-song of the great conflict:
"John Brown's body lies a-mouldering in the grave, But his soul is marching on."
And now, at the age of fifty-one, this child of the wilderness, this farm laborer, rail-sputter, flatboatman, this surveyor, lawyer, orator, statesman, and patriot, found himself elected by the great party which was pledged to prevent at all hazards the further extension of slavery, as the chief magistrate of the Republic, bound to carry out that purpose, to be the leader and ruler of the nation in its most trying hour.
Those who believe that there is a living Providence that overrules and conducts the affairs of nations, find in the elevation of this plain man to this extraordinary fortune and to this great duty, which he so fitly discharged, a signal vindication of their faith. Perhaps to this philosophical institution the judgment of our philosopher Emerson will commend itself as a just estimate of Lincoln's historical place.
"His occupying the chair of state was a triumph of the good sense of mankind and of the public conscience. He grew according to the need; his mind mastered the problem of the day: and as the problem grew, so did his comprehension of it. In the war there was no place for holiday magistrate, nor fair-weather sailor. The new pilot was hurried to the helm in a tornado. In four years—four years of battle days—his endurance, his fertility of resource, his magnanimity, were sorely tried, and never found wanting. There, by his courage, his justice, his even temper, his fertile counsel, his humanity, he stood a heroic figure in the centre of a heroic epoch. He is the true history of the American people in his time, the true representative of this continent—father of his country, the pulse of twenty millions throbbing in his heart, the thought of their mind—articulated in his tongue."
He was born great, as distinguished from those who achieve greatness or have it thrust upon them, and his inherent capacity, mental, moral, and physical, having been recognized by the educated intelligence of a free people, they happily chose him for their ruler in a day of deadly peril.
It is now forty years since I first saw and heard Abraham Lincoln, but the impression which he left on my mind is ineffaceable. After his great successes in the West he came to New York to make a political address. He appeared in every sense of the word like one of the plain people among whom he loved to be counted. At first sight there was nothing impressive or imposing about him—except that his great stature singled him out from the crowd: his clothes hung awkwardly on his giant frame; his face was of a dark pallor, without the slightest tinge of color; his seamed and rugged features bore the furrows of hardship and struggle; his deep-set eyes looked sad and anxious; his countenance in repose gave little evidence of that brain power which had raised him from the lowest to the highest station among his countrymen; as he talked to me before the meeting, he seemed ill at ease, with that sort of apprehension which a young man might feel before presenting himself to a new and strange audience, whose critical disposition he dreaded. It was a great audience, including all the noted men—all the learned and cultured of his party in New York editors, clergymen, statesmen, lawyers, merchants, critics. They were all very curious to hear him. His fame as a powerful speaker had preceded him, and exaggerated rumor of his wit—the worst forerunner of an orator—had reached the East. When Mr. Bryant presented him, on the high platform of the Cooper Institute, a vast sea of eager upturned faces greeted him, full of intense curiosity to see what this rude child of the people was like. He was equal to the occasion. When he spoke he was transformed; his eye kindled, his voice rang, his face shone and seemed to light up the whole assembly. For an hour and a half he held his audience in the hollow of his hand. His style of speech and manner of delivery were severely simple. What Lowell called "the grand simplicities of the Bible," with which he was so familiar, were reflected in his discourse. With no attempt at ornament or rhetoric, without parade or pretence, he spoke straight to the point. If any came expecting the turgid eloquence or the ribaldry of the frontier, they must have been startled at the earnest and sincere purity of his utterances. It was marvellous to see how this untutored man, by mere self-discipline and the chastening of his own spirit, had outgrown all meretricious arts, and found his own way to the grandeur and strength of absolute simplicity.
He spoke upon the theme which he had mastered so thoroughly. He demonstrated by copious historical proofs and masterly logic that the fathers who created the Constitution in order to form a more perfect union, to establish justice, and to secure the blessings of liberty to themselves and their posterity, intended to empower the Federal Government to exclude slavery from the Territories. In the kindliest spirit he protested against the avowed threat of the Southern States to destroy the Union if, in order to secure freedom in those vast regions out of which future States were to be carved, a Republican President were elected. He closed with an appeal to his audience, spoken with all the fire of his aroused and kindling conscience, with a full outpouring of his love of justice and liberty, to maintain their political purpose on that lofty and unassailable issue of right and wrong which alone could justify it, and not to be intimidated from their high resolve and sacred duty by any threats of destruction to the government or of ruin to themselves. He concluded with this telling sentence, which drove the whole argument home to all our hearts: "Let us have faith that right makes might, and in that faith let us to the end dare to do our duty as we understand it." That night the great hall, and the next day the whole city, rang with delighted applause and congratulations, and he who had come as a stranger departed with the laurels of great triumph.
Alas! in five years from that exulting night I saw him again, for the last time, in the same city, borne in his coffin through its draped streets. With tears and lamentations a heart-broken people accompanied him from Washington, the scene of his martyrdom, to his last resting-place in the young city of the West where he had worked his way to fame.
Never was a new ruler in a more desperate plight than Lincoln when he entered office on the fourth of March, 1861, four months after his election, and took his oath to support the Constitution and the Union. The intervening time had been busily employed by the Southern States in carrying out their threat of disunion in the event of his election. As soon as the fact was ascertained, seven of them had seceded and had seized upon the forts, arsenals, navy yards, and other public property of the United States within their boundaries, and were making every preparation for war. In the meantime the retiring President, who had been elected by the slave power, and who thought the seceding States could not lawfully be coerced, had done absolutely nothing. Lincoln found himself, by the Constitution, Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States, but with only a remnant of either at hand. Each was to be created on a great scale out of the unknown resources of a nation untried in war.
In his mild and conciliatory inaugural address, while appealing to the seceding States to return to their allegiance, he avowed his purpose to keep the solemn oath he had taken that day, to see that the laws of the Union were faithfully executed, and to use the troops to recover the forts, navy yards, and other property belonging to the government. It is probable, however, that neither side actually realized that war was inevitable, and that the other was determined to fight, until the assault on Fort Sumter presented the South as the first aggressor and roused the North to use every possible resource to maintain the government and the imperilled Union, and to vindicate the supremacy of the flag over every inch of the territory of the United States. The fact that Lincoln's first proclamation called for only 75,000 troops, to serve for three months, shows how inadequate was even his idea of what the future had in store. But from that moment Lincoln and his loyal supporters never faltered in their purpose. They knew they could win, that it was their duty to win, and that for America the whole hope of the future depended upon their winning; for now by the acts of the seceding States the issue of the election to secure or prevent the extension of slavery—stood transformed into a struggle to preserve or to destroy the Union.
We cannot follow this contest. You know its gigantic proportions; that it lasted four years instead of three months; that in its progress, instead of 75,000 men, more than 2,000,000 were enrolled on the side of the government alone; that the aggregate cost and loss to the nation approximated to 1,000,000,000 pounds sterling, and that not less than 300,000 brave and precious lives were sacrificed on each side. History has recorded how Lincoln bore himself during these four frightful years; that he was the real President, the responsible and actual head of the government, through it all; that he listened to all advice, heard all parties, and then, always realizing his responsibility to God and the nation, decided every great executive question for himself. His absolute honesty had become proverbial long before he was President. "Honest Abe Lincoln" was the name by which he had been known for years. His every act attested it.
In all the grandeur of the vast power that he wielded, he never ceased to be one of the plain people, as he always called them, never lost or impaired his perfect sympathy with them, was always in perfect touch with them and open to their appeals; and here lay the very secret of his personality and of his power, for the people in turn gave him their absolute confidence. His courage, his fortitude, his patience, his hopefulness, were sorely tried but never exhausted.
He was true as steel to his generals, but had frequent occasion to change them, as he found them inadequate. This serious and painful duty rested wholly upon him, and was perhaps his most important function as Commander-in-Chief; but when, at last, he recognized in General Grant the master of the situation, the man who could and would bring the war to a triumphant end, he gave it all over to him and upheld him with all his might. Amid all the pressure and distress that the burdens of office brought upon him, his unfailing sense of humor saved him; probably it made it possible for him to live under the burden. He had always been the great story-teller of the West, and he used and cultivated this faculty to relieve the weight of the load he bore.
It enabled him to keep the wonderful record of never having lost his temper, no matter what agony he had to bear. A whole night might be spent in recounting the stories of his wit, humor, and harmless sarcasm. But I will recall only two of his sayings, both about General Grant, who always found plenty of enemies and critics to urge the President to oust him from his command. One, I am sure, will interest all Scotchmen. They repeated with malicious intent the gossip that Grant drank. "What does he drink?" asked Lincoln. "Whiskey," was, of course, the answer; doubtless you can guess the brand. "Well," said the President, "just find out what particular kind he uses and I'll send a barrel to each of my other generals." The other must be as pleasing to the British as to the American ear. When pressed again on other grounds to get rid of Grant, he declared, "I can't spare that man, he fights!"
He was tender-hearted to a fault, and never could resist the appeals of wives and mothers of soldiers who had got into trouble and were under sentence of death for their offences. His Secretary of War and other officials complained that they never could get deserters shot. As surely as the women of the culprit's family could get at him he always gave way. Certainly you will all appreciate his exquisite sympathy with the suffering relatives of those who had fallen in battle. His heart bled with theirs. Never was there a more gentle and tender utterance than his letter to a mother who had given all her sons to her country, written at a time when the angel of death had visited almost every household in the land, and was already hovering over him.
"I have been shown," he says, "in the files of the War Department a statement that you are the mother of five sons who have died gloriously on the field of battle. I feel how weak and fruitless must be any words of mine which should attempt to beguile you from your grief for a loss so overwhelming but I cannot refrain from tendering to you the consolation which may be found in the thanks of the Republic they died to save. I pray that our Heavenly Father may assuage the anguish of your bereavement and leave you only the cherished memory of the loved and the lost, and the solemn pride that must be yours to have laid so costly a sacrifice upon the altar of freedom."
Hardly could your illustrious sovereign, from the depths of her queenly and womanly heart, have spoken words more touching and tender to soothe the stricken mothers of her own soldiers.
The Emancipation Proclamation, with which Mr. Lincoln delighted the country and the world on the first of January, 1863, will doubtless secure for him a foremost place in history among the philanthropists and benefactors of the race, as it rescued, from hopeless and degrading slavery, so many millions of his fellow-beings described in the law and existing in fact as "chattels-personal, in the hands of their owners and possessors, to all intents, constructions, and purposes whatsoever." Rarely does the happy fortune come to one man to render such a service to his kind—to proclaim liberty throughout the land unto all the inhabitants thereof.
Ideas rule the world, and never was there a more signal instance of this triumph of an idea than here. William Lloyd Garrison, who thirty years before had begun his crusade for the abolition of slavery, and had lived to see this glorious and unexpected consummation of the hopeless cause to which he had devoted his life, well described the proclamation as a "great historic event, sublime in its magnitude, momentous and beneficent in its far-reaching consequences, and eminently just and right alike to the oppressor and the oppressed."
Lincoln had always been heart and soul opposed to slavery. Tradition says that on the trip on the flatboat to New Orleans he formed his first and last opinion of slavery at the sight of negroes chained and scourged, and that then and there the iron entered into his soul. No boy could grow to manhood in those days as a poor white in Kentucky and Indiana, in close contact with slavery or in its neighborhood, without a growing consciousness of its blighting effects on free labor, as well as of its frightful injustice and cruelty. In the Legislature of Illinois, where the public sentiment was all for upholding the institution and violently against every movement for its abolition or restriction, upon the passage of resolutions to that effect he had the courage with one companion to put on record his protest, "believing that the institution of slavery is founded both in injustice and bad policy." No great demonstration of courage, you will say; but that was at a time when Garrison, for his abolition utterances, had been dragged by an angry mob through the streets of Boston with a rope around his body, and in the very year that Lovejoy in the same State of Illinois was slain by rioters while defending his press, from which he had printed antislavery appeals.
In Congress he brought in a bill for gradual abolition in the District of Columbia, with compensation to the owners, for until they raised treasonable hands against the life of the nation he always maintained that the property of the slaveholders, into which they had come by two centuries of descent, without fault on their part, ought not to be taken away from them without just compensation. He used to say that, one way or another, he had voted forty-two times for the Wilmot Proviso, which Mr. Wilmot of Pennsylvania moved as an addition to every bill which affected United States territory, "that neither slavery nor involuntary servitude shall ever exist in any part of the said territory," and it is evident that his condemnation of the system, on moral grounds as a crime against the human race, and on political grounds as a cancer that was sapping the vitals of the nation, and must master its whole being or be itself extirpated, grew steadily upon him until it culminated in his great speeches in the Illinois debate.
By the mere election of Lincoln to the Presidency, the further extension of slavery into the Territories was rendered forever impossible—Vox populi, vox Dei. Revolutions never go backward, and when founded on a great moral sentiment stirring the heart of an indignant people their edicts are irresistible and final. Had the slave power acquiesced in that election, had the Southern States remained under the Constitution and within the Union, and relied upon their constitutional and legal rights, their favorite institution, immoral as it was, blighting and fatal as it was, might have endured for another century. The great party that had elected him, unalterably determined against its extension, was nevertheless pledged not to interfere with its continuance in the States where it already existed. Of course, when new regions were forever closed against it, from its very nature it must have begun to shrink and to dwindle; and probably gradual and compensated emancipation, which appealed very strongly to the new President's sense of justice and expediency, would, in the progress of time, by a reversion to the ideas of the founders of the Republic, have found a safe outlet for both masters and slaves. But whom the gods wish to destroy they first make mad, and when seven States, afterwards increased to eleven, openly seceded from the Union, when they declared and began the war upon the nation, and challenged its mighty power to the desperate and protracted struggle for its life, and for the maintenance of its authority as a nation over its territory, they gave to Lincoln and to freedom the sublime opportunity of history.
In his first inaugural address, when as yet not a drop of precious blood had been shed, while he held out to them the olive branch in one hand, in the other he presented the guarantees of the Constitution, and after reciting the emphatic resolution of the convention that nominated him, that the maintenance inviolate of the "rights of the States, and especially the right of each State to order and control its own domestic institutions according to its own judgment exclusively, is essential to that balance of power on which the perfection and endurance of our political fabric depend," he reiterated this sentiment, and declared, with no mental reservation, "that all the protection which, consistently with the Constitution and the laws, can be given, will be cheerfully given to all the States when lawfully demanded for whatever cause as cheerfully to one section as to another."
When, however, these magnanimous overtures for peace and reunion were rejected; when the seceding States defied the Constitution and every clause and principle of it; when they persisted in staying out of the Union from which they had seceded, and proceeded to carve out of its territory a new and hostile empire based on slavery; when they flew at the throat of the nation and plunged it into the bloodiest war of the nineteenth century the tables were turned, and the belief gradually came to the mind of the President that if the Rebellion was not soon subdued by force of arms, if the war must be fought out to the bitter end, then to reach that end the salvation of the nation itself might require the destruction of slavery wherever it existed; that if the war was to continue on one side for Disunion, for no other purpose than to preserve slavery, it must continue on the other side for the Union, to destroy slavery.
As he said, "Events control me; I cannot control events," and as the dreadful war progressed and became more deadly and dangerous, the unalterable conviction was forced upon him that, in order that the frightful sacrifice of life and treasure on both sides might not be all in vain, it had become his duty as Commander-in-Chief of the Army, as a necessary war measure, to strike a blow at the Rebellion which, all others failing, would inevitably lead to its annihilation, by annihilating the very thing for which it was contending. His own words are the best:
"I understood that my oath to preserve the Constitution to the best of my ability imposed upon me the duty of preserving by every indispensable means that government—that nation—of which that Constitution was the organic law. Was it possible to lose the nation and yet preserve the Constitution? By general law, life and limb must be protected, yet often a limb must be amputated to save a life; but a life is never wisely given to save a limb. I felt that measures otherwise unconstitutional might become lawful by becoming indispensable to the preservation of the Constitution through the preservation of the nation. Right or wrong, I assumed this ground and now avow it. I could not feel that to the best of my ability I had ever tried to preserve the Constitution if to save slavery or any minor matter I should permit the wreck of government, country, and Constitution all together."
And so, at last, when in his judgment the indispensable necessity had come, he struck the fatal blow, and signed the proclamation which has made his name immortal. By it, the President, as Commander-in-Chief in time of actual armed rebellion, and as a fit and necessary war measure for suppressing the rebellion, proclaimed all persons held as slaves in the States and parts of States then in rebellion to be thenceforward free, and declared that the executive, with the army and navy, would recognize and maintain their freedom.
In the other great steps of the government, which led to the triumphant prosecution of the war, he necessarily shared the responsibility and the credit with the great statesmen who stayed up his hands in his cabinet, with Seward, Chase and Stanton, and the rest,—and with his generals and admirals, his soldiers and sailors, but this great act was absolutely his own. The conception and execution were exclusively his. He laid it before his cabinet as a measure on which his mind was made up and could not be changed, asking them only for suggestions as to details. He chose the time and the circumstances under which the Emancipation should be proclaimed and when it should take effect.
It came not an hour too soon; but public opinion in the North would not have sustained it earlier. In the first eighteen months of the war its ravages had extended from the Atlantic to beyond the Mississippi. Many victories in the West had been balanced and paralyzed by inaction and disasters in Virginia, only partially redeemed by the bloody and indecisive battle of Antietam; a reaction had set in from the general enthusiasm which had swept the Northern States after the assault upon Sumter. It could not truly be said that they had lost heart, but faction was raising its head. Heard through the land like the blast of a bugle, the proclamation rallied the patriotism of the country to fresh sacrifices and renewed ardor. It was a step that could not be revoked. It relieved the conscience of the nation from an incubus that had oppressed it from its birth. The United States were rescued from the false predicament in which they had been from the beginning, and the great popular heart leaped with new enthusiasm for "Liberty and Union, henceforth and forever, one and inseparable." It brought not only moral but material support to the cause of the government, for within two years 120,000 colored troops were enlisted in the military service and following the national flag, supported by all the loyalty of the North, and led by its choicest spirits. One mother said, when her son was offered the command of the first colored regiment, "If he accepts it I shall be as proud as if I had heard that he was shot." He was shot heading a gallant charge of his regiment.... The Confederates replied to a request of his friends for his body that they had "buried him under a layer of his niggers...;" but that mother has lived to enjoy thirty-six years of his glory, and Boston has erected its noblest monument to his memory.
The effect of the proclamation upon the actual progress of the war was not immediate, but wherever the Federal armies advanced they carried freedom with them, and when the summer came round the new spirit and force which had animated the heart of the government and people were manifest. In the first week of July the decisive battle of Gettysburg turned the tide of war, and the fall of Vicksburg made the great river free from its source to the Gulf.
On foreign nations the influence of the proclamation and of these new victories was of great importance. In those days, when there was no cable, it was not easy for foreign observers to appreciate what was really going on; they could not see clearly the true state of affairs, as in the last year of the nineteenth century we have been able, by our new electric vision, to watch every event at the antipodes and observe its effect. The Rebel emissaries, sent over to solicit intervention, spared no pains to impress upon the minds of public and private men and upon the press their own views of the character of the contest. The prospects of the Confederacy were always better abroad than at home. The stock markets of the world gambled upon its chances, and its bonds at one time were high in favor.
Such ideas as these were seriously held: that the North was fighting for empire and the South for independence; that the Southern States, instead of being the grossest oligarchies, essentially despotisms, founded on the right of one man to appropriate the fruit of other men's toil and to exclude them from equal rights, were real republics, feebler to be sure than their Northern rivals, but representing the same idea of freedom, and that the mighty strength of the nation was being put forth to crush them; that Jefferson Davis and the Southern leaders had created a nation; that the republican experiment had failed and the Union had ceased to exist. But the crowning argument to foreign minds was that it was an utter impossibility for the government to win in the contest; that the success of the Southern States, so far as separation was concerned, was as certain as any event yet future and contingent could be; that the subjugation of the South by the North, even if it could be accomplished, would prove a calamity to the United States and the world, and especially calamitous to the negro race; and that such a victory would necessarily leave the people of the South for many generations cherishing deadly hostility against the government and the North, and plotting always to recover their independence.
When Lincoln issued his proclamation he knew that all these ideas were founded in error; that the national resources were inexhaustible; that the government could and would win, and that if slavery were once finally disposed of, the only cause of difference being out of the way, the North and South would come together again, and by and by be as good friends as ever. In many quarters abroad the proclamation was welcomed with enthusiasm by the friends of America; but I think the demonstrations in its favor that brought more gladness to Lincoln's heart than any other were the meetings held in the manufacturing centres, by the very operatives upon whom the war bore the hardest, expressing the most enthusiastic sympathy with the proclamation, while they bore with heroic fortitude the grievous privations which the war entailed upon them. Mr. Lincoln's expectation when he announced to the world that all slaves in all States then in rebellion were set free must have been that the avowed position of his government, that the continuance of the war now meant the annihilation of slavery, would make intervention impossible for any foreign nation whose people were lovers of liberty—and so the result proved.
The growth and development of Lincoln's mental power and moral force, of his intense and magnetic personality, after the vast responsibilities of government were thrown upon him at the age of fifty-two, furnish a rare and striking illustration of the marvellous capacity and adaptability of the human intellect—of the sound mind in the sound body. He came to the discharge of the great duties of the Presidency with absolutely no experience in the administration of government, or of the vastly varied and complicated questions of foreign and domestic policy which immediately arose, and continued to press upon him during the rest of his life; but he mastered each as it came, apparently with the facility of a trained and experienced ruler. As Clarendon said of Cromwell, "His parts seemed to be raised by the demands of great station." His life through it all was one of intense labor, anxiety, and distress, without one hour of peaceful repose from first to last. But he rose to every occasion. He led public opinion, but did not march so far in advance of it as to fail of its effective support in every great emergency. He knew the heart and thought of the people, as no man not in constant and absolute sympathy with them could have known it, and so holding their confidence, he triumphed through and with them. Not only was there this steady growth of intellect, but the infinite delicacy of his nature and its capacity for refinement developed also, as exhibited in the purity and perfection of his language and style of speech. The rough backwoodsman, who had never seen the inside of a university, became in the end, by self-training and the exercise of his own powers of mind, heart, and soul, a master of style, and some of his utterances will rank with the best, the most perfectly adapted to the occasion which produced them.
Have you time to listen to his two-minutes speech at Gettysburg, at the dedication of the Soldiers' Cemetery? His whole soul was in it:
"Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field as a final resting-place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But in a larger sense we cannot dedicate—we cannot consecrate—we cannot hallow this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here have consecrated it far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember, what we say here but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us, the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion—that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation under God shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, and for the people shall not perish from the earth."
He lived to see his work indorsed by an overwhelming majority of his countrymen. In his second inaugural address, pronounced just forty days before his death, there is a single passage which well displays his indomitable will and at the same time his deep religious feeling, his sublime charity to the enemies of his country, and his broad and catholic humanity:
"If we shall suppose that American slavery is one of those offences which in the Providence of God must needs come, but which, having continued through the appointed time, He now wills to remove, and that He gives to both North and South this terrible war, as the woe due to those by whom the offence came, shall we discern therein any departure from those divine attributes which the believers in a living God always ascribe to Him? Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsmen's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid with another drawn by the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said, 'the judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.'
"With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right let us strive on to finish the work we are in to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan to do all which may achieve, and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves, and with all nations."
His prayer was answered. The forty days of life that remained to him were crowned with great historic events. He lived to see his Proclamation of Emancipation embodied in an amendment of the Constitution, adopted by Congress, and submitted to the States for ratification. The mighty scourge of war did speedily pass away, for it was given him to witness the surrender of the Rebel army and the fall of their capital, and the starry flag that he loved waving in triumph over the national soil. When he died by the madman's hand in the supreme hour of victory, the vanquished lost their best friend, and the human race one of its noblest examples; and all the friends of freedom and justice, in whose cause he lived and died, joined hands as mourners at his grave.
FELLOW CITIZENS:—Having become a candidate for the honorable office of one of your Representatives in the next General Assembly of this State, in according with an established custom and the principles of true Republicanism it becomes my duty to make known to you, the people whom I propose to represent, my sentiments with regard to local affairs.
Time and experience have verified to a demonstration the public utility of internal improvements. That the poorest and most thinly populated countries would be greatly benefited by the opening of good roads, and in the clearing of navigable streams within their limits, is what no person will deny. Yet it is folly to undertake works of this or any other without first knowing that we are able to finish them—as half-finished work generally proves to be labor lost. There cannot justly be any objection to having railroads and canals, any more than to other good things, provided they cost nothing. The only objection is to paying for them; and the objection arises from the want of ability to pay.
With respect to the County of Sangamon, some....
Yet, however desirable an object the construction of a railroad through our country may be, however high our imaginations may be heated at thoughts of it,—there is always a heart-appalling shock accompanying the amount of its cost, which forces us to shrink from our pleasing anticipations. The probable cost of this contemplated railroad is estimated at $290,000; the bare statement of which, in my opinion, is sufficient to justify the belief that the improvement of the Sangamon River is an object much better suited to our infant resources.......
What the cost of this work would be, I am unable to say. It is probable, however, that it would not be greater than is common to streams of the same length. Finally, I believe the improvement of the Sangamon River to be vastly important and highly desirable to the people of the county; and, if elected, any measure in the Legislature having this for its object, which may appear judicious, will meet my approbation and receive my support.
It appears that the practice of loaning money at exorbitant rates of interest has already been opened as a field for discussion; so I suppose I may enter upon it without claiming the honor or risking the danger which may await its first explorer. It seems as though we are never to have an end to this baneful and corroding system, acting almost as prejudicially to the general interests of the community as a direct tax of several thousand dollars annually laid on each county for the benefit of a few individuals only, unless there be a law made fixing the limits of usury. A law for this purpose, I am of opinion, may be made without materially injuring any class of people. In cases of extreme necessity, there could always be means found to cheat the law; while in all other cases it would have its intended effect. I would favor the passage of a law on this subject which might not be very easily evaded. Let it be such that the labor and difficulty of evading it could only be justified in cases of greatest necessity.
Upon the subject of education, not presuming to dictate any plan or system respecting it, I can only say that I view it as the most important subject which we as a people can be engaged in. That every man may receive at least a moderate education, and thereby be enabled to read the histories of his own and other countries, by which he may duly appreciate the value of our free institutions, appears to be an object of vital importance, even on this account alone, to say nothing of the advantages and satisfaction to be derived from all being able to read the Scriptures, and other works both of a religious and moral nature, for themselves.
For my part, I desire to see the time when education—and by its means, morality, sobriety, enterprise, and industry—shall become much more general than at present, and should be gratified to have it in my power to contribute something to the advancement of any measure which might have a tendency to accelerate that happy period.
With regard to existing laws, some alterations are thought to be necessary. Many respectable men have suggested that our estray laws, the law respecting the issuing of executions, the road law, and some others, are deficient in their present form, and require alterations. But, considering the great probability that the framers of those laws were wiser than myself, I should prefer not meddling with them, unless they were first attacked by others; in which case I should feel it both a privilege and a duty to take that stand which, in my view, might tend most to the advancement of justice.
But, fellow-citizens, I shall conclude. Considering the great degree of modesty which should always attend youth, it is probable I have already been more presuming than becomes me. However, upon the subjects of which I have treated, I have spoken as I have thought. I may be wrong in regard to any or all of them; but, holding it a sound maxim that it is better only sometimes to be right than at all times to be wrong, so soon as I discover my opinions to be erroneous, I shall be ready to renounce them.
Every man is said to have his peculiar ambition. Whether it be true or not, I can say, for one, that I have no other so great as that of being truly esteemed of my fellow-men, by rendering myself worthy of their esteem. How far I shall succeed in gratifying this ambition is yet to be developed. I am young, and unknown to many of you. I was born, and have ever remained, in the most humble walks of life. I have no wealthy or popular relations or friends to recommend me. My case is thrown exclusively upon the independent voters of the county; and, if elected, they will have conferred a favor upon me for which I shall be unremitting in my labors to compensate. But, if the good people in their wisdom shall see fit to keep me in the background, I have been too familiar with disappointments to be very much chagrined.
Your friend and fellow-citizen, A. LINCOLN.
New Salem, March 9, 1832.
E. C. BLANKENSHIP.
Dear Sir:—In regard to the time David Rankin served the enclosed discharge shows correctly—as well as I can recollect—having no writing to refer. The transfer of Rankin from my company occurred as follows: Rankin having lost his horse at Dixon's ferry and having acquaintance in one of the foot companies who were going down the river was desirous to go with them, and one Galishen being an acquaintance of mine and belonging to the company in which Rankin wished to go wished to leave it and join mine, this being the case it was agreed that they should exchange places and answer to each other's names—as it was expected we all would be discharged in very few days. As to a blanket—I have no knowledge of Rankin ever getting any. The above embraces all the facts now in my recollection which are pertinent to the case.
I shall take pleasure in giving any further information in my power should you call on me.
Your friend, A. LINCOLN.
Mr. SPEARS:
At your request I send you a receipt for the postage on your paper. I am somewhat surprised at your request. I will, however, comply with it. The law requires newspaper postage to be paid in advance, and now that I have waited a full year you choose to wound my feelings by insinuating that unless you get a receipt I will probably make you pay it again.
Respectfully, A. LINCOLN.
TO THE EDITOR OF THE "JOURNAL"—In your paper of last Saturday I see a communication, over the signature of "Many Voters," in which the candidates who are announced in the Journal are called upon to "show their hands." Agreed. Here's mine.
I go for all sharing the privileges of the government who assist in bearing its burdens. Consequently, I go for admitting all whites to the right of suffrage who pay taxes or bear arms (by no means excluding females).
If elected, I shall consider the whole people of Sangamon my constituents, as well those that oppose as those that support me.
While acting as their representative, I shall be governed by their will on all subjects upon which I have the means of knowing what their will is; and upon all others I shall do what my own judgment teaches me will best advance their interests. Whether elected or not, I go for distributing the proceeds of the sales of the public lands to the several States, to enable our State, in common with others, to dig canals and construct railroads without borrowing money and paying the interest on it. If alive on the first Monday in November, I shall vote for Hugh L. White for President.
Very respectfully, A. LINCOLN.
New Salem, June 21, 1836
DEAR COLONEL:—I am told that during my absence last week you passed through this place, and stated publicly that you were in possession of a fact or facts which, if known to the public, would entirely destroy the prospects of N. W. Edwards and myself at the ensuing election; but that, through favor to us, you should forbear to divulge them. No one has needed favors more than I, and, generally, few have been less unwilling to accept them; but in this case favor to me would be injustice to the public, and therefore I must beg your pardon for declining it. That I once had the confidence of the people of Sangamon, is sufficiently evident; and if I have since done anything, either by design or misadventure, which if known would subject me to a forfeiture of that confidence, he that knows of that thing, and conceals it, is a traitor to his country's interest.
I find myself wholly unable to form any conjecture of what fact or facts, real or supposed, you spoke; but my opinion of your veracity will not permit me for a moment to doubt that you at least believed what you said. I am flattered with the personal regard you manifested for me; but I do hope that, on more mature reflection, you will view the public interest as a paramount consideration, and therefore determine to let the worst come. I here assure you that the candid statement of facts on your part, however low it may sink me, shall never break the tie of personal friendship between us. I wish an answer to this, and you are at liberty to publish both, if you choose.
Very respectfully, A. LINCOLN.
MARY:—I have been sick ever since my arrival, or I should have written sooner. It is but little difference, however, as I have very little even yet to write. And more, the longer I can avoid the mortification of looking in the post-office for your letter and not finding it, the better. You see I am mad about that old letter yet. I don't like very well to risk you again. I'll try you once more, anyhow.
The new State House is not yet finished, and consequently the Legislature is doing little or nothing. The governor delivered an inflammatory political message, and it is expected there will be some sparring between the parties about it as soon as the two Houses get to business. Taylor delivered up his petition for the new county to one of our members this morning. I am told he despairs of its success, on account of all the members from Morgan County opposing it. There are names enough on the petition, I think, to justify the members from our county in going for it; but if the members from Morgan oppose it, which they say they will, the chance will be bad.
Our chance to take the seat of government to Springfield is better than I expected. An internal-improvement convention was held there since we met, which recommended a loan of several millions of dollars, on the faith of the State, to construct railroads. Some of the Legislature are for it, and some against it; which has the majority I cannot tell. There is great strife and struggling for the office of the United States Senator here at this time. It is probable we shall ease their pains in a few days. The opposition men have no candidate of their own, and consequently they will smile as complacently at the angry snarl of the contending Van Buren candidates and their respective friends as the Christian does at Satan's rage. You recollect that I mentioned at the outset of this letter that I had been unwell. That is the fact, though I believe I am about well now; but that, with other things I cannot account for, have conspired, and have gotten my spirits so low that I feel that I would rather be any place in the world than here. I really cannot endure the thought of staying here ten weeks. Write back as soon as you get this, and, if possible, say something that will please me, for really I have not been pleased since I left you. This letter is so dry and stupid that I am ashamed to send it, but with my present feelings I cannot do any better.
Give my best respects to Mr. and Mrs. Able and family.
Your friend, LINCOLN
Mr. CHAIRMAN:—Lest I should fall into the too common error of being mistaken in regard to which side I design to be upon, I shall make it my first care to remove all doubt on that point, by declaring that I am opposed to the resolution under consideration, in toto. Before I proceed to the body of the subject, I will further remark, that it is not without a considerable degree of apprehension that I venture to cross the track of the gentleman from Coles [Mr. Linder]. Indeed, I do not believe I could muster a sufficiency of courage to come in contact with that gentleman, were it not for the fact that he, some days since, most graciously condescended to assure us that he would never be found wasting ammunition on small game. On the same fortunate occasion, he further gave us to understand, that he regarded himself as being decidedly the superior of our common friend from Randolph [Mr. Shields]; and feeling, as I really do, that I, to say the most of myself, am nothing more than the peer of our friend from Randolph, I shall regard the gentleman from Coles as decidedly my superior also, and consequently, in the course of what I shall have to say, whenever I shall have occasion to allude to that gentleman, I shall endeavor to adopt that kind of court language which I understand to be due to decided superiority. In one faculty, at least, there can be no dispute of the gentleman's superiority over me and most other men, and that is, the faculty of entangling a subject, so that neither himself, or any other man, can find head or tail to it. Here he has introduced a resolution embracing ninety-nine printed lines across common writing paper, and yet more than one half of his opening speech has been made upon subjects about which there is not one word said in his resolution.
Though his resolution embraces nothing in regard to the constitutionality of the Bank, much of what he has said has been with a view to make the impression that it was unconstitutional in its inception. Now, although I am satisfied that an ample field may be found within the pale of the resolution, at least for small game, yet, as the gentleman has traveled out of it, I feel that I may, with all due humility, venture to follow him. The gentleman has discovered that some gentleman at Washington city has been upon the very eve of deciding our Bank unconstitutional, and that he would probably have completed his very authentic decision, had not some one of the Bank officers placed his hand upon his mouth, and begged him to withhold it. The fact that the individuals composing our Supreme Court have, in an official capacity, decided in favor of the constitutionality of the Bank, would, in my mind, seem a sufficient answer to this. It is a fact known to all, that the members of the Supreme Court, together with the Governor, form a Council of Revision, and that this Council approved this Bank charter. I ask, then, if the extra-judicial decision not quite but almost made by the gentleman at Washington, before whom, by the way, the question of the constitutionality of our Bank never has, nor never can come—is to be taken as paramount to a decision officially made by that tribunal, by which, and which alone, the constitutionality of the Bank can ever be settled? But, aside from this view of the subject, I would ask, if the committee which this resolution proposes to appoint are to examine into the Constitutionality of the Bank? Are they to be clothed with power to send for persons and papers, for this object? And after they have found the bank to be unconstitutional, and decided it so, how are they to enforce their decision? What will their decision amount to? They cannot compel the Bank to cease operations, or to change the course of its operations. What good, then, can their labors result in? Certainly none.
The gentleman asks, if we, without an examination, shall, by giving the State deposits to the Bank, and by taking the stock reserved for the State, legalize its former misconduct. Now I do not pretend to possess sufficient legal knowledge to decide whether a legislative enactment proposing to, and accepting from, the Bank, certain terms, would have the effect to legalize or wipe out its former errors, or not; but I can assure the gentleman, if such should be the effect, he has already got behind the settlement of accounts; for it is well known to all, that the Legislature, at its last session, passed a supplemental Bank charter, which the Bank has since accepted, and which, according to his doctrine, has legalized all the alleged violations of its original charter in the distribution of its stock.
I now proceed to the resolution. By examination it will be found that the first thirty-three lines, being precisely one third of the whole, relate exclusively to the distribution of the stock by the commissioners appointed by the State. Now, Sir, it is clear that no question can arise on this portion of the resolution, except a question between capitalists in regard to the ownership of stock. Some gentlemen have their stock in their hands, while others, who have more money than they know what to do with, want it; and this, and this alone, is the question, to settle which we are called on to squander thousands of the people's money. What interest, let me ask, have the people in the settlement of this question? What difference is it to them whether the stock is owned by Judge Smith or Sam Wiggins? If any gentleman be entitled to stock in the Bank, which he is kept out of possession of by others, let him assert his right in the Supreme Court, and let him or his antagonist, whichever may be found in the wrong, pay the costs of suit. It is an old maxim, and a very sound one, that he that dances should always pay the fiddler. Now, Sir, in the present case, if any gentlemen, whose money is a burden to them, choose to lead off a dance, I am decidedly opposed to the people's money being used to pay the fiddler. No one can doubt that the examination proposed by this resolution must cost the State some ten or twelve thousand dollars; and all this to settle a question in which the people have no interest, and about which they care nothing. These capitalists generally act harmoniously and in concert, to fleece the people, and now that they have got into a quarrel with themselves we are called upon to appropriate the people's money to settle the quarrel.
I leave this part of the resolution and proceed to the remainder. It will be found that no charge in the remaining part of the resolution, if true, amounts to the violation of the Bank charter, except one, which I will notice in due time. It might seem quite sufficient to say no more upon any of these charges or insinuations than enough to show they are not violations of the charter; yet, as they are ingeniously framed and handled, with a view to deceive and mislead, I will notice in their order all the most prominent of them. The first of these is in relation to a connection between our Bank and several banking institutions in other States. Admitting this connection to exist, I should like to see the gentleman from Coles, or any other gentleman, undertake to show that there is any harm in it. What can there be in such a connection, that the people of Illinois are willing to pay their money to get a peep into? By a reference to the tenth section of the Bank charter, any gentleman can see that the framers of the act contemplated the holding of stock in the institutions of other corporations. Why, then, is it, when neither law nor justice forbids it, that we are asked to spend our time and money in inquiring into its truth?
The next charge, in the order of time, is, that some officer, director, clerk or servant of the Bank, has been required to take an oath of secrecy in relation to the affairs of said Bank. Now, I do not know whether this be true or false—neither do I believe any honest man cares. I know that the seventh section of the charter expressly guarantees to the Bank the right of making, under certain restrictions, such by-laws as it may think fit; and I further know that the requiring an oath of secrecy would not transcend those restrictions. What, then, if the Bank has chosen to exercise this right? Whom can it injure? Does not every merchant have his secret mark? and who is ever silly enough to complain of it? I presume if the Bank does require any such oath of secrecy, it is done through a motive of delicacy to those individuals who deal with it. Why, Sir, not many days since, one gentleman upon this floor, who, by the way, I have no doubt is now ready to join this hue and cry against the Bank, indulged in a philippic against one of the Bank officials, because, as he said, he had divulged a secret.
Immediately following this last charge, there are several insinuations in the resolution, which are too silly to require any sort of notice, were it not for the fact that they conclude by saying, "to the great injury of the people at large." In answer to this I would say that it is strange enough, that the people are suffering these "great injuries," and yet are not sensible of it! Singular indeed that the people should be writhing under oppression and injury, and yet not one among them to be found to raise the voice of complaint. If the Bank be inflicting injury upon the people, why is it that not a single petition is presented to this body on the subject? If the Bank really be a grievance, why is it that no one of the real people is found to ask redress of it? The truth is, no such oppression exists. If it did, our people would groan with memorials and petitions, and we would not be permitted to rest day or night, till we had put it down. The people know their rights, and they are never slow to assert and maintain them, when they are invaded. Let them call for an investigation, and I shall ever stand ready to respond to the call. But they have made no such call. I make the assertion boldly, and without fear of contradiction, that no man, who does not hold an office, or does not aspire to one, has ever found any fault of the Bank. It has doubled the prices of the products of their farms, and filled their pockets with a sound circulating medium, and they are all well pleased with its operations. No, Sir, it is the politician who is the first to sound the alarm (which, by the way, is a false one.) It is he, who, by these unholy means, is endeavoring to blow up a storm that he may ride upon and direct. It is he, and he alone, that here proposes to spend thousands of the people's public treasure, for no other advantage to them than to make valueless in their pockets the reward of their industry. Mr. Chairman, this work is exclusively the work of politicians; a set of men who have interests aside from the interests of the people, and who, to say the most of them, are, taken as a mass, at least one long step removed from honest men. I say this with the greater freedom, because, being a politician myself, none can regard it as personal.
Again, it is charged, or rather insinuated, that officers of the Bank have loaned money at usurious rates of interest. Suppose this to be true, are we to send a committee of this House to inquire into it? Suppose the committee should find it true, can they redress the injured individuals? Assuredly not. If any individual had been injured in this way, is there not an ample remedy to be found in the laws of the land? Does the gentleman from Coles know that there is a statute standing in full force making it highly penal for an individual to loan money at a higher rate of interest than twelve per cent? If he does not he is too ignorant to be placed at the head of the committee which his resolution purposes and if he does, his neglect to mention it shows him to be too uncandid to merit the respect or confidence of any one.
But besides all this, if the Bank were struck from existence, could not the owners of the capital still loan it usuriously, as well as now? whatever the Bank, or its officers, may have done, I know that usurious transactions were much more frequent and enormous before the commencement of its operations than they have ever been since.
The next insinuation is, that the Bank has refused specie payments. This, if true is a violation of the charter. But there is not the least probability of its truth; because, if such had been the fact, the individual to whom payment was refused would have had an interest in making it public, by suing for the damages to which the charter entitles him. Yet no such thing has been done; and the strong presumption is, that the insinuation is false and groundless.
From this to the end of the resolution, there is nothing that merits attention—I therefore drop the particular examination of it.
By a general view of the resolution, it will be seen that a principal object of the committee is to examine into, and ferret out, a mass of corruption supposed to have been committed by the commissioners who apportioned the stock of the Bank. I believe it is universally understood and acknowledged that all men will ever act correctly unless they have a motive to do otherwise. If this be true, we can only suppose that the commissioners acted corruptly by also supposing that they were bribed to do so. Taking this view of the subject, I would ask if the Bank is likely to find it more difficult to bribe the committee of seven, which, we are about to appoint, than it may have found it to bribe the commissioners?
(Here Mr. Linder called to order. The Chair decided that Mr. Lincoln was not out of order. Mr. Linder appealed to the House, but, before the question was put, withdrew his appeal, saying he preferred to let the gentleman go on; he thought he would break his own neck. Mr. Lincoln proceeded:)
Another gracious condescension! I acknowledge it with gratitude. I know I was not out of order; and I know every sensible man in the House knows it. I was not saying that the gentleman from Coles could be bribed, nor, on the other hand, will I say he could not. In that particular I leave him where I found him. I was only endeavoring to show that there was at least as great a probability of any seven members that could be selected from this House being bribed to act corruptly, as there was that the twenty-four commissioners had been so bribed. By a reference to the ninth section of the Bank charter, it will be seen that those commissioners were John Tilson, Robert K. McLaughlin, Daniel Warm, A.G. S. Wight, John C. Riley, W. H. Davidson, Edward M. Wilson, Edward L. Pierson, Robert R. Green, Ezra Baker, Aquilla Wren, John Taylor, Samuel C. Christy, Edmund Roberts, Benjamin Godfrey, Thomas Mather, A. M. Jenkins, W. Linn, W. S. Gilman, Charles Prentice, Richard I. Hamilton, A.H. Buckner, W. F. Thornton, and Edmund D. Taylor.
These are twenty-four of the most respectable men in the State. Probably no twenty-four men could be selected in the State with whom the people are better acquainted, or in whose honor and integrity they would more readily place confidence. And I now repeat, that there is less probability that those men have been bribed and corrupted, than that any seven men, or rather any six men, that could be selected from the members of this House, might be so bribed and corrupted, even though they were headed and led on by "decided superiority" himself.
In all seriousness, I ask every reasonable man, if an issue be joined by these twenty-four commissioners, on the one part, and any other seven men, on the other part, and the whole depend upon the honor and integrity of the contending parties, to which party would the greatest degree of credit be due? Again: Another consideration is, that we have no right to make the examination. What I shall say upon this head I design exclusively for the law-loving and law-abiding part of the House. To those who claim omnipotence for the Legislature, and who in the plenitude of their assumed powers are disposed to disregard the Constitution, law, good faith, moral right, and everything else, I have not a word to say. But to the law-abiding part I say, examine the Bank charter, go examine the Constitution, go examine the acts that the General Assembly of this State has passed, and you will find just as much authority given in each and every of them to compel the Bank to bring its coffers to this hall and to pour their contents upon this floor, as to compel it to submit to this examination which this resolution proposes. Why, Sir, the gentleman from Coles, the mover of this resolution, very lately denied on this floor that the Legislature had any right to repeal or otherwise meddle with its own acts, when those acts were made in the nature of contracts, and had been accepted and acted on by other parties. Now I ask if this resolution does not propose, for this House alone, to do what he, but the other day, denied the right of the whole Legislature to do? He must either abandon the position he then took, or he must now vote against his own resolution. It is no difference to me, and I presume but little to any one else, which he does.
I am by no means the special advocate of the Bank. I have long thought that it would be well for it to report its condition to the General Assembly, and that cases might occur, when it might be proper to make an examination of its affairs by a committee. Accordingly, during the last session, while a bill supplemental to the Bank charter was pending before the House, I offered an amendment to the same, in these words: "The said corporation shall, at the next session of the General Assembly, and at each subsequent General Session, during the existence of its charter, report to the same the amount of debts due from said corporation; the amount of debts due to the same; the amount of specie in its vaults, and an account of all lands then owned by the same, and the amount for which such lands have been taken; and moreover, if said corporation shall at any time neglect or refuse to submit its books, papers, and all and everything necessary for a full and fair examination of its affairs, to any person or persons appointed by the General Assembly, for the purpose of making such examination, the said corporation shall forfeit its charter."
This amendment was negatived by a vote of 34 to 15. Eleven of the 34 who voted against it are now members of this House; and though it would be out of order to call their names, I hope they will all recollect themselves, and not vote for this examination to be made without authority, inasmuch as they refused to receive the authority when it was in their power to do so.
I have said that cases might occur, when an examination might be proper; but I do not believe any such case has now occurred; and if it has, I should still be opposed to making an examination without legal authority. I am opposed to encouraging that lawless and mobocratic spirit, whether in relation to the Bank or anything else, which is already abroad in the land and is spreading with rapid and fearful impetuosity, to the ultimate overthrow of every institution, of every moral principle, in which persons and property have hitherto found security.
But supposing we had the authority, I would ask what good can result from the examination? Can we declare the Bank unconstitutional, and compel it to desist from the abuses of its power, provided we find such abuses to exist? Can we repair the injuries which it may have done to individuals? Most certainly we can do none of these things. Why then shall we spend the public money in such employment? Oh, say the examiners, we can injure the credit of the Bank, if nothing else, Please tell me, gentlemen, who will suffer most by that? You cannot injure, to any extent, the stockholders. They are men of wealth—of large capital; and consequently, beyond the power of malice. But by injuring the credit of the Bank, you will depreciate the value of its paper in the hands of the honest and unsuspecting farmer and mechanic, and that is all you can do. But suppose you could effect your whole purpose; suppose you could wipe the Bank from existence, which is the grand ultimatum of the project, what would be the consequence? why, Sir, we should spend several thousand dollars of the public treasure in the operation, annihilate the currency of the State, render valueless in the hands of our people that reward of their former labors, and finally be once more under the comfortable obligation of paying the Wiggins loan, principal and interest.
January 27, 1837.
As a subject for the remarks of the evening, "The Perpetuation of our Political Institutions" is selected.
In the great journal of things happening under the sun, we, the American people, find our account running under date of the nineteenth century of the Christian era. We find ourselves in the peaceful possession of the fairest portion of the earth as regards extent of territory, fertility of soil, and salubrity of climate. We find ourselves under the government of a system of political institutions conducing more essentially to the ends of civil and religious liberty than any of which the history of former times tells us. We, when mounting the stage of existence, found ourselves the legal inheritors of these fundamental blessings. We toiled not in the acquirement or establishment of them; they are a legacy bequeathed us by a once hardy, brave, and patriotic, but now lamented and departed, race of ancestors. Theirs was the task (and nobly they performed it) to possess themselves, and through themselves us, of this goodly land, and to uprear upon its hills and its valleys a political edifice of liberty and equal rights; it is ours only to transmit these—the former unprofaned by the foot of an invader, the latter undecayed by the lapse of time and untorn by usurpation—to the latest generation that fate shall permit the world to know. This task gratitude to our fathers, justice to ourselves, duty to posterity, and love for our species in general, all imperatively require us faithfully to perform.
How then shall we perform it? At what point shall we expect the approach of danger? By what means shall we fortify against it? Shall we expect some transatlantic military giant to step the ocean and crush us at a blow? Never! All the armies of Europe, Asia, and Africa combined, with all the treasure of the earth (our own excepted) in their military chest, with a Bonaparte for a commander, could not by force take a drink from the Ohio or make a track on the Blue Ridge in a trial of a thousand years.
At what point then is the approach of danger to be expected? I answer: If it ever reach us it must spring up amongst us; it cannot come from abroad. If destruction be our lot we must ourselves be its author and finisher. As a nation of freemen we must live through all time, or die by suicide.
I hope I am over-wary; but if I am not, there is even now something of ill omen amongst us. I mean the increasing disregard for law which pervades the country—the growing disposition to substitute the wild and furious passions in lieu of the sober judgment of courts, and the worse than savage mobs for the executive ministers of justice. This disposition is awfully fearful in any community; and that it now exists in ours, though grating to our feelings to admit, it would be a violation of truth and an insult to our intelligence to deny. Accounts of outrages committed by mobs form the everyday news of the times. They have pervaded the country from New England to Louisiana; they are neither peculiar to the eternal snows of the former nor the burning suns of the latter; they are not the creature of climate, neither are they confined to the slave holding or the non-slave holding States. Alike they spring up among the pleasure-hunting masters of Southern slaves, and the order-loving citizens of the land of steady habits. Whatever then their cause may be, it is common to the whole country.
It would be tedious as well as useless to recount the horrors of all of them. Those happening in the State of Mississippi and at St. Louis are perhaps the most dangerous in example and revolting to humanity. In the Mississippi case they first commenced by hanging the regular gamblers—a set of men certainly not following for a livelihood a very useful or very honest occupation, but one which, so far from being forbidden by the laws, was actually licensed by an act of the Legislature passed but a single year before. Next, negroes suspected of conspiring to raise an insurrection were caught up and hanged in all parts of the State; then, white men supposed to be leagued with the negroes; and finally, strangers from neighboring States, going thither on business, were in many instances subjected to the same fate. Thus went on this process of hanging, from gamblers to negroes, from negroes to white citizens, and from these to strangers, till dead men were seen literally dangling from the boughs of trees upon every roadside, and in numbers almost sufficient to rival the native Spanish moss of the country as a drapery of the forest.
Turn then to that horror-striking scene at St. Louis. A single victim only was sacrificed there. This story is very short, and is perhaps the most highly tragic of anything of its length that has ever been witnessed in real life. A mulatto man by the name of McIntosh was seized in the street, dragged to the suburbs of the city, chained to a tree, and actually burned to death; and all within a single hour from the time he had been a freeman attending to his own business and at peace with the world.
Such are the effects of mob law, and such are the scenes becoming more and more frequent in this land so lately famed for love of law and order, and the stories of which have even now grown too familiar to attract anything more than an idle remark.
But you are perhaps ready to ask, "What has this to do with the perpetuation of our political institutions?" I answer, It has much to do with it. Its direct consequences are, comparatively speaking, but a small evil, and much of its danger consists in the proneness of our minds to regard its direct as its only consequences. Abstractly considered, the hanging of the gamblers at Vicksburg was of but little consequence. They constitute a portion of population that is worse than useless in any community; and their death, if no pernicious example be set by it, is never matter of reasonable regret with any one. If they were annually swept from the stage of existence by the plague or smallpox, honest men would perhaps be much profited by the operation. Similar too is the correct reasoning in regard to the burning of the negro at St. Louis. He had forfeited his life by the perpetration of an outrageous murder upon one of the most worthy and respectable citizens of the city, and had he not died as he did, he must have died by the sentence of the law in a very short time afterwards. As to him alone, it was as well the way it was as it could otherwise have been. But the example in either case was fearful. When men take it in their heads to-day to hang gamblers or burn murderers, they should recollect that in the confusion usually attending such transactions they will be as likely to hang or burn some one who is neither a gambler nor a murderer as one who is, and that, acting upon the example they set, the mob of to-morrow may, and probably will, hang or burn some of them by the very same mistake. And not only so: the innocent, those who have ever set their faces against violations of law in every shape, alike with the guilty fall victims to the ravages of mob law; and thus it goes on, step by step, till all the walls erected for the defense of the persons and property of individuals are trodden down and disregarded. But all this, even, is not the full extent of the evil. By such examples, by instances of the perpetrators of such acts going unpunished, the lawless in spirit are encouraged to become lawless in practice; and having been used to no restraint but dread of punishment, they thus become absolutely unrestrained. Having ever regarded government as their deadliest bane, they make a jubilee of the suspension of its operations, and pray for nothing so much as its total annihilation. While, on the other hand, good men, men who love tranquillity, who desire to abide by the laws and enjoy their benefits, who would gladly spill their blood in the defense of their country, seeing their property destroyed, their families insulted, and their lives endangered, their persons injured, and seeing nothing in prospect that forebodes a change for the better, become tired of and disgusted with a government that offers them no protection, and are not much averse to a change in which they imagine they have nothing to lose. Thus, then, by the operation of this mobocratic spirit which all must admit is now abroad in the land, the strongest bulwark of any government, and particularly of those constituted like ours, may effectually be broken down and destroyed—I mean the attachment of the people. Whenever this effect shall be produced among us; whenever the vicious portion of population shall be permitted to gather in bands of hundreds and thousands, and burn churches, ravage and rob provision-stores, throw printing presses into rivers, shoot editors, and hang and burn obnoxious persons at pleasure and with impunity, depend on it, this government cannot last. By such things the feelings of the best citizens will become more or less alienated from it, and thus it will be left without friends, or with too few, and those few too weak to make their friendship effectual. At such a time, and under such circumstances, men of sufficient talent and ambition will not be wanting to seize the opportunity, strike the blow, and overturn that fair fabric which for the last half century has been the fondest hope of the lovers of freedom throughout the world.
I know the American people are much attached to their government; I know they would suffer much for its sake; I know they would endure evils long and patiently before they would ever think of exchanging it for another,—yet, notwithstanding all this, if the laws be continually despised and disregarded, if their rights to be secure in their persons and property are held by no better tenure than the caprice of a mob, the alienation of their affections from the government is the natural consequence; and to that, sooner or later, it must come.
Here, then, is one point at which danger may be expected.
The question recurs, How shall we fortify against it? The answer is simple. Let every American, every lover of liberty, every well-wisher to his posterity swear by the blood of the Revolution never to violate in the least particular the laws of the country, and never to tolerate their violation by others. As the patriots of seventy-six did to the support of the Declaration of Independence, so to the support of the Constitution and laws let every American pledge his life, his property, and his sacred honor. Let every man remember that to violate the law is to trample on the blood of his father, and to tear the charter of his own and his children's liberty. Let reverence for the laws be breathed by every American mother to the lisping babe that prattles on her lap; let it be taught in schools, in seminaries, and in colleges; let it be written in primers, spelling books, and in almanacs; let it be preached from the pulpit, proclaimed in legislative halls, and enforced in courts of justice. And, in short, let it become the political religion of the nation; and let the old and the young, the rich and the poor, the grave and the gay of all sexes and tongues and colors and conditions, sacrifice unceasingly upon its altars.
While ever a state of feeling such as this shall universally or even very generally prevail throughout the nation, vain will be every effort, and fruitless every attempt, to subvert our national freedom.
When, I so pressingly urge a strict observance of all the laws, let me not be understood as saying there are no bad laws, or that grievances may not arise for the redress of which no legal provisions have been made. I mean to say no such thing. But I do mean to say that although bad laws, if they exist, should be repealed as soon as possible, still, while they continue in force, for the sake of example they should be religiously observed. So also in unprovided cases. If such arise, let proper legal provisions be made for them with the least possible delay, but till then let them, if not too intolerable, be borne with.
There is no grievance that is a fit object of redress by mob law. In any case that may arise, as, for instance, the promulgation of abolitionism, one of two positions is necessarily true—that is, the thing is right within itself, and therefore deserves the protection of all law and all good citizens, or it is wrong, and therefore proper to be prohibited by legal enactments; and in neither case is the interposition of mob law either necessary, justifiable, or excusable.
But it may be asked, Why suppose danger to our political institutions? Have we not preserved them for more than fifty years? And why may we not for fifty times as long?
We hope there is no sufficient reason. We hope all danger may be overcome; but to conclude that no danger may ever arise would itself be extremely dangerous. There are now, and will hereafter be, many causes, dangerous in their tendency, which have not existed heretofore, and which are not too insignificant to merit attention. That our government should have been maintained in its original form, from its establishment until now, is not much to be wondered at. It had many props to support it through that period, which now are decayed and crumbled away. Through that period it was felt by all to be an undecided experiment; now it is understood to be a successful one. Then, all that sought celebrity and fame and distinction expected to find them in the success of that experiment. Their all was staked upon it; their destiny was inseparably Alinked with it. Their ambition aspired to display before an admiring world a practical demonstration of the truth of a proposition which had hitherto been considered at best no better than problematical—namely, the capability of a people to govern themselves. If they succeeded they were to be immortalized; their names were to be transferred to counties, and cities, and rivers, and mountains; and to be revered and sung, toasted through all time. If they failed, they were to be called knaves and fools, and fanatics for a fleeting hour; then to sink and be forgotten. They succeeded. The experiment is successful, and thousands have won their deathless names in making it so. But the game is caught; and I believe it is true that with the catching end the pleasures of the chase. This field of glory is harvested, and the crop is already appropriated. But new reapers will arise, and they too will seek a field. It is to deny what the history of the world tells us is true, to suppose that men of ambition and talents will not continue to spring up amongst us. And when they do, they will as naturally seek the gratification of their ruling passion as others have done before them. The question then is, Can that gratification be found in supporting and in maintaining an edifice that has been erected by others? Most certainly it cannot. Many great and good men, sufficiently qualified for any task they should undertake, may ever be found whose ambition would aspire to nothing beyond a seat in Congress, a Gubernatorial or a Presidential chair; but such belong not to the family of the lion, or the tribe of the eagle. What! think you these places would satisfy an Alexander, a Caesar, or a Napoleon? Never! Towering genius disdains a beaten path. It seeks regions hitherto unexplored. It sees no distinction in adding story to story upon the monuments of fame erected to the memory of others. It denies that it is glory enough to serve under any chief. It scorns to tread in the footsteps of any predecessor, however illustrious. It thirsts and burns for distinction; and if possible, it will have it, whether at the expense of emancipating slaves or enslaving freemen. Is it unreasonable, then, to expect that some man possessed of the loftiest genius, coupled with ambition sufficient to push it to its utmost stretch, will at some time spring up among us? And when such an one does it will require the people to be united with each other, attached to the government and laws, and generally intelligent, to successfully frustrate his designs.
Distinction will be his paramount object, and although he would as willingly, perhaps more so, acquire it by doing good as harm, yet, that opportunity being past, and nothing left to be done in the way of building up, he would set boldly to the task of pulling down.
Here then is a probable case, highly dangerous, and such an one as could not have well existed heretofore.
Another reason which once was, but which, to the same extent, is now no more, has done much in maintaining our institutions thus far. I mean the powerful influence which the interesting scenes of the Revolution had upon the passions of the people as distinguished from their judgment. By this influence, the jealousy, envy, and avarice incident to our nature, and so common to a state of peace, prosperity, and conscious strength, were for the time in a great measure smothered and rendered inactive, while the deep-rooted principles of hate, and the powerful motive of revenge, instead of being turned against each other, were directed exclusively against the British nation. And thus, from the force of circumstances, the basest principles of our nature were either made to lie dormant, or to become the active agents in the advancement of the noblest of causes—that of establishing and maintaining civil and religious liberty.
But this state of feeling must fade, is fading, has faded, with the circumstances that produced it.
I do not mean to say that the scenes of the Revolution are now or ever will be entirely forgotten, but that, like everything else, they must fade upon the memory of the world, and grow more and more dim by the lapse of time. In history, we hope, they will be read of, and recounted, so long as the Bible shall be read; but even granting that they will, their influence cannot be what it heretofore has been. Even then they cannot be so universally known nor so vividly felt as they were by the generation just gone to rest. At the close of that struggle, nearly every adult male had been a participator in some of its scenes. The consequence was that of those scenes, in the form of a husband, a father, a son, or a brother, a living history was to be found in every family—a history bearing the indubitable testimonies of its own authenticity, in the limbs mangled, in the scars of wounds received, in the midst of the very scenes related—a history, too, that could be read and understood alike by all, the wise and the ignorant, the learned and the unlearned. But those histories are gone. They can be read no more forever. They were a fortress of strength; but what invading foeman could never do the silent artillery of time has done—the leveling of its walls. They are gone. They were a forest of giant oaks; but the all-restless hurricane has swept over them, and left only here and there a lonely trunk, despoiled of its verdure, shorn of its foliage, unshading and unshaded, to murmur in a few more gentle breezes, and to combat with its mutilated limbs a few more ruder storms, then to sink and be no more.
They were pillars of the temple of liberty; and now that they have crumbled away that temple must fall unless we, their descendants, supply their places with other pillars, hewn from the solid quarry of sober reason. Passion has helped us, but can do so no more. It will in future be our enemy. Reason cold, calculating, unimpassioned reason—must furnish all the materials for our future support and defense. Let those materials be moulded into general intelligence, sound morality, and in particular, a reverence for the Constitution and laws; and that we improved to the last, that we remained free to the last, that we revered his name to the last, that during his long sleep we permitted no hostile foot to pass over or desecrate his resting place, shall be that which to learn the last trump shall awaken our Washington.
Upon these let the proud fabric of freedom rest, as the rock of its basis; and as truly as has been said of the only greater institution, "the gates of hell shall not prevail against it."
The following protest was presented to the House, which was read and ordered to be spread in the journals, to wit:
"Resolutions upon the subject of domestic slavery having passed both branches of the General Assembly at its present session, the undersigned hereby protest against the passage of the same.
"They believe that the institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy, but that the promulgation of abolition doctrines tends rather to increase than abate its evils.
"They believe that the Congress of the United States has no power under the Constitution to interfere with the institution of slavery in the different States.
"They believe that the Congress of the United States has the power, under the Constitution, to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, but that the power ought not to be exercised, unless at the request of the people of the District.
"The difference between these opinions and those contained in the said resolutions is their reason for entering this protest.
"DAN STONE, "A. LINCOLN,
"Representatives from the County of Sangamon."
MISS MARY S. OWENS.
FRIEND MARY:—I have commenced two letters to send you before this, both of which displeased me before I got half done, and so I tore them up. The first I thought was not serious enough, and the second was on the other extreme. I shall send this, turn out as it may.
This thing of living in Springfield is rather a dull business, after all; at least it is so to me. I am quite as lonesome here as I ever was anywhere in my life. I have been spoken to by but one woman since I have been here, and should not have been by her if she could have avoided it. I 've never been to church yet, and probably shall not be soon. I stay away because I am conscious I should not know how to behave myself.
I am often thinking of what we said about your coming to live at Springfield. I am afraid you would not be satisfied. There is a great deal of flourishing about in carriages here, which it would be your doom to see without sharing it. You would have to be poor, without the means of hiding your poverty. Do you believe you could bear that patiently? Whatever woman may cast her lot with mine, should any ever do so, it is my intention to do all in my power to make her happy and contented; and there is nothing I can imagine that would make me more unhappy than to fail in the effort. I know I should be much happier with you than the way I am, provided I saw no signs of discontent in you. What you have said to me may have been in the way of jest, or I may have misunderstood you. If so, then let it be forgotten; if otherwise, I much wish you would think seriously before you decide. What I have said I will most positively abide by, provided you wish it. My opinion is that you had better not do it. You have not been accustomed to hardship, and it may be more severe than you now imagine. I know you are capable of thinking correctly on any subject, and if you deliberate maturely upon this subject before you decide, then I am willing to abide your decision.
You must write me a good long letter after you get this. You have nothing else to do, and though it might not seem interesting to you after you had written it, it would be a good deal of company to me in this "busy wilderness." Tell your sister I don't want to hear any more about selling out and moving. That gives me the "hypo" whenever I think of it.
Yours, etc., LINCOLN.
DEAR SIR:-Mr. Edwards tells me you wish to know whether the act to which your own incorporation provision was attached passed into a law. It did. You can organize under the general incorporation law as soon as you choose.
I also tacked a provision onto a fellow's bill to authorize the relocation of the road from Salem down to your town, but I am not certain whether or not the bill passed, neither do I suppose I can ascertain before the law will be published, if it is a law. Bowling Greene, Bennette Abe? and yourself are appointed to make the change. No news. No excitement except a little about the election of Monday next.
I suppose, of course, our friend Dr. Heney stands no chance in your diggings.
Your friend and humble servant, A. LINCOLN.
FRIEND MARY: You will no doubt think it rather strange that I should write you a letter on the same day on which we parted, and I can only account for it by supposing that seeing you lately makes me think of you more than usual; while at our late meeting we had but few expressions of thoughts. You must know that I cannot see you, or think of you, with entire indifference; and yet it may be that you are mistaken in regard to what my real feelings toward you are.
If I knew you were not, I should not have troubled you with this letter. Perhaps any other man would know enough without information; but I consider it my peculiar right to plead ignorance, and your bounden duty to allow the plea.
I want in all cases to do right; and most particularly so in all cases with women.
I want, at this particular time, more than any thing else to do right with you; and if I knew it would be doing right, as I rather suspect it would, to let you alone I would do it. And, for the purpose of making the matter as plain as possible, I now say that you can drop the subject, dismiss your thoughts (if you ever had any) from me for ever and leave this letter unanswered without calling forth one accusing murmur from me. And I will even go further and say that, if it will add anything to your comfort or peace of mind to do so, it is my sincere wish that you should. Do not understand by this that I wish to cut your acquaintance. I mean no such thing. What I do wish is that our further acquaintance shall depend upon yourself. If such further acquaintance would contribute nothing to your happiness, I am sure it would not to mine. If you feel yourself in any degree bound to me, I am now willing to release you, provided you wish it; while on the other hand I am willing and even anxious to bind you faster if I can be convinced that it will, in any considerable degree, add to your happiness. This, indeed, is the whole question with me. Nothing would make me more miserable than to believe you miserable, nothing more happy than to know you were so.
In what I have now said, I think I cannot be misunderstood; and to make myself understood is the only object of this letter.
If it suits you best not to answer this, farewell. A long life and a merry one attend you. But, if you conclude to write back, speak as plainly as I do. There can neither be harm nor danger in saying to me anything you think, just in the manner you think it. My respects to your sister.
Your friend, LINCOLN.
"SANGAMON JOURNAL," SPRINGFIELD, ILL., Aug. 19, 1837.
In accordance with our determination, as expressed last week, we present to the reader the articles which were published in hand-bill form, in reference to the case of the heirs of Joseph Anderson vs. James Adams. These articles can now be read uninfluenced by personal or party feeling, and with the sole motive of learning the truth. When that is done, the reader can pass his own judgment on the matters at issue.
We only regret in this case, that the publications were not made some weeks before the election. Such a course might have prevented the expressions of regret, which have often been heard since, from different individuals, on account of the disposition they made of their votes.
To the Public:
It is well known to most of you, that there is existing at this time considerable excitement in regard to Gen. Adams's titles to certain tracts of land, and the manner in which he acquired them. As I understand, the Gen. charges that the whole has been gotten up by a knot of lawyers to injure his election; and as I am one of the knot to which he refers, and as I happen to be in possession of facts connected with the matter, I will, in as brief a manner as possible, make a statement of them, together with the means by which I arrived at the knowledge of them.
Sometime in May or June last, a widow woman, by the name of Anderson, and her son, who resides in Fulton county, came to Springfield, for the purpose as they said of selling a ten acre lot of ground lying near town, which they claimed as the property of the deceased husband and father.
When they reached town they found the land was claimed by Gen. Adams. John T. Stuart and myself were employed to look into the matter, and if it was thought we could do so with any prospect of success, to commence a suit for the land. I went immediately to the recorder's office to examine Adams's title, and found that the land had been entered by one Dixon, deeded by Dixon to Thomas, by Thomas to one Miller, and by Miller to Gen. Adams. The oldest of these three deeds was about ten or eleven years old, and the latest more than five, all recorded at the same time, and that within less than one year. This I thought a suspicious circumstance, and I was thereby induced to examine the deeds very closely, with a view to the discovery of some defect by which to overturn the title, being almost convinced then it was founded in fraud. I discovered that in the deed from Thomas to Miller, although Miller's name stood in a sort of marginal note on the record book, it was nowhere in the deed itself. I told the fact to Talbott, the recorder, and proposed to him that he should go to Gen. Adams's and get the original deed, and compare it with the record, and thereby ascertain whether the defect was in the original or there was merely an error in the recording. As Talbott afterwards told me, he went to the General's, but not finding him at home, got the deed from his son, which, when compared with the record, proved what we had discovered was merely an error of the recorder. After Mr. Talbott corrected the record, he brought the original to our office, as I then thought and think yet, to show us that it was right. When he came into the room he handed the deed to me, remarking that the fault was all his own. On opening it, another paper fell out of it, which on examination proved to be an assignment of a judgment in the Circuit Court of Sangamon County from Joseph Anderson, the late husband of the widow above named, to James Adams, the judgment being in favor of said Anderson against one Joseph Miller. Knowing that this judgment had some connection with the land affair, I immediately took a copy of it, which is word for word, letter for letter and cross for cross as follows:
Joseph Anderson, vs. Joseph Miller.
Judgment in Sangamon Circuit Court against Joseph Miller obtained on a note originally 25 dolls and interest thereon accrued. I assign all my right, title and interest to James Adams which is in consideration of a debt I owe said Adams.
his JOSEPH x ANDERSON. mark.
As the copy shows, it bore date May 10, 1827; although the judgment assigned by it was not obtained until the October afterwards, as may be seen by any one on the records of the Circuit Court. Two other strange circumstances attended it which cannot be represented by a copy. One of them was, that the date "1827" had first been made "1837" and, without the figure "3," being fully obliterated, the figure "2" had afterwards been made on top of it; the other was that, although the date was ten years old, the writing on it, from the freshness of its appearance, was thought by many, and I believe by all who saw it, not to be more than a week old. The paper on which it was written had a very old appearance; and there were some old figures on the back of it which made the freshness of the writing on the face of it much more striking than I suppose it otherwise might have been. The reader's curiosity is no doubt excited to know what connection this assignment had with the land in question. The story is this: Dixon sold and deeded the land to Thomas; Thomas sold it to Anderson; but before he gave a deed, Anderson sold it to Miller, and took Miller's note for the purchase money. When this note became due, Anderson sued Miller on it, and Miller procured an injunction from the Court of Chancery to stay the collection of the money until he should get a deed for the land. Gen. Adams was employed as an attorney by Anderson in this chancery suit, and at the October term, 1827, the injunction was dissolved, and a judgment given in favor of Anderson against Miller; and it was provided that Thomas was to execute a deed for the land in favor of Miller and deliver it to Gen. Adams, to be held up by him till Miller paid the judgment, and then to deliver it to him. Miller left the county without paying the judgment. Anderson moved to Fulton county, where he has since died When the widow came to Springfield last May or June, as before mentioned, and found the land deeded to Gen. Adams by Miller, she was naturally led to inquire why the money due upon the judgment had not been sent to them, inasmuch as he, Gen. Adams, had no authority to deliver Thomas's deed to Miller until the money was paid. Then it was the General told her, or perhaps her son, who came with her, that Anderson, in his lifetime, had assigned the judgment to him, Gen. Adams. I am now told that the General is exhibiting an assignment of the same judgment bearing date "1828" and in other respects differing from the one described; and that he is asserting that no such assignment as the one copied by me ever existed; or if there did, it was forged between Talbott and the lawyers, and slipped into his papers for the purpose of injuring him. Now, I can only say that I know precisely such a one did exist, and that Ben. Talbott, Wm. Butler, C.R. Matheny, John T. Stuart, Judge Logan, Robert Irwin, P. C. Canedy and S. M. Tinsley, all saw and examined it, and that at least one half of them will swear that IT WAS IN GENERAL ADAMS'S HANDWRITING!! And further, I know that Talbott will swear that he got it out of the General's possession, and returned it into his possession again. The assignment which the General is now exhibiting purports to have been by Anderson in writing. The one I copied was signed with a cross.
I am told that Gen. Neale says that he will swear that he heard Gen. Adams tell young Anderson that the assignment made by his father was signed with a cross.
The above are 'facts,' as stated. I leave them without comment. I have given the names of persons who have knowledge of these facts, in order that any one who chooses may call on them and ascertain how far they will corroborate my statements. I have only made these statements because I am known by many to be one of the individuals against whom the charge of forging the assignment and slipping it into the General's papers has been made, and because our silence might be construed into a confession of its truth. I shall not subscribe my name; but I hereby authorize the editor of the Journal to give it up to any one that may call for it.
In the Republican of this morning a publication of Gen. Adams's appears, in which my name is used quite unreservedly. For this I thank the General. I thank him because it gives me an opportunity, without appearing obtrusive, of explaining a part of a former publication of mine, which appears to me to have been misunderstood by many.
In the former publication alluded to, I stated, in substance, that Mr. Talbott got a deed from a son of Gen. Adams's for the purpose of correcting a mistake that had occurred on the record of the said deed in the recorder's office; that he corrected the record, and brought the deed and handed it to me, and that on opening the deed, another paper, being the assignment of a judgment, fell out of it. This statement Gen. Adams and the editor of the Republican have seized upon as a most palpable evidence of fabrication and falsehood. They set themselves gravely about proving that the assignment could not have been in the deed when Talbott got it from young Adams, as he, Talbott, would have seen it when he opened the deed to correct the record. Now, the truth is, Talbott did see the assignment when he opened the deed, or at least he told me he did on the same day; and I only omitted to say so, in my former publication, because it was a matter of such palpable and necessary inference. I had stated that Talbott had corrected the record by the deed; and of course he must have opened it; and, just as the General and his friends argue, must have seen the assignment. I omitted to state the fact of Talbott's seeing the assignment, because its existence was so necessarily connected with other facts which I did state, that I thought the greatest dunce could not but understand it. Did I say Talbott had not seen it? Did I say anything that was inconsistent with his having seen it before? Most certainly I did neither; and if I did not, what becomes of the argument? These logical gentlemen can sustain their argument only by assuming that I did say negatively everything that I did not say affirmatively; and upon the same assumption, we may expect to find the General, if a little harder pressed for argument, saying that I said Talbott came to our office with his head downward, not that I actually said so, but because I omitted to say he came feet downward.
In his publication to-day, the General produces the affidavit of Reuben Radford, in which it is said that Talbott told Radford that he did not find the assignment in the deed, in the recording of which the error was committed, but that he found it wrapped in another paper in the recorder's office, upon which statement the Genl. comments as follows, to wit: "If it be true as stated by Talbott to Radford, that he found the assignment wrapped up in another paper at his office, that contradicts the statement of Lincoln that it fell out of the deed."
Is common sense to be abused with such sophistry? Did I say what Talbott found it in? If Talbott did find it in another paper at his office, is that any reason why he could not have folded it in a deed and brought it to my office? Can any one be so far duped as to be made believe that what may have happened at Talbot's office at one time is inconsistent with what happened at my office at another time?
Now Talbott's statement of the case as he makes it to me is this, that he got a bunch of deeds from young Adams, and that he knows he found the assignment in the bunch, but he is not certain which particular deed it was in, nor is he certain whether it was folded in the same deed out of which it was taken, or another one, when it was brought to my office. Is this a mysterious story? Is there anything suspicious about it?
"But it is useless to dwell longer on this point. Any man who is not wilfully blind can see at a flash, that there is no discrepancy, and Lincoln has shown that they are not only inconsistent with truth, but each other"—I can only say, that I have shown that he has done no such thing; and if the reader is disposed to require any other evidence than the General's assertion, he will be of my opinion.
Excepting the General's most flimsy attempt at mystification, in regard to a discrepance between Talbott and myself, he has not denied a single statement that I made in my hand-bill. Every material statement that I made has been sworn to by men who, in former times, were thought as respectable as General Adams. I stated that an assignment of a judgment, a copy of which I gave, had existed—Benj. Talbott, C. R. Matheny, Wm. Butler, and Judge Logan swore to its existence. I stated that it was said to be in Gen. Adams's handwriting—the same men swore it was in his handwriting. I stated that Talbott would swear that he got it out of Gen. Adams's possession—Talbott came forward and did swear it.
Bidding adieu to the former publication, I now propose to examine the General's last gigantic production. I now propose to point out some discrepancies in the General's address; and such, too, as he shall not be able to escape from. Speaking of the famous assignment, the General says: "This last charge, which was their last resort, their dying effort to render my character infamous among my fellow citizens, was manufactured at a certain lawyer's office in the town, printed at the office of the Sangamon Journal, and found its way into the world some time between two days just before the last election." Now turn to Mr. Keys' affidavit, in which you will find the following, viz.: "I certify that some time in May or the early part of June, 1837, I saw at Williams's corner a paper purporting to be an assignment from Joseph Anderson to James Adams, which assignment was signed by a mark to Anderson's name," etc. Now mark, if Keys saw the assignment on the last of May or first of June, Gen. Adams tells a falsehood when he says it was manufactured just before the election, which was on the 7th of August; and if it was manufactured just before the election, Keys tells a falsehood when he says he saw it on the last of May or first of June. Either Keys or the General is irretrievably in for it; and in the General's very condescending language, I say "Let them settle it between them."
Now again, let the reader, bearing in mind that General Adams has unequivocally said, in one part of his address, that the charge in relation to the assignment was manufactured just before the election, turn to the affidavit of Peter S. Weber, where the following will be found viz.: "I, Peter S. Weber, do certify that from the best of my recollection, on the day or day after Gen. Adams started for the Illinois Rapids, in May last, that I was at the house of Gen. Adams, sitting in the kitchen, situated on the back part of the house, it being in the afternoon, and that Benjamin Talbott came around the house, back into the kitchen, and appeared wild and confused, and that he laid a package of papers on the kitchen table and requested that they should be handed to Lucian. He made no apology for coming to the kitchen, nor for not handing them to Lucian himself, but showed the token of being frightened and confused both in demeanor and speech and for what cause I could not apprehend."
Commenting on Weber's affidavit, Gen. Adams asks, "Why this fright and confusion?" I reply that this is a question for the General himself. Weber says that it was in May, and if so, it is most clear that Talbott was not frightened on account of the assignment, unless the General lies when he says the assignment charge was manufactured just before the election. Is it not a strong evidence, that the General is not traveling with the pole-star of truth in his front, to see him in one part of his address roundly asserting that the assignment was manufactured just before the election, and then, forgetting that position, procuring Weber's most foolish affidavit, to prove that Talbott had been engaged in manufacturing it two months before?
In another part of his address, Gen. Adams says: "That I hold an assignment of said judgment, dated the 20th of May, 1828, and signed by said Anderson, I have never pretended to deny or conceal, but stated that fact in one of my circulars previous to the election, and also in answer to a bill in chancery." Now I pronounce this statement unqualifiedly false, and shall not rely on the word or oath of any man to sustain me in what I say; but will let the whole be decided by reference to the circular and answer in chancery of which the General speaks. In his circular he did speak of an assignment; but he did not say it bore date 20th of May, 1828; nor did he say it bore any date. In his answer in chancery, he did say that he had an assignment; but he did not say that it bore date the 20th May, 1828; but so far from it, he said on oath (for he swore to the answer) that as well as recollected, he obtained it in 1827. If any one doubts, let him examine the circular and answer for himself. They are both accessible.
It will readily be observed that the principal part of Adams's defense rests upon the argument that if he had been base enough to forge an assignment he would not have been fool enough to forge one that would not cover the case. This argument he used in his circular before the election. The Republican has used it at least once, since then; and Adams uses it again in his publication of to-day. Now I pledge myself to show that he is just such a fool that he and his friends have contended it was impossible for him to be. Recollect—he says he has a genuine assignment; and that he got Joseph Klein's affidavit, stating that he had seen it, and that he believed the signature to have been executed by the same hand that signed Anderson's name to the answer in chancery. Luckily Klein took a copy of this genuine assignment, which I have been permitted to see; and hence I know it does not cover the case. In the first place it is headed "Joseph Anderson vs. Joseph Miller," and heads off "Judgment in Sangamon Circuit Court." Now, mark, there never was a case in Sangamon Circuit Court entitled Joseph Anderson vs. Joseph Miller. The case mentioned in my former publication, and the only one between these parties that ever existed in the Circuit Court, was entitled Joseph Miller vs. Joseph Anderson, Miller being the plaintiff. What then becomes of all their sophistry about Adams not being fool enough to forge an assignment that would not cover the case? It is certain that the present one does not cover the case; and if he got it honestly, it is still clear that he was fool enough to pay for an assignment that does not cover the case.
The General asks for the proof of disinterested witnesses. Whom does he consider disinterested? None can be more so than those who have already testified against him. No one of them had the least interest on earth, so far as I can learn, to injure him. True, he says they had conspired against him; but if the testimony of an angel from Heaven were introduced against him, he would make the same charge of conspiracy. And now I put the question to every reflecting man, Do you believe that Benjamin Talbott, Chas. R. Matheny, William Butler and Stephen T. Logan, all sustaining high and spotless characters, and justly proud of them, would deliberately perjure themselves, without any motive whatever, except to injure a man's election; and that, too, a man who had been a candidate, time out of mind, and yet who had never been elected to any office?
Adams's assurance, in demanding disinterested testimony, is surpassing. He brings in the affidavit of his own son, and even of Peter S. Weber, with whom I am not acquainted, but who, I suppose, is some black or mulatto boy, from his being kept in the kitchen, to prove his points; but when such a man as Talbott, a man who, but two years ago, ran against Gen. Adams for the office of Recorder and beat him more than four votes to one, is introduced against him, he asks the community, with all the consequence of a lord, to reject his testimony.
I might easily write a volume, pointing out inconsistencies between the statements in Adams's last address with one another, and with other known facts; but I am aware the reader must already be tired with the length of this article. His opening statements, that he was first accused of being a Tory, and that he refuted that; that then the Sampson's ghost story was got up, and he refuted that; that as a last resort, a dying effort, the assignment charge was got up is all as false as hell, as all this community must know. Sampson's ghost first made its appearance in print, and that, too, after Keys swears he saw the assignment, as any one may see by reference to the files of papers; and Gen. Adams himself, in reply to the Sampson's ghost story, was the first man that raised the cry of toryism, and it was only by way of set-off, and never in seriousness, that it was bandied back at him. His effort is to make the impression that his enemies first made the charge of toryism and he drove them from that, then Sampson's ghost, he drove them from that, then finally the assignment charge was manufactured just before election. Now, the only general reply he ever made to the Sampson's ghost and tory charges he made at one and the same time, and not in succession as he states; and the date of that reply will show, that it was made at least a month after the date on which Keys swears he saw the Anderson assignment. But enough. In conclusion I will only say that I have a character to defend as well as Gen. Adams, but I disdain to whine about it as he does. It is true I have no children nor kitchen boys; and if I had, I should scorn to lug them in to make affidavits for me.
A. LINCOLN, September 6, 1837.
"SANGAMON JOURNAL," Springfield, Ill, Oct.28, 1837.
Such is the turn which things have taken lately, that when Gen. Adams writes a book, I am expected to write a commentary on it. In the Republican of this morning he has presented the world with a new work of six columns in length; in consequence of which I must beg the room of one column in the Journal. It is obvious that a minute reply cannot be made in one column to everything that can be said in six; and, consequently, I hope that expectation will be answered if I reply to such parts of the General's publication as are worth replying to.
It may not be improper to remind the reader that in his publication of Sept. 6th General Adams said that the assignment charge was manufactured just before the election; and that in reply I proved that statement to be false by Keys, his own witness. Now, without attempting to explain, he furnishes me with another witness (Tinsley) by which the same thing is proved, to wit, that the assignment was not manufactured just before the election; but that it was some weeks before. Let it be borne in mind that Adams made this statement—has himself furnished two witnesses to prove its falsehood, and does not attempt to deny or explain it. Before going farther, let a pin be stuck here, labeled "One lie proved and confessed." On the 6th of September he said he had before stated in the hand-bill that he held an assignment dated May 20th, 1828, which in reply I pronounced to be false, and referred to the hand-bill for the truth of what I said. This week he forgets to make any explanation of this. Let another pin be stuck here, labelled as before. I mention these things because, if, when I convict him in one falsehood, he is permitted to shift his ground and pass it by in silence, there can be no end to this controversy.
The first thing that attracts my attention in the General's present production is the information he is pleased to give to "those who are made to suffer at his (my) hands."
Under present circumstances, this cannot apply to me, for I am not a widow nor an orphan: nor have I a wife or children who might by possibility become such. Such, however, I have no doubt, have been, and will again be made to suffer at his hands! Hands! Yes, they are the mischievous agents. The next thing I shall notice is his favorite expression, "not of lawyers, doctors and others," which he is so fond of applying to all who dare expose his rascality. Now, let it be remembered that when he first came to this country he attempted to impose himself upon the community as a lawyer, and actually carried the attempt so far as to induce a man who was under a charge of murder to entrust the defence of his life in his hands, and finally took his money and got him hanged. Is this the man that is to raise a breeze in his favor by abusing lawyers? If he is not himself a lawyer, it is for the lack of sense, and not of inclination. If he is not a lawyer, he is a liar, for he proclaimed himself a lawyer, and got a man hanged by depending on him.
Passing over such parts of the article as have neither fact nor argument in them, I come to the question asked by Adams whether any person ever saw the assignment in his possession. This is an insult to common sense. Talbott has sworn once and repeated time and again, that he got it out of Adams's possession and returned it into the same possession. Still, as though he was addressing fools, he has assurance to ask if any person ever saw it in his possession.
Next I quote a sentence, "Now my son Lucian swears that when Talbott called for the deed, that he, Talbott, opened it and pointed out the error." True. His son Lucian did swear as he says; and in doing so, he swore what I will prove by his own affidavit to be a falsehood. Turn to Lucian's affidavit, and you will there see that Talbott called for the deed by which to correct an error on the record. Thus it appears that the error in question was on the record, and not in the deed. How then could Talbott open the deed and point out the error? Where a thing is not, it cannot be pointed out. The error was not in the deed, and of course could not be pointed out there. This does not merely prove that the error could not be pointed out, as Lucian swore it was; but it proves, too, that the deed was not opened in his presence with a special view to the error, for if it had been, he could not have failed to see that there was no error in it. It is easy enough to see why Lucian swore this. His object was to prove that the assignment was not in the deed when Talbott got it: but it was discovered he could not swear this safely, without first swearing the deed was opened—and if he swore it was opened, he must show a motive for opening it, and the conclusion with him and his father was that the pointing out the error would appear the most plausible.
For the purpose of showing that the assignment was not in the bundle when Talbott got it, is the story introduced into Lucian's affidavit that the deeds were counted. It is a remarkable fact, and one that should stand as a warning to all liars and fabricators, that in this short affidavit of Lucian's he only attempted to depart from the truth, so far as I have the means of knowing, in two points, to wit, in the opening the deed and pointing out the error and the counting of the deeds,—and in both of these he caught himself. About the counting, he caught himself thus—after saying the bundle contained five deeds and a lease, he proceeds, "and I saw no other papers than the said deed and lease." First he has six papers, and then he saw none but two; for "my son Lucian's" benefit, let a pin be stuck here.
Adams again adduces the argument, that he could not have forged the assignment, for the reason that he could have had no motive for it. With those that know the facts there is no absence of motive. Admitting the paper which he has filed in the suit to be genuine, it is clear that it cannot answer the purpose for which he designs it. Hence his motive for making one that he supposed would answer is obvious. His making the date too old is also easily enough accounted for. The records were not in his hands, and then, there being some considerable talk upon this particular subject, he knew he could not examine the records to ascertain the precise dates without subjecting himself to suspicion; and hence he concluded to try it by guess, and, as it turned out, missed it a little. About Miller's deposition I have a word to say. In the first place, Miller's answer to the first question shows upon its face that he had been tampered with, and the answer dictated to him. He was asked if he knew Joel Wright and James Adams; and above three-fourths of his answer consists of what he knew about Joseph Anderson, a man about whom nothing had been asked, nor a word said in the question—a fact that can only be accounted for upon the supposition that Adams had secretly told him what he wished him to swear to.
Another of Miller's answers I will prove both by common sense and the Court of Record is untrue. To one question he answers, "Anderson brought a suit against me before James Adams, then an acting justice of the peace in Sangamon County, before whom he obtained a judgment.
"Q.—Did you remove the same by injunction to the Sangamon Circuit Court? Ans.—I did remove it."
Now mark—it is said he removed it by injunction. The word "injunction" in common language imports a command that some person or thing shall not move or be removed; in law it has the same meaning. An injunction issuing out of chancery to a justice of the peace is a command to him to stop all proceedings in a named case until further orders. It is not an order to remove but to stop or stay something that is already moving. Besides this, the records of the Sangamon Circuit Court show that the judgment of which Miller swore was never removed into said Court by injunction or otherwise.
I have now to take notice of a part of Adams's address which in the order of time should have been noticed before. It is in these words: "I have now shown, in the opinion of two competent judges, that the handwriting of the forged assignment differed from mine, and by one of them that it could not be mistaken for mine." That is false. Tinsley no doubt is the judge referred to; and by reference to his certificate it will be seen that he did not say the handwriting of the assignment could not be mistaken for Adams's—nor did he use any other expression substantially, or anything near substantially, the same. But if Tinsley had said the handwriting could not be mistaken for Adams's, it would have been equally unfortunate for Adams: for it then would have contradicted Keys, who says, "I looked at the writing and judged it the said Adams's or a good imitation."
Adams speaks with much apparent confidence of his success on attending lawsuits, and the ultimate maintenance of his title to the land in question. Without wishing to disturb the pleasure of his dream, I would say to him that it is not impossible that he may yet be taught to sing a different song in relation to the matter.
At the end of Miller's deposition, Adams asks, "Will Mr. Lincoln now say that he is almost convinced my title to this ten acre tract of land is founded in fraud?" I answer, I will not. I will now change the phraseology so as to make it run—I am quite convinced, &c. I cannot pass in silence Adams's assertion that he has proved that the forged assignment was not in the deed when it came from his house by Talbott, the recorder. In this, although Talbott has sworn that the assignment was in the bundle of deeds when it came from his house, Adams has the unaccountable assurance to say that he has proved the contrary by Talbott. Let him or his friends attempt to show wherein he proved any such thing by Talbott.
In his publication of the 6th of September he hinted to Talbott, that he might be mistaken. In his present, speaking of Talbott and me he says "They may have been imposed upon." Can any man of the least penetration fail to see the object of this? After he has stormed and raged till he hopes and imagines he has got us a little scared he wishes to softly whisper in our ears, "If you'll quit I will." If he could get us to say that some unknown, undefined being had slipped the assignment into our hands without our knowledge, not a doubt remains but that he would immediately discover that we were the purest men on earth. This is the ground he evidently wishes us to understand he is willing to compromise upon. But we ask no such charity at his hands. We are neither mistaken nor imposed upon. We have made the statements we have because we know them to be true and we choose to live or die by them.
Esq. Carter, who is Adams's friend, personal and political, will recollect, that, on the 5th of this month, he (Adams), with a great affectation of modesty, declared that he would never introduce his own child as a witness. Notwithstanding this affectation of modesty, he has in his present publication introduced his child as witness; and as if to show with how much contempt he could treat his own declaration, he has had this same Esq. Carter to administer the oath to him. And so important a witness does he consider him, and so entirely does the whole of his entire present production depend upon the testimony of his child, that in it he has mentioned "my son," "my son Lucian," "Lucian, my son," and the like expressions no less than fifteen different times. Let it be remembered here, that I have shown the affidavit of "my darling son Lucian" to be false by the evidence apparent on its own face; and I now ask if that affidavit be taken away what foundation will the fabric have left to stand upon?
General Adams's publications and out-door maneuvering, taken in connection with the editorial articles of the Republican, are not more foolish and contradictory than they are ludicrous and amusing. One week the Republican notifies the public that Gen. Adams is preparing an instrument that will tear, rend, split, rive, blow up, confound, overwhelm, annihilate, extinguish, exterminate, burst asunder, and grind to powder all its slanderers, and particularly Talbott and Lincoln—all of which is to be done in due time.
Then for two or three weeks all is calm—not a word said. Again the Republican comes forth with a mere passing remark that "public" opinion has decided in favor of Gen. Adams, and intimates that he will give himself no more trouble about the matter. In the meantime Adams himself is prowling about and, as Burns says of the devil, "For prey, and holes and corners tryin'," and in one instance goes so far as to take an old acquaintance of mine several steps from a crowd and, apparently weighed down with the importance of his business, gravely and solemnly asks him if "he ever heard Lincoln say he was a deist."
Anon the Republican comes again. "We invite the attention of the public to General Adams's communication," &c. "The victory is a great one, the triumph is overwhelming." I really believe the editor of the Illinois Republican is fool enough to think General Adams leads off—"Authors most egregiously mistaken &c. Most woefully shall their presumption be punished," &c. (Lord have mercy on us.) "The hour is yet to come, yea, nigh at hand—(how long first do you reckon?)—when the Journal and its junto shall say, I have appeared too early." "Their infamy shall be laid bare to the public gaze." Suddenly the General appears to relent at the severity with which he is treating us and he exclaims: "The condemnation of my enemies is the inevitable result of my own defense." For your health's sake, dear Gen., do not permit your tenderness of heart to afflict you so much on our account. For some reason (perhaps because we are killed so quickly) we shall never be sensible of our suffering.
Farewell, General. I will see you again at court if not before—when and where we will settle the question whether you or the widow shall have the land.
A. LINCOLN. October 18, 1837.
DEAR MADAM:—Without apologizing for being egotistical, I shall make the history of so much of my life as has elapsed since I saw you the subject of this letter. And, by the way, I now discover that, in order to give a full and intelligible account of the things I have done and suffered since I saw you, I shall necessarily have to relate some that happened before.
It was, then, in the autumn of 1836 that a married lady of my acquaintance, and who was a great friend of mine, being about to pay a visit to her father and other relatives residing in Kentucky, proposed to me that on her return she would bring a sister of hers with her on condition that I would engage to become her brother-in-law with all convenient despatch. I, of course, accepted the proposal, for you know I could not have done otherwise had I really been averse to it; but privately, between you and me, I was most confoundedly well pleased with the project. I had seen the said sister some three years before, thought her intelligent and agreeable, and saw no good objection to plodding life through hand in hand with her. Time passed on; the lady took her journey and in due time returned, sister in company, sure enough. This astonished me a little, for it appeared to me that her coming so readily showed that she was a trifle too willing, but on reflection it occurred to me that she might have been prevailed on by her married sister to come without anything concerning me ever having been mentioned to her, and so I concluded that if no other objection presented itself, I would consent to waive this. All this occurred to me on hearing of her arrival in the neighborhood—for, be it remembered, I had not yet seen her, except about three years previous, as above mentioned. In a few days we had an interview, and, although I had seen her before, she did not look as my imagination had pictured her. I knew she was over-size, but she now appeared a fair match for Falstaff. I knew she was called an "old maid," and I felt no doubt of the truth of at least half of the appellation, but now, when I beheld her, I could not for my life avoid thinking of my mother; and this, not from withered features,—for her skin was too full of fat to permit of its contracting into wrinkles,—but from her want of teeth, weather-beaten appearance in general, and from a kind of notion that ran in my head that nothing could have commenced at the size of infancy and reached her present bulk in less than thirty-five or forty years; and in short, I was not at all pleased with her. But what could I do? I had told her sister that I would take her for better or for worse, and I made a point of honor and conscience in all things to stick to my word especially if others had been induced to act on it which in this case I had no doubt they had, for I was now fairly convinced that no other man on earth would have her, and hence the conclusion that they were bent on holding me to my bargain.
"Well," thought I, "I have said it, and, be the consequences what they may, it shall not be my fault if I fail to do it." At once I determined to consider her my wife; and, this done, all my powers of discovery were put to work in search of perfections in her which might be fairly set off against her defects. I tried to imagine her handsome, which, but for her unfortunate corpulency, was actually true. Exclusive of this no woman that I have ever seen has a finer face. I also tried to convince myself that the mind was much more to be valued than the person; and in this she was not inferior, as I could discover, to any with whom I had been acquainted.
Shortly after this, without coming to any positive understanding with her, I set out for Vandalia, when and where you first saw me. During my stay there I had letters from her which did not change my opinion of either her intellect or intention, but on the contrary confirmed it in both.
All this while, although I was fixed, "firm as the surge-repelling rock," in my resolution, I found I was continually repenting the rashness which had led me to make it. Through life, I have been in no bondage, either real or imaginary, from the thraldom of which I so much desired to be free. After my return home, I saw nothing to change my opinions of her in any particular. She was the same, and so was I. I now spent my time in planning how I might get along through life after my contemplated change of circumstances should have taken place, and how I might procrastinate the evil day for a time, which I really dreaded as much, perhaps more, than an Irishman does the halter.
After all my suffering upon this deeply interesting subject, here I am, wholly, unexpectedly, completely, out of the "scrape"; and now I want to know if you can guess how I got out of it——out, clear, in every sense of the term; no violation of word, honor, or conscience. I don't believe you can guess, and so I might as well tell you at once. As the lawyer says, it was done in the manner following, to wit: After I had delayed the matter as long as I thought I could in honor do (which, by the way, had brought me round into the last fall), I concluded I might as well bring it to a consummation without further delay; and so I mustered my resolution, and made the proposal to her direct; but, shocking to relate, she answered, No. At first I supposed she did it through an affectation of modesty, which I thought but ill became her under the peculiar circumstances of her case; but on my renewal of the charge, I found she repelled it with greater firmness than before. I tried it again and again but with the same success, or rather with the same want of success.
I finally was forced to give it up; at which I very unexpectedly found myself mortified almost beyond endurance. I was mortified, it seemed to me, in a hundred different ways. My vanity was deeply wounded by the reflection that I had been too stupid to discover her intentions, and at the same time never doubting that I understood them perfectly, and also that she, whom I had taught myself to believe nobody else would have, had actually rejected me with all my fancied greatness. And, to cap the whole, I then for the first time began to suspect that I was really a little in love with her. But let it all go. I'll try and outlive it. Others have been made fools of by the girls, but this can never with truth be said of me. I most emphatically in this instance, made a fool of myself. I have now come to the conclusion never again to think of marrying, and for this reason: I can never be satisfied with any one who would be blockhead enough to have me.
When you receive this, write me a long yarn about something to amuse me. Give my respects to Mr. Browning.
Your sincere friend, A. LINCOLN.
Mr. Lincoln, from Committee on Finance, to which the subject was referred, made a report on the subject of purchasing of the United States all the unsold lands lying within the limits of the State of Illinois, accompanied by resolutions that this State propose to purchase all unsold lands at twenty-five cents per acre, and pledging the faith of the State to carry the proposal into effect if the government accept the same within two years.
Mr. Lincoln thought the resolutions ought to be seriously considered. In reply to the gentleman from Adams, he said that it was not to enrich the State. The price of the lands may be raised, it was thought by some; by others, that it would be reduced. The conclusion in his mind was that the representatives in this Legislature from the country in which the lands lie would be opposed to raising the price, because it would operate against the settlement of the lands. He referred to the lands in the military tract. They had fallen into the hands of large speculators in consequence of the low price. He was opposed to a low price of land. He thought it was adverse to the interests of the poor settler, because speculators buy them up. He was opposed to a reduction of the price of public lands.
Mr. Lincoln referred to some official documents emanating from Indiana, and compared the progressive population of the two States. Illinois had gained upon that State under the public land system as it is. His conclusion was that ten years from this time Illinois would have no more public land unsold than Indiana now has. He referred also to Ohio. That State had sold nearly all her public lands. She was but twenty years ahead of us, and as our lands were equally salable—more so, as he maintained—we should have no more twenty years from now than she has at present.
Mr. Lincoln referred to the canal lands, and supposed that the policy of the State would be different in regard to them, if the representatives from that section of country could themselves choose the policy; but the representatives from other parts of the State had a veto upon it, and regulated the policy. He thought that if the State had all the lands, the policy of the Legislature would be more liberal to all sections.
He referred to the policy of the General Government. He thought that if the national debt had not been paid, the expenses of the government would not have doubled, as they had done since that debt was paid.
Mr. Redman informs me that you wish me to write you the particulars of a conversation between Dr. Felix and myself relative to you. The Dr. overtook me between Rushville and Beardstown.
He, after learning that I had lived at Springfield, asked if I was acquainted with you. I told him I was. He said you had lately been elected constable in Adams, but that you never would be again. I asked him why. He said the people there had found out that you had been sheriff or deputy sheriff in Sangamon County, and that you came off and left your securities to suffer. He then asked me if I did not know such to be the fact. I told him I did not think you had ever been sheriff or deputy sheriff in Sangamon, but that I thought you had been constable. I further told him that if you had left your securities to suffer in that or any other case, I had never heard of it, and that if it had been so, I thought I would have heard of it.
If the Dr. is telling that I told him anything against you whatever, I authorize you to contradict it flatly. We have no news here.
Your friend, as ever, A. LINCOLN.
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, December 20, 1839.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—It is peculiarly embarrassing to me to attempt a continuance of the discussion, on this evening, which has been conducted in this hall on several preceding ones. It is so because on each of those evenings there was a much fuller attendance than now, without any reason for its being so, except the greater interest the community feel in the speakers who addressed them then than they do in him who is to do so now. I am, indeed, apprehensive that the few who have attended have done so more to spare me mortification than in the hope of being interested in anything I may be able to say. This circumstance casts a damp upon my spirits, which I am sure I shall be unable to overcome during the evening. But enough of preface.
The subject heretofore and now to be discussed is the subtreasury scheme of the present administration, as a means of collecting, safe-keeping, transferring, and disbursing, the revenues of the nation, as contrasted with a national bank for the same purposes. Mr. Douglas has said that we (the Whigs) have not dared to meet them (the Locos) in argument on this question. I protest against this assertion. I assert that we have again and again, during this discussion, urged facts and arguments against the subtreasury which they have neither dared to deny nor attempted to answer. But lest some may be led to believe that we really wish to avoid the question, I now propose, in my humble way, to urge those arguments again; at the same time begging the audience to mark well the positions I shall take and the proof I shall offer to sustain them, and that they will not again permit Mr. Douglas or his friends to escape the force of them by a round and groundless assertion that we "dare not meet them in argument."
Of the subtreasury, then, as contrasted with a national bank for the before-enumerated purposes, I lay down the following propositions, to wit: (1) It will injuriously affect the community by its operation on the circulating medium. (2) It will be a more expensive fiscal agent. (3) It will be a less secure depository of the public money. To show the truth of the first proposition, let us take a short review of our condition under the operation of a national bank. It was the depository of the public revenues. Between the collection of those revenues and the disbursement of them by the government, the bank was permitted to and did actually loan them out to individuals, and hence the large amount of money actually collected for revenue purposes, which by any other plan would have been idle a great portion of the time, was kept almost constantly in circulation. Any person who will reflect that money is only valuable while in circulation will readily perceive that any device which will keep the government revenues in constant circulation, instead of being locked up in idleness, is no inconsiderable advantage. By the subtreasury the revenue is to be collected and kept in iron boxes until the government wants it for disbursement; thus robbing the people of the use of it, while the government does not itself need it, and while the money is performing no nobler office than that of rusting in iron boxes. The natural effect of this change of policy, every one will see, is to reduce the quantity of money in circulation. But, again, by the subtreasury scheme the revenue is to be collected in specie. I anticipate that this will be disputed. I expect to hear it said that it is not the policy of the administration to collect the revenue in specie. If it shall, I reply that Mr. Van Buren, in his message recommending the subtreasury, expended nearly a column of that document in an attempt to persuade Congress to provide for the collection of the revenue in specie exclusively; and he concludes with these words:
"It may be safely assumed that no motive of convenience to the citizens requires the reception of bank paper." In addition to this, Mr. Silas Wright, Senator from New York, and the political, personal and confidential friend of Mr. Van Buren, drafted and introduced into the Senate the first subtreasury bill, and that bill provided for ultimately collecting the revenue in specie. It is true, I know, that that clause was stricken from the bill, but it was done by the votes of the Whigs, aided by a portion only of the Van Buren senators. No subtreasury bill has yet become a law, though two or three have been considered by Congress, some with and some without the specie clause; so that I admit there is room for quibbling upon the question of whether the administration favor the exclusive specie doctrine or not; but I take it that the fact that the President at first urged the specie doctrine, and that under his recommendation the first bill introduced embraced it, warrants us in charging it as the policy of the party until their head as publicly recants it as he at first espoused it. I repeat, then, that by the subtreasury the revenue is to be collected in specie. Now mark what the effect of this must be. By all estimates ever made there are but between sixty and eighty millions of specie in the United States. The expenditures of the Government for the year 1838—the last for which we have had the report—were forty millions. Thus it is seen that if the whole revenue be collected in specie, it will take more than half of all the specie in the nation to do it. By this means more than half of all the specie belonging to the fifteen millions of souls who compose the whole population of the country is thrown into the hands of the public office-holders, and other public creditors comprising in number perhaps not more than one quarter of a million, leaving the other fourteen millions and three quarters to get along as they best can, with less than one half of the specie of the country, and whatever rags and shinplasters they may be able to put, and keep, in circulation. By this means, every office-holder and other public creditor may, and most likely will, set up shaver; and a most glorious harvest will the specie-men have of it,—each specie-man, upon a fair division, having to his share the fleecing of about fifty-nine rag-men. In all candor let me ask, was such a system for benefiting the few at the expense of the many ever before devised? And was the sacred name of Democracy ever before made to indorse such an enormity against the rights of the people?
I have already said that the subtreasury will reduce the quantity of money in circulation. This position is strengthened by the recollection that the revenue is to be collected in Specie, so that the mere amount of revenue is not all that is withdrawn, but the amount of paper circulation that the forty millions would serve as a basis to is withdrawn, which would be in a sound state at least one hundred millions. When one hundred millions, or more, of the circulation we now have shall be withdrawn, who can contemplate without terror the distress, ruin, bankruptcy, and beggary that must follow? The man who has purchased any article—say a horse—on credit, at one hundred dollars, when there are two hundred millions circulating in the country, if the quantity be reduced to one hundred millions by the arrival of pay-day, will find the horse but sufficient to pay half the debt; and the other half must either be paid out of his other means, and thereby become a clear loss to him, or go unpaid, and thereby become a clear loss to his creditor. What I have here said of a single case of the purchase of a horse will hold good in every case of a debt existing at the time a reduction in the quantity of money occurs, by whomsoever, and for whatsoever, it may have been contracted. It may be said that what the debtor loses the creditor gains by this operation; but on examination this will be found true only to a very limited extent. It is more generally true that all lose by it—the creditor by losing more of his debts than he gains by the increased value of those he collects; the debtor by either parting with more of his property to pay his debts than he received in contracting them, or by entirely breaking up his business, and thereby being thrown upon the world in idleness.
The general distress thus created will, to be sure, be temporary, because, whatever change may occur in the quantity of money in any community, time will adjust the derangement produced; but while that adjustment is progressing, all suffer more or less, and very many lose everything that renders life desirable. Why, then, shall we suffer a severe difficulty, even though it be but temporary, unless we receive some equivalent for it?
What I have been saying as to the effect produced by a reduction of the quantity of money relates to the whole country. I now propose to show that it would produce a peculiar and permanent hardship upon the citizens of those States and Territories in which the public lands lie. The land-offices in those States and Territories, as all know, form the great gulf by which all, or nearly all, the money in them is swallowed up. When the quantity of money shall be reduced, and consequently everything under individual control brought down in proportion, the price of those lands, being fixed by law, will remain as now. Of necessity it will follow that the produce or labor that now raises money sufficient to purchase eighty acres will then raise but sufficient to purchase forty, or perhaps not that much; and this difficulty and hardship will last as long, in some degree, as any portion of these lands shall remain undisposed of. Knowing, as I well do, the difficulty that poor people now encounter in procuring homes, I hesitate not to say that when the price of the public lands shall be doubled or trebled, or, which is the same thing, produce and labor cut down to one half or one third of their present prices, it will be little less than impossible for them to procure those homes at all....
Well, then, what did become of him? (Postmaster General Barry) Why, the President immediately expressed his high disapprobation of his almost unequaled incapacity and corruption by appointing him to a foreign mission, with a salary and outfit of $18,000 a year! The party now attempt to throw Barry off, and to avoid the responsibility of his sins. Did not the President indorse those sins when, on the very heel of their commission, he appointed their author to the very highest and most honorable office in his gift, and which is but a single step behind the very goal of American political ambition?
I return to another of Mr. Douglas's excuses for the expenditures of 1838, at the same time announcing the pleasing intelligence that this is the last one. He says that ten millions of that year's expenditure was a contingent appropriation, to prosecute an anticipated war with Great Britain on the Maine boundary question. Few words will settle this. First, that the ten millions appropriated was not made till 1839, and consequently could not have been expended in 1838; second, although it was appropriated, it has never been expended at all. Those who heard Mr. Douglas recollect that he indulged himself in a contemptuous expression of pity for me. "Now he's got me," thought I. But when he went on to say that five millions of the expenditure of 1838 were payments of the French indemnities, which I knew to be untrue; that five millions had been for the post-office, which I knew to be untrue; that ten millions had been for the Maine boundary war, which I not only knew to be untrue, but supremely ridiculous also; and when I saw that he was stupid enough to hope that I would permit such groundless and audacious assertions to go unexposed,—I readily consented that, on the score both of veracity and sagacity, the audience should judge whether he or I were the more deserving of the world's contempt.
Mr. Lamborn insists that the difference between the Van Buren party and the Whigs is that, although the former sometimes err in practice, they are always correct in principle, whereas the latter are wrong in principle; and, better to impress this proposition, he uses a figurative expression in these words: "The Democrats are vulnerable in the heel, but they are sound in the head and the heart." The first branch of the figure—that is, that the Democrats are vulnerable in the heel—I admit is not merely figuratively, but literally true. Who that looks but for a moment at their Swartwouts, their Prices, their Harringtons, and their hundreds of others, scampering away with the public money to Texas, to Europe, and to every spot of the earth where a villain may hope to find refuge from justice, can at all doubt that they are most distressingly affected in their heels with a species of "running itch"? It seems that this malady of their heels operates on these sound-headed and honest-hearted creatures very much like the cork leg in the comic song did on its owner: which, when he had once got started on it, the more he tried to stop it, the more it would run away. At the hazard of wearing this point threadbare, I will relate an anecdote which seems too strikingly in point to be omitted. A witty Irish soldier, who was always boasting of his bravery when no danger was near, but who invariably retreated without orders at the first charge of an engagement, being asked by his captain why he did so, replied: "Captain, I have as brave a heart as Julius Caesar ever had; but, somehow or other, whenever danger approaches, my cowardly legs will run away with it." So with Mr. Lamborn's party. They take the public money into their hand for the most laudable purpose that wise heads and honest hearts can dictate; but before they can possibly get it out again, their rascally "vulnerable heels" will run away with them.
Seriously this proposition of Mr. Lamborn is nothing more or less than a request that his party may be tried by their professions instead of their practices. Perhaps no position that the party assumes is more liable to or more deserving of exposure than this very modest request; and nothing but the unwarrantable length to which I have already extended these remarks forbids me now attempting to expose it. For the reason given, I pass it by.
I shall advert to but one more point. Mr. Lamborn refers to the late elections in the States, and from their results confidently predicts that every State in the Union will vote for Mr. Van Buren at the next Presidential election. Address that argument to cowards and to knaves; with the free and the brave it will effect nothing. It may be true; if it must, let it. Many free countries have lost their liberty, and ours may lose hers; but if she shall, be it my proudest plume, not that I was the last to desert, but that I never deserted her. I know that the great volcano at Washington, aroused and directed by the evil spirit that reigns there, is belching forth the lava of political corruption in a current broad and deep, which is sweeping with frightful velocity over the whole length and breadth of the land, bidding fair to leave unscathed no green spot or living thing; while on its bosom are riding, like demons on the waves of hell, the imps of that evil spirit, and fiendishly taunting all those who dare resist its destroying course with the hopelessness of their effort; and, knowing this, I cannot deny that all may be swept away. Broken by it I, too, may be; bow to it I never will. The probability that we may fall in the struggle ought not to deter us from the support of a cause we believe to be just; it shall not deter me. If ever I feel the soul within me elevate and expand to those dimensions not wholly unworthy of its almighty Architect, it is when I contemplate the cause of my country deserted by all the world beside, and I standing up boldly and alone, and hurling defiance at her victorious oppressors. Here, without contemplating consequences, before high heaven and in the face of the world, I swear eternal fidelity to the just cause, as I deem it, of the land of my life, my liberty, and my love. And who that thinks with me will not fearlessly adopt the oath that I take? Let none falter who thinks he is right, and we may succeed. But if, after all, we shall fail, be it so. We still shall have the proud consolation of saying to our consciences, and to the departed shade of our country's freedom, that the cause approved of our judgment, and adored of our hearts, in disaster, in chains, in torture, in death, we never faltered in defending.
DEAR STUART:
Dr. Henry will write you all the political news. I write this about some little matters of business. You recollect you told me you had drawn the Chicago Masark money, and sent it to the claimants. A hawk-billed Yankee is here besetting me at every turn I take, saying that Robert Kinzie never received the eighty dollars to which he was entitled. Can you tell me anything about the matter? Again, old Mr. Wright, who lives up South Fork somewhere, is teasing me continually about some deeds which he says he left with you, but which I can find nothing of. Can you tell me where they are? The Legislature is in session and has suffered the bank to forfeit its charter without benefit of clergy. There seems to be little disposition to resuscitate it.
Whenever a letter comes from you to Mrs.____________ I carry it to her, and then I see Betty; she is a tolerable nice "fellow" now. Maybe I will write again when I get more time.
Your friend as ever, A. LINCOLN
P. S.—The Democratic giant is here, but he is not much worth talking about. A.L.
January [1?], 1840.
To MESSRS ———
GENTLEMEN:—In obedience to a resolution of the Whig State convention, we have appointed you the Central Whig Committee of your county. The trust confided to you will be one of watchfulness and labor; but we hope the glory of having contributed to the overthrow of the corrupt powers that now control our beloved country will be a sufficient reward for the time and labor you will devote to it. Our Whig brethren throughout the Union have met in convention, and after due deliberation and mutual concessions have elected candidates for the Presidency and Vice-Presidency not only worthy of our cause, but worthy of the support of every true patriot who would have our country redeemed, and her institutions honestly and faithfully administered. To overthrow the trained bands that are opposed to us whose salaried officers are ever on the watch, and whose misguided followers are ever ready to obey their smallest commands, every Whig must not only know his duty, but must firmly resolve, whatever of time and labor it may cost, boldly and faithfully to do it. Our intention is to organize the whole State, so that every Whig can be brought to the polls in the coming Presidential contest. We cannot do this, however, without your co-operation; and as we do our duty, so we shall expect you to do yours. After due deliberation, the following is the plan of organization, and the duties required of each county committee:
(1) To divide their county into small districts, and to appoint in each a subcommittee, whose duty it shall be to make a perfect list of all the voters in their respective districts, and to ascertain with certainty for whom they will vote. If they meet with men who are doubtful as to the man they will support, such voters should be designated in separate lines, with the name of the man they will probably support.
(2) It will be the duty of said subcommittee to keep a constant watch on the doubtful voters, and from time to time have them talked to by those in whom they have the most confidence, and also to place in their hands such documents as will enlighten and influence them.
(3) It will also be their duty to report to you, at least once a month, the progress they are making, and on election days see that every Whig is brought to the polls.
(4) The subcommittees should be appointed immediately; and by the last of April, at least, they should make their first report.
(5) On the first of each month hereafter we shall expect to hear from you. After the first report of your subcommittees, unless there should be found a great many doubtful voters, you can tell pretty accurately the manner in which your county will vote. In each of your letters to us, you will state the number of certain votes both for and against us, as well as the number of doubtful votes, with your opinion of the manner in which they will be cast.
(6) When we have heard from all the counties, we shall be able to tell with similar accuracy the political complexion of the State. This information will be forwarded to you as soon as received.
(7) Inclosed is a prospectus for a newspaper to be continued until after the Presidential election. It will be superintended by ourselves, and every Whig in the State must take it. It will be published so low that every one can afford it. You must raise a fund and forward us for extra copies,—every county ought to send—fifty or one hundred dollars,—and the copies will be forwarded to you for distribution among our political opponents. The paper will be devoted exclusively to the great cause in which we are engaged. Procure subscriptions, and forward them to us immediately.
(8) Immediately after any election in your county, you must inform us of its results; and as early as possible after any general election we will give you the like information.
(9) A senator in Congress is to be elected by our next Legislature. Let no local interests divide you, but select candidates that can succeed.
(10) Our plan of operations will of course be concealed from every one except our good friends who of right ought to know them.
Trusting much in our good cause, the strength of our candidates, and the determination of the Whigs everywhere to do their duty, we go to the work of organization in this State confident of success. We have the numbers, and if properly organized and exerted, with the gallant Harrison at our head, we shall meet our foes and conquer them in all parts of the Union.
Address your letters to Dr. A. G. Henry, R. F, Barrett; A. Lincoln, E. D. Baker, J. F. Speed.
DEAR STUART:
I have never seen the prospects of our party so bright in these parts as they are now. We shall carry this county by a larger majority than we did in 1836, when you ran against May. I do not think my prospects, individually, are very flattering, for I think it probable I shall not be permitted to be a candidate; but the party ticket will succeed triumphantly. Subscriptions to the "Old Soldier" pour in without abatement. This morning I took from the post office a letter from Dubois enclosing the names of sixty subscribers, and on carrying it to Francis I found he had received one hundred and forty more from other quarters by the same day's mail. That is but an average specimen of every day's receipts. Yesterday Douglas, having chosen to consider himself insulted by something in the Journal, undertook to cane Francis in the street. Francis caught him by the hair and jammed him back against a market cart where the matter ended by Francis being pulled away from him. The whole affair was so ludicrous that Francis and everybody else (Douglass excepted) have been laughing about it ever since.
I send you the names of some of the V.B. men who have come out for Harrison about town, and suggest that you send them some documents.
Moses Coffman (he let us appoint him a delegate yesterday), Aaron Coffman, George Gregory, H. M. Briggs, Johnson (at Birchall's Bookstore), Michael Glyn, Armstrong (not Hosea nor Hugh, but a carpenter), Thomas Hunter, Moses Pileher (he was always a Whig and deserves attention), Matthew Crowder Jr., Greenberry Smith; John Fagan, George Fagan, William Fagan (these three fell out with us about Early, and are doubtful now), John M. Cartmel, Noah Rickard, John Rickard, Walter Marsh.
The foregoing should be addressed at Springfield.
Also send some to Solomon Miller and John Auth at Salisbury. Also to Charles Harper, Samuel Harper, and B. C. Harper, and T. J. Scroggins, John Scroggins at Pulaski, Logan County.
Speed says he wrote you what Jo Smith said about you as he passed here. We will procure the names of some of his people here, and send them to you before long. Speed also says you must not fail to send us the New York Journal he wrote for some time since.
Evan Butler is jealous that you never send your compliments to him. You must not neglect him next time.
Your friend, as ever, A. LINCOLN
In the Illinois House of Representatives, November 28, 1840, Mr. Lincoln offered the following:
Resolved, That so much of the governor's message as relates to fraudulent voting, and other fraudulent practices at elections, be referred to the Committee on Elections, with instructions to said committee to prepare and report to the House a bill for such an act as may in their judgment afford the greatest possible protection of the elective franchise against all frauds of all sorts whatever.
Resolved, That the Committee on Education be instructed to inquire into the expediency of providing by law for the examination as to the qualification of persons offering themselves as school teachers, that no teacher shall receive any part of the public school fund who shall not have successfully passed such examination, and that they report by bill or otherwise.
In the House of Representatives, Illinois, December 4, 1840, on presentation of a report respecting petition of H. N. Purple, claiming the seat of Mr. Phelps from Peoria, Mr. Lincoln moved that the House resolve itself into Committee of the Whole on the question, and take it up immediately. Mr. Lincoln considered the question of the highest importance whether an individual had a right to sit in this House or not. The course he should propose would be to take up the evidence and decide upon the facts seriatim.
Mr. Drummond wanted time; they could not decide in the heat of debate, etc.
Mr. Lincoln thought that the question had better be gone into now. In courts of law jurors were required to decide on evidence, without previous study or examination. They were required to know nothing of the subject until the evidence was laid before them for their immediate decision. He thought that the heat of party would be augmented by delay.
The Speaker called Mr. Lincoln to order as being irrelevant; no mention had been made of party heat.
Mr. Drummond said he had only spoken of debate. Mr. Lincoln asked what caused the heat, if it was not party? Mr. Lincoln concluded by urging that the question would be decided now better than hereafter, and he thought with less heat and excitement.
(Further debate, in which Lincoln participated.)
In the Illinois House of Representatives, December 4, 1840, House in Committee of the Whole on the bill providing for payment of interest on the State debt,—Mr. Lincoln moved to strike out the body and amendments of the bill, and insert in lieu thereof an amendment which in substance was that the governor be authorized to issue bonds for the payment of the interest; that these be called "interest bonds"; that the taxes accruing on Congress lands as they become taxable be irrevocably set aside and devoted as a fund to the payment of the interest bonds. Mr. Lincoln went into the reasons which appeared to him to render this plan preferable to that of hypothecating the State bonds. By this course we could get along till the next meeting of the Legislature, which was of great importance. To the objection which might be urged that these interest bonds could not be cashed, he replied that if our other bonds could, much more could these, which offered a perfect security, a fund being irrevocably set aside to provide for their redemption. To another objection, that we should be paying compound interest, he would reply that the rapid growth and increase of our resources was in so great a ratio as to outstrip the difficulty; that his object was to do the best that could be done in the present emergency. All agreed that the faith of the State must be preserved; this plan appeared to him preferable to a hypothecation of bonds, which would have to be redeemed and the interest paid. How this was to be done, he could not see; therefore he had, after turning the matter over in every way, devised this measure, which would carry us on till the next Legislature.
(Mr. Lincoln spoke at some length, advocating his measure.)
Lincoln advocated his measure, December 11, 1840.
December 12, 1840, he had thought some permanent provision ought to be made for the bonds to be hypothecated, but was satisfied taxation and revenue could not be connected with it now.
DEAR STUART: I am now the most miserable man living. If what I feel were equally distributed to the whole human family, there would not be one cheerful face on earth. Whether I shall ever be better, I cannot tell; I awfully forbode I shall not. To remain as I am is impossible. I must die or be better, as it appears to me.... I fear I shall be unable to attend any business here, and a change of scene might help me. If I could be myself, I would rather remain at home with Judge Logan. I can write no more.
In the House of Representatives January 23, 1841, while discussing the continuation of the Illinois and Michigan Canal, Mr. Moore was afraid the holders of the "scrip" would lose.
Mr. Napier thought there was no danger of that; and Mr. Lincoln said he had not examined to see what amount of scrip would probably be needed. The principal point in his mind was this, that nobody was obliged to take these certificates. It is altogether voluntary on their part, and if they apprehend it will fall in their hands they will not take it. Further the loss, if any there be, will fall on the citizens of that section of the country.
This scrip is not going to circulate over an extensive range of country, but will be confined chiefly to the vicinity of the canal. Now, we find the representatives of that section of the country are all in favor of the bill.
When we propose to protect their interests, they say to us: Leave us to take care of ourselves; we are willing to run the risk. And this is reasonable; we must suppose they are competent to protect their own interests, and it is only fair to let them do it.
Appeal to the People of the State of Illinois.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—When the General Assembly, now about adjourning, assembled in November last, from the bankrupt state of the public treasury, the pecuniary embarrassments prevailing in every department of society, the dilapidated state of the public works, and the impending danger of the degradation of the State, you had a right to expect that your representatives would lose no time in devising and adopting measures to avert threatened calamities, alleviate the distresses of the people, and allay the fearful apprehensions in regard to the future prosperity of the State. It was not expected by you that the spirit of party would take the lead in the councils of the State, and make every interest bend to its demands. Nor was it expected that any party would assume to itself the entire control of legislation, and convert the means and offices of the State, and the substance of the people, into aliment for party subsistence. Neither could it have been expected by you that party spirit, however strong its desires and unreasonable its demands, would have passed the sanctuary of the Constitution, and entered with its unhallowed and hideous form into the formation of the judiciary system.
At the early period of the session, measures were adopted by the dominant party to take possession of the State, to fill all public offices with party men, and make every measure affecting the interests of the people and the credit of the State operate in furtherance of their party views. The merits of men and measures therefore became the subject of discussion in caucus, instead of the halls of legislation, and decisions there made by a minority of the Legislature have been executed and carried into effect by the force of party discipline, without any regard whatever to the rights of the people or the interests of the State. The Supreme Court of the State was organized, and judges appointed, according to the provisions of the Constitution, in 1824. The people have never complained of the organization of that court; no attempt has ever before been made to change that department. Respect for public opinion, and regard for the rights and liberties of the people, have hitherto restrained the spirit of party from attacks upon the independence and integrity of the judiciary. The same judges have continued in office since 1824; their decisions have not been the subject of complaint among the people; the integrity and honesty of the court have not been questioned, and it has never been supposed that the court has ever permitted party prejudice or party considerations to operate upon their decisions. The court was made to consist of four judges, and by the Constitution two form a quorum for the transaction of business. With this tribunal, thus constituted, the people have been satisfied for near sixteen years. The same law which organized the Supreme Court in 1824 also established and organized circuit courts to be held in each county in the State, and five circuit judges were appointed to hold those courts. In 1826 the Legislature abolished these circuit courts, repealed the judges out of office, and required the judges of the Supreme Court to hold the circuit courts. The reasons assigned for this change were, first, that the business of the country could be better attended to by the four judges of the Supreme Court than by the two sets of judges; and, second, the state of the public treasury forbade the employment of unnecessary officers. In 1828 a circuit was established north of the Illinois River, in order to meet the wants of the people, and a circuit judge was appointed to hold the courts in that circuit.
In 1834 the circuit-court system was again established throughout the State, circuit judges appointed to hold the courts, and the judges of the Supreme Court were relieved from the performance of circuit court duties. The change was recommended by the then acting governor of the State, General W. L. D. Ewing, in the following terms:
"The augmented population of the State, the multiplied number of organized counties, as well as the increase of business in all, has long since convinced every one conversant with this department of our government of the indispensable necessity of an alteration in our judiciary system, and the subject is therefore recommended to the earnest patriotic consideration of the Legislature. The present system has never been exempt from serious and weighty objections. The idea of appealing from the circuit court to the same judges in the Supreme Court is recommended by little hopes of redress to the injured party below. The duties of the circuit, too, it may be added, consume one half of the year, leaving a small and inadequate portion of time (when that required for domestic purposes is deducted) to erect, in the decisions of the Supreme Court, a judicial monument of legal learning and research, which the talent and ability of the court might otherwise be entirely competent to."
With this organization of circuit courts the people have never complained. The only complaints which we have heard have come from circuits which were so large that the judges could not dispose of the business, and the circuits in which Judges Pearson and Ralston lately presided.
Whilst the honor and credit of the State demanded legislation upon the subject of the public debt, the canal, the unfinished public works, and the embarrassments of the people, the judiciary stood upon a basis which required no change—no legislative action. Yet the party in power, neglecting every interest requiring legislative action, and wholly disregarding the rights, wishes, and interests of the people, has, for the unholy purpose of providing places for its partisans and supplying them with large salaries, disorganized that department of the government. Provision is made for the election of five party judges of the Supreme Court, the proscription of four circuit judges, and the appointment of party clerks in more than half the counties of the State. Men professing respect for public opinion, and acknowledged to be leaders of the party, have avowed in the halls of legislation that the change in the judiciary was intended to produce political results favorable to their party and party friends. The immutable principles of justice are to make way for party interests, and the bonds of social order are to be rent in twain, in order that a desperate faction may be sustained at the expense of the people. The change proposed in the judiciary was supported upon grounds so destructive to the institutions of the country, and so entirely at war with the rights and liberties of the people, that the party could not secure entire unanimity in its support, three Democrats of the Senate and five of the House voting against the measure. They were unwilling to see the temples of justice and the seats of independent judges occupied by the tools of faction. The declarations of the party leaders, the selection of party men for judges, and the total disregard for the public will in the adoption of the measure, prove conclusively that the object has been not reform, but destruction; not the advancement of the highest interests of the State, but the predominance of party.
We cannot in this manner undertake to point out all the objections to this party measure; we present you with those stated by the Council of Revision upon returning the bill, and we ask for them a candid consideration.
Believing that the independence of the judiciary has been destroyed, that hereafter our courts will be independent of the people, and entirely dependent upon the Legislature; that our rights of property and liberty of conscience can no longer be regarded as safe from the encroachments of unconstitutional legislation; and knowing of no other remedy which can be adopted consistently with the peace and good order of society, we call upon you to avail yourselves of the opportunity afforded, and, at the next general election, vote for a convention of the people.
S. H. LITTLE, E. D. BAKER, J. J. HARDIN, E. B. WEBS, A. LINCOLN, J. GILLESPIE, Committee on behalf of the Whig members of the Legislature.
February 26, 1841
For the reasons thus presented, and for others no less apparent, the undersigned cannot assent to the passage of the bill, or permit it to become a law, without this evidence of their disapprobation; and they now protest against the reorganization of the judiciary, because—(1) It violates the great principles of free government by subjecting the judiciary to the Legislature. (2) It is a fatal blow at the independence of the judges and the constitutional term of their office. (3) It is a measure not asked for, or wished for, by the people. (4) It will greatly increase the expense of our courts, or else greatly diminish their utility. (5) It will give our courts a political and partisan character, thereby impairing public confidence in their decisions. (6) It will impair our standing with other States and the world. (7)It is a party measure for party purposes, from which no practical good to the people can possibly arise, but which may be the source of immeasurable evils.
The undersigned are well aware that this protest will be altogether unavailing with the majority of this body. The blow has already fallen, and we are compelled to stand by, the mournful spectators of the ruin it will cause.
[Signed by 35 members, among whom was Abraham Lincoln.]
DEAR SPEED:—We have had the highest state of excitement here for a week past that our community has ever witnessed; and, although the public feeling is somewhat allayed, the curious affair which aroused it is very far from being even yet cleared of mystery. It would take a quire of paper to give you anything like a full account of it, and I therefore only propose a brief outline. The chief personages in the drama are Archibald Fisher, supposed to be murdered, and Archibald Trailor, Henry Trailor, and William Trailor, supposed to have murdered him. The three Trailors are brothers: the first, Arch., as you know, lives in town; the second, Henry, in Clary's Grove; and the third, William, in Warren County; and Fisher, the supposed murdered, being without a family, had made his home with William. On Saturday evening, being the 29th of May, Fisher and William came to Henry's in a one-horse dearborn, and there stayed over Sunday; and on Monday all three came to Springfield (Henry on horseback) and joined Archibald at Myers's, the Dutch carpenter. That evening at supper Fisher was missing, and so next morning some ineffectual search was made for him; and on Tuesday, at one o'clock P.M., William and Henry started home without him. In a day or two Henry and one or two of his Clary-Grove neighbors came back for him again, and advertised his disappearance in the papers. The knowledge of the matter thus far had not been general, and here it dropped entirely, till about the 10th instant, when Keys received a letter from the postmaster in Warren County, that William had arrived at home, and was telling a very mysterious and improbable story about the disappearance of Fisher, which induced the community there to suppose he had been disposed of unfairly. Keys made this letter public, which immediately set the whole town and adjoining county agog. And so it has continued until yesterday. The mass of the people commenced a systematic search for the dead body, while Wickersham was despatched to arrest Henry Trailor at the Grove, and Jim Maxcy to Warren to arrest William. On Monday last, Henry was brought in, and showed an evident inclination to insinuate that he knew Fisher to be dead, and that Arch. and William had killed him. He said he guessed the body could be found in Spring Creek, between the Beardstown road and Hickox's mill. Away the people swept like a herd of buffalo, and cut down Hickox's mill-dam nolens volens, to draw the water out of the pond, and then went up and down and down and up the creek, fishing and raking, and raking and ducking and diving for two days, and, after all, no dead body found.
In the meantime a sort of scuffling-ground had been found in the brush in the angle, or point, where the road leading into the woods past the brewery and the one leading in past the brick-yard meet. From the scuffle-ground was the sign of something about the size of a man having been dragged to the edge of the thicket, where it joined the track of some small-wheeled carriage drawn by one horse, as shown by the road-tracks. The carriage-track led off toward Spring Creek. Near this drag-trail Dr. Merryman found two hairs, which, after a long scientific examination, he pronounced to be triangular human hairs, which term, he says, includes within it the whiskers, the hair growing under the arms and on other parts of the body; and he judged that these two were of the whiskers, because the ends were cut, showing that they had flourished in the neighborhood of the razor's operations. On Thursday last Jim Maxcy brought in William Trailor from Warren. On the same day Arch. was arrested and put in jail. Yesterday (Friday) William was put upon his examining trial before May and Lovely. Archibald and Henry were both present. Lamborn prosecuted, and Logan, Baker, and your humble servant defended. A great many witnesses were introduced and examined, but I shall only mention those whose testimony seemed most important. The first of these was Captain Ransdell. He swore that when William and Henry left Springfield for home on Tuesday before mentioned they did not take the direct route,—which, you know, leads by the butcher shop,—but that they followed the street north until they got opposite, or nearly opposite, May's new house, after which he could not see them from where he stood; and it was afterwards proved that in about an hour after they started, they came into the street by the butcher shop from toward the brickyard. Dr. Merryman and others swore to what is stated about the scuffle-ground, drag-trail, whiskers, and carriage tracks. Henry was then introduced by the prosecution. He swore that when they started for home they went out north, as Ransdell stated, and turned down west by the brick-yard into the woods, and there met Archibald; that they proceeded a small distance farther, when he was placed as a sentinel to watch for and announce the approach of any one that might happen that way; that William and Arch. took the dearborn out of the road a small distance to the edge of the thicket, where they stopped, and he saw them lift the body of a man into it; that they then moved off with the carriage in the direction of Hickox's mill, and he loitered about for something like an hour, when William returned with the carriage, but without Arch., and said they had put him in a safe place; that they went somehow he did not know exactly how—into the road close to the brewery, and proceeded on to Clary's Grove. He also stated that some time during the day William told him that he and Arch. had killed Fisher the evening before; that the way they did it was by him William knocking him down with a club, and Arch. then choking him to death.
An old man from Warren, called Dr. Gilmore, was then introduced on the part of the defense. He swore that he had known Fisher for several years; that Fisher had resided at his house a long time at each of two different spells—once while he built a barn for him, and once while he was doctored for some chronic disease; that two or three years ago Fisher had a serious hurt in his head by the bursting of a gun, since which he had been subject to continued bad health and occasional aberration of mind. He also stated that on last Tuesday, being the same day that Maxcy arrested William Trailor, he (the doctor) was from home in the early part of the day, and on his return, about eleven o'clock, found Fisher at his house in bed, and apparently very unwell; that he asked him how he came from Springfield; that Fisher said he had come by Peoria, and also told of several other places he had been at more in the direction of Peoria, which showed that he at the time of speaking did not know where he had been wandering about in a state of derangement. He further stated that in about two hours he received a note from one of Trailor's friends, advising him of his arrest, and requesting him to go on to Springfield as a witness, to testify as to the state of Fisher's health in former times; that he immediately set off, calling up two of his neighbors as company, and, riding all evening and all night, overtook Maxcy and William at Lewiston in Fulton County; that Maxcy refusing to discharge Trailor upon his statement, his two neighbors returned and he came on to Springfield. Some question being made as to whether the doctor's story was not a fabrication, several acquaintances of his (among whom was the same postmaster who wrote Keys, as before mentioned) were introduced as sort of compurgators, who swore that they knew the doctor to be of good character for truth and veracity, and generally of good character in every way.
Here the testimony ended, and the Trailors were discharged, Arch. and William expressing both in word and manner their entire confidence that Fisher would be found alive at the doctor's by Galloway, Mallory, and Myers, who a day before had been despatched for that purpose; which Henry still protested that no power on earth could ever show Fisher alive. Thus stands this curious affair. When the doctor's story was first made public, it was amusing to scan and contemplate the countenances and hear the remarks of those who had been actively in search for the dead body: some looked quizzical, some melancholy, and some furiously angry. Porter, who had been very active, swore he always knew the man was not dead, and that he had not stirred an inch to hunt for him; Langford, who had taken the lead in cutting down Hickox's mill-dam, and wanted to hang Hickox for objecting, looked most awfully woebegone: he seemed the "victim of unrequited affection," as represented in the comic almanacs we used to laugh over; and Hart, the little drayman that hauled Molly home once, said it was too damned bad to have so much trouble, and no hanging after all.
I commenced this letter on yesterday, since which I received yours of the 13th. I stick to my promise to come to Louisville. Nothing new here except what I have written. I have not seen ______ since my last trip, and I am going out there as soon as I mail this letter.
Yours forever, LINCOLN.
It having been charged in some of the public prints that Harry Wilton, late United States marshal for the district of Illinois, had used his office for political effect, in the appointment of deputies for the taking of the census for the year 1840, we, the undersigned, were called upon by Mr. Wilton to examine the papers in his possession relative to these appointments, and to ascertain therefrom the correctness or incorrectness of such charge. We accompanied Mr. Wilton to a room, and examined the matter as fully as we could with the means afforded us. The only sources of information bearing on the subject which were submitted to us were the letters, etc., recommending and opposing the various appointments made, and Mr. Wilton's verbal statements concerning the same. From these letters, etc., it appears that in some instances appointments were made in accordance with the recommendations of leading Whigs, and in opposition to those of leading Democrats; among which instances the appointments at Scott, Wayne, Madison, and Lawrence are the strongest. According to Mr. Wilton's statement of the seventy-six appointments we examined, fifty-four were of Democrats, eleven of Whigs, and eleven of unknown politics.
The chief ground of complaint against Mr. Wilton, as we had understood it, was because of his appointment of so many Democratic candidates for the Legislature, thus giving them a decided advantage over their Whig opponents; and consequently our attention was directed rather particularly to that point. We found that there were many such appointments, among which were those in Tazewell, McLean, Iroquois, Coles, Menard, Wayne, Washington, Fayette, etc.; and we did not learn that there was one instance in which a Whig candidate for the Legislature had been appointed. There was no written evidence before us showing us at what time those appointments were made; but Mr. Wilton stated that they all with one exception were made before those appointed became candidates for the Legislature, and the letters, etc., recommending them all bear date before, and most of them long before, those appointed were publicly announced candidates.
We give the foregoing naked facts and draw no conclusions from them.
Miss Mary Speed, Louisville, Ky.
MY FRIEND: By the way, a fine example was presented on board the boat for contemplating the effect of condition upon human happiness. A gentleman had purchased twelve negroes in different parts of Kentucky, and was taking them to a farm in the South. They were chained six and six together. A small iron clevis was around the left wrist of each, and this fastened to the main chain by a shorter one, at a convenient distance from the others, so that the negroes were strung together precisely like so many fish upon a trotline. In this condition they were being separated forever from the scenes of their childhood, their friends, their fathers and mothers, and brothers and sisters, and many of them from their wives and children, and going into perpetual slavery where the lash of the master is proverbially more ruthless and unrelenting than any other; and yet amid all these distressing circumstances, as we would think them, they were the most cheerful and apparently happy creatures on board. One, whose offence for which he had been sold was an overfondness for his wife, played the fiddle almost continually, and the others danced, sang, cracked jokes, and played various games with cards from day to day. How true it is that 'God tempers the wind to the shorn lamb,' or in other words, that he renders the worst of human conditions tolerable, while he permits the best to be nothing better than tolerable. To return to the narrative: When we reached Springfield I stayed but one day, when I started on this tedious circuit where I now am. Do you remember my going to the city, while I was in Kentucky, to have a tooth extracted, and making a failure of it? Well, that same old tooth got to paining me so much that about a week since I had it torn out, bringing with it a bit of the jawbone, the consequence of which is that my mouth is now so sore that I can neither talk nor eat.
Your sincere friend, A. LINCOLN.
MY DEAR SPEED:—Feeling, as you know I do, the deepest solicitude for the success of the enterprise you are engaged in, I adopt this as the last method I can adopt to aid you, in case (which God forbid!) you shall need any aid. I do not place what I am going to say on paper because I can say it better that way than I could by word of mouth, but, were I to say it orally before we part, most likely you would forget it at the very time when it might do you some good. As I think it reasonable that you will feel very badly some time between this and the final consummation of your purpose, it is intended that you shall read this just at such a time. Why I say it is reasonable that you will feel very badly yet, is because of three special causes added to the general one which I shall mention.
The general cause is, that you are naturally of a nervous temperament; and this I say from what I have seen of you personally, and what you have told me concerning your mother at various times, and concerning your brother William at the time his wife died. The first special cause is your exposure to bad weather on your journey, which my experience clearly proves to be very severe on defective nerves. The second is the absence of all business and conversation of friends, which might divert your mind, give it occasional rest from the intensity of thought which will sometimes wear the sweetest idea threadbare and turn it to the bitterness of death. The third is the rapid and near approach of that crisis on which all your thoughts and feelings concentrate.
If from all these causes you shall escape and go through triumphantly, without another "twinge of the soul," I shall be most happily but most egregiously deceived. If, on the contrary, you shall, as I expect you will at sometime, be agonized and distressed, let me, who have some reason to speak with judgment on such a subject, beseech you to ascribe it to the causes I have mentioned, and not to some false and ruinous suggestion of the Devil.
"But," you will say, "do not your causes apply to every one engaged in a like undertaking?" By no means. The particular causes, to a greater or less extent, perhaps do apply in all cases; but the general one,—nervous debility, which is the key and conductor of all the particular ones, and without which they would be utterly harmless,—though it does pertain to you, does not pertain to one in a thousand. It is out of this that the painful difference between you and the mass of the world springs.
I know what the painful point with you is at all times when you are unhappy; it is an apprehension that you do not love her as you should. What nonsense! How came you to court her? Was it because you thought she deserved it, and that you had given her reason to expect it? If it was for that why did not the same reason make you court Ann Todd, and at least twenty others of whom you can think, and to whom it would apply with greater force than to her? Did you court her for her wealth? Why, you know she had none. But you say you reasoned yourself into it. What do you mean by that? Was it not that you found yourself unable to reason yourself out of it? Did you not think, and partly form the purpose, of courting her the first time you ever saw her or heard of her? What had reason to do with it at that early stage? There was nothing at that time for reason to work upon. Whether she was moral, amiable, sensible, or even of good character, you did not, nor could then know, except, perhaps, you might infer the last from the company you found her in.
All you then did or could know of her was her personal appearance and deportment; and these, if they impress at all, impress the heart, and not the head.
Say candidly, were not those heavenly black eyes the whole basis of all your early reasoning on the subject? After you and I had once been at the residence, did you not go and take me all the way to Lexington and back, for no other purpose but to get to see her again, on our return on that evening to take a trip for that express object? What earthly consideration would you take to find her scouting and despising you, and giving herself up to another? But of this you have no apprehension; and therefore you cannot bring it home to your feelings.
I shall be so anxious about you that I shall want you to write by every mail.
Your friend, LINCOLN.
DEAR SPEED:—Your letter of the 25th January came to hand to-day. You well know that I do not feel my own sorrows much more keenly than I do yours, when I know of them; and yet I assure you I was not much hurt by what you wrote me of your excessively bad feeling at the time you wrote. Not that I am less capable of sympathizing with you now than ever, not that I am less your friend than ever, but because I hope and believe that your present anxiety and distress about her health and her life must and will forever banish those horrid doubts which I know you sometimes felt as to the truth of your affection for her. If they can once and forever be removed (and I almost feel a presentiment that the Almighty has sent your present affliction expressly for that object), surely nothing can come in their stead to fill their immeasurable measure of misery. The death-scenes of those we love are surely painful enough; but these we are prepared for and expect to see: they happen to all, and all know they must happen. Painful as they are, they are not an unlooked for sorrow. Should she, as you fear, be destined to an early grave, it is indeed a great consolation to know that she is so well prepared to meet it. Her religion, which you once disliked so much, I will venture you now prize most highly. But I hope your melancholy bodings as to her early death are not well founded. I even hope that ere this reaches you she will have returned with improved and still improving health, and that you will have met her, and forgotten the sorrows of the past in the enjoyments of the present. I would say more if I could, but it seems that I have said enough. It really appears to me that you yourself ought to rejoice, and not sorrow, at this indubitable evidence of your undying affection for her. Why, Speed, if you did not love her although you might not wish her death, you would most certainly be resigned to it. Perhaps this point is no longer a question with you, and my pertinacious dwelling upon it is a rude intrusion upon your feelings. If so, you must pardon me. You know the hell I have suffered on that point, and how tender I am upon it. You know I do not mean wrong. I have been quite clear of "hypo" since you left, even better than I was along in the fall. I have seen ______ but once. She seemed very cheerful, and so I said nothing to her about what we spoke of.
Old Uncle Billy Herndon is dead, and it is said this evening that Uncle Ben Ferguson will not live. This, I believe, is all the news, and enough at that unless it were better. Write me immediately on the receipt of this.
Your friend, as ever, LINCOLN.
DEAR SPEED:—Yours of the 1st instant came to hand three or four days ago. When this shall reach you, you will have been Fanny's husband several days. You know my desire to befriend you is everlasting; that I will never cease while I know how to do anything. But you will always hereafter be on ground that I have never occupied, and consequently, if advice were needed, I might advise wrong. I do fondly hope, however, that you will never again need any comfort from abroad. But should I be mistaken in this, should excessive pleasure still be accompanied with a painful counterpart at times, still let me urge you, as I have ever done, to remember, in the depth and even agony of despondency, that very shortly you are to feel well again. I am now fully convinced that you love her as ardently as you are capable of loving. Your ever being happy in her presence, and your intense anxiety about her health, if there were nothing else, would place this beyond all dispute in my mind. I incline to think it probable that your nerves will fail you occasionally for a while; but once you get them firmly guarded now that trouble is over forever. I think, if I were you, in case my mind were not exactly right, I would avoid being idle. I would immediately engage in some business, or go to making preparations for it, which would be the same thing. If you went through the ceremony calmly, or even with sufficient composure not to excite alarm in any present, you are safe beyond question, and in two or three months, to say the most, will be the happiest of men.
I would desire you to give my particular respects to Fanny; but perhaps you will not wish her to know you have received this, lest she should desire to see it. Make her write me an answer to my last letter to her; at any rate I would set great value upon a note or letter from her. Write me whenever you have leisure. Yours forever, A. LINCOLN. P. S.—I have been quite a man since you left.
G. B. SHELEDY, ESQ.:
Yours of the 10th is duly received. Judge Logan and myself are doing business together now, and we are willing to attend to your cases as you propose. As to the terms, we are willing to attend each case you prepare and send us for $10 (when there shall be no opposition) to be sent in advance, or you to know that it is safe. It takes $5.75 of cost to start upon, that is, $1.75 to clerk, and $2 to each of two publishers of papers. Judge Logan thinks it will take the balance of $20 to carry a case through. This must be advanced from time to time as the services are performed, as the officers will not act without. I do not know whether you can be admitted an attorney of the Federal court in your absence or not; nor is it material, as the business can be done in our names.
Thinking it may aid you a little, I send you one of our blank forms of Petitions. It, you will see, is framed to be sworn to before the Federal court clerk, and, in your cases, will have [to] be so far changed as to be sworn to before the clerk of your circuit court; and his certificate must be accompanied with his official seal. The schedules, too, must be attended to. Be sure that they contain the creditors' names, their residences, the amounts due each, the debtors' names, their residences, and the amounts they owe, also all property and where located.
Also be sure that the schedules are all signed by the applicants as well as the Petition. Publication will have to be made here in one paper, and in one nearest the residence of the applicant. Write us in each case where the last advertisement is to be sent, whether to you or to what paper.
I believe I have now said everything that can be of any advantage. Your friend as ever, A. LINCOLN.
I never encourage deceit, and falsehood, especially if you have got a bad memory, is the worst enemy a fellow can have. The fact is truth is your truest friend, no matter what the circumstances are. Notwithstanding this copy-book preamble, my boy, I am inclined to suggest a little prudence on your part. You see I have a congenital aversion to failure, and the sudden announcement to your Uncle Andrew of the success of your "lamp rubbing" might possibly prevent your passing the severe physical examination to which you will be subjected in order to enter the Military Academy. You see I should like to have a perfect soldier credited to dear old Illinois—no broken bones, scalp wounds, etc. So I think it might be wise to hand this letter from me in to your good uncle through his room-window after he has had a comfortable dinner, and watch its effect from the top of the pigeon-house.
I have just told the folks here in Springfield on this 111th anniversary of the birth of him whose name, mightiest in the cause of civil liberty, still mightiest in the cause of moral reformation, we mention in solemn awe, in naked, deathless splendor, that the one victory we can ever call complete will be that one which proclaims that there is not one slave or one drunkard on the face of God's green earth. Recruit for this victory.
Now, boy, on your march, don't you go and forget the old maxim that "one drop of honey catches more flies than a half-gallon of gall." Load your musket with this maxim, and smoke it in your pipe.
Although the temperance cause has been in progress for near twenty years, it is apparent to all that it is just now being crowned with a degree of success hitherto unparalleled.
The list of its friends is daily swelled by the additions of fifties, of hundreds, and of thousands. The cause itself seems suddenly transformed from a cold abstract theory to a living, breathing, active, and powerful chieftain, going forth "conquering and to conquer." The citadels of his great adversary are daily being stormed and dismantled; his temple and his altars, where the rites of his idolatrous worship have long been performed, and where human sacrifices have long been wont to be made, are daily desecrated and deserted. The triumph of the conqueror's fame is sounding from hill to hill, from sea to sea, and from land to land, and calling millions to his standard at a blast.
For this new and splendid success we heartily rejoice. That that success is so much greater now than heretofore is doubtless owing to rational causes; and if we would have it continue, we shall do well to inquire what those causes are.
The warfare heretofore waged against the demon intemperance has somehow or other been erroneous. Either the champions engaged or the tactics they adopted have not been the most proper. These champions for the most part have been preachers, lawyers, and hired agents. Between these and the mass of mankind there is a want of approachability, if the term be admissible, partially, at least, fatal to their success. They are supposed to have no sympathy of feeling or interest with those very persons whom it is their object to convince and persuade.
And again, it is so common and so easy to ascribe motives to men of these classes other than those they profess to act upon. The preacher, it is said, advocates temperance because he is a fanatic, and desires a union of the Church and State; the lawyer from his pride and vanity of hearing himself speak; and the hired agent for his salary. But when one who has long been known as a victim of intemperance bursts the fetters that have bound him, and appears before his neighbors "clothed and in his right mind," a redeemed specimen of long-lost humanity, and stands up, with tears of joy trembling in his eyes, to tell of the miseries once endured, now to be endured no more forever; of his once naked and starving children, now clad and fed comfortably; of a wife long weighed down with woe, weeping, and a broken heart, now restored to health, happiness, and a renewed affection; and how easily it is all done, once it is resolved to be done; how simple his language! there is a logic and an eloquence in it that few with human feelings can resist. They cannot say that he desires a union of Church and State, for he is not a church member; they cannot say he is vain of hearing himself speak, for his whole demeanor shows he would gladly avoid speaking at all; they cannot say he speaks for pay, for he receives none, and asks for none. Nor can his sincerity in any way be doubted, or his sympathy for those he would persuade to imitate his example be denied.
In my judgment, it is to the battles of this new class of champions that our late success is greatly, perhaps chiefly, owing. But, had the old-school champions themselves been of the most wise selecting, was their system of tactics the most judicious? It seems to me it was not. Too much denunciation against dram-sellers and dram-drinkers was indulged in. This I think was both impolitic and unjust. It was impolitic, because it is not much in the nature of man to be driven to anything; still less to be driven about that which is exclusively his own business; and least of all where such driving is to be submitted to at the expense of pecuniary interest or burning appetite. When the dram-seller and drinker were incessantly told not in accents of entreaty and persuasion, diffidently addressed by erring man to an erring brother, but in the thundering tones of anathema and denunciation with which the lordly judge often groups together all the crimes of the felon's life, and thrusts them in his face just ere he passes sentence of death upon him that they were the authors of all the vice and misery and crime in the land; that they were the manufacturers and material of all the thieves and robbers and murderers that infest the earth; that their houses were the workshops of the devil; and that their persons should be shunned by all the good and virtuous, as moral pestilences—I say, when they were told all this, and in this way, it is not wonderful that they were slow to acknowledge the truth of such denunciations, and to join the ranks of their denouncers in a hue and cry against themselves.
To have expected them to do otherwise than they did to have expected them not to meet denunciation with denunciation, crimination with crimination, and anathema with anathema—was to expect a reversal of human nature, which is God's decree and can never be reversed.
When the conduct of men is designed to be influenced, persuasion, kind, unassuming persuasion, should ever be adopted. It is an old and a true maxim that "a drop of honey catches more flies than a gallon of gall." So with men. If you would win a man to your cause, first convince him that you are his sincere friend. Therein is a drop of honey that catches his heart, which, say what he will, is the great highroad to his reason; and which, when once gained, you will find but little trouble in convincing his judgment of the justice of your cause, if indeed that cause really be a just one. On the contrary, assume to dictate to his judgment, or to command his action, or to mark him as one to be shunned and despised, and he will retreat within himself, close all the avenues to his head and his heart; and though your cause be naked truth itself, transformed to the heaviest lance, harder than steel, and sharper than steel can be made, and though you throw it with more than herculean force and precision, you shall be no more able to pierce him than to penetrate the hard shell of a tortoise with a rye straw. Such is man, and so must he be understood by those who would lead him, even to his own best interests.
On this point the Washingtonians greatly excel the temperance advocates of former times. Those whom they desire to convince and persuade are their old friends and companions. They know they are not demons, nor even the worst of men; they know that generally they are kind, generous, and charitable even beyond the example of their more staid and sober neighbors. They are practical philanthropists; and they glow with a generous and brotherly zeal that mere theorizers are incapable of feeling. Benevolence and charity possess their hearts entirely; and out of the abundance of their hearts their tongues give utterance; "love through all their actions runs, and all their words are mild." In this spirit they speak and act, and in the same they are heard and regarded. And when such is the temper of the advocate, and such of the audience, no good cause can be unsuccessful. But I have said that denunciations against dramsellers and dram-drinkers are unjust, as well as impolitic. Let us see. I have not inquired at what period of time the use of intoxicating liquors commenced; nor is it important to know. It is sufficient that, to all of us who now inhabit the world, the practice of drinking them is just as old as the world itself that is, we have seen the one just as long as we have seen the other. When all such of us as have now reached the years of maturity first opened our eyes upon the stage of existence, we found intoxicating liquor recognized by everybody, used by everybody, repudiated by nobody. It commonly entered into the first draught of the infant and the last draught of the dying man. From the sideboard of the parson down to the ragged pocket of the houseless loafer, it was constantly found. Physicians proscribed it in this, that, and the other disease; government provided it for soldiers and sailors; and to have a rolling or raising, a husking or "hoedown," anywhere about without it was positively insufferable. So, too, it was everywhere a respectable article of manufacture and merchandise. The making of it was regarded as an honorable livelihood, and he who could make most was the most enterprising and respectable. Large and small manufactories of it were everywhere erected, in which all the earthly goods of their owners were invested. Wagons drew it from town to town; boats bore it from clime to clime, and the winds wafted it from nation to nation; and merchants bought and sold it, by wholesale and retail, with precisely the same feelings on the part of the seller, buyer, and bystander as are felt at the selling and buying of ploughs, beef, bacon, or any other of the real necessaries of life. Universal public opinion not only tolerated but recognized and adopted its use.
It is true that even then it was known and acknowledged that many were greatly injured by it; but none seemed to think the injury arose from the use of a bad thing, but from the abuse of a very good thing. The victims of it were to be pitied and compassionated, just as are the heirs of consumption and other hereditary diseases. Their failing was treated as a misfortune, and not as a crime, or even as a disgrace. If, then, what I have been saying is true, is it wonderful that some should think and act now as all thought and acted twenty years ago? and is it just to assail, condemn, or despise them for doing so? The universal sense of mankind on any subject is an argument, or at least an influence, not easily overcome. The success of the argument in favor of the existence of an overruling Providence mainly depends upon that sense; and men ought not in justice to be denounced for yielding to it in any case, or giving it up slowly, especially when they are backed by interest, fixed habits, or burning appetites.
Another error, as it seems to me, into which the old reformers fell, was the position that all habitual drunkards were utterly incorrigible, and therefore must be turned adrift and damned without remedy in order that the grace of temperance might abound, to the temperate then, and to all mankind some hundreds of years thereafter. There is in this some thing so repugnant to humanity, so uncharitable, so cold-blooded and feelingless, that it, never did nor ever can enlist the enthusiasm of a popular cause. We could not love the man who taught it we could not hear him with patience. The heart could not throw open its portals to it, the generous man could not adopt it—it could not mix with his blood. It looked so fiendishly selfish, so like throwing fathers and brothers overboard to lighten the boat for our security, that the noble-minded shrank from the manifest meanness of the thing. And besides this, the benefits of a reformation to be effected by such a system were too remote in point of time to warmly engage many in its behalf. Few can be induced to labor exclusively for posterity, and none will do it enthusiastically. —Posterity has done nothing for us; and, theorize on it as we may, practically we shall do very little for it, unless we are made to think we are at the same time doing something for ourselves.
What an ignorance of human nature does it exhibit to ask or to expect a whole community to rise up and labor for the temporal happiness of others, after themselves shall be consigned to the dust, a majority of which community take no pains whatever to secure their own eternal welfare at no more distant day! Great distance in either time or space has wonderful power to lull and render quiescent the human mind. Pleasures to be enjoyed, or pains to be endured, after we shall be dead and gone are but little regarded even in our own cases, and much less in the cases of others. Still, in addition to this there is something so ludicrous in promises of good or threats of evil a great way off as to render the whole subject with which they are connected easily turned into ridicule. "Better lay down that spade you are stealing, Paddy; if you don't you'll pay for it at the day of judgment." "Be the powers, if ye'll credit me so long I'll take another jist."
By the Washingtonians this system of consigning the habitual drunkard to hopeless ruin is repudiated. They adopt a more enlarged philanthropy; they go for present as well as future good. They labor for all now living, as well as hereafter to live. They teach hope to all-despair to none. As applying to their cause, they deny the doctrine of unpardonable sin; as in Christianity it is taught, so in this they teach—"While—While the lamp holds out to burn, The vilest sinner may return." And, what is a matter of more profound congratulation, they, by experiment upon experiment and example upon example, prove the maxim to be no less true in the one case than in the other. On every hand we behold those who but yesterday were the chief of sinners, now the chief apostles of the cause. Drunken devils are cast out by ones, by sevens, by legions; and their unfortunate victims, like the poor possessed who were redeemed from their long and lonely wanderings in the tombs, are publishing to the ends of the earth how great things have been done for them.
To these new champions and this new system of tactics our late success is mainly owing, and to them we must mainly look for the final consummation. The ball is now rolling gloriously on, and none are so able as they to increase its speed and its bulk, to add to its momentum and its magnitude—even though unlearned in letters, for this task none are so well educated. To fit them for this work they have been taught in the true school. They have been in that gulf from which they would teach others the means of escape. They have passed that prison wall which others have long declared impassable; and who that has not shall dare to weigh opinions with them as to the mode of passing?
But if it be true, as I have insisted, that those who have suffered by intemperance personally, and have reformed, are the most powerful and efficient instruments to push the reformation to ultimate success, it does not follow that those who have not suffered have no part left them to perform. Whether or not the world would be vastly benefited by a total and final banishment from it of all intoxicating drinks seems to me not now an open question. Three fourths of mankind confess the affirmative with their tongues, and, I believe, all the rest acknowledge it in their hearts.
Ought any, then, to refuse their aid in doing what good the good of the whole demands? Shall he who cannot do much be for that reason excused if he do nothing? "But," says one, "what good can I do by signing the pledge? I never drank, even without signing." This question has already been asked and answered more than a million of times. Let it be answered once more. For the man suddenly or in any other way to break off from the use of drams, who has indulged in them for a long course of years and until his appetite for them has grown ten or a hundredfold stronger and more craving than any natural appetite can be, requires a most powerful moral effort. In such an undertaking he needs every moral support and influence that can possibly be brought to his aid and thrown around him. And not only so, but every moral prop should be taken from whatever argument might rise in his mind to lure him to his backsliding. When he casts his eyes around him, he should be able to see all that he respects, all that he admires, all that he loves, kindly and anxiously pointing him onward, and none beckoning him back to his former miserable "wallowing in the mire."
But it is said by some that men will think and act for themselves; that none will disuse spirits or anything else because his neighbors do; and that moral influence is not that powerful engine contended for. Let us examine this. Let me ask the man who could maintain this position most stiffly, what compensation he will accept to go to church some Sunday and sit during the sermon with his wife's bonnet upon his head? Not a trifle, I'll venture. And why not? There would be nothing irreligious in it, nothing immoral, nothing uncomfortable—then why not? Is it not because there would be something egregiously unfashionable in it? Then it is the influence of fashion; and what is the influence of fashion but the influence that other people's actions have on our actions—the strong inclination each of us feels to do as we see all our neighbors do? Nor is the influence of fashion confined to any particular thing or class of things; it is just as strong on one subject as another. Let us make it as unfashionable to withhold our names from the temperance cause as for husbands to wear their wives' bonnets to church, and instances will be just as rare in the one case as the other.
"But," say some, "we are no drunkards, and we shall not acknowledge ourselves such by joining a reformed drunkard's society, whatever our influence might be." Surely no Christian will adhere to this objection. If they believe as they profess, that Omnipotence condescended to take on himself the form of sinful man, and as such to die an ignominious death for their sakes, surely they will not refuse submission to the infinitely lesser condescension, for the temporal, and perhaps eternal, salvation of a large, erring, and unfortunate class of their fellow-creatures. Nor is the condescension very great. In my judgment such of us as have never fallen victims have been spared more by the absence of appetite than from any mental or moral superiority over those who have. Indeed, I believe if we take habitual drunkards as a class, their heads and their hearts will bear an advantageous comparison with those of any other class. There seems ever to have been a proneness in the brilliant and warm-blooded to fall into this vice—the demon of intemperance ever seems to have delighted in sucking the blood of genius and of generosity. What one of us but can call to mind some relative, more promising in youth than all his fellows, who has fallen a sacrifice to his rapacity? He ever seems to have gone forth like the Egyptian angel of death, commissioned to slay, if not the first, the fairest born of every family. Shall he now be arrested in his desolating career? In that arrest all can give aid that will; and who shall be excused that can and will not? Far around as human breath has ever blown he keeps our fathers, our brothers, our sons, and our friends prostrate in the chains of moral death. To all the living everywhere we cry, "Come sound the moral trump, that these may rise and stand up an exceeding great army." "Come from the four winds, O breath! and breathe upon these slain that they may live." If the relative grandeur of revolutions shall be estimated by the great amount of human misery they alleviate, and the small amount they inflict, then indeed will this be the grandest the world shall ever have seen.
Of our political revolution of '76 we are all justly proud. It has given us a degree of political freedom far exceeding that of any other nation of the earth. In it the world has found a solution of the long-mooted problem as to the capability of man to govern himself. In it was the germ which has vegetated, and still is to grow and expand into the universal liberty of mankind. But, with all these glorious results, past, present, and to come, it had its evils too. It breathed forth famine, swam in blood, and rode in fire; and long, long after, the orphan's cry and the widow's wail continued to break the sad silence that ensued. These were the price, the inevitable price, paid for the blessings it bought.
Turn now to the temperance revolution. In it we shall find a stronger bondage broken, a viler slavery manumitted, a greater tyrant deposed; in it, more of want supplied, more disease healed, more sorrow assuaged. By it no Orphans starving, no widows weeping. By it none wounded in feeling, none injured in interest; even the drammaker and dram-seller will have glided into other occupations so gradually as never to have felt the change, and will stand ready to join all others in the universal song of gladness. And what a noble ally this to the cause of political freedom, with such an aid its march cannot fail to be on and on, till every son of earth shall drink in rich fruition the sorrow-quenching draughts of perfect liberty. Happy day when-all appetites controlled, all poisons subdued, all matter subjected-mind, all-conquering mind, shall live and move, the monarch of the world. Glorious consummation! Hail, fall of fury! Reign of reason, all hail!
And when the victory shall be complete, when there shall be neither a slave nor a drunkard on the earth, how proud the title of that land which may truly claim to be the birthplace and the cradle of both those revolutions that shall have ended in that victory. How nobly distinguished that people who shall have planted and nurtured to maturity both the political and moral freedom of their species.
This is the one hundred and tenth anniversary of the birthday of Washington; we are met to celebrate this day. Washington is the mightiest name of earth long since mightiest in the cause of civil liberty, still mightiest in moral reformation. On that name no eulogy is expected. It cannot be. To add brightness to the sun or glory to the name of Washington is alike impossible. Let none attempt it. In solemn awe pronounce the name, and in its naked deathless splendor leave it shining on.
DEAR SPEED:—Yours of the 16th instant, announcing that Miss Fanny and you are "no more twain, but one flesh," reached me this morning. I have no way of telling you how much happiness I wish you both, though I believe you both can conceive it. I feel somewhat jealous of both of you now: you will be so exclusively concerned for one another, that I shall be forgotten entirely. My acquaintance with Miss Fanny (I call her this, lest you should think I am speaking of your mother) was too short for me to reasonably hope to long be remembered by her; and still I am sure I shall not forget her soon. Try if you cannot remind her of that debt she owes me—and be sure you do not interfere to prevent her paying it.
I regret to learn that you have resolved to not return to Illinois. I shall be very lonesome without you. How miserably things seem to be arranged in this world! If we have no friends, we have no pleasure; and if we have them, we are sure to lose them, and be doubly pained by the loss. I did hope she and you would make your home here; but I own I have no right to insist. You owe obligations to her ten thousand times more sacred than you can owe to others, and in that light let them be respected and observed. It is natural that she should desire to remain with her relatives and friends. As to friends, however, she could not need them anywhere: she would have them in abundance here.
Give my kind remembrance to Mr. Williamson and his family, particularly Miss Elizabeth; also to your mother, brother, and sisters. Ask little Eliza Davis if she will ride to town with me if I come there again. And finally, give Fanny a double reciprocation of all the love she sent me. Write me often, and believe me
Yours forever, LINCOLN.
P. S. Poor Easthouse is gone at last. He died awhile before day this morning. They say he was very loath to die....
DEAR SPEED:—I received yours of the 12th written the day you went down to William's place, some days since, but delayed answering it till I should receive the promised one of the 16th, which came last night. I opened the letter with intense anxiety and trepidation; so much so, that, although it turned out better than I expected, I have hardly yet, at a distance of ten hours, become calm.
I tell you, Speed, our forebodings (for which you and I are peculiar) are all the worst sort of nonsense. I fancied, from the time I received your letter of Saturday, that the one of Wednesday was never to come, and yet it did come, and what is more, it is perfectly clear, both from its tone and handwriting, that you were much happier, or, if you think the term preferable, less miserable, when you wrote it than when you wrote the last one before. You had so obviously improved at the very time I so much fancied you would have grown worse. You say that something indescribably horrible and alarming still haunts you. You will not say that three months from now, I will venture. When your nerves once get steady now, the whole trouble will be over forever. Nor should you become impatient at their being even very slow in becoming steady. Again you say, you much fear that that Elysium of which you have dreamed so much is never to be realized. Well, if it shall not, I dare swear it will not be the fault of her who is now your wife. I now have no doubt that it is the peculiar misfortune of both you and me to dream dreams of Elysium far exceeding all that anything earthly can realize. Far short of your dreams as you may be, no woman could do more to realize them than that same black-eyed Fanny. If you could but contemplate her through my imagination, it would appear ridiculous to you that any one should for a moment think of being unhappy with her. My old father used to have a saying that "If you make a bad bargain, hug it all the tighter"; and it occurs to me that if the bargain you have just closed can possibly be called a bad one, it is certainly the most pleasant one for applying that maxim to which my fancy can by any effort picture.
I write another letter, enclosing this, which you can show her, if she desires it. I do this because she would think strangely, perhaps, should you tell her that you received no letters from me, or, telling her you do, refuse to let her see them. I close this, entertaining the confident hope that every successive letter I shall have from you (which I here pray may not be few, nor far between) may show you possessing a more steady hand and cheerful heart than the last preceding it. As ever, your friend, LINCOLN.
DEAR SPEED:—Yours of the 10th instant was received three or four days since. You know I am sincere when I tell you the pleasure its contents gave me was, and is, inexpressible. As to your farm matter, I have no sympathy with you. I have no farm, nor ever expect to have, and consequently have not studied the subject enough to be much interested with it. I can only say that I am glad you are satisfied and pleased with it. But on that other subject, to me of the most intense interest whether in joy or sorrow, I never had the power to withhold my sympathy from you. It cannot be told how it now thrills me with joy to hear you say you are "far happier than you ever expected to be." That much I know is enough. I know you too well to suppose your expectations were not, at least, sometimes extravagant, and if the reality exceeds them all, I say, Enough, dear Lord. I am not going beyond the truth when I tell you that the short space it took me to read your last letter gave me more pleasure than the total sum of all I have enjoyed since the fatal 1st of January, 1841. Since then it seems to me I should have been entirely happy, but for the never-absent idea that there is one still unhappy whom I have contributed to make so. That still kills my soul. I cannot but reproach myself for even wishing to be happy while she is otherwise. She accompanied a large party on the railroad cars to Jacksonville last Monday, and on her return spoke, so that I heard of it, of having enjoyed the trip exceedingly. God be praised for that.
You know with what sleepless vigilance I have watched you ever since the commencement of your affair; and although I am almost confident it is useless, I cannot forbear once more to say that I think it is even yet possible for your spirits to flag down and leave you miserable. If they should, don't fail to remember that they cannot long remain so. One thing I can tell you which I know you will be glad to hear, and that is that I have seen—and scrutinized her feelings as well as I could, and am fully convinced she is far happier now than she has been for the last fifteen months past.
You will see by the last Sangamon Journal, that I made a temperance speech on the 22d of February, which I claim that Fanny and you shall read as an act of charity to me; for I cannot learn that anybody else has read it, or is likely to. Fortunately it is not very long, and I shall deem it a sufficient compliance with my request if one of you listens while the other reads it.
As to your Lockridge matter, it is only necessary to say that there has been no court since you left, and that the next commences to-morrow morning, during which I suppose we cannot fail to get a judgment.
I wish you would learn of Everett what he would take, over and above a discharge for all the trouble we have been at, to take his business out of our hands and give it to somebody else. It is impossible to collect money on that or any other claim here now; and although you know I am not a very petulant man, I declare I am almost out of patience with Mr. Everett's importunity. It seems like he not only writes all the letters he can himself, but gets everybody else in Louisville and vicinity to be constantly writing to us about his claim. I have always said that Mr. Everett is a very clever fellow, and I am very sorry he cannot be obliged; but it does seem to me he ought to know we are interested to collect his claim, and therefore would do it if we could.
I am neither joking nor in a pet when I say we would thank him to transfer his business to some other, without any compensation for what we have done, provided he will see the court cost paid, for which we are security.
The sweet violet you inclosed came safely to hand, but it was so dry, and mashed so flat, that it crumbled to dust at the first attempt to handle it. The juice that mashed out of it stained a place in the letter, which I mean to preserve and cherish for the sake of her who procured it to be sent. My renewed good wishes to her in particular, and generally to all such of your relations who know me.
As ever,
DEAR SPEED:—Yours of the 16th June was received only a day or two since. It was not mailed at Louisville till the 25th. You speak of the great time that has elapsed since I wrote you. Let me explain that. Your letter reached here a day or two after I started on the circuit. I was gone five or six weeks, so that I got the letters only a few weeks before Butler started to your country. I thought it scarcely worth while to write you the news which he could and would tell you more in detail. On his return he told me you would write me soon, and so I waited for your letter. As to my having been displeased with your advice, surely you know better than that. I know you do, and therefore will not labor to convince you. True, that subject is painful to me; but it is not your silence, or the silence of all the world, that can make me forget it. I acknowledge the correctness of your advice too; but before I resolve to do the one thing or the other, I must gain my confidence in my own ability to keep my resolves when they are made. In that ability you know I once prided myself as the only or chief gem of my character; that gem I lost—how and where you know too well. I have not yet regained it; and until I do, I cannot trust myself in any matter of much importance. I believe now that had you understood my case at the time as well as I understand yours afterward, by the aid you would have given me I should have sailed through clear, but that does not now afford me sufficient confidence to begin that or the like of that again.
You make a kind acknowledgment of your obligations to me for your present happiness. I am pleased with that acknowledgment. But a thousand times more am I pleased to know that you enjoy a degree of happiness worthy of an acknowledgment. The truth is, I am not sure that there was any merit with me in the part I took in your difficulty; I was drawn to it by a fate. If I would I could not have done less than I did. I always was superstitious; I believe God made me one of the instruments of bringing your Fanny and you together, which union I have no doubt He had fore-ordained. Whatever He designs He will do for me yet. "Stand still, and see the salvation of the Lord" is my text just now. If, as you say, you have told Fanny all, I should have no objection to her seeing this letter, but for its reference to our friend here: let her seeing it depend upon whether she has ever known anything of my affairs; and if she has not, do not let her.
I do not think I can come to Kentucky this season. I am so poor and make so little headway in the world, that I drop back in a month of idleness as much as I gain in a year's sowing. I should like to visit you again. I should like to see that "sis" of yours that was absent when I was there, though I suppose she would run away again if she were to hear I was coming.
My respects and esteem to all your friends there, and, by your permission, my love to your Fanny.
Ever yours,
Article written by Lincoln for the Sangamon Journal in ridicule of James Shields, who, as State Auditor, had declined to receive State Bank notes in payment of taxes. The above letter purported to come from a poor widow who, though supplied with State Bank paper, could not obtain a receipt for her tax bill. This, and another subsequent letter by Mary Todd, brought about the "Lincoln-Shields Duel."
DEAR Mr. PRINTER:
I see you printed that long letter I sent you a spell ago. I 'm quite encouraged by it, and can't keep from writing again. I think the printing of my letters will be a good thing all round—it will give me the benefit of being known by the world, and give the world the advantage of knowing what's going on in the Lost Townships, and give your paper respectability besides. So here comes another. Yesterday afternoon I hurried through cleaning up the dinner dishes and stepped over to neighbor S——— to see if his wife Peggy was as well as mout be expected, and hear what they called the baby. Well, when I got there and just turned round the corner of his log cabin, there he was, setting on the doorstep reading a newspaper. "How are you, Jeff?" says I. He sorter started when he heard me, for he hadn't seen me before. "Why," says he, "I 'm mad as the devil, Aunt 'Becca!" "What about?" says I; "ain't its hair the right color? None of that nonsense, Jeff; there ain't an honester woman in the Lost Townships than..."—"Than who?" says he; "what the mischief are you about?" I began to see I was running the wrong trail, and so says I, "Oh! nothing: I guess I was mistaken a little, that's all. But what is it you 're mad about?"
"Why," says he, "I've been tugging ever since harvest, getting out wheat and hauling it to the river to raise State Bank paper enough to pay my tax this year and a little school debt I owe; and now, just as I 've got it, here I open this infernal Extra Register, expecting to find it full of 'Glorious Democratic Victories' and 'High Comb'd Cocks,' when, lo and behold! I find a set of fellows, calling themselves officers of the State, have forbidden the tax collectors, and school commissioners to receive State paper at all; and so here it is dead on my hands. I don't now believe all the plunder I've got will fetch ready cash enough to pay my taxes and that school debt."
I was a good deal thunderstruck myself; for that was the first I had heard of the proclamation, and my old man was pretty much in the same fix with Jeff. We both stood a moment staring at one another without knowing what to say. At last says I, "Mr. S——— let me look at that paper." He handed it to me, when I read the proclamation over.
"There now," says he, "did you ever see such a piece of impudence and imposition as that?" I saw Jeff was in a good tune for saying some ill-natured things, and so I tho't I would just argue a little on the contrary side, and make him rant a spell if I could. "Why," says I, looking as dignified and thoughtful as I could, "it seems pretty tough, to be sure, to have to raise silver where there's none to be raised; but then, you see, 'there will be danger of loss' if it ain't done."
"Loss! damnation!" says he. "I defy Daniel Webster, I defy King Solomon, I defy the world—I defy—I defy—yes, I defy even you, Aunt 'Becca, to show how the people can lose anything by paying their taxes in State paper."
"Well," says I, "you see what the officers of State say about it, and they are a desarnin' set of men. But," says I, "I guess you 're mistaken about what the proclamation says. It don't say the people will lose anything by the paper money being taken for taxes. It only says 'there will be danger of loss'; and though it is tolerable plain that the people can't lose by paying their taxes in something they can get easier than silver, instead of having to pay silver; and though it's just as plain that the State can't lose by taking State Bank paper, however low it may be, while she owes the bank more than the whole revenue, and can pay that paper over on her debt, dollar for dollar;—still there is danger of loss to the 'officers of State'; and you know, Jeff, we can't get along without officers of State."
"Damn officers of State!" says he; "that's what Whigs are always hurrahing for."
"Now, don't swear so, Jeff," says I, "you know I belong to the meetin', and swearin' hurts my feelings."
"Beg pardon, Aunt 'Becca," says he; "but I do say it's enough to make Dr. Goddard swear, to have tax to pay in silver, for nothing only that Ford may get his two thousand a year, and Shields his twenty-four hundred a year, and Carpenter his sixteen hundred a year, and all without 'danger of loss' by taking it in State paper. Yes, yes: it's plain enough now what these officers of State mean by 'danger of loss.' Wash, I s'pose, actually lost fifteen hundred dollars out of the three thousand that two of these 'officers of State' let him steal from the treasury, by being compelled to take it in State paper. Wonder if we don't have a proclamation before long, commanding us to make up this loss to Wash in silver."
And so he went on till his breath run out, and he had to stop. I couldn't think of anything to say just then, and so I begun to look over the paper again. "Ay! here's another proclamation, or something like it."
"Another?" says Jeff; "and whose egg is it, pray?"
I looked to the bottom of it, and read aloud, "Your obedient servant, James Shields, Auditor."
"Aha!" says Jeff, "one of them same three fellows again. Well read it, and let's hear what of it."
I read on till I came to where it says, "The object of this measure is to suspend the collection of the revenue for the current year."
"Now stop, now stop!" says he; "that's a lie a'ready, and I don't want to hear of it."
"Oh, maybe not," says I.
"I say it-is-a-lie. Suspend the collection, indeed! Will the collectors, that have taken their oaths to make the collection, dare to end it? Is there anything in law requiring them to perjure themselves at the bidding of James Shields?
"Will the greedy gullet of the penitentiary be satisfied with swallowing him instead of all of them, if they should venture to obey him? And would he not discover some 'danger of loss,' and be off about the time it came to taking their places?
"And suppose the people attempt to suspend, by refusing to pay; what then? The collectors would just jerk up their horses and cows, and the like, and sell them to the highest bidder for silver in hand, without valuation or redemption. Why, Shields didn't believe that story himself; it was never meant for the truth. If it was true, why was it not writ till five days after the proclamation? Why did n't Carlin and Carpenter sign it as well as Shields? Answer me that, Aunt 'Becca. I say it's a lie, and not a well told one at that. It grins out like a copper dollar. Shields is a fool as well as a liar. With him truth is out of the question; and as for getting a good, bright, passable lie out of him, you might as well try to strike fire from a cake of tallow. I stick to it, it's all an infernal Whig lie!"
"A Whig lie! Highty tighty!"
"Yes, a Whig lie; and it's just like everything the cursed British Whigs do. First they'll do some divilment, and then they'll tell a lie to hide it. And they don't care how plain a lie it is; they think they can cram any sort of a one down the throats of the ignorant Locofocos, as they call the Democrats."
"Why, Jeff, you 're crazy: you don't mean to say Shields is a Whig!"
"Yes, I do."
"Why, look here! the proclamation is in your own Democratic paper, as you call it."
"I know it; and what of that? They only printed it to let us Democrats see the deviltry the Whigs are at."
"Well, but Shields is the auditor of this Loco—I mean this Democratic State."
"So he is, and Tyler appointed him to office."
"Tyler appointed him?"
"Yes (if you must chaw it over), Tyler appointed him; or, if it was n't him, it was old Granny Harrison, and that's all one. I tell you, Aunt 'Becca, there's no mistake about his being a Whig. Why, his very looks shows it; everything about him shows it: if I was deaf and blind, I could tell him by the smell. I seed him when I was down in Springfield last winter. They had a sort of a gatherin' there one night among the grandees, they called a fair. All the gals about town was there, and all the handsome widows and married women, finickin' about trying to look like gals, tied as tight in the middle, and puffed out at both ends, like bundles of fodder that had n't been stacked yet, but wanted stackin' pretty bad. And then they had tables all around the house kivered over with [———] caps and pincushions and ten thousand such little knick-knacks, tryin' to sell 'em to the fellows that were bowin', and scrapin' and kungeerin' about 'em. They would n't let no Democrats in, for fear they'd disgust the ladies, or scare the little gals, or dirty the floor. I looked in at the window, and there was this same fellow Shields floatin' about on the air, without heft or earthly substances, just like a lock of cat fur where cats had been fighting.
"He was paying his money to this one, and that one, and t' other one, and sufferin' great loss because it was n't silver instead of State paper; and the sweet distress he seemed to be in,—his very features, in the ecstatic agony of his soul, spoke audibly and distinctly, 'Dear girls, it is distressing, but I cannot marry you all. Too well I know how much you suffer; but do, do remember, it is not my fault that I am so handsome and so interesting.'
"As this last was expressed by a most exquisite contortion of his face, he seized hold of one of their hands, and squeezed, and held on to it about a quarter of an hour. 'Oh, my good fellow!' says I to myself, 'if that was one of our Democratic gals in the Lost Townships, the way you 'd get a brass pin let into you would be about up to the head.' He a Democrat! Fiddlesticks! I tell you, Aunt 'Becca, he's a Whig, and no mistake; nobody but a Whig could make such a conceity dunce of himself."
"Well," says I, "maybe he is; but, if he is, I 'm mistaken the worst sort. Maybe so, maybe so; but, if I am, I'll suffer by it; I'll be a Democrat if it turns out that Shields is a Whig, considerin' you shall be a Whig if he turns out a Democrat."
"A bargain, by jingoes!" says he; "but how will we find out?"
"Why," says I, "we'll just write and ax the printer."
"Agreed again!" says he; "and by thunder! if it does turn out that Shields is a Democrat, I never will——"
"Jefferson! Jefferson!"
"What do you want, Peggy?"
"Do get through your everlasting clatter some time, and bring me a gourd of water; the child's been crying for a drink this livelong hour."
"Let it die, then; it may as well die for water as to be taxed to death to fatten officers of State."
Jeff run off to get the water, though, just like he hadn't been saying anything spiteful, for he's a raal good-hearted fellow, after all, once you get at the foundation of him.
I walked into the house, and, "Why, Peggy," says I, "I declare we like to forgot you altogether."
"Oh, yes," says she, "when a body can't help themselves, everybody soon forgets 'em; but, thank God! by day after to-morrow I shall be well enough to milk the cows, and pen the calves, and wring the contrary ones' tails for 'em, and no thanks to nobody."
"Good evening, Peggy," says I, and so I sloped, for I seed she was mad at me for making Jeff neglect her so long.
And now, Mr. Printer, will you be sure to let us know in your next paper whether this Shields is a Whig or a Democrat? I don't care about it for myself, for I know well enough how it is already; but I want to convince Jeff. It may do some good to let him, and others like him, know who and what these officers of State are. It may help to send the present hypocritical set to where they belong, and to fill the places they now disgrace with men who will do more work for less pay, and take fewer airs while they are doing it. It ain't sensible to think that the same men who get us in trouble will change their course; and yet it's pretty plain if some change for the better is not made, it's not long that either Peggy or I or any of us will have a cow left to milk, or a calf's tail to wring.
Yours truly,
HON. HENRY CLAY, Lexington, Ky.
DEAR SIR:—We hear you are to visit Indianapolis, Indiana, on the 5th Of October next. If our information in this is correct we hope you will not deny us the pleasure of seeing you in our State. We are aware of the toil necessarily incident to a journey by one circumstanced as you are; but once you have embarked, as you have already determined to do, the toil would not be greatly augmented by extending the journey to our capital. The season of the year will be most favorable for good roads, and pleasant weather; and although we cannot but believe you would be highly gratified with such a visit to the prairie-land, the pleasure it would give us and thousands such as we is beyond all question. You have never visited Illinois, or at least this portion of it; and should you now yield to our request, we promise you such a reception as shall be worthy of the man on whom are now turned the fondest hopes of a great and suffering nation.
Please inform us at the earliest convenience whether we may expect you.
Very respectfully your obedient servants,
A. G. HENRY, A. T. BLEDSOE, C. BIRCHALL, A. LINCOLN, G. M. CABANNISS, ROB'T IRWIN, P. A. SAUNDERS, J. M. ALLEN, F. N. FRANCIS. Executive Committee "Clay Club."
(Clay's answer, September 6, 1842, declines with thanks.)
ABRA. LINCOLN, ESQ.:—I regret that my absence on public business compelled me to postpone a matter of private consideration a little longer than I could have desired. It will only be necessary, however, to account for it by informing you that I have been to Quincy on business that would not admit of delay. I will now state briefly the reasons of my troubling you with this communication, the disagreeable nature of which I regret, as I had hoped to avoid any difficulty with any one in Springfield while residing there, by endeavoring to conduct myself in such a way amongst both my political friends and opponents as to escape the necessity of any. Whilst thus abstaining from giving provocation, I have become the object of slander, vituperation, and personal abuse, which were I capable of submitting to, I would prove myself worthy of the whole of it.
In two or three of the last numbers of the Sangamon Journal, articles of the most personal nature and calculated to degrade me have made their appearance. On inquiring, I was informed by the editor of that paper, through the medium of my friend General Whitesides, that you are the author of those articles. This information satisfies me that I have become by some means or other the object of your secret hostility. I will not take the trouble of inquiring into the reason of all this; but I will take the liberty of requiring a full, positive, and absolute retraction of all offensive allusions used by you in these communications, in relation to my private character and standing as a man, as an apology for the insults conveyed in them.
This may prevent consequences which no one will regret more than myself.
Your obedient servant, JAS. SHIELDS.
JAS. SHIELDS, ESQ.:—Your note of to-day was handed me by General Whitesides. In that note you say you have been informed, through the medium of the editor of the Journal, that I am the author of certain articles in that paper which you deem personally abusive of you; and without stopping to inquire whether I really am the author, or to point out what is offensive in them, you demand an unqualified retraction of all that is offensive, and then proceed to hint at consequences.
Now, sir, there is in this so much assumption of facts and so much of menace as to consequences, that I cannot submit to answer that note any further than I have, and to add that the consequences to which I suppose you allude would be matter of as great regret to me as it possibly could to you.
Respectfully,
ABRA. LINCOLN, ESQ.:—In reply to my note of this date, you intimate that I assume facts and menace consequences, and that you cannot submit to answer it further. As now, sir, you desire it, I will be a little more particular. The editor of the Sangamon Journal gave me to understand that you are the author of an article which appeared, I think, in that paper of the 2d September instant, headed "The Lost Townships," and signed Rebecca or 'Becca. I would therefore take the liberty of asking whether you are the author of said article, or any other over the same signature which has appeared in any of the late numbers of that paper. If so, I repeat my request of an absolute retraction of all offensive allusions contained therein in relation to my private character and standing. If you are not the author of any of these articles, your denial will be sufficient. I will say further, it is not my intention to menace, but to do myself justice.
Your obedient servant, JAS. SHIELDS.
September 19, 1842.
In case Whitesides shall signify a wish to adjust this affair without further difficulty, let him know that if the present papers be withdrawn, and a note from Mr. Shields asking to know if I am the author of the articles of which he complains, and asking that I shall make him gentlemanly satisfaction if I am the author, and this without menace, or dictation as to what that satisfaction shall be, a pledge is made that the following answer shall be given:
"I did write the 'Lost Townships' letter which appeared in the Journal of the 2d instant, but had no participation in any form in any other article alluding to you. I wrote that wholly for political effect—I had no intention of injuring your personal or private character or standing as a man or a gentleman; and I did not then think, and do not now think, that that article could produce or has produced that effect against you; and had I anticipated such an effect I would have forborne to write it. And I will add that your conduct toward me, so far as I know, had always been gentlemanly; and that I had no personal pique against you, and no cause for any."
If this should be done, I leave it with you to arrange what shall and what shall not be published. If nothing like this is done, the preliminaries of the fight are to be—
First. Weapons: Cavalry broadswords of the largest size, precisely equal in all respects, and such as now used by the cavalry company at Jacksonville.
Second. Position: A plank ten feet long, and from nine to twelve inches broad, to be firmly fixed on edge, on the ground, as the line between us, which neither is to pass his foot over upon forfeit of his life. Next a line drawn on the ground on either side of said plank and parallel with it, each at the distance of the whole length of the sword and three feet additional from the plank; and the passing of his own such line by either party during the fight shall be deemed a surrender of the contest.
Third. Time: On Thursday evening at five o'clock, if you can get it so; but in no case to be at a greater distance of time than Friday evening at five o'clock.
Fourth. Place: Within three miles of Alton, on the opposite side of the river, the particular spot to be agreed on by you.
Any preliminary details coming within the above rules you are at liberty to make at your discretion; but you are in no case to swerve from these rules, or to pass beyond their limits.
DEAR SPEED:—You have heard of my duel with Shields, and I have now to inform you that the dueling business still rages in this city. Day before yesterday Shields challenged Butler, who accepted, and proposed fighting next morning at sunrise in Bob Allen's meadow, one hundred yards' distance, with rifles. To this Whitesides, Shields's second, said "No," because of the law. Thus ended duel No. 2. Yesterday Whitesides chose to consider himself insulted by Dr. Merryman, so sent him a kind of quasi-challenge, inviting him to meet him at the Planter's House in St. Louis on the next Friday, to settle their difficulty. Merryman made me his friend, and sent Whitesides a note, inquiring to know if he meant his note as a challenge, and if so, that he would, according to the law in such case made and provided, prescribe the terms of the meeting. Whitesides returned for answer that if Merryman would meet him at the Planter's House as desired, he would challenge him. Merryman replied in a note that he denied Whitesides's right to dictate time and place, but that he (Merryman) would waive the question of time, and meet him at Louisiana, Missouri. Upon my presenting this note to Whitesides and stating verbally its contents, he declined receiving it, saying he had business in St. Louis, and it was as near as Louisiana. Merryman then directed me to notify Whitesides that he should publish the correspondence between them, with such comments as he thought fit. This I did. Thus it stood at bedtime last night. This morning Whitesides, by his friend Shields, is praying for a new trial, on the ground that he was mistaken in Merryman's proposition to meet him at Louisiana, Missouri, thinking it was the State of Louisiana. This Merryman hoots at, and is preparing his publication; while the town is in a ferment, and a street fight somewhat anticipated.
But I began this letter not for what I have been writing, but to say something on that subject which you know to be of such infinite solicitude to me. The immense sufferings you endured from the first days of September till the middle of February you never tried to conceal from me, and I well understood. You have now been the husband of a lovely woman nearly eight months. That you are happier now than the day you married her I well know, for without you could not be living. But I have your word for it, too, and the returning elasticity of spirits which is manifested in your letters. But I want to ask a close question, "Are you now in feeling as well as judgment glad that you are married as you are?" From anybody but me this would be an impudent question, not to be tolerated; but I know you will pardon it in me. Please answer it quickly, as I am impatient to know. I have sent my love to your Fanny so often, I fear she is getting tired of it. However, I venture to tender it again.
Yours forever,
JAS. S. IRWIN ESQ.:
Owing to my absence, yours of the 22nd ult. was not received till this moment. Judge Logan and myself are willing to attend to any business in the Supreme Court you may send us. As to fees, it is impossible to establish a rule that will apply in all, or even a great many cases. We believe we are never accused of being very unreasonable in this particular; and we would always be easily satisfied, provided we could see the money—but whatever fees we earn at a distance, if not paid before, we have noticed, we never hear of after the work is done. We, therefore, are growing a little sensitive on that point.
Yours etc.,
The object of the meeting was stated by Mr. Lincoln of Springfield, who offered the following resolutions, which were unanimously adopted:
Resolved, That a tariff of duties on imported goods, producing sufficient revenue for the payment of the necessary expenditures of the National Government, and so adjusted as to protect American industry, is indispensably necessary to the prosperity of the American people.
Resolved, That we are opposed to direct taxation for the support of the National Government.
Resolved, That a national bank, properly restricted, is highly necessary and proper to the establishment and maintenance of a sound currency, and for the cheap and safe collection, keeping, and disbursing of the public revenue.
Resolved, That the distribution of the proceeds of the sales of the public lands, upon the principles of Mr. Clay's bill, accords with the best interests of the nation, and particularly with those of the State of Illinois.
Resolved, That we recommend to the Whigs of each Congressional district of the State to nominate and support at the approaching election a candidate of their own principles, regardless of the chances of success.
Resolved, That we recommend to the Whigs of all portions of the State to adopt and rigidly adhere to the convention system of nominating candidates.
Resolved, That we recommend to the Whigs of each Congressional district to hold a district convention on or before the first Monday of May next, to be composed of a number of delegates from each county equal to double the number of its representatives in the General Assembly, provided, each county shall have at least one delegate. Said delegates to be chosen by primary meetings of the Whigs, at such times and places as they in their respective counties may see fit. Said district conventions each to nominate one candidate for Congress, and one delegate to a national convention for the purpose of nominating candidates for President and Vice-President of the United States. The seven delegates so nominated to a national convention to have power to add two delegates to their own number, and to fill all vacancies.
Resolved, That A. T. Bledsoe, S. T. Logan, and A. Lincoln be appointed a committee to prepare an address to the people of the State.
Resolved, That N. W. Edwards, A. G. Henry, James H. Matheny, John C. Doremus, and James C. Conkling be appointed a Whig Central State Committee, with authority to fill any vacancy that may occur in the committee.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:-By a resolution of a meeting of such of the Whigs of the State as are now at Springfield, we, the undersigned, were appointed to prepare an address to you. The performance of that task we now undertake.
Several resolutions were adopted by the meeting; and the chief object of this address is to show briefly the reasons for their adoption.
The first of those resolutions declares a tariff of duties upon foreign importations, producing sufficient revenue for the support of the General Government, and so adjusted as to protect American industry, to be indispensably necessary to the prosperity of the American people; and the second declares direct taxation for a national revenue to be improper. Those two resolutions are kindred in their nature, and therefore proper and convenient to be considered together. The question of protection is a subject entirely too broad to be crowded into a few pages only, together with several other subjects. On that point we therefore content ourselves with giving the following extracts from the writings of Mr. Jefferson, General Jackson, and the speech of Mr. Calhoun:
"To be independent for the comforts of life, we must fabricate them ourselves. We must now place the manufacturer by the side of the agriculturalist. The grand inquiry now is, Shall we make our own comforts, or go without them at the will of a foreign nation? He, therefore, who is now against domestic manufactures must be for reducing us either to dependence on that foreign nation, or to be clothed in skins and to live like wild beasts in dens and caverns. I am not one of those; experience has taught me that manufactures are now as necessary to our independence as to our comfort." Letter of Mr. Jefferson to Benjamin Austin.
"I ask, What is the real situation of the agriculturalist? Where has the American farmer a market for his surplus produce? Except for cotton, he has neither a foreign nor a home market. Does not this clearly prove, when there is no market at home or abroad, that there [is] too much labor employed in agriculture? Common sense at once points out the remedy. Take from agriculture six hundred thousand men, women, and children, and you will at once give a market for more breadstuffs than all Europe now furnishes. In short, we have been too long subject to the policy of British merchants. It is time we should become a little more Americanized, and instead of feeding the paupers and laborers of England, feed our own; or else in a short time, by continuing our present policy, we shall all be rendered paupers ourselves."—General Jackson's Letter to Dr. Coleman.
"When our manufactures are grown to a certain perfection, as they soon will be, under the fostering care of government, the farmer will find a ready market for his surplus produce, and—what is of equal consequence—a certain and cheap supply of all he wants; his prosperity will diffuse itself to every class of the community." Speech of Hon. J. C. Calhoun on the Tariff.
The question of revenue we will now briefly consider. For several years past the revenues of the government have been unequal to its expenditures, and consequently loan after loan, sometimes direct and sometimes indirect in form, has been resorted to. By this means a new national debt has been created, and is still growing on us with a rapidity fearful to contemplate—a rapidity only reasonably to be expected in time of war. This state of things has been produced by a prevailing unwillingness either to increase the tariff or resort to direct taxation. But the one or the other must come. Coming expenditures must be met, and the present debt must be paid; and money cannot always be borrowed for these objects. The system of loans is but temporary in its nature, and must soon explode. It is a system not only ruinous while it lasts, but one that must soon fail and leave us destitute. As an individual who undertakes to live by borrowing soon finds his original means devoured by interest, and, next, no one left to borrow from, so must it be with a government.
We repeat, then, that a tariff sufficient for revenue, or a direct tax, must soon be resorted to; and, indeed, we believe this alternative is now denied by no one. But which system shall be adopted? Some of our opponents, in theory, admit the propriety of a tariff sufficient for a revenue, but even they will not in practice vote for such a tariff; while others boldly advocate direct taxation. Inasmuch, therefore, as some of them boldly advocate direct taxation, and all the rest—or so nearly all as to make exceptions needless—refuse to adopt the tariff, we think it is doing them no injustice to class them all as advocates of direct taxation. Indeed, we believe they are only delaying an open avowal of the system till they can assure themselves that the people will tolerate it. Let us, then, briefly compare the two systems. The tariff is the cheaper system, because the duties, being collected in large parcels at a few commercial points, will require comparatively few officers in their collection; while by the direct-tax system the land must be literally covered with assessors and collectors, going forth like swarms of Egyptian locusts, devouring every blade of grass and other green thing. And, again, by the tariff system the whole revenue is paid by the consumers of foreign goods, and those chiefly the luxuries, and not the necessaries, of life. By this system the man who contents himself to live upon the products of his own country pays nothing at all. And surely that country is extensive enough, and its products abundant and varied enough, to answer all the real wants of its people. In short, by this system the burthen of revenue falls almost entirely on the wealthy and luxurious few, while the substantial and laboring many who live at home, and upon home products, go entirely free. By the direct-tax system none can escape. However strictly the citizen may exclude from his premises all foreign luxuries,—fine cloths, fine silks, rich wines, golden chains, and diamond rings,—still, for the possession of his house, his barn, and his homespun, he is to be perpetually haunted and harassed by the tax-gatherer. With these views we leave it to be determined whether we or our opponents are the more truly democratic on the subject.
The third resolution declares the necessity and propriety of a national bank. During the last fifty years so much has been said and written both as to the constitutionality and expediency of such an institution, that we could not hope to improve in the least on former discussions of the subject, were we to undertake it. We, therefore, upon the question of constitutionality content ourselves with remarking the facts that the first national bank was established chiefly by the same men who formed the Constitution, at a time when that instrument was but two years old, and receiving the sanction, as President, of the immortal Washington; that the second received the sanction, as President, of Mr. Madison, to whom common consent has awarded the proud title of "Father of the Constitution"; and subsequently the sanction of the Supreme Court, the most enlightened judicial tribunal in the world. Upon the question of expediency, we only ask you to examine the history of the times during the existence of the two banks, and compare those times with the miserable present.
The fourth resolution declares the expediency of Mr. Clay's land bill. Much incomprehensible jargon is often used against the constitutionality of this measure. We forbear, in this place, attempting an answer to it, simply because, in our opinion, those who urge it are through party zeal resolved not to see or acknowledge the truth. The question of expediency, at least so far as Illinois is concerned, seems to us the clearest imaginable. By the bill we are to receive annually a large sum of money, no part of which we otherwise receive. The precise annual sum cannot be known in advance; it doubtless will vary in different years. Still it is something to know that in the last year—a year of almost unparalleled pecuniary pressure—it amounted to more than forty thousand dollars. This annual income, in the midst of our almost insupportable difficulties, in the days of our severest necessity, our political opponents are furiously resolving to take and keep from us. And for what? Many silly reasons are given, as is usual in cases where a single good one is not to be found. One is that by giving us the proceeds of the lands we impoverish the national treasury, and thereby render necessary an increase of the tariff. This may be true; but if so, the amount of it only is that those whose pride, whose abundance of means, prompt them to spurn the manufactures of our country, and to strut in British cloaks and coats and pantaloons, may have to pay a few cents more on the yard for the cloth that makes them. A terrible evil, truly, to the Illinois farmer, who never wore, nor ever expects to wear, a single yard of British goods in his whole life. Another of their reasons is that by the passage and continuance of Mr. Clay's bill, we prevent the passage of a bill which would give us more. This, if it were sound in itself, is waging destructive war with the former position; for if Mr. Clay's bill impoverishes the treasury too much, what shall be said of one that impoverishes it still more? But it is not sound in itself. It is not true that Mr. Clay's bill prevents the passage of one more favorable to us of the new States. Considering the strength and opposite interest of the old States, the wonder is that they ever permitted one to pass so favorable as Mr. Clay's. The last twenty-odd years' efforts to reduce the price of the lands, and to pass graduation bills and cession bills, prove the assertion to be true; and if there were no experience in support of it, the reason itself is plain. The States in which none, or few, of the public lands lie, and those consequently interested against parting with them except for the best price, are the majority; and a moment's reflection will show that they must ever continue the majority, because by the time one of the original new States (Ohio, for example) becomes populous and gets weight in Congress, the public lands in her limits are so nearly sold out that in every point material to this question she becomes an old State. She does not wish the price reduced, because there is none left for her citizens to buy; she does not wish them ceded to the States in which they lie, because they no longer lie in her limits, and she will get nothing by the cession. In the nature of things, the States interested in the reduction of price, in graduation, in cession, and in all similar projects, never can be the majority. Nor is there reason to hope that any of them can ever succeed as a Democratic party measure, because we have heretofore seen that party in full power, year after year, with many of their leaders making loud professions in favor of these projects, and yet doing nothing. What reason, then, is there to believe they will hereafter do better? In every light in which we can view this question, it amounts simply to this: Shall we accept our share of the proceeds under Mr. Clay's bill, or shall we rather reject that and get nothing?
The fifth resolution recommends that a Whig candidate for Congress be run in every district, regardless of the chances of success. We are aware that it is sometimes a temporary gratification, when a friend cannot succeed, to be able to choose between opponents; but we believe that that gratification is the seed-time which never fails to be followed by a most abundant harvest of bitterness. By this policy we entangle ourselves. By voting for our opponents, such of us as do it in some measure estop ourselves to complain of their acts, however glaringly wrong we may believe them to be. By this policy no one portion of our friends can ever be certain as to what course another portion may adopt; and by this want of mutual and perfect understanding our political identity is partially frittered away and lost. And, again, those who are thus elected by our aid ever become our bitterest persecutors. Take a few prominent examples. In 1830 Reynolds was elected Governor; in 1835 we exerted our whole strength to elect Judge Young to the United States Senate, which effort, though failing, gave him the prominence that subsequently elected him; in 1836 General Ewing, was so elected to the United States Senate; and yet let us ask what three men have been more perseveringly vindictive in their assaults upon all our men and measures than they? During the last summer the whole State was covered with pamphlet editions of misrepresentations against us, methodized into chapters and verses, written by two of these same men,—Reynolds and Young, in which they did not stop at charging us with error merely, but roundly denounced us as the designing enemies of human liberty, itself. If it be the will of Heaven that such men shall politically live, be it so; but never, never again permit them to draw a particle of their sustenance from us.
The sixth resolution recommends the adoption of the convention system for the nomination of candidates. This we believe to be of the very first importance. Whether the system is right in itself we do not stop to inquire; contenting ourselves with trying to show that, while our opponents use it, it is madness in us not to defend ourselves with it. Experience has shown that we cannot successfully defend ourselves without it. For examples, look at the elections of last year. Our candidate for governor, with the approbation of a large portion of the party, took the field without a nomination, and in open opposition to the system. Wherever in the counties the Whigs had held conventions and nominated candidates for the Legislature, the aspirants who were not nominated were induced to rebel against the nominations, and to become candidates, as is said, "on their own hook." And, go where you would into a large Whig county, you were sure to find the Whigs not contending shoulder to shoulder against the common enemy, but divided into factions, and fighting furiously with one another. The election came, and what was the result? The governor beaten, the Whig vote being decreased many thousands since 1840, although the Democratic vote had not increased any. Beaten almost everywhere for members of the Legislature,—Tazewell, with her four hundred Whig majority, sending a delegation half Democratic; Vermillion, with her five hundred, doing the same; Coles, with her four hundred, sending two out of three; and Morgan, with her two hundred and fifty, sending three out of four,—and this to say nothing of the numerous other less glaring examples; the whole winding up with the aggregate number of twenty-seven Democratic representatives sent from Whig counties. As to the senators, too, the result was of the same character. And it is most worthy to be remembered that of all the Whigs in the State who ran against the regular nominees, a single one only was elected. Although they succeeded in defeating the nominees almost by scores, they too were defeated, and the spoils chucklingly borne off by the common enemy.
We do not mention the fact of many of the Whigs opposing the convention system heretofore for the purpose of censuring them. Far from it. We expressly protest against such a conclusion. We know they were generally, perhaps universally, as good and true Whigs as we ourselves claim to be.
We mention it merely to draw attention to the disastrous result it produced, as an example forever hereafter to be avoided. That "union is strength" is a truth that has been known, illustrated, and declared in various ways and forms in all ages of the world. That great fabulist and philosopher Aesop illustrated it by his fable of the bundle of sticks; and he whose wisdom surpasses that of all philosophers has declared that "a house divided against itself cannot stand." It is to induce our friends to act upon this important and universally acknowledged truth that we urge the adoption of the convention system. Reflection will prove that there is no other way of practically applying it. In its application we know there will be incidents temporarily painful; but, after all, those incidents will be fewer and less intense with than without the system. If two friends aspire to the same office it is certain that both cannot succeed. Would it not, then, be much less painful to have the question decided by mutual friends some time before, than to snarl and quarrel until the day of election, and then both be beaten by the common enemy?
Before leaving this subject, we think proper to remark that we do not understand the resolution as intended to recommend the application of the convention system to the nomination of candidates for the small offices no way connected with politics; though we must say we do not perceive that such an application of it would be wrong.
The seventh resolution recommends the holding of district conventions in May next, for the purpose of nominating candidates for Congress. The propriety of this rests upon the same reasons with that of the sixth, and therefore needs no further discussion.
The eighth and ninth also relate merely to the practical application of the foregoing, and therefore need no discussion.
Before closing, permit us to add a few reflections on the present condition and future prospects of the Whig party. In almost all the States we have fallen into the minority, and despondency seems to prevail universally among us. Is there just cause for this? In 1840 we carried the nation by more than a hundred and forty thousand majority. Our opponents charged that we did it by fraudulent voting; but whatever they may have believed, we know the charge to be untrue. Where, now, is that mighty host? Have they gone over to the enemy? Let the results of the late elections answer. Every State which has fallen off from the Whig cause since 1840 has done so not by giving more Democratic votes than they did then, but by giving fewer Whig. Bouck, who was elected Democratic Governor of New York last fall by more than 15,000 majority, had not then as many votes as he had in 1840, when he was beaten by seven or eight thousand. And so has it been in all the other States which have fallen away from our cause. From this it is evident that tens of thousands in the late elections have not voted at all. Who and what are they? is an important question, as respects the future. They can come forward and give us the victory again. That all, or nearly all, of them are Whigs is most apparent. Our opponents, stung to madness by the defeat of 1840, have ever since rallied with more than their usual unanimity. It has not been they that have been kept from the polls. These facts show what the result must be, once the people again rally in their entire strength. Proclaim these facts, and predict this result; and although unthinking opponents may smile at us, the sagacious ones will "believe and tremble." And why shall the Whigs not all rally again? Are their principles less dear now than in 1840? Have any of their doctrines since then been discovered to be untrue? It is true, the victory of 1840 did not produce the happy results anticipated; but it is equally true, as we believe, that the unfortunate death of General Harrison was the cause of the failure. It was not the election of General Harrison that was expected to produce happy effects, but the measures to be adopted by his administration. By means of his death, and the unexpected course of his successor, those measures were never adopted. How could the fruits follow? The consequences we always predicted would follow the failure of those measures have followed, and are now upon us in all their horrors. By the course of Mr. Tyler the policy of our opponents has continued in operation, still leaving them with the advantage of charging all its evils upon us as the results of a Whig administration. Let none be deceived by this somewhat plausible, though entirely false charge. If they ask us for the sufficient and sound currency we promised, let them be answered that we only promised it through the medium of a national bank, which they, aided by Mr. Tyler, prevented our establishing. And let them be reminded, too, that their own policy in relation to the currency has all the time been, and still is, in full operation. Let us then again come forth in our might, and by a second victory accomplish that which death prevented in the first. We can do it. When did the Whigs ever fail if they were fully aroused and united? Even in single States, under such circumstances, defeat seldom overtakes them. Call to mind the contested elections within the last few years, and particularly those of Moore and Letcher from Kentucky, Newland and Graham from North Carolina, and the famous New Jersey case. In all these districts Locofocoism had stalked omnipotent before; but when the whole people were aroused by its enormities on those occasions, they put it down, never to rise again.
We declare it to be our solemn conviction, that the Whigs are always a majority of this nation; and that to make them always successful needs but to get them all to the polls and to vote unitedly. This is the great desideratum. Let us make every effort to attain it. At every election, let every Whig act as though he knew the result to depend upon his action. In the great contest of 1840 some more than twenty one hundred thousand votes were cast, and so surely as there shall be that many, with the ordinary increase added, cast in 1844 that surely will a Whig be elected President of the United States.
A. LINCOLN. S. T. LOGAN. A. T. BLEDSOE.
March 4, 1843.
FRIEND BENNETT:
Your letter of this day was handed me by Mr. Miles. It is too late now to effect the object you desire. On yesterday morning the most of the Whig members from this district got together and agreed to hold the convention at Tremont in Tazewell County. I am sorry to hear that any of the Whigs of your county, or indeed of any county, should longer be against conventions. On last Wednesday evening a meeting of all the Whigs then here from all parts of the State was held, and the question of the propriety of conventions was brought up and fully discussed, and at the end of the discussion a resolution recommending the system of conventions to all the Whigs of the State was unanimously adopted. Other resolutions were also passed, all of which will appear in the next Journal. The meeting also appointed a committee to draft an address to the people of the State, which address will also appear in the next journal.
In it you will find a brief argument in favor of conventions—and although I wrote it myself I will say to you that it is conclusive upon the point and can not be reasonably answered. The right way for you to do is hold your meeting and appoint delegates any how, and if there be any who will not take part, let it be so. The matter will work so well this time that even they who now oppose will come in next time.
The convention is to be held at Tremont on the 5th of April and according to the rule we have adopted your county is to have delegates—being double your representation.
If there be any good Whig who is disposed to stick out against conventions get him at least to read the arguement in their favor in the address.
Yours as ever,
DEAR SPEED:—We had a meeting of the Whigs of the county here on last Monday to appoint delegates to a district convention; and Baker beat me, and got the delegation instructed to go for him. The meeting, in spite of my attempt to decline it, appointed me one of the delegates; so that in getting Baker the nomination I shall be fixed a good deal like a fellow who is made a groomsman to a man that has cut him out and is marrying his own dear "gal." About the prospects of your having a namesake at our town, can't say exactly yet.
FRIEND MORRIS:
Your letter of the a 3 d, was received on yesterday morning, and for which (instead of an excuse, which you thought proper to ask) I tender you my sincere thanks. It is truly gratifying to me to learn that, while the people of Sangamon have cast me off, my old friends of Menard, who have known me longest and best, stick to me. It would astonish, if not amuse, the older citizens to learn that I (a stranger, friendless, uneducated, penniless boy, working on a flatboat at ten dollars per month) have been put down here as the candidate of pride, wealth, and aristocratic family distinction. Yet so, chiefly, it was. There was, too, the strangest combination of church influence against me. Baker is a Campbellite; and therefore, as I suppose, with few exceptions got all that church. My wife has some relations in the Presbyterian churches, and some with the Episcopal churches; and therefore, wherever it would tell, I was set down as either the one or the other, while it was everywhere contended that no Christian ought to go for me, because I belonged to no church, was suspected of being a deist, and had talked about fighting a duel. With all these things, Baker, of course, had nothing to do. Nor do I complain of them. As to his own church going for him, I think that was right enough, and as to the influences I have spoken of in the other, though they were very strong, it would be grossly untrue and unjust to charge that they acted upon them in a body or were very near so. I only mean that those influences levied a tax of a considerable per cent. upon my strength throughout the religious controversy. But enough of this.
You say that in choosing a candidate for Congress you have an equal right with Sangamon, and in this you are undoubtedly correct. In agreeing to withdraw if the Whigs of Sangamon should go against me, I did not mean that they alone were worth consulting, but that if she, with her heavy delegation, should be against me, it would be impossible for me to succeed, and therefore I had as well decline. And in relation to Menard having rights, permit me fully to recognize them, and to express the opinion that, if she and Mason act circumspectly, they will in the convention be able so far to enforce their rights as to decide absolutely which one of the candidates shall be successful. Let me show the reason of this. Hardin, or some other Morgan candidate, will get Putnam, Marshall, Woodford, Tazewell, and Logan—making sixteen. Then you and Mason, having three, can give the victory to either side.
You say you shall instruct your delegates for me, unless I object. I certainly shall not object. That would be too pleasant a compliment for me to tread in the dust. And besides, if anything should happen (which, however, is not probable) by which Baker should be thrown out of the fight, I would be at liberty to accept the nomination if I could get it. I do, however, feel myself bound not to hinder him in any way from getting the nomination. I should despise myself were I to attempt it. I think, then, it would be proper for your meeting to appoint three delegates and to instruct them to go for some one as the first choice, some one else as a second, and perhaps some one as a third; and if in those instructions I were named as the first choice, it would gratify me very much. If you wish to hold the balance of power, it is important for you to attend to and secure the vote of Mason also: You should be sure to have men appointed delegates that you know you can safely confide in. If yourself and James Short were appointed from your county, all would be safe; but whether Jim's woman affair a year ago might not be in the way of his appointment is a question. I don't know whether you know it, but I know him to be as honorable a man as there is in the world. You have my permission, and even request, to show this letter to Short; but to no one else, unless it be a very particular friend who you know will not speak of it.
Yours as ever, A. LINCOLN.
P. S Will you write me again?
FRIEND MORRIS:
I have heard it intimated that Baker has been attempting to get you or Miles, or both of you, to violate the instructions of the meeting that appointed you, and to go for him. I have insisted, and still insist, that this cannot be true. Surely Baker would not do the like. As well might Hardin ask me to vote for him in the convention. Again, it is said there will be an attempt to get up instructions in your county requiring you to go for Baker. This is all wrong. Upon the same rule, Why might not I fly from the decision against me in Sangamon, and get up instructions to their delegates to go for me? There are at least twelve hundred Whigs in the county that took no part, and yet I would as soon put my head in the fire as to attempt it. Besides, if any one should get the nomination by such extraordinary means, all harmony in the district would inevitably be lost. Honest Whigs (and very nearly all of them are honest) would not quietly abide such enormities. I repeat, such an attempt on Baker's part cannot be true. Write me at Springfield how the matter is. Don't show or speak of this letter.
FRIEND HARDIN:
Butler informs me that he received a letter from you, in which you expressed some doubt whether the Whigs of Sangamon will support you cordially. You may, at once, dismiss all fears on that subject. We have already resolved to make a particular effort to give you the very largest majority possible in our county. From this, no Whig of the county dissents. We have many objects for doing it. We make it a matter of honor and pride to do it; we do it because we love the Whig cause; we do it because we like you personally; and last, we wish to convince you that we do not bear that hatred to Morgan County that you people have so long seemed to imagine. You will see by the journals of this week that we propose, upon pain of losing a barbecue, to give you twice as great a majority in this county as you shall receive in your own. I got up the proposal.
Who of the five appointed is to write the district address? I did the labor of writing one address this year, and got thunder for my reward. Nothing new here.
Yours as ever, A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—I wish you would measure one of the largest of those swords we took to Alton and write me the length of it, from tip of the point to tip of the hilt, in feet and inches. I have a dispute about the length.
A. L.
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
SELECTION OF CONGRESSIONAL CANDIDATES
VERSES WRITTEN BY LINCOLN AFTER A VISIT TO HIS OLD HOME IN INDIANA
RESOLUTIONS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REMARKS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
DESIRE FOR SECOND TERM IN CONGRESS
SPEECH ON DECLARATION OF WAR ON MEXICO
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, JANUARY 19, 1848.
TO WILLIAM H. HERNDON—LEGAL WORK
REGARDING SPEECH ON MEXICAN WAR
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REPORT IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
REMARKS IN THE UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, MARCH 29, 1848.
REMARKS IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
DEFENSE OF MEXICAN WAR POSITION
SPEECH IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
OPPORTUNITIES FOR YOUNG POLITICIANS
SALARY OF JUDGE IN WESTERN VIRGINIA
YOUNG v.s. OLD—POLITICAL JEALOUSY
SPEECH DELIVERED AT WORCESTER, MASS., ON SEPT. 12, 1848.
HIS FATHER'S REQUEST FOR MONEY
BILL GRANTING LANDS TO THE STATES TO MAKE RAILWAYS AND CANALS
ON FEDERAL POLITICAL APPOINTMENTS
MORE POLITICAL PATRONAGE REQUESTS
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
REQUEST FOR GENERAL LAND-OFFICE APPPOINTMENT
RESOLUTIONS OF SYMPATHY WITH THE CAUSE OF HUNGARIAN FREEDOM,
RESOLUTIONS ON THE DEATH OF JUDGE NATHANIEL POPE.
PETITION ON BEHALF OF ONE JOSHUA GIPSON
REPLY TO SENATOR DOUGLAS—PEORIA SPEECH
RESPONSE TO A PRO-SLAVERY FRIEND
SPEECH DELIVERED BEFORE THE FIRST REPUBLICAN STATE CONVENTION
ON THE DANGER OF THIRD-PARTIES
TO HENRY O'CONNER, MUSCATINE, IOWA.
AFTER THE DEMOCRATIC VICTORY OF BUCHANAN
ARGUMENT IN THE ROCK ISLAND BRIDGE CASE.
ANOTHER POLITICAL PATRONAGE REFERENCE
DEAR SPEED:—Yours of the 9th instant is duly received, which I do not meet as a "bore," but as a most welcome visitor. I will answer the business part of it first.
In relation to our Congress matter here, you were right in supposing I would support the nominee. Neither Baker nor I, however, is the man, but Hardin, so far as I can judge from present appearances. We shall have no split or trouble about the matter; all will be harmony. In relation to the "coming events" about which Butler wrote you, I had not heard one word before I got your letter; but I have so much confidence in the judgment of Butler on such a subject that I incline to think there may be some reality in it. What day does Butler appoint? By the way, how do "events" of the same sort come on in your family? Are you possessing houses and lands, and oxen and asses, and men-servants and maid-servants, and begetting sons and daughters? We are not keeping house, but boarding at the Globe Tavern, which is very well kept now by a widow lady of the name of Beck. Our room (the same that Dr. Wallace occupied there) and boarding only costs us four dollars a week. Ann Todd was married something more than a year since to a fellow by the name of Campbell, and who, Mary says, is pretty much of a "dunce," though he has a little money and property. They live in Boonville, Missouri, and have not been heard from lately enough for me to say anything about her health. I reckon it will scarcely be in our power to visit Kentucky this year. Besides poverty and the necessity of attending to business, those "coming events," I suspect, would be somewhat in the way. I most heartily wish you and your Fanny would not fail to come. Just let us know the time, and we will have a room provided for you at our house, and all be merry together for a while. Be sure to give my respects to your mother and family; assure her that if ever I come near her, I will not fail to call and see her. Mary joins in sending love to your Fanny and you.
Yours as ever,
DEAR HARDIN: Knowing that you have correspondents enough, I have forborne to trouble you heretofore; and I now only do so to get you to set a matter right which has got wrong with one of our best friends. It is old Uncle Thomas Campbell of Spring Creek—(Berlin P.O.). He has received several documents from you, and he says they are old newspapers and documents, having no sort of interest in them. He is, therefore, getting a strong impression that you treat him with disrespect. This, I know, is a mistaken impression; and you must correct it. The way, I leave to yourself. Rob't W. Canfield says he would like to have a document or two from you.
The Locos (Democrats) here are in considerable trouble about Van Buren's letter on Texas, and the Virginia electors. They are growing sick of the Tariff question; and consequently are much confounded at V.B.'s cutting them off from the new Texas question. Nearly half the leaders swear they won't stand it. Of those are Ford, T. Campbell, Ewing, Calhoun and others. They don't exactly say they won't vote for V.B., but they say he will not be the candidate, and that they are for Texas anyhow.
As ever yours,
DEAR GENERAL:
I do not wish to join in your proposal of a new plan for the selection of a Whig candidate for Congress because:
1st. I am entirely satisfied with the old system under which you and Baker were successively nominated and elected to Congress; and because the Whigs of the district are well acquainted with the system, and, so far as I know or believe, are well satisfied with it. If the old system be thought to be vague, as to all the delegates of the county voting the same way, or as to instructions to them as to whom they are to vote for, or as to filling vacancies, I am willing to join in a provision to make these matters certain.
2d. As to your proposals that a poll shall be opened in every precinct, and that the whole shall take place on the same day, I do not personally object. They seem to me to be not unfair; and I forbear to join in proposing them only because I choose to leave the decision in each county to the Whigs of the county, to be made as their own judgment and convenience may dictate.
3d. As to your proposed stipulation that all the candidates shall remain in their own counties, and restrain their friends in the same it seems to me that on reflection you will see the fact of your having been in Congress has, in various ways, so spread your name in the district as to give you a decided advantage in such a stipulation. I appreciate your desire to keep down excitement; and I promise you to "keep cool" under all circumstances.
4th. I have already said I am satisfied with the old system under which such good men have triumphed and that I desire no departure from its principles. But if there must be a departure from it, I shall insist upon a more accurate and just apportionment of delegates, or representative votes, to the constituent body, than exists by the old, and which you propose to retain in your new plan. If we take the entire population of the counties as shown by the late census, we shall see by the old plan, and by your proposed new plan,
Morgan County, with a population 16,541, has but ....... 8 votes While Sangamon with 18,697—2156 greater has but ....... 8 " So Scott with 6553 has ................................. 4 " While Tazewell with 7615 1062 greater has but .......... 4 " So Mason with 3135 has ................................. 1 vote While Logan with 3907, 772 greater, has but ............ 1 "
And so on in a less degree the matter runs through all the counties, being not only wrong in principle, but the advantage of it being all manifestly in your favor with one slight exception, in the comparison of two counties not here mentioned.
Again, if we take the Whig votes of the counties as shown by the late Presidential election as a basis, the thing is still worse.
It seems to me most obvious that the old system needs adjustment in nothing so much as in this; and still, by your proposal, no notice is taken of it. I have always been in the habit of acceding to almost any proposal that a friend would make and I am truly sorry that I cannot in this. I perhaps ought to mention that some friends at different places are endeavoring to secure the honor of the sitting of the convention at their towns respectively, and I fear that they would not feel much complimented if we shall make a bargain that it should sit nowhere.
Yours as ever,
FRIEND WILLIAMS:
The Supreme Court adjourned this morning for the term. Your cases of Reinhardt vs. Schuyler, Bunce vs. Schuyler, Dickhut vs. Dunell, and Sullivan vs. Andrews are continued. Hinman vs. Pope I wrote you concerning some time ago. McNutt et al. vs. Bean and Thompson is reversed and remanded.
Fitzpatrick vs. Brady et al. is reversed and remanded with leave to complainant to amend his bill so as to show the real consideration given for the land.
Bunce against Graves the court confirmed, wherefore, in accordance with your directions, I moved to have the case remanded to enable you to take a new trial in the court below. The court allowed the motion; of which I am glad, and I guess you are.
This, I believe, is all as to court business. The canal men have got their measure through the Legislature pretty much or quite in the shape they desired. Nothing else now.
Yours as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, October 3, 1845
When I saw you at home, it was agreed that I should write to you and your brother Madison. Until I then saw you I was not aware of your being what is generally called an abolitionist, or, as you call yourself, a Liberty man, though I well knew there were many such in your country.
I was glad to hear that you intended to attempt to bring about, at the next election in Putnam, a Union of the Whigs proper and such of the Liberty men as are Whigs in principle on all questions save only that of slavery. So far as I can perceive, by such union neither party need yield anything on the point in difference between them. If the Whig abolitionists of New York had voted with us last fall, Mr. Clay would now be President, Whig principles in the ascendant, and Texas not annexed; whereas, by the division, all that either had at stake in the contest was lost. And, indeed, it was extremely probable, beforehand, that such would be the result. As I always understood, the Liberty men deprecated the annexation of Texas extremely; and this being so, why they should refuse to cast their votes [so] as to prevent it, even to me seemed wonderful. What was their process of reasoning, I can only judge from what a single one of them told me. It was this: "We are not to do evil that good may come." This general proposition is doubtless correct; but did it apply? If by your votes you could have prevented the extension, etc., of slavery would it not have been good, and not evil, so to have used your votes, even though it involved the casting of them for a slaveholder? By the fruit the tree is to be known. An evil tree cannot bring forth good fruit. If the fruit of electing Mr. Clay would have been to prevent the extension of slavery, could the act of electing have been evil?
But I will not argue further. I perhaps ought to say that individually I never was much interested in the Texas question. I never could see much good to come of annexation, inasmuch as they were already a free republican people on our own model. On the other hand, I never could very clearly see how the annexation would augment the evil of slavery. It always seemed to me that slaves would be taken there in about equal numbers, with or without annexation. And if more were taken because of annexation, still there would be just so many the fewer left where they were taken from. It is possibly true, to some extent, that, with annexation, some slaves may be sent to Texas and continued in slavery that otherwise might have been liberated. To whatever extent this may be true, I think annexation an evil. I hold it to be a paramount duty of us in the free States, due to the Union of the States, and perhaps to liberty itself (paradox though it may seem), to let the slavery of the other States alone; while, on the other hand, I hold it to be equally clear that we should never knowingly lend ourselves, directly or indirectly, to prevent that slavery from dying a natural death—to find new places for it to live in when it can no longer exist in the old. Of course I am not now considering what would be our duty in cases of insurrection among the slaves. To recur to the Texas question, I understand the Liberty men to have viewed annexation as a much greater evil than ever I did; and I would like to convince you, if I could, that they could have prevented it, if they had chosen. I intend this letter for you and Madison together; and if you and he or either shall think fit to drop me a line, I shall be pleased.
Yours with respect,
Dr. ROBERT BOAL, Lacon, Ill.
DEAR DOCTOR:—Since I saw you last fall, I have often thought of writing to you, as it was then understood I would, but, on reflection, I have always found that I had nothing new to tell you. All has happened as I then told you I expected it would—Baker's declining, Hardin's taking the track, and so on.
If Hardin and I stood precisely equal, if neither of us had been to Congress, or if we both had, it would only accord with what I have always done, for the sake of peace, to give way to him; and I expect I should do it. That I can voluntarily postpone my pretensions, when they are no more than equal to those to which they are postponed, you have yourself seen. But to yield to Hardin under present circumstances seems to me as nothing else than yielding to one who would gladly sacrifice me altogether. This I would rather not submit to. That Hardin is talented, energetic, usually generous and magnanimous, I have before this affirmed to you and do not deny. You know that my only argument is that "turn about is fair play." This he, practically at least, denies.
If it would not be taxing you too much, I wish you would write me, telling the aspect of things in your country, or rather your district; and also, send the names of some of your Whig neighbors, to whom I might, with propriety, write. Unless I can get some one to do this, Hardin, with his old franking list, will have the advantage of me. My reliance for a fair shake (and I want nothing more) in your country is chiefly on you, because of your position and standing, and because I am acquainted with so few others. Let me hear from you soon.
Yours truly,
JOHN BENNETT. FRIEND JOHN:
Nathan Dresser is here, and speaks as though the contest between Hardin and me is to be doubtful in Menard County. I know he is candid and this alarms me some. I asked him to tell me the names of the men that were going strong for Hardin, he said Morris was about as strong as any-now tell me, is Morris going it openly? You remember you wrote me that he would be neutral. Nathan also said that some man, whom he could not remember, had said lately that Menard County was going to decide the contest and that made the contest very doubtful. Do you know who that was? Don't fail to write me instantly on receiving this, telling me all—particularly the names of those who are going strong against me.
Yours as ever,
DEAR SIR:—You perhaps know that General Hardin and I have a contest for the Whig nomination for Congress for this district.
He has had a turn and my argument is "turn about is fair play."
I shall be pleased if this strikes you as a sufficient argument.
Yours truly,
DEAR SIR:—I thank you for the promptness with which you answered my letter from Bloomington. I also thank you for the frankness with which you comment upon a certain part of my letter; because that comment affords me an opportunity of trying to express myself better than I did before, seeing, as I do, that in that part of my letter, you have not understood me as I intended to be understood.
In speaking of the "dissatisfaction" of men who yet mean to do no wrong, etc., I mean no special application of what I said to the Whigs of Morgan, or of Morgan & Scott. I only had in my mind the fact that previous to General Hardin's withdrawal some of his friends and some of mine had become a little warm; and I felt, and meant to say, that for them now to meet face to face and converse together was the best way to efface any remnant of unpleasant feeling, if any such existed.
I did not suppose that General Hardin's friends were in any greater need of having their feelings corrected than mine were. Since I saw you at Jacksonville, I have had no more suspicion of the Whigs of Morgan than of those of any other part of the district. I write this only to try to remove any impression that I distrust you and the other Whigs of your country.
Yours truly,
DEAR SIR:—It is a matter of high moral obligation, if not of necessity, for me to attend the Coles and Edwards courts. I have some cases in both of them, in which the parties have my promise, and are depending upon me. The court commences in Coles on the second Monday, and in Edgar on the third. Your court in Morgan commences on the fourth Monday; and it is my purpose to be with you then, and make a speech. I mention the Coles and Edgar courts in order that if I should not reach Jacksonville at the time named you may understand the reason why. I do not, however, think there is much danger of my being detained; as I shall go with a purpose not to be, and consequently shall engage in no new cases that might delay me.
Yours truly,
[In December, 1847, when Lincoln was stumping for Clay, he crossed into Indiana and revisited his old home. He writes: "That part of the country is within itself as unpoetical as any spot on earth; but still seeing it and its objects and inhabitants aroused feelings in me which were certainly poetry; though whether my expression of these feelings is poetry, is quite another question."]
Near twenty years have passed away Since here I bid farewell To woods and fields, and scenes of play, And playmates loved so well. Where many were, but few remain Of old familiar things; But seeing them to mind again The lost and absent brings. The friends I left that parting day, How changed, as time has sped! Young childhood grown, strong manhood gray, And half of all are dead. I hear the loved survivors tell How naught from death could save, Till every sound appears a knell, And every spot a grave. I range the fields with pensive tread, And pace the hollow rooms, And feel (companion of the dead) I 'm living in the tombs. VERSES WRITTEN BY LINCOLN CONCERNING A SCHOOL-FELLOW WHO BECAME INSANE—(A FRAGMENT). And when at length the drear and long Time soothed thy fiercer woes, How plaintively thy mournful song Upon the still night rose I've heard it oft as if I dreamed, Far distant, sweet and lone; The funeral dirge it ever seemed Of reason dead and gone. Air held her breath; trees with the spell Seemed sorrowing angels round, Whose swelling tears in dewdrops fell Upon the listening ground. But this is past, and naught remains That raised thee o'er the brute; Thy piercing shrieks and soothing strains Are like, forever mute. Now fare thee well! More thou the cause Than subject now of woe. All mental pangs by time's kind laws Hast lost the power to know. O Death! thou awe-inspiring prince That keepst the world in fear, Why dost thou tear more blest ones hence, And leave him lingering here?
SPRINGFIELD, October 22, 1846.
DEAR SPEED:—You, no doubt, assign the suspension of our correspondence to the true philosophic cause; though it must be confessed by both of us that this is rather a cold reason for allowing a friendship such as ours to die out by degrees. I propose now that, upon receipt of this, you shall be considered in my debt, and under obligations to pay soon, and that neither shall remain long in arrears hereafter. Are you agreed?
Being elected to Congress, though I am very grateful to our friends for having done it, has not pleased me as much as I expected.
We have another boy, born the 10th of March. He is very much such a child as Bob was at his age, rather of a longer order. Bob is "short and low," and I expect always will be. He talks very plainly,—almost as plainly as anybody. He is quite smart enough. I sometimes fear that he is one of the little rare-ripe sort that are smarter at about five than ever after. He has a great deal of that sort of mischief that is the offspring of such animal spirits. Since I began this letter, a messenger came to tell me Bob was lost; but by the time I reached the house his mother had found him and had him whipped, and by now, very likely, he is run away again. Mary has read your letter, and wishes to be remembered to Mrs. Speed and you, in which I most sincerely join her.
As ever yours,
MESSRS. MORRIS AND BROWN.
GENTLEMEN:—Your second letter on the matter of Thornton and others, came to hand this morning. I went at once to see Logan, and found that he is not engaged against you, and that he has so sent you word by Mr. Butterfield, as he says. He says that some time ago, a young man (who he knows not) came to him, with a copy of the affidavit, to engage him to aid in getting the Governor to grant the warrant; and that he, Logan, told the man, that in his opinion, the affidavit was clearly insufficient, upon which the young man left, without making any engagement with him. If the Governor shall arrive before I leave, Logan and I will both attend to the matter, and he will attend to it, if he does not come till after I leave; all upon the condition that the Governor shall not have acted upon the matter, before his arrival here. I mention this condition because, I learned this morning from the Secretary of State, that he is forwarding to the Governor, at Palestine, all papers he receives in the case, as fast as he receives them. Among the papers forwarded will be your letter to the Governor or Secretary of, I believe, the same date and about the same contents of your last letter to me; so that the Governor will, at all events have your points and authorities. The case is a clear one on our side; but whether the Governor will view it so is another thing.
Yours as ever,
DEAR WILLIAM:—You may remember that about a year ago a man by the name of Wilson (James Wilson, I think) paid us twenty dollars as an advance fee to attend to a case in the Supreme Court for him, against a Mr. Campbell, the record of which case was in the hands of Mr. Dixon of St. Louis, who never furnished it to us. When I was at Bloomington last fall I met a friend of Wilson, who mentioned the subject to me, and induced me to write to Wilson, telling him I would leave the ten dollars with you which had been left with me to pay for making abstracts in the case, so that the case may go on this winter; but I came away, and forgot to do it. What I want now is to send you the money, to be used accordingly, if any one comes on to start the case, or to be retained by you if no one does.
There is nothing of consequence new here. Congress is to organize to-morrow. Last night we held a Whig caucus for the House, and nominated Winthrop of Massachusetts for speaker, Sargent of Pennsylvania for sergeant-at-arms, Homer of New Jersey door-keeper, and McCormick of District of Columbia postmaster. The Whig majority in the House is so small that, together with some little dissatisfaction, [it] leaves it doubtful whether we will elect them all.
This paper is too thick to fold, which is the reason I send only a half-sheet.
Yours as ever, A. LINCOLN.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Your letter, advising me of the receipt of our fee in the bank case, is just received, and I don't expect to hear another as good a piece of news from Springfield while I am away. I am under no obligations to the bank; and I therefore wish you to buy bank certificates, and pay my debt there, so as to pay it with the least money possible. I would as soon you should buy them of Mr. Ridgely, or any other person at the bank, as of any one else, provided you can get them as cheaply. I suppose, after the bank debt shall be paid, there will be some money left, out of which I would like to have you pay Lavely and Stout twenty dollars, and Priest and somebody (oil-makers) ten dollars, for materials got for house-painting. If there shall still be any left, keep it till you see or hear from me.
I shall begin sending documents so soon as I can get them. I wrote you yesterday about a "Congressional Globe." As you are all so anxious for me to distinguish myself, I have concluded to do so before long.
Yours truly,
Whereas, The President of the United States, in his message of May 11, 1846, has declared that "the Mexican Government not only refused to receive him [the envoy of the United States], or to listen to his propositions, but, after a long-continued series of menaces, has at last invaded our territory and shed the blood of our fellow-citizens on our own soil";
And again, in his message of December 8, 1846, that "we had ample cause of war against Mexico long before the breaking out of hostilities; but even then we forbore to take redress into our own hands until Mexico herself became the aggressor, by invading our soil in hostile array, and shedding the blood of our citizens";
And yet again, in his message of December 7, 1847, that "the Mexican Government refused even to hear the terms of adjustment which he [our minister of peace] was authorized to propose, and finally, under wholly unjustifiable pretexts, involved the two countries in war, by invading the territory of the State of Texas, striking the first blow, and shedding the blood of our citizens on our own soil";
And whereas, This House is desirous to obtain a full knowledge of all the facts which go to establish whether the particular spot on which the blood of our citizens was so shed was or was not at that time our own soil: therefore,
Resolved, By the House of Representatives, that the President of the United States be respectfully requested to inform this House:
First. Whether the spot on which the blood of our citizens was shed, as in his message declared, was or was not within the territory of Spain, at least after the treaty of 1819, until the Mexican revolution.
Second. Whether that spot is or is not within the territory which was wrested from Spain by the revolutionary government of Mexico.
Third. Whether that spot is or is not within a settlement of people, which settlement has existed ever since long before the Texas revolution, and until its inhabitants fled before the approach of the United States army.
Fourth. Whether that settlement is or is not isolated from any and all other settlements by the Gulf and the Rio Grande on the south and west, and by wide uninhabited regions on the north and east.
Fifth. Whether the people of that settlement, or a majority of them, or any of them, have ever submitted themselves to the government or laws of Texas or of the United States, by consent or by compulsion, either by accepting office, or voting at elections, or paying tax, or serving on juries, or having process served upon them, or in any other way.
Sixth. Whether the people of that settlement did or did not flee from the approach of the United States army, leaving unprotected their homes and their growing crops, before the blood was shed, as in the message stated; and whether the first blood, so shed, was or was not shed within the inclosure of one of the people who had thus fled from it.
Seventh. Whether our citizens, whose blood was shed, as in his message declared, were or were not, at that time, armed officers and soldiers, sent into that settlement by the military order of the President, through the Secretary of War.
Eighth. Whether the military force of the United States was or was not so sent into that settlement after General Taylor had more than once intimated to the War Department that, in his opinion, no such movement was necessary to the defence or protection of Texas.
Mr. Lincoln said he had made an effort, some few days since, to obtain the floor in relation to this measure [resolution to direct Postmaster-General to make arrangements with railroad for carrying the mails—in Committee of the Whole], but had failed. One of the objects he had then had in view was now in a great measure superseded by what had fallen from the gentleman from Virginia who had just taken his seat. He begged to assure his friends on the other side of the House that no assault whatever was meant upon the Postmaster-General, and he was glad that what the gentleman had now said modified to a great extent the impression which might have been created by the language he had used on a previous occasion. He wanted to state to gentlemen who might have entertained such impressions, that the Committee on the Post-office was composed of five Whigs and four Democrats, and their report was understood as sustaining, not impugning, the position taken by the Postmaster-General. That report had met with the approbation of all the Whigs, and of all the Democrats also, with the exception of one, and he wanted to go even further than this. [Intimation was informally given Mr. Lincoln that it was not in order to mention on the floor what had taken place in committee.] He then observed that if he had been out of order in what he had said he took it all back so far as he could. He had no desire, he could assure gentlemen, ever to be out of order—though he never could keep long in order.
Mr. Lincoln went on to observe that he differed in opinion, in the present case, from his honorable friend from Richmond [Mr. Botts]. That gentleman, had begun his remarks by saying that if all prepossessions in this matter could be removed out of the way, but little difficulty would be experienced in coming to an agreement. Now, he could assure that gentleman that he had himself begun the examination of the subject with prepossessions all in his favor. He had long and often heard of him, and, from what he had heard, was prepossessed in his favor. Of the Postmaster-General he had also heard, but had no prepossessions in his favor, though certainly none of an opposite kind. He differed, however, with that gentleman in politics, while in this respect he agreed with the gentleman from Virginia [Mr. Botts], whom he wished to oblige whenever it was in his power. That gentleman had referred to the report made to the House by the Postmaster-General, and had intimated an apprehension that gentlemen would be disposed to rely, on that report alone, and derive their views of the case from that document alone. Now it so happened that a pamphlet had been slipped into his [Mr. Lincoln's] hand before he read the report of the Postmaster-General; so that, even in this, he had begun with prepossessions in favor of the gentleman from Virginia.
As to the report, he had but one remark to make: he had carefully examined it, and he did not understand that there was any dispute as to the facts therein stated the dispute, if he understood it, was confined altogether to the inferences to be drawn from those facts. It was a difference not about facts, but about conclusions. The facts were not disputed. If he was right in this, he supposed the House might assume the facts to be as they were stated, and thence proceed to draw their own conclusions.
The gentleman had said that the Postmaster-General had got into a personal squabble with the railroad company. Of this Mr. Lincoln knew nothing, nor did he need or desire to know anything, because it had nothing whatever to do with a just conclusion from the premises. But the gentleman had gone on to ask whether so great a grievance as the present detention of the Southern mail ought not to be remedied. Mr. Lincoln would assure the gentleman that if there was a proper way of doing it, no man was more anxious than he that it should be done. The report made by the committee had been intended to yield much for the sake of removing that grievance. That the grievance was very great there was no dispute in any quarter. He supposed that the statements made by the gentleman from Virginia to show this were all entirely correct in point of fact. He did suppose that the interruptions of regular intercourse, and all the other inconveniences growing out of it, were all as that gentleman had stated them to be; and certainly, if redress could be rendered, it was proper it should be rendered as soon as possible. The gentleman said that in order to effect this no new legislative action was needed; all that was necessary was that the Postmaster-General should be required to do what the law, as it stood, authorized and required him to do.
We come then, said Mr. Lincoln, to the law. Now the Postmaster-General says he cannot give to this company more than two hundred and thirty-seven dollars and fifty cents per railroad mile of transportation, and twelve and a half per cent. less for transportation by steamboats. He considers himself as restricted by law to this amount; and he says, further, that he would not give more if he could, because in his apprehension it would not be fair and just.
WASHINGTON, January 8, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Your letter of December 27 was received a day or two ago. I am much obliged to you for the trouble you have taken, and promise to take in my little business there. As to speech making, by way of getting the hang of the House I made a little speech two or three days ago on a post-office question of no general interest. I find speaking here and elsewhere about the same thing. I was about as badly scared, and no worse as I am when I speak in court. I expect to make one within a week or two, in which I hope to succeed well enough to wish you to see it.
It is very pleasant to learn from you that there are some who desire that I should be reelected. I most heartily thank them for their kind partiality; and I can say, as Mr. Clay said of the annexation of Texas, that "personally I would not object" to a reelection, although I thought at the time, and still think, it would be quite as well for me to return to the law at the end of a single term. I made the declaration that I would not be a candidate again, more from a wish to deal fairly with others, to keep peace among our friends, and to keep the district from going to the enemy, than for any cause personal to myself; so that if it should so happen that nobody else wishes to be elected, I could not refuse the people the right of sending me again. But to enter myself as a competitor of others, or to authorize any one so to enter me is what my word and honor forbid.
I got some letters intimating a probability of so much difficulty amongst our friends as to lose us the district; but I remember such letters were written to Baker when my own case was under consideration, and I trust there is no more ground for such apprehension now than there was then. Remember I am always glad to receive a letter from you.
Most truly your friend,
JANUARY 12, 1848.
MR CHAIRMAN:—Some if not all the gentlemen on the other side of the House who have addressed the committee within the last two days have spoken rather complainingly, if I have rightly understood them, of the vote given a week or ten days ago declaring that the war with Mexico was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President. I admit that such a vote should not be given in mere party wantonness, and that the one given is justly censurable if it have no other or better foundation. I am one of those who joined in that vote; and I did so under my best impression of the truth of the case. How I got this impression, and how it may possibly be remedied, I will now try to show. When the war began, it was my opinion that all those who because of knowing too little, or because of knowing too much, could not conscientiously approve the conduct of the President in the beginning of it should nevertheless, as good citizens and patriots, remain silent on that point, at least till the war should be ended. Some leading Democrats, including ex-President Van Buren, have taken this same view, as I understand them; and I adhered to it and acted upon it, until since I took my seat here; and I think I should still adhere to it were it not that the President and his friends will not allow it to be so. Besides the continual effort of the President to argue every silent vote given for supplies into an indorsement of the justice and wisdom of his conduct; besides that singularly candid paragraph in his late message in which he tells us that Congress with great unanimity had declared that "by the act of the Republic of Mexico, a state of war exists between that government and the United States," when the same journals that informed him of this also informed him that when that declaration stood disconnected from the question of supplies sixty-seven in the House, and not fourteen merely, voted against it; besides this open attempt to prove by telling the truth what he could not prove by telling the whole truth-demanding of all who will not submit to be misrepresented, in justice to themselves, to speak out, besides all this, one of my colleagues [Mr. Richardson] at a very early day in the session brought in a set of resolutions expressly indorsing the original justice of the war on the part of the President. Upon these resolutions when they shall be put on their passage I shall be compelled to vote; so that I cannot be silent if I would. Seeing this, I went about preparing myself to give the vote understandingly when it should come. I carefully examined the President's message, to ascertain what he himself had said and proved upon the point. The result of this examination was to make the impression that, taking for true all the President states as facts, he falls far short of proving his justification; and that the President would have gone further with his proof if it had not been for the small matter that the truth would not permit him. Under the impression thus made I gave the vote before mentioned. I propose now to give concisely the process of the examination I made, and how I reached the conclusion I did. The President, in his first war message of May, 1846, declares that the soil was ours on which hostilities were commenced by Mexico, and he repeats that declaration almost in the same language in each successive annual message, thus showing that he deems that point a highly essential one. In the importance of that point I entirely agree with the President. To my judgment it is the very point upon which he should be justified, or condemned. In his message of December, 1846, it seems to have occurred to him, as is certainly true, that title-ownership-to soil or anything else is not a simple fact, but is a conclusion following on one or more simple facts; and that it was incumbent upon him to present the facts from which he concluded the soil was ours on which the first blood of the war was shed.
Accordingly, a little below the middle of page twelve in the message last referred to, he enters upon that task; forming an issue and introducing testimony, extending the whole to a little below the middle of page fourteen. Now, I propose to try to show that the whole of this—issue and evidence—is from beginning to end the sheerest deception. The issue, as he presents it, is in these words: "But there are those who, conceding all this to be true, assume the ground that the true western boundary of Texas is the Nueces, instead of the Rio Grande; and that, therefore, in marching our army to the east bank of the latter river, we passed the Texas line and invaded the territory of Mexico." Now this issue is made up of two affirmatives and no negative. The main deception of it is that it assumes as true that one river or the other is necessarily the boundary; and cheats the superficial thinker entirely out of the idea that possibly the boundary is somewhere between the two, and not actually at either. A further deception is that it will let in evidence which a true issue would exclude. A true issue made by the President would be about as follows: "I say the soil was ours, on which the first blood was shed; there are those who say it was not."
I now proceed to examine the President's evidence as applicable to such an issue. When that evidence is analyzed, it is all included in the following propositions:
(1) That the Rio Grande was the western boundary of Louisiana as we purchased it of France in 1803.
(2) That the Republic of Texas always claimed the Rio Grande as her eastern boundary.
(3) That by various acts she had claimed it on paper.
(4) That Santa Anna in his treaty with Texas recognized the Rio Grande as her boundary.
(5) That Texas before, and the United States after, annexation had exercised jurisdiction beyond the Nueces—between the two rivers.
(6) That our Congress understood the boundary of Texas to extend beyond the Nueces.
Now for each of these in its turn. His first item is that the Rio Grande was the western boundary of Louisiana, as we purchased it of France in 1803; and seeming to expect this to be disputed, he argues over the amount of nearly a page to prove it true, at the end of which he lets us know that by the treaty of 1803 we sold to Spain the whole country from the Rio Grande eastward to the Sabine. Now, admitting for the present that the Rio Grande was the boundary of Louisiana, what under heaven had that to do with the present boundary between us and Mexico? How, Mr. Chairman, the line that once divided your land from mine can still be the boundary between us after I have sold my land to you is to me beyond all comprehension. And how any man, with an honest purpose only of proving the truth, could ever have thought of introducing such a fact to prove such an issue is equally incomprehensible. His next piece of evidence is that "the Republic of Texas always claimed this river [Rio Grande] as her western boundary." That is not true, in fact. Texas has claimed it, but she has not always claimed it. There is at least one distinguished exception. Her State constitution the republic's most solemn and well-considered act, that which may, without impropriety, be called her last will and testament, revoking all others-makes no such claim. But suppose she had always claimed it. Has not Mexico always claimed the contrary? So that there is but claim against claim, leaving nothing proved until we get back of the claims and find which has the better foundation. Though not in the order in which the President presents his evidence, I now consider that class of his statements which are in substance nothing more than that Texas has, by various acts of her Convention and Congress, claimed the Rio Grande as her boundary, on paper. I mean here what he says about the fixing of the Rio Grande as her boundary in her old constitution (not her State constitution), about forming Congressional districts, counties, etc. Now all of this is but naked claim; and what I have already said about claims is strictly applicable to this. If I should claim your land by word of mouth, that certainly would not make it mine; and if I were to claim it by a deed which I had made myself, and with which you had had nothing to do, the claim would be quite the same in substance—or rather, in utter nothingness. I next consider the President's statement that Santa Anna in his treaty with Texas recognized the Rio Grande as the western boundary of Texas. Besides the position so often taken, that Santa Anna while a prisoner of war, a captive, could not bind Mexico by a treaty, which I deem conclusive—besides this, I wish to say something in relation to this treaty, so called by the President, with Santa Anna. If any man would like to be amused by a sight of that little thing which the President calls by that big name, he can have it by turning to Niles's Register, vol. 1, p. 336. And if any one should suppose that Niles's Register is a curious repository of so mighty a document as a solemn treaty between nations, I can only say that I learned to a tolerable degree of certainty, by inquiry at the State Department, that the President himself never saw it anywhere else. By the way, I believe I should not err if I were to declare that during the first ten years of the existence of that document it was never by anybody called a treaty—that it was never so called till the President, in his extremity, attempted by so calling it to wring something from it in justification of himself in connection with the Mexican War. It has none of the distinguishing features of a treaty. It does not call itself a treaty. Santa Anna does not therein assume to bind Mexico; he assumes only to act as the President—Commander-in-Chief of the Mexican army and navy; stipulates that the then present hostilities should cease, and that he would not himself take up arms, nor influence the Mexican people to take up arms, against Texas during the existence of the war of independence. He did not recognize the independence of Texas; he did not assume to put an end to the war, but clearly indicated his expectation of its continuance; he did not say one word about boundary, and, most probably, never thought of it. It is stipulated therein that the Mexican forces should evacuate the territory of Texas, passing to the other side of the Rio Grande; and in another article it is stipulated that, to prevent collisions between the armies, the Texas army should not approach nearer than within five leagues—of what is not said, but clearly, from the object stated, it is of the Rio Grande. Now, if this is a treaty recognizing the Rio Grande as the boundary of Texas, it contains the singular feature of stipulating that Texas shall not go within five leagues of her own boundary.
Next comes the evidence of Texas before annexation, and the United States afterwards, exercising jurisdiction beyond the Nueces and between the two rivers. This actual exercise of jurisdiction is the very class or quality of evidence we want. It is excellent so far as it goes; but does it go far enough? He tells us it went beyond the Nueces, but he does not tell us it went to the Rio Grande. He tells us jurisdiction was exercised between the two rivers, but he does not tell us it was exercised over all the territory between them. Some simple-minded people think it is possible to cross one river and go beyond it without going all the way to the next, that jurisdiction may be exercised between two rivers without covering all the country between them. I know a man, not very unlike myself, who exercises jurisdiction over a piece of land between the Wabash and the Mississippi; and yet so far is this from being all there is between those rivers that it is just one hundred and fifty-two feet long by fifty feet wide, and no part of it much within a hundred miles of either. He has a neighbor between him and the Mississippi—that is, just across the street, in that direction—whom I am sure he could neither persuade nor force to give up his habitation; but which nevertheless he could certainly annex, if it were to be done by merely standing on his own side of the street and claiming it, or even sitting down and writing a deed for it.
But next the President tells us the Congress of the United States understood the State of Texas they admitted into the Union to extend beyond the Nueces. Well, I suppose they did. I certainly so understood it. But how far beyond? That Congress did not understand it to extend clear to the Rio Grande is quite certain, by the fact of their joint resolutions for admission expressly leaving all questions of boundary to future adjustment. And it may be added that Texas herself is proven to have had the same understanding of it that our Congress had, by the fact of the exact conformity of her new constitution to those resolutions.
I am now through the whole of the President's evidence; and it is a singular fact that if any one should declare the President sent the army into the midst of a settlement of Mexican people who had never submitted, by consent or by force, to the authority of Texas or of the United States, and that there and thereby the first blood of the war was shed, there is not one word in all the which would either admit or deny the declaration. This strange omission it does seem to me could not have occurred but by design. My way of living leads me to be about the courts of justice; and there I have sometimes seen a good lawyer, struggling for his client's neck in a desperate case, employing every artifice to work round, befog, and cover up with many words some point arising in the case which he dared not admit and yet could not deny. Party bias may help to make it appear so, but with all the allowance I can make for such bias, it still does appear to me that just such, and from just such necessity, is the President's struggle in this case.
Sometime after my colleague [Mr. Richardson] introduced the resolutions I have mentioned, I introduced a preamble, resolution, and interrogations, intended to draw the President out, if possible, on this hitherto untrodden ground. To show their relevancy, I propose to state my understanding of the true rule for ascertaining the boundary between Texas and Mexico. It is that wherever Texas was exercising jurisdiction was hers; and wherever Mexico was exercising jurisdiction was hers; and that whatever separated the actual exercise of jurisdiction of the one from that of the other was the true boundary between them. If, as is probably true, Texas was exercising jurisdiction along the western bank of the Nueces, and Mexico was exercising it along the eastern bank of the Rio Grande, then neither river was the boundary: but the uninhabited country between the two was. The extent of our territory in that region depended not on any treaty-fixed boundary (for no treaty had attempted it), but on revolution. Any people anywhere being inclined and having the power have the right to rise up and shake off the existing government, and form a new one that suits them better. This is a most valuable, a most sacred right—a right which we hope and believe is to liberate the world. Nor is this right confined to cases in which the whole people of an existing government may choose to exercise it. Any portion of such people that can may revolutionize and make their own of so much of the territory as they inhabit. More than this, a majority of any portion of such people may revolutionize, putting down a minority, intermingled with or near about them, who may oppose this movement. Such minority was precisely the case of the Tories of our own revolution. It is a quality of revolutions not to go by old lines or old laws, but to break up both, and make new ones.
As to the country now in question, we bought it of France in 1803, and sold it to Spain in 1819, according to the President's statements. After this, all Mexico, including Texas, revolutionized against Spain; and still later Texas revolutionized against Mexico. In my view, just so far as she carried her resolution by obtaining the actual, willing or unwilling, submission of the people, so far the country was hers, and no farther. Now, sir, for the purpose of obtaining the very best evidence as to whether Texas had actually carried her revolution to the place where the hostilities of the present war commenced, let the President answer the interrogatories I proposed, as before mentioned, or some other similar ones. Let him answer fully, fairly, and candidly. Let him answer with facts and not with arguments. Let him remember he sits where Washington sat, and so remembering, let him answer as Washington would answer. As a nation should not, and the Almighty will not, be evaded, so let him attempt no evasion—no equivocation. And if, so answering, he can show that the soil was ours where the first blood of the war was shed,—that it was not within an inhabited country, or, if within such, that the inhabitants had submitted themselves to the civil authority of Texas or of the United States, and that the same is true of the site of Fort Brown, then I am with him for his justification. In that case I shall be most happy to reverse the vote I gave the other day. I have a selfish motive for desiring that the President may do this—I expect to gain some votes, in connection with the war, which, without his so doing, will be of doubtful propriety in my own judgment, but which will be free from the doubt if he does so. But if he can not or will not do this,—if on any pretence or no pretence he shall refuse or omit it then I shall be fully convinced of what I more than suspect already that he is deeply conscious of being in the wrong; that he feels the blood of this war, like the blood of Abel, is crying to heaven against him; that originally having some strong motive—what, I will not stop now to give my opinion concerning to involve the two countries in a war, and trusting to escape scrutiny by fixing the public gaze upon the exceeding brightness of military glory,—that attractive rainbow that rises in showers of blood, that serpent's eye that charms to destroy,—he plunged into it, and was swept on and on till, disappointed in his calculation of the ease with which Mexico might be subdued, he now finds himself he knows not where. How like the half insane mumbling of a fever dream is the whole war part of his late message! At one time telling us that Mexico has nothing whatever that we can get—but territory; at another showing us how we can support the war by levying contributions on Mexico. At one time urging the national honor, the security of the future, the prevention of foreign interference, and even the good of Mexico herself as among the objects of the war; at another telling us that "to reject indemnity, by refusing to accept a cession of territory, would be to abandon all our just demands, and to wage the war, bearing all its expenses, without a purpose or definite object." So then this national honor, security of the future, and everything but territorial indemnity may be considered the no-purposes and indefinite objects of the war! But, having it now settled that territorial indemnity is the only object, we are urged to seize, by legislation here, all that he was content to take a few months ago, and the whole province of Lower California to boot, and to still carry on the war to take all we are fighting for, and still fight on. Again, the President is resolved under all circumstances to have full territorial indemnity for the expenses of the war; but he forgets to tell us how we are to get the excess after those expenses shall have surpassed the value of the whole of the Mexican territory. So again, he insists that the separate national existence of Mexico shall be maintained; but he does not tell us how this can be done, after we shall have taken all her territory. Lest the questions I have suggested be considered speculative merely, let me be indulged a moment in trying to show they are not. The war has gone on some twenty months; for the expenses of which, together with an inconsiderable old score, the President now claims about one half of the Mexican territory, and that by far the better half, so far as concerns our ability to make anything out of it. It is comparatively uninhabited; so that we could establish land-offices in it, and raise some money in that way. But the other half is already inhabited, as I understand it, tolerably densely for the nature of the country, and all its lands, or all that are valuable, already appropriated as private property. How then are we to make anything out of these lands with this encumbrance on them? or how remove the encumbrance? I suppose no one would say we should kill the people, or drive them out, or make slaves of them, or confiscate their property. How, then, can we make much out of this part of the territory? If the prosecution of the war has in expenses already equalled the better half of the country, how long its future prosecution will be in equalling the less valuable half is not a speculative, but a practical, question, pressing closely upon us. And yet it is a question which the President seems never to have thought of. As to the mode of terminating the war and securing peace, the President is equally wandering and indefinite. First, it is to be done by a more vigorous prosecution of the war in the vital parts of the enemy's country; and after apparently talking himself tired on this point, the President drops down into a half-despairing tone, and tells us that "with a people distracted and divided by contending factions, and a government subject to constant changes by successive revolutions, the continued success of our arms may fail to secure a satisfactory peace." Then he suggests the propriety of wheedling the Mexican people to desert the counsels of their own leaders, and, trusting in our protestations, to set up a government from which we can secure a satisfactory peace; telling us that "this may become the only mode of obtaining such a peace." But soon he falls into doubt of this too; and then drops back on to the already half-abandoned ground of "more vigorous prosecution." All this shows that the President is in nowise satisfied with his own positions. First he takes up one, and in attempting to argue us into it he argues himself out of it, then seizes another and goes through the same process, and then, confused at being able to think of nothing new, he snatches up the old one again, which he has some time before cast off. His mind, taxed beyond its power, is running hither and thither, like some tortured creature on a burning surface, finding no position on which it can settle down and be at ease.
Again, it is a singular omission in this message that it nowhere intimates when the President expects the war to terminate. At its beginning, General Scott was by this same President driven into disfavor if not disgrace, for intimating that peace could not be conquered in less than three or four months. But now, at the end of about twenty months, during which time our arms have given us the most splendid successes, every department and every part, land and water, officers and privates, regulars and volunteers, doing all that men could do, and hundreds of things which it had ever before been thought men could not do—after all this, this same President gives a long message, without showing us that as to the end he himself has even an imaginary conception. As I have before said, he knows not where he is. He is a bewildered, confounded, and miserably perplexed man. God grant he may be able to show there is not something about his conscience more painful than his mental perplexity.
The following is a copy of the so-called "treaty" referred to in the speech:
"Articles of Agreement entered into between his Excellency David G. Burnet, President of the Republic of Texas, of the one part, and his Excellency General Santa Anna, President-General-in-Chief of the Mexican army, of the other part: "Article I. General Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna agrees that he will not take up arms, nor will he exercise his influence to cause them to be taken up, against the people of Texas during the present war of independence. "Article II. All hostilities between the Mexican and Texan troops will cease immediately, both by land and water. "Article III. The Mexican troops will evacuate the territory of Texas, passing to the other side of the Rio Grande Del Norte. "Article IV. The Mexican army, in its retreat, shall not take the property of any person without his consent and just indemnification, using only such articles as may be necessary for its subsistence, in cases when the owner may not be present, and remitting to the commander of the army of Texas, or to the commissioners to be appointed for the adjustment of such matters, an account of the value of the property consumed, the place where taken, and the name of the owner, if it can be ascertained. "Article V. That all private property, including cattle, horses, negro slaves, or indentured persons, of whatever denomination, that may have been captured by any portion of the Mexican army, or may have taken refuge in the said army, since the commencement of the late invasion, shall be restored to the commander of the Texan army, or to such other persons as may be appointed by the Government of Texas to receive them. "Article VI. The troops of both armies will refrain from coming in contact with each other; and to this end the commander of the army of Texas will be careful not to approach within a shorter distance than five leagues. "Article VII. The Mexican army shall not make any other delay on its march than that which is necessary to take up their hospitals, baggage, etc., and to cross the rivers; any delay not necessary to these purposes to be considered an infraction of this agreement. "Article VIII. By an express, to be immediately despatched, this agreement shall be sent to General Vincente Filisola and to General T. J. Rusk, commander of the Texan army, in order that they may be apprised of its stipulations; and to this end they will exchange engagements to comply with the same. "Article IX. That all Texan prisoners now in the possession of the Mexican army, or its authorities, be forthwith released, and furnished with free passports to return to their homes; in consideration of which a corresponding number of Mexican prisoners, rank and file, now in possession of the Government of Texas shall be immediately released; the remainder of the Mexican prisoners that continue in the possession of the Government of Texas to be treated with due humanity,—any extraordinary comforts that may be furnished them to be at the charge of the Government of Mexico. "Article X. General Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna will be sent to Vera Cruz as soon as it shall be deemed proper. "The contracting parties sign this instrument for the abovementioned purposes, in duplicate, at the port of Velasco, this fourteenth day of May, 1836. "DAVID G. BURNET, President, "JAS. COLLINGSWORTH, Secretary of State, "ANTONIO LOPEZ DE SANTA ANNA, "B. HARDIMAN, Secretary of the Treasury, "P. W. GRAYSON, Attorney-General."
Mr. Lincoln, from the Committee on the Post-office and Post Roads, made the following report:
The Committee on the Post-office and Post Roads, to whom was referred the petition of Messrs. Saltmarsh and Fuller, report: That, as proved to their satisfaction, the mail routes from Milledgeville to Athens, and from Warrenton to Decatur, in the State of Georgia (numbered 2366 and 2380), were let to Reeside and Avery at $1300 per annum for the former and $1500 for the latter, for the term of four years, to commence on the first day of January, 1835; that, previous to the time for commencing the service, Reeside sold his interest therein to Avery; that on the 5th of May, 1835, Avery sold the whole to these petitioners, Saltmarsh and Fuller, to take effect from the beginning, January a 1835; that at this time, the Assistant Postmaster-General, being called on for that purpose, consented to the transfer of the contracts from Reeside and Avery to these petitioners, and promised to have proper entries of the transfer made on the books of the department, which, however, was neglected to be done; that the petitioners, supposing all was right, in good faith commenced the transportation of the mail on these routes, and after difficulty arose, still trusting that all would be made right, continued the service till December a 1837; that they performed the service to the entire satisfaction of the department, and have never been paid anything for it except $——; that the difficulty occurred as follows:
Mr. Barry was Postmaster-General at the times of making the contracts and the attempted transfer of them; Mr. Kendall succeeded Mr. Barry, and finding Reeside apparently in debt to the department, and these contracts still standing in the names of Reeside and Avery, refused to pay for the services under them, otherwise than by credits to Reeside; afterward, however, he divided the compensation, still crediting one half to Reeside, and directing the other to be paid to the order of Avery, who disclaimed all right to it. After discontinuing the service, these petitioners, supposing they might have legal redress against Avery, brought suit against him in New Orleans; in which suit they failed, on the ground that Avery had complied with his contract, having done so much toward the transfer as they had accepted and been satisfied with. Still later the department sued Reeside on his supposed indebtedness, and by a verdict of the jury it was determined that the department was indebted to him in a sum much beyond all the credits given him on the account above stated. Under these circumstances, the committee consider the petitioners clearly entitled to relief, and they report a bill accordingly; lest, however, there should be some mistake as to the amount which they have already received, we so frame it as that, by adjustment at the department, they may be paid so much as remains unpaid for services actually performed by them not charging them with the credits given to Reeside. The committee think it not improbable that the petitioners purchased the right of Avery to be paid for the service from the 1st of January, till their purchase on May 11, 1835; but, the evidence on this point being very vague, they forbear to report in favor of allowing it.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Inclosed you find a letter of Louis W. Chandler. What is wanted is that you shall ascertain whether the claim upon the note described has received any dividend in the Probate Court of Christian County, where the estate of Mr. Overbon Williams has been administered on. If nothing is paid on it, withdraw the note and send it to me, so that Chandler can see the indorser of it. At all events write me all about it, till I can somehow get it off my hands. I have already been bored more than enough about it; not the least of which annoyance is his cursed, unreadable, and ungodly handwriting.
I have made a speech, a copy of which I will send you by next mail.
Yours as ever,
WASHINGTON, February 1, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Your letter of the 19th ultimo was received last night, and for which I am much obliged. The only thing in it that I wish to talk to you at once about is that because of my vote for Ashmun's amendment you fear that you and I disagree about the war. I regret this, not because of any fear we shall remain disagreed after you have read this letter, but because if you misunderstand I fear other good friends may also. That vote affirms that the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President; and I will stake my life that if you had been in my place you would have voted just as I did. Would you have voted what you felt and knew to be a lie? I know you would not. Would you have gone out of the House—skulked the vote? I expect not. If you had skulked one vote, you would have had to skulk many more before the end of the session. Richardson's resolutions, introduced before I made any move or gave any vote upon the subject, make the direct question of the justice of the war; so that no man can be silent if he would. You are compelled to speak; and your only alternative is to tell the truth or a lie. I cannot doubt which you would do.
This vote has nothing to do in determining my votes on the questions of supplies. I have always intended, and still intend, to vote supplies; perhaps not in the precise form recommended by the President, but in a better form for all purposes, except Locofoco party purposes. It is in this particular you seem mistaken. The Locos are untiring in their efforts to make the impression that all who vote supplies or take part in the war do of necessity approve the President's conduct in the beginning of it; but the Whigs have from the beginning made and kept the distinction between the two. In the very first act nearly all the Whigs voted against the preamble declaring that war existed by the act of Mexico; and yet nearly all of them voted for the supplies. As to the Whig men who have participated in the war, so far as they have spoken in my hearing they do not hesitate to denounce as unjust the President's conduct in the beginning of the war. They do not suppose that such denunciation is directed by undying hatred to him, as The Register would have it believed. There are two such Whigs on this floor (Colonel Haskell and Major James) The former fought as a colonel by the side of Colonel Baker at Cerro Gordo, and stands side by side with me in the vote that you seem dissatisfied with. The latter, the history of whose capture with Cassius Clay you well know, had not arrived here when that vote was given; but, as I understand, he stands ready to give just such a vote whenever an occasion shall present. Baker, too, who is now here, says the truth is undoubtedly that way; and whenever he shall speak out, he will say so. Colonel Doniphan, too, the favorite Whig of Missouri, and who overran all Northern Mexico, on his return home in a public speech at St. Louis condemned the administration in relation to the war. If I remember, G. T. M. Davis, who has been through almost the whole war, declares in favor of Mr. Clay; from which I infer that he adopts the sentiments of Mr. Clay, generally at least. On the other hand, I have heard of but one Whig who has been to the war attempting to justify the President's conduct. That one was Captain Bishop, editor of the Charleston Courier, and a very clever fellow. I do not mean this letter for the public, but for you. Before it reaches you, you will have seen and read my pamphlet speech, and perhaps been scared anew by it. After you get over your scare, read it over again, sentence by sentence, and tell me honestly what you think of it. I condensed all I could for fear of being cut off by the hour rule, and when I got through I had spoken but forty-five minutes.
Yours forever,
DEAR WILLIAM:—I just take my pen to say that Mr. Stephens, of Georgia, a little, slim, pale-faced, consumptive man, with a voice like Logan's, has just concluded the very best speech of an hour's length I ever heard. My old withered dry eyes are full of tears yet.
If he writes it out anything like he delivered it, our people shall see a good many copies of it.
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, February 15, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Your letter of the 29th January was received last night. Being exclusively a constitutional argument, I wish to submit some reflections upon it in the same spirit of kindness that I know actuates you. Let me first state what I understand to be your position. It is that if it shall become necessary to repel invasion, the President may, without violation of the Constitution, cross the line and invade the territory of another country, and that whether such necessity exists in any given case the President is the sole judge.
Before going further consider well whether this is or is not your position. If it is, it is a position that neither the President himself, nor any friend of his, so far as I know, has ever taken. Their only positions are—first, that the soil was ours when the hostilities commenced; and second, that whether it was rightfully ours or not, Congress had annexed it, and the President for that reason was bound to defend it; both of which are as clearly proved to be false in fact as you can prove that your house is mine. The soil was not ours, and Congress did not annex or attempt to annex it. But to return to your position. Allow the President to invade a neighboring nation whenever he shall deem it necessary to repel an invasion, and you allow him to do so whenever he may choose to say he deems it necessary for such purpose, and you allow him to make war at pleasure. Study to see if you can fix any limit to his power in this respect, after having given him so much as you propose. If to-day he should choose to say he thinks it necessary to invade Canada to prevent the British from invading us, how could you stop him? You may say to him,—"I see no probability of the British invading us"; but he will say to you, "Be silent: I see it, if you don't."
The provision of the Constitution giving the war making power to Congress was dictated, as I understand it, by the following reasons: kings had always been involving and impoverishing their people in wars, pretending generally, if not always, that the good of the people was the object. This our convention understood to be the most oppressive of all kingly oppressions, and they resolved to so frame the Constitution that no one man should hold the power of bringing this oppression upon us. But your view destroys the whole matter, and places our President where kings have always stood. Write soon again.
Yours truly,
Mr. Lincoln, from the Committee on the Postoffice and Post Roads, made the following report:
The Committee on the Post-office and Post Roads, to whom was referred the resolution of the House of Representatives entitled "An Act authorizing postmasters at county seats of justice to receive subscriptions for newspapers and periodicals, to be paid through the agency of the Post-office Department, and for other purposes," beg leave to submit the following report:
The committee have reason to believe that a general wish pervades the community at large that some such facility as the proposed measure should be granted by express law, for subscribing, through the agency of the Post-office Department, to newspapers and periodicals which diffuse daily, weekly, or monthly intelligence of passing events. Compliance with this general wish is deemed to be in accordance with our republican institutions, which can be best sustained by the diffusion of knowledge and the due encouragement of a universal, national spirit of inquiry and discussion of public events through the medium of the public press. The committee, however, has not been insensible to its duty of guarding the Post-office Department against injurious sacrifices for the accomplishment of this object, whereby its ordinary efficacy might be impaired or embarrassed. It has therefore been a subject of much consideration; but it is now confidently hoped that the bill herewith submitted effectually obviates all objections which might exist with regard to a less matured proposition.
The committee learned, upon inquiry, that the Post-office Department, in view of meeting the general wish on this subject, made the experiment through one if its own internal regulations, when the new postage system went into operation on the first of July, 1845, and that it was continued until the thirtieth of September, 1847. But this experiment, for reasons hereafter stated, proved unsatisfactory, and it was discontinued by order of the Postmaster-General. As far as the committee can at present ascertain, the following seem to have been the principal grounds of dissatisfaction in this experiment:
(1) The legal responsibility of postmasters receiving newspaper subscriptions, or of their sureties, was not defined.
(2) The authority was open to all postmasters instead of being limited to those of specific offices.
(3) The consequence of this extension of authority was that, in innumerable instances, the money, without the previous knowledge or control of the officers of the department who are responsible for the good management of its finances, was deposited in offices where it was improper such funds should be placed; and the repayment was ordered, not by the financial officers, but by the postmasters, at points where it was inconvenient to the department so to disburse its funds.
(4) The inconvenience of accumulating uncertain and fluctuating sums at small offices was felt seriously in consequent overpayments to contractors on their quarterly collecting orders; and, in case of private mail routes, in litigation concerning the misapplication of such funds to the special service of supplying mails.
(5) The accumulation of such funds on draft offices could not be known to the financial clerks of the department in time to control it, and too often this rendered uncertain all their calculations of funds in hand.
(6) The orders of payment were for the most part issued upon the principal offices, such as New York, Philadelphia, Boston, Baltimore, etc., where the large offices of publishers are located, causing an illimitable and uncontrollable drain of the department funds from those points where it was essential to husband them for its own regular disbursements. In Philadelphia alone this drain averaged $5000 per quarter; and in other cities of the seaboard it was proportionate.
(7) The embarrassment of the department was increased by the illimitable, uncontrollable, and irresponsible scattering of its funds from concentrated points suitable for its distributions, to remote, unsafe, and inconvenient offices, where they could not be again made available till collected by special agents, or were transferred at considerable expense into the principal disbursing offices again.
(8) There was a vast increase of duties thrown upon the limited force before necessary to conduct the business of the department; and from the delay of obtaining vouchers impediments arose to the speedy settlement of accounts with present or retired post-masters, causing postponements which endangered the liability of sureties under the act of limitations, and causing much danger of an increase of such cases.
(9) The most responsible postmasters (at the large offices) were ordered by the least responsible (at small offices) to make payments upon their vouchers, without having the means of ascertaining whether these vouchers were genuine or forged, or if genuine, whether the signers were in or out of office, or solvent or defaulters.
(10) The transaction of this business for subscribers and publishers at the public expense, an the embarrassment, inconvenience, and delay of the department's own business occasioned by it, were not justified by any sufficient remuneration of revenue to sustain the department, as required in every other respect with regard to its agency.
The committee, in view of these objections, has been solicitous to frame a bill which would not be obnoxious to them in principle or in practical effect.
It is confidently believed that by limiting the offices for receiving subscriptions to less than one tenth of the number authorized by the experiment already tried, and designating the county seat in each county for the purpose, the control of the department will be rendered satisfactory; particularly as it will be in the power of the Auditor, who is the officer required by law to check the accounts, to approve or disapprove of the deposits, and to sanction not only the payments, but to point out the place of payment. If these payments should cause a drain on the principal offices of the seaboard, it will be compensated by the accumulation of funds at county seats, where the contractors on those routes can be paid to that extent by the department's drafts, with more local convenience to themselves than by drafts on the seaboard offices.
The legal responsibility for these deposits is defined, and the accumulation of funds at the point of deposit, and the repayment at points drawn upon, being known to and controlled by the Auditor, will not occasion any such embarrassments as were before felt; the record kept by the Auditor on the passing of the certificates through his hands will enable him to settle accounts without the delay occasioned by vouchers being withheld; all doubt or uncertainty as to the genuineness of certificates, or the propriety of their issue, will be removed by the Auditor's examination and approval; and there can be no risk of loss of funds by transmission, as the certificate will not be payable till sanctioned by the Auditor, and after his sanction the payor need not pay it unless it is presented by the publisher or his known clerk or agent.
The main principle of equivalent for the agency of the department is secured by the postage required to be paid upon the transmission of the certificates, augmenting adequately the post-office revenue.
The committee, conceiving that in this report all the difficulties of the subject have been fully and fairly stated, and that these difficulties have been obviated by the plan proposed in the accompanying bill, and believing that the measure will satisfactorily meet the wants and wishes of a very large portion of the community, beg leave to recommend its adoption.
Mr. Lincoln, from the Committee on the Postoffice and Post Roads, made the following report:
The Committee on the Post-office and Post Roads, to whom was referred the petition of H. M. Barney, postmaster at Brimfield, Peoria County, Illinois, report: That they have been satisfied by evidence, that on the 15th of December, 1847, said petitioner had his store, with some fifteen hundred dollars' worth of goods, together with all the papers of the post-office, entirely destroyed by fire; and that the specie funds of the office were melted down, partially lost and partially destroyed; that this large individual loss entirely precludes the idea of embezzlement; that the balances due the department of former quarters had been only about twenty-five dollars; and that owing to the destruction of papers, the exact amount due for the quarter ending December 31, 1847, cannot be ascertained. They therefore report a joint resolution, releasing said petitioner from paying anything for the quarter last mentioned.
The bill for raising additional military force for limited time, etc., was reported from Committee on judiciary; similar bills had been reported from Committee on, Public Lands and Military Committee.
Mr. Lincoln said if there was a general desire on the part of the House to pass the bill now he should be glad to have it done—concurring, as he did generally, with the gentleman from Arkansas [Mr. Johnson] that the postponement might jeopard the safety of the proposition. If, however, a reference was to be made, he wished to make a very few remarks in relation to the several subjects desired by the gentlemen to be embraced in amendments to the ninth section of the act of the last session of Congress. The first amendment desired by members of this House had for its only object to give bounty lands to such persons as had served for a time as privates, but had never been discharged as such, because promoted to office. That subject, and no other, was embraced in this bill. There were some others who desired, while they were legislating on this subject, that they should also give bounty lands to the volunteers of the War of 1812. His friend from Maryland said there were no such men. He [Mr. L.] did not say there were many, but he was very confident there were some. His friend from Kentucky near him, [Mr. Gaines] told him he himself was one.
There was still another proposition touching this matter; that was, that persons entitled to bounty lands should by law be entitled to locate these lands in parcels, and not be required to locate them in one body, as was provided by the existing law.
Now he had carefully drawn up a bill embracing these three separate propositions, which he intended to propose as a substitute for all these bills in the House, or in Committee of the Whole on the State of the Union, at some suitable time. If there was a disposition on the part of the House to act at once on this separate proposition, he repeated that, with the gentlemen from Arkansas, he should prefer it lest they should lose all. But if there was to be a reference, he desired to introduce his bill embracing the three propositions, thus enabling the committee and the House to act at the same time, whether favorably or unfavorably, upon all. He inquired whether an amendment was now in order.
The Speaker replied in the negative.
DEAR WILLIAMS:—I have not seen in the papers any evidence of a movement to send a delegate from your circuit to the June convention. I wish to say that I think it all-important that a delegate should be sent. Mr. Clay's chance for an election is just no chance at all. He might get New York, and that would have elected in 1844, but it will not now, because he must now, at the least, lose Tennessee, which he had then, and in addition the fifteen new votes of Florida, Texas, Iowa, and Wisconsin. I know our good friend Browning is a great admirer of Mr. Clay, and I therefore fear he is favoring his nomination. If he is, ask him to discard feeling, and try if he can possibly, as a matter of judgment, count the votes necessary to elect him.
In my judgment we can elect nobody but General Taylor; and we cannot elect him without a nomination. Therefore don't fail to send a delegate.
Your friend as ever,
A bill for the admission of Wisconsin into the Union had been passed.
Mr. Lincoln moved to reconsider the vote by which the bill was passed. He stated to the House that he had made this motion for the purpose of obtaining an opportunity to say a few words in relation to a point raised in the course of the debate on this bill, which he would now proceed to make if in order. The point in the case to which he referred arose on the amendment that was submitted by the gentleman from Vermont [Mr. Collamer] in Committee of the Whole on the State of the Union, and which was afterward renewed in the House, in relation to the question whether the reserved sections, which, by some bills heretofore passed, by which an appropriation of land had been made to Wisconsin, had been enhanced in value, should be reduced to the minimum price of the public lands. The question of the reduction in value of those sections was to him at this time a matter very nearly of indifference. He was inclined to desire that Wisconsin should be obliged by having it reduced. But the gentleman from Indiana [Mr. C. B. Smith], the chairman of the Committee on Territories, yesterday associated that question with the general question, which is now to some extent agitated in Congress, of making appropriations of alternate sections of land to aid the States in making internal improvements, and enhancing the price of the sections reserved, and the gentleman from Indiana took ground against that policy. He did not make any special argument in favor of Wisconsin, but he took ground generally against the policy of giving alternate sections of land, and enhancing the price of the reserved sections. Now he [Mr. Lincoln] did not at this time take the floor for the purpose of attempting to make an argument on the general subject. He rose simply to protest against the doctrine which the gentleman from Indiana had avowed in the course of what he [Mr. Lincoln] could not but consider an unsound argument.
It might, however, be true, for anything he knew, that the gentleman from Indiana might convince him that his argument was sound; but he [Mr. Lincoln] feared that gentleman would not be able to convince a majority in Congress that it was sound. It was true the question appeared in a different aspect to persons in consequence of a difference in the point from which they looked at it. It did not look to persons residing east of the mountains as it did to those who lived among the public lands. But, for his part, he would state that if Congress would make a donation of alternate sections of public land for the purpose of internal improvements in his State, and forbid the reserved sections being sold at $1.25, he should be glad to see the appropriation made; though he should prefer it if the reserved sections were not enhanced in price. He repeated, he should be glad to have such appropriations made, even though the reserved sections should be enhanced in price. He did not wish to be understood as concurring in any intimation that they would refuse to receive such an appropriation of alternate sections of land because a condition enhancing the price of the reserved sections should be attached thereto. He believed his position would now be understood: if not, he feared he should not be able to make himself understood.
But, before he took his seat, he would remark that the Senate during the present session had passed a bill making appropriations of land on that principle for the benefit of the State in which he resided the State of Illinois. The alternate sections were to be given for the purpose of constructing roads, and the reserved sections were to be enhanced in value in consequence. When that bill came here for the action of this House—it had been received, and was now before the Committee on Public Lands—he desired much to see it passed as it was, if it could be put in no more favorable form for the State of Illinois. When it should be before this House, if any member from a section of the Union in which these lands did not lie, whose interest might be less than that which he felt, should propose a reduction of the price of the reserved sections to $1.25, he should be much obliged; but he did not think it would be well for those who came from the section of the Union in which the lands lay to do so.—He wished it, then, to be understood that he did not join in the warfare against the principle which had engaged the minds of some members of Congress who were favorable to the improvements in the western country. There was a good deal of force, he admitted, in what fell from the chairman of the Committee on Territories. It might be that there was no precise justice in raising the price of the reserved sections to $2.50 per acre. It might be proper that the price should be enhanced to some extent, though not to double the usual price; but he should be glad to have such an appropriation with the reserved sections at $2.50; he should be better pleased to have the price of those sections at something less; and he should be still better pleased to have them without any enhancement at all.
There was one portion of the argument of the gentleman from Indiana, the chairman of the Committee on Territories [Mr. Smith], which he wished to take occasion to say that he did not view as unsound. He alluded to the statement that the General Government was interested in these internal improvements being made, inasmuch as they increased the value of the lands that were unsold, and they enabled the government to sell the lands which could not be sold without them. Thus, then, the government gained by internal improvements as well as by the general good which the people derived from them, and it might be, therefore, that the lands should not be sold for more than $1.50 instead of the price being doubled. He, however, merely mentioned this in passing, for he only rose to state, as the principle of giving these lands for the purposes which he had mentioned had been laid hold of and considered favorably, and as there were some gentlemen who had constitutional scruples about giving money for these purchases who would not hesitate to give land, that he was not willing to have it understood that he was one of those who made war against that principle. This was all he desired to say, and having accomplished the object with which he rose, he withdrew his motion to reconsider.
WASHINGTON, April 30,1848.
DEAR WASHBURNE:
I have this moment received your very short note asking me if old Taylor is to be used up, and who will be the nominee. My hope of Taylor's nomination is as high—a little higher than it was when you left. Still, the case is by no means out of doubt. Mr. Clay's letter has not advanced his interests any here. Several who were against Taylor, but not for anybody particularly, before, are since taking ground, some for Scott and some for McLean. Who will be nominated neither I nor any one else can tell. Now, let me pray to you in turn. My prayer is that you let nothing discourage or baffle you, but that, in spite of every difficulty, you send us a good Taylor delegate from your circuit. Make Baker, who is now with you, I suppose, help about it. He is a good hand to raise a breeze.
General Ashley, in the Senate from Arkansas, died yesterday. Nothing else new beyond what you see in the papers.
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, May 21, 1848. DEAR SIR:
....Not in view of all the facts. There are facts which you have kept out of view. It is a fact that the United States army in marching to the Rio Grande marched into a peaceful Mexican settlement, and frightened the inhabitants away from their homes and their growing crops. It is a fact that Fort Brown, opposite Matamoras, was built by that army within a Mexican cotton-field, on which at the time the army reached it a young cotton crop was growing, and which crop was wholly destroyed and the field itself greatly and permanently injured by ditches, embankments, and the like. It is a fact that when the Mexicans captured Captain Thornton and his command, they found and captured them within another Mexican field.
Now I wish to bring these facts to your notice, and to ascertain what is the result of your reflections upon them. If you deny that they are facts, I think I can furnish proofs which shall convince you that you are mistaken. If you admit that they are facts, then I shall be obliged for a reference to any law of language, law of States, law of nations, law of morals, law of religions, any law, human or divine, in which an authority can be found for saying those facts constitute "no aggression."
Possibly you consider those acts too small for notice. Would you venture to so consider them had they been committed by any nation on earth against the humblest of our people? I know you would not. Then I ask, is the precept "Whatsoever ye would that men should do to you, do ye even so to them" obsolete? of no force? of no application?
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, June 12, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAMS:—On my return from Philadelphia, where I had been attending the nomination of "Old Rough," (Zachary Taylor) I found your letter in a mass of others which had accumulated in my absence. By many, and often, it had been said they would not abide the nomination of Taylor; but since the deed has been done, they are fast falling in, and in my opinion we shall have a most overwhelming, glorious triumph. One unmistakable sign is that all the odds and ends are with us—Barnburners, Native Americans, Tyler men, disappointed office-seeking Locofocos, and the Lord knows what. This is important, if in nothing else, in showing which way the wind blows. Some of the sanguine men have set down all the States as certain for Taylor but Illinois, and it as doubtful. Cannot something be done even in Illinois? Taylor's nomination takes the Locos on the blind side. It turns the war thunder against them. The war is now to them the gallows of Haman, which they built for us, and on which they are doomed to be hanged themselves.
Excuse this short letter. I have so many to write that I cannot devote much time to any one.
Yours as ever,
In Committee of the Whole on the State of the Union, on the Civil and Diplomatic Appropriation Bill:
Mr. CHAIRMAN:—I wish at all times in no way to practise any fraud upon the House or the committee, and I also desire to do nothing which may be very disagreeable to any of the members. I therefore state in advance that my object in taking the floor is to make a speech on the general subject of internal improvements; and if I am out of order in doing so, I give the chair an opportunity of so deciding, and I will take my seat.
The Chair: I will not undertake to anticipate what the gentleman may say on the subject of internal improvements. He will, therefore, proceed in his remarks, and if any question of order shall be made, the chair will then decide it.
Mr. Lincoln: At an early day of this session the President sent us what may properly be called an internal improvement veto message. The late Democratic convention, which sat at Baltimore, and which nominated General Cass for the Presidency, adopted a set of resolutions, now called the Democratic platform, among which is one in these words:
"That the Constitution does not confer upon the General Government the power to commence and carry on a general system of internal improvements."
General Cass, in his letter accepting the nomination, holds this language:
"I have carefully read the resolutions of the Democratic national convention, laying down the platform of our political faith, and I adhere to them as firmly as I approve them cordially."
These things, taken together, show that the question of internal improvements is now more distinctly made—has become more intense—than at any former period. The veto message and the Baltimore resolution I understand to be, in substance, the same thing; the latter being the more general statement, of which the former is the amplification the bill of particulars. While I know there are many Democrats, on this floor and elsewhere, who disapprove that message, I understand that all who voted for General Cass will thereafter be counted as having approved it, as having indorsed all its doctrines.
I suppose all, or nearly all, the Democrats will vote for him. Many of them will do so not because they like his position on this question, but because they prefer him, being wrong on this, to another whom they consider farther wrong on other questions. In this way the internal improvement Democrats are to be, by a sort of forced consent, carried over and arrayed against themselves on this measure of policy. General Cass, once elected, will not trouble himself to make a constitutional argument, or perhaps any argument at all, when he shall veto a river or harbor bill; he will consider it a sufficient answer to all Democratic murmurs to point to Mr. Polk's message, and to the Democratic platform. This being the case, the question of improvements is verging to a final crisis; and the friends of this policy must now battle, and battle manfully, or surrender all. In this view, humble as I am, I wish to review, and contest as well as I may, the general positions of this veto message. When I say general positions, I mean to exclude from consideration so much as relates to the present embarrassed state of the treasury in consequence of the Mexican War.
Those general positions are: that internal improvements ought not to be made by the General Government—First. Because they would overwhelm the treasury Second. Because, while their burdens would be general, their benefits would be local and partial, involving an obnoxious inequality; and Third. Because they would be unconstitutional. Fourth. Because the States may do enough by the levy and collection of tonnage duties; or if not—Fifth. That the Constitution may be amended. "Do nothing at all, lest you do something wrong," is the sum of these positions is the sum of this message. And this, with the exception of what is said about constitutionality, applying as forcibly to what is said about making improvements by State authority as by the national authority; so that we must abandon the improvements of the country altogether, by any and every authority, or we must resist and repudiate the doctrines of this message. Let us attempt the latter.
The first position is, that a system of internal improvements would overwhelm the treasury. That in such a system there is a tendency to undue expansion, is not to be denied. Such tendency is founded in the nature of the subject. A member of Congress will prefer voting for a bill which contains an appropriation for his district, to voting for one which does not; and when a bill shall be expanded till every district shall be provided for, that it will be too greatly expanded is obvious. But is this any more true in Congress than in a State Legislature? If a member of Congress must have an appropriation for his district, so a member of a Legislature must have one for his county. And if one will overwhelm the national treasury, so the other will overwhelm the State treasury. Go where we will, the difficulty is the same. Allow it to drive us from the halls of Congress, and it will, just as easily, drive us from the State Legislatures. Let us, then, grapple with it, and test its strength. Let us, judging of the future by the past, ascertain whether there may not be, in the discretion of Congress, a sufficient power to limit and restrain this expansive tendency within reasonable and proper bounds. The President himself values the evidence of the past. He tells us that at a certain point of our history more than two hundred millions of dollars had been applied for to make improvements; and this he does to prove that the treasury would be overwhelmed by such a system. Why did he not tell us how much was granted? Would not that have been better evidence? Let us turn to it, and see what it proves. In the message the President tells us that "during the four succeeding years embraced by the administration of President Adams, the power not only to appropriate money, but to apply it, under the direction and authority of the General Government, as well to the construction of roads as to the improvement of harbors and rivers, was fully asserted and exercised." This, then, was the period of greatest enormity. These, if any, must have been the days of the two hundred millions. And how much do you suppose was really expended for improvements during that four years? Two hundred millions? One hundred? Fifty? Ten? Five? No, sir; less than two millions. As shown by authentic documents, the expenditures on improvements during 1825, 1826, 1827, and 1828 amounted to one million eight hundred and seventy-nine thousand six hundred and twenty-seven dollars and one cent. These four years were the period of Mr. Adams's administration, nearly and substantially. This fact shows that when the power to make improvements "was fully asserted and exercised," the Congress did keep within reasonable limits; and what has been done, it seems to me, can be done again.
Now for the second portion of the message—namely, that the burdens of improvements would be general, while their benefits would be local and partial, involving an obnoxious inequality. That there is some degree of truth in this position, I shall not deny. No commercial object of government patronage can be so exclusively general as to not be of some peculiar local advantage. The navy, as I understand it, was established, and is maintained at a great annual expense, partly to be ready for war when war shall come, and partly also, and perhaps chiefly, for the protection of our commerce on the high seas. This latter object is, for all I can see, in principle the same as internal improvements. The driving a pirate from the track of commerce on the broad ocean, and the removing of a snag from its more narrow path in the Mississippi River, cannot, I think, be distinguished in principle. Each is done to save life and property, and for nothing else.
The navy, then, is the most general in its benefits of all this class of objects; and yet even the navy is of some peculiar advantage to Charleston, Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York, and Boston, beyond what it is to the interior towns of Illinois. The next most general object I can think of would be improvements on the Mississippi River and its tributaries. They touch thirteen of our States-Pennsylvania, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, Louisiana, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Wisconsin, and Iowa. Now I suppose it will not be denied that these thirteen States are a little more interested in improvements on that great river than are the remaining seventeen. These instances of the navy and the Mississippi River show clearly that there is something of local advantage in the most general objects. But the converse is also true. Nothing is so local as to not be of some general benefit. Take, for instance, the Illinois and Michigan Canal. Considered apart from its effects, it is perfectly local. Every inch of it is within the State of Illinois. That canal was first opened for business last April. In a very few days we were all gratified to learn, among other things, that sugar had been carried from New Orleans through this canal to Buffalo in New York. This sugar took this route, doubtless, because it was cheaper than the old route. Supposing benefit of the reduction in the cost of carriage to be shared between seller and the buyer, result is that the New Orleans merchant sold his sugar a little dearer, and the people of Buffalo sweetened their coffee a little cheaper, than before,—a benefit resulting from the canal, not to Illinois, where the canal is, but to Louisiana and New York, where it is not. In other transactions Illinois will, of course, have her share, and perhaps the larger share too, of the benefits of the canal; but this instance of the sugar clearly shows that the benefits of an improvement are by no means confined to the particular locality of the improvement itself. The just conclusion from all this is that if the nation refuse to make improvements of the more general kind because their benefits may be somewhat local, a State may for the same reason refuse to make an improvement of a local kind because its benefits may be somewhat general. A State may well say to the nation, "If you will do nothing for me, I will do nothing for you." Thus it is seen that if this argument of "inequality" is sufficient anywhere, it is sufficient everywhere, and puts an end to improvements altogether. I hope and believe that if both the nation and the States would, in good faith, in their respective spheres do what they could in the way of improvements, what of inequality might be produced in one place might be compensated in another, and the sum of the whole might not be very unequal.
But suppose, after all, there should be some degree of inequality. Inequality is certainly never to be embraced for its own sake; but is every good thing to be discarded which may be inseparably connected with some degree of it? If so, we must discard all government. This Capitol is built at the public expense, for the public benefit; but does any one doubt that it is of some peculiar local advantage to the property-holders and business people of Washington? Shall we remove it for this reason? And if so, where shall we set it down, and be free from the difficulty? To make sure of our object, shall we locate it nowhere, and have Congress hereafter to hold its sessions, as the loafer lodged, "in spots about"? I make no allusion to the present President when I say there are few stronger cases in this world of "burden to the many and benefit to the few," of "inequality," than the Presidency itself is by some thought to be. An honest laborer digs coal at about seventy cents a day, while the President digs abstractions at about seventy dollars a day. The coal is clearly worth more than the abstractions, and yet what a monstrous inequality in the prices! Does the President, for this reason, propose to abolish the Presidency? He does not, and he ought not. The true rule, in determining to embrace or reject anything, is not whether it have any evil in it, but whether it have more of evil than of good. There are few things wholly evil or wholly good. Almost everything, especially of government policy, is an inseparable compound of the two; so that our best judgment of the preponderance between them is continually demanded. On this principle the President, his friends, and the world generally act on most subjects. Why not apply it, then, upon this question? Why, as to improvements, magnify the evil, and stoutly refuse to see any good in them?
Mr. Chairman, on the third position of the message the constitutional question—I have not much to say. Being the man I am, and speaking, where I do, I feel that in any attempt at an original constitutional argument I should not be and ought not to be listened to patiently. The ablest and the best of men have gone over the whole ground long ago. I shall attempt but little more than a brief notice of what some of them have said. In relation to Mr. Jefferson's views, I read from Mr. Polk's veto message:
"President Jefferson, in his message to Congress in 1806, recommended an amendment of the Constitution, with a view to apply an anticipated surplus in the treasury 'to the great purposes of the public education, roads, rivers, canals, and such other objects of public improvement as it may be thought proper to add to the constitutional enumeration of the federal powers'; and he adds: 'I suppose an amendment to the Constitution, by consent of the States, necessary, because the objects now recommended are not among those enumerated in the Constitution, and to which it permits the public moneys to be applied.' In 1825, he repeated in his published letters the opinion that no such power has been conferred upon Congress."
I introduce this not to controvert just now the constitutional opinion, but to show that, on the question of expediency, Mr. Jefferson's opinion was against the present President; that this opinion of Mr. Jefferson, in one branch at least, is in the hands of Mr. Polk like McFingal's gun—"bears wide and kicks the owner over."
But to the constitutional question. In 1826 Chancellor Kent first published his Commentaries on American law. He devoted a portion of one of the lectures to the question of the authority of Congress to appropriate public moneys for internal improvements. He mentions that the subject had never been brought under judicial consideration, and proceeds to give a brief summary of the discussion it had undergone between the legislative and executive branches of the government. He shows that the legislative branch had usually been for, and the executive against, the power, till the period of Mr. J.Q. Adams's administration, at which point he considers the executive influence as withdrawn from opposition, and added to the support of the power. In 1844 the chancellor published a new edition of his Commentaries, in which he adds some notes of what had transpired on the question since 1826. I have not time to read the original text on the notes; but the whole may be found on page 267, and the two or three following pages, of the first volume of the edition of 1844. As to what Chancellor Kent seems to consider the sum of the whole, I read from one of the notes:
"Mr. Justice Story, in his Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States, Vol. II., pp. 429-440, and again pp. 519-538, has stated at large the arguments for and against the proposition that Congress have a constitutional authority to lay taxes and to apply the power to regulate commerce as a means directly to encourage and protect domestic manufactures; and without giving any opinion of his own on the contested doctrine, he has left the reader to draw his own conclusions. I should think, however, from the arguments as stated, that every mind which has taken no part in the discussion, and felt no prejudice or territorial bias on either side of the question, would deem the arguments in favor of the Congressional power vastly superior."
It will be seen that in this extract the power to make improvements is not directly mentioned; but by examining the context, both of Kent and Story, it will be seen that the power mentioned in the extract and the power to make improvements are regarded as identical. It is not to be denied that many great and good men have been against the power; but it is insisted that quite as many, as great and as good, have been for it; and it is shown that, on a full survey of the whole, Chancellor Kent was of opinion that the arguments of the latter were vastly superior. This is but the opinion of a man; but who was that man? He was one of the ablest and most learned lawyers of his age, or of any age. It is no disparagement to Mr. Polk, nor indeed to any one who devotes much time to politics, to be placed far behind Chancellor Kent as a lawyer. His attitude was most favorable to correct conclusions. He wrote coolly, and in retirement. He was struggling to rear a durable monument of fame; and he well knew that truth and thoroughly sound reasoning were the only sure foundations. Can the party opinion of a party President on a law question, as this purely is, be at all compared or set in opposition to that of such a man, in such an attitude, as Chancellor Kent? This constitutional question will probably never be better settled than it is, until it shall pass under judicial consideration; but I do think no man who is clear on the questions of expediency need feel his conscience much pricked upon this.
Mr. Chairman, the President seems to think that enough may be done, in the way of improvements, by means of tonnage duties under State authority, with the consent of the General Government. Now I suppose this matter of tonnage duties is well enough in its own sphere. I suppose it may be efficient, and perhaps sufficient, to make slight improvements and repairs in harbors already in use and not much out of repair. But if I have any correct general idea of it, it must be wholly inefficient for any general beneficent purposes of improvement. I know very little, or rather nothing at all, of the practical matter of levying and collecting tonnage duties; but I suppose one of its principles must be to lay a duty for the improvement of any particular harbor upon the tonnage coming into that harbor; to do otherwise—to collect money in one harbor, to be expended on improvements in another—would be an extremely aggravated form of that inequality which the President so much deprecates. If I be right in this, how could we make any entirely new improvement by means of tonnage duties? How make a road, a canal, or clear a greatly obstructed river? The idea that we could involves the same absurdity as the Irish bull about the new boots. "I shall niver git 'em on," says Patrick, "till I wear 'em a day or two, and stretch 'em a little." We shall never make a canal by tonnage duties until it shall already have been made awhile, so the tonnage can get into it.
After all, the President concludes that possibly there may be some great objects of improvement which cannot be effected by tonnage duties, and which it therefore may be expedient for the General Government to take in hand. Accordingly he suggests, in case any such be discovered, the propriety of amending the Constitution. Amend it for what? If, like Mr. Jefferson, the President thought improvements expedient, but not constitutional, it would be natural enough for him to recommend such an amendment. But hear what he says in this very message:
"In view of these portentous consequences, I cannot but think that this course of legislation should be arrested, even were there nothing to forbid it in the fundamental laws of our Union."
For what, then, would he have the Constitution amended? With him it is a proposition to remove one impediment merely to be met by others which, in his opinion, cannot be removed, to enable Congress to do what, in his opinion, they ought not to do if they could.
Here Mr. Meade of Virginia inquired if Mr. Lincoln understood the President to be opposed, on grounds of expediency, to any and every improvement.
Mr. Lincoln answered: In the very part of his message of which I am speaking, I understand him as giving some vague expression in favor of some possible objects of improvement; but in doing so I understand him to be directly on the teeth of his own arguments in other parts of it. Neither the President nor any one can possibly specify an improvement which shall not be clearly liable to one or another of the objections he has urged on the score of expediency. I have shown, and might show again, that no work—no object—can be so general as to dispense its benefits with precise equality; and this inequality is chief among the "portentous consequences" for which he declares that improvements should be arrested. No, sir. When the President intimates that something in the way of improvements may properly be done by the General Government, he is shrinking from the conclusions to which his own arguments would force him. He feels that the improvements of this broad and goodly land are a mighty interest; and he is unwilling to confess to the people, or perhaps to himself, that he has built an argument which, when pressed to its conclusions, entirely annihilates this interest.
I have already said that no one who is satisfied of the expediency of making improvements needs be much uneasy in his conscience about its constitutionality. I wish now to submit a few remarks on the general proposition of amending the Constitution. As a general rule, I think we would much better let it alone. No slight occasion should tempt us to touch it. Better not take the first step, which may lead to a habit of altering it. Better, rather, habituate ourselves to think of it as unalterable. It can scarcely be made better than it is. New provisions would introduce new difficulties, and thus create and increase appetite for further change. No, sir; let it stand as it is. New hands have never touched it. The men who made it have done their work, and have passed away. Who shall improve on what they did?
Mr. Chairman, for the purpose of reviewing this message in the least possible time, as well as for the sake of distinctness, I have analyzed its arguments as well as I could, and reduced them to the propositions I have stated. I have now examined them in detail. I wish to detain the committee only a little while longer with some general remarks upon the subject of improvements. That the subject is a difficult one, cannot be denied. Still it is no more difficult in Congress than in the State Legislatures, in the counties, or in the smallest municipal districts which anywhere exist. All can recur to instances of this difficulty in the case of county roads, bridges, and the like. One man is offended because a road passes over his land, and another is offended because it does not pass over his; one is dissatisfied because the bridge for which he is taxed crosses the river on a different road from that which leads from his house to town; another cannot bear that the county should be got in debt for these same roads and bridges; while not a few struggle hard to have roads located over their lands, and then stoutly refuse to let them be opened until they are first paid the damages. Even between the different wards and streets of towns and cities we find this same wrangling and difficulty. Now these are no other than the very difficulties against which, and out of which, the President constructs his objections of "inequality," "speculation," and "crushing the treasury." There is but a single alternative about them: they are sufficient, or they are not. If sufficient, they are sufficient out of Congress as well as in it, and there is the end. We must reject them as insufficient, or lie down and do nothing by any authority. Then, difficulty though there be, let us meet and encounter it. "Attempt the end, and never stand to doubt; nothing so hard, but search will find it out." Determine that the thing can and shall be done, and then we shall find the way. The tendency to undue expansion is unquestionably the chief difficulty.
How to do something, and still not do too much, is the desideratum. Let each contribute his mite in the way of suggestion. The late Silas Wright, in a letter to the Chicago convention, contributed his, which was worth something; and I now contribute mine, which may be worth nothing. At all events, it will mislead nobody, and therefore will do no harm. I would not borrow money. I am against an overwhelming, crushing system. Suppose that, at each session, Congress shall first determine how much money can, for that year, be spared for improvements; then apportion that sum to the most important objects. So far all is easy; but how shall we determine which are the most important? On this question comes the collision of interests. I shall be slow to acknowledge that your harbor or your river is more important than mine, and vice versa. To clear this difficulty, let us have that same statistical information which the gentleman from Ohio [Mr. Vinton] suggested at the beginning of this session. In that information we shall have a stern, unbending basis of facts—a basis in no wise subject to whim, caprice, or local interest. The prelimited amount of means will save us from doing too much, and the statistics will save us from doing what we do in wrong places. Adopt and adhere to this course, and, it seems to me, the difficulty is cleared.
One of the gentlemen from South Carolina [Mr. Rhett] very much deprecates these statistics. He particularly objects, as I understand him, to counting all the pigs and chickens in the land. I do not perceive much force in the objection. It is true that if everything be enumerated, a portion of such statistics may not be very useful to this object. Such products of the country as are to be consumed where they are produced need no roads or rivers, no means of transportation, and have no very proper connection with this subject. The surplus—that which is produced in one place to be consumed in another; the capacity of each locality for producing a greater surplus; the natural means of transportation, and their susceptibility of improvement; the hindrances, delays, and losses of life and property during transportation, and the causes of each, would be among the most valuable statistics in this connection. From these it would readily appear where a given amount of expenditure would do the most good. These statistics might be equally accessible, as they would be equally useful, to both the nation and the States. In this way, and by these means, let the nation take hold of the larger works, and the States the smaller ones; and thus, working in a meeting direction, discreetly, but steadily and firmly, what is made unequal in one place may be equalized in another, extravagance avoided, and the whole country put on that career of prosperity which shall correspond with its extent of territory, its natural resources, and the intelligence and enterprise of its people.
WASHINGTON, June 22, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAM:—Last night I was attending a sort of caucus of the Whig members, held in relation to the coming Presidential election. The whole field of the nation was scanned, and all is high hope and confidence. Illinois is expected to better her condition in this race. Under these circumstances, judge how heartrending it was to come to my room and find and read your discouraging letter of the 15th. We have made no gains, but have lost "H. R. Robinson, Turner, Campbell, and four or five more." Tell Arney to reconsider, if he would be saved. Baker and I used to do something, but I think you attach more importance to our absence than is just. There is another cause. In 1840, for instance, we had two senators and five representatives in Sangamon; now we have part of one senator and two representatives. With quite one third more people than we had then, we have only half the sort of offices which are sought by men of the speaking sort of talent. This, I think, is the chief cause. Now, as to the young men. You must not wait to be brought forward by the older men. For instance, do you suppose that I should ever have got into notice if I had waited to be hunted up and pushed forward by older men? You young men get together and form a "Rough and Ready Club," and have regular meetings and speeches. Take in everybody you can get. Harrison Grimsley, L. A. Enos, Lee Kimball, and C. W. Matheny will do to begin the thing; but as you go along gather up all the shrewd, wild boys about town, whether just of age, or a little under age, Chris. Logan, Reddick Ridgely, Lewis Zwizler, and hundreds such. Let every one play the part he can play best,—some speak, some sing, and all "holler." Your meetings will be of evenings; the older men, and the women, will go to hear you; so that it will not only contribute to the election of "Old Zach," but will be an interesting pastime, and improving to the intellectual faculties of all engaged. Don't fail to do this.
You ask me to send you all the speeches made about "Old Zach," the war, etc. Now this makes me a little impatient. I have regularly sent you the Congressional Globe and Appendix, and you cannot have examined them, or you would have discovered that they contain every speech made by every man in both houses of Congress, on every subject, during the session. Can I send any more? Can I send speeches that nobody has made? Thinking it would be most natural that the newspapers would feel interested to give at least some of the speeches to their readers, I at the beginning of the session made arrangements to have one copy of the Globe and Appendix regularly sent to each Whig paper of the district. And yet, with the exception of my own little speech, which was published in two only of the then five, now four, Whig papers, I do not remember having seen a single speech, or even extract from one, in any single one of those papers. With equal and full means on both sides, I will venture that the State Register has thrown before its readers more of Locofoco speeches in a month than all the Whig papers of the district have done of Whig speeches during the session.
If you wish a full understanding of the war, I repeat what I believe I said to you in a letter once before, that the whole, or nearly so, is to be found in the speech of Dixon of Connecticut. This I sent you in pamphlet as well as in the Globe. Examine and study every sentence of that speech thoroughly, and you will understand the whole subject. You ask how Congress came to declare that war had existed by the act of Mexico. Is it possible you don't understand that yet? You have at least twenty speeches in your possession that fully explain it. I will, however, try it once more. The news reached Washington of the commencement of hostilities on the Rio Grande, and of the great peril of General Taylor's army. Everybody, Whigs and Democrats, was for sending them aid, in men and money. It was necessary to pass a bill for this. The Locos had a majority in both houses, and they brought in a bill with a preamble saying: Whereas, War exists by the act of Mexico, therefore we send General Taylor money. The Whigs moved to strike out the preamble, so that they could vote to send the men and money, without saying anything about how the war commenced; but being in the minority, they were voted down, and the preamble was retained. Then, on the passage of the bill, the question came upon them, Shall we vote for preamble and bill together, or against both together? They did not want to vote against sending help to General Taylor, and therefore they voted for both together. Is there any difficulty in understanding this? Even my little speech shows how this was; and if you will go to the library, you may get the Journal of 1845-46, in which you will find the whole for yourself.
We have nothing published yet with special reference to the Taylor race; but we soon will have, and then I will send them to everybody. I made an internal-improvement speech day before yesterday, which I shall send home as soon as I can get it written out and printed,—and which I suppose nobody will read.
Your friend as ever,
Discussion as to salary of judge of western Virginia:—Wishing to increase it from $1800 to $2500.
Mr. Lincoln said he felt unwilling to be either unjust or ungenerous, and he wanted to understand the real case of this judicial officer. The gentleman from Virginia had stated that he had to hold eleven courts. Now everybody knew that it was not the habit of the district judges of the United States in other States to hold anything like that number of courts; and he therefore took it for granted that this must happen under a peculiar law which required that large number of courts to be holden every year; and these laws, he further supposed, were passed at the request of the people of that judicial district. It came, then, to this: that the people in the western district of Virginia had got eleven courts to be held among them in one year, for their own accommodation; and being thus better accommodated than neighbors elsewhere, they wanted their judge to be a little better paid. In Illinois there had been until the present season but one district court held in the year. There were now to be two. Could it be that the western district of Virginia furnished more business for a judge than the whole State of Illinois?
[FRAGMENT]
The question of a national bank is at rest. Were I President, I should not urge its reagitation upon Congress; but should Congress see fit to pass an act to establish such an institution, I should not arrest it by the veto, unless I should consider it subject to some constitutional objection from which I believe the two former banks to have been free.
WASHINGTON, July 10, 1848.
DEAR WILLIAM:
Your letter covering the newspaper slips was received last night. The subject of that letter is exceedingly painful to me, and I cannot but think there is some mistake in your impression of the motives of the old men. I suppose I am now one of the old men; and I declare on my veracity, which I think is good with you, that nothing could afford me more satisfaction than to learn that you and others of my young friends at home were doing battle in the contest and endearing themselves to the people and taking a stand far above any I have ever been able to reach in their admiration. I cannot conceive that other men feel differently. Of course I cannot demonstrate what I say; but I was young once, and I am sure I was never ungenerously thrust back. I hardly know what to say. The way for a young man to rise is to improve himself every way he can, never suspecting that anybody wishes to hinder him. Allow me to assure you that suspicion and jealousy never did help any man in any situation. There may sometimes be ungenerous attempts to keep a young man down; and they will succeed, too, if he allows his mind to be diverted from its true channel to brood over the attempted injury. Cast about and see if this feeling has not injured every person you have ever known to fall into it.
Now, in what I have said I am sure you will suspect nothing but sincere friendship. I would save you from a fatal error. You have been a studious young man. You are far better informed on almost all subjects than I ever have been. You cannot fail in any laudable object unless you allow your mind to be improperly directed. I have some the advantage of you in the world's experience, merely by being older; and it is this that induces me to advise. You still seem to be a little mistaken about the Congressional Globe and Appendix. They contain all of the speeches that are published in any way. My speech and Dayton's speech which you say you got in pamphlet form are both word for word in the Appendix. I repeat again, all are there.
Your friend, as ever,
Mr. SPEAKER, our Democratic friends seem to be in a great distress because they think our candidate for the Presidency don't suit us. Most of them cannot find out that General Taylor has any principles at all; some, however, have discovered that he has one, but that one is entirely wrong. This one principle is his position on the veto power. The gentleman from Tennessee [Mr. Stanton] who has just taken his seat, indeed, has said there is very little, if any, difference on this question between General Taylor and all the Presidents; and he seems to think it sufficient detraction from General Taylor's position on it that it has nothing new in it. But all others whom I have heard speak assail it furiously. A new member from Kentucky [Mr. Clark], of very considerable ability, was in particular concerned about it. He thought it altogether novel and unprecedented for a President or a Presidential candidate to think of approving bills whose constitutionality may not be entirely clear to his own mind. He thinks the ark of our safety is gone unless Presidents shall always veto such bills as in their judgment may be of doubtful constitutionality. However clear Congress may be on their authority to pass any particular act, the gentleman from Kentucky thinks the President must veto it if he has doubts about it. Now I have neither time nor inclination to argue with the gentleman on the veto power as an original question; but I wish to show that General Taylor, and not he, agrees with the earlier statesmen on this question. When the bill chartering the first Bank of the United States passed Congress, its constitutionality was questioned. Mr. Madison, then in the House of Representatives, as well as others, had opposed it on that ground. General Washington, as President, was called on to approve or reject it. He sought and obtained on the constitutionality question the separate written opinions of Jefferson, Hamilton, and Edmund Randolph,—they then being respectively Secretary of State, Secretary of the Treasury, and Attorney general. Hamilton's opinion was for the power; while Randolph's and Jefferson's were both against it. Mr. Jefferson, after giving his opinion deciding only against the constitutionality of the bill, closes his letter with the paragraph which I now read:
"It must be admitted, however, that unless the President's mind, on a view of everything which is urged for and against this bill, is tolerably clear that it is unauthorized by the Constitution,—if the pro and con hang so even as to balance his judgment, a just respect for the wisdom of the legislature would naturally decide the balance in favor of their opinion. It is chiefly for cases where they are clearly misled by error, ambition, or interest, that the Constitution has placed a check in the negative of the President.
"THOMAS JEFFERSON.
"February 15, 1791."
General Taylor's opinion, as expressed in his Allison letter, is as I now read:
"The power given by the veto is a high conservative power; but, in my opinion, should never be exercised except in cases of clear violation of the Constitution, or manifest haste and want of consideration by Congress."
It is here seen that, in Mr. Jefferson's opinion, if on the constitutionality of any given bill the President doubts, he is not to veto it, as the gentleman from Kentucky would have him do, but is to defer to Congress and approve it. And if we compare the opinion of Jefferson and Taylor, as expressed in these paragraphs, we shall find them more exactly alike than we can often find any two expressions having any literal difference. None but interested faultfinders, I think, can discover any substantial variation.
But gentlemen on the other side are unanimously agreed that General Taylor has no other principles. They are in utter darkness as to his opinions on any of the questions of policy which occupy the public attention. But is there any doubt as to what he will do on the prominent questions if elected? Not the least. It is not possible to know what he will or would do in every imaginable case, because many questions have passed away, and others doubtless will arise which none of us have yet thought of; but on the prominent questions of currency, tariff, internal improvements, and Wilmot Proviso, General Taylor's course is at least as well defined as is General Cass's. Why, in their eagerness to get at General Taylor, several Democratic members here have desired to know whether, in case of his election, a bankrupt law is to be established. Can they tell us General Cass's opinion on this question?
[Some member answered, "He is against it."]
Aye, how do you know he is? There is nothing about it in the platform, nor elsewhere, that I have seen. If the gentleman knows of anything which I do not know he can show it. But to return. General Taylor, in his Allison letter, says:
"Upon the subject of the tariff, the currency, the improvement of our great highways, rivers, lakes, and harbors, the will of the people, as expressed through their representatives in Congress, ought to be respected and carried out by the executive."
Now this is the whole matter. In substance, it is this: The people say to General Taylor, "If you are elected, shall we have a national bank?" He answers, "Your will, gentlemen, not mine." "What about the tariff?" "Say yourselves." "Shall our rivers and harbors be improved?" "Just as you please. If you desire a bank, an alteration of the tariff, internal improvements, any or all, I will not hinder you. If you do not desire them, I will not attempt to force them on you. Send up your members of Congress from the various districts, with opinions according to your own, and if they are for these measures, or any of them, I shall have nothing to oppose; if they are not for them, I shall not, by any appliances whatever, attempt to dragoon them into their adoption."
Now can there be any difficulty in understanding this? To you Democrats it may not seem like principle; but surely you cannot fail to perceive the position plainly enough. The distinction between it and the position of your candidate is broad and obvious, and I admit you have a clear right to show it is wrong if you can; but you have no right to pretend you cannot see it at all. We see it, and to us it appears like principle, and the best sort of principle at that—the principle of allowing the people to do as they please with their own business. My friend from Indiana (C. B. Smith) has aptly asked, "Are you willing to trust the people?" Some of you answered substantially, "We are willing to trust the people; but the President is as much the representative of the people as Congress." In a certain sense, and to a certain extent, he is the representative of the people. He is elected by them, as well as Congress is; but can he, in the nature of things know the wants of the people as well as three hundred other men, coming from all the various localities of the nation? If so, where is the propriety of having a Congress? That the Constitution gives the President a negative on legislation, all know; but that this negative should be so combined with platforms and other appliances as to enable him, and in fact almost compel him, to take the whole of legislation into his own hands, is what we object to, is what General Taylor objects to, and is what constitutes the broad distinction between you and us. To thus transfer legislation is clearly to take it from those who understand with minuteness the interests of the people, and give it to one who does not and cannot so well understand it. I understand your idea that if a Presidential candidate avow his opinion upon a given question, or rather upon all questions, and the people, with full knowledge of this, elect him, they thereby distinctly approve all those opinions. By means of it, measures are adopted or rejected contrary to the wishes of the whole of one party, and often nearly half of the other. Three, four, or half a dozen questions are prominent at a given time; the party selects its candidate, and he takes his position on each of these questions. On all but one his positions have already been indorsed at former elections, and his party fully committed to them; but that one is new, and a large portion of them are against it. But what are they to do? The whole was strung together; and they must take all, or reject all. They cannot take what they like, and leave the rest. What they are already committed to being the majority, they shut their eyes, and gulp the whole. Next election, still another is introduced in the same way. If we run our eyes along the line of the past, we shall see that almost if not quite all the articles of the present Democratic creed have been at first forced upon the party in this very way. And just now, and just so, opposition to internal improvements is to be established if General Cass shall be elected. Almost half the Democrats here are for improvements; but they will vote for Cass, and if he succeeds, their vote will have aided in closing the doors against improvements. Now this is a process which we think is wrong. We prefer a candidate who, like General Taylor, will allow the people to have their own way, regardless of his private opinions; and I should think the internal-improvement Democrats, at least, ought to prefer such a candidate. He would force nothing on them which they don't want, and he would allow them to have improvements which their own candidate, if elected, will not.
Mr. Speaker, I have said General Taylor's position is as well defined as is that of General Cass. In saying this, I admit I do not certainly know what he would do on the Wilmot Proviso. I am a Northern man or rather a Western Free-State man, with a constituency I believe to be, and with personal feelings I know to be, against the extension of slavery. As such, and with what information I have, I hope and believe General Taylor, if elected, would not veto the proviso. But I do not know it. Yet if I knew he would, I still would vote for him. I should do so because, in my judgment, his election alone can defeat General Cass; and because, should slavery thereby go to the territory we now have, just so much will certainly happen by the election of Cass, and in addition a course of policy leading to new wars, new acquisitions of territory and still further extensions of slavery. One of the two is to be President. Which is preferable?
But there is as much doubt of Cass on improvements as there is of Taylor on the proviso. I have no doubt myself of General Cass on this question; but I know the Democrats differ among themselves as to his position. My internal-improvement colleague [Mr. Wentworth] stated on this floor the other day that he was satisfied Cass was for improvements, because he had voted for all the bills that he [Mr. Wentworth] had. So far so good. But Mr. Polk vetoed some of these very bills. The Baltimore convention passed a set of resolutions, among other things, approving these vetoes, and General Cass declares, in his letter accepting the nomination, that he has carefully read these resolutions, and that he adheres to them as firmly as he approves them cordially. In other words, General Cass voted for the bills, and thinks the President did right to veto them; and his friends here are amiable enough to consider him as being on one side or the other, just as one or the other may correspond with their own respective inclinations. My colleague admits that the platform declares against the constitutionality of a general system of improvements, and that General Cass indorses the platform; but he still thinks General Cass is in favor of some sort of improvements. Well, what are they? As he is against general objects, those he is for must be particular and local. Now this is taking the subject precisely by the wrong end. Particularity expending the money of the whole people for an object which will benefit only a portion of them—is the greatest real objection to improvements, and has been so held by General Jackson, Mr. Polk, and all others, I believe, till now. But now, behold, the objects most general—nearest free from this objection—are to be rejected, while those most liable to it are to be embraced. To return: I cannot help believing that General Cass, when he wrote his letter of acceptance, well understood he was to be claimed by the advocates of both sides of this question, and that he then closed the door against all further expressions of opinion purposely to retain the benefits of that double position. His subsequent equivocation at Cleveland, to my mind, proves such to have been the case.
One word more, and I shall have done with this branch of the subject. You Democrats, and your candidate, in the main are in favor of laying down in advance a platform—a set of party positions—as a unit, and then of forcing the people, by every sort of appliance, to ratify them, however unpalatable some of them may be. We and our candidate are in favor of making Presidential elections and the legislation of the country distinct matters; so that the people can elect whom they please, and afterward legislate just as they please, without any hindrance, save only so much as may guard against infractions of the Constitution, undue haste, and want of consideration. The difference between us is clear as noonday. That we are right we cannot doubt. We hold the true Republican position. In leaving the people's business in their hands, we cannot be wrong. We are willing, and even anxious, to go to the people on this issue.
But I suppose I cannot reasonably hope to convince you that we have any principles. The most I can expect is to assure you that we think we have and are quite contented with them. The other day one of the gentlemen from Georgia [Mr. Iverson], an eloquent man, and a man of learning, so far as I can judge, not being learned myself, came down upon us astonishingly. He spoke in what the 'Baltimore American' calls the "scathing and withering style." At the end of his second severe flash I was struck blind, and found myself feeling with my fingers for an assurance of my continued existence. A little of the bone was left, and I gradually revived. He eulogized Mr. Clay in high and beautiful terms, and then declared that we had deserted all our principles, and had turned Henry Clay out, like an old horse, to root. This is terribly severe. It cannot be answered by argument—at least I cannot so answer it. I merely wish to ask the gentleman if the Whigs are the only party he can think of who sometimes turn old horses out to root. Is not a certain Martin Van Buren an old horse which your own party have turned out to root? and is he not rooting a little to your discomfort about now? But in not nominating Mr. Clay we deserted our principles, you say. Ah! In what? Tell us, ye men of principle, what principle we violated. We say you did violate principle in discarding Van Buren, and we can tell you how. You violated the primary, the cardinal, the one great living principle of all democratic representative government—the principle that the representative is bound to carry out the known will of his constituents. A large majority of the Baltimore convention of 1844 were, by their constituents, instructed to procure Van Buren 's nomination if they could. In violation—in utter glaring contempt of this, you rejected him; rejected him, as the gentleman from New York [Mr. Birdsall] the other day expressly admitted, for availability—that same "general availability" which you charge upon us, and daily chew over here, as something exceedingly odious and unprincipled. But the gentleman from Georgia [Mr. Iverson] gave us a second speech yesterday, all well considered and put down in writing, in which Van Buren was scathed and withered a "few" for his present position and movements. I cannot remember the gentleman's precise language; but I do remember he put Van Buren down, down, till he got him where he was finally to "stink" and "rot."
Mr. Speaker, it is no business or inclination of mine to defend Martin Van Buren in the war of extermination now waging between him and his old admirers. I say, "Devil take the hindmost"—and the foremost. But there is no mistaking the origin of the breach; and if the curse of "stinking" and "rotting" is to fall on the first and greatest violators of principle in the matter, I disinterestedly suggest that the gentleman from Georgia and his present co-workers are bound to take it upon themselves. But the gentleman from Georgia further says we have deserted all our principles, and taken shelter under General Taylor's military coat-tail, and he seems to think this is exceedingly degrading. Well, as his faith is, so be it unto him. But can he remember no other military coat-tail under which a certain other party have been sheltering for near a quarter of a century? Has he no acquaintance with the ample military coat tail of General Jackson? Does he not know that his own party have run the five last Presidential races under that coat-tail, and that they are now running the sixth under the same cover? Yes, sir, that coat-tail was used not only for General Jackson himself, but has been clung to, with the grip of death, by every Democratic candidate since. You have never ventured, and dare not now venture, from under it. Your campaign papers have constantly been "Old Hickories," with rude likenesses of the old general upon them; hickory poles and hickory brooms your never-ending emblems; Mr. Polk himself was "Young Hickory," or something so; and even now your campaign paper here is proclaiming that Cass and Butler are of the true "Hickory stripe." Now, sir, you dare not give it up. Like a horde of hungry ticks you have stuck to the tail of the Hermitage Lion to the end of his life; and you are still sticking to it, and drawing a loathsome sustenance from it, after he is dead. A fellow once advertised that he had made a discovery by which he could make a new man out of an old one, and have enough of the stuff left to make a little yellow dog. Just such a discovery has General Jackson's popularity been to you. You not only twice made President of him out of it, but you have had enough of the stuff left to make Presidents of several comparatively small men since; and it is your chief reliance now to make still another.
Mr. Speaker, old horses and military coat-tails, or tails of any sort, are not figures of speech such as I would be the first to introduce into discussions here; but as the gentleman from Georgia has thought fit to introduce them, he and you are welcome to all you have made, or can make by them. If you have any more old horses, trot them out; any more tails, just cock them and come at us. I repeat, I would not introduce this mode of discussion here; but I wish gentlemen on the other side to understand that the use of degrading figures is a game at which they may not find themselves able to take all the winnings.
["We give it up!"]
Aye, you give it up, and well you may; but for a very different reason from that which you would have us understand. The point—the power to hurt—of all figures consists in the truthfulness of their application; and, understanding this, you may well give it up. They are weapons which hit you, but miss us.
But in my hurry I was very near closing this subject of military tails before I was done with it. There is one entire article of the sort I have not discussed yet,—I mean the military tail you Democrats are now engaged in dovetailing into the great Michigander [Cass]. Yes, sir; all his biographies (and they are legion) have him in hand, tying him to a military tail, like so many mischievous boys tying a dog to a bladder of beans. True, the material they have is very limited, but they drive at it might and main. He invaded Canada without resistance, and he outvaded it without pursuit. As he did both under orders, I suppose there was to him neither credit nor discredit in them; but they constitute a large part of the tail. He was not at Hull's surrender, but he was close by; he was volunteer aid to General Harrison on the day of the battle of the Thames; and as you said in 1840 Harrison was picking huckleberries two miles off while the battle was fought, I suppose it is a just conclusion with you to say Cass was aiding Harrison to pick huckleberries. This is about all, except the mooted question of the broken sword. Some authors say he broke it, some say he threw it away, and some others, who ought to know, say nothing about it. Perhaps it would be a fair historical compromise to say, if he did not break it, he did not do anything else with it.
By the way, Mr. Speaker, did you know I am a military hero? Yes, sir; in the days of the Black Hawk war I fought, bled, and came away. Speaking of General Cass's career reminds me of my own. I was not at Stiliman's defeat, but I was about as near it as Cass was to Hull's surrender; and, like him, I saw the place very soon afterward. It is quite certain I did not break my sword, for I had none to break; but I bent a musket pretty badly on one occasion. If Cass broke his sword, the idea is he broke it in desperation; I bent the musket by accident. If General Cass went in advance of me in picking huckleberries, I guess I surpassed him in charges upon the wild onions. If he saw any live, fighting Indians, it was more than I did; but I had a good many bloody struggles with the mosquitoes, and although I never fainted from the loss of blood, I can truly say I was often very hungry. Mr. Speaker, if I should ever conclude to doff whatever our Democratic friends may suppose there is of black-cockade federalism about me, and therefore they shall take me up as their candidate for the Presidency, I protest they shall not make fun of me, as they have of General Cass, by attempting to write me into a military hero.
While I have General Cass in hand, I wish to say a word about his political principles. As a specimen, I take the record of his progress in the Wilmot Proviso. In the Washington Union of March 2, 1847, there is a report of a speech of General Cass, made the day before in the Senate, on the Wilmot Proviso, during the delivery of which Mr. Miller of New Jersey is reported to have interrupted him as follows, to wit:
"Mr. Miller expressed his great surprise at the change in the sentiments of the Senator from Michigan, who had been regarded as the great champion of freedom in the Northwest, of which he was a distinguished ornament. Last year the Senator from Michigan was understood to be decidedly in favor of the Wilmot Proviso; and as no reason had been stated for the change, he [Mr. Miller] could not refrain from the expression of his extreme surprise."
To this General Cass is reported to have replied as follows, to wit:
"Mr. Cass said that the course of the Senator from New Jersey was most extraordinary. Last year he [Mr. Cass] should have voted for the proposition, had it come up. But circumstances had altogether changed. The honorable Senator then read several passages from the remarks, as given above, which he had committed to writing, in order to refute such a charge as that of the Senator from New Jersey."
In the "remarks above reduced to writing" is one numbered four, as follows, to wit:
"Fourth. Legislation now would be wholly inoperative, because no territory hereafter to be acquired can be governed without an act of Congress providing for its government; and such an act, on its passage, would open the whole subject, and leave the Congress called on to pass it free to exercise its own discretion, entirely uncontrolled by any declaration found on the statute-book."
In Niles's Register, vol. lxxiii., p. 293, there is a letter of General Cass to ——— Nicholson, of Nashville, Tennessee, dated December 24, 1847, from which the following are correct extracts:
"The Wilmot Proviso has been before the country some time. It has been repeatedly discussed in Congress and by the public press. I am strongly impressed with the opinion that a great change has been going on in the public mind upon this subject,—in my own as well as others',—and that doubts are resolving themselves into convictions that the principle it involves should be kept out of the national legislature, and left to the people of the confederacy in their respective local governments.... Briefly, then, I am opposed to the exercise of any jurisdiction by Congress over this matter; and I am in favor of leaving the people of any territory which may be hereafter acquired the right to regulate it themselves, under the general principles of the Constitution. Because—'First. I do not see in the Constitution any grant of the requisite power to Congress; and I am not disposed to extend a doubtful precedent beyond its necessity,—the establishment of territorial governments when needed,—leaving to the inhabitants all the right compatible with the relations they bear to the confederation."
These extracts show that in 1846 General Cass was for the proviso at once; that in March, 1847, he was still for it, but not just then; and that in December, 1847, he was against it altogether. This is a true index to the whole man. When the question was raised in 1846, he was in a blustering hurry to take ground for it. He sought to be in advance, and to avoid the uninteresting position of a mere follower; but soon he began to see glimpses of the great Democratic ox-goad waving in his face, and to hear indistinctly a voice saying, "Back! Back, sir! Back a little!" He shakes his head, and bats his eyes, and blunders back to his position of March, 1847; but still the goad waves, and the voice grows more distinct and sharper still, "Back, sir! Back, I say! Further back!"—and back he goes to the position of December, 1847, at which the goad is still, and the voice soothingly says, "So! Stand at that!"
Have no fears, gentlemen, of your candidate. He exactly suits you, and we congratulate you upon it. However much you may be distressed about our candidate, you have all cause to be contented and happy with your own. If elected, he may not maintain all or even any of his positions previously taken; but he will be sure to do whatever the party exigency for the time being may require; and that is precisely what you want. He and Van Buren are the same "manner of men"; and, like Van Buren, he will never desert you till you first desert him.
Mr. Speaker, I adopt the suggestion of a friend, that General Cass is a general of splendidly successful charges—charges, to be sure, not upon the public enemy, but upon the public treasury. He was Governor of Michigan territory, and ex-officio Superintendent of Indian Affairs, from the 9th of October, 1813, till the 31st of July, 1831—a period of seventeen years, nine months, and twenty-two days. During this period he received from the United States treasury, for personal services and personal expenses, the aggregate sum of ninety-six thousand and twenty eight dollars, being an average of fourteen dollars and seventy-nine cents per day for every day of the time. This large sum was reached by assuming that he was doing service at several different places, and in several different capacities in the same place, all at the same time. By a correct analysis of his accounts during that period, the following propositions may be deduced:
First. He was paid in three different capacities during the whole of the time: that is to say—(1) As governor a salary at the rate per year of $2000. (2) As estimated for office rent, clerk hire, fuel, etc., in superintendence of Indian affairs in Michigan, at the rate per year of $1500. (3) As compensation and expenses for various miscellaneous items of Indian service out of Michigan, an average per year of $625.
Second. During part of the time—that is, from the 9th of October, 1813, to the 29th of May, 1822 he was paid in four different capacities; that is to say, the three as above, and, in addition thereto, the commutation of ten rations per day, amounting per year to $730.
Third. During another part of the time—that is, from the beginning of 1822 to the 31st of July, '83 he was also paid in four different capacities; that is to say, the first three, as above (the rations being dropped after the 29th of May, 1822), and, in addition thereto, for superintending Indian Agencies at Piqua, Ohio; Fort Wayne, Indiana; and Chicago, Illinois, at the rate per year of $1500. It should be observed here that the last item, commencing at the beginning of 1822, and the item of rations, ending on the 29th of May, 1822, lap on each other during so much of the time as lies between those two dates.
Fourth. Still another part of the time—that is, from the 31st of October, 1821, to the 29th of May, 1822—he was paid in six different capacities; that is to say, the three first, as above; the item of rations, as above; and, in addition thereto, another item of ten rations per day while at Washington settling his accounts, being at the rate per year of $730; and also an allowance for expenses traveling to and from Washington, and while there, of $1022, being at the rate per year of $1793.
Fifth. And yet during the little portion of the time which lies between the 1st of January, 1822, and the 29th of May, 1822, he was paid in seven different capacities; that is to say, the six last mentioned, and also, at the rate of $1500 per year, for the Piqua, Fort Wayne, and Chicago service, as mentioned above.
These accounts have already been discussed some here; but when we are amongst them, as when we are in the Patent Office, we must peep about a good deal before we can see all the curiosities. I shall not be tedious with them. As to the large item of $1500 per year—amounting in the aggregate to $26,715 for office rent, clerk hire, fuel, etc., I barely wish to remark that, so far as I can discover in the public documents, there is no evidence, by word or inference, either from any disinterested witness or of General Cass himself, that he ever rented or kept a separate office, ever hired or kept a clerk, or even used any extra amount of fuel, etc., in consequence of his Indian services. Indeed, General Cass's entire silence in regard to these items, in his two long letters urging his claims upon the government, is, to my mind, almost conclusive that no such claims had any real existence.
But I have introduced General Cass's accounts here chiefly to show the wonderful physical capacities of the man. They show that he not only did the labor of several men at the same time, but that he often did it at several places, many hundreds of miles apart, at the same time. And at eating, too, his capacities are shown to be quite as wonderful. From October, 1821, to May, 1822, he eat ten rations a day in Michigan, ten rations a day here in Washington, and near five dollars' worth a day on the road between the two places! And then there is an important discovery in his example—the art of being paid for what one eats, instead of having to pay for it. Hereafter if any nice young man should owe a bill which he cannot pay in any other way, he can just board it out. Mr. Speaker, we have all heard of the animal standing in doubt between two stacks of hay and starving to death. The like of that would never happen to General Cass. Place the stacks a thousand miles apart, he would stand stock-still midway between them, and eat them both at once, and the green grass along the line would be apt to suffer some, too, at the same time. By all means make him President, gentlemen. He will feed you bounteously—if—if there is any left after he shall have helped himself.
But, as General Taylor is, par excellence, the hero of the Mexican War, and as you Democrats say we Whigs have always opposed the war, you think it must be very awkward and embarrassing for us to go for General Taylor. The declaration that we have always opposed the war is true or false, according as one may understand the term "oppose the war." If to say "the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President" by opposing the war, then the Whigs have very generally opposed it. Whenever they have spoken at all, they have said this; and they have said it on what has appeared good reason to them. The marching an army into the midst of a peaceful Mexican settlement, frightening the inhabitants away, leaving their growing crops and other property to destruction, to you may appear a perfectly amiable, peaceful, unprovoking procedure; but it does not appear so to us. So to call such an act, to us appears no other than a naked, impudent absurdity, and we speak of it accordingly. But if, when the war had begun, and had become the cause of the country, the giving of our money and our blood, in common with yours, was support of the war, then it is not true that we have always opposed the war. With few individual exceptions, you have constantly had our votes here for all the necessary supplies. And, more than this, you have had the services, the blood, and the lives of our political brethren in every trial and on every field. The beardless boy and the mature man, the humble and the distinguished—you have had them. Through suffering and death, by disease and in battle they have endured and fought and fell with you. Clay and Webster each gave a son, never to be returned. From the State of my own residence, besides other worthy but less known Whig names, we sent Marshall, Morrison, Baker, and Hardin; they all fought, and one fell, and in the fall of that one we lost our best Whig man. Nor were the Whigs few in number, or laggard in the day of danger. In that fearful, bloody, breathless struggle at Buena Vista, where each man's hard task was to beat back five foes or die himself, of the five high officers who perished, four were Whigs.
In speaking of this, I mean no odious comparison between the lion-hearted Whigs and the Democrats who fought there. On other occasions, and among the lower officers and privates on that occasion, I doubt not the proportion was different. I wish to do justice to all. I think of all those brave men as Americans, in whose proud fame, as an American, I too have a share. Many of them, Whigs and Democrats are my constituents and personal friends; and I thank them,—more than thank them,—one and all, for the high imperishable honor they have conferred on our common State.
But the distinction between the cause of the President in beginning the war, and the cause of the country after it was begun, is a distinction which you cannot perceive. To you the President and the country seem to be all one. You are interested to see no distinction between them; and I venture to suggest that probably your interest blinds you a little. We see the distinction, as we think, clearly enough; and our friends who have fought in the war have no difficulty in seeing it also. What those who have fallen would say, were they alive and here, of course we can never know; but with those who have returned there is no difficulty. Colonel Haskell and Major Gaines, members here, both fought in the war, and both of them underwent extraordinary perils and hardships; still they, like all other Whigs here, vote, on the record, that the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President. And even General Taylor himself, the noblest Roman of them all, has declared that as a citizen, and particularly as a soldier, it is sufficient for him to know that his country is at war with a foreign nation, to do all in his power to bring it to a speedy and honorable termination by the most vigorous and energetic operations, without inquiry about its justice, or anything else connected with it.
Mr. Speaker, let our Democratic friends be comforted with the assurance that we are content with our position, content with our company, and content with our candidate; and that although they, in their generous sympathy, think we ought to be miserable, we really are not, and that they may dismiss the great anxiety they have on our account.
Mr. Speaker, I see I have but three minutes left, and this forces me to throw out one whole branch of my subject. A single word on still another. The Democrats are keen enough to frequently remind us that we have some dissensions in our ranks. Our good friend from Baltimore immediately before me [Mr. McLane] expressed some doubt the other day as to which branch of our party General Taylor would ultimately fall into the hands of. That was a new idea to me. I knew we had dissenters, but I did not know they were trying to get our candidate away from us. I would like to say a word to our dissenters, but I have not the time. Some such we certainly have; have you none, gentlemen Democrats? Is it all union and harmony in your ranks? no bickerings? no divisions? If there be doubt as to which of our divisions will get our candidate, is there no doubt as to which of your candidates will get your party? I have heard some things from New York; and if they are true, one might well say of your party there, as a drunken fellow once said when he heard the reading of an indictment for hog-stealing. The clerk read on till he got to and through the words, "did steal, take, and carry away ten boars, ten sows, ten shoats, and ten pigs," at which he exclaimed, "Well, by golly, that is the most equally divided gang of hogs I ever did hear of!" If there is any other gang of hogs more equally divided than the Democrats of New York are about this time, I have not heard of it.
Mr. Kellogg then introduced to the meeting the Hon. Abram Lincoln, Whig member of Congress from Illinois, a representative of free soil.
Mr. Lincoln has a very tall and thin figure, with an intellectual face, showing a searching mind, and a cool judgment. He spoke in a clear and cool and very eloquent manner, for an hour and a half, carrying the audience with him in his able arguments and brilliant illustrations—only interrupted by warm and frequent applause. He began by expressing a real feeling of modesty in addressing an audience "this side of the mountains," a part of the country where, in the opinion of the people of his section, everybody was supposed to be instructed and wise. But he had devoted his attention to the question of the coming Presidential election, and was not unwilling to exchange with all whom he might the ideas to which he had arrived. He then began to show the fallacy of some of the arguments against Gen. Taylor, making his chief theme the fashionable statement of all those who oppose him ("the old Locofocos as well as the new") that he has no principles, and that the Whig party have abandoned their principles by adopting him as their candidate. He maintained that Gen. Taylor occupied a high and unexceptionable Whig ground, and took for his first instance and proof of this the statement in the Allison letter—with regard to the bank, tariff, rivers and harbors, etc.—that the will of the people should produce its own results, without executive influence. The principle that the people should do what—under the Constitution—as they please, is a Whig principle. All that Gen. Taylor is not only to consent to, but appeal to the people to judge and act for themselves. And this was no new doctrine for Whigs. It was the "platform" on which they had fought all their battles, the resistance of executive influence, and the principle of enabling the people to frame the government according to their will. Gen. Taylor consents to be the candidate, and to assist the people to do what they think to be their duty, and think to be best in their national affairs, but because he don't want to tell what we ought to do, he is accused of having no principles. The Whigs here maintained for years that neither the influence, the duress, or the prohibition of the executive should control the legitimately expressed will of the people; and now that, on that very ground, Gen. Taylor says that he should use the power given him by the people to do, to the best of his judgment, the will of the people, he is accused of want of principle, and of inconsistency in position.
Mr. Lincoln proceeded to examine the absurdity of an attempt to make a platform or creed for a national party, to all parts of which all must consent and agree, when it was clearly the intention and the true philosophy of our government, that in Congress all opinions and principles should be represented, and that when the wisdom of all had been compared and united, the will of the majority should be carried out. On this ground he conceived (and the audience seemed to go with him) that Gen. Taylor held correct, sound republican principles.
Mr. Lincoln then passed to the subject of slavery in the States, saying that the people of Illinois agreed entirely with the people of Massachusetts on this subject, except perhaps that they did not keep so constantly thinking about it. All agreed that slavery was an evil, but that we were not responsible for it and cannot affect it in States of this Union where we do not live. But the question of the extension of slavery to new territories of this country is a part of our responsibility and care, and is under our control. In opposition to this Mr. L. believed that the self-named "Free Soil" party was far behind the Whigs. Both parties opposed the extension. As he understood it the new party had no principle except this opposition. If their platform held any other, it was in such a general way that it was like the pair of pantaloons the Yankee pedlar offered for sale, "large enough for any man, small enough for any boy." They therefore had taken a position calculated to break down their single important declared object. They were working for the election of either Gen. Cass or Gen. Taylor. The speaker then went on to show, clearly and eloquently, the danger of extension of slavery, likely to result from the election of Gen. Cass. To unite with those who annexed the new territory to prevent the extension of slavery in that territory seemed to him to be in the highest degree absurd and ridiculous. Suppose these gentlemen succeed in electing Mr. Van Buren, they had no specific means to prevent the extension of slavery to New Mexico and California, and Gen. Taylor, he confidently believed, would not encourage it, and would not prohibit its restriction. But if Gen. Cass was elected, he felt certain that the plans of farther extension of territory would be encouraged, and those of the extension of slavery would meet no check. The "Free Soil" mart in claiming that name indirectly attempts a deception, by implying that Whigs were not Free Soil men. Declaring that they would "do their duty and leave the consequences to God" merely gave an excuse for taking a course they were not able to maintain by a fair and full argument. To make this declaration did not show what their duty was. If it did we should have no use for judgment, we might as well be made without intellect; and when divine or human law does not clearly point out what is our duty, we have no means of finding out what it is but by using our most intelligent judgment of the consequences. If there were divine law or human law for voting for Martin Van Buren, or if a fair examination of the consequences and just reasoning would show that voting for him would bring about the ends they pretended to wish—then he would give up the argument. But since there was no fixed law on the subject, and since the whole probable result of their action would be an assistance in electing Gen. Cass, he must say that they were behind the Whigs in their advocacy of the freedom of the soil.
Mr. Lincoln proceeded to rally the Buffalo convention for forbearing to say anything—after all the previous declarations of those members who were formerly Whigs—on the subject of the Mexican War, because the Van Burens had been known to have supported it. He declared that of all the parties asking the confidence of the country, this new one had less of principle than any other.
He wondered whether it was still the opinion of these Free Soil gentlemen, as declared in the "whereas" at Buffalo, that the Whig and Democratic parties were both entirely dissolved and absorbed into their own body. Had the Vermont election given them any light? They had calculated on making as great an impression in that State as in any part of the Union, and there their attempts had been wholly ineffectual. Their failure was a greater success than they would find in any other part of the Union.
Mr. Lincoln went on to say that he honestly believed that all those who wished to keep up the character of the Union; who did not believe in enlarging our field, but in keeping our fences where they are and cultivating our present possessions, making it a garden, improving the morals and education of the people, devoting the administrations to this purpose; all real Whigs, friends of good honest government—the race was ours. He had opportunities of hearing from almost every part of the Union from reliable sources and had not heard of a county in which we had not received accessions from other parties. If the true Whigs come forward and join these new friends, they need not have a doubt. We had a candidate whose personal character and principles he had already described, whom he could not eulogize if he would. Gen. Taylor had been constantly, perseveringly, quietly standing up, doing his duty and asking no praise or reward for it. He was and must be just the man to whom the interests, principles, and prosperity of the country might be safely intrusted. He had never failed in anything he had undertaken, although many of his duties had been considered almost impossible.
Mr. Lincoln then went into a terse though rapid review of the origin of the Mexican War and the connection of the administration and General Taylor with it, from which he deduced a strong appeal to the Whigs present to do their duty in the support of General Taylor, and closed with the warmest aspirations for and confidence in a deserved success.
At the close of his truly masterly and convincing speech, the audience gave three enthusiastic cheers for Illinois, and three more for the eloquent Whig member from the State.
WASHINGTON, Dec. 24, 1848.
MY DEAR FATHER:—Your letter of the 7th was received night before last. I very cheerfully send you the twenty dollars, which sum you say is necessary to save your land from sale. It is singular that you should have forgotten a judgment against you; and it is more singular that the plaintiff should have let you forget it so long; particularly as I suppose you always had property enough to satisfy a judgment of that amount. Before you pay it, it would be well to be sure you have not paid, or at least, that you cannot prove you have paid it.
Give my love to mother and all the connections. Affectionately your son,
Resolved, That the Committee on the District of Columbia be instructed to report a bill in substance as follows:
Sec. 1. Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States, in Congress assembled, That no person not now within the District of Columbia, nor now owned by any person or persons now resident within it, nor hereafter born within it, shall ever be held in slavery within said District.
Sec. 2. That no person now within said District, or now owned by any person or persons now resident within the same, or hereafter born within it, shall ever be held in slavery without the limits of said District: Provided, That officers of the Government of the United States, being citizens of the slaveholding States, coming into said District on public business, and remaining only so long as may be reasonably necessary for that object, may be attended into and out of said District, and while there, by the necessary servants of themselves and their families, without their right to hold such servants in service being thereby impaired.
Sec. 3. That all children born of slave mothers within said District, on or after the first day of January, in the year of our Lord eighteen hundred and fifty, shall be free; but shall be reasonably supported and educated by the respective owners of their mothers, or by their heirs or representatives, and shall owe reasonable service as apprentices to such owners, heirs, or representatives, until they respectively arrive at the age of __ years, when they shall be entirely free; and the municipal authorities of Washington and Georgetown, within their respective jurisdictional limits, are hereby empowered and required to make all suitable and necessary provision for enforcing obedience to this section, on the part of both masters and apprentices.
Sec. 4. That all persons now within this District, lawfully held as slaves, or now owned by any person or persons now resident within said District, shall remain such at the will of their respective owners, their heirs, and legal representatives: Provided, That such owner, or his legal representative, may at any time receive from the Treasury of the United States the full value of his or her slave, of the class in this section mentioned, upon which such slave shall be forthwith and forever free: And provided further, That the President of the United States, the Secretary of State, and the Secretary of the Treasury shall be a board for determining the value of such slaves as their owners may desire to emancipate under this section, and whose duty it shall be to hold a session for the purpose on the first Monday of each calendar month, to receive all applications, and, on satisfactory evidence in each case that the person presented for valuation is a slave, and of the class in this section mentioned, and is owned by the applicant, shall value such slave at his or her full cash value, and give to the applicant an order on the Treasury for the amount, and also to such slave a certificate of freedom.
Sec. 5. That the municipal authorities of Washington and Georgetown, within their respective jurisdictional limits, are hereby empowered and required to provide active and efficient means to arrest and deliver up to their owners all fugitive slaves escaping into said District.
Sec. 6. That the election officers within said District of Columbia are hereby empowered and required to open polls, at all the usual places of holding elections, on the first Monday of April next, and receive the vote of every free white male citizen above the age of twenty-one years, having resided within said District for the period of one year or more next preceding the time of such voting for or against this act, to proceed in taking said votes, in all respects not herein specified, as at elections under the municipal laws, and with as little delay as possible to transmit correct statements of the votes so cast to the President of the United States; and it shall be the duty of the President to canvass said votes immediately, and if a majority of them be found to be for this act, to forthwith issue his proclamation giving notice of the fact; and this act shall only be in full force and effect on and after the day of such proclamation.
Sec. 7. That involuntary servitude for the punishment of crime, whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall in no wise be prohibited by this act.
Sec. 8. That for all the purposes of this act, the jurisdictional limits of Washington are extended to all parts of the District of Columbia not now included within the present limits of Georgetown.
Mr. Lincoln said he had not risen for the purpose of making a speech, but only for the purpose of meeting some of the objections to the bill. If he understood those objections, the first was that if the bill were to become a law, it would be used to lock large portions of the public lands from sale, without at last effecting the ostensible object of the bill—the construction of railroads in the new States; and secondly, that Congress would be forced to the abandonment of large portions of the public lands to the States for which they might be reserved, without their paying for them. This he understood to be the substance of the objections of the gentleman from Ohio to the passage of the bill.
If he could get the attention of the House for a few minutes, he would ask gentlemen to tell us what motive could induce any State Legislature, or individual, or company of individuals, of the new States, to expend money in surveying roads which they might know they could not make.
(A voice: They are not required to make the road.)
Mr. Lincoln continued: That was not the case he was making. What motive would tempt any set of men to go into an extensive survey of a railroad which they did not intend to make? What good would it do? Did men act without motive? Did business men commonly go into an expenditure of money which could be of no account to them? He generally found that men who have money were disposed to hold on to it, unless they could see something to be made by its investment. He could not see what motive of advantage to the new States could be subserved by merely keeping the public lands out of market, and preventing their settlement. As far as he could see, the new States were wholly without any motive to do such a thing. This, then, he took to be a good answer to the first objection.
In relation to the fact assumed, that after a while, the new States having got hold of the public lands to a certain extent, they would turn round and compel Congress to relinquish all claim to them, he had a word to say, by way of recurring to the history of the past. When was the time to come (he asked) when the States in which the public lands were situated would compose a majority of the representation in Congress, or anything like it? A majority of Representatives would very soon reside west of the mountains, he admitted; but would they all come from States in which the public lands were situated? They certainly would not; for, as these Western States grew strong in Congress, the public lands passed away from them, and they got on the other side of the question; and the gentleman from Ohio [Mr. Vinton] was an example attesting that fact.
Mr. Vinton interrupted here to say that he had stood on this question just where he was now, for five and twenty years.
Mr. Lincoln was not making an argument for the purpose of convicting the gentleman of any impropriety at all. He was speaking of a fact in history, of which his State was an example. He was referring to a plain principle in the nature of things. The State of Ohio had now grown to be a giant. She had a large delegation on that floor; but was she now in favor of granting lands to the new States, as she used to be? The New England States, New York, and the Old Thirteen were all rather quiet upon the subject; and it was seen just now that a member from one of the new States was the first man to rise up in opposition. And such would be with the history of this question for the future. There never would come a time when the people residing in the States embracing the public lands would have the entire control of this subject; and so it was a matter of certainty that Congress would never do more in this respect than what would be dictated by a just liberality. The apprehension, therefore, that the public lands were in danger of being wrested from the General Government by the strength of the delegation in Congress from the new States, was utterly futile. There never could be such a thing. If we take these lands (said he) it will not be without your consent. We can never outnumber you. The result is that all fear of the new States turning against the right of Congress to the public domain must be effectually quelled, as those who are opposed to that interest must always hold a vast majority here, and they will never surrender the whole or any part of the public lands unless they themselves choose to do so. That was all he desired to say.
WASHINGTON, March 9, 1849.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
DEAR SIR: Colonel R. D. Baker and myself are the only Whig members of Congress from Illinois of the Thirtieth, and he of the Thirty-first. We have reason to think the Whigs of that State hold us responsible, to some extent, for the appointments which may be made of our citizens. We do not know you personally, and our efforts to you have so far been unavailing. I therefore hope I am not obtrusive in saying in this way, for him and myself, that when a citizen of Illinois is to be appointed in your department, to an office either in or out of the State, we most respectfully ask to be heard.
Your obedient servant,
WASHINGTON, March 10, 1849.
HON. SECRETARY OF STATE.
SIR:—There are several applicants for the office of United States Marshal for the District of Illinois. Among the most prominent of them are Benjamin Bond, Esq., of Carlyle, and Thomas, Esq., of Galena. Mr. Bond I know to be personally every way worthy of the office; and he is very numerously and most respectably recommended. His papers I send to you; and I solicit for his claims a full and fair consideration.
Having said this much, I add that in my individual judgment the appointment of Mr. Thomas would be the better.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
(Indorsed on Mr. Bond's papers.)
In this and the accompanying envelope are the recommendations of about two hundred good citizens of all parts of Illinois, that Benjamin Bond be appointed marshal for that district. They include the names of nearly all our Whigs who now are, or have ever been, members of the State Legislature, besides forty-six of the Democratic members of the present Legislature, and many other good citizens. I add that from personal knowledge I consider Mr. Bond every way worthy of the office, and qualified to fill it. Holding the individual opinion that the appointment of a different gentleman would be better, I ask especial attention and consideration for his claims, and for the opinions expressed in his favor by those over whom I can claim no superiority.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE HOME DEPARTMENT.
DEAR SIR:—I recommend that Walter Davis be appointed receiver of the land-office at this place, whenever there shall be a vacancy. I cannot say that Mr. Herndon, the present incumbent, has failed in the proper discharge of any of the duties of the office. He is a very warm partisan, and openly and actively opposed to the election of General Taylor. I also understand that since General Taylor's election he has received a reappointment from Mr. Polk, his old commission not having expired. Whether this is true the records of the department will show. I may add that the Whigs here almost universally desire his removal.
I give no opinion of my own, but state the facts, and express the hope that the department will act in this as in all other cases on some proper general rule.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—The land district to which this office belongs is very nearly if not entirely within my district; so that Colonel Baker, the other Whig representative, claims no voice in the appointment. A. L.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE HOME DEPARTMENT.
DEAR SIR:—I recommend that Turner R. King, now of Pekin, Illinois, be appointed register of the land-office at this place whenever there shall be a vacancy.
I do not know that Mr. Barret, the present incumbent, has failed in the proper discharge of any of his duties in the office. He is a decided partisan, and openly and actively opposed the election of General Taylor. I understand, too, that since the election of General Taylor, Mr. Barret has received a reappointment from Mr. Polk, his old commission not having expired. Whether this be true, the records of the department will show.
Whether he should be removed I give no opinion, but merely express the wish that the department may act upon some proper general rule, and that Mr. Barret's case may not be made an exception to it.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.-The land district to which this office belongs is very nearly if not entirely within my district; so that Colonel Baker, the other Whig representative, claims no voice in the appointment. A. L.
HON. POSTMASTER-GENERAL.
DEAR Sir:—I recommend that Abner Y. Ellis be appointed postmaster at this place, whenever there shall be a vacancy. J. R. Diller, the present incumbent, I cannot say has failed in the proper discharge of any of the duties of the office. He, however, has been an active partisan in opposition to us.
Located at the seat of government of the State, he has been, for part if not the whole of the time he has held the office, a member of the Democratic State Central Committee, signing his name to their addresses and manifestoes; and has been, as I understand, reappointed by Mr. Polk since General Taylor's election. These are the facts of the case as I understand them, and I give no opinion of mine as to whether he should or should not be removed. My wish is that the department may adopt some proper general rule for such cases, and that Mr. Diller may not be made an exception to it, one way or the other.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—This office, with its delivery, is entirely within my district; so that Colonel Baker, the other Whig representative, claims no voice in the appointment.L.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE HOME DEPARTMENT.
DEAR SIR:—I recommend that William Butler be appointed pension agent for the Illinois agency, when the place shall be vacant. Mr. Hurst, the present incumbent, I believe has performed the duties very well. He is a decided partisan, and I believe expects to be removed. Whether he shall, I submit to the department. This office is not confined to my district, but pertains to the whole State; so that Colonel Baker has an equal right with myself to be heard concerning it. However, the office is located here; and I think it is not probable that any one would desire to remove from a distance to take it.
Your obedient servant,
DEAR THOMPSON: A tirade is still kept up against me here for recommending T. R. King. This morning it is openly avowed that my supposed influence at Washington shall be broken down generally, and King's prospects defeated in particular. Now, what I have done in this matter I have done at the request of you and some other friends in Tazewell; and I therefore ask you to either admit it is wrong or come forward and sustain me. If the truth will permit, I propose that you sustain me in the following manner: copy the inclosed scrap in your own handwriting and get everybody (not three or four, but three or four hundred) to sign it, and then send it to me. Also, have six, eight or ten of our best known Whig friends there write to me individual letters, stating the truth in this matter as they understand it. Don't neglect or delay in the matter. I understand information of an indictment having been found against him about three years ago, for gaming or keeping a gaming house, has been sent to the department. I shall try to take care of it at the department till your action can be had and forwarded on.
Yours as ever,
HON. SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
DEAR SIR:—I regret troubling you so often in relation to the land-offices here, but I hope you will perceive the necessity of it, and excuse me. On the 7th of April I wrote you recommending Turner R. King for register, and Walter Davis for receiver. Subsequently I wrote you that, for a private reason, I had concluded to transpose them. That private reason was the request of an old personal friend who himself desired to be receiver, but whom I felt it my duty to refuse a recommendation. He said if I would transpose King and Davis he would be satisfied. I thought it a whim, but, anxious to oblige him, I consented. Immediately he commenced an assault upon King's character, intending, as I suppose, to defeat his appointment, and thereby secure another chance for himself. This double offence of bad faith to me and slander upon a good man is so totally outrageous that I now ask to have King and Davis placed as I originally recommended,—that is, King for register and Davis for receiver.
An effort is being made now to have Mr. Barret, the present register, retained. I have already said he has done the duties of the office well, and I now add he is a gentleman in the true sense. Still, he submits to be the instrument of his party to injure us. His high character enables him to do it more effectually. Last year he presided at the convention which nominated the Democratic candidate for Congress in this district, and afterward ran for the State Senate himself, not desiring the seat, but avowedly to aid and strengthen his party. He made speech after speech with a degree of fierceness and coarseness against General Taylor not quite consistent with his habitually gentlemanly deportment. At least one (and I think more) of those who are now trying to have him retained was himself an applicant for this very office, and, failing to get my recommendation, now takes this turn.
In writing you a third time in relation to these offices, I stated that I supposed charges had been forwarded to you against King, and that I would inquire into the truth of them. I now send you herewith what I suppose will be an ample defense against any such charges. I ask attention to all the papers, but particularly to the letters of Mr. David Mack, and the paper with the long list of names. There is no mistake about King's being a good man. After the unjust assault upon him, and considering the just claims of Tazewell County, as indicated in the letters I inclose you, it would in my opinion be injustice, and withal a blunder, not to appoint him, at least as soon as any one is appointed to either of the offices here.
Your obedient servant,
DEAR GILLESPIE:
Butterfield will be commissioner of the Gen'l Land Office, unless prevented by strong and speedy efforts. Ewing is for him, and he is only not appointed yet because Old Zach. hangs fire.
I have reliable information of this. Now, if you agree with me that this appointment would dissatisfy rather than gratify the Whigs of this State, that it would slacken their energies in future contests, that his appointment in '41 is an old sore with them which they will not patiently have reopened,—in a word that his appointment now would be a fatal blunder to the administration and our political men here in Illinois, write Crittenden to that effect. He can control the matter. Were you to write Ewing I fear the President would never hear of your letter. This may be mere suspicion. You might write directly to Old Zach. You will be the best judge of the propriety of that. Not a moment's time is to be lost.
Let this be confidential except with Mr. Edwards and a few others whom you know I would trust just as I do you.
Yours as ever,
[Confidential]
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, May 25, 1849.
HON. E. EMBREE
DEAR SIR:—I am about to ask a favor of you, one which I hope will not cost you much. I understand the General Land-Office is about to be given to Illinois, and that Mr. Ewing desires Justin Butterfield, of Chicago, to be the man. I give you my word, the appointment of Mr. Butterfield will be an egregious political blunder. It will give offence to the whole Whig party here, and be worse than a dead loss to the administration of so much of its patronage. Now, if you can conscientiously do so, I wish you to write General Taylor at once, saying that either I or the man I recommend should in your opinion be appointed to that office, if any one from Illinois shall be. I restrict my request to Illinois because you may have a man from your own State, and I do not ask to interfere with that.
Your friend as ever,
Application for Patent:
What I claim as my invention, and desire to secure by letters patent, is the combination of expansible buoyant chambers placed at the sides of a vessel with the main shaft or shafts by means of the sliding spars, which pass down through the buoyant chambers and are made fast to their bottoms and the series of ropes and pulleys or their equivalents in such a manner that by turning the main shaft or shafts in one direction the buoyant chambers will be forced downward into the water, and at the same time expanded and filled with air for buoying up the vessel by the displacement of water, and by turning the shafts in an opposite direction the buoyant chambers will be contracted into a small space and secured against injury.
HON. SECRETARY OF INTERIOR.
DEAR SIR:—Vandalia, the receiver's office at which place is the subject of the within, is not in my district; and I have been much perplexed to express any preference between Dr. Stapp and Mr. Remann. If any one man is better qualified for such an office than all others, Dr. Stapp is that man; still, I believe a large majority of the Whigs of the district prefer Mr. Remann, who also is a good man. Perhaps the papers on file will enable you to judge better than I can. The writers of the within are good men, residing within the land district.
Your obt. servant,
DEAR WILLIAM:—Your two letters were received last night. I have a great many letters to write, and so cannot write very long ones. There must be some mistake about Walter Davis saying I promised him the post-office. I did not so promise him. I did tell him that if the distribution of the offices should fall into my hands, he should have something; and if I shall be convinced he has said any more than this, I shall be disappointed. I said this much to him because, as I understand, he is of good character, is one of the young men, is of the mechanics, and always faithful and never troublesome; a Whig, and is poor, with the support of a widow mother thrown almost exclusively on him by the death of his brother. If these are wrong reasons, then I have been wrong; but I have certainly not been selfish in it, because in my greatest need of friends he was against me, and for Baker.
Yours as ever,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S. Let the above be confidential.
Mr. Edwards is unquestionably offended with me in connection with the matter of the General Land-Office. He wrote a letter against me which was filed at the department.
The better part of one's life consists of his friendships; and, of them, mine with Mr. Edwards was one of the most cherished. I have not been false to it. At a word I could have had the office any time before the department was committed to Mr. Butterfield, at least Mr. Ewing and the President say as much. That word I forbore to speak, partly for other reasons, but chiefly for Mr. Edwards' sake, losing the office (that he might gain it) I was always for; but to lose his friendship, by the effort for him, would oppress me very much, were I not sustained by the utmost consciousness of rectitude. I first determined to be an applicant, unconditionally, on the 2nd of June; and I did so then upon being informed by a telegraphic despatch that the question was narrowed down to Mr. B and myself, and that the Cabinet had postponed the appointment three weeks, for my benefit. Not doubting that Mr. Edwards was wholly out of the question I, nevertheless, would not then have become an applicant had I supposed he would thereby be brought to suspect me of treachery to him. Two or three days afterwards a conversation with Levi Davis convinced me Mr. Edwards was dissatisfied; but I was then too far in to get out. His own letter, written on the 25th of April, after I had fully informed him of all that had passed, up to within a few days of that time, gave assurance I had that entire confidence from him which I felt my uniform and strong friendship for him entitled me to. Among other things it says, "Whatever course your judgment may dictate as proper to be pursued, shall never be excepted to by me." I also had had a letter from Washington, saying Chambers, of the Republic, had brought a rumor then, that Mr. E had declined in my favor, which rumor I judged came from Mr. E himself, as I had not then breathed of his letter to any living creature. In saying I had never, before the 2nd of June, determined to be an applicant, unconditionally, I mean to admit that, before then, I had said substantially I would take the office rather than it should be lost to the State, or given to one in the State whom the Whigs did not want; but I aver that in every instance in which I spoke of myself, I intended to keep, and now believe I did keep, Mr. E above myself. Mr. Edwards' first suspicion was that I had allowed Baker to overreach me, as his friend, in behalf of Don Morrison. I knew this was a mistake; and the result has proved it. I understand his view now is, that if I had gone to open war with Baker I could have ridden him down, and had the thing all my own way. I believe no such thing. With Baker and some strong man from the Military tract & elsewhere for Morrison, and we and some strong man from the Wabash & elsewhere for Mr. E, it was not possible for either to succeed. I believed this in March, and I know it now. The only thing which gave either any chance was the very thing Baker & I proposed,—an adjustment with themselves.
You may wish to know how Butterfield finally beat me. I can not tell you particulars now, but will when I see you. In the meantime let it be understood I am not greatly dissatisfied,—I wish the offer had been so bestowed as to encourage our friends in future contests, and I regret exceedingly Mr. Edwards' feelings towards me. These two things away, I should have no regrets,—at least I think I would not.
Write me soon.
Your friend, as ever,
At a meeting to express sympathy with the cause of Hungarian freedom, Dr. Todd, Thos. Lewis, Hon. A. Lincoln, and Wm. Carpenter were appointed a committee to present appropriate resolutions, which reported through Hon. A. Lincoln the following:
Resolved, That, in their present glorious struggle for liberty, the Hungarians command our highest admiration and have our warmest sympathy.
Resolved, That they have our most ardent prayers for their speedy triumph and final success.
Resolved, That the Government of the United States should acknowledge the independence of Hungary as a nation of freemen at the very earliest moment consistent with our amicable relations with the government against which they are contending.
Resolved, That, in the opinion of this meeting, the immediate acknowledgment of the independence of Hungary by our government is due from American freemen to their struggling brethren, to the general cause of republican liberty, and not violative of the just rights of any nation or people.
Dr. WILLIAM FITHIAN, Danville, Ill.
DEAR DOCTOR:—Your letter of the 9th was received a day or two ago. The notes and mortgages you enclosed me were duly received. I also got the original Blanchard mortgage from Antrim Campbell, with whom Blanchard had left it for you. I got a decree of foreclosure on the whole; but, owing to there being no redemption on the sale to be under the Blanchard mortgage, the court allowed Mobley till the first of March to pay the money, before advertising for sale. Stuart was empowered by Mobley to appear for him, and I had to take such decree as he would consent to, or none at all. I cast the matter about in my mind and concluded that as I could not get a decree we would put the accrued interest at interest, and thereby more than match the fact of throwing the Blanchard debt back from twelve to six per cent., it was better to do it. This is the present state of the case.
I can well enough understand and appreciate your suggestions about the Land-Office at Danville; but in my present condition, I can do nothing.
Yours, as ever,
DEAR SIR:—On my return from Kentucky I found your letter of the 7th of November, and have delayed answering it till now for the reason I now briefly state. From the beginning of our acquaintance I had felt the greatest kindness for you and had supposed it was reciprocated on your part. Last summer, under circumstances which I mentioned to you, I was painfully constrained to withhold a recommendation which you desired, and shortly afterwards I learned, in such a way as to believe it, that you were indulging in open abuse of me. Of course my feelings were wounded. On receiving your last letter the question occurred whether you were attempting to use me at the same time you would injure me, or whether you might not have been misrepresented to me. If the former, I ought not to answer you; if the latter, I ought, and so I have remained in suspense. I now enclose you the letter, which you may use if you see fit.
Yours, etc.,
Circuit and District Court of the U. S. in and for the State and District of Illinois. Monday, June 3, 1850.
On the opening of the Court this morning, the Hon. A. Lincoln, a member of the Bar of this Court, suggested the death of the Hon. Nathaniel Pope, late a judge of this Court, since the adjournment of the last term; whereupon, in token of respect for the memory of the deceased, it is ordered that the Court do now adjourn until to-morrow morning at ten o'clock.
The Hon. Stephen T. Logan, the Hon. Norman H. Purple, the Hon. David L. Gregg, the Hon. A. Lincoln, and George W. Meeker, Esq., were appointed a Committee to prepare resolutions.
Whereupon, the Hon. Stephen T. Logan, in behalf of the Committee, presented the following preamble and resolutions:
Whereas The Hon. Nathaniel Pope, District Judge of the United States Court for the District of Illinois, having departed this life during the last vacation of said Court, and the members of the Bar of said Court, entertaining the highest veneration for his memory, a profound respect for his ability, great experience, and learning as a judge, and cherishing for his many virtues, public and private, his earnest simplicity of character and unostentatious deportment, both in his public and private relations, the most lively and affectionate recollections, have
Resolved, That, as a manifestation of their deep sense of the loss which has been sustained in his death, they will wear the usual badge of mourning during the residue of the term.
Resolved, That the Chairman communicate to the family of the deceased a copy of these proceedings, with an assurance of our sincere condolence on account of their heavy bereavement.
Resolved, That the Hon. A. Williams, District Attorney of this Court, be requested in behalf of the meeting to present these proceedings to the Circuit Court, and respectfully to ask that they may be entered on the records.
E. N. POWELL, Sec'y. SAMUEL H. TREAT, Ch'n.
JULY 1, 1850
DISCOURAGE LITIGATION. Persuade your neighbors to compromise whenever you can. Point out to them how the nominal winner is often a real loser—in fees, expenses, and waste of time. As a peace-maker the lawyer has a superior opportunity of being a good man. There will still be business enough.
Never stir up litigation. A worse man can scarcely be found than one who does this. Who can be more nearly a fiend than he who habitually over-hauls the register of deeds in search of defects in titles, whereon to stir up strife, and put money in his pocket? A moral tone ought to be infused into the profession which should drive such men out of it.
The matter of fees is important, far beyond the mere question of bread and butter involved. Properly attended to, fuller justice is done to both lawyer and client. An exorbitant fee should never be claimed. As a general rule never take your whole fee in advance, nor any more than a small retainer. When fully paid beforehand, you are more than a common mortal if you can feel the same interest in the case as if something was still in prospect for you, as well as for your client. And when you lack interest in the case the job will very likely lack skill and diligence in the performance. Settle the amount of fee and take a note in advance. Then you will feel that you are working for something, and you are sure to do your work faithfully and well. Never sell a fee note—at least not before the consideration service is performed. It leads to negligence and dishonesty—negligence by losing interest in the case, and dishonesty in refusing to refund when you have allowed the consideration to fail.
This idea of a refund or reduction of charges from the lawyer in a failed case is a new one to me—but not a bad one.
DEAR JOHNSTON:—Your request for eighty dollars I do not think it best to comply with now. At the various times when I have helped you a little you have said to me, "We can get along very well now"; but in a very short time I find you in the same difficulty again. Now, this can only happen by some defect in your conduct. What that defect is, I think I know. You are not lazy, and still you are an idler. I doubt whether, since I saw you, you have done a good whole day's work in any one day. You do not very much dislike to work, and still you do not work much merely because it does not seem to you that you could get much for it. This habit of uselessly wasting time is the whole difficulty; it is vastly important to you, and still more so to your children, that you should break the habit. It is more important to them, because they have longer to live, and can keep out of an idle habit before they are in it, easier than they can get out after they are in.
You are now in need of some money; and what I propose is, that you shall go to work, "tooth and nail," for somebody who will give you money for it. Let father and your boys take charge of your things at home, prepare for a crop, and make the crop, and you go to work for the best money wages, or in discharge of any debt you owe, that you can get; and, to secure you a fair reward for your labor, I now promise you, that for every dollar you will, between this and the first of May, get for your own labor, either in money or as your own indebtedness, I will then give you one other dollar. By this, if you hire yourself at ten dollars a month, from me you will get ten more, making twenty dollars a month for your work. In this I do not mean you shall go off to St. Louis, or the lead mines, or the gold mines in California, but I mean for you to go at it for the best wages you can get close to home in Coles County. Now, if you will do this, you will be soon out of debt, and, what is better, you will have a habit that will keep you from getting in debt again. But, if I should now clear you out of debt, next year you would be just as deep in as ever. You say you would almost give your place in heaven for seventy or eighty dollars. Then you value your place in heaven very cheap, for I am sure you can, with the offer I make, get the seventy or eighty dollars for four or five months' work. You say if I will furnish you the money you will deed me the land, and, if you don't pay the money back, you will deliver possession. Nonsense! If you can't now live with the land, how will you then live without it? You have always been kind to me, and I do not mean to be unkind to you. On the contrary, if you will but follow my advice, you will find it worth more than eighty times eighty dollars to you.
Affectionately your brother,
C. HOYT, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—Our case is decided against us. The decision was announced this morning. Very sorry, but there is no help. The history of the case since it came here is this. On Friday morning last, Mr. Joy filed his papers, and entered his motion for a mandamus, and urged me to take up the motion as soon as possible. I already had the points and authority sent me by you and by Mr. Goodrich, but had not studied them. I began preparing as fast as possible.
The evening of the same day I was again urged to take up the case. I refused on the ground that I was not ready, and on which plea I also got off over Saturday. But on Monday (the 14th) I had to go into it. We occupied the whole day, I using the large part. I made every point and used every authority sent me by yourself and by Mr. Goodrich; and in addition all the points I could think of and all the authorities I could find myself. When I closed the argument on my part, a large package was handed me, which proved to be the plat you sent me.
The court received it of me, but it was not different from the plat already on the record. I do not think I could ever have argued the case better than I did. I did nothing else, but prepare to argue and argue this case, from Friday morning till Monday evening. Very sorry for the result; but I do not think it could have been prevented.
Your friend, as ever,
DEAR BROTHER:—On the day before yesterday I received a letter from Harriet, written at Greenup. She says she has just returned from your house, and that father is very low and will hardly recover. She also says you have written me two letters, and that, although you do not expect me to come now, you wonder that I do not write.
I received both your letters, and although I have not answered them it is not because I have forgotten them, or been uninterested about them, but because it appeared to me that I could write nothing which would do any good. You already know I desire that neither father nor mother shall be in want of any comfort, either in health or sickness, while they live; and I feel sure you have not failed to use my name, if necessary, to procure a doctor, or anything else for father in his present sickness. My business is such that I could hardly leave home now, if it was not as it is, that my own wife is sick abed. (It is a case of baby-sickness, and I suppose is not dangerous.) I sincerely hope father may recover his health, but at all events, tell him to remember to call upon and confide in our great and good and merciful Maker, who will not turn away from him in any extremity. He notes the fall of a sparrow, and numbers the hairs of our heads, and He will not forget the dying man who puts his trust in Him. Say to him that if we could meet now it is doubtful whether it would not be more painful than pleasant, but that if it be his lot to go now, he will soon have a joyous meeting with many loved ones gone before, and where the rest of us, through the help of God, hope ere long to join them.
Write to me again when you receive this.
Affectionately,
MAY 13, 1851. TO THE HONORABLE, THE JUDGE OF THE COUNTY COURT IN AND FOR THE COUNTY OF SANGAMON AND STATE OF ILLINOIS:
Your Petitioner, Joshua Gipson, respectfully represents that on or about the 21st day of December, 1850, a judgment was rendered against your Petitioner for costs, by J. C. Spugg, one of the Justices of the Peace in and for said County of Sangamon, in a suit wherein your Petitioner was plaintiff and James L. and C. B. Gerard were defendants; that said judgment was not the result of negligence on the part of your Petitioner; that said judgment, in his opinion, is unjust and erroneous in this, that the defendants were at that time and are indebted to this Petitioner in the full amount of the principal and interest of the note sued on, the principal being, as affiant remembers and believes, thirty-one dollars and eighty two cents; and that, as affiant is informed and believes, the defendants succeeded in the trial of said cause by proving old claims against your petitioner, in set-off against said note, which claims had been settled, adjusted and paid before said note was executed. Your Petitioner further states that the reasons of his not being present at said trial, as he was not, and of its not being in his power to take an appeal in the ordinary way, as it was not, were that your Petitioner then resided in Edgar County about one hundred and twenty miles from where defendants resided; that a very short time before the suit was commenced your Petitioner was in Sangamon County for the purpose of collecting debts due him, and with the rest, the note in question, which note had then been given more than a year, that your Petitioner then saw the defendant J. L. Gerard who is the principal in said note, and solicited payment of the same; that said defendant then made no pretense that he did not owe the same, but on the contrary expressly promised that he would come into Springfield, in a very few days and either pay the money, or give a new note, payable by the then next Christmas; that your Petitioner accordingly left said note with said J. C. Spugg, with directions to give defendant full time to pay the money or give the new note as above, and if he did neither to sue; and then affiant came home to Edgar County, not having the slightest suspicion that if suit should be brought, the defendants would make any defense whatever; and your Petitioner never did in any way learn that said suit had been commenced until more than twenty days after it had been decided against him. He therefore prays for a writ of Certiorari.
HIS JOSHUA x GIPSON MARK
DEAR BROTHER: Inclosed is the deed for the land. We are all well, and have nothing in the way of news. We have had no Cholera here for about two weeks.
Give my love to all, and especially to Mother.
Yours as ever,
DEAR BROTHER:
When I came into Charleston day before yesterday I learned that you are anxious to sell the land where you live, and move to Missouri. I have been thinking of this ever since, and cannot but think such a notion is utterly foolish. What can you do in Missouri better than here? Is the land richer? Can you there, any more than here, raise corn and wheat and oats without work? Will anybody there, any more than here, do your work for you? If you intend to go to work, there is no better place than right where you are; if you do not intend to go to work you cannot get along anywhere. Squirming and crawling about from place to place can do no good. You have raised no crop this year, and what you really want is to sell the land, get the money and spend it. Part with the land you have, and, my life upon it, you will never after own a spot big enough to bury you in. Half you will get for the land you spend in moving to Missouri, and the other half you will eat and drink and wear out, and no foot of land will be bought. Now I feel it is my duty to have no hand in such a piece of foolery. I feel that it is so even on your own account, and particularly on Mother's account. The eastern forty acres I intend to keep for Mother while she lives; if you will not cultivate it, it will rent for enough to support her; at least it will rent for something. Her dower in the other two forties she can let you have, and no thanks to me.
Now do not misunderstand this letter. I do not write it in any unkindness. I write it in order, if possible, to get you to face the truth, which truth is, you are destitute because you have idled away all your time. Your thousand pretenses for not getting along better are all nonsense; they deceive nobody but yourself. Go to work is the only cure for your case.
A word for Mother: Chapman tells me he wants you to go and live with him. If I were you I would try it awhile. If you get tired of it (as I think you will not) you can return to your own home. Chapman feels very kindly to you; and I have no doubt he will make your situation very pleasant.
Sincerely yours,
Chapman tells me he wants you to go and live with him. If I were you I would try it awhile. If you get tired of it (as I think you will not) you can return to your own home. Chapman feels very kindly to you; and I have no doubt he will make your situation very pleasant.
Sincerely your son,
DEAR BROTHER:—When I wrote you before, I had not received your letter. I still think as I did, but if the land can be sold so that I get three hundred dollars to put to interest for Mother, I will not object, if she does not. But before I will make a deed, the money must be had, or secured beyond all doubt, at ten per cent.
As to Abram, I do not want him, on my own account; but I understand he wants to live with me, so that he can go to school and get a fair start in the world, which I very much wish him to have. When I reach home, if I can make it convenient to take, I will take him, provided there is no mistake between us as to the object and terms of my taking him. In haste, as ever,
DEAR BROTHER:—Your letter of the 22d is just received. Your proposal about selling the east forty acres of land is all that I want or could claim for myself; but I am not satisfied with it on Mother's account—I want her to have her living, and I feel that it is my duty, to some extent, to see that she is not wronged. She had a right of dower (that is, the use of one-third for life) in the other two forties; but, it seems, she has already let you take that, hook and line. She now has the use of the whole of the east forty, as long as she lives; and if it be sold, of course she is entitled to the interest on all the money it brings, as long as she lives; but you propose to sell it for three hundred dollars, take one hundred away with you, and leave her two hundred at 8 per cent., making her the enormous sum of 16 dollars a year. Now, if you are satisfied with treating her in that way, I am not. It is true that you are to have that forty for two hundred dollars, at Mother's death, but you are not to have it before. I am confident that land can be made to produce for Mother at least $30 a year, and I can not, to oblige any living person, consent that she shall be put on an allowance of sixteen dollars a year.
Yours, etc.,
On the fourth day of July, 1776, the people of a few feeble and oppressed colonies of Great Britain, inhabiting a portion of the Atlantic coast of North America, publicly declared their national independence, and made their appeal to the justice of their cause and to the God of battles for the maintenance of that declaration. That people were few in number and without resources, save only their wise heads and stout hearts. Within the first year of that declared independence, and while its maintenance was yet problematical, while the bloody struggle between those resolute rebels and their haughty would-be masters was still waging,—of undistinguished parents and in an obscure district of one of those colonies Henry Clay was born. The infant nation and the infant child began the race of life together. For three quarters of a century they have travelled hand in hand. They have been companions ever. The nation has passed its perils, and it is free, prosperous, and powerful. The child has reached his manhood, his middle age, his old age, and is dead. In all that has concerned the nation the man ever sympathized; and now the nation mourns the man.
The day after his death one of the public journals, opposed to him politically, held the following pathetic and beautiful language, which I adopt partly because such high and exclusive eulogy, originating with a political friend, might offend good taste, but chiefly because I could not in any language of my own so well express my thoughts:
"Alas, who can realize that Henry Clay is dead! Who can realize that never again that majestic form shall rise in the council-chambers of his country to beat back the storms of anarchy which may threaten, or pour the oil of peace upon the troubled billows as they rage and menace around! Who can realize that the workings of that mighty mind have ceased, that the throbbings of that gallant heart are stilled, that the mighty sweep of that graceful arm will be felt no more, and the magic of that eloquent tongue, which spake as spake no other tongue besides, is hushed hushed for ever! Who can realize that freedom's champion, the champion of a civilized world and of all tongues and kindreds of people, has indeed fallen! Alas, in those dark hours of peril and dread which our land has experienced, and which she may be called to experience again, to whom now may her people look up for that counsel and advice which only wisdom and experience and patriotism can give, and which only the undoubting confidence of a nation will receive? Perchance in the whole circle of the great and gifted of our land there remains but one on whose shoulders the mighty mantle of the departed statesman may fall; one who while we now write is doubtless pouring his tears over the bier of his brother and friend brother, friend, ever, yet in political sentiment as far apart as party could make them. Ah, it is at times like these that the petty distinctions of mere party disappear. We see only the great, the grand, the noble features of the departed statesman; and we do not even beg permission to bow at his feet and mingle our tears with those who have ever been his political adherents—we do [not] beg this permission, we claim it as a right, though we feel it as a privilege. Henry Clay belonged to his country—to the world; mere party cannot claim men like him. His career has been national, his fame has filled the earth, his memory will endure to the last syllable of recorded time.
"Henry Clay is dead! He breathed his last on yesterday, at twenty minutes after eleven, in his chamber at Washington. To those who followed his lead in public affairs, it more appropriately belongs to pronounce his eulogy and pay specific honors to the memory of the illustrious dead. But all Americans may show the grief which his death inspires, for his character and fame are national property. As on a question of liberty he knew no North, no South, no East, no West, but only the Union which held them all in its sacred circle, so now his countrymen will know no grief that is not as wide-spread as the bounds of the confederacy. The career of Henry Clay was a public career. From his youth he has been devoted to the public service, at a period, too, in the world's history justly regarded as a remarkable era in human affairs. He witnessed in the beginning the throes of the French Revolution. He saw the rise and fall of Napoleon. He was called upon to legislate for America and direct her policy when all Europe was the battlefield of contending dynasties, and when the struggle for supremacy imperilled the rights of all neutral nations. His voice spoke war and peace in the contest with Great Britain.
"When Greece rose against the Turks and struck for liberty, his name was mingled with the battle-cry of freedom. When South America threw off the thraldom of Spain, his speeches were read at the head of her armies by Bolivar. His name has been, and will continue to be, hallowed in two hemispheres, for it is
"'One of the few, the immortal names
That were not born to die!'
"To the ardent patriot and profound statesman he added a quality possessed by few of the gifted on earth. His eloquence has not been surpassed. In the effective power to move the heart of man, Clay was without an equal, and the heaven-born endowment, in the spirit of its origin, has been most conspicuously exhibited against intestine feud. On at least three important occasions he has quelled our civil commotions by a power and influence which belonged to no other statesman of his age and times. And in our last internal discord, when this Union trembled to its centre, in old age he left the shades of private life, and gave the death-blow to fraternal strife, with the vigor of his earlier years, in a series of senatorial efforts which in themselves would bring immortality by challenging comparison with the efforts of any statesman in any age. He exorcised the demon which possessed the body politic, and gave peace to a distracted land. Alas! the achievement cost him his life. He sank day by day to the tomb his pale but noble brow bound with a triple wreath, put there by a grateful country. May his ashes rest in peace, while his spirit goes to take its station among the great and good men who preceded him."
While it is customary and proper upon occasions like the present to give a brief sketch of the life of the deceased, in the case of Mr. Clay it is less necessary than most others; for his biography has been written and rewritten and read and reread for the last twenty-five years; so that, with the exception of a few of the latest incidents of his life, all is as well known as it can be. The short sketch which I give is, therefore, merely to maintain the connection of this discourse.
Henry Clay was born on the twelfth day of April, 1777, in Hanover County, Virginia. Of his father, who died in the fourth or fifth year of Henry's age, little seems to be known, except that he was a respectable man and a preacher of the Baptist persuasion. Mr. Clay's education to the end of life was comparatively limited. I say "to the end of life," because I have understood that from time to time he added something to his education during the greater part of his whole life. Mr. Clay's lack of a more perfect early education, however it may be regretted generally, teaches at least one profitable lesson: it teaches that in this country one can scarcely be so poor but that, if he will, he can acquire sufficient education to get through the world respectably. In his twenty-third year Mr. Clay was licensed to practise law, and emigrated to Lexington, Kentucky. Here he commenced and continued the practice till the year 1803, when he was first elected to the Kentucky Legislature. By successive elections he was continued in the Legislature till the latter part of 1806, when he was elected to fill a vacancy of a single session in the United States Senate. In 1807 he was again elected to the Kentucky House of Representatives, and by that body chosen Speaker. In 1808 he was re-elected to the same body. In 1809 he was again chosen to fill a vacancy of two years in the United States Senate. In 1811 he was elected to the United States House of Representatives, and on the first day of taking his seat in that body he was chosen its Speaker. In 1813 he was again elected Speaker. Early in 1814, being the period of our last British war, Mr. Clay was sent as commissioner, with others, to negotiate a treaty of peace, which treaty was concluded in the latter part of the same year. On his return from Europe he was again elected to the lower branch of Congress, and on taking his seat in December, 1815, was called to his old post-the Speaker's chair, a position in which he was retained by successive elections, with one brief intermission, till the inauguration of John Quincy Adams, in March, 1825. He was then appointed Secretary of State, and occupied that important station till the inauguration of General Jackson, in March, 1829. After this he returned to Kentucky, resumed the practice of law, and continued it till the autumn of 1831, when he was by the Legislature of Kentucky again placed in the United States Senate. By a reelection he was continued in the Senate till he resigned his seat and retired, in March, 1848. In December, 1849, he again took his seat in the Senate, which he again resigned only a few months before his death.
By the foregoing it is perceived that the period from the beginning of Mr. Clay's official life in 1803 to the end of 1852 is but one year short of half a century, and that the sum of all the intervals in it will not amount to ten years. But mere duration of time in office constitutes the smallest part of Mr. Clay's history. Throughout that long period he has constantly been the most loved and most implicitly followed by friends, and the most dreaded by opponents, of all living American politicians. In all the great questions which have agitated the country, and particularly in those fearful crises, the Missouri question, the nullification question, and the late slavery question, as connected with the newly acquired territory, involving and endangering the stability of the Union, his has been the leading and most conspicuous part. In 1824 he was first a candidate for the Presidency, and was defeated; and, although he was successively defeated for the same office in 1832 and in 1844, there has never been a moment since 1824 till after 1848 when a very large portion of the American people did not cling to him with an enthusiastic hope and purpose of still elevating him to the Presidency. With other men, to be defeated was to be forgotten; but with him defeat was but a trifling incident, neither changing him nor the world's estimate of him. Even those of both political parties who have been preferred to him for the highest office have run far briefer courses than he, and left him still shining high in the heavens of the political world. Jackson, Van Buren, Harnson, Polk, and Taylor all rose after, and set long before him. The spell—the long-enduring spell—with which the souls of men were bound to him is a miracle. Who can compass it? It is probably true he owed his pre-eminence to no one quality, but to a fortunate combination of several. He was surpassingly eloquent; but many eloquent men fail utterly, and they are not, as a class, generally successful. His judgment was excellent; but many men of good judgment live and die unnoticed. His will was indomitable; but this quality often secures to its owner nothing better than a character for useless obstinacy. These, then, were Mr. Clay's leading qualities. No one of them is very uncommon; but all together are rarely combined in a single individual, and this is probably the reason why such men as Henry Clay are so rare in the world.
Mr. Clay's eloquence did not consist, as many fine specimens of eloquence do, of types and figures, of antithesis and elegant arrangement of words and sentences, but rather of that deeply earnest and impassioned tone and manner which can proceed only from great sincerity, and a thorough conviction in the speaker of the justice and importance of his cause. This it is that truly touches the chords of sympathy; and those who heard Mr. Clay never failed to be moved by it, or ever afterward forgot the impression. All his efforts were made for practical effect. He never spoke merely to be heard. He never delivered a Fourth of July oration, or a eulogy on an occasion like this. As a politician or statesman, no one was so habitually careful to avoid all sectional ground. Whatever he did he did for the whole country. In the construction of his measures, he ever carefully surveyed every part of the field, and duly weighed every conflicting interest. Feeling as he did, and as the truth surely is, that the world's best hope depended on the continued union of these States, he was ever jealous of and watchful for whatever might have the slightest tendency to separate them.
Mr. Clay's predominant sentiment, from first to last, was a deep devotion to the cause of human liberty—a strong sympathy with the oppressed everywhere, and an ardent wish for their elevation. With him this was a primary and all-controlling passion. Subsidiary to this was the conduct of his whole life. He loved his country partly because it was his own country, and mostly because it was a free country; and he burned with a zeal for its advancement, prosperity, and glory, because he saw in such the advancement, prosperity, and glory of human liberty, human right, and human nature. He desired the prosperity of his countrymen, partly because they were his countrymen, but chiefly to show to the world that free men could be prosperous.
That his views and measures were always the wisest needs not to be affirmed; nor should it be on this occasion, where so many thinking differently join in doing honor to his memory. A free people in times of peace and quiet when pressed by no common danger-naturally divide into parties. At such times the man who is of neither party is not, cannot be, of any consequence. Mr. Clay therefore was of a party. Taking a prominent part, as he did, in all the great political questions of his country for the last half century, the wisdom of his course on many is doubted and denied by a large portion of his countrymen; and of such it is not now proper to speak particularly. But there are many others, about his course upon which there is little or no disagreement amongst intelligent and patriotic Americans. Of these last are the War of 1812, the Missouri question, nullification, and the now recent compromise measures. In 1812 Mr. Clay, though not unknown, was still a young man. Whether we should go to war with Great Britain being the question of the day, a minority opposed the declaration of war by Congress, while the majority, though apparently inclined to war, had for years wavered, and hesitated to act decisively. Meanwhile British aggressions multiplied, and grew more daring and aggravated. By Mr. Clay more than any other man the struggle was brought to a decision in Congress. The question, being now fully before Congress, came up in a variety of ways in rapid succession, on most of which occasions Mr. Clay spoke. Adding to all the logic of which the subject was susceptible that noble inspiration which came to him as it came to no other, he aroused and nerved and inspired his friends, and confounded and bore down all opposition. Several of his speeches on these occasions were reported and are still extant, but the best of them all never was. During its delivery the reporters forgot their vocation, dropped their pens, and sat enchanted from near the beginning to quite the close. The speech now lives only in the memory of a few old men, and the enthusiasm with which they cherish their recollection of it is absolutely astonishing. The precise language of this speech we shall never know; but we do know we cannot help knowing—that with deep pathos it pleaded the cause of the injured sailor, that it invoked the genius of the Revolution, that it apostrophized the names of Otis, of Henry, and of Washington, that it appealed to the interests, the pride, the honor, and the glory of the nation, that it shamed and taunted the timidity of friends, that it scorned and scouted and withered the temerity of domestic foes, that it bearded and defied the British lion, and, rising and swelling and maddening in its course, it sounded the onset, till the charge, the shock, the steady struggle, and the glorious victory all passed in vivid review before the entranced hearers.
Important and exciting as was the war question of 1812, it never so alarmed the sagacious statesmen of the country for the safety of the Republic as afterward did the Missouri question. This sprang from that unfortunate source of discord—negro slavery. When our Federal Constitution was adopted, we owned no territory beyond the limits or ownership of the States, except the territory northwest of the River Ohio and east of the Mississippi. What has since been formed into the States of Maine, Kentucky and Tennessee, was, I believe, within the limits of or owned by Massachusetts, Virginia, and North Carolina. As to the Northwestern Territory, provision had been made even before the adoption of the Constitution that slavery should never go there. On the admission of States into the Union, carved from the territory we owned before the Constitution, no question, or at most no considerable question, arose about slavery—those which were within the limits of or owned by the old States following respectively the condition of the parent State, and those within the Northwest Territory following the previously made provision. But in 1803 we purchased Louisiana of the French, and it included with much more what has since been formed into the State of Missouri. With regard to it, nothing had been done to forestall the question of slavery. When, therefore, in 1819, Missouri, having formed a State constitution without excluding slavery, and with slavery already actually existing within its limits, knocked at the door of the Union for admission, almost the entire representation of the non-slaveholding States objected. A fearful and angry struggle instantly followed. This alarmed thinking men more than any previous question, because, unlike all the former, it divided the country by geographical lines. Other questions had their opposing partisans in all localities of the country and in almost every family, so that no division of the Union could follow such without a separation of friends to quite as great an extent as that of opponents. Not so with the Missouri question. On this a geographical line could be traced, which in the main would separate opponents only. This was the danger. Mr. Jefferson, then in retirement, wrote:
"I had for a long time ceased to read newspapers or to pay any attention to public affairs, confident they were in good hands and content to be a passenger in our bark to the shore from which I am not distant. But this momentous question, like a firebell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the knell of the Union. It is hushed, indeed, for the moment. But this is a reprieve only, not a final sentence. A geographical line coinciding with a marked principle, moral and political, once conceived and held up to the angry passions of men, will never be obliterated, and every irritation will mark it deeper and deeper. I can say with conscious truth that there is not a man on earth who would sacrifice more than I would to relieve us from this heavy reproach in any practicable way.
"The cession of that kind of property—for it is so misnamed—is a bagatelle which would not cost me a second thought if in that way a general emancipation and expatriation could be effected, and gradually and with due sacrifices I think it might be. But as it is, we have the wolf by the ears, and we can neither hold him nor safely let him go. Justice is in one scale, and self-preservation in the other."
Mr. Clay was in Congress, and, perceiving the danger, at once engaged his whole energies to avert it. It began, as I have said, in 1819; and it did not terminate till 1821. Missouri would not yield the point; and Congress that is, a majority in Congress—by repeated votes showed a determination not to admit the State unless it should yield. After several failures, and great labor on the part of Mr. Clay to so present the question that a majority could consent to the admission, it was by a vote rejected, and, as all seemed to think, finally. A sullen gloom hung over the nation. All felt that the rejection of Missouri was equivalent to a dissolution of the Union, because those States which already had what Missouri was rejected for refusing to relinquish would go with Missouri. All deprecated and deplored this, but none saw how to avert it. For the judgment of members to be convinced of the necessity of yielding was not the whole difficulty; each had a constituency to meet and to answer to. Mr. Clay, though worn down and exhausted, was appealed to by members to renew his efforts at compromise. He did so, and by some judicious modifications of his plan, coupled with laborious efforts with individual members and his own overmastering eloquence upon that floor, he finally secured the admission of the State. Brightly and captivating as it had previously shown, it was now perceived that his great eloquence was a mere embellishment, or at most but a helping hand to his inventive genius and his devotion to his country in the day of her extreme peril.
After the settlement of the Missouri question, although a portion of the American people have differed with Mr. Clay, and a majority even appear generally to have been opposed to him on questions of ordinary administration, he seems constantly to have been regarded by all as the man for the crisis. Accordingly, in the days of nullification, and more recently in the reappearance of the slavery question connected with our territory newly acquired of Mexico, the task of devising a mode of adjustment seems to have been cast upon Mr. Clay by common consent—and his performance of the task in each case was little else than a literal fulfilment of the public expectation.
Mr. Clay's efforts in behalf of the South Americans, and afterward in behalf of the Greeks, in the times of their respective struggles for civil liberty, are among the finest on record, upon the noblest of all themes, and bear ample corroboration of what I have said was his ruling passion—a love of liberty and right, unselfishly, and for their own sakes.
Having been led to allude to domestic slavery so frequently already, I am unwilling to close without referring more particularly to Mr. Clay's views and conduct in regard to it. He ever was on principle and in feeling opposed to slavery. The very earliest, and one of the latest, public efforts of his life, separated by a period of more than fifty years, were both made in favor of gradual emancipation. He did not perceive that on a question of human right the negroes were to be excepted from the human race. And yet Mr. Clay was the owner of slaves. Cast into life when slavery was already widely spread and deeply seated, he did not perceive, as I think no wise man has perceived, how it could be at once eradicated without producing a greater evil even to the cause of human liberty itself. His feeling and his judgment, therefore, ever led him to oppose both extremes of opinion on the subject. Those who would shiver into fragments the Union of these States, tear to tatters its now venerated Constitution, and even burn the last copy of the Bible, rather than slavery should continue a single hour, together with all their more halting sympathizers, have received, and are receiving, their just execration; and the name and opinions and influence of Mr. Clay are fully and, as I trust, effectually and enduringly arrayed against them. But I would also, if I could, array his name, opinions, and influence against the opposite extreme—against a few but an increasing number of men who, for the sake of perpetuating slavery, are beginning to assail and to ridicule the white man's charter of freedom, the declaration that "all men are created free and equal." So far as I have learned, the first American of any note to do or attempt this was the late John C. Calhoun; and if I mistake not, it soon after found its way into some of the messages of the Governor of South Carolina. We, however, look for and are not much shocked by political eccentricities and heresies in South Carolina. But only last year I saw with astonishment what purported to be a letter of a very distinguished and influential clergyman of Virginia, copied, with apparent approbation, into a St. Louis newspaper, containing the following to me very unsatisfactory language:
"I am fully aware that there is a text in some Bibles that is not in mine. Professional abolitionists have made more use of it than of any passage in the Bible. It came, however, as I trace it, from Saint Voltaire, and was baptized by Thomas Jefferson, and since almost universally regarded as canonical authority`All men are born free and equal.'
"This is a genuine coin in the political currency of our generation. I am sorry to say that I have never seen two men of whom it is true. But I must admit I never saw the Siamese Twins, and therefore will not dogmatically say that no man ever saw a proof of this sage aphorism."
This sounds strangely in republican America. The like was not heard in the fresher days of the republic. Let us contrast with it the language of that truly national man whose life and death we now commemorate and lament: I quote from a speech of Mr. Clay delivered before the American Colonization Society in 1827:
"We are reproached with doing mischief by the agitation of this question. The society goes into no household to disturb its domestic tranquillity. It addresses itself to no slaves to weaken their obligations of obedience. It seeks to affect no man's property. It neither has the power nor the will to affect the property of any one contrary to his consent. The execution of its scheme would augment instead of diminishing the value of property left behind. The society, composed of free men, conceals itself only with the free. Collateral consequences we are not responsible for. It is not this society which has produced the great moral revolution which the age exhibits. What would they who thus reproach us have done? If they would repress all tendencies toward liberty and ultimate emancipation, they must do more than put down the benevolent efforts of this society. They must go back to the era of our liberty and independence, and muzzle the cannon which thunders its annual joyous return. They must renew the slave trade, with all its train of atrocities. They must suppress the workings of British philanthropy, seeking to meliorate the condition of the unfortunate West Indian slave. They must arrest the career of South American deliverance from thraldom. They must blow out the moral lights around us and extinguish that greatest torch of all which America presents to a benighted world—pointing the way to their rights, their liberties, and their happiness. And when they have achieved all those purposes their work will be yet incomplete. They must penetrate the human soul, and eradicate the light of reason and the love of liberty. Then, and not till then, when universal darkness and despair prevail, can you perpetuate slavery and repress all sympathy and all humane and benevolent efforts among free men in behalf of the unhappy portion of our race doomed to bondage."
The American Colonization Society was organized in 1816. Mr. Clay, though not its projector, was one of its earliest members; and he died, as for many preceding years he had been, its president. It was one of the most cherished objects of his direct care and consideration, and the association of his name with it has probably been its very greatest collateral support. He considered it no demerit in the society that it tended to relieve the slave-holders from the troublesome presence of the free negroes; but this was far from being its whole merit in his estimation. In the same speech from which we have quoted he says:
"There is a moral fitness in the idea of returning to Africa her children, whose ancestors have been torn from her by the ruthless hand of fraud and violence. Transplanted in a foreign land, they will carry back to their native soil the rich fruits of religion, civilization, law, and liberty. May it not be one of the great designs of the Ruler of the universe, whose ways are often inscrutable by short-sighted mortals, thus to transform an original crime into a signal blessing to that most unfortunate portion of the globe?"
This suggestion of the possible ultimate redemption of the African race and African continent was made twenty-five years ago. Every succeeding year has added strength to the hope of its realization. May it indeed be realized. Pharaoh's country was cursed with plagues, and his hosts were lost in the Red Sea, for striving to retain a captive people who had already served them more than four hundred years. May like disasters never befall us! If, as the friends of colonization hope, the present and coming generations of our countrymen shall by any means succeed in freeing our land from the dangerous presence of slavery, and at the same time in restoring a captive people to their long-lost fatherland with bright prospects for the future, and this too so gradually that neither races nor individuals shall have suffered by the change, it will indeed be a glorious consummation. And if to such a consummation the efforts of Mr. Clay shall have contributed, it will be what he most ardently wished, and none of his labors will have been more valuable to his country and his kind.
But Henry Clay is dead. His long and eventful life is closed. Our country is prosperous and powerful; but could it have been quite all it has been, and is, and is to be, without Henry Clay? Such a man the times have demanded, and such in the providence of God was given us. But he is gone. Let us strive to deserve, as far as mortals may, the continued care of Divine Providence, trusting that in future national emergencies He will not fail to provide us the instruments of safety and security.
NOTE. We are indebted for a copy of this speech to the courtesy of Major Wm. H. Bailhache, formerly one of the proprietors of the Illinois State Journal.
SPRINGFIELD, November 1, 1852
A leading article in the Daily Register of this morning has induced some of our friends to request our opinion on the election laws as applicable to challenged voters. We have examined the present constitution of the State, the election law of 1849, and the unrepealed parts of the election law in the revised code of 1845; and we are of the opinion that any person taking the oath prescribed in the act of 1849 is entitled to vote unless counter-proof be made satisfactory to a majority of the judges that such oath is untrue; and that for the purpose of obtaining such counter-proof, the proposed voter may be asked questions in the way of cross-examination, and other independent testimony may be received. We base our opinion as to receiving counter-proof upon the unrepealed Section nineteen of the election law in the revised code.
A. LINCOLN, B. S. EDWARDS S. T. LOGAN. S. H. TREAT
Mr. JOSHUA R. STANFORD.
SIR:—I hope the subject-matter of this letter will appear a sufficient apology to you for the liberty I, a total stranger, take in addressing you. The persons here holding two lots under a conveyance made by you, as the attorney of Daniel M. Baily, now nearly twenty-two years ago, are in great danger of losing the lots, and very much, perhaps all, is to depend on the testimony you give as to whether you did or did not account to Baily for the proceeds received by you on this sale of the lots. I, therefore, as one of the counsel, beg of you to fully refresh your recollection by any means in your power before the time you may be called on to testify. If persons should come about you, and show a disposition to pump you on the subject, it may be no more than prudent to remember that it may be possible they design to misrepresent you and embarrass the real testimony you may ultimately give. It may be six months or a year before you are called on to testify.
Respectfully,
SPRINGFIELD, June 22, 1854.
O. L. DAVIS, ESQ.
DEAR SIR:—You, no doubt, remember the enclosed memorandum being handed me in your office. I have just made the desired search, and find that no such deed has ever been here. Campbell, the auditor, says that if it were here, it would be in his office, and that he has hunted for it a dozen times, and could never find it. He says that one time and another, he has heard much about the matter, that it was not a deed for Right of Way, but a deed, outright, for Depot-ground—at least, a sale for Depot-ground, and there may never have been a deed. He says, if there is a deed, it is most probable General Alexander, of Paris, has it.
Yours truly,
[Confidential]
SPRINGFIELD, Sept. 7, 1854.
HON. J. M. PALMER.
DEAR SIR:—You know how anxious I am that this Nebraska measure shall be rebuked and condemned everywhere. Of course I hope something from your position; yet I do not expect you to do anything which may be wrong in your own judgment; nor would I have you do anything personally injurious to yourself. You are, and always have been, honestly and sincerely a Democrat; and I know how painful it must be to an honest, sincere man to be urged by his party to the support of a measure which in his conscience he believes to be wrong. You have had a severe struggle with yourself, and you have determined not to swallow the wrong. Is it not just to yourself that you should, in a few public speeches, state your reasons, and thus justify yourself? I wish you would; and yet I say, don't do it, if you think it will injure you. You may have given your word to vote for Major Harris; and if so, of course you will stick to it. But allow me to suggest that you should avoid speaking of this; for it probably would induce some of your friends in like manner to cast their votes. You understand. And now let me beg your pardon for obtruding this letter upon you, to whom I have ever been opposed in politics. Had your party omitted to make Nebraska a test of party fidelity, you probably would have been the Democratic candidate for Congress in the district. You deserved it, and I believe it would have been given you. In that case I should have been quite happy that Nebraska was to be rebuked at all events. I still should have voted for the Whig candidate; but I should have made no speeches, written no letters; and you would have been elected by at least a thousand majority.
Yours truly,
A. B. MOREAU, ESQ.
SIR:—Stranger though I am, personally, being a brother in the faith, I venture to write you. Yates can not come to your court next week. He is obliged to be at Pike court where he has a case, with a fee of five hundred dollars, two hundred dollars already paid. To neglect it would be unjust to himself, and dishonest to his client. Harris will be with you, head up and tail up, for Nebraska. You must have some one to make an anti-Nebraska speech. Palmer is the best, if you can get him, I think. Jo. Gillespie, if you can not get Palmer, and somebody anyhow, if you can get neither. But press Palmer hard. It is in his Senatorial district, I believe.
Yours etc.,
OCTOBER 16, 1854.
I do not rise to speak now, if I can stipulate with the audience to meet me here at half-past six or at seven o'clock. It is now several minutes past five, and Judge Douglas has spoken over three hours. If you hear me at all, I wish you to hear me through. It will take me as long as it has taken him. That will carry us beyond eight o'clock at night. Now, every one of you who can remain that long can just as well get his supper, meet me at seven, and remain an hour or two later. The Judge has already informed you that he is to have an hour to reply to me. I doubt not but you have been a little surprised to learn that I have consented to give one of his high reputation and known ability this advantage of me. Indeed, my consenting to it, though reluctant, was not wholly unselfish, for I suspected, if it were understood that the Judge was entirely done, you Democrats would leave and not hear me; but by giving him the close, I felt confident you would stay for the fun of hearing him skin me.
The audience signified their assent to the arrangement, and adjourned to seven o'clock P.M., at which time they reassembled, and Mr. Lincoln spoke substantially as follows:
The repeal of the Missouri Compromise, and the propriety of its restoration, constitute the subject of what I am about to say. As I desire to present my own connected view of this subject, my remarks will not be specifically an answer to Judge Douglas; yet, as I proceed, the main points he has presented will arise, and will receive such respectful attention as I may be able to give them. I wish further to say that I do not propose to question the patriotism or to assail the motives of any man or class of men, but rather to confine myself strictly to the naked merits of the question. I also wish to be no less than national in all the positions I may take, and whenever I take ground which others have thought, or may think, narrow, sectional, and dangerous to the Union, I hope to give a reason which will appear sufficient, at least to some, why I think differently.
And as this subject is no other than part and parcel of the larger general question of domestic slavery, I wish to make and to keep the distinction between the existing institution and the extension of it so broad and so clear that no honest man can misunderstand me, and no dishonest one successfully misrepresent me.
In order to a clear understanding of what the Missouri Compromise is, a short history of the preceding kindred subjects will perhaps be proper.
When we established our independence, we did not own or claim the country to which this compromise applies. Indeed, strictly speaking, the Confederacy then owned no country at all; the States respectively owned the country within their limits, and some of them owned territory beyond their strict State limits. Virginia thus owned the Northwestern Territory—the country out of which the principal part of Ohio, all Indiana, all Illinois, all Michigan, and all Wisconsin have since been formed. She also owned (perhaps within her then limits) what has since been formed into the State of Kentucky. North Carolina thus owned what is now the State of Tennessee; and South Carolina and Georgia owned, in separate parts, what are now Mississippi and Alabama. Connecticut, I think, owned the little remaining part of Ohio, being the same where they now send Giddings to Congress and beat all creation in making cheese.
These territories, together with the States themselves, constitute all the country over which the Confederacy then claimed any sort of jurisdiction. We were then living under the Articles of Confederation, which were superseded by the Constitution several years afterward. The question of ceding the territories to the General Government was set on foot. Mr. Jefferson,—the author of the Declaration of Independence, and otherwise a chief actor in the Revolution; then a delegate in Congress; afterward, twice President; who was, is, and perhaps will continue to be, the most distinguished politician of our history; a Virginian by birth and continued residence, and withal a slaveholder,—conceived the idea of taking that occasion to prevent slavery ever going into the Northwestern Territory. He prevailed on the Virginia Legislature to adopt his views, and to cede the Territory, making the prohibition of slavery therein a condition of the deed. (Jefferson got only an understanding, not a condition of the deed to this wish.) Congress accepted the cession with the condition; and the first ordinance (which the acts of Congress were then called) for the government of the Territory provided that slavery should never be permitted therein. This is the famed "Ordinance of '87," so often spoken of.
Thenceforward for sixty-one years, and until, in 1848, the last scrap of this Territory came into the Union as the State of Wisconsin, all parties acted in quiet obedience to this ordinance. It is now what Jefferson foresaw and intended—the happy home of teeming millions of free, white, prosperous people, and no slave among them.
Thus, with the author of the Declaration of Independence, the policy of prohibiting slavery in new territory originated. Thus, away back to the Constitution, in the pure, fresh, free breath of the Revolution, the State of Virginia and the national Congress put that policy into practice. Thus, through more than sixty of the best years of the republic, did that policy steadily work to its great and beneficent end. And thus, in those five States, and in five millions of free, enterprising people, we have before us the rich fruits of this policy.
But now new light breaks upon us. Now Congress declares this ought never to have been, and the like of it must never be again. The sacred right of self-government is grossly violated by it. We even find some men who drew their first breath—and every other breath of their lives—under this very restriction, now live in dread of absolute suffocation if they should be restricted in the "sacred right" of taking slaves to Nebraska. That perfect liberty they sigh for—the liberty of making slaves of other people, Jefferson never thought of, their own fathers never thought of, they never thought of themselves, a year ago. How fortunate for them they did not sooner become sensible of their great misery! Oh, how difficult it is to treat with respect such assaults upon all we have ever really held sacred!
But to return to history. In 1803 we purchased what was then called Louisiana, of France. It included the present States of Louisiana, Arkansas, Missouri, and Iowa; also the Territory of Minnesota, and the present bone of contention, Kansas and Nebraska. Slavery already existed among the French at New Orleans, and to some extent at St. Louis. In 1812 Louisiana came into the Union as a slave State, without controversy. In 1818 or '19, Missouri showed signs of a wish to come in with slavery. This was resisted by Northern members of Congress; and thus began the first great slavery agitation in the nation. This controversy lasted several months, and became very angry and exciting—the House of Representatives voting steadily for the prohibition of slavery in Missouri, and the Senate voting as steadily against it. Threats of the breaking up of the Union were freely made, and the ablest public men of the day became seriously alarmed. At length a compromise was made, in which, as in all compromises, both sides yielded something. It was a law, passed on the 6th of March, 1820, providing that Missouri might come into the Union with slavery, but that in all the remaining part of the territory purchased of France which lies north of thirty-six degrees and thirty minutes north latitude, slavery should never be permitted. This provision of law is the "Missouri Compromise." In excluding slavery north of the line, the same language is employed as in the Ordinance of 1787. It directly applied to Iowa, Minnesota, and to the present bone of contention, Kansas and Nebraska. Whether there should or should not be slavery south of that line, nothing was said in the law. But Arkansas constituted the principal remaining part south of the line; and it has since been admitted as a slave State, without serious controversy. More recently, Iowa, north of the line, came in as a free State without controversy. Still later, Minnesota, north of the line, had a territorial organization without controversy. Texas, principally south of the line, and west of Arkansas, though originally within the purchase from France, had, in 1819, been traded off to Spain in our treaty for the acquisition of Florida. It had thus become a part of Mexico. Mexico revolutionized and became independent of Spain. American citizens began settling rapidly with their slaves in the southern part of Texas. Soon they revolutionized against Mexico, and established an independent government of their own, adopting a constitution with slavery, strongly resembling the constitutions of our slave States. By still another rapid move, Texas, claiming a boundary much farther west than when we parted with her in 1819, was brought back to the United States, and admitted into the Union as a slave State. Then there was little or no settlement in the northern part of Texas, a considerable portion of which lay north of the Missouri line; and in the resolutions admitting her into the Union, the Missouri restriction was expressly extended westward across her territory. This was in 1845, only nine years ago.
Thus originated the Missouri Compromise; and thus has it been respected down to 1845. And even four years later, in 1849, our distinguished Senator, in a public address, held the following language in relation to it:
"The Missouri Compromise has been in practical operation for about a quarter of a century, and has received the sanction and approbation of men of all parties in every section of the Union. It has allayed all sectional jealousies and irritations growing out of this vexed question, and harmonized and tranquillized the whole country. It has given to Henry Clay, as its prominent champion, the proud sobriquet of the 'Great Pacificator,' and by that title, and for that service, his political friends had repeatedly appealed to the people to rally under his standard as a Presidential candidate, as the man who had exhibited the patriotism and power to suppress an unholy and treasonable agitation, and preserve the Union. He was not aware that any man or any party, from any section of the Union, had ever urged as an objection to Mr. Clay that he was the great champion of the Missouri Compromise. On the contrary, the effort was made by the opponents of Mr. Clay to prove that he was not entitled to the exclusive merit of that great patriotic measure, and that the honor was equally due to others, as well as to him, for securing its adoption; that it had its origin in the hearts of all patriotic men, who desired to preserve and perpetuate the blessings of our glorious Union—an origin akin to that of the Constitution of the United States, conceived in the same spirit of fraternal affection, and calculated to remove forever the only danger which seemed to threaten, at some distant day, to sever the social bond of union. All the evidences of public opinion at that day seemed to indicate that this compromise had been canonized in the hearts of the American people, as a sacred thing which no ruthless hand would ever be reckless enough to disturb."
I do not read this extract to involve Judge Douglas in an inconsistency. If he afterward thought he had been wrong, it was right for him to change. I bring this forward merely to show the high estimate placed on the Missouri Compromise by all parties up to so late as the year 1849.
But going back a little in point of time. Our war with Mexico broke out in 1846. When Congress was about adjourning that session, President Polk asked them to place two millions of dollars under his control, to be used by him in the recess, if found practicable and expedient, in negotiating a treaty of peace with Mexico, and acquiring some part of her territory. A bill was duly gotten up for the purpose, and was progressing swimmingly in the House of Representatives, when a member by the name of David Wilmot, a Democrat from Pennsylvania, moved as an amendment, "Provided, that in any territory thus acquired there never shall be slavery."
This is the origin of the far-famed Wilmot Proviso. It created a great flutter; but it stuck like wax, was voted into the bill, and the bill passed with it through the House. The Senate, however, adjourned without final action on it, and so both appropriation and proviso were lost for the time. The war continued, and at the next session the President renewed his request for the appropriation, enlarging the amount, I think, to three millions. Again came the proviso, and defeated the measure. Congress adjourned again, and the war went on. In December, 1847, the new Congress assembled. I was in the lower House that term. The Wilmot Proviso, or the principle of it, was constantly coming up in some shape or other, and I think I may venture to say I voted for it at least forty times during the short time I was there. The Senate, however, held it in check, and it never became a law. In the spring of 1848 a treaty of peace was made with Mexico, by which we obtained that portion of her country which now constitutes the Territories of New Mexico and Utah and the present State of California. By this treaty the Wilmot Proviso was defeated, in so far as it was intended to be a condition of the acquisition of territory. Its friends, however, were still determined to find some way to restrain slavery from getting into the new country. This new acquisition lay directly west of our old purchase from France, and extended west to the Pacific Ocean, and was so situated that if the Missouri line should be extended straight west, the new country would be divided by such extended line, leaving some north and some south of it. On Judge Douglas's motion, a bill, or provision of a bill, passed the Senate to so extend the Missouri line. The proviso men in the House, including myself, voted it down, because, by implication, it gave up the southern part to slavery, while we were bent on having it all free.
In the fall of 1848 the gold-mines were discovered in California. This attracted people to it with unprecedented rapidity, so that on, or soon after, the meeting of the new Congress in December, 1849, she already had a population of nearly a hundred thousand, had called a convention, formed a State constitution excluding slavery, and was knocking for admission into the Union. The proviso men, of course, were for letting her in, but the Senate, always true to the other side, would not consent to her admission, and there California stood, kept out of the Union because she would not let slavery into her borders. Under all the circumstances, perhaps, this was not wrong. There were other points of dispute connected with the general question of Slavery, which equally needed adjustment. The South clamored for a more efficient fugitive slave law. The North clamored for the abolition of a peculiar species of slave trade in the District of Columbia, in connection with which, in view from the windows of the Capitol, a sort of negro livery-stable, where droves of negroes were collected, temporarily kept, and finally taken to Southern markets, precisely like droves of horses, had been openly maintained for fifty years. Utah and New Mexico needed territorial governments; and whether slavery should or should not be prohibited within them was another question. The indefinite western boundary of Texas was to be settled. She was a slave State, and consequently the farther west the slavery men could push her boundary, the more slave country they secured; and the farther east the slavery opponents could thrust the boundary back, the less slave ground was secured. Thus this was just as clearly a slavery question as any of the others.
These points all needed adjustment, and they were held up, perhaps wisely, to make them help adjust one another. The Union now, as in 1820, was thought to be in danger, and devotion to the Union rightfully inclined men to yield somewhat in points where nothing else could have so inclined them. A compromise was finally effected. The South got their new fugitive slave law, and the North got California, (by far the best part of our acquisition from Mexico) as a free State. The South got a provision that New Mexico and Utah, when admitted as States, may come in with or without slavery as they may then choose; and the North got the slave trade abolished in the District of Columbia.. The North got the western boundary of Texas thrown farther back eastward than the South desired; but, in turn, they gave Texas ten millions of dollars with which to pay her old debts. This is the Compromise of 1850.
Preceding the Presidential election of 1852, each of the great political parties, Democrats and Whigs, met in convention and adopted resolutions indorsing the Compromise of '50, as a "finality," a final settlement, so far as these parties could make it so, of all slavery agitation. Previous to this, in 1851, the Illinois Legislature had indorsed it.
During this long period of time, Nebraska (the Nebraska Territory, not the State of as we know it now) had remained substantially an uninhabited country, but now emigration to and settlement within it began to take place. It is about one third as large as the present United States, and its importance, so long overlooked, begins to come into view. The restriction of slavery by the Missouri Compromise directly applies to it—in fact was first made, and has since been maintained expressly for it. In 1853, a bill to give it a territorial government passed the House of Representatives, and, in the hands of Judge Douglas, failed of passing only for want of time. This bill contained no repeal of the Missouri Compromise. Indeed, when it was assailed because it did not contain such repeal, Judge Douglas defended it in its existing form. On January 4, 1854, Judge Douglas introduces a new bill to give Nebraska territorial government. He accompanies this bill with a report, in which last he expressly recommends that the Missouri Compromise shall neither be affirmed nor repealed. Before long the bill is so modified as to make two territories instead of one, calling the southern one Kansas.
Also, about a month after the introduction of the bill, on the Judge's own motion it is so amended as to declare the Missouri Compromise inoperative and void; and, substantially, that the people who go and settle there may establish slavery, or exclude it, as they may see fit. In this shape the bill passed both branches of Congress and became a law.
This is the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. The foregoing history may not be precisely accurate in every particular, but I am sure it is sufficiently so for all the use I shall attempt to make of it, and in it we have before us the chief material enabling us to judge correctly whether the repeal of the Missouri Compromise is right or wrong. I think, and shall try to show, that it is wrong—wrong in its direct effect, letting slavery into Kansas and Nebraska, and wrong in its prospective principle, allowing it to spread to every other part of the wide world where men can be found inclined to take it.
This declared indifference, but, as I must think, covert real zeal, for the spread of slavery, I cannot but hate. I hate it because of the monstrous injustice of slavery itself. I hate it because it deprives our republican example of its just influence in the world; enables the enemies of free institutions with plausibility to taunt us as hypocrites; causes the real friends of freedom to doubt our sincerity; and especially because it forces so many good men among ourselves into an open war with the very fundamental principles of civil liberty, criticizing the Declaration of Independence, and insisting that there is no right principle of action but self-interest.
Before proceeding let me say that I think I have no prejudice against the Southern people. They are just what we would be in their situation. If slavery did not now exist among them, they would not introduce it. If it did now exist among us, we should not instantly give it up. This I believe of the masses North and South. Doubtless there are individuals on both sides who would not hold slaves under any circumstances, and others who would gladly introduce slavery anew if it were out of existence. We know that some Southern men do free their slaves, go North and become tip-top abolitionists, while some Northern ones go South and become most cruel slave masters.
When Southern people tell us that they are no more responsible for the origin of slavery than we are, I acknowledge the fact. When it is said that the institution exists, and that it is very difficult to get rid of it in any satisfactory way, I can understand and appreciate the saying. I surely will not blame them for not doing what I should not know how to do myself. If all earthly power were given me, I should not know what to do as to the existing institution. My first impulse would be to free all the slaves, and send them to Liberia, to their own native land. But a moment's reflection would convince me that whatever of high hope (as I think there is) there may be in this in the long run, its sudden execution is impossible. If they were all landed there in a day, they would all perish in the next ten days; and there are not surplus shipping and surplus money enough to carry them there in many times ten days. What then? Free them all, and keep them among us as underlings? Is it quite certain that this betters their condition? I think I would not hold one in slavery at any rate, yet the point is not clear enough for me to denounce people upon. What next? Free them, and make them politically and socially our equals? My own feelings will not admit of this, and if mine would, we well know that those of the great mass of whites will not. Whether this feeling accords with justice and sound judgment is not the sole question, if indeed it is any part of it. A universal feeling, whether well or ill founded, cannot be safely disregarded. We cannot then make them equals. It does seem to me that systems of gradual emancipation might be adopted, but for their tardiness in this I will not undertake to judge our brethren of the South.
When they remind us of their constitutional rights, I acknowledge them—not grudgingly, but fully and fairly; and I would give them any legislation for the reclaiming of their fugitives which should not in its stringency be more likely to carry a free man into slavery than our ordinary criminal laws are to hang an innocent one.
But all this, to my judgment, furnishes no more excuse for permitting slavery to go into our own free territory than it would for reviving the African slave trade by law. The law which forbids the bringing of slaves from Africa, and that which has so long forbidden the taking of them into Nebraska, can hardy be distinguished on any moral principle, and the repeal of the former could find quite as plausible excuses as that of the latter.
The arguments by which the repeal of the Missouri Compromise is sought to be justified are these:
First. That the Nebraska country needed a territorial government.
Second. That in various ways the public had repudiated that compromise and demanded the repeal, and therefore should not now complain of it. And, lastly, That the repeal establishes a principle which is intrinsically right.
I will attempt an answer to each of them in its turn.
First, then: If that country was in need of a territorial organization, could it not have had it as well without as with a repeal? Iowa and Minnesota, to both of which the Missouri restriction applied, had, without its repeal, each in succession, territorial organizations. And even the year before, a bill for Nebraska itself was within an ace of passing without the repealing clause, and this in the hands of the same men who are now the champions of repeal. Why no necessity then for repeal? But still later, when this very bill was first brought in, it contained no repeal. But, say they, because the people had demanded, or rather commanded, the repeal, the repeal was to accompany the organization whenever that should occur.
Now, I deny that the public ever demanded any such thing—ever repudiated the Missouri Compromise, ever commanded its repeal. I deny it, and call for the proof. It is not contended, I believe, that any such command has ever been given in express terms. It is only said that it was done in principle. The support of the Wilmot Proviso is the first fact mentioned to prove that the Missouri restriction was repudiated in principle, and the second is the refusal to extend the Missouri line over the country acquired from Mexico. These are near enough alike to be treated together. The one was to exclude the chances of slavery from the whole new acquisition by the lump, and the other was to reject a division of it, by which one half was to be given up to those chances. Now, whether this was a repudiation of the Missouri line in principle depends upon whether the Missouri law contained any principle requiring the line to be extended over the country acquired from Mexico. I contend it did not. I insist that it contained no general principle, but that it was, in every sense, specific. That its terms limit it to the country purchased from France is undenied and undeniable. It could have no principle beyond the intention of those who made it. They did not intend to extend the line to country which they did not own. If they intended to extend it in the event of acquiring additional territory, why did they not say so? It was just as easy to say that "in all the country west of the Mississippi which we now own, or may hereafter acquire, there shall never be slavery," as to say what they did say; and they would have said it if they had meant it. An intention to extend the law is not only not mentioned in the law, but is not mentioned in any contemporaneous history. Both the law itself, and the history of the times, are a blank as to any principle of extension; and by neither the known rules of construing statutes and contracts, nor by common sense, can any such principle be inferred.
Another fact showing the specific character of the Missouri law—showing that it intended no more than it expressed, showing that the line was not intended as a universal dividing line between Free and Slave territory, present and prospective, north of which slavery could never go—is the fact that by that very law Missouri came in as a slave State, north of the line. If that law contained any prospective principle, the whole law must be looked to in order to ascertain what the principle was. And by this rule the South could fairly contend that, inasmuch as they got one slave State north of the line at the inception of the law, they have the right to have another given them north of it occasionally, now and then, in the indefinite westward extension of the line. This demonstrates the absurdity of attempting to deduce a prospective principle from the Missouri Compromise line.
When we voted for the Wilmot Proviso we were voting to keep slavery out of the whole Mexican acquisition, and little did we think we were thereby voting to let it into Nebraska lying several hundred miles distant. When we voted against extending the Missouri line, little did we think we were voting to destroy the old line, then of near thirty years' standing.
To argue that we thus repudiated the Missouri Compromise is no less absurd than it would be to argue that because we have so far forborne to acquire Cuba, we have thereby, in principle, repudiated our former acquisitions and determined to throw them out of the Union. No less absurd than it would be to say that because I may have refused to build an addition to my house, I thereby have decided to destroy the existing house! And if I catch you setting fire to my house, you will turn upon me and say I instructed you to do it!
The most conclusive argument, however, that while for the Wilmot Proviso, and while voting against the extension of the Missouri line, we never thought of disturbing the original Missouri Compromise, is found in the fact that there was then, and still is, an unorganized tract of fine country, nearly as large as the State of Missouri, lying immediately west of Arkansas and south of the Missouri Compromise line, and that we never attempted to prohibit slavery as to it. I wish particular attention to this. It adjoins the original Missouri Compromise line by its northern boundary, and consequently is part of the country into which by implication slavery was permitted to go by that compromise. There it has lain open ever s, and there it still lies, and yet no effort has been made at any time to wrest it from the South. In all our struggles to prohibit slavery within our Mexican acquisitions, we never so much as lifted a finger to prohibit it as to this tract. Is not this entirely conclusive that at all times we have held the Missouri Compromise as a sacred thing, even when against ourselves as well as when for us?
Senator Douglas sometimes says the Missouri line itself was in principle only an extension of the line of the Ordinance of '87—that is to say, an extension of the Ohio River. I think this is weak enough on its face. I will remark, however, that, as a glance at the map will show, the Missouri line is a long way farther south than the Ohio, and that if our Senator in proposing his extension had stuck to the principle of jogging southward, perhaps it might not have been voted down so readily.
But next it is said that the compromises of '50, and the ratification of them by both political parties in '52, established a new principle which required the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. This again I deny. I deny it, and demand the proof. I have already stated fully what the compromises of '50 are. That particular part of those measures from which the virtual repeal of the Missouri Compromise is sought to be inferred (for it is admitted they contain nothing about it in express terms) is the provision in the Utah and New Mexico laws which permits them when they seek admission into the Union as States to come in with or without slavery, as they shall then see fit. Now I insist this provision was made for Utah and New Mexico, and for no other place whatever. It had no more direct reference to Nebraska than it had to the territories of the moon. But, say they, it had reference to Nebraska in principle. Let us see. The North consented to this provision, not because they considered it right in itself, but because they were compensated—paid for it.
They at the same time got California into the Union as a free State. This was far the best part of all they had struggled for by the Wilmot Proviso. They also got the area of slavery somewhat narrowed in the settlement of the boundary of Texas. Also they got the slave trade abolished in the District of Columbia.
For all these desirable objects the North could afford to yield something; and they did yield to the South the Utah and New Mexico provision. I do not mean that the whole North, or even a majority, yielded, when the law passed; but enough yielded—when added to the vote of the South, to carry the measure. Nor can it be pretended that the principle of this arrangement requires us to permit the same provision to be applied to Nebraska, without any equivalent at all. Give us another free State; press the boundary of Texas still farther back; give us another step toward the destruction of slavery in the District, and you present us a similar case. But ask us not to repeat, for nothing, what you paid for in the first instance. If you wish the thing again, pay again. That is the principle of the compromises of '50, if, indeed, they had any principles beyond their specific terms—it was the system of equivalents.
Again, if Congress, at that time, intended that all future Territories should, when admitted as States, come in with or without slavery at their own option, why did it not say so? With such a universal provision, all know the bills could not have passed. Did they, then—could they-establish a principle contrary to their own intention? Still further, if they intended to establish the principle that, whenever Congress had control, it should be left to the people to do as they thought fit with slavery, why did they not authorize the people of the District of Columbia, at their option, to abolish slavery within their limits?
I personally know that this has not been left undone because it was unthought of. It was frequently spoken of by members of Congress, and by citizens of Washington, six years ago; and I heard no one express a doubt that a system of gradual emancipation, with compensation to owners, would meet the approbation of a large majority of the white people of the District. But without the action of Congress they could say nothing; and Congress said "No." In the measures of 1850, Congress had the subject of slavery in the District expressly on hand. If they were then establishing the principle of allowing the people to do as they please with slavery, why did they not apply the principle to that people?
Again it is claimed that by the resolutions of the Illinois Legislature, passed in 1851, the repeal of the Missouri Compromise was demanded. This I deny also. Whatever may be worked out by a criticism of the language of those resolutions, the people have never understood them as being any more than an indorsement of the compromises of 1850, and a release of our senators from voting for the Wilmot Proviso. The whole people are living witnesses that this only was their view. Finally, it is asked, "If we did not mean to apply the Utah and New Mexico provision to all future territories, what did we mean when we, in 1852, indorsed the compromises of 1850?"
For myself I can answer this question most easily. I meant not to ask a repeal or modification of the Fugitive Slave law. I meant not to ask for the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia. I meant not to resist the admission of Utah and New Mexico, even should they ask to come in as slave States. I meant nothing about additional Territories, because, as I understood, we then had no Territory whose character as to slavery was not already settled. As to Nebraska, I regarded its character as being fixed by the Missouri Compromise for thirty years—as unalterably fixed as that of my own home in Illinois. As to new acquisitions, I said, "Sufficient unto the day is the evil thereof." When we make new acquisitions, we will, as heretofore, try to manage them somehow. That is my answer; that is what I meant and said; and I appeal to the people to say each for himself whether that is not also the universal meaning of the free States.
And now, in turn, let me ask a few questions. If, by any or all these matters, the repeal of the Missouri Compromise was commanded, why was not the command sooner obeyed? Why was the repeal omitted in the Nebraska Bill of 1853? Why was it omitted in the original bill of 1854? Why in the accompanying report was such a repeal characterized as a departure from the course pursued in 1850 and its continued omission recommended?
I am aware Judge Douglas now argues that the subsequent express repeal is no substantial alteration of the bill. This argument seems wonderful to me. It is as if one should argue that white and black are not different. He admits, however, that there is a literal change in the bill, and that he made the change in deference to other senators who would not support the bill without. This proves that those other senators thought the change a substantial one, and that the Judge thought their opinions worth deferring to. His own opinions, therefore, seem not to rest on a very firm basis, even in his own mind; and I suppose the world believes, and will continue to believe, that precisely on the substance of that change this whole agitation has arisen.
I conclude, then, that the public never demanded the repeal of the Missouri Compromise.
I now come to consider whether the appeal with its avowed principles, is intrinsically right. I insist that it is not. Take the particular case. A controversy had arisen between the advocates and opponents of slavery, in relation to its establishment within the country we had purchased of France. The southern, and then best, part of the purchase was already in as a slave State. The controversy was settled by also letting Missouri in as a slave State; but with the agreement that within all the remaining part of the purchase, north of a certain line, there should never be slavery. As to what was to be done with the remaining part, south of the line, nothing was said; but perhaps the fair implication was, it should come in with slavery if it should so choose. The southern part, except a portion heretofore mentioned, afterward did come in with slavery, as the State of Arkansas. All these many years, since 1820, the northern part had remained a wilderness. At length settlements began in it also. In due course Iowa came in as a free State, and Minnesota was given a territorial government, without removing the slavery restriction. Finally, the sole remaining part north of the line—Kansas and Nebraska—was to be organized; and it is proposed, and carried, to blot out the old dividing line of thirty-four years' standing, and to open the whole of that country to the introduction of slavery. Now this, to my mind, is manifestly unjust. After an angry and dangerous controversy, the parties made friends by dividing the bone of contention. The one party first appropriates her own share, beyond all power to be disturbed in the possession of it, and then seizes the share of the other party. It is as if two starving men had divided their only loaf, the one had hastily swallowed his half, and then grabbed the other's half just as he was putting it to his mouth.
Let me here drop the main argument, to notice what I consider rather an inferior matter. It is argued that slavery will not go to Kansas and Nebraska, in any event. This is a palliation, a lullaby. I have some hope that it will not; but let us not be too confident. As to climate, a glance at the map shows that there are five slave States—Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri, and also the District of Columbia, all north of the Missouri Compromise line. The census returns of 1850 show that within these there are eight hundred and sixty-seven thousand two hundred and seventy-six slaves, being more than one fourth of all the slaves in the nation.
It is not climate, then, that will keep slavery out of these Territories. Is there anything in the peculiar nature of the country? Missouri adjoins these Territories by her entire western boundary, and slavery is already within every one of her western counties. I have even heard it said that there are more slaves in proportion to whites in the northwestern county of Missouri than within any other county in the State. Slavery pressed entirely up to the old western boundary of the State, and when rather recently a part of that boundary at the northwest was moved out a little farther west, slavery followed on quite up to the new line. Now, when the restriction is removed, what is to prevent it from going still farther? Climate will not, no peculiarity of the country will, nothing in nature will. Will the disposition of the people prevent it? Those nearest the scene are all in favor of the extension. The Yankees who are opposed to it may be most flumerous; but, in military phrase, the battlefield is too far from their base of operations.
But it is said there now is no law in Nebraska on the subject of slavery, and that, in such case, taking a slave there operates his freedom. That is good book-law, but it is not the rule of actual practice. Wherever slavery is it has been first introduced without law. The oldest laws we find concerning it are not laws introducing it, but regulating it as an already existing thing. A white man takes his slave to Nebraska now. Who will inform the negro that he is free? Who will take him before court to test the question of his freedom? In ignorance of his legal emancipation he is kept chopping, splitting, and plowing. Others are brought, and move on in the same track. At last, if ever the time for voting comes on the question of slavery the institution already, in fact, exists in the country, and cannot well be removed. The fact of its presence, and the difficulty of its removal, will carry the vote in its favor. Keep it out until a vote is taken, and a vote in favor of it cannot be got in any population of forty thousand on earth, who have been drawn together by the ordinary motives of emigration and settlement. To get slaves into the Territory simultaneously with the whites in the incipient stages of settlement is the precise stake played for and won in this Nebraska measure.
The question is asked us: "If slaves will go in notwithstanding the general principle of law liberates them, why would they not equally go in against positive statute law—go in, even if the Missouri restriction were maintained!" I answer, because it takes a much bolder man to venture in with his property in the latter case than in the former; because the positive Congressional enactment is known to and respected by all, or nearly all, whereas the negative principle that no law is free law is not much known except among lawyers. We have some experience of this practical difference. In spite of the Ordinance of '87, a few negroes were brought into Illinois, and held in a state of quasi-slavery, not enough, however, to carry a vote of the people in favor of the institution when they came to form a constitution. But into the adjoining Missouri country, where there was no Ordinance of '87,—was no restriction,—they were carried ten times, nay, a hundred times, as fast, and actually made a slave State. This is fact-naked fact.
Another lullaby argument is that taking slaves to new countries does not increase their number, does not make any one slave who would otherwise be free. There is some truth in this, and I am glad of it; but it is not wholly true. The African slave trade is not yet effectually suppressed; and, if we make a reasonable deduction for the white people among us who are foreigners and the descendants of foreigners arriving here since 1808, we shall find the increase of the black population outrunning that of the white to an extent unaccountable, except by supposing that some of them, too, have been coming from Africa. If this be so, the opening of new countries to the institution increases the demand for and augments the price of slaves, and so does, in fact, make slaves of freemen, by causing them to be brought from Africa and sold into bondage.
But however this may be, we know the opening of new countries to slavery tends to the perpetuation of the institution, and so does keep men in slavery who would otherwise be free. This result we do not feel like favoring, and we are under no legal obligation to suppress our feelings in this respect.
Equal justice to the South, it is said, requires us to consent to the extension of slavery to new countries. That is to say, inasmuch as you do not object to my taking my hog to Nebraska, therefore I must not object to your taking your slave. Now, I admit that this is perfectly logical if there is no difference between hogs and negroes. But while you thus require me to deny the humanity of the negro, I wish to ask whether you of the South, yourselves, have ever been willing to do as much? It is kindly provided that of all those who come into the world only a small percentage are natural tyrants. That percentage is no larger in the slave States than in the free. The great majority South, as well as North, have human sympathies, of which they can no more divest themselves than they can of their sensibility to physical pain. These sympathies in the bosoms of the Southern people manifest, in many ways, their sense of the wrong of slavery, and their consciousness that, after all, there is humanity in the negro. If they deny this, let me address them a few plain questions. In 1820 you (the South) joined the North, almost unanimously, in declaring the African slave trade piracy, and in annexing to it the punishment of death. Why did you do this? If you did not feel that it was wrong, why did you join in providing that men should be hung for it? The practice was no more than bringing wild negroes from Africa to such as would buy them. But you never thought of hanging men for catching and selling wild horses, wild buffaloes, or wild bears.
Again, you have among you a sneaking individual of the class of native tyrants known as the "slavedealer." He watches your necessities, and crawls up to buy your slave, at a speculating price. If you cannot help it, you sell to him; but if you can help it, you drive him from your door. You despise him utterly. You do not recognize him as a friend, or even as an honest man. Your children must not play with his; they may rollick freely with the little negroes, but not with the slave-dealer's children. If you are obliged to deal with him, you try to get through the job without so much as touching him. It is common with you to join hands with the men you meet, but with the slave-dealer you avoid the ceremony—instinctively shrinking from the snaky contact. If he grows rich and retires from business, you still remember him, and still keep up the ban of non-intercourse upon him and his family. Now, why is this? You do not so treat the man who deals in corn, cotton, or tobacco.
And yet again: There are in the United States and Territories, including the District of Columbia, 433,643 free blacks. At five hundred dollars per head they are worth over two hundred millions of dollars. How comes this vast amount of property to be running about without owners? We do not see free horses or free cattle running at large. How is this? All these free blacks are the descendants of slaves, or have been slaves themselves; and they would be slaves now but for something which has operated on their white owners, inducing them at vast pecuniary sacrifice to liberate them. What is that something? Is there any mistaking it? In all these cases it is your sense of justice and human sympathy continually telling you that the poor negro has some natural right to himself—that those who deny it and make mere merchandise of him deserve kickings, contempt, and death.
And now why will you ask us to deny the humanity of the slave, and estimate him as only the equal of the hog? Why ask us to do what you will not do yourselves? Why ask us to do for nothing what two hundred millions of dollars could not induce you to do?
But one great argument in support of the repeal of the Missouri Compromise is still to come. That argument is "the sacred right of self-government." It seems our distinguished Senator has found great difficulty in getting his antagonists, even in the Senate, to meet him fairly on this argument. Some poet has said:
"Fools rush in where angels fear to tread."
At the hazard of being thought one of the fools of this quotation, I meet that argument—I rush in—I take that bull by the horns. I trust I understand and truly estimate the right of self-government. My faith in the proposition that each man should do precisely as he pleases with all which is exclusively his own lies at the foundation of the sense of justice there is in me. I extend the principle to communities of men as well as to individuals. I so extend it because it is politically wise, as well as naturally just; politically wise in saving us from broils about matters which do not concern us. Here, or at Washington, I would not trouble myself with the oyster laws of Virginia, or the cranberry laws of Indiana. The doctrine of self-government is right,—absolutely and eternally right,—but it has no just application as here attempted. Or perhaps I should rather say that whether it has such application depends upon whether a negro is or is not a man. If he is not a man, in that case he who is a man may as a matter of self-government do just what he pleases with him. But if the negro is a man, is it not to that extent a total destruction of self-government to say that he too shall not govern himself? When the white man governs himself, that is self-government; but when he governs himself and also governs another man, that is more than self-government—that is despotism. If the negro is a man, why, then, my ancient faith teaches me that "all men are created equal," and that there can be no moral right in connection with one man's making a slave of another.
Judge Douglas frequently, with bitter irony and sarcasm, paraphrases our argument by saying: "The white people of Nebraska are good enough to govern themselves, but they are not good enough to govern a few miserable negroes!"
Well, I doubt not that the people of Nebraska are and will continue to be as good as the average of people elsewhere. I do not say the contrary. What I do say is that no man is good enough to govern another man without that other's consent. I say this is the leading principle, the sheet-anchor of American republicanism. Our Declaration of Independence says:
"We hold these truths to be self-evident: That all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. That to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, DERIVING THEIR JUST POWERS PROM THE CONSENT OF THE GOVERNED."
I have quoted so much at this time merely to show that, according to our ancient faith, the just powers of government are derived from the consent of the governed. Now the relation of master and slave is pro tanto a total violation of this principle. The master not only governs the slave without his consent, but he governs him by a set of rules altogether different from those which he prescribes for himself. Allow all the governed an equal voice in the government, and that, and that only, is self-government.
Let it not be said that I am contending for the establishment of political and social equality between the whites and blacks. I have already said the contrary. I am not combating the argument of necessity, arising from the fact that the blacks are already among us; but I am combating what is set up as moral argument for allowing them to be taken where they have never yet been—arguing against the extension of a bad thing, which, where it already exists, we must of necessity manage as we best can.
In support of his application of the doctrine of self-government, Senator Douglas has sought to bring to his aid the opinions and examples of our Revolutionary fathers. I am glad he has done this. I love the sentiments of those old-time men, and shall be most happy to abide by their opinions. He shows us that when it was in contemplation for the colonies to break off from Great Britain, and set up a new government for themselves, several of the States instructed their delegates to go for the measure, provided each State should be allowed to regulate its domestic concerns in its own way. I do not quote; but this in substance. This was right; I see nothing objectionable in it. I also think it probable that it had some reference to the existence of slavery among them. I will not deny that it had. But had it any reference to the carrying of slavery into new countries? That is the question, and we will let the fathers themselves answer it.
This same generation of men, and mostly the same individuals of the generation who declared this principle, who declared independence, who fought the war of the Revolution through, who afterward made the Constitution under which we still live—these same men passed the Ordinance of '87, declaring that slavery should never go to the Northwest Territory.
I have no doubt Judge Douglas thinks they were very inconsistent in this. It is a question of discrimination between them and him. But there is not an inch of ground left for his claiming that their opinions, their example, their authority, are on his side in the controversy.
Again, is not Nebraska, while a Territory, a part of us? Do we not own the country? And if we surrender the control of it, do we not surrender the right of self-government? It is part of ourselves. If you say we shall not control it, because it is only part, the same is true of every other part; and when all the parts are gone, what has become of the whole? What is then left of us? What use for the General Government, when there is nothing left for it to govern?
But you say this question should be left to the people of Nebraska, because they are more particularly interested. If this be the rule, you must leave it to each individual to say for himself whether he will have slaves. What better moral right have thirty-one citizens of Nebraska to say that the thirty-second shall not hold slaves than the people of the thirty-one States have to say that slavery shall not go into the thirty-second State at all?
But if it is a sacred right for the people of Nebraska to take and hold slaves there, it is equally their sacred right to buy them where they can buy them cheapest; and that, undoubtedly, will be on the coast of Africa, provided you will consent not to hang them for going there to buy them. You must remove this restriction, too, from the sacred right of self-government. I am aware you say that taking slaves from the States to Nebraska does not make slaves of freemen; but the African slave-trader can say just as much. He does not catch free negroes and bring them here. He finds them already slaves in the hands of their black captors, and he honestly buys them at the rate of a red cotton handkerchief a head. This is very cheap, and it is a great abridgment of the sacred right of self-government to hang men for engaging in this profitable trade.
Another important objection to this application of the right of self-government is that it enables the first few to deprive the succeeding many of a free exercise of the right of self-government. The first few may get slavery in, and the subsequent many cannot easily get it out. How common is the remark now in the slave States, "If we were only clear of our slaves, how much better it would be for us." They are actually deprived of the privilege of governing themselves as they would, by the action of a very few in the beginning. The same thing was true of the whole nation at the time our Constitution was formed.
Whether slavery shall go into Nebraska, or other new Territories, is not a matter of exclusive concern to the people who may go there. The whole nation is interested that the best use shall be made of these Territories. We want them for homes of free white people. This they cannot be, to any considerable extent, if slavery shall be planted within them. Slave States are places for poor white people to remove from, not to remove to. New free States are the places for poor people to go to, and better their condition. For this use the nation needs these Territories.
Still further: there are constitutional relations between the slave and free States which are degrading to the latter. We are under legal obligations to catch and return their runaway slaves to them: a sort of dirty, disagreeable job, which, I believe, as a general rule, the slaveholders will not perform for one another. Then again, in the control of the government—the management of the partnership affairs—they have greatly the advantage of us. By the Constitution each State has two senators, each has a number of representatives in proportion to the number of its people, and each has a number of Presidential electors equal to the whole number of its senators and representatives together. But in ascertaining the number of the people for this purpose, five slaves are counted as being equal to three whites. The slaves do not vote; they are only counted and so used as to swell the influence of the white people's votes. The practical effect of this is more aptly shown by a comparison of the States of South Carolina and Maine. South Carolina has six representatives, and so has Maine; South Carolina has eight Presidential electors, and so has Maine. This is precise equality so far; and of course they are equal in senators, each having two. Thus in the control of the government the two States are equals precisely. But how are they in the number of their white people? Maine has 581,813, while South Carolina has 274,567; Maine has twice as many as South Carolina, and 32,679 over. Thus, each white man in South Carolina is more than the double of any man in Maine. This is all because South Carolina, besides her free people, has 384,984 slaves. The South Carolinian has precisely the same advantage over the white man in every other free State as well as in Maine. He is more than the double of any one of us in this crowd. The same advantage, but not to the same extent, is held by all the citizens of the slave States over those of the free; and it is an absolute truth, without an exception, that there is no voter in any slave State but who has more legal power in the government than any voter in any free State. There is no instance of exact equality; and the disadvantage is against us the whole chapter through. This principle, in the aggregate, gives the slave States in the present Congress twenty additional representatives, being seven more than the whole majority by which they passed the Nebraska Bill.
Now all this is manifestly unfair; yet I do not mention it to complain of it, in so far as it is already settled. It is in the Constitution, and I do not for that cause, or any other cause, propose to destroy, or alter, or disregard the Constitution. I stand to it, fairly, fully, and firmly.
But when I am told I must leave it altogether to other people to say whether new partners are to be bred up and brought into the firm, on the same degrading terms against me, I respectfully demur. I insist that whether I shall be a whole man or only the half of one, in comparison with others is a question in which I am somewhat concerned, and one which no other man can have a sacred right of deciding for me. If I am wrong in this, if it really be a sacred right of self-government in the man who shall go to Nebraska to decide whether he will be the equal of me or the double of me, then, after he shall have exercised that right, and thereby shall have reduced me to a still smaller fraction of a man than I already am, I should like for some gentleman, deeply skilled in the mysteries of sacred rights, to provide himself with a microscope, and peep about, and find out, if he can, what has become of my sacred rights. They will surely be too small for detection with the naked eye.
Finally, I insist that if there is anything which it is the duty of the whole people to never intrust to any hands but their own, that thing is the preservation and perpetuity of their own liberties and institutions. And if they shall think as I do, that the extension of slavery endangers them more than any or all other causes, how recreant to themselves if they submit The question, and with it the fate of their country, to a mere handful of men bent only on seif-interest. If this question of slavery extension were an insignificant one, one having no power to do harm—it might be shuffled aside in this way; and being, as it is, the great Behemoth of danger, shall the strong grip of the nation be loosened upon him, to intrust him to the hands of such feeble keepers?
I have done with this mighty argument of self-government. Go, sacred thing! Go in peace.
But Nebraska is urged as a great Union-saving measure. Well, I too go for saving the Union. Much as I hate slavery, I would consent to the extension of it rather than see the Union dissolved, just as I would consent to any great evil to avoid a greater one. But when I go to Union-saving, I must believe, at least, that the means I employ have some adaptation to the end. To my mind, Nebraska has no such adaptation.
"It hath no relish of salvation in it."
It is an aggravation, rather, of the only one thing which ever endangers the Union. When it came upon us, all was peace and quiet. The nation was looking to the forming of new bends of union, and a long course of peace and prosperity seemed to lie before us. In the whole range of possibility, there scarcely appears to me to have been anything out of which the slavery agitation could have been revived, except the very project of repealing the Missouri Compromise. Every inch of territory we owned already had a definite settlement of the slavery question, by which all parties were pledged to abide. Indeed, there was no uninhabited country on the continent which we could acquire, if we except some extreme northern regions which are wholly out of the question.
In this state of affairs the Genius of Discord himself could scarcely have invented a way of again setting us by the ears but by turning back and destroying the peace measures of the past. The counsels of that Genius seem to have prevailed. The Missouri Compromise was repealed; and here we are in the midst of a new slavery agitation, such, I think, as we have never seen before. Who is responsible for this? Is it those who resist the measure, or those who causelessly brought it forward, and pressed it through, having reason to know, and in fact knowing, it must and would be so resisted? It could not but be expected by its author that it would be looked upon as a measure for the extension of slavery, aggravated by a gross breach of faith.
Argue as you will and long as you will, this is the naked front and aspect of the measure. And in this aspect it could not but produce agitation. Slavery is founded in the selfishness of man's nature—opposition to it in his love of justice. These principles are at eternal antagonism, and when brought into collision so fiercely as slavery extension brings them, shocks and throes and convulsions must ceaselessly follow. Repeal the Missouri Compromise, repeal all compromises, repeal the Declaration of Independence, repeal all past history, you still cannot repeal human nature. It still will be the abundance of man's heart that slavery extension is wrong, and out of the abundance of his heart his mouth will continue to speak.
The structure, too, of the Nebraska Bill is very peculiar. The people are to decide the question of slavery for themselves; but when they are to decide, or how they are to decide, or whether, when the question is once decided, it is to remain so or is to be subject to an indefinite succession of new trials, the law does not say. Is it to be decided by the first dozen settlers who arrive there, or is it to await the arrival of a hundred? Is it to be decided by a vote of the people or a vote of the Legislature, or, indeed, by a vote of any sort? To these questions the law gives no answer. There is a mystery about this; for when a member proposed to give the Legislature express authority to exclude slavery, it was hooted down by the friends of the bill. This fact is worth remembering. Some Yankees in the East are sending emigrants to Nebraska to exclude slavery from it; and, so far as I can judge, they expect the question to be decided by voting in some way or other. But the Missourians are awake, too. They are within a stone's-throw of the contested ground. They hold meetings and pass resolutions, in which not the slightest allusion to voting is made. They resolve that slavery already exists in the Territory; that more shall go there; that they, remaining in Missouri, will protect it, and that abolitionists shall be hung or driven away. Through all this bowie knives and six-shooters are seen plainly enough, but never a glimpse of the ballot-box.
And, really, what is the result of all this? Each party within having numerous and determined backers without, is it not probable that the contest will come to blows and bloodshed? Could there be a more apt invention to bring about collision and violence on the slavery question than this Nebraska project is? I do not charge or believe that such was intended by Congress; but if they had literally formed a ring and placed champions within it to fight out the controversy, the fight could be no more likely to come off than it is. And if this fight should begin, is it likely to take a very peaceful, Union-saving turn? Will not the first drop of blood so shed be the real knell of the Union?
The Missouri Compromise ought to be restored. For the sake of the Union, it ought to be restored. We ought to elect a House of Representatives which will vote its restoration. If by any means we omit to do this, what follows? Slavery may or may not be established in Nebraska. But whether it be or not, we shall have repudiated—discarded from the councils of the nation—the spirit of compromise; for who, after this, will ever trust in a national compromise? The spirit of mutual concession—that spirit which first gave us the Constitution, and which has thrice saved the Union—we shall have strangled and cast from us forever. And what shall we have in lieu of it? The South flushed with triumph and tempted to excess; the North, betrayed as they believe, brooding on wrong and burning for revenge. One side will provoke, the other resent. The one will taunt, the other defy; one aggresses, the other retaliates. Already a few in the North defy all constitutional restraints, resist the execution of the Fugitive Slave law, and even menace the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. Already a few in the South claim the constitutional right to take and to hold slaves in the free States, demand the revival of the slave trade, and demand a treaty with Great Britain by which fugitive slaves may be reclaimed from Canada. As yet they are but few on either side. It is a grave question for lovers of the union whether the final destruction of the Missouri Compromise, and with it the spirit of all compromise, will or will not embolden and embitter each of these, and fatally increase the number of both.
But restore the compromise, and what then? We thereby restore the national faith, the national confidence, the national feeling of brotherhood. We thereby reinstate the spirit of concession and compromise, that spirit which has never failed us in past perils, and which may be safely trusted for all the future. The South ought to join in doing this. The peace of the nation is as dear to them as to us. In memories of the past and hopes of the future, they share as largely as we. It would be on their part a great act—great in its spirit, and great in its effect. It would be worth to the nation a hundred years purchase of peace and prosperity. And what of sacrifice would they make? They only surrender to us what they gave us for a consideration long, long ago; what they have not now asked for, struggled or cared for; what has been thrust upon them, not less to their astonishment than to ours.
But it is said we cannot restore it; that though we elect every member of the lower House, the Senate is still against us. It is quite true that of the senators who passed the Nebraska Bill a majority of the whole Senate will retain their seats in spite of the elections of this and the next year. But if at these elections their several constituencies shall clearly express their will against Nebraska, will these senators disregard their will? Will they neither obey nor make room for those who will?
But even if we fail to technically restore the compromise, it is still a great point to carry a popular vote in favor of the restoration. The moral weight of such a vote cannot be estimated too highly. The authors of Nebraska are not at all satisfied with the destruction of the compromise—an indorsement of this principle they proclaim to be the great object. With them, Nebraska alone is a small matter—to establish a principle for future use is what they particularly desire.
The future use is to be the planting of slavery wherever in the wide world local and unorganized opposition cannot prevent it. Now, if you wish to give them this indorsement, if you wish to establish this principle, do so. I shall regret it, but it is your right. On the contrary, if you are opposed to the principle,—intend to give it no such indorsement, let no wheedling, no sophistry, divert you from throwing a direct vote against it.
Some men, mostly Whigs, who condemn the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, nevertheless hesitate to go for its restoration, lest they be thrown in company with the abolitionists. Will they allow me, as an old Whig, to tell them, good-humoredly, that I think this is very silly? Stand with anybody that stands right. Stand with him while he is right, and part with him when he goes wrong. Stand with the abolitionist in restoring the Missouri Compromise, and stand against him when he attempts to repeal the Fugitive Slave law. In the latter case you stand with the Southern disunionist. What of that? You are still right. In both cases you are right. In both cases you oppose the dangerous extremes. In both you stand on middle ground, and hold the ship level and steady. In both you are national, and nothing less than national. This is the good old Whig ground. To desert such ground because of any company is to be less than a Whig—less than a man—less than an American.
I particularly object to the new position which the avowed principle of this Nebraska law gives to slavery in the body politic. I object to it because it assumes that there can be moral right in the enslaving of one man by another. I object to it as a dangerous dalliance for a free people—a sad evidence that, feeling prosperity, we forget right; that liberty, as a principle, we have ceased to revere. I object to it because the fathers of the republic eschewed and rejected it. The argument of "necessity" was the only argument they ever admitted in favor of slavery; and so far, and so far only, as it carried them did they ever go. They found the institution existing among us, which they could not help, and they cast blame upon the British king for having permitted its introduction.
The royally appointed Governor of Georgia in the early 1700's was threatened by the King with removal if he continued to oppose slavery in his colony—at that time the King of England made a small profit on every slave imported to the colonies. The later British criticism of the United States for not eradicating slavery in the early 1800's, combined with their tacit support of the 'Confederacy' during the Civil War is a prime example of the irony and hypocrisy of politics: that self-interest will ever overpower right.
Before the Constitution they prohibited its introduction into the Northwestern Territory, the only country we owned then free from it. At the framing and adoption of the Constitution, they forbore to so much as mention the word "slave" or "slavery" in the whole instrument. In the provision for the recovery of fugitives, the slave is spoken of as a "person held to service or labor." In that prohibiting the abolition of the African slave trade for twenty years, that trade is spoken of as "the migration or importation of such persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit," etc. These are the only provisions alluding to slavery. Thus the thing is hid away in the Constitution, just as an afflicted man hides away a wen or cancer which he dares not cut out at once, lest he bleed to death,—with the promise, nevertheless, that the cutting may begin at a certain time. Less than this our fathers could not do, and more they would not do. Necessity drove them so far, and farther they would not go. But this is not all. The earliest Congress under the Constitution took the same view of slavery. They hedged and hemmed it in to the narrowest limits of necessity.
In 1794 they prohibited an outgoing slave trade—that is, the taking of slaves from the United States to sell. In 1798 they prohibited the bringing of slaves from Africa into the Mississippi Territory, this Territory then comprising what are now the States of Mississippi and Alabama. This was ten years before they had the authority to do the same thing as to the States existing at the adoption of the Constitution. In 1800 they prohibited American citizens from trading in slaves between foreign countries, as, for instance, from Africa to Brazil. In 1803 they passed a law in aid of one or two slave-State laws in restraint of the internal slave trade. In 1807, in apparent hot haste, they passed the law, nearly a year in advance,—to take effect the first day of 1808, the very first day the Constitution would permit, prohibiting the African slave trade by heavy pecuniary and corporal penalties. In 1820, finding these provisions ineffectual, they declared the slave trade piracy, and annexed to it the extreme penalty of death. While all this was passing in the General Government, five or six of the original slave States had adopted systems of gradual emancipation, by which the institution was rapidly becoming extinct within their limits. Thus we see that the plain, unmistakable spirit of that age toward slavery was hostility to the principle and toleration only by necessity.
But now it is to be transformed into a "sacred right." Nebraska brings it forth, places it on the highroad to extension and perpetuity, and with a pat on its back says to it, "Go, and God speed you." Henceforth it is to be the chief jewel of the nation the very figure-head of the ship of state. Little by little, but steadily as man's march to the grave, we have been giving up the old for the new faith. Near eighty years ago we began by declaring that all men are created equal; but now from that beginning we have run down to the other declaration, that for some men to enslave others is a "sacred right of self-government." These principles cannot stand together. They are as opposite as God and Mammon; and who ever holds to the one must despise the other. When Pettit, in connection with his support of the Nebraska Bill, called the Declaration of Independence "a self-evident lie," he only did what consistency and candor require all other Nebraska men to do. Of the forty-odd Nebraska senators who sat present and heard him, no one rebuked him. Nor am I apprised that any Nebraska newspaper, or any Nebraska orator, in the whole nation has ever yet rebuked him. If this had been said among Marion's men, Southerners though they were, what would have become of the man who said it? If this had been said to the men who captured Andre, the man who said it would probably have been hung sooner than Andre was. If it had been said in old Independence Hall seventy-eight years ago, the very doorkeeper would have throttled the man and thrust him into the street. Let no one be deceived. The spirit of seventy-six and the spirit of Nebraska are utter antagonisms; and the former is being rapidly displaced by the latter.
Fellow-countrymen, Americans, South as well as North, shall we make no effort to arrest this? Already the liberal party throughout the world express the apprehension that "the one retrograde institution in America is undermining the principles of progress, and fatally violating the noblest political system the world ever saw." This is not the taunt of enemies, but the warning of friends. Is it quite safe to disregard it—to despise it? Is there no danger to liberty itself in discarding the earliest practice and first precept of our ancient faith? In our greedy chase to make profit of the negro, let us beware lest we "cancel and tear in pieces" even the white man's charter of freedom.
Our republican robe is soiled and trailed in the dust. Let us repurify it. Let us turn and wash it white in the spirit, if not the blood, of the Revolution. Let us turn slavery from its claims of "moral right," back upon its existing legal rights and its arguments of "necessity." Let us return it to the position our fathers gave it, and there let it rest in peace. Let us readopt the Declaration of Independence, and with it the practices and policy which harmonize with it. Let North and South, let all Americans—let all lovers of liberty everywhere join in the great and good work. If we do this, we shall not only have saved the Union, but we shall have so saved it as to make and to keep it forever worthy of the saving. We shall have so saved it that the succeeding millions of free happy people the world over shall rise up and call us blessed to the latest generations.
At Springfield, twelve days ago, where I had spoken substantially as I have here, Judge Douglas replied to me; and as he is to reply to me here, I shall attempt to anticipate him by noticing some of the points he made there. He commenced by stating I had assumed all the way through that the principle of the Nebraska Bill would have the effect of extending slavery. He denied that this was intended or that this effect would follow.
I will not reopen the argument upon this point. That such was the intention the world believed at the start, and will continue to believe. This was the countenance of the thing, and both friends and enemies instantly recognized it as such. That countenance cannot now be changed by argument. You can as easily argue the color out of the negro's skin. Like the "bloody hand," you may wash it and wash it, the red witness of guilt still sticks and stares horribly at you.
Next he says that Congressional intervention never prevented slavery anywhere; that it did not prevent it in the Northwestern Territory, nor in Illinois; that, in fact, Illinois came into the Union as a slave State; that the principle of the Nebraska Bill expelled it from Illinois, from several old States, from everywhere.
Now this is mere quibbling all the way through. If the Ordinance of '87 did not keep slavery out of the Northwest Territory, how happens it that the northwest shore of the Ohio River is entirely free from it, while the southeast shore, less than a mile distant, along nearly the whole length of the river, is entirely covered with it?
If that ordinance did not keep it out of Illinois, what was it that made the difference between Illinois and Missouri? They lie side by side, the Mississippi River only dividing them, while their early settlements were within the same latitude. Between 1810 and 1820 the number of slaves in Missouri increased 7211, while in Illinois in the same ten years they decreased 51. This appears by the census returns. During nearly all of that ten years both were Territories, not States. During this time the ordinance forbade slavery to go into Illinois, and nothing forbade it to go into Missouri. It did go into Missouri, and did not go into Illinois. That is the fact. Can any one doubt as to the reason of it? But he says Illinois came into the Union as a slave State. Silence, perhaps, would be the best answer to this flat contradiction of the known history of the country. What are the facts upon which this bold assertion is based? When we first acquired the country, as far back as 1787, there were some slaves within it held by the French inhabitants of Kaskaskia. The territorial legislation admitted a few negroes from the slave States as indentured servants. One year after the adoption of the first State constitution, the whole number of them was—what do you think? Just one hundred and seventeen, while the aggregate free population was 55,094,—about four hundred and seventy to one. Upon this state of facts the people framed their constitution prohibiting the further introduction of slavery, with a sort of guaranty to the owners of the few indentured servants, giving freedom to their children to be born thereafter, and making no mention whatever of any supposed slave for life. Out of this small matter the Judge manufactures his argument that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State. Let the facts be the answer to the argument.
The principles of the Nebraska Bill, he says, expelled slavery from Illinois. The principle of that bill first planted it here—that is, it first came because there was no law to prevent it, first came before we owned the country; and finding it here, and having the Ordinance of '87 to prevent its increasing, our people struggled along, and finally got rid of it as best they could.
But the principle of the Nebraska Bill abolished slavery in several of the old States. Well, it is true that several of the old States, in the last quarter of the last century, did adopt systems of gradual emancipation by which the institution has finally become extinct within their limits; but it may or may not be true that the principle of the Nebraska Bill was the cause that led to the adoption of these measures. It is now more than fifty years since the last of these States adopted its system of emancipation.
If the Nebraska Bill is the real author of the benevolent works, it is rather deplorable that it has for so long a time ceased working altogether. Is there not some reason to suspect that it was the principle of the Revolution, and not the principle of the Nebraska Bill, that led to emancipation in these old States? Leave it to the people of these old emancipating States, and I am quite certain they will decide that neither that nor any other good thing ever did or ever will come of the Nebraska Bill.
In the course of my main argument, Judge Douglas interrupted me to say that the principle of the Nebraska Bill was very old; that it originated when God made man, and placed good and evil before him, allowing him to choose for himself, being responsible for the choice he should make. At the time I thought this was merely playful, and I answered it accordingly. But in his reply to me he renewed it as a serious argument. In seriousness, then, the facts of this proposition are not true as stated. God did not place good and evil before man, telling him to make his choice. On the contrary, he did tell him there was one tree of the fruit of which he should not eat, upon pain of certain death. I should scarcely wish so strong a prohibition against slavery in Nebraska.
But this argument strikes me as not a little remarkable in another particular—in its strong resemblance to the old argument for the "divine right of kings." By the latter, the king is to do just as he pleases with his white subjects, being responsible to God alone. By the former, the white man is to do just as he pleases with his black slaves, being responsible to God alone. The two things are precisely alike, and it is but natural that they should find similar arguments to sustain them.
I had argued that the application of the principle of self-government, as contended for, would require the revival of the African slave trade; that no argument could be made in favor of a man's right to take slaves to Nebraska which could not be equally well made in favor of his right to bring them from the coast of Africa. The Judge replied that the Constitution requires the suppression of the foreign slave trade, but does not require the prohibition of slavery in the Territories. That is a mistake in point of fact. The Constitution does not require the action of Congress in either case, and it does authorize it in both. And so there is still no difference between the cases.
In regard to what I have said of the advantage the slave States have over the free in the matter of representation, the Judge replied that we in the free States count five free negroes as five white people, while in the slave States they count five slaves as three whites only; and that the advantage, at last, was on the side of the free States.
Now, in the slave States they count free negroes just as we do; and it so happens that, besides their slaves, they have as many free negroes as we have, and thirty thousand over. Thus, their free negroes more than balance ours; and their advantage over us, in consequence of their slaves, still remains as I stated it.
In reply to my argument that the compromise measures of 1850 were a system of equivalents, and that the provisions of no one of them could fairly be carried to other subjects without its corresponding equivalent being carried with it, the Judge denied outright that these measures had any connection with or dependence upon each other. This is mere desperation. If they had no connection, why are they always spoken of in connection? Why has he so spoken of them a thousand times? Why has he constantly called them a series of measures? Why does everybody call them a compromise? Why was California kept out of the Union six or seven months, if it was not because of its connection with the other measures? Webster's leading definition of the verb "to compromise" is "to adjust and settle a difference, by mutual agreement, with concessions of claims by the parties." This conveys precisely the popular understanding of the word "compromise."
We knew, before the Judge told us, that these measures passed separately, and in distinct bills, and that no two of them were passed by the votes of precisely the same members. But we also know, and so does he know, that no one of them could have passed both branches of Congress but for the understanding that the others were to pass also. Upon this understanding, each got votes which it could have got in no other way. It is this fact which gives to the measures their true character; and it is the universal knowledge of this fact that has given them the name of "compromises," so expressive of that true character.
I had asked: "If, in carrying the Utah and New Mexico laws to Nebraska, you could clear away other objection, how could you leave Nebraska 'perfectly free' to introduce slavery before she forms a constitution, during her territorial government, while the Utah and New Mexico laws only authorize it when they form constitutions and are admitted into the Union?" To this Judge Douglas answered that the Utah and New Mexico laws also authorized it before; and to prove this he read from one of their laws, as follows: "That the legislative power of said Territory shall extend to all rightful subjects of legislation, consistent with the Constitution of the United States and the provisions of this act."
Now it is perceived from the reading of this that there is nothing express upon the subject, but that the authority is sought to be implied merely for the general provision of "all rightful subjects of legislation." In reply to this I insist, as a legal rule of construction, as well as the plain, popular view of the matter, that the express provision for Utah and New Mexico coming in with slavery, if they choose, when they shall form constitutions, is an exclusion of all implied authority on the same subject; that Congress having the subject distinctly in their minds when they made the express provision, they therein expressed their whole meaning on that subject.
The Judge rather insinuated that I had found it convenient to forget the Washington territorial law passed in 1853. This was a division of Oregon, organizing the northern part as the Territory of Washington. He asserted that by this act the Ordinance of '87, theretofore existing in Oregon, was repealed; that nearly all the members of Congress voted for it, beginning in the House of Representatives with Charles Allen of Massachusetts, and ending with Richard Yates of Illinois; and that he could not understand how those who now opposed the Nebraska Bill so voted there, unless it was because it was then too soon after both the great political parties had ratified the compromises of 1850, and the ratification therefore was too fresh to be then repudiated.
Now I had seen the Washington act before, and I have carefully examined it since; and I aver that there is no repeal of the Ordinance of '87, or of any prohibition of slavery, in it. In express terms, there is absolutely nothing in the whole law upon the subject—in fact, nothing to lead a reader to think of the subject. To my judgment it is equally free from everything from which repeal can be legally implied; but, however this may be, are men now to be entrapped by a legal implication, extracted from covert language, introduced perhaps for the very purpose of entrapping them? I sincerely wish every man could read this law quite through, carefully watching every sentence and every line for a repeal of the Ordinance of '87, or anything equivalent to it.
Another point on the Washington act: If it was intended to be modeled after the Utah and New Mexico acts, as Judge Douglas insists, why was it not inserted in it, as in them, that Washington was to come in with or without slavery as she may choose at the adoption of her constitution? It has no such provision in it; and I defy the ingenuity of man to give a reason for the omission, other than that it was not intended to follow the Utah and New Mexico laws in regard to the question of slavery.
The Washington act not only differs vitally from the Utah and New Mexico acts, but the Nebraska act differs vitally from both. By the latter act the people are left "perfectly free" to regulate their own domestic concerns, etc.; but in all the former, all their laws are to be submitted to Congress, and if disapproved are to be null. The Washington act goes even further; it absolutely prohibits the territorial Legislature, by very strong and guarded language, from establishing banks or borrowing money on the faith of the Territory. Is this the sacred right of self-government we hear vaunted so much? No, sir; the Nebraska Bill finds no model in the acts of '50 or the Washington act. It finds no model in any law from Adam till to-day. As Phillips says of Napoleon, the Nebraska act is grand, gloomy and peculiar, wrapped in the solitude of its own originality, without a model and without a shadow upon the earth.
In the course of his reply Senator Douglas remarked in substance that he had always considered this government was made for the white people and not for the negroes. Why, in point of mere fact, I think so too. But in this remark of the Judge there is a significance which I think is the key to the great mistake (if there is any such mistake) which he has made in this Nebraska measure. It shows that the Judge has no very vivid impression that the negro is human, and consequently has no idea that there can be any moral question in legislating about him. In his view the question of whether a new country shall be slave or free is a matter of as utter indifference as it is whether his neighbor shall plant his farm with tobacco or stock it with horned cattle. Now, whether this view is right or wrong, it is very certain that the great mass of mankind take a totally different view. They consider slavery a great moral wrong, and their feeling against it is not evanescent, but eternal. It lies at the very foundation of their sense of justice, and it cannot be trifled with. It is a great and durable element of popular action, and I think no statesman can safely disregard it.
Our Senator also objects that those who oppose him in this matter do not entirely agree with one another. He reminds me that in my firm adherence to the constitutional rights of the slave States I differ widely from others who are cooperating with me in opposing the Nebraska Bill, and he says it is not quite fair to oppose him in this variety of ways. He should remember that he took us by surprise—astounded us by this measure. We were thunderstruck and stunned, and we reeled and fell in utter confusion. But we rose, each fighting, grasping whatever he could first reach—a scythe, a pitchfork, a chopping-ax, or a butcher's cleaver. We struck in the direction of the sound, and we were rapidly closing in upon him. He must not think to divert us from our purpose by showing us that our drill, our dress, and our weapons are not entirely perfect and uniform. When the storm shall be past he shall find us still Americans, no less devoted to the continued union and prosperity of the country than heretofore.
Finally, the Judge invokes against me the memory of Clay and Webster, They were great men, and men of great deeds. But where have I assailed them? For what is it that their lifelong enemy shall now make profit by assuming to defend them against me, their lifelong friend? I go against the repeal of the Missouri Compromise; did they ever go for it? They went for the Compromise of 1850; did I ever go against them? They were greatly devoted to the Union; to the small measure of my ability was I ever less so? Clay and Webster were dead before this question arose; by what authority shall our Senator say they would espouse his side of it if alive? Mr. Clay was the leading spirit in making the Missouri Compromise; is it very credible that if now alive he would take the lead in the breaking of it? The truth is that some support from Whigs is now a necessity with the Judge, and for this it is that the names of Clay and Webster are invoked. His old friends have deserted him in such numbers as to leave too few to live by. He came to his own, and his own received him not; and lo! he turns unto the Gentiles.
A word now as to the Judge's desperate assumption that the compromises of 1850 had no connection with one another; that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State, and some other similar ones. This is no other than a bold denial of the history of the country. If we do not know that the compromises of 1850 were dependent on each other; if we do not know that Illinois came into the Union as a free State,—we do not know anything. If we do not know these things, we do not know that we ever had a Revolutionary War or such a chief as Washington. To deny these things is to deny our national axioms,—or dogmas, at least,—and it puts an end to all argument. If a man will stand up and assert, and repeat and reassert, that two and two do not make four, I know nothing in the power of argument that can stop him. I think I can answer the Judge so long as he sticks to the premises; but when he flies from them, I cannot work any argument into the consistency of a mental gag and actually close his mouth with it. In such a case I can only commend him to the seventy thousand answers just in from Pennsylvania, Ohio, and Indiana.
CLINTON, De WITT Co., Nov. 10, 1854
DEAR SIR:—You used to express a good deal of partiality for me, and if you are still so, now is the time. Some friends here are really for me for the U.S. Senate, and I should be very grateful if you could make a mark for me among your members. Please write me at all events, giving me the names, post-offices, and "political position" of members round about you. Direct to Springfield.
Let this be confidential.
Yours truly,
November 27, 1854 T. J. HENDERSON, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—It has come round that a whig may, by possibility, be elected to the United States Senate, and I want the chance of being the man. You are a member of the Legislature, and have a vote to give. Think it over, and see whether you can do better than to go for me.
Write me, at all events; and let this be confidential.
Yours truly,
DEAR SIR:—I have really got it into my head to try to be United States Senator, and, if I could have your support, my chances would be reasonably good. But I know, and acknowledge, that you have as just claims to the place as I have; and therefore I cannot ask you to yield to me, if you are thinking of becoming a candidate, yourself. If, however, you are not, then I should like to be remembered affectionately by you; and also to have you make a mark for me with the Anti-Nebraska members down your way.
If you know, and have no objection to tell, let me know whether Trumbull intends to make a push. If he does, I suppose the two men in St. Clair, and one, or both, in Madison, will be for him. We have the Legislature, clearly enough, on joint ballot, but the Senate is very close, and Cullom told me to-day that the Nebraska men will stave off the election, if they can. Even if we get into joint vote, we shall have difficulty to unite our forces. Please write me, and let this be confidential.
Your friend, as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., December 6, 1854.
SIR:—I understand it is in contemplation to displace the present clerk and appoint a new one for the Circuit and District Courts of Illinois. I am very friendly to the present incumbent, and, both for his own sake and that of his family, I wish him to be retained so long as it is possible for the court to do so.
In the contingency of his removal, however, I have recommended William Butler as his successor, and I do not wish what I write now to be taken as any abatement of that recommendation.
William J. Black is also an applicant for the appointment, and I write this at the solicitation of his friends to say that he is every way worthy of the office, and that I doubt not the conferring it upon him will give great satisfaction.
Your ob't servant,
HON. T. J. HENDERSON.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 11th was received last night, and for which I thank you. Of course I prefer myself to all others; yet it is neither in my heart nor my conscience to say I am any better man than Mr. Williams. We shall have a terrible struggle with our adversaries. They are desperate and bent on desperate deeds. I accidentally learned of one of the leaders here writing to a member south of here, in about the following language:
We are beaten. They have a clean majority of at least nine, on joint ballot. They outnumber us, but we must outmanage them. Douglas must be sustained. We must elect the Speaker; and we must elect a Nebraska United States Senator, or "elect none at all." Similar letters, no doubt, are written to every Nebraska member. Be considering how we can best meet, and foil, and beat them. I send you, by mail, a copy of my Peoria speech. You may have seen it before, or you may not think it worth seeing now.
Do not speak of the Nebraska letter mentioned above; I do not wish it to become public, that I received such information.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, February 9, 1855 MY DEAR SIR:
I began with 44 votes, Shields 41, and Trumbull 5,—yet Trumbull was elected. In fact 47 different members voted for me,—getting three new ones on the second ballot, and losing four old ones. How came my 47 to yield to Trumbull's 5? It was Governor Matteson's work. He has been secretly a candidate ever since (before, even) the fall election.
All the members round about the canal were Anti-Nebraska, but were nevertheless nearly all Democrats and old personal friends of his. His plan was to privately impress them with the belief that he was as good Anti-Nebraska as any one else—at least could be secured to be so by instructions, which could be easily passed.
The Nebraska men, of course, were not for Matteson; but when they found they could elect no avowed Nebraska man, they tardily determined to let him get whomever of our men he could, by whatever means he could, and ask him no questions.
The Nebraska men were very confident of the election of Matteson, though denying that he was a candidate, and we very much believing also that they would elect him. But they wanted first to make a show of good faith to Shields by voting for him a few times, and our secret Matteson men also wanted to make a show of good faith by voting with us a few times. So we led off. On the seventh ballot, I think, the signal was given to the Nebraska men to turn to Matteson, which they acted on to a man, with one exception. . . Next ballot the remaining Nebraska man and one pretended Anti went over to him, giving him 46. The next still another, giving him 47, wanting only three of an election. In the meantime our friends, with a view of detaining our expected bolters, had been turning from me to Trumbull till he had risen to 35 and I had been reduced to 15. These would never desert me except by my direction; but I became satisfied that if we could prevent Matteson's election one or two ballots more, we could not possibly do so a single ballot after my friends should begin to return to me from Trumbull. So I determined to strike at once, and accordingly advised my remaining friends to go for him, which they did and elected him on the tenth ballot.
Such is the way the thing was done. I think you would have done the same under the circumstances.
I could have headed off every combination and been elected, had it not been for Matteson's double game—and his defeat now gives me more pleasure than my own gives me pain. On the whole, it is perhaps as well for our general cause that Trumbull is elected. The Nebraska men confess that they hate it worse than anything that could have happened. It is a great consolation to see them worse whipped than I am.
Yours forever,
SPRINGFIELD, MARCH 10, 1855
GENTLEMEN:—Yours of the 5th is received, as also was that of 15th Dec, last, inclosing bond of Clift to Pray. When I received the bond I was dabbling in politics, and of course neglecting business. Having since been beaten out I have gone to work again.
As I do not practice in Rushville, I to-day open a correspondence with Henry E. Dummer, Esq., of Beardstown, Ill., with the view of getting the job into his hands. He is a good man if he will undertake it.
Write me whether I shall do this or return the bond to you.
Yours respectfully,
HON. O. H. BROWNING.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter to Judge Logan has been shown to us by him; and, with his consent, we answer it. When it became probable that there would be a vacancy on the Supreme Bench, public opinion, on this side of the river, seemed to be universally directed to Logan as the proper man to fill it. I mean public opinion on our side in politics, with very small manifestation in any different direction by the other side. The result is, that he has been a good deal pressed to allow his name to be used, and he has consented to it, provided it can be done with perfect cordiality and good feeling on the part of all our own friends. We, the undersigned, are very anxious for it; and the more so now that he has been urged, until his mind is turned upon the matter. We, therefore are very glad of your letter, with the information it brings us, mixed only with a regret that we can not elect Logan and Walker both. We shall be glad, if you will hoist Logan's name, in your Quincy papers.
Very truly your friends,
A. LINCOLN, B. S. EWARDS, JOHN T. STUART.
H. C. WHITNEY, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your note containing election news is received; and for which I thank you. It is all of no use, however. Logan is worse beaten than any other man ever was since elections were invented—beaten more than twelve hundred in this county. It is conceded on all hands that the Prohibitory law is also beaten.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, August 24, 1855
DEAR SPEED:—You know what a poor correspondent I am. Ever since I received your very agreeable letter of the 22d of May, I have been intending to write you an answer to it. You suggest that in political action, now, you and I would differ. I suppose we would; not quite as much, however, as you may think. You know I dislike slavery, and you fully admit the abstract wrong of it. So far there is no cause of difference. But you say that sooner than yield your legal right to the slave, especially at the bidding of those who are not themselves interested, you would see the Union dissolved. I am not aware that any one is bidding you yield that right; very certainly I am not. I leave that matter entirely to yourself. I also acknowledge your rights and my obligations under the Constitution in regard to your slaves. I confess I hate to see the poor creatures hunted down and caught and carried back to their stripes and unrequited toil; but I bite my lips and keep quiet. In 1841 you and I had together a tedious low-water trip on a steamboat from Louisville to St. Louis. You may remember, as I well do, that from Louisville to the mouth of the Ohio there were on board ten or a dozen slaves shackled together with irons. That sight was a continued torment to me, and I see something like it every time I touch the Ohio or any other slave border. It is not fair for you to assume that I have no interest in a thing which has, and continually exercises, the power of making me miserable. You ought rather to appreciate how much the great body of the Northern people do crucify their feelings, in order to maintain their loyalty to the Constitution and the Union. I do oppose the extension of slavery because my judgment and feeling so prompt me, and I am under no obligations to the contrary. If for this you and I must differ, differ we must. You say, if you were President, you would send an army and hang the leaders of the Missouri outrages upon the Kansas elections; still, if Kansas fairly votes herself a slave State she must be admitted or the Union must be dissolved. But how if she votes herself a slave State unfairly, that is, by the very means for which you say you would hang men? Must she still be admitted, or the Union dissolved? That will be the phase of the question when it first becomes a practical one. In your assumption that there may be a fair decision of the slavery question in Kansas, I plainly see you and I would differ about the Nebraska law. I look upon that enactment not as a law, but as a violence from the beginning. It was conceived in violence, is maintained in violence, and is being executed in violence. I say it was conceived in violence, because the destruction of the Missouri Compromise, under the circumstances, was nothing less than violence. It was passed in violence because it could not have passed at all but for the votes of many members in violence of the known will of their constituents. It is maintained in violence, because the elections since clearly demand its repeal; and the demand is openly disregarded.
You say men ought to be hung for the way they are executing the law; I say the way it is being executed is quite as good as any of its antecedents. It is being executed in the precise way which was intended from the first, else why does no Nebraska man express astonishment or condemnation? Poor Reeder is the only public man who has been silly enough to believe that anything like fairness was ever intended, and he has been bravely undeceived.
That Kansas will form a slave constitution, and with it will ask to be admitted into the Union, I take to be already a settled question, and so settled by the very means you so pointedly condemn. By every principle of law ever held by any court North or South, every negro taken to Kansas is free; yet, in utter disregard of this,—in the spirit of violence merely,—that beautiful Legislature gravely passes a law to hang any man who shall venture to inform a negro of his legal rights. This is the subject and real object of the law. If, like Haman, they should hang upon the gallows of their own building, I shall not be among the mourners for their fate. In my humble sphere, I shall advocate the restoration of the Missouri Compromise so long as Kansas remains a Territory, and when, by all these foul means, it seeks to come into the Union as a slave State, I shall oppose it. I am very loath in any case to withhold my assent to the enjoyment of property acquired or located in good faith; but I do not admit that good faith in taking a negro to Kansas to be held in slavery is a probability with any man. Any man who has sense enough to be the controller of his own property has too much sense to misunderstand the outrageous character of the whole Nebraska business. But I digress. In my opposition to the admission of Kansas I shall have some company, but we may be beaten. If we are, I shall not on that account attempt to dissolve the Union. I think it probable, however, we shall be beaten. Standing as a unit among yourselves, You can, directly and indirectly, bribe enough of our men to carry the day, as you could on the open proposition to establish a monarchy. Get hold of some man in the North whose position and ability is such that he can make the support of your measure, whatever it may be, a Democratic party necessity, and the thing is done. Apropos of this, let me tell you an anecdote. Douglas introduced the Nebraska Bill in January. In February afterward there was a called session of the Illinois Legislature. Of the one hundred members composing the two branches of that body, about seventy were Democrats. These latter held a caucus in which the Nebraska Bill was talked of, if not formally discussed. It was thereby discovered that just three, and no more, were in favor of the measure. In a day or two Douglas's orders came on to have resolutions passed approving the bill; and they were passed by large majorities!!!! The truth of this is vouched for by a bolting Democratic member. The masses, too, Democratic as well as Whig, were even nearer unanimous against it; but, as soon as the party necessity of supporting it became apparent, the way the Democrats began to see the wisdom and justice of it was perfectly astonishing.
You say that if Kansas fairly votes herself a free State, as a Christian you will rejoice at it. All decent slaveholders talk that way, and I do not doubt their candor. But they never vote that way. Although in a private letter or conversation you will express your preference that Kansas shall be free, you would vote for no man for Congress who would say the same thing publicly. No such man could be elected from any district in a slave State. You think Stringfellow and company ought to be hung; and yet at the next Presidential election you will vote for the exact type and representative of Stringfellow. The slave-breeders and slave-traders are a small, odious, and detested class among you; and yet in politics they dictate the course of all of you, and are as completely your masters as you are the master of your own negroes. You inquire where I now stand. That is a disputed point. I think I am a Whig; but others say there are no Whigs, and that I am an Abolitionist. When I was at Washington, I voted for the Wilmot Proviso as good as forty times; and I never heard of any one attempting to un-Whig me for that. I now do no more than oppose the extension of slavery. I am not a Know-Nothing; that is certain. How could I be? How can any one who abhors the oppression of negroes be in favor of degrading classes of white people? Our progress in degeneracy appears to me to be pretty rapid. As a nation we began by declaring that "all men are created equal." We now practically read it "all men are created equal, except negroes." When the Know-Nothings get control, it will read "all men are created equal, except negroes and foreigners and Catholics." When it comes to this, I shall prefer emigrating to some country where they make no pretense of loving liberty,—to Russia, for instance, where despotism can be taken pure, and without the base alloy of hypocrisy.
Mary will probably pass a day or two in Louisville in October. My kindest regards to Mrs. Speed. On the leading subject of this letter I have more of her sympathy than I have of yours; and yet let me say I am,
Your friend forever,
SPRINGFIELD, February 13, 1856.
R. P. MORGAN, ESQ.:
Says Tom to John, "Here's your old rotten wheelbarrow. I've broke it usin' on it. I wish you would mend it, 'case I shall want to borrow it this arternoon." Acting on this as a precedent, I say, "Here's your old 'chalked hat,—I wish you would take it and send me a new one, 'case I shall want to use it the first of March."
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
(A 'chalked hat' was the common term, at that time, for a railroad pass.)
[From the Report by William C. Whitney.]
(Mr. Whitney's notes were made at the time, but not written out until 1896. He does not claim that the speech, as here reported, is literally correct only that he has followed the argument, and that in many cases the sentences are as Mr. Lincoln spoke them.)
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND GENTLEMEN: I was over at [Cries of "Platform!" "Take the platform!"]—I say, that while I was at Danville Court, some of our friends of Anti-Nebraska got together in Springfield and elected me as one delegate to represent old Sangamon with them in this convention, and I am here certainly as a sympathizer in this movement and by virtue of that meeting and selection. But we can hardly be called delegates strictly, inasmuch as, properly speaking, we represent nobody but ourselves. I think it altogether fair to say that we have no Anti-Nebraska party in Sangamon, although there is a good deal of Anti-Nebraska feeling there; but I say for myself, and I think I may speak also for my colleagues, that we who are here fully approve of the platform and of all that has been done [A voice, "Yes!"], and even if we are not regularly delegates, it will be right for me to answer your call to speak. I suppose we truly stand for the public sentiment of Sangamon on the great question of the repeal, although we do not yet represent many numbers who have taken a distinct position on the question.
We are in a trying time—it ranges above mere party—and this movement to call a halt and turn our steps backward needs all the help and good counsels it can get; for unless popular opinion makes itself very strongly felt, and a change is made in our present course, blood will flow on account of Nebraska, and brother's hands will be raised against brother!
[The last sentence was uttered in such an earnest, impressive, if not, indeed, tragic, manner, as to make a cold chill creep over me. Others gave a similar experience.]
I have listened with great interest to the earnest appeal made to Illinois men by the gentleman from Lawrence [James S. Emery] who has just addressed us so eloquently and forcibly. I was deeply moved by his statement of the wrongs done to free-State men out there. I think it just to say that all true men North should sympathize with them, and ought to be willing to do any possible and needful thing to right their wrongs. But we must not promise what we ought not, lest we be called on to perform what we cannot; we must be calm and moderate, and consider the whole difficulty, and determine what is possible and just. We must not be led by excitement and passion to do that which our sober judgments would not approve in our cooler moments. We have higher aims; we will have more serious business than to dally with temporary measures.
We are here to stand firmly for a principle—to stand firmly for a right. We know that great political and moral wrongs are done, and outrages committed, and we denounce those wrongs and outrages, although we cannot, at present, do much more. But we desire to reach out beyond those personal outrages and establish a rule that will apply to all, and so prevent any future outrages.
We have seen to-day that every shade of popular opinion is represented here, with Freedom, or rather Free Soil, as the basis. We have come together as in some sort representatives of popular opinion against the extension of slavery into territory now free in fact as well as by law, and the pledged word of the statesmen of the nation who are now no more. We come—we are here assembled together—to protest as well as we can against a great wrong, and to take measures, as well as we now can, to make that wrong right; to place the nation, as far as it may be possible now, as it was before the repeal of the Missouri Compromise; and the plain way to do this is to restore the Compromise, and to demand and determine that Kansas shall be free! [Immense applause.] While we affirm, and reaffirm, if necessary, our devotion to the principles of the Declaration of Independence, let our practical work here be limited to the above. We know that there is not a perfect agreement of sentiment here on the public questions which might be rightfully considered in this convention, and that the indignation which we all must feel cannot be helped; but all of us must give up something for the good of the cause. There is one desire which is uppermost in the mind, one wish common to us all, to which no dissent will be made; and I counsel you earnestly to bury all resentment, to sink all personal feeling, make all things work to a common purpose in which we are united and agreed about, and which all present will agree is absolutely necessary—which must be done by any rightful mode if there be such: Slavery must be kept out of Kansas! [Applause.] The test—the pinch—is right there. If we lose Kansas to freedom, an example will be set which will prove fatal to freedom in the end. We, therefore, in the language of the Bible, must "lay the axe to the root of the tree." Temporizing will not do longer; now is the time for decision—for firm, persistent, resolute action. [Applause.]
The Nebraska Bill, or rather Nebraska law, is not one of wholesome legislation, but was and is an act of legislative usurpation, whose result, if not indeed intention, is to make slavery national; and unless headed off in some effective way, we are in a fair way to see this land of boasted freedom converted into a land of slavery in fact. [Sensation.] Just open your two eyes, and see if this be not so. I need do no more than state, to command universal approval, that almost the entire North, as well as a large following in the border States, is radically opposed to the planting of slavery in free territory. Probably in a popular vote throughout the nation nine tenths of the voters in the free States, and at least one-half in the border States, if they could express their sentiments freely, would vote NO on such an issue; and it is safe to say that two thirds of the votes of the entire nation would be opposed to it. And yet, in spite of this overbalancing of sentiment in this free country, we are in a fair way to see Kansas present itself for admission as a slave State. Indeed, it is a felony, by the local law of Kansas, to deny that slavery exists there even now. By every principle of law, a negro in Kansas is free; yet the bogus Legislature makes it an infamous crime to tell him that he is free!
Statutes of Kansas, 1555, chapter 151, Sec. 12: If any free person, by speaking or by writing, assert or maintain that persons have not the right to hold slaves in this Territory, or shall introduce into this Territory, print, publish, write, circulate . . . any book, paper, magazine, pamphlet, or circular containing any denial of the right of persons to hold slaves in this Territory such person shall be deemed guilty of felony, and punished by imprisonment at hard labor for a term of not less than two years. Sec. 13. No person who is conscientiously opposed to holding slaves, or who does not admit the right to hold slaves in this Territory, shall sit as a juror on the trial of any prosecution for any violation of any Sections of this Act.
The party lash and the fear of ridicule will overawe justice and liberty; for it is a singular fact, but none the less a fact, and well known by the most common experience, that men will do things under the terror of the party lash that they would not on any account or for any consideration do otherwise; while men who will march up to the mouth of a loaded cannon without shrinking will run from the terrible name of "Abolitionist," even when pronounced by a worthless creature whom they, with good reason, despise. For instance—to press this point a little—Judge Douglas introduced his Nebraska Bill in January; and we had an extra session of our Legislature in the succeeding February, in which were seventy-five Democrats; and at a party caucus, fully attended, there were just three votes, out of the whole seventy-five, for the measure. But in a few days orders came on from Washington, commanding them to approve the measure; the party lash was applied, and it was brought up again in caucus, and passed by a large majority. The masses were against it, but party necessity carried it; and it was passed through the lower house of Congress against the will of the people, for the same reason. Here is where the greatest danger lies that, while we profess to be a government of law and reason, law will give way to violence on demand of this awful and crushing power. Like the great Juggernaut—I think that is the name—the great idol, it crushes everything that comes in its way, and makes a [?]—or, as I read once, in a blackletter law book, "a slave is a human being who is legally not a person but a thing." And if the safeguards to liberty are broken down, as is now attempted, when they have made things of all the free negroes, how long, think you, before they will begin to make things of poor white men? [Applause.] Be not deceived. Revolutions do not go backward. The founder of the Democratic party declared that all men were created equal. His successor in the leadership has written the word "white" before men, making it read "all white men are created equal." Pray, will or may not the Know-Nothings, if they should get in power, add the word "Protestant," making it read "all Protestant white men...?"
Meanwhile the hapless negro is the fruitful subject of reprisals in other quarters. John Pettit, whom Tom Benton paid his respects to, you will recollect, calls the immortal Declaration "a self-evident lie"; while at the birthplace of freedom—in the shadow of Bunker Hill and of the "cradle of liberty," at the home of the Adamses and Warren and Otis—Choate, from our side of the house, dares to fritter away the birthday promise of liberty by proclaiming the Declaration to be "a string of glittering generalities"; and the Southern Whigs, working hand in hand with proslavery Democrats, are making Choate's theories practical. Thomas Jefferson, a slaveholder, mindful of the moral element in slavery, solemnly declared that he trembled for his country when he remembered that God is just; while Judge Douglas, with an insignificant wave of the hand, "don't care whether slavery is voted up or voted down." Now, if slavery is right, or even negative, he has a right to treat it in this trifling manner. But if it is a moral and political wrong, as all Christendom considers it to be, how can he answer to God for this attempt to spread and fortify it? [Applause.]
But no man, and Judge Douglas no more than any other, can maintain a negative, or merely neutral, position on this question; and, accordingly, he avows that the Union was made by white men and for white men and their descendants. As matter of fact, the first branch of the proposition is historically true; the government was made by white men, and they were and are the superior race. This I admit. But the corner-stone of the government, so to speak, was the declaration that "all men are created equal," and all entitled to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness." [Applause.]
And not only so, but the framers of the Constitution were particular to keep out of that instrument the word "slave," the reason being that slavery would ultimately come to an end, and they did not wish to have any reminder that in this free country human beings were ever prostituted to slavery. [Applause.] Nor is it any argument that we are superior and the negro inferior—that he has but one talent while we have ten. Let the negro possess the little he has in independence; if he has but one talent, he should be permitted to keep the little he has. [Applause:] But slavery will endure no test of reason or logic; and yet its advocates, like Douglas, use a sort of bastard logic, or noisy assumption it might better be termed, like the above, in order to prepare the mind for the gradual, but none the less certain, encroachments of the Moloch of slavery upon the fair domain of freedom. But however much you may argue upon it, or smother it in soft phrase, slavery can only be maintained by force—by violence. The repeal of the Missouri Compromise was by violence. It was a violation of both law and the sacred obligations of honor, to overthrow and trample under foot a solemn compromise, obtained by the fearful loss to freedom of one of the fairest of our Western domains. Congress violated the will and confidence of its constituents in voting for the bill; and while public sentiment, as shown by the elections of 1854, demanded the restoration of this compromise, Congress violated its trust by refusing simply because it had the force of numbers to hold on to it. And murderous violence is being used now, in order to force slavery on to Kansas; for it cannot be done in any other way. [Sensation.]
The necessary result was to establish the rule of violence—force, instead of the rule of law and reason; to perpetuate and spread slavery, and in time to make it general. We see it at both ends of the line. In Washington, on the very spot where the outrage was started, the fearless Sumner is beaten to insensibility, and is now slowly dying; while senators who claim to be gentlemen and Christians stood by, countenancing the act, and even applauding it afterward in their places in the Senate. Even Douglas, our man, saw it all and was within helping distance, yet let the murderous blows fall unopposed. Then, at the other end of the line, at the very time Sumner was being murdered, Lawrence was being destroyed for the crime of freedom. It was the most prominent stronghold of liberty in Kansas, and must give way to the all-dominating power of slavery. Only two days ago, Judge Trumbull found it necessary to propose a bill in the Senate to prevent a general civil war and to restore peace in Kansas.
We live in the midst of alarms; anxiety beclouds the future; we expect some new disaster with each newspaper we read. Are we in a healthful political state? Are not the tendencies plain? Do not the signs of the times point plainly the way in which we are going? [Sensation.]
In the early days of the Constitution slavery was recognized, by South and North alike, as an evil, and the division of sentiment about it was not controlled by geographical lines or considerations of climate, but by moral and philanthropic views. Petitions for the abolition of slavery were presented to the very first Congress by Virginia and Massachusetts alike. To show the harmony which prevailed, I will state that a fugitive slave law was passed in 1793, with no dissenting voice in the Senate, and but seven dissenting votes in the House. It was, however, a wise law, moderate, and, under the Constitution, a just one. Twenty-five years later, a more stringent law was proposed and defeated; and thirty-five years after that, the present law, drafted by Mason of Virginia, was passed by Northern votes. I am not, just now, complaining of this law, but I am trying to show how the current sets; for the proposed law of 1817 was far less offensive than the present one. In 1774 the Continental Congress pledged itself, without a dissenting vote, to wholly discontinue the slave trade, and to neither purchase nor import any slave; and less than three months before the passage of the Declaration of Independence, the same Congress which adopted that declaration unanimously resolved "that no slave be imported into any of the thirteen United Colonies." [Great applause.]
On the second day of July, 1776, the draft of a Declaration of Independence was reported to Congress by the committee, and in it the slave trade was characterized as "an execrable commerce," as "a piratical warfare," as the "opprobrium of infidel powers," and as "a cruel war against human nature." [Applause.] All agreed on this except South Carolina and Georgia, and in order to preserve harmony, and from the necessity of the case, these expressions were omitted. Indeed, abolition societies existed as far south as Virginia; and it is a well-known fact that Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Lee, Henry, Mason, and Pendleton were qualified abolitionists, and much more radical on that subject than we of the Whig and Democratic parties claim to be to-day. On March 1, 1784, Virginia ceded to the confederation all its lands lying northwest of the Ohio River. Jefferson, Chase of Maryland, and Howell of Rhode Island, as a committee on that and territory thereafter to be ceded, reported that no slavery should exist after the year 1800. Had this report been adopted, not only the Northwest, but Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Mississippi also would have been free; but it required the assent of nine States to ratify it. North Carolina was divided, and thus its vote was lost; and Delaware, Georgia, and New Jersey refused to vote. In point of fact, as it was, it was assented to by six States. Three years later on a square vote to exclude slavery from the Northwest, only one vote, and that from New York, was against it. And yet, thirty-seven years later, five thousand citizens of Illinois, out of a voting mass of less than twelve thousand, deliberately, after a long and heated contest, voted to introduce slavery in Illinois; and, to-day, a large party in the free State of Illinois are willing to vote to fasten the shackles of slavery on the fair domain of Kansas, notwithstanding it received the dowry of freedom long before its birth as a political community. I repeat, therefore, the question: Is it not plain in what direction we are tending? [Sensation.] In the colonial time, Mason, Pendleton, and Jefferson were as hostile to slavery in Virginia as Otis, Ames, and the Adamses were in Massachusetts; and Virginia made as earnest an effort to get rid of it as old Massachusetts did. But circumstances were against them and they failed; but not that the good will of its leading men was lacking. Yet within less than fifty years Virginia changed its tune, and made negro-breeding for the cotton and sugar States one of its leading industries. [Laughter and applause.]
In the Constitutional Convention, George Mason of Virginia made a more violent abolition speech than my friends Lovejoy or Codding would desire to make here to-day—a speech which could not be safely repeated anywhere on Southern soil in this enlightened year. But, while there were some differences of opinion on this subject even then, discussion was allowed; but as you see by the Kansas slave code, which, as you know, is the Missouri slave code, merely ferried across the river, it is a felony to even express an opinion hostile to that foul blot in the land of Washington and the Declaration of Independence. [Sensation.]
In Kentucky—my State—in 1849, on a test vote, the mighty influence of Henry Clay and many other good then there could not get a symptom of expression in favor of gradual emancipation on a plain issue of marching toward the light of civilization with Ohio and Illinois; but the State of Boone and Hardin and Henry Clay, with a nigger under each arm, took the black trail toward the deadly swamps of barbarism. Is there—can there be—any doubt about this thing? And is there any doubt that we must all lay aside our prejudices and march, shoulder to shoulder, in the great army of Freedom? [Applause.]
Every Fourth of July our young orators all proclaim this to be "the land of the free and the home of the brave!" Well, now, when you orators get that off next year, and, may be, this very year, how would you like some old grizzled farmer to get up in the grove and deny it? [Laughter.] How would you like that? But suppose Kansas comes in as a slave State, and all the "border ruffians" have barbecues about it, and free-State men come trailing back to the dishonored North, like whipped dogs with their tails between their legs, it is—ain't it?—evident that this is no more the "land of the free"; and if we let it go so, we won't dare to say "home of the brave" out loud. [Sensation and confusion.]
Can any man doubt that, even in spite of the people's will, slavery will triumph through violence, unless that will be made manifest and enforced? Even Governor Reeder claimed at the outset that the contest in Kansas was to be fair, but he got his eyes open at last; and I believe that, as a result of this moral and physical violence, Kansas will soon apply for admission as a slave State. And yet we can't mistake that the people don't want it so, and that it is a land which is free both by natural and political law. No law, is free law! Such is the understanding of all Christendom. In the Somerset case, decided nearly a century ago, the great Lord Mansfield held that slavery was of such a nature that it must take its rise in positive (as distinguished from natural) law; and that in no country or age could it be traced back to any other source. Will some one please tell me where is the positive law that establishes slavery in Kansas? [A voice: "The bogus laws."] Aye, the bogus laws! And, on the same principle, a gang of Missouri horse-thieves could come into Illinois and declare horse-stealing to be legal [Laughter], and it would be just as legal as slavery is in Kansas. But by express statute, in the land of Washington and Jefferson, we may soon be brought face to face with the discreditable fact of showing to the world by our acts that we prefer slavery to freedom—darkness to light! [Sensation.]
It is, I believe, a principle in law that when one party to a contract violates it so grossly as to chiefly destroy the object for which it is made, the other party may rescind it. I will ask Browning if that ain't good law. [Voices: "Yes!"] Well, now if that be right, I go for rescinding the whole, entire Missouri Compromise and thus turning Missouri into a free State; and I should like to know the difference—should like for any one to point out the difference—between our making a free State of Missouri and their making a slave State of Kansas. [Great applause.] There ain't one bit of difference, except that our way would be a great mercy to humanity. But I have never said, and the Whig party has never said, and those who oppose the Nebraska Bill do not as a body say, that they have any intention of interfering with slavery in the slave States. Our platform says just the contrary. We allow slavery to exist in the slave States, not because slavery is right or good, but from the necessities of our Union. We grant a fugitive slave law because it is so "nominated in the bond"; because our fathers so stipulated—had to—and we are bound to carry out this agreement. But they did not agree to introduce slavery in regions where it did not previously exist. On the contrary, they said by their example and teachings that they did not deem it expedient—did n't consider it right—to do so; and it is wise and right to do just as they did about it. [Voices: "Good!"] And that it what we propose—not to interfere with slavery where it exists (we have never tried to do it), and to give them a reasonable and efficient fugitive slave law. [A voice: "No!"] I say YES! [Applause.] It was part of the bargain, and I 'm for living up to it; but I go no further; I'm not bound to do more, and I won't agree any further. [Great applause.]
We, here in Illinois, should feel especially proud of the provision of the Missouri Compromise excluding slavery from what is now Kansas; for an Illinois man, Jesse B. Thomas, was its father. Henry Clay, who is credited with the authorship of the Compromise in general terms, did not even vote for that provision, but only advocated the ultimate admission by a second compromise; and Thomas was, beyond all controversy, the real author of the "slavery restriction" branch of the Compromise. To show the generosity of the Northern members toward the Southern side: on a test vote to exclude slavery from Missouri, ninety voted not to exclude, and eighty-seven to exclude, every vote from the slave States being ranged with the former and fourteen votes from the free States, of whom seven were from New England alone; while on a vote to exclude slavery from what is now Kansas, the vote was one hundred and thirty-four for, to forty-two against. The scheme, as a whole, was, of course, a Southern triumph. It is idle to contend otherwise, as is now being done by the Nebraskites; it was so shown by the votes and quite as emphatically by the expressions of representative men. Mr. Lowndes of South Carolina was never known to commit a political mistake; his was the great judgment of that section; and he declared that this measure "would restore tranquillity to the country—a result demanded by every consideration of discretion, of moderation, of wisdom, and of virtue." When the measure came before President Monroe for his approval, he put to each member of his cabinet this question: "Has Congress the constitutional power to prohibit slavery in a Territory?" And John C. Calhoun and William H. Crawford from the South, equally with John Quincy Adams, Benjamin Rush, and Smith Thompson from the North, alike answered, "Yes!" without qualification or equivocation; and this measure, of so great consequence to the South, was passed; and Missouri was, by means of it, finally enabled to knock at the door of the Republic for an open passage to its brood of slaves. And, in spite of this, Freedom's share is about to be taken by violence—by the force of misrepresentative votes, not called for by the popular will. What name can I, in common decency, give to this wicked transaction? [Sensation.]
But even then the contest was not over; for when the Missouri constitution came before Congress for its approval, it forbade any free negro or mulatto from entering the State. In short, our Illinois "black laws" were hidden away in their constitution [Laughter], and the controversy was thus revived. Then it was that Mr. Clay's talents shone out conspicuously, and the controversy that shook the union to its foundation was finally settled to the satisfaction of the conservative parties on both sides of the line, though not to the extremists on either, and Missouri was admitted by the small majority of six in the lower House. How great a majority, do you think, would have been given had Kansas also been secured for slavery? [A voice: "A majority the other way."] "A majority the other way," is answered. Do you think it would have been safe for a Northern man to have confronted his constituents after having voted to consign both Missouri and Kansas to hopeless slavery? And yet this man Douglas, who misrepresents his constituents and who has exerted his highest talents in that direction, will be carried in triumph through the State and hailed with honor while applauding that act. [Three groans for "Dug!"] And this shows whither we are tending. This thing of slavery is more powerful than its supporters—even than the high priests that minister at its altar. It debauches even our greatest men. It gathers strength, like a rolling snowball, by its own infamy. Monstrous crimes are committed in its name by persons collectively which they would not dare to commit as individuals. Its aggressions and encroachments almost surpass belief. In a despotism, one might not wonder to see slavery advance steadily and remorselessly into new dominions; but is it not wonderful, is it not even alarming, to see its steady advance in a land dedicated to the proposition that "all men are created equal"? [Sensation.]
It yields nothing itself; it keeps all it has, and gets all it can besides. It really came dangerously near securing Illinois in 1824; it did get Missouri in 1821. The first proposition was to admit what is now Arkansas and Missouri as one slave State. But the territory was divided and Arkansas came in, without serious question, as a slave State; and afterwards Missouri, not, as a sort of equality, free, but also as a slave State. Then we had Florida and Texas; and now Kansas is about to be forced into the dismal procession. [Sensation.] And so it is wherever you look. We have not forgotten—it is but six years since—how dangerously near California came to being a slave State. Texas is a slave State, and four other slave States may be carved from its vast domain. And yet, in the year 1829, slavery was abolished throughout that vast region by a royal decree of the then sovereign of Mexico. Will you please tell me by what right slavery exists in Texas to-day? By the same right as, and no higher or greater than, slavery is seeking dominion in Kansas: by political force—peaceful, if that will suffice; by the torch (as in Kansas) and the bludgeon (as in the Senate chamber), if required. And so history repeats itself; and even as slavery has kept its course by craft, intimidation, and violence in the past, so it will persist, in my judgment, until met and dominated by the will of a people bent on its restriction.
We have, this very afternoon, heard bitter denunciations of Brooks in Washington, and Titus, Stringfellow, Atchison, Jones, and Shannon in Kansas—the battle-ground of slavery. I certainly am not going to advocate or shield them; but they and their acts are but the necessary outcome of the Nebraska law. We should reserve our highest censure for the authors of the mischief, and not for the catspaws which they use. I believe it was Shakespeare who said, "Where the offence lies, there let the axe fall"; and, in my opinion, this man Douglas and the Northern men in Congress who advocate "Nebraska" are more guilty than a thousand Joneses and Stringfellows, with all their murderous practices, can be. [Applause.]
We have made a good beginning here to-day. As our Methodist friends would say, "I feel it is good to be here." While extremists may find some fault with the moderation of our platform, they should recollect that "the battle is not always to the strong, nor the race to the swift." In grave emergencies, moderation is generally safer than radicalism; and as this struggle is likely to be long and earnest, we must not, by our action, repel any who are in sympathy with us in the main, but rather win all that we can to our standard. We must not belittle nor overlook the facts of our condition—that we are new and comparatively weak, while our enemies are entrenched and relatively strong. They have the administration and the political power; and, right or wrong, at present they have the numbers. Our friends who urge an appeal to arms with so much force and eloquence should recollect that the government is arrayed against us, and that the numbers are now arrayed against us as well; or, to state it nearer to the truth, they are not yet expressly and affirmatively for us; and we should repel friends rather than gain them by anything savoring of revolutionary methods. As it now stands, we must appeal to the sober sense and patriotism of the people. We will make converts day by day; we will grow strong by calmness and moderation; we will grow strong by the violence and injustice of our adversaries. And, unless truth be a mockery and justice a hollow lie, we will be in the majority after a while, and then the revolution which we will accomplish will be none the less radical from being the result of pacific measures. The battle of freedom is to be fought out on principle. Slavery is a violation of the eternal right. We have temporized with it from the necessities of our condition; but as sure as God reigns and school children read, THAT BLACK FOUL LIE CAN NEVER BE CONSECRATED INTO GOD'S HALLOWED TRUTH! [Immense applause lasting some time.]
One of our greatest difficulties is, that men who know that slavery is a detestable crime and ruinous to the nation are compelled, by our peculiar condition and other circumstances, to advocate it concretely, though damning it in the raw. Henry Clay was a brilliant example of this tendency; others of our purest statesmen are compelled to do so; and thus slavery secures actual support from those who detest it at heart. Yet Henry Clay perfected and forced through the compromise which secured to slavery a great State as well as a political advantage. Not that he hated slavery less, but that he loved the whole Union more. As long as slavery profited by his great compromise, the hosts of proslavery could not sufficiently cover him with praise; but now that this compromise stands in their way—
"....they never mention him, His name is never heard: Their lips are now forbid to speak That once familiar word."
They have slaughtered one of his most cherished measures, and his ghost would arise to rebuke them. [Great applause.]
Now, let us harmonize, my friends, and appeal to the moderation and patriotism of the people: to the sober second thought; to the awakened public conscience. The repeal of the sacred Missouri Compromise has installed the weapons of violence: the bludgeon, the incendiary torch, the death-dealing rifle, the bristling cannon—the weapons of kingcraft, of the inquisition, of ignorance, of barbarism, of oppression. We see its fruits in the dying bed of the heroic Sumner; in the ruins of the "Free State" hotel; in the smoking embers of the Herald of Freedom; in the free-State Governor of Kansas chained to a stake on freedom's soil like a horse-thief, for the crime of freedom. [Applause.] We see it in Christian statesmen, and Christian newspapers, and Christian pulpits applauding the cowardly act of a low bully, WHO CRAWLED UPON HIS VICTIM BEHIND HIS BACK AND DEALT THE DEADLY BLOW. [Sensation and applause.] We note our political demoralization in the catch-words that are coming into such common use; on the one hand, "freedom-shriekers," and sometimes "freedom-screechers" [Laughter], and, on the other hand, "border-ruffians," and that fully deserved. And the significance of catch-words cannot pass unheeded, for they constitute a sign of the times. Everything in this world "jibes" in with everything else, and all the fruits of this Nebraska Bill are like the poisoned source from which they come. I will not say that we may not sooner or later be compelled to meet force by force; but the time has not yet come, and, if we are true to ourselves, may never come. Do not mistake that the ballot is stronger than the bullet. Therefore let the legions of slavery use bullets; but let us wait patiently till November and fire ballots at them in return; and by that peaceful policy I believe we shall ultimately win. [Applause.]
It was by that policy that here in Illinois the early fathers fought the good fight and gained the victory. In 1824 the free men of our State, led by Governor Coles (who was a native of Maryland and President Madison's private secretary), determined that those beautiful groves should never re-echo the dirge of one who has no title to himself. By their resolute determination, the winds that sweep across our broad prairies shall never cool the parched brow, nor shall the unfettered streams that bring joy and gladness to our free soil water the tired feet, of a slave; but so long as those heavenly breezes and sparkling streams bless the land, or the groves and their fragrance or memory remain, the humanity to which they minister SHALL BE FOREVER FREE! [Great applause] Palmer, Yates, Williams, Browning, and some more in this convention came from Kentucky to Illinois (instead of going to Missouri), not only to better their conditions, but also to get away from slavery. They have said so to me, and it is understood among us Kentuckians that we don't like it one bit. Now, can we, mindful of the blessings of liberty which the early men of Illinois left to us, refuse a like privilege to the free men who seek to plant Freedom's banner on our Western outposts? ["No!" "No!"] Should we not stand by our neighbors who seek to better their conditions in Kansas and Nebraska? ["Yes!" "Yes!"] Can we as Christian men, and strong and free ourselves, wield the sledge or hold the iron which is to manacle anew an already oppressed race? ["No!" "No!"] "Woe unto them," it is written, "that decree unrighteous decrees and that write grievousness which they have prescribed." Can we afford to sin any more deeply against human liberty? ["No!" "No!"]
One great trouble in the matter is, that slavery is an insidious and crafty power, and gains equally by open violence of the brutal as well as by sly management of the peaceful. Even after the Ordinance of 1787, the settlers in Indiana and Illinois (it was all one government then) tried to get Congress to allow slavery temporarily, and petitions to that end were sent from Kaskaskia, and General Harrison, the Governor, urged it from Vincennes, the capital. If that had succeeded, good-bye to liberty here. But John Randolph of Virginia made a vigorous report against it; and although they persevered so well as to get three favorable reports for it, yet the United States Senate, with the aid of some slave States, finally squelched if for good. [Applause.] And that is why this hall is to-day a temple for free men instead of a negro livery-stable. [Great applause and laughter.] Once let slavery get planted in a locality, by ever so weak or doubtful a title, and in ever so small numbers, and it is like the Canada thistle or Bermuda grass—you can't root it out. You yourself may detest slavery; but your neighbor has five or six slaves, and he is an excellent neighbor, or your son has married his daughter, and they beg you to help save their property, and you vote against your interests and principle to accommodate a neighbor, hoping that your vote will be on the losing side. And others do the same; and in those ways slavery gets a sure foothold. And when that is done the whole mighty Union—the force of the nation—is committed to its support. And that very process is working in Kansas to-day. And you must recollect that the slave property is worth a billion of dollars; while free-State men must work for sentiment alone. Then there are "blue lodges"—as they call them—everywhere doing their secret and deadly work.
It is a very strange thing, and not solvable by any moral law that I know of, that if a man loses his horse, the whole country will turn out to help hang the thief; but if a man but a shade or two darker than I am is himself stolen, the same crowd will hang one who aids in restoring him to liberty. Such are the inconsistencies of slavery, where a horse is more sacred than a man; and the essence of squatter or popular sovereignty—I don't care how you call it—is that if one man chooses to make a slave of another, no third man shall be allowed to object. And if you can do this in free Kansas, and it is allowed to stand, the next thing you will see is shiploads of negroes from Africa at the wharf at Charleston, for one thing is as truly lawful as the other; and these are the bastard notions we have got to stamp out, else they will stamp us out. [Sensation and applause.]
Two years ago, at Springfield, Judge Douglas avowed that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State, and that slavery was weeded out by the operation of his great, patent, everlasting principle of "popular sovereignty." [Laughter.] Well, now, that argument must be answered, for it has a little grain of truth at the bottom. I do not mean that it is true in essence, as he would have us believe. It could not be essentially true if the Ordinance of '87 was valid. But, in point of fact, there were some degraded beings called slaves in Kaskaskia and the other French settlements when our first State constitution was adopted; that is a fact, and I don't deny it. Slaves were brought here as early as 1720, and were kept here in spite of the Ordinance of 1787 against it. But slavery did not thrive here. On the contrary, under the influence of the ordinance the number decreased fifty-one from 1810 to 1820; while under the influence of squatter sovereignty, right across the river in Missouri, they increased seven thousand two hundred and eleven in the same time; and slavery finally faded out in Illinois, under the influence of the law of freedom, while it grew stronger and stronger in Missouri, under the law or practice of "popular sovereignty." In point of fact there were but one hundred and seventeen slaves in Illinois one year after its admission, or one to every four hundred and seventy of its population; or, to state it in another way, if Illinois was a slave State in 1820, so were New York and New Jersey much greater slave States from having had greater numbers, slavery having been established there in very early times. But there is this vital difference between all these States and the Judge's Kansas experiment: that they sought to disestablish slavery which had been already established, while the Judge seeks, so far as he can, to disestablish freedom, which had been established there by the Missouri Compromise. [Voices: "Good!"]
The Union is under-going a fearful strain; but it is a stout old ship, and has weathered many a hard blow, and "the stars in their courses," aye, an invisible Power, greater than the puny efforts of men, will fight for us. But we ourselves must not decline the burden of responsibility, nor take counsel of unworthy passions. Whatever duty urges us to do or to omit must be done or omitted; and the recklessness with which our adversaries break the laws, or counsel their violation, should afford no example for us. Therefore, let us revere the Declaration of Independence; let us continue to obey the Constitution and the laws; let us keep step to the music of the Union. Let us draw a cordon, so to speak, around the slave States, and the hateful institution, like a reptile poisoning itself, will perish by its own infamy. [Applause.]
But we cannot be free men if this is, by our national choice, to be a land of slavery. Those who deny freedom to others deserve it not for themselves; and, under the rule of a just God, cannot long retain it.[Loud applause.]
Did you ever, my friends, seriously reflect upon the speed with which we are tending downwards? Within the memory of men now present the leading statesman of Virginia could make genuine, red-hot abolitionist speeches in old Virginia! and, as I have said, now even in "free Kansas" it is a crime to declare that it is "free Kansas." The very sentiments that I and others have just uttered would entitle us, and each of us, to the ignominy and seclusion of a dungeon; and yet I suppose that, like Paul, we were "free born." But if this thing is allowed to continue, it will be but one step further to impress the same rule in Illinois. [Sensation.]
The conclusion of all is, that we must restore the Missouri Compromise. We must highly resolve that Kansas must be free! [Great applause.] We must reinstate the birthday promise of the Republic; we must reaffirm the Declaration of Independence; we must make good in essence as well as in form Madison's avowal that "the word slave ought not to appear in the Constitution"; and we must even go further, and decree that only local law, and not that time-honored instrument, shall shelter a slaveholder. We must make this a land of liberty in fact, as it is in name. But in seeking to attain these results—so indispensable if the liberty which is our pride and boast shall endure—we will be loyal to the Constitution and to the "flag of our Union," and no matter what our grievance—even though Kansas shall come in as a slave State; and no matter what theirs—even if we shall restore the compromise—WE WILL SAY TO THE SOUTHERN DISUNIONISTS, WE WON'T GO OUT OF THE UNION, AND YOU SHAN'T!
[This was the climax; the audience rose to its feet en masse, applauded, stamped, waved handkerchiefs, threw hats in the air, and ran riot for several minutes. The arch-enchanter who wrought this transformation looked, meanwhile, like the personification of political justice.]
But let us, meanwhile, appeal to the sense and patriotism of the people, and not to their prejudices; let us spread the floods of enthusiasm here aroused all over these vast prairies, so suggestive of freedom. Let us commence by electing the gallant soldier Governor (Colonel) Bissell who stood for the honor of our State alike on the plains and amidst the chaparral of Mexico and on the floor of Congress, while he defied the Southern Hotspur; and that will have a greater moral effect than all the border ruffians can accomplish in all their raids on Kansas. There is both a power and a magic in popular opinion. To that let us now appeal; and while, in all probability, no resort to force will be needed, our moderation and forbearance will stand US in good stead when, if ever, WE MUST MAKE AN APPEAL TO BATTLE AND TO THE GOD OF HOSTS! [Immense applause and a rush for the orator.]
One can realize with this ability to move people's minds that the Southern Conspiracy were right to hate this man. He, better than any at the time was able to uncover their stratagems and tear down their sophisms and contradictions.
SPRINGFIELD, July 9, 1856.
DEAR WHITNEY:—I now expect to go to Chicago on the 15th, and I probably shall remain there or thereabouts for about two weeks.
It turned me blind when I first heard Swett was beaten and Lovejoy nominated; but, after much reflection, I really believe it is best to let it stand. This, of course, I wish to be confidential.
Lamon did get your deeds. I went with him to the office, got them, and put them in his hands myself.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, July 12, 1856
Your's of the 29th of June was duly received. I did not answer it because it plagued me. This morning I received another from Judd and Peck, written by consultation with you. Now let me tell you why I am plagued:
1. I can hardly spare the time.
2. I am superstitious. I have scarcely known a party preceding an election to call in help from the neighboring States but they lost the State. Last fall, our friends had Wade, of Ohio, and others, in Maine; and they lost the State. Last spring our adversaries had New Hampshire full of South Carolinians, and they lost the State. And so, generally, it seems to stir up more enemies than friends.
Have the enemy called in any foreign help? If they have a foreign champion there I should have no objection to drive a nail in his track. I shall reach Chicago on the night of the 15th, to attend to a little business in court. Consider the things I have suggested, and write me at Chicago. Especially write me whether Browning consents to visit you.
Your obedient servant,
AUGUST 1, 1856.
You further charge us with being disunionists. If you mean that it is our aim to dissolve the Union, I for myself answer that it is untrue; for those who act with me I answer that it is untrue. Have you heard us assert that as our aim? Do you really believe that such is our aim? Do you find it in our platform, our speeches, our conventions, or anywhere? If not, withdraw the charge.
But you may say that, though it is not our aim, it will be the result if we succeed, and that we are therefore disunionists in fact. This is a grave charge you make against us, and we certainly have a right to demand that you specify in what way we are to dissolve the Union. How are we to effect this?
The only specification offered is volunteered by Mr. Fillmore in his Albany speech. His charge is that if we elect a President and Vice-President both from the free States, it will dissolve the Union. This is open folly. The Constitution provides that the President and Vice-President of the United States shall be of different States, but says nothing as to the latitude and longitude of those States. In 1828 Andrew Jackson, of Tennessee, and John C. Calhoun, of South Carolina, were elected President and Vice-President, both from slave States; but no one thought of dissolving the Union then on that account. In 1840 Harrison, of Ohio, and Tyler, of Virginia, were elected. In 1841 Harrison died and John Tyler succeeded to the Presidency, and William R. King, of Alabama, was elected acting Vice-President by the Senate; but no one supposed that the Union was in danger. In fact, at the very time Mr. Fillmore uttered this idle charge, the state of things in the United States disproved it. Mr. Pierce, of New Hampshire, and Mr. Bright, of Indiana, both from free States, are President and Vice-President, and the Union stands and will stand. You do not pretend that it ought to dissolve the Union, and the facts show that it won't; therefore the charge may be dismissed without further consideration.
No other specification is made, and the only one that could be made is that the restoration of the restriction of 1820, making the United States territory free territory, would dissolve the Union. Gentlemen, it will require a decided majority to pass such an act. We, the majority, being able constitutionally to do all that we purpose, would have no desire to dissolve the Union. Do you say that such restriction of slavery would be unconstitutional, and that some of the States would not submit to its enforcement? I grant you that an unconstitutional act is not a law; but I do not ask and will not take your construction of the Constitution. The Supreme Court of the United States is the tribunal to decide such a question, and we will submit to its decisions; and if you do also, there will be an end of the matter. Will you? If not, who are the disunionists—you or we? We, the majority, would not strive to dissolve the Union; and if any attempt is made, it must be by you, who so loudly stigmatize us as disunionists. But the Union, in any event, will not be dissolved. We don't want to dissolve it, and if you attempt it we won't let you. With the purse and sword, the army and navy and treasury, in our hands and at our command, you could not do it. This government would be very weak indeed if a majority with a disciplined army and navy and a well-filled treasury could not preserve itself when attacked by an unarmed, undisciplined, unorganized minority. All this talk about the dissolution of the Union is humbug, nothing but folly. We do not want to dissolve the Union; you shall not.
SPRINGFIELD, AUG. 4, 1856
DEAR SIR:—I understand you are a Fillmore man. If, as between Fremont and Buchanan, you really prefer the election of Buchanan, then burn this without reading a line further. But if you would like to defeat Buchanan and his gang, allow me a word with you: Does any one pretend that Fillmore can carry the vote of this State? I have not heard a single man pretend so. Every vote taken from Fremont and given to Fillmore is just so much in favor of Buchanan. The Buchanan men see this; and hence their great anxiety in favor of the Fillmore movement. They know where the shoe pinches. They now greatly prefer having a man of your character go for Fillmore than for Buchanan because they expect several to go with you, who would go for Fremont if you were to go directly for Buchanan.
I think I now understand the relative strength of the three parties in this State as well as any one man does, and my opinion is that to-day Buchanan has alone 85,000, Fremont 78,000, and Fillmore 21,000.
This gives B. the State by 7000 and leaves him in the minority of the whole 14,000.
Fremont and Fillmore men being united on Bissell, as they already are, he cannot be beaten. This is not a long letter, but it contains the whole story.
Yours as ever,
DEAR DUBOIS: Your letter on the same sheet with Mr. Miller's is just received. I have been absent four days. I do not know when your court sits.
Trumbull has written the committee here to have a set of appointments made for him commencing here in Springfield, on the 11th of Sept., and to extend throughout the south half of the State. When he goes to Lawrenceville, as he will, I will strain every nerve to be with you and him. More than that I cannot promise now.
Yours as truly as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, September 8, 1856.
DEAR SIR:—I understand you are a Fillmore man. Let me prove to you that every vote withheld from Fremont and given to Fillmore in this State actually lessens Fillmore's chance of being President. Suppose Buchanan gets all the slave States and Pennsylvania, and any other one State besides; then he is elected, no matter who gets all the rest. But suppose Fillmore gets the two slave States of Maryland and Kentucky; then Buchanan is not elected; Fillmore goes into the House of Representatives, and may be made President by a compromise. But suppose, again, Fillmore's friends throw away a few thousand votes on him in Indiana and Illinois; it will inevitably give these States to Buchanan, which will more than compensate him for the loss of Maryland and Kentucky, will elect him, and leave Fillmore no chance in the House of Representatives or out of it.
This is as plain as adding up the weight of three small hogs. As Mr. Fillmore has no possible chance to carry Illinois for himself, it is plainly to his interest to let Fremont take it, and thus keep it out of the hands of Buchanan. Be not deceived. Buchanan is the hard horse to beat in this race. Let him have Illinois, and nothing can beat him; and he will get Illinois if men persist in throwing away votes upon Mr. Fillmore. Does some one persuade you that Mr. Fillmore can carry Illinois? Nonsense! There are over seventy newspapers in Illinois opposing Buchanan, only three or four of which support Mr. Fillmore, all the rest going for Fremont. Are not these newspapers a fair index of the proportion of the votes? If not, tell me why.
Again, of these three or four Fillmore newspapers, two, at least, are supported in part by the Buchanan men, as I understand. Do not they know where the shoe pinches? They know the Fillmore movement helps them, and therefore they help it. Do think these things over, and then act according to your judgment.
Yours very truly,
Dr. R. BOAL, Lacon, Ill.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 8th inviting me to be with [you] at Lacon on the 30th is received. I feel that I owe you and our friends of Marshall a good deal, and I will come if I can; and if I do not get there, it will be because I shall think my efforts are now needed farther south.
Present my regards to Mrs. Boal, and believe [me], as ever,
Your friend,
DEAR SIR:—Yours, inviting me to attend a mass-meeting on the 23d inst., is received. It would be very pleasant to strike hands with the Fremonters of Iowa, who have led the van so splendidly, in this grand charge which we hope and believe will end in a most glorious victory. All thanks, all honor to Iowa! But Iowa is out of all danger, and it is no time for us, when the battle still rages, to pay holiday visits to Iowa. I am sure you will excuse me for remaining in Illinois, where much hard work is still to be done.
Yours very truly,
We have another annual Presidential message. Like a rejected lover making merry at the wedding of his rival, the President felicitates himself hugely over the late Presidential election. He considers the result a signal triumph of good principles and good men, and a very pointed rebuke of bad ones. He says the people did it. He forgets that the "people," as he complacently calls only those who voted for Buchanan, are in a minority of the whole people by about four hundred thousand votes—one full tenth of all the votes. Remembering this, he might perceive that the "rebuke" may not be quite as durable as he seems to think—that the majority may not choose to remain permanently rebuked by that minority.
The President thinks the great body of us Fremonters, being ardently attached to liberty, in the abstract, were duped by a few wicked and designing men. There is a slight difference of opinion on this. We think he, being ardently attached to the hope of a second term, in the concrete, was duped by men who had liberty every way. He is the cat's-paw. By much dragging of chestnuts from the fire for others to eat, his claws are burnt off to the gristle, and he is thrown aside as unfit for further use. As the fool said of King Lear, when his daughters had turned him out of doors, "He 's a shelled peascod" ("That 's a sheal'd peascod").
So far as the President charges us "with a desire to change the domestic institutions of existing States," and of "doing everything in our power to deprive the Constitution and the laws of moral authority," for the whole party on belief, and for myself on knowledge, I pronounce the charge an unmixed and unmitigated falsehood.
Our government rests in public opinion. Whoever can change public opinion can change the government practically just so much. Public opinion, on any subject, always has a "central idea," from which all its minor thoughts radiate. That "central idea" in our political public opinion at the beginning was, and until recently has continued to be, "the equality of men." And although it has always submitted patiently to whatever of inequality there seemed to be as matter of actual necessity, its constant working has been a steady progress toward the practical equality of all men. The late Presidential election was a struggle by one party to discard that central idea and to substitute for it the opposite idea that slavery is right in the abstract, the workings of which as a central idea may be the perpetuity of human slavery and its extension to all countries and colors. Less than a year ago the Richmond Enquirer, an avowed advocate of slavery, regardless of color, in order to favor his views, invented the phrase "State equality," and now the President, in his message, adopts the Enquirer's catch-phrase, telling us the people "have asserted the constitutional equality of each and all of the States of the Union as States." The President flatters himself that the new central idea is completely inaugurated; and so indeed it is, so far as the mere fact of a Presidential election can inaugurate it. To us it is left to know that the majority of the people have not yet declared for it, and to hope that they never will.
All of us who did not vote for Mr. Buchanan, taken together, are a majority of four hundred thousand. But in the late contest we were divided between Fremont and Fillmore. Can we not come together for the future? Let every one who really believes and is resolved that free society is not and shall not be a failure, and who can conscientiously declare that in the last contest he has done only what he thought best—let every such one have charity to believe that every other one can say as much. Thus let bygones be bygones; let past differences as nothing be; and with steady eye on the real issue let us reinaugurate the good old "central idea" of the republic. We can do it. The human heart is with us; God is with us. We shall again be able, not to declare that "all States as States are equal," nor yet that "all citizens as citizens are equal," but to renew the broader, better declaration, including both these and much more, that "all men are created equal."
DEAR SIR:-When I was at Chicago two weeks ago I saw Mr. Arnold, and from a remark of his I inferred he was thinking of the speakership, though I think he was not anxious about it. He seemed most anxious for harmony generally, and particularly that the contested seats from Peoria and McDonough might be rightly determined. Since I came home I had a talk with Cullom, one of our American representatives here, and he says he is for you for Speaker and also that he thinks all the Americans will be for you, unless it be Gorin, of Macon, of whom he cannot speak. If you would like to be Speaker go right up and see Arnold. He is talented, a practised debater, and, I think, would do himself more credit on the floor than in the Speaker's seat. Go and see him; and if you think fit, show him this letter.
Your friend as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., February 10, 1857.
DEAR SIR:—Your note about the little paragraph in the Republican was received yesterday, since which time I have been too unwell to notice it. I had not supposed you wrote or approved it. The whole originated in mistake. You know by the conversation with me that I thought the establishment of the paper unfortunate, but I always expected to throw no obstacle in its way, and to patronize it to the extent of taking and paying for one copy. When the paper was brought to my house, my wife said to me, "Now are you going to take another worthless little paper?" I said to her evasively, "I have not directed the paper to be left." From this, in my absence, she sent the message to the carrier. This is the whole story.
Yours truly,
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I am here to-night partly by the invitation of some of you, and partly by my own inclination. Two weeks ago Judge Douglas spoke here on the several subjects of Kansas, the Dred Scott decision, and Utah. I listened to the speech at the time, and have the report of it since. It was intended to controvert opinions which I think just, and to assail (politically, not personally) those men who, in common with me, entertain those opinions. For this reason I wished then, and still wish, to make some answer to it, which I now take the opportunity of doing.
I begin with Utah. If it prove to be true, as is probable, that the people of Utah are in open rebellion to the United States, then Judge Douglas is in favor of repealing their territorial organization, and attaching them to the adjoining States for judicial purposes. I say, too, if they are in rebellion, they ought to be somehow coerced to obedience; and I am not now prepared to admit or deny that the Judge's mode of coercing them is not as good as any. The Republicans can fall in with it without taking back anything they have ever said. To be sure, it would be a considerable backing down by Judge Douglas from his much-vaunted doctrine of self-government for the Territories; but this is only additional proof of what was very plain from the beginning, that that doctrine was a mere deceitful pretense for the benefit of slavery. Those who could not see that much in the Nebraska act itself, which forced governors, and secretaries, and judges on the people of the Territories without their choice or consent, could not be made to see, though one should rise from the dead.
But in all this it is very plain the Judge evades the only question the Republicans have ever pressed upon the Democracy in regard to Utah. That question the Judge well knew to be this: "If the people of Utah peacefully form a State constitution tolerating polygamy, will the Democracy admit them into the Union?" There is nothing in the United States Constitution or law against polygamy; and why is it not a part of the Judge's "sacred right of self-government" for the people to have it, or rather to keep it, if they choose? These questions, so far as I know, the Judge never answers. It might involve the Democracy to answer them either way, and they go unanswered.
As to Kansas. The substance of the Judge's speech on Kansas is an effort to put the free-State men in the wrong for not voting at the election of delegates to the constitutional convention. He says:
"There is every reason to hope and believe that the law will be fairly interpreted and impartially executed, so as to insure to every bona fide inhabitant the free and quiet exercise of the elective franchise."
It appears extraordinary that Judge Douglas should make such a statement. He knows that, by the law, no one can vote who has not been registered; and he knows that the free-State men place their refusal to vote on the ground that but few of them have been registered. It is possible that this is not true, but Judge Douglas knows it is asserted to be true in letters, newspapers, and public speeches, and borne by every mail and blown by every breeze to the eyes and ears of the world. He knows it is boldly declared that the people of many whole counties, and many whole neighborhoods in others, are left unregistered; yet he does not venture to contradict the declaration, or to point out how they can vote without being registered; but he just slips along, not seeming to know there is any such question of fact, and complacently declares: "There is every reason to hope and believe that the law will be fairly and impartially executed, so as to insure to every bona fide inhabitant the free and quiet exercise of the elective franchise."
I readily agree that if all had a chance to vote they ought to have voted. If, on the contrary, as they allege, and Judge Douglas ventures not to particularly contradict, few only of the free-State men had a chance to vote, they were perfectly right in staying from the polls in a body.
By the way, since the Judge spoke, the Kansas election has come off. The Judge expressed his confidence that all the Democrats in Kansas would do their duty-including "free-State Democrats," of course. The returns received here as yet are very incomplete; but so far as they go, they indicate that only about one sixth of the registered voters have really voted; and this, too, when not more, perhaps, than one half of the rightful voters have been registered, thus showing the thing to have been altogether the most exquisite farce ever enacted. I am watching with considerable interest to ascertain what figure "the free-State Democrats" cut in the concern. Of course they voted,—all Democrats do their duty,—and of course they did not vote for slave-State candidates. We soon shall know how many delegates they elected, how many candidates they had pledged to a free State, and how many votes were cast for them.
Allow me to barely whisper my suspicion that there were no such things in Kansas as "free-State Democrats"—that they were altogether mythical, good only to figure in newspapers and speeches in the free States. If there should prove to be one real living free-State Democrat in Kansas, I suggest that it might be well to catch him, and stuff and preserve his skin as an interesting specimen of that soon-to-be extinct variety of the genus Democrat.
And now as to the Dred Scott decision. That decision declares two propositions—first, that a negro cannot sue in the United States courts; and secondly, that Congress cannot prohibit slavery in the Territories. It was made by a divided court dividing differently on the different points. Judge Douglas does not discuss the merits of the decision, and in that respect I shall follow his example, believing I could no more improve on McLean and Curtis than he could on Taney.
He denounces all who question the correctness of that decision, as offering violent resistance to it. But who resists it? Who has, in spite of the decision, declared Dred Scott free, and resisted the authority of his master over him?
Judicial decisions have two uses—first, to absolutely determine the case decided, and secondly, to indicate to the public how other similar cases will be decided when they arise. For the latter use, they are called "precedents" and "authorities."
We believe as much as Judge Douglas (perhaps more) in obedience to, and respect for, the judicial department of government. We think its decisions on constitutional questions, when fully settled, should control not only the particular cases decided, but the general policy of the country, subject to be disturbed only by amendments of the Constitution as provided in that instrument itself. More than this would be revolution. But we think the Dred Scott decision is erroneous. We know the court that made it has often overruled its own decisions, and we shall do what we can to have it to overrule this. We offer no resistance to it.
Judicial decisions are of greater or less authority as precedents according to circumstances. That this should be so accords both with common sense and the customary understanding of the legal profession.
If this important decision had been made by the unanimous concurrence of the judges, and without any apparent partisan bias, and in accordance with legal public expectation and with the steady practice of the departments throughout our history, and had been in no part based on assumed historical facts which are not really true; or, if wanting in some of these, it had been before the court more than once, and had there been affirmed and reaffirmed through a course of years, it then might be, perhaps would be, factious, nay, even revolutionary, not to acquiesce in it as a precedent.
But when, as is true, we find it wanting in all these claims to the public confidence, it is not resistance, it is not factious, it is not even disrespectful, to treat it as not having yet quite established a settled doctrine for the country. But Judge Douglas considers this view awful. Hear him:
"The courts are the tribunals prescribed by the Constitution and created by the authority of the people to determine, expound, and enforce the law. Hence, whoever resists the final decision of the highest judicial tribunal aims a deadly blow at our whole republican system of government—a blow which, if successful, would place all our rights and liberties at the mercy of passion, anarchy, and violence. I repeat, therefore, that if resistance to the decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States, in a matter like the points decided in the Dred Scott case, clearly within their jurisdiction as defined by the Constitution, shall be forced upon the country as a political issue, it will become a distinct and naked issue between the friends and enemies of the Constitution—the friends and the enemies of the supremacy of the laws."
Why, this same Supreme Court once decided a national bank to be constitutional; but General Jackson, as President of the United States, disregarded the decision, and vetoed a bill for a recharter, partly on constitutional ground, declaring that each public functionary must support the Constitution "as he understands it." But hear the General's own words. Here they are, taken from his veto message:
"It is maintained by the advocates of the bank that its constitutionality, in all its features, ought to be considered as settled by precedent, and by the decision of the Supreme Court. To this conclusion I cannot assent. Mere precedent is a dangerous source of authority, and should not be regarded as deciding questions of constitutional power, except where the acquiescence of the people and the States can be considered as well settled. So far from this being the case on this subject, an argument against the bank might be based on precedent. One Congress, in 1791, decided in favor of a bank; another, in 1811, decided against it. One Congress, in 1815, decided against a bank; another, in 1816, decided in its favor. Prior to the present Congress, therefore, the precedents drawn from that course were equal. If we resort to the States, the expressions of legislative, judicial, and executive opinions against the bank have been probably to those in its favor as four to one. There is nothing in precedent, therefore, which, if its authority were admitted, ought to weigh in favor of the act before me."
I drop the quotations merely to remark that all there ever was in the way of precedent up to the Dred Scott decision, on the points therein decided, had been against that decision. But hear General Jackson further:
"If the opinion of the Supreme Court covered the whole ground of this act, it ought not to control the coordinate authorities of this government. The Congress, the executive, and the courts must, each for itself, be guided by its own opinion of the Constitution. Each public officer who takes an oath to support the Constitution swears that he will support it as he understands it, and not as it is understood by others."
Again and again have I heard Judge Douglas denounce that bank decision and applaud General Jackson for disregarding it. It would be interesting for him to look over his recent speech, and see how exactly his fierce philippics against us for resisting Supreme Court decisions fall upon his own head. It will call to mind a long and fierce political war in this country, upon an issue which, in his own language, and, of course, in his own changeless estimation, "was a distinct issue between the friends and the enemies of the Constitution," and in which war he fought in the ranks of the enemies of the Constitution.
I have said, in substance, that the Dred Scott decision was in part based on assumed historical facts which were not really true, and I ought not to leave the subject without giving some reasons for saying this; I therefore give an instance or two, which I think fully sustain me. Chief Justice Taney, in delivering the opinion of the majority of the court, insists at great length that negroes were no part of the people who made, or for whom was made, the Declaration of Independence, or the Constitution of the United States.
On the contrary, Judge Curtis, in his dissenting opinion, shows that in five of the then thirteen States—to wit, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, New York, New Jersey, and North Carolina—free negroes were voters, and in proportion to their numbers had the same part in making the Constitution that the white people had. He shows this with so much particularity as to leave no doubt of its truth; and as a sort of conclusion on that point, holds the following language:
"The Constitution was ordained and established by the people of the United States, through the action, in each State, of those persons who were qualified by its laws to act thereon in behalf of themselves and all other citizens of the State. In some of the States, as we have seen, colored persons were among those qualified by law to act on the subject. These colored persons were not only included in the body of 'the people of the United States' by whom the Constitution was ordained and established; but in at least five of the States they had the power to act, and doubtless did act, by their suffrages, upon the question of its adoption."
Again, Chief Justice Taney says:
"It is difficult at this day to realize the state of public opinion, in relation to that unfortunate race, which prevailed in the civilized and enlightened portions of the world at the time of the Declaration of Independence, and when the Constitution of the United States was framed and adopted."
And again, after quoting from the Declaration, he says:
"The general words above quoted would seem to include the whole human family, and if they were used in a similar instrument at this day, would be so understood."
In these the Chief Justice does not directly assert, but plainly assumes as a fact, that the public estimate of the black man is more favorable now than it was in the days of the Revolution. This assumption is a mistake. In some trifling particulars the condition of that race has been ameliorated; but as a whole, in this country, the change between then and now is decidedly the other way, and their ultimate destiny has never appeared so hopeless as in the last three or four years. In two of the five States—New Jersey and North Carolina—that then gave the free negro the right of voting, the right has since been taken away, and in a third—New York—it has been greatly abridged; while it has not been extended, so far as I know, to a single additional State, though the number of the States has more than doubled. In those days, as I understand, masters could, at their own pleasure, emancipate their slaves; but since then such legal restraints have been made upon emancipation as to amount almost to prohibition. In those days Legislatures held the unquestioned power to abolish slavery in their respective States, but now it is becoming quite fashionable for State constitutions to withhold that power from the Legislatures. In those days, by common consent, the spread of the black man's bondage to the new countries was prohibited, but now Congress decides that it will not continue the prohibition, and the Supreme Court decides that it could not if it would. In those days our Declaration of Independence was held sacred by all, and thought to include all; but now, to aid in making the bondage of the negro universal and eternal, it is assailed and sneered at and construed and hawked at and torn, till, if its framers could rise from their graves, they could not at all recognize it. All the powers of earth seem rapidly combining against him. Mammon is after him, ambition follows, philosophy follows, and the theology of the day fast joining the cry. They have him in his prison house; they have searched his person, and left no prying instrument with him. One after another they have closed the heavy iron doors upon him; and now they have him, as it were, bolted in with a lock of hundred keys, which can never be unlocked without the concurrence of every key—the keys in the hands of a hundred different men, and they scattered to hundred different and distant places; and they stand musing as to what invention, in all the dominions of mind and matter, can be produced to make the impossibility of his escape more complete than it is.
It is grossly incorrect to say or assume that the public estimate of the negro is more favorable now than it was at the origin of the government.
Three years and a half ago, Judge Douglas brought forward his famous Nebraska Bill. The country was at once in a blaze. He scorned all opposition, and carried it through Congress. Since then he has seen himself superseded in a Presidential nomination by one indorsing the general doctrine of his measure, but at the same time standing clear of the odium of its untimely agitation and its gross breach of national faith; and he has seen that successful rival constitutionally elected, not by the strength of friends, but by the division of adversaries, being in a popular minority of nearly four hundred thousand votes. He has seen his chief aids in his own State, Shields and Richardson, politically speaking, successively tried, convicted, and executed for an offence not their own but his. And now he sees his own case standing next on the docket for trial.
There is a natural disgust in the minds of nearly all white people at the idea of an indiscriminate amalgamation of the white and black races; and Judge Douglas evidently is basing his chief hope upon the chances of his being able to appropriate the benefit of this disgust to himself. If he can, by much drumming and repeating, fasten the odium of that idea upon his adversaries, he thinks he can struggle through the storm. He therefore clings to this hope, as a drowning man to the last plank. He makes an occasion for lugging it in from the opposition to the Dred Scott decision. He finds the Republicans insisting that the Declaration of Independence includes all men, black as well as white, and forthwith he boldly denies that it includes negroes at all, and proceeds to argue gravely that all who contend it does, do so only because they want to vote, and eat, and sleep, and marry with negroes. He will have it that they cannot be consistent else. Now I protest against the counterfeit logic which concludes that, because I do not want a black woman for a slave I must necessarily want her for a wife. I need not have her for either. I can just leave her alone. In some respects she certainly is not my equal; but in her natural right to eat the bread she earns with her own hands, without asking leave of any one else, she is my equal and the equal of all others.
Chief Justice Taney, in his opinion in the Dred Scott case, admits that the language of the Declaration is broad enough to include the whole human family, but he and Judge Douglas argue that the authors of that instrument did not intend to include negroes, by the fact that they did not at once actually place them on an equality with the whites. Now this grave argument comes to just nothing at all, by the other fact that they did not at once, or ever afterward, actually place all white people on an equality with one another. And this is the staple argument of both the Chief Justice and the Senator for doing this obvious violence to the plain, unmistakable language of the Declaration.
I think the authors of that notable instrument intended to include all men, but they did not intend to declare all men equal in all respects. They did not mean to say all were equal in color, size, intellect, moral developments, or social capacity. They defined with tolerable distinctness in what respects they did consider all men created equal—equal with "certain inalienable rights, among which are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness." This they said, and this they meant. They did not mean to assert the obvious untruth that all were then actually enjoying that equality, nor yet that they were about to confer it immediately upon them. In fact, they had no power to confer such a boon. They meant simply to declare the right, so that enforcement of it might follow as fast as circumstances should permit.
They meant to set up a standard maxim for free society, which should be familiar to all, and revered by all; constantly looked to, constantly labored for, and, even though never perfectly attained, constantly approximated, and thereby constantly spreading and deepening its influence and augmenting the happiness and value of life to all people of all colors everywhere. The assertion that "all men are created equal" was of no practical use in effecting our separation from Great Britain; and it was placed in the Declaration not for that, but for future use. Its authors meant it to be—as thank God, it is now proving itself—stumbling-block to all those who in after times might seek to turn a free people back into the hateful paths of despotism. They knew the proneness of prosperity to breed tyrants, and they meant when such should reappear in this fair land and commence their vocation, they should find left for them at least one hard nut to crack.
I have now briefly expressed my view of the meaning and object of that part of the Declaration of Independence which declares that "all men are created equal."
Now let us hear Judge Douglas's view of the same subject, as I find it in the printed report of his late speech. Here it is:
"No man can vindicate the character, motives, and conduct of the signers of the Declaration of Independence, except upon the hypothesis that they referred to the white race alone, and not to the African, when they declared all men to have been created equal; that they were speaking of British subjects on this continent being equal to British subjects born and residing in Great Britain; that they were entitled to the same inalienable rights, and among them were enumerated life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. The Declaration was adopted for the purpose of justifying the colonists in the eyes of the civilized world in withdrawing their allegiance from the British crown, and dissolving their connection with the mother country."
My good friends, read that carefully over some leisure hour, and ponder well upon it; see what a mere wreck—mangled ruin—it makes of our once glorious Declaration.
"They were speaking of British subjects on this continent being equal to British subjects born and residing in Great Britain"! Why, according to this, not only negroes but white people outside of Great Britain and America were not spoken of in that instrument. The English, Irish, and Scotch, along with white Americans, were included, to be sure, but the French, Germans, and other white people of the world are all gone to pot along with the Judge's inferior races!
I had thought the Declaration promised something better than the condition of British subjects; but no, it only meant that we should be equal to them in their own oppressed and unequal condition. According to that, it gave no promise that, having kicked off the king and lords of Great Britain, we should not at once be saddled with a king and lords of our own.
I had thought the Declaration contemplated the progressive improvement in the condition of all men everywhere; but no, it merely "was adopted for the purpose of justifying the colonists in the eyes of the civilized world in withdrawing their allegiance from the British crown, and dissolving their connection with the mother country." Why, that object having been effected some eighty years ago, the Declaration is of no practical use now—mere rubbish—old wadding left to rot on the battlefield after the victory is won.
I understand you are preparing to celebrate the "Fourth," to-morrow week. What for? The doings of that day had no reference to the present; and quite half of you are not even descendants of those who were referred to at that day. But I suppose you will celebrate, and will even go so far as to read the Declaration. Suppose, after you read it once in the old-fashioned way, you read it once more with Judge Douglas's version. It will then run thus:
"We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all British subjects who were on this continent eighty-one years ago were created equal to all British subjects born and then residing in Great Britain."
And now I appeal to all—to Democrats as well as others—are you really willing that the Declaration shall thus be frittered away?—thus left no more, at most, than an interesting memorial of the dead past?—thus shorn of its vitality and practical value, and left without the germ or even the suggestion of the individual rights of man in it?
But Judge Douglas is especially horrified at the thought of the mixing of blood by the white and black races. Agreed for once—a thousand times agreed. There are white men enough to marry all the white women and black men enough to many all the black women; and so let them be married. On this point we fully agree with the Judge, and when he shall show that his policy is better adapted to prevent amalgamation than ours, we shall drop ours and adopt his. Let us see. In 1850 there were in the United States 405,751 mulattoes. Very few of these are the offspring of whites and free blacks; nearly all have sprung from black slaves and white masters. A separation of the races is the only perfect preventive of amalgamation; but as an immediate separation is impossible, the next best thing is to keep them apart where they are not already together. If white and black people never get together in Kansas, they will never mix blood in Kansas. That is at least one self-evident truth. A few free colored persons may get into the free States, in any event; but their number is too insignificant to amount to much in the way of mixing blood. In 1850 there were in the free States 56,649 mulattoes; but for the most part they were not born there—they came from the slave States, ready made up. In the same year the slave States had 348,874 mulattoes, all of home production. The proportion of free mulattoes to free blacks—the only colored classes in the free States is much greater in the slave than in the free States. It is worthy of note, too, that among the free States those which make the colored man the nearest equal to the white have proportionably the fewest mulattoes, the least of amalgamation. In New Hampshire, the State which goes farthest toward equality between the races, there are just 184 mulattoes, while there are in Virginia—how many do you think?—79,775, being 23,126 more than in all the free States together.
These statistics show that slavery is the greatest source of amalgamation, and next to it, not the elevation, but the degradation of the free blacks. Yet Judge Douglas dreads the slightest restraints on the spread of slavery, and the slightest human recognition of the negro, as tending horribly to amalgamation!
The very Dred Scott case affords a strong test as to which party most favors amalgamation, the Republicans or the dear Union-saving Democracy. Dred Scott, his wife, and two daughters were all involved in the suit. We desired the court to have held that they were citizens so far at least as to entitle them to a hearing as to whether they were free or not; and then, also, that they were in fact and in law really free. Could we have had our way, the chances of these black girls ever mixing their blood with that of white people would have been diminished at least to the extent that it could not have been without their consent. But Judge Douglas is delighted to have them decided to be slaves, and not human enough to have a hearing, even if they were free, and thus left subject to the forced concubinage of their masters, and liable to become the mothers of mulattoes in spite of themselves: the very state of case that produces nine tenths of all the mulattoes all the mixing of blood in the nation.
Of course, I state this case as an illustration only, not meaning to say or intimate that the master of Dred Scott and his family, or any more than a percentage of masters generally, are inclined to exercise this particular power which they hold over their female slaves.
I have said that the separation of the races is the only perfect preventive of amalgamation. I have no right to say all the members of the Republican party are in favor of this, nor to say that as a party they are in favor of it. There is nothing in their platform directly on the subject. But I can say a very large proportion of its members are for it, and that the chief plank in their platform—opposition to the spread of slavery—is most favorable to that separation.
Such separation, if ever effected at all, must be effected by colonization; and no political party, as such, is now doing anything directly for colonization. Party operations at present only favor or retard colonization incidentally. The enterprise is a difficult one; but "where there is a will there is a way," and what colonization needs most is a hearty will. Will springs from the two elements of moral sense and self-interest. Let us be brought to believe it is morally right, and at the same time favorable to, or at least not against, our interest to transfer the African to his native clime, and we shall find a way to do it, however great the task may be. The children of Israel, to such numbers as to include four hundred thousand fighting men, went out of Egyptian bondage in a body.
How differently the respective courses of the Democratic and Republican parties incidentally, bear on the question of forming a will—a public sentiment—for colonization, is easy to see. The Republicans inculcate, with whatever of ability they can, that the negro is a man, that his bondage is cruelly wrong, and that the field of his oppression ought not to be enlarged. The Democrats deny his manhood; deny, or dwarf to insignificance, the wrong of his bondage; so far as possible crush all sympathy for him, and cultivate and excite hatred and disgust against him; compliment themselves as Union-savers for doing so; and call the indefinite outspreading of his bondage "a sacred right of self-government."
The plainest print cannot be read through a gold eagle; and it will be ever hard to find many men who will send a slave to Liberia, and pay his passage, while they can send him to a new country—Kansas, for instance—and sell him for fifteen hundred dollars, and the rise.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 14th is received, and I am much obliged for the legal information you give.
You can scarcely be more anxious than I that the next election in Iowa should result in favor of the Republicans. I lost nearly all the working part of last year, giving my time to the canvass; and I am altogether too poor to lose two years together. I am engaged in a suit in the United States Court at Chicago, in which the Rock Island Bridge Company is a party. The trial is to commence on the 8th of September, and probably will last two or three weeks. During the trial it is not improbable that all hands may come over and take a look at the bridge, and, if it were possible to make it hit right, I could then speak at Davenport. My courts go right on without cessation till late in November. Write me again, pointing out the more striking points of difference between your old and new constitutions, and also whether Democratic and Republican party lines were drawn in the adoption of it, and which were for and which were against it. If, by possibility, I could get over among you it might be of some advantage to know these things in advance.
Yours very truly,
Hurd et al. vs Railroad Bridge Co.
United States Circuit Court, Hon. John McLean, Presiding Judge.
13th day, Tuesday, Sept. 22, 1857.
Mr. A. Lincoln addressed the jury. He said he did not purpose to assail anybody, that he expected to grow earnest as he proceeded but not ill-natured. "There is some conflict of testimony in the case," he said, "but one quarter of such a number of witnesses seldom agree, and even if all were on one side some discrepancy might be expected. We are to try and reconcile them, and to believe that they are not intentionally erroneous as long as we can." He had no prejudice, he said, against steamboats or steamboat men nor any against St. Louis, for he supposed they went about this matter as other people would do in their situation. "St. Louis," he continued, "as a commercial place may desire that this bridge should not stand, as it is adverse to her commerce, diverting a portion of it from the river; and it may be that she supposes that the additional cost of railroad transportation upon the productions of Iowa will force them to go to St. Louis if this bridge is removed. The meetings in St. Louis are connected with this case only as some witnesses are in it, and thus has some prejudice added color to their testimony." The last thing that would be pleasing to him, Mr. Lincoln said, would be to have one of these great channels, extending almost from where it never freezes to where it never thaws, blocked up, but there is a travel from east to west whose demands are not less important than those of the river. It is growing larger and larger, building up new countries with a rapidity never before seen in the history of the world. He alluded to the astonishing growth of Illinois, having grown within his memory to a population of a million and a half; to Iowa and the other young rising communities of the Northwest.
"This current of travel," said he, "has its rights as well as that of north and south. If the river had not the advantage in priority and legislation we could enter into free competition with it and we could surpass it. This particular railroad line has a great importance and the statement of its business during a little less than a year shows this importance. It is in evidence that from September 8, 1856, to August 8, 1857, 12,586 freight cars and 74,179 passengers passed over this bridge. Navigation was closed four days short of four months last year, and during this time while the river was of no use this road and bridge were valuable. There is, too, a considerable portion of time when floating or thin ice makes the river useless while the bridge is as useful as ever. This shows that this bridge must be treated with respect in this court and is not to be kicked about with contempt. The other day Judge Wead alluded to the strike of the contending interest and even a dissolution of the Union. The proper mode for all parties in this affair is to 'live and let live,' and then we will find a cessation of this trouble about the bridge. What mood were the steamboat men in when this bridge was burned? Why, there was a shouting and ringing of bells and whistling on all the boats as it fell. It was a jubilee, a greater celebration than follows an excited election. The first thing I will proceed to is the record of Mr. Gurney and the complaint of Judge Wead that the record did not extend back over all the time from the completion of the bridge. The principal part of the navigation after the bridge was burned passed through the span. When the bridge was repaired and the boats were a second time confined to the draw it was provided that this record should be kept. That is the simple history of that book.
"From April 19th, 1856, to May 6th—seventeen days—there were twenty accidents and all the time since then there have been but twenty hits, including seven accidents, so that the dangers of this place are tapering off and as the boatmen get cool the accidents get less. We may soon expect if this ratio is kept up that there will be no accidents at all.
"Judge Wead said, while admitting that the floats went straight through, there was a difference between a float and a boat, but I do not remember that he indulged us with an argument in support of this statement. Is it because there is a difference in size? Will not a small body and a large one float the same way under the same influence? True a flatboat will float faster than an egg shell and the egg shell might be blown away by the wind, but if under the same influence they would go the same way. Logs, floats, boards, various things the witnesses say all show the same current. Then is not this test reliable? At all depths too the direction of the current is the same. A series of these floats would make a line as long as a boat and would show any influence upon any part and all parts of the boat.
"I will now speak of the angular position of the piers. What is the amount of the angle? The course of the river is a curve and the pier is straight. If a line is produced from the upper end of the long pier straight with the pier to a distance of 350 feet, and a line is drawn from a point in the channel opposite this point to the head of the pier, Colonel Nason says they will form an angle of twenty degrees. But the angle if measured at the pier is seven degrees; that is, we would have to move the pier seven degrees to make it exactly straight with the current. Would that make the navigation better or worse? The witnesses of the plaintiff seem to think it was only necessary to say that the pier formed an angle with the current and that settled the matter. Our more careful and accurate witnesses say that, though they had been accustomed to seeing the piers placed straight with the current, yet they could see that here the current had been made straight by us in having made this slight angle; that the water now runs just right, that it is straight and cannot be improved. They think that if the pier was changed the eddy would be divided and the navigation improved.
"I am not now going to discuss the question what is a material obstruction. We do not greatly differ about the law. The cases produced here are, I suppose, proper to be taken into consideration by the court in instructing a jury. Some of them I think are not exactly in point, but I am still willing to trust his honor, Judge McLean, and take his instructions as law. What is reasonable skill and care? This is a thing of which the jury are to judge. I differ from the other side when it says that they are bound to exercise no more care than was taken before the building of the bridge. If we are allowed by the Legislature to build the bridge which will require them to do more than before, when a pilot comes along, it is unreasonable for him to dash on heedless of this structure which has been legally put there. The Afton came there on the 5th and lay at Rock Island until next morning. When a boat lies up the pilot has a holiday, and would not any of these jurors have then gone around to the bridge and gotten acquainted with the place? Pilot Parker has shown here that he does not understand the draw. I heard him say that the fall from the head to the foot of the pier was four feet; he needs information. He could have gone there that day and seen there was no such fall. He should have discarded passion and the chances are that he would have had no disaster at all. He was bound to make himself acquainted with the place.
"McCammon says that the current and the swell coming from the long pier drove her against the long pier. In other words drove her toward the very pier from which the current came! It is an absurdity, an impossibility. The only recollection I can find for this contradiction is in a current which White says strikes out from the long pier and then like a ram's horn turns back, and this might have acted somehow in this manner.
"It is agreed by all that the plaintiff's boat was destroyed and that it was destroyed upon the head of the short pier; that she moved from the channel where she was with her bow above the head of the long pier, till she struck the short one, swung around under the bridge and there was crowded and destroyed.
"I shall try to prove that the average velocity of the current through the draw with the boat in it should be five and a half miles an hour; that it is slowest at the head of the pier and swiftest at the foot of the pier. Their lowest estimate in evidence is six miles an hour, their highest twelve miles. This was the testimony of men who had made no experiment, only conjecture. We have adopted the most exact means. The water runs swiftest in high water and we have taken the point of nine feet above low water. The water when the Afton was lost was seven feet above low water, or at least a foot lower than our time. Brayton and his assistants timed the instruments, the best instruments known in measuring currents. They timed them under various circumstances and they found the current five miles an hour and no more. They found that the water at the upper end ran slower than five miles; that below it was swifter than five miles, but that the average was five miles. Shall men who have taken no care, who conjecture, some of whom speak of twenty miles an hour, be believed against those who have had such a favorable and well improved opportunity? They should not even qualify the result. Several men have given their opinion as to the distance of the steamboat Carson, and I suppose if one should go and measure that distance you would believe him in preference to all of them.
"These measurements were made when the boat was not in the draw. It has been ascertained what is the area of the cross section of this stream and the area of the face of the piers, and the engineers say that the piers being put there will increase the current proportionally as the space is decreased. So with the boat in the draw. The depth of the channel was twenty-two feet, the width one hundred and sixteen feet; multiply these and you have the square-feet across the water of the draw, viz.: 2552 feet. The Afton was 35 feet wide and drew 5 feet, making a fourteenth of the sum. Now, one-fourteenth of five miles is five-fourteenths of one mile—about one third of a mile—the increase of the current. We will call the current five and a half miles per hour. The next thing I will try to prove is that the plaintiff's (?) boat had power to run six miles an hour in that current. It had been testified that she was a strong, swift boat, able to run eight miles an hour up stream in a current of four miles an hour, and fifteen miles down stream. Strike the average and you will find what is her average—about eleven and a half miles. Take the five and a half miles which is the speed of the current in the draw and it leaves the power of that boat in that draw at six miles an hour, 528 feet per minute and 8 4/5 feet to the second.
"Next I propose to show that there are no cross currents. I know their witnesses say that there are cross currents—that, as one witness says, there were three cross currents and two eddies; so far as mere statement, without experiment, and mingled with mistakes, can go, they have proved. But can these men's testimony be compared with the nice, exact, thorough experiments of our witnesses? Can you believe that these floats go across the currents? It is inconceivable that they could not have discovered every possible current. How do boats find currents that floats cannot discover? We assume the position then that those cross currents are not there. My next proposition is that the Afton passed between the S. B. Carson and the Iowa shore. That is undisputed.
"Next I shall show that she struck first the short pier, then the long pier, then the short one again and there she stopped." Mr. Lincoln then cited the testimony of eighteen witnesses on this point.
"How did the boat strike when she went in? Here is an endless variety of opinion. But ten of them say what pier she struck; three of them testify that she struck first the short, then the long and then the short for the last time. None of the rest substantially contradict this. I assume that these men have got the truth because I believe it an established fact. My next proposition is that after she struck the short and long pier and before she got back to the short pier the boat got right with her bow up. So says the pilot Parker—that he got her through until her starboard wheel passed the short pier. This would make her head about even with the head of the long pier. He says her head was as high or higher than the head of the long pier. Other witnesses confirmed this one. The final stroke was in the splash door aft the wheel. Witnesses differ, but the majority say that she struck thus."
Court adjourned.
14th day, Wednesday, Sept. 23, 1857.
Mr. A. LINCOLN resumed. He said he should conclude as soon as possible. He said the colored map of the plaintiff which was brought in during one stage of the trial showed itself that the cross currents alleged did not exist. That the current as represented would drive an ascending boat to the long pier but not to the short pier, as they urge. He explained from a model of a boat where the splash door is, just behind the wheel. The boat struck on the lower shoulder of the short pier as she swung around in the splash door; then as she went on around she struck the point or end of the pier, where she rested. "Her engineers," said Mr. Lincoln, "say the starboard wheel then was rushing around rapidly. Then the boat must have struck the upper point of the pier so far back as not to disturb the wheel. It is forty feet from the stern of the Afton to the splash door, and thus it appears that she had but forty feet to go to clear the pier. How was it that the Afton with all her power flanked over from the channel to the short pier without moving one foot ahead? Suppose she was in the middle of the draw, her wheel would have been 31 feet from the short pier. The reason she went over thus is her starboard wheel was not working. I shall try to establish the fact that the wheel was not running and that after she struck she went ahead strong on this same wheel. Upon the last point the witnesses agree, that the starboard wheel was running after she struck, and no witnesses say that it was running while she was out in the draw flanking over."
Mr. Lincoln read from the testimonies of various witnesses to prove that the starboard wheel was not working while the Afton was out in the stream.
"Other witnesses show that the captain said something of the machinery of the wheel, and the inference is that he knew the wheel was not working. The fact is undisputed that she did not move one inch ahead while she was moving this 31 feet sideways. There is evidence proving that the current there is only five miles an hour, and the only explanation is that her power was not all used—that only one wheel was working. The pilot says he ordered the engineers to back her up. The engineers differ from him and said they kept on going ahead. The bow was so swung that the current pressed it over; the pilot pressed the stern over with the rudder, though not so fast but that the bow gained on it, and only one wheel being in motion the boat nearly stood still so far as motion up and down is concerned, and thus she was thrown upon this pier. The Afton came into the draw after she had just passed the Carson, and as the Carson no doubt kept the true course the Afton going around her got out of the proper way, got across the current into the eddy which is west of a straight line drawn down from the long pier, was compelled to resort to these changes of wheels, which she did not do with sufficient adroitness to save her. Was it not her own fault that she entered wrong, so far wrong that she never got right? Is the defence to blame for that?
"For several days we were entertained with depositions about boats 'smelling a bar.' Why did the Afton then, after she had come up smelling so close to the long pier sheer off so strangely. When she got to the centre of the very nose she was smelling she seemed suddenly to have lost her sense of smell and to have flanked over to the short pier."
Mr. Lincoln said there was no practicability in the project of building a tunnel under the river, for there "is not a tunnel that is a successful project in this world. A suspension bridge cannot be built so high but that the chimneys of the boats will grow up till they cannot pass. The steamboat men will take pains to make them grow. The cars of a railroad cannot without immense expense rise high enough to get even with a suspension bridge or go low enough to get through a tunnel; such expense is unreasonable.
"The plaintiffs have to establish that the bridge is a material obstruction and that they have managed their boat with reasonable care and skill. As to the last point high winds have nothing to do with it, for it was not a windy day. They must show due skill and care. Difficulties going down stream will not do, for they were going up stream. Difficulties with barges in tow have nothing to do with the accident, for they had no barge." Mr. Lincoln said he had much more to say, many things he could suggest to the jury, but he wished to close to save time.
BLOOMINGTON, Dec. 19, 1857.
J. M. Douglas of the I. C. R. R. Co. is here and will carry this letter. He says they have a large sum (near $90,000) which they will pay into the treasury now, if they have an assurance that they shall not be sued before Jan., 1859—otherwise not. I really wish you could consent to this. Douglas says they cannot pay more, and I believe him.
I do not write this as a lawyer seeking an advantage for a client; but only as a friend, only urging you to do what I think I would do if I were in your situation. I mean this as private and confidential only, but I feel a good deal of anxiety about it.
Yours as ever,
MY DEAR SIR: This morning Col. McClernand showed me a petition for a mandamus against the Secretary of State to compel him to certify the apportionment act of last session; and he says it will be presented to the court to-morrow morning. We shall be allowed three or four days to get up a return, and I, for one, want the benefit of consultation with you.
Please come right up.
Yours as ever,
MY DEAR SIR: Yesterday morning the court overruled the demurrer to Hatches return in the mandamus case. McClernand was present; said nothing about pleading over; and so I suppose the matter is ended.
The court gave no reason for the decision; but Peck tells me confidentially that they were unanimous in the opinion that even if the Gov'r had signed the bill purposely, he had the right to scratch his name off so long as the bill remained in his custody and control.
Yours as ever,
HENRY C. WHITNEY, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—Coming home from Bloomington last night I found your letter of the 15th.
I know of no express statute or decisions as to what a J. P. upon the expiration of his term shall do with his docket books, papers, unfinished business, etc., but so far as I know, the practice has been to hand over to the successor, and to cease to do anything further whatever, in perfect analogy to Sections 110 and 112, and I have supposed and do suppose this is the law. I think the successor may forthwith do whatever the retiring J. P. might have done. As to the proviso to Section 114 I think it was put in to cover possible cases, by way of caution, and not to authorize the J. P. to go forward and finish up whatever might have been begun by him.
The view I take, I believe, is the Common law principle, as to retiring officers and their successors, to which I remember but one exception, which is the case of Sheriff and ministerial officers of that class.
I have not had time to examine this subject fully, but I have great confidence I am right. You must not think of offering me pay for this.
Mr. John O. Johnson is my friend; I gave your name to him. He is doing the work of trying to get up a Republican organization. I do not suppose "Long John" ever saw or heard of him. Let me say to you confidentially, that I do not entirely appreciate what the Republican papers of Chicago are so constantly saying against "Long John." I consider those papers truly devoted to the Republican cause, and not unfriendly to me; but I do think that more of what they say against "Long John" is dictated by personal malice than themselves are conscious of. We can not afford to lose the services of "Long John" and I do believe the unrelenting warfare made upon him is injuring our cause. I mean this to be confidential.
If you quietly co-operate with Mr. J. O. Johnson on getting up an organization, I think it will be right.
Your friend as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, Feb.19, 1858.
MY DEAR SIR:
Mr. G. A. Sutton is an applicant for superintendent of the addition of the Insane Asylum, and I understand it partly depends on you whether he gets it.
Sutton is my fellow-townsman and friend, and I therefore wish to say for him that he is a man of sterling integrity and as a master mechanic and builder not surpassed by any in our city, or any I have known anywhere, as far as I can judge. I hope you will consider me as being really interested for Mr. Sutton and not as writing merely to relieve myself of importunity. Please show this to Col. William Ross and let him consider it as much intended for him as for yourself.
Your friend as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, JUNE 11, 1858
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 9th written at Joliet is just received. Two or three days ago I learned that McLean had appointed delegates in favor of Lovejoy, and thenceforward I have considered his renomination a fixed fact. My opinion—if my opinion is of any consequence in this case, in which it is no business of mine to interfere—remains unchanged, that running an independent candidate against Lovejoy will not do; that it will result in nothing but disaster all round. In the first place, whosoever so runs will be beaten and will be spotted for life; in the second place, while the race is in progress, he will be under the strongest temptation to trade with the Democrats, and to favor the election of certain of their friends to the Legislature; thirdly, I shall be held responsible for it, and Republican members of the Legislature who are partial to Lovejoy will for that purpose oppose us; and lastly, it will in the end lose us the district altogether. There is no safe way but a convention; and if in that convention, upon a common platform which all are willing to stand upon, one who has been known as an abolitionist, but who is now occupying none but common ground, can get the majority of the votes to which all look for an election, there is no safe way but to submit.
As to the inclination of some Republicans to favor Douglas, that is one of the chances I have to run, and which I intend to run with patience.
I write in the court room. Court has opened, and I must close.
Yours as ever,
The compiler of the Dictionary of Congress states that while preparing that work for publication, in 1858, he sent to Mr. Lincoln the usual request for a sketch of his life, and received the following reply:
Born February 12, 1809, in Hardin County, Kentucky. Education, defective. Profession, a lawyer. Have been a captain of volunteers in Black Hawk war. Postmaster at a very small office. Four times a member of the Illinois Legislature and was a member of the lower house of Congress.
Yours, etc.,
A. LINCOLN.
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
SPEECH AT CHICAGO, JULY 10, 1858.
SPEECH AT SPRINGFIELD, JULY 17, 1858.
CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN LINCOLN AND DOUGLAS
FIRST JOINT DEBATE, AT OTTAWA,
SECOND JOINT DEBATE, AT FREEPORT,
THIRD JOINT DEBATE, AT JONESBORO,
POLITICAL SPEECHES & DEBATES of LINCOLN WITH DOUGLAS In the Senatorial Campaign of 1858 in Illinois SPEECH AT SPRINGFIELD, JUNE 17, 1858
[The following speech was delivered at Springfield, Ill., at the close of the Republican State Convention held at that time and place, and by which Convention Mr. LINCOLN had been named as their candidate for United States Senator. Mr. DOUGLAS was not present.]
Mr. PRESIDENT AND GENTLEMEN OF THE CONVENTION:—If we could first know where we are, and whither we are tending, we could better judge what to do, and how to do it. We are now far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of that policy, that agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented. In my opinion, it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. "A house divided against itself cannot stand." I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved; I do not expect the house to fall; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South.
Have we no tendency to the latter condition?
Let any one who doubts, carefully contemplate that now almost complete legal combination-piece of machinery, so to speak compounded of the Nebraska doctrine and the Dred Scott decision. Let him consider, not only what work the machinery is adapted to do, and how well adapted, but also let him study the history of its construction, and trace, if he can, or rather fail, if he can, to trace the evidences of design, and concert of action, among its chief architects, from the beginning.
The new year of 1854 found slavery excluded from more than half the States by State Constitutions, and from most of the National territory by Congressional prohibition. Four days later, commenced the struggle which ended in repealing that Congressional prohibition. This opened all the National territory to slavery, and was the first point gained.
But, so far, Congress only had acted, and an indorsement by the people, real or apparent, was indispensable to save the point already gained, and give chance for more.
This necessity had not been overlooked, but had been provided for, as well as might be, in the notable argument of "squatter sovereignty," otherwise called "sacred right of self-government," which latter phrase, though expressive of the only rightful basis of any government, was so perverted in this attempted use of it as to amount to just this: That if any one man choose to enslave another, no third man shall be allowed to object. That argument was incorporated into the Nebraska Bill itself, in the language which follows:
"It being the true intent and meaning of this Act not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State, nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States."
Then opened the roar of loose declamation in favor of "squatter sovereignty," and "sacred right of self-government." "But," said opposition members, "let us amend the bill so as to expressly declare that the people of the Territory may exclude slavery." "Not we," said the friends of the measure, and down they voted the amendment.
While the Nebraska Bill was passing through Congress, a law case, involving the question of a negro's freedom, by reason of his owner having voluntarily taken him first into a free State, and then into a territory covered by the Congressional Prohibition, and held him as a slave for a long time in each, was passing through the United States Circuit Court for the District of Missouri; and both Nebraska Bill and lawsuit were brought to a decision in the same month of May, 1854. The negro's name was "Dred Scott," which name now designates the decision finally made in the case. Before the then next Presidential election, the law case came to, and was argued in, the Supreme Court of the United States; but the decision of it was deferred until after the election. Still, before the election, Senator Trumbull, on the floor of the Senate, requested the leading advocate of the Nebraska Bill to state his opinion whether the people of a territory can constitutionally exclude slavery from their limits; and the latter answers: "That is a question for the Supreme Court."
The election came. Mr. Buchanan was elected, and the indorsement, such as it was, secured. That was the second point gained. The indorsement, however, fell short of a clear popular majority by nearly four hundred thousand votes,(approximately 10% of the vote) and so, perhaps, was not overwhelmingly reliable and satisfactory. The outgoing President, in his last annual message, as impressively as possible echoed back upon the people the weight and authority of the indorsement. The Supreme Court met again, did not announce their decision, but ordered a reargument. The Presidential inauguration came, and still no decision of the court; but the incoming President, in his inaugural address, fervently exhorted the people to abide by the forth-coming decision, whatever it might be. Then, in a few days, came the decision.
The reputed author of the Nebraska Bill finds an early occasion to make a speech at this capital indorsing the Dred Scott decision, and vehemently denouncing all opposition to it. The new President, too, seizes the early occasion of the Silliman letter to indorse and strongly construe that decision, and to express his astonishment that any different view had ever been entertained!
At length a squabble springs up between the President and the author of the Nebraska Bill, on the mere question of fact, whether the Lecompton Constitution was or was not in any just sense made by the people of Kansas; and in that quarrel the latter declares that all he wants is a fair vote for the people, and that he cares not whether slavery be voted down or voted up. I do not understand his declaration, that he cares not whether slavery be voted down or voted up, to be intended by him other than as an apt definition of the policy he would impress upon the public mind,—the principle for which he declares he has suffered so much, and is ready to suffer to the end. And well may he cling to that principle! If he has any parental feeling, well may he cling to it. That principle is the only shred left of his original Nebraska doctrine. Under the Dred Scott decision "squatter sovereignty" squatted out of existence, tumbled down like temporary scaffolding; like the mould at the foundry, served through one blast, and fell back into loose sand; helped to carry an election, and then was kicked to the winds. His late joint struggle with the Republicans, against the Lecompton Constitution, involves nothing of the original Nebraska doctrine. That struggle was made on a point—the right of a people to make their own constitution—upon which he and the Republicans have never differed.
The several points of the Dred Scott decision, in connection with Senator Douglas's "care not" policy, constitute the piece of machinery, in its present state of advancement. This was the third point gained. The working points of that machinery are:
Firstly, That no negro slave, imported as such from Africa, and no descendant of such slave, can ever be a citizen of any State, in the sense of that term as used in the Constitution of the United States. This point is made in order to deprive the negro, in every possible event, of the benefit of that provision of the United States Constitution which declares that "The citizens of each State shall be entitled to all privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States."
Secondly, That, "subject to the Constitution of the United States," neither Congress nor a Territorial Legislature can exclude slavery from any United States Territory. This point is made in order that individual men may fill up the Territories with slaves, without danger of losing them as property, and thus to enhance the chances of permanency to the institution through all the future.
Thirdly, That whether the holding a negro in actual slavery in a free State makes him free, as against the holder, the United States courts will not decide, but will leave to be decided by the courts of any slave State the negro may be forced into by the master. This point is made, not to be pressed immediately; but, if acquiesced in for a while, and apparently indorsed by the people at an election, then to sustain the logical conclusion that what Dred Scott's master might lawfully do with Dred Scott, in the free State of Illinois, every other master may lawfully do with any other one, or one thousand slaves, in Illinois, or in any other free State.
Auxiliary to all this, and working hand in hand with it, the Nebraska doctrine, or what is left of it, is to educate and mould public opinion, at least Northern public opinion, not to care whether slavery is voted down or voted up. This shows exactly where we now are; and partially, also, wither we are tending.
It will throw additional light on the latter, to go back and run the mind over the string of historical facts already stated. Several things will now appear less dark and mysterious than they did when they were transpiring. The people were to be left "perfectly free," "subject only to the Constitution." What the Constitution had to do with it, outsiders could not then see. Plainly enough now,—it was an exactly fitted niche, for the Dred Scott decision to afterward come in, and declare the perfect freedom of the people to be just no freedom at all. Why was the amendment, expressly declaring the right of the people, voted down? Plainly enough now,—the adoption of it would have spoiled the niche for the Dred Scott decision. Why was the court decision held up? Why even a Senator's individual opinion withheld, till after the Presidential election? Plainly enough now,—the speaking out then would have damaged the "perfectly free" argument upon which the election was to be carried. Why the outgoing President's felicitation on the indorsement? Why the delay of a reargument? Why the incoming President's advance exhortation in favor of the decision? These things look like the cautious patting and petting of a spirited horse preparatory to mounting him, when it is dreaded that he may give the rider a fall. And why the hasty after-indorsement of the decision by the President and others?
We cannot absolutely know that all these exact adaptations are the result of preconcert. But when we see a lot of framed timbers, different portions of which we know have been gotten out at different times and places and by different workmen, Stephen, Franklin, Roger, and James, for instance, and when we see these timbers joined together, and see they exactly make the frame of a house or a mill, all the tenons and mortises exactly fitting, and all the lengths and proportions of the different pieces exactly adapted to their respective places, and not a piece too many or too few,—not omitting even scaffolding,—or, if a single piece be lacking, we see the place in the frame exactly fitted and prepared yet to bring such piece in,—in such a case, we find it impossible not to believe that Stephen and Franklin and Roger and James all understood one another from the beginning, and all worked upon a common plan or draft drawn up before the first blow was struck.
It should not be overlooked that by the Nebraska Bill the people of a State as well as Territory were to be left "perfectly free," "subject only to the Constitution." Why mention a State? They were legislating for Territories, and not for or about States. Certainly the people of a State are and ought to be subject to the Constitution of the United States; but why is mention of this lugged into this merely Territorial law? Why are the people of a Territory and the people of a State therein lumped together, and their relation to the Constitution therefore treated as being precisely the same? While the opinion of the court, by Chief Justice Taney, in the Dred Scott case, and the separate opinions of all the concurring Judges, expressly declare that the Constitution of the United States neither permits Congress nor a Territorial Legislature to exclude slavery from any United States Territory, they all omit to declare whether or not the same Constitution permits a State, or the people of a State, to exclude it. Possibly, this is a mere omission; but who can be quite sure, if McLean or Curtis had sought to get into the opinion a declaration of unlimited power in the people of a State to exclude slavery from their limits, just as Chase and Mace sought to get such declaration, in behalf of the people of a Territory, into the Nebraska Bill,—I ask, who can be quite sure that it would not have been voted down in the one case as it had been in the other? The nearest approach to the point of declaring the power of a State over slavery is made by Judge Nelson. He approaches it more than once, Using the precise idea, and almost the language, too, of the Nebraska Act. On one occasion, his exact language is, "Except in cases where the power is restrained by the Constitution of the United States, the law of the State is supreme over the subject of slavery within its jurisdiction." In what cases the power of the States is so restrained by the United States Constitution, is left an open question, precisely as the same question, as to the restraint on the power of the Territories, was left open in the Nebraska Act. Put this and that together, and we have another nice little niche, which we may, ere long, see filled with another Supreme Court decision, declaring that the Constitution of the United States does not permit a State to exclude slavery from its limits. And this may especially be expected if the doctrine of "care not whether slavery be voted down or voted up" shall gain upon the public mind sufficiently to give promise that such a decision can be maintained when made.
Such a decision is all that slavery now lacks of being alike lawful in all the States. Welcome or unwelcome, such decision is probably coming, and will soon be upon us, unless the power of the present political dynasty shall be met and overthrown. We shall lie down pleasantly dreaming that the people of Missouri are on the verge of making their State free, and we shall awake to the reality instead that the Supreme Court has made Illinois a slave State. To meet and overthrow the power of that dynasty is the work now before all those who would prevent that consummation. That is what we have to do. How can we best do it?
There are those who denounce us openly to their friends, and yet whisper to us softly that Senator Douglas is the aptest instrument there is with which to effect that object. They wish us to infer all, from the fact that he now has a little quarrel with the present head of the dynasty, and that he has regularly voted with us on a single point, upon which he and we have never differed. They remind us that he is a great man, and that the largest of us are very small ones. Let this be granted. But "a living dog is better than a dead lion." Judge Douglas, if not a dead lion, for this work is at least a caged and toothless one. How can he oppose the advances of slavery? He don't care anything about it. His avowed mission is impressing the "public heart" to care nothing about it. A leading Douglas Democratic newspaper thinks Douglas's superior talent will be needed to resist the revival of the African slave trade. Does Douglas believe an effort to revive that trade is approaching? He has not said so. Does he really think so? But if it is, how can he resist it? For years he has labored to prove it a sacred right of white men to take negro slaves into the new Territories. Can he possibly show that it is less a sacred right to buy them where they can be bought cheapest? And unquestionably they can be bought cheaper in Africa than in Virginia. He has done all in his power to reduce the whole question of slavery to one of a mere right of property; and, as such, how can he oppose the foreign slave trade, how can he refuse that trade in that "property" shall be "perfectly free,"—unless he does it as a protection to the home production? And as the home producers will probably not ask the protection, he will be wholly without a ground of opposition.
Senator Douglas holds, we know, that a man may rightfully be wiser to-day than he was yesterday; that he may rightfully change when he finds himself wrong. But can we, for that reason, run ahead, and infer that he will make any particular change, of which he himself has given no intimation? Can we safely base our action upon any such vague inference? Now, as ever, I wish not to misrepresent Judge Douglas's position, question his motives, or do aught that can be personally offensive to him. Whenever, if ever, he and we can come together on principle so that our cause may have assistance from his great ability, I hope to have interposed no adventitious obstacles. But clearly he is not now with us; he does not pretend to be,—he does not promise ever to be.
Our cause, then, must be intrusted to, and conducted by, its own undoubted friends,—those whose hands are free, whose hearts are in the work, who do care for the result. Two years ago the Republicans of the nation mustered over thirteen hundred thousand strong. We did this under the single impulse of resistance to a common danger, with every external circumstance against us. Of strange, discordant, and even hostile elements we gathered from the four winds, and formed and fought the battle through, under the constant hot fire of a disciplined, proud, and pampered enemy. Did we brave all then to falter now,—now, when that same enemy is wavering, dissevered, and belligerent? The result is not doubtful. We shall not fail; if we stand firm, we shall not fail. Wise counsels may accelerate, or mistakes delay it, but, sooner or later, the victory is sure to come.
DELIVERED AT CHICAGO, SATURDAY EVENING, JULY 10, 1858.
(Mr. DOUGLAS WAS NOT PRESENT.)
[Mr. LINCOLN was introduced by C. L. Wilson, Esq., and as he made his appearance he was greeted with a perfect storm of applause. For some moments the enthusiasm continued unabated. At last, when by a wave of his hand partial silence was restored, Mr. LINCOLN said,]
MY FELLOW-CITIZENS:—On yesterday evening, upon the occasion of the reception given to Senator Douglas, I was furnished with a seat very convenient for hearing him, and was otherwise very courteously treated by him and his friends, and for which I thank him and them. During the course of his remarks my name was mentioned in such a way as, I suppose, renders it at least not improper that I should make some sort of reply to him. I shall not attempt to follow him in the precise order in which he addressed the assembled multitude upon that occasion, though I shall perhaps do so in the main.
There was one question to which he asked the attention of the crowd, which I deem of somewhat less importance—at least of propriety—for me to dwell upon than the others, which he brought in near the close of his speech, and which I think it would not be entirely proper for me to omit attending to, and yet if I were not to give some attention to it now, I should probably forget it altogether. While I am upon this subject, allow me to say that I do not intend to indulge in that inconvenient mode sometimes adopted in public speaking, of reading from documents; but I shall depart from that rule so far as to read a little scrap from his speech, which notices this first topic of which I shall speak,—that is, provided I can find it in the paper:
"I have made up my mind to appeal to the people against the combination that has been made against me; the Republican leaders having formed an alliance, an unholy and unnatural alliance, with a portion of unscrupulous Federal office-holders. I intend to fight that allied army wherever I meet them. I know they deny the alliance; but yet these men who are trying to divide the Democratic party for the purpose of electing a Republican Senator in my place are just as much the agents and tools of the supporters of Mr. Lincoln. Hence I shall deal with this allied army just as the Russians dealt with the Allies at Sebastopol,—that is, the Russians did not stop to inquire, when they fired a broadside, whether it hit an Englishman, a Frenchman, or a Turk. Nor will I stop to inquire, nor shall I hesitate, whether my blows shall hit the Republican leaders or their allies, who are holding the Federal offices, and yet acting in concert with them."
Well, now, gentlemen, is not that very alarming? Just to think of it! right at the outset of his canvass, I, a poor, kind, amiable, intelligent gentleman,—I am to be slain in this way! Why, my friend the Judge is not only, as it turns out, not a dead lion, nor even a living one,—he is the rugged Russian Bear!
But if they will have it—for he says that we deny it—that there is any such alliance, as he says there is,—and I don't propose hanging very much upon this question of veracity,—but if he will have it that there is such an alliance, that the Administration men and we are allied, and we stand in the attitude of English, French, and Turk, he occupying the position of the Russian, in that case I beg that he will indulge us while we barely suggest to him that these allies took Sebastopol.
Gentlemen, only a few more words as to this alliance. For my part, I have to say that whether there be such an alliance depends, so far as I know, upon what may be a right definition of the term alliance. If for the Republican party to see the other great party to which they are opposed divided among themselves, and not try to stop the division, and rather be glad of it,—if that is an alliance, I confess I am in; but if it is meant to be said that the Republicans had formed an alliance going beyond that, by which there is contribution of money or sacrifice of principle on the one side or the other, so far as the Republican party is concerned,—if there be any such thing, I protest that I neither know anything of it, nor do I believe it. I will, however, say,—as I think this branch of the argument is lugged in,—I would before I leave it state, for the benefit of those concerned, that one of those same Buchanan men did once tell me of an argument that he made for his opposition to Judge Douglas. He said that a friend of our Senator Douglas had been talking to him, and had, among other things, said to him:
"...why, you don't want to beat Douglas?" "Yes," said he, "I do want to beat him, and I will tell you why. I believe his original Nebraska Bill was right in the abstract, but it was wrong in the time that it was brought forward. It was wrong in the application to a Territory in regard to which the question had been settled; it was brought forward at a time when nobody asked him; it was tendered to the South when the South had not asked for it, but when they could not well refuse it; and for this same reason he forced that question upon our party. It has sunk the best men all over the nation, everywhere; and now, when our President, struggling with the difficulties of this man's getting up, has reached the very hardest point to turn in the case, he deserts him and I am for putting him where he will trouble us no more."
Now, gentlemen, that is not my argument; that is not my argument at all. I have only been stating to you the argument of a Buchanan man. You will judge if there is any force in it.
Popular sovereignty! Everlasting popular sovereignty! Let us for a moment inquire into this vast matter of popular sovereignty. What is popular sovereignty? We recollect that at an early period in the history of this struggle there was another name for the same thing,—"squatter sovereignty." It was not exactly popular sovereignty, but squatter sovereignty. What do those terms mean? What do those terms mean when used now? And vast credit is taken by our friend the Judge in regard to his support of it, when he declares the last years of his life have been, and all the future years of his life shall be, devoted to this matter of popular sovereignty. What is it? Why, it is the sovereignty of the people! What was squatter sovereignty? I suppose, if it had any significance at all, it was the right of the people to govern themselves, to be sovereign in their own affairs while they were squatted down in a country not their own, while they had squatted on a Territory that did not belong to them, in the sense that a State belongs to the people who inhabit it, when it belonged to the nation; such right to govern themselves was called "squatter sovereignty."
Now, I wish you to mark: What has become of that squatter sovereignty? what has become of it? Can you get anybody to tell you now that the people of a Territory have any authority to govern themselves, in regard to this mooted question of slavery, before they form a State constitution? No such thing at all; although there is a general running fire, and although there has been a hurrah made in every speech on that side, assuming that policy had given the people of a Territory the right to govern themselves upon this question, yet the point is dodged. To-day it has been decided—no more than a year ago it was decided—by the Supreme Court of the United States, and is insisted upon to-day that the people of a Territory have no right to exclude slavery from a Territory; that if any one man chooses to take slaves into a Territory, all the rest of the people have no right to keep them out. This being so, and this decision being made one of the points that the Judge approved, and one in the approval of which he says he means to keep me down,—put me down I should not say, for I have never been up,—he says he is in favor of it, and sticks to it, and expects to win his battle on that decision, which says that there is no such thing as squatter sovereignty, but that any one man may take slaves into a Territory, and all the other men in the Territory may be opposed to it, and yet by reason of the Constitution they cannot prohibit it. When that is so, how much is left of this vast matter of squatter sovereignty, I should like to know?
When we get back, we get to the point of the right of the people to make a constitution. Kansas was settled, for example, in 1854. It was a Territory yet, without having formed a constitution, in a very regular way, for three years. All this time negro slavery could be taken in by any few individuals, and by that decision of the Supreme Court, which the Judge approves, all the rest of the people cannot keep it out; but when they come to make a constitution, they may say they will not have slavery. But it is there; they are obliged to tolerate it some way, and all experience shows it will be so, for they will not take the negro slaves and absolutely deprive the owners of them. All experience shows this to be so. All that space of time that runs from the beginning of the settlement of the Territory until there is sufficiency of people to make a State constitution,—all that portion of time popular sovereignty is given up. The seal is absolutely put down upon it by the court decision, and Judge Douglas puts his own upon the top of that; yet he is appealing to the people to give him vast credit for his devotion to popular sovereignty.
Again, when we get to the question of the right of the people to form a State constitution as they please, to form it with slavery or without slavery, if that is anything new, I confess I don't know it. Has there ever been a time when anybody said that any other than the people of a Territory itself should form a constitution? What is now in it that Judge Douglas should have fought several years of his life, and pledge himself to fight all the remaining years of his life for? Can Judge Douglas find anybody on earth that said that anybody else should form a constitution for a people? [A voice, "Yes."] Well, I should like you to name him; I should like to know who he was. [Same voice, "John Calhoun."]
No, sir, I never heard of even John Calhoun saying such a thing. He insisted on the same principle as Judge Douglas; but his mode of applying it, in fact, was wrong. It is enough for my purpose to ask this crowd whenever a Republican said anything against it. They never said anything against it, but they have constantly spoken for it; and whoever will undertake to examine the platform, and the speeches of responsible men of the party, and of irresponsible men, too, if you please, will be unable to find one word from anybody in the Republican ranks opposed to that popular sovereignty which Judge Douglas thinks that he has invented. I suppose that Judge Douglas will claim, in a little while, that he is the inventor of the idea that the people should govern themselves; that nobody ever thought of such a thing until he brought it forward. We do not remember that in that old Declaration of Independence it is said that:
"We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; that to secure these rights, governments are instituted among men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed."
There is the origin of popular sovereignty. Who, then, shall come in at this day and claim that he invented it?
The Lecompton Constitution connects itself with this question, for it is in this matter of the Lecompton Constitution that our friend Judge Douglas claims such vast credit. I agree that in opposing the Lecompton Constitution, so far as I can perceive, he was right. I do not deny that at all; and, gentlemen, you will readily see why I could not deny it, even if I wanted to. But I do not wish to; for all the Republicans in the nation opposed it, and they would have opposed it just as much without Judge Douglas's aid as with it. They had all taken ground against it long before he did. Why, the reason that he urges against that constitution I urged against him a year before. I have the printed speech in my hand. The argument that he makes, why that constitution should not be adopted, that the people were not fairly represented nor allowed to vote, I pointed out in a speech a year ago, which I hold in my hand now, that no fair chance was to be given to the people. ["Read it, Read it."] I shall not waste your time by trying to read it. ["Read it, Read it."] Gentlemen, reading from speeches is a very tedious business, particularly for an old man that has to put on spectacles, and more so if the man be so tall that he has to bend over to the light.
A little more, now, as to this matter of popular sovereignty and the Lecompton Constitution. The Lecompton Constitution, as the Judge tells us, was defeated. The defeat of it was a good thing or it was not. He thinks the defeat of it was a good thing, and so do I, and we agree in that. Who defeated it?
[A voice: Judge Douglas.]
Yes, he furnished himself, and if you suppose he controlled the other Democrats that went with him, he furnished three votes; while the Republicans furnished twenty.
That is what he did to defeat it. In the House of Representatives he and his friends furnished some twenty votes, and the Republicans furnished ninety odd. Now, who was it that did the work?
[A voice: Douglas.]
Why, yes, Douglas did it! To be sure he did.
Let us, however, put that proposition another way. The Republicans could not have done it without Judge Douglas. Could he have done it without them? Which could have come the nearest to doing it without the other?
[A voice: Who killed the bill?]
[Another voice: Douglas.]
Ground was taken against it by the Republicans long before Douglas did it. The proportion of opposition to that measure is about five to one.
[A voice: Why don't they come out on it?]
You don't know what you are talking about, my friend. I am quite willing to answer any gentleman in the crowd who asks an intelligent question.
Now, who in all this country has ever found any of our friends of Judge Douglas's way of thinking, and who have acted upon this main question, that has ever thought of uttering a word in behalf of Judge Trumbull?
[A voice: We have.]
I defy you to show a printed resolution passed in a Democratic meeting—I take it upon myself to defy any man to show a printed resolution of a Democratic meeting, large or small—in favor of Judge Trumbull, or any of the five to one Republicans who beat that bill. Everything must be for the Democrats! They did everything, and the five to the one that really did the thing they snub over, and they do not seem to remember that they have an existence upon the face of the earth.
Gentlemen, I fear that I shall become tedious. I leave this branch of the subject to take hold of another. I take up that part of Judge Douglas's speech in which he respectfully attended to me.
Judge Douglas made two points upon my recent speech at Springfield. He says they are to be the issues of this campaign. The first one of these points he bases upon the language in a speech which I delivered at Springfield, which I believe I can quote correctly from memory. I said there that "we are now far into the fifth year since a policy was instituted for the avowed object, and with the confident promise, of putting an end to slavery agitation; under the operation of that policy, that agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented." "I believe it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. 'A house divided against itself cannot stand.' I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free." "I do not expect the Union to be dissolved,"—I am quoting from my speech, "—I do not expect the house to fall, but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the spread of it and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward until it shall become alike lawful in all the States, north as well as south."
What is the paragraph? In this paragraph, which I have quoted in your hearing, and to which I ask the attention of all, Judge Douglas thinks he discovers great political heresy. I want your attention particularly to what he has inferred from it. He says I am in favor of making all the States of this Union uniform in all their internal regulations; that in all their domestic concerns I am in favor of making them entirely uniform. He draws this inference from the language I have quoted to you. He says that I am in favor of making war by the North upon the South for the extinction of slavery; that I am also in favor of inviting (as he expresses it) the South to a war upon the North for the purpose of nationalizing slavery. Now, it is singular enough, if you will carefully read that passage over, that I did not say that I was in favor of anything in it. I only said what I expected would take place. I made a prediction only,—it may have been a foolish one, perhaps. I did not even say that I desired that slavery should be put in course of ultimate extinction. I do say so now, however, so there need be no longer any difficulty about that. It may be written down in the great speech.
Gentlemen, Judge Douglas informed you that this speech of mine was probably carefully prepared. I admit that it was. I am not master of language; I have not a fine education; I am not capable of entering into a disquisition upon dialectics, as I believe you call it; but I do not believe the language I employed bears any such construction as Judge Douglas puts upon it. But I don't care about a quibble in regard to words. I know what I meant, and I will not leave this crowd in doubt, if I can explain it to them, what I really meant in the use of that paragraph.
I am not, in the first place, unaware that this government has endured eighty-two years half slave and half free. I know that. I am tolerably well acquainted with the history of the country, and I know that it has endured eighty-two years half slave and half free. I believe—and that is what I meant to allude to there—I believe it has endured because during all that time, until the introduction of the Nebraska Bill, the public mind did rest all the time in the belief that slavery was in course of ultimate extinction. That was what gave us the rest that we had through that period of eighty-two years,—at least, so I believe. I have always hated slavery, I think, as much as any Abolitionist,—I have been an Old Line Whig,—I have always hated it; but I have always been quiet about it until this new era of the introduction of the Nebraska Bill began. I always believed that everybody was against it, and that it was in course of ultimate extinction. [Pointing to Mr. Browning, who stood near by.] Browning thought so; the great mass of the nation have rested in the belief that slavery was in course of ultimate extinction. They had reason so to believe.
The adoption of the Constitution and its attendant history led the people to believe so; and that such was the belief of the framers of the Constitution itself, why did those old men, about the time of the adoption of the Constitution, decree that slavery should not go into the new Territory, where it had not already gone? Why declare that within twenty years the African slave trade, by which slaves are supplied, might be cut off by Congress? Why were all these acts? I might enumerate more of these acts; but enough. What were they but a clear indication that the framers of the Constitution intended and expected the ultimate extinction of that institution? And now, when I say, as I said in my speech that Judge Douglas has quoted from, when I say that I think the opponents of slavery will resist the farther spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest with the belief that it is in course of ultimate extinction, I only mean to say that they will place it where the founders of this government originally placed it.
I have said a hundred times, and I have now no inclination to take it back, that I believe there is no right, and ought to be no inclination, in the people of the free States to enter into the slave States and interfere with the question of slavery at all. I have said that always; Judge Douglas has heard me say it, if not quite a hundred times, at least as good as a hundred times; and when it is said that I am in favor of interfering with slavery where it exists, I know it is unwarranted by anything I have ever intended, and, as I believe, by anything I have ever said. If, by any means, I have ever used language which could fairly be so construed (as, however, I believe I never have), I now correct it.
So much, then, for the inference that Judge Douglas draws, that I am in favor of setting the sections at war with one another. I know that I never meant any such thing, and I believe that no fair mind can infer any such thing from anything I have ever said.
Now, in relation to his inference that I am in favor of a general consolidation of all the local institutions of the various States. I will attend to that for a little while, and try to inquire, if I can, how on earth it could be that any man could draw such an inference from anything I said. I have said, very many times, in Judge Douglas's hearing, that no man believed more than I in the principle of self-government; that it lies at the bottom of all my ideas of just government, from beginning to end. I have denied that his use of that term applies properly. But for the thing itself, I deny that any man has ever gone ahead of me in his devotion to the principle, whatever he may have done in efficiency in advocating it. I think that I have said it in your hearing, that I believe each individual is naturally entitled to do as he pleases with himself and the fruit of his labor, so far as it in no wise interferes with any other man's rights; that each community as a State has a right to do exactly as it pleases with all the concerns within that State that interfere with the right of no other State; and that the General Government, upon principle, has no right to interfere with anything other than that general class of things that does concern the whole. I have said that at all times. I have said, as illustrations, that I do not believe in the right of Illinois to interfere with the cranberry laws of Indiana, the oyster laws of Virginia, or the liquor laws of Maine. I have said these things over and over again, and I repeat them here as my sentiments.
How is it, then, that Judge Douglas infers, because I hope to see slavery put where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, that I am in favor of Illinois going over and interfering with the cranberry laws of Indiana? What can authorize him to draw any such inference?
I suppose there might be one thing that at least enabled him to draw such an inference that would not be true with me or many others: that is, because he looks upon all this matter of slavery as an exceedingly little thing,—this matter of keeping one sixth of the population of the whole nation in a state of oppression and tyranny unequaled in the world. He looks upon it as being an exceedingly little thing,—only equal to the question of the cranberry laws of Indiana; as something having no moral question in it; as something on a par with the question of whether a man shall pasture his land with cattle, or plant it with tobacco; so little and so small a thing that he concludes, if I could desire that anything should be done to bring about the ultimate extinction of that little thing, I must be in favor of bringing about an amalgamation of all the other little things in the Union. Now, it so happens—and there, I presume, is the foundation of this mistake—that the Judge thinks thus; and it so happens that there is a vast portion of the American people that do not look upon that matter as being this very little thing. They look upon it as a vast moral evil; they can prove it as such by the writings of those who gave us the blessings of liberty which we enjoy, and that they so looked upon it, and not as an evil merely confining itself to the States where it is situated; and while we agree that, by the Constitution we assented to, in the States where it exists, we have no right to interfere with it, because it is in the Constitution; and we are by both duty and inclination to stick by that Constitution, in all its letter and spirit, from beginning to end.
So much, then, as to my disposition—my wish to have all the State legislatures blotted out, and to have one consolidated government, and a uniformity of domestic regulations in all the States, by which I suppose it is meant, if we raise corn here, we must make sugar-cane grow here too, and we must make those which grow North grow in the South. All this I suppose he understands I am in favor of doing. Now, so much for all this nonsense; for I must call it so. The Judge can have no issue with me on a question of establishing uniformity in the domestic regulations of the States.
A little now on the other point,—the Dred Scott decision. Another of the issues he says that is to be made with me is upon his devotion to the Dred Scott decision, and my opposition to it.
I have expressed heretofore, and I now repeat, my opposition to the Dred Scott decision; but I should be allowed to state the nature of that opposition, and I ask your indulgence while I do so. What is fairly implied by the term Judge Douglas has used, "resistance to the decision"? I do not resist it. If I wanted to take Dred Scott from his master, I would be interfering with property, and that terrible difficulty that Judge Douglas speaks of, of interfering with property, would arise. But I am doing no such thing as that, but all that I am doing is refusing to obey it as a political rule. If I were in Congress, and a vote should come up on a question whether slavery should be prohibited in a new Territory, in spite of the Dred Scott decision, I would vote that it should.
That is what I should do. Judge Douglas said last night that before the decision he might advance his opinion, and it might be contrary to the decision when it was made; but after it was made he would abide by it until it was reversed. Just so! We let this property abide by the decision, but we will try to reverse that decision. We will try to put it where Judge Douglas would not object, for he says he will obey it until it is reversed. Somebody has to reverse that decision, since it is made, and we mean to reverse it, and we mean to do it peaceably.
What are the uses of decisions of courts? They have two uses. As rules of property they have two uses. First, they decide upon the question before the court. They decide in this case that Dred Scott is a slave. Nobody resists that, not only that, but they say to everybody else that persons standing just as Dred Scott stands are as he is. That is, they say that when a question comes up upon another person, it will be so decided again, unless the court decides in another way, unless the court overrules its decision. Well, we mean to do what we can to have the court decide the other way. That is one thing we mean to try to do.
The sacredness that Judge Douglas throws around this decision is a degree of sacredness that has never been before thrown around any other decision. I have never heard of such a thing. Why, decisions apparently contrary to that decision, or that good lawyers thought were contrary to that decision, have been made by that very court before. It is the first of its kind; it is an astonisher in legal history. It is a new wonder of the world. It is based upon falsehood in the main as to the facts; allegations of facts upon which it stands are not facts at all in many instances, and no decision made on any question—the first instance of a decision made under so many unfavorable circumstances—thus placed, has ever been held by the profession as law, and it has always needed confirmation before the lawyers regarded it as settled law. But Judge Douglas will have it that all hands must take this extraordinary decision, made under these extraordinary circumstances, and give their vote in Congress in accordance with it, yield to it, and obey it in every possible sense. Circumstances alter cases. Do not gentlemen here remember the case of that same Supreme Court some twenty-five or thirty years ago deciding that a National Bank was constitutional? I ask, if somebody does not remember that a National Bank was declared to be constitutional? Such is the truth, whether it be remembered or not. The Bank charter ran out, and a recharter was granted by Congress. That recharter was laid before General Jackson. It was urged upon him, when he denied the constitutionality of the Bank, that the Supreme Court had decided that it was constitutional; and General Jackson then said that the Supreme Court had no right to lay down a rule to govern a coordinate branch of the government, the members of which had sworn to support the Constitution; that each member had sworn to support that Constitution as he understood it. I will venture here to say that I have heard Judge Douglas say that he approved of General Jackson for that act. What has now become of all his tirade about "resistance of the Supreme Court"?
My fellow-citizens, getting back a little,—for I pass from these points,—when Judge Douglas makes his threat of annihilation upon the "alliance," he is cautious to say that that warfare of his is to fall upon the leaders of the Republican party. Almost every word he utters, and every distinction he makes, has its significance. He means for the Republicans who do not count themselves as leaders, to be his friends; he makes no fuss over them; it is the leaders that he is making war upon. He wants it understood that the mass of the Republican party are really his friends. It is only the leaders that are doing something that are intolerant, and that require extermination at his hands. As this is dearly and unquestionably the light in which he presents that matter, I want to ask your attention, addressing myself to the Republicans here, that I may ask you some questions as to where you, as the Republican party, would be placed if you sustained Judge Douglas in his present position by a re-election? I do not claim, gentlemen, to be unselfish; I do not pretend that I would not like to go to the United States Senate,—I make no such hypocritical pretense; but I do say to you that in this mighty issue it is nothing to you—nothing to the mass of the people of the nation,—whether or not Judge Douglas or myself shall ever be heard of after this night; it may be a trifle to either of us, but in connection with this mighty question, upon which hang the destinies of the nation, perhaps, it is absolutely nothing: but where will you be placed if you reindorse Judge Douglas? Don't you know how apt he is, how exceedingly anxious he is at all times, to seize upon anything and everything to persuade you that something he has done you did yourselves? Why, he tried to persuade you last night that our Illinois Legislature instructed him to introduce the Nebraska Bill. There was nobody in that Legislature ever thought of such a thing; and when he first introduced the bill, he never thought of it; but still he fights furiously for the proposition, and that he did it because there was a standing instruction to our Senators to be always introducing Nebraska bills. He tells you he is for the Cincinnati platform, he tells you he is for the Dred Scott decision. He tells you, not in his speech last night, but substantially in a former speech, that he cares not if slavery is voted up or down; he tells you the struggle on Lecompton is past; it may come up again or not, and if it does, he stands where he stood when, in spite of him and his opposition, you built up the Republican party. If you indorse him, you tell him you do not care whether slavery be voted up or down, and he will close or try to close your mouths with his declaration, repeated by the day, the week, the month, and the year. Is that what you mean? [Cries of "No," one voice "Yes."] Yes, I have no doubt you who have always been for him, if you mean that. No doubt of that, soberly I have said, and I repeat it. I think, in the position in which Judge Douglas stood in opposing the Lecompton Constitution, he was right; he does not know that it will return, but if it does we may know where to find him, and if it does not, we may know where to look for him, and that is on the Cincinnati platform. Now, I could ask the Republican party, after all the hard names that Judge Douglas has called them by all his repeated charges of their inclination to marry with and hug negroes; all his declarations of Black Republicanism,—by the way, we are improving, the black has got rubbed off,—but with all that, if he be indorsed by Republican votes, where do you stand? Plainly, you stand ready saddled, bridled, and harnessed, and waiting to be driven over to the slavery extension camp of the nation,—just ready to be driven over, tied together in a lot, to be driven over, every man with a rope around his neck, that halter being held by Judge Douglas. That is the question. If Republican men have been in earnest in what they have done, I think they had better not do it; but I think that the Republican party is made up of those who, as far as they can peaceably, will oppose the extension of slavery, and who will hope for its ultimate extinction. If they believe it is wrong in grasping up the new lands of the continent and keeping them from the settlement of free white laborers, who want the land to bring up their families upon; if they are in earnest, although they may make a mistake, they will grow restless, and the time will come when they will come back again and reorganize, if not by the same name, at least upon the same principles as their party now has. It is better, then, to save the work while it is begun. You have done the labor; maintain it, keep it. If men choose to serve you, go with them; but as you have made up your organization upon principle, stand by it; for, as surely as God reigns over you, and has inspired your mind, and given you a sense of propriety, and continues to give you hope, so surely will you still cling to these ideas, and you will at last come back again after your wanderings, merely to do your work over again.
We were often,—more than once, at least,—in the course of Judge Douglas's speech last night, reminded that this government was made for white men; that he believed it was made for white men. Well, that is putting it into a shape in which no one wants to deny it; but the Judge then goes into his passion for drawing inferences that are not warranted. I protest, now and forever, against that counterfeit logic which presumes that because I did not want a negro woman for a slave, I do necessarily want her for a wife. My understanding is that I need not have her for either, but, as God made us separate, we can leave one another alone, and do one another much good thereby. There are white men enough to marry all the white women, and enough black men to marry all the black women; and in God's name let them be so married. The Judge regales us with the terrible enormities that take place by the mixture of races; that the inferior race bears the superior down. Why, Judge, if we do not let them get together in the Territories, they won't mix there.
[A voice: "Three cheers for Lincoln".—The cheers were given with a hearty good-will.]
I should say at least that that is a self-evident truth.
Now, it happens that we meet together once every year, sometimes about the 4th of July, for some reason or other. These 4th of July gatherings I suppose have their uses. If you will indulge me, I will state what I suppose to be some of them.
We are now a mighty nation; we are thirty or about thirty millions of people, and we own and inhabit about one fifteenth part of the dry land of the whole earth. We run our memory back over the pages of history for about eighty-two years, and we discover that we were then a very small people in point of numbers, vastly inferior to what we are now, with a vastly less extent of country, with vastly less of everything we deem desirable among men; we look upon the change as exceedingly advantageous to us and to our posterity, and we fix upon something that happened away back, as in some way or other being connected with this rise of prosperity. We find a race of men living in that day whom we claim as our fathers and grandfathers; they were iron men; they fought for the principle that they were contending for; and we understood that by what they then did it has followed that the degree of prosperity which we now enjoy has come to us. We hold this annual celebration to remind ourselves of all the good done in this process of time, of how it was done and who did it, and how we are historically connected with it; and we go from these meetings in better humor with ourselves, we feel more attached the one to the other, and more firmly bound to the country we inhabit. In every way we are better men in the age and race and country in which we live, for these celebrations. But after we have done all this we have not yet reached the whole. There is something else connected with it. We have—besides these, men descended by blood from our ancestors—among us perhaps half our people who are not descendants at all of these men; they are men who have come from Europe, German, Irish, French, and Scandinavian,—men that have come from Europe themselves, or whose ancestors have come hither and settled here, finding themselves our equals in all things. If they look back through this history to trace their connection with those days by blood, they find they have none, they cannot carry themselves back into that glorious epoch and make themselves feel that they are part of us; but when they look through that old Declaration of Independence, they find that those old men say that "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal"; and then they feel that that moral sentiment, taught in that day, evidences their relation to those men, that it is the father of all moral principle in them, and that they have a right to claim it as though they were blood of the blood, and flesh of the flesh, of the men who wrote that Declaration; and so they are. That is the electric cord in that Declaration that Clinks the hearts of patriotic and liberty-loving men together, that will link those patriotic hearts as long as the love of freedom exists in the minds of men throughout the world.
Now, sirs, for the purpose of squaring things with this idea of "don't care if slavery is voted up or voted down," for sustaining the Dred Scott decision, for holding that the Declaration of Independence did not mean anything at all, we have Judge Douglas giving his exposition of what the Declaration of Independence means, and we have him saying that the people of America are equal to the people of England. According to his construction, you Germans are not connected with it. Now, I ask you in all soberness if all these things, if indulged in, if ratified, if confirmed and indorsed, if taught to our children, and repeated to them, do not tend to rub out the sentiment of liberty in the country, and to transform this government into a government of some other form. Those arguments that are made, that the inferior race are to be treated with as much allowance as they are capable of enjoying; that as much is to be done for them as their condition will allow,—what are these arguments? They are the arguments that kings have made for enslaving the people in all ages of the world. You will find that all the arguments in favor of kingcraft were of this class; they always bestrode the necks of the people not that they wanted to do it, but because the people were better off for being ridden. That is their argument, and this argument of the Judge is the same old serpent that says, You work, and I eat; you toil, and I will enjoy the fruits of it. Turn in whatever way you will, whether it come from the mouth of a king, an excuse for enslaving the people of his country, or from the mouth of men of one race as a reason for enslaving the men of another race, it is all the same old serpent; and I hold, if that course of argumentation that is made for the purpose of convincing the public mind that we should not care about this should be granted, it does not stop with the negro. I should like to know, if taking this old Declaration of Independence, which declares that all men are equal upon principle, and making exceptions to it, where will it stop? If one man says it does not mean a negro, why not another say it does not mean some other man? If that Declaration is not the truth, let us get the statute book, in which we find it, and tear it out! Who is so bold as to do it? If it is not true, let us tear it out! [Cries of "No, no."] Let us stick to it, then; let us stand firmly by it, then.
It may be argued that there are certain conditions that make necessities and impose them upon us; and to the extent that a necessity is imposed upon a man, he must submit to it. I think that was the condition in which we found ourselves when we established this government. We had slavery among us, we could not get our Constitution unless we permitted them to remain in slavery, we could not secure the good we did secure if we grasped for more; and having by necessity submitted to that much, it does not destroy the principle that is the charter of our liberties. Let that charter stand as our standard.
My friend has said to me that I am a poor hand to quote Scripture. I will try it again, however. It is said in one of the admonitions of our Lord, "As your Father in heaven is perfect, be ye also perfect." The Savior, I suppose, did not expect that any human creature could be perfect as the Father in heaven; but he said, "As your Father in heaven is perfect, be ye also perfect." He set that up as a standard; and he who did most towards reaching that standard attained the highest degree of moral perfection. So I say in relation to the principle that all men are created equal, let it be as nearly reached as we can. If we cannot give freedom to every creature, let us do nothing that will impose slavery upon any other creature. Let us then turn this government back into the channel in which the framers of the Constitution originally placed it. Let us stand firmly by each other. If we do not do so, we are turning in the contrary direction, that our friend Judge Douglas proposes—not intentionally—as working in the traces tends to make this one universal slave nation. He is one that runs in that direction, and as such I resist him.
My friends, I have detained you about as long as I desired to do, and I have only to say: Let us discard all this quibbling about this man and the other man, this race and that race and the other race being inferior, and therefore they must be placed in an inferior position; discarding our standard that we have left us. Let us discard all these things, and unite as one people throughout this land, until we shall once more stand up declaring that all men are created equal.
My friends, I could not, without launching off upon some new topic, which would detain you too long, continue to-night. I thank you for this most extensive audience that you have furnished me to-night. I leave you, hoping that the lamp of liberty will burn in your bosoms until there shall no longer be a doubt that all men are created free and equal.
(Mr. Douglas was not present.)
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—Another election, which is deemed an important one, is approaching, and, as I suppose, the Republican party will, without much difficulty, elect their State ticket. But in regard to the Legislature, we, the Republicans, labor under some disadvantages. In the first place, we have a Legislature to elect upon an apportionment of the representation made several years ago, when the proportion of the population was far greater in the South (as compared with the North) than it now is; and inasmuch as our opponents hold almost entire sway in the South, and we a correspondingly large majority in the North, the fact that we are now to be represented as we were years ago, when the population was different, is to us a very great disadvantage. We had in the year 1855, according to law, a census, or enumeration of the inhabitants, taken for the purpose of a new apportionment of representation. We know what a fair apportionment of representation upon that census would give us. We know that it could not, if fairly made, fail to give the Republican party from six to ten more members of the Legislature than they can probably get as the law now stands. It so happened at the last session of the Legislature that our opponents, holding the control of both branches of the Legislature, steadily refused to give us such an apportionment as we were rightly entitled to have upon the census already taken. The Legislature steadily refused to give us such an apportionment as we were rightfully entitled to have upon the census taken of the population of the State. The Legislature would pass no bill upon that subject, except such as was at least as unfair to us as the old one, and in which, in some instances, two men in the Democratic regions were allowed to go as far toward sending a member to the Legislature as three were in the Republican regions. Comparison was made at the time as to representative and senatorial districts, which completely demonstrated that such was the fact. Such a bill was passed and tendered to the Republican Governor for his signature; but, principally for the reasons I have stated, he withheld his approval, and the bill fell without becoming a law.
Another disadvantage under which we labor is that there are one or two Democratic Senators who will be members of the next Legislature, and will vote for the election of Senator, who are holding over in districts in which we could, on all reasonable calculation, elect men of our own, if we only had the chance of an election. When we consider that there are but twenty-five Senators in the Senate, taking two from the side where they rightfully belong, and adding them to the other, is to us a disadvantage not to be lightly regarded. Still, so it is; we have this to contend with. Perhaps there is no ground of complaint on our part. In attending to the many things involved in the last general election for President, Governor, Auditor, Treasurer, Superintendent of Public Instruction, Members of Congress, of the Legislature, County Officers, and so on, we allowed these things to happen by want of sufficient attention, and we have no cause to complain of our adversaries, so far as this matter is concerned. But we have some cause to complain of the refusal to give us a fair apportionment.
There is still another disadvantage under which we labor, and to which I will ask your attention. It arises out of the relative positions of the two persons who stand before the State as candidates for the Senate. Senator Douglas is of world-wide renown. All the anxious politicians of his party, or who have been of his party for years past, have been looking upon him as certainly, at no distant day, to be the President of the United States. They have seen in his round, jolly, fruitful face post-offices, land-offices, marshalships, and cabinet appointments, charge-ships and foreign missions bursting and sprouting out in wonderful exuberance, ready to be laid hold of by their greedy hands. And as they have been gazing upon this attractive picture so long, they cannot, in the little distraction that has taken place in the party, bring themselves to give up the charming hope; but with greedier anxiety they rush about him, sustain him, and give him marches, triumphal entries, and receptions beyond what even in the days of his highest prosperity they could have brought about in his favor. On the contrary, nobody has ever expected me to be President. In my poor, lean, lank face, nobody has ever seen that any cabbages were sprouting out. These are disadvantages all, taken together, that the Republicans labor under. We have to fight this battle upon principle, and upon principle alone. I am, in a certain sense, made the standard-bearer in behalf of the Republicans. I was made so merely because there had to be some one so placed,—I being in nowise preferable to any other one of twenty-five, perhaps a hundred, we have in the Republican ranks. Then I say I wish it to be distinctly understood and borne in mind that we have to fight this battle without many—perhaps without any of the external aids which are brought to bear against us. So I hope those with whom I am surrounded have principle enough to nerve themselves for the task, and leave nothing undone that can be fairly done to bring about the right result.
After Senator Douglas left Washington, as his movements were made known by the public prints, he tarried a considerable time in the city of New York; and it was heralded that, like another Napoleon, he was lying by and framing the plan of his campaign. It was telegraphed to Washington City, and published in the Union, that he was framing his plan for the purpose of going to Illinois to pounce upon and annihilate the treasonable and disunion speech which Lincoln had made here on the 16th of June. Now, I do suppose that the Judge really spent some time in New York maturing the plan of the campaign, as his friends heralded for him. I have been able, by noting his movements since his arrival in Illinois, to discover evidences confirmatory of that allegation. I think I have been able to see what are the material points of that plan. I will, for a little while, ask your attention to some of them. What I shall point out, though not showing the whole plan, are, nevertheless, the main points, as I suppose.
They are not very numerous. The first is popular sovereignty. The second and third are attacks upon my speech made on the 16th of June. Out of these three points—drawing within the range of popular sovereignty the question of the Lecompton Constitution—he makes his principal assault. Upon these his successive speeches are substantially one and the same. On this matter of popular sovereignty I wish to be a little careful. Auxiliary to these main points, to be sure, are their thunderings of cannon, their marching and music, their fizzlegigs and fireworks; but I will not waste time with them. They are but the little trappings of the campaign.
Coming to the substance,—the first point, "popular sovereignty." It is to be labeled upon the cars in which he travels; put upon the hacks he rides in; to be flaunted upon the arches he passes under, and the banners which wave over him. It is to be dished up in as many varieties as a French cook can produce soups from potatoes. Now, as this is so great a staple of the plan of the campaign, it is worth while to examine it carefully; and if we examine only a very little, and do not allow ourselves to be misled, we shall be able to see that the whole thing is the most arrant Quixotism that was ever enacted before a community. What is the matter of popular sovereignty? The first thing, in order to understand it, is to get a good definition of what it is, and after that to see how it is applied.
I suppose almost every one knows that, in this controversy, whatever has been said has had reference to the question of negro slavery. We have not been in a controversy about the right of the people to govern themselves in the ordinary matters of domestic concern in the States and Territories. Mr. Buchanan, in one of his late messages (I think when he sent up the Lecompton Constitution) urged that the main point to which the public attention had been directed was not in regard to the great variety of small domestic matters, but was directed to the question of negro slavery; and he asserts that if the people had had a fair chance to vote on that question there was no reasonable ground of objection in regard to minor questions. Now, while I think that the people had not had given, or offered, them a fair chance upon that slavery question, still, if there had been a fair submission to a vote upon that main question, the President's proposition would have been true to the utmost. Hence, when hereafter I speak of popular sovereignty, I wish to be understood as applying what I say to the question of slavery only, not to other minor domestic matters of a Territory or a State.
Does Judge Douglas, when he says that several of the past years of his life have been devoted to the question of "popular sovereignty," and that all the remainder of his life shall be devoted to it, does he mean to say that he has been devoting his life to securing to the people of the Territories the right to exclude slavery from the Territories? If he means so to say he means to deceive; because he and every one knows that the decision of the Supreme Court, which he approves and makes especial ground of attack upon me for disapproving, forbids the people of a Territory to exclude slavery. This covers the whole ground, from the settlement of a Territory till it reaches the degree of maturity entitling it to form a State Constitution. So far as all that ground is concerned, the Judge is not sustaining popular sovereignty, but absolutely opposing it. He sustains the decision which declares that the popular will of the Territory has no constitutional power to exclude slavery during their territorial existence. This being so, the period of time from the first settlement of a Territory till it reaches the point of forming a State Constitution is not the thing that the Judge has fought for or is fighting for, but, on the contrary, he has fought for, and is fighting for, the thing that annihilates and crushes out that same popular sovereignty.
Well, so much being disposed of, what is left? Why, he is contending for the right of the people, when they come to make a State Constitution, to make it for themselves, and precisely as best suits themselves. I say again, that is quixotic. I defy contradiction when I declare that the Judge can find no one to oppose him on that proposition. I repeat, there is nobody opposing that proposition on principle. Let me not be misunderstood. I know that, with reference to the Lecompton Constitution, I may be misunderstood; but when you understand me correctly, my proposition will be true and accurate. Nobody is opposing, or has opposed, the right of the people, when they form a constitution, to form it for themselves. Mr. Buchanan and his friends have not done it; they, too, as well as the Republicans and the Anti-Lecompton Democrats, have not done it; but on the contrary, they together have insisted on the right of the people to form a constitution for themselves. The difference between the Buchanan men on the one hand, and the Douglas men and the Republicans on the other, has not been on a question of principle, but on a question of fact.
The dispute was upon the question of fact, whether the Lecompton Constitution had been fairly formed by the people or not. Mr. Buchanan and his friends have not contended for the contrary principle any more than the Douglas men or the Republicans. They have insisted that whatever of small irregularities existed in getting up the Lecompton Constitution were such as happen in the settlement of all new Territories. The question was, Was it a fair emanation of the people? It was a question of fact, and not of principle. As to the principle, all were agreed. Judge Douglas voted with the Republicans upon that matter of fact.
He and they, by their voices and votes, denied that it was a fair emanation of the people. The Administration affirmed that it was. With respect to the evidence bearing upon that question of fact, I readily agree that Judge Douglas and the Republicans had the right on their side, and that the Administration was wrong. But I state again that, as a matter of principle, there is no dispute upon the right of a people in a Territory, merging into a State, to form a constitution for themselves without outside interference from any quarter. This being so, what is Judge Douglas going to spend his life for? Is he going to spend his life in maintaining a principle that nobody on earth opposes? Does he expect to stand up in majestic dignity, and go through his apotheosis and become a god in the maintaining of a principle which neither man nor mouse in all God's creation is opposing? Now something in regard to the Lecompton Constitution more specially; for I pass from this other question of popular sovereignty as the most arrant humbug that has ever been attempted on an intelligent community.
As to the Lecompton Constitution, I have already said that on the question of fact, as to whether it was a fair emanation of the people or not, Judge Douglas, with the Republicans and some Americans, had greatly the argument against the Administration; and while I repeat this, I wish to know what there is in the opposition of Judge Douglas to the Lecompton Constitution that entitles him to be considered the only opponent to it,—as being par excellence the very quintessence of that opposition. I agree to the rightfulness of his opposition. He in the Senate and his class of men there formed the number three and no more. In the House of Representatives his class of men—the Anti-Lecompton Democrats—formed a number of about twenty. It took one hundred and twenty to defeat the measure, against one hundred and twelve. Of the votes of that one hundred and twenty, Judge Douglas's friends furnished twenty, to add to which there were six Americans and ninety-four Republicans. I do not say that I am precisely accurate in their numbers, but I am sufficiently so for any use I am making of it.
Why is it that twenty shall be entitled to all the credit of doing that work, and the hundred none of it? Why, if, as Judge Douglas says, the honor is to be divided and due credit is to be given to other parties, why is just so much given as is consonant with the wishes, the interests, and advancement of the twenty? My understanding is, when a common job is done, or a common enterprise prosecuted, if I put in five dollars to your one, I have a right to take out five dollars to your one. But he does not so understand it. He declares the dividend of credit for defeating Lecompton upon a basis which seems unprecedented and incomprehensible.
Let us see. Lecompton in the raw was defeated. It afterward took a sort of cooked-up shape, and was passed in the English bill. It is said by the Judge that the defeat was a good and proper thing. If it was a good thing, why is he entitled to more credit than others for the performance of that good act, unless there was something in the antecedents of the Republicans that might induce every one to expect them to join in that good work, and at the same time something leading them to doubt that he would? Does he place his superior claim to credit on the ground that he performed a good act which was never expected of him? He says I have a proneness for quoting Scripture. If I should do so now, it occurs that perhaps he places himself somewhat upon the ground of the parable of the lost sheep which went astray upon the mountains, and when the owner of the hundred sheep found the one that was lost, and threw it upon his shoulders and came home rejoicing, it was said that there was more rejoicing over the one sheep that was lost and had been found than over the ninety and nine in the fold. The application is made by the Saviour in this parable, thus: "Verily, I say unto you, there is more rejoicing in heaven over one sinner that repenteth, than over ninety and nine just persons that need no repentance."
And now, if the Judge claims the benefit of this parable, let him repent. Let him not come up here and say: "I am the only just person; and you are the ninety-nine sinners!" Repentance before forgiveness is a provision of the Christian system, and on that condition alone will the Republicans grant his forgiveness.
How will he prove that we have ever occupied a different position in regard to the Lecompton Constitution or any principle in it? He says he did not make his opposition on the ground as to whether it was a free or slave constitution, and he would have you understand that the Republicans made their opposition because it ultimately became a slave constitution. To make proof in favor of himself on this point, he reminds us that he opposed Lecompton before the vote was taken declaring whether the State was to be free or slave. But he forgets to say that our Republican Senator, Trumbull, made a speech against Lecompton even before he did.
Why did he oppose it? Partly, as he declares, because the members of the convention who framed it were not fairly elected by the people; that the people were not allowed to vote unless they had been registered; and that the people of whole counties, some instances, were not registered. For these reasons he declares the Constitution was not an emanation, in any true sense, from the people. He also has an additional objection as to the mode of submitting the Constitution back to the people. But bearing on the question of whether the delegates were fairly elected, a speech of his, made something more than twelve months ago, from this stand, becomes important. It was made a little while before the election of the delegates who made Lecompton. In that speech he declared there was every reason to hope and believe the election would be fair; and if any one failed to vote, it would be his own culpable fault.
I, a few days after, made a sort of answer to that speech. In that answer I made, substantially, the very argument with which he combated his Lecompton adversaries in the Senate last winter. I pointed to the facts that the people could not vote without being registered, and that the time for registering had gone by. I commented on it as wonderful that Judge Douglas could be ignorant of these facts which every one else in the nation so well knew.
I now pass from popular sovereignty and Lecompton. I may have occasion to refer to one or both.
When he was preparing his plan of campaign, Napoleon-like, in New York, as appears by two speeches I have heard him deliver since his arrival in Illinois, he gave special attention to a speech of mine, delivered here on the 16th of June last. He says that he carefully read that speech. He told us that at Chicago a week ago last night and he repeated it at Bloomington last night. Doubtless, he repeated it again to-day, though I did not hear him. In the first two places—Chicago and Bloomington I heard him; to-day I did not. He said he had carefully examined that speech,—when, he did not say; but there is no reasonable doubt it was when he was in New York preparing his plan of campaign. I am glad he did read it carefully. He says it was evidently prepared with great care. I freely admit it was prepared with care. I claim not to be more free from errors than others,—perhaps scarcely so much; but I was very careful not to put anything in that speech as a matter of fact, or make any inferences, which did not appear to me to be true and fully warrantable. If I had made any mistake, I was willing to be corrected; if I had drawn any inference in regard to Judge Douglas or any one else which was not warranted, I was fully prepared to modify it as soon as discovered. I planted myself upon the truth and the truth only, so far as I knew it, or could be brought to know it.
Having made that speech with the most kindly feelings toward Judge Douglas, as manifested therein, I was gratified when I found that he had carefully examined it, and had detected no error of fact, nor any inference against him, nor any misrepresentations of which he thought fit to complain. In neither of the two speeches I have mentioned did he make any such complaint. I will thank any one who will inform me that he, in his speech to-day, pointed out anything I had stated respecting him as being erroneous. I presume there is no such thing. I have reason to be gratified that the care and caution used in that speech left it so that he, most of all others interested in discovering error, has not been able to point out one thing against him which he could say was wrong. He seizes upon the doctrines he supposes to be included in that speech, and declares that upon them will turn the issues of this campaign. He then quotes, or attempts to quote, from my speech. I will not say that he wilfully misquotes, but he does fail to quote accurately. His attempt at quoting is from a passage which I believe I can quote accurately from memory. I shall make the quotation now, with some comments upon it, as I have already said, in order that the Judge shall be left entirely without excuse for misrepresenting me. I do so now, as I hope, for the last time. I do this in great caution, in order that if he repeats his misrepresentation it shall be plain to all that he does so wilfully. If, after all, he still persists, I shall be compelled to reconstruct the course I have marked out for myself, and draw upon such humble resources, as I have, for a new course, better suited to the real exigencies of the case. I set out in this campaign with the intention of conducting it strictly as a gentleman, in substance at least, if not in the outside polish. The latter I shall never be; but that which constitutes the inside of a gentleman I hope I understand, and am not less inclined to practice than others. It was my purpose and expectation that this canvass would be conducted upon principle, and with fairness on both sides, and it shall not be my fault if this purpose and expectation shall be given up.
He charges, in substance, that I invite a war of sections; that I propose all the local institutions of the different States shall become consolidated and uniform. What is there in the language of that speech which expresses such purpose or bears such construction? I have again and again said that I would not enter into any of the States to disturb the institution of slavery. Judge Douglas said, at Bloomington, that I used language most able and ingenious for concealing what I really meant; and that while I had protested against entering into the slave States, I nevertheless did mean to go on the banks of the Ohio and throw missiles into Kentucky, to disturb them in their domestic institutions.
I said in that speech, and I meant no more, that the institution of slavery ought to be placed in the very attitude where the framers of this government placed it and left it. I do not understand that the framers of our Constitution left the people of the free States in the attitude of firing bombs or shells into the slave States. I was not using that passage for the purpose for which he infers I did use it. I said:
"We are now far advanced into the fifth year since a policy was created for the avowed object and with the confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of that policy that agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented. In my opinion it will not cease till a crisis shall have been reached and passed. 'A house divided against itself cannot stand.' I believe that this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free; it will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South."
Now, you all see, from that quotation, I did not express my wish on anything. In that passage I indicated no wish or purpose of my own; I simply expressed my expectation. Cannot the Judge perceive a distinction between a purpose and an expectation? I have often expressed an expectation to die, but I have never expressed a wish to die. I said at Chicago, and now repeat, that I am quite aware this government has endured, half slave and half free, for eighty-two years. I understand that little bit of history. I expressed the opinion I did because I perceived—or thought I perceived—a new set of causes introduced. I did say at Chicago, in my speech there, that I do wish to see the spread of slavery arrested, and to see it placed where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction. I said that because I supposed, when the public mind shall rest in that belief, we shall have peace on the slavery question. I have believed—and now believe—the public mind did rest on that belief up to the introduction of the Nebraska Bill.
Although I have ever been opposed to slavery, so far I rested in the hope and belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. For that reason it had been a minor question with me. I might have been mistaken; but I had believed, and now believe, that the whole public mind, that is, the mind of the great majority, had rested in that belief up to the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. But upon that event I became convinced that either I had been resting in a delusion, or the institution was being placed on a new basis, a basis for making it perpetual, national, and universal. Subsequent events have greatly confirmed me in that belief. I believe that bill to be the beginning of a conspiracy for that purpose. So believing, I have since then considered that question a paramount one. So believing, I thought the public mind will never rest till the power of Congress to restrict the spread of it shall again be acknowledged and exercised on the one hand or, on the other, all resistance be entirely crushed out. I have expressed that opinion, and I entertain it to-night. It is denied that there is any tendency to the nationalization of slavery in these States.
Mr. Brooks, of South Carolina, in one of his speeches, when they were presenting him canes, silver plate, gold pitchers, and the like, for assaulting Senator Sumner, distinctly affirmed his opinion that when this Constitution was formed it was the belief of no man that slavery would last to the present day. He said, what I think, that the framers of our Constitution placed the institution of slavery where the public mind rested in the hope that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. But he went on to say that the men of the present age, by their experience, have become wiser than the framers of the Constitution, and the invention of the cotton gin had made the perpetuity of slavery a necessity in this country.
As another piece of evidence tending to this same point: Quite recently in Virginia, a man—the owner of slaves—made a will providing that after his death certain of his slaves should have their freedom if they should so choose, and go to Liberia, rather than remain in slavery. They chose to be liberated. But the persons to whom they would descend as property claimed them as slaves. A suit was instituted, which finally came to the Supreme Court of Virginia, and was therein decided against the slaves upon the ground that a negro cannot make a choice; that they had no legal power to choose, could not perform the condition upon which their freedom depended.
I do not mention this with any purpose of criticizing it, but to connect it with the arguments as affording additional evidence of the change of sentiment upon this question of slavery in the direction of making it perpetual and national. I argue now as I did before, that there is such a tendency; and I am backed, not merely by the facts, but by the open confession in the slave States.
And now as to the Judge's inference that because I wish to see slavery placed in the course of ultimate extinction,—placed where our fathers originally placed it,—I wish to annihilate the State Legislatures, to force cotton to grow upon the tops of the Green Mountains, to freeze ice in Florida, to cut lumber on the broad Illinois prairie,—that I am in favor of all these ridiculous and impossible things.
It seems to me it is a complete answer to all this to ask if, when Congress did have the fashion of restricting slavery from free territory; when courts did have the fashion of deciding that taking a slave into a free country made him free,—I say it is a sufficient answer to ask if any of this ridiculous nonsense about consolidation and uniformity did actually follow. Who heard of any such thing because of the Ordinance of '87? because of the Missouri restriction? because of the numerous court decisions of that character?
Now, as to the Dred Scott decision; for upon that he makes his last point at me. He boldly takes ground in favor of that decision.
This is one half the onslaught, and one third of the entire plan of the campaign. I am opposed to that decision in a certain sense, but not in the sense which he puts it. I say that in so far as it decided in favor of Dred Scott's master, and against Dred Scott and his family, I do not propose to disturb or resist the decision.
I never have proposed to do any such thing. I think that in respect for judicial authority my humble history would not suffer in comparison with that of Judge Douglas. He would have the citizen conform his vote to that decision; the member of Congress, his; the President, his use of the veto power. He would make it a rule of political action for the people and all the departments of the government. I would not. By resisting it as a political rule, I disturb no right of property, create no disorder, excite no mobs.
When he spoke at Chicago, on Friday evening of last week, he made this same point upon me. On Saturday evening I replied, and reminded him of a Supreme Court decision which he opposed for at least several years. Last night, at Bloomington, he took some notice of that reply, but entirely forgot to remember that part of it.
He renews his onslaught upon me, forgetting to remember that I have turned the tables against himself on that very point. I renew the effort to draw his attention to it. I wish to stand erect before the country, as well as Judge Douglas, on this question of judicial authority; and therefore I add something to the authority in favor of my own position. I wish to show that I am sustained by authority, in addition to that heretofore presented. I do not expect to convince the Judge. It is part of the plan of his campaign, and he will cling to it with a desperate grip. Even turn it upon him,—the sharp point against him, and gaff him through,—he will still cling to it till he can invent some new dodge to take the place of it.
In public speaking it is tedious reading from documents; but I must beg to indulge the practice to a limited extent. I shall read from a letter written by Mr. Jefferson in 1820, and now to be found in the seventh volume of his correspondence, at page 177. It seems he had been presented by a gentleman of the name of Jarvis with a book, or essay, or periodical, called the Republican, and he was writing in acknowledgment of the present, and noting some of its contents. After expressing the hope that the work will produce a favorable effect upon the minds of the young, he proceeds to say:
"That it will have this tendency may be expected, and for that reason I feel an urgency to note what I deem an error in it, the more requiring notice as your opinion is strengthened by that of many others. You seem, in pages 84 and 148, to consider the judges as the ultimate arbiters of all constitutional questions,—a very dangerous doctrine indeed, and one which would place us under the despotism of an oligarchy. Our judges are as honest as other men, and not more so. They have, with others, the same passions for party, for power, and the privilege of their corps. Their maxim is, 'Boni judicis est ampliare jurisdictionem'; and their power is the more dangerous as they are in office for life, and not responsible, as the other functionaries are, to the elective control. The Constitution has erected no such single tribunal, knowing that, to whatever hands confided, with the corruptions of time and party, its members would become despots. It has more wisely made all the departments co-equal and co-sovereign with themselves."
Thus we see the power claimed for the Supreme Court by Judge Douglas, Mr. Jefferson holds, would reduce us to the despotism of an oligarchy.
Now, I have said no more than this,—in fact, never quite so much as this; at least I am sustained by Mr. Jefferson.
Let us go a little further. You remember we once had a National Bank. Some one owed the bank a debt; he was sued, and sought to avoid payment on the ground that the bank was unconstitutional. The case went to the Supreme Court, and therein it was decided that the bank was constitutional. The whole Democratic party revolted against that decision. General Jackson himself asserted that he, as President, would not be bound to hold a National Bank to be constitutional, even though the court had decided it to be so. He fell in precisely with the view of Mr. Jefferson, and acted upon it under his official oath, in vetoing a charter for a National Bank. The declaration that Congress does not possess this constitutional power to charter a bank has gone into the Democratic platform, at their National Conventions, and was brought forward and reaffirmed in their last Convention at Cincinnati. They have contended for that declaration, in the very teeth of the Supreme Court, for more than a quarter of a century. In fact, they have reduced the decision to an absolute nullity. That decision, I repeat, is repudiated in the Cincinnati platform; and still, as if to show that effrontery can go no further, Judge Douglas vaunts in the very speeches in which he denounces me for opposing the Dred Scott decision that he stands on the Cincinnati platform.
Now, I wish to know what the Judge can charge upon me, with respect to decisions of the Supreme Court, which does not lie in all its length, breadth, and proportions at his own door. The plain truth is simply this: Judge Douglas is for Supreme Court decisions when he likes and against them when he does not like them. He is for the Dred Scott decision because it tends to nationalize slavery; because it is part of the original combination for that object. It so happens, singularly enough, that I never stood opposed to a decision of the Supreme Court till this, on the contrary, I have no recollection that he was ever particularly in favor of one till this. He never was in favor of any nor opposed to any, till the present one, which helps to nationalize slavery.
Free men of Sangamon, free men of Illinois, free men everywhere, judge ye between him and me upon this issue.
He says this Dred Scott case is a very small matter at most,—that it has no practical effect; that at best, or rather, I suppose, at worst, it is but an abstraction. I submit that the proposition that the thing which determines whether a man is free or a slave is rather concrete than abstract. I think you would conclude that it was, if your liberty depended upon it, and so would Judge Douglas, if his liberty depended upon it. But suppose it was on the question of spreading slavery over the new Territories that he considers it as being merely an abstract matter, and one of no practical importance. How has the planting of slavery in new countries always been effected? It has now been decided that slavery cannot be kept out of our new Territories by any legal means. In what do our new Territories now differ in this respect from the old Colonies when slavery was first planted within them? It was planted, as Mr. Clay once declared, and as history proves true, by individual men, in spite of the wishes of the people; the Mother Government refusing to prohibit it, and withholding from the people of the Colonies the authority to prohibit it for themselves. Mr. Clay says this was one of the great and just causes of complaint against Great Britain by the Colonies, and the best apology we can now make for having the institution amongst us. In that precise condition our Nebraska politicians have at last succeeded in placing our own new Territories; the government will not prohibit slavery within them, nor allow the people to prohibit it.
I defy any man to find any difference between the policy which originally planted slavery in these Colonies and that policy which now prevails in our new Territories. If it does not go into them, it is only because no individual wishes it to go. The Judge indulged himself doubtless to-day with the question as to what I am going to do with or about the Dred Scott decision. Well, Judge, will you please tell me what you did about the bank decision? Will you not graciously allow us to do with the Dred Scott decision precisely as you did with the bank decision? You succeeded in breaking down the moral effect of that decision: did you find it necessary to amend the Constitution, or to set up a court of negroes in order to do it?
There is one other point. Judge Douglas has a very affectionate leaning toward the Americans and Old Whigs. Last evening, in a sort of weeping tone, he described to us a death-bed scene. He had been called to the side of Mr. Clay, in his last moments, in order that the genius of "popular sovereignty" might duly descend from the dying man and settle upon him, the living and most worthy successor. He could do no less than promise that he would devote the remainder of his life to "popular sovereignty"; and then the great statesman departs in peace. By this part of the "plan of the campaign" the Judge has evidently promised himself that tears shall be drawn down the cheeks of all Old Whigs, as large as half-grown apples.
Mr. Webster, too, was mentioned; but it did not quite come to a death-bed scene as to him. It would be amusing, if it were not disgusting, to see how quick these compromise-breakers administer on the political effects of their dead adversaries, trumping up claims never before heard of, and dividing the assets among themselves. If I should be found dead to-morrow morning, nothing but my insignificance could prevent a speech being made on my authority, before the end of next week. It so happens that in that "popular sovereignty" with which Mr. Clay was identified, the Missouri Compromise was expressly reversed; and it was a little singular if Mr. Clay cast his mantle upon Judge Douglas on purpose to have that compromise repealed.
Again, the Judge did not keep faith with Mr. Clay when he first brought in his Nebraska Bill. He left the Missouri Compromise unrepealed, and in his report accompanying the bill he told the world he did it on purpose. The manes of Mr. Clay must have been in great agony till thirty days later, when "popular sovereignty" stood forth in all its glory.
One more thing. Last night Judge Douglas tormented himself with horrors about my disposition to make negroes perfectly equal with white men in social and political relations. He did not stop to show that I have said any such thing, or that it legitimately follows from anything I have said, but he rushes on with his assertions. I adhere to the Declaration of Independence. If Judge Douglas and his friends are not willing to stand by it, let them come up and amend it. Let them make it read that all men are created equal except negroes. Let us have it decided whether the Declaration of Independence, in this blessed year of 1858, shall be thus amended. In his construction of the Declaration last year, he said it only meant that Americans in America were equal to Englishmen in England. Then, when I pointed out to him that by that rule he excludes the Germans, the Irish, the Portuguese, and all the other people who have come among us since the revolution, he reconstructs his construction. In his last speech he tells us it meant Europeans.
I press him a little further, and ask if it meant to include the Russians in Asia; or does he mean to exclude that vast population from the principles of our Declaration of Independence? I expect ere long he will introduce another amendment to his definition. He is not at all particular. He is satisfied with anything which does not endanger the nationalizing of negro slavery. It may draw white men down, but it must not lift negroes up.
Who shall say, "I am the superior, and you are the inferior"?
My declarations upon this subject of negro slavery may be misrepresented, but cannot be misunderstood. I have said that I do not understand the Declaration to mean that all men were created equal in all respects. They are not our equal in color; but I suppose that it does mean to declare that all men are equal in some respects; they are equal in their right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness." Certainly the negro is not our equal in color, perhaps not in many other respects; still, in the right to put into his mouth the bread that his own hands have earned, he is the equal of every other man, white or black. In pointing out that more has been given you, you cannot be justified in taking away the little which has been given him. All I ask for the negro is that if you do not like him, let him alone. If God gave him but little, that little let him enjoy.
When our government was established we had the institution of slavery among us. We were in a certain sense compelled to tolerate its existence. It was a sort of necessity. We had gone through our struggle and secured our own independence. The framers of the Constitution found the institution of slavery amongst their own institutions at the time. They found that by an effort to eradicate it they might lose much of what they had already gained. They were obliged to bow to the necessity. They gave power to Congress to abolish the slave trade at the end of twenty years. They also prohibited it in the Territories where it did not exist. They did what they could, and yielded to the necessity for the rest. I also yield to all which follows from that necessity. What I would most desire would be the separation of the white and black races.
One more point on this Springfield speech which Judge Douglas says he has read so carefully. I expressed my belief in the existence of a conspiracy to perpetuate and nationalize slavery. I did not profess to know it, nor do I now. I showed the part Judge Douglas had played in the string of facts constituting to my mind the proof of that conspiracy. I showed the parts played by others.
I charged that the people had been deceived into carrying the last Presidential election, by the impression that the people of the Territories might exclude slavery if they chose, when it was known in advance by the conspirators that the court was to decide that neither Congress nor the people could so exclude slavery. These charges are more distinctly made than anything else in the speech.
Judge Douglas has carefully read and reread that speech. He has not, so far as I know, contradicted those charges. In the two speeches which I heard he certainly did not. On this own tacit admission, I renew that charge. I charge him with having been a party to that conspiracy and to that deception for the sole purpose of nationalizing slavery.
[The following is the correspondence between the two rival candidates for the United States Senate]
HON. S. A. DOUGLAS:
My dear Sir,—Will it be agreeable to you to make an arrangement for you and myself to divide time, and address the same audiences the present canvass? Mr. Judd, who will hand you this, is authorized to receive your answer; and, if agreeable to you, to enter into the terms of such arrangement.
Your obedient servant,
Dear Sir,—Your letter dated yesterday, accepting my proposition for a joint discussion at one prominent point in each Congressional District, as stated in my previous letter, was received this morning.
The times and places designated are as follows:
Ottawa, La Salle County August 21st, 1858.
Freeport, Stephenson County " 27th,
Jonesboro, Union County, September 15th,
Charleston, Coles County " 18th,
Galesburgh, Knox County October 7th,
Quincy, Adams County " 13th,
Alton, Madison County " 15th,
I agree to your suggestion that we shall alternately open and close the discussion. I will speak at Ottawa one hour, you can reply, occupying an hour and a half, and I will then follow for half an hour. At Freeport, you shall open the discussion and speak one hour; I will follow for an hour and a half, and you can then reply for half an hour. We will alternate in like manner in each successive place.
Very respectfully, your obedient servant,
Dear Sir,—Yours of yesterday, naming places, times, and terms for joint discussions between us, was received this morning. Although, by the terms, as you propose, you take four openings and closes, to my three, I accede, and thus close the arrangement. I direct this to you at Hillsborough, and shall try to have both your letter and this appear in the Journal and Register of Monday morning.
Your obedient servant,
Mr. LINCOLN'S REPLY
MY FELLOW-CITIZENS:—When a man hears himself somewhat misrepresented, it provokes him, at least, I find it so with myself; but when misrepresentation becomes very gross and palpable, it is more apt to amuse him. The first thing I see fit to notice is the fact that Judge Douglas alleges, after running through the history of the old Democratic and the old Whig parties, that Judge Trumbull and myself made an arrangement in 1854, by which I was to have the place of General Shields in the United States Senate, and Judge Trumbull was to have the place of Judge Douglas. Now, all I have to say upon that subject is that I think no man not even Judge Douglas can prove it, because it is not true. I have no doubt he is "conscientious" in saying it. As to those resolutions that he took such a length of time to read, as being the platform of the Republican party in 1854, I say I never had anything to do with them, and I think Trumbull never had. Judge Douglas cannot show that either of us ever did have anything to do with them.
I believe this is true about those resolutions: There was a call for a convention to form a Republican party at Springfield, and I think that my friend Mr. Lovejoy, who is here upon this stand, had a hand in it. I think this is true, and I think if he will remember accurately he will be able to recollect that he tried to get me into it, and I would not go in. I believe it is also true that I went away from Springfield when the convention was in session, to attend court in Tazewell county. It is true they did place my name, though without authority, upon the committee, and afterward wrote me to attend the meeting of the committee; but I refused to do so, and I never had anything to do with that organization. This is the plain truth about all that matter of the resolutions.
Now, about this story that Judge Douglas tells of Trumbull bargaining to sell out the old Democratic party, and Lincoln agreeing to sell out the old Whig party, I have the means of knowing about that: Judge Douglas cannot have; and I know there is no substance to it whatever. Yet I have no doubt he is "conscientious" about it. I know that after Mr. Lovejoy got into the Legislature that winter, he complained of me that I had told all the old Whigs of his district that the old Whig party was good enough for them, and some of them voted against him because I told them so. Now, I have no means of totally disproving such charges as this which the Judge makes. A man cannot prove a negative; but he has a right to claim that when a man makes an affirmative charge, he must offer some proof to show the truth of what he says. I certainly cannot introduce testimony to show the negative about things, but I have a right to claim that if a man says he knows a thing, then he must show how he knows it. I always have a right to claim this, and it is not satisfactory to me that he may be "conscientious" on the subject.
Now, gentlemen, I hate to waste my time on such things; but in regard to that general Abolition tilt that Judge Douglas makes, when he says that I was engaged at that time in selling out and Abolitionizing the old Whig party, I hope you will permit me to read a part of a printed speech that I made then at Peoria, which will show altogether a different view of the position I took in that contest of 1854.
[Voice: "Put on your specs."]
Mr. LINCOLN: Yes, sir, I am obliged to do so; I am no longer a young man.
"This is the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. The foregoing history may not be precisely accurate in every particular, but I am sure it is sufficiently so for all the uses I shall attempt to make of it, and in it we have before us the chief materials enabling us to correctly judge whether the repeal of the Missouri Compromise is right or wrong.
"I think, and shall try to show, that it is wrong—wrong in its direct effect, letting slavery into Kansas and Nebraska, and wrong in its prospective principle, allowing it to spread to every other part of the wide world where men can be found inclined to take it.
"This declared indifference, but, as I must think, covert real zeal for the spread of slavery, I cannot but hate. I hate it because of the monstrous injustice of slavery itself. I hate it because it deprives our republican example of its just influence in the world,—enables the enemies of free institutions, with plausibility, to taunt us as hypocrites; causes the real friends of freedom to doubt our sincerity, and especially because it forces so many really good men amongst ourselves into an open war with the very fundamental principles of civil liberty, criticizing the Declaration of Independence, and insisting that there is no right principle of action but self-interest.
"Before proceeding, let me say I think I have no prejudice against the Southern people. They are just what we would be in their situation. If slavery did not now exist among them, they would not introduce it. If it did now exist among us, we should not instantly give it up. This I believe of the masses north and south. Doubtless there are individuals on both sides who would not hold slaves under any circumstances; and others who would gladly introduce slavery anew, if it were out of existence. We know that some Southern men do free their slaves, go north, and become tip-top Abolitionists; while some Northern ones go south and become most cruel slave-masters.
"When Southern people tell us they are no more responsible for the origin of slavery than we, I acknowledge the fact. When it is said that the institution exists, and that it is very difficult to get rid of it, in any satisfactory way, I can understand and appreciate the saying. I will not blame them for not doing what I should not know how to do myself. If all earthly power were given me, I should not know what to do, as to the existing institution. My first impulse would be to free all the slaves and send them to Liberia,—to their own native land. But a moment's reflection would convince me that whatever of high hope (as I think there is) there may be in this in the long term, its sudden execution is impossible. If they were all landed there in a day, they would all perish in the next ten days; and there are not surplus shipping and surplus money enough in the world to carry them there in many times ten days. What then? Free them all and keep them among us as underlings? Is it quite certain that this betters their condition? I think I would not hold one in slavery, at any rate; yet the point is not clear enough to me to denounce people upon. What next? Free them, and make them politically and socially our equals? My own feelings will not admit of this; and if mine would, we well know that those of the great mass of white people will not. Whether this feeling accords with justice and sound judgment, is not the sole question, if, indeed, it is any part of it. A universal feeling, whether well or ill founded, cannot be safely disregarded. We cannot, then, make them equals. It does seem to me that systems of gradual emancipation might be adopted; but for their tardiness in this I will not undertake to judge our brethren of the South.
"When they remind us of their constitutional rights, I acknowledge them, not grudgingly, but fully and fairly; and I would give them any legislation for the reclaiming of their fugitives, which should not, in its stringency, be more likely to carry a free man into slavery than Our ordinary criminal laws are to hang an innocent one.
"But all this, to my judgment, furnishes no more excuse for permitting slavery to go into our own free territory than it would for reviving the African slave-trade by law. The law which forbids the bringing of slaves from Africa, and that which has so long forbid the taking of them to Nebraska, can hardly be distinguished on any moral principle; and the repeal of the former could find quite as plausible excuses as that of the latter."
I have reason to know that Judge Douglas knows that I said this. I think he has the answer here to one of the questions he put to me. I do not mean to allow him to catechize me unless he pays back for it in kind. I will not answer questions one after another, unless he reciprocates; but as he has made this inquiry, and I have answered it before, he has got it without my getting anything in return. He has got my answer on the Fugitive Slave law.
Now, gentlemen, I don't want to read at any greater length; but this is the true complexion of all I have ever said in regard to the institution of slavery and the black race. This is the whole of it; and anything that argues me into his idea of perfect social and political equality with the negro is but a specious and fantastic arrangement of words, by which a man can prove a horse-chestnut to be a chestnut horse. I will say here, while upon this subject, that I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so. I have no purpose to introduce political and social equality between the white and the black races. There is a physical difference between the two which, in my judgment, will probably forever forbid their living together upon the footing of perfect equality; and inasmuch as it becomes a necessity that there must be a difference, I, as well as Judge Douglas, am in favor of the race to which I belong having the superior position. I have never said anything to the contrary, but I hold that, notwithstanding all this, there is no reason in the world why the negro is not entitled to all the natural rights enumerated in the Declaration of Independence, the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. I hold that he is as much entitled to these as the white man. I agree with Judge Douglas he is not my equal in many respects, certainly not in color, perhaps not in moral or intellectual endowment. But in the right to eat the bread, without the leave of anybody else, which his own hand earns, he is my equal, and the equal of Judge Douglas, and the equal of every living man.
Now I pass on to consider one or two more of these little follies. The Judge is woefully at fault about his early friend Lincoln being a "grocery-keeper." I don't know as it would be a great sin, if I had been; but he is mistaken. Lincoln never kept a grocery anywhere in the world. It is true that Lincoln did work the latter part of one winter in a little stillhouse, up at the head of a hollow. And so I think my friend the Judge is equally at fault when he charges me at the time when I was in Congress of having opposed our soldiers who were fighting in the Mexican war. The Judge did not make his charge very distinctly, but I can tell you what he can prove, by referring to the record. You remember I was an old Whig, and whenever the Democratic party tried to get me to vote that the war had been righteously begun by the President, I would not do it. But whenever they asked for any money, or landwarrants, or anything to pay the soldiers there, during all that time, I gave the same vote that Judge Douglas did. You can think as you please as to whether that was consistent. Such is the truth, and the Judge has the right to make all he can out of it. But when he, by a general charge, conveys the idea that I withheld supplies from the soldiers who were fighting in the Mexican war, or did anything else to hinder the soldiers, he is, to say the least, grossly and altogether mistaken, as a consultation of the records will prove to him.
As I have not used up so much of my time as I had supposed, I will dwell a little longer upon one or two of these minor topics upon which the Judge has spoken. He has read from my speech in Springfield, in which I say that "a house divided against itself cannot stand" Does the Judge say it can stand? I don't know whether he does or not. The Judge does not seem to be attending to me just now, but I would like to know if it is his opinion that a house divided against itself can stand. If he does, then there is a question of veracity, not between him and me, but between the Judge and an Authority of a somewhat higher character.
Now, my friends, I ask your attention to this matter for the purpose of saying something seriously. I know that the Judge may readily enough agree with me that the maxim which was put forth by the Savior is true, but he may allege that I misapply it; and the Judge has a right to urge that, in my application, I do misapply it, and then I have a right to show that I do not misapply it, When he undertakes to say that because I think this nation, so far as the question of slavery is concerned, will all become one thing or all the other, I am in favor of bringing about a dead uniformity in the various States, in all their institutions, he argues erroneously. The great variety of the local institutions in the States, springing from differences in the soil, differences in the face of the country, and in the climate, are bonds of Union. They do not make "a house divided against itself," but they make a house united. If they produce in one section of the country what is called for, by the wants of another section, and this other section can supply the wants of the first, they are not matters of discord, but bonds of union, true bonds of union. But can this question of slavery be considered as among these varieties in the institutions of the country? I leave it to you to say whether, in the history of our government, this institution of slavery has not always failed to be a bond of union, and, on the contrary, been an apple of discord and an element of division in the house. I ask you to consider whether, so long as the moral constitution of men's minds shall continue to be the same, after this generation and assemblage shall sink into the grave, and another race shall arise, with the same moral and intellectual development we have, whether, if that institution is standing in the same irritating position in which it now is, it will not continue an element of division? If so, then I have a right to say that, in regard to this question, the Union is a house divided against itself; and when the Judge reminds me that I have often said to him that the institution of slavery has existed for eighty years in some States, and yet it does not exist in some others, I agree to the fact, and I account for it by looking at the position in which our fathers originally placed it—restricting it from the new Territories where it had not gone, and legislating to cut off its source by the abrogation of the slave trade, thus putting the seal of legislation against its spread. The public mind did rest in the belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. But lately, I think—and in this I charge nothing on the Judge's motives—lately, I think that he, and those acting with him, have placed that institution on a new basis, which looks to the perpetuity and nationalization of slavery. And while it is placed upon this new basis, I say, and I have said, that I believe we shall not have peace upon the question until the opponents of slavery arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction; or, on the other hand, that its advocates will push it forward until it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South. Now, I believe if we could arrest the spread, and place it where Washington and Jefferson and Madison placed it, it would be in the course of ultimate extinction, and the public mind would, as for eighty years past, believe that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. The crisis would be past, and the institution might be let alone for a hundred years, if it should live so long, in the States where it exists; yet it would be going out of existence in the way best for both the black and the white races.
[A voice: "Then do you repudiate popular sovereignty?"]
Well, then, let us talk about popular sovereignty! what is popular sovereignty? Is it the right of the people to have slavery or not have it, as they see fit, in the Territories? I will state—and I have an able man to watch me—my understanding is that popular sovereignty, as now applied to the question of slavery, does allow the people of a Territory to have slavery if they want to, but does not allow them not to have it if they do not want it. I do not mean that if this vast concourse of people were in a Territory of the United States, any one of them would be obliged to have a slave if he did not want one; but I do say that, as I understand the Dred Scott decision, if any one man wants slaves, all the rest have no way of keeping that one man from holding them.
When I made my speech at Springfield, of which the Judge complains, and from which he quotes, I really was not thinking of the things which he ascribes to me at all. I had no thought in the world that I was doing anything to bring about a war between the free and slave states. I had no thought in the world that I was doing anything to bring about a political and social equality of the black and white races. It never occurred to me that I was doing anything or favoring anything to reduce to a dead uniformity all the local institutions of the various States. But I must say, in all fairness to him, if he thinks I am doing something which leads to these bad results, it is none the better that I did not mean it. It is just as fatal to the country, if I have any influence in producing it, whether I intend it or not. But can it be true that placing this institution upon the original basis—the basis upon which our fathers placed it—can have any tendency to set the Northern and the Southern States at war with one another, or that it can have any tendency to make the people of Vermont raise sugar-cane, because they raise it in Louisiana, or that it can compel the people of Illinois to cut pine logs on the Grand Prairie, where they will not grow, because they cut pine logs in Maine, where they do grow? The Judge says this is a new principle started in regard to this question. Does the Judge claim that he is working on the plan of the founders of government? I think he says in some of his speeches indeed, I have one here now—that he saw evidence of a policy to allow slavery to be south of a certain line, while north of it it should be excluded, and he saw an indisposition on the part of the country to stand upon that policy, and therefore he set about studying the subject upon original principles, and upon original principles he got up the Nebraska Bill! I am fighting it upon these "original principles," fighting it in the Jeffersonian, Washingtonian, and Madisonian fashion.
Now, my friends, I wish you to attend for a little while to one or two other things in that Springfield speech. My main object was to show, so far as my humble ability was capable of showing, to the people of this country what I believed was the truth,—that there was a tendency, if not a conspiracy, among those who have engineered this slavery question for the last four or five years, to make slavery perpetual and universal in this nation. Having made that speech principally for that object, after arranging the evidences that I thought tended to prove my proposition, I concluded with this bit of comment:
"We cannot absolutely know that these exact adaptations are the result of preconcert; but when we see a lot of framed timbers, different portions of which we know have been gotten out at different times and places, and by different workmen—Stephen, Franklin, Roger, and James, for instance,—and when we see these timbers joined together, and see they exactly make the frame of a house or a mill, all the tenons and mortises exactly fitting, and all the lengths and proportions of the different pieces exactly adapted to their respective places, and not a piece too many or too few,—not omitting even the scaffolding,—or if a single piece be lacking, we see the place in the frame exactly fitted and prepared yet to bring such piece in,—in such a case we feel it impossible not to believe that Stephen and Franklin and Roger and James all understood one another from the beginning, and all worked upon a common plan or draft drawn before the first blow was struck."
When my friend Judge Douglas came to Chicago on the 9th of July, this speech having been delivered on the 16th of June, he made an harangue there, in which he took hold of this speech of mine, showing that he had carefully read it; and while he paid no attention to this matter at all, but complimented me as being a "kind, amiable, and intelligent gentleman," notwithstanding I had said this, he goes on and eliminates, or draws out, from my speech this tendency of mine to set the States at war with one another, to make all the institutions uniform, and set the niggers and white people to marrying together. Then, as the Judge had complimented me with these pleasant titles (I must confess to my weakness), I was a little "taken," for it came from a great man. I was not very much accustomed to flattery, and it came the sweeter to me. I was rather like the Hoosier, with the gingerbread, when he said he reckoned he loved it better than any other man, and got less of it. As the Judge had so flattered me, I could not make up my mind that he meant to deal unfairly with me; so I went to work to show him that he misunderstood the whole scope of my speech, and that I really never intended to set the people at war with one another. As an illustration, the next time I met him, which was at Springfield, I used this expression, that I claimed no right under the Constitution, nor had I any inclination, to enter into the slave States and interfere with the institutions of slavery. He says upon that: Lincoln will not enter into the slave States, but will go to the banks of the Ohio, on this side, and shoot over! He runs on, step by step, in the horse-chestnut style of argument, until in the Springfield speech he says: "Unless he shall be successful in firing his batteries until he shall have extinguished slavery in all the States the Union shall be dissolved." Now, I don't think that was exactly the way to treat "a kind, amiable, intelligent gentleman." I know if I had asked the Judge to show when or where it was I had said that, if I didn't succeed in firing into the slave States until slavery should be extinguished, the Union should be dissolved, he could not have shown it. I understand what he would do. He would say: I don't mean to quote from you, but this was the result of what you say. But I have the right to ask, and I do ask now, Did you not put it in such a form that an ordinary reader or listener would take it as an expression from me?
In a speech at Springfield, on the night of the 17th, I thought I might as well attend to my own business a little, and I recalled his attention as well as I could to this charge of conspiracy to nationalize slavery. I called his attention to the fact that he had acknowledged in my hearing twice that he had carefully read the speech, and, in the language of the lawyers, as he had twice read the speech, and still had put in no plea or answer, I took a default on him. I insisted that I had a right then to renew that charge of conspiracy. Ten days afterward I met the Judge at Clinton,—that is to say, I was on the ground, but not in the discussion,—and heard him make a speech. Then he comes in with his plea to this charge, for the first time; and his plea when put in, as well as I can recollect it, amounted to this: that he never had any talk with Judge Taney or the President of the United States with regard to the Dred Scott decision before it was made. I (Lincoln) ought to know that the man who makes a charge without knowing it to be true falsifies as much as he who knowingly tells a falsehood; and, lastly, that he would pronounce the whole thing a falsehood; but, he would make no personal application of the charge of falsehood, not because of any regard for the "kind, amiable, intelligent gentleman," but because of his own personal self-respect! I have understood since then (but [turning to Judge Douglas] will not hold the Judge to it if he is not willing) that he has broken through the "self-respect," and has got to saying the thing out. The Judge nods to me that it is so. It is fortunate for me that I can keep as good-humored as I do, when the Judge acknowledges that he has been trying to make a question of veracity with me. I know the Judge is a great man, while I am only a small man, but I feel that I have got him. I demur to that plea. I waive all objections that it was not filed till after default was taken, and demur to it upon the merits. What if Judge Douglas never did talk with Chief Justice Taney and the President before the Dred Scott decision was made, does it follow that he could not have had as perfect an understanding without talking as with it? I am not disposed to stand upon my legal advantage. I am disposed to take his denial as being like an answer in chancery, that he neither had any knowledge, information, or belief in the existence of such a conspiracy. I am disposed to take his answer as being as broad as though he had put it in these words. And now, I ask, even if he had done so, have not I a right to prove it on him, and to offer the evidence of more than two witnesses, by whom to prove it; and if the evidence proves the existence of the conspiracy, does his broader answer denying all knowledge, information, or belief, disturb the fact? It can only show that he was used by conspirators, and was not a leader of them.
Now, in regard to his reminding me of the moral rule that persons who tell what they do not know to be true falsify as much as those who knowingly tell falsehoods. I remember the rule, and it must be borne in mind that in what I have read to you, I do not say that I know such a conspiracy to exist. To that I reply, I believe it. If the Judge says that I do not believe it, then he says what he does not know, and falls within his own rule, that he who asserts a thing which he does not know to be true, falsifies as much as he who knowingly tells a falsehood. I want to call your attention to a little discussion on that branch of the case, and the evidence which brought my mind to the conclusion which I expressed as my belief. If, in arraying that evidence I had stated anything which was false or erroneous, it needed but that Judge Douglas should point it out, and I would have taken it back, with all the kindness in the world. I do not deal in that way. If I have brought forward anything not a fact, if he will point it out, it will not even ruffle me to take it back. But if he will not point out anything erroneous in the evidence, is it not rather for him to show, by a comparison of the evidence, that I have reasoned falsely, than to call the "kind, amiable, intelligent gentleman" a liar? If I have reasoned to a false conclusion, it is the vocation of an able debater to show by argument that I have wandered to an erroneous conclusion. I want to ask your attention to a portion of the Nebraska Bill, which Judge Douglas has quoted: "It being the true intent and meaning of this Act, not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State, nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States."
Thereupon Judge Douglas and others began to argue in favor of "popular sovereignty," the right of the people to have slaves if they wanted them, and to exclude slavery if they did not want them. "But," said, in substance, a Senator from Ohio (Mr. Chase, I believe), "we more than suspect that you do not mean to allow the people to exclude slavery if they wish to; and if you do mean it, accept an amendment which I propose, expressly authorizing the people to exclude slavery."
I believe I have the amendment here before me, which was offered, and under which the people of the Territory, through their representatives, might, if they saw fit, prohibit the existence of slavery therein. And now I state it as a fact, to be taken back if there is any mistake about it, that Judge Douglas and those acting with him voted that amendment down. I now think that those men who voted it down had a real reason for doing so. They know what that reason was. It looks to us, since we have seen the Dred Scott decision pronounced, holding that "under the Constitution" the people cannot exclude slavery, I say it looks to outsiders, poor, simple, "amiable, intelligent gentlemen," as though the niche was left as a place to put that Dred Scott decision in,—a niche which would have been spoiled by adopting the amendment. And now, I say again, if this was not the reason, it will avail the Judge much more to calmly and good-humoredly point out to these people what that other reason was for voting the amendment down, than, swelling himself up, to vociferate that he may be provoked to call somebody a liar.
Again: There is in that same quotation from the Nebraska Bill this clause: "It being the true intent and meaning of this bill not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State." I have always been puzzled to know what business the word "State" had in that connection. Judge Douglas knows. He put it there. He knows what he put it there for. We outsiders cannot say what he put it there for. The law they were passing was not about States, and was not making provisions for States. What was it placed there for? After seeing the Dred Scott decision, which holds that the people cannot exclude slavery from a Territory, if another Dred Scott decision shall come, holding that they cannot exclude it from a State, we shall discover that when the word was originally put there, it was in view of something which was to come in due time, we shall see that it was the other half of something. I now say again, if there is any different reason for putting it there, Judge Douglas, in a good-humored way, without calling anybody a liar, can tell what the reason was.
When the Judge spoke at Clinton, he came very near making a charge of falsehood against me. He used, as I found it printed in a newspaper, which, I remember, was very nearly like the real speech, the following language:
"I did not answer the charge [of conspiracy] before, for the reason that I did not suppose there was a man in America with a heart so corrupt as to believe such a charge could be true. I have too much respect for Mr. Lincoln to suppose he is serious in making the charge."
I confess this is rather a curious view, that out of respect for me he should consider I was making what I deemed rather a grave charge in fun. I confess it strikes me rather strangely. But I let it pass. As the Judge did not for a moment believe that there was a man in America whose heart was so "corrupt" as to make such a charge, and as he places me among the "men in America" who have hearts base enough to make such a charge, I hope he will excuse me if I hunt out another charge very like this; and if it should turn out that in hunting I should find that other, and it should turn out to be Judge Douglas himself who made it, I hope he will reconsider this question of the deep corruption of heart he has thought fit to ascribe to me. In Judge Douglas's speech of March 22, 1858, which I hold in my hand, he says:
"In this connection there is another topic to which I desire to allude. I seldom refer to the course of newspapers, or notice the articles which they publish in regard to myself; but the course of the Washington Union has been so extraordinary for the last two or three months, that I think it well enough to make some allusion to it. It has read me out of the Democratic party every other day, at least for two or three months, and keeps reading me out, and, as if it had not succeeded, still continues to read me out, using such terms as 'traitor,' 'renegade,' 'deserter,' and other kind and polite epithets of that nature. Sir, I have no vindication to make of my Democracy against the Washington Union, or any other newspapers. I am willing to allow my history and action for the last twenty years to speak for themselves as to my political principles and my fidelity to political obligations. The Washington Union has a personal grievance. When its editor was nominated for public printer, I declined to vote for him, and stated that at some time I might give my reasons for doing so. Since I declined to give that vote, this scurrilous abuse, these vindictive and constant attacks have been repeated almost daily on me. Will any friend from Michigan read the article to which I allude?"
This is a part of the speech. You must excuse me from reading the entire article of the Washington Union, as Mr. Stuart read it for Mr. Douglas. The Judge goes on and sums up, as I think, correctly:
"Mr. President, you here find several distinct propositions advanced boldly by the Washington Union editorially, and apparently authoritatively; and any man who questions any of them is denounced as an Abolitionist, a Free-soiler, a fanatic. The propositions are, first, that the primary object of all government at its original institution is the protection of person and property; second, that the Constitution of the United States declares that the citizens of each State shall be entitled to all the privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States; and that, therefore, thirdly, all State laws, whether organic or otherwise, which prohibit the citizens of one State from settling in another with their slave property, and especially declaring it forfeited, are direct violations of the original intention of the government and Constitution of the United States; and, fourth, that the emancipation of the slaves of the Northern States was a gross outrage of the rights of property, inasmuch as it was involuntarily done on the part of the owner.
"Remember that this article was published in the Union on the 17th of November, and on the 18th appeared the first article giving the adhesion of the Union, to the Lecompton Constitution. It was in these words:
"KANSAS AND HER CONSTITUTION.—The vexed question is settled. The problem is saved. The dead point of danger is passed. All serious trouble to Kansas affairs is over and gone..."
And a column nearly of the same sort. Then, when you come to look into the Lecompton Constitution, you find the same doctrine incorporated in it which was put forth editorially in the Union. What is it?
"ARTICLE 7, Section I. The right of property is before and higher than any constitutional sanction; and the right of the owner of a slave to such slave and its increase is the same and as inviolable as the right of the owner of any property whatever."
Then in the schedule is a provision that the Constitution may be amended after 1864 by a two-thirds vote:
"But no alteration shall be made to affect the right of property in the ownership of slaves."
"It will be seen by these clauses in the Lecompton Constitution that they are identical in spirit with the authoritative article in the Washington Union of the day previous to its indorsement of this Constitution."
I pass over some portions of the speech, and I hope that any one who feels interested in this matter will read the entire section of the speech, and see whether I do the Judge injustice. He proceeds:
"When I saw that article in the Union of the 17th of November, followed by the glorification of the Lecompton Constitution on the 10th of November, and this clause in the Constitution asserting the doctrine that a State has no right to prohibit slavery within its limits, I saw that there was a fatal blow being struck at the sovereignty of the States of this Union."
I stop the quotation there, again requesting that it may all be read. I have read all of the portion I desire to comment upon. What is this charge that the Judge thinks I must have a very corrupt heart to make? It was a purpose on the part of certain high functionaries to make it impossible for the people of one State to prohibit the people of any other State from entering it with their "property," so called, and making it a slave State. In other words, it was a charge implying a design to make the institution of slavery national. And now I ask your attention to what Judge Douglas has himself done here. I know he made that part of the speech as a reason why he had refused to vote for a certain man for public printer; but when we get at it, the charge itself is the very one I made against him, that he thinks I am so corrupt for uttering. Now, whom does he make that charge against? Does he make it against that newspaper editor merely? No; he says it is identical in spirit with the Lecompton Constitution, and so the framers of that Constitution are brought in with the editor of the newspaper in that "fatal blow being struck." He did not call it a "conspiracy." In his language, it is a "fatal blow being struck." And if the words carry the meaning better when changed from a "conspiracy" into a "fatal blow being struck," I will change my expression, and call it "fatal blow being struck." We see the charge made not merely against the editor of the Union, but all the framers of the Lecompton Constitution; and not only so, but the article was an authoritative article. By whose authority? Is there any question but he means it was by the authority of the President and his Cabinet,—the Administration?
Is there any sort of question but he means to make that charge? Then there are the editors of the Union, the framers of the Lecompton Constitution, the President of the United States and his Cabinet, and all the supporters of the Lecompton Constitution, in Congress and out of Congress, who are all involved in this "fatal blow being struck." I commend to Judge Douglas's consideration the question of how corrupt a man's heart must be to make such a charge!
Now, my friends, I have but one branch of the subject, in the little time I have left, to which to call your attention; and as I shall come to a close at the end of that branch, it is probable that I shall not occupy quite all the time allotted to me. Although on these questions I would like to talk twice as long as I have, I could not enter upon another head and discuss it properly without running over my time. I ask the attention of the people here assembled and elsewhere to the course that Judge Douglas is pursuing every day as bearing upon this question of making slavery national. Not going back to the records, but taking the speeches he makes, the speeches he made yesterday and day before, and makes constantly all over the country, I ask your attention to them. In the first place, what is necessary to make the institution national? Not war. There is no danger that the people of Kentucky will shoulder their muskets, and, with a young nigger stuck on every bayonet, march into Illinois and force them upon us. There is no danger of our going over there and making war upon them. Then what is necessary for the nationalization of slavery? It is simply the next Dred Scott decision. It is merely for the Supreme Court to decide that no State under the Constitution can exclude it, just as they have already decided that under the Constitution neither Congress nor the Territorial Legislature can do it. When that is decided and acquiesced in, the whole thing is done. This being true, and this being the way, as I think, that slavery is to be made national, let us consider what Judge Douglas is doing every day to that end. In the first place, let us see what influence he is exerting on public sentiment. In this and like communities, public sentiment is everything. With public sentiment, nothing can fail; without it, nothing can succeed. Consequently, he who moulds public sentiment goes deeper than he who enacts statutes or pronounces decisions. He makes statutes and decisions possible or impossible to be executed. This must be borne in mind, as also the additional fact that Judge Douglas is a man of vast influence, so great that it is enough for many men to profess to believe anything when they once find out Judge Douglas professes to believe it. Consider also the attitude he occupies at the head of a large party,—a party which he claims has a majority of all the voters in the country. This man sticks to a decision which forbids the people of a Territory from excluding slavery, and he does so, not because he says it is right in itself,—he does not give any opinion on that,—but because it has been decided by the court; and being decided by the court, he is, and you are, bound to take it in your political action as law, not that he judges at all of its merits, but because a decision of the court is to him a "Thus saith the Lord." He places it on that ground alone; and you will bear in mind that thus committing himself unreservedly to this decision commits him to the next one just as firmly as to this. He did not commit himself on account of the merit or demerit of the decision, but it is a "Thus saith the Lord." The next decision, as much as this, will be a "Thus saith the Lord." There is nothing that can divert or turn him away from this decision. It is nothing that I point out to him that his great prototype, General Jackson, did not believe in the binding force of decisions. It is nothing to him that Jefferson did not so believe. I have said that I have often heard him approve of Jackson's course in disregarding the decision of the Supreme Court pronouncing a National Bank constitutional. He says I did not hear him say so. He denies the accuracy of my recollection. I say he ought to know better than I, but I will make no question about this thing, though it still seems to me that I heard him say it twenty times. I will tell him, though, that he now claims to stand on the Cincinnati platform, which affirms that Congress cannot charter a National Bank, in the teeth of that old standing decision that Congress can charter a bank. And I remind him of another piece of history on the question of respect for judicial decisions, and it is a piece of Illinois history belonging to a time when the large party to which Judge Douglas belonged were displeased with a decision of the Supreme Court of Illinois, because they had decided that a Governor could not remove a Secretary of State. You will find the whole story in Ford's History of Illinois, and I know that Judge Douglas will not deny that he was then in favor of over-slaughing that decision by the mode of adding five new judges, so as to vote down the four old ones. Not only so, but it ended in the Judge's sitting down on that very bench as one of the five new judges to break down the four old ones It was in this way precisely that he got his title of judge. Now, when the Judge tells me that men appointed conditionally to sit as members of a court will have to be catechized beforehand upon some subject, I say, "You know, Judge; you have tried it." When he says a court of this kind will lose the confidence of all men, will be prostituted and disgraced by such a proceeding, I say, "You know best, Judge; you have been through the mill." But I cannot shake Judge Douglas's teeth loose from the Dred Scott decision. Like some obstinate animal (I mean no disrespect) that will hang on when he has once got his teeth fixed, you may cut off a leg, or you may tear away an arm, still he will not relax his hold. And so I may point out to the Judge, and say that he is bespattered all over, from the beginning of his political life to the present time, with attacks upon judicial decisions; I may cut off limb after limb of his public record, and strive to wrench him from a single dictum of the court,—yet I cannot divert him from it. He hangs, to the last, to the Dred Scott decision. These things show there is a purpose strong as death and eternity for which he adheres to this decision, and for which he will adhere to all other decisions of the same court.
[A HIBERNIAN: "Give us something besides Dred Scott."]
Yes; no doubt you want to hear something that don't hurt. Now, having spoken of the Dred Scott decision, one more word, and I am done. Henry Clay, my beau-ideal of a statesman, the man for whom I fought all my humble life, Henry Clay once said of a class of men who would repress all tendencies to liberty and ultimate emancipation that they must, if they would do this, go back to the era of our Independence, and muzzle the cannon which thunders its annual joyous return; they must blow out the moral lights around us; they must penetrate the human soul, and eradicate there the love of liberty; and then, and not till then, could they perpetuate slavery in this country! To my thinking, Judge Douglas is, by his example and vast influence, doing that very thing in this community, when he says that the negro has nothing in the Declaration of Independence. Henry Clay plainly understood the contrary. Judge Douglas is going back to the era of our Revolution, and, to the extent of his ability, muzzling the cannon which thunders its annual joyous return. When he invites any people, willing to have slavery, to establish it, he is blowing out the moral lights around us. When he says he "cares not whether slavery is voted down or up,"—that it is a sacred right of self-government,—he is, in my judgment, penetrating the human soul and eradicating the light of reason and the love of liberty in this American people. And now I will only say that when, by all these means and appliances, Judge Douglas shall succeed in bringing public sentiment to an exact accordance with his own views; when these vast assemblages shall echo back all these sentiments; when they shall come to repeat his views and to avow his principles, and to say all that he says on these mighty questions,—then it needs only the formality of the second Dred Scott decision, which he indorses in advance, to make slavery alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South.
My friends, that ends the chapter. The Judge can take his half-hour.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—On Saturday last, Judge Douglas and myself first met in public discussion. He spoke one hour, I an hour and a half, and he replied for half an hour. The order is now reversed. I am to speak an hour, he an hour and a half, and then I am to reply for half an hour. I propose to devote myself during the first hour to the scope of what was brought within the range of his half-hour speech at Ottawa. Of course there was brought within the scope in that half-hour's speech something of his own opening speech. In the course of that opening argument Judge Douglas proposed to me seven distinct interrogatories. In my speech of an hour and a half, I attended to some other parts of his speech, and incidentally, as I thought, intimated to him that I would answer the rest of his interrogatories on condition only that he should agree to answer as many for me. He made no intimation at the time of the proposition, nor did he in his reply allude at all to that suggestion of mine. I do him no injustice in saying that he occupied at least half of his reply in dealing with me as though I had refused to answer his interrogatories. I now propose that I will answer any of the interrogatories, upon condition that he will answer questions from me not exceeding the same number. I give him an opportunity to respond.
The Judge remains silent. I now say that I will answer his interrogatories, whether he answers mine or not; and that after I have done so, I shall propound mine to him.
I have supposed myself, since the organization of the Republican party at Bloomington, in May, 1856, bound as a party man by the platforms of the party, then and since. If in any interrogatories which I shall answer I go beyond the scope of what is within these platforms, it will be perceived that no one is responsible but myself.
Having said thus much, I will take up the Judge's interrogatories as I find them printed in the Chicago Times, and answer them seriatim. In order that there may be no mistake about it, I have copied the interrogatories in writing, and also my answers to them. The first one of these interrogatories is in these words:
Question 1.—"I desire to know whether Lincoln to-day stands, as he did in 1854, in favor of the unconditional repeal of the Fugitive Slave law?" Answer:—I do not now, nor ever did, stand in favor of the unconditional repeal of the Fugitive Slave law.
Q. 2.—"I desire him to answer whether he stands pledged to-day, as he did in 1854, against the admission of any more slave States into the Union, even if the people want them?" Answer:—I do not now, nor ever did, stand pledged against the admission of any more slave States into the Union.
Q. 3.—"I want to know whether he stands pledged against the admission of a new State into the Union with such a constitution as the people of that State may see fit to make?" Answer:—I do not stand pledged against the admission of a new State into the Union, with such a constitution as the people of that State may see fit to make.
Q. 4.—"I want to know whether he stands to-day pledged to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia?" Answer:—I do not stand to-day pledged to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia.
Q. 5.—"I desire him to answer whether he stands pledged to the prohibition of the slave-trade between the different States?" Answer:—I do not stand pledged to the prohibition of the slave-trade between the different States.
Q. 6.—"I desire to know whether he stands pledged to prohibit slavery in all the Territories of the United States, north as well as south of the Missouri Compromise line?" Answer:—I am impliedly, if not expressly, pledged to a belief in the right and duty of Congress to prohibit slavery in all the United States 'Territories.
Q. 7.—"I desire him to answer whether he is opposed to the acquisition of any new territory unless slavery is first prohibited therein?" Answer:—I am not generally opposed to honest acquisition of territory; and, in any given case, I would or would not oppose such acquisition, accordingly as I might think such acquisition would or would not aggravate the slavery question among ourselves.
Now, my friends, it will be perceived, upon an examination of these questions and answers, that so far I have only answered that I was not pledged to this, that, or the other. The Judge has not framed his interrogatories to ask me anything more than this, and I have answered in strict accordance with the interrogatories, and have answered truly, that I am not pledged at all upon any of the points to which I have answered. But I am not disposed to hang upon the exact form of his interrogatory. I am rather disposed to take up at least some of these questions, and state what I really think upon them.
As to the first one, in regard to the Fugitive Slave law, I have never hesitated to say, and I do not now hesitate to say, that I think, under the Constitution of the United States, the people of the Southern States are entitled to a Congressional Fugitive Slave law. Having said that, I have had nothing to say in regard to the existing Fugitive Slave law, further than that I think it should have been framed so as to be free from some of the objections that pertain to it, without lessening its efficiency. And inasmuch as we are not now in an agitation in regard to an alteration or modification of that law, I would not be the man to introduce it as a new subject of agitation upon the general question of slavery.
In regard to the other question, of whether I am pledged to the admission of any more slave States into the Union, I state to you very frankly that I would be exceedingly sorry ever to be put in a position of having to pass upon that question. I should be exceedingly glad to know that there would never be another slave State admitted into the Union; but I must add that if slavery shall be kept out of the Territories during the territorial existence of any one given Territory, and then the people shall, having a fair chance and a clear field, when they come to adopt the constitution, do such an extraordinary thing as to adopt a slave constitution, uninfluenced by the actual presence of the institution among them, I see no alternative, if we own the country, but to admit them into the Union.
The third interrogatory is answered by the answer to the second, it being, as I conceive, the same as the second.
The fourth one is in regard to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia. In relation to that, I have my mind very distinctly made up. I should be exceedingly glad to see slavery abolished in the District of Columbia. I believe that Congress possesses the constitutional power to abolish it. Yet as a member of Congress, I should not, with my present views, be in favor of endeavoring to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, unless it would be upon these conditions: First, that the abolition should be gradual; second, that it should be on a vote of the majority of qualified voters in the District; and third, that compensation should be made to unwilling owners. With these three conditions, I confess I would be exceedingly glad to see Congress abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, and, in the language of Henry Clay, "sweep from our capital that foul blot upon our nation."
In regard to the fifth interrogatory, I must say here that, as to the question of the abolition of the slave-trade between the different States, I can truly answer, as I have, that I am pledged to nothing about it. It is a subject to which I have not given that mature consideration that would make me feel authorized to state a position so as to hold myself entirely bound by it. In other words, that question has never been prominently enough before me to induce me to investigate whether we really have the constitutional power to do it. I could investigate it if I had sufficient time to bring myself to a conclusion upon that subject; but I have not done so, and I say so frankly to you here, and to Judge Douglas. I must say, however, that if I should be of opinion that Congress does possess the constitutional power to abolish the slave-trade among the different States, I should still not be in favor of the exercise of that power, unless upon some conservative principle as I conceive it, akin to what I have said in relation to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia.
My answer as to whether I desire that slavery should be prohibited in all the Territories of the United States is full and explicit within itself, and cannot be made clearer by any comments of mine. So I suppose in regard to the question whether I am opposed to the acquisition of any more territory unless slavery is first prohibited therein, my answer is such that I could add nothing by way of illustration, or making myself better understood, than the answer which I have placed in writing.
Now in all this the Judge has me, and he has me on the record. I suppose he had flattered himself that I was really entertaining one set of opinions for one place, and another set for another place; that I was afraid to say at one place what I uttered at another. What I am saying here I suppose I say to a vast audience as strongly tending to Abolitionism as any audience in the State of Illinois, and I believe I am saying that which, if it would be offensive to any persons and render them enemies to myself, would be offensive to persons in this audience.
I now proceed to propound to the Judge the interrogatories, so far as I have framed them. I will bring forward a new installment when I get them ready. I will bring them forward now only reaching to number four. The first one is:
Question 1.—If the people of Kansas shall, by means entirely unobjectionable in all other respects, adopt a State constitution, and ask admission into the Union under it, before they have the requisite number of inhabitants according to the English bill,—some ninety-three thousand,—will you vote to admit them?
Q. 2.—Can the people of a United States Territory, in any lawful way, against the wish of any citizen of the United States, exclude slavery from its limits prior to the formation of a State constitution?
Q. 3. If the Supreme Court of the United States shall decide that States cannot exclude slavery from their limits, are you in favor of acquiescing in, adopting, and following such decision as a rule of political action?
Q. 4. Are you in favor of acquiring additional territory, in disregard of how such acquisition may affect the nation on the slavery question?
As introductory to these interrogatories which Judge Douglas propounded to me at Ottawa, he read a set of resolutions which he said Judge Trumbull and myself had participated in adopting, in the first Republican State Convention, held at Springfield in October, 1854. He insisted that I and Judge Trumbull, and perhaps the entire Republican party, were responsible for the doctrines contained in the set of resolutions which he read, and I understand that it was from that set of resolutions that he deduced the interrogatories which he propounded to me, using these resolutions as a sort of authority for propounding those questions to me. Now, I say here to-day that I do not answer his interrogatories because of their springing at all from that set of resolutions which he read. I answered them because Judge Douglas thought fit to ask them. I do not now, nor ever did, recognize any responsibility upon myself in that set of resolutions. When I replied to him on that occasion, I assured him that I never had anything to do with them. I repeat here to today that I never in any possible form had anything to do with that set of resolutions It turns out, I believe, that those resolutions were never passed in any convention held in Springfield.
It turns out that they were never passed at any convention or any public meeting that I had any part in. I believe it turns out, in addition to all this, that there was not, in the fall of 1854, any convention holding a session in Springfield, calling itself a Republican State Convention; yet it is true there was a convention, or assemblage of men calling themselves a convention, at Springfield, that did pass some resolutions. But so little did I really know of the proceedings of that convention, or what set of resolutions they had passed, though having a general knowledge that there had been such an assemblage of men there, that when Judge Douglas read the resolutions, I really did not know but they had been the resolutions passed then and there. I did not question that they were the resolutions adopted. For I could not bring myself to suppose that Judge Douglas could say what he did upon this subject without knowing that it was true. I contented myself, on that occasion, with denying, as I truly could, all connection with them, not denying or affirming whether they were passed at Springfield. Now, it turns out that he had got hold of some resolutions passed at some convention or public meeting in Kane County. I wish to say here, that I don't conceive that in any fair and just mind this discovery relieves me at all. I had just as much to do with the convention in Kane County as that at Springfield. I am as much responsible for the resolutions at Kane County as those at Springfield,—the amount of the responsibility being exactly nothing in either case; no more than there would be in regard to a set of resolutions passed in the moon.
I allude to this extraordinary matter in this canvass for some further purpose than anything yet advanced. Judge Douglas did not make his statement upon that occasion as matters that he believed to be true, but he stated them roundly as being true, in such form as to pledge his veracity for their truth. When the whole matter turns out as it does, and when we consider who Judge Douglas is, that he is a distinguished Senator of the United States; that he has served nearly twelve years as such; that his character is not at all limited as an ordinary Senator of the United States, but that his name has become of world-wide renown,—it is most extraordinary that he should so far forget all the suggestions of justice to an adversary, or of prudence to himself, as to venture upon the assertion of that which the slightest investigation would have shown him to be wholly false. I can only account for his having done so upon the supposition that that evil genius which has attended him through his life, giving to him an apparent astonishing prosperity, such as to lead very many good men to doubt there being any advantage in virtue over vice,—I say I can only account for it on the supposition that that evil genius has as last made up its mind to forsake him.
And I may add that another extraordinary feature of the Judge's conduct in this canvass—made more extraordinary by this incident—is, that he is in the habit, in almost all the speeches he makes, of charging falsehood upon his adversaries, myself and others. I now ask whether he is able to find in anything that Judge Trumbull, for instance, has said, or in anything that I have said, a justification at all compared with what we have, in this instance, for that sort of vulgarity.
I have been in the habit of charging as a matter of belief on my part that, in the introduction of the Nebraska Bill into Congress, there was a conspiracy to make slavery perpetual and national. I have arranged from time to time the evidence which establishes and proves the truth of this charge. I recurred to this charge at Ottawa. I shall not now have time to dwell upon it at very great length; but inasmuch as Judge Douglas, in his reply of half an hour, made some points upon me in relation to it, I propose noticing a few of them.
The Judge insists that, in the first speech I made, in which I very distinctly made that charge, he thought for a good while I was in fun! that I was playful; that I was not sincere about it; and that he only grew angry and somewhat excited when he found that I insisted upon it as a matter of earnestness. He says he characterized it as a falsehood so far as I implicated his moral character in that transaction. Well, I did not know, till he presented that view, that I had implicated his moral character. He is very much in the habit, when he argues me up into a position I never thought of occupying, of very cosily saying he has no doubt Lincoln is "conscientious" in saying so. He should remember that I did not know but what he was ALTOGETHER "CONSCIENTIOUS" in that matter. I can conceive it possible for men to conspire to do a good thing, and I really find nothing in Judge Douglas's course of arguments that is contrary to or inconsistent with his belief of a conspiracy to nationalize and spread slavery as being a good and blessed thing; and so I hope he will understand that I do not at all question but that in all this matter he is entirely "conscientious."
But to draw your attention to one of the points I made in this case, beginning at the beginning: When the Nebraska Bill was introduced, or a short time afterward, by an amendment, I believe, it was provided that it must be considered "the true intent and meaning of this Act not to legislate slavery into any State or Territory, or to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their own domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States." I have called his attention to the fact that when he and some others began arguing that they were giving an increased degree of liberty to the people in the Territories over and above what they formerly had on the question of slavery, a question was raised whether the law was enacted to give such unconditional liberty to the people; and to test the sincerity of this mode of argument, Mr. Chase, of Ohio, introduced an amendment, in which he made the law—if the amendment were adopted—expressly declare that the people of the Territory should have the power to exclude slavery if they saw fit. I have asked attention also to the fact that Judge Douglas and those who acted with him voted that amendment down, notwithstanding it expressed exactly the thing they said was the true intent and meaning of the law. I have called attention to the fact that in subsequent times a decision of the Supreme Court has been made, in which it has been declared that a Territorial Legislature has no constitutional right to exclude slavery. And I have argued and said that for men who did, intend that the people of the Territory should have the right to exclude slavery absolutely and unconditionally, the voting down of Chase's amendment is wholly inexplicable. It is a puzzle, a riddle. But I have said, that with men who did look forward to such a decision, or who had it in contemplation that such a decision of the Supreme Court would or might be made, the voting down of that amendment would be perfectly rational and intelligible. It would keep Congress from coming in collision with the decision when it was made. Anybody can conceive that if there was an intention or expectation that such a decision was to follow, it would not be a very desirable party attitude to get into for the Supreme Court—all or nearly all its members belonging to the same party—to decide one way, when the party in Congress had decided the other way. Hence it would be very rational for men expecting such a decision to keep the niche in that law clear for it. After pointing this out, I tell Judge Douglas that it looks to me as though here was the reason why Chase's amendment was voted down. I tell him that, as he did it, and knows why he did it, if it was done for a reason different from this, he knows what that reason was and can tell us what it was. I tell him, also, it will be vastly more satisfactory to the country for him to give some other plausible, intelligible reason why it was voted down than to stand upon his dignity and call people liars. Well, on Saturday he did make his answer; and what do you think it was? He says if I had only taken upon myself to tell the whole truth about that amendment of Chase's, no explanation would have been necessary on his part or words to that effect. Now, I say here that I am quite unconscious of having suppressed anything material to the case, and I am very frank to admit if there is any sound reason other than that which appeared to me material, it is quite fair for him to present it. What reason does he propose? That when Chase came forward with his amendment expressly authorizing the people to exclude slavery from the limits of every Territory, General Cass proposed to Chase, if he (Chase) would add to his amendment that the people should have the power to introduce or exclude, they would let it go. This is substantially all of his reply. And because Chase would not do that, they voted his amendment down. Well, it turns out, I believe, upon examination, that General Cass took some part in the little running debate upon that amendment, and then ran away and did not vote on it at all. Is not that the fact? So confident, as I think, was General Cass that there was a snake somewhere about, he chose to run away from the whole thing. This is an inference I draw from the fact that, though he took part in the debate, his name does not appear in the ayes and noes. But does Judge Douglas's reply amount to a satisfactory answer?
[Cries of "Yes," "Yes," and "No," "No."]
There is some little difference of opinion here. But I ask attention to a few more views bearing on the question of whether it amounts to a satisfactory answer. The men who were determined that that amendment should not get into the bill, and spoil the place where the Dred Scott decision was to come in, sought an excuse to get rid of it somewhere. One of these ways—one of these excuses—was to ask Chase to add to his proposed amendment a provision that the people might introduce slavery if they wanted to. They very well knew Chase would do no such thing, that Mr. Chase was one of the men differing from them on the broad principle of his insisting that freedom was better than slavery,—a man who would not consent to enact a law, penned with his own hand, by which he was made to recognize slavery on the one hand, and liberty on the other, as precisely equal; and when they insisted on his doing this, they very well knew they insisted on that which he would not for a moment think of doing, and that they were only bluffing him. I believe (I have not, since he made his answer, had a chance to examine the journals or Congressional Globe and therefore speak from memory)—I believe the state of the bill at that time, according to parliamentary rules, was such that no member could propose an additional amendment to Chase's amendment. I rather think this is the truth,—the Judge shakes his head. Very well. I would like to know, then, if they wanted Chase's amendment fixed over, why somebody else could not have offered to do it? If they wanted it amended, why did they not offer the amendment? Why did they not put it in themselves? But to put it on the other ground: suppose that there was such an amendment offered, and Chase's was an amendment to an amendment; until one is disposed of by parliamentary law, you cannot pile another on. Then all these gentlemen had to do was to vote Chase's on, and then, in the amended form in which the whole stood, add their own amendment to it, if they wanted to put it in that shape. This was all they were obliged to do, and the ayes and noes show that there were thirty-six who voted it down, against ten who voted in favor of it. The thirty-six held entire sway and control. They could in some form or other have put that bill in the exact shape they wanted. If there was a rule preventing their amending it at the time, they could pass that, and then, Chase's amendment being merged, put it in the shape they wanted. They did not choose to do so, but they went into a quibble with Chase to get him to add what they knew he would not add, and because he would not, they stand upon the flimsy pretext for voting down what they argued was the meaning and intent of their own bill. They left room thereby for this Dred Scott decision, which goes very far to make slavery national throughout the United States.
I pass one or two points I have, because my time will very soon expire; but I must be allowed to say that Judge Douglas recurs again, as he did upon one or two other occasions, to the enormity of Lincoln, an insignificant individual like Lincoln,—upon his ipse dixit charging a conspiracy upon a large number of members of Congress, the Supreme Court, and two Presidents, to nationalize slavery. I want to say that, in the first place, I have made no charge of this sort upon my ipse dixit. I have only arrayed the evidence tending to prove it, and presented it to the understanding of others, saying what I think it proves, but giving you the means of judging whether it proves it or not. This is precisely what I have done. I have not placed it upon my ipse dixit at all. On this occasion, I wish to recall his attention to a piece of evidence which I brought forward at Ottawa on Saturday, showing that he had made substantially the same charge against substantially the same persons, excluding his dear self from the category. I ask him to give some attention to the evidence which I brought forward that he himself had discovered a "fatal blow being struck" against the right of the people to exclude slavery from their limits, which fatal blow he assumed as in evidence in an article in the Washington Union, published "by authority." I ask by whose authority? He discovers a similar or identical provision in the Lecompton Constitution. Made by whom? The framers of that Constitution. Advocated by whom? By all the members of the party in the nation, who advocated the introduction of Kansas into the Union under the Lecompton Constitution. I have asked his attention to the evidence that he arrayed to prove that such a fatal blow was being struck, and to the facts which he brought forward in support of that charge,—being identical with the one which he thinks so villainous in me. He pointed it, not at a newspaper editor merely, but at the President and his Cabinet and the members of Congress advocating the Lecompton Constitution and those framing that instrument. I must again be permitted to remind him that although my ipse dixit may not be as great as his, yet it somewhat reduces the force of his calling my attention to the enormity of my making a like charge against him.
Go on, Judge Douglas.
MY FRIENDS:—It will readily occur to you that I cannot, in half an hour, notice all the things that so able a man as Judge Douglas can say in an hour and a half; and I hope, therefore, if there be anything that he has said upon which you would like to hear something from me, but which I omit to comment upon, you will bear in mind that it would be expecting an impossibility for me to go over his whole ground. I can but take up some of the points that he has dwelt upon, and employ my half-hour specially on them.
The first thing I have to say to you is a word in regard to Judge Douglas's declaration about the "vulgarity and blackguardism" in the audience, that no such thing, as he says, was shown by any Democrat while I was speaking. Now, I only wish, by way of reply on this subject, to say that while I was speaking, I used no "vulgarity or blackguardism" toward any Democrat.
Now, my friends, I come to all this long portion of the Judge's speech,—perhaps half of it,—which he has devoted to the various resolutions and platforms that have been adopted in the different counties in the different Congressional districts, and in the Illinois legislature, which he supposes are at variance with the positions I have assumed before you to-day. It is true that many of these resolutions are at variance with the positions I have here assumed. All I have to ask is that we talk reasonably and rationally about it. I happen to know, the Judge's opinion to the contrary notwithstanding, that I have never tried to conceal my opinions, nor tried to deceive any one in reference to them. He may go and examine all the members who voted for me for United States Senator in 1855, after the election of 1854. They were pledged to certain things here at home, and were determined to have pledges from me; and if he will find any of these persons who will tell him anything inconsistent with what I say now, I will resign, or rather retire from the race, and give him no more trouble. The plain truth is this: At the introduction of the Nebraska policy, we believed there was a new era being introduced in the history of the Republic, which tended to the spread and perpetuation of slavery. But in our opposition to that measure we did not agree with one another in everything. The people in the north end of the State were for stronger measures of opposition than we of the central and southern portions of the State, but we were all opposed to the Nebraska doctrine. We had that one feeling and that one sentiment in common. You at the north end met in your conventions and passed your resolutions. We in the middle of the State and farther south did not hold such conventions and pass the same resolutions, although we had in general a common view and a common sentiment. So that these meetings which the Judge has alluded to, and the resolutions he has read from, were local, and did not spread over the whole State. We at last met together in 1886, from all parts of the State, and we agreed upon a common platform. You, who held more extreme notions, either yielded those notions, or, if not wholly yielding them, agreed to yield them practically, for the sake of embodying the opposition to the measures which the opposite party were pushing forward at that time. We met you then, and if there was anything yielded, it was for practical purposes. We agreed then upon a platform for the party throughout the entire State of Illinois, and now we are all bound, as a party, to that platform.
And I say here to you, if any one expects of me—in case of my election—that I will do anything not signified by our Republican platform and my answers here to-day, I tell you very frankly that person will be deceived. I do not ask for the vote of any one who supposes that I have secret purposes or pledges that I dare not speak out. Cannot the Judge be satisfied? If he fears, in the unfortunate case of my election, that my going to Washington will enable me to advocate sentiments contrary to those which I expressed when you voted for and elected me, I assure him that his fears are wholly needless and groundless. Is the Judge really afraid of any such thing? I'll tell you what he is afraid of. He is afraid we'll all pull together. This is what alarms him more than anything else. For my part, I do hope that all of us, entertaining a common sentiment in opposition to what appears to us a design to nationalize and perpetuate slavery, will waive minor differences on questions which either belong to the dead past or the distant future, and all pull together in this struggle. What are your sentiments? If it be true that on the ground which I occupy—ground which I occupy as frankly and boldly as Judge Douglas does his,—my views, though partly coinciding with yours, are not as perfectly in accordance with your feelings as his are, I do say to you in all candor, go for him, and not for me. I hope to deal in all things fairly with Judge Douglas, and with the people of the State, in this contest. And if I should never be elected to any office, I trust I may go down with no stain of falsehood upon my reputation, notwithstanding the hard opinions Judge Douglas chooses to entertain of me.
The Judge has again addressed himself to the Abolition tendencies of a speech of mine made at Springfield in June last. I have so often tried to answer what he is always saying on that melancholy theme that I almost turn with disgust from the discussion,—from the repetition of an answer to it. I trust that nearly all of this intelligent audience have read that speech. If you have, I may venture to leave it to you to inspect it closely, and see whether it contains any of those "bugaboos" which frighten Judge Douglas.
The Judge complains that I did not fully answer his questions. If I have the sense to comprehend and answer those questions, I have done so fairly. If it can be pointed out to me how I can more fully and fairly answer him, I aver I have not the sense to see how it is to be done. He says I do not declare I would in any event vote for the admission of a slave State into the Union. If I have been fairly reported, he will see that I did give an explicit answer to his interrogatories; I did not merely say that I would dislike to be put to the test, but I said clearly, if I were put to the test, and a Territory from which slavery had been excluded should present herself with a State constitution sanctioning slavery,—a most extraordinary thing, and wholly unlikely to happen,—I did not see how I could avoid voting for her admission. But he refuses to understand that I said so, and he wants this audience to understand that I did not say so. Yet it will be so reported in the printed speech that he cannot help seeing it.
He says if I should vote for the admission of a slave State I would be voting for a dissolution of the Union, because I hold that the Union cannot permanently exist half slave and half free. I repeat that I do not believe this government can endure permanently half slave and half free; yet I do not admit, nor does it at all follow, that the admission of a single slave State will permanently fix the character and establish this as a universal slave nation. The Judge is very happy indeed at working up these quibbles. Before leaving the subject of answering questions, I aver as my confident belief, when you come to see our speeches in print, that you will find every question which he has asked me more fairly and boldly and fully answered than he has answered those which I put to him. Is not that so? The two speeches may be placed side by side, and I will venture to leave it to impartial judges whether his questions have not been more directly and circumstantially answered than mine.
Judge Douglas says he made a charge upon the editor of the Washington Union, alone, of entertaining a purpose to rob the States of their power to exclude slavery from their limits. I undertake to say, and I make the direct issue, that he did not make his charge against the editor of the Union alone. I will undertake to prove by the record here that he made that charge against more and higher dignitaries than the editor of the Washington Union. I am quite aware that he was shirking and dodging around the form in which he put it, but I can make it manifest that he leveled his "fatal blow" against more persons than this Washington editor. Will he dodge it now by alleging that I am trying to defend Mr. Buchanan against the charge? Not at all. Am I not making the same charge myself? I am trying to show that you, Judge Douglas, are a witness on my side. I am not defending Buchanan, and I will tell Judge Douglas that in my opinion, when he made that charge, he had an eye farther north than he has to-day. He was then fighting against people who called him a Black Republican and an Abolitionist. It is mixed all through his speech, and it is tolerably manifest that his eye was a great deal farther north than it is to-day. The Judge says that though he made this charge, Toombs got up and declared there was not a man in the United States, except the editor of the Union, who was in favor of the doctrines put forth in that article. And thereupon I understand that the Judge withdrew the charge. Although he had taken extracts from the newspaper, and then from the Lecompton Constitution, to show the existence of a conspiracy to bring about a "fatal blow," by which the States were to be deprived of the right of excluding slavery, it all went to pot as soon as Toombs got up and told him it was not true. It reminds me of the story that John Phoenix, the California railroad surveyor, tells. He says they started out from the Plaza to the Mission of Dolores. They had two ways of determining distances. One was by a chain and pins taken over the ground. The other was by a "go-it-ometer,"—an invention of his own,—a three-legged instrument, with which he computed a series of triangles between the points. At night he turned to the chain-man to ascertain what distance they had come, and found that by some mistake he had merely dragged the chain over the ground, without keeping any record. By the "go-it-ometer," he found he had made ten miles. Being skeptical about this, he asked a drayman who was passing how far it was to the Plaza. The drayman replied it was just half a mile; and the surveyor put it down in his book,—just as Judge Douglas says, after he had made his calculations and computations, he took Toombs's statement. I have no doubt that after Judge Douglas had made his charge, he was as easily satisfied about its truth as the surveyor was of the drayman's statement of the distance to the Plaza. Yet it is a fact that the man who put forth all that matter which Douglas deemed a "fatal blow" at State sovereignty was elected by the Democrats as public printer.
Now, gentlemen, you may take Judge Douglas's speech of March 22, 1858, beginning about the middle of page 21, and reading to the bottom of page 24, and you will find the evidence on which I say that he did not make his charge against the editor of the Union alone. I cannot stop to read it, but I will give it to the reporters. Judge Douglas said:
"Mr. President, you here find several distinct propositions advanced boldly by the Washington Union editorially, and apparently authoritatively, and every man who questions any of them is denounced as an Abolitionist, a Free-soiler, a fanatic. The propositions are, first, that the primary object of all government at its original institution is the protection of persons and property; second, that the Constitution of the United States declares that the citizens of each State shall be entitled to all the privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States; and that, therefore, thirdly, all State laws, whether organic or otherwise, which prohibit the citizens of one State from settling in another with their slave property, and especially declaring it forfeited, are direct violations of the original intention of the Government and Constitution of the United States; and, fourth, that the emancipation of the slaves of the Northern States was a gross outrage on the rights of property, in as much as it was involuntarily done on the part of the owner.
"Remember that this article was published in the Union on the 17th of November, and on the 18th appeared the first article giving the adhesion of the Union to the Lecompton Constitution. It was in these words:
"'KANSAS AND HER CONSTITUTION.—The vexed question is settled. The problem is solved. The dead point of danger is passed. All serious trouble to Kansas affairs is over and gone...."
"And a column, nearly, of the same sort. Then, when you come to look into the Lecompton Constitution, you find the same doctrine incorporated in it which was put forth editorially in the Union. What is it?
"'ARTICLE 7, Section i. The right of property is before and higher than any constitutional sanction; and the right of the owner of a slave to such slave and its increase is the same and as invariable as the right of the owner of any property whatever.'
"Then in the schedule is a provision that the Constitution may be amended after 1864 by a two-thirds vote.
"'But no alteration shall be made to affect the right of property in the ownership of slaves.'
"It will be seen by these clauses in the Lecompton Constitution that they are identical in spirit with this authoritative article in the Washington Union of the day previous to its indorsement of this Constitution.
"When I saw that article in the Union of the 17th of November, followed by the glorification of the Lecompton Constitution on the 18th of November, and this clause in the Constitution asserting the doctrine that a State has no right to prohibit slavery within its limits, I saw that there was a fatal blow being struck at the sovereignty of the States of this Union."
Here he says, "Mr. President, you here find several distinct propositions advanced boldly, and apparently authoritatively." By whose authority, Judge Douglas? Again, he says in another place, "It will be seen by these clauses in the Lecompton Constitution that they are identical in spirit with this authoritative article." By whose authority,—who do you mean to say authorized the publication of these articles? He knows that the Washington Union is considered the organ of the Administration. I demand of Judge Douglas by whose authority he meant to say those articles were published, if not by the authority of the President of the United States and his Cabinet? I defy him to show whom he referred to, if not to these high functionaries in the Federal Government. More than this, he says the articles in that paper and the provisions of the Lecompton Constitution are "identical," and, being identical, he argues that the authors are co-operating and conspiring together. He does not use the word "conspiring," but what other construction can you put upon it? He winds up:
"When I saw that article in the Union of the 17th of November, followed by the glorification of the Lecompton Constitution on the 18th of November, and this clause in the Constitution asserting the doctrine that a State has no right to prohibit slavery within its limits, I saw that there was a fatal blow being struck at the sovereignty of the States of this Union."
I ask him if all this fuss was made over the editor of this newspaper. It would be a terribly "fatal blow" indeed which a single man could strike, when no President, no Cabinet officer, no member of Congress, was giving strength and efficiency to the movement. Out of respect to Judge Douglas's good sense I must believe he did n't manufacture his idea of the "fatal" character of that blow out of such a miserable scapegrace as he represents that editor to be. But the Judge's eye is farther south now. Then, it was very peculiarly and decidedly north. His hope rested on the idea of visiting the great "Black Republican" party, and making it the tail of his new kite. He knows he was then expecting from day to day to turn Republican, and place himself at the head of our organization. He has found that these despised "Black Republicans" estimate him by a standard which he has taught them none too well. Hence he is crawling back into his old camp, and you will find him eventually installed in full fellowship among those whom he was then battling, and with whom he now pretends to be at such fearful variance.
Mr. LINCOLN'S REPLY.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—There is very much in the principles that Judge Douglas has here enunciated that I most cordially approve, and over which I shall have no controversy with him. In so far as he has insisted that all the States have the right to do exactly as they please about all their domestic relations, including that of slavery, I agree entirely with him. He places me wrong in spite of all I can tell him, though I repeat it again and again, insisting that I have no difference with him upon this subject. I have made a great many speeches, some of which have been printed, and it will be utterly impossible for him to find anything that I have ever put in print contrary to what I now say upon this subject. I hold myself under constitutional obligations to allow the people in all the States, without interference, direct or indirect, to do exactly as they please; and I deny that I have any inclination to interfere with them, even if there were no such constitutional obligation. I can only say again that I am placed improperly—altogether improperly, in spite of all I can say—when it is insisted that I entertain any other view or purposes in regard to that matter.
While I am upon this subject, I will make some answers briefly to certain propositions that Judge Douglas has put. He says, "Why can't this Union endure permanently half slave and half free?" I have said that I supposed it could not, and I will try, before this new audience, to give briefly some of the reasons for entertaining that opinion. Another form of his question is, "Why can't we let it stand as our fathers placed it?" That is the exact difficulty between us. I say that Judge Douglas and his friends have changed it from the position in which our fathers originally placed it. I say, in the way our father's originally left the slavery question, the institution was in the course of ultimate extinction, and the public mind rested in the belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. I say when this government was first established it was the policy of its founders to prohibit the spread of slavery into the new Territories of the United States, where it had not existed. But Judge Douglas and his friends have broken up that policy, and placed it upon a new basis, by which it is to become national and perpetual. All I have asked or desired anywhere is that it should be placed back again upon the basis that the fathers of our government originally placed it upon. I have no doubt that it would become extinct, for all time to come, if we but readopted the policy of the fathers, by restricting it to the limits it has already covered, restricting it from the new Territories.
I do not wish to dwell at great length on this branch of the subject at this time, but allow me to repeat one thing that I have stated before. Brooks—the man who assaulted Senator Sumner on the floor of the Senate, and who was complimented with dinners, and silver pitchers, and gold-headed canes, and a good many other things for that feat—in one of his speeches declared that when this government was originally established, nobody expected that the institution of slavery would last until this day. That was but the opinion of one man, but it was such an opinion as we can never get from Judge Douglas or anybody in favor of slavery, in the North, at all. You can sometimes get it from a Southern man. He said at the same time that the framers of our government did not have the knowledge that experience has taught us; that experience and the invention of the cotton-gin have taught us that the perpetuation of slavery is a necessity. He insisted, therefore, upon its being changed from the basis upon which the fathers of the government left it to the basis of its perpetuation and nationalization.
I insist that this is the difference between Judge Douglas and myself,—that Judge Douglas is helping that change along. I insist upon this government being placed where our fathers originally placed it.
I remember Judge Douglas once said that he saw the evidences on the statute books of Congress of a policy in the origin of government to divide slavery and freedom by a geographical line; that he saw an indisposition to maintain that policy, and therefore he set about studying up a way to settle the institution on the right basis,—the basis which he thought it ought to have been placed upon at first; and in that speech he confesses that he seeks to place it, not upon the basis that the fathers placed it upon, but upon one gotten up on "original principles." When he asks me why we cannot get along with it in the attitude where our fathers placed it, he had better clear up the evidences that he has himself changed it from that basis, that he has himself been chiefly instrumental in changing the policy of the fathers. Any one who will read his speech of the 22d of last March will see that he there makes an open confession, showing that he set about fixing the institution upon an altogether different set of principles. I think I have fully answered him when he asks me why we cannot let it alone upon the basis where our fathers left it, by showing that he has himself changed the whole policy of the government in that regard.
Now, fellow-citizens, in regard to this matter about a contract that was made between Judge Trumbull and myself, and all that long portion of Judge Douglas's speech on this subject,—I wish simply to say what I have said to him before, that he cannot know whether it is true or not, and I do know that there is not a word of truth in it. And I have told him so before. I don't want any harsh language indulged in, but I do not know how to deal with this persistent insisting on a story that I know to be utterly without truth. It used to be a fashion amongst men that when a charge was made, some sort of proof was brought forward to establish it, and if no proof was found to exist, the charge was dropped. I don't know how to meet this kind of an argument. I don't want to have a fight with Judge Douglas, and I have no way of making an argument up into the consistency of a corn-cob and stopping his mouth with it. All I can do is—good-humoredly—to say that, from the beginning to the end of all that story about a bargain between Judge Trumbull and myself, there is not a word of truth in it. I can only ask him to show some sort of evidence of the truth of his story. He brings forward here and reads from what he contends is a speech by James H. Matheny, charging such a bargain between Trumbull and myself. My own opinion is that Matheny did do some such immoral thing as to tell a story that he knew nothing about. I believe he did. I contradicted it instantly, and it has been contradicted by Judge Trumbull, while nobody has produced any proof, because there is none. Now, whether the speech which the Judge brings forward here is really the one Matheny made, I do not know, and I hope the Judge will pardon me for doubting the genuineness of this document, since his production of those Springfield resolutions at Ottawa. I do not wish to dwell at any great length upon this matter. I can say nothing when a long story like this is told, except it is not true, and demand that he who insists upon it shall produce some proof. That is all any man can do, and I leave it in that way, for I know of no other way of dealing with it.
[In an argument on the lines of: "Yes, you did.—No, I did not." It bears on the former to prove his point, not on the negative to "prove" that he did not—even if he easily can do so.]
The Judge has gone over a long account of the old Whig and Democratic parties, and it connects itself with this charge against Trumbull and myself. He says that they agreed upon a compromise in regard to the slavery question in 1850; that in a National Democratic Convention resolutions were passed to abide by that compromise as a finality upon the slavery question. He also says that the Whig party in National Convention agreed to abide by and regard as a finality the Compromise of 1850. I understand the Judge to be altogether right about that; I understand that part of the history of the country as stated by him to be correct I recollect that I, as a member of that party, acquiesced in that compromise. I recollect in the Presidential election which followed, when we had General Scott up for the presidency, Judge Douglas was around berating us Whigs as Abolitionists, precisely as he does to-day,—not a bit of difference. I have often heard him. We could do nothing when the old Whig party was alive that was not Abolitionism, but it has got an extremely good name since it has passed away.
[It almost a natural law that, when dead—no matter how bad we were—we are automatically beatified.]
When that Compromise was made it did not repeal the old Missouri Compromise. It left a region of United States territory half as large as the present territory of the United States, north of the line of 36 degrees 30 minutes, in which slavery was prohibited by Act of Congress. This Compromise did not repeal that one. It did not affect or propose to repeal it. But at last it became Judge Douglas's duty, as he thought (and I find no fault with him), as Chairman of the Committee on Territories, to bring in a bill for the organization of a territorial government,—first of one, then of two Territories north of that line. When he did so, it ended in his inserting a provision substantially repealing the Missouri Compromise. That was because the Compromise of 1850 had not repealed it. And now I ask why he could not have let that Compromise alone? We were quiet from the agitation of the slavery question. We were making no fuss about it. All had acquiesced in the Compromise measures of 1850. We never had been seriously disturbed by any Abolition agitation before that period. When he came to form governments for the Territories north of the line of 36 degrees 30 minutes, why could he not have let that matter stand as it was standing? Was it necessary to the organization of a Territory? Not at all. Iowa lay north of the line, and had been organized as a Territory and come into the Union as a State without disturbing that Compromise. There was no sort of necessity for destroying it to organize these Territories. But, gentlemen, it would take up all my time to meet all the little quibbling arguments of Judge Douglas to show that the Missouri Compromise was repealed by the Compromise of 1850. My own opinion is, that a careful investigation of all the arguments to sustain the position that that Compromise was virtually repealed by the Compromise of 1850 would show that they are the merest fallacies. I have the report that Judge Douglas first brought into Congress at the time of the introduction of the Nebraska Bill, which in its original form did not repeal the Missouri Compromise, and he there expressly stated that he had forborne to do so because it had not been done by the Compromise of 1850. I close this part of the discussion on my part by asking him the question again, "Why, when we had peace under the Missouri Compromise, could you not have let it alone?"
In complaining of what I said in my speech at Springfield, in which he says I accepted my nomination for the senatorship (where, by the way, he is at fault, for if he will examine it, he will find no acceptance in it), he again quotes that portion in which I said that "a house divided against itself cannot stand." Let me say a word in regard to that matter.
He tries to persuade us that there must be a variety in the different institutions of the States of the Union; that that variety necessarily proceeds from the variety of soil, climate, of the face of the country, and the difference in the natural features of the States. I agree to all that. Have these very matters ever produced any difficulty amongst us? Not at all. Have we ever had any quarrel over the fact that they have laws in Louisiana designed to regulate the commerce that springs from the production of sugar? Or because we have a different class relative to the production of flour in this State? Have they produced any differences? Not at all. They are the very cements of this Union. They don't make the house a house divided against itself. They are the props that hold up the house and sustain the Union.
But has it been so with this element of slavery? Have we not always had quarrels and difficulties over it? And when will we cease to have quarrels over it? Like causes produce like effects. It is worth while to observe that we have generally had comparative peace upon the slavery question, and that there has been no cause for alarm until it was excited by the effort to spread it into new territory. Whenever it has been limited to its present bounds, and there has been no effort to spread it, there has been peace. All the trouble and convulsion has proceeded from efforts to spread it over more territory. It was thus at the date of the Missouri Compromise. It was so again with the annexation of Texas; so with the territory acquired by the Mexican war; and it is so now. Whenever there has been an effort to spread it, there has been agitation and resistance. Now, I appeal to this audience (very few of whom are my political friends), as national men, whether we have reason to expect that the agitation in regard to this subject will cease while the causes that tend to reproduce agitation are actively at work? Will not the same cause that produced agitation in 1820, when the Missouri Compromise was formed, that which produced the agitation upon the annexation of Texas, and at other times, work out the same results always? Do you think that the nature of man will be changed, that the same causes that produced agitation at one time will not have the same effect at another?
This has been the result so far as my observation of the slavery question and my reading in history extends. What right have we then to hope that the trouble will cease,—that the agitation will come to an end,—until it shall either be placed back where it originally stood, and where the fathers originally placed it, or, on the other hand, until it shall entirely master all opposition? This is the view I entertain, and this is the reason why I entertained it, as Judge Douglas has read from my Springfield speech.
Now, my friends, there is one other thing that I feel myself under some sort of obligation to mention. Judge Douglas has here to-day—in a very rambling way, I was about saying—spoken of the platforms for which he seeks to hold me responsible. He says, "Why can't you come out and make an open avowal of principles in all places alike?" and he reads from an advertisement that he says was used to notify the people of a speech to be made by Judge Trumbull at Waterloo. In commenting on it he desires to know whether we cannot speak frankly and manfully, as he and his friends do. How, I ask, do his friends speak out their own sentiments? A Convention of his party in this State met on the 21st of April at Springfield, and passed a set of resolutions which they proclaim to the country as their platform. This does constitute their platform, and it is because Judge Douglas claims it is his platform—that these are his principles and purposes—that he has a right to declare he speaks his sentiments "frankly and manfully." On the 9th of June Colonel John Dougherty, Governor Reynolds, and others, calling themselves National Democrats, met in Springfield and adopted a set of resolutions which are as easily understood, as plain and as definite in stating to the country and to the world what they believed in and would stand upon, as Judge Douglas's platform Now, what is the reason that Judge Douglas is not willing that Colonel Dougherty and Governor Reynolds should stand upon their own written and printed platform as well as he upon his? Why must he look farther than their platform when he claims himself to stand by his platform?
Again, in reference to our platform: On the 16th of June the Republicans had their Convention and published their platform, which is as clear and distinct as Judge Douglas's. In it they spoke their principles as plainly and as definitely to the world. What is the reason that Judge Douglas is not willing I should stand upon that platform? Why must he go around hunting for some one who is supporting me or has supported me at some time in his life, and who has said something at some time contrary to that platform? Does the Judge regard that rule as a good one? If it turn out that the rule is a good one for me—that I am responsible for any and every opinion that any man has expressed who is my friend,—then it is a good rule for him. I ask, is it not as good a rule for him as it is for me? In my opinion, it is not a good rule for either of us. Do you think differently, Judge?
[Mr. DOUGLAS: I do not.]
Judge Douglas says he does not think differently. I am glad of it. Then can he tell me why he is looking up resolutions of five or six years ago, and insisting that they were my platform, notwithstanding my protest that they are not, and never were my platform, and my pointing out the platform of the State Convention which he delights to say nominated me for the Senate? I cannot see what he means by parading these resolutions, if it is not to hold me responsible for them in some way. If he says to me here that he does not hold the rule to be good, one way or the other, I do not comprehend how he could answer me more fully if he answered me at greater length. I will therefore put in as my answer to the resolutions that he has hunted up against me, what I, as a lawyer, would call a good plea to a bad declaration. I understand that it is an axiom of law that a poor plea may be a good plea to a bad declaration. I think that the opinions the Judge brings from those who support me, yet differ from me, is a bad declaration against me; but if I can bring the same things against him, I am putting in a good plea to that kind of declaration, and now I propose to try it.
At Freeport, Judge Douglas occupied a large part of his time in producing resolutions and documents of various sorts, as I understood, to make me somehow responsible for them; and I propose now doing a little of the same sort of thing for him. In 1850 a very clever gentleman by the name of Thompson Campbell, a personal friend of Judge Douglas and myself, a political friend of Judge Douglas and opponent of mine, was a candidate for Congress in the Galena District. He was interrogated as to his views on this same slavery question. I have here before me the interrogatories, and Campbell's answers to them—I will read them:
"1st. Will you, if elected, vote for and cordially support a bill prohibiting slavery in the Territories of the United States?
"2d. Will you vote for and support a bill abolishing slavery in the District of Columbia?
"3d. Will you oppose the admission of any Slave States which may be formed out of Texas or the Territories?
"4th. Will you vote for and advocate the repeal of the Fugitive Slave law passed at the recent session of Congress?
"5th. Will you advocate and vote for the election of a Speaker of the House of Representatives who shall be willing to organize the committees of that House so as to give the Free States their just influence in the business of legislation?
"6th. What are your views, not only as to the constitutional right of Congress to prohibit the slave-trade between the States, but also as to the expediency of exercising that right immediately?"
"To the first and second interrogatories, I answer unequivocally in the affirmative.
"To the third interrogatory I reply, that I am opposed to the admission of any more Slave States into the Union, that may be formed out of Texas or any other Territory.
"To the fourth and fifth interrogatories I unhesitatingly answer in the affirmative.
"To the sixth interrogatory I reply, that so long as the Slave States continue to treat slaves as articles of commerce, the Constitution confers power on Congress to pass laws regulating that peculiar COMMERCE, and that the protection of Human Rights imperatively demands the interposition of every constitutional means to prevent this most inhuman and iniquitous traffic.
"T. CAMPBELL."
I want to say here that Thompson Campbell was elected to Congress on that platform, as the Democratic candidate in the Galena District, against Martin P. Sweet.
[Judge DOUGLAS: Give me the date of the letter.]
The time Campbell ran was in 1850. I have not the exact date here. It was some time in 1850 that these interrogatories were put and the answer given. Campbell was elected to Congress, and served out his term. I think a second election came up before he served out his term, and he was not re-elected. Whether defeated or not nominated, I do not know. [Mr. Campbell was nominated for re-election by the Democratic party, by acclamation.] At the end of his term his very good friend Judge Douglas got him a high office from President Pierce, and sent him off to California. Is not that the fact? Just at the end of his term in Congress it appears that our mutual friend Judge Douglas got our mutual friend Campbell a good office, and sent him to California upon it. And not only so, but on the 27th of last month, when Judge Douglas and myself spoke at Freeport in joint discussion, there was his same friend Campbell, come all the way from California, to help the Judge beat me; and there was poor Martin P. Sweet standing on the platform, trying to help poor me to be elected. That is true of one of Judge Douglas's friends.
So again, in that same race of 1850, there was a Congressional Convention assembled at Joliet, and it nominated R. S. Molony for Congress, and unanimously adopted the following resolution:
"Resolved, That we are uncompromisingly opposed to the extension of slavery; and while we would not make such opposition a ground of interference with the interests of the States where it exists, yet we moderately but firmly insist that it is the duty of Congress to oppose its extension into Territory now free, by all means compatible with the obligations of the Constitution, and with good faith to our sister States; that these principles were recognized by the Ordinance of 1787, which received the sanction of Thomas Jefferson, who is acknowledged by all to be the great oracle and expounder of our faith."
Subsequently the same interrogatories were propounded to Dr. Molony which had been addressed to Campbell as above, with the exception of the 6th, respecting the interstate slave trade, to which Dr. Molony, the Democratic nominee for Congress, replied as follows:
"I received the written interrogatories this day, and, as you will see by the La Salle Democrat and Ottawa Free Trader, I took at Peru on the 5th, and at Ottawa on the 7th, the affirmative side of interrogatories 1st and 2d; and in relation to the admission of any more Slave States from Free Territory, my position taken at these meetings, as correctly reported in said papers, was emphatically and distinctly opposed to it. In relation to the admission of any more Slave States from Texas, whether I shall go against it or not will depend upon the opinion that I may hereafter form of the true meaning and nature of the resolutions of annexation. If, by said resolutions, the honor and good faith of the nation is pledged to admit more Slave States from Texas when she (Texas) may apply for the admission of such State, then I should, if in Congress, vote for their admission. But if not so PLEDGED and bound by sacred contract, then a bill for the admission of more Slave States from Texas would never receive my vote.
"To your fourth interrogatory I answer most decidedly in the affirmative, and for reasons set forth in my reported remarks at Ottawa last Monday.
"To your fifth interrogatory I also reply in the affirmative most cordially, and that I will use my utmost exertions to secure the nomination and election of a man who will accomplish the objects of said interrogatories. I most cordially approve of the resolutions adopted at the Union meeting held at Princeton on the 27th September ult.
"Yours, etc., R. S. MOLONY."
All I have to say in regard to Dr. Molony is that he was the regularly nominated Democratic candidate for Congress in his district; was elected at that time; at the end of his term was appointed to a land-office at Danville. (I never heard anything of Judge Douglas's instrumentality in this.) He held this office a considerable time, and when we were at Freeport the other day there were handbills scattered about notifying the public that after our debate was over R. S. Molony would make a Democratic speech in favor of Judge Douglas. That is all I know of my own personal knowledge. It is added here to this resolution, and truly I believe, that among those who participated in the Joliet Convention, and who supported its nominee, with his platform as laid down in the resolution of the Convention and in his reply as above given, we call at random the following names, all of which are recognized at this day as leading Democrats:
"Cook County,—E. B. Williams, Charles McDonell, Arno Voss, Thomas Hoyne, Isaac Cook."
I reckon we ought to except Cook.
"F. C. Sherman. "Will,—Joel A. Matteson, S. W. Bowen. "Kane,—B. F. Hall, G. W. Renwick, A. M. Herrington, Elijah Wilcox. "McHenry,—W. M. Jackson, Enos W. Smith, Neil Donnelly. La Salle,—John Hise, William Reddick."
William Reddick! another one of Judge Douglas's friends that stood on the stand with him at Ottawa, at the time the Judge says my knees trembled so that I had to be carried away. The names are all here:
"Du Page,—Nathan Allen. "De Kalb,—Z. B. Mayo."
Here is another set of resolutions which I think are apposite to the matter in hand.
On the 28th of February of the same year a Democratic District Convention was held at Naperville to nominate a candidate for Circuit Judge. Among the delegates were Bowen and Kelly of Will; Captain Naper, H. H. Cody, Nathan Allen, of Du Page; W. M. Jackson, J. M. Strode, P. W. Platt, and Enos W. Smith of McHenry; J. Horssnan and others of Winnebago. Colonel Strode presided over the Convention. The following resolutions were unanimously adopted,—the first on motion of P. W. Platt, the second on motion of William M. Jackson:
"Resolved, That this Convention is in favor of the Wilmot Proviso, both in Principle and Practice, and that we know of no good reason why any person should oppose the largest latitude in Free Soil, Free Territory and Free speech.
"Resolved, That in the opinion of this Convention, the time has arrived when all men should be free, whites as well as others."
[Judge DOUGLAS: What is the date of those resolutions?]
I understand it was in 1850, but I do not know it. I do not state a thing and say I know it, when I do not. But I have the highest belief that this is so. I know of no way to arrive at the conclusion that there is an error in it. I mean to put a case no stronger than the truth will allow. But what I was going to comment upon is an extract from a newspaper in De Kalb County; and it strikes me as being rather singular, I confess, under the circumstances. There is a Judge Mayo in that county, who is a candidate for the Legislature, for the purpose, if he secures his election, of helping to re-elect Judge Douglas. He is the editor of a newspaper [De Kalb County Sentinel], and in that paper I find the extract I am going to read. It is part of an editorial article in which he was electioneering as fiercely as he could for Judge Douglas and against me. It was a curious thing, I think, to be in such a paper. I will agree to that, and the Judge may make the most of it:
"Our education has been such that we have been rather in favor of the equality of the blacks; that is, that they should enjoy all the privileges of the whites where they reside. We are aware that this is not a very popular doctrine. We have had many a confab with some who are now strong 'Republicans' we taking the broad ground of equality, and they the opposite ground.
"We were brought up in a State where blacks were voters, and we do not know of any inconvenience resulting from it, though perhaps it would not work as well where the blacks are more numerous. We have no doubt of the right of the whites to guard against such an evil, if it is one. Our opinion is that it would be best for all concerned to have the colored population in a State by themselves [in this I agree with him]; but if within the jurisdiction of the United States, we say by all means they should have the right to have their Senators and Representatives in Congress, and to vote for President. With us 'worth makes the man, and want of it the fellow.' We have seen many a 'nigger' that we thought more of than some white men."
That is one of Judge Douglas's friends. Now, I do not want to leave myself in an attitude where I can be misrepresented, so I will say I do not think the Judge is responsible for this article; but he is quite as responsible for it as I would be if one of my friends had said it. I think that is fair enough.
I have here also a set of resolutions passed by a Democratic State Convention in Judge Douglas's own good State of Vermont, that I think ought to be good for him too:
"Resolved, That liberty is a right inherent and inalienable in man, and that herein all men are equal.
"Resolved, That we claim no authority in the Federal Government to abolish slavery in the several States, but we do claim for it Constitutional power perpetually to prohibit the introduction of slavery into territory now free, and abolish it wherever, under the jurisdiction of Congress, it exists.
"Resolved, That this power ought immediately to be exercised in prohibiting the introduction and existence of slavery in New Mexico and California, in abolishing slavery and the slave-trade in the District of Columbia, on the high seas, and wherever else, under the Constitution, it can be reached.
"Resolved, That no more Slave States should be admitted into the Federal Union.
"Resolved, That the Government ought to return to its ancient policy, not to extend, nationalize, or encourage, but to limit, localize, and discourage slavery."
At Freeport I answered several interrogatories that had been propounded to me by Judge Douglas at the Ottawa meeting. The Judge has not yet seen fit to find any fault with the position that I took in regard to those seven interrogatories, which were certainly broad enough, in all conscience, to cover the entire ground. In my answers, which have been printed, and all have had the opportunity of seeing, I take the ground that those who elect me must expect that I will do nothing which will not be in accordance with those answers. I have some right to assert that Judge Douglas has no fault to find with them. But he chooses to still try to thrust me upon different ground, without paying any attention to my answers, the obtaining of which from me cost him so much trouble and concern. At the same time I propounded four interrogatories to him, claiming it as a right that he should answer as many interrogatories for me as I did for him, and I would reserve myself for a future instalment when I got them ready. The Judge, in answering me upon that occasion, put in what I suppose he intends as answers to all four of my interrogatories. The first one of these interrogatories I have before me, and it is in these words:
"Question 1.—If the people of Kansas shall, by means entirely unobjectionable in all other respects, adopt a State constitution, and ask admission into the Union under it, before they have the requisite number of inhabitants according to the English bill,"—some ninety-three thousand,—"will you vote to admit them?"
As I read the Judge's answer in the newspaper, and as I remember it as pronounced at the time, he does not give any answer which is equivalent to yes or no,—I will or I won't. He answers at very considerable length, rather quarreling with me for asking the question, and insisting that Judge Trumbull had done something that I ought to say something about, and finally getting out such statements as induce me to infer that he means to be understood he will, in that supposed case, vote for the admission of Kansas. I only bring this forward now for the purpose of saying that if he chooses to put a different construction upon his answer, he may do it. But if he does not, I shall from this time forward assume that he will vote for the admission of Kansas in disregard of the English bill. He has the right to remove any misunderstanding I may have. I only mention it now, that I may hereafter assume this to be the true construction of his answer, if he does not now choose to correct me.
The second interrogatory that I propounded to him was this:
"Question 2.—Can the people of a United States Territory, in any lawful way, against the wish of any citizen of the United States, exclude slavery from its limits prior to the formation of a State Constitution?"
To this Judge Douglas answered that they can lawfully exclude slavery from the Territory prior to the formation of a constitution. He goes on to tell us how it can be done. As I understand him, he holds that it can be done by the Territorial Legislature refusing to make any enactments for the protection of slavery in the Territory, and especially by adopting unfriendly legislation to it. For the sake of clearness, I state it again: that they can exclude slavery from the Territory, 1st, by withholding what he assumes to be an indispensable assistance to it in the way of legislation; and, 2d, by unfriendly legislation. If I rightly understand him, I wish to ask your attention for a while to his position.
In the first place, the Supreme Court of the United States has decided that any Congressional prohibition of slavery in the Territories is unconstitutional; that they have reached this proposition as a conclusion from their former proposition, that the Constitution of the United States expressly recognizes property in slaves, and from that other Constitutional provision, that no person shall be deprived of property without due process of law. Hence they reach the conclusion that as the Constitution of the United States expressly recognizes property in slaves, and prohibits any person from being deprived of property without due process of law, to pass an Act of Congress by which a man who owned a slave on one side of a line would be deprived of him if he took him on the other side, is depriving him of that property without due process of law. That I understand to be the decision of the Supreme Court. I understand also that Judge Douglas adheres most firmly to that decision; and the difficulty is, how is it possible for any power to exclude slavery from the Territory, unless in violation of that decision? That is the difficulty.
In the Senate of the United States, in 1850, Judge Trumbull, in a speech substantially, if not directly, put the same interrogatory to Judge Douglas, as to whether the people of a Territory had the lawful power to exclude slavery prior to the formation of a constitution. Judge Douglas then answered at considerable length, and his answer will be found in the Congressional Globe, under date of June 9th, 1856. The Judge said that whether the people could exclude slavery prior to the formation of a constitution or not was a question to be decided by the Supreme Court. He put that proposition, as will be seen by the Congressional Globe, in a variety of forms, all running to the same thing in substance,—that it was a question for the Supreme Court. I maintain that when he says, after the Supreme Court have decided the question, that the people may yet exclude slavery by any means whatever, he does virtually say that it is not a question for the Supreme Court. He shifts his ground. I appeal to you whether he did not say it was a question for the Supreme Court? Has not the Supreme Court decided that question? when he now says the people may exclude slavery, does he not make it a question for the people? Does he not virtually shift his ground and say that it is not a question for the Court, but for the people? This is a very simple proposition,—a very plain and naked one. It seems to me that there is no difficulty in deciding it. In a variety of ways he said that it was a question for the Supreme Court. He did not stop then to tell us that, whatever the Supreme Court decides, the people can by withholding necessary "police regulations" keep slavery out. He did not make any such answer I submit to you now whether the new state of the case has not induced the Judge to sheer away from his original ground. Would not this be the impression of every fair-minded man?
I hold that the proposition that slavery cannot enter a new country without police regulations is historically false. It is not true at all. I hold that the history of this country shows that the institution of slavery was originally planted upon this continent without these "police regulations," which the Judge now thinks necessary for the actual establishment of it. Not only so, but is there not another fact: how came this Dred Scott decision to be made? It was made upon the case of a negro being taken and actually held in slavery in Minnesota Territory, claiming his freedom because the Act of Congress prohibited his being so held there. Will the Judge pretend that Dred Scott was not held there without police regulations? There is at least one matter of record as to his having been held in slavery in the Territory, not only without police regulations, but in the teeth of Congressional legislation supposed to be valid at the time. This shows that there is vigor enough in slavery to plant itself in a new country even against unfriendly legislation. It takes not only law, but the enforcement of law to keep it out. That is the history of this country upon the subject.
I wish to ask one other question. It being understood that the Constitution of the United States guarantees property in slaves in the Territories, if there is any infringement of the right of that property, would not the United States courts, organized for the government of the Territory, apply such remedy as might be necessary in that case? It is a maxim held by the courts that there is no wrong without its remedy; and the courts have a remedy for whatever is acknowledged and treated as a wrong.
Again: I will ask you, my friends, if you were elected members of the Legislature, what would be the first thing you would have to do before entering upon your duties? Swear to support the Constitution of the United States. Suppose you believe, as Judge Douglas does, that the Constitution of the United States guarantees to your neighbor the right to hold slaves in that Territory; that they are his property: how can you clear your oaths unless you give him such legislation as is necessary to enable him to enjoy that property? What do you understand by supporting the Constitution of a State, or of the United States? Is it not to give such constitutional helps to the rights established by that Constitution as may be practically needed? Can you, if you swear to support the Constitution, and believe that the Constitution establishes a right, clear your oath, without giving it support? Do you support the Constitution if, knowing or believing there is a right established under it which needs specific legislation, you withhold that legislation? Do you not violate and disregard your oath? I can conceive of nothing plainer in the world. There can be nothing in the words "support the Constitution," if you may run counter to it by refusing support to any right established under the Constitution. And what I say here will hold with still more force against the Judge's doctrine of "unfriendly legislation." How could you, having sworn to support the Constitution, and believing it guaranteed the right to hold slaves in the Territories, assist in legislation intended to defeat that right? That would be violating your own view of the Constitution. Not only so, but if you were to do so, how long would it take the courts to hold your votes unconstitutional and void? Not a moment.
Lastly, I would ask: Is not Congress itself under obligation to give legislative support to any right that is established under the United States Constitution? I repeat the question: Is not Congress itself bound to give legislative support to any right that is established in the United States Constitution? A member of Congress swears to support the Constitution of the United States: and if he sees a right established by that Constitution which needs specific legislative protection, can he clear his oath without giving that protection? Let me ask you why many of us who are opposed to slavery upon principle give our acquiescence to a Fugitive Slave law? Why do we hold ourselves under obligations to pass such a law, and abide by it when it is passed? Because the Constitution makes provision that the owners of slaves shall have the right to reclaim them. It gives the right to reclaim slaves; and that right is, as Judge Douglas says, a barren right, unless there is legislation that will enforce it.
The mere declaration, "No person held to service or labor in one State under the laws thereof, escaping into another, shall in consequence of any law or regulation therein be discharged from such service or labor, but shall be delivered up on claim of the party to whom such service or labor may be due," is powerless without specific legislation to enforce it. Now, on what ground would a member of Congress, who is opposed to slavery in the abstract, vote for a Fugitive law, as I would deem it my duty to do? Because there is a constitutional right which needs legislation to enforce it. And although it is distasteful to me, I have sworn to support the Constitution; and having so sworn, I cannot conceive that I do support it if I withhold from that right any necessary legislation to make it practical. And if that is true in regard to a Fugitive Slave law, is the right to have fugitive slaves reclaimed any better fixed in the Constitution than the right to hold slaves in the Territories? For this decision is a just exposition of the Constitution, as Judge Douglas thinks. Is the one right any better than the other? Is there any man who, while a member of Congress, would give support to the one any more than the other? If I wished to refuse to give legislative support to slave property in the Territories, if a member of Congress, I could not do it, holding the view that the Constitution establishes that right. If I did it at all, it would be because I deny that this decision properly construes the Constitution. But if I acknowledge, with Judge Douglas, that this decision properly construes the Constitution, I cannot conceive that I would be less than a perjured man if I should refuse in Congress to give such protection to that property as in its nature it needed.
At the end of what I have said here I propose to give the Judge my fifth interrogatory, which he may take and answer at his leisure. My fifth interrogatory is this:
If the slaveholding citizens of a United States Territory should need and demand Congressional legislation for the protection of their slave property in such Territory, would you, as a member of Congress, vote for or against such legislation?
[Judge DOUGLAS: Will you repeat that? I want to answer that question.]
If the slaveholding citizens of a United States Territory should need and demand Congressional legislation for the protection of their slave property in such Territory, would you, as a member of Congress, vote for or against such legislation?
I am aware that in some of the speeches Judge Douglas has made, he has spoken as if he did not know or think that the Supreme Court had decided that a Territorial Legislature cannot exclude slavery. Precisely what the Judge would say upon the subject—whether he would say definitely that he does not understand they have so decided, or whether he would say he does understand that the court have so decided,—I do not know; but I know that in his speech at Springfield he spoke of it as a thing they had not decided yet; and in his answer to me at Freeport, he spoke of it, so far, again, as I can comprehend it, as a thing that had not yet been decided. Now, I hold that if the Judge does entertain that view, I think that he is not mistaken in so far as it can be said that the court has not decided anything save the mere question of jurisdiction. I know the legal arguments that can be made,—that after a court has decided that it cannot take jurisdiction in a case, it then has decided all that is before it, and that is the end of it. A plausible argument can be made in favor of that proposition; but I know that Judge Douglas has said in one of his speeches that the court went forward, like honest men as they were, and decided all the points in the case. If any points are really extra-judicially decided, because not necessarily before them, then this one as to the power of the Territorial Legislature, to exclude slavery is one of them, as also the one that the Missouri Compromise was null and void. They are both extra-judicial, or neither is, according as the court held that they had no jurisdiction in the case between the parties, because of want of capacity of one party to maintain a suit in that court. I want, if I have sufficient time, to show that the court did pass its opinion; but that is the only thing actually done in the case. If they did not decide, they showed what they were ready to decide whenever the matter was before them. What is that opinion? After having argued that Congress had no power to pass a law excluding slavery from a United States Territory, they then used language to this effect: That inasmuch as Congress itself could not exercise such a power, it followed as a matter of course that it could not authorize a Territorial government to exercise it; for the Territorial Legislature can do no more than Congress could do. Thus it expressed its opinion emphatically against the power of a Territorial Legislature to exclude slavery, leaving us in just as little doubt on that point as upon any other point they really decided.
Now, my fellow-citizens, I will detain you only a little while longer; my time is nearly out. I find a report of a speech made by Judge Douglas at Joliet, since we last met at Freeport,—published, I believe, in the Missouri Republican, on the 9th of this month, in which Judge Douglas says:
"You know at Ottawa I read this platform, and asked him if he concurred in each and all of the principles set forth in it. He would not answer these questions. At last I said frankly, I wish you to answer them, because when I get them up here where the color of your principles are a little darker than in Egypt, I intend to trot you down to Jonesboro. The very notice that I was going to take him down to Egypt made him tremble in his knees so that he had to be carried from the platform. He laid up seven days, and in the meantime held a consultation with his political physicians; they had Lovejoy and Farnsworth and all the leaders of the Abolition party, they consulted it all over, and at last Lincoln came to the conclusion that he would answer, so he came up to Freeport last Friday."
Now, that statement altogether furnishes a subject for philosophical contemplation. I have been treating it in that way, and I have really come to the conclusion that I can explain it in no other way than by believing the Judge is crazy. If he was in his right mind I cannot conceive how he would have risked disgusting the four or five thousand of his own friends who stood there and knew, as to my having been carried from the platform, that there was not a word of truth in it.
[Judge DOUGLAS: Did n't they carry you off?]
There that question illustrates the character of this man Douglas exactly. He smiles now, and says, "Did n't they carry you off?" but he said then "he had to be carried off"; and he said it to convince the country that he had so completely broken me down by his speech that I had to be carried away. Now he seeks to dodge it, and asks, "Did n't they carry you off?" Yes, they did. But, Judge Douglas, why didn't you tell the truth? I would like to know why you did n't tell the truth about it. And then again "He laid up seven days." He put this in print for the people of the country to read as a serious document. I think if he had been in his sober senses he would not have risked that barefacedness in the presence of thousands of his own friends who knew that I made speeches within six of the seven days at Henry, Marshall County, Augusta, Hancock County, and Macomb, McDonough County, including all the necessary travel to meet him again at Freeport at the end of the six days. Now I say there is no charitable way to look at that statement, except to conclude that he is actually crazy. There is another thing in that statement that alarmed me very greatly as he states it, that he was going to "trot me down to Egypt." Thereby he would have you infer that I would not come to Egypt unless he forced me—that I could not be got here unless he, giant-like, had hauled me down here. That statement he makes, too, in the teeth of the knowledge that I had made the stipulation to come down here and that he himself had been very reluctant to enter into the stipulation. More than all this: Judge Douglas, when he made that statement, must have been crazy and wholly out of his sober senses, or else he would have known that when he got me down here, that promise—that windy promise—of his powers to annihilate me, would n't amount to anything. Now, how little do I look like being carried away trembling? Let the Judge go on; and after he is done with his half-hour, I want you all, if I can't go home myself, to let me stay and rot here; and if anything happens to the Judge, if I cannot carry him to the hotel and put him to bed, let me stay here and rot. I say, then, here is something extraordinary in this statement. I ask you if you know any other living man who would make such a statement? I will ask my friend Casey, over there, if he would do such a thing? Would he send that out and have his men take it as the truth? Did the Judge talk of trotting me down to Egypt to scare me to death? Why, I know this people better than he does. I was raised just a little east of here. I am a part of this people. But the Judge was raised farther north, and perhaps he has some horrid idea of what this people might be induced to do. But really I have talked about this matter perhaps longer than I ought, for it is no great thing; and yet the smallest are often the most difficult things to deal with. The Judge has set about seriously trying to make the impression that when we meet at different places I am literally in his clutches—that I am a poor, helpless, decrepit mouse, and that I can do nothing at all. This is one of the ways he has taken to create that impression. I don't know any other way to meet it except this. I don't want to quarrel with him—to call him a liar; but when I come square up to him I don't know what else to call him if I must tell the truth out. I want to be at peace, and reserve all my fighting powers for necessary occasions. My time now is very nearly out, and I give up the trifle that is left to the Judge, to let him set my knees trembling again, if he can.
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
THE LINCOLN-DOUGLAS DEBATES II
LINCOLN AND DOUGLAS FOURTH DEBATE, AT CHARLESTON, SEPTEMBER 18, 1858.
FIFTH JOINT DEBATE, AT GALESBURGH, OCTOBER 7, 1858
SIXTH JOINT DEBATE, AT QUINCY, OCTOBER 13, 1858.
LAST DEBATE, AT ALTON, OCTOBER 15, 1858
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—It will be very difficult for an audience so large as this to hear distinctly what a speaker says, and consequently it is important that as profound silence be preserved as possible.
While I was at the hotel to-day, an elderly gentleman called upon me to know whether I was really in favor of producing a perfect equality between the negroes and white people. While I had not proposed to myself on this occasion to say much on that subject, yet as the question was asked me I thought I would occupy perhaps five minutes in saying something in regard to it. I will say, then, that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of bringing about in any way the social and political equality of the white and black races; that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of making voters or jurors of negroes, nor of qualifying them to hold office, nor to intermarry with white people; and I will say, in addition to this, that there is a physical difference between the white and black races which I believe will forever forbid the two races living together on terms of social and political equality. And in as much as they cannot so live, while they do remain together there must be the position of superior and inferior, and I as much as any other man am in favor of having the superior position assigned to the white race. I say upon this occasion I do not perceive that because the white man is to have the superior position the negro should be denied everything. I do not understand that because I do not want a negro woman for a slave I must necessarily want her for a wife. My understanding is that I can just let her alone. I am now in my fiftieth year, and I certainly never have had a black woman for either a slave or a wife. So it seems to me quite possible for us to get along without making either slaves or wives of negroes. I will add to this that I have never seen, to my knowledge, a man, woman, or child who was in favor of producing a perfect equality, social and political, between negroes and white men. I recollect of but one distinguished instance that I ever heard of so frequently as to be entirely satisfied of its correctness, and that is the case of Judge Douglas's old friend Colonel Richard M. Johnson. I will also add to the remarks I have made (for I am not going to enter at large upon this subject), that I have never had the least apprehension that I or my friends would marry negroes if there was no law to keep them from it; but as Judge Douglas and his friends seem to be in great apprehension that they might, if there were no law to keep them from it, I give him the most solemn pledge that I will to the very last stand by the law of this State which forbids the marrying of white people with negroes. I will add one further word, which is this: that I do not understand that there is any place where an alteration of the social and political relations of the negro and the white man can be made, except in the State Legislature,—not in the Congress of the United States; and as I do not really apprehend the approach of any such thing myself, and as Judge Douglas seems to be in constant horror that some such danger is rapidly approaching, I propose as the best means to prevent it that the Judge be kept at home, and placed in the State Legislature to fight the measure. I do not propose dwelling longer at this time on this subject.
When Judge Trumbull, our other Senator in Congress, returned to Illinois in the month of August, he made a speech at Chicago, in which he made what may be called a charge against Judge Douglas, which I understand proved to be very offensive to him. The Judge was at that time out upon one of his speaking tours through the country, and when the news of it reached him, as I am informed, he denounced Judge Trumbull in rather harsh terms for having said what he did in regard to that matter. I was traveling at that time, and speaking at the same places with Judge Douglas on subsequent days, and when I heard of what Judge Trumbull had said of Douglas, and what Douglas had said back again, I felt that I was in a position where I could not remain entirely silent in regard to the matter. Consequently, upon two or three occasions I alluded to it, and alluded to it in no other wise than to say that in regard to the charge brought by Trumbull against Douglas, I personally knew nothing, and sought to say nothing about it; that I did personally know Judge Trumbull; that I believed him to be a man of veracity; that I believed him to be a man of capacity sufficient to know very well whether an assertion he was making, as a conclusion drawn from a set of facts, was true or false; and as a conclusion of my own from that, I stated it as my belief if Trumbull should ever be called upon, he would prove everything he had said. I said this upon two or three occasions. Upon a subsequent occasion, Judge Trumbull spoke again before an audience at Alton, and upon that occasion not only repeated his charge against Douglas, but arrayed the evidence he relied upon to substantiate it. This speech was published at length; and subsequently at Jacksonville Judge Douglas alluded to the matter. In the course of his speech, and near the close of it, he stated in regard to myself what I will now read:
"Judge Douglas proceeded to remark that he should not hereafter occupy his time in refuting such charges made by Trumbull, but that, Lincoln having indorsed the character of Trumbull for veracity, he should hold him (Lincoln) responsible for the slanders."
I have done simply what I have told you, to subject me to this invitation to notice the charge. I now wish to say that it had not originally been my purpose to discuss that matter at all But in-as-much as it seems to be the wish of Judge Douglas to hold me responsible for it, then for once in my life I will play General Jackson, and to the just extent I take the responsibility.
I wish to say at the beginning that I will hand to the reporters that portion of Judge Trumbull's Alton speech which was devoted to this matter, and also that portion of Judge Douglas's speech made at Jacksonville in answer to it. I shall thereby furnish the readers of this debate with the complete discussion between Trumbull and Douglas. I cannot now read them, for the reason that it would take half of my first hour to do so. I can only make some comments upon them. Trumbull's charge is in the following words:
"Now, the charge is, that there was a plot entered into to have a constitution formed for Kansas, and put in force, without giving the people an opportunity to vote upon it, and that Mr. Douglas was in the plot."
I will state, without quoting further, for all will have an opportunity of reading it hereafter, that Judge Trumbull brings forward what he regards as sufficient evidence to substantiate this charge.
It will be perceived Judge Trumbull shows that Senator Bigler, upon the floor of the Senate, had declared there had been a conference among the senators, in which conference it was determined to have an enabling act passed for the people of Kansas to form a constitution under, and in this conference it was agreed among them that it was best not to have a provision for submitting the constitution to a vote of the people after it should be formed. He then brings forward to show, and showing, as he deemed, that Judge Douglas reported the bill back to the Senate with that clause stricken out. He then shows that there was a new clause inserted into the bill, which would in its nature prevent a reference of the constitution back for a vote of the people,—if, indeed, upon a mere silence in the law, it could be assumed that they had the right to vote upon it. These are the general statements that he has made.
I propose to examine the points in Judge Douglas's speech in which he attempts to answer that speech of Judge Trumbull's. When you come to examine Judge Douglas's speech, you will find that the first point he makes is:
"Suppose it were true that there was such a change in the bill, and that I struck it out,—is that a proof of a plot to force a constitution upon them against their will?"
His striking out such a provision, if there was such a one in the bill, he argues, does not establish the proof that it was stricken out for the purpose of robbing the people of that right. I would say, in the first place, that that would be a most manifest reason for it. It is true, as Judge Douglas states, that many Territorial bills have passed without having such a provision in them. I believe it is true, though I am not certain, that in some instances constitutions framed under such bills have been submitted to a vote of the people with the law silent upon the subject; but it does not appear that they once had their enabling acts framed with an express provision for submitting the constitution to be framed to a vote of the people, then that they were stricken out when Congress did not mean to alter the effect of the law. That there have been bills which never had the provision in, I do not question; but when was that provision taken out of one that it was in? More especially does the evidence tend to prove the proposition that Trumbull advanced, when we remember that the provision was stricken out of the bill almost simultaneously with the time that Bigler says there was a conference among certain senators, and in which it was agreed that a bill should be passed leaving that out. Judge Douglas, in answering Trumbull, omits to attend to the testimony of Bigler, that there was a meeting in which it was agreed they should so frame the bill that there should be no submission of the constitution to a vote of the people. The Judge does not notice this part of it. If you take this as one piece of evidence, and then ascertain that simultaneously Judge Douglas struck out a provision that did require it to be submitted, and put the two together, I think it will make a pretty fair show of proof that Judge Douglas did, as Trumbull says, enter into a plot to put in force a constitution for Kansas, without giving the people any opportunity of voting upon it.
But I must hurry on. The next proposition that Judge Douglas puts is this:
"But upon examination it turns out that the Toombs bill never did contain a clause requiring the constitution to be submitted."
This is a mere question of fact, and can be determined by evidence. I only want to ask this question: Why did not Judge Douglas say that these words were not stricken out of the Toomb's bill, or this bill from which it is alleged the provision was stricken out,—a bill which goes by the name of Toomb's, because he originally brought it forward? I ask why, if the Judge wanted to make a direct issue with Trumbull, did he not take the exact proposition Trumbull made in his speech, and say it was not stricken out? Trumbull has given the exact words that he says were in the Toomb's bill, and he alleges that when the bill came back, they were stricken out. Judge Douglas does not say that the words which Trumbull says were stricken out were not so stricken out, but he says there was no provision in the Toomb's bill to submit the constitution to a vote of the people. We see at once that he is merely making an issue upon the meaning of the words. He has not undertaken to say that Trumbull tells a lie about these words being stricken out, but he is really, when pushed up to it, only taking an issue upon the meaning of the words. Now, then, if there be any issue upon the meaning of the words, or if there be upon the question of fact as to whether these words were stricken out, I have before me what I suppose to be a genuine copy of the Toomb's bill, in which it can be shown that the words Trumbull says were in it were, in fact, originally there. If there be any dispute upon the fact, I have got the documents here to show they were there. If there be any controversy upon the sense of the words,—whether these words which were stricken out really constituted a provision for submitting the matter to a vote of the people,—as that is a matter of argument, I think I may as well use Trumbull's own argument. He says that the proposition is in these words:
"That the following propositions be and the same are hereby offered to the said Convention of the people of Kansas when formed, for their free acceptance or rejection; which, if accepted by the Convention and ratified by the people at the election for the adoption of the constitution, shall be obligatory upon the United States and the said State of Kansas."
Now, Trumbull alleges that these last words were stricken out of the bill when it came back, and he says this was a provision for submitting the constitution to a vote of the people; and his argument is this:
"Would it have been possible to ratify the land propositions at the election for the adoption of the constitution, unless such an election was to be held?"
This is Trumbull's argument. Now, Judge Douglas does not meet the charge at all, but he stands up and says there was no such proposition in that bill for submitting the constitution to be framed to a vote of the people. Trumbull admits that the language is not a direct provision for submitting it, but it is a provision necessarily implied from another provision. He asks you how it is possible to ratify the land proposition at the election for the adoption of the constitution, if there was no election to be held for the adoption of the constitution. And he goes on to show that it is not any less a law because the provision is put in that indirect shape than it would be if it were put directly. But I presume I have said enough to draw attention to this point, and I pass it by also.
Another one of the points that Judge Douglas makes upon Trumbull, and at very great length, is, that Trumbull, while the bill was pending, said in a speech in the Senate that he supposed the constitution to be made would have to be submitted to the people. He asks, if Trumbull thought so then, what ground is there for anybody thinking otherwise now? Fellow-citizens, this much may be said in reply: That bill had been in the hands of a party to which Trumbull did not belong. It had been in the hands of the committee at the head of which Judge Douglas stood. Trumbull perhaps had a printed copy of the original Toomb's bill. I have not the evidence on that point except a sort of inference I draw from the general course of business there. What alterations, or what provisions in the way of altering, were going on in committee, Trumbull had no means of knowing, until the altered bill was reported back. Soon afterwards, when it was reported back, there was a discussion over it, and perhaps Trumbull in reading it hastily in the altered form did not perceive all the bearings of the alterations. He was hastily borne into the debate, and it does not follow that because there was something in it Trumbull did not perceive, that something did not exist. More than this, is it true that what Trumbull did can have any effect on what Douglas did? Suppose Trumbull had been in the plot with these other men, would that let Douglas out of it? Would it exonerate Douglas that Trumbull did n't then perceive he was in the plot? He also asks the question: Why did n't Trumbull propose to amend the bill, if he thought it needed any amendment? Why, I believe that everything Judge Trumbull had proposed, particularly in connection with this question of Kansas and Nebraska, since he had been on the floor of the Senate, had been promptly voted down by Judge Douglas and his friends. He had no promise that an amendment offered by him to anything on this subject would receive the slightest consideration. Judge Trumbull did bring to the notice of the Senate at that time the fact that there was no provision for submitting the constitution about to be made for the people of Kansas to a vote of the people. I believe I may venture to say that Judge Douglas made some reply to this speech of Judge Trumbull's, but he never noticed that part of it at all. And so the thing passed by. I think, then, the fact that Judge Trumbull offered no amendment does not throw much blame upon him; and if it did, it does not reach the question of fact as to what Judge Douglas was doing. I repeat, that if Trumbull had himself been in the plot, it would not at all relieve the others who were in it from blame. If I should be indicted for murder, and upon the trial it should be discovered that I had been implicated in that murder, but that the prosecuting witness was guilty too, that would not at all touch the question of my crime. It would be no relief to my neck that they discovered this other man who charged the crime upon me to be guilty too.
Another one of the points Judge Douglas makes upon Judge Trumbull is, that when he spoke in Chicago he made his charge to rest upon the fact that the bill had the provision in it for submitting the constitution to a vote of the people when it went into his Judge Douglas's hands, that it was missing when he reported it to the Senate, and that in a public speech he had subsequently said the alterations in the bill were made while it was in committee, and that they were made in consultation between him (Judge Douglas) and Toomb's. And Judge Douglas goes on to comment upon the fact of Trumbull's adducing in his Alton speech the proposition that the bill not only came back with that proposition stricken out, but with another clause and another provision in it, saying that "until the complete execution of this Act there shall be no election in said Territory,"—which, Trumbull argued, was not only taking the provision for submitting to a vote of the people out of the bill, but was adding an affirmative one, in that it prevented the people from exercising the right under a bill that was merely silent on the question. Now, in regard to what he says, that Trumbull shifts the issue, that he shifts his ground,—and I believe he uses the term that, "it being proven false, he has changed ground," I call upon all of you, when you come to examine that portion of Trumbull's speech (for it will make a part of mine), to examine whether Trumbull has shifted his ground or not. I say he did not shift his ground, but that he brought forward his original charge and the evidence to sustain it yet more fully, but precisely as he originally made it. Then, in addition thereto, he brought in a new piece of evidence. He shifted no ground. He brought no new piece of evidence inconsistent with his former testimony; but he brought a new piece, tending, as he thought, and as I think, to prove his proposition. To illustrate: A man brings an accusation against another, and on trial the man making the charge introduces A and B to prove the accusation. At a second trial he introduces the same witnesses, who tell the same story as before, and a third witness, who tells the same thing, and in addition gives further testimony corroborative of the charge. So with Trumbull. There was no shifting of ground, nor inconsistency of testimony between the new piece of evidence and what he originally introduced.
But Judge Douglas says that he himself moved to strike out that last provision of the bill, and that on his motion it was stricken out and a substitute inserted. That I presume is the truth. I presume it is true that that last proposition was stricken out by Judge Douglas. Trumbull has not said it was not; Trumbull has himself said that it was so stricken out. He says: "I am now speaking of the bill as Judge Douglas reported it back. It was amended somewhat in the Senate before it passed, but I am speaking of it as he brought it back." Now, when Judge Douglas parades the fact that the provision was stricken out of the bill when it came back, he asserts nothing contrary to what Trumbull alleges. Trumbull has only said that he originally put it in, not that he did not strike it out. Trumbull says it was not in the bill when it went to the committee. When it came back it was in, and Judge Douglas said the alterations were made by him in consultation with Toomb's. Trumbull alleges, therefore, as his conclusion, that Judge Douglas put it in. Then, if Douglas wants to contradict Trumbull and call him a liar, let him say he did not put it in, and not that he did n't take it out again. It is said that a bear is sometimes hard enough pushed to drop a cub; and so I presume it was in this case. I presume the truth is that Douglas put it in, and afterward took it out. That, I take it, is the truth about it. Judge Trumbull says one thing, Douglas says another thing, and the two don't contradict one another at all. The question is, what did he put it in for? In the first place, what did he take the other provision out of the bill for,—the provision which Trumbull argued was necessary for submitting the constitution to a vote of the people? What did he take that out for; and, having taken it out, what did he put this in for? I say that in the run of things it is not unlikely forces conspire to render it vastly expedient for Judge Douglas to take that latter clause out again. The question that Trumbull has made is that Judge Douglas put it in; and he don't meet Trumbull at all unless he denies that.
In the clause of Judge Douglas's speech upon this subject he uses this language toward Judge Trumbull. He says:
"He forges his evidence from beginning to end; and by falsifying the record, he endeavors to bolster up his false charge."
Well, that is a pretty serious statement—Trumbull forges his evidence from beginning to end. Now, upon my own authority I say that it is not true. What is a forgery? Consider the evidence that Trumbull has brought forward. When you come to read the speech, as you will be able to, examine whether the evidence is a forgery from beginning to end. He had the bill or document in his hand like that [holding up a paper]. He says that is a copy of the Toomb's bill,—the amendment offered by Toomb's. He says that is a copy of the bill as it was introduced and went into Judge Douglas's hands. Now, does Judge Douglas say that is a forgery? That is one thing Trumbull brought forward. Judge Douglas says he forged it from beginning to end! That is the "beginning," we will say. Does Douglas say that is a forgery? Let him say it to-day, and we will have a subsequent examination upon this subject. Trumbull then holds up another document like this, and says that is an exact copy of the bill as it came back in the amended form out of Judge Douglas's hands. Does Judge Douglas say that is a forgery? Does he say it in his general sweeping charge? Does he say so now? If he does not, then take this Toomb's bill and the bill in the amended form, and it only needs to compare them to see that the provision is in the one and not in the other; it leaves the inference inevitable that it was taken out.
But, while I am dealing with this question, let us see what Trumbull's other evidence is. One other piece of evidence I will read. Trumbull says there are in this original Toomb's bill these words:
"That the following propositions be and the same are hereby offered to the said Convention of the people of Kansas, when formed, for their free acceptance or rejection; which, if accepted by the Convention and ratified by the people at the election for the adoption of the constitution, shall be obligatory upon the United States and the said State of Kansas."
Now, if it is said that this is a forgery, we will open the paper here and see whether it is or not. Again, Trumbull says, as he goes along, that Mr. Bigler made the following statement in his place in the Senate, December 9, 1857:
"I was present when that subject was discussed by senators before the bill was introduced, and the question was raised and discussed, whether the constitution, when formed, should be submitted to a vote of the people. It was held by those most intelligent on the subject that, in view of all the difficulties surrounding that Territory, the danger of any experiment at that time of a popular vote, it would be better there should be no such provision in the Toomb's bill; and it was my understanding, in all the intercourse I had, that the Convention would make a constitution, and send it here, without submitting it to the popular vote."
Then Trumbull follows on:
"In speaking of this meeting again on the 21st December, 1857 [Congressional Globe, same vol., page 113], Senator Bigler said:
"'Nothing was further from my mind than to allude to any social or confidential interview. The meeting was not of that character. Indeed, it was semi-official, and called to promote the public good. My recollection was clear that I left the conference under the impression that it had been deemed best to adopt measures to admit Kansas as a State through the agency of one popular election, and that for delegates to this Convention. This impression was stronger because I thought the spirit of the bill infringed upon the doctrine of non-intervention, to which I had great aversion; but with the hope of accomplishing a great good, and as no movement had been made in that direction in the Territory, I waived this objection, and concluded to support the measure. I have a few items of testimony as to the correctness of these impressions, and with their submission I shall be content. I have before me the bill reported by the senator from Illinois on the 7th of March, 1856, providing for the admission of Kansas as a State, the third section of which reads as follows:
"That the following propositions be, and the same are hereby offered to the said Convention of the people of Kansas, when formed, for their free acceptance or rejection; which, if accepted by the Convention and ratified by the people at the election for the adoption of the constitution, shall be obligatory upon the United States and the said State of Kansas."
The bill read in his place by the senator from Georgia on the 25th of June, and referred to the Committee on Territories, contained the same section word for word. Both these bills were under consideration at the conference referred to; but, sir, when the senator from Illinois reported the Toombs bill to the Senate with amendments, the next morning, it did not contain that portion of the third section which indicated to the Convention that the constitution should be approved by the people. The words "and ratified by the people at the election for the adoption of the constitution" had been stricken out.
Now, these things Trumbull says were stated by Bigler upon the floor of the Senate on certain days, and that they are recorded in the Congressional Globe on certain pages. Does Judge Douglas say this is a forgery? Does he say there is no such thing in the Congressional Globe? What does he mean when he says Judge Trumbull forges his evidence from beginning to end? So again he says in another place that Judge Douglas, in his speech, December 9, 1857 (Congressional Globe, part I., page 15), stated:
"That during the last session of Congress, I [Mr. Douglas] reported a bill from the Committee on Territories, to authorize the people of Kansas to assemble and form a constitution for themselves. Subsequently the senator from Georgia [Mr. Toombs] brought forward a substitute for my bill, which, after having been modified by him and myself in consultation, was passed by the Senate."
Now, Trumbull says this is a quotation from a speech of Douglas, and is recorded in the Congressional Globe. Is it a forgery? Is it there or not? It may not be there, but I want the Judge to take these pieces of evidence, and distinctly say they are forgeries if he dare do it.
[A voice: "He will."]
Well, sir, you had better not commit him. He gives other quotations,—another from Judge Douglas. He says:
"I will ask the senator to show me an intimation, from any one member of the Senate, in the whole debate on the Toombs bill, and in the Union, from any quarter, that the constitution was not to be submitted to the people. I will venture to say that on all sides of the chamber it was so understood at the time. If the opponents of the bill had understood it was not, they would have made the point on it; and if they had made it, we should certainly have yielded to it, and put in the clause. That is a discovery made since the President found out that it was not safe to take it for granted that that would be done, which ought in fairness to have been done."
Judge Trumbull says Douglas made that speech, and it is recorded. Does Judge Douglas say it is a forgery, and was not true? Trumbull says somewhere, and I propose to skip it, but it will be found by any one who will read this debate, that he did distinctly bring it to the notice of those who were engineering the bill, that it lacked that provision; and then he goes on to give another quotation from Judge Douglas, where Judge Trumbull uses this language:
"Judge Douglas, however, on the same day and in the same debate, probably recollecting or being reminded of the fact that I had objected to the Toombs bill when pending that it did not provide for a submission of the constitution to the people, made another statement, which is to be found in the same volume of the Globe, page 22, in which he says: 'That the bill was silent on this subject was true, and my attention was called to that about the time it was passed; and I took the fair construction to be, that powers not delegated were reserved, and that of course the constitution would be submitted to the people.'
"Whether this statement is consistent with the statement just before made, that had the point been made it would have been yielded to, or that it was a new discovery, you will determine."
So I say. I do not know whether Judge Douglas will dispute this, and yet maintain his position that Trumbull's evidence "was forged from beginning to end." I will remark that I have not got these Congressional Globes with me. They are large books, and difficult to carry about, and if Judge Douglas shall say that on these points where Trumbull has quoted from them there are no such passages there, I shall not be able to prove they are there upon this occasion, but I will have another chance. Whenever he points out the forgery and says, "I declare that this particular thing which Trumbull has uttered is not to be found where he says it is," then my attention will be drawn to that, and I will arm myself for the contest, stating now that I have not the slightest doubt on earth that I will find every quotation just where Trumbull says it is. Then the question is, How can Douglas call that a forgery? How can he make out that it is a forgery? What is a forgery? It is the bringing forward something in writing or in print purporting to be of certain effect when it is altogether untrue. If you come forward with my note for one hundred dollars when I have never given such a note, there is a forgery. If you come forward with a letter purporting to be written by me which I never wrote, there is another forgery. If you produce anything in writing or in print saying it is so and so, the document not being genuine, a forgery has been committed. How do you make this forgery when every piece of the evidence is genuine? If Judge Douglas does say these documents and quotations are false and forged, he has a full right to do so; but until he does it specifically, we don't know how to get at him. If he does say they are false and forged, I will then look further into it, and presume I can procure the certificates of the proper officers that they are genuine copies. I have no doubt each of these extracts will be found exactly where Trumbull says it is. Then I leave it to you if Judge Douglas, in making his sweeping charge that Judge Trumbull's evidence is forged from beginning to end, at all meets the case,—if that is the way to get at the facts. I repeat again, if he will point out which one is a forgery, I will carefully examine it, and if it proves that any one of them is really a forgery, it will not be me who will hold to it any longer. I have always wanted to deal with everyone I meet candidly and honestly. If I have made any assertion not warranted by facts, and it is pointed out to me, I will withdraw it cheerfully. But I do not choose to see Judge Trumbull calumniated, and the evidence he has brought forward branded in general terms "a forgery from beginning to end." This is not the legal way of meeting a charge, and I submit it to all intelligent persons, both friends of Judge Douglas and of myself, whether it is.
The point upon Judge Douglas is this: The bill that went into his hands had the provision in it for a submission of the constitution to the people; and I say its language amounts to an express provision for a submission, and that he took the provision out. He says it was known that the bill was silent in this particular; but I say, Judge Douglas, it was not silent when you got it. It was vocal with the declaration, when you got it, for a submission of the constitution to the people. And now, my direct question to Judge Douglas is, to answer why, if he deemed the bill silent on this point, he found it necessary to strike out those particular harmless words. If he had found the bill silent and without this provision, he might say what he does now. If he supposes it was implied that the constitution would be submitted to a vote of the people, how could these two lines so encumber the statute as to make it necessary to strike them out? How could he infer that a submission was still implied, after its express provision had been stricken from the bill? I find the bill vocal with the provision, while he silenced it. He took it out, and although he took out the other provision preventing a submission to a vote of the people, I ask, Why did you first put it in? I ask him whether he took the original provision out, which Trumbull alleges was in the bill. If he admits that he did take it, I ask him what he did it for. It looks to us as if he had altered the bill. If it looks differently to him,—if he has a different reason for his action from the one we assign him—he can tell it. I insist upon knowing why he made the bill silent upon that point when it was vocal before he put his hands upon it.
I was told, before my last paragraph, that my time was within three minutes of being out. I presume it is expired now; I therefore close.
FELLOW-CITIZENS: It follows as a matter of course that a half-hour answer to a speech of an hour and a half can be but a very hurried one. I shall only be able to touch upon a few of the points suggested by Judge Douglas, and give them a brief attention, while I shall have to totally omit others for the want of time.
Judge Douglas has said to you that he has not been able to get from me an answer to the question whether I am in favor of negro citizenship. So far as I know the Judge never asked me the question before. He shall have no occasion to ever ask it again, for I tell him very frankly that I am not in favor of negro citizenship. This furnishes me an occasion for saying a few words upon the subject. I mentioned in a certain speech of mine, which has been printed, that the Supreme Court had decided that a negro could not possibly be made a citizen; and without saying what was my ground of complaint in regard to that, or whether I had any ground of complaint, Judge Douglas has from that thing manufactured nearly everything that he ever says about my disposition to produce an equality between the negroes and the white people. If any one will read my speech, he will find I mentioned that as one of the points decided in the course of the Supreme Court opinions, but I did not state what objection I had to it. But Judge Douglas tells the people what my objection was when I did not tell them myself. Now, my opinion is that the different States have the power to make a negro a citizen under the Constitution of the United States if they choose. The Dred Scott decision decides that they have not that power. If the State of Illinois had that power, I should be opposed to the exercise of it. That is all I have to say about it.
Judge Douglas has told me that he heard my speeches north and my speeches south; that he had heard me at Ottawa and at Freeport in the north and recently at Jonesboro in the south, and there was a very different cast of sentiment in the speeches made at the different points. I will not charge upon Judge Douglas that he wilfully misrepresents me, but I call upon every fair-minded man to take these speeches and read them, and I dare him to point out any difference between my speeches north and south. While I am here perhaps I ought to say a word, if I have the time, in regard to the latter portion of the Judge's speech, which was a sort of declamation in reference to my having said I entertained the belief that this government would not endure half slave and half free. I have said so, and I did not say it without what seemed to me to be good reasons. It perhaps would require more time than I have now to set forth these reasons in detail; but let me ask you a few questions. Have we ever had any peace on this slavery question? When are we to have peace upon it, if it is kept in the position it now occupies? How are we ever to have peace upon it? That is an important question. To be sure, if we will all stop, and allow Judge Douglas and his friends to march on in their present career until they plant the institution all over the nation, here and wherever else our flag waves, and we acquiesce in it, there will be peace. But let me ask Judge Douglas how he is going to get the people to do that? They have been wrangling over this question for at least forty years. This was the cause of the agitation resulting in the Missouri Compromise; this produced the troubles at the annexation of Texas, in the acquisition of the territory acquired in the Mexican War. Again, this was the trouble which was quieted by the Compromise of 1850, when it was settled "forever" as both the great political parties declared in their National Conventions. That "forever" turned out to be just four years, when Judge Douglas himself reopened it. When is it likely to come to an end? He introduced the Nebraska Bill in 1854 to put another end to the slavery agitation. He promised that it would finish it all up immediately, and he has never made a speech since, until he got into a quarrel with the President about the Lecompton Constitution, in which he has not declared that we are just at the end of the slavery agitation. But in one speech, I think last winter, he did say that he did n't quite see when the end of the slavery agitation would come. Now he tells us again that it is all over and the people of Kansas have voted down the Lecompton Constitution. How is it over? That was only one of the attempts at putting an end to the slavery agitation—one of these "final settlements." Is Kansas in the Union? Has she formed a constitution that she is likely to come in under? Is not the slavery agitation still an open question in that Territory? Has the voting down of that constitution put an end to all the trouble? Is that more likely to settle it than every one of these previous attempts to settle the slavery agitation? Now, at this day in the history of the world we can no more foretell where the end of this slavery agitation will be than we can see the end of the world itself. The Nebraska-Kansas Bill was introduced four years and a half ago, and if the agitation is ever to come to an end we may say we are four years and a half nearer the end. So, too, we can say we are four years and a half nearer the end of the world, and we can just as clearly see the end of the world as we can see the end of this agitation. The Kansas settlement did not conclude it. If Kansas should sink to-day, and leave a great vacant space in the earth's surface, this vexed question would still be among us. I say, then, there is no way of putting an end to the slavery agitation amongst us but to put it back upon the basis where our fathers placed it; no way but to keep it out of our new Territories,—to restrict it forever to the old States where it now exists. Then the public mind will rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction. That is one way of putting an end to the slavery agitation.
The other way is for us to surrender and let Judge Douglas and his friends have their way and plant slavery over all the States; cease speaking of it as in any way a wrong; regard slavery as one of the common matters of property, and speak of negroes as we do of our horses and cattle. But while it drives on in its state of progress as it is now driving, and as it has driven for the last five years, I have ventured the opinion, and I say to-day, that we will have no end to the slavery agitation until it takes one turn or the other. I do not mean that when it takes a turn toward ultimate extinction it will be in a day, nor in a year, nor in two years. I do not suppose that in the most peaceful way ultimate extinction would occur in less than a hundred years at least; but that it will occur in the best way for both races, in God's own good time, I have no doubt. But, my friends, I have used up more of my time than I intended on this point.
Now, in regard to this matter about Trumbull and myself having made a bargain to sell out the entire Whig and Democratic parties in 1854: Judge Douglas brings forward no evidence to sustain his charge, except the speech Matheny is said to have made in 1856, in which he told a cock-and-bull story of that sort, upon the same moral principles that Judge Douglas tells it here to-day. This is the simple truth. I do not care greatly for the story, but this is the truth of it: and I have twice told Judge Douglas to his face that from beginning to end there is not one word of truth in it. I have called upon him for the proof, and he does not at all meet me as Trumbull met him upon that of which we were just talking, by producing the record. He did n't bring the record because there was no record for him to bring. When he asks if I am ready to indorse Trumbull's veracity after he has broken a bargain with me, I reply that if Trumbull had broken a bargain with me I would not be likely to indorse his veracity; but I am ready to indorse his veracity because neither in that thing, nor in any other, in all the years that I have known Lyman Trumbull, have I known him to fail of his word or tell a falsehood large or small. It is for that reason that I indorse Lyman Trumbull.
[Mr. JAMES BROWN (Douglas postmaster): "What does Ford's History say about him?"]
Some gentleman asks me what Ford's History says about him. My own recollection is that Ford speaks of Trumbull in very disrespectful terms in several portions of his book, and that he talks a great deal worse of Judge Douglas. I refer you, sir, to the History for examination.
Judge Douglas complains at considerable length about a disposition on the part of Trumbull and myself to attack him personally. I want to attend to that suggestion a moment. I don't want to be unjustly accused of dealing illiberally or unfairly with an adversary, either in court or in a political canvass or anywhere else. I would despise myself if I supposed myself ready to deal less liberally with an adversary than I was willing to be treated myself. Judge Douglas in a general way, without putting it in a direct shape, revives the old charge against me in reference to the Mexican War. He does not take the responsibility of putting it in a very definite form, but makes a general reference to it. That charge is more than ten years old. He complains of Trumbull and myself because he says we bring charges against him one or two years old. He knows, too, that in regard to the Mexican War story the more respectable papers of his own party throughout the State have been compelled to take it back and acknowledge that it was a lie.
[Here Mr. LINCOLN turned to the crowd on the platform, and, selecting HON. ORLANDO B. FICKLIN, led him forward and said:]
I do not mean to do anything with Mr. FICKLIN except to present his face and tell you that he personally knows it to be a lie! He was a member of Congress at the only time I was in Congress, and [FICKLIN] knows that whenever there was an attempt to procure a vote of mine which would indorse the origin and justice of the war, I refused to give such indorsement and voted against it; but I never voted against the supplies for the army, and he knows, as well as Judge Douglas, that whenever a dollar was asked by way of compensation or otherwise for the benefit of the soldiers I gave all the votes that FICKLIN or Douglas did, and perhaps more.
[Mr. FICKLIN: My friends, I wish to say this in reference to the matter: Mr. Lincoln and myself are just as good personal friends as Judge Douglas and myself. In reference to this Mexican War, my recollection is that when Ashmun's resolution [amendment] was offered by Mr. Ashmun of Massachusetts, in which he declared that the Mexican War was unnecessary and unconstitutionally commenced by the President-my recollection is that Mr. Lincoln voted for that resolution.]
That is the truth. Now, you all remember that was a resolution censuring the President for the manner in which the war was begun. You know they have charged that I voted against the supplies, by which I starved the soldiers who were out fighting the battles of their country. I say that FICKLIN knows it is false. When that charge was brought forward by the Chicago Times, the Springfield Register [Douglas's organ] reminded the Times that the charge really applied to John Henry; and I do know that John Henry is now making speeches and fiercely battling for Judge Douglas. If the Judge now says that he offers this as a sort of setoff to what I said to-day in reference to Trumbull's charge, then I remind him that he made this charge before I said a word about Trumbull's. He brought this forward at Ottawa, the first time we met face to face; and in the opening speech that Judge Douglas made he attacked me in regard to a matter ten years old. Is n't he a pretty man to be whining about people making charges against him only two years old!
The Judge thinks it is altogether wrong that I should have dwelt upon this charge of Trumbull's at all. I gave the apology for doing so in my opening speech. Perhaps it did n't fix your attention. I said that when Judge Douglas was speaking at place—where I spoke on the succeeding day he used very harsh language about this charge. Two or three times afterward I said I had confidence in Judge Trumbull's veracity and intelligence; and my own opinion was, from what I knew of the character of Judge Trumbull, that he would vindicate his position and prove whatever he had stated to be true. This I repeated two or three times; and then I dropped it, without saying anything more on the subject for weeks—perhaps a month. I passed it by without noticing it at all till I found, at Jacksonville, Judge Douglas in the plenitude of his power is not willing to answer Trumbull and let me alone, but he comes out there and uses this language: "He should not hereafter occupy his time in refuting such charges made by Trumbull but that, Lincoln having indorsed the character of Trumbull for veracity, he should hold him [Lincoln] responsible for the slanders." What was Lincoln to do? Did he not do right, when he had the fit opportunity of meeting Judge Douglas here, to tell him he was ready for the responsibility? I ask a candid audience whether in doing thus Judge Douglas was not the assailant rather than I? Here I meet him face to face, and say I am ready to take the responsibility, so far as it rests on me.
Having done so I ask the attention of this audience to the question whether I have succeeded in sustaining the charge, and whether Judge Douglas has at all succeeded in rebutting it? You all heard me call upon him to say which of these pieces of evidence was a forgery. Does he say that what I present here as a copy of the original Toombs bill is a forgery? Does he say that what I present as a copy of the bill reported by himself is a forgery, or what is presented as a transcript from the Globe of the quotations from Bigler's speech is a forgery? Does he say the quotations from his own speech are forgeries? Does he say this transcript from Trumbull's speech is a forgery?
["He didn't deny one of them."]
I would then like to know how it comes about that when each piece of a story is true the whole story turns out false. I take it these people have some sense; they see plainly that Judge Douglas is playing cuttle-fish, a small species of fish that has no mode of defending itself when pursued except by throwing out a black fluid, which makes the water so dark the enemy cannot see it, and thus it escapes. Ain't the Judge playing the cuttle-fish?
Now, I would ask very special attention to the consideration of Judge Douglas's speech at Jacksonville; and when you shall read his speech of to-day, I ask you to watch closely and see which of these pieces of testimony, every one of which he says is a forgery, he has shown to be such. Not one of them has he shown to be a forgery. Then I ask the original question, if each of the pieces of testimony is true, how is it possible that the whole is a falsehood?
In regard to Trumbull's charge that he [Douglas] inserted a provision into the bill to prevent the constitution being submitted to the people, what was his answer? He comes here and reads from the Congressional Globe to show that on his motion that provision was struck out of the bill. Why, Trumbull has not said it was not stricken out, but Trumbull says he [Douglas] put it in; and it is no answer to the charge to say he afterwards took it out. Both are perhaps true. It was in regard to that thing precisely that I told him he had dropped the cub. Trumbull shows you that by his introducing the bill it was his cub. It is no answer to that assertion to call Trumbull a liar merely because he did not specially say that Douglas struck it out. Suppose that were the case, does it answer Trumbull? I assert that you [pointing to an individual] are here to-day, and you undertake to prove me a liar by showing that you were in Mattoon yesterday. I say that you took your hat off your head, and you prove me a liar by putting it on your head. That is the whole force of Douglas's argument.
Now, I want to come back to my original question. Trumbull says that Judge Douglas had a bill with a provision in it for submitting a constitution to be made to a vote of the people of Kansas. Does Judge Douglas deny that fact? Does he deny that the provision which Trumbull reads was put in that bill? Then Trumbull says he struck it out. Does he dare to deny that? He does not, and I have the right to repeat the question,—Why Judge Douglas took it out? Bigler has said there was a combination of certain senators, among whom he did not include Judge Douglas, by which it was agreed that the Kansas Bill should have a clause in it not to have the constitution formed under it submitted to a vote of the people. He did not say that Douglas was among them, but we prove by another source that about the same time Douglas comes into the Senate with that provision stricken out of the bill. Although Bigler cannot say they were all working in concert, yet it looks very much as if the thing was agreed upon and done with a mutual understanding after the conference; and while we do not know that it was absolutely so, yet it looks so probable that we have a right to call upon the man who knows the true reason why it was done to tell what the true reason was. When he will not tell what the true reason was, he stands in the attitude of an accused thief who has stolen goods in his possession, and when called to account refuses to tell where he got them. Not only is this the evidence, but when he comes in with the bill having the provision stricken out, he tells us in a speech, not then but since, that these alterations and modifications in the bill had been made by HIM, in consultation with Toombs, the originator of the bill. He tells us the same to-day. He says there were certain modifications made in the bill in committee that he did not vote for. I ask you to remember, while certain amendments were made which he disapproved of, but which a majority of the committee voted in, he has himself told us that in this particular the alterations and modifications were made by him, upon consultation with Toombs. We have his own word that these alterations were made by him, and not by the committee. Now, I ask, what is the reason Judge Douglas is so chary about coming to the exact question? What is the reason he will not tell you anything about How it was made, BY WHOM it was made, or that he remembers it being made at all? Why does he stand playing upon the meaning of words and quibbling around the edges of the evidence? If he can explain all this, but leaves it unexplained, I have the right to infer that Judge Douglas understood it was the purpose of his party, in engineering that bill through, to make a constitution, and have Kansas come into the Union with that constitution, without its being submitted to a vote of the people. If he will explain his action on this question, by giving a better reason for the facts that happened than he has done, it will be satisfactory. But until he does that—until he gives a better or more plausible reason than he has offered against the evidence in the case—I suggest to him it will not avail him at all that he swells himself up, takes on dignity, and calls people liars. Why, sir, there is not a word in Trumbull's speech that depends on Trumbull's veracity at all. He has only arrayed the evidence and told you what follows as a matter of reasoning. There is not a statement in the whole speech that depends on Trumbull's word. If you have ever studied geometry, you remember that by a course of reasoning Euclid proves that all the angles in a triangle are equal to two right angles. Euclid has shown you how to work it out. Now, if you undertake to disprove that proposition, and to show that it is erroneous, would you prove it to be false by calling Euclid a liar? They tell me that my time is out, and therefore I close.
MY FELLOW-CITIZENS: A very large portion of the speech which Judge Douglas has addressed to you has previously been delivered and put in print. I do not mean that for a hit upon the Judge at all.—-If I had not been interrupted, I was going to say that such an answer as I was able to make to a very large portion of it had already been more than once made and published. There has been an opportunity afforded to the public to see our respective views upon the topics discussed in a large portion of the speech which he has just delivered. I make these remarks for the purpose of excusing myself for not passing over the entire ground that the Judge has traversed. I however desire to take up some of the points that he has attended to, and ask your attention to them, and I shall follow him backwards upon some notes which I have taken, reversing the order, by beginning where he concluded.
The Judge has alluded to the Declaration of Independence, and insisted that negroes are not included in that Declaration; and that it is a slander upon the framers of that instrument to suppose that negroes were meant therein; and he asks you: Is it possible to believe that Mr. Jefferson, who penned the immortal paper, could have supposed himself applying the language of that instrument to the negro race, and yet held a portion of that race in slavery? Would he not at once have freed them? I only have to remark upon this part of the Judge's speech (and that, too, very briefly, for I shall not detain myself, or you, upon that point for any great length of time), that I believe the entire records of the world, from the date of the Declaration of Independence up to within three years ago, may be searched in vain for one single affirmation, from one single man, that the negro was not included in the Declaration of Independence; I think I may defy Judge Douglas to show that he ever said so, that Washington ever said so, that any President ever said so, that any member of Congress ever said so, or that any living man upon the whole earth ever said so, until the necessities of the present policy of the Democratic party, in regard to slavery, had to invent that affirmation. And I will remind Judge Douglas and this audience that while Mr. Jefferson was the owner of slaves, as undoubtedly he was, in speaking upon this very subject he used the strong language that "he trembled for his country when he remembered that God was just"; and I will offer the highest premium in my power to Judge Douglas if he will show that he, in all his life, ever uttered a sentiment at all akin to that of Jefferson.
The next thing to which I will ask your attention is the Judge's comments upon the fact, as he assumes it to be, that we cannot call our public meetings as Republican meetings; and he instances Tazewell County as one of the places where the friends of Lincoln have called a public meeting and have not dared to name it a Republican meeting. He instances Monroe County as another, where Judge Trumbull and Jehu Baker addressed the persons whom the Judge assumes to be the friends of Lincoln calling them the "Free Democracy." I have the honor to inform Judge Douglas that he spoke in that very county of Tazewell last Saturday, and I was there on Tuesday last; and when he spoke there, he spoke under a call not venturing to use the word "Democrat." [Turning to Judge Douglas.] what think you of this?
So, again, there is another thing to which I would ask the Judge's attention upon this subject. In the contest of 1856 his party delighted to call themselves together as the "National Democracy"; but now, if there should be a notice put up anywhere for a meeting of the "National Democracy," Judge Douglas and his friends would not come. They would not suppose themselves invited. They would understand that it was a call for those hateful postmasters whom he talks about.
Now a few words in regard to these extracts from speeches of mine which Judge Douglas has read to you, and which he supposes are in very great contrast to each other. Those speeches have been before the public for a considerable time, and if they have any inconsistency in them, if there is any conflict in them, the public have been able to detect it. When the Judge says, in speaking on this subject, that I make speeches of one sort for the people of the northern end of the State, and of a different sort for the southern people, he assumes that I do not understand that my speeches will be put in print and read north and south. I knew all the while that the speech that I made at Chicago, and the one I made at Jonesboro and the one at Charleston, would all be put in print, and all the reading and intelligent men in the community would see them and know all about my opinions. And I have not supposed, and do not now suppose, that there is any conflict whatever between them. But the Judge will have it that if we do not confess that there is a sort of inequality between the white and black races which justifies us in making them slaves, we must then insist that there is a degree of equality that requires us to make them our wives. Now, I have all the while taken a broad distinction in regard to that matter; and that is all there is in these different speeches which he arrays here; and the entire reading of either of the speeches will show that that distinction was made. Perhaps by taking two parts of the same speech he could have got up as much of a conflict as the one he has found. I have all the while maintained that in so far as it should be insisted that there was an equality between the white and black races that should produce a perfect social and political equality, it was an impossibility. This you have seen in my printed speeches, and with it I have said that in their right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness," as proclaimed in that old Declaration, the inferior races are our equals. And these declarations I have constantly made in reference to the abstract moral question, to contemplate and consider when we are legislating about any new country which is not already cursed with the actual presence of the evil,—slavery. I have never manifested any impatience with the necessities that spring from the actual presence of black people amongst us, and the actual existence of slavery amongst us where it does already exist; but I have insisted that, in legislating for new countries where it does not exist there is no just rule other than that of moral and abstract right! With reference to those new countries, those maxims as to the right of a people to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness" were the just rules to be constantly referred to. There is no misunderstanding this, except by men interested to misunderstand it. I take it that I have to address an intelligent and reading community, who will peruse what I say, weigh it, and then judge whether I advanced improper or unsound views, or whether I advanced hypocritical, and deceptive, and contrary views in different portions of the country. I believe myself to be guilty of no such thing as the latter, though, of course, I cannot claim that I am entirely free from all error in the opinions I advance.
The Judge has also detained us awhile in regard to the distinction between his party and our party. His he assumes to be a national party, ours a sectional one. He does this in asking the question whether this country has any interest in the maintenance of the Republican party. He assumes that our party is altogether sectional, that the party to which he adheres is national; and the argument is, that no party can be a rightful party—and be based upon rightful principles—unless it can announce its principles everywhere. I presume that Judge Douglas could not go into Russia and announce the doctrine of our national Democracy; he could not denounce the doctrine of kings and emperors and monarchies in Russia; and it may be true of this country that in some places we may not be able to proclaim a doctrine as clearly true as the truth of democracy, because there is a section so directly opposed to it that they will not tolerate us in doing so. Is it the true test of the soundness of a doctrine that in some places people won't let you proclaim it? Is that the way to test the truth of any doctrine? Why, I understood that at one time the people of Chicago would not let Judge Douglas preach a certain favorite doctrine of his. I commend to his consideration the question whether he takes that as a test of the unsoundness of what he wanted to preach.
There is another thing to which I wish to ask attention for a little while on this occasion. What has always been the evidence brought forward to prove that the Republican party is a sectional party? The main one was that in the Southern portion of the Union the people did not let the Republicans proclaim their doctrines amongst them. That has been the main evidence brought forward,—that they had no supporters, or substantially none, in the Slave States. The South have not taken hold of our principles as we announce them; nor does Judge Douglas now grapple with those principles. We have a Republican State Platform, laid down in Springfield in June last stating our position all the way through the questions before the country. We are now far advanced in this canvass. Judge Douglas and I have made perhaps forty speeches apiece, and we have now for the fifth time met face to face in debate, and up to this day I have not found either Judge Douglas or any friend of his taking hold of the Republican platform, or laying his finger upon anything in it that is wrong. I ask you all to recollect that. Judge Douglas turns away from the platform of principles to the fact that he can find people somewhere who will not allow us to announce those principles. If he had great confidence that our principles were wrong, he would take hold of them and demonstrate them to be wrong. But he does not do so. The only evidence he has of their being wrong is in the fact that there are people who won't allow us to preach them. I ask again, is that the way to test the soundness of a doctrine?
I ask his attention also to the fact that by the rule of nationality he is himself fast becoming sectional. I ask his attention to the fact that his speeches would not go as current now south of the Ohio River as they have formerly gone there I ask his attention to the fact that he felicitates himself to-day that all the Democrats of the free States are agreeing with him, while he omits to tell us that the Democrats of any slave State agree with him. If he has not thought of this, I commend to his consideration the evidence in his own declaration, on this day, of his becoming sectional too. I see it rapidly approaching. Whatever may be the result of this ephemeral contest between Judge Douglas and myself, I see the day rapidly approaching when his pill of sectionalism, which he has been thrusting down the throats of Republicans for years past, will be crowded down his own throat.
Now, in regard to what Judge Douglas said (in the beginning of his speech) about the Compromise of 1850 containing the principles of the Nebraska Bill, although I have often presented my views upon that subject, yet as I have not done so in this canvass, I will, if you please, detain you a little with them. I have always maintained, so far as I was able, that there was nothing of the principle of the Nebraska Bill in the Compromise of 1850 at all,—nothing whatever. Where can you find the principle of the Nebraska Bill in that Compromise? If anywhere, in the two pieces of the Compromise organizing the Territories of New Mexico and Utah. It was expressly provided in these two acts that when they came to be admitted into the Union they should be admitted with or without slavery, as they should choose, by their own constitutions. Nothing was said in either of those acts as to what was to be done in relation to slavery during the Territorial existence of those Territories, while Henry Clay constantly made the declaration (Judge Douglas recognizing him as a leader) that, in his opinion, the old Mexican laws would control that question during the Territorial existence, and that these old Mexican laws excluded slavery. How can that be used as a principle for declaring that during the Territorial existence as well as at the time of framing the constitution the people, if you please, might have slaves if they wanted them? I am not discussing the question whether it is right or wrong; but how are the New Mexican and Utah laws patterns for the Nebraska Bill? I maintain that the organization of Utah and New Mexico did not establish a general principle at all. It had no feature of establishing a general principle. The acts to which I have referred were a part of a general system of Compromises. They did not lay down what was proposed as a regular policy for the Territories, only an agreement in this particular case to do in that way, because other things were done that were to be a compensation for it. They were allowed to come in in that shape, because in another way it was paid for, considering that as a part of that system of measures called the Compromise of 1850, which finally included half-a-dozen acts. It included the admission of California as a free State, which was kept out of the Union for half a year because it had formed a free constitution. It included the settlement of the boundary of Texas, which had been undefined before, which was in itself a slavery question; for if you pushed the line farther west, you made Texas larger, and made more slave territory; while, if you drew the line toward the east, you narrowed the boundary and diminished the domain of slavery, and by so much increased free territory. It included the abolition of the slave trade in the District of Columbia. It included the passage of a new Fugitive Slave law. All these things were put together, and, though passed in separate acts, were nevertheless, in legislation (as the speeches at the time will show), made to depend upon each other. Each got votes with the understanding that the other measures were to pass, and by this system of compromise, in that series of measures, those two bills—the New Mexico and Utah bills—were passed: and I say for that reason they could not be taken as models, framed upon their own intrinsic principle, for all future Territories. And I have the evidence of this in the fact that Judge Douglas, a year afterward, or more than a year afterward, perhaps, when he first introduced bills for the purpose of framing new Territories, did not attempt to follow these bills of New Mexico and Utah; and even when he introduced this Nebraska Bill, I think you will discover that he did not exactly follow them. But I do not wish to dwell at great length upon this branch of the discussion. My own opinion is, that a thorough investigation will show most plainly that the New Mexico and Utah bills were part of a system of compromise, and not designed as patterns for future Territorial legislation; and that this Nebraska Bill did not follow them as a pattern at all.
The Judge tells, in proceeding, that he is opposed to making any odious distinctions between free and slave States. I am altogether unaware that the Republicans are in favor of making any odious distinctions between the free and slave States. But there is still a difference, I think, between Judge Douglas and the Republicans in this. I suppose that the real difference between Judge Douglas and his friends, and the Republicans on the contrary, is, that the Judge is not in favor of making any difference between slavery and liberty; that he is in favor of eradicating, of pressing out of view, the questions of preference in this country for free or slave institutions; and consequently every sentiment he utters discards the idea that there is any wrong in slavery. Everything that emanates from him or his coadjutors in their course of policy carefully excludes the thought that there is anything wrong in slavery. All their arguments, if you will consider them, will be seen to exclude the thought that there is anything whatever wrong in slavery. If you will take the Judge's speeches, and select the short and pointed sentences expressed by him,—as his declaration that he "don't care whether slavery is voted up or down,"—you will see at once that this is perfectly logical, if you do not admit that slavery is wrong. If you do admit that it is wrong, Judge Douglas cannot logically say he don't care whether a wrong is voted up or voted down. Judge Douglas declares that if any community wants slavery they have a right to have it. He can say that logically, if he says that there is no wrong in slavery; but if you admit that there is a wrong in it, he cannot logically say that anybody has a right to do wrong. He insists that upon the score of equality the owners of slaves and owners of property—of horses and every other sort of property—should be alike, and hold them alike in a new Territory. That is perfectly logical if the two species of property are alike and are equally founded in right. But if you admit that one of them is wrong, you cannot institute any equality between right and wrong. And from this difference of sentiment,—the belief on the part of one that the institution is wrong, and a policy springing from that belief which looks to the arrest of the enlargement of that wrong, and this other sentiment, that it is no wrong, and a policy sprung from that sentiment, which will tolerate no idea of preventing the wrong from growing larger, and looks to there never being an end to it through all the existence of things,—arises the real difference between Judge Douglas and his friends on the one hand and the Republicans on the other. Now, I confess myself as belonging to that class in the country who contemplate slavery as a moral, social, and political evil, having due regard for its actual existence amongst us and the difficulties of getting rid of it in any satisfactory way, and to all the constitutional obligations which have been thrown about it; but, nevertheless, desire a policy that looks to the prevention of it as a wrong, and looks hopefully to the time when as a wrong it may come to an end.
Judge Douglas has again, for, I believe, the fifth time, if not the seventh, in my presence, reiterated his charge of a conspiracy or combination between the National Democrats and Republicans. What evidence Judge Douglas has upon this subject I know not, inasmuch as he never favors us with any. I have said upon a former occasion, and I do not choose to suppress it now, that I have no objection to the division in the Judge's party. He got it up himself. It was all his and their work. He had, I think, a great deal more to do with the steps that led to the Lecompton Constitution than Mr. Buchanan had; though at last, when they reached it, they quarreled over it, and their friends divided upon it. I am very free to confess to Judge Douglas that I have no objection to the division; but I defy the Judge to show any evidence that I have in any way promoted that division, unless he insists on being a witness himself in merely saying so. I can give all fair friends of Judge Douglas here to understand exactly the view that Republicans take in regard to that division. Don't you remember how two years ago the opponents of the Democratic party were divided between Fremont and Fillmore? I guess you do. Any Democrat who remembers that division will remember also that he was at the time very glad of it, and then he will be able to see all there is between the National Democrats and the Republicans. What we now think of the two divisions of Democrats, you then thought of the Fremont and Fillmore divisions. That is all there is of it.
But if the Judge continues to put forward the declaration that there is an unholy and unnatural alliance between the Republicans and the National Democrats, I now want to enter my protest against receiving him as an entirely competent witness upon that subject. I want to call to the Judge's attention an attack he made upon me in the first one of these debates, at Ottawa, on the 21st of August. In order to fix extreme Abolitionism upon me, Judge Douglas read a set of resolutions which he declared had been passed by a Republican State Convention, in October, 1854, at Springfield, Illinois, and he declared I had taken part in that Convention. It turned out that although a few men calling themselves an anti-Nebraska State Convention had sat at Springfield about that time, yet neither did I take any part in it, nor did it pass the resolutions or any such resolutions as Judge Douglas read. So apparent had it become that the resolutions which he read had not been passed at Springfield at all, nor by a State Convention in which I had taken part, that seven days afterward, at Freeport, Judge Douglas declared that he had been misled by Charles H. Lanphier, editor of the State Register, and Thomas L. Harris, member of Congress in that district, and he promised in that speech that when he went to Springfield he would investigate the matter. Since then Judge Douglas has been to Springfield, and I presume has made the investigation; but a month has passed since he has been there, and, so far as I know, he has made no report of the result of his investigation. I have waited as I think sufficient time for the report of that investigation, and I have some curiosity to see and hear it. A fraud, an absolute forgery was committed, and the perpetration of it was traced to the three,—Lanphier, Harris, and Douglas. Whether it can be narrowed in any way so as to exonerate any one of them, is what Judge Douglas's report would probably show.
It is true that the set of resolutions read by Judge Douglas were published in the Illinois State Register on the 16th of October, 1854, as being the resolutions of an anti-Nebraska Convention which had sat in that same month of October, at Springfield. But it is also true that the publication in the Register was a forgery then, and the question is still behind, which of the three, if not all of them, committed that forgery. The idea that it was done by mistake is absurd. The article in the Illinois State Register contains part of the real proceedings of that Springfield Convention, showing that the writer of the article had the real proceedings before him, and purposely threw out the genuine resolutions passed by the Convention and fraudulently substituted the others. Lanphier then, as now, was the editor of the Register, so that there seems to be but little room for his escape. But then it is to be borne in mind that Lanphier had less interest in the object of that forgery than either of the other two. The main object of that forgery at that time was to beat Yates and elect Harris to Congress, and that object was known to be exceedingly dear to Judge Douglas at that time. Harris and Douglas were both in Springfield when the Convention was in session, and although they both left before the fraud appeared in the Register, subsequent events show that they have both had their eyes fixed upon that Convention.
The fraud having been apparently successful upon the occasion, both Harris and Douglas have more than once since then been attempting to put it to new uses. As the fisherman's wife, whose drowned husband was brought home with his body full of eels, said when she was asked what was to be done with him, "Take the eels out and set him again," so Harris and Douglas have shown a disposition to take the eels out of that stale fraud by which they gained Harris's election, and set the fraud again more than once. On the 9th of July, 1856, Douglas attempted a repetition of it upon Trumbull on the floor of the Senate of the United States, as will appear from the appendix of the Congressional Globe of that date.
On the 9th of August, Harris attempted it again upon Norton in the House of Representatives, as will appear by the same documents,—the appendix to the Congressional Globe of that date. On the 21st of August last, all three—Lanphier, Douglas, and Harris—reattempted it upon me at Ottawa. It has been clung to and played out again and again as an exceedingly high trump by this blessed trio. And now that it has been discovered publicly to be a fraud we find that Judge Douglas manifests no surprise at it at all. He makes no complaint of Lanphier, who must have known it to be a fraud from the beginning. He, Lanphier, and Harris are just as cozy now and just as active in the concoction of new schemes as they were before the general discovery of this fraud. Now, all this is very natural if they are all alike guilty in that fraud, and it is very unnatural if any one of them is innocent. Lanphier perhaps insists that the rule of honor among thieves does not quite require him to take all upon himself, and consequently my friend Judge Douglas finds it difficult to make a satisfactory report upon his investigation. But meanwhile the three are agreed that each is "a most honorable man."
Judge Douglas requires an indorsement of his truth and honor by a re-election to the United States Senate, and he makes and reports against me and against Judge Trumbull, day after day, charges which we know to be utterly untrue, without for a moment seeming to think that this one unexplained fraud, which he promised to investigate, will be the least drawback to his claim to belief. Harris ditto. He asks a re-election to the lower House of Congress without seeming to remember at all that he is involved in this dishonorable fraud! The Illinois State Register, edited by Lanphier, then, as now, the central organ of both Harris and Douglas, continues to din the public ear with this assertion, without seeming to suspect that these assertions are at all lacking in title to belief.
After all, the question still recurs upon us, How did that fraud originally get into the State Register? Lanphier then, as now, was the editor of that paper. Lanphier knows. Lanphier cannot be ignorant of how and by whom it was originally concocted. Can he be induced to tell, or, if he has told, can Judge Douglas be induced to tell how it originally was concocted? It may be true that Lanphier insists that the two men for whose benefit it was originally devised shall at least bear their share of it! How that is, I do not know, and while it remains unexplained I hope to be pardoned if I insist that the mere fact of Judge Douglas making charges against Trumbull and myself is not quite sufficient evidence to establish them!
While we were at Freeport, in one of these joint discussions, I answered certain interrogatories which Judge Douglas had propounded to me, and then in turn propounded some to him, which he in a sort of way answered. The third one of these interrogatories I have with me, and wish now to make some comments upon it. It was in these words: "If the Supreme Court of States cannot exclude slavery from their limits, are you in favor of acquiescing in, adhering to, and following such decision as a rule of political action?"
To this interrogatory Judge Douglas made no answer in any just sense of the word. He contented himself with sneering at the thought that it was possible for the Supreme Court ever to make such a decision. He sneered at me for propounding the interrogatory. I had not propounded it without some reflection, and I wish now to address to this audience some remarks upon it.
In the second clause of the sixth article, I believe it is, of the Constitution of the United States, we find the following language:
"This Constitution and the laws of the United States which shall be made in pursuance thereof, and all treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the land; and the judges in every State shall be bound thereby, anything in the Constitution or laws of any State to the contrary notwithstanding."
The essence of the Dred Scott case is compressed into the sentence which I will now read:
"Now, as we have already said in an earlier part of this opinion, upon a different point, the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution."
I repeat it, "The right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution"! What is it to be "affirmed" in the Constitution? Made firm in the Constitution, so made that it cannot be separated from the Constitution without breaking the Constitution; durable as the Constitution, and part of the Constitution. Now, remembering the provision of the Constitution which I have read—affirming that that instrument is the supreme law of the land; that the judges of every State shall be bound by it, any law or constitution of any State to the contrary notwithstanding; that the right of property in a slave is affirmed in that Constitution, is made, formed into, and cannot be separated from it without breaking it; durable as the instrument; part of the instrument;—what follows as a short and even syllogistic argument from it? I think it follows, and I submit to the consideration of men capable of arguing whether, as I state it, in syllogistic form, the argument has any fault in it:
Nothing in the Constitution or laws of any State can destroy a right distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution of the United States.
The right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution of the United States.
Therefore, nothing in the Constitution or laws of any State can destroy the right of property in a slave.
I believe that no fault can be pointed out in that argument; assuming the truth of the premises, the conclusion, so far as I have capacity at all to understand it, follows inevitably. There is a fault in it as I think, but the fault is not in the reasoning; but the falsehood in fact is a fault of the premises. I believe that the right of property in a slave is not distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution, and Judge Douglas thinks it is. I believe that the Supreme Court and the advocates of that decision may search in vain for the place in the Constitution where the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed I say, therefore, that I think one of the premises is not true in fact. But it is true with Judge Douglas. It is true with the Supreme Court who pronounced it. They are estopped from denying it, and being estopped from denying it, the conclusion follows that, the Constitution of the United States being the supreme law, no constitution or law can interfere with it. It being affirmed in the decision that the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution, the conclusion inevitably follows that no State law or constitution can destroy that right. I then say to Judge Douglas and to all others that I think it will take a better answer than a sneer to show that those who have said that the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution, are not prepared to show that no constitution or law can destroy that right. I say I believe it will take a far better argument than a mere sneer to show to the minds of intelligent men that whoever has so said is not prepared, whenever public sentiment is so far advanced as to justify it, to say the other. This is but an opinion, and the opinion of one very humble man; but it is my opinion that the Dred Scott decision, as it is, never would have been made in its present form if the party that made it had not been sustained previously by the elections. My own opinion is, that the new Dred Scott decision, deciding against the right of the people of the States to exclude slavery, will never be made if that party is not sustained by the elections. I believe, further, that it is just as sure to be made as to-morrow is to come, if that party shall be sustained. I have said, upon a former occasion, and I repeat it now, that the course of arguement that Judge Douglas makes use of upon this subject (I charge not his motives in this), is preparing the public mind for that new Dred Scott decision. I have asked him again to point out to me the reasons for his first adherence to the Dred Scott decision as it is. I have turned his attention to the fact that General Jackson differed with him in regard to the political obligation of a Supreme Court decision. I have asked his attention to the fact that Jefferson differed with him in regard to the political obligation of a Supreme Court decision. Jefferson said that "Judges are as honest as other men, and not more so." And he said, substantially, that whenever a free people should give up in absolute submission to any department of government, retaining for themselves no appeal from it, their liberties were gone. I have asked his attention to the fact that the Cincinnati platform, upon which he says he stands, disregards a time-honored decision of the Supreme Court, in denying the power of Congress to establish a National Bank. I have asked his attention to the fact that he himself was one of the most active instruments at one time in breaking down the Supreme Court of the State of Illinois because it had made a decision distasteful to him,—a struggle ending in the remarkable circumstance of his sitting down as one of the new Judges who were to overslaugh that decision; getting his title of Judge in that very way.
So far in this controversy I can get no answer at all from Judge Douglas upon these subjects. Not one can I get from him, except that he swells himself up and says, "All of us who stand by the decision of the Supreme Court are the friends of the Constitution; all you fellows that dare question it in any way are the enemies of the Constitution." Now, in this very devoted adherence to this decision, in opposition to all the great political leaders whom he has recognized as leaders, in opposition to his former self and history, there is something very marked. And the manner in which he adheres to it,—not as being right upon the merits, as he conceives (because he did not discuss that at all), but as being absolutely obligatory upon every one simply because of the source from whence it comes, as that which no man can gainsay, whatever it may be,—this is another marked feature of his adherence to that decision. It marks it in this respect, that it commits him to the next decision, whenever it comes, as being as obligatory as this one, since he does not investigate it, and won't inquire whether this opinion is right or wrong. So he takes the next one without inquiring whether it is right or wrong. He teaches men this doctrine, and in so doing prepares the public mind to take the next decision when it comes, without any inquiry. In this I think I argue fairly (without questioning motives at all) that Judge Douglas is most ingeniously and powerfully preparing the public mind to take that decision when it comes; and not only so, but he is doing it in various other ways. In these general maxims about liberty, in his assertions that he "don't care whether slavery is voted up or voted down,"; that "whoever wants slavery has a right to have it"; that "upon principles of equality it should be allowed to go everywhere"; that "there is no inconsistency between free and slave institutions"—in this he is also preparing (whether purposely or not) the way for making the institution of slavery national! I repeat again, for I wish no misunderstanding, that I do not charge that he means it so; but I call upon your minds to inquire, if you were going to get the best instrument you could, and then set it to work in the most ingenious way, to prepare the public mind for this movement, operating in the free States, where there is now an abhorrence of the institution of slavery, could you find an instrument so capable of doing it as Judge Douglas, or one employed in so apt a way to do it?
I have said once before, and I will repeat it now, that Mr. Clay, when he was once answering an objection to the Colonization Society, that it had a tendency to the ultimate emancipation of the slaves, said that:
"Those who would repress all tendencies to liberty and ultimate emancipation must do more than put down the benevolent efforts of the Colonization Society: they must go back to the era of our liberty and independence, and muzzle the cannon that thunders its annual joyous return; they must blow out the moral lights around us; they must penetrate the human soul, and eradicate the light of reason and the love of liberty!"
And I do think—I repeat, though I said it on a former occasion—that Judge Douglas and whoever, like him, teaches that the negro has no share, humble though it may be, in the Declaration of Independence, is going back to the era of our liberty and independence, and, so far as in him lies, muzzling the cannon that thunders its annual joyous return; that he is blowing out the moral lights around us, when he contends that whoever wants slaves has a right to hold them; that he is penetrating, so far as lies in his power, the human soul, and eradicating the light of reason and the love of liberty, when he is in every possible way preparing the public mind, by his vast influence, for making the institution of slavery perpetual and national.
There is, my friends, only one other point to which I will call your attention for the remaining time that I have left me, and perhaps I shall not occupy the entire time that I have, as that one point may not take me clear through it.
Among the interrogatories that Judge Douglas propounded to me at Freeport, there was one in about this language:
"Are you opposed to the acquisition of any further territory to the United States, unless slavery shall first be prohibited therein?"
I answered, as I thought, in this way: that I am not generally opposed to the acquisition of additional territory, and that I would support a proposition for the acquisition of additional territory according as my supporting it was or was not calculated to aggravate this slavery question amongst us. I then proposed to Judge Douglas another interrogatory, which was correlative to that: "Are you in favor of acquiring additional territory, in disregard of how it may affect us upon the slavery question?" Judge Douglas answered,—that is, in his own way he answered it. I believe that, although he took a good many words to answer it, it was a little more fully answered than any other. The substance of his answer was that this country would continue to expand; that it would need additional territory; that it was as absurd to suppose that we could continue upon our present territory, enlarging in population as we are, as it would be to hoop a boy twelve years of age, and expect him to grow to man's size without bursting the hoops. I believe it was something like that. Consequently, he was in favor of the acquisition of further territory as fast as we might need it, in disregard of how it might affect the slavery question. I do not say this as giving his exact language, but he said so substantially; and he would leave the question of slavery, where the territory was acquired, to be settled by the people of the acquired territory. ["That's the doctrine."] May be it is; let us consider that for a while. This will probably, in the run of things, become one of the concrete manifestations of this slavery question. If Judge Douglas's policy upon this question succeeds, and gets fairly settled down, until all opposition is crushed out, the next thing will be a grab for the territory of poor Mexico, an invasion of the rich lands of South America, then the adjoining islands will follow, each one of which promises additional slave-fields. And this question is to be left to the people of those countries for settlement. When we get Mexico, I don't know whether the Judge will be in favor of the Mexican people that we get with it settling that question for themselves and all others; because we know the Judge has a great horror for mongrels, and I understand that the people of Mexico are most decidedly a race of mongrels. I understand that there is not more than one person there out of eight who is pure white, and I suppose from the Judge's previous declaration that when we get Mexico, or any considerable portion of it, that he will be in favor of these mongrels settling the question, which would bring him somewhat into collision with his horror of an inferior race.
It is to be remembered, though, that this power of acquiring additional territory is a power confided to the President and the Senate of the United States. It is a power not under the control of the representatives of the people any further than they, the President and the Senate, can be considered the representatives of the people. Let me illustrate that by a case we have in our history. When we acquired the territory from Mexico in the Mexican War, the House of Representatives, composed of the immediate representatives of the people, all the time insisted that the territory thus to be acquired should be brought in upon condition that slavery should be forever prohibited therein, upon the terms and in the language that slavery had been prohibited from coming into this country. That was insisted upon constantly and never failed to call forth an assurance that any territory thus acquired should have that prohibition in it, so far as the House of Representatives was concerned. But at last the President and Senate acquired the territory without asking the House of Representatives anything about it, and took it without that prohibition. They have the power of acquiring territory without the immediate representatives of the people being called upon to say anything about it, and thus furnishing a very apt and powerful means of bringing new territory into the Union, and, when it is once brought into the country, involving us anew in this slavery agitation. It is therefore, as I think, a very important question for due consideration of the American people, whether the policy of bringing in additional territory, without considering at all how it will operate upon the safety of the Union in reference to this one great disturbing element in our national politics, shall be adopted as the policy of the country. You will bear in mind that it is to be acquired, according to the Judge's view, as fast as it is needed, and the indefinite part of this proposition is that we have only Judge Douglas and his class of men to decide how fast it is needed. We have no clear and certain way of determining or demonstrating how fast territory is needed by the necessities of the country. Whoever wants to go out filibustering, then, thinks that more territory is needed. Whoever wants wider slave-fields feels sure that some additional territory is needed as slave territory. Then it is as easy to show the necessity of additional slave-territory as it is to assert anything that is incapable of absolute demonstration. Whatever motive a man or a set of men may have for making annexation of property or territory, it is very easy to assert, but much less easy to disprove, that it is necessary for the wants of the country.
And now it only remains for me to say that I think it is a very grave question for the people of this Union to consider, whether, in view of the fact that this slavery question has been the only one that has ever endangered our Republican institutions, the only one that has ever threatened or menaced a dissolution of the Union, that has ever disturbed us in such a way as to make us fear for the perpetuity of our liberty,—in view of these facts, I think it is an exceedingly interesting and important question for this people to consider whether we shall engage in the policy of acquiring additional territory, discarding altogether from our consideration, while obtaining new territory, the question how it may affect us in regard to this, the only endangering element to our liberties and national greatness. The Judge's view has been expressed. I, in my answer to his question, have expressed mine. I think it will become an important and practical question. Our views are before the public. I am willing and anxious that they should consider them fully; that they should turn it about and consider the importance of the question, and arrive at a just conclusion as to whether it is or is not wise in the people of this Union, in the acquisition of new territory, to consider whether it will add to the disturbance that is existing amongst us—whether it will add to the one only danger that has ever threatened the perpetuity of the Union or our own liberties. I think it is extremely important that they shall decide, and rightly decide, that question before entering upon that policy.
And now, my friends, having said the little I wish to say upon this head, whether I have occupied the whole of the remnant of my time or not, I believe I could not enter upon any new topic so as to treat it fully, without transcending my time, which I would not for a moment think of doing. I give way to Judge Douglas.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN: I have had no immediate conference with Judge Douglas, but I will venture to say that he and I will perfectly agree that your entire silence, both when I speak and when he speaks, will be most agreeable to us.
In the month of May, 1856, the elements in the State of Illinois which have since been consolidated into the Republican party assembled together in a State Convention at Bloomington. They adopted at that time what, in political language, is called a platform. In June of the same year the elements of the Republican party in the nation assembled together in a National Convention at Philadelphia. They adopted what is called the National Platform. In June, 1858,—the present year,—the Republicans of Illinois reassembled at Springfield, in State Convention, and adopted again their platform, as I suppose not differing in any essential particular from either of the former ones, but perhaps adding something in relation to the new developments of political progress in the country.
The Convention that assembled in June last did me the honor, if it be one, and I esteem it such, to nominate me as their candidate for the United States Senate. I have supposed that, in entering upon this canvass, I stood generally upon these platforms. We are now met together on the 13th of October of the same year, only four months from the adoption of the last platform, and I am unaware that in this canvass, from the beginning until to-day, any one of our adversaries has taken hold of our platforms, or laid his finger upon anything that he calls wrong in them.
In the very first one of these joint discussions between Senator Douglas and myself, Senator Douglas, without alluding at all to these platforms, or any one of them, of which I have spoken, attempted to hold me responsible for a set of resolutions passed long before the meeting of either one of these conventions of which I have spoken. And as a ground for holding me responsible for these resolutions, he assumed that they had been passed at a State Convention of the Republican party, and that I took part in that Convention. It was discovered afterward that this was erroneous, that the resolutions which he endeavored to hold me responsible for had not been passed by any State Convention anywhere, had not been passed at Springfield, where he supposed they had, or assumed that they had, and that they had been passed in no convention in which I had taken part. The Judge, nevertheless, was not willing to give up the point that he was endeavoring to make upon me, and he therefore thought to still hold me to the point that he was endeavoring to make, by showing that the resolutions that he read had been passed at a local convention in the northern part of the State, although it was not a local convention that embraced my residence at all, nor one that reached, as I suppose, nearer than one hundred and fifty or two hundred miles of where I was when it met, nor one in which I took any part at all. He also introduced other resolutions, passed at other meetings, and by combining the whole, although they were all antecedent to the two State Conventions and the one National Convention I have mentioned, still he insisted, and now insists, as I understand, that I am in some way responsible for them.
At Jonesboro, on our third meeting, I insisted to the Judge that I was in no way rightfully held responsible for the proceedings of this local meeting or convention, in which I had taken no part, and in which I was in no way embraced; but I insisted to him that if he thought I was responsible for every man or every set of men everywhere, who happen to be my friends, the rule ought to work both ways, and he ought to be responsible for the acts and resolutions of all men or sets of men who were or are now his supporters and friends, and gave him a pretty long string of resolutions, passed by men who are now his friends, and announcing doctrines for which he does not desire to be held responsible.
This still does not satisfy Judge Douglas. He still adheres to his proposition, that I am responsible for what some of my friends in different parts of the State have done, but that he is not responsible for what his have done. At least, so I understand him. But in addition to that, the Judge, at our meeting in Galesburgh, last week, undertakes to establish that I am guilty of a species of double dealing with the public; that I make speeches of a certain sort in the north, among the Abolitionists, which I would not make in the south, and that I make speeches of a certain sort in the south which I would not make in the north. I apprehend, in the course I have marked out for myself, that I shall not have to dwell at very great length upon this subject.
As this was done in the Judge's opening speech at Galesburgh, I had an opportunity, as I had the middle speech then, of saying something in answer to it. He brought forward a quotation or two from a speech of mine delivered at Chicago, and then, to contrast with it, he brought forward an extract from a speech of mine at Charleston, in which he insisted that I was greatly inconsistent, and insisted that his conclusion followed, that I was playing a double part, and speaking in one region one way, and in another region another way. I have not time now to dwell on this as long as I would like, and wish only now to requote that portion of my speech at Charleston which the Judge quoted, and then make some comments upon it. This he quotes from me as being delivered at Charleston, and I believe correctly:
"I will say, then, that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of bringing about in any way the social and political equality of the white and black races; that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of making voters or jurors of negroes, nor of qualifying them to hold office, nor to intermarry with white people; and I will say, in addition to this, that there is a physical difference between the white and black races which will forever forbid the two races living together on terms of social and political equality. And inasmuch as they cannot so live while they do remain together, there must be the position of superior and inferior. I am as much as any other man in favor of having the superior position assigned to the white race."
This, I believe, is the entire quotation from Charleston speech, as Judge Douglas made it his comments are as follows:
"Yes, here you find men who hurrah for Lincoln, and say he is right when he discards all distinction between races, or when he declares that he discards the doctrine that there is such a thing as a superior and inferior race; and Abolitionists are required and expected to vote for Mr. Lincoln because he goes for the equality of races, holding that in the Declaration of Independence the white man and negro were declared equal, and endowed by divine law with equality. And down South, with the old-line Whigs, with the Kentuckians, the Virginians and the Tennesseeans, he tells you that there is a physical difference between the races, making the one superior, the other inferior, and he is in favor of maintaining the superiority of the white race over the negro."
Those are the Judges comments. Now, I wish to show you that a month, or only lacking three days of a month, before I made the speech at Charleston, which the Judge quotes from, he had himself heard me say substantially the same thing It was in our first meeting, at Ottawa—and I will say a word about where it was, and the atmosphere it was in, after a while—but at our first meeting, at Ottawa, I read an extract from an old speech of mine, made nearly four years ago, not merely to show my sentiments, but to show that my sentiments were long entertained and openly expressed; in which extract I expressly declared that my own feelings would not admit a social and political equality between the white and black races, and that even if my own feelings would admit of it, I still knew that the public sentiment of the country would not, and that such a thing was an utter impossibility, or substantially that. That extract from my old speech the reporters by some sort of accident passed over, and it was not reported. I lay no blame upon anybody. I suppose they thought that I would hand it over to them, and dropped reporting while I was giving it, but afterward went away without getting it from me. At the end of that quotation from my old speech, which I read at Ottawa, I made the comments which were reported at that time, and which I will now read, and ask you to notice how very nearly they are the same as Judge Douglas says were delivered by me down in Egypt. After reading, I added these words:
"Now, gentlemen, I don't want to read at any great length; but this is the true complexion of all I have ever said in regard to the institution of slavery or the black race, and this is the whole of it: anything that argues me into his idea of perfect social and political equality with the negro, is but a specious and fantastical arrangement of words by which a man can prove a horse-chestnut to be a chestnut horse. I will say here, while upon this subject, that I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution in the States where it exists. I believe I have no right to do so. I have no inclination to do so. I have no purpose to introduce political and social equality between the white and black races. There is a physical difference between the two which, in my judgment, will probably forever forbid their living together on the footing of perfect equality; and inasmuch as it becomes a necessity that there must be a difference, I, as well as Judge Douglas, am in favor of the race to which I belong having the superior position. I have never said anything to the contrary, but I hold that, notwithstanding all this, there is no reason in the world why the negro is not entitled to all the rights enumerated in the Declaration of Independence,—the right of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. I hold that he is as much entitled to these as the white man. I agree with Judge Douglas that he is not my equal in many respects, certainly not in color, perhaps not in intellectual and moral endowments; but in the right to eat the bread, without the leave of anybody else, which his own hand earns, he is my equal and the equal of Judge Douglas, and the equal of every other man."
I have chiefly introduced this for the purpose of meeting the Judge's charge that the quotation he took from my Charleston speech was what I would say down South among the Kentuckians, the Virginians, etc., but would not say in the regions in which was supposed to be more of the Abolition element. I now make this comment: That speech from which I have now read the quotation, and which is there given correctly—perhaps too much so for good taste—was made away up North in the Abolition District of this State par excellence, in the Lovejoy District, in the personal presence of Lovejoy, for he was on the stand with us when I made it. It had been made and put in print in that region only three days less than a month before the speech made at Charleston, the like of which Judge Douglas thinks I would not make where there was any Abolition element. I only refer to this matter to say that I am altogether unconscious of having attempted any double-dealing anywhere; that upon one occasion I may say one thing, and leave other things unsaid, and vice versa, but that I have said anything on one occasion that is inconsistent with what I have said elsewhere, I deny, at least I deny it so far as the intention is concerned. I find that I have devoted to this topic a larger portion of my time than I had intended. I wished to show, but I will pass it upon this occasion, that in the sentiment I have occasionally advanced upon the Declaration of Independence I am entirely borne out by the sentiments advanced by our old Whig leader, Henry Clay, and I have the book here to show it from but because I have already occupied more time than I intended to do on that topic, I pass over it.
At Galesburgh, I tried to show that by the Dred Scott decision, pushed to its legitimate consequences, slavery would be established in all the States as well as in the Territories. I did this because, upon a former occasion, I had asked Judge Douglas whether, if the Supreme Court should make a decision declaring that the States had not the power to exclude slavery from their limits, he would adopt and follow that decision as a rule of political action; and because he had not directly answered that question, but had merely contented himself with sneering at it, I again introduced it, and tried to show that the conclusion that I stated followed inevitably and logically from the proposition already decided by the court. Judge Douglas had the privilege of replying to me at Galesburgh, and again he gave me no direct answer as to whether he would or would not sustain such a decision if made. I give him his third chance to say yes or no. He is not obliged to do either, probably he will not do either; but I give him the third chance. I tried to show then that this result, this conclusion, inevitably followed from the point already decided by the court. The Judge, in his reply, again sneers at the thought of the court making any such decision, and in the course of his remarks upon this subject uses the language which I will now read. Speaking of me, the Judge says:
"He goes on and insists that the Dred Scott decision would carry slavery into the free States, notwithstanding the decision itself says the contrary." And he adds:
"Mr. Lincoln knows that there is no member of the Supreme Court that holds that doctrine. He knows that every one of them in their opinions held the reverse."
I especially introduce this subject again for the purpose of saying that I have the Dred Scott decision here, and I will thank Judge Douglas to lay his finger upon the place in the entire opinions of the court where any one of them "says the contrary." It is very hard to affirm a negative with entire confidence. I say, however, that I have examined that decision with a good deal of care, as a lawyer examines a decision and, so far as I have been able to do so, the court has nowhere in its opinions said that the States have the power to exclude slavery, nor have they used other language substantially that, I also say, so far as I can find, not one of the concurring judges has said that the States can exclude slavery, nor said anything that was substantially that. The nearest approach that any one of them has made to it, so far as I can find, was by Judge Nelson, and the approach he made to it was exactly, in substance, the Nebraska Bill,—that the States had the exclusive power over the question of slavery, so far as they are not limited by the Constitution of the United States. I asked the question, therefore, if the non-concurring judges, McLean or Curtis, had asked to get an express declaration that the States could absolutely exclude slavery from their limits, what reason have we to believe that it would not have been voted down by the majority of the judges, just as Chase's amendment was voted down by Judge Douglas and his compeers when it was offered to the Nebraska Bill.
Also, at Galesburgh, I said something in regard to those Springfield resolutions that Judge Douglas had attempted to use upon me at Ottawa, and commented at some length upon the fact that they were, as presented, not genuine. Judge Douglas in his reply to me seemed to be somewhat exasperated. He said he would never have believed that Abraham Lincoln, as he kindly called me, would have attempted such a thing as I had attempted upon that occasion; and among other expressions which he used toward me, was that I dared to say forgery, that I had dared to say forgery [turning to Judge Douglas]. Yes, Judge, I did dare to say forgery. But in this political canvass the Judge ought to remember that I was not the first who dared to say forgery. At Jacksonville, Judge Douglas made a speech in answer to something said by Judge Trumbull, and at the close of what he said upon that subject, he dared to say that Trumbull had forged his evidence. He said, too, that he should not concern himself with Trumbull any more, but thereafter he should hold Lincoln responsible for the slanders upon him. When I met him at Charleston after that, although I think that I should not have noticed the subject if he had not said he would hold me responsible for it, I spread out before him the statements of the evidence that Judge Trumbull had used, and I asked Judge Douglas, piece by piece, to put his finger upon one piece of all that evidence that he would say was a forgery! When I went through with each and every piece, Judge Douglas did not dare then to say that any piece of it was a forgery. So it seems that there are some things that Judge Douglas dares to do, and some that he dares not to do.
[A voice: It is the same thing with you.]
Yes, sir, it is the same thing with me. I do dare to say forgery when it is true, and don't dare to say forgery when it is false. Now I will say here to this audience and to Judge Douglas I have not dared to say he committed a forgery, and I never shall until I know it; but I did dare to say—just to suggest to the Judge—that a forgery had been committed, which by his own showing had been traced to him and two of his friends. I dared to suggest to him that he had expressly promised in one of his public speeches to investigate that matter, and I dared to suggest to him that there was an implied promise that when he investigated it he would make known the result. I dared to suggest to the Judge that he could not expect to be quite clear of suspicion of that fraud, for since the time that promise was made he had been with those friends, and had not kept his promise in regard to the investigation and the report upon it. I am not a very daring man, but I dared that much, Judge, and I am not much scared about it yet. When the Judge says he would n't have believed of Abraham Lincoln that he would have made such an attempt as that he reminds me of the fact that he entered upon this canvass with the purpose to treat me courteously; that touched me somewhat. It sets me to thinking. I was aware, when it was first agreed that Judge Douglas and I were to have these seven joint discussions, that they were the successive acts of a drama, perhaps I should say, to be enacted, not merely in the face of audiences like this, but in the face of the nation, and to some extent, by my relation to him, and not from anything in myself, in the face of the world; and I am anxious that they should be conducted with dignity and in the good temper which would be befitting the vast audiences before which it was conducted. But when Judge Douglas got home from Washington and made his first speech in Chicago, the evening afterward I made some sort of a reply to it. His second speech was made at Bloomington, in which he commented upon my speech at Chicago and said that I had used language ingeniously contrived to conceal my intentions, or words to that effect. Now, I understand that this is an imputation upon my veracity and my candor. I do not know what the Judge understood by it, but in our first discussion, at Ottawa, he led off by charging a bargain, somewhat corrupt in its character, upon Trumbull and myself,—that we had entered into a bargain, one of the terms of which was that Trumbull was to Abolitionize the old Democratic party, and I (Lincoln) was to Abolitionize the old Whig party; I pretending to be as good an old-line Whig as ever. Judge Douglas may not understand that he implicated my truthfulness and my honor when he said I was doing one thing and pretending another; and I misunderstood him if he thought he was treating me in a dignified way, as a man of honor and truth, as he now claims he was disposed to treat me. Even after that time, at Galesburgh, when he brings forward an extract from a speech made at Chicago and an extract from a speech made at Charleston, to prove that I was trying to play a double part, that I was trying to cheat the public, and get votes upon one set of principles at one place, and upon another set of principles at another place,—I do not understand but what he impeaches my honor, my veracity, and my candor; and because he does this, I do not understand that I am bound, if I see a truthful ground for it, to keep my hands off of him. As soon as I learned that Judge Douglas was disposed to treat me in this way, I signified in one of my speeches that I should be driven to draw upon whatever of humble resources I might have,—to adopt a new course with him. I was not entirely sure that I should be able to hold my own with him, but I at least had the purpose made to do as well as I could upon him; and now I say that I will not be the first to cry "Hold." I think it originated with the Judge, and when he quits, I probably will. But I shall not ask any favors at all. He asks me, or he asks the audience, if I wish to push this matter to the point of personal difficulty. I tell him, no. He did not make a mistake, in one of his early speeches, when he called me an "amiable" man, though perhaps he did when he called me an "intelligent" man. It really hurts me very much to suppose that I have wronged anybody on earth. I again tell him, no! I very much prefer, when this canvass shall be over, however it may result, that we at least part without any bitter recollections of personal difficulties.
The Judge, in his concluding speech at Galesburgh, says that I was pushing this matter to a personal difficulty, to avoid the responsibility for the enormity of my principles. I say to the Judge and this audience, now, that I will again state our principles, as well as I hastily can, in all their enormity, and if the Judge hereafter chooses to confine himself to a war upon these principles, he will probably not find me departing from the same course.
We have in this nation this element of domestic slavery. It is a matter of absolute certainty that it is a disturbing element. It is the opinion of all the great men who have expressed an opinion upon it, that it is a dangerous element. We keep up a controversy in regard to it. That controversy necessarily springs from difference of opinion; and if we can learn exactly—can reduce to the lowest elements—what that difference of opinion is, we perhaps shall be better prepared for discussing the different systems of policy that we would propose in regard to that disturbing element. I suggest that the difference of opinion, reduced to its lowest of terms, is no other than the difference between the men who think slavery a wrong and those who do not think it wrong. The Republican party think it wrong; we think it is a moral, a social, and a political wrong. We think it as a wrong not confining itself merely to the persons or the States where it exists, but that it is a wrong in its tendency, to say the least, that extends itself to the existence of the whole nation. Because we think it wrong, we propose a course of policy that shall deal with it as a wrong. We deal with it as with any other wrong, in so far as we can prevent its growing any larger, and so deal with it that in the run of time there may be some promise of an end to it. We have a due regard to the actual presence of it amongst us, and the difficulties of getting rid of it in any satisfactory way, and all the constitutional obligations thrown about it. I suppose that in reference both to its actual existence in the nation, and to our constitutional obligations, we have no right at all to disturb it in the States where it exists, and we profess that we have no more inclination to disturb it than we have the right to do it. We go further than that: we don't propose to disturb it where, in one instance, we think the Constitution would permit us. We think the Constitution would permit us to disturb it in the District of Columbia. Still, we do not propose to do that, unless it should be in terms which I don't suppose the nation is very likely soon to agree to,—the terms of making the emancipation gradual, and compensating the unwilling owners. Where we suppose we have the constitutional right, we restrain ourselves in reference to the actual existence of the institution and the difficulties thrown about it. We also oppose it as an evil so far as it seeks to spread itself. We insist on the policy that shall restrict it to its present limits. We don't suppose that in doing this we violate anything due to the actual presence of the institution, or anything due to the constitutional guaranties thrown around it.
We oppose the Dred Scott decision in a certain way, upon which I ought perhaps to address you a few words. We do not propose that when Dred Scott has been decided to be a slave by the court, we, as a mob, will decide him to be free. We do not propose that, when any other one, or one thousand, shall be decided by that court to be slaves, we will in any violent way disturb the rights of property thus settled; but we nevertheless do oppose that decision as a political rule which shall be binding on the voter to vote for nobody who thinks it wrong, which shall be binding on the members of Congress or the President to favor no measure that does not actually concur with the principles of that decision. We do not propose to be bound by it as a political rule in that way, because we think it lays the foundation, not merely of enlarging and spreading out what we consider an evil, but it lays the foundation for spreading that evil into the States themselves. We propose so resisting it as to have it reversed if we can, and a new judicial rule established upon this subject.
I will add this: that if there be any man who does not believe that slavery is wrong in the three aspects which I have mentioned, or in any one of them, that man is misplaced, and ought to leave us; while on the other hand, if there be any man in the Republican party who is impatient over the necessity springing from its actual presence, and is impatient of the constitutional guaranties thrown around it, and would act in disregard of these, he too is misplaced, standing with us. He will find his place somewhere else; for we have a due regard, so far as we are capable of understanding them, for all these things. This, gentlemen, as well as I can give it, is a plain statement of our principles in all their enormity. I will say now that there is a sentiment in the country contrary to me,—a sentiment which holds that slavery is not wrong, and therefore it goes for the policy that does not propose dealing with it as a wrong. That policy is the Democratic policy, and that sentiment is the Democratic sentiment. If there be a doubt in the mind of any one of this vast audience that this is really the central idea of the Democratic party in relation to this subject, I ask him to bear with me while I state a few things tending, as I think, to prove that proposition. In the first place, the leading man—I think I may do my friend Judge Douglas the honor of calling him such advocating the present Democratic policy never himself says it is wrong. He has the high distinction, so far as I know, of never having said slavery is either right or wrong. Almost everybody else says one or the other, but the Judge never does. If there be a man in the Democratic party who thinks it is wrong, and yet clings to that party, I suggest to him, in the first place, that his leader don't talk as he does, for he never says that it is wrong. In the second place, I suggest to him that if he will examine the policy proposed to be carried forward, he will find that he carefully excludes the idea that there is anything wrong in it. If you will examine the arguments that are made on it, you will find that every one carefully excludes the idea that there is anything wrong in slavery. Perhaps that Democrat who says he is as much opposed to slavery as I am will tell me that I am wrong about this. I wish him to examine his own course in regard to this matter a moment, and then see if his opinion will not be changed a little. You say it is wrong; but don't you constantly object to anybody else saying so? Do you not constantly argue that this is not the right place to oppose it? You say it must not be opposed in the free States, because slavery is not here; it must not be opposed in the slave States, because it is there; it must not be opposed in politics, because that will make a fuss; it must not be opposed in the pulpit, because it is not religion. Then where is the place to oppose it? There is no suitable place to oppose it. There is no place in the country to oppose this evil overspreading the continent, which you say yourself is coming. Frank Blair and Gratz Brown tried to get up a system of gradual emancipation in Missouri, had an election in August, and got beat, and you, Mr. Democrat, threw up your hat, and hallooed "Hurrah for Democracy!" So I say, again, that in regard to the arguments that are made, when Judge Douglas Says he "don't care whether slavery is voted up or voted down," whether he means that as an individual expression of sentiment, or only as a sort of statement of his views on national policy, it is alike true to say that he can thus argue logically if he don't see anything wrong in it; but he cannot say so logically if he admits that slavery is wrong. He cannot say that he would as soon see a wrong voted up as voted down. When Judge Douglas says that whoever or whatever community wants slaves, they have a right to have them, he is perfectly logical, if there is nothing wrong in the institution; but if you admit that it is wrong, he cannot logically say that anybody has a right to do wrong. When he says that slave property and horse and hog property are alike to be allowed to go into the Territories, upon the principles of equality, he is reasoning truly, if there is no difference between them as property; but if the one is property held rightfully, and the other is wrong, then there is no equality between the right and wrong; so that, turn it in anyway you can, in all the arguments sustaining the Democratic policy, and in that policy itself, there is a careful, studied exclusion of the idea that there is anything wrong in slavery. Let us understand this. I am not, just here, trying to prove that we are right, and they are wrong. I have been stating where we and they stand, and trying to show what is the real difference between us; and I now say that whenever we can get the question distinctly stated, can get all these men who believe that slavery is in some of these respects wrong to stand and act with us in treating it as a wrong,—then, and not till then, I think we will in some way come to an end of this slavery agitation.
MY FRIENDS:—Since Judge Douglas has said to you in his conclusion that he had not time in an hour and a half to answer all I had said in an hour, it follows of course that I will not be able to answer in half an hour all that he said in an hour and a half.
I wish to return to Judge Douglas my profound thanks for his public annunciation here to-day, to be put on record, that his system of policy in regard to the institution of slavery contemplates that it shall last forever. We are getting a little nearer the true issue of this controversy, and I am profoundly grateful for this one sentence. Judge Douglas asks you, Why cannot the institution of slavery, or rather, why cannot the nation, part slave and part free, continue as our fathers made it, forever? In the first place, I insist that our fathers did not make this nation half slave and half free, or part slave and part free. I insist that they found the institution of slavery existing here. They did not make it so but they left it so because they knew of no way to get rid of it at that time. When Judge Douglas undertakes to say that, as a matter of choice, the fathers of the government made this nation part slave and part free, he assumes what is historically a falsehood. More than that: when the fathers of the government cut off the source of slavery by the abolition of the slave-trade, and adopted a system of restricting it from the new Territories where it had not existed, I maintain that they placed it where they understood, and all sensible men understood, it was in the course of ultimate extinction; and when Judge Douglas asks me why it cannot continue as our fathers made it, I ask him why he and his friends could not let it remain as our fathers made it?
It is precisely all I ask of him in relation to the institution of slavery, that it shall be placed upon the basis that our fathers placed it upon. Mr. Brooks, of South Carolina, once said, and truly said, that when this government was established, no one expected the institution of slavery to last until this day, and that the men who formed this government were wiser and better than the men of these days; but the men of these days had experience which the fathers had not, and that experience had taught them the invention of the cotton-gin, and this had made the perpetuation of the institution of slavery a necessity in this country. Judge Douglas could not let it stand upon the basis which our fathers placed it, but removed it, and put it upon the cotton-gin basis. It is a question, therefore, for him and his friends to answer, why they could not let it remain where the fathers of the government originally placed it. I hope nobody has understood me as trying to sustain the doctrine that we have a right to quarrel with Kentucky, or Virginia, or any of the slave States, about the institution of slavery,—thus giving the Judge an opportunity to be eloquent and valiant against us in fighting for their rights. I expressly declared in my opening speech that I had neither the inclination to exercise, nor the belief in the existence of, the right to interfere with the States of Kentucky or Virginia in doing as they pleased with slavery Or any other existing institution. Then what becomes of all his eloquence in behalf of the rights of States, which are assailed by no living man?
But I have to hurry on, for I have but a half hour. The Judge has informed me, or informed this audience, that the Washington Union is laboring for my election to the United States Senate. This is news to me,—not very ungrateful news either. [Turning to Mr. W. H. Carlin, who was on the stand]—I hope that Carlin will be elected to the State Senate, and will vote for me. [Mr. Carlin shook his head.] Carlin don't fall in, I perceive, and I suppose he will not do much for me; but I am glad of all the support I can get, anywhere, if I can get it without practicing any deception to obtain it. In respect to this large portion of Judge Douglas's speech in which he tries to show that in the controversy between himself and the Administration party he is in the right, I do not feel myself at all competent or inclined to answer him. I say to him, "Give it to them,—give it to them just all you can!" and, on the other hand, I say to Carlin, and Jake Davis, and to this man Wogley up here in Hancock, "Give it to Douglas, just pour it into him!"
Now, in regard to this matter of the Dred Scott decision, I wish to say a word or two. After all, the Judge will not say whether, if a decision is made holding that the people of the States cannot exclude slavery, he will support it or not. He obstinately refuses to say what he will do in that case. The judges of the Supreme Court as obstinately refused to say what they would do on this subject. Before this I reminded him that at Galesburgh he said the judges had expressly declared the contrary, and you remember that in my Opening speech I told him I had the book containing that decision here, and I would thank him to lay his finger on the place where any such thing was said. He has occupied his hour and a half, and he has not ventured to try to sustain his assertion. He never will. But he is desirous of knowing how we are going to reverse that Dred Scott decision. Judge Douglas ought to know how. Did not he and his political friends find a way to reverse the decision of that same court in favor of the constitutionality of the National Bank? Didn't they find a way to do it so effectually that they have reversed it as completely as any decision ever was reversed, so far as its practical operation is concerned?
And let me ask you, did n't Judge Douglas find a way to reverse the decision of our Supreme Court when it decided that Carlin's father—old Governor Carlin had not the constitutional power to remove a Secretary of State? Did he not appeal to the "MOBS," as he calls them? Did he not make speeches in the lobby to show how villainous that decision was, and how it ought to be overthrown? Did he not succeed, too, in getting an act passed by the Legislature to have it overthrown? And did n't he himself sit down on that bench as one of the five added judges, who were to overslaugh the four old ones, getting his name of "judge" in that way, and no other? If there is a villainy in using disrespect or making opposition to Supreme Court decisions, I commend it to Judge Douglas's earnest consideration. I know of no man in the State of Illinois who ought to know so well about how much villainy it takes to oppose a decision of the Supreme Court as our honorable friend Stephen A. Douglas.
Judge Douglas also makes the declaration that I say the Democrats are bound by the Dred Scott decision, while the Republicans are not. In the sense in which he argues, I never said it; but I will tell you what I have said and what I do not hesitate to repeat to-day. I have said that as the Democrats believe that decision to be correct, and that the extension of slavery is affirmed in the National Constitution, they are bound to support it as such; and I will tell you here that General Jackson once said each man was bound to support the Constitution "as he understood it." Now, Judge Douglas understands the Constitution according to the Dred Scott decision, and he is bound to support it as he understands it. I understand it another way, and therefore I am bound to support it in the way in which I understand it. And as Judge Douglas believes that decision to be correct, I will remake that argument if I have time to do so. Let me talk to some gentleman down there among you who looks me in the face. We will say you are a member of the Territorial Legislature, and, like Judge Douglas, you believe that the right to take and hold slaves there is a constitutional right The first thing you do is to swear you will support the Constitution, and all rights guaranteed therein; that you will, whenever your neighbor needs your legislation to support his constitutional rights, not withhold that legislation. If you withhold that necessary legislation for the support of the Constitution and constitutional rights, do you not commit perjury? I ask every sensible man if that is not so? That is undoubtedly just so, say what you please. Now, that is precisely what Judge Douglas says, that this is a constitutional right. Does the Judge mean to say that the Territorial Legislature in legislating may, by withholding necessary laws, or by passing unfriendly laws, nullify that constitutional right? Does he mean to say that? Does he mean to ignore the proposition so long and well established in law, that what you cannot do directly, you cannot do indirectly? Does he mean that? The truth about the matter is this: Judge Douglas has sung paeans to his "Popular Sovereignty" doctrine until his Supreme Court, co-operating with him, has squatted his Squatter Sovereignty out. But he will keep up this species of humbuggery about Squatter Sovereignty. He has at last invented this sort of do-nothing sovereignty,—that the people may exclude slavery by a sort of "sovereignty" that is exercised by doing nothing at all. Is not that running his Popular Sovereignty down awfully? Has it not got down as thin as the homeopathic soup that was made by boiling the shadow of a pigeon that had starved to death? But at last, when it is brought to the test of close reasoning, there is not even that thin decoction of it left. It is a presumption impossible in the domain of thought. It is precisely no other than the putting of that most unphilosophical proposition, that two bodies can occupy the same space at the same time. The Dred Scott decision covers the whole ground, and while it occupies it, there is no room even for the shadow of a starved pigeon to occupy the same ground.
Judge Douglas, in reply to what I have said about having upon a previous occasion made the speech at Ottawa as the one he took an extract from at Charleston, says it only shows that I practiced the deception twice. Now, my friends, are any of you obtuse enough to swallow that? Judge Douglas had said I had made a speech at Charleston that I would not make up north, and I turned around and answered him by showing I had made that same speech up north,—had made it at Ottawa; made it in his hearing; made it in the Abolition District,—in Lovejoy's District,—in the personal presence of Lovejoy himself,—in the same atmosphere exactly in which I had made my Chicago speech, of which he complains so much.
Now, in relation to my not having said anything about the quotation from the Chicago speech: he thinks that is a terrible subject for me to handle. Why, gentlemen, I can show you that the substance of the Chicago speech I delivered two years ago in "Egypt," as he calls it. It was down at Springfield. That speech is here in this book, and I could turn to it and read it to you but for the lack of time. I have not now the time to read it. ["Read it, read it."] No, gentlemen, I am obliged to use discretion in disposing most advantageously of my brief time. The Judge has taken great exception to my adopting the heretical statement in the Declaration of Independence, that "all men are created equal," and he has a great deal to say about negro equality. I want to say that in sometimes alluding to the Declaration of Independence, I have only uttered the sentiments that Henry Clay used to hold. Allow me to occupy your time a moment with what he said. Mr. Clay was at one time called upon in Indiana, and in a way that I suppose was very insulting, to liberate his slaves; and he made a written reply to that application, and one portion of it is in these words:
"What is the foundation of this appeal to me in Indiana to liberate the slaves under my care in Kentucky? It is a general declaration in the act announcing to the world the independence of the thirteen American colonies, that men are created equal. Now, as an abstract principle, there is no doubt of the truth of that declaration, and it is desirable in the original construction of society, and in organized societies, to keep it in view as a great fundamental principle."
When I sometimes, in relation to the organization of new societies in new countries, where the soil is clean and clear, insisted that we should keep that principle in view, Judge Douglas will have it that I want a negro wife. He never can be brought to understand that there is any middle ground on this subject. I have lived until my fiftieth year, and have never had a negro woman either for a slave or a wife, and I think I can live fifty centuries, for that matter, without having had one for either. I maintain that you may take Judge Douglas's quotations from my Chicago speech, and from my Charleston speech, and the Galesburgh speech,—in his speech of to-day,—and compare them over, and I am willing to trust them with you upon his proposition that they show rascality or double-dealing. I deny that they do.
The Judge does not seem at all disposed to have peace, but I find he is disposed to have a personal warfare with me. He says that my oath would not be taken against the bare word of Charles H. Lanphier or Thomas L. Harris. Well, that is altogether a matter of opinion. It is certainly not for me to vaunt my word against oaths of these gentlemen, but I will tell Judge Douglas again the facts upon which I "dared" to say they proved a forgery. I pointed out at Galesburgh that the publication of these resolutions in the Illinois State Register could not have been the result of accident, as the proceedings of that meeting bore unmistakable evidence of being done by a man who knew it was a forgery; that it was a publication partly taken from the real proceedings of the Convention, and partly from the proceedings of a convention at another place, which showed that he had the real proceedings before him, and taking one part of the resolutions, he threw out another part, and substituted false and fraudulent ones in their stead. I pointed that out to him, and also that his friend Lanphier, who was editor of the Register at that time and now is, must have known how it was done. Now, whether he did it, or got some friend to do it for him, I could not tell, but he certainly knew all about it. I pointed out to Judge Douglas that in his Freeport speech he had promised to investigate that matter. Does he now say that he did not make that promise? I have a right to ask why he did not keep it. I call upon him to tell here to-day why he did not keep that promise? That fraud has been traced up so that it lies between him, Harris, and Lanphier. There is little room for escape for Lanphier. Lanphier is doing the Judge good service, and Douglas desires his word to be taken for the truth. He desires Lanphier to be taken as authority in what he states in his newspaper. He desires Harris to be taken as a man of vast credibility; and when this thing lies among them, they will not press it to show where the guilt really belongs. Now, as he has said that he would investigate it, and implied that he would tell us the result of his investigation, I demand of him to tell why he did not investigate it, if he did not; and if he did, why he won't tell the result. I call upon him for that.
This is the third time that Judge Douglas has assumed that he learned about these resolutions by Harris's attempting to use them against Norton on the floor of Congress. I tell Judge Douglas the public records of the country show that he himself attempted it upon Trumbull a month before Harris tried them on Norton; that Harris had the opportunity of learning it from him, rather than he from Harris. I now ask his attention to that part of the record on the case. My friends, I am not disposed to detain you longer in regard to that matter.
I am told that I still have five minutes left. There is another matter I wish to call attention to. He says, when he discovered there was a mistake in that case, he came forward magnanimously, without my calling his attention to it, and explained it. I will tell you how he became so magnanimous. When the newspapers of our side had discovered and published it, and put it beyond his power to deny it, then he came forward and made a virtue of necessity by acknowledging it. Now he argues that all the point there was in those resolutions, although never passed at Springfield, is retained by their being passed at other localities. Is that true? He said I had a hand in passing them, in his opening speech, that I was in the convention and helped to pass them. Do the resolutions touch me at all? It strikes me there is some difference between holding a man responsible for an act which he has not done and holding him responsible for an act that he has done. You will judge whether there is any difference in the "spots." And he has taken credit for great magnanimity in coming forward and acknowledging what is proved on him beyond even the capacity of Judge Douglas to deny; and he has more capacity in that way than any other living man.
Then he wants to know why I won't withdraw the charge in regard to a conspiracy to make slavery national, as he has withdrawn the one he made. May it please his worship, I will withdraw it when it is proven false on me as that was proven false on him. I will add a little more than that, I will withdraw it whenever a reasonable man shall be brought to believe that the charge is not true. I have asked Judge Douglas's attention to certain matters of fact tending to prove the charge of a conspiracy to nationalize slavery, and he says he convinces me that this is all untrue because Buchanan was not in the country at that time, and because the Dred Scott case had not then got into the Supreme Court; and he says that I say the Democratic owners of Dred Scott got up the case. I never did say that I defy Judge Douglas to show that I ever said so, for I never uttered it. [One of Mr. Douglas's reporters gesticulated affirmatively at Mr. Lincoln.] I don't care if your hireling does say I did, I tell you myself that I never said the "Democratic" owners of Dred Scott got up the case. I have never pretended to know whether Dred Scott's owners were Democrats, or Abolitionists, or Freesoilers or Border Ruffians. I have said that there is evidence about the case tending to show that it was a made-up case, for the purpose of getting that decision. I have said that that evidence was very strong in the fact that when Dred Scott was declared to be a slave, the owner of him made him free, showing that he had had the case tried and the question settled for such use as could be made of that decision; he cared nothing about the property thus declared to be his by that decision. But my time is out, and I can say no more.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—I have been somewhat, in my own mind, complimented by a large portion of Judge Douglas's speech,—I mean that portion which he devotes to the controversy between himself and the present Administration. This is the seventh time Judge Douglas and myself have met in these joint discussions, and he has been gradually improving in regard to his war with the Administration. At Quincy, day before yesterday, he was a little more severe upon the Administration than I had heard him upon any occasion, and I took pains to compliment him for it. I then told him to give it to them with all the power he had; and as some of them were present, I told them I would be very much obliged if they would give it to him in about the same way. I take it he has now vastly improved upon the attack he made then upon the Administration. I flatter myself he has really taken my advice on this subject. All I can say now is to re-commend to him and to them what I then commended,—to prosecute the war against one another in the most vigorous manner. I say to them again: "Go it, husband!—Go it, bear!"
There is one other thing I will mention before I leave this branch of the discussion,—although I do not consider it much of my business, anyway. I refer to that part of the Judge's remarks where he undertakes to involve Mr. Buchanan in an inconsistency. He reads something from Mr. Buchanan, from which he undertakes to involve him in an inconsistency; and he gets something of a cheer for having done so. I would only remind the Judge that while he is very valiantly fighting for the Nebraska Bill and the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, it has been but a little while since he was the valiant advocate of the Missouri Compromise. I want to know if Buchanan has not as much right to be inconsistent as Douglas has? Has Douglas the exclusive right, in this country, of being on all sides of all questions? Is nobody allowed that high privilege but himself? Is he to have an entire monopoly on that subject?
So far as Judge Douglas addressed his speech to me, or so far as it was about me, it is my business to pay some attention to it. I have heard the Judge state two or three times what he has stated to-day, that in a speech which I made at Springfield, Illinois, I had in a very especial manner complained that the Supreme Court in the Dred Scott case had decided that a negro could never be a citizen of the United States. I have omitted by some accident heretofore to analyze this statement, and it is required of me to notice it now. In point of fact it is untrue. I never have complained especially of the Dred Scott decision because it held that a negro could not be a citizen, and the Judge is always wrong when he says I ever did so complain of it. I have the speech here, and I will thank him or any of his friends to show where I said that a negro should be a citizen, and complained especially of the Dred Scott decision because it declared he could not be one. I have done no such thing; and Judge Douglas, so persistently insisting that I have done so, has strongly impressed me with the belief of a predetermination on his part to misrepresent me. He could not get his foundation for insisting that I was in favor of this negro equality anywhere else as well as he could by assuming that untrue proposition. Let me tell this audience what is true in regard to that matter; and the means by which they may correct me if I do not tell them truly is by a recurrence to the speech itself. I spoke of the Dred Scott decision in my Springfield speech, and I was then endeavoring to prove that the Dred Scott decision was a portion of a system or scheme to make slavery national in this country. I pointed out what things had been decided by the court. I mentioned as a fact that they had decided that a negro could not be a citizen; that they had done so, as I supposed, to deprive the negro, under all circumstances, of the remotest possibility of ever becoming a citizen and claiming the rights of a citizen of the United States under a certain clause of the Constitution. I stated that, without making any complaint of it at all. I then went on and stated the other points decided in the case; namely, that the bringing of a negro into the State of Illinois and holding him in slavery for two years here was a matter in regard to which they would not decide whether it would make him free or not; that they decided the further point that taking him into a United States Territory where slavery was prohibited by Act of Congress did not make him free, because that Act of Congress, as they held, was unconstitutional. I mentioned these three things as making up the points decided in that case. I mentioned them in a lump, taken in connection with the introduction of the Nebraska Bill, and the amendment of Chase, offered at the time, declaratory of the right of the people of the Territories to exclude slavery, which was voted down by the friends of the bill. I mentioned all these things together, as evidence tending to prove a combination and conspiracy to make the institution of slavery national. In that connection and in that way I mentioned the decision on the point that a negro could not be a citizen, and in no other connection.
Out of this Judge Douglas builds up his beautiful fabrication of my purpose to introduce a perfect social and political equality between the white and black races. His assertion that I made an "especial objection" (that is his exact language) to the decision on this account is untrue in point of fact.
Now, while I am upon this subject, and as Henry Clay has been alluded to, I desire to place myself, in connection with Mr. Clay, as nearly right before this people as may be. I am quite aware what the Judge's object is here by all these allusions. He knows that we are before an audience having strong sympathies southward, by relationship, place of birth, and so on. He desires to place me in an extremely Abolition attitude. He read upon a former occasion, and alludes, without reading, to-day to a portion of a speech which I delivered in Chicago. In his quotations from that speech, as he has made them upon former occasions, the extracts were taken in such a way as, I suppose, brings them within the definition of what is called garbling,—taking portions of a speech which, when taken by themselves, do not present the entire sense of the speaker as expressed at the time. I propose, therefore, out of that same speech, to show how one portion of it which he skipped over (taking an extract before and an extract after) will give a different idea, and the true idea I intended to convey. It will take me some little time to read it, but I believe I will occupy the time that way.
You have heard him frequently allude to my controversy with him in regard to the Declaration of Independence. I confess that I have had a struggle with Judge Douglas on that matter, and I will try briefly to place myself right in regard to it on this occasion. I said—and it is between the extracts Judge Douglas has taken from this speech, and put in his published speeches:
"It may be argued that there are certain conditions that make necessities and impose them upon us, and to the extent that a necessity is imposed upon a man he must submit to it. I think that was the condition in which we found ourselves when we established this government. We had slaves among us, we could not get our Constitution unless we permitted them to remain in slavery, we could not secure the good we did secure if we grasped for more; and having by necessity submitted to that much, it does not destroy the principle that is the charter of our liberties. Let the charter remain as our standard."
Now, I have upon all occasions declared as strongly as Judge Douglas against the disposition to interfere with the existing institution of slavery. You hear me read it from the same speech from which he takes garbled extracts for the purpose of proving upon me a disposition to interfere with the institution of slavery, and establish a perfect social and political equality between negroes and white people.
Allow me while upon this subject briefly to present one other extract from a speech of mine, more than a year ago, at Springfield, in discussing this very same question, soon after Judge Douglas took his ground that negroes were, not included in the Declaration of Independence:
"I think the authors of that notable instrument intended to include all men, but they did not mean to declare all men equal in all respects. They did not mean to say all men were equal in color, size, intellect, moral development, or social capacity. They defined with tolerable distinctness in what they did consider all men created equal,—equal in certain inalienable rights, among which are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. This they said, and this they meant. They did not mean to assert the obvious untruth that all were then actually enjoying that equality, or yet that they were about to confer it immediately upon them. In fact they had no power to confer such a boon. They meant simply to declare the right, so that the enforcement of it might follow as fast as circumstances should permit.
"They meant to set up a standard maxim for free society which should be familiar to all,—constantly looked to, constantly labored for, and even, though never perfectly attained, constantly approximated, and thereby constantly spreading and deepening its influence, and augmenting the happiness and value of life to all people, of all colors, everywhere."
There again are the sentiments I have expressed in regard to the Declaration of Independence upon a former occasion,—sentiments which have been put in print and read wherever anybody cared to know what so humble an individual as myself chose to say in regard to it.
At Galesburgh, the other day, I said, in answer to Judge Douglas, that three years ago there never had been a man, so far as I knew or believed, in the whole world, who had said that the Declaration of Independence did not include negroes in the term "all men." I reassert it to-day. I assert that Judge Douglas and all his friends may search the whole records of the country, and it will be a matter of great astonishment to me if they shall be able to find that one human being three years ago had ever uttered the astounding sentiment that the term "all men" in the Declaration did not include the negro. Do not let me be misunderstood. I know that more than three years ago there were men who, finding this assertion constantly in the way of their schemes to bring about the ascendency and perpetuation of slavery, denied the truth of it. I know that Mr. Calhoun and all the politicians of his school denied the truth of the Declaration. I know that it ran along in the mouth of some Southern men for a period of years, ending at last in that shameful, though rather forcible, declaration of Pettit of Indiana, upon the floor of the United States Senate, that the Declaration of Independence was in that respect "a self-evident lie," rather than a self-evident truth. But I say, with a perfect knowledge of all this hawking at the Declaration without directly attacking it, that three years ago there never had lived a man who had ventured to assail it in the sneaking way of pretending to believe it, and then asserting it did not include the negro. I believe the first man who ever said it was Chief Justice Taney in the Dred Scott case, and the next to him was our friend Stephen A. Douglas. And now it has become the catchword of the entire party. I would like to call upon his friends everywhere to consider how they have come in so short a time to view this matter in a way so entirely different from their former belief; to ask whether they are not being borne along by an irresistible current,—whither, they know not.
In answer to my proposition at Galesburgh last week, I see that some man in Chicago has got up a letter, addressed to the Chicago Times, to show, as he professes, that somebody had said so before; and he signs himself "An Old-Line Whig," if I remember correctly. In the first place, I would say he was not an old-line Whig. I am somewhat acquainted with old-line Whigs from the origin to the end of that party; I became pretty well acquainted with them, and I know they always had some sense, whatever else you could ascribe to them. I know there never was one who had not more sense than to try to show by the evidence he produces that some men had, prior to the time I named, said that negroes were not included in the term "all men" in the Declaration of Independence. What is the evidence he produces? I will bring forward his evidence, and let you see what he offers by way of showing that somebody more than three years ago had said negroes were not included in the Declaration. He brings forward part of a speech from Henry Clay,—the part of the speech of Henry Clay which I used to bring forward to prove precisely the contrary. I guess we are surrounded to some extent to-day by the old friends of Mr. Clay, and they will be glad to hear anything from that authority. While he was in Indiana a man presented a petition to liberate his negroes, and he (Mr. Clay) made a speech in answer to it, which I suppose he carefully wrote out himself and caused to be published. I have before me an extract from that speech which constitutes the evidence this pretended "Old-Line Whig" at Chicago brought forward to show that Mr. Clay did n't suppose the negro was included in the Declaration of Independence. Hear what Mr. Clay said:
"And what is the foundation of this appeal to me in Indiana to liberate the slaves under my care in Kentucky? It is a general declaration in the act announcing to the world the independence of the thirteen American colonies, that all men are created equal. Now, as an abstract principle, there is no doubt of the truth of that declaration; and it is desirable, in the original construction of society and in organized societies, to keep it in view as a great fundamental principle. But, then, I apprehend that in no society that ever did exist, or ever shall be formed, was or can the equality asserted among the members of the human race be practically enforced and carried out. There are portions, large portions, women, minors, insane, culprits, transient sojourners, that will always probably remain subject to the government of another portion of the community.
"That declaration, whatever may be the extent of its import, was made by the delegations of the thirteen States. In most of them slavery existed, and had long existed, and was established by law. It was introduced and forced upon the colonies by the paramount law of England. Do you believe that in making that declaration the States that concurred in it intended that it should be tortured into a virtual emancipation of all the slaves within their respective limits? Would Virginia and other Southern States have ever united in a declaration which was to be interpreted into an abolition of slavery among them? Did any one of the thirteen colonies entertain such a design or expectation? To impute such a secret and unavowed purpose, would be to charge a political fraud upon the noblest band of patriots that ever assembled in council,—a fraud upon the Confederacy of the Revolution; a fraud upon the union of those States whose Constitution not only recognized the lawfulness of slavery, but permitted the importation of slaves from Africa until the year 1808."
This is the entire quotation brought forward to prove that somebody previous to three years ago had said the negro was not included in the term "all men" in the Declaration. How does it do so? In what way has it a tendency to prove that? Mr. Clay says it is true as an abstract principle that all men are created equal, but that we cannot practically apply it in all eases. He illustrates this by bringing forward the cases of females, minors, and insane persons, with whom it cannot be enforced; but he says it is true as an abstract principle in the organization of society as well as in organized society and it should be kept in view as a fundamental principle. Let me read a few words more before I add some comments of my own. Mr. Clay says, a little further on:
"I desire no concealment of my opinions in regard to the institution of slavery. I look upon it as a great evil, and deeply lament that we have derived it from the parental government and from our ancestors. I wish every slave in the United States was in the country of his ancestors. But here they are, and the question is, How can they be best dealt with? If a state of nature existed, and we were about to lay the foundations of society, no man would be more strongly opposed than I should be to incorporate the institution of slavery amongst its elements."
Now, here in this same book, in this same speech, in this same extract, brought forward to prove that Mr. Clay held that the negro was not included in the Declaration of Independence, is no such statement on his part, but the declaration that it is a great fundamental truth which should be constantly kept in view in the organization of society and in societies already organized. But if I say a word about it; if I attempt, as Mr. Clay said all good men ought to do, to keep it in view; if, in this "organized society," I ask to have the public eye turned upon it; if I ask, in relation to the organization of new Territories, that the public eye should be turned upon it, forthwith I am vilified as you hear me to-day. What have I done that I have not the license of Henry Clay's illustrious example here in doing? Have I done aught that I have not his authority for, while maintaining that in organizing new Territories and societies this fundamental principle should be regarded, and in organized society holding it up to the public view and recognizing what he recognized as the great principle of free government?
And when this new principle—this new proposition that no human being ever thought of three years ago—is brought forward, I combat it as having an evil tendency, if not an evil design. I combat it as having a tendency to dehumanize the negro, to take away from him the right of ever striving to be a man. I combat it as being one of the thousand things constantly done in these days to prepare the public mind to make property, and nothing but property, of the negro in all the States of this Union.
But there is a point that I wish, before leaving this part of the discussion, to ask attention to. I have read and I repeat the words of Henry Clay:
"I desire no concealment of my opinions in regard to the institution of slavery. I look upon it as a great evil, and deeply lament that we have derived it from the parental government and from our ancestors. I wish every slave in the United States was in the country of his ancestors. But here they are, and the question is, How can they be best dealt with? If a state of nature existed, and we were about to lay the foundations of society, no man would be more strongly opposed than I should be to incorporate the institution of slavery amongst its elements."
The principle upon which I have insisted in this canvass is in relation to laying the foundations of new societies. I have never sought to apply these principles to the old States for the purpose of abolishing slavery in those States. It is nothing but a miserable perversion of what I have said, to assume that I have declared Missouri, or any other slave State, shall emancipate her slaves; I have proposed no such thing. But when Mr. Clay says that in laying the foundations of society in our Territories where it does not exist, he would be opposed to the introduction of slavery as an element, I insist that we have his warrant—his license—for insisting upon the exclusion of that element which he declared in such strong and emphatic language was most hurtful to him.
Judge Douglas has again referred to a Springfield speech in which I said "a house divided against itself cannot stand." The Judge has so often made the entire quotation from that speech that I can make it from memory. I used this language:
"We are now far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to the slavery agitation. Under the operation of this policy, that agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented. In my opinion it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. 'A house divided against itself cannot stand.' I believe this government cannot endure permanently, half slave and half free. I do not expect the house to fall, but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South."
That extract and the sentiments expressed in it have been extremely offensive to Judge Douglas. He has warred upon them as Satan wars upon the Bible. His perversions upon it are endless. Here now are my views upon it in brief:
I said we were now far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to the slavery agitation. Is it not so? When that Nebraska Bill was brought forward four years ago last January, was it not for the "avowed object" of putting an end to the slavery agitation? We were to have no more agitation in Congress; it was all to be banished to the Territories. By the way, I will remark here that, as Judge Douglas is very fond of complimenting Mr. Crittenden in these days, Mr. Crittenden has said there was a falsehood in that whole business, for there was no slavery agitation at that time to allay. We were for a little while quiet on the troublesome thing, and that very allaying plaster of Judge Douglas's stirred it up again. But was it not understood or intimated with the "confident promise" of putting an end to the slavery agitation? Surely it was. In every speech you heard Judge Douglas make, until he got into this "imbroglio," as they call it, with the Administration about the Lecompton Constitution, every speech on that Nebraska Bill was full of his felicitations that we were just at the end of the slavery agitation. The last tip of the last joint of the old serpent's tail was just drawing out of view. But has it proved so? I have asserted that under that policy that agitation "has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented." When was there ever a greater agitation in Congress than last winter? When was it as great in the country as to-day?
There was a collateral object in the introduction of that Nebraska policy, which was to clothe the people of the Territories with a superior degree of self-government, beyond what they had ever had before. The first object and the main one of conferring upon the people a higher degree of "self-government" is a question of fact to be determined by you in answer to a single question. Have you ever heard or known of a people anywhere on earth who had as little to do as, in the first instance of its use, the people of Kansas had with this same right of "self-government "? In its main policy and in its collateral object, it has been nothing but a living, creeping lie from the time of its introduction till to-day.
I have intimated that I thought the agitation would not cease until a crisis should have been reached and passed. I have stated in what way I thought it would be reached and passed. I have said that it might go one way or the other. We might, by arresting the further spread of it, and placing it where the fathers originally placed it, put it where the public mind should rest in the belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. Thus the agitation may cease. It may be pushed forward until it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South. I have said, and I repeat, my wish is that the further spread of it may be arrested, and that it may be where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction—I have expressed that as my wish I entertain the opinion, upon evidence sufficient to my mind, that the fathers of this government placed that institution where the public mind did rest in the belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction. Let me ask why they made provision that the source of slavery—the African slave-trade—should be cut off at the end of twenty years? Why did they make provision that in all the new territory we owned at that time slavery should be forever inhibited? Why stop its spread in one direction, and cut off its source in another, if they did not look to its being placed in the course of its ultimate extinction?
Again: the institution of slavery is only mentioned in the Constitution of the United States two or three times, and in neither of these cases does the word "slavery" or "negro race" occur; but covert language is used each time, and for a purpose full of significance. What is the language in regard to the prohibition of the African slave-trade? It runs in about this way:
"The migration or importation of such persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit, shall not be prohibited by the Congress prior to the year one thousand eight hundred and eight."
The next allusion in the Constitution to the question of slavery and the black race is on the subject of the basis of representation, and there the language used is:
"Representatives and direct taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole number of free persons, including those bound to service for a term of years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three-fifths of all other persons."
It says "persons," not slaves, not negroes; but this "three-fifths" can be applied to no other class among us than the negroes.
Lastly, in the provision for the reclamation of fugitive slaves, it is said:
"No person held to service or labor in one State, under the laws thereof, escaping into another, shall in consequence of any law or regulation therein be discharged from such service or labor, but shall be delivered up, on claim of the party to whom such service or labor may be due."
There again there is no mention of the word "negro" or of slavery. In all three of these places, being the only allusions to slavery in the instrument, covert language is used. Language is used not suggesting that slavery existed or that the black race were among us. And I understand the contemporaneous history of those times to be that covert language was used with a purpose, and that purpose was that in our Constitution, which it was hoped and is still hoped will endure forever,—when it should be read by intelligent and patriotic men, after the institution of slavery had passed from among us,—there should be nothing on the face of the great charter of liberty suggesting that such a thing as negro slavery had ever existed among us. This is part of the evidence that the fathers of the government expected and intended the institution of slavery to come to an end. They expected and intended that it should be in the course of ultimate extinction. And when I say that I desire to see the further spread of it arrested, I only say I desire to see that done which the fathers have first done. When I say I desire to see it placed where the public mind will rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, I only say I desire to see it placed where they placed it. It is not true that our fathers, as Judge Douglas assumes, made this government part slave and part free. Understand the sense in which he puts it. He assumes that slavery is a rightful thing within itself,—was introduced by the framers of the Constitution. The exact truth is, that they found the institution existing among us, and they left it as they found it. But in making the government they left this institution with many clear marks of disapprobation upon it. They found slavery among them, and they left it among them because of the difficulty—the absolute impossibility—of its immediate removal. And when Judge Douglas asks me why we cannot let it remain part slave and part free, as the fathers of the government made it, he asks a question based upon an assumption which is itself a falsehood; and I turn upon him and ask him the question, when the policy that the fathers of the government had adopted in relation to this element among us was the best policy in the world, the only wise policy, the only policy that we can ever safely continue upon that will ever give us peace, unless this dangerous element masters us all and becomes a national institution,—I turn upon him and ask him why he could not leave it alone. I turn and ask him why he was driven to the necessity of introducing a new policy in regard to it. He has himself said he introduced a new policy. He said so in his speech on the 22d of March of the present year, 1858. I ask him why he could not let it remain where our fathers placed it. I ask, too, of Judge Douglas and his friends why we shall not again place this institution upon the basis on which the fathers left it. I ask you, when he infers that I am in favor of setting the free and slave States at war, when the institution was placed in that attitude by those who made the Constitution, did they make any war? If we had no war out of it when thus placed, wherein is the ground of belief that we shall have war out of it if we return to that policy? Have we had any peace upon this matter springing from any other basis? I maintain that we have not. I have proposed nothing more than a return to the policy of the fathers.
I confess, when I propose a certain measure of policy, it is not enough for me that I do not intend anything evil in the result, but it is incumbent on me to show that it has not a tendency to that result. I have met Judge Douglas in that point of view. I have not only made the declaration that I do not mean to produce a conflict between the States, but I have tried to show by fair reasoning, and I think I have shown to the minds of fair men, that I propose nothing but what has a most peaceful tendency. The quotation that I happened to make in that Springfield Speech, that "a house divided against itself cannot stand," and which has proved so offensive to the judge, was part and parcel of the same thing. He tries to show that variety in the democratic institutions of the different States is necessary and indispensable. I do not dispute it. I have no controversy with Judge Douglas about that. I shall very readily agree with him that it would be foolish for us to insist upon having a cranberry law here in Illinois, where we have no cranberries, because they have a cranberry law in Indiana, where they have cranberries. I should insist that it would be exceedingly wrong in us to deny to Virginia the right to enact oyster laws, where they have oysters, because we want no such laws here. I understand, I hope, quite as well as Judge Douglas or anybody else, that the variety in the soil and climate and face of the country, and consequent variety in the industrial pursuits and productions of a country, require systems of law conforming to this variety in the natural features of the country. I understand quite as well as Judge Douglas that if we here raise a barrel of flour more than we want, and the Louisianians raise a barrel of sugar more than they want, it is of mutual advantage to exchange. That produces commerce, brings us together, and makes us better friends. We like one another the more for it. And I understand as well as Judge Douglas, or anybody else, that these mutual accommodations are the cements which bind together the different parts of this Union; that instead of being a thing to "divide the house,"—figuratively expressing the Union,—they tend to sustain it; they are the props of the house, tending always to hold it up.
But when I have admitted all this, I ask if there is any parallel between these things and this institution of slavery? I do not see that there is any parallel at all between them. Consider it. When have we had any difficulty or quarrel amongst ourselves about the cranberry laws of Indiana, or the oyster laws of Virginia, or the pine-lumber laws of Maine, or the fact that Louisiana produces sugar, and Illinois flour? When have we had any quarrels over these things? When have we had perfect peace in regard to this thing which I say is an element of discord in this Union? We have sometimes had peace, but when was it? It was when the institution of slavery remained quiet where it was. We have had difficulty and turmoil whenever it has made a struggle to spread itself where it was not. I ask, then, if experience does not speak in thunder-tones telling us that the policy which has given peace to the country heretofore, being returned to, gives the greatest promise of peace again. You may say, and Judge Douglas has intimated the same thing, that all this difficulty in regard to the institution of slavery is the mere agitation of office-seekers and ambitious Northern politicians. He thinks we want to get "his place," I suppose. I agree that there are office-seekers amongst us. The Bible says somewhere that we are desperately selfish. I think we would have discovered that fact without the Bible. I do not claim that I am any less so than the average of men, but I do claim that I am not more selfish than Judge Douglas.
But is it true that all the difficulty and agitation we have in regard to this institution of slavery spring from office-seeking, from the mere ambition of politicians? Is that the truth? How many times have we had danger from this question? Go back to the day of the Missouri Compromise. Go back to the nullification question, at the bottom of which lay this same slavery question. Go back to the time of the annexation of Texas. Go back to the troubles that led to the Compromise of 1850. You will find that every time, with the single exception of the Nullification question, they sprung from an endeavor to spread this institution. There never was a party in the history of this country, and there probably never will be, of sufficient strength to disturb the general peace of the country. Parties themselves may be divided and quarrel on minor questions, yet it extends not beyond the parties themselves. But does not this question make a disturbance outside of political circles? Does it not enter into the churches and rend them asunder? What divided the great Methodist Church into two parts, North and South? What has raised this constant disturbance in every Presbyterian General Assembly that meets? What disturbed the Unitarian Church in this very city two years ago? What has jarred and shaken the great American Tract Society recently, not yet splitting it, but sure to divide it in the end? Is it not this same mighty, deep-seated power that somehow operates on the minds of men, exciting and stirring them up in every avenue of society,—in politics, in religion, in literature, in morals, in all the manifold relations of life? Is this the work of politicians? Is that irresistible power, which for fifty years has shaken the government and agitated the people, to be stifled and subdued by pretending that it is an exceedingly simple thing, and we ought not to talk about it? If you will get everybody else to stop talking about it, I assure you I will quit before they have half done so. But where is the philosophy or statesmanship which assumes that you can quiet that disturbing element in our society which has disturbed us for more than half a century, which has been the only serious danger that has threatened our institutions,—I say, where is the philosophy or the statesmanship based on the assumption that we are to quit talking about it, and that the public mind is all at once to cease being agitated by it? Yet this is the policy here in the North that Douglas is advocating, that we are to care nothing about it! I ask you if it is not a false philosophy. Is it not a false statesmanship that undertakes to build up a system of policy upon the basis of caring nothing about the very thing that everybody does care the most about—a thing which all experience has shown we care a very great deal about?
The Judge alludes very often in the course of his remarks to the exclusive right which the States have to decide the whole thing for themselves. I agree with him very readily that the different States have that right. He is but fighting a man of straw when he assumes that I am contending against the right of the States to do as they please about it. Our controversy with him is in regard to the new Territories. We agree that when the States come in as States they have the right and the power to do as they please. We have no power as citizens of the free-States, or in our Federal capacity as members of the Federal Union through the General Government, to disturb slavery in the States where it exists. We profess constantly that we have no more inclination than belief in the power of the government to disturb it; yet we are driven constantly to defend ourselves from the assumption that we are warring upon the rights of the Sates. What I insist upon is, that the new Territories shall be kept free from it while in the Territorial condition. Judge Douglas assumes that we have no interest in them,—that we have no right whatever to interfere. I think we have some interest. I think that as white men we have. Do we not wish for an outlet for our surplus population, if I may so express myself? Do we not feel an interest in getting to that outlet with such institutions as we would like to have prevail there? If you go to the Territory opposed to slavery, and another man comes upon the same ground with his slave, upon the assumption that the things are equal, it turns out that he has the equal right all his way, and you have no part of it your way. If he goes in and makes it a slave Territory, and by consequence a slave State, is it not time that those who desire to have it a free State were on equal ground? Let me suggest it in a different way. How many Democrats are there about here ["A thousand"] who have left slave States and come into the free State of Illinois to get rid of the institution of slavery? [Another voice: "A thousand and one."] I reckon there are a thousand and one. I will ask you, if the policy you are now advocating had prevailed when this country was in a Territorial condition, where would you have gone to get rid of it? Where would you have found your free State or Territory to go to? And when hereafter, for any cause, the people in this place shall desire to find new homes, if they wish to be rid of the institution, where will they find the place to go to?
Now, irrespective of the moral aspect of this question as to whether there is a right or wrong in enslaving a negro, I am still in favor of our new Territories being in such a condition that white men may find a home,—may find some spot where they can better their condition; where they can settle upon new soil and better their condition in life. I am in favor of this, not merely (I must say it here as I have elsewhere) for our own people who are born amongst us, but as an outlet for free white people everywhere the world over—in which Hans, and Baptiste, and Patrick, and all other men from all the world, may find new homes and better their conditions in life.
I have stated upon former occasions, and I may as well state again, what I understand to be the real issue in this controversy between Judge Douglas and myself. On the point of my wanting to make war between the free and the slave States, there has been no issue between us. So, too, when he assumes that I am in favor of producing a perfect social and political equality between the white and black races. These are false issues, upon which Judge Douglas has tried to force the controversy. There is no foundation in truth for the charge that I maintain either of these propositions. The real issue in this controversy—the one pressing upon every mind—is the sentiment on the part of one class that looks upon the institution of slavery as a wrong, and of another class that does not look upon it as a wrong. The sentiment that contemplates the institution of slavery in this country as a wrong is the sentiment of the Republican party. It is the sentiment around which all their actions, all their arguments, circle, from which all their propositions radiate. They look upon it as being a moral, social, and political wrong; and while they contemplate it as such, they nevertheless have due regard for its actual existence among us, and the difficulties of getting rid of it in any satisfactory way, and to all the constitutional obligations thrown about it. Yet, having a due regard for these, they desire a policy in regard to it that looks to its not creating any more danger. They insist that it should, as far as may be, be treated as a wrong; and one of the methods of treating it as a wrong is to make provision that it shall grow no larger. They also desire a policy that looks to a peaceful end of slavery at some time. These are the views they entertain in regard to it as I understand them; and all their sentiments, all their arguments and propositions, are brought within this range. I have said, and I repeat it here, that if there be a man amongst us who does not think that the institution of slavery is wrong in any one of the aspects of which I have spoken, he is misplaced, and ought not to be with us. And if there be a man amongst us who is so impatient of it as a wrong as to disregard its actual presence among us and the difficulty of getting rid of it suddenly in a satisfactory way, and to disregard the constitutional obligations thrown about it, that man is misplaced if he is on our platform. We disclaim sympathy with him in practical action. He is not placed properly with us.
On this subject of treating it as a wrong, and limiting its spread, let me say a word. Has anything ever threatened the existence of this Union save and except this very institution of slavery? What is it that we hold most dear amongst us? Our own liberty and prosperity. What has ever threatened our liberty and prosperity, save and except this institution of slavery? If this is true, how do you propose to improve the condition of things by enlarging slavery, by spreading it out and making it bigger? You may have a wen or cancer upon your person, and not be able to cut it out, lest you bleed to death; but surely it is no way to cure it, to engraft it and spread it over your whole body. That is no proper way of treating what you regard a wrong. You see this peaceful way of dealing with it as a wrong, restricting the spread of it, and not allowing it to go into new countries where it has not already existed. That is the peaceful way, the old-fashioned way, the way in which the fathers themselves set us the example.
On the other hand, I have said there is a sentiment which treats it as not being wrong. That is the Democratic sentiment of this day. I do not mean to say that every man who stands within that range positively asserts that it is right. That class will include all who positively assert that it is right, and all who, like Judge Douglas, treat it as indifferent and do not say it is either right or wrong. These two classes of men fall within the general class of those who do not look upon it as a wrong. And if there be among you anybody who supposes that he, as a Democrat, can consider himself "as much opposed to slavery as anybody," I would like to reason with him. You never treat it as a wrong. What other thing that you consider as a wrong do you deal with as you deal with that? Perhaps you say it is wrong—but your leader never does, and you quarrel with anybody who says it is wrong. Although you pretend to say so yourself, you can find no fit place to deal with it as a wrong. You must not say anything about it in the free States, because it is not here. You must not say anything about it in the slave States, because it is there. You must not say anything about it in the pulpit, because that is religion, and has nothing to do with it. You must not say anything about it in politics, because that will disturb the security of "my place." There is no place to talk about it as being a wrong, although you say yourself it is a wrong. But, finally, you will screw yourself up to the belief that if the people of the slave States should adopt a system of gradual emancipation on the slavery question, you would be in favor of it. You would be in favor of it. You say that is getting it in the right place, and you would be glad to see it succeed. But you are deceiving yourself. You all know that Frank Blair and Gratz Brown, down there in St. Louis, undertook to introduce that system in Missouri. They fought as valiantly as they could for the system of gradual emancipation which you pretend you would be glad to see succeed. Now, I will bring you to the test. After a hard fight they were beaten, and when the news came over here, you threw up your hats and hurrahed for Democracy. More than that, take all the argument made in favor of the system you have proposed, and it carefully excludes the idea that there is anything wrong in the institution of slavery. The arguments to sustain that policy carefully exclude it. Even here to-day you heard Judge Douglas quarrel with me because I uttered a wish that it might sometime come to an end. Although Henry Clay could say he wished every slave in the United States was in the country of his ancestors, I am denounced by those pretending to respect Henry Clay for uttering a wish that it might sometime, in some peaceful way, come to an end. The Democratic policy in regard to that institution will not tolerate the merest breath, the slightest hint, of the least degree of wrong about it. Try it by some of Judge Douglas's arguments. He says he "don't care whether it is voted up or voted down" in the Territories. I do not care myself, in dealing with that expression, whether it is intended to be expressive of his individual sentiments on the subject, or only of the national policy he desires to have established. It is alike valuable for my purpose. Any man can say that who does not see anything wrong in slavery; but no man can logically say it who does see a wrong in it, because no man can logically say he don't care whether a wrong is voted up or voted down. He may say he don't care whether an indifferent thing is voted up or down, but he must logically have a choice between a right thing and a wrong thing. He contends that whatever community wants slaves has a right to have them. So they have, if it is not a wrong. But if it is a wrong, he cannot say people have a right to do wrong. He says that upon the score of equality slaves should be allowed to go in a new Territory, like other property. This is strictly logical if there is no difference between it and other property. If it and other property are equal, this argument is entirely logical. But if you insist that one is wrong and the other right, there is no use to institute a comparison between right and wrong. You may turn over everything in the Democratic policy from beginning to end, whether in the shape it takes on the statute book, in the shape it takes in the Dred Scott decision, in the shape it takes in conversation, or the shape it takes in short maxim-like arguments,—it everywhere carefully excludes the idea that there is anything wrong in it.
That is the real issue. That is the issue that will continue in this country when these poor tongues of Judge Douglas and myself shall be silent. It is the eternal struggle between these two principles—right and wrong—throughout the world. They are the two principles that have stood face to face from the beginning of time, and will ever continue to struggle. The one is the common right of humanity, and the other the divine right of kings. It is the same principle in whatever shape it develops itself. It is the same spirit that says, "You work and toil and earn bread, and I'll eat it." No matter in what shape it comes, whether from the mouth of a king who seeks to bestride the people of his own nation and live by the fruit of their labor, or from one race of men as an apology for enslaving another race, it is the same tyrannical principle. I was glad to express my gratitude at Quincy, and I re-express it here, to Judge Douglas,—that he looks to no end of the institution of slavery. That will help the people to see where the struggle really is. It will hereafter place with us all men who really do wish the wrong may have an end. And whenever we can get rid of the fog which obscures the real question, when we can get Judge Douglas and his friends to avow a policy looking to its perpetuation,—we can get out from among that class of men and bring them to the side of those who treat it as a wrong. Then there will soon be an end of it, and that end will be its "ultimate extinction." Whenever the issue can be distinctly made, and all extraneous matter thrown out so that men can fairly see the real difference between the parties, this controversy will soon be settled, and it will be done peaceably too. There will be no war, no violence. It will be placed again where the wisest and best men of the world placed it. Brooks of South Carolina once declared that when this Constitution was framed its framers did not look to the institution existing until this day. When he said this, I think he stated a fact that is fully borne out by the history of the times. But he also said they were better and wiser men than the men of these days, yet the men of these days had experience which they had not, and by the invention of the cotton-gin it became a necessity in this country that slavery should be perpetual. I now say that, willingly or unwillingly—purposely or without purpose, Judge Douglas has been the most prominent instrument in changing the position of the institution of slavery,—which the fathers of the government expected to come to an end ere this, and putting it upon Brooks's cotton-gin basis; placing it where he openly confesses he has no desire there shall ever be an end of it.
I understand I have ten minutes yet. I will employ it in saying something about this argument Judge Douglas uses, while he sustains the Dred Scott decision, that the people of the Territories can still somehow exclude slavery. The first thing I ask attention to is the fact that Judge Douglas constantly said, before the decision, that whether they could or not, was a question for the Supreme Court. But after the court had made the decision he virtually says it is not a question for the Supreme Court, but for the people. And how is it he tells us they can exclude it? He says it needs "police regulations," and that admits of "unfriendly legislation." Although it is a right established by the Constitution of the United States to take a slave into a Territory of the United States and hold him as property, yet unless the Territorial Legislature will give friendly legislation, and more especially if they adopt unfriendly legislation, they can practically exclude him. Now, without meeting this proposition as a matter of fact, I pass to consider the real constitutional obligation. Let me take the gentleman who looks me in the face before me, and let us suppose that he is a member of the Territorial Legislature. The first thing he will do will be to swear that he will support the Constitution of the United States. His neighbor by his side in the Territory has slaves and needs Territorial legislation to enable him to enjoy that constitutional right. Can he withhold the legislation which his neighbor needs for the enjoyment of a right which is fixed in his favor in the Constitution of the United States which he has sworn to support? Can he withhold it without violating his oath? And, more especially, can he pass unfriendly legislation to violate his oath? Why, this is a monstrous sort of talk about the Constitution of the United States! There has never been as outlandish or lawless a doctrine from the mouth of any respectable man on earth. I do not believe it is a constitutional right to hold slaves in a Territory of the United States. I believe the decision was improperly made and I go for reversing it. Judge Douglas is furious against those who go for reversing a decision. But he is for legislating it out of all force while the law itself stands. I repeat that there has never been so monstrous a doctrine uttered from the mouth of a respectable man.
I suppose most of us (I know it of myself) believe that the people of the Southern States are entitled to a Congressional Fugitive Slave law,—that is a right fixed in the Constitution. But it cannot be made available to them without Congressional legislation. In the Judge's language, it is a "barren right," which needs legislation before it can become efficient and valuable to the persons to whom it is guaranteed. And as the right is constitutional, I agree that the legislation shall be granted to it, and that not that we like the institution of slavery. We profess to have no taste for running and catching niggers, at least, I profess no taste for that job at all. Why then do I yield support to a Fugitive Slave law? Because I do not understand that the Constitution, which guarantees that right, can be supported without it. And if I believed that the right to hold a slave in a Territory was equally fixed in the Constitution with the right to reclaim fugitives, I should be bound to give it the legislation necessary to support it. I say that no man can deny his obligation to give the necessary legislation to support slavery in a Territory, who believes it is a constitutional right to have it there. No man can, who does not give the Abolitionists an argument to deny the obligation enjoined by the Constitution to enact a Fugitive State law. Try it now. It is the strongest Abolition argument ever made. I say if that Dred Scott decision is correct, then the right to hold slaves in a Territory is equally a constitutional right with the right of a slaveholder to have his runaway returned. No one can show the distinction between them. The one is express, so that we cannot deny it. The other is construed to be in the Constitution, so that he who believes the decision to be correct believes in the right. And the man who argues that by unfriendly legislation, in spite of that constitutional right, slavery may be driven from the Territories, cannot avoid furnishing an argument by which Abolitionists may deny the obligation to return fugitives, and claim the power to pass laws unfriendly to the right of the slaveholder to reclaim his fugitive. I do not know how such an arguement may strike a popular assembly like this, but I defy anybody to go before a body of men whose minds are educated to estimating evidence and reasoning, and show that there is an iota of difference between the constitutional right to reclaim a fugitive and the constitutional right to hold a slave, in a Territory, provided this Dred Scott decision is correct, I defy any man to make an argument that will justify unfriendly legislation to deprive a slaveholder of his right to hold his slave in a Territory, that will not equally, in all its length, breadth, and thickness, furnish an argument for nullifying the Fugitive Slave law. Why, there is not such an Abolitionist in the nation as Douglas, after all!
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
THE WRITINGS OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN, Volume Five, 1858-1862
TO SYDNEY SPRING, GRAYVILLE, ILL.
TO JOHN MATHERS, JACKSONVILLE, ILL.
TO DR. WILLIAM FITHIAN, DANVILLE, ILL.
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT PARIS, ILL.,
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT EDWARDSVILLE, ILL.,
SENATORIAL ELECTION LOST AND OUT OF MONEY
REALIZATION THAT DEBATES MUST BE SAVED
A LEGAL OPINION BY ABRAHAM LINCOLN.
TO THE GOVERNOR, AUDITOR, AND TREASURER OF THE STATE OF ILLINOIS.
FIRST SUGGESTION OF A PRESIDENTIAL OFFER.
SPEECH AT CINCINNATI OHIO, SEPTEMBER 17, 1859
FRAGMENT OF SPEECH AT LEAVENWORTH, KANSAS,
TO G. W. DOLE, G. S. HUBBARD, AND W. H. BROWN.
ON NOMINATION TO THE NATIONAL TICKET
SPEECH AT NEW HAVEN, CONNECTICUT, MARCH 6, 1860
RESPONSE TO AN ELECTOR'S REQUEST FOR MONEY
ACCUSATION OF HAVING BEEN PAID FOR A POLITICAL SPEECH
TELEGRAM TO A MEMBER OF THE ILLINOIS DELEGATION
REPLY TO THE COMMITTEE SENT BY THE CHICAGO CONVENTION TO INFORM
ACCEPTANCE OF NOMINATION AS REPUBLICAN CANDIDATE FOR PRESIDENT
FORM OF REPLY PREPARED BY MR. LINCOLN,
SLOW TO LISTEN TO CRIMINATIONS
EARLY INFORMATION ON ARMY DEFECTION IN SOUTH
BLOCKING "COMPROMISE" ON SLAVERY ISSUE
SOME FORTS SURRENDERED TO THE SOUTH
SUPPORT OF THE FUGITIVE SLAVE CLAUSE
ATTEMPT TO FORM A COALITION CABINET
FAREWELL ADDRESS AT SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS,
REMARKS AT TOLONO, ILLINOIS, FEBRUARY 11, 1861
REPLY TO ADDRESS OF WELCOME, INDIANAPOLIS,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF INDIANA, AT INDIANAPOLIS,
ADDRESS TO THE GERMAN CLUB OF CINCINNATI, OHIO,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF OHIO AT COLUMBUS
ADDRESS AT STEUBENVILLE, OHIO,
ADDRESS AT PITTSBURGH, PENNSYLVANIA
ADDRESS AT ROCHESTER, NEW YORK,
ADDRESS AT SYRACUSE, NEW YORK,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF ALBANY, NEW YORK
REPLY TO GOVERNOR MORGAN OF NEW YORK, AT ALBANY,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF NEW YORK, AT ALBANY,
ADDRESS AT POUGHKEEPSIE, NEW YORK,
ADDRESS AT PEEKSKILL, NEW YORK,
REMARKS AT THE ASTOR HOUSE, NEW YORK CITY, FEBRUARY 19, 1861
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF NEW YORK CITY,
ADDRESS AT JERSEY CITY, NEW JERSEY
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF NEWARK, NEW JERSEY,
ADDRESS IN TRENTON AT THE TRENTON HOUSE,
ADDRESS TO THE SENATE OF NEW JERSEY
ADDRESS TO THE ASSEMBLY OF NEW JERSEY,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA,
ADDRESS IN THE HALL OF INDEPENDENCE, PHILADELPHIA,
REPLY TO THE WILMINGTON DELEGATION,
ADDRESS AT LANCASTER, PENNSYLVANIA,
ADDRESS TO THE LEGISLATURE OF PENNSYLVANIA, AT HARRISBURG,
REPLY TO THE MAYOR OF WASHINGTON, D.C.,
REPLY TO A SERENADE AT WASHINGTON, D.C.,
WASHINGTON, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 1861
FIRST INAUGURAL ADDRESS, MARCH 4, 1861
REPLY TO THE PENNSYLVANIA DELEGATION,
REPLY TO THE MASSACHUSETTS DELEGATION,
NOTE ASKING CABINET OPINIONS ON FORT SUMTER.
ON ROYAL ARBITRATION OF AMERICAN BOUNDARY LINE
RESPONSE TO SENATE INQUIRY RE. FORT SUMTER
PREPARATION OF FIRST NAVAL ACTION
TO THE COMMANDANT OF THE NEW YORK NAVY-YARD.
RELIEF EXPEDITION FOR FORT SUMTER
ORDER TO CAPTAIN SAMUEL MERCER.
SECRETARY SEWARD'S BID FOR POWER
REPLY TO SECRETARY SEWARD'S MEMORANDUM
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE FROM THE VIRGINIA CONVENTION, APRIL 13, 1861
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR 75,000 MILITIA,
PROCLAMATION OF BLOCKADE, APRIL 19, 1861
TO GOVERNOR HICKS AND MAYOR BROWN.
ORDER TO DEFEND FROM A MARYLAND INSURRECTION
PROCLAMATION OF BLOCKADE, APRIL 27, 1861
REMARKS TO A MILITARY COMPANY, WASHINGTON, APRIL 27, 1861
LOCALIZED REPEAL OF WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS
MILITARY ENROLLMENT OF ST. LOUIS CITIZENS
CONDOLENCE OVER FAILURE OF FT. SUMTER RELIEF
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR 42,034 VOLUNTEERS,
COMMUNICATION WITH VICE-PRESIDENT
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS IN FLORIDA,
PRESIDENT LINCOLN'S CORRECTIONS OF A DIPLOMATIC DESPATCH
LETTER OF CONDOLENCE TO ONE OF FIRST CASUALTIES
MEMORANDUM ABOUT INDIANA REGIMENTS.
ORDER AUTHORIZING GENERAL SCOTT TO SUSPEND THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS, JULY
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS IN SPECIAL SESSION,
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE INTERIOR.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MEMORANDA OF MILITARY POLICY SUGGESTED BY THE BULL RUN DEFEAT. JULY 23,
TO THE GOVERNOR OF NEW JERSEY.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
ORDER TO UNITED STATES MARSHALS.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
PROCLAMATION OF A NATIONAL FAST-DAY, AUGUST 12, 1861.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR O. P. MORTON.
PROCLAMATION FORBIDDING INTERCOURSE WITH REBEL STATES, AUGUST 16, 1861.
MEMORANDUM FOR A PLAN OF CAMPAIGN
ORDER AUTHORIZING SUSPENSION OF THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS.
TO GENERAL CURTIS, WITH INCLOSURES.
ORDER RETIRING GENERAL SCOTT AND APPOINTING
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON.
ORDER APPROVING THE PLAN OF GOVERNOR GAMBLE OF MISSOURI.
REPLY TO THE MINISTER FROM SWEDEN.
INDORSEMENT AUTHORIZING MARTIAL LAW IN SAINT LOUIS.
OFFER TO COOPERATE AND GIVE SPECIAL LINE OF INFORMATION TO HORACE GREELEY
ORDER AUTHORIZING GENERAL HALLECK TO SUSPEND THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
LETTER OF REPRIMAND TO GENERAL HUNTER
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. C. BUELL.
MESSAGES OF DISAPPOINTMENT WITH HIS GENERALS
INDORSEMENT ON LETTER FROM GENERAL HALLECK,
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO. 1
PRESIDENT'S SPECIAL WAR ORDER NO. 1.
OPPOSITION TO McCLELLAN'S PLANS
TO GENERALS D. HUNTER AND J. H. LANE.
EXECUTIVE ORDER NO. 1, RELATING TO POLITICAL PRISONERS.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. WASHINGTON CITY, February 15, 1862
EXECUTIVE ORDER NO. 2.—IN RELATION TO STATE PRISONERS.
ORDER RELATING TO COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE.
SPEECH TO THE PERUVIAN MINISTER,
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS RECOMMENDING COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION.
INDORSEMENT ON LETTER FROM GOVERNOR YATES.
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO.2.
PRESIDENT'S GENERAL WAR ORDER NO.3.
INTERVIEW BETWEEN THE PRESIDENT AND SOME BORDER SLAVE STATE
PRESIDENT'S SPECIAL WAR ORDER NO.3.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL MCCLELLAN.
SPEECH TO A PARTY OF MASSACHUSETTS GENTLEMAN
INSTRUCTION TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
PROCLAMATION RECOMMENDING THANKSGIVING FOR VICTORIES,
ABOLISHING SLAVERY IN WASHINGTON, D.C.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE, MAY 1, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
RESPONSE TO EVANGELICAL LUTHERANS, MAY 6, 1862
TELEGRAM TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH.
FURTHER REPRIMAND OF McCLELLAN
TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH,
PROCLAMATION RAISING THE BLOCKADE OF CERTAIN PORTS.
SYDNEY SPRING, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter introducing Mr. Faree was duly received. There was no opening to nominate him for Superintendent of Public Instruction, but through him Egypt made a most valuable contribution to the convention. I think it may be fairly said that he came off the lion of the day—or rather of the night. Can you not elect him to the Legislature? It seems to me he would be hard to beat. What objection could be made to him? What is your Senator Martin saying and doing? What is Webb about?
Please write me. Yours truly,
H. C. WHITNEY, ESQ.
DEAR SIR:—Your letter enclosing the attack of the Times upon me was received this morning. Give yourself no concern about my voting against the supplies. Unless you are without faith that a lie can be successfully contradicted, there is not a word of truth in the charge, and I am just considering a little as to the best shape to put a contradiction in. Show this to whomever you please, but do not publish it in the paper.
Your friend as ever,
JAMES W. SOMERS, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 22nd, inclosing a draft of two hundred dollars, was duly received. I have paid it on the judgment, and herewith you have the receipt. I do not wish to say anything as to who shall be the Republican candidate for the Legislature in your district, further than that I have full confidence in Dr. Hull. Have you ever got in the way of consulting with McKinley in political matters? He is true as steel, and his judgment is very good. The last I heard from him, he rather thought Weldon, of De Witt, was our best timber for representative, all things considered. But you there must settle it among yourselves. It may well puzzle older heads than yours to understand how, as the Dred Scott decision holds, Congress can authorize a Territorial Legislature to do everything else, and cannot authorize them to prohibit slavery. That is one of the things the court can decide, but can never give an intelligible reason for.
Yours very truly,
A. CAMPBELL, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—In 1856 you gave me authority to draw on you for any sum not exceeding five hundred dollars. I see clearly that such a privilege would be more available now than it was then. I am aware that times are tighter now than they were then. Please write me at all events, and whether you can now do anything or not I shall continue grateful for the past.
Yours very truly,
HON. JOSEPH GILLESPIE.
MY DEAR SIR:—I write this to say that from the specimens of Douglas Democracy we occasionally see here from Madison, we learn that they are making very confident calculation of beating you and your friends for the lower house, in that county. They offer to bet upon it. Billings and Job, respectively, have been up here, and were each as I learn, talking largely about it. If they do so, it can only be done by carrying the Fillmore men of 1856 very differently from what they seem to [be] going in the other party. Below is the vote of 1856, in your district:
Counties.
Counties. Buchanan. Fremont. Fillmore.
Bond............ 607 153 659
Madison......... 1451 1111 1658
Montgomery...... 992 162 686
—— —— ——
3050 1426 3003
By this you will see, if you go through the calculation, that if they get one quarter of the Fillmore votes, and you three quarters, they will beat you 125 votes. If they get one fifth, and you four fifths, you beat them 179. In Madison, alone, if our friends get 1000 of the Fillmore votes, and their opponents the remainder, 658, we win by just two votes.
This shows the whole field, on the basis of the election of 1856.
Whether, since then, any Buchanan, or Fremonters, have shifted ground, and how the majority of new votes will go, you can judge better than I.
Of course you, on the ground, can better determine your line of tactics than any one off the ground; but it behooves you to be wide awake and actively working.
Don't neglect it; and write me at your first leisure. Yours as ever,
JNO. MATHERS, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your kind and interesting letter of the 19th was duly received. Your suggestions as to placing one's self on the offensive rather than the defensive are certainly correct. That is a point which I shall not disregard. I spoke here on Saturday night. The speech, not very well reported, appears in the State journal of this morning. You doubtless will see it; and I hope that you will perceive in it that I am already improving. I would mail you a copy now, but have not one [at] hand. I thank you for your letter and shall be pleased to hear from you again.
Yours very truly,
HON. J. GILLESPIE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your doleful letter of the 8th was received on my return from Chicago last night. I do hope you are worse scared than hurt, though you ought to know best. We must not lose the district. We must make a job of it, and save it. Lay hold of the proper agencies, and secure all the Americans you can, at once. I do hope, on closer inspection, you will find they are not half gone. Make a little test. Run down one of the poll-books of the Edwardsville precinct, and take the first hundred known American names. Then quietly ascertain how many of them are actually going for Douglas. I think you will find less than fifty. But even if you find fifty, make sure of the other fifty, that is, make sure of all you can, at all events. We will set other agencies to work which shall compensate for the loss of a good many Americans. Don't fail to check the stampede at once. Trumbull, I think, will be with you before long.
There is much he cannot do, and some he can. I have reason to hope there will be other help of an appropriate kind. Write me again.
Yours as ever,
Hon. B. C. COOK.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have a letter from a very true and intelligent man insisting that there is a plan on foot in La Salle and Bureau to run Douglas Republicans for Congress and for the Legislature in those counties, if they can only get the encouragement of our folks nominating pretty extreme abolitionists.
It is thought they will do nothing if our folks nominate men who are not very obnoxious to the charge of abolitionism. Please have your eye upon this. Signs are looking pretty fair.
Yours very truly,
HON. J. M. PALMER.
DEAR SIR:—Since we parted last evening no new thought has occurred to [me] on the subject of which we talked most yesterday.
I have concluded, however, to speak at your town on Tuesday, August 31st, and have promised to have it so appear in the papers of to-morrow. Judge Trumbull has not yet reached here.
Yours as ever,
ALEXANDER SYMPSON, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 6th received. If life and health continue I shall pretty likely be at Augusta on the 25th.
Things look reasonably well. Will tell you more fully when I see you.
Yours truly,
J. O. CUNNINGHAM, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 18th, signed as secretary of the Republican club, is received. In the matter of making speeches I am a good deal pressed by invitations from almost all quarters, and while I hope to be at Urbana some time during the canvass, I cannot yet say when. Can you not see me at Monticello on the 6th of September?
Douglas and I, for the first time this canvass, crossed swords here yesterday; the fire flew some, and I am glad to know I am yet alive. There was a vast concourse of people—more than could get near enough to hear.
Yours as ever,
As I would not be a slave, so I would not be a master. This expresses my idea of democracy. Whatever differs from this, to the extent of the difference, is no democracy.
HON. B. C. COOK.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have a letter from a very true friend, and intelligent man, writing that there is a plan on foot in La Salle and Bureau, to run Douglas Republican for Congress and for the Legislature in those counties, if they can only get the encouragement of our folks nominating pretty extreme abolitionists. It is thought they will do nothing if our folks nominate men who are not very [undecipherable word looks like "obnoxious"] to the charge of abolitionism. Please have your eye upon this. Signs are looking pretty fair.
Yours very truly,
DEAR DOCTOR:—Yours of the 1st was received this morning, as also one from Mr. Harmon, and one from Hiram Beckwith on the same subject. You will see by the Journal that I have been appointed to speak at Danville on the 22d of Sept.,—the day after Douglas speaks there. My recent experience shows that speaking at the same place the next day after D. is the very thing,—it is, in fact, a concluding speech on him. Please show this to Messrs. Harmon and Beckwith; and tell them they must excuse me from writing separate letters to them.
Yours as ever,
A. LINCOLN
P. S.—Give full notice to all surrounding country. A.L.
Let us inquire what Judge Douglas really invented when he introduced the Nebraska Bill? He called it Popular Sovereignty. What does that mean? It means the sovereignty of the people over their own affairs—in other words, the right of the people to govern themselves. Did Judge Douglas invent this? Not quite. The idea of popular sovereignty was floating about several ages before the author of the Nebraska Bill was born—indeed, before Columbus set foot on this continent. In the year 1776 it took form in the noble words which you are all familiar with: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal," etc. Was not this the origin of popular sovereignty as applied to the American people? Here we are told that governments are instituted among men deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. If that is not popular sovereignty, then I have no conception of the meaning of words. If Judge Douglas did not invent this kind of popular sovereignty, let us pursue the inquiry and find out what kind he did invent. Was it the right of emigrants to Kansas and Nebraska to govern themselves, and a lot of "niggers," too, if they wanted them? Clearly this was no invention of his because General Cass put forth the same doctrine in 1848 in his so called Nicholson letter, six years before Douglas thought of such a thing. Then what was it that the "Little Giant" invented? It never occurred to General Cass to call his discovery by the odd name of popular sovereignty. He had not the face to say that the right of the people to govern "niggers" was the right of the people to govern themselves. His notions of the fitness of things were not moulded to the brazenness of calling the right to put a hundred "niggers" through under the lash in Nebraska a "sacred" right of self-government. And here I submit to you was Judge Douglas's discovery, and the whole of it: He discovered that the right to breed and flog negroes in Nebraska was popular sovereignty.
The questions are sometimes asked "What is all this fuss that is being made about negroes? What does it amount to? And where will it end?" These questions imply that those who ask them consider the slavery question a very insignificant matter they think that it amounts to little or nothing and that those who agitate it are extremely foolish. Now it must be admitted that if the great question which has caused so much trouble is insignificant, we are very foolish to have anything to do with it—if it is of no importance we had better throw it aside and busy ourselves with something else. But let us inquire a little into this insignificant matter, as it is called by some, and see if it is not important enough to demand the close attention of every well-wisher of the Union. In one of Douglas's recent speeches, I find a reference to one which was made by me in Springfield some time ago. The judge makes one quotation from that speech that requires some little notice from me at this time. I regret that I have not my Springfield speech before me, but the judge has quoted one particular part of it so often that I think I can recollect it. It runs I think as follows:
"We are now far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of that policy that agitation has not only not ceased but has constantly augmented. In my opinion it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed.
"A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved. I do not expect the house to fall, but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction; or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South."
Judge Douglas makes use of the above quotation, and finds a great deal of fault with it. He deals unfairly with me, and tries to make the people of this State believe that I advocated dangerous doctrines in my Springfield speech. Let us see if that portion of my Springfield speech of which Judge Douglas complains so bitterly, is as objectionable to others as it is to him. We are, certainly, far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. On the fourth day of January, 1854, Judge Douglas introduced the Kansas-Nebraska bill. He initiated a new policy, and that policy, so he says, was to put an end to the agitation of the slavery question. Whether that was his object or not I will not stop to discuss, but at all events some kind of a policy was initiated; and what has been the result? Instead of the quiet and good feeling which were promised us by the self-styled author of Popular Sovereignty, we have had nothing but ill-feeling and agitation. According to Judge Douglas, the passage of the Nebraska bill would tranquilize the whole country—there would be no more slavery agitation in or out of Congress, and the vexed question would be left entirely to the people of the Territories. Such was the opinion of Judge Douglas, and such were the opinions of the leading men of the Democratic Party. Even as late as the spring of 1856 Mr. Buchanan said, a short time subsequent to his nomination by the Cincinnati convention, that the territory of Kansas would be tranquil in less than six weeks. Perhaps he thought so, but Kansas has not been and is not tranquil, and it may be a long time before she may be so.
We all know how fierce the agitation was in Congress last winter, and what a narrow escape Kansas had from being admitted into the Union with a constitution that was detested by ninety-nine hundredths of her citizens. Did the angry debates which took place at Washington during the last season of Congress lead you to suppose that the slavery agitation was settled?
An election was held in Kansas in the month of August, and the constitution which was submitted to the people was voted down by a large majority. So Kansas is still out of the Union, and there is a probability that she will remain out for some time. But Judge Douglas says the slavery question is settled. He says the bill he introduced into the Senate of the United States on the 4th day of January, 1854, settled the slavery question forever! Perhaps he can tell us how that bill settled the slavery question, for if he is able to settle a question of such great magnitude he ought to be able to explain the manner in which he does it. He knows and you know that the question is not settled, and that his ill-timed experiment to settle it has made it worse than it ever was before.
And now let me say a few words in regard to Douglas's great hobby of negro equality. He thinks—he says at least—that the Republican party is in favor of allowing whites and blacks to intermarry, and that a man can't be a good Republican unless he is willing to elevate black men to office and to associate with them on terms of perfect equality. He knows that we advocate no such doctrines as these, but he cares not how much he misrepresents us if he can gain a few votes by so doing. To show you what my opinion of negro equality was in times past, and to prove to you that I stand on that question where I always stood, I will read you a few extracts from a speech that was made by me in Peoria in 1854. It was made in reply to one of Judge Douglas's speeches.
(Mr. Lincoln then read a number of extracts which had the ring of the true metal. We have rarely heard anything with which we have been more pleased. And the audience after hearing the extracts read, and comparing their conservative sentiments with those now advocated by Mr. Lincoln, testified their approval by loud applause. How any reasonable man can hear one of Mr. Lincoln's speeches without being converted to Republicanism is something that we can't account for. Ed.)
Slavery, continued Mr. Lincoln, is not a matter of little importance, it overshadows every other question in which we are interested. It has divided the Methodist and Presbyterian churches, and has sown discord in the American Tract Society. The churches have split and the society will follow their example before long. So it will be seen that slavery is agitated in the religious as well as in the political world. Judge Douglas is very much afraid in the triumph that the Republican party will lead to a general mixture of the white and black races. Perhaps I am wrong in saying that he is afraid, so I will correct myself by saying that he pretends to fear that the success of our party will result in the amalgamation of the blacks and whites. I think I can show plainly, from documents now before me, that Judge Douglas's fears are groundless. The census of 1800 tells us that in that year there were over four hundred thousand mulattoes in the United States. Now let us take what is called an Abolition State—the Republican, slavery-hating State of New Hampshire—and see how many mulattoes we can find within her borders. The number amounts to just one hundred and eighty-four. In the Old Dominion—in the Democratic and aristocratic State of Virginia—there were a few more mulattoes than the Census-takers found in New Hampshire. How many do you suppose there were? Seventy-nine thousand, seven hundred and seventy-five—twenty-three thousand more than there were in all the free States! In the slave States there were in 1800, three hundred and forty-eight thousand mulattoes all of home production; and in the free States there were less than sixty thousand mulattoes—and a large number of them were imported from the South.
I have been requested to give a concise statement of the difference, as I understand it, between the Democratic and Republican parties, on the leading issues of the campaign. This question has been put to me by a gentleman whom I do not know. I do not even know whether he is a friend of mine or a supporter of Judge Douglas in this contest, nor does that make any difference. His question is a proper one. Lest I should forget it, I will give you my answer before proceeding with the line of argument I have marked out for this discussion.
The difference between the Republican and the Democratic parties on the leading issues of this contest, as I understand it, is that the former consider slavery a moral, social and political wrong, while the latter do not consider it either a moral, a social or a political wrong; and the action of each, as respects the growth of the country and the expansion of our population, is squared to meet these views. I will not affirm that the Democratic party consider slavery morally, socially and politically right, though their tendency to that view has, in my opinion, been constant and unmistakable for the past five years. I prefer to take, as the accepted maxim of the party, the idea put forth by Judge Douglas, that he "don't care whether slavery is voted down or voted up." I am quite willing to believe that many Democrats would prefer that slavery should be always voted down, and I know that some prefer that it be always voted up; but I have a right to insist that their action, especially if it be their constant action, shall determine their ideas and preferences on this subject. Every measure of the Democratic party of late years, bearing directly or indirectly on the slavery question, has corresponded with this notion of utter indifference whether slavery or freedom shall outrun in the race of empire across to the Pacific—every measure, I say, up to the Dred Scott decision, where, it seems to me, the idea is boldly suggested that slavery is better than freedom. The Republican party, on the contrary, hold that this government was instituted to secure the blessings of freedom, and that slavery is an unqualified evil to the negro, to the white man, to the soil, and to the State. Regarding it as an evil, they will not molest it in the States where it exists, they will not overlook the constitutional guards which our fathers placed around it; they will do nothing that can give proper offence to those who hold slaves by legal sanction; but they will use every constitutional method to prevent the evil from becoming larger and involving more negroes, more white men, more soil, and more States in its deplorable consequences. They will, if possible, place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in course of ultimate peaceable extinction in God's own good time. And to this end they will, if possible, restore the government to the policy of the fathers, the policy of preserving the new Territories from the baneful influence of human bondage, as the Northwestern Territories were sought to be preserved by the Ordinance of 1787, and the Compromise Act of 1820. They will oppose, in all its length and breadth, the modern Democratic idea, that slavery is as good as freedom, and ought to have room for expansion all over the continent, if people can be found to carry it. All, or nearly all, of Judge Douglas's arguments are logical, if you admit that slavery is as good and as right as freedom, and not one of them is worth a rush if you deny it. This is the difference, as I understand it, between the Republican and Democratic parties.
My friends, I have endeavored to show you the logical consequences of the Dred Scott decision, which holds that the people of a Territory cannot prevent the establishment of slavery in their midst. I have stated what cannot be gainsaid, that the grounds upon which this decision is made are equally applicable to the free States as to the free Territories, and that the peculiar reasons put forth by Judge Douglas for indorsing this decision commit him, in advance, to the next decision and to all other decisions corning from the same source. And when, by all these means, you have succeeded in dehumanizing the negro; when you have put him down and made it impossible for him to be but as the beasts of the field; when you have extinguished his soul in this world and placed him where the ray of hope is blown out as in the darkness of the damned, are you quite sure that the demon you have roused will not turn and rend you? What constitutes the bulwark of our own liberty and independence? It is not our frowning battlements, our bristling sea coasts, our army and our navy. These are not our reliance against tyranny All of those may be turned against us without making us weaker for the struggle. Our reliance is in the love of liberty which God has planted in us. Our defense is in the spirit which prizes liberty as the heritage of all men, in all lands everywhere. Destroy this spirit and you have planted the seeds of despotism at your own doors. Familiarize yourselves with the chains of bondage and you prepare your own limbs to wear them. Accustomed to trample on the rights of others, you have lost the genius of your own independence and become the fit subjects of the first cunning tyrant who rises among you. And let me tell you, that all these things are prepared for you by the teachings of history, if the elections shall promise that the next Dred Scott decision and all future decisions will be quietly acquiesced in by the people.
TO "LINNIE":
A sweet plaintive song did I hear
And I fancied that she was the singer.
May emotions as pure as that song set astir
Be the wont that the future shall bring her.
SPRINGFIELD, OCT 18, 1858 HON. J. U. BROWN.
MY DEAR SIR:—I do not perceive how I can express myself more plainly than I have in the fore-going extracts. In four of them I have expressly disclaimed all intention to bring about social and political equality between the white and black races and in all the rest I have done the same thing by clear implication.
I have made it equally plain that I think the negro is included in the word "men" used in the Declaration of Independence.
I believe the declaration that "all men are created equal" is the great fundamental principle upon which our free institutions rest; that negro slavery is violative of that principle; but that, by our frame of government, that principle has not been made one of legal obligation; that by our frame of government, States which have slavery are to retain it, or surrender it at their own pleasure; and that all others—individuals, free States and national Government—are constitutionally bound to leave them alone about it.
I believe our Government was thus framed because of the necessity springing from the actual presence of slavery, when it was framed.
That such necessity does not exist in the Territories when slavery is not present.
In his Mendenhall speech Mr. Clay says: "Now as an abstract principle there is no doubt of the truth of that declaration (all men created equal), and it is desirable, in the original construction of society, to keep it in view as a great fundamental principle."
Again, in the same speech Mr. Clay says: "If a state of nature existed and we were about to lay the foundations of society, no man would be more strongly opposed than I should to incorporate the institution of slavery among its elements."
Exactly so. In our new free Territories, a state of nature does exist. In them Congress lays the foundations of society; and in laying those foundations, I say, with Mr. Clay, it is desirable that the declaration of the equality of all men shall be kept in view as a great fundamental principle, and that Congress, which lays the foundations of society, should, like Mr. Clay, be strongly opposed to the incorporation of slavery and its elements.
But it does not follow that social and political equality between whites and blacks must be incorporated because slavery must not. The declaration does not so require.
Yours as ever,
A. LINCOLN
[Newspaper cuttings of Lincoln's speeches at Peoria, in 1854, at Springfield, Ottawa, Chicago, and Charleston, in 1858. They were pasted in a little book in which the above letter was also written.]
A. SYMPSON, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Since parting with you this morning I heard some things which make me believe that Edmunds and Morrill will spend this week among the National Democrats, trying to induce them to content themselves by voting for Jake Davis, and then to vote for the Douglas candidates for senator and representative. Have this headed off, if you can. Call Wagley's attention to it and have him and the National Democrat for Rep. to counteract it as far as they can.
Yours as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, NOVEMBER 16, 1858 HON. N. B. JUDD
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 15th is just received. I wrote you the same day. As to the pecuniary matter, I am willing to pay according to my ability; but I am the poorest hand living to get others to pay. I have been on expenses so long without earning anything that I am absolutely without money now for even household purposes. Still, if you can put in two hundred and fifty dollars for me toward discharging the debt of the committee, I will allow it when you and I settle the private matter between us. This, with what I have already paid, and with an outstanding note of mine, will exceed my subscription of five hundred dollars. This, too, is exclusive of my ordinary expenses during the campaign, all of which, being added to my loss of time and business, bears pretty heavily upon one no better off in [this] world's goods than I; but as I had the post of honor, it is not for me to be over nice. You are feeling badly,—"And this too shall pass away," never fear.
Yours as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, November 19, 1858.
HENRY ASBURY, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 13th was received some days ago. The fight must go on. The cause of civil liberty must not be surrendered at the end of one or even one hundred defeats. Douglas had the ingenuity to be supported in the late contest both as the best means to break down and to uphold the slave interest. No ingenuity can keep these antagonistic elements in harmony long. Another explosion will soon come.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, Nov.20, 1858
DR. C. H. RAY
MY DEAR SIR:—I wish to preserve a set of the late debates (if they may be called so), between Douglas and myself. To enable me to do so, please get two copies of each number of your paper containing the whole, and send them to me by express; and I will pay you for the papers and for your trouble. I wish the two sets in order to lay one away in the [undecipherable word] and to put the other in a scrapbook. Remember, if part of any debate is on both sides of the sheet it will take two sets to make one scrap-book.
I believe, according to a letter of yours to Hatch, you are "feeling like h-ll yet." Quit that—you will soon feel better. Another "blow up" is coming; and we shall have fun again. Douglas managed to be supported both as the best instrument to down and to uphold the slave power; but no ingenuity can long keep the antagonism in harmony.
Yours as ever,
H. C. WHITNEY, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—Being desirous of preserving in some permanent form the late joint discussion between Douglas and myself, ten days ago I wrote to Dr. Ray, requesting him to forward to me by express two sets of the numbers of the Tribune which contain the reports of those discussions. Up to date I have no word from him on the subject. Will you, if in your power, procure them and forward them to me by express? If you will, I will pay all charges, and be greatly obliged, to boot. Hoping to visit you before long, I remain
As ever your friend,
H. D. SHARPE, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Your very kind letter of Nov. 9th was duly received. I do not know that you expected or desired an answer; but glancing over the contents of yours again, I am prompted to say that, while I desired the result of the late canvass to have been different, I still regard it as an exceeding small matter. I think we have fairly entered upon a durable struggle as to whether this nation is to ultimately become all slave or all free, and though I fall early in the contest, it is nothing if I shall have contributed, in the least degree, to the final rightful result.
Respectfully yours,
ALEXANDER SYMPSON, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—I expect the result of the election went hard with you. So it did with me, too, perhaps not quite so hard as you may have supposed. I have an abiding faith that we shall beat them in the long run. Step by step the objects of the leaders will become too plain for the people to stand them. I write merely to let you know that I am neither dead nor dying. Please give my respects to your good family, and all inquiring friends.
Yours as ever,
Legislation and adjudication must follow and conform to the progress of society.
The progress of society now begins to produce cases of the transfer for debts of the entire property of railroad corporations; and to enable transferees to use and enjoy the transferred property, legislation and adjudication begin to be necessary.
Shall this class of legislation just now beginning with us be general or special?
Special legislation always trenches upon the judicial department; and in so far violates Section Two of the Constitution. (Read it.)
Just reasoning—policy—is in favor of general legislation—else the Legislature will be loaded down with the investigation of smaller cases—a work which the courts ought to perform, and can perform much more perfectly. How can the Legislature rightly decide the facts between P. & B. and S.C.
It is said that under a general law, whenever a R. R. Co. gets tired of its debts, it may transfer fraudulently to get rid of them. So they may—so may individuals; and which—the Legislature or the courts—is best suited to try the question of fraud in either case?
It is said, if a purchaser have acquired legal rights, let him not be robbed of them, but if he needs legislation let him submit to just terms to obtain it.
Let him, say we, have general law in advance (guarded in every possible way against fraud), so that, when he acquires a legal right, he will have no occasion to wait for additional legislation; and if he has practiced fraud let the courts so decide.
The 11th Section of the Act of Congress, approved Feb. 11, 1805, prescribing rules for the subdivision of sections of land within the United States system of surveys, standing unrepealed, in my opinion, is binding on the respective purchasers of different parts of the same section, and furnishes the true rule for surveyors in establishing lines between them. That law, being in force at the time each became a purchaser, becomes a condition of the purchase.
And, by that law, I think the true rule for dividing into quarters any interior section or sections, which is not fractional, is to run straight lines through the section from the opposite quarter section corners, fixing the point where such straight lines cross, or intersect each other, as the middle or centre of the section.
Nearly, perhaps quite, all the original surveys are to some extent erroneous, and in some of the sections, greatly so. In each of the latter, it is obvious that a more equitable mode of division than the above might be adopted; but as error is infinitely various perhaps no better single rules can be prescribed.
At all events I think the above has been prescribed by the competent authority.
SPRINGFIELD, Jany. 6, 1859.
M. W. DELAHAY, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR: Your second letter in relation to my being with you at your Republican convention was duly received. It is not at hand just now, but I have the impression from it that the convention was to be at Leavenworth; but day before yesterday a friend handed me a letter from Judge M. F. Caraway, in which he also expresses a wish for me to come, and he fixes the place at Ossawatomie. This I believe is off of the river, and will require more time and labor to get to it. It will push me hard to get there without injury to my own business; but I shall try to do it, though I am not yet quite certain I shall succeed.
I should like to know before coming, that while some of you wish me to come, there may not be others who would quite as lief I would stay away. Write me again.
Yours as ever,
W. M. MORRIS, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Your kind note inviting me to deliver a lecture at Galesburg is received. I regret to say I cannot do so now; I must stick to the courts awhile. I read a sort of lecture to three different audiences during the last month and this; but I did so under circumstances which made it a waste of no time whatever.
Yours very truly,
GENTLEMEN:—Your kind note inviting me to attend a festival in Boston, on the 28th instant, in honor of the birthday of Thomas Jefferson, was duly received. My engagements are such that I cannot attend.
Bearing in mind that about seventy years ago two great political parties were first formed in this country, that Thomas Jefferson was the head of one of them and Boston the headquarters of the other, it is both curious and interesting that those supposed to descend politically from the party opposed to Jefferson should now be celebrating his birthday in their own original seat of empire, while those claiming political descent from him have nearly ceased to breathe his name everywhere.
Remembering, too, that the Jefferson party was formed upon its supposed superior devotion to the personal rights of men, holding the rights of property to be secondary only, and greatly inferior, and assuming that the so-called Democracy of to-day are the Jefferson, and their opponents the anti-Jefferson, party, it will be equally interesting to note how completely the two have changed hands as to the principle upon which they were originally supposed to be divided. The Democracy of to-day hold the liberty of one man to be absolutely nothing, when in conflict with another man's right of property; Republicans, on the contrary, are for both the man and the dollar, but in case of conflict the man before the dollar.
I remember being once much amused at seeing two partially intoxicated men engaged in a fight with their great-coats on, which fight, after a long and rather harmless contest, ended in each having fought himself out of his own coat and into that of the other. If the two leading parties of this day are really identical with the two in the days of Jefferson and Adams, they have performed the same feat as the two drunken men.
But soberly, it is now no child's play to save the principles of Jefferson from total overthrow in this nation. One would state with great confidence that he could convince any sane child that the simpler propositions of Euclid are true; but nevertheless he would fail, utterly, with one who should deny the definitions and axioms. The principles of Jefferson are the definitions and axioms of free society. And yet they are denied and evaded, with no small show of success. One dashingly calls them "glittering generalities." Another bluntly calls them "self-evident lies." And others insidiously argue that they apply to "superior races." These expressions, differing in form, are identical in object and effect—the supplanting the principles of free government, and restoring those of classification, caste, and legitimacy. They would delight a convocation of crowned heads plotting against the people. They are the vanguard, the miners and sappers, of returning despotism. We must repulse them, or they will subjugate us. This is a world of compensation; and he who would be no slave must consent to have no slave. Those who deny freedom to others deserve it not for themselves, and, under a just God, cannot long retain it. All honor to Jefferson to the man who, in the concrete pressure of a struggle for national independence by a single people, had the coolness, forecast, and capacity to introduce into a mere revolutionary document an abstract truth, applicable to all men and all times, and so to embalm it there that to-day and in all coming days it shall be a rebuke and a stumbling-block to the very harbingers of reappearing tyranny and oppression.
Your obedient servant,
DR. THEODORE CANISIUS.
DEAR SIR:—Your note asking, in behalf of yourself and other German citizens, whether I am for or against the constitutional provision in regard to naturalized citizens, lately adopted by Massachusetts, and whether I am for or against a fusion of the Republicans and other opposition elements for the canvass of 1860, is received.
Massachusetts is a sovereign and independent State; and it is no privilege of mine to scold her for what she does. Still, if from what she has done an inference is sought to be drawn as to what I would do, I may without impropriety speak out. I say, then, that, as I understand the Massachusetts provision, I am against its adoption in Illinois, or in any other place where I have a right to oppose it. Understanding the spirit of our institutions to aim at the elevation of men, I am opposed to whatever tends to degrade them. I have some little notoriety for commiserating the oppressed negro; and I should be strangely inconsistent if I could favor any project for curtailing the existing rights of white men, even though born in different lands, and speaking different languages from myself. As to the matter of fusion, I am for it if it can be had on Republican grounds; and I am not for it on any other terms. A fusion on any other terms would be as foolish as unprincipled. It would lose the whole North, while the common enemy would still carry the whole South. The question of men is a different one. There are good, patriotic men and able statesmen in the South whom I would cheerfully support, if they would now place themselves on Republican ground, but I am against letting down the Republican standard a hairsbreadth.
I have written this hastily, but I believe it answers your questions substantially.
Yours truly,
In reply to your inquiry; requesting our written opinion as to what your duty requires you to do in executing the latter clause of the Seventh Section of "An Act in relation to the payment of the principal and interest of the State debt," approved Feb'y 22, 1859, we reply that said last clause of said section is certainly indefinite, general, and ambiguous in its description of the bonds to be issued by you; giving no time at which the bonds are to be made payable, no place at which either principal or interest are to be paid, and no rate of interest which the bonds are to bear; nor any other description except that they are to be coupon bonds, which in commercial usage means interest-paying bonds with obligations or orders attached to them for the payment of annual or semiannual interest; there is we suppose no difficulty in ascertaining, if this act stood alone, what ought to be the construction of the terms "coupon bonds" and that it, would mean bonds bearing interest from the time of issuing the same. And under this act considered by itself the creditors would have a right to require such bonds. But your inquiry in regard to a class of bonds on which no interest is to be paid or shall begin to run until January 1, 1860, is whether the Act of February 18, 1857, would not authorize you to refuse to give bonds with any coupons attached payable before the first day of July, 1860. We have very maturely considered this question and have arrived at the conclusion that you have a right to use such measures as will secure the State against the loss of six months' interest on these bonds by the indefiniteness of the Act of 1859. While it cannot be denied that the letter of the laws favor the construction claimed by some of the creditors that interest-bearing bonds were required to be issued to them, inasmuch as the restriction that no interest is to run on said bonds until 1st January, 1860, relates solely to the bonds issued under the Act of 1857. And the Act of 1859 directing you to issue new bonds does not contain this restriction, but directs you to issue coupon bonds. Nevertheless the very indefiniteness and generality of the Act of 1859, giving no rate of interest, no time due, no place of payment, no postponement of the time when interest commences, necessarily implies that the Legislature intended to invest you with a discretion to impose such terms and restrictions as would protect the interest of the State; and we think you have a right and that it is your duty to see that the State Bonds are so issued that the State shall not lose six months' interest. Two plans present themselves either of which will secure the State. 1st. If in literal compliance with the law you issue bonds bearing interest from 1st July, 1859, you may deduct from the bonds presented three thousand from every $100,000 of bonds and issue $97,000 of coupon bonds; by this plan $3000 out of $100,000 of principal would be extinguished in consideration of paying $2910 interest on the first of January, 1860—and the interest on the $3000 would forever cease; this would be no doubt most advantageous to the State. But if the Auditor will not consent to this, then, 2nd. Cut off of each bond all the coupons payable before 1st July, 1860.
One of these plans would undoubtedly have been prescribed by the Legislature if its attention had been directed to this question.
May 28, 1859.
SPRINGFIELD, December 25, 1858.
H. C. WHITNEY, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have just received yours of the 23rd inquiring whether I received the newspapers you sent me by express. I did receive them, and am very much obliged. There is some probability that my scrap-book will be reprinted, and if it shall, I will save you a copy.
Your friend as ever,
HON. SAMUEL GALLOWAY.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your very complimentary, not to say flattering, letter of the 23d inst. is received. Dr. Reynolds had induced me to expect you here; and I was disappointed not a little by your failure to come. And yet I fear you have formed an estimate of me which can scarcely be sustained on a personal acquaintance.
Two things done by the Ohio Republican convention—the repudiation of Judge Swan, and the "plank" for a repeal of the Fugitive Slave Law—I very much regretted. These two things are of a piece; and they are viewed by many good men, sincerely opposed to slavery, as a struggle against, and in disregard of, the Constitution itself. And it is the very thing that will greatly endanger our cause, if it be not kept out of our national convention. There is another thing our friends are doing which gives me some uneasiness. It is their leaning toward "popular sovereignty." There are three substantial objections to this: First, no party can command respect which sustains this year what it opposed last. Secondly, Douglas (who is the most dangerous enemy of liberty, because the most insidious one) would have little support in the North, and by consequence, no capital to trade on in the South, if it were not for his friends thus magnifying him and his humbug. But lastly, and chiefly, Douglas's popular sovereignty, accepted by the public mind as a just principle, nationalizes slavery, and revives the African slave trade inevitably.
Taking slaves into new Territories, and buying slaves in Africa, are identical things, identical rights or identical wrongs, and the argument which establishes one will establish the other. Try a thousand years for a sound reason why Congress shall not hinder the people of Kansas from having slaves, and, when you have found it, it will be an equally good one why Congress should not hinder the people of Georgia from importing slaves from Africa.
As to Governor Chase, I have a kind side for him. He was one of the few distinguished men of the nation who gave us, in Illinois, their sympathy last year. I never saw him, but suppose him to be able and right-minded; but still he may not be the most suitable as a candidate for the Presidency.
I must say I do not think myself fit for the Presidency. As you propose a correspondence with me, I shall look for your letters anxiously.
I have not met Dr. Reynolds since receiving your letter; but when I shall, I will present your respects as requested.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL. Sept. 6, 1859.
HAWKINS TAYLOR, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 3d is just received. There is some mistake about my expected attendance of the U.S. Court in your city on the 3d Tuesday of this month. I have had no thought of being there.
It is bad to be poor. I shall go to the wall for bread and meat if I neglect my business this year as well as last. It would please me much to see the city and good people of Keokuk, but for this year it is little less than an impossibility. I am constantly receiving invitations which I am compelled to decline. I was pressingly urged to go to Minnesota; and I now have two invitations to go to Ohio. These last are prompted by Douglas going there; and I am really tempted to make a flying trip to Columbus and Cincinnati.
I do hope you will have no serious trouble in Iowa. What thinks Grimes about it? I have not known him to be mistaken about an election in Iowa. Present my respects to Col. Carter, and any other friends, and believe me
Yours truly,
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE STATE OF OHIO: I cannot fail to remember that I appear for the first time before an audience in this now great State,—an audience that is accustomed to hear such speakers as Corwin, and Chase, and Wade, and many other renowned men; and, remembering this, I feel that it will be well for you, as for me, that you should not raise your expectations to that standard to which you would have been justified in raising them had one of these distinguished men appeared before you. You would perhaps be only preparing a disappointment for yourselves, and, as a consequence of your disappointment, mortification to me. I hope, therefore, that you will commence with very moderate expectations; and perhaps, if you will give me your attention, I shall be able to interest you to a moderate degree.
Appearing here for the first time in my life, I have been somewhat embarrassed for a topic by way of introduction to my speech; but I have been relieved from that embarrassment by an introduction which the Ohio Statesman newspaper gave me this morning. In this paper I have read an article, in which, among other statements, I find the following:
"In debating with Senator Douglas during the memorable contest of last fall, Mr. Lincoln declared in favor of negro suffrage, and attempted to defend that vile conception against the Little Giant."
I mention this now, at the opening of my remarks, for the purpose of making three comments upon it. The first I have already announced,—it furnishes me an introductory topic; the second is to show that the gentleman is mistaken; thirdly, to give him an opportunity to correct it.
In the first place, in regard to this matter being a mistake. I have found that it is not entirely safe, when one is misrepresented under his very nose, to allow the misrepresentation to go uncontradicted. I therefore propose, here at the outset, not only to say that this is a misrepresentation, but to show conclusively that it is so; and you will bear with me while I read a couple of extracts from that very "memorable" debate with Judge Douglas last year, to which this newspaper refers. In the first pitched battle which Senator Douglas and myself had, at the town of Ottawa, I used the language which I will now read. Having been previously reading an extract, I continued as follows:
"Now, gentlemen, I don't want to read at any greater length, but this is the true complexion of all I have ever said in regard to the institution of slavery and the black race. This is the whole of it; and anything that argues me into his idea of perfect social and political equality with the negro, is but a specious and fantastic arrangement of words, by which a man can prove a horse-chestnut to be a chestnut horse. I will say here, while upon this subject, that I have no purpose directly or indirectly to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so. I have no purpose to introduce political and social equality between the white and the black races. There is a physical difference between the two which, in my judgment, will probably forbid their ever living together upon the footing of perfect equality; and inasmuch as it becomes a necessity that there must be a difference, I, as well as Judge Douglas, am in favor of the race to which I belong having the superior position. I have never said anything to the contrary, but I hold that, notwithstanding all this, there is no reason in the world why the negro is not entitled to all the natural rights enumerated in the Declaration of Independence,—the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. I hold that he is as much entitled to these as the white man. I agree with judge Douglas, he is not my equal in many respects,—certainly not in color, perhaps not in moral or intellectual endowments. But in the right to eat the bread, without leave of anybody else, which his own hand earns, he is my equal, and the equal of Judge Douglas, and the equal of every living man."
Upon a subsequent occasion, when the reason for making a statement like this occurred, I said:
"While I was at the hotel to-day an elderly gentleman called upon me to know whether I was really in favor of producing perfect equality between the negroes and white people. While I had not proposed to myself on this occasion to say much on that subject, yet, as the question was asked me, I thought I would occupy perhaps five minutes in saying something in regard to it. I will say, then, that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of bringing about in any way the social and political equality of the white and black races; that I am not, nor ever have been, in favor of making voters or jurors of negroes, nor of qualifying them to hold office, or intermarry with the white people; and I will say in addition to this that there is a physical difference between the white and black races which I believe will forever forbid the two races living together on terms of social and political equality. And inasmuch as they can not so live, while they do remain together there must be the position of superior and inferior, and I, as much as any other man, am in favor of having the superior position assigned to the white race. I say upon this occasion I do not perceive that because the white man is to have the superior position, the negro should be denied everything. I do not understand that because I do not want a negro woman for a slave, I must necessarily want her for a wife. My understanding is that I can just let her alone. I am now in my fiftieth year, and I certainly never have had a black woman for either a slave or a wife. So it seems to me quite possible for us to get along without making either slaves or wives of negroes. I will add to this that I have never seen, to my knowledge, a man, woman, or child, who was in favor of producing perfect equality, social and political, between negroes and white men. I recollect of but one distinguished instance that I ever heard of so frequently as to be satisfied of its correctness, and that is the case of Judge Douglas's old friend Colonel Richard M. Johnson. I will also add to the remarks I have made (for I am not going to enter at large upon this subject), that I have never had the least apprehension that I or my friends would marry negroes, if there was no law to keep them from it; but as judge Douglas and his friends seem to be in great apprehension that they might, if there were no law to keep them from it, I give him the most solemn pledge that I will to the very last stand by the law of the State which forbids the marrying of white people with negroes."
There, my friends, you have briefly what I have, upon former occasions, said upon this subject to which this newspaper, to the extent of its ability, has drawn the public attention. In it you not only perceive, as a probability, that in that contest I did not at any time say I was in favor of negro suffrage, but the absolute proof that twice—once substantially, and once expressly—I declared against it. Having shown you this, there remains but a word of comment upon that newspaper article. It is this, that I presume the editor of that paper is an honest and truth-loving man, and that he will be greatly obliged to me for furnishing him thus early an opportunity to correct the misrepresentation he has made, before it has run so long that malicious people can call him a liar.
The Giant himself has been here recently. I have seen a brief report of his speech. If it were otherwise unpleasant to me to introduce the subject of the negro as a topic for discussion, I might be somewhat relieved by the fact that he dealt exclusively in that subject while he was here. I shall, therefore, without much hesitation or diffidence, enter upon this subject.
The American people, on the first day of January, 1854, found the African slave trade prohibited by a law of Congress. In a majority of the States of this Union, they found African slavery, or any other sort of slavery, prohibited by State constitutions. They also found a law existing, supposed to be valid, by which slavery was excluded from almost all the territory the United States then owned. This was the condition of the country, with reference to the institution of slavery, on the first of January, 1854. A few days after that, a bill was introduced into Congress, which ran through its regular course in the two branches of the national legislature, and finally passed into a law in the month of May, by which the Act of Congress prohibiting slavery from going into the Territories of the United States was repealed. In connection with the law itself, and, in fact, in the terms of the law, the then existing prohibition was not only repealed, but there was a declaration of a purpose on the part of Congress never thereafter to exercise any power that they might have, real or supposed, to prohibit the extension or spread of slavery. This was a very great change; for the law thus repealed was of more than thirty years' standing. Following rapidly upon the heels of this action of Congress, a decision of the Supreme Court is made, by which it is declared that Congress, if it desires to prohibit the spread of slavery into the Territories, has no constitutional power to do so. Not only so, but that decision lays down principles which, if pushed to their logical conclusion,—I say pushed to their logical conclusion,—would decide that the constitutions of free States, forbidding slavery, are themselves unconstitutional. Mark me, I do not say the judges said this, and let no man say I affirm the judges used these words; but I only say it is my opinion that what they did say, if pressed to its logical conclusion, will inevitably result thus.
Looking at these things, the Republican party, as I understand its principles and policy, believes that there is great danger of the institution of slavery being spread out and extended until it is ultimately made alike lawful in all the States of this Union; so believing, to prevent that incidental and ultimate consummation is the original and chief purpose of the Republican organization. I say "chief purpose" of the Republican organization; for it is certainly true that if the National House shall fall into the hands of the Republicans, they will have to attend to all the other matters of national house-keeping, as well as this. The chief and real purpose of the Republican party is eminently conservative. It proposes nothing save and except to restore this government to its original tone in regard to this element of slavery, and there to maintain it, looking for no further change in reference to it than that which the original framers of the Government themselves expected and looked forward to.
The chief danger to this purpose of the Republican party is not just now the revival of the African slave trade, or the passage of a Congressional slave code, or the declaring of a second Dred Scott decision, making slavery lawful in all the States. These are not pressing us just now. They are not quite ready yet. The authors of these measures know that we are too strong for them; but they will be upon us in due time, and we will be grappling with them hand to hand, if they are not now headed off. They are not now the chief danger to the purpose of the Republican organization; but the most imminent danger that now threatens that purpose is that insidious Douglas popular sovereignty. This is the miner and sapper. While it does not propose to revive the African slave trade, nor to pass a slave code, nor to make a second Dred Scott decision, it is preparing us for the onslaught and charge of these ultimate enemies when they shall be ready to come on, and the word of command for them to advance shall be given. I say this "Douglas popular sovereignty"; for there is a broad distinction, as I now understand it, between that article and a genuine popular sovereignty.
I believe there is a genuine popular sovereignty. I think a definition of "genuine popular sovereignty," in the abstract, would be about this: That each man shall do precisely as he pleases with himself, and with all those things which exclusively concern him. Applied to government, this principle would be, that a general government shall do all those things which pertain to it, and all the local governments shall do precisely as they please in respect to those matters which exclusively concern them. I understand that this government of the United States, under which we live, is based upon this principle; and I am misunderstood if it is supposed that I have any war to make upon that principle.
Now, what is judge Douglas's popular sovereignty? It is, as a principle, no other than that if one man chooses to make a slave of another man neither that other man nor anybody else has a right to object. Applied in government, as he seeks to apply it, it is this: If, in a new Territory into which a few people are beginning to enter for the purpose of making their homes, they choose to either exclude slavery from their limits or to establish it there, however one or the other may affect the persons to be enslaved, or the infinitely greater number of persons who are afterwards to inhabit that Territory, or the other members of the families of communities, of which they are but an incipient member, or the general head of the family of States as parent of all, however their action may affect one or the other of these, there is no power or right to interfere. That is Douglas's popular sovereignty applied.
He has a good deal of trouble with popular sovereignty. His explanations explanatory of explanations explained are interminable. The most lengthy, and, as I suppose, the most maturely considered of this long series of explanations is his great essay in Harper's Magazine. I will not attempt to enter on any very thorough investigation of his argument as there made and presented. I will nevertheless occupy a good portion of your time here in drawing your attention to certain points in it. Such of you as may have read this document will have perceived that the judge early in the document quotes from two persons as belonging to the Republican party, without naming them, but who can readily be recognized as being Governor Seward of New York and myself. It is true that exactly fifteen months ago this day, I believe, I for the first time expressed a sentiment upon this subject, and in such a manner that it should get into print, that the public might see it beyond the circle of my hearers; and my expression of it at that time is the quotation that Judge Douglas makes. He has not made the quotation with accuracy, but justice to him requires me to say that it is sufficiently accurate not to change the sense.
The sense of that quotation condensed is this: that this slavery element is a durable element of discord among us, and that we shall probably not have perfect peace in this country with it until it either masters the free principle in our government, or is so far mastered by the free principle as for the public mind to rest in the belief that it is going to its end. This sentiment, which I now express in this way, was, at no great distance of time, perhaps in different language, and in connection with some collateral ideas, expressed by Governor Seward. Judge Douglas has been so much annoyed by the expression of that sentiment that he has constantly, I believe, in almost all his speeches since it was uttered, been referring to it. I find he alluded to it in his speech here, as well as in the copyright essay. I do not now enter upon this for the purpose of making an elaborate argument to show that we were right in the expression of that sentiment. In other words, I shall not stop to say all that might properly be said upon this point, but I only ask your attention to it for the purpose of making one or two points upon it.
If you will read the copyright essay, you will discover that judge Douglas himself says a controversy between the American Colonies and the Government of Great Britain began on the slavery question in 1699, and continued from that time until the Revolution; and, while he did not say so, we all know that it has continued with more or less violence ever since the Revolution.
Then we need not appeal to history, to the declarations of the framers of the government, but we know from judge Douglas himself that slavery began to be an element of discord among the white people of this country as far back as 1699, or one hundred and sixty years ago, or five generations of men,—counting thirty years to a generation. Now, it would seem to me that it might have occurred to Judge Douglas, or anybody who had turned his attention to these facts, that there was something in the nature of that thing, slavery, somewhat durable for mischief and discord.
There is another point I desire to make in regard to this matter, before I leave it. From the adoption of the Constitution down to 1820 is the precise period of our history when we had comparative peace upon this question,—the precise period of time when we came nearer to having peace about it than any other time of that entire one hundred and sixty years in which he says it began, or of the eighty years of our own Constitution. Then it would be worth our while to stop and examine into the probable reason of our coming nearer to having peace then than at any other time. This was the precise period of time in which our fathers adopted, and during which they followed, a policy restricting the spread of slavery, and the whole Union was acquiescing in it. The whole country looked forward to the ultimate extinction of the institution. It was when a policy had been adopted, and was prevailing, which led all just and right-minded men to suppose that slavery was gradually coming to an end, and that they might be quiet about it, watching it as it expired. I think Judge Douglas might have perceived that too; and whether he did or not, it is worth the attention of fair-minded men, here and elsewhere, to consider whether that is not the truth of the case. If he had looked at these two facts,—that this matter has been an element of discord for one hundred and sixty years among this people, and that the only comparative peace we have had about it was when that policy prevailed in this government which he now wars upon, he might then, perhaps, have been brought to a more just appreciation of what I said fifteen months ago,—that "a house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe that this government cannot endure permanently, half slave and half free. I do not expect the house to fall, I do not expect the Union to dissolve; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind will rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward until it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South." That was my sentiment at that time. In connection with it, I said: "We are now far into the fifth year since a policy was inaugurated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of the policy that agitation has not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented." I now say to you here that we are advanced still farther into the sixth year since that policy of Judge Douglas—that popular sovereignty of his—for quieting the slavery question was made the national policy. Fifteen months more have been added since I uttered that sentiment; and I call upon you and all other right-minded men to say whether that fifteen months have belied or corroborated my words.
While I am here upon this subject, I cannot but express gratitude that this true view of this element of discord among us—as I believe it is—is attracting more and more attention. I do not believe that Governor Seward uttered that sentiment because I had done so before, but because he reflected upon this subject and saw the truth of it. Nor do I believe because Governor Seward or I uttered it that Mr. Hickman of Pennsylvania, in, different language, since that time, has declared his belief in the utter antagonism which exists between the principles of liberty and slavery. You see we are multiplying. Now, while I am speaking of Hickman, let me say, I know but little about him. I have never seen him, and know scarcely anything about the man; but I will say this much of him: Of all the anti-Lecompton Democracy that have been brought to my notice, he alone has the true, genuine ring of the metal. And now, without indorsing anything else he has said, I will ask this audience to give three cheers for Hickman. [The audience responded with three rousing cheers for Hickman.]
Another point in the copyright essay to which I would ask your attention is rather a feature to be extracted from the whole thing, than from any express declaration of it at any point. It is a general feature of that document, and, indeed, of all of Judge Douglas's discussions of this question, that the Territories of the United States and the States of this Union are exactly alike; that there is no difference between them at all; that the Constitution applies to the Territories precisely as it does to the States; and that the United States Government, under the Constitution, may not do in a State what it may not do in a Territory, and what it must do in a State it must do in a Territory. Gentlemen, is that a true view of the case? It is necessary for this squatter sovereignty, but is it true?
Let us consider. What does it depend upon? It depends altogether upon the proposition that the States must, without the interference of the General Government, do all those things that pertain exclusively to themselves,—that are local in their nature, that have no connection with the General Government. After Judge Douglas has established this proposition, which nobody disputes or ever has disputed, he proceeds to assume, without proving it, that slavery is one of those little, unimportant, trivial matters which are of just about as much consequence as the question would be to me whether my neighbor should raise horned cattle or plant tobacco; that there is no moral question about it, but that it is altogether a matter of dollars and cents; that when a new Territory is opened for settlement, the first man who goes into it may plant there a thing which, like the Canada thistle or some other of those pests of the soil, cannot be dug out by the millions of men who will come thereafter; that it is one of those little things that is so trivial in its nature that it has nor effect upon anybody save the few men who first plant upon the soil; that it is not a thing which in any way affects the family of communities composing these States, nor any way endangers the General Government. Judge Douglas ignores altogether the very well known fact that we have never had a serious menace to our political existence, except it sprang from this thing, which he chooses to regard as only upon a par with onions and potatoes.
Turn it, and contemplate it in another view. He says that, according to his popular sovereignty, the General Government may give to the Territories governors, judges, marshals, secretaries, and all the other chief men to govern them, but they, must not touch upon this other question. Why? The question of who shall be governor of a Territory for a year or two, and pass away, without his track being left upon the soil, or an act which he did for good or for evil being left behind, is a question of vast national magnitude; it is so much opposed in its nature to locality that the nation itself must decide it: while this other matter of planting slavery upon a soil,—a thing which, once planted, cannot be eradicated by the succeeding millions who have as much right there as the first comers, or, if eradicated, not without infinite difficulty and a long struggle, he considers the power to prohibit it as one of these little local, trivial things that the nation ought not to say a word about; that it affects nobody save the few men who are there.
Take these two things and consider them together, present the question of planting a State with the institution of slavery by the side of a question who shall be Governor of Kansas for a year or two, and is there a man here, is there a man on earth, who would not say the governor question is the little one, and the slavery question is the great one? I ask any honest Democrat if the small, the local, and the trivial and temporary question is not, Who shall be governor? while the durable, the important, and the mischievous one is, Shall this soil be planted with slavery?
This is an idea, I suppose, which has arisen in Judge Douglas's mind from his peculiar structure. I suppose the institution of slavery really looks small to him. He is so put up by nature that a lash upon his back would hurt him, but a lash upon anybody else's back does not hurt him. That is the build of the man, and consequently he looks upon the matter of slavery in this unimportant light.
Judge Douglas ought to remember, when he is endeavoring to force this policy upon the American people, that while he is put up in that way, a good many are not. He ought to remember that there was once in this country a man by the name of Thomas Jefferson, supposed to be a Democrat,—a man whose principles and policy are not very prevalent amongst Democrats to-day, it is true; but that man did not take exactly this view of the insignificance of the element of slavery which our friend judge Douglas does. In contemplation of this thing, we all know he was led to exclaim, "I tremble for my country when I remember that God is just!" We know how he looked upon it when he thus expressed himself. There was danger to this country,—danger of the avenging justice of God, in that little unimportant popular sovereignty question of judge Douglas. He supposed there was a question of God's eternal justice wrapped up in the enslaving of any race of men, or any man, and that those who did so braved the arm of Jehovah; that when a nation thus dared the Almighty, every friend of that nation had cause to dread his wrath. Choose ye between Jefferson and Douglas as to what is the true view of this element among us.
There is another little difficulty about this matter of treating the Territories and States alike in all things, to which I ask your attention, and I shall leave this branch of the case. If there is no difference between them, why not make the Territories States at once? What is the reason that Kansas was not fit to come into the Union when it was organized into a Territory, in Judge Douglas's view? Can any of you tell any reason why it should not have come into the Union at once? They are fit, as he thinks, to decide upon the slavery question,—the largest and most important with which they could possibly deal: what could they do by coming into the Union that they are not fit to do, according to his view, by staying out of it? Oh, they are not fit to sit in Congress and decide upon the rates of postage, or questions of ad valorem or specific duties on foreign goods, or live-oak timber contracts, they are not fit to decide these vastly important matters, which are national in their import, but they are fit, "from the jump," to decide this little negro question. But, gentlemen, the case is too plain; I occupy too much time on this head, and I pass on.
Near the close of the copyright essay, the judge, I think, comes very near kicking his own fat into the fire. I did not think, when I commenced these remarks, that I would read that article, but I now believe I will:
"This exposition of the history of these measures shows conclusively that the authors of the Compromise measures of 1850 and of the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854, as well as the members of the Continental Congress of 1774., and the founders of our system of government subsequent to the Revolution, regarded the people of the Territories and Colonies as political communities which were entitled to a free and exclusive power of legislation in their provisional legislatures, where their representation could alone be preserved, in all cases of taxation and internal polity."
When the judge saw that putting in the word "slavery" would contradict his own history, he put in what he knew would pass synonymous with it, "internal polity." Whenever we find that in one of his speeches, the substitute is used in this manner; and I can tell you the reason. It would be too bald a contradiction to say slavery; but "internal polity" is a general phrase, which would pass in some quarters, and which he hopes will pass with the reading community for the same thing.
"This right pertains to the people collectively, as a law-abiding and peaceful community, and not in the isolated individuals who may wander upon the public domain in violation of the law. It can only be exercised where there are inhabitants sufficient to constitute a government, and capable of performing its various functions and duties,—a fact to be ascertained and determined by" who do you think? Judge Douglas says "by Congress!" "Whether the number shall be fixed at ten, fifteen or twenty thousand inhabitants, does not affect the principle."
Now, I have only a few comments to make. Popular sovereignty, by his own words, does not pertain to the few persons who wander upon the public domain in violation of law. We have his words for that. When it does pertain to them, is when they are sufficient to be formed into an organized political community, and he fixes the minimum for that at ten thousand, and the maximum at twenty thousand. Now, I would like to know what is to be done with the nine thousand? Are they all to be treated, until they are large enough to be organized into a political community, as wanderers upon the public land, in violation of law? And if so treated and driven out, at what point of time would there ever be ten thousand? If they were not driven out, but remained there as trespassers upon the public land in violation of the law, can they establish slavery there? No; the judge says popular sovereignty don't pertain to them then. Can they exclude it then? No; popular sovereignty don't pertain to them then. I would like to know, in the case covered by the essay, what condition the people of the Territory are in before they reach the number of ten thousand?
But the main point I wish to ask attention to is, that the question as to when they shall have reached a sufficient number to be formed into a regular organized community is to be decided "by Congress." Judge Douglas says so. Well, gentlemen, that is about all we want. No, that is all the Southerners want. That is what all those who are for slavery want. They do not want Congress to prohibit slavery from coming into the new Territories, and they do not want popular sovereignty to hinder it; and as Congress is to say when they are ready to be organized, all that the South has to do is to get Congress to hold off. Let Congress hold off until they are ready to be admitted as a State, and the South has all it wants in taking slavery into and planting it in all the Territories that we now have or hereafter may have. In a word, the whole thing, at a dash of the pen, is at last put in the power of Congress; for if they do not have this popular sovereignty until Congress organizes them, I ask if it at last does not come from Congress? If, at last, it amounts to anything at all, Congress gives it to them. I submit this rather for your reflection than for comment. After all that is said, at last, by a dash of the pen, everything that has gone before is undone, and he puts the whole question under the control of Congress. After fighting through more than three hours, if you undertake to read it, he at last places the whole matter under the control of that power which he has been contending against, and arrives at a result directly contrary to what he had been laboring to do. He at last leaves the whole matter to the control of Congress.
There are two main objects, as I understand it, of this Harper's Magazine essay. One was to show, if possible, that the men of our Revolutionary times were in favor of his popular sovereignty, and the other was to show that the Dred Scott decision had not entirely squelched out this popular sovereignty. I do not propose, in regard to this argument drawn from the history of former times, to enter into a detailed examination of the historical statements he has made. I have the impression that they are inaccurate in a great many instances,—sometimes in positive statement, but very much more inaccurate by the suppression of statements that really belong to the history. But I do not propose to affirm that this is so to any very great extent, or to enter into a very minute examination of his historical statements. I avoid doing so upon this principle,—that if it were important for me to pass out of this lot in the least period of time possible, and I came to that fence, and saw by a calculation of my known strength and agility that I could clear it at a bound, it would be folly for me to stop and consider whether I could or not crawl through a crack. So I say of the whole history contained in his essay where he endeavored to link the men of the Revolution to popular sovereignty. It only requires an effort to leap out of it, a single bound to be entirely successful. If you read it over, you will find that he quotes here and there from documents of the Revolutionary times, tending to show that the people of the colonies were desirous of regulating their own concerns in their own way, that the British Government should not interfere; that at one time they struggled with the British Government to be permitted to exclude the African slave trade,—if not directly, to be permitted to exclude it indirectly, by taxation sufficient to discourage and destroy it. From these and many things of this sort, judge Douglas argues that they were in favor of the people of our own Territories excluding slavery if they wanted to, or planting it there if they wanted to, doing just as they pleased from the time they settled upon the Territory. Now, however his history may apply and whatever of his argument there may be that is sound and accurate or unsound and inaccurate, if we can find out what these men did themselves do upon this very question of slavery in the Territories, does it not end the whole thing? If, after all this labor and effort to show that the men of the Revolution were in favor of his popular sovereignty and his mode of dealing with slavery in the Territories, we can show that these very men took hold of that subject, and dealt with it, we can see for ourselves how they dealt with it. It is not a matter of argument or inference, but we know what they thought about it.
It is precisely upon that part of the history of the country that one important omission is made by Judge Douglas. He selects parts of the history of the United States upon the subject of slavery, and treats it as the whole, omitting from his historical sketch the legislation of Congress in regard to the admission of Missouri, by which the Missouri Compromise was established and slavery excluded from a country half as large as the present United States. All this is left out of his history, and in nowise alluded to by him, so far as I can remember, save once, when he makes a remark, that upon his principle the Supreme Court were authorized to pronounce a decision that the act called the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional. All that history has been left out. But this part of the history of the country was not made by the men of the Revolution.
There was another part of our political history, made by the very men who were the actors in the Revolution, which has taken the name of the Ordinance of '87. Let me bring that history to your attention. In 1784, I believe, this same Mr. Jefferson drew up an ordinance for the government of the country upon which we now stand, or, rather, a frame or draft of an ordinance for the government of this country, here in Ohio, our neighbors in Indiana, us who live in Illinois, our neighbors in Wisconsin and Michigan. In that ordinance, drawn up not only for the government of that Territory, but for the Territories south of the Ohio River, Mr. Jefferson expressly provided for the prohibition of slavery. Judge Douglas says, and perhaps is right, that that provision was lost from that ordinance. I believe that is true. When the vote was taken upon it, a majority of all present in the Congress of the Confederation voted for it; but there were so many absentees that those voting for it did not make the clear majority necessary, and it was lost. But three years after that, the Congress of the Confederation were together again, and they adopted a new ordinance for the government of this Northwest Territory, not contemplating territory south of the river, for the States owning that territory had hitherto refrained from giving it to the General Government; hence they made the ordinance to apply only to what the Government owned. In fact, the provision excluding slavery was inserted aside, passed unanimously, or at any rate it passed and became a part of the law of the land. Under that ordinance we live. First here in Ohio you were a Territory; then an enabling act was passed, authorizing you to form a constitution and State Government, provided it was republican and not in conflict with the Ordinance of '87. When you framed your constitution and presented it for admission, I think you will find the legislation upon the subject will show that, whereas you had formed a constitution that was republican, and not in conflict with the Ordinance of '87, therefore you were admitted upon equal footing with the original States. The same process in a few years was gone through with in Indiana, and so with Illinois, and the same substantially with Michigan and Wisconsin.
Not only did that Ordinance prevail, but it was constantly looked to whenever a step was taken by a new Territory to become a State. Congress always turned their attention to it, and in all their movements upon this subject they traced their course by that Ordinance of '87. When they admitted new States, they advertised them of this Ordinance, as a part of the legislation of the country. They did so because they had traced the Ordinance of '87 throughout the history of this country. Begin with the men of the Revolution, and go down for sixty entire years, and until the last scrap of that Territory comes into the Union in the form of the State of Wisconsin, everything was made to conform with the Ordinance of '87, excluding slavery from that vast extent of country.
I omitted to mention in the right place that the Constitution of the United States was in process of being framed when that Ordinance was made by the Congress of the Confederation; and one of the first Acts of Congress itself, under the new Constitution itself, was to give force to that Ordinance by putting power to carry it out in the hands of the new officers under the Constitution, in the place of the old ones, who had been legislated out of existence by the change in the Government from the Confederation to the Constitution. Not only so, but I believe Indiana once or twice, if not Ohio, petitioned the General Government for the privilege of suspending that provision and allowing them to have slaves. A report made by Mr. Randolph, of Virginia, himself a slaveholder, was directly against it, and the action was to refuse them the privilege of violating the Ordinance of '87.
This period of history, which I have run over briefly, is, I presume, as familiar to most of this assembly as any other part of the history of our country. I suppose that few of my hearers are not as familiar with that part of history as I am, and I only mention it to recall your attention to it at this time. And hence I ask how extraordinary a thing it is that a man who has occupied a position upon the floor of the Senate of the United States, who is now in his third term, and who looks to see the government of this whole country fall into his own hands, pretending to give a truthful and accurate history o the slavery question in this country, should so entirely ignore the whole of that portion of our history—the most important of all. Is it not a most extraordinary spectacle that a man should stand up and ask for any confidence in his statements who sets out as he does with portions of history, calling upon the people to believe that it is a true and fair representation, when the leading part and controlling feature of the whole history is carefully suppressed?
But the mere leaving out is not the most remarkable feature of this most remarkable essay. His proposition is to establish that the leading men of the Revolution were for his great principle of nonintervention by the government in the question of slavery in the Territories, while history shows that they decided, in the cases actually brought before them, in exactly the contrary way, and he knows it. Not only did they so decide at that time, but they stuck to it during sixty years, through thick and thin, as long as there was one of the Revolutionary heroes upon the stage of political action. Through their whole course, from first to last, they clung to freedom. And now he asks the community to believe that the men of the Revolution were in favor of his great principle, when we have the naked history that they themselves dealt with this very subject matter of his principle, and utterly repudiated his principle, acting upon a precisely contrary ground. It is as impudent and absurd as if a prosecuting attorney should stand up before a jury and ask them to convict A as the murderer of B, while B was walking alive before them.
I say, again, if judge Douglas asserts that the men of the Revolution acted upon principles by which, to be consistent with themselves, they ought to have adopted his popular sovereignty, then, upon a consideration of his own argument, he had a right to make you believe that they understood the principles of government, but misapplied them, that he has arisen to enlighten the world as to the just application of this principle. He has a right to try to persuade you that he understands their principles better than they did, and, therefore, he will apply them now, not as they did, but as they ought to have done. He has a right to go before the community and try to convince them of this, but he has no right to attempt to impose upon any one the belief that these men themselves approved of his great principle. There are two ways of establishing a proposition. One is by trying to demonstrate it upon reason, and the other is, to show that great men in former times have thought so and so, and thus to pass it by the weight of pure authority. Now, if Judge Douglas will demonstrate somehow that this is popular sovereignty,—the right of one man to make a slave of another, without any right in that other or any one else to object,—demonstrate it as Euclid demonstrated propositions,—there is no objection. But when he comes forward, seeking to carry a principle by bringing to it the authority of men who themselves utterly repudiate that principle, I ask that he shall not be permitted to do it.
I see, in the judge's speech here, a short sentence in these words: "Our fathers, when they formed this government under which we live, understood this question just as well, and even better than, we do now." That is true; I stick to that. I will stand by Judge Douglas in that to the bitter end. And now, Judge Douglas, come and stand by me, and truthfully show how they acted, understanding it better than we do. All I ask of you, Judge Douglas, is to stick to the proposition that the men of the Revolution understood this subject better than we do now, and with that better understanding they acted better than you are trying to act now.
I wish to say something now in regard to the Dred Scott decision, as dealt with by Judge Douglas. In that "memorable debate" between Judge Douglas and myself, last year, the judge thought fit to commence a process of catechising me, and at Freeport I answered his questions, and propounded some to him. Among others propounded to him was one that I have here now. The substance, as I remember it, is, "Can the people of a United States Territory, under the Dred Scott decision, in any lawful way, against the wish of any citizen of the United States, exclude slavery from its limits, prior to the formation of a State constitution?" He answered that they could lawfully exclude slavery from the United States Territories, notwithstanding the Dred Scot decision. There was something about that answer that has probably been a trouble to the judge ever since.
The Dred Scott decision expressly gives every citizen of the United States a right to carry his slaves into the United States Territories. And now there was some inconsistency in saying that the decision was right, and saying, too, that the people of the Territory could lawfully drive slavery out again. When all the trash, the words, the collateral matter, was cleared away from it, all the chaff was fanned out of it, it was a bare absurdity,—no less than that a thing may be lawfully driven away from where it has a lawful right to be. Clear it of all the verbiage, and that is the naked truth of his proposition,—that a thing may be lawfully driven from the place where it has a lawful right to stay. Well, it was because the judge could n't help seeing this that he has had so much trouble with it; and what I want to ask your especial attention to, just now, is to remind you, if you have not noticed the fact, that the judge does not any longer say that the people can exclude slavery. He does not say so in the copyright essay; he did not say so in the speech that he made here; and, so far as I know, since his re-election to the Senate he has never said, as he did at Freeport, that the people of the Territories can exclude slavery. He desires that you, who wish the Territories to remain free, should believe that he stands by that position; but he does not say it himself. He escapes to some extent the absurd position I have stated, by changing his language entirely. What he says now is something different in language, and we will consider whether it is not different in sense too. It is now that the Dred Scott decision, or rather the Constitution under that decision, does not carry slavery into the Territories beyond the power of the people of the Territories to control it as other property. He does not say the people can drive it out, but they can control it as other property. The language is different; we should consider whether the sense is different. Driving a horse out of this lot is too plain a proposition to be mistaken about; it is putting him on the other side of the fence. Or it might be a sort of exclusion of him from the lot if you were to kill him and let the worms devour him; but neither of these things is the same as "controlling him as other property." That would be to feed him, to pamper him, to ride him, to use and abuse him, to make the most money out of him, "as other property"; but, please you, what do the men who are in favor of slavery want more than this? What do they really want, other than that slavery, being in the Territories, shall be controlled as other property? If they want anything else, I do not comprehend it. I ask your attention to this, first, for the purpose of pointing out the change of ground the judge has made; and, in the second place, the importance of the change,—that that change is not such as to give you gentlemen who want his popular sovereignty the power to exclude the institution or drive it out at all. I know the judge sometimes squints at the argument that in controlling it as other property by unfriendly legislation they may control it to death; as you might, in the case of a horse, perhaps, feed him so lightly and ride him so much that he would die. But when you come to legislative control, there is something more to be attended to. I have no doubt, myself, that if the Territories should undertake to control slave property as other property that is, control it in such a way that it would be the most valuable as property, and make it bear its just proportion in the way of burdens as property, really deal with it as property,—the Supreme Court of the United States will say, "God speed you, and amen." But I undertake to give the opinion, at least, that if the Territories attempt by any direct legislation to drive the man with his slave out of the Territory, or to decide that his slave is free because of his being taken in there, or to tax him to such an extent that he cannot keep him there, the Supreme Court will unhesitatingly decide all such legislation unconstitutional, as long as that Supreme Court is constructed as the Dred Scott Supreme Court is. The first two things they have already decided, except that there is a little quibble among lawyers between the words "dicta" and "decision." They have already decided a negro cannot be made free by Territorial legislation.
What is the Dred Scott decision? Judge Douglas labors to show that it is one thing, while I think it is altogether different. It is a long opinion, but it is all embodied in this short statement: "The Constitution of the United States forbids Congress to deprive a man of his property, without due process of law; the right of property in slaves is distinctly and expressly affirmed in that Constitution: therefore, if Congress shall undertake to say that a man's slave is no longer his slave when he crosses a certain line into a Territory, that is depriving him of his property without due process of law, and is unconstitutional." There is the whole Dred Scott decision. They add that if Congress cannot do so itself, Congress cannot confer any power to do so; and hence any effort by the Territorial Legislature to do either of these things is absolutely decided against. It is a foregone conclusion by that court.
Now, as to this indirect mode by "unfriendly legislation," all lawyers here will readily understand that such a proposition cannot be tolerated for a moment, because a legislature cannot indirectly do that which it cannot accomplish directly. Then I say any legislation to control this property, as property, for its benefit as property, would be hailed by this Dred Scott Supreme Court, and fully sustained; but any legislation driving slave property out, or destroying it as property, directly or indirectly, will most assuredly, by that court, be held unconstitutional.
Judge Douglas says if the Constitution carries slavery into the Territories, beyond the power of the people of the Territories to control it as other property; then it follows logically that every one who swears to support the Constitution of the United States must give that support to that property which it needs. And, if the Constitution carries slavery into the Territories, beyond the power of the people, to control it as other property, then it also carries it into the States, because the Constitution is the supreme law of the land. Now, gentlemen, if it were not for my excessive modesty, I would say that I told that very thing to Judge Douglas quite a year ago. This argument is here in print, and if it were not for my modesty, as I said, I might call your attention to it. If you read it, you will find that I not only made that argument, but made it better than he has made it since.
There is, however, this difference: I say now, and said then, there is no sort of question that the Supreme Court has decided that it is the right of the slave holder to take his slave and hold him in the Territory; and saying this, judge Douglas himself admits the conclusion. He says if that is so, this consequence will follow; and because this consequence would follow, his argument is, the decision cannot, therefore, be that way,—"that would spoil my popular sovereignty; and it cannot be possible that this great principle has been squelched out in this extraordinary way. It might be, if it were not for the extraordinary consequences of spoiling my humbug."
Another feature of the judge's argument about the Dred Scott case is, an effort to show that that decision deals altogether in declarations of negatives; that the Constitution does not affirm anything as expounded by the Dred Scott decision, but it only declares a want of power a total absence of power, in reference to the Territories. It seems to be his purpose to make the whole of that decision to result in a mere negative declaration of a want of power in Congress to do anything in relation to this matter in the Territories. I know the opinion of the Judges states that there is a total absence of power; but that is, unfortunately; not all it states: for the judges add that the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution. It does not stop at saying that the right of property in a slave is recognized in the Constitution, is declared to exist somewhere in the Constitution, but says it is affirmed in the Constitution. Its language is equivalent to saying that it is embodied and so woven in that instrument that it cannot be detached without breaking the Constitution itself. In a word, it is part of the Constitution.
Douglas is singularly unfortunate in his effort to make out that decision to be altogether negative, when the express language at the vital part is that this is distinctly affirmed in the Constitution. I think myself, and I repeat it here, that this decision does not merely carry slavery into the Territories, but by its logical conclusion it carries it into the States in which we live. One provision of that Constitution is, that it shall be the supreme law of the land,—I do not quote the language,—any constitution or law of any State to the contrary notwithstanding. This Dred Scott decision says that the right of property in a slave is affirmed in that Constitution which is the supreme law of the land, any State constitution or law notwithstanding. Then I say that to destroy a thing which is distinctly affirmed and supported by the supreme law of the land, even by a State constitution or law, is a violation of that supreme law, and there is no escape from it. In my judgment there is no avoiding that result, save that the American people shall see that constitutions are better construed than our Constitution is construed in that decision. They must take care that it is more faithfully and truly carried out than it is there expounded.
I must hasten to a conclusion. Near the beginning of my remarks I said that this insidious Douglas popular sovereignty is the measure that now threatens the purpose of the Republican party to prevent slavery from being nationalized in the United States. I propose to ask your attention for a little while to some propositions in affirmance of that statement. Take it just as it stands, and apply it as a principle; extend and apply that principle elsewhere; and consider where it will lead you. I now put this proposition, that Judge Douglas's popular sovereignty applied will reopen the African slave trade; and I will demonstrate it by any variety of ways in which you can turn the subject or look at it.
The Judge says that the people of the Territories have the right, by his principle, to have slaves, if they want them. Then I say that the people in Georgia have the right to buy slaves in Africa, if they want them; and I defy any man on earth to show any distinction between the two things,—to show that the one is either more wicked or more unlawful; to show, on original principles, that one is better or worse than the other; or to show, by the Constitution, that one differs a whit from the other. He will tell me, doubtless, that there is no constitutional provision against people taking slaves into the new Territories, and I tell him that there is equally no constitutional provision against buying slaves in Africa. He will tell you that a people, in the exercise of popular sovereignty, ought to do as they please about that thing, and have slaves if they want them; and I tell you that the people of Georgia are as much entitled to popular sovereignty and to buy slaves in Africa, if they want them, as the people of the Territory are to have slaves if they want them. I ask any man, dealing honestly with himself, to point out a distinction.
I have recently seen a letter of Judge Douglas's in which, without stating that to be the object, he doubtless endeavors to make a distinction between the two. He says he is unalterably opposed to the repeal of the laws against the African slave trade. And why? He then seeks to give a reason that would not apply to his popular sovereignty in the Territories. What is that reason? "The abolition of the African slave trade is a compromise of the Constitution!" I deny it. There is no truth in the proposition that the abolition of the African slave trade is a compromise of the Constitution. No man can put his finger on anything in the Constitution, or on the line of history, which shows it. It is a mere barren assertion, made simply for the purpose of getting up a distinction between the revival of the African slave trade and his "great principle."
At the time the Constitution of the United States was adopted, it was expected that the slave trade would be abolished. I should assert and insist upon that, if judge Douglas denied it. But I know that it was equally expected that slavery would be excluded from the Territories, and I can show by history that in regard to these two things public opinion was exactly alike, while in regard to positive action, there was more done in the Ordinance of '87 to resist the spread of slavery than was ever done to abolish the foreign slave trade. Lest I be misunderstood, I say again that at the time of the formation of the Constitution, public expectation was that the slave trade would be abolished, but no more so than the spread of slavery in the Territories should be restrained. They stand alike, except that in the Ordinance of '87 there was a mark left by public opinion, showing that it was more committed against the spread of slavery in the Territories than against the foreign slave trade.
Compromise! What word of compromise was there about it? Why, the public sense was then in favor of the abolition of the slave trade; but there was at the time a very great commercial interest involved in it, and extensive capital in that branch of trade. There were doubtless the incipient stages of improvement in the South in the way of farming, dependent on the slave trade, and they made a proposition to Congress to abolish the trade after allowing it twenty years,—a sufficient time for the capital and commerce engaged in it to be transferred to other channel. They made no provision that it should be abolished in twenty years; I do not doubt that they expected it would be, but they made no bargain about it. The public sentiment left no doubt in the minds of any that it would be done away. I repeat, there is nothing in the history of those times in favor of that matter being a compromise of the constitution. It was the public expectation at the time, manifested in a thousand ways, that the spread of slavery should also be restricted.
Then I say, if this principle is established, that there is no wrong in slavery, and whoever wants it has a right to have it, is a matter of dollars and cents, a sort of question as to how they shall deal with brutes, that between us and the negro here there is no sort of question, but that at the South the question is between the negro and the crocodile, that is all, it is a mere matter of policy, there is a perfect right, according to interest, to do just as you please,—when this is done, where this doctrine prevails, the miners and sappers will have formed public opinion for the slave trade. They will be ready for Jeff. Davis and Stephens and other leaders of that company to sound the bugle for the revival of the slave trade, for the second Dred Scott decision, for the flood of slavery to be poured over the free States, while we shall be here tied down and helpless and run over like sheep.
It is to be a part and parcel of this same idea to say to men who want to adhere to the Democratic party, who have always belonged to that party, and are only looking about for some excuse to stick to it, but nevertheless hate slavery, that Douglas's popular sovereignty is as good a way as any to oppose slavery. They allow themselves to be persuaded easily, in accordance with their previous dispositions, into this belief, that it is about as good a way of opposing slavery as any, and we can do that without straining our old party ties or breaking up old political associations. We can do so without being called negro-worshipers. We can do that without being subjected to the jibes and sneers that are so readily thrown out in place of argument where no argument can be found. So let us stick to this popular sovereignty,—this insidious popular sovereignty.
Now let me call your attention to one thing that has really happened, which shows this gradual and steady debauching of public opinion, this course of preparation for the revival of the slave trade, for the Territorial slave code, and the new Dred Scott decision that is to carry slavery into the Free States. Did you ever, five years ago, hear of anybody in the world saying that the negro had no share in the Declaration of National Independence; that it does not mean negroes at all; and when "all men" were spoken of, negroes were not included?
I am satisfied that five years ago that proposition was not put upon paper by any living being anywhere. I have been unable at any time to find a man in an audience who would declare that he had ever known of anybody saying so five years ago. But last year there was not a Douglas popular sovereign in Illinois who did not say it. Is there one in Ohio but declares his firm belief that the Declaration of Independence did not mean negroes at all? I do not know how this is; I have not been here much; but I presume you are very much alike everywhere. Then I suppose that all now express the belief that the Declaration of Independence never did mean negroes. I call upon one of them to say that he said it five years ago.
If you think that now, and did not think it then, the next thing that strikes me is to remark that there has been a change wrought in you,—and a very significant change it is, being no less than changing the negro, in your estimation, from the rank of a man to that of a brute. They are taking him down and placing him, when spoken of, among reptiles and crocodiles, as Judge Douglas himself expresses it.
Is not this change wrought in your minds a very important change? Public opinion in this country is everything. In a nation like ours, this popular sovereignty and squatter sovereignty have already wrought a change in the public mind to the extent I have stated. There is no man in this crowd who can contradict it.
Now, if you are opposed to slavery honestly, as much as anybody, I ask you to note that fact, and the like of which is to follow, to be plastered on, layer after layer, until very soon you are prepared to deal with the negro every where as with the brute. If public sentiment has not been debauched already to this point, a new turn of the screw in that direction is all that is wanting; and this is constantly being done by the teachers of this insidious popular sovereignty. You need but one or two turns further, until your minds, now ripening under these teachings, will be ready for all these things, and you will receive and support, or submit to, the slave trade, revived with all its horrors, a slave code enforced in our Territories, and a new Dred Scott decision to bring slavery up into the very heart of the free North. This, I must say, is but carrying out those words prophetically spoken by Mr. Clay,—many, many years ago,—I believe more than thirty years, when he told an audience that if they would repress all tendencies to liberty and ultimate emancipation they must go back to the era of our independence, and muzzle the cannon which thundered its annual joyous return on the Fourth of July; they must blow out the moral lights around us; they must penetrate the human soul, and eradicate the love of liberty: but until they did these things, and others eloquently enumerated by him, they could not repress all tendencies to ultimate emancipation.
I ask attention to the fact that in a pre-eminent degree these popular sovereigns are at this work: blowing out the moral lights around us; teaching that the negro is no longer a man, but a brute; that the Declaration has nothing to do with him; that he ranks with the crocodile and the reptile; that man, with body and soul, is a matter of dollars and cents. I suggest to this portion of the Ohio Republicans, or Democrats, if there be any present, the serious consideration of this fact that there is now going on among you a steady process of debauching public opinion on this subject. With this, my friends, I bid you adieu.
My Fellow-Citizens of the State of Ohio: This is the first time in my life that I have appeared before an audience in so great a city as this: I therefore—though I am no longer a young man—make this appearance under some degree of embarrassment. But I have found that when one is embarrassed, usually the shortest way to get through with it is to quit talking or thinking about it, and go at something else.
I understand that you have had recently with you my very distinguished friend Judge Douglas, of Illinois; and I understand, without having had an opportunity (not greatly sought, to be sure) of seeing a report of the speech that he made here, that he did me the honor to mention my humble name. I suppose that he did so for the purpose of making some objection to some sentiment at some time expressed by me. I should expect, it is true, that judge Douglas had reminded you, or informed you, if you had never before heard it, that I had once in my life declared it as my opinion that this government cannot endure permanently, half slave and half free; that a house divided against itself cannot stand, and, as I had expressed it, I did not expect the house to fall, that I did not expect the Union to be dissolved, but that I did expect that it would cease to be divided, that it would become all one thing, or all the other; that either the opponents of slavery would arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind would rest in the belief that it was in the course of ultimate extinction, or the friends of slavery will push it forward until it becomes alike lawful in all the States, old or new, free as well as slave. I did, fifteen months ago, express that opinion, and upon many occasions Judge Douglas has denounced it, and has greatly, intentionally or unintentionally, misrepresented my purpose in the expression of that opinion.
I presume, without having seen a report of his speech, that he did so here. I presume that he alluded also to that opinion, in different language, having been expressed at a subsequent time by Governor Seward of New York, and that he took the two in a lump and denounced them; that he tried to point out that there was something couched in this opinion which led to the making of an entire uniformity of the local institutions of the various States of the Union, in utter disregard of the different States, which in their nature would seem to require a variety of institutions and a variety of laws, conforming to the differences in the nature of the different States.
Not only so: I presume he insisted that this was a declaration of war between the free and slave States, that it was the sounding to the onset of continual war between the different States, the slave and free States.
This charge, in this form, was made by Judge Douglas on, I believe, the 9th of July, 1858, in Chicago, in my hearing. On the next evening, I made some reply to it. I informed him that many of the inferences he drew from that expression of mine were altogether foreign to any purpose entertained by me, and in so far as he should ascribe these inferences to me, as my purpose, he was entirely mistaken; and in so far as he might argue that, whatever might be my purpose, actions conforming to my views would lead to these results, he might argue and establish if he could; but, so far as purposes were concerned, he was totally mistaken as to me.
When I made that reply to him, I told him, on the question of declaring war between the different States of the Union, that I had not said that I did not expect any peace upon this question until slavery was exterminated; that I had only said I expected peace when that institution was put where the public mind should rest in the belief that it was in course of ultimate extinction; that I believed, from the organization of our government until a very recent period of time, the institution had been placed and continued upon such a basis; that we had had comparative peace upon that question through a portion of that period of time, only because the public mind rested in that belief in regard to it, and that when we returned to that position in relation to that matter, I supposed we should again have peace as we previously had. I assured him, as I now, assure you, that I neither then had, nor have, or ever had, any purpose in any way of interfering with the institution of slavery, where it exists. I believe we have no power, under the Constitution of the United States, or rather under the form of government under which we live, to interfere with the institution of slavery, or any other of the institutions of our sister States, be they free or slave States. I declared then, and I now re-declare, that I have as little inclination to interfere with the institution of slavery where it now exists, through the instrumentality of the General Government, or any other instrumentality, as I believe we have no power to do so. I accidentally used this expression: I had no purpose of entering into the slave States to disturb the institution of slavery. So, upon the first occasion that Judge Douglas got an opportunity to reply to me, he passed by the whole body of what I had said upon that subject, and seized upon the particular expression of mine that I had no purpose of entering into the slave States to disturb the institution of slavery. "Oh, no," said he, "he [Lincoln] won't enter into the slave States to disturb the institution of slavery, he is too prudent a man to do such a thing as that; he only means that he will go on to the line between the free and slave States, and shoot over at them. This is all he means to do. He means to do them all the harm he can, to disturb them all he can, in such a way as to keep his own hide in perfect safety."
Well, now, I did not think, at that time, that that was either a very dignified or very logical argument but so it was, I had to get along with it as well as I could.
It has occurred to-me here to-night that if I ever do shoot over the line at the people on the other side of the line into a slave State, and purpose to do so, keeping my skin safe, that I have now about the best chance I shall ever have. I should not wonder if there are some Kentuckians about this audience—we are close to Kentucky; and whether that be so or not, we are on elevated ground, and, by speaking distinctly, I should not wonder if some of the Kentuckians would hear me on the other side of the river. For that reason I propose to address a portion of what I have to say to the Kentuckians.
I say, then, in the first place, to the Kentuckians, that I am what they call, as I understand it, a "Black Republican." I think slavery is wrong, morally and politically. I desire that it should be no further spread in—these United States, and I should not object if it should gradually terminate in the whole Union. While I say this for myself, I say to you Kentuckians that I understand you differ radically with me upon this proposition; that you believe slavery is a good thing; that slavery is right; that it ought to be extended and perpetuated in this Union. Now, there being this broad difference between us, I do not pretend, in addressing myself to you Kentuckians, to attempt proselyting you; that would be a vain effort. I do not enter upon it. I only propose to try to show you that you ought to nominate for the next Presidency, at Charleston, my distinguished friend Judge Douglas. In all that there is a difference between you and him, I understand he is sincerely for you, and more wisely for you than you are for yourselves. I will try to demonstrate that proposition. Understand, now, I say that I believe he is as sincerely for you, and more wisely for you, than you are for yourselves.
What do you want more than anything else to make successful your views of slavery,—to advance the outspread of it, and to secure and perpetuate the nationality of it? What do you want more than anything else? What—is needed absolutely? What is indispensable to you? Why, if I may, be allowed to answer the question, it is to retain a hold upon the North, it is to retain support and strength from the free States. If you can get this support and strength from the free States, you can succeed. If you do not get this support and this strength from the free States, you are in the minority, and you are beaten at once.
If that proposition be admitted,—and it is undeniable,—then the next thing I say to you is, that Douglas, of all the men in this nation, is the only man that affords you any hold upon the free States; that no other man can give you any strength in the free States. This being so, if you doubt the other branch of the proposition, whether he is for you—whether he is really for you, as I have expressed it,—I propose asking your attention for a while to a few facts.
The issue between you and me, understand, is, that I think slavery is wrong, and ought not to be outspread; and you think it is right, and ought to be extended and perpetuated. [A voice, "Oh, Lord!"] That is my Kentuckian I am talking to now.
I now proceed to try to show you that Douglas is as sincerely for you and more wisely for you than you are for yourselves.
In the first place, we know that in a government like this, in a government of the people, where the voice of all the men of the country, substantially, enters into the execution—or administration, rather—of the government, in such a government, what lies at the bottom of all of it is public opinion. I lay down the proposition, that Judge Douglas is not only the man that promises you in advance a hold upon the North, and support in the North, but he constantly moulds public opinion to your ends; that in every possible way he can he constantly moulds the public opinion of the North to your ends; and if there are a few things in which he seems to be against you,—a few things which he says that appear to be against you, and a few that he forbears to say which you would like to have him say you ought to remember that the saying of the one, or the forbearing to say the other, would lose his hold upon the North, and, by consequence, would lose his capacity to serve you.
Upon this subject of moulding public opinion I call your attention to the fact—for a well established fact it is—that the Judge never says your institution of slavery is wrong. There is not a public man in the United States, I believe, with the exception of Senator Douglas, who has not, at some time in his life, declared his opinion whether the thing is right or wrong; but Senator Douglas never declares it is wrong. He leaves himself at perfect liberty to do all in your favor which he would be hindered from doing if he were to declare the thing to be wrong. On the contrary, he takes all the chances that he has for inveigling the sentiment of the North, opposed to slavery, into your support, by never saying it is right. This you ought to set down to his credit: You ought to give him full credit for this much; little though it be, in comparison to the whole which he does for you.
Some other, things I will ask your attention to. He said upon the floor of the United States Senate, and he has repeated it, as I understand, a great many times, that he does not care whether slavery is "voted up or voted down." This again shows you, or ought to show you, if you would reason upon it, that he does not believe it to be wrong; for a man may say when he sees nothing wrong in a thing; that he, dues not care whether it be voted up or voted down but no man can logically say that he cares not whether a thing goes up or goes down which to him appears to be wrong. You therefore have a demonstration in this that to Judge Douglas's mind your favorite institution, which you would have spread out and made perpetual, is no wrong.
Another thing he tells you, in a speech made at Memphis in Tennessee, shortly after the canvass in Illinois, last year. He there distinctly told the people that there was a "line drawn by the Almighty across this continent, on the one side of which the soil must always be cultivated by slaves"; that he did not pretend to know exactly where that line was, but that there was such a line. I want to ask your attention to that proposition again; that there is one portion of this continent where the Almighty has signed the soil shall always be cultivated by slaves; that its being cultivated by slaves at that place is right; that it has the direct sympathy and authority of the Almighty. Whenever you can get these Northern audiences to adopt the opinion that slavery is right on the other side of the Ohio, whenever you can get them, in pursuance of Douglas's views, to adopt that sentiment, they will very readily make the other argument, which is perfectly logical, that that which is right on that side of the Ohio cannot be wrong on this, and that if you have that property on that side of the Ohio, under the seal and stamp of the Almighty, when by any means it escapes over here it is wrong to have constitutions and laws "to devil" you about it. So Douglas is moulding the public opinion of the North, first to say that the thing is right in your State over the Ohio River, and hence to say that that which is right there is not wrong here, and that all laws and constitutions here recognizing it as being wrong are themselves wrong, and ought to be repealed and abrogated. He will tell you, men of Ohio, that if you choose here to have laws against slavery, it is in conformity to the idea that your climate is not suited to it, that your climate is not suited to slave labor, and therefore you have constitutions and laws against it.
Let us attend to that argument for a little while and see if it be sound. You do not raise sugar-cane (except the new-fashioned sugar-cane, and you won't raise that long), but they do raise it in Louisiana. You don't raise it in Ohio, because you can't raise it profitably, because the climate don't suit it. They do raise it in Louisiana, because there it is profitable. Now, Douglas will tell you that is precisely the slavery question: that they do have slaves there because they are profitable, and you don't have them here because they are not profitable. If that is so, then it leads to dealing with the one precisely as with the other. Is there, then, anything in the constitution or laws of Ohio against raising sugar-cane? Have you found it necessary to put any such provision in your law? Surely not! No man desires to raise sugar-cane in Ohio, but if any man did desire to do so, you would say it was a tyrannical law that forbids his doing so; and whenever you shall agree with Douglas, whenever your minds are brought to adopt his argument, as surely you will have reached the conclusion that although it is not profitable in Ohio, if any man wants it, is wrong to him not to let him have it.
In this matter Judge Douglas is preparing the public mind for you of Kentucky to make perpetual that good thing in your estimation, about which you and I differ.
In this connection, let me ask your attention to another thing. I believe it is safe to assert that five years ago no living man had expressed the opinion that the negro had no share in the Declaration of Independence. Let me state that again: five years ago no living man had expressed the opinion that the negro had no share in the Declaration of Independence. If there is in this large audience any man who ever knew of that opinion being put upon paper as much as five years ago, I will be obliged to him now or at a subsequent time to show it.
If that be true I wish you then to note the next fact: that within the space of five years Senator Douglas, in the argument of this question, has got his entire party, so far as I know, without exception, in saying that the negro has no share in the Declaration of Independence. If there be now in all these United States one Douglas man that does not say this, I have been unable upon any occasion to scare him up. Now, if none of you said this five years ago, and all of you say it now, that is a matter that you Kentuckians ought to note. That is a vast change in the Northern public sentiment upon that question.
Of what tendency is that change? The tendency of that change is to bring the public mind to the conclusion that when men are spoken of, the negro is not meant; that when negroes are spoken of, brutes alone are contemplated. That change in public sentiment has already degraded the black man in the estimation of Douglas and his followers from the condition of a man of some sort, and assigned him to the condition of a brute. Now, you Kentuckians ought to give Douglas credit for this. That is the largest possible stride that can be made in regard to the perpetuation of your thing of slavery.
A voice: Speak to Ohio men, and not to Kentuckians!
Mr. LINCOLN: I beg permission to speak as I please.
In Kentucky perhaps, in many of the slave States certainly, you are trying to establish the rightfulness of slavery by reference to the Bible. You are trying to show that slavery existed in the Bible times by divine ordinance. Now, Douglas is wiser than you, for your own benefit, upon that subject. Douglas knows that whenever you establish that slavery was—right by the Bible, it will occur that that slavery was the slavery of the white man, of men without reference to color; and he knows very well that you may entertain that idea in Kentucky as much as you please, but you will never win any Northern support upon it. He makes a wiser argument for you: he makes the argument that the slavery of the black man; the slavery of the man who has a skin of a different color from your own, is right. He thereby brings to your support Northern voters who could not for a moment be brought by your own argument of the Bible right of slavery. Will you give him credit for that? Will you not say that in this matter he is more wisely for you than you are for yourselves?
Now, having established with his entire party this doctrine, having been entirely successful in that branch of his efforts in your behalf, he is ready for another.
At this same meeting at Memphis he declared that in all contests between the negro and the white man he was for the white man, but that in all questions between the negro and the crocodile he was for the negro. He did not make that declaration accidentally at Memphis. He made it a great many times in the canvass in Illinois last year (though I don't know that it was reported in any of his speeches there, but he frequently made it). I believe he repeated it at Columbus, and I should not wonder if he repeated it here. It is, then, a deliberate way of expressing himself upon that subject. It is a matter of mature deliberation with him thus to express himself upon that point of his case. It therefore requires deliberate attention.
The first inference seems to be that if you do not enslave the negro, you are wronging the white man in some way or other, and that whoever is opposed to the negro being enslaved, is, in some way or other, against the white man. Is not that a falsehood? If there was a necessary conflict between the white man and the negro, I should be for the white man as much as Judge Douglas; but I say there is no such necessary conflict. I say that there is room enough for us all to be free, and that it not only does not wrong the white man that the negro should be free, but it positively wrongs the mass of the white men that the negro should be enslaved; that the mass of white men are really injured by the effects of slave labor in the vicinity of the fields of their own labor.
But I do not desire to dwell upon this branch of the question more than to say that this assumption of his is false, and I do hope that that fallacy will not long prevail in the minds of intelligent white men. At all events, you ought to thank Judge Douglas for it; it is for your benefit it is made.
The other branch of it is, that in the struggle between the negro and the crocodile; he is for the negro. Well, I don't know that there is any struggle between the negro and the crocodile, either. I suppose that if a crocodile (or, as we old Ohio River boatmen used to call them, alligators) should come across a white man, he would kill him if he could; and so he would a negro. But what, at last, is this proposition? I believe it is a sort of proposition in proportion, which may be stated thus: "As the negro is to the white man, so is the crocodile to the negro; and as the negro may rightfully treat the crocodile as a beast or reptile, so the white man may rightfully treat the negro as a beast or a reptile." That is really the "knip" of all that argument of his.
Now, my brother Kentuckians, who believe in this, you ought to thank Judge Douglas for having put that in a much more taking way than any of yourselves have done.
Again, Douglas's great principle, "popular sovereignty," as he calls it, gives you, by natural consequence, the revival of the slave trade whenever you want it. If you question this, listen awhile, consider awhile what I shall advance in support of that proposition.
He says that it is the sacred right of the man who goes into the Territories to have slavery if he wants it. Grant that for argument's sake. Is it not the sacred right of the man who don't go there equally to buy slaves in Africa, if he wants them? Can you point out the difference? The man who goes into the Territories of Kansas and Nebraska, or any other new Territory, with the sacred right of taking a slave there which belongs to him, would certainly have no more right to take one there than I would, who own no slave, but who would desire to buy one and take him there. You will not say you, the friends of Judge Douglas but that the man who does not own a slave has an equal right to buy one and take him to the Territory as the other does.
A voice: I want to ask a question. Don't foreign nations interfere with the slave trade?
Mr. LINCOLN: Well! I understand it to be a principle of Democracy to whip foreign nations whenever, they interfere with us.
Voice: I only asked for information. I am a Republican myself.
Mr. LINCOLN: You and I will be on the best terms in the world, but I do not wish to be diverted from the point I was trying to press.
I say that Douglas's popular sovereignty, establishing his sacred right in the people, if you please, if carried to its logical conclusion gives equally the sacred right to the people of the States or the Territories themselves to buy slaves wherever they can buy them cheapest; and if any man can show a distinction, I should like to hear him try it. If any man can show how the people of Kansas have a better right to slaves, because they want them, than the people of Georgia have to buy them in Africa, I want him to do it. I think it cannot be done. If it is "popular sovereignty" for the people to have slaves because they want them, it is popular sovereignty for them to buy them in Africa because they desire to do so.
I know that Douglas has recently made a little effort, not seeming to notice that he had a different theory, has made an effort to get rid of that. He has written a letter, addressed to somebody, I believe, who resides in Iowa, declaring his opposition to the repeal of the laws that prohibit the Africa slave trade. He bases his opposition to such repeal upon the ground that these laws are themselves one of the compromises of the Constitution of the United States. Now, it would be very interesting to see Judge Douglas or any of his friends turn, to the Constitution of the United States and point out that compromise, to show where there is any compromise in the Constitution, or provision in the Constitution; express or implied, by which the administrators of that Constitution are under any obligation to repeal the African slave trade. I know, or at least I think I know, that the framers of that Constitution did expect the African slave trade would be abolished at the end of twenty years, to which time their prohibition against its being abolished extended there is abundant contemporaneous history to show that the framers of the Constitution expected it to be abolished. But while they so expected, they gave nothing for that expectation, and they put no provision in the Constitution requiring it should be so abolished. The migration or importation of such persons as the States shall see fit to admit shall not be prohibited, but a certain tax might be levied upon such importation. But what was to be done after that time? The Constitution is as silent about that as it is silent, personally, about myself. There is absolutely nothing in it about that subject; there is only the expectation of the framers of the Constitution that the slave trade would be abolished at the end of that time; and they expected it would be abolished, owing to public sentiment, before that time; and the put that provision in, in order that it should not be abolished before that time, for reasons which I suppose they thought to be sound ones, but which I will not now try to enumerate before you.
But while, they expected the slave trade would be abolished at that time, they expected that the spread of slavery into the new Territories should also be restricted. It is as easy to prove that the framers of the Constitution of the United States expected that slavery should be prohibited from extending into the new Territories, as it is to prove that it was expected that the slave trade should be abolished. Both these things were expected. One was no more expected than the other, and one was no more a compromise of the Constitution than the other. There was nothing said in the Constitution in regard to the spread of slavery into the Territory. I grant that; but there was something very important said about it by the same generation of men in the adoption of the old Ordinance of '87, through the influence of which you here in Ohio, our neighbors in Indiana, we in Illinois, our neighbors in Michigan and Wisconsin, are happy, prosperous, teeming millions of free men. That generation of men, though not to the full extent members of the convention that framed the Constitution, were to some extent members of that convention, holding seats at the same time in one body and the other, so that if there was any compromise on either of these subjects, the strong evidence is that that compromise was in favor of the restriction of slavery from the new Territories.
But Douglas says that he is unalterably opposed to the repeal of those laws because, in his view, it is a compromise of the Constitution. You Kentuckians, no doubt, are somewhat offended with that. You ought not to be! You ought to be patient! You ought to know that if he said less than that, he would lose the power of "lugging" the Northern States to your support. Really, what you would push him to do would take from him his entire power to serve you. And you ought to remember how long, by precedent, Judge Douglas holds himself obliged to stick by compromises. You ought to remember that by the time you yourselves think you are ready to inaugurate measures for the revival of the African slave trade, that sufficient time will have arrived, by precedent, for Judge Douglas to break through, that compromise. He says now nothing more strong than he said in 1849 when he declared in favor of Missouri Compromise,—and precisely four years and a quarter after he declared that Compromise to be a sacred thing, which "no ruthless hand would ever daze to touch," he himself brought forward the measure ruthlessly to destroy it. By a mere calculation of time it will only be four years more until he is ready to take back his profession about the sacredness of the Compromise abolishing the slave trade. Precisely as soon as you are ready to have his services in that direction, by fair calculation, you may be sure of having them.
But you remember and set down to Judge Douglas's debt, or discredit, that he, last year, said the people of Territories can, in spite of the Dred Scott decision, exclude your slaves from those Territories; that he declared, by "unfriendly legislation" the extension of your property into the new Territories may be cut off, in the teeth of the decision of the Supreme Court of the United States.
He assumed that position at Freeport on the 27th of August, 1858. He said that the people of the Territories can exclude slavery, in so many words: You ought, however, to bear in mind that he has never said it since. You may hunt in every speech that he has since made, and he has never used that expression once. He has never seemed to notice that he is stating his views differently from what he did then; but by some sort of accident, he has always really stated it differently. He has always since then declared that "the Constitution does not carry slavery into the Territories of the United States beyond the power of the people legally to control it, as other property." Now, there is a difference in the language used upon that former occasion and in this latter day. There may or may not be a difference in the meaning, but it is worth while considering whether there is not also a difference in meaning.
What is it to exclude? Why, it is to drive it out. It is in some way to put it out of the Territory. It is to force it across the line, or change its character so that, as property, it is out of existence. But what is the controlling of it "as other property"? Is controlling it as other property the same thing as destroying it, or driving it away? I should think not. I should think the controlling of it as other property would be just about what you in Kentucky should want. I understand the controlling of property means the controlling of it for the benefit of the owner of it. While I have no doubt the Supreme Court of the United States would say "God speed" to any of the Territorial Legislatures that should thus control slave property, they would sing quite a different tune if, by the pretence of controlling it, they were to undertake to pass laws which virtually excluded it,—and that upon a very well known principle to all lawyers, that what a Legislature cannot directly do, it cannot do by indirection; that as the Legislature has not the power to drive slaves out, they have no power, by indirection, by tax, or by imposing burdens in any way on that property, to effect the same end, and that any attempt to do so would be held by the Dred Scott court unconstitutional.
Douglas is not willing to stand by his first proposition that they can exclude it, because we have seen that that proposition amounts to nothing more nor less than the naked absurdity that you may lawfully drive out that which has a lawful right to remain. He admitted at first that the slave might be lawfully taken into the Territories under the Constitution of the United States, and yet asserted that he might be lawfully driven out. That being the proposition, it is the absurdity I have stated. He is not willing to stand in the face of that direct, naked, and impudent absurdity; he has, therefore, modified his language into that of being "controlled as other property."
The Kentuckians don't like this in Douglas! I will tell you where it will go. He now swears by the court. He was once a leading man in Illinois to break down a court, because it had made a decision he did not like. But he now not only swears by the court, the courts having got to working for you, but he denounces all men that do not swear by the courts, as unpatriotic, as bad citizens. When one of these acts of unfriendly legislation shall impose such heavy burdens as to, in effect, destroy property in slaves in a Territory, and show plainly enough that there can be no mistake in the purpose of the Legislature to make them so burdensome, this same Supreme Court will decide that law to be unconstitutional, and he will be ready to say for your benefit "I swear by the court; I give it up"; and while that is going on he has been getting all his men to swear by the courts, and to give it up with him. In this again he serves you faithfully, and, as I say, more wisely than you serve yourselves.
Again: I have alluded in the beginning of these remarks to the fact that Judge Douglas has made great complaint of my having expressed the opinion that this government "cannot endure permanently, half slave and half free." He has complained of Seward for using different language, and declaring that there is an "irrepressible conflict" between the principles of free and slave labor. [A voice: "He says it is not original with Seward. That it is original with Lincoln."] I will attend to that immediately, sir. Since that time, Hickman of Pennsylvania expressed the same sentiment. He has never denounced Mr. Hickman: why? There is a little chance, notwithstanding that opinion in the mouth of Hickman, that he may yet be a Douglas man. That is the difference! It is not unpatriotic to hold that opinion if a man is a Douglas man.
But neither I, nor Seward, nor Hickman is entitled to the enviable or unenviable distinction of having first expressed that idea. That same idea was expressed by the Richmond Enquirer, in Virginia, in 1856,—quite two years before it was expressed by the first of us. And while Douglas was pluming himself that in his conflict with my humble self, last year, he had "squelched out" that fatal heresy, as he delighted to call it, and had suggested that if he only had had a chance to be in New York and meet Seward he would have "squelched" it there also, it never occurred to him to breathe a word against Pryor. I don't think that you can discover that Douglas ever talked of going to Virginia to "squelch" out that idea there. No. More than that. That same Roger A. Pryor was brought to Washington City and made the editor of the par excellence Douglas paper, after making use of that expression, which, in us, is so unpatriotic and heretical. From all this, my Kentucky friends may see that this opinion is heretical in his view only when it is expressed by men suspected of a desire that the country shall all become free, and not when expressed by those fairly known to entertain the desire that the whole country shall become slave. When expressed by that class of men, it is in nowise offensive to him. In this again, my friends of Kentucky, you have Judge Douglas with you.
There is another reason why you Southern people ought to nominate Douglas at your convention at Charleston. That reason is the wonderful capacity of the man,—the power he has of doing what would seem to be impossible. Let me call your attention to one of these apparently impossible things:
Douglas had three or four very distinguished men of the most extreme anti-slavery views of any men in the Republican party expressing their desire for his re-election to the Senate last year. That would, of itself, have seemed to be a little wonderful; but that wonder is heightened when we see that Wise of Virginia, a man exactly opposed to them, a man who believes in the divine right of slavery, was also expressing his desire that Douglas should be reelected; that another man that may be said to be kindred to Wise, Mr. Breckinridge, the Vice-President, and of your own State, was also agreeing with the anti-slavery men in the North that Douglas ought to be re-elected. Still to heighten the wonder, a senator from Kentucky, whom I have always loved with an affection as tender and endearing as I have ever loved any man, who was opposed to the anti-slavery men for reasons which seemed sufficient to him, and equally opposed to Wise and Breckinridge, was writing letters into Illinois to secure the reelection of Douglas. Now, that all these conflicting elements should be brought, while at daggers' points with one another, to support him, is a feat that is worthy for you to note and consider. It is quite probable that each of these classes of men thought, by the re-election of Douglas, their peculiar views would gain something: it is probable that the anti-slavery men thought their views would gain something; that Wise and Breckinridge thought so too, as regards their opinions; that Mr. Crittenden thought that his views would gain something, although he was opposed to both these other men. It is probable that each and all of them thought that they were using Douglas; and it is yet an unsolved problem whether he was not using them all. If he was, then it is for you to consider whether that power to perform wonders is one for you lightly to throw away.
There is one other thing that I will say to you, in this relation. It is but my opinion, I give it to you without a fee. It is my opinion that it is for you to take him or be defeated; and that if you do take him you may be beaten. You will surely be beaten if you do not take him. We, the Republicans and others forming the opposition of the country, intend to "stand by our guns," to be patient and firm, and in the long run to beat you, whether you take him or not. We know that before we fairly beat you we have to beat you both together. We know that you are "all of a feather," and that we have to beat you all together, and we expect to do it. We don't intend to be very impatient about it. We mean to be as deliberate and calm about it as it is possible to be, but as firm and resolved as it is possible for men to be. When we do as we say,—beat you,—you perhaps want to know what we will do with you.
I will tell you, so far as I am authorized to speak for the opposition, what we mean to do with you. We mean to treat you, as near as we possibly can, as Washington, Jefferson, and Madison treated you. We mean to leave you alone, and in no way interfere with your institution; to abide by all and every compromise of the Constitution, and, in a word, coming back to the original proposition, to treat you, so far as degenerated men (if we have degenerated) may, according to the examples of those noble fathers, Washington, Jefferson, and Madison. We mean to remember that you are as good as we; that there is no difference between us other than the difference of circumstances. We mean to recognize and bear in mind always that you have as good hearts in your bosoms as other people, or as we claim to have, and treat you accordingly. We mean to marry your girls when we have a chance, the white ones I mean; and I have the honor to inform you that I once did have a chance in that way.
I have told you what we mean to do. I want to know, now, when that thing takes place, what do you mean to do? I often hear it intimated that you mean to divide the Union whenever a Republican, or anything like it, is elected President of the United States. [A voice: "That is so."] "That is so," one of them says; I wonder if he is a Kentuckian? [A voice: "He is a Douglas man."] Well, then, I want to know what you are going to do with your half of it? Are you going to split the Ohio down through, and push your half off a piece? Or are you going to keep it right alongside of us outrageous fellows? Or are you going to build up a wall some way between your country and ours, by which that movable property of yours can't come over here any more, to the danger of your losing it? Do you think you can better yourselves, on that subject, by leaving us here under no obligation whatever to return those specimens of your movable property that come hither? You have divided the Union because we would not do right with you, as you think, upon that subject; when we cease to be under obligations to do anything for you, how much better off do you think you will be? Will you make war upon us and kill us all? Why, gentlemen, I think you are as gallant and as brave men as live; that you can fight as bravely in a good cause, man for man, as any other people living; that you have shown yourselves capable of this upon various occasions: but, man for man, you are not better than we are, and there are not so many of you as there are of us. You will never make much of a hand at whipping us. If we were fewer in numbers than you, I think that you could whip us; if we were equal, it would likely be a drawn battle; but being inferior in numbers, you will make nothing by attempting to master us.
But perhaps I have addressed myself as long, or longer, to the Kentuckians than I ought to have done, inasmuch as I have said that whatever course you take we intend in the end to beat you. I propose to address a few remarks to our friends, by way of discussing with them the best means of keeping that promise that I have in good faith made.
It may appear a little episodical for me to mention the topic of which I will speak now. It is a favorite position of Douglas's that the interference of the General Government, through the Ordinance of '87, or through any other act of the General Government never has made or ever can make a free State; the Ordinance of '87 did not make free States of Ohio, Indiana, or Illinois; that these States are free upon his "great principle" of popular sovereignty, because the people of those several States have chosen to make them so. At Columbus, and probably here, he undertook to compliment the people that they themselves have made the State of Ohio free, and that the Ordinance of '87 was not entitled in any degree to divide the honor with them. I have no doubt that the people of the State of Ohio did make her free according to their own will and judgment, but let the facts be remembered.
In 1802, I believe, it was you who made your first constitution, with the clause prohibiting slavery, and you did it, I suppose, very nearly unanimously; but you should bear in mind that you—speaking of you as one people—that you did so unembarrassed by the actual presence of the institution amongst you; that you made it a free State not with the embarrassment upon you of already having among you many slaves, which if they had been here, and you had sought to make a free State, you would not know what to do with. If they had been among you, embarrassing difficulties, most probably, would have induced you to tolerate a slave constitution instead of a free one, as indeed these very difficulties have constrained every people on this continent who have adopted slavery.
Pray what was it that made you free? What kept you free? Did you not find your country free when you came to decide that Ohio should be a free State? It is important to inquire by what reason you found it so. Let us take an illustration between the States of Ohio and Kentucky. Kentucky is separated by this River Ohio, not a mile wide. A portion of Kentucky, by reason of the course of the Ohio, is farther north than this portion of Ohio, in which we now stand. Kentucky is entirely covered with slavery; Ohio is entirely free from it: What made that difference? Was it climate? No. A portion of Kentucky was farther north than this portion of Ohio. Was it soil? No. There is nothing in the soil of the one more favorable to slave than the other. It was not climate or soil that mused one side of the line to be entirely covered with slavery, and the other side free of it. What was it? Study over it. Tell us, if you can, in all the range of conjecture, if there be anything you can conceive of that made that difference, other than that there was no law of any sort keeping it out of Kentucky, while the Ordinance of '87 kept it out of Ohio. If there is any other reason than this, I confess that it is wholly beyond my power to conceive of it. This, then, I offer to combat the idea that that Ordinance has never made any State free.
I don't stop at this illustration. I come to the State of Indiana; and what I have said as between Kentucky and Ohio, I repeat as between Indiana and Kentucky: it is equally applicable. One additional argument is applicable also to Indiana. In her Territorial condition she more than once petitioned Congress to abrogate the Ordinance entirely, or at least so far as to suspend its operation for a time, in order that they should exercise the "popular sovereignty" of having slaves if they wanted them. The men then controlling the General Government, imitating the men of the Revolution, refused Indiana that privilege. And so we have the evidence that Indiana supposed she could have slaves, if it were not for that Ordinance; that she besought Congress to put that barrier out of the way; that Congress refused to do so; and it all ended at last in Indiana being a free State. Tell me not then that the Ordinance of '87 had nothing to do with making Indiana a free State, when we find some men chafing against, and only restrained by, that barrier.
Come down again to our State of Illinois. The great Northwest Territory, including Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, and Wisconsin, was acquired first, I believe, by the British Government, in part at least, from the French. Before the establishment of our independence it became a part of Virginia, enabling Virginia afterward to transfer it to the General Government. There were French settlements in what is now Illinois, and at the same time there were French settlements in what is now Missouri, in the tract of country that was not purchased till about 1803. In these French settlements negro slavery had existed for many years, perhaps more than a hundred; if not as much as two hundred years,—at Kaskaskia, in Illinois, and at St. Genevieve, or Cape Girardeau, perhaps, in Missouri. The number of slaves was not very great, but there was about the same number in each place. They were there when we acquired the Territory. There was no effort made to break up the relation of master and slave, and even the Ordinance of 1787 was not so enforced as to destroy that slavery in Illinois; nor did the Ordinance apply to Missouri at all.
What I want to ask your attention to; at this point, is that Illinois and Missouri came into the Union about the same time, Illinois in the latter part of 1818, and Missouri, after a struggle, I believe sometime in 1820. They had been filling up with American people about the same period of time; their progress enabling them to come into the Union about the same time. At the end of that ten years, in which they had been so preparing (for it was about that period of time), the number of slaves in Illinois had actually decreased; while in Missouri, beginning with very few, at the end of that ten years there were about ten thousand. This being so, and it being remembered that Missouri and Illinois are, to a certain extent, in the same parallel of latitude, that the northern half of Missouri and the southern half of Illinois are in the same parallel of latitude, so that climate would have the same effect upon one as upon the other, and that in the soil there is no material difference so far as bears upon the question of slavery being settled upon one or the other,—there being none of those natural causes to produce a difference in filling them, and yet there being a broad difference to their filling up, we are led again to inquire what was the cause of that difference.
It is most natural to say that in Missouri there was no law to keep that country from filling up with slaves, while in Illinois there was the Ordinance of The Ordinance being there, slavery decreased during that ten years; the Ordinance not being in the other, it increased from a few to ten thousand. Can anybody doubt the reason of the difference?
I think all these facts most abundantly prove that my friend Judge Douglas's proposition, that the Ordinance of '87, or the national restriction of slavery, never had a tendency to make a free State, is a fallacy,—a proposition without the shadow or substance of truth about it.
Douglas sometimes says that all the States (and it is part of this same proposition I have been discussing) that have become free have become so upon his "great principle"; that the State of Illinois itself came into the Union as a slave State, and that the people, upon the "great principle" of popular sovereignty, have since made it a free State. Allow me but a little while to state to you what facts there are to justify him in saying that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State.
I have mentioned to you that there were a few old French slaves there. They numbered, I think, one or two hundred. Besides that, there had been a Territorial law for indenturing black persons. Under that law, in violation of the Ordinance of '87, but without any enforcement of the Ordinance to overthrow the system, there had been a small number of slaves introduced as indentured persons. Owing to this, the clause for the prohibition of slavery was slightly modified. Instead of running like yours, that neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except for crime, of which the party shall have been duly convicted, should exist in the State, they said that neither slavery nor involuntary servitude should thereafter be introduced; and that the children of indentured servants should be born free; and nothing was said about the few old French slaves. Out of this fact, that the clause for prohibiting slavery was modified because of the actual presence of it, Douglas asserts again and again that Illinois came into the Union as a slave State. How far the facts sustain the conclusion that he draws, it is for intelligent and impartial men to decide. I leave it with you, with these remarks, worthy of being remembered, that that little thing, those few indentured servants being there, was of itself sufficient to modify a constitution made by a people ardently desiring to have a free constitution; showing the power of the actual presence of the institution of slavery to prevent any people, however anxious to make a free State, from making it perfectly so.
I have been detaining you longer, perhaps, than I ought to do.
I am in some doubt whether to introduce another topic upon which I could talk a while. [Cries of "Go on," and "Give us it."] It is this, then: Douglas's Popular sovereignty, as a principle, is simply this: If one man chooses to make a slave of another man, neither that man nor anybody else has a right to object. Apply it to government, as he seeks to apply it, and it is this: If, in a new Territory into which a few people are beginning to enter for the purpose of making their homes, they choose to either exclude slavery from their limits, or to establish it there, however one or the other may affect the persons to be enslaved, or the infinitely greater number of persons who are afterward to inhabit that Territory, or the other members of the family of communities of which they are but an incipient member, or the general head of the family of States as parent of all, however their action may affect one or the other of these, there is no power or right to interfere. That is Douglas's popular sovereignty applied. Now, I think that there is a real popular sovereignty in the world. I think the definition of popular sovereignty, in the abstract, would be about this: that each man shall do precisely as he pleases with himself, and with all those things which exclusively concern him. Applied in government, this principle would be that a general government shall do all those things which pertain to it, and all the local governments shall do precisely as they please in respect to those matters which exclusively concern them.
Douglas looks upon slavery as so insignificant that the people must decide that question for themselves; and yet they are not fit to decide who shall be their governor, judge, or secretary, or who shall be any of their officers. These are vast national matters in his estimation; but the little matter in his estimation is that of planting slavery there. That is purely of local interest, which nobody should be allowed to say a word about.
Labor is the great source from which nearly all, if not all, human comforts and necessities are drawn. There is a difference in opinion about the elements of labor in society. Some men assume that there is necessary connection between capital and labor, and that connection draws within it the whole of the labor of the community. They assume that nobody works unless capital excites them to work. They begin next to consider what is the best way. They say there are but two ways: one is to hire men, and to allure them to labor by their consent; the other is to buy the men, and drive them, to it, and that is slavery. Having assumed that, they proceed to discuss the question of whether the laborers themselves are better off in the condition of slaves or of hired laborers, and they usually decide that they are better off in the condition of slaves.
In the first place, I say that the whole thing is a mistake. That there is a certain relation between capital and labor, I admit. That it does exist, and rightfully exists, I think is true. That men who are industrious, and sober, and honest in the pursuit of their own interests should after a while accumulate capital, and after that should be allowed to enjoy it in peace, and also, if they should choose, when they have accumulated it, to use it to save themselves from actual labor, and hire other people to labor for them, is right. In doing so they do not wrong the man they employ, for they find men who have not of their own land to work upon, or shops to work in, and who are benefited by working for others, hired laborers, receiving their capital for it. Thus a few men, that own capital, hire a few others, and these establish the relation of capital and labor rightfully, a relation of which I make no complaint. But I insist that that relation, after all, does not embrace more than one eighth of the labor of the country.
[The speaker proceeded to argue that the hired laborer, with his ability to become an employer, must have every precedence over him who labors under the inducement of force. He continued:]
I have taken upon myself in the name of some of you to say that we expect upon these principles to ultimately beat them. In order to do so, I think we want and must have a national policy in regard to the institution of slavery that acknowledges and deals with that institution as being wrong. Whoever desires the prevention of the spread of slavery and the nationalization of that institution yields all when he yields to any policy that either recognizes slavery as being right or as being an indifferent thing. Nothing will make you successful but setting up a policy which shall treat the thing as being wrong: When I say this, I do not mean to say that this General Government is charged with the duty of redressing or preventing all the wrongs in the world, but I do think that it is charged with preventing and redressing all wrongs which are wrongs to itself. This Government is expressly charged with the duty of providing for the general welfare. We believe that the spreading out and perpetuity of the institution of slavery impairs the general welfare. We believe—nay, we know—that that is the only thing that has ever threatened the perpetuity of the Union itself. The only thing which has ever menaced the destruction of the government under which we live is this very thing. To repress this thing, we think, is, Providing for the general welfare. Our friends in Kentucky differ from us. We need not make our argument for them, but we who think it is wrong in all its relations, or in some of them at least, must decide as to our own actions and our own course, upon our own judgment.
I say that we must not interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists, because the Constitution forbids it, and the general welfare does not require us to do so. We must not withhold an efficient Fugitive Slave law, because the Constitution requires us, as I understand it, not to withhold such a law. But we must prevent the outspreading of the institution, because neither the Constitution nor general welfare requires us to extend it. We must prevent the revival of the African slave trade, and the enacting by Congress of a Territorial slave code. We must prevent each of these things being done by either Congresses or courts. The people of these United States are the rightful masters of both Congresses and courts, not to overthrow the Constitution, but to overthrow the men who pervert the Constitution.
To do these things we must employ instrumentalities. We must hold conventions; we must adopt platforms, if we conform to ordinary custom; we must nominate candidates; and we must carry elections. In all these things, I think that we ought to keep in view our real purpose, and in none do anything that stands adverse to our purpose. If we shall adopt a platform that fails to recognize or express our purpose, or elect a man that declares himself inimical to our purpose, we not only take nothing by our success, but we tacitly admit that we act upon no other principle than a desire to have "the loaves and fishes," by which, in the end, our apparent success is really an injury to us.
I know that this is very desirable with me, as with everybody else, that all the elements of the opposition shall unite in the next Presidential election and in all future time. I am anxious that that should be; but there are things seriously to be considered in relation to that matter. If the terms can be arranged, I am in favor of the union. But suppose we shall take up some man, and put him upon one end or the other of the ticket, who declares himself against us in regard to the prevention of the spread of slavery, who turns up his nose and says he is tired of hearing anything more about it, who is more against us than against the enemy, what will be the issue? Why, he will get no slave States, after all,—he has tried that already until being beat is the rule for him. If we nominate him upon that ground, he will not carry a slave State; and not only so, but that portion of our men who are high-strung upon the principle we really fight for will not go for him, and he won't get a single electoral vote anywhere, except, perhaps, in the State of Maryland. There is no use in saying to us that we are stubborn and obstinate because we won't do some such thing as this. We cannot do it. We cannot get our men to vote it. I speak by the card, that we cannot give the State of Illinois in such case by fifty thousand. We would be flatter down than the "Negro Democracy" themselves have the heart to wish to see us.
After saying this much let me say a little on the other side. There are plenty of men in the slave States that are altogether good enough for me to be either President or Vice-President, provided they will profess their sympathy with our purpose, and will place themselves on the ground that our men, upon principle, can vote for them. There are scores of them, good men in their character for intelligence and talent and integrity. If such a one will place himself upon the right ground, I am for his occupying one place upon the next Republican or opposition ticket. I will heartily go for him. But unless he does so place himself, I think it a matter of perfect nonsense to attempt to bring about a union upon any other basis; that if a union be made, the elements will scatter so that there can be no success for such a ticket, nor anything like success. The good old maxims of the Bible axe applicable, and truly applicable, to human affairs, and in this, as in other things, we may say here that he who is not for us is against us; he who gathereth not with us, scattereth. I should be glad to have some of the many good and able and noble men of the South to place themselves where we can confer upon them the high honor of an election upon one or the other end of our ticket. It would do my soul good to do that thing. It would enable us to teach them that, inasmuch as we select one of their own number to carry out our principles, we are free from the charge that we mean more than we say.
But, my friends, I have detained you much longer than I expected to do. I believe I may do myself the compliment to say that you have stayed and heard me with great patience, for which I return you my most sincere thanks.
CLINTON, October 11, 1859
Dr. EDWARD WALLACE.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am here just now attending court. Yesterday, before I left Springfield, your brother, Dr. William S. Wallace, showed me a letter of yours, in which you kindly mention my name, inquiring for my tariff views, and suggest the propriety of my writing a letter upon the subject. I was an old Henry-Clay-Tariff Whig. In old times I made more speeches on that subject than any other.
I have not since changed my views. I believe yet, if we could have a moderate, carefully adjusted protective tariff, so far acquiesced in as not to be a perpetual subject of political strife, squabbles changes, and uncertainties, it would be better for us. Still it is my opinion that just now the revival of that question will not advance the cause itself, or the man who revives it.
I have not thought much on the subject recently, but my general impression is that the necessity for a protective tariff will ere long force its old opponents to take it up; and then its old friends can join in and establish it on a more firm and durable basis. We, the Old Whigs, have been entirely beaten out on the tariff question, and we shall not be able to re-establish the policy until the absence of it shall have demonstrated the necessity for it in the minds of men heretofore opposed to it. With this view, I should prefer to not now write a public letter on the subject. I therefore wish this to be considered confidential. I shall be very glad to receive a letter from you.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, November, 2, 1859.
WM. DUNGY, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of October 27 is received. When a mortgage is given to secure two notes, and one of the notes is sold and assigned, if the mortgaged premises are only sufficient to pay one note, the one assigned will take it all. Also, an execution from a judgment on the assigned note may take it all; it being the same thing in substance. There is redemption on execution sales from the United States Court just as from any other court.
You did not mention the name of the plaintiff or defendant in the suit, and so I can tell nothing about it as to sales, bids, etc. Write again.
Yours truly,
............. But you Democrats are for the Union; and you greatly fear the success of the Republicans would destroy the Union. Why? Do the Republicans declare against the Union? Nothing like it. Your own statement of it is that if the Black Republicans elect a President, you "won't stand it." You will break up the Union. If we shall constitutionally elect a President, it will be our duty to see that you submit. Old John Brown has been executed for treason against a State. We cannot object, even though he agreed with us in thinking slavery wrong. That cannot excuse violence, bloodshed and treason. It could avail him nothing that he might think himself right. So, if we constitutionally elect a President, and therefore you undertake to destroy the Union, it will be our duty to deal with you as old John Brown has been dealt with. We shall try to do our duty. We hope and believe that in no section will a majority so act as to render such extreme measures necessary.
MESSRS. DOLE, HUBBARD & BROWN.
GENT.:—Your favor of the 12th is at hand, and it gives me pleasure to be able to answer it. It is not my intention to take part in any of the rivalries for the gubernatorial nomination; but the fear of being misunderstood upon that subject ought not to deter me from doing justice to Mr. Judd, and preventing a wrong being done to him by the use of nay name in connection with alleged wrongs to me.
In answer to your first question, as to whether Mr. Judd was guilty of any unfairness to me at the time of Senator Trumbull's election, I answer unhesitatingly in the negative; Mr. Judd owed no political allegiance to any party whose candidate I was. He was in the Senate, holding over, having been elected by a Democratic Constituency. He never was in any caucus of the friends who sought to make me U. S. Senator, never gave me any promises or pledges to support me, and subsequent events have greatly tended to prove the wisdom, politically, of Mr. Judd's course. The election of Judge Trumbull strongly tended to sustain and preserve the position of that lion of the Democrats who condemned the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, and left them in a position of joining with us in forming the Republican party, as was done at the Bloomington convention in 1856.
During the canvass of 1858 for the senatorship my belief was, and still is, that I had no more sincere and faithful friend than Mr. Judd—certainly none whom I trusted more. His position as chairman of the State Central Committee led to my greater intercourse with him, and to my giving him a larger share of my confidence, than with or to almost any other friend; and I have never suspected that that confidence was, to any degree, misplaced.
My relations with Mr. Judo since the organization of the Republican party, in, our State, in 1856, and especially since the adjournment of the Legislature in Feb., 1857, have been so very intimate that I deem it an impossibility that he could have been dealing treacherously with me. He has also, at all times, appeared equally true and faithful to the party. In his position as chairman of the committee, I believe he did all that any man could have done. The best of us are liable to commit errors, which become apparent by subsequent developments; but I do not know of a single error, even, committed by Mr. Judd, since he and I have acted together politically.
I, had occasionally heard these insinuations against Mr. Judd, before the receipt of your letter; and in no instance have I hesitated to pronounce them wholly unjust, to the full extent of my knowledge and belief. I have been, and still am, very anxious to take no part between the many friends, all good and true, who are mentioned as candidates for a Republican gubernatorial nomination; but I can not feel that my own honor is quite clear if I remain silent when I hear any one of them assailed about matters of which I believe I know more than his assailants.
I take pleasure in adding that, of all the avowed friends I had in the canvass of last year, I do not suspect any of having acted treacherously to me, or to our cause; and that there is not one of them in whose honesty, honor, and integrity I, today, have greater confidence than I have in those of Mr. Judd.
I dislike to appear before the public in this matter; but you are at liberty to make such use of this letter as you may think justice requires.
Yours very truly,
MESSRS. G. M. PARSONS AND OTHERS, CENTRAL EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE, ETC.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter of the 7th instant, accompanied by a similar one from the governor-elect, the Republican State officers, and the Republican members of the State Board of Equalization of Ohio, both requesting of me, for publication in permanent form, copies of the political debates between Senator Douglas and myself last year, has been received. With my grateful acknowledgments to both you and them for the very flattering terms in which the request is communicated, I transmit you the copies. The copies I send you are as reported and printed by the respective friends of Senator Douglas and myself, at the time—that is, his by his friends, and mine by mine. It would be an unwarrantable liberty for us to change a word or a letter in his, and the changes I have made in mine, you perceive, are verbal only, and very few in number. I wish the reprint to be precisely as the copies I send, without any comment whatever.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, December 20, 1859.
J. W. FELL, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Herewith is a little sketch, as you requested. There is not much of it, for the reason, I suppose, that there is not much of me. If anything be made out of it, I wish it to be modest, and not to go beyond the material. If it were thought necessary to incorporate anything from any of my speeches I suppose there would be no objection. Of course it must not appear to have been written by myself.
Yours very truly, A. LINCOLN
———
I was born February 12, 1809, in Hardin County, Kentucky. My parents were both born in Virginia, of undistinguished families—second families, perhaps I should say. My mother, who died in my tenth year, was of a family of the name of Hanks, some of whom now reside in Adams, and others in Macon County, Illinois. My paternal grandfather, Abraham Lincoln, emigrated from Rockingham County, Virginia, to Kentucky about 1781 or 1782, where a year or two later he was killed by the Indians, not in battle, but by stealth, when he was laboring to open a farm in the forest. His ancestors, who were Quakers, went to Virginia from Berks County, Pennsylvania. An effort to identify them with the New England family of the same name ended in nothing more definite than a similarity of Christian names in both families, such as Enoch, Levi, Mordecai, Solomon, Abraham, and the like.
My father, at the death of his father, was but six years of age, and he grew up literally without education. He removed from Kentucky to what is now Spencer County, Indiana, in my eighth year. We reached our new home about the time that State came into the Union. It was a wild region, with many bears and other wild animals still in the woods. There I grew up. There were some schools, so called, but no qualification was ever required of a teacher beyond "readin', writin', and cipherin"' to the Rule of Three. If a straggler supposed to understand Latin happened to sojourn in the neighborhood he was looked upon as a wizard. There was absolutely nothing to excite ambition for education. Of course, when I came of age I did not know much. Still, somehow, I could read, write, and cipher to the Rule of Three, but that was all. I have not been to school since. The little advance I now have upon this store of education I have picked up from time to time under the pressure of necessity.
I was raised to farm work, which I continued till I was twenty-two. At twenty-one I came to Illinois, Macon County. Then I got to New Salem, at that time in Sangamon, now in Menard County, where I remained a year as a sort of clerk in a store. Then came the Black Hawk war; and I was elected a captain of volunteers, a success which gave me more pleasure than any I have had since. I went the campaign, was elected, ran for the Legislature the same year (1832), and was beaten—the only time I ever have been beaten by the people. The next and three succeeding biennial elections I was elected to the Legislature. I was not a candidate afterward. During this legislative period I had studied law, and removed to Springfield to practice it. In 1846 I was once elected to the lower House of Congress. Was not a candidate for re-election. From 1849 to 1854, both inclusive, practiced law more assiduously than ever before. Always a Whig in politics; and generally on the Whig electoral tickets, making active canvasses. I was losing interest in politics when the repeal of the Missouri Compromise aroused me again. What I have done since then is pretty well known.
If any personal description of me is thought desirable, it may be said I am, in height, six feet four inches, nearly; lean in flesh, weighing on an average one hundred and eighty pounds; dark complexion, with coarse black hair and gray eyes. No other marks or brands recollected.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, FEBRUARY 9, 1859 HON. N. B. JUDD.
DEAR Sir:—I am not in a position where it would hurt much for me to not be nominated on the national ticket; but I am where it would hurt some for me to not get the Illinois delegates. What I expected when I wrote the letter to Messrs. Dole and others is now happening. Your discomfited assailants are most bitter against me; and they will, for revenge upon me, lay to the Bates egg in the South, and to the Seward egg in the North, and go far toward squeezing me out in the middle with nothing. Can you help me a little in this matter in your end of the vineyard. I mean this to be private.
Yours as ever,
SPEECH AT THE COOPER INSTITUTE, NEW YORK FEBRUARY 27, 1860
MR. PRESIDENT AND FELLOW-CITIZENS OF NEW YORK:—The facts with which I shall deal this evening are mainly old and familiar; nor is there anything new in the general use I shall make of them. If there shall be any novelty, it will be in the mode of presenting the facts, and the inferences and observations following that presentation.
In his speech last autumn at Columbus, Ohio, as reported in the New York Times, Senator Douglas said:
"Our fathers, when they framed the Government under which we live, understood this question just as well, and even better than we do now."
I fully indorse this, and I adopt it as a text for this discourse. I so adopt it because it furnishes a precise and an agreed starting-point for a discussion between Republicans and that wing of the Democracy headed by Senator Douglas. It simply leaves the inquiry: What was the understanding those fathers had of the question mentioned?
What is the frame of Government under which we live?
The answer must be—the Constitution of the United States. That Constitution consists of the original, framed in 1787 (and under which the present Government first went into operation), and twelve subsequently framed amendments, the first ten of which were framed in 1789.
Who were our fathers that framed the Constitution? I suppose the "thirty-nine" who signed the original instrument may be fairly called our fathers who framed that part of the present Government. It is almost exactly true to say they framed it, and it is altogether true to say they fairly represented the opinion and sentiment of the whole nation at that time.
Their names, being familiar to nearly all, and accessible to quite all, need not now be repeated.
I take these "thirty-nine," for the present, as being our "fathers who framed the Government under which we live."
What is the question which, according to the text, those fathers understood "just as well, and even better than we do now"?
It is this: Does the proper division of local from Federal authority, or anything in the Constitution, forbid our Federal Government to control as to slavery in our Federal Territories?
Upon this Senator Douglas holds the affirmative, and Republicans the negative. This affirmation and denial form an issue, and this issue—this question is precisely what the text declares our fathers understood "better than we."
Let us now inquire whether the "thirty-nine," or any of them, acted upon this question; and if they did, how they acted upon it—how they expressed that better understanding.
In 1784, three years before the Constitution—the United States then owning the Northwestern Territory, and no other—the Congress of the Confederation had before them the question of prohibiting slavery in that Territory; and four of the "thirty nine" who afterward framed the Constitution were in that Congress and voted on that question. Of these, Roger Sherman, Thomas Mifflin, and Hugh Williamson voted for the prohibition, thus showing that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor anything else, properly forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory. The other of the four—James McHenry voted against the prohibition, showing that, for some cause, he thought it improper to vote for it.
In 1787, still before the Constitution, but while the convention was in session framing it, and while the Northwestern Territory still was the only Territory owned by the United States, the same question of prohibiting slavery in the Territory again came before the Congress of the Confederation; and two more of the "thirty-nine" who afterward signed the Constitution were in that Congress, and voted on the question. They were William Blount and William Few; and they both voted for the prohibition thus showing that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor anything else, properly forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory. This time the prohibition became a law, being part of what is now well known as the Ordinance of '87.
The question of Federal control of slavery in the Territories seems not to have been directly before the convention which framed the original Constitution; and hence it is not recorded that the "thirty-nine," or any of them, while engaged on that instrument, expressed any opinion on that precise question.
In 1789, by the first Congress which sat under the Constitution, an act was passed to enforce the Ordinance of '87, including the prohibition of slavery in the Northwestern Territory. The bill for this act was reported by one of the "thirty-nine," Thomas Fitzsimmons, then a member of the House of Representatives from Pennsylvania. It went through all its stages without a word of opposition, and finally passed both branches without yeas and nays, which is equivalent to a unanimous passage. In this Congress there were sixteen of the thirty-nine fathers who framed the original Constitution. They were John Langdon, Nicholas Gilman, Wm. S. Johnnson, Roger Sherman, Robert Morris, Thos. Fitzsimmons, William Few, Abraham Baldwin, Rufus King, William Paterson, George Claimer, Richard Bassett, George Read, Pierce Butler, Daniel Carroll, James Madison.
This shows that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor anything in the Constitution, properly forbade Congress to prohibit slavery in the Federal territory; else both their fidelity to correct principles and their oath to support the Constitution would have constrained them to oppose the prohibition.
Again: George Washington, another of the "thirty nine," was then President of the United States, and, as such, approved and signed the bill; thus completing its validity as a law, and thus showing that, in his understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor anything in the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
No great while after the adoption of the original Constitution, North Carolina ceded to the Federal Government the country now constituting the State of Tennessee; and, a few years later, Georgia ceded that which now constitutes the States of Mississippi and Alabama. In both deeds of cession it was made a condition by the ceding States that the Federal Government should not prohibit slavery in the ceded country. Besides this, slavery was then actually in the ceded country. Under these circumstances, Congress, on taking charge of these countries, did not absolutely prohibit slavery within them. But they did interfere with it—take control of it—even there, to a certain extent. In 1798, Congress organized the Territory of Mississippi: In the act of organization they prohibited the bringing of slaves into the Territory from any place without the United States, by fine and giving freedom to slaves so brought. This act passed both branches of Congress without yeas and nays. In that Congress were three of the "thirty-nine" who framed the original Constitution. They were John Langdon, George Read, and Abraham Baldwin. They all, probably, voted for it. Certainly they would have placed their opposition to it upon record, if, in their understanding, any line dividing local from Federal authority, or anything in the Constitution, properly forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
In 1803, the Federal Government purchased the Louisiana country. Our former territorial acquisitions came from certain of our own States; but this Louisiana country was acquired from a foreign nation. In 1804, Congress gave a territorial organization to that part of it which now constitutes the State of Lousiana. New Orleans, lying within that part, was an old and comparatively large city. There were other considerable towns and settlements, and slavery was extensively and thoroughly intermingled with the people. Congress did not, in the Territorial Act, prohibit slavery; but they did interfere with it take control of it—in a more marked and extensive way than they did in the case of Mississippi. The substance of the provision therein made in relation to slaves was:
First. That no slave should be imported into the Territory from foreign parts.
Second. That no slave should be carried into it who had been imported into the United States since the first day of May, 1798.
Third. That no slave should be carried into it except by the owner, and for his own use as a settler; the penalty in all the cases being a fine upon the violator of the law, and freedom to the slave.
This act also was passed without yeas and nays. In the Congress which passed it there were two of the "thirty-nine." They were Abraham Baldwin and Jonathan Dayton. As stated in the case of Mississippi, it is probable they both voted for it. They would not have allowed it to pass without recording their opposition to it, if, in their understanding, it violated either the line properly dividing local from Federal authority, or any provision of the Constitution.
In 1819-20 came and passed the Missouri question. Many votes were taken, by yeas and nays, in both branches of Congress, upon the various phases of the general question. Two of the "thirty-nine"—Rufus King and Charles Pinckney were members of that Congress. Mr. King steadily voted for slavery prohibition and against all compromises, while Mr. Pinckney as steadily voted against slavery prohibition, and against all compromises. By this, Mr. King showed that, in his understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor anything in the Constitution, was violated by Congress prohibiting slavery in Federal territory; while Mr. Pinckney, by his vote, showed that in his understanding there was some sufficient reason for opposing such prohibition in that case.
The cases I have mentioned are the only acts of the "thirty-nine," or of any of them, upon the direct issue, which I have been able to discover.
To enumerate the persons who thus acted, as being four in 1784, two in 1787, seventeen in 1789, three in 1798, two in 1804, and two in 1819-20—there would be thirty of them. But this would be counting, John Langdon, Roger Sherman, William Few, Rufus King, and George Read, each twice, and Abraham Baldwin three times. The true number of those of the "thirty-nine" whom I have shown to have acted upon the question which, by the text, they understood better than we, is twenty-three, leaving sixteen not shown to have acted upon it in any way.
Here, then, we have twenty-three out of our thirty-nine fathers "who framed the Government under which we live," who have, upon their official responsibility and their corporal oaths, acted upon the very question which the text affirms they "understood just as well, and even better than we do now"; and twenty-one of them—a clear majority of the whole "thirty-nine"—so acting upon it as to make them guilty of gross political impropriety and wilful perjury, if, in their understanding, any proper division between local and Federal authority, or anything in the Constitution they had made themselves, and sworn to support, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. Thus the twenty-one acted; and, as actions speak louder than words, so actions under such responsibilities speak still louder.
Two of the twenty-three voted against Congressional prohibition of slavery in the Federal Territories, in the instances in which they acted upon the question. But for what reasons they so voted is not known. They may have done so because they thought a proper division of local from Federal authority, or some provision or principle of the Constitution, stood in the way; or they may, without any such question, have voted against the prohibition on what appeared to them to be sufficient grounds of expediency. No one who has sworn to support the Constitution can conscientiously vote for what he understands to be an unconstitutional measure, however expedient he may think it; but one may and ought to vote against a measure which he deems constitutional, if, at the same time, he deems it inexpedient. It therefore would be unsafe to set down even the two who voted against the prohibition as having done so because, in their understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or anything in the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
The remaining sixteen of the "thirty-nine," so far as I have discovered, have left no record of their understanding upon the direct question of Federal control on slavery in the Federal Territories. But there is much reason to believe that their understanding upon that question would not have appeared different from that of their twenty-three compeers, had it been manifested at all.
For the purpose of adhering rigidly to the text, I have purposely omitted whatever understanding may have been manifested by any person, however distinguished, other than the thirty-nine fathers who framed the original Constitution; and, for the same reason, I have also omitted whatever understanding may have been manifested by any of the "thirty tine" even on any other phase of the general question of slavery. If we should look into their acts and declarations on those other phases, as the foreign slave trade, and the morality and policy of slavery generally, it would appear to us that on the direct question of Federal control of slavery in Federal Territories, the sixteen, if they had acted at all, would probably have acted just as the twenty-three did. Among that sixteen were several of the most noted anti-slavery men of those times—as Dr. Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and Gouverneur Morris while there was not one now known to have been otherwise, unless it may be John Rutledge, of South Carolina.
The sum of the whole is, that of our thirty-nine fathers who framed the original Constitution, twenty-one—a clear majority of the whole—certainly understood that no proper division of local from Federal authority, nor any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control slavery in the Federal Territories; whilst all the rest probably had the same understanding. Such, unquestionably, was the understanding of our fathers who framed the original Constitution; and the text affirms that they understood the question "better than we."
But, so far, I have been considering the understanding of the question manifested by the framers of the original Constitution. In and by the original instrument, a mode was provided for amending it; and, as I have already stated, the present frame of "the Government under which we live" consists of that original, and twelve amendatory articles framed and adopted since. Those who now insist that Federal control of slavery in Federal Territories violates the Constitution, point us to the provisions which they suppose it thus violates; and, as I understand, they all fix upon provisions in these amendatory articles, and not in the original instrument. The Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott case, plant themselves upon the fifth amendment, which provides that no person shall be deprived of "life, liberty, or property without due process of law"; while Senator Douglas and his peculiar adherents plant themselves upon the tenth amendment, providing that "the powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution" "are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."
Now, it so happens that these amendments were framed by the first Congress which sat under the Constitution—the identical Congress which passed the act already mentioned, enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the Northwestern Territory. Not only was it the same Congress, but they were the identical same individual men who, at the same session, and at the same time within the session, had under consideration, and in progress toward maturity, these Constitutional amendments, and this act prohibiting slavery in all the territory the nation then owned. The Constitutional amendments were introduced before and passed after the act enforcing the Ordinance of '87; so that, during the whole pendency of the act to enforce the Ordinance, the Constitutional amendments were also pending.
The seventy-six members of that Congress, including sixteen of the framers of the original Constitution, as before stated, were pre-eminently our fathers who framed that part of "the Government under which we live," which is now claimed as forbidding the Federal Government to control slavery in the Federal Territories.
Is it not a little presumptuous in any one at this day to affirm that the two things which that Congress deliberately framed, and carried to maturity at the same time, are absolutely inconsistent with each other? And does not such affirmation become impudently absurd when coupled with the other affirmation from the same mouth, that those who did the two things alleged to be inconsistent understood whether they really were inconsistent better than we—better than he who affirms that they are inconsistent?
It is surely safe to assume that the thirty-nine framers of the original Constitution, and the seventy-six members of the Congress which framed the amendments thereto, taken together, do certainly include those who may be fairly called "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live." And, so assuming, I defy any man to show that any one of them ever, in his whole life, declared that, in his understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. I go a step further. I defy any one to show that any living man in the world ever did, prior to the beginning of the present century (and I might almost say prior to the beginning of the last half of the present century), declare that, in his understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. To those who now so declare, I give not only "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live," but with them all other living men within the century in which it was framed, among whom to search, and they shall not be able to find the evidence of a single man agreeing with them.
Now and here let me guard a little against being misunderstood. I do not mean to say we are bound to follow implicitly in whatever our fathers did. To do so would be to discard all the lights of current experience to reject all progress, all improvement. What I do say is that, if we would supplant the opinions and policy of our fathers in any case, we should do so upon evidence so conclusive, and argument so clear, that even their great authority, fairly considered and weighed, cannot stand; and most surely not in a case whereof we ourselves declare they understood the question better than we.
If any man at this day sincerely believes that proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbids the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories, he is right to say so, and to enforce his position by all truthful evidence and fair argument which he can. But he has no right to mislead others who have less access to history, and less leisure to study it, into the false belief that "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live" were of the same opinion thus substituting falsehood and deception for truthful evidence and fair argument. If any man at this day sincerely believes "our fathers, who framed the Government under which we live," used and applied principles, in other cases, which ought to have led them to understand that a proper division of local from Federal authority, or some part of the Constitution, forbids the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories, he is right to say so. But he should, at the same time, brave the responsibility of declaring that, in his opinion, he understands their principles better than they did themselves; and especially should he not shirk that responsibility by asserting that they "understood the question just as well, and even better than we do now."
But enough! Let all who believe that "our fathers, who framed the Government under which we live, understood this question just as well, and even better than we do now," speak as they spoke, and act as they acted upon it. This is all Republicans ask—all Republicans desire—in relation to slavery. As those fathers marked it, so let it be again marked, as an evil not to be extended, but to be tolerated and protected only because of, and so far as, its actual presence among us makes that toleration and protection a necessity. Let all the guaranties those fathers gave it be not grudgingly, but fully and fairly maintained. For this Republicans contend, and with this, so far as I know or believe, they will be content.
And now, if they would listen—as I suppose they will not—I would address a few words to the Southern people.
I would say to them: You consider yourselves a reasonable and a just people; and I consider that in the general qualities of reason and justice you are not inferior to any other people. Still, when you speak of us Republicans, you do so only to denounce us as reptiles, or, at the best, as no better than outlaws. You will grant a hearing to pirates or murderers, but nothing like it to "Black Republicans." In all your contentions with one another, each of you deems an unconditional condemnation of "Black Republicanism" as the first thing to be attended to. Indeed, such condemnation of us seems to be an indispensable prerequisite license, so to speak among you, to be admitted or permitted to speak at all: Now; can you, or not, be prevailed upon to pause, and to consider whether this is quite just to us, or even to yourselves? Bring forward your charges and specifications, and then be patient long enough to hear us deny or justify.
You say we are sectional. We deny it. That makes an issue; and the burden of proof is upon you. You produce your proof; and what is it? Why, that our party has no existence in your section—gets no votes in your section. The fact is substantially true; but does it prove the issue? If it does, then in case we should, without change of principle, begin to get votes in your section, we should thereby cease to be sectional. You cannot escape this conclusion; and yet, are you willing to abide by it? If you are, you will probably soon find that we have ceased to be sectional, for we shall get votes in your section this very year. You will then begin to discover, as the truth plainly is, that your proof, does not touch the issue. The fact that we get no votes in your section is a fact of your making, and not of ours. And if there be fault in that fact, that fault is primarily yours, and remains so until you show that we repel you by, some wrong principle or practice. If we do repel you by any wrong principle or practice, the fault is ours; but this brings you to where you ought to have started to a discussion of the right or wrong of our principle. If our principle, put in practice, would wrong your section for the benefit of ours, or for any other object, then our principle, and we with it, are sectional, and are justly opposed and denounced as such. Meet us, then, on the question of whether our principle, put in practice, would wrong your section; and so meet us as if it were possible that something may be said on our side. Do you accept the challenge? No! Then you really believe that the principle which "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live" thought so clearly right as to adopt it, and indorse it again and again, upon their official oaths, is in fact so clearly wrong as to demand your condemnation without a moment's consideration.
Some of you delight to flaunt in our faces the warning against sectional parties given by Washington in his Farewell Address. Less than eight years before Washington gave that warning, he had, as President of the United States, approved and signed an act of Congress enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the Northwestern Territory, which act embodied the policy of the Government upon that subject up to, and at, the very moment he penned that warning; and about one year after he penned it, he wrote La Fayette that he considered that prohibition a wise measure, expressing in the same connection his hope that we should at some time have a confederacy of free States.
Bearing this in mind, and seeing that sectionalism has since arisen upon this same subject, is that warning a weapon in your hands against us, or in our hands against you? Could Washington himself speak, would he cast the blame of that sectionalism upon us, who sustain his policy, or upon you, who repudiate it? We respect that warning of Washington, and we commend it to you, together with his example pointing to the right application of it.
But you say you are conservative—eminently conservative—while we are revolutionary, destructive, or something, of the sort. What is conservatism? Is it not adherence to the old and tried, against a new and untried? We stick to, contend for, the identical old policy on the point in controversy which was adopted by "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live"; while you with one accord reject, and scout, and spit upon that old policy and insist upon substituting something new. True, you disagree among yourselves as to what that substitute shall be. You are divided on new propositions and plans, but you are unanimous in rejecting and denouncing the old policy of the fathers. Some of you are for reviving the foreign slave trade; some for a Congressional slave code for the Territories; some for Congress forbidding the Territories to prohibit slavery within their limits; some for maintaining slavery in the Territories through the judiciary; some for the "gur-reat pur-rinciple" that "if one man would enslave another, no third man should object," fantastically called "popular sovereignty"; but never a man among you in favor of Federal prohibition of slavery in Federal Territories, according to the practice of "our fathers who framed the Government under which we live." Not one of all your various plans can show a precedent or an advocate in the century within which our Government originated. Consider, then, whether your claim of conservatism for yourselves, and your charge of destructiveness against us, are based on the most clear and stable foundations.
Again: You say we have made the slavery question more prominent than it formerly was. We deny it. We admit that it is more prominent, but we deny that we made it so. It was not we, but you, who discarded the old policy of the fathers. We resisted and still resist your innovation; and thence comes the greater prominence of the question. Would you have that question reduced to its former proportions? Go back to that old policy. What has been will be again, under the same conditions. If you would have the peace of the old times, readopt the precepts and policy of the old times.
You charge that we stir up insurrections among your slaves. We deny it; and what is your proof'? Harper's Ferry! John Brown!! John Brown was no Republican; and you have failed to implicate a single Republican in his Harper's Ferry enterprise. If any member of our party is guilty in that matter you know it or you do not know it. If you do know it, you are inexcusable for not designating the man and proving the fact. If you do not know it, you are inexcusable for asserting it, and especially for persisting in the assertion after you have tried and failed to make the proof. You need not be told that persisting in a charge which one does not know to be true is simply malicious slander.
Some of you admit that no Republican designedly aided or encouraged the Harper's Ferry affair, but still insist that our doctrines and declarations necessarily lead to such results. We do not believe it. We know we hold to no doctrine, and make no declaration, which were not held to and made by our fathers who framed the Government under which we live. You never dealt fairly by us in relation to this affair. When it occurred, some important State elections were near at hand, and you were in evident glee with the belief that, by charging the blame upon us, you could get an advantage of us in those elections. The elections came, and your expectations were not quite fulfilled. Every Republican man knew that, as to himself at least, your charge was a slander, and he was not much inclined by it to cast his vote in your favor. Republican doctrines and declarations are accompanied with a continued protest against any interference whatever with your slaves, or with you about your slaves. Surely, this does not encourage them to revolt. True, we do, in common with "our fathers, who framed the Government under which we live," declare our belief that slavery is wrong; but the slaves do not hear us declare even this. For any thing we say or do, the slaves would scarcely know there is a Republican party. I believe they would not, in fact, generally know it but for your misrepresentations of us in their hearing. In your political contests among yourselves, each faction charges the other with sympathy with Black Republicanism; and then, to give point to the charge, defines Black Republicanism to simply be insurrection, blood, and thunder among the slaves.
Slave insurrections are no more common now than they were before the Republican party was organized. What induced the Southampton insurrection, twenty-eight years ago, in which, at least, three times as many lives were lost as at Harper's Ferry? You can scarcely stretch your very elastic fancy to the conclusion that Southampton was "got up by Black Republicanism." In the present state of things in the United States, I do not think a general or even a very extensive slave insurrection is possible. The indispensable concert of action cannot be attained. The slaves have no means of rapid communication; nor can incendiary freemen, black or white, supply it. The explosive materials are everywhere in parcels; but there neither are, nor can be supplied the indispensable connecting trains.
Much is said by Southern people about the affection of slaves for their masters and mistresses; and a part of it, at least, is true. A plot for an uprising could scarcely be devised and communicated to twenty individuals before some one of them, to save the life of a favorite master or mistress, would divulge it. This is the rule; and the slave revolution in Hayti was not an exception to it, but a case occurring under peculiar circumstances. The gunpowder plot of British history, though not connected with slaves, was more in point. In that case, only about twenty were admitted to the secret; and yet one of them, in his anxiety to save a friend, betrayed the plot to that friend, and, by consequence, averted the calamity. Occasional poisonings from the kitchen, and open or stealthy assassinations in the field, and local revolts, extending to a score or so, will continue to occur as the natural results of slavery; but no general insurrection of slaves, as I think, can happen in this country for a long time. Whoever much fears or much hopes for such an event will be alike disappointed.
In the language of Mr. Jefferson, uttered many years ago, "It is still in our power to direct the process of emancipation and deportation peaceably, and in such slow degrees as that the evil will wear off insensibly, and their places be, pari passu, filled up by free white laborers. If, on the contrary, it is left to force itself on, human nature must shudder at the prospect held up."
Mr. Jefferson did not mean to say, nor do I, that the power of emancipation is in the Federal Government. He spoke of Virginia; and, as to the power of emancipation, I speak of the slave holding States only. The Federal Government, however, as we insist, has the power of restraining the extension of the institution—the power to insure that a slave insurrection shall never occur on any American soil which is now free from slavery.
John Brown's effort was peculiar. It was not a slave insurrection. It was an attempt by white men to get up a revolt among slaves, in which the slaves refused to participate. In fact, it was so absurd that the slaves, with all their ignorance, saw plainly enough it could not succeed. That affair, in its philosophy, corresponds with the many attempts related in history at the assassination of kings and emperors. An enthusiast broods over the oppression of a people till he fancies himself commissioned by Heaven to liberate them. He ventures the attempt, which ends in little else than his own execution. Orsini's attempt on Louis Napoleon and John Brown's attempt at Harper's Ferry were, in their philosophy, precisely the same. The eagerness to cast blame on old England in the one case, and on New England in the other, does not disprove the sameness of the two things.
And how much would it avail you, if you could, by the use of John Brown, Helper's Book, and the like, break up the Republican organization? Human action can be modified to some extent, but human nature cannot be changed. There is a judgment and a feeling against slavery in this nation, which cast at least a million and a half of votes. You cannot destroy that judgment and feeling—that sentiment—by breaking up the political organization which rallies around it. You can scarcely scatter and disperse an army which has been formed into order in the face of your heaviest fire; but if you could, how much would you gain by forcing the sentiment which created it out of the peaceful channel of the ballot-box, into some other channel? What would that other channel probably be? Would the number of John Browns be lessened or enlarged by the operation?
But you will break up the Union rather than submit to a denial of your constitutional rights.
That has a somewhat reckless sound; but it would be palliated, if not fully justified, were we proposing, by the mere force of numbers, to deprive you of some right plainly written down in the Constitution. But we are proposing no such thing.
When you make these declarations, you have a specific and well-understood allusion to an assumed constitutional right of yours to take slaves into the Federal Territories, and to hold them there as property. But no such right is specifically written in the Constitution. That instrument is literally silent about any such right. We, on the contrary, deny that such a right has any existence in the Constitution, even by implication.
Your purpose, then, plainly stated, is that you will destroy the Government unless you be allowed to construe and enforce the Constitution as you please on all points in dispute between you and us. You will rule or ruin, in all events.
This, plainly stated, is your language. Perhaps you will say the Supreme Court has decided the disputed constitutional question in your favor. Not quite so. But, waiving the lawyer's distinction between dictum and decision, the court have decided the question for you in a sort of way. The court have substantially said it is your constitutional right to take slaves into the Federal Territories, and to hold them there as property. When I say, the decision was made in a sort of way, I mean it was made in a divided court, by a bare majority of the judges, and they not quite agreeing with one another in the reasons for making it; that it is so made as that its avowed supporters disagree with one another about its meaning, and that it was mainly based upon a mistaken statement of fact—the statement in the opinion that "the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution."
An inspection of the Constitution will show that the right of property in a slave is not "distinctly and expressly affirmed" in it. Bear in mind, the judges do not pledge their judicial opinion that such right is impliedly affirmed in the Constitution; but they pledge their veracity that it is "distinctly and expressly" affirmed there—"distinctly," that is, not mingled with anything else; "expressly," that is, in words meaning just that, without the aid of any inference, and susceptible of no other meaning.
If they had only pledged their judicial opinion that such right is affirmed in the instrument by implication, it would be open to others to show that neither the word "slave" nor "slavery" is to be found in the Constitution, nor the word "property" even, in any connection with language alluding to the things slave or slavery; and that wherever in that instrument the slave is alluded to, he is called a "person"; and wherever his master's legal right in relation to him is alluded to, it is spoken of as "service or labor which may be due," as a debt payable in service or labor. Also, it would be open to show, by contemporaneous history, that this mode of alluding to slaves and slavery, instead of speaking of them, was employed on purpose to exclude from the Constitution the idea that there could be property in man.
To show all this, is easy and certain.
When this obvious mistake of the judges shall be brought to their notice, is it not reasonable to expect that they will withdraw the mistaken statement, and reconsider the conclusion based upon it?
And then it is to be remembered that "our fathers; who framed the Government under which we live",—the men who made the Constitution—decided this same constitutional question in our favor, long ago; decided it without division among themselves, when making the decision, without division among themselves about the meaning of it after it was made, and, so far as any evidence is left, without basing it upon any mistaken statement of facts.
Under all these circumstances, do you really feel yourselves justified to break up this Government unless such a court decision as yours is shall be at once submitted to as a conclusive and final rule of political action? But you will not abide the election of a Republican President! In that supposed event, you say, you will destroy the Union; and then, you say, the great crime of having destroyed it will be upon us! That is cool. A highwayman holds a pistol to my ear, and mutters through his teeth, "stand and deliver, or I shall kill you, and then you'll be a murderer!"
To be sure, what the robber demanded of me-my money was my own, and I had a clear right to keep it; but it was no more my own than my vote is my own; and the threat of death to me, to extort my money, and the threat of destruction to the Union, to extort my vote, can scarcely be distinguished in principle.
A few words now to Republicans: It is exceedingly desirable that all parts of this great confederacy shall be at peace and in harmony one with another. Let us Republicans do our part to have it so. Even though much provoked, let us do nothing through passion and ill temper. Even though the Southern people will not so much as listen to us, let us calmly consider their demands, and yield to them if, in our deliberate view of our duty, we possibly can. Judging by all they say and do, and by the subject and nature of their controversy with us, let us determine, if we can, what will satisfy them.
Will they be satisfied if the Territories be unconditionally surrendered to them? We know they will not. In all their present complaints against us, the Territories are scarcely mentioned. Invasions and insurrections are the rage now. Will it satisfy them if, in the future, we have nothing to do with invasions and, insurrections? We know it will not. We so know because we know we never had anything to do with invasions and insurrections; and yet this total abstaining does not exempt us from the charge and the denunciation.
The question recurs, what will satisfy them? Simply this: We must not only let them alone, but we must, somehow, convince them that we do let them alone. This, we know by experience, is no easy task. We have been so trying to convince them from the very beginning of our organization, but with no success. In all our platforms and speeches we have constantly protested our purpose to let them alone; but this has had no tendency to convince them. Alike unavailing to convince them is the fact that they have never detected a man of us in any attempt to disturb them.
These natural and apparently adequate means all failing, what will convince them? This, and this only: cease to call slavery wrong, and join them in calling it right. And this must be done thoroughly—done in acts as well as in words. Silence will not be tolerated—we must place ourselves avowedly with them. Senator Douglas's new sedition law must be enacted and enforced, suppressing all declarations that slavery is wrong, whether made in politics, in presses, in pulpits; or in private. We must arrest and return their fugitive slaves with greedy pleasure. We must pull down our free State constitutions. The whole atmosphere must be disinfected from all taint of opposition to slavery, before they will cease to believe that all their troubles proceed from us.
I am quite aware they do not state their case precisely in this way. Most of them would probably say to us, "Let us alone, do nothing to us, and say what you please about slavery." But we do let them alone have never disturbed them—so that after all it is what we say which dissatisfies them. They will continue to accuse us of doing, until we cease saying.
I am also aware they have not as yet, in terms, demanded the overthrow of our free State constitutions. Yet those constitutions declare the wrong of slavery, with more solemn emphasis than do all other sayings against it; and when all these other sayings shall have been silenced, the overthrow of these constitutions will be demanded, and nothing be left to resist the demand. It is nothing to the contrary, that they do not demand the whole of this just now. Demanding what they do, and for the reason they do, they can voluntarily stop nowhere short of this consummation. Holding, as they do, that slavery is morally right, and socially elevating, they cannot cease to demand a full national recognition of it, as a legal right and a social blessing.
Nor can we justifiably withhold this on any ground save our conviction that slavery is wrong. If slavery is right, all words, acts, laws, and constitutions against it are themselves wrong, and should be silenced and swept away. If it is right, we cannot justly object to its nationality its universality; if it is wrong, they cannot justly insist upon its extension—its enlargement. All they ask we could readily grant if we thought slavery right; all we ask they could as readily grant, if they thought it wrong. Their thinking it right and our thinking it wrong is the precise fact upon which depends the whole controversy. Thinking it right, as they do, they are not to blame for desiring its full recognition, as being right; but thinking it wrong, as we do, can we yield to them? Can we cast our votes with their view, and against our own? In view of our moral, social, and political responsibilities, can we do this? Wrong as we think slavery is, we can yet afford to let it alone where it is, because that much is due to the necessity arising from its actual presence in the nation; but can we, while our votes will prevent it, allow it to spread into the national Territories, and to overrun us here in these free States? If our sense of duty forbids this, then let us stand by our duty, fearlessly and effectively. Let us be diverted by none of those sophistical contrivances wherewith we are so industriously plied and belabored-contrivances such as groping for some middle ground between the right and the wrong, vain as the search for a man who should be neither a living man nor a dead man-such as a policy of "don't care" on a question about which all true men do care—such as Union appeals beseeching true Union men to yield to Disunionists, reversing the divine rule, and calling, not the sinners, but the righteous to repentance—such as invocations to Washington, imploring men to unsay what Washington said, and undo what Washington did.
Neither let us be slandered from our duty by false accusations against us, nor frightened from it by menaces of destruction to the Government nor of dungeons to ourselves. LET US HAVE FAITH THAT RIGHT MAKES MIGHT, AND IN THAT FAITH LET US, TO THE END, DARE TO DO OUR DUTY AS WE UNDERSTAND IT.
MR. PRESIDENT, AND FELLOW-CITIZENS OF NEW HAVEN:—If the Republican party of this nation shall ever have the national House entrusted to its keeping, it will be the duty of that party to attend to all the affairs of national housekeeping. Whatever matters of importance may come up, whatever difficulties may arise in its way of administration of the Government, that party will then have to attend to. It will then be compelled to attend to other questions, besides this question which now assumes an overwhelming importance—the question of slavery. It is true that in the organization of the Republican party this question of slavery was more important than any other: indeed, so much more important has it become that no more national question can even get a hearing just at present. The old question of tariff—a matter that will remain one of the chief affairs of national house-keeping to all time; the question of the management of financial affairs; the question of the disposition of the public domain how shall it be managed for the purpose of getting it well settled, and of making there the homes of a free and happy people? these will remain open and require attention for a great while yet, and these questions will have to be attended to by whatever party has the control of the Government. Yet, just now, they cannot even obtain a hearing, and I do not propose to detain you upon these topics or what sort of hearing they should have when opportunity shall come.
For, whether we will or not, the question of slavery is the question, the all-absorbing topic of the day. It is true that all of us—and by that I mean, not the Republican party alone, but the whole American people, here and elsewhere—all of us wish this question settled, wish it out of the way. It stands in the way, and prevents the adjustment, and the giving of necessary attention to other questions of national house-keeping. The people of the whole nation agree that this question ought to be settled, and yet it is not settled. And the reason is that they are not yet agreed how it shall be settled. All wish it done, but some wish one way and some another, and some a third, or fourth, or fifth; different bodies are pulling in different directions, and none of them, having a decided majority, are able to accomplish the common object.
In the beginning of the year 1854, a new policy was inaugurated with the avowed object and confident promise that it would entirely and forever put an end to the slavery agitation. It was again and again declared that under this policy, when once successfully established, the country would be forever rid of this whole question. Yet under the operation of that policy this agitation has not only not ceased, but it has been constantly augmented. And this too, although, from the day of its introduction, its friends, who promised that it would wholly end all agitation, constantly insisted, down to the time that the Lecompton Bill was introduced, that it was working admirably, and that its inevitable tendency was to remove the question forever from the politics of the country. Can you call to mind any Democratic speech, made after the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, down to the time of the Lecompton Bill, in which it was not predicted that the slavery agitation was just at an end, that "the abolition excitement was played out," "the Kansas question was dead," "they have made the most they can out of this question and it is now forever settled"? But since the Lecompton Bill no Democrat, within my experience, has ever pretended that he could see the end. That cry has been dropped. They themselves do not pretend, now, that the agitation of this subject has come to an end yet.
The truth is that this question is one of national importance, and we cannot help dealing with it; we must do something about it, whether we will or not. We cannot avoid it; the subject is one we cannot avoid considering; we can no more avoid it than a man can live without eating. It is upon us; it attaches to the body politic as much and closely as the natural wants attach to our natural bodies. Now I think it important that this matter should be taken up in earnest, and really settled: And one way to bring about a true settlement of the question is to understand its true magnitude.
There have been many efforts made to settle it. Again and again it has been fondly hoped that it was settled; but every time it breaks out afresh, and more violently than ever. It was settled, our fathers hoped, by the Missouri Compromise, but it did not stay settled. Then the compromises of 1850 were declared to be a full and final settlement of the question. The two great parties, each in national convention, adopted resolutions declaring that the settlement made by the Compromise of 1850 was a finality that it would last forever. Yet how long before it was unsettled again? It broke out again in 1854, and blazed higher and raged more furiously than ever before, and the agitation has not rested since.
These repeated settlements must have some faults about them. There must be some inadequacy in their very nature to the purpose to which they were designed. We can only speculate as to where that fault, that inadequacy, is, but we may perhaps profit by past experiences.
I think that one of the causes of these repeated failures is that our best and greatest men have greatly underestimated the size of this question. They have constantly brought forward small cures for great sores—plasters too small to cover the wound. That is one reason that all settlements have proved temporary—so evanescent.
Look at the magnitude of this subject: One sixth of our population, in round numbers—not quite one sixth, and yet more than a seventh,—about one sixth of the whole population of the United States are slaves. The owners of these slaves consider them property. The effect upon the minds of the owners is that of property, and nothing else it induces them to insist upon all that will favorably affect its value as property, to demand laws and institutions and a public policy that shall increase and secure its value, and make it durable, lasting, and universal. The effect on the minds of the owners is to persuade them that there is no wrong in it. The slaveholder does not like to be considered a mean fellow for holding that species of property, and hence, he has to struggle within himself and sets about arguing himself into the belief that slavery is right. The property influences his mind. The dissenting minister who argued some theological point with one of the established church was always met with the reply, "I can't see it so." He opened a Bible and pointed him a passage, but the orthodox minister replied, "I can't see it so." Then he showed him a single word—"Can you see that?" "Yes, I see it," was the reply. The dissenter laid a guinea over the word and asked, "Do you see it now?" So here. Whether the owners of this species of property do really see it as it is, it is not for me to say, but if they do, they see it as it is through two thousand millions of dollars, and that is a pretty thick coating. Certain it is that they do not see it as we see it. Certain it is that this two thousand millions of dollars, invested in this species of property, all so concentrated that the mind can grasp it at once—this immense pecuniary interest—has its influence upon their minds.
But here in Connecticut and at the North slavery does not exist, and we see it through no such medium.
To us it appears natural to think that slaves are human beings; men, not property; that some of the things, at least, stated about men in the Declaration of Independence apply to them as well as to us. I say we think, most of us, that this charter of freedom applies to the slaves as well as to ourselves; that the class of arguments put forward to batter down that idea are also calculated to break down the very idea of a free government, even for white men, and to undermine the very foundations of free society. We think slavery a great moral wrong, and, while we do not claim the right to touch it where it exists, we wish to treat it as a wrong in the Territories, where our votes will reach it. We think that a respect for ourselves, a regard for future generations and for the God that made us, require that we put down this wrong where our votes will properly reach it. We think that species of labor an injury to free white men—in short, we think slavery a great moral, social, and political evil, tolerable only because, and so far as, its actual existence makes it necessary to tolerate it, and that beyond that it ought to be treated as a wrong.
Now these two ideas, the property idea that slavery is right, and the idea that it is wrong, come into collision, and do actually produce that irrepressible conflict which Mr. Seward has been so roundly abused for mentioning. The two ideas conflict, and must conflict.
Again, in its political aspect, does anything in any way endanger the perpetuity of this Union but that single thing, slavery? Many of our adversaries are anxious to claim that they are specially devoted to the Union, and take pains to charge upon us hostility to the Union. Now we claim that we are the only true Union men, and we put to them this one proposition: Whatever endangers this Union, save and except slavery? Did any other thing ever cause a moment's fear? All men must agree that this thing alone has ever endangered the perpetuity of the Union. But if it was threatened by any other influence, would not all men say that the best thing that could be done, if we could not or ought not to destroy it, would be at least to keep it from growing any larger? Can any man believe, that the way to save the Union is to extend and increase the only thing that threatens the Union, and to suffer it to grow bigger and bigger?
Whenever this question shall be settled, it must be settled on some philosophical basis. No policy that does not rest upon some philosophical opinion can be permanently maintained. And hence there are but two policies in regard to slavery that can be at all maintained. The first, based on the property view that slavery is right, conforms to that idea throughout, and demands that we shall do everything for it that we ought to do if it were right. We must sweep away all opposition, for opposition to the right is wrong; we must agree that slavery is right, and we must adopt the idea that property has persuaded the owner to believe that slavery is morally right and socially elevating. This gives a philosophical basis for a permanent policy of encouragement.
The other policy is one that squares with the idea that slavery is wrong, and it consists in doing everything that we ought to do if it is wrong. Now, I don't wish to be misunderstood, nor to leave a gap down to be misrepresented, even. I don't mean that we ought to attack it where it exists. To me it seems that if we were to form a government anew, in view of the actual presence of slavery we should find it necessary to frame just such a government as our fathers did—giving to the slaveholder the entire control where the system was established, while we possessed the power to restrain it from going outside those limits. From the necessities of the case we should be compelled to form just such a government as our blessed fathers gave us; and, surely, if they have so made it, that adds another reason why we should let slavery alone where it exists.
If I saw a venomous snake crawling in the road, any man would say I might seize the nearest stick and kill it; but if I found that snake in bed with my children, that would be another question. I might hurt the children more than the snake, and it might bite them. Much more if I found it in bed with my neighbor's children, and I had bound myself by a solemn compact not to meddle with his children under any circumstances, it would become me to let that particular mode of getting rid of the gentleman alone. But if there was a bed newly made up, to which the children were to be taken, and it was proposed to take a batch of young snakes and put them there with them, I take it no man would say there was any question how I ought to decide!
That is just the case. The new Territories are the newly made bed to which our children are to go, and it lies with the nation to say whether they shall have snakes mixed up with them or not. It does not seem as if there could be much hesitation what our policy should be!
Now I have spoken of a policy based on the idea that slavery is wrong, and a policy based on the idea that it is right. But an effort has been made for a policy that shall treat it as neither right nor wrong. It is based upon utter indifference. Its leading advocate [Douglas] has said, "I don't care whether it be voted up or down." "It is merely a matter of dollars and cents." "The Almighty has drawn a line across this continent, on one side of which all soil must forever be cultivated by slave labor, and on the other by free." "When the struggle is between the white man and the negro, I am for the white man; when it is between the negro and the crocodile, I am for the negro." Its central idea is indifference. It holds that it makes no more difference to us whether the Territories become free or slave States than whether my neighbor stocks his farm with horned cattle or puts in tobacco. All recognize this policy, the plausible sugar-coated name of which is "popular sovereignty."
This policy chiefly stands in the way of a permanent settlement of the question. I believe there is no danger of its becoming the permanent policy of the country, for it is based on a public indifference. There is nobody that "don't care." All the people do care one way or the other! I do not charge that its author, when he says he "don't care," states his individual opinion; he only expresses his policy for the government. I understand that he has never said as an individual whether he thought slavery right or wrong—and he is the only man in the nation that has not! Now such a policy may have a temporary run; it may spring up as necessary to the political prospects of some gentleman; but it is utterly baseless: the people are not indifferent, and it can therefore have no durability or permanence.
But suppose it could: Then it could be maintained only by a public opinion that shall say, "We don't care." There must be a change in public opinion; the public mind must be so far debauched as to square with this policy of caring not at all. The people must come to consider this as "merely a question of dollars and cents," and to believe that in some places the Almighty has made slavery necessarily eternal. This policy can be brought to prevail if the people can be brought round to say honestly, "We don't care"; if not, it can never be maintained. It is for you to say whether that can be done.
You are ready to say it cannot, but be not too fast! Remember what a long stride has been taken since the repeal of the Missouri Compromise! Do you know of any Democrat, of either branch of the party—do you know one who declares that he believes that the Declaration of Independence has any application to the negro? Judge Taney declares that it has not, and Judge Douglas even vilifies me personally and scolds me roundly for saying that the Declaration applies to all men, and that negroes are men. Is there a Democrat here who does not deny that the Declaration applies to the negro? Do any of you know of one? Well, I have tried before perhaps fifty audiences, some larger and some smaller than this, to find one such Democrat, and never yet have I found one who said I did not place him right in that. I must assume that Democrats hold that, and now, not one of these Democrats can show that he said that five years ago! I venture to defy the whole party to produce one man that ever uttered the belief that the Declaration did not apply to negroes, before the repeal of the Missouri Compromise! Four or five years ago we all thought negroes were men, and that when "all men" were named, negroes were included. But the whole Democratic party has deliberately taken negroes from the class of men and put them in the class of brutes. Turn it as you will it is simply the truth! Don't be too hasty, then, in saying that the people cannot be brought to this new doctrine, but note that long stride. One more as long completes the journey from where negroes are estimated as men to where they are estimated as mere brutes—as rightful property!
That saying "In the struggle between white men and the negro," etc., which I know came from the same source as this policy—that saying marks another step. There is a falsehood wrapped up in that statement. "In the struggle between the white man and the negro" assumes that there is a struggle, in which either the white man must enslave the negro or the negro must enslave the white. There is no such struggle! It is merely the ingenious falsehood to degrade and brutalize the negro. Let each let the other alone, and there is no struggle about it. If it was like two wrecked seamen on a narrow plank, when each must push the other off or drown himself, I would push the negro off or a white man either, but it is not; the plank is large enough for both. This good earth is plenty broad enough for white man and negro both, and there is no need of either pushing the other off.
So that saying, "In the struggle between the negro and the crocodile," etc., is made up from the idea that down where the crocodile inhabits, a white man can't labor; it must be nothing else but crocodile or negro; if the negro does not the crocodile must possess the earth; in that case he declares for the negro. The meaning of the whole is just this: As a white man is to a negro, so is a negro to a crocodile; and as the negro may rightfully treat the crocodile, so may the white man rightfully treat the negro. This very dear phrase coined by its author, and so dear that he deliberately repeats it in many speeches, has a tendency to still further brutalize the negro, and to bring public opinion to the point of utter indifference whether men so brutalized are enslaved or not. When that time shall come, if ever, I think that policy to which I refer may prevail. But I hope the good freemen of this country will never allow it to come, and until then the policy can never be maintained.
Now consider the effect of this policy. We in the States are not to care whether freedom or slavery gets the better, but the people in the Territories may care. They are to decide, and they may think what they please; it is a matter of dollars and cents! But are not the people of the Territories detailed from the States? If this feeling of indifference this absence of moral sense about the question prevails in the States, will it not be carried into the Territories? Will not every man say, "I don't care, it is nothing to me"? If any one comes that wants slavery, must they not say, "I don't care whether freedom or slavery be voted up or voted down"? It results at last in nationalizing the institution of slavery. Even if fairly carried out, that policy is just as certain to nationalize slavery as the doctrine of Jeff Davis himself. These are only two roads to the same goal, and "popular sovereignty" is just as sure and almost as short as the other.
What we want, and all we want, is to have with us the men who think slavery wrong. But those who say they hate slavery, and are opposed to it, but yet act with the Democratic party—where are they? Let us apply a few tests. You say that you think slavery is wrong, but you denounce all attempts to restrain it. Is there anything else that you think wrong that you are not willing to deal with as wrong? Why are you so careful, so tender, of this one wrong and no other? You will not let us do a single thing as if it was wrong; there is no place where you will even allow it to be called wrong! We must not call it wrong in the free States, because it is not there, and we must not call it wrong in the slave States, because it is there; we must not call it wrong in politics because that is bringing morality into politics, and we must not call it wrong in the pulpit because that is bringing politics into religion; we must not bring it into the Tract Society or the other societies, because those are such unsuitable places—and there is no single place, according to you, where this wrong thing can properly be called wrong!
Perhaps you will plead that if the people of the slave States should themselves set on foot an effort for emancipation, you would wish them success, and bid them God-speed. Let us test that: In 1858 the emancipation party of Missouri, with Frank Blair at their head, tried to get up a movement for that purpose, and having started a party contested the State. Blair was beaten, apparently if not truly, and when the news came to Connecticut, you, who knew that Frank Blair was taking hold of this thing by the right end, and doing the only thing that you say can properly be done to remove this wrong—did you bow your heads in sorrow because of that defeat? Do you, any of you, know one single Democrat that showed sorrow over that result? Not one! On the contrary every man threw up his hat, and hallooed at the top of his lungs, "Hooray for Democracy!"
Now, gentlemen, the Republicans desire to place this great question of slavery on the very basis on which our fathers placed it, and no other. It is easy to demonstrate that "our fathers, who framed this Government under which we live," looked on slavery as wrong, and so framed it and everything about it as to square with the idea that it was wrong, so far as the necessities arising from its existence permitted. In forming the Constitution they found the slave trade existing, capital invested in it, fields depending upon it for labor, and the whole system resting upon the importation of slave labor. They therefore did not prohibit the slave trade at once, but they gave the power to prohibit it after twenty years. Why was this? What other foreign trade did they treat in that way? Would they have done this if they had not thought slavery wrong?
Another thing was done by some of the same men who framed the Constitution, and afterwards adopted as their own the act by the first Congress held under that Constitution, of which many of the framers were members, that prohibited the spread of slavery into Territories. Thus the same men, the framers of the Constitution, cut off the supply and prohibited the spread of slavery, and both acts show conclusively that they considered that the thing was wrong.
If additional proof is wanted it can be found in the phraseology of the Constitution. When men are framing a supreme law and chart of government, to secure blessings and prosperity to untold generations yet to come, they use language as short and direct and plain as can be found, to express their meaning In all matters but this of slavery the framers of the Constitution used the very clearest, shortest, and most direct language. But the Constitution alludes to slavery three times without mentioning it once The language used becomes ambiguous, roundabout, and mystical. They speak of the "immigration of persons," and mean the importation of slaves, but do not say so. In establishing a basis of representation they say "all other persons," when they mean to say slaves—why did they not use the shortest phrase? In providing for the return of fugitives they say "persons held to service or labor." If they had said slaves it would have been plainer, and less liable to misconstruction. Why did n't they do it? We cannot doubt that it was done on purpose. Only one reason is possible, and that is supplied us by one of the framers of the Constitution—and it is not possible for man to conceive of any other—they expected and desired that the system would come to an end, and meant that when it did, the Constitution should not show that there ever had been a slave in this good free country of ours.
I will dwell on that no longer. I see the signs of approaching triumph of the Republicans in the bearing of their political adversaries. A great deal of their war with us nowadays is mere bushwhacking. At the battle of Waterloo, when Napoleon's cavalry had charged again and again upon the unbroken squares of British infantry, at last they were giving up the attempt, and going off in disorder, when some of the officers in mere vexation and complete despair fired their pistols at those solid squares. The Democrats are in that sort of extreme desperation; it is nothing else. I will take up a few of these arguments.
There is "the irrepressible conflict." How they rail at Seward for that saying! They repeat it constantly; and, although the proof has been thrust under their noses again and again that almost every good man since the formation of our Government has uttered that same sentiment, from General Washington, who "trusted that we should yet have a confederacy of free States," with Jefferson, Jay, Monroe, down to the latest days, yet they refuse to notice that at all, and persist in railing at Seward for saying it. Even Roger A. Pryor, editor of the Richmond Enquirer, uttered the same sentiment in almost the same language, and yet so little offence did it give the Democrats that he was sent for to Washington to edit the States—the Douglas organ there—while Douglas goes into hydrophobia and spasms of rage because Seward dared to repeat it. This is what I call bushwhacking, a sort of argument that they must know any child can see through.
Another is John Brown: "You stir up insurrections, you invade the South; John Brown! Harper's Ferry!" Why, John Brown was not a Republican! You have never implicated a single Republican in that Harper's Ferry enterprise. We tell you that if any member of the Republican party is guilty in that matter, you know it or you do not know it. If you do know it, you are inexcusable not to designate the man and prove the fact. If you do not know it, you are inexcusable to assert it, and especially to persist in the assertion after you have tried and failed to make the proof. You need not be told that persisting in a charge which one does not know to be true is simply malicious slander. Some of you admit that no Republican designedly aided or encouraged the Harper's Ferry affair, but still insist that our doctrines and declarations necessarily lead to such results. We do not believe it. We know we hold to no doctrines, and make no declarations, which were not held to and made by our fathers who framed the Government 'under which we live, and we cannot see how declarations that were patriotic when they made them are villainous when we make them. You never dealt fairly by us in relation to that affair—and I will say frankly that I know of nothing in your character that should lead us to suppose that you would. You had just been soundly thrashed in elections in several States, and others were soon to come. You rejoiced at the occasion, and only were troubled that there were not three times as many killed in the affair. You were in evident glee; there was no sorrow for the killed nor for the peace of Virginia disturbed; you were rejoicing that by charging Republicans with this thing you might get an advantage of us in New York, and the other States. You pulled that string as tightly as you could, but your very generous and worthy expectations were not quite fulfilled. Each Republican knew that the charge was a slander as to himself at least, and was not inclined by it to cast his vote in your favor. It was mere bushwhacking, because you had nothing else to do. You are still on that track, and I say, go on! If you think you can slander a woman into loving you or a man into voting for you, try it till you are satisfied!
Another specimen of this bushwhacking, that "shoe strike." Now be it understood that I do not pretend to know all about the matter. I am merely going to speculate a little about some of its phases. And at the outset, I am glad to see that a system of labor prevails in New England under which laborers can strike when they want to, where they are not obliged to work under all circumstances, and are not tied down and obliged to labor whether you pay them or not! I like the system which lets a man quit when he wants to, and wish it might prevail everywhere. One of the reasons why I am opposed to slavery is just here. What is the true condition of the laborer? I take it that it is best for all to leave each man free to acquire property as fast as he can. Some will get wealthy. I don't believe in a law to prevent a man from getting rich; it would do more harm than good. So, while we do not propose any war upon capital, we do wish to allow the humblest man an equal chance to get rich with everybody else. When one starts poor, as most do in the race of life, free society is such that he knows he can better his condition; he knows that there is no fixed condition of labor for his whole life. I am not ashamed to confess that twenty-five years ago I was a hired laborer, mauling rails, at work on a flatboat—just what might happen to any poor man's son! I want every man to have a chance—and I believe a Black man is entitled to it—in which he can better his condition; when he may look forward and hope to be a hired laborer this year and the next, work for himself afterward, and finally to hire men to work for him! That is the system. Up here in New England, you have a soil that scarcely sprouts black-eyed beans, and yet where will you find wealthy men so wealthy, and poverty so rarely in extremity? There is not another such place on earth! I desire that if you get too thick here, and find it hard to better your condition on this soil, you may have a chance to strike and go somewhere else, where you may not be degraded, nor have your families corrupted, by forced rivalry with negro slaves. I want you to have a clean bed and no snakes in it! Then you can better your condition, and so it may go on and on in one endless round so long as man exists on the face of the earth!
Now, to come back to this shoe strike,—if, as the senator from Illinois asserts, this is caused by withdrawal of Southern votes, consider briefly how you will meet the difficulty. You have done nothing, and have protested that you have done nothing, to injure the South. And yet, to get back the shoe trade, you must leave off doing something which you are now doing. What is it? You must stop thinking slavery wrong! Let your institutions be wholly changed; let your State constitutions be subverted; glorify slavery, and so you will get back the shoe trade—for what? You have brought owned labor with it, to compete with your own labor, to underwork you, and to degrade you! Are you ready to get back the trade on those terms?
But the statement is not correct. You have not lost that trade; orders were never better than now! Senator Mason, a Democrat, comes into the Senate in homespun, a proof that the dissolution of the Union has actually begun! but orders are the same. Your factories have not struck work, neither those where they make anything for coats, nor for pants nor for shirts, nor for ladies' dresses. Mr. Mason has not reached the manufacturers who ought to have made him a coat and pants! To make his proof good for anything he should have come into the Senate barefoot!
Another bushwhacking contrivance; simply that, nothing else! I find a good many people who are very much concerned about the loss of Southern trade. Now either these people are sincere or they are not. I will speculate a little about that. If they are sincere, and are moved by any real danger of the loss of Southern trade, they will simply get their names on the white list, and then, instead of persuading Republicans to do likewise, they will be glad to keep you away! Don't you see that they cut off competition? They would not be whispering around to Republicans to come in and share the profits with them. But if they are not sincere, and are merely trying to fool Republicans out of their votes, they will grow very anxious about your pecuniary prospects; they are afraid you are going to get broken up and ruined; they do not care about Democratic votes, oh, no, no, no! You must judge which class those belong to whom you meet: I leave it to you to determine from the facts.
Let us notice some more of the stale charges against Republicans. You say we are sectional. We deny it. That makes an issue; and the burden of proof is upon you. You produce your proof; and what is it? Why, that our party has no existence in your section—gets no votes in your section. The fact is substantially true; but does it prove the issue? If it does, then in case we should, without change of principle, begin to get votes in your section, we should thereby cease to be sectional. You cannot escape this conclusion; and yet, are you willing to abide by it? If you are, you will probably soon find that we have ceased to be sectional, for we shall get votes in your section this very year. The fact that we get no votes in your section is a fact of your making and not of ours. And if there be fault in that fact, that fault is primarily yours, and remains so until you show that we repel you by some wrong principle or practice. If we ours; but this brings you to where you ought to have started—to a discussion of the right or wrong of our principle. If our principle, put in practice, would wrong your section for the benefit of ours, or for any other object, then our principle, and we with it, are sectional, and are justly opposed and denounced as such. Meet us, then, on the question of whether our principle put in practice would wrong your section; and so meet it as if it were possible that something may be said on our side. Do you accept the challenge? No? Then you really believe that the principle which our fathers who framed the Government under which we live thought so clearly right as to adopt it, and indorse it again and again, upon their official oaths, is in fact so clearly wrong as to demand our condemnation without a moment's consideration. Some of you delight to flaunt in our faces the warning against sectional parties given by Washington in his Farewell Address. Less than eight years before Washington gave that warning, he had, as President of the United States, approved and signed an act of Congress enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the Northwestern Territory, which act embodied the policy of government upon that subject, up to and at the very moment he penned that warning; and about one year after he penned it he wrote La Fayette that he considered that prohibition a wise measure, expressing in the same connection his hope that we should sometime have a confederacy of free States.
Bearing this in mind, and seeing that sectionalism has since arisen upon this same subject, is that warning a weapon in your hands against us, or in our hands against you? Could Washington himself speak, would he cast the blame of that sectionalism upon us, who sustain his policy, or upon you, who repudiate it? We respect that warning of Washington, and we commend it to you, together with his example pointing to the right application of it.
But you say you are conservative—eminently conservative—while we are revolutionary, destructive, or something of the sort. What is conservatism? Is it not adherence to the old and tried, against the new and untried? We stick to, contend for, the identical old policy on the point in controversy which was adopted by our fathers who framed the Government under which we live; while you with one accord reject and scout and spit upon that old policy, and insist upon substituting something new.
True, you disagree among yourselves as to what that substitute shall be. You have considerable variety of new propositions and plans, but you are unanimous in rejecting and denouncing the old policy of the fathers. Some of you are for reviving the foreign slave-trade; some for a congressional slave code for the Territories; some for Congress forbidding the Territories to prohibit slavery within their limits; some for maintaining slavery in the Territories through the judiciary; some for the "gur-reat pur-rinciple" that if one man would enslave another, no third man should object—fantastically called "popular sovereignty." But never a man among you in favor of prohibition of slavery in Federal Territories, according to the practice of our fathers who framed the Government under which we live. Not one of all your various plans can show a precedent or an advocate in the century within which our Government originated. And yet you draw yourselves up and say, "We are eminently conservative."
It is exceedingly desirable that all parts of this great confederacy shall be at peace, and in harmony one with another. Let us Republicans do our part to have it so. Even though much provoked, let us do nothing through passion and ill-temper. Even though the Southern people will not so much as listen to us, let us calmly consider their demands, and yield to them if, in our deliberate view of our duty, we possibly can. Judging by all they say and do, and by the subject and nature of their controversy with us, let us determine, if we can, what will satisfy them.
Will they be satisfied if the Territories be unconditionally surrendered to them? We know they will not. In all their present complaints against us, the Territories are scarcely mentioned. Invasions and insurrections are the rage now. Will it satisfy them, in the future, if we have nothing to do with invasions and insurrections? We know it will not. We so know because we know we never had anything to do with invasions and insurrections; and yet this total abstaining does not exempt us from the charge and the denunciation.
The question recurs, what will satisfy them? Simply this: we must not only let them alone, but we must, somehow, convince them that we do let them alone. This, we know by experience, is no easy task. We have been so trying to convince them, from the very beginning of our organization, but with no success. In all our platforms and speeches, we have constantly protested our purpose to let them alone; but this had no tendency to convince them. Alike unavailing to convince them is the fact that they have never detected a man of us in any attempt to disturb them.
These natural and apparently adequate means all failing, what will convince them? This, and this only: cease to call slavery wrong, and join them in calling it right. And this must be done thoroughly—done in acts as well as in words. Silence will not be tolerated—we must place ourselves avowedly with them. Douglas's new sedition law must be enacted and enforced, suppressing all declarations that slavery is wrong, whether made in politics, in presses, in pulpits, or in private. We must arrest and return their fugitive slaves with greedy pleasure. We must pull down our free State constitutions. The whole atmosphere must be disinfected of all taint of opposition to slavery, before they will cease to believe that all their troubles proceed from us. So long as we call slavery wrong, whenever a slave runs away they will overlook the obvious fact that he ran away because he was oppressed, and declare he was stolen off. Whenever a master cuts his slaves with a lash, and they cry out under it, he will overlook the obvious fact that the negroes cry out because they are hurt, and insist that they were put up to it by some rascally abolitionist.
I am quite aware that they do not state their case precisely in this way. Most of them would probably say to us, "Let us alone, do nothing to us, and say what you please about slavery." But we do let them alone—have never disturbed them—so that, after all, it is what we say which dissatisfies them. They will continue to accuse us of doing, until we cease saying.
I am also aware that they have not as yet in terms demanded the overthrow of our free-State constitutions. Yet those constitutions declare the wrong of slavery with more solemn emphasis than do all other sayings against it; and when all these other sayings shall have been silenced, the overthrow of these constitutions will be demanded. It is nothing to the contrary that they do not demand the whole of this just now. Demanding what they do, and for the reason they do, they can voluntarily stop nowhere short of this consummation. Holding as they do that slavery is morally right, and socially elevating, they cannot cease to demand a full national recognition of it, as a legal right, and a social blessing.
Nor can we justifiably withhold this on any ground save our conviction that slavery is wrong. If slavery is right, all words, acts, laws, and constitutions against it are themselves wrong and should be silenced and swept away. If it is right, we cannot justly object to its nationality—its universality: if it is wrong, they cannot justly insist upon its extension—its enlargement. All they ask, we could readily grant, if we thought slavery right; all we ask, they could as readily grant, if they thought it wrong. Their thinking it right and our thinking it wrong is the precise fact on which depends the whole controversy. Thinking it right as they do, they are not to blame for desiring its full recognition, as being right; but, thinking it wrong, as we do, can we yield to them? Can we cast our votes with their view, and against our own? In view of our moral, social, and political responsibilities, can we do this?
Wrong as we think slavery is, we can yet afford to let it alone where it is because that much is due to the necessity arising from its actual presence in the nation; but can we, while our votes will prevent it, allow it to spread into the national Territories, and to overrun us here in these free States?
If our sense of duty forbids this, then let us stand by our duty, fearlessly and effectively. Let us be diverted by none of those sophistical contrivances wherewith we are so industriously plied and belabored—contrivances such as groping for some middle ground between the right and the wrong, vain as the search for a man who would be neither a living man nor a dead man—such as a policy of "don't care" on a question about which all free men do care—such as Union appeals beseeching true Union men to yield to Disunionists, reversing the divine rule, and caning, not the sinners, but the righteous to repentance—such as invocations of Washington, imploring men to unsay what Washington did.
Neither let us be slandered from our duty by false accusations against us, nor frightened from it by menaces of destruction to the Government, nor of dungeons to ourselves. Let us have faith that right makes might; and in that faith, let us, to the end, dare to do our duty as we understand it.
[As Mr. Lincoln concluded his address, there was witnessed the wildest scene of enthusiasm and excitement that has been in New Haven for years. The Palladium editorially says: "We give up most of our space to-day to a very full report of the eloquent speech of the HON. Abraham Lincoln, of Illinois, delivered last night at Union Hall."]
As to your kind wishes for myself, allow me to say I cannot enter the ring on the money basis—first, because in the main it is wrong; and secondly, I have not and cannot get the money.
I say, in the main, the use of money is wrong; but for certain objects in a political contest, the use of some is both right and indispensable. With me, as with yourself, the long struggle has been one of great pecuniary loss.
I now distinctly say this—if you shall be appointed a delegate to Chicago, I will furnish one hundred dollars to bear the expenses of the trip.
Your friend as ever,
A. LINCOLN.
[Extract from a letter to a Kansas delegate.]
JAMES W. SOMERS, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Reaching home three days ago, I found your letter of February 26th. Considering your difficulty of hearing, I think you had better settle in Chicago, if, as you say, a good man already in fair practice there will take you into partnership. If you had not that difficulty, I still should think it an even balance whether you would not better remain in Chicago, with such a chance for copartnership.
If I went west, I think I would go to Kansas, to Leavenworth or Atchison. Both of them are and will continue to be fine growing places.
I believe I have said all I can, and I have said it with the deepest interest for your welfare.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, April 6, 1860
C. F. MCNEIL, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Reaching home yesterday, I found yours of the 23d March, inclosing a slip from The Middleport Press. It is not true that I ever charged anything for a political speech in my life; but this much is true: Last October I was requested by letter to deliver some sort of speech in Mr. Beecher's church, in Brooklyn—two hundred dollars being offered in the first letter. I wrote that I could do it in February, provided they would take a political speech if I could find time to get up no other. They agreed; and subsequently I informed them the speech would have to be a political one. When I reached New York, I for the first time learned that the place was changed to "Cooper Institute." I made the speech, and left for New Hampshire, where I have a son at school, neither asking for pay nor having any offered me. Three days after a check for two hundred dollars was sent to me at New Hampshire; and I took it, and did not know it was wrong. My understanding now is—though I knew nothing of it at the time—that they did charge for admittance to the Cooper Institute, and that they took in more than twice two hundred dollars.
I have made this explanation to you as a friend; but I wish no explanation made to our enemies. What they want is a squabble and a fuss, and that they can have if we explain; and they cannot have it if we don't.
When I returned through New York from New England, I was told by the gentlemen who sent me the Check that a drunken vagabond in the club, having learned something about the two hundred dollars, made the exhibition out of which The Herald manufactured the article quoted by The Press of your town.
My judgment is, and therefore my request is, that you give no denial and no explanation.
Thanking you for your kind interest in the matter, I remain, Yours truly,
HAWKINS TAYLOR, Esq.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 15th is just received. It surprises me that you have written twice, without receiving an answer. I have answered all I ever received from you; and certainly one since my return from the East.
Opinions here, as to the prospect of Douglas being nominated, are quite conflicting—some very confident he will, and others that he will not be. I think his nomination possible, but that the chances are against him.
I am glad there is a prospect of your party passing this way to Chicago. Wishing to make your visit here as pleasant as we can, we wish you to notify us as soon as possible whether you come this way, how many, and when you will arrive.
Yours very truly,
I authorize no bargains and will be bound by none.
MAY 19, 1860.
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND GENTLEMEN OF THE COMMITTEE:—I tender to you, and through you to the Republican National Convention, and all the people represented in it, my profoundest thanks for the high honor done me, which you now formally announce. Deeply and even painfully sensible of the great responsibility which is inseparable from this high honor—a responsibility which I could almost wish had fallen upon some one of the far more eminent men and experienced statesmen whose distinguished names were before the convention—I shall, by your leave, consider more fully the resolutions of the convention, denominated their platform, and without any unnecessary or unreasonable delay respond to you, Mr. Chairman, in writing—not doubting that the platform will be found satisfactory, and the nomination gratefully accepted.
And now I will not longer defer the pleasure of taking you, and each of you, by the hand.
TO GEORGE ASHMUN AND OTHERS.
SPRINGFIELD ILLINOIS, May 23, 1860
HON. GEORGE ASHMUN, President of Republican National Convention.
SIR:—I accept the nomination tendered me by the convention over which you presided, and of which I am formally apprised in the letter of yourself and others, acting as a committee of the convention for that purpose.
The declaration of principles and sentiments which accompanies your letter meets my approval; and it shall be my care not to violate or disregard it in any part.
Imploring the assistance of Divine Providence, and with due regard to the views and feelings of all who were represented in the convention, to the rights of all the States and Territories and people of the nation, to the inviolability of the Constitution, and the perpetual union, harmony, and prosperity of all—I am most happy to co-operate for the practical success of the principles declared by the convention.
Your obliged friend and fellow-citizen,
HON. C. B. SMITH.
MY DEAR SIR:-Yours of the 21st was duly received, but have found no time until now to say a word in the way of answer. I am indeed much indebted to Indiana; and, as my home friends tell me, much to you personally. Your saying, you no longer consider it a doubtful State is very gratifying. The thing starts well everywhere—too well, I almost fear, to last. But we are in, and stick or go through must be the word.
Let me hear from Indiana occasionally.
Your friend, as ever,
WITH WHICH HIS PRIVATE SECRETARY WAS INSTRUCTED TO ANSWER A NUMEROUS CLASS OF LETTERS IN THE CAMPAIGN OF 1860.
(Doctrine.)
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, ———, 1860
DEAR SIR:—Your letter to Mr. Lincoln of and by which you seek to obtain his opinions on certain political points, has been received by him. He has received others of a similar character, but he also has a greater number of the exactly opposite character. The latter class beseech him to write nothing whatever upon any point of political doctrine. They say his positions were well known when he was nominated, and that he must not now embarrass the canvass by undertaking to shift or modify them. He regrets that he cannot oblige all, but you perceive it is impossible for him to do so.
Yours, etc.,
HON. E. B. WASHBURNE.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have several letters from you written since the nomination, but till now have found no moment to say a word by way of answer. Of course I am glad that the nomination is well received by our friends, and I sincerely thank you for so informing me. So far as I can learn, the nominations start well everywhere; and, if they get no back-set, it would seem as if they are going through. I hope you will write often; and as you write more rapidly than I do, don't make your letters so short as mine.
Yours very truly,
HON. SAMUEL HAYCRAFT.
MY DEAR SIR:—Like yourself I belonged to the old Whig party from its origin to its close. I never belonged to the American party organization, nor ever to a party called a Union party; though I hope I neither am or ever have been less devoted to the Union than yourself or any other patriotic man.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL. June 4, 1860
HON. GEORGE ASHMUN.
MY DEAR SIR:—It seems as if the question whether my first name is "Abraham" or "Abram" will never be settled. It is "Abraham," and if the letter of acceptance is not yet in print, you may, if you think fit, have my signature thereto printed "Abraham Lincoln." Exercise your judgment about this.
Yours as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., June 19, 1860
HON. SAM'L GALLOWAY.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your very kind letter of the 15th is received. Messrs. Follett, Foster, & Co.'s Life of me is not by my authority; and I have scarcely been so much astounded by anything, as by their public announcement that it is authorized by me. They have fallen into some strange misunderstanding. I certainly knew they contemplated publishing a biography, and I certainly did not object to their doing so, upon their own responsibility. I even took pains to facilitate them. But, at the same time, I made myself tiresome, if not hoarse, with repeating to Mr. Howard, their only agent seen by me, my protest that I authorized nothing—would be responsible for nothing. How they could so misunderstand me, passes comprehension. As a matter wholly my own, I would authorize no biography, without time and opportunity [sic] to carefully examine and consider every word of it and, in this case, in the nature of things, I can have no such time and Opportunity [sic]. But, in my present position, when, by the lessons of the past, and the united voice of all discreet friends, I can neither write nor speak a word for the public, how dare I to send forth, by my authority, a volume of hundreds of pages, for adversaries to make points upon without end? Were I to do so, the convention would have a right to re-assemble and substitute another name for mine.
For these reasons, I would not look at the proof sheets—I am determined to maintain the position of [sic] truly saying I never saw the proof sheets, or any part of their work, before its publication.
Now, do not mistake me—I feel great kindness for Messrs. F., F., & Co.—do not think they have intentionally done wrong. There may be nothing wrong in their proposed book—I sincerely hope there will not. I barely suggest that you, or any of the friends there, on the party account, look it over, and exclude what you may think would embarrass the party bearing in mind, at all times, that I authorize nothing—will be responsible for nothing.
Your friend, as ever,
A. LINCOLN.
[The custom then, and it may have been a good one, was for the Presidential candidate to do no personal canvassing or speaking—or as we have it now "running for election." He stayed at home and kept his mouth shut. Ed.]
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN. MY DEAR SIR:—It appears to me that you and I ought to be acquainted, and accordingly I write this as a sort of introduction of myself to you. You first entered the Senate during the single term I was a member of the House of Representatives, but I have no recollection that we were introduced. I shall be pleased to receive a line from you.
The prospect of Republican success now appears very flattering, so far as I can perceive. Do you see anything to the contrary?
Yours truly,
HON. A. JONAS.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 20th is received. I suppose as good or even better men than I may have been in American or Know-Nothing lodges; but in point of fact, I never was in one at Quincy or elsewhere. I was never in Quincy but one day and two nights while Know-Nothing lodges were in existence, and you were with me that day and both those nights. I had never been there before in my life, and never afterward, till the joint debate with Douglas in 1858. It was in 1854 when I spoke in some hall there, and after the speaking, you, with others, took me to an oyster-saloon, passed an hour there, and you walked with me to, and parted with me at, the Quincy House, quite late at night. I left by stage for Naples before daylight in the morning, having come in by the same route after dark the evening, previous to the speaking, when I found you waiting at the Quincy House to meet me. A few days after I was there, Richardson, as I understood, started this same story about my having been in a Know-Nothing lodge. When I heard of the charge, as I did soon after; I taxed my recollection for some incident which could have suggested it; and I remembered that on parting with you the last night I went to the office of the hotel to take my stage-passage for the morning, was told that no stage-office for that line was kept there, and that I must see the driver before retiring, to insure his calling for me in the morning; and a servant was sent with me to find the driver, who, after taking me a square or two, stopped me, and stepped perhaps a dozen steps farther, and in my hearing called to some one, who answered him, apparently from the upper part of a building, and promised to call with the stage for me at the Quincy House. I returned, and went to bed, and before day the stage called and took me. This is all.
That I never was in a Know-Nothing lodge in Quincy, I should expect could be easily proved by respectable men who were always in the lodges and never saw me there. An affidavit of one or two such would put the matter at rest.
And now a word of caution. Our adversaries think they can gain a point if they could force me to openly deny the charge, by which some degree of offence would be given to the Americans. For this reason it must not publicly appear that I am paying any attention to the charge.
Yours truly,
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 9th, inclosing the letter of HON. John Minor Botts, was duly received. The latter is herewith returned according to your request. It contains one of the many assurances I receive from the South, that in no probable event will there be any very formidable effort to break up the Union. The people of the South have too much of good sense and good temper to attempt the ruin of the government rather than see it administered as it was administered by the men who made it. At least so I hope and believe. I thank you both for your own letter and a sight of that of Mr. Botts.
Yours very truly,
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 13th was received this morning. Douglas is managing the Bell element with great adroitness. He had his men in Kentucky to vote for the Bell candidate, producing a result which has badly alarmed and damaged Breckenridge, and at the same time has induced the Bell men to suppose that Bell will certainly be President, if they can keep a few of the Northern States away from us by throwing them to Douglas. But you, better than I, understand all this.
I think there will be the most extraordinary effort ever made to carry New York for Douglas. You and all others who write me from your State think the effort cannot succeed, and I hope you are right. Still, it will require close watching and great efforts on the other side.
Herewith I send you a copy of a letter written at New York, which sufficiently explains itself, and which may or may not give you a valuable hint. You have seen that Bell tickets have been put on the track both here and in Indiana. In both cases the object has been, I think, the same as the Hunt movement in New York—to throw States to Douglas. In our State, we know the thing is engineered by Douglas men, and we do not believe they can make a great deal out of it.
Yours very truly,
(Private.)
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., Aug. 31, 1860
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 27th is duly received. It consists almost exclusively of a historical detail of some local troubles, among some of our friends in Pennsylvania; and I suppose its object is to guard me against forming a prejudice against Mr. McC———____, I have not heard near so much upon that subject as you probably suppose; and I am slow to listen to criminations among friends, and never expose their quarrels on either side. My sincere wish is that both sides will allow bygones to be bygones, and look to the present and future only.
Yours very truly,
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am annoyed some by a letter from a friend in Chicago, in which the following passage occurs: "Hamlin has written Colfax that two members of Congress will, he fears, be lost in Maine, the first and sixth districts; and that Washburne's majority for governor will not exceed six thousand."
I had heard something like this six weeks ago, but had been assured since that it was not so. Your secretary of state,—Mr. Smith, I think,—whom you introduced to me by letter, gave this assurance; more recently, Mr. Fessenden, our candidate for Congress in one of those districts, wrote a relative here that his election was sure by at least five thousand, and that Washburne's majority would be from 14,000 to 17,000; and still later, Mr. Fogg, of New Hampshire, now at New York serving on a national committee, wrote me that we were having a desperate fight in Maine, which would end in a splendid victory for us.
Such a result as you seem to have predicted in Maine, in your letter to Colfax, would, I fear, put us on the down-hill track, lose us the State elections in Pennsylvania and Indiana, and probably ruin us on the main turn in November.
You must not allow it.
Yours very truly,
HON. E. B. WASHBURNE.
MY DEAR SIR: Yours of the 5th was received last evening. I was right glad to see it. It contains the freshest "posting" which I now have. It relieved me some from a little anxiety I had about Maine. Jo Medill, on August 30th, wrote me that Colfax had a letter from Mr. Hamlin saying we were in great danger of losing two members of Congress in Maine, and that your brother would not have exceeding six thousand majority for Governor. I addressed you at once, at Galena, asking for your latest information. As you are at Washington, that letter you will receive some time after the Maine election.
Yours very truly,
DEAR WILLIAM:—I cannot give you details, but it is entirely certain that Pennsylvania and Indiana have gone Republican very largely. Pennsylvania 25,000, and Indiana 5000 to 10,000. Ohio of course is safe.
Yours as ever,
L. MONTGOMERY BOND, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR: I certainly am in no temper and have no purpose to embitter the feelings of the South, but whether I am inclined to such a course as would in fact embitter their feelings you can better judge by my published speeches than by anything I would say in a short letter if I were inclined now, as I am not, to define my position anew.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., October 19, 1860
MISS GRACE BEDELL.
MY DEAR LITTLE MISS:—Your very agreeable letter of the 15th is received. I regret the necessity of saying I have no daughter. I have three sons—one seventeen, one nine, and one seven. They with their mother constitute my whole family. As to the whiskers, as I have never worn any, do you not think that people would call it a piece of silly affectation were I to begin wearing them now?
I am your true friend and sincere well-wisher,
(Private and Confidential.) SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, October 26, 1860
MAJOR DAVID HUNTER
MY DEAR SIR:—Your very kind letter of the 20th was duly received, for which please accept my thanks. I have another letter, from a writer unknown to me, saying the officers of the army at Fort Kearny have determined in case of Republican success at the approaching Presidential election, to take themselves, and the arms at that point, south, for the purpose of resistance to the government. While I think there are many chances to one that this is a humbug, it occurs to me that any real movement of this sort in the Army would leak out and become known to you. In such case, if it would not be unprofessional or dishonorable (of which you are to be judge), I shall be much obliged if you will apprise me of it.
Yours very truly,
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am anxious for a personal interview with you at as early a day as possible. Can you, without much inconvenience, meet me at Chicago? If you can, please name as early a day as you conveniently can, and telegraph me, unless there be sufficient time before the day named to communicate by mail.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., Nov.13, 1860
HON. SAMUEL HAYCRAFT.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 9th is just received. I can only answer briefly. Rest fully assured that the good people of the South who will put themselves in the same temper and mood towards me which you do will find no cause to complain of me.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN. CELEBRATION OF LINCOLN'S ELECTION, REMARKS AT THE MEETING AT SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS NOVEMBER 20, 1860
FRIENDS AND FELLOW-CITIZENS:—Please excuse me on this occasion from making a speech. I thank you in common with all those who have thought fit by their votes to indorse the Republican cause. I rejoice with you in the success which has thus far attended that cause. Yet in all our rejoicings let us neither express nor cherish any hard feelings toward any citizen who by his vote has differed with us. Let us at all times remember that all American citizens are brothers of a common country, and should dwell together in the bonds of fraternal feeling. Let me again beg you to accept my thanks, and to excuse me from further speaking at this time.
HON. A. H. STEPHENS.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have read in the newspapers your speech recently delivered (I think) before the Georgia Legislature, or its assembled members. If you have revised it, as is probable, I shall be much obliged if you will send me a copy.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, December 8, 1860
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 4th was duly received. The inclosed to Governor Seward covers two notes to him, copies of which you find open for your inspection. Consult with Judge Trumbull; and if you and he see no reason to the contrary, deliver the letter to Governor Seward at once. If you see reason to the contrary write me at once.
I have an intimation that Governor Banks would yet accept a place in the Cabinet. Please ascertain and write me how this is,
Yours very truly,
(Private and Confidential.)
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., December 13, 1860
HON. E. B. WASHBURNE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your long letter received. Prevent, as far as possible, any of our friends from demoralizing themselves and our cause by entertaining propositions for compromise of any sort on "slavery extension." There is no possible compromise upon it but which puts us under again, and leaves all our work to do over again. Whether it be a Missouri line or Eli Thayer's popular sovereignty, it is all the same. Let either be done, and immediately filibustering and extending slavery recommences. On that point hold firm, as with a chain of steel.
Yours as ever,
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, DECEMBER 17, 1860
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 11th was received two days ago. Should the convocation of governors of which you speak seem desirous to know my views on the present aspect of things, tell them you judge from my speeches that I will be inflexible on the territorial question; but I probably think either the Missouri line extended, or Douglas's and Eli Thayer's popular sovereignty would lose us everything we gain by the election; that filibustering for all south of us and making slave States of it would follow in spite of us, in either case; also that I probably think all opposition, real and apparent, to the fugitive slave clause of the Constitution ought to be withdrawn.
I believe you can pretend to find but little, if anything, in my speeches, about secession. But my opinion is that no State can in any way lawfully get out of the Union without the consent of the others; and that it is the duty of the President and other government functionaries to run the machine as it is.
Truly yours,
(Confidential)
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, December 21, 1860
HON. E. B. WASHBURNE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Last night I received your letter giving an account of your interview with General Scott, and for which I thank you. Please present my respects to the General, and tell him, confidentially, I shall be obliged to him to be as well prepared as he can to either hold or retake the forts, as the case may require, at and after the inauguration.
Yours as ever,
HON. ALEXANDER STEVENS
MY DEAR SIR:—Your obliging answer to my short note is just received, and for which please accept my thanks. I fully appreciate the present peril the country is in, and the weight of responsibility on me. Do the people of the South really entertain fear that a Republican administration would, directly or indirectly, interfere with the slaves, or with them about the slaves? If they do, I wish to assure you, as once a friend, and still, I hope, not an enemy, that there is no cause for such fears. The South would be in no more danger in this respect than it was in the days of Washington. I suppose, however, this does not meet the case. You think slavery is right and ought to be extended, while we think it is wrong and ought to be restricted. That, I suppose, is the rub. It certainly is the only substantial difference between us.
Yours very truly,
December [22?], 1860
Resolved: That the fugitive slave clause of the Constitution ought to be enforced by a law of Congress, with efficient provisions for that object, not obliging private persons to assist in its execution, but punishing all who resist it, and with the usual safeguards to liberty, securing free men against being surrendered as slaves.
That all State laws, if there be such, really or apparently in conflict with such law of Congress, ought to be repealed; and no opposition to the execution of such law of Congress ought to be made.
That the Federal Union must be preserved.
Prepared for the consideration of the Republican members of the Senate Committee of Thirteen.
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS December 22, 1860
MAJOR DAVID HUNTER.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am much obliged by the receipt of yours of the 18th. The most we can do now is to watch events, and be as well prepared as possible for any turn things may take. If the forts fall, my judgment is that they are to be retaken. When I shall determine definitely my time of starting to Washington, I will notify you.
Yours truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., Dec 24, 1860
HON. I. N. MORRIS.
MY DEAR SIR:—Without supposing that you and I are any nearer together, politically, than heretofore, allow me to tender you my sincere thanks for your Union resolution, expressive of views upon which we never were, and, I trust, never will be at variance.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILLINOIS, December 14, 1860.
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN.
MY DEAR SIR:—I need a man of Democratic antecedents from New England. I cannot get a fair share of that element in without. This stands in the way of Mr. Adams. I think of Governor Banks, Mr. Welles, and Mr. Tuck. Which of them do the New England delegation prefer? Or shall I decide for myself?
Yours as ever,
TO WILLIAM H. SEWARD.
(Private.)
SPRINGFIELD. ILL., January 3, 1861.
HON. W. H. SEWARD.
DEAR SIR:—Yours without signature was received last night. I have been considering your suggestions as to my reaching Washington somewhat earlier than is usual. It seems to me the inauguration is not the most dangerous point for us. Our adversaries have us now clearly at disadvantage on the second Wednesday of February, when the votes should be officially counted. If the two houses refuse to meet at all, or meet without a quorum of each, where shall we be? I do not think that this counting is constitutionally essential to the election, but how are we to proceed in the absence of it? In view of this, I think it is best for me not to attempt appearing in Washington till the result of that ceremony is known.
It certainly would be of some advantage if you could know who are to be at the heads of the War and Navy departments, but until I can ascertain definitely whether I can get any suitable men from the South, and who, and how many, I can not well decide. As yet, I have no word from Mr. Gilmer in answer to my request for an interview with him. I look for something on the subject, through you, before long.
Yours very truly,
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., January 12, 1861
HON. W. H. SEWARD.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 8th received. I still hope Mr. Gilmer will, on a fair understanding with us, consent to take a place in the Cabinet. The preference for him over Mr. Hunt or Mr. Gentry is that, up to date—he has a living position in the South, while they have not. He is only better than Winter Davis in that he is farther south. I fear, if we could get, we could not safely take more than one such man—that is, not more than one who opposed us in the election—the danger being to lose the confidence of our own friends. Your selection for the State Department having become public, I am happy to find scarcely any objection to it. I shall have trouble with every other Northern Cabinet appointment—so much so that I shall have to defer them as long as possible to avoid being teased into insanity, to make changes.
Your obedient servant,
SIR:—Your letter of the 30th ult. inviting me, on behalf of the Legislature of New York, to pass through that State on my way to Washington, and tendering me the hospitalities of her authorities and people, has been duly received. With the feelings of deep gratitude to you and them for this testimonial of regard and esteem I beg you to notify them that I accept the invitation so kindly tendered.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN
P.S.—Please let the ceremonies be only such as to take the least time possible. A. L.
SPRINGFIELD, ILL., February 4, 1861
DEAR SIR:—I have both your letter to myself and that to Judge Davis, in relation to a certain gentleman in your State claiming to dispense patronage in my name, and also to be authorized to use my name to advance the chances of Mr. Greeley for an election to the United States Senate.
It is very strange that such things should be said by any one. The gentleman you mention did speak to me of Mr. Greeley in connection with the senatorial election, and I replied in terms of kindness toward Mr. Greeley, which I really feel, but always with an expressed protest that my name must not be used in the senatorial election in favor of or against any one. Any other representation of me is a misrepresentation.
As to the matter of dispensing patronage, it perhaps will surprise you to learn that I have information that you claim to have my authority to arrange that matter in New York. I do not believe you have so claimed; but still so some men say. On that subject you know all I have said to you is "justice to all," and I have said nothing more particular to any one. I say this to reassure you that I have not changed my position.
In the hope, however, that you will not use my name in the matter, I am,
Yours truly,
MY FRIENDS:—One who has never been placed in a like position cannot understand my feelings at this hour, nor the oppressive sadness I feel at this parting. For more than twenty-five years I have lived among you, and during all that time I have received nothing but kindness at your hands. Here the most cherished ties of earth were assumed. Here my children were born, and here one of them lies buried. To you, my friends, I owe all that I have, all that I am. All the strange checkered past seems to crowd upon my mind. To-day I leave you. I go to assume a task more difficult than that which devolved upon General Washington. Unless the great God who assisted him shall be with and aid me I cannot prevail; but if the same almighty arm that directed and protected him shall guide and support me I shall not fail; I shall succeed. Let us pray that the God of our fathers may not forsake us now. To Him I commend you all. Permit me to ask that with equal sincerity and faith you will all invoke His wisdom and goodness for me.
With these words I must leave you; for how long I know not. Friends, one and all, I must now wish you an affectionate farewell.
I am leaving you on an errand of national importance, attended, as you are aware, with considerable difficulties. Let us believe, as some poet has expressed it, "Behind the cloud the sun is still shining." I bid you an affectionate farewell.
GOVERNOR MORTON AND FELLOW CITIZENS OF THE STATE OF INDIANA:
Most heartily do I thank you for this magnificent reception, and while I cannot take to myself any share of the compliment thus paid, more than that which pertains to a mere instrument, an accidental instrument, perhaps I should say, of a great cause, I yet must look upon it as a most magnificent reception, and as such most heartily do thank you for it. You have been pleased to address yourself to me chiefly in behalf of this glorious Union in which we live, in all of which you have my hearty sympathy, and, as far as may be within my power, will have, one and inseparable, my hearty consideration. While I do not expect, upon this occasion, or until I get to Washington, to attempt any lengthy speech, I will only say to the salvation of the Union there needs but one single thing—the hearts of a people like yours.
The people—when they rise in mass in behalf of the Union and the liberties of their country, truly may it be said, "The gates of hell cannot prevail against them." In all trying positions in which I shall be placed—and, doubtless, I shall be placed in many such—my reliance will be placed upon you and the people of the United States; and I wish you to remember, now and forever, that it is your business, and not mine; that if the union of these States and the liberties of this people shall be lost, it is but little to any one man of fifty-two years of age, but a great deal to the thirty millions of people who inhabit these United States, and to their posterity in all coming time. It is your business to rise up and preserve the Union and liberty for yourselves, and not for me.
I desire they should be constitutionally performed. I, as already intimated, am but an accidental instrument, temporary, and to serve but for a limited time; and I appeal to you again to constantly bear in mind that with you, and not with politicians, not with Presidents, not with office-seekers, but with you is the question, Shall the Union and shall the liberties of this country be preserved to the latest generations?
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE STATE OF INDIANA:—I am here to thank you much for this magnificent welcome, and still more for the generous support given by your State to that political cause which I think is the true and just cause of the whole country and the whole world.
Solomon says there is "a time to keep silence," and when men wrangle by the mouth with no certainty that they mean the same thing while using the same word, it perhaps were as well if they would keep silence.
The words "coercion" and "invasion" are much used in these days, and often with some temper and hot blood. Let us make sure, if we can, the meaning of those who use them. Let us get the exact definitions of these words, not from dictionaries, but from the men themselves, who certainly deprecate the things they would represent by the use of the words.
What, then, is coercion? What is invasion? Would the marching of an army into South Carolina, without the consent of her people, and with hostile intent toward them, be invasion? I certainly think it would, and it would be coercion also, if the South Carolinians were forced to submit. But if the United States should merely hold and retake its own forts and other property, and collect the duties on foreign importations, or even withhold the mails from places where they were habitually violated, would any or all of these things be invasion or coercion? Do our professed lovers of the Union, who spitefully resolve that they will resist coercion and invasion, understand that such things as these, on the part of the United States, would be coercion or invasion of a State? If so, their idea of means to preserve the object of their great affection would seem to be exceedingly thin and airy. If sick, the little pills of the homoeopathist would be much too large for it to swallow. In their view, the Union, as a family relation, would seem to be no regular marriage, but rather a sort of "free-love" arrangement, to be maintained on passional attraction.
By the way, in what consists the special sacredness of a State? I speak not of the position assigned to a State in the Union by the Constitution, for that is a bond we all recognize. That position, however, a State cannot carry out of the Union with it. I speak of that assumed primary right of a State to rule all which is less than itself, and to ruin all which is larger than itself. If a State and a county, in a given case, should be equal in number of inhabitants, in what, as a matter of principle, is the State better than the county? Would an exchange of name be an exchange of rights? Upon what principle, upon what rightful principle, may a State, being no more than one fiftieth part of the nation in soil and population, break up the nation, and then coerce a proportionably large subdivision of itself in the most arbitrary way? What mysterious right to play tyrant is conferred on a district of country, with its people, by merely calling it a State? Fellow-citizens, I am not asserting anything. I am merely asking questions for you to consider. And now allow me to bid you farewell.
CINCINNATI, OHIO, FEBRUARY 12, 1861
Mr. MAYOR, AND GENTLEMEN:—Twenty-four hours ago, at the capital of Indiana, I said to myself, "I have never seen so many people assembled together in winter weather." I am no longer able to say that. But it is what might reasonably have been expected—that this great city of Cincinnati would thus acquit herself on such an occasion. My friends, I am entirely overwhelmed by the magnificence of the reception which has been given, I will not say to me, but to the President-elect of the United States of America. Most heartily do I thank you, one and all, for it.
I have spoken but once before this in Cincinnati. That was a year previous to the late Presidential election. On that occasion, in a playful manner, but with sincere words, I addressed much of what I said to the Kentuckians. I gave my opinion that we, as Republicans, would ultimately beat them as Democrats, but that they could postpone that result longer by nominating Senator Douglas for the Presidency than they could by any other way. They did not, in any true sense of the word, nominate Mr. Douglas, and the result has come certainly as soon as ever I expected. I also told them how I expected they would be treated after they should have been beaten, and I now wish to call their attention to what I then said upon that subject. I then said:
"When we do as we say, beat you, you perhaps want to know what we will do with you. I will tell you, as far as I am authorized to speak for the Opposition, what we mean to do with you. We mean to treat you, as near as we possibly can, as Washington, Jefferson, and Madison treated you. We mean to leave you alone, and in no way to interfere with your institutions; to abide by all and every compromise of the Constitution, and, in a word, coming back to the original proposition, to treat you so far as degenerate men, if we have degenerated, may, according to the example of those noble fathers, Washington, Jefferson, and Madison.
"We mean to remember that you are as good as we; that there is no difference between us other than the difference of circumstances. We mean to recognize and bear in mind always that you have as good hearts in your bosoms as other people, or as we claim to have, and treat you accordingly."
Fellow-citizens of Kentucky—friends and brethren, may I call you in my new position?—I see no occasion and feel no inclination to retract a word of this. If it shall not be made good, be assured the fault shall not be mine.
Mr. CHAIRMAN:—I thank you and those whom you represent for the compliment you have paid me by tendering me this address. In so far as there is an allusion to our present national difficulties, which expresses, as you have said, the views of the gentlemen present, I shall have to beg pardon for not entering fully upon the questions which the address you have now read suggests.
I deem it my duty—a duty which I owe to my constituents—to you, gentlemen, that I should wait until the last moment for a development of the present national difficulties before I express myself decidedly as to what course I shall pursue. I hope, then, not to be false to anything that you have expected of me.
I agree with you, Mr. Chairman, that the working men are the basis of all governments, for the plain reason that they are all the more numerous, and as you added that those were the sentiments of the gentlemen present, representing not only the working class, but citizens of other callings than those of the mechanic, I am happy to concur with you in these sentiments, not only of the native-born citizens, but also of the Germans and foreigners from other countries.
Mr. Chairman, I hold that while man exists it is his duty to improve not only his own condition, but to assist in ameliorating the condition of mankind; and therefore, without entering upon the details of the question, I will simply say that I am for those means which will give the greatest good to the greatest number.
In regard to the Homestead law, I have to say that, in so far as the government lands can be disposed of, I am in favor of cutting up the wild lands into parcels, so that every poor man may have a home.
In regard to the Germans and foreigners, I esteem them no better than other people, nor any worse. It is not my nature, when I see a people borne down by the weight of their shackles—the oppression of tyranny—to make their life more bitter by heaping upon them greater burdens; but rather would I do all in my power to raise the yoke than to add anything that would tend to crush them.
Inasmuch as our own country is extensive and new, and the countries of Europe are densely populated, if there are any abroad who desire to make this the land of their adoption, it is not in my heart to throw aught in their way to prevent them from coming to the United States.
Mr. Chairman and gentlemen, I will bid you an affectionate farewell.
Mr. PRESIDENT AND Mr. SPEAKER, AND GENTLEMEN OF THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF OHIO:—It is true, as has been said by the president of the Senate, that very great responsibility rests upon me in the position to which the votes of the American people have called me. I am deeply sensible of that weighty responsibility. I cannot but know what you all know, that without a name, perhaps without a reason why I should have a name, there has fallen upon me a task such as did not rest even upon the Father of his Country; and so feeling, I can turn and look for that support without which it will be impossible for me to perform that great task. I turn, then, and look to the American people and to that God who has never forsaken them. Allusion has been made to the interest felt in relation to the policy of the new administration. In this I have received from some a degree of credit for having kept silence, and from others some deprecation. I still think that I was right.
In the varying and repeatedly shifting scenes of the present, and without a precedent which could enable me to judge by the past, it has seemed fitting that before speaking upon the difficulties of the country I should have gained a view of the whole field, being at liberty to modify and change the course of policy as future events may make a change necessary.
I have not maintained silence from any want of real anxiety. It is a good thing that there is no more than anxiety, for there is nothing going wrong. It is a consoling circumstance that when we look out there is nothing that really hurts anybody. We entertain different views upon political questions, but nobody is suffering anything. This is a most consoling circumstance, and from it we may conclude that all we want is time, patience, and a reliance on that God who has never forsaken this people.
Fellow-citizens, what I have said I have said altogether extemporaneously, and I will now come to a close.
I fear that the great confidence placed in my ability is unfounded. Indeed, I am sure it is. Encompassed by vast difficulties as I am, nothing shall be wanting on my part, if sustained by God and the American people. I believe the devotion to the Constitution is equally great on both sides of the river. It is only the different understanding of that instrument that causes difficulty. The only dispute on both sides is, "What are their rights?" If the majority should not rule, who would be the judge? Where is such a judge to be found? We should all be bound by the majority of the American people; if not, then the minority must control. Would that be right? Would it be just or generous? Assuredly not. I reiterate that the majority should rule. If I adopt a wrong policy, the opportunity for condemnation will occur in four years' time. Then I can be turned out, and a better man with better views put in my place.
I most cordially thank his Honor Mayor Wilson, and the citizens of Pittsburg generally, for their flattering reception. I am the more grateful because I know that it is not given to me alone, but to the cause I represent, which clearly proves to me their good-will, and that sincere feeling is at the bottom of it. And here I may remark that in every short address I have made to the people, in every crowd through which I have passed of late, some allusion has been made to the present distracted condition of the country. It is natural to expect that I should say something on this subject; but to touch upon it at all would involve an elaborate discussion of a great many questions and circumstances, requiring more time than I can at present command, and would, perhaps, unnecessarily commit me upon matters which have not yet fully developed themselves. The condition of the country is an extraordinary one, and fills the mind of every patriot with anxiety. It is my intention to give this subject all the consideration I possibly can before specially deciding in regard to it, so that when I do speak it may be as nearly right as possible. When I do speak I hope I may say nothing in opposition to the spirit of the Constitution, contrary to the integrity of the Union, or which will prove inimical to the liberties of the people, or to the peace of the whole country. And furthermore, when the time arrives for me to speak on this great subject, I hope I may say nothing to disappoint the people generally throughout the country, especially if the expectation has been based upon anything which I may have heretofore said. Notwithstanding the troubles across the river [the speaker pointing southwardly across the Monongahela, and smiling], there is no crisis but an artificial one. What is there now to warrant the condition of affairs presented by our friends over the river? Take even their own view of the questions involved, and there is nothing to justify the course they are pursuing. I repeat, then, there is no crisis, excepting such a one as may be gotten up at any time by turbulent men aided by designing politicians, My advice to them, under such circumstances, is to keep cool. If the great American people only keep their temper on both sides of the line, the troubles will come to an end, and the question which now distracts the country will be settled, just as surely as all other difficulties of a like character which have originated in this government have been adjusted. Let the people on both sides keep their self-possession, and just as other clouds have cleared away in due time, so will this great nation continue to prosper as heretofore. But, fellow-citizens, I have spoken longer on this subject than I intended at the outset.
It is often said that the tariff is the specialty of Pennsylvania. Assuming that direct taxation is not to be adopted, the tariff question must be as durable as the government itself. It is a question of national housekeeping. It is to the government what replenishing the meal-tub is to the family. Every varying circumstances will require frequent modifications as to the amount needed and the sources of supply. So far there is little difference of opinion among the people. It is as to whether, and how far, duties on imports shall be adjusted to favor home production in the home market, that controversy begins. One party insists that such adjustment oppresses one class for the advantage of another; while the other party argues that, with all its incidents, in the long run all classes are benefited. In the Chicago platform there is a plank upon this subject which should be a general law to the incoming administration. We should do neither more nor less than we gave the people reason to believe we would when they gave us their votes. Permit me, fellow-citizens, to read the tariff plank of the Chicago platform, or rather have it read in your hearing by one who has younger eyes.
[Mr. Lincoln's private secretary then read Section 12 of the Chicago platform, as follows:]
"That, while providing revenue for the support of the General Government by duties upon imports, sound policy requires such an adjustment of these imposts as will encourage the development of the industrial interest of the whole country; and we commend that policy of national exchanges which secures to working-men liberal wages, to agriculture remunerating prices, to mechanics and manufacturers adequate return for their skill, labor, and enterprise, and to the nation commercial prosperity and independence."
As with all general propositions, doubtless, there will be shades of difference in construing this. I have by no means a thoroughly matured judgment upon this subject, especially as to details; some general ideas are about all. I have long thought it would be to our advantage to produce any necessary article at home which can be made of as good quality and with as little labor at home as abroad, at least by the difference of the carrying from abroad. In such case the carrying is demonstrably a dead loss of labor. For instance, labor being the true standard of value, is it not plain that if equal labor get a bar of railroad iron out of a mine in England and another out of a mine in Pennsylvania, each can be laid down in a track at home cheaper than they could exchange countries, at least by the carriage? If there be a present cause why one can be both made and carried cheaper in money price than the other can be made without carrying, that cause is an unnatural and injurious one, and ought gradually, if not rapidly, to be removed. The condition of the treasury at this time would seem to render an early revision of the tariff indispensable. The Morrill [tariff] bill, now pending before Congress, may or may not become a law. I am not posted as to its particular provisions, but if they are generally satisfactory, and the bill shall now pass, there will be an end for the present. If, however, it shall not pass, I suppose the whole subject will be one of the most pressing and important for the next Congress. By the Constitution, the executive may recommend measures which he may think proper, and he may veto those he thinks improper, and it is supposed that he may add to these certain indirect influences to affect the action of Congress. My political education strongly inclines me against a very free use of any of these means by the executive to control the legislation of the country. As a rule, I think it better that Congress should originate as well as perfect its measures without external bias. I therefore would rather recommend to every gentleman who knows he is to be a member of the next Congress to take an enlarged view, and post himself thoroughly, so as to contribute his part to such an adjustment of the tariff as shall produce a sufficient revenue, and in its other bearings, so far as possible, be just and equal to all sections of the country and classes of the people.
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND FELLOW-CITIZENS OF CLEVELAND:—We have been marching about two miles through snow, rain, and deep mud. The large numbers that have turned out under these circumstances testify that you are in earnest about something or other. But do I think so meanly of you as to suppose that that earnestness is about me personally? I would be doing you an injustice to suppose you did. You have assembled to testify your respect for the Union, the Constitution, and the laws; and here let me say that it is with you, the people, to advance the great cause of the Union and the Constitution, and not with any one man. It rests with you alone. This fact is strongly impressed upon my mind at present. In a community like this, whose appearance testifies to their intelligence, I am convinced that the cause of liberty and the Union can never be in danger. Frequent allusion is made to the excitement at present existing in our national politics, and it is as well that I should also allude to it here. I think that there is no occasion for any excitement. 'The crisis, as it is called, is altogether an artificial crisis. In all parts of the nation there are differences of opinion on politics. There are differences of opinion even here. You did not all vote for the person who now addresses you. What is happening now will not hurt those who are farther away from here. Have they not all their rights now as they ever have had? Do they not have their fugitive slaves returned now as ever? Have they not the same Constitution that they have lived under for seventy-odd years? Have they not a position as citizens of this common country, and have we any power to change that position? What, then, is the matter with them? Why all this excitement? Why all these complaints?
As I said before, this crisis is all artificial! It has no foundation in facts. It is not argued up, as the saying is, and cannot, therefore, be argued down. Let it alone and it will go down of itself.
[Mr. Lincoln then said that they must be content with a few words from him, as he was tired, etc. Having been given to understand that the crowd was not all Republican, but consisted of men of all parties, he continued:]
This is as it should be. If Judge Douglas had been elected and had been here on his way to Washington, as I am to-night, the Republicans should have joined his supporters in welcoming him, just as his friends have joined with mine tonight. If all do not join now to save the good old ship of the Union this voyage, nobody will have a chance to pilot her on another voyage.
Mr. MAYOR AND FELLOW-CITIZENS OF BUFFALO AND THE STATE OF NEW YORK:—I am here to thank you briefly for this grand reception given to me, not personally, but as the representative of our great and beloved country. Your worthy mayor has been pleased to mention, in his address to me, the fortunate and agreeable journey which I have had from home, on my rather circuitous route to the Federal capital. I am very happy that he was enabled in truth to congratulate myself and company on that fact. It is true we have had nothing thus far to mar the pleasure of the trip. We have not been met alone by those who assisted in giving the election to me—I say not alone by them, but by the whole population of the country through which we have passed. This is as it should be. Had the election fallen to any other of the distinguished candidates instead of myself, under the peculiar circumstances, to say the least, it would have been proper for all citizens to have greeted him as you now greet me. It is an evidence of the devotion of the whole people to the Constitution, the Union, and the perpetuity of the liberties of this country. I am unwilling on any occasion that I should be so meanly thought of as to have it supposed for a moment that these demonstrations are tendered to me personally. They are tendered to the country, to the institutions of the country, and to the perpetuity of the liberties of the country, for which these institutions were made and created.
Your worthy mayor has thought fit to express the hope that I may be able to relieve the country from the present, or, I should say, the threatened difficulties. I am sure I bring a heart true to the work. For the ability to perform it, I must trust in that Supreme Being who has never forsaken this favored land, through the instrumentality of this great and intelligent people. Without that assistance I shall surely fail; with it, I cannot fail. When we speak of threatened difficulties to the Country, it is natural that it should be expected that something should be said by myself with regard to particular measures. Upon more mature reflection, however, others will agree with me that, when it is considered that these difficulties are without precedent, and have never been acted upon by any individual situated as I am, it is most proper I should wait and see the developments, and get all the light possible, so that when I do speak authoritatively, I may be as near right as possible. When I shall speak authoritatively, I hope to say nothing inconsistent with the Constitution, the Union, the rights of all the States, of each State, and of each section of the country, and not to disappoint the reasonable expectations of those who have confided to me their votes. In this connection allow me to say that you, as a portion of the great American people, need only to maintain your composure, stand up to your sober convictions of right, to your obligations to the Constitution, and act in accordance with those sober convictions, and the clouds now on the horizon will be dispelled, and we shall have a bright and glorious future; and when this generation has passed away, tens of thousands will inhabit this country where only thousands inhabit it now. I do not propose to address you at length; I have no voice for it. Allow me again to thank you for this magnificent reception, and bid you farewell.
I confess myself, after having seen many large audiences since leaving home, overwhelmed with this vast number of faces at this hour of the morning. I am not vain enough to believe that you are here from any wish to see me as an individual, but because I am for the time being the representative of the American people. I could not, if I would, address you at any length. I have not the strength, even if I had the time, for a speech at each of these many interviews that are afforded me on my way to Washington. I appear merely to see you, and to let you see me, and to bid you farewell. I hope it will be understood that it is from no disinclination to oblige anybody that I do not address you at greater length.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—I See you have erected a very fine and handsome platform here for me, and I presume you expected me to speak from it. If I should go upon it, you would imagine that I was about to deliver you a much longer speech than I am. I wish you to understand that I mean no discourtesy to you by thus declining. I intend discourtesy to no one. But I wish you to understand that, though I am unwilling to go upon this platform, you are not at liberty to draw inferences concerning any other platform with which my name has been or is connected. I wish you long life and prosperity individually, and pray that with the perpetuity of those institutions under which we have all so long lived and prospered, our happiness may be secured, our future made brilliant, and the glorious destiny of our country established forever. I bid you a kind farewell.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—I have no speech to make to you; and no time to speak in. I appear before you that I may see you, and that you may see me; and I am willing to admit that so far as the ladies are concerned I have the best of the bargain, though I wish it to be understood that I do not make the same acknowledgment concerning the men.
MR. MAYOR:—I can hardly appropriate to myself the flattering terms in which you communicate the tender of this reception, as personal to myself. I most gratefully accept the hospitalities tendered to me, and will not detain you or the audience with any extended remarks at this time. I presume that in the two or three courses through which I shall have to go, I shall have to repeat somewhat, and I will therefore only express to you my thanks for this kind reception.
GOVERNOR MORGAN:—I was pleased to receive an invitation to visit the capital of the great Empire State of this nation while on my way to the Federal capital. I now thank you, Mr. Governor, and you, the people of the capital of the State of New York, for this most hearty and magnificent welcome. If I am not at fault, the great Empire State at this time contains a larger population than did the whole of the United States of America at the time they achieved their national independence, and I was proud—to be invited to visit its capital, to meet its citizens, as I now have the honor to do. I am notified by your governor that this reception is tendered by citizens without distinction of party. Because of this I accept it the more gladly. In this country, and in any country where freedom of thought is tolerated, citizens attach themselves to political parties. It is but an ordinary degree of charity to attribute this act to the supposition that, in thus attaching themselves to the various parties, each man in his own judgment supposes he thereby best advances the interests of the whole country. And when an election is past it is altogether befitting a free people, as I suppose, that, until the next election, they should be one people. The reception you have extended me to-day is not given to me personally,—it should not be so,—but as the representative, for the time being, of the majority of the nation. If the election had fallen to any of the more distinguished citizens who received the support of the people, this same honor should have greeted him that greets me this day, in testimony of the universal, unanimous devotion of the whole people to the Constitution, the Union, and to the perpetual liberties of succeeding generations in this country.
I have neither the voice nor the strength to address you at any greater length. I beg you will therefore accept my most grateful thanks for this manifest devotion—not to me, but the institutions of this great and glorious country.
MR. PRESIDENT AND GENTLEMEN OF THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK:—It is with feelings of great diffidence, and, I may say, with feelings of awe, perhaps greater than I have recently experienced, that I meet you here in this place. The history of this great State, the renown of those great men who have stood here, and have spoken here, and have been heard here, all crowd around my fancy, and incline me to shrink from any attempt to address you. Yet I have some confidence given me by the generous manner in which you have invited me, and by the still more generous manner in which you have received me, to speak further. You have invited and received me without distinction of party. I cannot for a moment suppose that this has been done in any considerable degree with reference to my personal services, but that it is done in so far as I am regarded, at this time, as the representative of the majesty of this great nation. I doubt not this is the truth, and the whole truth of the case, and this is as it should be. It is much more gratifying to me that this reception has been given to me as the elected representative of a free people, than it could possibly be if tendered merely as an evidence of devotion to me, or to any one man personally.
And now I think it were more fitting that I should close these hasty remarks. It is true that, while I hold myself, without mock modesty, the humblest of all individuals that have ever been elevated to the Presidency, I have a more difficult task to perform than any one of them.
You have generously tendered me the support—the united support—of the great Empire State. For this, in behalf of the nation—in behalf of the present and future of the nation—in behalf of civil and religious liberty for all time to come, most gratefully do I thank you. I do not propose to enter into an explanation of any particular line of policy, as to our present difficulties, to be adopted by the incoming administration. I deem it just to you, to myself, to all, that I should see everything, that I should hear everything, that I should have every light that can be brought within my reach, in order that, when I do so speak, I shall have enjoyed every opportunity to take correct and true ground; and for this reason I do not propose to speak at this time of the policy of the Government. But when the time comes, I shall speak, as well as I am able, for the good of the present and future of this country for the good both of the North and of the South—for the good of the one and the other, and of all sections of the country. In the meantime, if we have patience, if we restrain ourselves, if we allow ourselves not to run off in a passion, I still have confidence that the Almighty, the Maker of the universe, will, through the instrumentality of this great and intelligent people, bring us through this as He has through all the other difficulties of our country. Relying on this, I again thank you for this generous reception.
MR. MAYOR AND CITIZENS OF TROY:—I thank you very kindly for this great reception. Since I left my home it has not been my fortune to meet an assemblage more numerous and more orderly than this. I am the more gratified at this mark of your regard since you assure me it is tendered, not to the individual but to the high office you have called me to fill. I have neither strength nor time to make any extended remarks on this occasion, and I can only repeat to you my sincere thanks for the kind reception you have thought proper to extend to me.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—It is altogether impossible I should make myself heard by any considerable portion of this vast assemblage; but, although I appear before you mainly for the purpose of seeing you, and to let you see rather than hear me, I cannot refrain from saying that I am highly gratified—as much here, indeed, under the circumstances, as I have been anywhere on my route—to witness this noble demonstration—made, not in honor of an individual, but of the man who at this time humbly, but earnestly, represents the majesty of the nation.
This reception, like all the others that have been tendered to me, doubtless emanates from all the political parties, and not from one alone. As such I accept it the more gratefully, since it indicates an earnest desire on the part of the whole people, with out regard to political differences, to save—not the country, because the country will save itself but to save the institutions of the country, those institutions under which, in the last three quarters of a century, we have grown to a great, and intelligent, and a happy people—the greatest, the most intelligent, and the happiest people in the world. These noble manifestations indicate, with unerring certainty, that the whole people are willing to make common cause for this object; that if, as it ever must be, some have been successful in the recent election and some have been beaten, if some are satisfied and some are dissatisfied, the defeated party are not in favor of sinking the ship, but are desirous of running it through the tempest in safety, and willing, if they think the people have committed an error in their verdict now, to wait in the hope of reversing it and setting it right next time. I do not say that in the recent election the people did the wisest thing, that could have been done—indeed, I do not think they did; but I do say that in accepting the great trust committed to me, which I do with a determination to endeavor to prove worthy of it, I must rely upon you, upon the people of the whole country, for support; and with their sustaining aid, even I, humble as I am, cannot fail to carry the ship of state safely through the storm.
I have now only to thank you warmly for your kind attendance, and bid you all an affectionate farewell.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I see that you are providing a platform for me. I shall have to decline standing upon it, because the president of the company tells me that I shall not have time to wait until it is brought to me. As I said yesterday, under similar circumstances at another gathering, you must not draw the inference that I have any intention of deserting any platform with which I have a legitimate connection because I do not stand on yours. Allow me to thank you for this splendid reception, and I now bid you farewell.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—I have but a moment to stand before you to listen to and return your kind greeting. I thank you for this reception, and for the pleasant manner in which it is tendered to me by our mutual friends. I will say in a single sentence, in regard to the difficulties that lie before me and our beloved country, that if I can only be as generously and unanimously sustained as the demonstrations I have witnessed indicate I shall be, I shall not fail; but without your sustaining hands I am sure that neither I nor any other man can hope to surmount these difficulties. I trust that in the course I shall pursue I shall be sustained not only by the party that elected me, but by the patriotic people of the whole country.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—I appear before you not to make a speech. I have not sufficient time, if I had the strength, to repeat speeches at every station where the people kindly gather to welcome me as we go along. If I had the strength, and should take the time, I should not get to Washington until after the inauguration, which you must be aware would not fit exactly. That such an untoward event might not transpire, I know you will readily forego any further remarks; and I close by bidding you farewell.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I have stepped before you merely in compliance with what appears to be your wish, and not with the purpose of making a speech. I do not propose making a speech this afternoon. I could not be heard by any but a small fraction of you, at best; but, what is still worse than that, I have nothing just now to say that is worthy of your hearing. I beg you to believe that I do not now refuse to address you from any disposition to disoblige you, but to the contrary. But, at the same time, I beg of you to excuse me for the present.
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND GENTLEMEN:—I am rather an old man to avail myself of such an excuse as I am now about to do. Yet the truth is so distinct, and presses itself so distinctly upon me, that I cannot well avoid it—and that is, that I did not understand when I was brought into this room that I was to be brought here to make a speech. It was not intimated to me that I was brought into the room where Daniel Webster and Henry Clay had made speeches, and where one in my position might be expected to do something like those men or say something worthy of myself or my audience. I therefore beg you to make allowance for the circumstances in which I have been by surprise brought before you. Now I have been in the habit of thinking and sometimes speaking upon political questions that have for some years past agitated the country; and, if I were disposed to do so, and we could take up some one of the issues, as the lawyers call them, and I were called upon to make an argument about it to the best of my ability, I could do so without much preparation. But that is not what you desire to have done here to-night.
I have been occupying a position, since the Presidential election, of silence—of avoiding public speaking, of avoiding public writing. I have been doing so because I thought, upon full consideration, that was the proper course for me to take. I am brought before you now, and required to make a speech, when you all approve more than anything else of the fact that I have been keeping silence. And now it seems to me that the response you give to that remark ought to justify me in closing just here. I have not kept silence since the Presidential election from any party wantonness, or from any indifference to the anxiety that pervades the minds of men about the aspect of the political affairs of this country. I have kept silence for the reason that I supposed it was peculiarly proper that I should do so until the time came when, according to the custom of the country, I could speak officially.
I still suppose that, while the political drama being enacted in this country at this time is rapidly shifting its scenes—forbidding an anticipation with any degree of certainty to-day of what we shall see to-morrow—it is peculiarly fitting that I should see it all, up to the last minute, before I should take ground that I might be disposed, by the shifting of the scenes afterward, also to shift. I have said several times upon this journey, and I now repeat it to you, that when the time does come, I shall then take the ground that I think is right—right for the North, for the South, for the East, for the West, for the whole country. And in doing so I hope to feel no necessity pressing upon me to say anything in conflict with the Constitution, in conflict with the continued union of these States, in conflict with the perpetuation of the liberties of this people, or anything in conflict with anything whatever that I have ever given you reason to expect from me. And now, my friends, have I said enough? [Loud cries of "No, no!" and, "Three cheers for LINCOLN!"] Now, my friends, there appears to be a difference of opinion between you and me, and I really feel called upon to decide the question myself.
Mr. MAYOR:—It is with feelings of deep gratitude that I make my acknowledgments for the reception that has been given me in the great commercial city of New York. I cannot but remember that it is done by the people who do not, by a large majority, agree with me in political sentiment. It is the more grateful to me because in this I see that for the great principles of our Government the people are pretty nearly or quite unanimous. In regard to the difficulties that confront us at this time, and of which you have seen fit to speak so becomingly and so justly, I can only say I agree with the sentiments expressed. In my devotion to the Union I hope I am behind no man in the nation. As to my wisdom in conducting affairs so as to tend to the preservation of the Union, I fear too great confidence may have been placed in me. I am sure I bring a heart devoted to the work. There is nothing that could ever bring me to consent—willingly to consent—to the destruction of this Union (in which not only the great city of New York, but the whole country, has acquired its greatness), unless it would be that thing for which the Union itself was made. I understand that the ship is made for the carrying and preservation of the cargo; and so long as the ship is safe with the cargo, it shall not be abandoned. This Union shall never be abandoned, unless the possibility of its existence shall cease to exist without the necessity of throwing passengers and cargo overboard. So long, then, as it is possible that the prosperity and liberties of this people can be preserved within this Union, it shall be my purpose at all tunes to preserve it. And now, Mr. Mayor, renewing my thanks for this cordial reception, allow me to come to a close.
MR. DAYTON AND GENTLEMEN OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY:—I shall only thank you briefly for this very kind reception given me, not personally, but as the temporary representative of the majesty of the nation. To the kindness of your hearts, and of the hearts of your brethren in your State, I should be very proud to respond, but I shall not have strength to address you or other assemblages at length, even if I had the time to do so. I appear before you, therefore, for little else than to greet you, and to briefly say farewell. You have done me the very high honor to present your reception courtesies to me through your great man a man with whom it is an honor to be associated anywhere, and in owning whom no State can be poor. He has said enough, and by the saying of it suggested enough, to require a response of an hour, well considered. I could not in an hour make a worthy response to it. I therefore, ladies and gentlemen of New Jersey, content myself with saying, most heartily do I indorse all the sentiments he has expressed. Allow me, most gratefully, to bid you farewell.
MR. MAYOR:—I thank you for this reception at the city of Newark. With regard to the great work of which you speak, I will say that I bring to it a heart filled with love for my country, and an honest desire to do what is right. I am sure, however, that I have not the ability to do anything unaided of God, and that without His support and that of this free, happy, prosperous, and intelligent people, no man can succeed in doing that the importance of which we all comprehend. Again thanking you for the reception you have given me, I will now bid you farewell, and proceed upon my journey.
I have been invited by your representatives to the Legislature to visit this the capital of your honored State, and in acknowledging their kind invitation, compelled to respond to the welcome of the presiding officers of each body, and I suppose they intended I should speak to you through them, as they are the representatives of all of you; and if I were to speak again here, I should only have to repeat in a great measure much that I have said, which would be disgusting to my friends around me who have met here. I have no speech to make, but merely appear to see you and let you look at me; and as to the latter I think I have greatly the best of the bargain. My friends, allow me to bid you farewell.
MR. PRESIDENT AND GENTLEMEN OF THE SENATE OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY:—I am very grateful to you for the honorable reception of which I have been the object. I cannot but remember the place that New Jersey holds in our early history. In the Revolutionary struggle few of the States among the Old Thirteen had more of the battle-fields of the country within their limits than New Jersey. May I be pardoned if, upon this occasion, I mention that away back in my childhood, the earliest days of my being able to read, I got hold of a small book, such a one as few of the younger members have ever seen Weems's Life of Washington. I remember all the accounts there given of the battle-fields and struggles for the liberties of the country; and none fixed themselves upon my imagination so deeply as the struggle here at Trenton, New Jersey. The crossing of the river, the contest with the Hessians, the great hardships endured at that time, all fixed themselves on my memory more than any single Revolutionary event; and you all know, for you have all been boys, how these early impressions last longer than any others. I recollect thinking then, boy even though I was, that there must have been something more than common that these men struggled for. I am exceedingly anxious that that thing that something even more than national independence, that something that held out a great promise to all the people of the world to all time to come—I am exceedingly anxious that this Union, the Constitution, and the liberties of the people shall be perpetuated in accordance with the original idea for which that struggle was made; and I shall be most happy indeed if I shall be a humble instrument in the hands of the Almighty, and of this his almost chosen people, for perpetuating the object of that great struggle. You give me this reception, as I understand, without distinction of party. I learn that this body is composed of a majority of gentlemen who, in the exercise of their best judgment in the choice of a chief magistrate, did not think I was the man. I understand, nevertheless, that they come forward here to greet me as the constitutionally elected President of the United States—as citizens of the United States to meet the man who, for the time being, is the representative of the majesty of the nation—united by the single purpose to perpetuate the Constitution, the union, and the liberties of the people. As such, I accept this reception more gratefully than I could do did I believe it were tendered to me as an individual.
MR. SPEAKER AND GENTLEMEN: I have just enjoyed the honor of a reception by the other branch of this Legislature, and I return to you and them my thanks for the reception which the people of New Jersey have given through their chosen representatives to me as the representative, for the time being, of the majesty of the people of the United States. I appropriate to myself very little of the demonstrations of respect with which I have been greeted. I think little should be given to any man, but that it should be a manifestation of adherence to the Union and the Constitution. I understand myself to be received here by the representatives of the people of New Jersey, a majority of whom differ in opinion from those with whom I have acted. This manifestation is therefore to be regarded by me as expressing their devotion to the Union, the Constitution, and the liberties of the people.
You, Mr. Speaker, have well said that this is a time when the bravest and wisest look with doubt and awe upon the aspect presented by our national affairs. Under these circumstances you will readily see why I should not speak in detail of the course I shall deem it best to pursue. It is proper that I should avail myself of all the information and all the time at my command, in order that when the time arrives in which I must speak officially, I shall be able to take the ground which I deem best and safest, and from which I may have no occasion to swerve. I shall endeavor to take the ground I deem most just to the North, the East, the West, the South, and the whole country. I shall take it, I hope, in good temper, certainly with no malice toward any section. I shall do all that may be in my power to promote a peaceful settlement of all our difficulties. The man does not live who is more devoted to peace than I am, none who would do more to preserve it, but it may be necessary to put the foot down firmly. And if I do my duty and do right, you will sustain me, will you not? [Loud cheers, and cries of "Yes, yes; we will."] Received as I am by the members of a Legislature the majority of whom do not agree with me in political sentiments, I trust that I may have their assistance in piloting the ship of state through this voyage, surrounded by perils as it is; for if it should suffer wreck now, there will be no pilot ever needed for another voyage.
Gentlemen, I have already spoken longer than I intended, and must beg leave to stop here.
MR. MAYOR AND FELLOW-CITIZENS OF PHILADELPHIA:—I appear before you to make no lengthy speech, but to thank you for this reception. The reception you have given me to-night is not to me, the man, the individual, but to the man who temporarily represents, or should represent, the majesty of the nation. It is true, as your worthy mayor has said, that there is great anxiety amongst the citizens of the United States at this time. I deem it a happy circumstance that this dissatisfied portion of our fellow-citizens does not point us to anything in which they are being injured or about to be injured; for which reason I have felt all the while justified in concluding that the crisis, the panic, the anxiety of the country at this time is artificial. If there be those who differ with me upon this subject, they have not pointed out the substantial difficulty that exists. I do not mean to say that an artificial panic may not do considerable harm; that it has done such I do not deny. The hope that has been expressed by your mayor, that I may be able to restore peace, harmony, and prosperity to the country, is most worthy of him; and most happy, indeed, will I be if I shall be able to verify and fulfil that hope. I promise you that I bring to the work a sincere heart. Whether I will bring a head equal to that heart will be for future times to determine. It were useless for me to speak of details of plans now; I shall speak officially next Monday week, if ever. If I should not speak then, it were useless for me to do so now. If I do speak then, it is useless for me to do so now. When I do speak, I shall take such ground as I deem best calculated to restore peace, harmony, and prosperity to the country, and tend to the perpetuity of the nation and the liberty of these States and these people. Your worthy mayor has expressed the wish, in which I join with him, that it were convenient for me to remain in your city long enough to consult your merchants and manufacturers; or, as it were, to listen to those breathings rising within the consecrated walls wherein the Constitution of the United States and, I will add, the Declaration of Independence, were originally framed and adopted. I assure you and your mayor that I had hoped on this occasion, and upon all occasions during my life, that I shall do nothing inconsistent with the teachings of these holy and most sacred walls. I have never asked anything that does not breathe from those walls. All my political warfare has been in favor of the teachings that come forth from these sacred walls. May my right hand forget its cunning and my tongue cleave to the roof of my mouth if ever I prove false to those teachings. Fellow-citizens, I have addressed you longer than I expected to do, and now allow me to bid you goodnight.
MR. CUYLER:—I am filled with deep emotion at finding myself standing here, in this place, where were collected together the wisdom, the devotion to principle, from which sprang the institutions under which we live. You have kindly suggested to me that in my hands is the task of restoring peace to the present distracted condition of the country. I can say in return, sir, that all the political sentiments I entertain have been drawn, so far as I have been able to draw them, from the sentiments which originated and were given to the world from this hall. I have never had a feeling politically that did not spring from the sentiments embodied in the Declaration of Independence. I have often pondered over the dangers which were incurred by the men who assembled here and framed and adopted that Declaration of Independence. I have pondered over the toils that were endured by the officers and soldiers of the army who achieved that independence. I have often inquired of myself what great principle or idea it was that kept the confederacy so long together. It was not the mere matter of separation of the colonies from the motherland, but that sentiment in the Declaration of Independence which gave liberty, not alone to the people of this country, but, I hope, to the world for all future time. It was that which gave promise that in due time the weight would be lifted from the shoulders of all men. This is the sentiment embodied in the Declaration of Independence. Now, my friends, can the country be saved upon that basis? If it can, I will consider myself one of the happiest men in the world if I can help to save it. If it cannot be saved upon that principle, it will be truly awful. But if this country cannot be saved without giving up that principle, I was about to say I would rather be assassinated on this spot than surrender it. Now, in my view of the present aspect of affairs, there need be no bloodshed or war. There is no necessity for it. I am not in favor of such a course, and I may say, in advance, that there will be no bloodshed unless it is forced upon the Government, and then it will be compelled to act in self-defence.
My friends; this is wholly an unexpected speech, and I did not expect to be called upon to say a word when I came here. I supposed it was merely to do something toward raising the flag. I may, therefore, have said something indiscreet. I have said nothing but what I am willing to live by and, if it be the pleasure of Almighty God, die by.
MR. CHAIRMAN:—I feel highly flattered by the encomiums you have seen fit to bestow upon me. Soon after the nomination of General Taylor, I attended a political meeting in the city of Wilmington, and have since carried with me a fond remembrance of the hospitalities of the city on that occasion. The programme established provides for my presence in Harrisburg in twenty-four hours from this time. I expect to be in Washington on Saturday. It is, therefore, an impossibility that I should accept your kind invitation. There are no people whom I would more gladly accommodate than those of Delaware; but circumstances forbid, gentlemen. With many regrets for the character of the reply I am compelled to give you, I bid you adieu.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN OF OLD LANCASTER:—I appear not to make a speech. I have not time to make a speech at length, and not strength to make them on every occasion; and, worse than all, I have none to make. There is plenty of matter to speak about in these times, but it is well known that the more a man speaks the less he is understood—the more he says one thing, the more his adversaries contend he meant something else. I shall soon have occasion to speak officially, and then I will endeavor to put my thoughts just as plain as I can express myself—true to the Constitution and Union of all the States, and to the perpetual liberty of all the people. Until I so speak, there is no need to enter upon details. In conclusion, I greet you most heartily, and bid you an affectionate farewell.
MR. SPEAKER OF THE SENATE, AND ALSO MR. SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES, AND GENTLEMEN OF THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF THE STATE OF PENNSYLVANIA:—I appear before you only for a very few brief remarks in response to what has been said to me. I thank you most sincerely for this reception, and the generous words in which support has been promised me upon this occasion. I thank your great commonwealth for the overwhelming support it recently gave, not me personally, but the cause which I think a just one, in the late election.
Allusion has been made to the fact—the interesting fact perhaps we should say—that I for the first time appear at the capital of the great commonwealth of Pennsylvania upon the birthday of the Father of his Country. In connection with that beloved anniversary connected with the history of this country, I have already gone through one exceedingly interesting scene this morning in the ceremonies at Philadelphia. Under the kind conduct of gentlemen there, I was for the first time allowed the privilege of standing in old Independence Hall to have a few words addressed to me there, and opening up to me an opportunity of manifesting my deep regret that I had not more time to express something of my own feelings excited by the occasion, that had been really the feelings of my whole life.
Besides this, our friends there had provided a magnificent flag of the country. They had arranged it so that I was given the honor of raising it to the head of its staff, and when it went up I was pleased that it went to its place by the strength of my own feeble arm. When, according to the arrangement, the cord was pulled, and it floated gloriously to the wind, without an accident, in the bright, glowing sunshine of the morning, I could not help hoping that there was in the entire success of that beautiful ceremony at least something of an omen of what is to come. Nor could I help feeling then, as I have often felt, that in the whole of that proceeding I was a very humbled instrument. I had not provided the flag; I had not made the arrangements for elevating it to its place; I had applied but a very small portion of even my feeble strength in raising it. In the whole transaction I was in the hands of the people who had arranged it, and if I can have the same generous co-operation of the people of this nation, I think the flag of our country may yet be kept flaunting gloriously.
I recur for a moment but to repeat some words uttered at the hotel in regard to what has been said about the military support which the General Government may expect from the commonwealth of Pennsylvania in a proper emergency. To guard against any possible mistake do I recur to this. It is not with any pleasure that I contemplate the possibility that a necessity may arise in this country for the use of the military arm. While I am exceedingly gratified to see the manifestation upon your streets of your military force here, and exceedingly gratified at your promise to use that force upon a proper emergency—while I make these acknowledgments I desire to repeat, in order to preclude any possible misconstruction, that I do most sincerely hope that we shall have no use for them; that it will never become their duty to shed blood, and most especially never to shed fraternal blood. I promise that so far as I may have wisdom to direct, if so painful a result shall in any wise be brought about, it shall be through no fault of mine.
Allusion has also been made by one of your honored speakers to some remarks recently made by myself at Pittsburg in regard to what is supposed to be the especial interest of this great commonwealth of Pennsylvania. I now wish only to say in regard to that matter, that the few remarks which I uttered on that occasion were rather carefully worded. I took pains that they should be so. I have seen no occasion since to add to them or subtract from them. I leave them precisely as they stand, adding only now that I am pleased to have an expression from you, gentlemen of Pennsylvania, signifying that they are satisfactory to you.
And now, gentlemen of the General Assembly of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, allow me again to return to you my most sincere thanks.
Mr. MAYOR:—I thank you, and through you the municipal authorities of this city who accompany you, for this welcome. And as it is the first time in my life, since the present phase of politics has presented itself in this country, that I have said anything publicly within a region of country where the institution of slavery exists, I will take this occasion to say that I think very much of the ill feeling that has existed and still exists between the people in the section from which I came and the people here, is dependent upon a misunderstanding of one another. I therefore avail myself of this opportunity to assure you, Mr. Mayor, and all the gentlemen present, that I have not now, and never have had, any other than as kindly feelings toward you as to the people of my own section. I have not now, and never have had, any disposition to treat you in any respect otherwise than as my own neighbors. I have not now any purpose to withhold from you any of the benefits of the Constitution, under any circumstances, that I would not feel myself constrained to withhold from my own neighbors; and I hope, in a word, that when we shall become better acquainted—and I say it with great confidence—we shall like each other better. I thank you for the kindness of this reception.
MY FRIENDS:—I suppose that I may take this as a compliment paid to me, and as such please accept my thanks for it. I have reached this city of Washington under circumstances considerably differing from those under which any other man has ever reached it. I am here for the purpose of taking an official position amongst the people, almost all of whom were politically opposed to me, and are yet opposed to me, as I suppose.
I propose no lengthy address to you. I only propose to say, as I did on yesterday, when your worthy mayor and board of aldermen called upon me, that I thought much of the ill feeling that has existed between you and the people of your surroundings and that people from among whom I came, has depended, and now depends, upon a misunderstanding.
I hope that, if things shall go along as prosperously as I believe we all desire they may, I may have it in my power to remove something of this misunderstanding; that I may be enabled to convince you, and the people of your section of the country, that we regard you as in all things our equals, and in all things entitled to the same respect and the same treatment that we claim for ourselves; that we are in no wise disposed, if it were in our power, to oppress you, to deprive you of any of your rights under the Constitution of the United States, or even narrowly to split hairs with you in regard to these rights, but are determined to give you, as far as lies in our hands, all your rights under the Constitution—not grudgingly, but fully and fairly. I hope that, by thus dealing with you, we will become better acquainted, and be better friends.
And now, my friends, with these few remarks, and again returning my thanks for this compliment, and expressing my desire to hear a little more of your good music, I bid you good-night.
[During the struggle over the appointments of LINCOLN's Cabinet, the President-elect spoke as follows:]
Gentlemen, it is evident that some one must take the responsibility of these appointments, and I will do it. My Cabinet is completed. The positions are not definitely assigned, and will not be until I announce them privately to the gentlemen whom I have selected as my Constitutional advisers.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE UNITED STATES:—In compliance with a custom as old as the Government itself, I appear before you to address you briefly, and to take in your presence the oath prescribed by the Constitution of the United States to be taken by the President "before he enters on the execution of his office."
I do not consider it necessary at present for me to discuss those matters of administration about which there is no special anxiety or excitement.
Apprehension seems to exist among the people of the Southern States that by the accession of a Republican administration their property and their peace and personal security are to be endangered. There has never been any reasonable cause for such apprehension. Indeed, the most ample evidence to the contrary has all the while existed and been open to their inspection. It is found in nearly all the published speeches of him who now addresses you. I do but quote from one of those speeches when I declare that
"I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so."
Those who nominated and elected me did so with full knowledge that I had made this and many similar declarations, and had never recanted them. And, more than this, they placed in the platform for my acceptance, and as a law to themselves and to me, the clear and emphatic resolution which I now read:
"Resolved, That the maintenance inviolate of the rights of the States, and especially the right of each State to order and control its own domestic institutions according to its own judgment exclusively, is essential to that balance of power on which the perfection and endurance of our political fabric depend, and we denounce the lawless invasion by armed force of the soil of any State or Territory, no matter under what pretext, as amongst the gravest of crimes."
I now reiterate these sentiments; and, in doing so, I only press upon the public attention the most conclusive evidence of which the case is susceptible, that the property, peace, and security of no section are to be in any wise endangered by the now incoming administration. I add, too, that all the protection which, consistently with the Constitution and the laws, can be given, will be cheerfully given to all the States when lawfully demanded, for whatever cause—as cheerfully to one section as to another.
There is much controversy about the delivering up of fugitives from service or labor. The clause I now read is as plainly written in the Constitution as any other of its provisions:
"No person held to service or labor in one State, under the laws thereof, escaping into another, shall in consequence of any law or regulation therein be discharged from such service or labor, but shall be delivered up on claim of the party to whom such service or labor may be due."
It is scarcely questioned that this provision was intended by those who made it for the reclaiming of what we call fugitive slaves; and the intention of the lawgiver is the law. All members of Congress swear their support to the whole Constitution—to this provision as much as to any other. To the proposition, then, that slaves whose cases come within the terms of this clause "shall be delivered up," their oaths are unanimous. Now, if they would make the effort in good temper, could they not with nearly equal unanimity frame and pass a law by means of which to keep good that unanimous oath?
There is some difference of opinion whether this clause should be enforced by national or by State authority; but surely that difference is not a very material one. If the slave is to be surrendered, it can be of but little consequence to him or to others by which authority it is done. And should any one in any case be content that his oath shall go unkept on a merely unsubstantial controversy as to how it shall be kept?
Again, in any law upon this subject, ought not all the safeguards of liberty known in civilized and humane jurisprudence to be introduced, so that a free man be not, in any case, surrendered as a slave? And might it not be well at the same time to provide by law for the enforcement of that clause in the Constitution which guarantees that "the citizens of each State shall be entitled to all privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States"?
I take the official oath to-day with no mental reservations, and with no purpose to construe the Constitution or laws by any hypercritical rules. And, while I do not choose now to specify particular acts of Congress as proper to be enforced, I do suggest that it will be much safer for all, both in official and private stations, to conform to and abide by all those acts which stand unrepealed, than to violate any of them, trusting to find impunity in having them held to be unconstitutional.
It is seventy-two years since the first inauguration of a President under our national Constitution. During that period fifteen different and greatly distinguished citizens have, in succession, administered the executive branch of the Government. They have conducted it through many perils, and generally with great success. Yet, with all this scope of precedent, I now enter upon the same task for the brief constitutional term of four years under great and peculiar difficulty. A disruption of the Federal Union, heretofore only menaced, is now formidably attempted.
I hold that, in contemplation of universal law and of the Constitution, the Union of these States is perpetual. Perpetuity is implied, if not expressed, in the fundamental law of all national governments. It is safe to assert that no government proper ever had a provision in its organic law for its own termination. Continue to execute all the express provisions of our national Constitution, and the Union will endure forever—it being impossible to destroy it except by some action not provided for in the instrument itself.
Again, if the United States be not a government proper, but an association of States in the nature of contract merely, can it as a contract be peaceably unmade by less than all the parties who made it? One party to a contract may violate it—break it, so to speak; but does it not require all to lawfully rescind it?
Descending from these general principles, we find the proposition that in legal contemplation the Union is perpetual confirmed by the history of the Union itself. The Union is much older than the Constitution. It was formed, in fact, by the Articles of Association in 1774. It was matured and continued by the Declaration of Independence in 1776. It was further matured, and the faith of all the then thirteen States expressly plighted and engaged that it should be perpetual, by the Articles of Confederation in 1778. And, finally, in 1787 one of the declared objects for ordaining and establishing the Constitution was "to form a more perfect Union."
But if the destruction of the Union by one or by a part only of the States be lawfully possible, the Union is less perfect than before the Constitution, having lost the vital element of perpetuity.
It follows from these views that no State upon its own mere motion can lawfully get out of the Union; that resolves and ordinances to that effect are legally void; and that acts of violence, within any State or States, against the authority of the United States, are insurrectionary or revolutionary, according to circumstances.
I therefore consider that, in view of the Constitution and the laws, the Union is unbroken; and to the extent of my ability I shall take care, as the Constitution itself expressly enjoins upon me, that the laws of the Union be faithfully executed in all the States. Doing this I deem to be only a simple duty on my part; and I shall perform it so far as practicable, unless my rightful masters, the American people, shall withhold the requisite means, or in some authoritative manner direct the contrary. I trust this will not be regarded as a menace, but only as the declared purpose of the Union that it will constitutionally defend and maintain itself.
In doing this there needs to be no bloodshed or violence; and there shall be none, unless it be forced upon the national authority. The power confided to me will be used to hold, occupy, and possess the property and places belonging to the Government, and to collect the duties and imposts; but beyond what may be necessary for these objects, there will be no invasion, no using of force against or among the people anywhere. Where hostility to the United States, in any interior locality, shall be so great and universal as to prevent competent resident citizens from holding the Federal offices, there will be no attempt to force obnoxious strangers among the people for that object. While the strict legal right may exist in the government to enforce the exercise of these offices, the attempt to do so would be so irritating, and so nearly impracticable withal, that I deem it better to forego for the time the uses of such offices.
The mails, unless repelled, will continue to be furnished in all parts of the Union. So far as possible, the people everywhere shall have that sense of perfect security which is most favorable to calm thought and reflection. The course here indicated will be followed unless current events and experience shall show a modification or change to be proper, and in every case and exigency my best discretion will be exercised according to circumstances actually existing, and with a view and a hope of a peaceful solution of the national troubles and the restoration of fraternal sympathies and affections.
That there are persons in one section or another who seek to destroy the Union at all events, and are glad of any pretext to do it, I will neither affirm nor deny; but if there be such, I need address no word to them. To those, however, who really love the Union may I not speak?
Before entering upon so grave a matter as the destruction of our national fabric, with all its benefits, its memories, and its hopes, would it not be wise to ascertain precisely why we do it? Will you hazard so desperate a step while there is any possibility that any portion of the ills you fly from have no real existence? Will you, while the certain ills you fly to are greater than all the real ones you fly from—will you risk the commission of so fearful a mistake?
All profess to be content in the Union if all constitutional rights can be maintained. Is it true, then, that any right, plainly written in the Constitution, has been denied? I think not. Happily the human mind is so constituted that no party can reach to the audacity of doing this. Think, if you can, of a single instance in which a plainly written provision of the Constitution has ever been denied. If by the mere force of numbers a majority should deprive a minority of any clearly written constitutional right, it might, in a moral point of view, justify revolution—certainly would if such a right were a vital one. But such is not our case. All the vital rights of minorities and of individuals are so plainly assured to them by affirmations and negations, guaranties and prohibitions, in the Constitution, that controversies never arise concerning them. But no organic law can ever be framed with a provision specifically applicable to every question which may occur in practical administration. No foresight can anticipate, nor any document of reasonable length contain, express provisions for all possible questions. Shall fugitives from labor be surrendered by national or by State authority? The Constitution does not expressly say. May Congress prohibit slavery in the Territories? The Constitution does not expressly say. Must Congress protect slavery in the Territories? The Constitution does not expressly say.
From questions of this class spring all our constitutional controversies, and we divide upon them into majorities and minorities. If the minority will not acquiesce, the majority must, or the Government must cease. There is no other alternative; for continuing the Government is acquiescence on one side or the other.
If a minority in such case will secede rather than acquiesce, they make a precedent which in turn will divide and ruin them; for a minority of their own will secede from them whenever a majority refuses to be controlled by such minority. For instance, why may not any portion of a new confederacy a year or two hence arbitrarily secede again, precisely as portions of the present Union now claim to secede from it? All who cherish disunion sentiments are now being educated to the exact temper of doing this.
Is there such perfect identity of interests among the States to compose a new Union as to produce harmony only, and prevent renewed secession?
Plainly, the central idea of secession is the essence of anarchy. A majority held in restraint by constitutional checks and limitations, and always changing easily with deliberate changes of popular opinions and sentiments, is the only true sovereign of a free people. Whoever rejects it does, of necessity, fly to anarchy or to despotism. Unanimity is impossible; the rule of a minority, as a permanent arrangement, is wholly inadmissible; so that, rejecting the majority principle, anarchy or despotism in some form is all that is left.
I do not forget the position assumed by some, that constitutional questions are to be decided by the Supreme Court; nor do I deny that such decisions must be binding, in any case, upon the parties to a suit, as to the object of that suit, while they are also entitled to very high respect and consideration in all parallel cases by all other departments of the government. And, while it is obviously possible that such decision may be erroneous in any given case, still the evil effect following it, being limited to that particular case, with the chance that it may be overruled and never become a precedent for other cases, can better be borne than could the evils of a different practice. At the same time, the candid citizen must confess that if the policy of the government, upon vital questions affecting the whole people, is to be irrevocably fixed by decisions of the Supreme Court, the instant they are made, in ordinary litigation between parties in personal actions, the people will have ceased to be their own rulers, having to that extent practically resigned the government into the hands of that eminent tribunal. Nor is there in this view any assault upon the court or the judges. It is a duty from which they may not shrink to decide cases properly brought before them, and it is no fault of theirs if others seek to turn their decisions to political purposes.
One section of our country believes slavery is right, and ought to be extended, while the other believes it is wrong, and ought not to be extended. This is the only substantial dispute. The fugitive slave clause of the Constitution and the law for the suppression of the foreign slave trade are each as well enforced, perhaps, as any law can ever be in a community where the moral sense of the people imperfectly supports the law itself. The great body of the people abide by the dry legal obligation in both cases, and a few break over in each. This, I think, cannot be perfectly cured; and it would be worse in both cases after the separation of the sections than before. The foreign slave trade, now imperfectly suppressed, would be ultimately revived, without restriction, in one section, while fugitive slaves, now only partially surrendered, would not be surrendered at all by the other.
Physically speaking, we cannot separate. We cannot remove our respective sections from each other, nor build an impassable wall between them. A husband and wife may be divorced and go out of the presence and beyond the reach of each other; but the different parts of our country cannot do this. They cannot but remain face to face, and intercourse, either amicable or hostile, must continue between them. Is it possible, then, to make that intercourse more advantageous or more satisfactory after separation than before? Can aliens make treaties easier than friends can make laws? Can treaties be more faithfully enforced between aliens than laws can among friends? Suppose you go to war, you cannot fight always; and when, after much loss on both sides, and no gain on either, you cease fighting, the identical old questions as to terms of intercourse are again upon you.
This country, with its institutions, belongs to the people who inhabit it. Whenever they shall grow weary of the existing government, they can exercise their constitutional right of amending it, or their revolutionary right to dismember or overthrow it. I cannot be ignorant of the fact that many worthy and patriotic citizens are desirous of having the national Constitution amended. While I make no recommendation of amendments, I fully recognize the rightful authority of the people over the whole subject, to be exercised in either of the modes prescribed in the instrument itself, and I should, under existing circumstances, favor rather than oppose a fair opportunity being afforded the people to act upon it. I will venture to add that to me the convention mode seems preferable, in that it allows amendments to originate with the people themselves, instead of only permitting them to take or reject propositions originated by others not especially chosen for the purpose, and which might not be precisely such as they would wish to either accept or refuse. I understand a proposed amendment to the Constitution which amendment, however, I have not seen—has passed Congress, to the effect that the Federal Government shall never interfere with the domestic institutions of the States, including that of persons held to service. To avoid misconstruction of what I have said, I depart from my purpose not to speak of particular amendments so far as to say that, holding such a provision to now be implied constitutional law, I have no objection to its being made express and irrevocable.
The chief magistrate derives all his authority from the people, and they have conferred none upon him to fix terms for the separation of the States. The people themselves can do this also if they choose; but the executive, as such, has nothing to do with it. His duty is to administer the present government, as it came to his hands, and to transmit it, unimpaired by him, to his successors.
Why should there not be a patient confidence in the ultimate justice of the people? Is there any better or equal hope in the world? In our present differences is either party without faith of being in the right? If the Almighty Ruler of nations, with his eternal truth and justice, be on your side of the North, or on yours of the South, that truth and that justice will surely prevail by the judgment of this great tribunal of the American people.
By the frame of the government under which we live, this same people have wisely given their public servants but little power for mischief; and have, with equal wisdom, provided for the return of that little to their own hands at very short intervals. While the people retain their virtue and vigilance, no administration, by any extreme of wickedness or folly, can very seriously injure the government in the short space of four years.
My countrymen, one and all, think calmly and well upon this whole subject. Nothing valuable can be lost by taking time. If there be an object to hurry any of you in hot haste to a step which you would never take deliberately, that object will be frustrated by taking time; but no good object can be frustrated by it. Such of you as are now dissatisfied still have the old Constitution unimpaired, and, on the sensitive point, the laws of your own framing under it; while the new administration will have no immediate power, if it would, to change either. If it were admitted that you who are dissatisfied hold the right side in the dispute, there still is no single good reason for precipitate action. Intelligence, patriotism, Christianity, and a firm reliance on Him who has never yet forsaken this favored land, are still competent to adjust in the best way all our present difficulty.
In your hands, my dissatisfied fellow-countrymen, and not in mine, is the momentous issue of civil war. The government will not assail you. You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors. You have no oath registered in heaven to destroy the government, while I shall have the most solemn one to "preserve, protect, and defend" it.
I am loath to close. We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies. Though passion may have strained, it must not break, our bonds of affection. The mystic chords of memory, stretching from every battle-field and patriot grave to every living heart and hearthstone all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, March 4, 1861.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your note of the 2d instant, asking to withdraw your acceptance of my invitation to take charge of the State Department, was duly received. It is the subject of the most painful solicitude with me, and I feel constrained to beg that you will countermand the withdrawal. The public interest, I think, demands that you should; and my personal feelings are deeply enlisted in the same direction. Please consider and answer by 9 A.M. to-morrow.
Your obedient servant,
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND GENTLEMEN OF THE PENNSYLVANIAN DELEGATION:—As I have so frequently said heretofore, when I have had occasion to address the people of the Keystone, in my visits to that State, I can now but repeat the assurance of my gratification at the support you gave me at the election, and at the promise of a continuation of that support which is now tendered to me.
Allusion has been made to the hope that you entertain that you have a President and a government. In respect to that I wish to say to you that in the position I have assumed I wish to do more than I have ever given reason to believe I would do. I do not wish you to believe that I assume to be any better than others who have gone before me. I prefer rather to have it understood that if we ever have a government on the principles we profess, we should remember, while we exercise our opinion, that others have also rights to the exercise of their opinions, and that we should endeavor to allow these rights, and act in such a manner as to create no bad feeling. I hope we have a government and a President. I hope, and wish it to be understood, that there may be no allusion to unpleasant differences.
We must remember that the people of all the States are entitled to all the privileges and immunities of the citizens of the several States. We should bear this in mind, and act in such a way as to say nothing insulting or irritating. I would inculcate this idea, so that we may not, like Pharisees, set ourselves up to be better than other people.
Now, my friends, my public duties are pressing to-day, and will prevent my giving more time to you. Indeed, I should not have left them now, but I could not well deny myself to so large and respectable a body.
I am thankful for this renewed assurance of kind feeling and confidence, and the support of the old Bay State, in so far as you, Mr. Chairman, have expressed, in behalf of those whom you represent, your sanction of what I have enunciated in my inaugural address. This is very grateful to my feelings. The object was one of great delicacy, in presenting views at the opening of an administration under the peculiar circumstances attending my entrance upon the official duties connected with the Government. I studied all the points with great anxiety, and presented them with whatever of ability and sense of justice I could bring to bear. If it met the approbation of our good friends in Massachusetts, I shall be exceedingly gratified, while I hope it will meet the approbation of friends everywhere. I am thankful for the expressions of those who have voted with us; and like every other man of you, I like them as certainly as I do others. As the President in the administration of the Government, I hope to be man enough not to know one citizen of the United States from another, nor one section from another. I shall be gratified to have good friends of Massachusetts and others who have thus far supported me in these national views still to support me in carrying them out.
MY DEAR SIR:—Herewith is the diplomatic address and my reply. To whom the reply should be addressed—that is, by what title or style—I do not quite understand, and therefore I have left it blank.
Will you please bring with you to-day the message from the War Department, with General Scott's note upon it, which we had here yesterday? I wish to examine the General's opinion, which I have not yet done.
Yours very truly
Mr. FIGANIERE AND GENTLEMEN OF THE DIPLOMATIC BODY:—Please accept my sincere thanks for your kind congratulations. It affords me pleasure to confirm the confidence you so generously express in the friendly disposition of the United States, through me, towards the sovereigns and governments you respectively represent. With equal satisfaction I accept the assurance you are pleased to give, that the same disposition is reciprocated by your sovereigns, your governments, and yourselves.
Allow me to express the hope that these friendly relations may remain undisturbed, and also my fervent wishes for the health and happiness of yourselves personally.
HON. SECRETARY OF STATE. DEAR SIR:—What think you of sending ministers at once as follows: Dayton to England; Fremont to France; Clay to Spain; Corwin to Mexico?
We need to have these points guarded as strongly and quickly as possible. This is suggestion merely, and not dictation.
Your obedient servant,
HON. JACOB COLLAMER. MY DEAR SIR:—God help me. It is said I have offended you. I hope you will tell me how.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
March 14, 1861. DEAR SIR:—I am entirely unconscious that you have any way offended me. I cherish no sentiment towards you but that of kindness and confidence. Your humble servant, J. COLLAMER.
[Returned with indorsement:]
Very glad to know that I have n't.
HON. P. M. G.
DEAR SIR:—The bearer of this, Mr. C. T. Hempstow, is a Virginian who wishes to get, for his son, a small place in your Dept. I think Virginia should be heard, in such cases.
THE HONORABLE SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—Assuming it to be possible to now provision Fort Sumter, under all the circumstances is it wise to attempt it? Please give me your opinion in writing on this question.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
[Same to other members of the Cabinet.]
The Senate has transmitted to me a copy of the message sent by my predecessor to that body on the 21st of February last, proposing to take its advice on the subject of a proposition made by the British Government through its minister here to refer the matter in controversy between that government and the Government of the United States to the arbitrament of the King of Sweden and Norway, the King of the Netherlands, or the Republic of the Swiss Confederation.
In that message my predecessor stated that he wished to present to the Senate the precise questions following, namely:
"Will the Senate approve a treaty referring to either of the sovereign powers above named the dispute now existing between the governments of the United States and Great Britain concerning the boundary line between Vancouver's Island and the American continent? In case the referee shall find himself unable to decide where the line is by the description of it in the treaty of June 15, 1846, shall he be authorized to establish a line according to the treaty as nearly as possible? Which of the three powers named by Great Britain as an arbiter shall be chosen by the United States?"
I find no reason to disapprove of the course of my predecessor in this important matter; but, on the contrary, I not only shall receive the advice of the Senate thereon cheerfully, but I respectfully ask the Senate for their advice on the three questions before recited.
ABRAHAM LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, March 16, 1861
EXECUTIVE MANSION, MARCH 18, 1861 HON. SECRETARY OF STATE.
MY DEAR SIR:—I believe it is a necessity with us to make the appointments I mentioned last night—that is, Charles F. Adams to England, William L. Dayton to France, George P. Marsh to Sardinia, and Anson Burlingame to Austria. These gentlemen all have my highest esteem, but no one of them is originally suggested by me except Mr. Dayton. Mr. Adams I take because you suggested him, coupled with his eminent fitness for the place. Mr. Marsh and Mr. Burlingame I take because of the intense pressure of their respective States, and their fitness also.
The objection to this card is that locally they are so huddled up—three being in New England and two from a single State. I have considered this, and will not shrink from the responsibility. This, being done, leaves but five full missions undisposed of—Rome, China, Brazil, Peru, and Chili. And then what about Carl Schurz; or, in other words, what about our German friends?
Shall we put the card through, and arrange the rest afterward? What say you?
Your obedient servant,
TO MASTER GEO. EVANS PATTEN.
WHOM IT MAY CONCERN:—I did see and talk with Master Geo. Evans Patten last May at Springfield, Ill.
Respectfully,
A. LINCOLN.
[Written because of a denial that any interview with young Patten, then a schoolboy, had ever taken place.]
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:—I have received a copy of the resolution of the Senate, passed on the 25th instant, requesting me, if in my opinion not incompatible with the public interest, to communicate to the Senate the despatches of Major Robert Anderson to the War Department during the time he has been in command of Fort Sumter. On examination of the correspondence thus called for, I have, with the highest respect for the Senate, come to the conclusion that at the present moment the publication of it would be inexpedient.
A. LINCOLN WASHINGTON, MARCH 16, 1861
EXECUTIVE MANSION, MARCH 29, 1861 HONORABLE SECRETARY OF WAR.
SIR:—I desire that an expedition to move by sea be got ready to sail as early as the 6th of April next, the whole according to memorandum attached, and that you cooperate with the Secretary of the Navy for that object.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
[Inclosure.]
Steamers Pocahontas at Norfolk, Paunee at Washington, Harriet Lane at New York, to be under sailing orders for sea, with stores, etc., for one month. Three hundred men to be kept ready for departure from on board the receiving-ships at New York. Two hundred men to be ready to leave Governor's Island in New York. Supplies for twelve months for one hundred men to be put in portable shape, ready for instant shipping. A large steamer and three tugs conditionally engaged.
DEAR STUART:
Cousin Lizzie shows me your letter of the 27th. The question of giving her the Springfield post-office troubles me. You see I have already appointed William Jayne a Territorial governor and Judge Trumbull's brother to a land-office. Will it do for me to go on and justify the declaration that Trumbull and I have divided out all the offices among our relatives? Dr. Wallace, you know, is needy, and looks to me; and I personally owe him much.
I see by the papers, a vote is to be taken as to the post-office. Could you not set up Lizzie and beat them all? She, being here, need know nothing of it, so therefore there would be no indelicacy on her part.
Yours as ever,
TO THE COMMANDANT OF THE NAVY-YARD, Brooklyn, N. Y.
Fit out the Powhatan to go to sea at the earnest possible moment under sealed orders. Orders by a confidential messenger go forward to-morrow.
LIEUTENANT D. D. PORTER, United States Navy.
SIR:—You will proceed to New York, and with the least possible delay, assuming command of any naval steamer available, proceed to Pensacola Harbor, and at any cost or risk prevent any expedition from the mainland reaching Fort Pickens or Santa Rosa Island.
You will exhibit this order to any naval officer at Pensacola, if you deem it necessary, after you have established yourself within the harbor, and will request co-operation by the entrance of at least one other steamer.
This order, its object, and your destination will be communicated to no person whatever until you reach the harbor of Pensacola.
A. LINCOLN.
Recommended, WILLIAM H. SEWARD.
WASHINGTON, EXECUTIVE MANSION, April 1, 1861.
All officers of the army and navy to whom this order may be exhibited will aid by every means in their power the expedition under the command of Colonel Harvey Brown, supplying him with men and material, and co-operating with him as he may desire.
WASHINGTON CITY, April 1, 1861
SIR:—Circumstances render it necessary to place in command of your ship (and for a special purpose) an officer who is fully informed and instructed in relation to the wishes of the Government, and you will therefore consider yourself detached. But in taking this step the Government does not in the least reflect upon your efficiency or patriotism; on the contrary, have the fullest confidence in your ability to perform any duty required of you. Hoping soon to be able to give you a better command than the one you now enjoy, and trusting that you will have full confidence in the disposition of the Government toward you, I remain, etc.,
Some thoughts for the President's Consideration,
First. We are at the end of a month's administration, and yet without a policy either domestic or foreign.
Second. This, however, is not culpable, and it has even been unavoidable. The presence of the Senate, with the need to meet applications for patronage, have prevented attention to other and more grave matters.
Third. But further delay to adopt and prosecute our policies for both domestic and foreign affairs would not only bring scandal on the administration, but danger upon the country.
Fourth. To do this we must dismiss the applicants for office. But how? I suggest that we make the local appointments forthwith, leaving foreign or general ones for ulterior and occasional action.
Fifth. The policy at home. I am aware that my views are singular, and perhaps not sufficiently explained. My system is built upon this idea as a ruling one, namely, that we must CHANGE THE QUESTION BEFORE THE PUBLIC FROM ONE UPON SLAVERY, OR ABOUT SLAVERY, for a question upon UNION OR DISUNION: In other words, from what would be regarded as a party question, to one of patriotism or union.
The occupation or evacuation of Fort Sumter, although not in fact a slavery or a party question, is so regarded. Witness the temper manifested by the Republicans in the free States, and even by the Union men in the South.
I would therefore terminate it as a safe means for changing the issue. I deem it fortunate that the last administration created the necessity.
For the rest, I would simultaneously defend and reinforce all the ports in the gulf, and have the navy recalled from foreign stations to be prepared for a blockade. Put the island of Key West under martial law.
This will raise distinctly the question of union or disunion. I would maintain every fort and possession in the South.
FOR FOREIGN NATIONS,
I would demand explanations from Spain and France, categorically, at once.
I would seek explanations from Great Britain and Russia, and send agents into Canada, Mexico, and Central America to rouse a vigorous continental spirit of independence on this continent against European intervention.
And, if satisfactory explanations are not received from Spain and France,
Would convene Congress and declare war against them.
But whatever policy we adopt, there must be an energetic prosecution of it.
For this purpose it must be somebody's business to pursue and direct it incessantly.
Either the President must do it himself, and be all the while active in it, or Devolve it on some member of his Cabinet. Once adopted, debates on it must end, and all agree and abide.
It is not in my especial province; But I neither seek to evade nor assume responsibility.
HON. W. H. SEWARD.
MY DEAR SIR:—Since parting with you I have been considering your paper dated this day, and entitled "Some Thoughts for the President's Consideration." The first proposition in it is, "First, We are at the end of a month's administration, and yet without a policy either domestic or foreign."
At the beginning of that month, in the inaugural, I said: "The power confided to me will be used to hold, occupy, and possess the property and places belonging to the Government, and to Collect the duties and imposts." This had your distinct approval at the time; and, taken in connection with the order I immediately gave General Scott, directing him to employ every means in his power to strengthen and hold the forts, comprises the exact domestic policy you now urge, with the single exception that it does not propose to abandon Fort Sumter.
Again, I do not perceive how the reinforcement of Fort Sumter would be done on a slavery or a party issue, while that of Fort Pickens would be on a more national and patriotic one.
The news received yesterday in regard to St. Domingo certainly brings a new item within the range of our foreign policy; but up to that time we have been preparing circulars and instructions to ministers and the like, all in perfect harmony, without even a suggestion that we had no foreign policy.
Upon your Closing propositions—that,
"Whatever policy we adopt, there must be an energetic prosecution of it.
"For this purpose it must be somebody's business to pursue and direct it incessantly.
"Either the President must do it himself, and be all the while active in it, or,
"Devolve it on some member of his Cabinet. Once adopted, debates on it must end, and all agree and abide"—
I remark that if this must be done, I must do it. When a general line of policy is adopted, I apprehend there is no danger of its being changed without good reason, or continuing to be a subject of unnecessary debate; still, upon points arising in its progress I wish, and suppose I am entitled to have, the advice of all the Cabinet.
Your obedient servant,
HON. WILLIAM BALLARD PRESTON, ALEXANDER H. H. STUART, GEORGE W. RANDOLPH, Esq.
GENTLEMEN:—As a committee of the Virginia Convention now in Session, you present me a preamble and resolution in these words:
"Whereas, in the opinion of this Convention, the uncertainty which prevails in the public mind as to the policy which the Federal Executive intends to pursue toward the seceded States is extremely injurious to the industrial and commercial interests of the country, tends to keep up an excitement which is unfavorable to the adjustment of pending difficulties, and threatens a disturbance of the public peace: therefore
"Resolved, that a committee of three delegates be appointed by this Convention to wait upon the President of the United States, present to him this preamble and resolution, and respectfully ask him to communicate to this Convention the policy which the Federal Executive intends to pursue in regard to the Confederate States.
"Adopted by the Convention of the State of Virginia, Richmond, April 8, 1861."
In answer I have to say that, having at the beginning of my official term expressed my intended policy as plainly as I was able, it is with deep regret and some mortification I now learn that there is great and injurious uncertainty in the public mind as to what that policy is, and what course I intend to pursue. Not having as yet seen occasion to change, it is now my purpose to pursue the course marked out in the inaugural address. I commend a careful consideration of the whole document as the best expression I can give of my purposes.
As I then and therein said, I now repeat: "The power confided to me will be used to hold, occupy, and possess the property and places belonging to the Government, and to collect the duties and imposts; but beyond what is necessary for these objects, there will be no invasion, no using of force against or among the people anywhere." By the words "property and places belonging to the Government," I chiefly allude to the military posts and property which were in the possession of the Government when it came to my hands.
But if, as now appears to be true, in pursuit of a purpose to drive the United States authority from these places, an unprovoked assault has been made upon Fort Sumter, I shall hold myself at liberty to repossess, if I can, like places which had been seized before the Government was devolved upon me. And in every event I shall, to the extent of my ability, repel force by force. In case it proves true that Fort Sumter has been assaulted, as is reported, I shall perhaps cause the United States mails to be withdrawn from all the States which claim to have seceded, believing that the commencement of actual war against the Government justifies and possibly demands this.
I scarcely need to say that I consider the military posts and property situated within the States which claim to have seceded as yet belonging to the Government of the United States as much as they did before the supposed secession.
Whatever else I may do for the purpose, I shall not attempt to collect the duties and imposts by any armed invasion of any part of the country; not meaning by this, however, that I may not land a force deemed necessary to relieve a fort upon a border of the country.
From the fact that I have quoted a part of the inaugural address, it must not be inferred that I repudiate any other part, the whole of which I reaffirm, except so far as what I now say of the mails may be regarded as a modification.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas the laws of the United States have been for some time past and now are opposed, and the execution thereof obstructed, in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas, by combinations too powerful to be suppressed by the ordinary course of judicial proceedings, or by the powers vested in the marshals bylaw:
Now, therefore, I, A. LINCOLN, President of the United States, in virtue of the power in me vested by the Constitution and the laws, have thought fit to call forth, and hereby do call forth, the militia of the several States of the Union, to the aggregate number of seventy-five thousand, in order to suppress said combinations, and to cause the laws to be duly executed.
The details for this object will be immediately communicated to the State authorities through the War Department.
I appeal to all loyal citizens to favor, facilitate, and aid this effort to maintain the honor, the integrity, and the existence of our National Union, and the perpetuity of popular government; and to redress wrongs already long enough endured.
I deem it proper to say that the first service assigned to the forces hereby called forth will probably be to repossess the forts, places, and property which have been seized from the Union; and in every event the utmost care will be observed, consistently with the objects aforesaid, to avoid any devastation, any destruction of or interference with property, or any disturbance of peaceful citizens in any part of the country.
And I hereby command the persons composing the combinations aforesaid to disperse and retire peacefully to their respective abodes within twenty days from date.
Deeming that the present condition of public affairs presents an extraordinary occasion, I do hereby, in virtue of the power in me vested by the Constitution, convene both Houses of Congress. Senators and Representatives are therefore summoned to assemble at their respective chambers, at twelve o'clock noon, on Thursday, the fourth day of July next, then and there to consider and determine such measures as, in their wisdom, the public safety and interest may seem to demand.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this fifteenth day of April, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-one, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-fifth.
A. LINCOLN
By the President:
WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
A Proclamation.
Whereas an insurrection against the Government of the United States has broken out in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas, and the laws of the United States for the collection of the revenue cannot be effectually executed therein conformably to that provision of the Constitution which requires duties to be uniform throughout the United States:
And Whereas a combination of persons engaged in such insurrection have threatened to grant pretended letters of marque to authorize the bearers thereof to commit assaults on the lives, vessels, and property of good citizens of the country lawfully engaged in commerce on the high seas, and in waters of the United States:
And Whereas an executive proclamation has been already issued requiring the persons engaged in these disorderly proceedings to desist therefrom, calling out a militia force for the purpose of repressing the same, and convening Congress in extraordinary session to deliberate and determine thereon:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham LINCOLN, President of the United States, with a view to the same purposes before mentioned, and to the protection of the public peace, and the lives and property of quiet and orderly citizens pursuing their lawful occupations, until Congress shall have assembled and deliberated on the said unlawful proceedings, or until the same shall have ceased, have further deemed it advisable to set on foot a blockade of the ports within the States aforesaid, in pursuance of the laws of the United States, and of the law of nations in such case provided. For this purpose a competent force will be posted so as to prevent entrance and exit of vessels from the ports aforesaid. If, therefore, with a view to violate such blockade, a vessel shall approach or shall attempt to leave either of the said ports, she will be duly warned by the commander of one of the blockading vessels, who will indorse on her register the fact and date of such warning, and if the same vessel shall again attempt to enter or leave the blockaded port, she will be captured and sent to the nearest convenient port, for such proceedings against her and her cargo, as prize, as may be deemed advisable.
And I hereby proclaim and declare that if any person, under the pretended authority of the said States, or under any other pretense, shall molest a vessel of the United States, or the persons or cargo on board of her, such person will be held amenable to the laws of the United States for the prevention and punishment of piracy.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this nineteenth day of April, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-one, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-fifth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
GOVERNOR HICKS AND MAYOR BROWN.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter by Messrs. Bond, Dobbin, and Brune is received. I tender you both my sincere thanks for your efforts to keep the peace in the trying situation in which you are placed.
For the future troops must be brought here, but I make no point of bringing them through Baltimore. Without any military knowledge myself, of course I must leave details to General Scott. He hastily said this morning in the presence of these gentlemen, "March them around Baltimore, and not through it." I sincerely hope the General, on fuller reflection, will consider this practical and proper, and that you will not object to it. By this a collision of the people of Baltimore with the troops will be avoided, unless they go out of their way to seek it. I hope you will exert your influence to prevent this.
Now and ever I shall do all in my power for peace consistently with the maintenance of the Government.
Your obedient servant,
GOVERNOR HICKS:
I desire to consult with you and the Mayor of Baltimore relative to preserving the peace of Maryland. Please come immediately by special train, which you can take at Baltimore; or, if necessary, one can be sent from here. Answer forthwith.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL SCOTT.
MY DEAR SIR—The Maryland Legislature assembles to-morrow at Annapolis, and not improbably will take action to arm the people of that State against the United States. The question has been submitted to and considered by me whether it would not be justifiable, upon the ground of necessary defense, for you, as General in Chief of the United States Army, to arrest or disperse the members of that body. I think it would not be justifiable nor efficient for the desired object.
First. They have a clearly legal right to assemble, and we cannot know in advance that their action will not be lawful and peaceful, and if we wait until they shall have acted their arrest or dispersion will not lessen the effect of their action.
Secondly. We cannot permanently prevent their action. If we arrest them, we cannot long hold them as prisoners, and when liberated they will immediately reassemble and take their action; and precisely the same if we simply disperse them—they will immediately reassemble in some other place.
I therefore conclude that it is only left to the Commanding General to watch and await their action, which, if it shall be to arm their people against the United States, he is to adopt the most prompt and efficient means to counteract, even, if necessary, to the bombardment of their cities and, in the extremist necessity, the suspension of the writ of habeas corpus.
Your obedient servant,
A Proclamation.
Whereas, for the reasons assigned in my proclamation of the nineteenth instant, a blockade of the ports of the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas was ordered to be established:
And whereas, since that date, public property of the United States has been seized, the collection of the revenue obstructed, and duly commissioned officers of the United States, while engaged in executing the orders of their superiors, have been arrested and held in custody as prisoners, or have been impeded in the discharge of their official duties, without due legal process, by persons claiming to act under authorities of the States of Virginia and North Carolina:
An efficient blockade of the ports of those States will also be established.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twenty seventh day of April, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-one, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-fifth.
I have desired as sincerely as any man, and I sometimes think more than any other man, that our present difficulties might be settled without the shedding of blood. I will not say that all hope has yet gone; but if the alternative is presented whether the Union is to be broken in fragments and the liberties of the people lost, or blood be shed, you will probably make the choice with which I shall not be dissatisfied.
TO THE COMMANDING GENERAL, ARMY OF THE UNITED STATES.
You are engaged in suppressing an insurrection against the laws of the United States. If at any point on or in the vicinity of any military line which is now or which shall be used between the City of Philadelphia and the city of Washington you find resistance which renders it necessary to suspend the writ of habeas corpus for the public safety, you personally, or through the officer in command at the point at which resistance occurs, are authorized to suspend that writ.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, April 17, 1861
TO CAPTAIN NATHANIEL LYON.
CAPT. NATHANIEL LYON, Commanding Department of the West.
SIR:—The President of the United States directs that you enroll in the military service of the United States the loyal citizens of Saint Louis and vicinity, not exceeding, with those heretofore enlisted, ten thousand in number, for the purpose of maintaining the authority of the United States; for the protection of the peaceful inhabitants of Missouri; and you will, if deemed necessary for that purpose by yourself, by Messrs. Oliver F. Ferny, John How, James O. Broadhead, Samuel T. Glover, J. Wilzie, Francis P. Blair, Jr., proclaim martial law in the city of Saint Louis.
The additional force hereby authorized shall be discharged in part or in whole, if enlisted. As soon as it appears to you and the gentlemen above mentioned that there is no danger of an attempt on the part of the enemies of the Government to take military possession of the city of Saint Louis, or put the city in control of the combination against the Government of the United States; and whilst such additional force remains in the service the same shall be governed by the Rules and Articles of War, and such special regulations as you may prescribe. I shall like the force hereafter directed to be enrolled to be under your command.
The arms and other military stores in the Saint Louis Arsenal not needed for the forces of the United States in Missouri must be removed to Springfield, or some other safe place of deposit in the State of Illinois, as speedily as practicable, by the ordnance officers in charge at Saint Louis.
(Indorsement.)
It is revolutionary times, and therefore I do not object to the irregularity of this. W. S.
Approved, April 30, 1861.
A. LINCOLN.
Colonel Thomas will make this order. SIMON CAMERON, Secretary of War.
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 1, 1861
CAPTAIN G. V. Fox.
MY DEAR SIR:—I sincerely regret that the failure of the late attempt to provision Fort Sumter should be the source of any annoyance to you.
The practicability of your plan was not, in fact, brought to a test. By reason of a gale, well known in advance to be possible and not improbable, the tugs, an essential part of the plan, never reached the ground; while, by an accident for which you were in no wise responsible, and possibly I to some extent was, you were deprived of a war vessel, with her men, which you deemed of great importance to the enterprise.
I most cheerfully and truly declare that the failure of the undertaking has not lowered you a particle, while the qualities you developed in the effort have greatly heightened you in my estimation.
For a daring and dangerous enterprise of a similar character you would to-day be the man of all my acquaintances whom I would select. You and I both anticipated that the cause of the country would be advanced by making the attempt to provision Fort Sumter, even if it should fail; and it is no small consolation now to feel that our anticipation is justified by the result.
Very truly your friend,
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES.
A Proclamation..
Whereas existing exigencies demand immediate and adequate measures for the protection of the National Constitution and the preservation of the National Union by the suppression of the insurrectionary combinations now existing in several States for opposing the laws of the Union and obstructing the execution thereof, to which end a military force in addition to that called forth by my proclamation of the 15th day of April in the present year appears to be indispensably necessary:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States and Commander in Chief of the Army and Navy thereof and of the militia of the several States when called into actual service, do hereby call into the service of the United States 42,034 volunteers to serve for the period of three years, unless sooner discharged, and to be mustered into service as infantry and cavalry. The proportions of each arm and the details of enrollment and organization will be made known through the Department of War.
And I also direct that the Regular Army of the United States be increased by the addition of eight regiments of infantry, one regiment of cavalry, and one regiment of artillery, making altogether a maximum aggregate increase of 22,714 officers and enlisted men, the details of which increase will also be made known through the Department of War.
And I further direct the enlistment for not less than one or more than three years of 18,000 seamen, in addition to the present force, for the naval service of the United States. The details of the enlistment and organization will be made known through the Department of the Navy.
The call for volunteers hereby made and the direction for the increase of the Regular Army and for the enlistment of seamen hereby given, together with the plan of organization adopted for the volunteer and for the regular forces hereby authorized, will be submitted to Congress as soon as assembled.
In the meantime I earnestly invoke the co-operation of all good citizens in the measures hereby adopted for the effectual suppression of unlawful violence, for the impartial enforcement of constitutional laws, and for the speediest possible restoration of peace and order, and with these of happiness and prosperity, throughout our country.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my band and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 6, 1861
HON. H. HAMLIN, New York.
MY DEAR SIR:-Please advise me at the close of each day what troops left during the day, where going, and by what route; what remaining at New York, and what expected in the next day. Give the numbers, as near as convenient, and what corps they are. This information, reaching us daily, will be very useful as well as satisfactory.
Yours very truly,
TO ALL WHO SHALL SEE THESE PRESENTS, GREETING:
Know ye that, reposing special trust and confidence in the patriotism, valor, fidelity, and ability of Colonel Robert Anderson, U. S. Army, I have empowered him, and do hereby empower him, to receive into the army of the United States as many regiments of volunteer troops from the State of Kentucky and from the western part of the State of Virginia as shall be willing to engage in the Service of the United States for the term of three years, upon the terms and according to the plan proposed by the proclamation of May 3, 1861, and General Orders No. 15, from the War Department, of May 4, 1861.
The troops whom he receives shall be on the same footing in every respect as those of the like kind called for in the proclamation above cited, except that the officers shall be commissioned by the United States. He is therefore carefully and diligently to discharge the duty hereby devolved upon him by doing and performing all manner of things thereunto belonging.
Given under my hand, at the city of Washington, this 7th day of May, A. D. 1861, and in the eighty-fifth year of the independence of the United States.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: SIMON CAMERON, Secretary of War,
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OP AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas an insurrection exists in the State of Florida, by which the lives, liberty, and property of loyal citizens of the United States are endangered:
And whereas it is deemed proper that all needful measures should be taken for the protection of such citizens and all officers of the United States in the discharge of their public duties in the State aforesaid:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham LINCOLN, President of the United States, do hereby direct the commander of the forces of the United States on the Florida coast to permit no person to exercise any office or authority upon the islands of Key West, the Tortugas, and Santa Rosa, which may be inconsistent with the laws and Constitution of the United States, authorizing him at the same time, if he shall find it necessary, to suspend there the writ of habeas corpus, and to remove from the vicinity of the United States fortresses all dangerous or suspected persons.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.....................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY.
SIR:-Lieut. D. D. Porter was placed in command of the steamer Powhatan, and Captain Samuel Mercer was detached therefrom, by my special order, and neither of them is responsible for any apparent or real irregularity on their part or in connection with that vessel.
Hereafter Captain Porter is relieved from that special service and placed under the direction of the Navy Department, from which he will receive instructions and to which he will report.
Very respectfully,
NO. 10.
DEPARTMENT OF STATE. WASHINGTON, May 21, 1861
SIR:—-Mr. Dallas, in a brief despatch of May 2d (No. 333), tells us that Lord John Russell recently requested an interview with him on account of the solicitude which his lordship felt concerning the effect of certain measures represented as likely to be adopted by the President. In that conversation the British secretary told Mr. Dallas that the three representatives of the Southern Confederacy were then in London, that Lord John Russell had not yet seen them, but that he was not unwilling to see them unofficially. He further informed Mr. Dallas that an understanding exists between the British and French governments which would lead both to take one and the same course as to recognition. His lordship then referred to the rumor of a meditated blockade by us of Southern ports, and a discontinuance of them as ports of entry. Mr. Dallas answered that he knew nothing on those topics, and therefore
(The President's corrections, both in notes and text, are in caps. All matter between brackets was to be marked out.)
could say nothing. He added that you were expected to arrive in two weeks. Upon this statement Lord John Russell acquiesced in the expediency of waiting for the full knowledge you were expected to bring.
Mr. Dallas transmitted to us some newspaper reports of ministerial explanations made in Parliament.
You will base no proceedings on parliamentary debates further than to seek explanations when necessary and communicate them to this department. [We intend to have a clear and simple record of whatever issue may arise between us and Great Britain.]
The President [is surprised and grieved] regrets that Mr. Dallas did not protest against the proposed unofficial intercourse between the British Government and the missionaries of the insurgents [as well as against the demand for explanations made by the British Government]. It is due, however, to Mr. Dallas to say that our instructions had been given only to you and not to him, and that his loyalty and fidelity, too rare in these times [among our late representatives abroad, are confessed and] are appreciated.
Intercourse of any kind with the so-called commissioners is liable to be construed as a recognition of the authority which appointed them. Such intercourse would be none the less [wrongful] hurtful to us for being called unofficial, and it might be even more injurious, because we should have no means of knowing what points might be resolved by it. Moreover, unofficial intercourse is useless and meaningless if it is not expected to ripen into official intercourse and direct recognition. It is left doubtful here whether the proposed unofficial intercourse has yet actually begun. Your own [present] antecedent instructions are deemed explicit enough, and it is hoped that you have not misunderstood them. You will in any event desist from all intercourse whatever, unofficial as well as official, with the British Government, so long as it shall continue intercourse of either kind with the domestic enemies of this country [confining yourself to a delivery of a copy of this paper to the Secretary of State. After doing this.] When intercourse shall have been arrested for this cause, you will communicate with this department and receive further directions.
Lord John Russell has informed us of an understanding between the British and French governments that they will act together in regard to our affairs. This communication, however, loses something of its value from the circumstance that the communication was withheld until after knowledge of the fact had been acquired by us from other sources. We know also another fact that has not yet been officially communicated to us—namely, that other European States are apprised by France and England of their agreement, and are expected to concur with or follow them in whatever measures they adopt on the subject of recognition. The United States have been impartial and just in all their conduct toward the several nations of Europe. They will not complain, however, of the combination now announced by the two leading powers, although they think they had a right to expect a more independent, if not a more friendly, course from each of them. You will take no notice of that or any other alliance. Whenever the European governments shall see fit to communicate directly with us, we shall be, as heretofore, frank and explicit in our reply.
As to the blockade, you will say that by [the] our own laws [of nature] and the laws of nature and the laws of nations, this Government has a clear right to suppress insurrection. An exclusion of commerce from national ports which have been seized by the insurgents, in the equitable form of blockade, is the proper means to that end. You will [admit] not insist that our blockade is [not] to be respected if it be not maintained by a competent force; but passing by that question as not now a practical, or at least an urgent, one, you will add that [it] the blockade is now, and it will continue to be so maintained, and therefore we expect it to be respected by Great Britain. You will add that we have already revoked the exequatur of a Russian consul who had enlisted in the military service of the insurgents, and we shall dismiss or demand the recall of every foreign agent, consular or diplomatic, who shall either disobey the Federal laws or disown the Federal authority.
As to the recognition of the so-called Southern Confederacy, it is not to be made a subject of technical definition. It is, of course, [quasi] direct recognition to publish an acknowledgment of the sovereignty and independence of a new power. It is [quasi] direct recognition to receive its ambassadors, ministers, agents, or commissioners officially. A concession of belligerent rights is liable to be construed as a recognition of them. No one of these proceedings will [be borne] pass [unnoticed] unquestioned by the United States in this case.
Hitherto recognition has been moved only on the assumption that the so-called Confederate States are de facto a self-sustaining power. Now, after long forbearance, designed to soothe discontent and avert the need of civil war, the land and naval forces of the United States have been put in motion to repress the insurrection. The true character of the pretended new State is at once revealed. It is seen to be a power existing in pronunciamento only, It has never won a field. It has obtained no forts that were not virtually betrayed into its hands or seized in breach of trust. It commands not a single port on the coast nor any highway out from its pretended capital by land. Under these circumstances Great Britain is called upon to intervene and give it body and independence by resisting our measures of suppression. British recognition would be British intervention to create within our own territory a hostile state by overthrowing this republic itself. [When this act of intervention is distinctly performed, we from that hour shall cease to be friends, and become once more, as we have twice before been forced to be, enemies of Great Britain.]
As to the treatment of privateers in the insurgent service, you will say that this is a question exclusively our own. We treat them as pirates. They are our own citizens, or persons employed by our citizens, preying on the commerce of our country. If Great Britain shall choose to recognize them as lawful belligerents, and give them shelter from our pursuit and punishment, the laws of nations afford an adequate and proper remedy [and we shall avail ourselves of it. And while you need not say this in advance, be sure that you say nothing inconsistent with it.]
Happily, however, her Britannic Majesty's government can avoid all these difficulties. It invited us in 1856 to accede to the declaration of the Congress of Paris, of which body Great Britain was herself a member, abolishing privateering everywhere in all cases and forever. You already have our authority to propose to her our accession to that declaration. If she refuse to receive it, it can only be because she is willing to become the patron of privateering when aimed at our devastation.
These positions are not elaborately defended now, because to vindicate them would imply a possibility of our waiving them.
1 We are not insensible of the grave importance of
1 (Drop all from this line to the end, and in lieu of it write, "This paper is for your own guidance only, and not [sic] to be read or shown to any one.")
(Secretary Seward, when the despatch was returned to him, added an introductory paragraph stating that the document was strictly confidential. For this reason these last two paragraphs remained as they are here printed.)
this occasion. We see how, upon the result of the debate in which we are engaged, a war may ensue between the United States and one, two, or even more European nations. War in any case is as exceptionable from the habits as it is revolting from the sentiments of the American people. But if it come, it will be fully seen that it results from the action of Great Britain, not our own; that Great Britain will have decided to fraternize with our domestic enemy, either without waiting to hear from you our remonstrances and our warnings, or after having heard them. War in defense of national life is not immoral, and war in defense of independence is an inevitable part of the discipline of nations.
The dispute will be between the European and the American branches of the British race. All who belong to that race will especially deprecate it, as they ought. It may well be believed that men of every race and kindred will deplore it. A war not unlike it between the same parties occurred at the close of the last century. Europe atoned by forty years of suffering for the error that Great Britain committed in provoking that contest. If that nation shall now repeat the same great error, the social convulsions which will follow may not be so long, but they will be more general. When they shall have ceased, it will, we think, be seen, whatever may have been the fortunes of other nations, that it is not the United States that will have come out of them with its precious Constitution altered or its honestly obtained dominion in any degree abridged. Great Britain has but to wait a few months and all her present inconveniences will cease with all our own troubles. If she take a different course, she will calculate for herself the ultimate as well as the immediate consequences, and will consider what position she will hold when she shall have forever lost the sympathies and the affections of the only nation on whose sympathies and affections she has a natural claim. In making that calculation she will do well to remember that in the controversy she proposes to open we shall be actuated by neither pride, nor passion, nor cupidity, nor ambition; but we shall stand simply on the principle of self-preservation, and that our cause will involve the independence of nations and the rights of human nature.
I am, Sir, respectfully your obedient servant, W. H. S.
CHARLES FRANCIS ADAMS, Esq., etc,
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR. MY DEAR SIR:—Why cannot Colonel Small's Philadelphia regiment be received? I sincerely wish it could. There is something strange about it. Give these gentlemen an interview, and take their regiment.
Yours truly,
GOVERNOR E. D. MORGAN, Albany, N.Y.
I wish to see you face to face to clear these difficulties about forwarding troops from New York.
CAPT. DAHLGREEN.
MY DEAR SIR:—Allow me to introduce Col. J. A. McLernand, M.C. of my own district in Illinois. If he should desire to visit Fortress Monroe, please introduce him to the captain of one of the vessels in our service, and pass him down and back.
Yours very truly,
TO THE FATHER AND MOTHER OF COL. ELMER E. ELLSWORTH.
MY DEAR SIR AND MADAME:—In the untimely loss of your noble son, our affliction here is scarcely less than your own. So much of promised usefulness to one's country, and of bright hopes for one's self and friends, have never been so suddenly dashed as in his fall. In size, in years, and in youthful appearance a boy only, his power to command men was surpassingly great. This power, combined with a fine intellectual and indomitable energy, and a taste altogether military, constituted in him, as seemed to me, the best natural talent in that department I ever knew. And yet he was singularly modest and deferential in social intercourse. My acquaintance with him began less than two years ago; yet, through the latter half of the intervening period, it was as intense as the disparity of our ages and my engrossing engagements would permit. To me he appeared to have no indulgences or pastimes, and I never heard him utter a profane or an intemperate word. What was conclusive of his good heart, he never forgot his parents. The honors he labored for so laudably, and for which, in the sad end, he so gallantly gave his life, he meant for them no less than for himself.
In the hope that it may be no intrusion upon the sacredness of your sorrow, I have ventured to address you this tribute to the memory of my young friend and your brave and early fallen son.
May God give you the consolation which is beyond all early power.
Sincerely your friend in common affliction,
COL. W. A. BARTLETT, New York.
The Naval Brigade was to go to Fort Monroe without trouble to the government, and must so go or not at all.
The government has already accepted ten regiments from the State of Indiana. I think at least six more ought to be received from that State, two to be those of Colonel James W. McMillan and Colonel William L. Brown, and the other four to be designated by the Governor of the State of Indiana, and to be received into the volunteer service of the United States according to the "Plan of Organization" in the General Orders of the War Department, No.15. When they report to Major-General McClellan in condition to pass muster according to that order, and with the approval of the Secretary of War to be indorsed hereon, and left in his department, I direct that the whole six, or any smaller number of such regiments, be received.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—There is, it seems, a regiment in Massachusetts commanded by Fletcher Webster, and which HON. Daniel Webster's old friends very much wish to get into the service. If it can be received with the approval of your department and the consent of the Governor of Massachusetts I shall indeed be much gratified. Give Mr. Ashmun a chance to explain fully.
Yours truly,
MY DEAR SIR—I think it is entirely safe to accept a fifth regiment from Michigan, and with your approbation I should say a regiment presented by Col. T. B. W. Stockton, ready for service within two weeks from now, will be received. Look at Colonel Stockton's testimonials.
Yours truly,
HON. SECRETARY Of WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—With your concurrence, and that of the Governor of Indiana, I am in favor of accepting into what we call the three years' service any number not exceeding four additional regiments from that State. Probably they should come from the triangular region between the Ohio and Wabash Rivers, including my own old boyhood home. Please see HON. C. M. Allen, Speaker of the Indiana House of Representatives, and unless you perceive good reason to the contrary, draw up an order for him according to the above.
Yours truly,
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR. MY DEAR SIR:—With your concurrence, and that of the Governor of Ohio, I am in favor of receiving into what we call the three years' service any number not exceeding six additional regiments from that State, unless you perceive good reasons to the contrary. Please see HON. John A. Gurley, who bears this, and make an order corresponding with the above.
Yours truly,
Hon. N. W. EDWARDS MY DEAR SIR:
....When you wrote me some time ago in reference to looking up something in the departments here, I thought I would inquire into the thing and write you, but the extraordinary pressure upon me diverted me from it, and soon it passed out of my mind. The thing you proposed, it seemed to me, I ought to understand myself before it was set on foot by my direction or permission; and I really had no time to make myself acquainted with it. Nor have I yet. And yet I am unwilling, of course, that you should be deprived of a chance to make something, if it can be done without injustice to the Government, or to any individual. If you choose to come here and point out to me how this can be done I shall not only not object, but shall be gratified to be able to oblige you.
Your friend as ever
MY DEAR SIR:—Since you spoke to me yesterday about General J. H. Lane, of Kansas, I have been reflecting upon the subject, and have concluded that we need the service of such a man out there at once; that we had better appoint him a brigadier-general of volunteers to-day, and send him off with such authority to raise a force (I think two regiments better than three, but as to this I am not particular) as you think will get him into actual work quickest. Tell him, when he starts, to put it through not to be writing or telegraphing back here, but put it through.
Yours truly,
General Lane has been authorized to raise two additional regiments of volunteers.
SIMON CAMERON, Secretary o f War.
GENTLEMEN OF THE KENTUCKY DELEGATION WHO ARE FOR THE UNION:
I somewhat wish to authorize my friend Jesse Bayles to raise a Kentucky regiment, but I do not wish to do it without your consent. If you consent, please write so at the bottom of this.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
We consent: R. MALLORY. H. GRIDER. G. W. DUNLAP. J. S. JACKSON. C. A. WICKLIFFE.
I repeat, I would like for Col. Bayles to raise a regiment of cavalry whenever the Union men of Kentucky desire or consent to it.
2, 1861 TO THE COMMANDING GENERAL, ARMY OF THE UNITED STATES:
You are engaged in suppressing an insurrection against the laws of the United States. If at any point on or in the vicinity of any military line which is now or which shall be used between the city of New York and the city of Washington you find resistance which renders it necessary to suspend the writ of habeas corpus for the public safety, you personally, or through the officer in command at the point where resistance occurs, are authorized to suspend that writ.
Given under my hand and the seal of the United States at the city of Washington, this second day of July, A.D. 1861, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-fifth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
HON. SECRETARY OF STATE.
MY DEAR SIR:—General Scott had sent me a copy of the despatch of which you kindly sent one. Thanks to both him and you. Please assemble the Cabinet at twelve to-day to look over the message and reports.
And now, suppose you step over at once and let us see General Scott (and) General Cameron about assigning a position to General Fremont.
Yours as ever,
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:—Having been convened on an extraordinary occasion, as authorized by the Constitution, your attention is not called to any ordinary subject of legislation.
At the beginning of the present Presidential term, four months ago, the functions of the Federal Government were found to be generally suspended within the several States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Florida, excepting only those of the Post-Office Department.
Within these States all the forts, arsenals, dockyards, custom-houses, and the like, including the movable and stationary property in and about them, had been seized, and were held in open hostility to this government, excepting only Forts Pickens, Taylor, and Jefferson, on and near the Florida coast, and Fort Sumter, in Charleston Harbor, South Carolina. The forts thus seized had been put in improved condition, new ones had been built, and armed forces had been organized and were organizing, all avowedly with the same hostile purpose.
The forts remaining in the possession of the Federal Government in and near these States were either besieged or menaced by warlike preparations, and especially Fort Sumter was nearly surrounded by well-protected hostile batteries, with guns equal in quality to the best of its own, and outnumbering the latter as perhaps ten to one. A disproportionate share of the Federal muskets and rifles had somehow found their way into these States, and had been seized to be used against the government. Accumulations of the public revenue lying within them had been seized for the same object. The navy was scattered in distant seas, leaving but a very small part of it within the immediate reach of the government. Officers of the Federal army and navy had resigned in great numbers; and of those resigning a large proportion had taken up arms against the government. Simultaneously, and in connection with all this, the purpose to sever the Federal Union was openly avowed. In accordance with this purpose, an ordinance had been adopted in each of these States, declaring the States respectively to be separated from the national Union. A formula for instituting a combined government of these States had been promulgated; and this illegal organization, in the character of confederate States, was already invoking recognition, aid, and intervention from foreign powers.
Finding this condition of things, and believing it to be an imperative duty upon the incoming executive to prevent, if possible, the consummation of such attempt to destroy the Federal Union, a choice of means to that end became indispensable. This choice was made and was declared in the inaugural address. The policy chosen looked to the exhaustion of all peaceful measures before a resort to any stronger ones. It sought only to hold the public places and property not already wrested from the government, and to collect the revenue, relying for the rest on time, discussion, and the ballot-box. It promised a continuance of the mails, at government expense, to the very people who were resisting the government; and it gave repeated pledges against any disturbance to any of the people, or any of their rights. Of all that which a President might constitutionally and justifiably do in such a case, everything was forborne without which it was believed possible to keep the government on foot.
On the 5th of March (the present incumbent's first full day in office), a letter of Major Anderson, commanding at Fort Sumter, written on the 28th of February and received at the War Department on the 4th of March, was by that department placed in his hands. This letter expressed the professional opinion of the writer that reinforcements could not be thrown into that fort within the time for his relief, rendered necessary by the limited supply of provisions, and with a view of holding possession of the same, with a force of less than twenty thousand good and well-disciplined men. This opinion was concurred in by all the officers of his command, and their memoranda on the subject were made inclosures of Major Anderson's letter. The whole was immediately laid before Lieutenant-General Scott, who at once concurred with Major Anderson in opinion. On reflection, however, he took full time, consulting with other officers, both of the army and the navy, and at the end of four days came reluctantly but decidedly to the same conclusion as before. He also stated at the same time that no such sufficient force was then at the control of the government, or could be raised and brought to the ground within the time when the provisions in the fort would be exhausted. In a purely military point of view, this reduced the duty of the administration in the case to the mere matter of getting the garrison safely out of the fort.
It was believed, however, that to so abandon that position, under the circumstances, would be utterly ruinous; that the necessity under which it was to be done would not be fully understood; that by many it would be construed as a part of a voluntary policy; that at home it would discourage the friends of the Union, embolden its adversaries, and go far to insure to the latter a recognition abroad; that in fact, it would be our national destruction consummated. This could not be allowed. Starvation was not yet upon the garrison, and ere it would be reached Fort Pickens might be reinforced. This last would be a clear indication of policy, and would better enable the country to accept the evacuation of Fort Sumter as a military necessity. An order was at once directed to be sent for the landing of the troops from the steamship Brooklyn into Fort Pickens. This order could not go by land, but must take the longer and slower route by sea. The first return news from the order was received just one week before the fall of Fort Sumter. The news itself was that the officer commanding the Sabine, to which vessel the troops had been transferred from the Brooklyn, acting upon some quasi armistice of the late administration (and of the existence of which the present administration, up to the time the order was despatched, had only too vague and uncertain rumors to fix attention), had refused to land the troops. To now reinforce Fort Pickens before a crisis would be reached at Fort Sumter was impossible—rendered so by the near exhaustion of provisions in the latter-named fort. In precaution against such a conjuncture, the government had, a few days before, commenced preparing an expedition as well adapted as might be to relieve Fort Sumter, which expedition was intended to be ultimately used, or not, according to circumstances. The strongest anticipated case for using it was now presented, and it was resolved to send it forward. As had been intended in this contingency, it was also resolved to notify the governor of South Carolina that he might expect an attempt would be made to provision the fort; and that, if the attempt should not be resisted, there would be no effort to throw in men, arms, or ammunition, without further notice, or in case of an attack upon the fort. This notice was accordingly given; whereupon the fort was attacked and bombarded to its fall, without even awaiting the arrival of the provisioning expedition.
It is thus seen that the assault upon and reduction of Fort Sumter was in no sense a matter of self-defense on the part of the assailants. They well knew that the garrison in the fort could by no possibility commit aggression upon them. They knew—they were expressly notified—that the giving of bread to the few brave and hungry men of the garrison was all which would on that occasion be attempted, unless themselves, by resisting so much, should provoke more. They knew that this government desired to keep the garrison in the fort, not to assail them, but merely to maintain visible possession, and thus to preserve the Union from actual and immediate dissolution—trusting, as hereinbefore stated, to time, discussion, and the ballot-box for final adjustment; and they assailed and reduced the fort for precisely the reverse object—to drive out the visible authority of the Federal Union, and thus force it to immediate dissolution. That this was their object the executive well understood; and having said to them in the inaugural address, "You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors," he took pains not only to keep this declaration good, but also to keep the case so free from the power of ingenious sophistry that the world should not be able to misunderstand it. By the affair at Fort Sumter, with its surrounding circumstances, that point was reached. Then and thereby the assailants of the government began the conflict of arms, without a gun in sight or in expectancy to return their fire, save only the few in the fort sent to that harbor years before for their own protection, and still ready to give that protection in whatever was lawful. In this act, discarding all else, they have forced upon the country the distinct issue, "immediate dissolution or blood."
And this issue embraces more than the fate of these United States. It presents to the whole family of man the question whether a constitutional republic or democracy—a government of the people by the same people—can or cannot maintain its territorial integrity against its own domestic foes. It presents the question whether discontented individuals, too few in numbers to control administration according to organic law in any case, can always, upon the pretenses made in this case, or on any other pretenses, or arbitrarily without any pretense, break up their government, and thus practically put an end to free government upon the earth. It forces us to ask: Is there in all republics this inherent and fatal weakness? Must a government, of necessity, be too strong for the liberties of its own people, or too weak to maintain its own existence?
So viewing the issue, no choice was left but to call out the war power of the government, and so to resist force employed for its destruction by force for its preservation.
The call was made, and the response of the country was most gratifying, surpassing in unanimity and spirit the most sanguine expectation. Yet none of the States commonly called slave States, except Delaware, gave a regiment through regular State organization. A few regiments have been organized within some others of those States by individual enterprise, and received into the government service. Of course the seceded States, so called (and to which Texas had been joined about the time of the inauguration), gave no troops to the cause of the Union.
The border States, so called, were not uniform in their action, some of them being almost for the Union, while in others—as Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas—the Union sentiment was nearly repressed and silenced. The course taken in Virginia was the most remarkable—perhaps the most important. A convention elected by the people of that State to consider this very question of disrupting the Federal Union was in session at the capital of Virginia when Fort Sumter fell. To this body the people had chosen a large majority of professed Union men. Almost immediately after the fall of Sumter, many members of that majority went over to the original disunion minority, and with them adopted an ordinance for withdrawing the State from the Union. Whether this change was wrought by their great approval of the assault upon Sumter, or their great resentment at the government's resistance to that assault, is not definitely known. Although they submitted the ordinance for ratification to a vote of the people, to be taken on a day then somewhat more than a month distant, the convention and the Legislature (which was also in session at the same time and place), with leading men of the State not members of either, immediately commenced acting as if the State were already out of the Union. They pushed military preparations vigorously forward all over the State. They seized the United States armory at Harper's Ferry, and the navy-yard at Gosport, near Norfolk. They received perhaps invited—into their State large bodies of troops, with their warlike appointments, from the so-called seceded States. They formally entered into a treaty of temporary alliance and co-operation with the so-called "Confederate States," and sent members to their congress at Montgomery. And finally, they permitted the insurrectionary government to be transferred to their capital at Richmond.
The people of Virginia have thus allowed this giant insurrection to make its nest within her borders; and this government has no choice left but to deal with it where it finds it. And it has the less regret as the loyal citizens have, in due form, claimed its protection. Those loyal citizens this government is bound to recognize and protect, as being Virginia.
In the border States, so called,—in fact, the middle States,—there are those who favor a policy which they call "armed neutrality"; that is, an arming of those States to prevent the Union forces passing one way, or the disunion the other, over their soil. This would be disunion completed. Figuratively speaking, it would be the building of an impassable wall along the line of separation—and yet not quite an impassable one, for under the guise of neutrality it would tie the hands of Union men and freely pass supplies from among them to the insurrectionists, which it could not do as an open enemy. At a stroke it would take all the trouble off the hands of secession, except only what proceeds from the external blockade. It would do for the disunionists that which, of all things, they most desire—feed them well and give them disunion without a struggle of their own. It recognizes no fidelity to the Constitution, no obligation to maintain the Union; and while very many who have favored it are doubtless loyal citizens, it is, nevertheless, very injurious in effect.
Recurring to the action of the government, it may be stated that at first a call was made for 75,000 militia; and, rapidly following this, a proclamation was issued for closing the ports of the insurrectionary districts by proceedings in the nature of blockade. So far all was believed to be strictly legal. At this point the insurrectionists announced their purpose to enter upon the practice of privateering.
Other calls were made for volunteers to serve for three years, unless sooner discharged, and also for large additions to the regular army and navy. These measures, whether strictly legal or not, were ventured upon, under what appeared to be a popular demand and a public necessity; trusting then, as now, that Congress would readily ratify them. It is believed that nothing has been done beyond the constitutional competency of Congress.
Soon after the first call for militia, it was considered a duty to authorize the commanding general in proper cases, according to his discretion, to suspend the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus, or, in other words, to arrest and detain, without resort to the ordinary processes and forms of law, such individuals as he might deem dangerous to the public safety. This authority has purposely been exercised but very sparingly. Nevertheless, the legality and propriety of what has been done under it are questioned, and the attention of the country has been called to the proposition that one who has sworn to "take care that the laws be faithfully executed" should not himself violate them. Of course some consideration was given to the questions of power and propriety before this matter was acted upon. The whole of the laws which were required to be faithfully executed were being resisted and failing of execution in nearly one third of the States. Must they be allowed to finally fail of execution, even had it been perfectly clear that by the use of the means necessary to their execution some single law, made in such extreme tenderness of the citizen's liberty that, practically, it relieves more of the guilty than of the innocent, should to a very limited extent be violated? To state the question more directly, are all the laws but one to go unexecuted, and the government itself go to pieces lest that one be violated? Even in such a case, would not the official oath be broken if the government should be overthrown when it was believed that disregarding the single law would tend to preserve it? But it was not believed that this question was presented. It was not believed that any law was violated. The provision of the Constitution that "the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus shall not be suspended, unless when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require it," is equivalent to a provision—is a provision—that such privilege may be suspended when, in case of rebellion or invasion, the public safety does require it. It was decided that we have a case of rebellion, and that the public safety does require the qualified suspension of the privilege of the writ which was authorized to be made. Now it is insisted that Congress, and not the executive, is vested with this power. But the Constitution itself is silent as to which or who is to exercise the power; and as the provision was plainly made for a dangerous emergency, it cannot be believed the framers of the instrument intended that in every case the danger should run its course until Congress could be called together, the very assembling of which might be prevented, as was intended in this case, by the rebellion.
No more extended argument is now offered, as an opinion at some length will probably be presented by the attorney-general. Whether there shall be any legislation upon the subject, and if any, what, is submitted entirely to the better judgment of Congress.
The forbearance of this government had been so extraordinary and so long continued as to lead some foreign nations to shape their action as if they supposed the early destruction of our national Union was probable. While this, on discovery, gave the executive some concern, he is now happy to say that the sovereignty and rights of the United States are now everywhere practically respected by foreign powers; and a general sympathy with the country is manifested throughout the world.
The reports of the Secretaries of the Treasury, War, and the Navy will give the information in detail deemed necessary and convenient for your deliberation and action; while the executive and all the departments will stand ready to supply omissions, or to communicate new facts considered important for you to know.
It is now recommended that you give the legal means for making this contest a short and decisive one: that you place at the control of the government for the work at least four hundred thousand men and $400,000,000. That number of men is about one-tenth of those of proper ages within the regions where, apparently, all are willing to engage; and the sum is less than a twenty-third part of the money value owned by the men who seem ready to devote the whole. A debt of $600,000,000 now is a less sum per head than was the debt of our Revolution when we came out of that struggle; and the money value in the country now bears even a greater proportion to what it was then than does the population. Surely each man has as strong a motive now to preserve our liberties as each had then to establish them.
A right result at this time will be worth more to the world than ten times the men and ten times the money. The evidence reaching us from the country leaves no doubt that the material for the work is abundant, and that it needs only the hand of legislation to give it legal sanction, and the hand of the executive to give it practical shape and efficiency. One of the greatest perplexities of the government is to avoid receiving troops faster than it can provide for them. In a word, the people will save their government if the government itself will do its part only indifferently well.
It might seem, at first thought, to be of little difference whether the present movement at the South be called "secession" or "rebellion." The movers, however, well understand the difference. At the beginning they knew they could never raise their treason to any respectable magnitude by any name which implies violation of law. They knew their people possessed as much of moral sense, as much of devotion to law and order, and as much pride in and reverence for the history and government of their common country as any other civilized and patriotic people. They knew they could make no advancement directly in the teeth of these strong and noble sentiments. Accordingly, they commenced by an insidious debauching of the public mind. They invented an ingenious sophism which, if conceded, was followed by perfectly logical steps, through all the incidents, to the complete destruction of the Union. The sophism itself is that any State of the Union may consistently with the national Constitution, and therefore lawfully and peacefully, withdraw from the Union without the consent of the Union or of any other State. The little disguise that the supposed right is to be exercised only for just cause, themselves to be the sole judges of its justice, is too thin to merit any notice.
With rebellion thus sugar-coated they have been drugging the public mind of their section for more than thirty years, and until at length they have brought many good men to a willingness to take up arms against the government the day after some assemblage of men have enacted the farcical pretense of taking their State out of the Union, who could have been brought to no such thing the day before.
This sophism derives much, perhaps the whole, of its currency from the assumption that there is some omnipotent and sacred supremacy pertaining to a State—to each State of our Federal Union. Our States have neither more nor less power than that reserved to them in the Union by the Constitution—no one of them ever having been a State out of the Union. The original ones passed into the Union even before they cast off their British colonial dependence; and the new ones each came into the Union directly from a condition of dependence, excepting Texas. And even Texas in its temporary independence was never designated a State. The new ones only took the designation of States on coming into the Union, while that name was first adopted for the old ones in and by the Declaration of Independence. Therein the "United Colonies" were declared to be "free and independent States"; but even then the object plainly was not to declare their independence of one another or of the Union, but directly the contrary, as their mutual pledge and their mutual action before, at the time, and afterward, abundantly show. The express plighting of faith by each and all of the original thirteen in the Articles of Confederation, two years later, that the Union shall be perpetual, is most conclusive. Having never been States either in substance or in name outside of the Union, whence this magical omnipotence of "State rights," asserting a claim of power to lawfully destroy the Union itself? Much is said about the "sovereignty" of the States; but the word even is not in the national Constitution, nor, as is believed, in any of the State constitutions. What is "sovereignty" in the political sense of the term? Would it be far wrong to define it as "a political community without a political superior"? Tested by this, no one of our States except Texas ever was a sovereignty. And even Texas gave up the character on coming into the Union; by which act she acknowledged the Constitution of the United States, and the laws and treaties of the United States made in pursuance of the Constitution, to be for her the supreme law of the land. The States have their status in the Union, and they have no other legal status. If they break from this, they can only do so against law and by revolution. The Union, and not themselves separately, procured their independence and their liberty. By conquest or purchase the Union gave each of them whatever of independence or liberty it has. The Union is older than any of the States, and, in fact, it created them as States. Originally some dependent colonies made the Union, and, in turn, the Union threw off their old dependence for them, and made them States, such as they are. Not one of them ever had a State constitution independent of the Union. Of course, it is not forgotten that all the new States framed their constitutions before they entered the Union nevertheless, dependent upon and preparatory to coming into the Union.
Unquestionably the States have the powers and rights reserved to them in and by the national Constitution; but among these surely are not included all conceivable powers, however mischievous or destructive, but, at most, such only as were known in the world at the time as governmental powers; and certainly a power to destroy the government itself had never been known as a governmental, as a merely administrative power. This relative matter of national power and State rights, as a principle, is no other than the principle of generality and locality. Whatever concerns the whole should be confided to the whole—to the General Government; while whatever concerns only the State should be left exclusively to the State. This is all there is of original principle about it. Whether the national Constitution in defining boundaries between the two has applied the principle with exact accuracy, is not to be questioned. We are all bound by that defining, without question.
What is now combated is the position that secession is consistent with the Constitution—is lawful and peaceful. It is not contended that there is any express law for it; and nothing should ever be implied as law which leads to unjust or absurd consequences. The nation purchased with money the countries out of which several of these States were formed. Is it just that they shall go off without leave and without refunding? The nation paid very large sums (in the aggregate, I believe, nearly a hundred millions) to relieve Florida of the aboriginal tribes. Is it just that she shall now be off without consent or without making any return? The nation is now in debt for money applied to the benefit of these so-called seceding States in common with the rest. Is it just either that creditors shall go unpaid or the remaining States pay the whole? A part of the present national debt was contracted to pay the old debts of Texas. Is it just that she shall leave and pay no part of this herself?
Again, if one State may secede, so may another; and when all shall have seceded, none is left to pay the debts. Is this quite just for creditors? Did we notify them of this sage view of ours when we borrowed their money? If we now recognize this doctrine by allowing the seceders to go in peace, it is difficult to see what we can do if others choose to go or to extort terms upon which they will promise to remain.
The seceders insist that our Constitution admits of secession. They have assumed to make a national constitution of their own, in which of necessity they have either discarded or retained the right of secession as they insist it exists in ours. If they have discarded it, they thereby admit that on principle it ought not to be in ours. If they have retained it, by their own construction of ours, they show that to be consistent they must secede from one another whenever they shall find it the easiest way of settling their debts, or effecting any other selfish or unjust object. The principle itself is one of disintegration and upon which no government can possibly endure.
If all the States save one should assert the power to drive that one out of the Union, it is presumed the whole class of seceder politicians would at once deny the power and denounce the act as the greatest outrage upon State rights. But suppose that precisely the same act, instead of being called "driving the one out," should be called "the seceding of the others from that one," it would be exactly what the seceders claim to do, unless, indeed, they make the point that the one, because it is a minority, may rightfully do what the others, because they are a majority, may not rightfully do. These politicians are subtle and profound on the rights of minorities. They are not partial to that power which made the Constitution and speaks from the preamble calling itself "We, the People."
It may well be questioned whether there is to-day a majority of the legally qualified voters of any State except perhaps South Carolina in favor of disunion. There is much reason to believe that the Union men are the majority in many, if not in every other one, of the so-called seceded States. The contrary has not been demonstrated in any one of them. It is ventured to affirm this even of Virginia and Tennessee; for the result of an election held in military camps, where the bayonets are all on one side of the question voted upon, can scarcely be considered as demonstrating popular sentiment. At such an election, all that large class who are at once for the Union and against coercion would be coerced to vote against the Union.
It may be affirmed without extravagance that the free institutions we enjoy have developed the powers and improved the condition of our whole people beyond any example in the world. Of this we now have a striking and an impressive illustration. So large an army as the government has now on foot was never before known without a soldier in it but who has taken his place there of his own free choice. But more than this, there are many single regiments whose members, one and another, possess full practical knowledge of all the arts, sciences, professions, and whatever else, whether useful or elegant, is known in the world; and there is scarcely one from which there could not be selected a President, a Cabinet, a Congress, and perhaps a court, abundantly competent to administer the government itself. Nor do I say this is not true also in the army of our late friends, now adversaries in this contest; but if it is, so much better the reason why the government which has conferred such benefits on both them and us should not be broken up. Whoever in any section proposes to abandon such a government would do well to consider in deference to what principle it is that he does it; what better he is likely to get in its stead; whether the substitute will give, or be intended to give, so much of good to the people. There are some foreshadowings on this subject. Our adversaries have adopted some declarations of independence in which, unlike the good old one, penned by Jefferson, they omit the words "all men are created equal." Why? They have adopted a temporary national constitution, in the preamble of which, unlike our good old one, signed by Washington, they omit "We, the People," and substitute, "We, the deputies of the sovereign and independent States." Why? Why this deliberate pressing out of view the rights of men and the authority of the people?
This is essentially a people's contest. On the side of the Union it is a struggle for maintaining in the world that form and substance of government whose leading object is to elevate the condition of men to lift artificial weights from all shoulders; to clear the paths of laudable pursuit for all; to afford all an unfettered start, and a fair chance in the race of life. Yielding to partial and temporary departures, from necessity; this is the leading object of the government for whose existence we contend.
I am most happy to believe that the plain people understand and appreciate this. It is worthy of note that, while in this the government's hour of trial large numbers of those in the army and navy who have been favored with the offices have resigned and proved false to the hand which had pampered them, not one common soldier or common sailor is known to have deserted his flag.
Great honor is due to those officers who remained true, despite the example of their treacherous associates; but the greatest honor, and most important fact of all, is the unanimous firmness of the common soldiers and common sailors. To the last man, so far as known, they have successfully resisted the traitorous efforts of those whose commands, but an hour before, they obeyed as absolute law. This is the patriotic instinct of the plain people. They understand, without an argument, that the destroying of the government which was made by Washington means no good to them.
Our popular government has often been called an experiment. Two points in it our people have already settled—the successful establishing and the successful administering of it. One still remains—its successful maintenance against a formidable internal attempt to overthrow it. It is now for them to demonstrate to the world that those who can fairly carry an election can also suppress a rebellion; that ballots are the rightful and peaceful successors of bullets; and that when ballots have fairly and constitutionally decided, there can be no successful appeal back to bullets; that there can be no successful appeal, except to ballots themselves, at succeeding elections. Such will be a great lesson of peace: teaching men that what they cannot take by an election, neither can they take it by a war; teaching all the folly of being the beginners of a war.
Lest there be some uneasiness in the minds of candid men as to what is to be the course of the government toward the Southern States after the rebellion shall have been suppressed, the executive deems it proper to say it will be his purpose then, as ever, to be guided by the Constitution and the laws; and that he probably will have no different understanding of the powers and duties of the Federal Government relatively to the rights of the States and the people, under the Constitution, than that expressed in the inaugural address.
He desires to preserve the government, that it may be administered for all as it was administered by the men who made it. Loyal citizens everywhere have the right to claim this of their government, and the government has no right to withhold or neglect it. It is not perceived that in giving it there is any coercion, any conquest, or any subjugation, in any just sense of those terms.
The Constitution provides, and all the States have accepted the provision, that "the United States shall guarantee to every State in this Union a republican form of government." But if a State may lawfully go out of the Union, having done so it may also discard the republican form of government, so that to prevent its going out is an indispensable means to the end of maintaining the guarantee mentioned; and when an end is lawful and obligatory, the indispensable means to it are also lawful and obligatory.
It was with the deepest regret that the executive found the duty of employing the war power in defense of the government forced upon him. He could but perform this duty or surrender the existence of the government. No compromise by public servants could, in this case, be a cure; not that compromises are not often proper, but that no popular government can long survive a marked precedent that those who carry an election can only save the government from immediate destruction by giving up the main point upon which the people gave the election. The people themselves, and not their servants, can safely reverse their own deliberate decisions.
As a private citizen the executive could not have consented that these institutions shall perish; much less could he in betrayal of so vast and so sacred a trust as these free people had confided to him. He felt that he had no moral right to shrink, nor even to count the chances of his own life, in what might follow. In full view of his great responsibility he has, so far, done what he has deemed his duty. You will now, according to your own judgment, perform yours. He sincerely hopes that your views and your action may so accord with his as to assure all faithful citizens who have been disturbed in their rights of a certain and speedy restoration to them, under the Constitution and the laws.
And having thus chosen our course, without guile and with pure purpose, let us renew our trust in God, and go forward without fear and with manly hearts.
A. LINCOLN,
July 4, 1861
HON. SEC. OF INTERIOR.
MY DEAR SIR:—Please ask the Comr. of Indian Affairs, and of the Gen'l Land Office to come with you, and see me at once. I want the assistance of all of you in overhauling the list of appointments a little before I send them to the Senate.
Yours truly,
In answer to the resolution of the House of Representatives of the 9th instant, requesting a copy of correspondence upon the subject of the incorporation of the Dominican republic with the Spanish monarchy, I transmit a report from the Secretary of State; to whom the resolution was referred.
WASHINGTON, July 11, 1861.
I transmit to Congress a copy of correspondence between the Secretary of State and her Britannic Majesty's envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary accredited to this government, relative to the exhibition of the products of industry of all nations, which is to take place at London in the course of next year. As citizens of the United States may justly pride themselves upon their proficiency in industrial arts, it is desirable that they should have proper facilities toward taking part in the exhibition. With this view I recommend such legislation by Congress at this session as may be necessary for that purpose.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, July 16, 1861
As the United States have, in common with Great Britain and France, a deep interest in the preservation and development of the fisheries adjacent to the northeastern coast and islands of this continent, it seems proper that we should concert with the governments of those countries such measures as may be conducive to those important objects. With this view I transmit to Congress a copy of a correspondence between the Secretary of State and the British minister here, in which the latter proposes, on behalf of his government, the appointment of a joint commission to inquire into the matter, in order that such ulterior measures may be adopted as may be advisable for the objects proposed. Such legislation recommended as may be necessary to enable the executive to provide for a commissioner on behalf of the United States:
WASHINGTON, JULY 19, 1861. A. LINCOLN.
ADJUTANT-GENERAL:
I have agreed, and do agree, that the two Indian regiments named within shall be accepted if the act of Congress shall admit it. Let there be no further question about it.
1861
1. Let the plan for making the blockade effective be pushed forward with all possible despatch.
2. Let the volunteer forces at Fort Monroe and vicinity under General Butler be constantly drilled, disciplined, and instructed without more for the present.
3. Let Baltimore be held as now, with a gentle but firm and certain hand.
4. Let the force now under Patterson or Banks be strengthened and made secure in its position.
5. Let the forces in Western Virginia act till further orders according to instructions or orders from General McClellan.
6. [Let] General Fremont push forward his organization and operations in the West as rapidly as possible, giving rather special attention to Missouri.
7. Let the forces late before Manassas, except the three-months men, be reorganized as rapidly as possible in their camps here and about Arlington.
8. Let the three-months forces who decline to enter the longer service be discharged as rapidly as circumstances will permit.
9. Let the new volunteer forces be brought forward as fast as possible, and especially into the camps on the two sides of the river here.
When the foregoing shall be substantially attended to:
1. Let Manassas Junction (or some point on one or other of the railroads near it) and Strasburg be seized, and permanently held, with an open line from Washington to Manassas, and an open line from Harper's Ferry to Strasburg the military men to find the way of doing these.
2. This done, a joint movement from Cairo on Memphis; and from Cincinnati on East Tennessee.
THE GOVERNOR OF NEW JERSEY.
SIR:—Together with the regiments of three years' volunteers which the government already has in service in your State, enough to make eight in all, if tendered in a reasonable time, will be accepted, the new regiments to be taken, as far as convenient, from the three months' men and officers just discharged, and to be organized, equipped, and sent forward as fast as single regiments are ready, On the same terms as were those already in the service from that State.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
[Indorsement.]
This order is entered in the War Department, and the Governor of New Jersey is authorized to furnish the regiments with wagons and horses.
S. CAMERON, Secretary of War.
In answer to the resolution of the House of Representatives of the 22d instant; requesting a copy of the correspondence between this, government and foreign powers with reference to maritime right, I transmit a report from the Secretary of State.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, July 25, 1861
In answer to the resolution of the House of Representatives of the 15th instant, requesting a copy of the correspondence between this government and foreign powers on the subject of the existing insurrection in the United States, I transmit a report from the Secretary of State.
WASHINGTON, July 25, 1861.
MR CHASE:—The bearer, Mr. ———, wants ——— in the custom house at Baltimore. If his recommendations are satisfactory, and I recollect them to have been so, the fact that he is urged by the Methodists should be in his favor, as they complain of us some.
In answer to the resolution of the House of Representatives of the 24th instant, asking the grounds, reasons, and evidence upon which the police Commissioners of Baltimore were arrested and are now detained as prisoners at Port McHenry, I have to state that it is judged to be incompatible with the public interest at this time to furnish the information called for by the resolution.
A. LINCOLN. WASHINGTON, JULY 27, 1861
In answer to the resolution of the Senate of the 19th instant requesting information concerning the quasi armistice alluded to in my message of the 4th instant, I transmit a report from the Secretary of the Navy.
In answer to the resolution of the Senate of the 23d instant requesting information concerning the imprisonment of Lieutenant John J. Worden (John L. Worden) of the United States navy, I transmit a report from the Secretary of the Navy.
A. LINCOLN.
July 30, 1861
The Marshals of the United States in the vicinity of forts where political prisoners are held will supply decent lodging and sustenance for such prisoners unless they shall prefer to provide in those respects for themselves, in which case they will be allowed to do so by the commanding officer in charge.
Approved, and the Secretary of the State will transmit the order to the Marshals, to the Lieutenant-General, and the Secretary of the Interior.
In answer to the resolution of the House of Representatives of yesterday, requesting information regarding the imprisonment of loyal citizens of the United States by the forces now in rebellion against this government, I transmit a report from the Secretary of State, and the copy of a telegraphic despatch by which it was accompanied.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, August 2, 1861.
In answer to the resolution of your honorable body of date July 31, 1861, requesting the President to inform the Senate whether the Hon. James H. Lane, a member of that body from Kansas, has been appointed a brigadier-general in the army of the United States, and if so, whether he has accepted such appointment, I have the honor to transmit herewith certain papers, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, which, taken together, explain themselves, and which contain all the information I possess upon the questions propounded.
It was my intention, as shown by my letter of June 20, 1861, to appoint Hon. James H. Lane, of Kansas, a brigadier-general of United States volunteers in anticipation of the act of Congress, since passed, for raising such volunteers; and I have no further knowledge upon the subject, except as derived from the papers herewith enclosed.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, August 5, 1861
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR
MY DEAR SIR:—The within paper, as you see, is by HON. John S. Phelps and HON. Frank P. Blair, Jr., both members of the present Congress from Missouri. The object is to get up an efficient force of Missourians in the southwestern part of the State. It ought to be done, and Mr. Phelps ought to have general superintendence of it. I see by a private report to me from the department that eighteen regiments are already accepted from Missouri. Can it not be arranged that part of them (not yet organized, as I understand) may be taken from the locality mentioned and put under the control of Mr. Phelps, and let him have discretion to accept them for a shorter term than three years—or the war—understanding, however, that he will get them for the full term if he can? I hope this can be done, because Mr. Phelps is too zealous and efficient and understands his ground too well for us to lose his service. Of course provision for arming, equipping, etc., must be made. Mr. Phelps is here, and wishes to carry home with him authority for this matter.
Yours truly,
A Proclamation.
Whereas a joint committee of both houses of Congress has waited on the President of the United States and requested him to "recommend a day of public humiliation, prayer, and fasting to be observed by the people of the United States with religious solemnities and the offering of fervent supplications to Almighty God for the safety and welfare of these States, His blessings on their arms, and a speedy restoration of peace"; and
Whereas it is fit and becoming in all people at all times to acknowledge and revere the supreme government of God, to bow in humble submission to His chastisements, to confess and deplore their sins and transgressions in the full conviction that the fear of the Lord is the beginning of wisdom, and to pray with all fervency and contrition for the pardon of their past offences and for a blessing upon their present and prospective action; and
Whereas when our own beloved country, once, by the blessing of God, united, prosperous, and happy, is now afflicted with faction and civil war, it is peculiarly fit for us to recognize the hand of God in this terrible visitation, and in sorrowful remembrance of our own faults and crimes as a nation and as individuals to humble ourselves before Him and to pray for His mercy-to pray that we may be spared further punishment, though most justly deserved, that our arms may be blessed and made effectual for the re-establishment of order, law, and peace throughout the wide extent of our country, and that the inestimable boon of civil and religious liberty, earned under His guidance and blessing by the labors and sufferings of our fathers, may be restored in all its original excellence.
Therefore I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do appoint the last Thursday in September next as a day of humiliation, prayer, and fasting for all the people of the nation. And I do earnestly recommend to all the people, and especially to all ministers and teachers of religion of all denominations and to all heads of families, to observe and keep that day according to their several creeds and modes of worship in all humility and with all religious solemnity, to the end that the united prayer of the nation may ascend to the Throne of Grace and bring down plentiful blessings upon our country.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand
and caused the seal of the United States to
[SEAL.]
be affixed, this twelfth day of August, A. D.
1861, and of the independence of the United
States of America the eighty-sixth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
HON. JAMES POLLOCK.
MY DEAR SIR:—You must make a job for the bearer of this—make a job of it with the collector and have it done. You can do it for me and you must.
Yours as ever,
GOVERNOR MORTON, Indiana: Start your four regiments to St. Louis at the earliest moment possible. Get such harness as may be necessary for your rifled gums. Do not delay a single regiment, but hasten everything forward as soon as any one regiment is ready. Have your three additional regiments organized at once. We shall endeavor to send you the arms this week.
TO MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
Been answering your messages since day before yesterday. Do you receive the answers? The War Department has notified all the governors you designate to forward all available force. So telegraphed you. Have you received these messages? Answer immediately.
A Proclamation.
Whereas on the fifteenth day of April, eighteen hundred and sixty-one, the President of the United States, in view of an insurrection against the laws, Constitution, and government of the United States which had broken out within the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas, and in pursuance of the provisions of the act entitled "An act to provide for calling forth the militia to execute the laws of the Union, suppress insurrections, and repel invasions, and to repeal the act now in force for that purpose," approved February twenty-eighth, seventeen hundred and ninety-five, did call forth the militia to suppress said insurrection, and to cause the laws of the Union to be duly executed, and the insurgents have failed to disperse by the time directed by the President; and whereas such insurrection has since broken out and yet exists within the States of Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas; and whereas the insurgents in all the said States claim to act under the authority thereof, and such claim is not disclaimed or repudiated by the persons exercising the functions of government in such State or States, or in the part or parts thereof in which such combinations exist, nor has such insurrection been suppressed by said States:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, in pursuance of an act of Congress approved July thirteen, eighteen hundred and sixty-one, do hereby declare that the inhabitants of the said States of Georgia, South Carolina, Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama, Louisiana, Texas, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Florida (except the inhabitants of that part of the State of Virginia lying west of the Allegheny Mountains, and of such other parts of that State, and the other States hereinbefore named, as may maintain a loyal adhesion to the Union and the Constitution, or may be time to time occupied and controlled by forces of the United States engaged in the dispersion of said insurgents), are in a state of insurrection against the United States, and that all commercial intercourse between the same and the inhabitants thereof, with the exceptions aforesaid, and the citizens of other States and other parts of the United States, is unlawful, and will remain unlawful until such insurrection shall cease or has been suppressed; that all goods and chattels, wares and merchandise, coming from any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, into other parts of the United States, without the special license and permission of the President, through the Secretary of the Treasury, or proceeding to any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, by land or water, together with the vessel or vehicle conveying the same, or conveying persons to or from said States, with said exceptions, will be forfeited to the United States; and that from and after fifteen days from the issuing of this proclamation all ships and vessels belonging in whole or in part to any citizen or inhabitant of any of said States, with said exceptions, found at sea, or in any port of the United States, will be forfeited to the United States; and I hereby enjoin upon all district attorneys, marshals, and officers of the revenue and of the military and naval forces of the United States to be vigilant in the execution of said act, and in the enforcement of the penalties and forfeitures imposed or declared by it; leaving any party who may think himself aggrieved thereby to his application to the Secretary of the Treasury for the remission of any penalty or forfeiture, which the said Secretary is authorized by law to grant if, in his judgment, the special circumstances of any case shall require such remission.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand,....
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of Sate.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—Unless there be reason to the contrary, not known to me, make out a commission for Simon B. Buckner, of Kentucky, as a brigadier-general of volunteers. It is to be put into the hands of General Anderson, and delivered to General Buckner or not, at the discretion of General Anderson. Of course it is to remain a secret unless and until the commission is delivered.
Yours truly, A. LINCOLN
Same day made.
[Indorsement.]
To HIS EXCELLENCY B. MAGOFFIN, Governor of the State of Kentucky.
SIR:—Your letter of the 19th instant, in which you urge the "removal from the limits of Kentucky of the military force now organized and in camp within that State," is received.
I may not possess full and precisely accurate knowledge upon this subject; but I believe it is true that there is a military force in camp within Kentucky, acting by authority of the United States, which force is not very large, and is not now being augmented.
I also believe that some arms have been furnished to this force by the United States.
I also believe this force consists exclusively of Kentuckians, having their camp in the immediate vicinity of their own homes, and not assailing or menacing any of the good people of Kentucky.
In all I have done in the premises I have acted upon the urgent solicitation of many Kentuckians, and in accordance with what I believed, and still believe, to be the wish of a majority of all the Union-loving people of Kentucky.
While I have conversed on this subject with many eminent men of Kentucky, including a large majority of her members of Congress, I do not remember that any one of them, or any other person, except your Excellency and the bearers of your Excellency's letter, has urged me to remove the military force from Kentucky or to disband it. One other very worthy citizen of Kentucky did solicit me to have the augmenting of the force suspended for a time.
Taking all the means within my reach to form a judgment, I do not believe it is the popular wish of Kentucky that this force shall be removed beyond her limits; and, with this impression, I must respectfully decline to so remove it.
I most cordially sympathize with your Excellency in the wish to preserve the peace of my own native State, Kentucky. It is with regret I search, and cannot find, in your not very short letter, any declaration or intimation that you entertain any desire for the preservation of the Federal Union.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT.
MY DEAR SIR:—Two points in your proclamation of August 30 give me some anxiety.
First. Should you shoot a man, according to the proclamation, the Confederates would very certainly shoot our best men in their hands in retaliation; and so, man for man, indefinitely. It is, therefore, my order that you allow no man to be shot under the proclamation without first having my approbation or consent.
Second. I think there is great danger that the closing paragraph, in relation to the confiscation of property and the liberating slaves of traitorous owners, will alarm our Southern Union friends and turn them against us; perhaps ruin our rather fair prospect for Kentucky. Allow me, therefore, to ask that you will, as of your own motion, modify that paragraph so as to conform to the first and fourth sections of the act of Congress entitled "An act to confiscate property used for insurrectionary purposes," approved August 6, 1861, and a copy of which act I herewith send you.
This letter is written in a spirit of caution, and not of censure. I send it by special messenger, in order that it may certainly and speedily reach you.
Yours very truly,
WASHBURN OF MAINE, FAIRBANKS OF VERMONT, BERRY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE, ANDREW OF MASSACHUSETTS, BUCKINGHAM OF CONNECTICUT, AND SPRAGUE OF RHODE ISLAND.
WAR DEPARTMENT, September 11, 1861.
General Butler proposes raising in New England six regiments, to be recruited and commanded by himself, and to go on special service.
I shall be glad if you, as governor of ———, will answer by telegraph if you consent.
MAJOR-GENERAL JOHN C. FREMONT.
SIR:-Yours of the 8th, in answer to mine of the 2d instant, is just received. Assuming that you, upon the ground, could better judge of the necessities of your position than I could at this distance, on seeing your proclamation of August 30 I perceived no general objection to it. The particular clause, however, in relation to the confiscation of property and the liberation of slaves appeared to me to be objectionable in its nonconformity to the act of Congress passed the 6th of last August upon the same subjects; and hence I wrote you, expressing my wish that that clause should be modified accordingly. Your answer, just received, expresses the preference on your part that I should make an open order for the modification, which I very cheerfully do. It is therefore ordered that the said clause of said proclamation be so modified, held, and construed as to conform to, and not to transcend, the provisions on the same subject contained in the act of Congress entitled "An act to confiscate property used for insurrectionary purposes," approved August 6, 1861, and that said act be published at length with this order.
Your obedient servant,
Mrs. GENERAL FREMONT.
MY DEAR MADAM:—Your two notes of to-day are before me. I answered the letter you bore me from General Fremont on yesterday, and not hearing from you during the day, I sent the answer to him by mail. It is not exactly correct, as you say you were told by the elder Mr. Blair, to say that I sent Postmaster-General Blair to St. Louis to examine into that department and report. Postmaster-General Blair did go, with my approbation, to see and converse with General Fremont as a friend. I do not feel authorized to furnish you with copies of letters in my possession without the consent of the writers. No impression has been made on my mind against the honor or integrity of General Fremont, and I now enter my protest against being understood as acting in any hostility toward him.
Your obedient servant,
HON. JOSEPH HOLT.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of this day in relation to the late proclamation of General Fremont is received yesterday I addressed a letter to him, by mail, on the same subject, and which is to be made public when he receives it. I herewith send you a copy of that letter, which perhaps shows my position as distinctly as any new one I could write. I will thank you not to make it public until General Fremont shall have had time to receive the original.
Your obedient servant,
DEAR SIR:—Since conversing with you I have concluded to request you to frame an order for recruiting North Carolinians at Fort Hatteras. I suggest it to be so framed as for us to accept a smaller force—even a company—if we cannot get a regiment or more. What is necessary to now say about officers you will judge. Governor Seward says he has a nephew (Clarence A. Seward, I believe) who would be willing to go and play colonel and assist in raising the force. Still it is to be considered whether the North Carolinians will not prefer officers of their own. I should expect they would.
Yours very truly,
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR. MY DEAR SIR:—To guard against misunderstanding, I think fit to say that the joint expedition of the army and navy agreed upon some time since, and in which General T. W. Sherman was and is to bear a conspicuous part, is in no wise to be abandoned, but must be ready to move by the 1st of, or very early in, October. Let all preparations go forward accordingly.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
Governor Morton telegraphs as follows: "Colonel Lane, just arrived by special train, represents Owensborough, forty miles above Evansville, in possession of secessionists. Green River is navigable. Owensborough must be seized. We want a gunboat sent up from Paducah for that purpose." Send up the gunboat if, in your discretion, you think it right. Perhaps you had better order those in charge of the Ohio River to guard it vigilantly at all points.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON SEPTEMBER 22, 1861 HON. O. H. BROWNING.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 17th is just received; and coming from you, I confess it astonishes me. That you should object to my adhering to a law which you had assisted in making and presenting to me less than a month before is odd enough. But this is a very small part. General Fremont's proclamation as to confiscation of property and the liberation of slaves is purely political and not within the range of military law or necessity. If a commanding general finds a necessity to seize the farm of a private owner for a pasture, an encampment, or a fortification, he has the right to do so, and to so hold it as long as the necessity lasts; and this is within military law, because within military necessity. But to say the farm shall no longer belong to the owner, or his heirs forever, and this as well when the farm is not needed for military purposes as when it is, is purely political, without the savor of military law about it. And the same is true of slaves. If the general needs them, he can seize them and use them; but when the need is past, it is not for him to fix their permanent future condition. That must be settled according to laws made by law-makers, and not by military proclamations. The proclamation in the point in question is simply "dictatorship." It assumes that the general may do anything he pleases confiscate the lands and free the slaves of loyal people, as well as of disloyal ones. And going the whole figure, I have no doubt, would be more popular with some thoughtless people than that which has been done, But I cannot assume this reckless position, nor allow others to assume it on my responsibility.
You speak of it as being the only means of saving the government. On the contrary, it is itself the surrender of the government. Can it be pretended that it is any longer the Government of the United States—any government of constitution and laws wherein a general or a president may make permanent rules of property by proclamation? I do not say Congress might not with propriety pass a law on the point, just such as General Fremont proclaimed.
I do not say I might not, as a member of Congress, vote for it. What I object to is, that I, as President, shall expressly or impliedly seize and exercise the permanent legislative functions of the government.
So much as to principle. Now as to policy. No doubt the thing was popular in some quarters, and would have been more so if it had been a general declaration of emancipation. The Kentucky Legislature would not budge till that proclamation was modified; and General Anderson telegraphed me that on the news of General Fremont having actually issued deeds of manumission, a whole company of our volunteers threw down their arms and disbanded. I was so assured as to think it probable that the very arms we had furnished Kentucky would be turned against us. I think to lose Kentucky is nearly the same as to lose the whole game. Kentucky gone, we cannot hold Missouri, nor, as I think, Maryland. These all against us, and the job on our hands is too large for us. We would as well consent to separation at once, including the surrender of this Capital. On the contrary, if you will give up your restlessness for new positions, and back me manfully on the grounds upon which you and other kind friends gave me the election and have approved in my public documents, we shall go through triumphantly. You must not understand I took my course on the proclamation because of Kentucky. I took the same ground in a private letter to General Fremont before I heard from Kentucky.
You think I am inconsistent because I did not also forbid General Fremont to shoot men under the proclamation. I understand that part to be within military law, but I also think, and so privately wrote General Fremont, that it is impolitic in this, that our adversaries have the power, and will certainly exercise it, to shoot as many of our men as we shoot of theirs. I did not say this in the public letter, because it is a subject I prefer not to discuss in the hearing of our enemies.
There has been no thought of removing General Fremont on any ground connected with his proclamation, and if there has been any wish for his removal on any ground, our mutual friend Sam. Glover can probably tell you what it was. I hope no real necessity for it exists on any ground.
Your friend, as ever,
On or about the 5th of October (the exact date to be determined hereafter) I wish a movement made to seize and hold a point on the railroad connecting Virginia and Tennessee near the mountain-pass called Cumberland Gap. That point is now guarded against us by Zollicoffer, with 6000 or 8000 rebels at Barboursville Ky.,—say twenty-five miles from the Gap, toward Lexington. We have a force of 5000 or 6000 under General Thomas, at Camp Dick Robinson, about twenty-five miles from Lexington and seventy-five from Zollicoffer's camp, On the road between the two. There is not a railroad anywhere between Lexington and the point to be seized, and along the whole length of which the Union sentiment among the people largely predominates. We have military possession of the railroad from Cincinnati to Lexington, and from Louisville to Lexington, and some home guards, under General Crittenden, are on the latter line. We have possession of the railroad from Louisville to Nashville, Tenn., so far as Muldraugh's Hill, about forty miles, and the rebels have possession of that road all south of there. At the Hill we have a force of 8000, under General Sherman, and about an equal force of rebels is a very short distance south, under General Buckner.
We have a large force at Paducah, and a smaller at Port Holt, both on the Kentucky side, with some at Bird's Point, Cairo, Mound City, Evansville, and New Albany, all on the other side, and all which, with the gunboats on the river, are perhaps sufficient to guard the Ohio from Louisville to its mouth.
About supplies of troops, my general idea is that all from Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, and Kansas, not now elsewhere, be left to Fremont. All from Indiana and Michigan, not now elsewhere, be sent to Anderson at Louisville. All from Ohio needed in western Virginia be sent there, and any remainder be sent to Mitchell at Cincinnati, for Anderson. All east of the mountains be appropriated to McClellan and to the coast.
As to movements, my idea is that the one for the coast and that on Cumberland Gap be simultaneous, and that in the meantime preparation, vigilant watching, and the defensive only be acted upon; this, however, not to apply to Fremont's operations in northern and middle Missouri. That before these movements Thomas and Sherman shall respectively watch but not attack Zollicoffer and Buckner. That when the coast and Gap movements shall be ready Sherman is merely to stand fast, while all at Cincinnati and all at Louisville, with all on the line, concentrate rapidly at Lexington, and thence to Thomas's camp, joining him, and the whole thence upon the Gap. It is for the military men to decide whether they can find a pass through the mountains at or near the Gap which cannot be defended by the enemy with a greatly inferior force, and what is to be done in regard to this.
The coast and Gap movements made, Generals McClellan and Fremont, in their respective departments, will avail themselves of any advantages the diversions may present.
[He was entirely unable to get this started, Sherman would have taken an active part if given him, the others were too busy getting lines of communication guarded—and discovering many "critical" supply items that had not been sent them. Also the commanding general did not like it. D.W.]
HONORABLE SECRETARY OF STATE.
DEAR SIR:—Please see Mr. Walker, well vouched as a Union man and son-in-law of Governor Morehead, and pleading for his release. I understand the Kentucky arrests were not made by special direction from here, and I am willing if you are that any of the parties may be released when James Guthrie and James Speed think they should be.
Yours truly,
GREAT AND GOOD FRIEND:—I have received from Mr. Thayer, Consul-General of the United States at Alexandria, a full account of the liberal, enlightened, and energetic proceedings which, on his complaint, you have adopted in bringing to speedy and condign punishment the parties, subjects of your Highness in Upper Egypt, who were concerned in an act of criminal persecution against Faris, an agent of certain Christian missionaries in Upper Egypt. I pray your Highness to be assured that these proceedings, at once so prompt and so just, will be regarded as a new and unmistakable proof equally of your Highness's friendship for the United States and of the firmness, integrity and wisdom, with which the government of your Highness is conducted. Wishing you great prosperity and success, I am your friend,
A. LINCOLN.
HIS HIGHNESS MOHAMMED SAID PACHA, Viceroy of Egypt and its Dependencies, etc.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL WINFIELD SCOTT:
The military line of the United States for the suppression of the insurrection may be extended so far as Bangor, in Maine. You and any officer acting under your authority are hereby authorized to suspend the writ of habeas corpus in any place between that place and the city of Washington.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
HON. SEC. OF INTERIOR.
DEAR SIR:—How is this? I supposed I was appointing for register of wills a citizen of this District. Now the commission comes to me "Moses Kelly, of New Hampshire." I do not like this.
Yours truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, October 17, 1861
MAJOR RAMSEY.
MY DEAR SIR:—The lady bearer of this says she has two sons who want to work. Set them at it if possible. Wanting to work is so rare a want that it should be encouraged.
Yours truly,
GENERAL THOMAS SHERMAN, Annapolis, Md.:
Your despatch of yesterday received and shown to General McClellan. I have promised him not to direct his army here without his consent. I do not think I shall come to Annapolis.
BRIGADIER-GENERAL S. R. CURTIS.
MY DEAR SIR:—Herewith is a document—half letter, half order—which, wishing you to see, but not to make public, I send unsealed. Please read it and then inclose it to the officer who may be in command of the Department of the West at the time it reaches him. I cannot now know whether Fremont or Hunter will then be in command.
Yours truly,
DEAR SIR:—On receipt of this, with the accompanying inclosures, you will take safe, certain, and suitable measures to have the inclosure addressed to Major-General Fremont delivered to him with all reasonable despatch, subject to these conditions only: that if, when General Fremont shall be reached by the messenger—yourself or any one sent by you—he shall then have, in personal command, fought and won a battle, or shall then be actually in a battle, or shall then be in the immediate presence of the enemy in expectation of a battle, it is not to be delivered, but held for further orders. After, and not till after, the delivery to General Fremont, let the inclosure addressed to General Hunter be delivered to him.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
(General Orders No. 18.) HEADQUARTERS OF THE ARMY,
WASHINGTON, October 24, 1861
Major-General Fremont, of the United States Army, the present commander of the Western Department of the same, will, on the receipt of this order, call Major-General Hunter, of the United States Volunteers, to relieve him temporarily in that command, when he (Major-General Fremont) will report to general headquarters by letter for further orders.
WINFIELD SCOTT. By command: E. D. TOWNSEND, Assistant Adjutant-General.
SIR:—The command of the Department of the West having devolved upon you, I propose to offer you a few suggestions. Knowing how hazardous it is to bind down a distant commander in the field to specific lines and operations, as so much always depends on a knowledge of localities and passing events, it is intended, therefore, to leave a considerable margin for the exercise of your judgment and discretion.
The main rebel army (Price's) west of the Mississippi is believed to have passed Dade County in full retreat upon northwestern Arkansas, leaving Missouri almost freed from the enemy, excepting in the southeast of the State. Assuming this basis of fact, it seems desirable, as you are not likely to overtake Price, and are in danger of making too long a line from your own base of supplies and reinforcements, that you should give up the pursuit, halt your main army, divide it into two corps of observation, one occupying Sedalia and the other Rolla, the present termini of railroads; then recruit the condition of both corps by re-establishing and improving their discipline and instructions, perfecting their clothing and equipments, and providing less uncomfortable quarters. Of course, both railroads must be guarded and kept open, judiciously employing just so much force as is necessary for this. From these two points, Sedalia and Rolla, and especially in judicious cooperation with Lane on the Kansas border, it would be so easy to concentrate and repel any army of the enemy returning on Missouri from the southwest, that it is not probable any such attempt will be made before or during the approaching cold weather. Before spring the people of Missouri will probably be in no favorable mood to renew for next year the troubles which have so much afflicted and impoverished them during this. If you adopt this line of policy, and if, as I anticipate, you will see no enemy in great force approaching, you will have a surplus of force which you can withdraw from these points and direct to others as may be needed, the railroads furnishing ready means of reinforcing these main points if occasion requires. Doubtless local uprisings will for a time continue to occur, but these can be met by detachments and local forces of our own, and will ere long tire out of themselves.
While, as stated in the beginning of the letter, a large discretion must be and is left with yourself, I feel sure that an indefinite pursuit of Price or an attempt by this long and circuitous route to reach Memphis will be exhaustive beyond endurance, and will end in the loss of the whole force engaged in it.
Your obedient servant,
WAR DEPARTMENT, ADJUTANT-GENERAL'S OFFICE
WASHINGTON, November 1, 1861
The following order from the President of the United States, announcing the retirement from active command of the honored veteran Lieutenant general Winfield Scott, will be read by the army with profound regret:
On the 1st day of November, A.D. 1861, upon his own application to the President of the United States, Brevet Lieutenant-General Winfield Scott is ordered to be placed, and hereby is placed, upon the list of retired officers of the army of the United States, without reduction in his current pay, subsistence, or allowances.
The American people will hear with sadness and deep emotion that General Scott has withdrawn from the active control of the army, while the President and a unanimous Cabinet express their own and the nation's sympathy in his personal affliction and their profound sense of the important public services rendered by him to his country during his long and brilliant career, among which will ever be gratefully distinguished his faithful devotion to the Constitution, the Union, and the flag when assailed by parricidal rebellion.
A. LINCOLN
The President is pleased to direct that Major general George B. McClellan assume the command of the army of the United States. The headquarters of the army will be established in the city of Washington. All communications intended for the commanding general will hereafter be addressed direct to the adjutant-general. The duplicate returns, orders, and other papers heretofore sent to the assistant adjutant-general, headquarters of the army, will be discontinued.
By order of the Secretary of War: L. THOMAS, Adjutant General.
November 5, 1861.
The Governor of the State of Missouri, acting under the direction of the convention of that State, proposes to the Government of the United States that he will raise a military force to serve within the State as State militia during the war there, to cooperate with the troops in the service of the United States in repelling the invasion of the State and suppressing rebellion therein; the said State militia to be embodied and to be held in the camp and in the field, drilled, disciplined, and governed according to the Army Regulations and subject to the Articles of War; the said State militia not to be ordered out of the State except for the immediate defense of the State of Missouri, but to co-operate with the troops in the service of the United States in military operations within the State or necessary to its defense, and when officers of the State militia act with officers in the service of the United States of the same grade the officers of the United States service shall command the combined force; the State militia to be armed, equipped, clothed, subsisted, transported, and paid by the United States during such time as they shall be actually engaged as an embodied military force in service in accordance with regulations of the United States Army or general orders as issued from time to time.
In order that the Treasury of the United States may not be burdened with the pay of unnecessary officers, the governor proposes that, although the State law requires him to appoint upon the general staff an adjutant-general, a commissary-general, an inspector-general, a quartermaster-general, a paymaster-general, and a surgeon-general, each with the rank of colonel of cavalry, yet he proposes that the Government of the United States pay only the adjutant-general, the quartermaster-general, and inspector-general, their services being necessary in the relations which would exist between the State militia and the United States. The governor further proposes that while he is allowed by the State law to appoint aides-de-camp to the governor at his discretion, with the rank of colonel, three only shall be reported to the United States for payment. He also proposes that the State militia shall be commanded by a single major-general and by such number of brigadier-generals as shall allow one for a brigade of not less than four regiments, and that no greater number of staff officers shall be appointed for regimental, brigade, and division duties than as provided for in the act of Congress of the 22d July, 1861; and that, whatever be the rank of such officers as fixed by the law of the State, the compensation that they shall receive from the United States shall only be that which belongs to the rank given by said act of Congress to officers in the United States service performing the same duties.
The field officers of a regiment in the State militia are one colonel, one lieutenant-colonel, and one major, and the company officers are a captain, a first lieutenant, and a second lieutenant. The governor proposes that, as the money to be disbursed is the money of the United States, such staff officers in the service of the United States as may be necessary to act as disbursing officers for the State militia shall be assigned by the War Department for that duty; or, if such cannot be spared from their present duty, he will appoint such persons disbursing officers for the State militia as the President of the United States may designate. Such regulations as may be required, in the judgment of the President, to insure regularity of returns and to protect the United States from any fraudulent practices shall be observed and obeyed by all in office in the State militia.
The above propositions are accepted on the part of the United States, and the Secretary of War is directed to make the necessary orders upon the Ordnance, Quartermaster's, Commissary, Pay, and Medical departments to carry this agreement into effect. He will cause the necessary staff officers in the United States service to be detailed for duty in connection with the Missouri State militia, and will order them to make the necessary provision in their respective offices for fulfilling this agreement. All requisitions upon the different officers of the United States under this agreement to be made in substance in the same mode for the Missouri State militia as similar requisitions are made for troops in the service of the United States; and the Secretary of War will cause any additional regulations that may be necessary to insure regularity and economy in carrying this agreement into effect to be adopted and communicated to the Governor of Missouri for the government of the Missouri State militia.
[Indorsement.]
November 6, 1861.
This plan approved, with the modification that the governor stipulates that when he commissions a major-general of militia it shall be the same person at the time in command of the United States Department of the West; and in case the United States shall change such commander of the department, he (the governor) will revoke the State commission given to the person relieved and give one to the person substituted to the United States command of said department.
SIR:—I receive with great pleasure a Minister from Sweden. That pleasure is enhanced by the information which preceded your arrival here, that his Majesty, your sovereign, had selected you to fill the mission upon the grounds of your derivation from an ancestral stock identified with the most glorious era of your country's noble history, and your own eminent social and political standing in Sweden. This country, sir, maintains, and means to maintain, the rights of human nature, and the capacity of men for self-government. The history of Sweden proves that this is the faith of the people of Sweden, and we know that it is the faith and practice of their respected sovereign. Rest assured, therefore, that we shall be found always just and paternal in our transactions with your government, and that nothing will be omitted on my part to make your residence in this capital agreeable to yourself and satisfactory to your government.
GENERAL McCLELLAN,
For the President of the United States.
No written authority is found here to declare and enforce martial law in this department. Please send me such written authority and telegraph me that it has been sent by mail.
H. W. HALLECK, Major-General.
[Indorsement.] November 21, 1861.
If General McClellan and General Halleck deem it necessary to declare and maintain martial law in Saint Louis, the same is hereby authorized.
WASHINGTON, November 21, 1861
DEAR GOVERNOR:—I have thought over the interview which Mr. Gilmore has had with Mr. Greeley, and the proposal that Greeley has made to Gilmore, namely, that he [Gilmore] shall communicate to him [Greeley] all that he learns from you of the inner workings of the administration, in return for his [Greeley's] giving such aid as he can to the new magazine, and allowing you [Walker] from time to time the use of his [Greeley's] columns when it is desirable to feel of, or forestall, public opinion on important subjects. The arrangement meets my unqualified approval, and I shall further it to the extent of my ability, by opening to you—as I do now—fully the policy of the Government,—its present views and future intentions when formed, giving you permission to communicate them to Gilmore for Greeley; and in case you go to Europe I will give these things direct to Gilmore. But all this must be on the express and explicit understanding that the fact of these communications coming from me shall be absolutely confidential,—not to be disclosed by Greeley to his nearest friend, or any of his subordinates. He will be, in effect, my mouthpiece, but I must not be known to be the speaker.
I need not tell you that I have the highest confidence in Mr. Greeley. He is a great power. Having him firmly behind me will be as helpful to me as an army of one hundred thousand men.
This was to be most severely regretted, when Greeley became a traitor to the cause, editorialized for compromise and separation—and promoted McClellan as Democratic candidate for the Presidency.
That he has ever kicked the traces has been owing to his not being fully informed. Tell Gilmore to say to him that, if he ever objects to my policy, I shall be glad to have him state to me his views frankly and fully. I shall adopt his if I can. If I cannot, I will at least tell him why. He and I should stand together, and let no minor differences come between us; for we both seek one end, which is the saving of our country. Now, Governor, this is a longer letter than I have written in a month,—longer than I would have written for any other man than Horace Greeley.
Your friend, truly,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—The sooner Gilmore sees Greeley the better, as you may before long think it wise to ventilate our policy on the Trent affair.
MAJOR-GENERAL H. W. HALLECK, Commanding in the Department of Missouri.
GENERAL:—As an insurrection exists in the United States, and is in arms in the State of Missouri, you are hereby authorized and empowered to suspend the writ of habeas corpus within the limits of the military division under your command, and to exercise martial law as you find it necessary in your discretion to secure the public safety and the authority of the United States.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed at Washington, this second day of December, A.D. 1861.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:—In the midst of unprecedented political troubles we have cause of great gratitude to God for unusual good health and most abundant harvests.
You will not be surprised to learn that in the peculiar exigencies of the times our intercourse with foreign nations has been attended with profound solicitude, chiefly turning upon our own domestic affairs.
A disloyal portion of the American people have during the whole year been engaged in an attempt to divide and destroy the Union. A nation which endures factious domestic division is exposed to disrespect abroad, and one party, if not both, is sure sooner or later to invoke foreign intervention.
Nations thus tempted to interfere are not always able to resist the counsels of seeming expediency and ungenerous ambition, although measures adopted under such influences seldom fail to be unfortunate and injurious to those adopting them.
The disloyal citizens of the United States who have offered the ruin of our country in return for the aid and comfort which they have invoked abroad have received less patronage and encouragement than they probably expected. If it were just to suppose, as the insurgents have seemed to assume, that foreign nations in this case, discarding all moral, social, and treaty obligations, would act solely and selfishly for the most speedy restoration of commerce, including especially the acquisition of cotton, those nations appear as yet not to have seen their way to their object more directly or clearly through the destruction than through the preservation of the Union. If we could dare to believe that foreign nations are actuated by no higher principle than this, I am quite sure a sound argument could be made to show them that they can reach their aim more readily and easily by aiding to crush this rebellion than by giving encouragement to it.
The principal lever relied on by the insurgents for exciting foreign nations to hostility against us, as already intimated, is the embarrassment of commerce. Those nations, however, not improbably saw from the first that it was the Union which made as well our foreign as our domestic commerce. They can scarcely have failed to perceive that the effort for disunion produces the existing difficulty, and that one strong nation promises more durable peace and a more extensive, valuable, and reliable commerce than can the same nation broken into hostile fragments.
It is not my purpose to review our discussions with foreign states, because, whatever might be their wishes or dispositions, the integrity of our country and the stability of our government mainly depend not upon them, but on the loyalty, virtue, patriotism, and intelligence of the American people. The correspondence itself, with the usual reservations, is herewith submitted.
I venture to hope it will appear that we have practiced prudence and liberality toward foreign powers, averting causes of irritation and with firmness maintaining our own rights and honor.
Since, however, it is apparent that here, as in every other state, foreign dangers necessarily attend domestic difficulties, I recommend that adequate and ample measures be adopted for maintaining the public defenses on every side. While under this general recommendation provision for defending our seacoast line readily occurs to the mind, I also in the same connection ask the attention of Congress to our great lakes and rivers. It is believed that some fortifications and depots of arms and munitions, with harbor and navigation improvements, all at well-selected points upon these, would be of great importance to the national defense and preservation I ask attention to the views of the Secretary of War, expressed in his report, upon the same general subject.
I deem it of importance that the loyal regions of east Tennessee and western North Carolina should be connected with Kentucky and other faithful parts of the Union by rail-road. I therefore recommend, as a military measure, that Congress provide for the construction of such rail-road as speedily as possible. Kentucky will no doubt co-operate, and through her Legislature make the most judicious selection of a line. The northern terminus must connect with some existing railroad, and whether the route shall be from Lexington or Nicholasville to the Cumberland Gap, or from Lebanon to the Tennessee line, in the direction of Knoxville, or on some still different line, can easily be determined. Kentucky and the General Government co-operating, the work can be completed in a very short time, and when done it will be not only of vast present usefulness but also a valuable permanent improvement, worth its cost in all the future.
Some treaties, designed chiefly for the interests of commerce, and having no grave political importance, have been negotiated, and will be submitted to the Senate for their consideration.
Although we have failed to induce some of the commercial powers to adopt a desirable melioration of the rigor of maritime war, we have removed all obstructions from the way of this humane reform except such as are merely of temporary and accidental occurrence.
I invite your attention to the correspondence between her Britannic Majesty's minister accredited to this government and the Secretary of State relative to the detention of the British ship Perthshire in June last by the United States steamer Massachusetts for a supposed breach of the blockade. As this detention was occasioned by an obvious misapprehension of the facts, and as justice requires that we should commit no belligerent act not founded in strict right as sanctioned by public law, I recommend that an appropriation be made to satisfy the reasonable demand of the owners of the vessel for her detention.
I repeat the recommendation of my predecessor in his annual message to Congress in December last in regard to the disposition of the surplus which will probably remain after satisfying the claims of American citizens against China, pursuant to the awards of the commissioners under the act of the 3d of March, 1859. If, however, it should not be deemed advisable to carry that recommendation into effect, I would suggest that authority be given for investing the principal, or the proceeds of the surplus referred to, in good securities, with a view to the satisfaction of such other just claims of our citizens against China as are not unlikely to arise hereafter in the course of our extensive trade with that empire.
By the act of the 5th of August last Congress authorized the President to instruct the commanders of suitable vessels to defend themselves against and to capture pirates. His authority has been exercised in a single instance only. For the more effectual protection of our extensive and valuable commerce in the Eastern seas especially, it seems to me that it would also be advisable to authorize the commanders of sailing vessels to recapture any prizes which pirates may make of United States vessels and their cargoes, and the consular courts now established by law in Eastern countries to adjudicate the cases in the event that this should not be objected to by the local authorities.
If any good reason exists why we should persevere longer in withholding our recognition of the independence and sovereignty of Haiti and Liberia, I am unable to discern it. Unwilling, however, to inaugurate a novel policy in regard to them without the approbation of Congress, I submit for your consideration the expediency of an appropriation for maintaining a charge d'affaires near each of those new States. It does not admit of doubt that important commercial advantages might be secured by favorable treaties with them.
The operations of the treasury during the period which has elapsed since your adjournment have been conducted with signal success. The patriotism of the people has placed at the disposal of the government the large means demanded by the public exigencies. Much of the national loan has been taken by citizens of the industrial classes, whose confidence in their country's faith and zeal for their country's deliverance from present peril have induced them to contribute to the support of the government the whole of their limited acquisitions. This fact imposes peculiar obligations to economy in disbursement and energy in action.
The revenue from all sources, including loans, for the financial year ending on the 30th of June, 1861, was $86,835,900.27, and the expenditures for the same period, including payments on account of the public debt, were $84,578,834.47, leaving a balance in the treasury on the 1st of July of $2,257,065.80. For the first quarter of the financial year ending on the 30th of September, 1861, the receipts from all sources, including the balance of the 1st of July, were $102,532,509.27, and the expenses $98,239733.09, leaving a balance on the 1st of October, 1861, of $4,292,776.18.
Estimates for the remaining three quarters of the year and for the financial year 1863, together with his views of ways and means for meeting the demands contemplated by them, will be submitted to Congress by the Secretary of the Treasury. It is gratifying to know that the expenditures made necessary by the rebellion are not beyond the resources of the loyal people, and to believe that the same patriotism which has thus far sustained the government will continue to sustain it till peace and union shall again bless the land.
I respectfully refer to the report of the Secretary of War for information respecting the numerical strength of the army and for recommendations having in view an increase of its efficiency and the well-being of the various branches of the service intrusted to his care. It is gratifying to know that the patriotism of the people has proved equal to the occasion, and that the number of troops tendered greatly exceeds the force which Congress authorized me to call into the field.
I refer with pleasure to those portions of his report which make allusion to the creditable degree of discipline already attained by our troops and to the excellent sanitary condition of the entire army.
The recommendation of the Secretary for an organization of the militia upon a uniform basis is a subject of vital importance to the future safety of the country, and is commended to the serious attention of Congress.
The large addition to the regular army, in connection with the defection that has so considerably diminished the number of its officers, gives peculiar importance to his recommendation for increasing the corps of cadets to the greatest capacity of the Military Academy.
By mere omission, I presume, Congress has failed to provide chaplains for hospitals occupied by volunteers. This subject was brought to my notice, and I was induced to draw up the form of a letter, one copy of which, properly addressed, has been delivered to each of the persons, and at the dates respectively named and stated in a schedule, containing also the form of the letter, marked A, and herewith transmitted.
These gentlemen, I understand, entered upon the duties designated at the times respectively stated in the schedule, and have labored faithfully therein ever since. I therefore recommend that they be compensated at the same rate as chaplains in the army. I further suggest that general provision be made for chaplains to serve at hospitals, as well as with regiments.
The report of the Secretary of the Navy presents in detail the operations of that branch of the service, the activity and energy which have characterized its administration, and the results of measures to increase its efficiency and power such have been the additions, by construction and purchase, that it may almost be said a navy has been created and brought into service since our difficulties commenced.
Besides blockading our extensive coast, squadrons larger than ever before assembled under our flag have been put afloat and performed deeds which have increased our naval renown.
I would invite special attention to the recommendation of the Secretary for a more perfect organization of the navy by introducing additional grades in the service.
The present organization is defective and unsatisfactory, and the suggestions submitted by the department will, it is believed, if adopted, obviate the difficulties alluded to, promote harmony, and increase the efficiency of the navy.
There are three vacancies on the bench of the Supreme Court—two by the decease of Justices Daniel and McLean and one by the resignation of Justice Campbell. I have so far forborne making nominations to fill these vacancies for reasons which I will now state. Two of the outgoing judges resided within the States now overrun by revolt, so that if successors were appointed in the same localities they could not now serve upon their circuits; and many of the most competent men there probably would not take the personal hazard of accepting to serve, even here, upon the Supreme bench. I have been unwilling to throw all the appointments north-ward, thus disabling myself from doing justice to the South on the return of peace; although I may remark that to transfer to the North one which has heretofore been in the South would not, with reference to territory and population, be unjust.
During the long and brilliant judicial career of Judge McLean his circuit grew into an empire-altogether too large for any one judge to give the courts therein more than a nominal attendance—rising in population from 1,470,018 in 1830 to 6,151,405 in 1860.
Besides this, the country generally has outgrown our present judicial system. If uniformity was at all intended, the system requires that all the States shall be accommodated with circuit courts, attended by Supreme judges, while, in fact, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Kansas, Florida, Texas, California, and Oregon have never had any such courts. Nor can this well be remedied without a change in the system, because the adding of judges to the Supreme Court, enough for the accommodation of all parts of the country with circuit courts, would create a court altogether too numerous for a judicial body of any sort. And the evil, if it be one, will increase as new States come into the Union. Circuit courts are useful or they are not useful. If useful, no State should be denied them; if not useful, no State should have them. Let them be provided for all or abolished as to all.
Three modifications occur to me, either of which, I think, would be an improvement upon our present system. Let the Supreme Court be of convenient number in every event; then, first, let the whole country be divided into circuits of convenient size, the Supreme judges to serve in a number of them corresponding to their own number, and independent circuit judges be provided for all the rest; or, secondly, let the Supreme judges be relieved from circuit duties and circuit judges provided for all the circuits; or, thirdly, dispense with circuit courts altogether, leaving the judicial functions wholly to the district courts and an independent Supreme Court.
I respectfully recommend to the consideration of Congress the present condition of the statute laws, with the hope that Congress will be able to find an easy remedy for many of the inconveniences and evils which constantly embarrass those engaged in the practical administration of them. Since the Organization of the government, Congress has enacted some 5000 acts and joint resolutions, which fill more than 6000 closely printed pages and are scattered through many volumes. Many of these acts have been drawn in haste and without sufficient caution, so that their provisions are often obscure in themselves or in conflict with each other, or at least so doubtful as to render it very difficult for even the best-informed persons to ascertain precisely what the statute law really is.
It seems to me very important that the statute laws should be made as plain and intelligible as possible, and be reduced to as small a compass as may consist with the fullness and precision of the will of the Legislature and the perspicuity of its language. This well done would, I think, greatly facilitate the labors of those whose duty it is to assist in the administration of the laws, and would be a lasting benefit to the people, by placing before them in a more accessible and intelligible form the laws which so deeply concern their interests and their duties.
I am informed by some whose opinions I respect that all the acts of Congress now in force and of a permanent and general nature might be revised and rewritten so as to be embraced in one volume (or at most two volumes) of ordinary and convenient size; and I respectfully recommend to Congress to consider of the subject, and if my suggestion be approved to devise such plan as to their wisdom shall seem most proper for the attainment of the end proposed.
One of the unavoidable consequences of the present insurrection is the entire suppression in many places of all the ordinary means of administering civil justice by the officers and in the forms of existing law. This is the case, in whole or in part, in all the insurgent States; and as our armies advance upon and take possession of parts of those States the practical evil becomes more apparent. There are no courts or officers to whom the citizens of other States may apply for the enforcement of their lawful claims against citizens of the insurgent States, and there is a vast amount of debt constituting such claims. Some have estimated it as high as $200,000,000, due in large part from insurgents in open rebellion to loyal citizens who are even now making great sacrifices in the discharge of their patriotic duty to support the government.
Under these circumstances I have been urgently solicited to establish, by military power, courts to administer summary justice in such cases. I have thus far declined to do it, not because I had any doubt that the end proposed—the collection of the debts—was just and right in itself, but because I have been unwilling to go beyond the pressure of necessity in the unusual exercise of power. But the powers of Congress, I suppose, are equal to the anomalous occasion, and therefore I refer the whole matter to Congress, with the hope that a plan maybe devised for the administration of justice in all such parts of the insurgent States and Territories as may be under the control of this government, whether by a voluntary return to allegiance and order or by the power of our arms; this, however, not to be a permanent institution, but a temporary substitute, and to cease as soon as the ordinary courts can be reestablished in peace.
It is important that some more convenient means should be provided, if possible, for the adjustment of claims against the government, especially in view of their increased number by reason of the war. It is as much the duty of government to render prompt justice against itself in favor of citizens as it is to administer the same between private individuals. The investigation and adjudication of claims in their nature belong to the judicial department. Besides, it is apparent that the attention of Congress will be more than usually engaged for some time to come with great national questions. It was intended by the organization of the Court of Claims mainly to remove this branch of business from the halls of Congress; but, while the court has proved to be an effective and valuable means of investigation, it in great degree fails to effect the object of its creation for want of power to make its judgments final.
Fully aware of the delicacy, not to say the danger of the subject, I commend to your careful consideration whether this power of making judgments final may not properly be given to the court, reserving the right of appeal on questions of law to the Supreme Court, with such other provisions as experience may have shown to be necessary.
I ask attention to the report of the Postmaster general, the following being a summary statement of the condition of the department:
The revenue from all sources during the fiscal year ending June 30, 1861, including the annual permanent appropriation of $700,000 for the transportation of "free mail matter," was $9,049,296.40, being about 2 per cent. less than the revenue for 1860.
The expenditures were $13,606,759.11, showing a decrease of more than 8 per cent. as compared with those of the previous year and leaving an excess of expenditure over the revenue for the last fiscal year of $4,557,462.71.
The gross revenue for the year ending June 30, 1863, is estimated at an increase of 4 per cent. on that of 1861, making $8,683,000, to which should be added the earnings of the department in carrying free matter, viz., $700,000, making $9,383,000.
The total expenditures for 1863 are estimated at $12,528,000, leaving an estimated deficiency of $3,145,000 to be supplied from the treasury in addition to the permanent appropriation.
The present insurrection shows, I think, that the extension of this District across the Potomac River at the time of establishing the capital here was eminently wise, and consequently that the relinquishment of that portion of it which lies within the State of Virginia was unwise and dangerous. I submit for your consideration the expediency of regaining that part of the District and the restoration of the original boundaries thereof through negotiations with the State of Virginia.
The report of the Secretary of the Interior, with the accompanying documents, exhibits the condition of the several branches of the public business pertaining to that department. The depressing influences of the insurrection have been specially felt in the operations of the Patent and General Land Offices. The cash receipts from the sales of public lands during the past year have exceeded the expenses of our land system only about $200,000. The sales have been entirely suspended in the Southern States, while the interruptions to the business of the country and the diversion of large numbers of men from labor to military service have obstructed settlements in the new States and Territories of the Northwest.
The receipts of the Patent Office have declined in nine months about $100,000.00 rendering a large reduction of the force employed necessary to make it self-sustaining.
The demands upon the Pension Office will be largely increased by the insurrection. Numerous applications for pensions, based upon the casualties of the existing war, have already been made. There is reason to believe that many who are now upon the pension rolls and in receipt of the bounty of the government are in the ranks of the insurgent army or giving them aid and comfort. The Secretary of the Interior has directed a suspension of the payment of the pensions of such persons upon proof of their disloyalty. I recommend that Congress authorize that officer to cause the names of such persons to be stricken from the pension rolls.
The relations of the government with the Indian tribes have been greatly disturbed by the insurrection, especially in the southern superintendency and in that of New Mexico. The Indian country south of Kansas is in the possession of insurgents from Texas and Arkansas. The agents of the United States appointed since the 4th of March for this superintendency have been unable to reach their posts, while the most of those who were in office before that time have espoused the insurrectionary cause, and assume to exercise the powers of agents by virtue of commissions from the insurrectionists. It has been stated in the public press that a portion of those Indians have been organized as a military force and are attached to the army of the insurgents. Although the government has no official information upon this subject, letters have been written to the Commissioner of Indian Affairs by several prominent chiefs giving assurance of their loyalty to the United States and expressing a wish for the presence of Federal troops to protect them. It is believed that upon the repossession of the country by the Federal forces the Indians will readily cease all hostile demonstrations and resume their former relations to the government.
Agriculture, confessedly the largest interest of the nation, has not a department nor a bureau, but a clerkship only, assigned to it in the government. While it is fortunate that this great interest is so independent in its nature as not to have demanded and extorted more from the government, I respectfully ask Congress to consider whether something more cannot be given voluntarily with general advantage.
Annual reports exhibiting the condition of our agriculture, commerce, and manufactures would present a fund of information of great practical value to the country. While I make no suggestion as to details, I venture the opinion that an agricultural and statistical bureau might profitably be organized.
The execution of the laws for the suppression of the African slave trade has been confided to the Department of the Interior. It is a subject of gratulation that the efforts which have been made for the suppression of this inhuman traffic have been recently attended with unusual success. Five vessels being fitted out for the slave trade have been seized and condemned. Two mates of vessels engaged in the trade and one person in equipping a vessel as a slaver have been convicted and subjected to the penalty of fine and imprisonment, and one captain, taken with a cargo of Africans on board his vessel, has been convicted of the highest grade of offense under our laws, the punishment of which is death.
The Territories of Colorado, Dakota, and Nevada, created by the last Congress, have been organized, and civil administration has been inaugurated therein under auspices especially gratifying when it is considered that the leaven of treason was found existing in some of these new countries when the Federal officers arrived there.
The abundant natural resources of these Territories, with the security and protection afforded by organized government, will doubtless invite to them a large immigration when peace shall restore the business of the country to its accustomed channels. I submit the resolutions of the Legislature of Colorado, which evidence the patriotic spirit of the people of the Territory. So far the authority of the United States has been upheld in all the Territories, as it is hoped it will be in the future. I commend their interests and defense to the enlightened and generous care of Congress.
I recommend to the favorable consideration of Congress the interests of the District of Columbia. The insurrection has been the cause of much suffering and sacrifice to its inhabitants, and as they have no representative in Congress that body should not overlook their just claims upon the government.
At your late session a joint resolution was adopted authorizing the President to take measures for facilitating a proper representation of the industrial interests of the United States at the exhibition of the industry of all nations to be holden at London in the year 1862. I regret to say I have been unable to give personal attention to this subject—a subject at once so interesting in itself and so extensively and intimately connected with the material prosperity of the world. Through the Secretaries of State and of the Interior a plan or system has been devised and partly matured, and which will be laid before you.
Under and by virtue of the act of Congress entitled "An act to confiscate property used for insurrectionary purposes," approved August 6, 1861, the legal claims of certain persons to the labor and service of certain other persons have become forfeited, and numbers of the latter thus liberated are already dependent on the United States, and must be provided for in some way. Besides this, it is not impossible that some of the States will pass similar enactments for their own benefit respectively, and by operation of which persons of the same class will be thrown upon them for disposal. In such case I recommend that Congress provide for accepting such persons from such States, according to some mode of valuation, in lieu, pro tanto, of direct taxes, or upon some other plan to be agreed on with such States respectively; that such persons, on such acceptance by the General Government, be at once deemed free, and that in any event steps be taken for colonizing both classes (or the one first mentioned if the other shall not be brought into existence) at some place or places in a climate congenial to them. It might be well to consider, too, whether the free colored people already in the United States could not, so far as individuals may desire, be included in such colonization.
To carry out the plan of colonization may involve the acquiring of territory, and also the appropriation of money beyond that to be expended in the territorial acquisition. Having practised the acquisition of territory for nearly sixty years, the question of constitutional power to do so is no longer an open one with us. The power was questioned at first by Mr. Jefferson, who, however, in the purchase of Louisiana, yielded his scruples on the plea of great expediency. If it be said that the only legitimate object of acquiring territory is to furnish homes for white men, this measure effects that object, for emigration of colored men leaves additional room for white men remaining or coming here. Mr. Jefferson, however, placed the importance of procuring Louisiana more on political and commercial grounds than on providing room for population.
On this whole proposition, including the appropriation of money with the acquisition of territory, does not the expediency amount to absolute necessity—that without which the government itself cannot be perpetuated?
The war continues. In considering the policy to be adopted for suppressing the insurrection I have been anxious and careful that the inevitable conflict for this purpose shall not degenerate into a violent and remorseless revolutionary struggle. I have therefore in every case thought it proper to keep the integrity of the Union prominent as the primary object of the contest on our part, leaving all questions which are not of vital military importance to the more deliberate action of the Legislature.
In the exercise of my best discretion I have adhered to the blockade of the ports held by the insurgents, instead of putting in force by proclamation the law of Congress enacted at the late session for closing those ports.
So also, obeying the dictates of prudence, as well as the obligations of law, instead of transcending I have adhered to the act of Congress to confiscate property used for insurrectionary purposes. If a new law upon the same subject shall be proposed, its propriety will be duly considered. The Union must be preserved, and hence all indispensable means must be employed. We should not be in haste to determine that radical and extreme measures, which may reach the loyal as well as the disloyal, are indispensable.
The inaugural address at the beginning of the Administration and the message to Congress at the late special session were both mainly devoted to topics domestic controversy out of which the insurrection and consequent war have sprung. Nothing now occurs to add or subtract to or from the principles or general purposes stated and expressed in those documents.
The last ray of hope for preserving the Union peaceably expired at the assault upon Fort Sumter, and a general review of what has occurred since may not be unprofitable. What was painfully uncertain then is much better defined and more distinct now, and the progress of events is plainly in the right direction. The insurgents confidently claimed a strong support from north of Mason and Dixon's line, and the friends of the Union were not free from apprehension on the point. This, however, was soon settled definitely, and on the right side. South of the line noble little Delaware led off right from the first. Maryland was made to seem against the Union. Our soldiers were assaulted, bridges were burned, and railroads torn up within her limits, and we were many days at one time without the ability to bring a single regiment over her soil to the capital. Now her bridges and railroads are repaired and open to the government; she already gives seven regiments to the cause of the Union, and none to the enemy; and her people, at a regular election, have sustained the Union by a larger majority and a larger aggregate vote than they ever before gave to any candidate or any question. Kentucky, too, for some time in doubt, is now decidedly and, I think, unchangeably ranged on the side of the Union. Missouri is comparatively quiet, and, I believe, can, not again be overrun by the insurrectionists. These three States of Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri, neither of which would promise a single soldier at first, have now an aggregate of not less than forty thousand in the field for the Union, while of their citizens certainly not more than a third of that number, and they of doubtful whereabouts and doubtful existence, are in arms against us. After a somewhat bloody struggle of months, winter closes on the Union people of western Virginia, leaving them masters of their own country.
An insurgent force of about fifteen hundred, for months dominating the narrow peninsular region constituting the counties of Accomac and Northampton, and known as Eastern Shore of Virginia, together with some contiguous parts of Maryland, have laid down their arms, and the people there have renewed their allegiance to and accepted the protection of the old flag. This leaves no armed insurrectionist north of the Potomac or east of the Chesapeake.
Also we have obtained a footing at each of the isolated points on the southern coast of Hatteras, Port Royal, Tybee Island (near Savannah), and Ship Island; and we likewise have some general accounts of popular movements in behalf of the Union in North Carolina and Tennessee.
These things demonstrate that the cause of the Union is advancing steadily and certainly southward.
Since your last adjournment Lieutenant-General Scott has retired from the head of the army. During his long life the nation has not been unmindful of his merit; yet on calling to mind how faithfully, ably, and brilliantly he has served the country, from a time far back in our history, when few of the now living had been born, and thenceforward continually, I cannot but think we are still his debtors. I submit, therefore, for your consideration what further mark of recognition is due to him, and to ourselves as a grateful people.
With the retirement of General Scott came the Executive duty of appointing in his stead a general-in-chief of the army. It is a fortunate circumstance that neither in council nor country was there, so far as I know, any difference of opinion as to the proper person to be selected. The retiring chief repeatedly expressed his judgment in favor of General McClellan for the position, and in this the nation seemed to give a unanimous concurrence. The designation of General McClellan is therefore in considerable degree the selection of the country as well as of the Executive, and hence there is better reason to hope there will be given him the confidence and cordial support thus by fair implication promised, and without which he cannot with so full efficiency serve the country.
It has been said that one bad general is better than two good ones, and the saying is true if taken to mean no more than that an army is better directed by a single mind, though inferior, than by two superior ones at variance and cross-purposes with each other.
And the same is true in all joint operations wherein those engaged can have none but a common end in view and can differ only as to the choice of means. In a storm at sea no one on hoard can wish the ship to sink, and yet not unfrequently all go down together because too many will direct and no single mind can be allowed to control.
It continues to develop that the insurrection is largely, if not exclusively, a war upon the first principle of popular government—the rights of the people. Conclusive evidence of this is found in the most grave and maturely considered public documents, as well as in the general tone of the insurgents. In those documents we find the abridgment of the existing right of suffrage and the denial to the people of all right to participate in the selection of public officers except the legislative boldly advocated, with labored arguments to prove that large control of the people in government is the source of all political evil. Monarchy itself is sometimes hinted at as a possible refuge from the power of the people.
In my present position I could scarcely be justified were I to omit raising a warning voice against this approach of returning despotism. It is not needed nor fitting here that a general argument should be made in favor of popular institutions, but there is one point, with its connections, not so hackneyed as most others, to which I ask a brief attention. It is the effort to place capital on an equal footing with, if not above, labor in the structure of government. It is assumed that labor is available only in connection with capital; that nobody labors unless somebody else, owning capital, somehow by the use of it induces him to labor. This assumed, it is next considered whether it is best that capital shall hire laborers, and thus induce them to work by their own consent, or buy them and drive them to it without their consent. Having proceeded so far, it is naturally concluded that all laborers are either hired laborers or what we call slaves. And further, it is assumed that whoever is once a hired laborer is fixed in that condition for life.
Now there is no such relation between capital and labor as assumed, nor is there any such thing as a free man being fixed for life in the condition of a hired laborer. Both these assumptions are false, and all inferences from them are groundless.
Labor is prior to and independent of capital. Capital is only the fruit of labor, and could never have existed if labor had not first existed. Labor is the superior of capital, and deserves much the higher consideration. Capital has its rights, which are as worthy of protection as any other rights. Nor is it denied that there is, and probably always will be, a relation between labor and capital producing mutual benefits. The error is in assuming that the whole labor of community exists within that relation. A few men own capital, and that few avoid labor themselves, and with their capital hire or buy another few to labor for them. A large majority belong to neither class—neither work for others nor have others working for them. In most of the Southern States a majority of the whole people of all colors are neither slaves nor masters, while in the Northern a large majority are neither hirers nor hired. Men, with their families—wives, sons, and daughters,—work for themselves on their farms, in their houses, and in their shops, taking the whole product to themselves, and asking no favors of capital on the one hand nor of hired laborers or slaves on the other. It is not forgotten that a considerable number of persons mingle their own labor with capital; that is, they labor with their own hands and also buy or hire others to labor for them; but this is only a mixed and not a distinct class. No principle stated is disturbed by the existence of this mixed class.
Again, as has already been said, there is not of necessity any such thing as the free hired laborer being fixed to that condition for life. Many independent men everywhere in these States a few years back in their lives were hired laborers. The prudent, penniless beginner in the world labors for wages awhile, saves a surplus with which to buy tools or land for himself, then labors on his own account another while, and at length hires another new beginner to help him. This is the just and generous and prosperous system which opens the way to all, gives hope to all, and consequent energy and progress and improvement of condition to all. No men living are more worthy to be trusted than those who toil up from poverty; none less inclined to take or touch aught which they have not honestly earned. Let them beware of surrendering a political power which they already possess, and which if surrendered will surely be used to close the door of advancement against such as they and to fix new disabilities and burdens upon them till all of liberty shall be lost.
From the first taking of our national census to the last are seventy years, and we find our population at the end of the period eight times as great as it was at the beginning. The increase of those other things which men deem desirable has been even greater. We thus have at one view what the popular principle, applied to government through the machinery of the States and the Union, has produced in a given time, and also what if firmly maintained it promises for the future. There are already among us those who if the Union be preserved will live to see it contain 200,000,000. The struggle of to-day is not altogether for to-day; it is for a vast future also. With a reliance on Providence all the more firm and earnest, let us proceed in the great task which events have devolved upon us.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I transmit to Congress a letter from the secretary of the executive committee of the commission appointed to represent the interests of those American citizens who may desire to become exhibitors at the industrial exhibition to be held in London in 1862, and a memorial of that commission, with a report of the executive committee thereof and copies of circulars announcing the decisions of Her Majesty's commissioners in London, giving directions to be observed in regard to articles intended for exhibition, and also of circular forms of application, demands for space, approvals, etc., according to the rules prescribed by the British commissioners.
As these papers fully set forth the requirements necessary to enable those citizens of the United States who may wish to become exhibitors to avail themselves of the privileges of the exhibition, I commend them to your early consideration, especially in view of the near approach of the time when the exhibition will begin.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
Dec.31, 1861
MAJOR-GENERAL HUNTER.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 23d is received, and I am constrained to say it is difficult to answer so ugly a letter in good temper. I am, as you intimate, losing much of the great confidence I placed in you, not from any act or omission of yours touching the public service, up to the time you were sent to Leavenworth, but from the flood of grumbling despatches and letters I have seen from you since. I knew you were being ordered to Leavenworth at the time it was done; and I aver that with as tender a regard for your honor and your sensibilities as I had for my own, it never occurred to me that you were being "humiliated, insulted, and disgraced"; nor have I, up to this day, heard an intimation that you have been wronged, coming from any one but yourself. No one has blamed you for the retrograde movement from Springfield, nor for the information you gave General Cameron; and this you could readily understand, if it were not for your unwarranted assumption that the ordering you to Leavenworth must necessarily have been done as a punishment for some fault. I thought then, and think yet, the position assigned to you is as responsible, and as honorable, as that assigned to Buell—I know that General McClellan expected more important results from it. My impression is that at the time you were assigned to the new Western Department, it had not been determined to replace General Sherman in Kentucky; but of this I am not certain, because the idea that a command in Kentucky was very desirable, and one in the farther West undesirable, had never occurred to me. You constantly speak of being placed in command of only 3000. Now, tell me, is this not mere impatience? Have you not known all the while that you are to command four or five times that many.
I have been, and am sincerely your friend; and if, as such, I dare to make a suggestion, I would say you are adopting the best possible way to ruin yourself. "Act well your part, there all the honor lies." He who does something at the head of one regiment, will eclipse him who does nothing at the head of a hundred.
Your friend, as ever,
GENERAL H. W. HALLECK, St. Louis, Missouri:
General McClellan is sick. Are General Buell and yourself in concert? When he moves on Bowling Green, what hinders it being reinforced from Columbus? A simultaneous movement by you on Columbus might prevent it.
A. LINCOLN.
[Similar despatch to Buell same date.]
BRIGADIER-GENERAL BUELL, Louisville:
General McClellan should not yet be disturbed with business. I think you better get in concert with General Halleck at once. I write you to-night. I also telegraph and write Halleck.
DEAR GENERAL HALLECK:
General McClellan is not dangerously ill, as I hope, but would better not be disturbed with business. I am very anxious that, in case of General Buell's moving toward Nashville, the enemy shall not be greatly reinforced, and I think there is danger he will be from Columbus. It seems to me that a real or feigned attack upon Columbus from up the river at the same time would either prevent this or compensate for it by throwing Columbus into our hands. I wrote General Buell a letter similar to this, meaning that he and you shall communicate and act in concert, unless it be your judgment and his that there is no necessity for it. You and he will understand much better than I how to do it. Please do not lose time in this matter.
Yours very truly,
In view of the recent declaration of the people of Maryland of their adhesion to the Union, so distinctly made in their recent election, the President directs that all the prisoners who having heretofore been arrested in that State are now detained in military custody by the President's authority, be released from their imprisonment on the following conditions, namely: that if they were holding any civil or military offices when arrested, the terms of which have expired, they shall not resume or reclaim such office; and secondly, all persons availing themselves of this proclamation shall engage by oath or parole of honor to maintain the Union and the Constitution of the United States, and in no way to aid or abet by arms, counsel, conversation, or information of any kind the existing insurrection against the Government of the United States.
To guard against misapprehension it is proper to state that this proclamation does not apply to prisoners of war.
To THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
I transmit to Congress a copy of a letter to the Secretary of State from James R. Partridge, secretary to the executive committee to the in exhibition to be held in London in the course present year, and a copy of the correspond which it refers, relative to a vessel for the of taking such articles as persons in this country may wish to exhibit on that occasion. As it appears no naval vessel can be spared for the purpose, I recommend that authority be given to charter a suitable merchant vessel, in order that facilities similar to those afforded by the government exhibition of 1851 may also be extended to citizens of the United States who may desire to contribute to the exhibition of this year.
WASHINGTON, January 4, 1862.
GENERAL BUELL:
Have arms gone forward for East Tennessee? Please tell me the progress and condition of the movement in that direction. Answer.
January 6, 1862.
BRIGADIER-GENERAL BUELL.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your despatch of yesterday has been received, and it disappoints and distresses me. I have shown it to General McClellan, who says he will write you to-day. I am not competent to criticize your views, and therefore what I offer is in justification of myself. Of the two, I would rather have a point on the railroad south of Cumberland Gap than Nashville. First, because it cuts a great artery of the enemy's communication, which Nashville does not; and secondly, because it is in the midst of loyal people who would rally around it, while Nashville is not. Again, I cannot see why the movement on East Tennessee would not be a diversion in your favor rather than a disadvantage, assuming that a movement toward Nashville is the main object. But my distress is that our friends in East Tennessee are being hanged and driven to despair, and even now, I fear, are thinking of taking rebel arms for the sake of personal protection. In this we lose the most valuable stake we have in the South. My despatch, to which yours is an answer, was sent with the knowledge of Senator Johnson and Representative Maynard of East Tennessee, and they will be upon me to know the answer, which I cannot safely show them. They would despair, possibly resign to go and save their families somehow, or die with them. I do not intend this to be an order in any sense, but merely, as intimated before, to show you the grounds of my anxiety.
Yours very truly,
BRIGADIER-GENERAL D.C. BUELL, Louisville:
Please name as early a day as you safely can on or before which you can be ready to move southward in concert with Major-General Halleck. Delay is ruining us, and it is indispensable for me to have something definite. I send a like despatch to Major-General Halleck.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I transmit to Congress a translation of an instruction to the minister of his Majesty the Emperor of Austria accredited to this government, and a copy of a note to that minister from the Secretary of State relative to the questions involved in the taking from the British steamer Trent of certain citizens of the United States by order of Captain Wilkes of the United States Navy. This correspondence may be considered as a sequel to that previously communicated to Congress relating to the same subject.
HEADQUARTERS DEPARTMENT OF THE MISSOURI ST. Louis, January 6, 1862.
To His EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT:
In reply to your Excellency's letter of the 1st instant, I have to state that on receiving your telegram I immediately communicated with General Buell and have since sent him all the information I could obtain of the enemy's movements about Columbus and Camp Beauregard. No considerable force has been sent from those places to Bowling Green. They have about 22,000 men at Columbus, and the place is strongly fortified. I have at Cairo, Port Holt, and Paducah only about 15,000, which, after leaving guards at these places, would give me but little over 10,000 men with which to assist General Buell. It would be madness to attempt anything serious with such a force, and I cannot at the present time withdraw any from Missouri without risking the loss of this State. The troops recently raised in other States of this department have, without my knowledge, been sent to Kentucky and Kansas.
I am satisfied that the authorities at Washington do not appreciate the difficulties with which we have to contend here. The operations of Lane, Jennison, and others have so enraged the people of Missouri that it is estimated that there is a majority of 80,000 against the government. We are virtually in an enemy's country. Price and others have a considerable army in the southwest, against which I am operating with all my available force.
This city and most of the middle and northern counties are insurrectionary,—burning bridges, destroying telegraph lines, etc.,—and can be kept down only by the presence of troops. A large portion of the foreign troops organized by General Fremont are unreliable; indeed, many of them are already mutinous. They have been tampered with by politicians, and made to believe that if they get up a mutiny and demand Fremont's return the government will be forced to restore him to duty here. It is believed that some high officers are in the plot I have already been obliged to disarm several of these organizations, and I am daily expecting more serious outbreaks. Another grave difficulty is the want of proper general officers to command the troops and enforce order and discipline, and especially to protect public property from robbery and plunder. Some of the brigadier-generals assigned to this department are entirely ignorant of their duties and unfit for any command. I assure you, Mr. President, it is very difficult to accomplish much with such means. I am in the condition of a carpenter who is required to build a bridge with a dull axe, a broken saw, and rotten timber. It is true that I have some very good green timber, which will answer the purpose as soon as I can get it into shape and season it a little.
I know nothing of General Buell's intended operations, never having received any information in regard to the general plan of campaign. If it be intended that his column shall move on Bowling Green while another moves from Cairo or Paducah on Columbus or Camp Beauregard, it will be a repetition of the same strategic error which produced the disaster of Bull Run. To operate on exterior lines against an enemy occupying a central position will fail, as it always has failed, in ninety-nine cases out of a hundred. It is condemned by every military authority I have ever read.
General Buell's army and the forces at Paducah occupy precisely the same position in relation to each other and to the enemy as did the armies of McDowell and Patterson before the battle of Bull Run.
Very respectfully, your obedient servant,
H. W. HALLECK, Major-General
[Indorsement]
The within is a copy of a letter just received from General Halleck. It is exceedingly discouraging. As everywhere else, nothing can be done.
GOVERNOR JOHN A. ANDREW, Boston:
I will be greatly obliged if you will arrange; somehow with General Butler to officer his two un-officered regiments.
BRIGADIER-GENERAL BUELL.
MY DEAR SIR—Your despatch of yesterday is received, in which you say, "I received your letter and General McClellan's, and will at once devote my efforts to your views and his." In the midst of my many cares I have not seen, nor asked to see, General McClellan's letter to you. For my own views, I have not offered and do not now offer them as orders; and while I am glad to have them respectfully considered, I would blame you to follow them contrary to your own clear judgment, unless I should put them in the form of orders. As to General McClellan's views, you understand your duty in regard to them better than I do.
With this preliminary I state my general idea of this war to be, that we have the greater numbers and the enemy has the greater facility of concentrating forces upon points of collision; that we must fail unless we can find some way of making our advantage an overmatch for his; and that this can only be done by menacing him with superior forces at different points at the same time, so that we can safely attack one or both if he makes no change; and if he weakens one to strengthen the other, forbear to attack the strengthened one, but seize and hold the weakened one, gaining so much.
To illustrate: Suppose last summer, when Winchester ran away to reinforce Manassas, we had forborne to attack Manassas, but had seized and held Winchester. I mention this to illustrate and not to criticise. I did not lose confidence in McDowell, and I think less harshly of Patterson than some others seem to.... Applying the principle to your case, my idea is that Halleck shall menace Columbus and "down river" generally, while you menace Bowling Green and East Tennessee. If the enemy shall concentrate at Bowling Green, do not retire from his front, yet do not fight him there either, but seize Columbus and East Tennessee, one or both, left exposed by the concentration at Bowling Green. It is a matter of no small anxiety to me, and which I am sure you will not overlook, that the East Tennessee line is so long and over so bad a road.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
(Indorsement.)
Having to-day written General Buell a letter, it occurs to me to send General Halleck a copy of it.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK.
MY DEAR SIR:—The Germans are true and patriotic and so far as they have got cross in Missouri it is upon mistake and misunderstanding. Without a knowledge of its contents, Governor Koerner, of Illinois, will hand you this letter. He is an educated and talented German gentleman, as true a man as lives. With his assistance you can set everything right with the Germans.... My clear judgment is that, with reference to the German element in your command, you should have Governor Koerner with you; and if agreeable to you and him, I will make him a brigadier-general, so that he can afford to give his time. He does not wish to command in the field, though he has more military knowledge than some who do. If he goes into the place, he will simply be an efficient, zealous, and unselfish assistant to you. I say all this upon intimate personal acquaintance with Governor Koerner.
Yours very truly,
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I transmit to Congress a translation of an instruction to the minister of his Majesty the King of Prussia accredited to this government, and a copy of a note to that minister from the Secretary of State relating to the capture and detention of certain citizens of the United States, passengers on board the British steamer Trent, by order of Captain Wilkes of the United States Navy.
January 20, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN,
Commanding Armies of the United States:
You or any officer you may designate will in your discretion suspend the writ of habeas corpus so far as may relate to Major Chase, lately of the Engineer Corps of the Army of the United States, now alleged to be guilty of treasonable practices against this government.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD.
Ordered, That the 22d day of February, 1862, be the day for a general movement of the land and the naval forces of the United States against the insurgent forces.
That especially the army at and about Fortress Monroe, the Army of the Potomac, the Army of Western Virginia, the army near Munfordville, Kentucky, the army and flotilla at Cairo, and a naval force in the Gulf of Mexico, be ready for a movement on that day.
That all other forces, both land and naval, with their respective commanders, obey existing orders for the time, and be ready to obey additional orders when duly given.
That the heads of departments, and especially the Secretaries of War and of the Navy, with all their subordinates, and the General-in-chief, with all other commanders and subordinates of land and naval forces, will severally be held to their strict and full responsibilities for the prompt execution of this order.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—It is my wish that the expedition commonly called the "Lane Expedition" shall be, as much as has been promised at the adjutant-general's office, under the supervision of General McClellan, and not any more. I have not intended, and do not now intend, that it shall be a great, exhausting affair, but a snug, sober column of 10,000 or 15,000. General Lane has been told by me many times that he is under the command of General Hunter, and assented to it as often as told. It was the distinct agreement between him and me, when I appointed him, that he was to be under Hunter.
Yours truly,
Ordered, That all the disposable force of the Army of the Potomac, after providing safely for the defence of Washington, be formed into an expedition for the immediate object of seizing and occupying a point upon the railroad southwestward of what is known as Manassas Junction, all details to be in the discretion of the commander-in-chief, and the expedition to move before or on the 22d day of February next.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, February 3, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL MCCLELLAN.
DEAR SIR—You and I have distinct and different plans for a movement of the Army of the Potomac—yours to be down the Chesapeake, up the Rappahannock to Urbana, and across land to the terminus of the railroad on the York River; mine to move directly to a point on the railroad southwest of Manassas.
If you will give me satisfactory answers to the following questions, I shall gladly yield my plan to yours.
First. Does not your plan involve a greatly larger expenditure of time and money than mine?
Second. Wherein is a victory more certain by your plan than mine?
Third. Wherein is a victory more valuable by your plan than mine?
Fourth. In fact, would it not be less valuable in this, that it would break no great line of the enemy's communications, while mine would?
Fifth. In case of disaster, would not a retreat be more difficult by your plan than mine?
Yours truly,
First. Suppose the enemy should attack us in force before we reach the Occoquan, what?
Second. Suppose the enemy in force shall dispute the crossing of the Occoquan, what? In view of this, might it not be safest for us to cross the Occoquan at Coichester, rather than at the village of Occoquan? This would cost the enemy two miles of travel to meet us, but would, on the contrary, leave us two miles farther from our ultimate destination.
Third. Suppose we reach Maple Valley without an attack, will we not be attacked there in force by the enemy marching by the several roads from Manassas; and if so, what?
DEAR WILLIAM:—Yours of January 30th just received. Do just as you say about the money matter.
As you well know, I have not time to write a letter of respectable length. God bless you, says
Your friend,
A. LINCOLN, PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA,
To all to whom these Presents shall come, Greeting:
Whereas it appears that at a term of the Circuit Court of the United States of America for the Southern District of New York held in the month of November, A.D. 1861, Nathaniel Gordon was indicted and convicted for being engaged in the slave trade, and was by the said court sentenced to be put to death by hanging by the neck, on Friday the 7th day of February, AD. 1862:
And whereas a large number of respectable citizens have earnestly besought me to commute the said sentence of the said Nathaniel Gordon to a term of imprisonment for life, which application I have felt it to be my duty to refuse:
And whereas it has seemed to me probable that the unsuccessful application made for the commutation of his sentence may have prevented the said Nathaniel Gordon from making the necessary preparation for the awful change which awaits him;
Now, therefore, be it known, that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, have granted and do hereby grant unto him, the said Nathaniel Gordon, a respite of the above recited sentence, until Friday the twenty-first day of February, A.D. 1862, between the hours of twelve o'clock at noon and three o'clock in the afternoon of the said day, when the said sentence shall be executed.
In granting this respite, it becomes my painful duty to admonish the prisoner that, relinquishing all expectation of pardon by human authority, he refer himself alone to the mercy of the common God and Father of all men.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto signed my name and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the City of Washington, this fourth day of February, A.D. 1862, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-sixth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
To THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
The third section of the "Act further to promote the efficiency of the Navy," approved December 21, 1862, provides:
"That the President of the United States, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate, shall have the authority to detail from the retired list of the navy for the command of squadrons and single ships such officers as he may believe that the good of the service requires to be thus placed in command; and such officers may, if upon the recommendation of the President of the United States they shall receive a vote of thanks of Congress for their services and gallantry in action against an enemy, be restored to the active list, and not otherwise."
In conformity with this law, Captain Samuel F. Du Pont, of the navy, was nominated to the Senate for continuance as the flag-officer in command of the squadron which recently rendered such important service to the Union in the expedition to the coast of South Carolina.
Believing that no occasion could arise which would more fully correspond with the intention of the law, or be more pregnant with happy influence as an example, I cordially recommend that Captain Samuel F. Du Pont receive a vote of thanks of Congress for his services and gallantry displayed in the capture of Forts Walker and Beauregard, commanding the entrance of Port Royal Harbor, on the 7th of November, 1861.
MAJOR-GENERAL HUNTER AND BRIGADIER-GENERAL LANE, Leavenworth, Kansas:
My wish has been and is to avail the government of the services of both General Hunter and General Lane, and, so far as possible, to personally oblige both. General Hunter is the senior officer, and must command when they serve together; though in so far as he can consistently with the public service and his own honor oblige General Lane, he will also oblige me. If they cannot come to an amicable understanding, General Lane must report to General Hunter for duty, according to the rules, or decline the service.
The breaking out of a formidable insurrection based on a conflict of political ideas, being an event without precedent in the United States, was necessarily attended by great confusion and perplexity of the public mind. Disloyalty before unsuspected suddenly became bold, and treason astonished the world by bringing at once into the field military forces superior in number to the standing army of the United States.
Every department of the government was paralyzed by treason. Defection appeared in the Senate, in the House of Representatives, in the Cabinet, in the Federal courts; ministers and consuls returned from foreign countries to enter the insurrectionary councils of land or naval forces; commanding and other officers of the army and in the navy betrayed our councils or deserted their posts for commands in the insurgent forces. Treason was flagrant in the revenue and in the post-office service, as well as in the Territorial governments and in the Indian reserves.
Not only governors, judges, legislators, and ministerial officers in the States, but even whole States rushed one after another with apparent unanimity into rebellion. The capital was besieged and its connection with all the States cut off. Even in the portions of the country which were most loyal, political combinations and secret societies were formed furthering the work of disunion, while, from motives of disloyalty or cupidity or from excited passions or perverted sympathies, individuals were found furnishing men, money, and materials of war and supplies to the insurgents' military and naval forces. Armies, ships, fortifications, navy yards, arsenals, military posts, and garrisons one after another were betrayed or abandoned to the insurgents.
Congress had not anticipated, and so had not provided for, the emergency. The municipal authorities were powerless and inactive. The judicial machinery seemed as if it had been designed, not to sustain the government, but to embarrass and betray it.
Foreign intervention, openly invited and industriously instigated by the abettors of the insurrection, became imminent, and has only been prevented by the practice of strict and impartial justice, with the most perfect moderation, in our intercourse with nations.
The public mind was alarmed and apprehensive, though fortunately not distracted or disheartened. It seemed to be doubtful whether the Federal Government, which one year before had been thought a model worthy of universal acceptance, had indeed the ability to defend and maintain itself.
Some reverses, which, perhaps, were unavoidable, suffered by newly levied and inefficient forces, discouraged the loyal and gave new hopes to the insurgents. Voluntary enlistments seemed about to cease and desertions commenced. Parties speculated upon the question whether conscription had not become necessary to fill up the armies of the United States.
In this emergency the President felt it his duty to employ with energy the extraordinary powers which the Constitution confides to him in cases of insurrection. He called into the field such military and naval forces, unauthorized by the existing laws, as seemed necessary. He directed measures to prevent the use of the post-office for treasonable correspondence. He subjected passengers to and from foreign countries to new passport regulations, and he instituted a blockade, suspended the writ of habeas corpus in various places, and caused persons who were represented to him as being or about to engage in disloyal and treasonable practices to be arrested by special civil as well as military agencies and detained in military custody when necessary to prevent them and deter others from such practices. Examinations of such cases were instituted, and some of the persons so arrested have been discharged from time to time under circumstances or upon conditions compatible, as was thought, with the public safety.
Meantime a favorable change of public opinion has occurred. The line between loyalty and disloyalty is plainly defined. The whole structure of the government is firm and stable. Apprehension of public danger and facilities for treasonable practices have diminished with the passions which prompted heedless persons to adopt them. The insurrection is believed to have culminated and to be declining.
The President, in view of these facts, and anxious to favor a return to the normal course of the administration as far as regard for the public welfare will allow, directs that all political prisoners or state prisoners now held in military custody be released on their subscribing to a parole engaging them to render no aid or comfort to the enemies in hostility to the United States.
The Secretary of War will, however, in his discretion, except from the effect of this order any persons detained as spies in the service of the insurgents, or others whose release at the present moment may be deemed incompatible with the public safety.
To all persons who shall be so released, and who shall keep their parole, the President grants an amnesty for any past offences of treason or disloyalty which they may have comminuted.
Extraordinary arrests will hereafter be made under the direction of the military authorities alone.
By order of the President EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
The third section of the "Act further to promote the efficiency of the Navy," approved December 21, 1861, provides
"That the President of the United States, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate, shall have the authority to detail from the retired list of the navy for the command of squadrons and single ships such officers as he may believe that the good of the service requires to be thus placed in command; and such officers may, if upon the recommendation of the President of the United States they shall receive a vote of thanks of Congress for their services and gallantry in action against an enemy, be restored to the active list, and not otherwise."
In conformity with this law, Captain Louis M. Goldsborough, of the navy, was nominated to the Senate for continuance as the flag-officer in command of the North Atlantic Blockading Squadron, which recently rendered such important service to the Union in the expedition to the coast of North Carolina.
Believing that no occasion could arise which would more fully correspond with the intention of the law or be more pregnant with happy influence as an example, I cordially recommend that Captain Louis M. Goldsborough receive a vote of thanks of Congress for his services and gallantry displayed in the combined attack of the forces commanded by him and Brigadier-General Burnside in the capture of Roanoke Island and the destruction of rebel gunboats On the 7th, 8th, and 10th of February, 1862.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
February 16, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, St. Louis, Missouri:
You have Fort Donelson safe, unless Grant shall be overwhelmed from outside; to prevent which latter will, I think, require all the vigilance, energy, and skill of yourself and Buell, acting in full co-operation. Columbus will not get at Grant, but the force from Bowling Green will. They hold the railroad from Bowling Green to within a few miles of Fort Donelson, with the bridge at Clarksville undisturbed. It is unsafe to rely that they will not dare to expose Nashville to Buell. A small part of their force can retire slowly toward Nashville, breaking up the railroad as they go, and keep Buell out of that city twenty days. Meanwhile Nashville will be abundantly defended by forces from all South and perhaps from hers at Manassas. Could not a cavalry force from General Thomas on the upper Cumberland dash across, almost unresisted, and cut the railroad at or near Knoxville, Tennessee? In the midst of a bombardment at Fort Donelson, why could not a gunboat run up and destroy the bridge at Clarksville? Our success or failure at Fort Donelson is vastly important, and I beg you to put your soul in the effort. I send a copy of this to Buell.
It is ordered:
First. That a special commission of two persons, one of military rank and the other in civil life, be appointed to examine the cases of the state prisoners remaining in the military custody of the United States, and to determine whether in view of the public Safety and the existing rebellion they should be discharged, or remain in military custody, or be remitted to the civil tribunals for trial.
Second. That Major-General John A. Dix, commanding in Baltimore, and the HON. Edwards Pierrepont, of New York, be, and they are hereby, appointed commissioners for the purpose above mentioned; and they are authorized to examine, hear, and determine the cases aforesaid ex parte and in a summary manner, at such times and places as in their discretion they may appoint, and make full report to the War Department.
By order of the President EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Considering that the existing circumstances of the country allow a partial restoration of commercial intercourse between the inhabitants of those parts of the United States heretofore declared to be in insurrection and the citizens of the loyal States of the Union, and exercising the authority and discretion confided to me by the act of Congress, approved July 13, 1861, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," I hereby license and permit such commercial intercourse in all cases within the rules and regulations which have been or may be prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury for conducting and carrying on the same on the inland waters and ways of the United States.
WASHINGTON, February 28, 1862.
The United States have no enmities, animosities, or rivalries, and no interests which conflict with the welfare, safety, and rights or interests of any other nation. Their own prosperity, happiness, and aggrandizement are sought most safely and advantageously through the preservation not only of peace on their own part, but peace among all other nations. But while the United States are thus a friend to all other nations, they do not seek to conceal the fact that they cherish especial sentiments of friendship for, and sympathies with, those who, like themselves, have founded their institutions on the principle of the equal rights of men; and such nations being more prominently neighbors of the United States, the latter are co-operating with them in establishing civilization and culture on the American continent. Such being the general principles which govern the United States in their foreign relations, you may be assured, sir, that in all things this government will deal justly, frankly, and, if it be possible, even liberally with Peru, whose liberal sentiments toward us you have so kindly expressed.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:—I recommend the adoption of a joint resolution by your honorable bodies which shall be substantially as follows:
"Resolved, That the United States ought to co-operate with any State which may adopt gradual abolishment of slavery, giving to such State pecuniary aid, to be used by such State, in its discretion, to compensate for the inconveniences, public and private, produced by such change of system."
If the proposition contained in the resolution does not meet the approval of Congress and the country, there is the end; but if it does command such approval, I deem it of importance that the States and people immediately interested should be at once distinctly notified of the fact, so that they may begin to consider whether to accept or reject it. The Federal Government would find its highest interest in such a measure, as one of the most efficient means of self-preservation. The leaders of the existing insurrection entertain the hope that this government will ultimately be forced to acknowledge the independence of some part of the disaffected region, and that all the slave States north of such part will then say, "The Union for which we have struggled being already gone, we now choose to go with the Southern section." To deprive them of this hope substantially ends the rebellion, and the initiation of emancipation completely deprives them of it as to all the States initiating it. The point is not that all the States tolerating slavery would very soon, if at all, initiate emancipation; but that, while the offer is equally made to all, the more northern shall by such initiation make it certain to the more southern that in no event will the former ever join the latter in their proposed confederacy. I say "initiation" because, in my judgment, gradual and not sudden emancipation is better for all. In the mere financial or pecuniary view, any member of Congress with the census tables and treasury reports before him can readily see for himself how very soon the current expenditures of this war would purchase, at fair valuation, all the slaves in any named State. Such a proposition on the part of the General Government sets up no claim of a right by Federal authority to interfere with slavery within State limits, referring, as it does, the absolute control of the subject in each case to the State and its people immediately interested. It is proposed as a matter of perfectly free choice with them.
In the annual message last December, I thought fit to say, "The Union must be preserved, and hence all indispensable means must be employed." I said this not hastily, but deliberately. War has been made and continues to be an indispensable means to this end. A practical reacknowledgment of the national authority would render the war unnecessary, and it would at once cease. If, however, resistance continues, the war must also continue; and it is impossible to foresee all the incidents which may attend and all the ruin which may follow it. Such as may seem indispensable or may obviously promise great efficiency toward ending the struggle must and will come.
The proposition now made (though an offer only), I hope it may be esteemed no offense to ask whether the pecuniary consideration tendered would not be of more value to the States and private persons concerned than are the institution and property in it in the present aspect of affairs.
While it is true that the adoption of the proposed resolution would be merely initiatory, and not within itself a practical measure, it is recommended in the hope that it would soon lead to important practical results. In full view of my great responsibility to my God and to my country, I earnestly beg the attention of Congress and the people to the subject.
HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, SECRETARY OF WAR, Washington, D. C.
SIR:—The government at my special request a few months since contracted for fourteen batteries of the James rifled gun, 6-pounder calibre, and a limited quantity of the James projectiles, weighing about fourteen pounds each. The reports showing the superiority of this gun and projectile, both as regards range, accuracy, and execution, for field service over that of all others at the battle of Fort Donelson, leads me to request that there be furnished to the State of Illinois in the shortest time practicable seven batteries of 12-pounder calibre James rifled guns, with carriages, harness, implements, etc., complete and ready for field service, together with the following fixed ammunition to each gun, viz., 225 shells, 225 canister, and 50 solid projectiles, weighing about 24 pounds each, and also 200 shells, 100 canister, and 100 solid projectiles for each of the guns of the fourteen batteries named above, weighing about 14 pounds each, all to be of the James model.
Very respectfully,
RICHARD YATES, Governor of Illinois.
[Indorsement.]
March 8, 1862.
The within is from the Governor of Illinois. I understand the seven additional batteries now sought are to be 6-gun batteries, and the object is to mix them with the fourteen batteries they already have so as to make each battery consist of four 6-pounders and two 12-pounders. I shall be very glad to have the requisition filled if it can be without detriment to the service.
March 8, 1862.
Ordered: 1. That the major-general commanding the Army of the Potomac proceed forthwith to organize that part of the said army destined to enter upon active operations (including the reserve, but excluding the troops to be left in the fortifications about Washington) into four army corps, to be commanded according to seniority of rank, as follows:
First Corps to consist of four divisions, and to be commanded by Major-General I. McDowell. Second Corps to consist of three divisions, and to be commanded by Brigadier-General E. V. Sumner. Third Corps to consist of three divisions, and to be commanded by Brigadier-General S. P. Heintzelman. Fourth Corps to consist of three divisions, and to be commanded by Brigadier-General E. D. Keyes.
2. That the divisions now commanded by the officers above assigned to the commands of army corps shall be embraced in and form part of their respective corps.
3. The forces left for the defense of Washington will be placed in command of Brigadier-General James S. Wadsworth, who shall also be military governor of the District of Columbia.
4. That this order be executed with such promptness and dispatch as not to delay the commencement of the operations already directed to be underwritten by the Army of the Potomac.
5. A fifth army corps, to be commanded by Major general N. P. Banks, will be formed from his own and General Shields's (late General Lander's) divisions.
Ordered: That no change of the base of operations of the Army of the Potomac shall be made without leaving in and about Washington such a force as in the opinion of the general-in-chief and the commanders of all the army corps shall leave said city entirely secure.
That no more than two army corps (about 50,000 troops) of said Army of the Potomac shall be moved en route for a new base of operations until the navigation of the Potomac from Washington to the Chesapeake Bay shall be freed from enemy's batteries and other obstructions, or until the President shall hereafter give express permission.
That any movements as aforesaid en route for a new base of operations which may be ordered by the general-in-chief, and which may be intended to move upon the Chesapeake Bay, shall begin to move upon the bay as early as the 18th day of March instant, and the general-in-chief shall be responsible that it so move as early as that day.
Ordered, That the army and navy co-operate in an immediate effort to capture the enemy's batteries upon the Potomac between Washington and the Chesapeake Bay.
MEMORANDUM
"DEAR SIR:—I called, at the request of the President, to ask you to come to the White House tomorrow morning, at nine o'clock, and bring such of your colleagues as are in town."
WASHINGTON, March 10, 1862.
Yesterday, on my return from church, I found Mr. Postmaster-General Blair in my room, writing the above note, which he immediately suspended, and verbally communicated the President's invitation, and stated that the President's purpose was to have some conversation with the delegations of Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, Virginia, and Delaware, in explanation of his message of the 6th instant.
This morning these delegations, or such of them as were in town, assembled at the White House at the appointed time, and after some little delay were admitted to an audience. Mr. Leary and myself were the only members from Maryland present, and, I think, were the only members of the delegation at that time in the city. I know that Mr. Pearoe, of the Senate, and Messrs. Webster and Calvert, of the House, were absent.
After the usual salutations, and we were seated, the President said, in substance, that he had invited us to meet him to have some conversation with us in explanation of his message of the 6th; that since he had sent it in several of the gentlemen then present had visited him, but had avoided any allusion to the message, and he therefore inferred that the import of the message had been misunderstood, and was regarded as inimical to the interests we represented; and he had resolved he would talk with us, and disabuse our minds of that erroneous opinion.
The President then disclaimed any intent to injure the interests or wound the sensibilities of the slave States. On the contrary, his purpose was to protect the one and respect the other; that we were engaged in a terrible, wasting, and tedious war; immense armies were in the field, and must continue in the field as long as the war lasts; that these armies must, of necessity, be brought into contact with slaves in the States we represented and in other States as they advanced; that slaves would come to the camps, and continual irritation was kept up; that he was constantly annoyed by conflicting and antagonistic complaints: on the one side a certain class complained if the slave was not protected by the army; persons were frequently found who, participating in these views, acted in a way unfriendly to the slaveholder; on the other hand, slaveholders complained that their rights were interfered with, their slaves induced to abscond and protected within the lines; these complaints were numerous, loud and deep; were a serious annoyance to him and embarrassing to the progress of the war; that it kept alive a spirit hostile to the government in the States we represented; strengthened the hopes of the Confederates that at some day the border States would unite with them, and thus tend to prolong the war; and he was of opinion, if this resolution should be adopted by Congress and accepted by our States, these causes of irritation and these hopes would be removed, and more would be accomplished toward shortening the war than could be hoped from the greatest victory achieved by Union armies; that he made this proposition in good faith, and desired it to be accepted, if at all, voluntarily, and in the same patriotic spirit in which it was made; that emancipation was a subject exclusively under the control of the States, and must be adopted or rejected by each for itself; that he did not claim nor had this government any right to coerce them for that purpose; that such was no part of his purpose in making this proposition, and he wished it to be clearly understood; that he did not expect us there to be prepared to give him an answer, but he hoped we would take the subject into serious consideration, confer with one another, and then take such course as we felt our duty and the interests of our constituents required of us.
Mr. Noell, of Missouri, said that in his State slavery was not considered a permanent institution; that natural causes were there in operation which would at no distant day extinguish it, and he did not think that this proposition was necessary for that; and, besides that, he and his friends felt solicitous as to the message on account of the different constructions which the resolution and message had received. The New York Tribune was for it, and understood it to mean that we must accept gradual emancipation according to the plan suggested, or get something worse.
The President replied that he must not be expected to quarrel with the New York Tribune before the right time; he hoped never to have to do it; he would not anticipate events. In respect to emancipation in Missouri, he said that what had been observed by Mr. Noell was probably true, but the operation of these natural causes had not prevented the irritating conduct to which he had referred, or destroyed the hopes of the Confederates that Missouri would at some time merge herself alongside of them, which, in his judgment, the passage of this resolution by Congress and its acceptance by Missouri would accomplish.
Mr. Crisfield, of Maryland, asked what would be the effect of the refusal of the State to accept this proposal, and he desired to know if the President looked to any policy beyond the acceptance or rejection of this scheme.
The President replied that he had no designs beyond the actions of the States on this particular subject. He should lament their refusal to accept it, but he had no designs beyond their refusal of it.
Mr. Menzies, of Kentucky, inquired if the President thought there was any power except in the States themselves to carry out his scheme of emancipation.
The President replied that he thought there could not be. He then went off into a course of remarks not qualifying the foregoing declaration nor material to be repeated to a just understanding of his meaning.
Mr. Crisfield said he did not think the people of Maryland looked upon slavery as a permanent institution; and he did not know that they would be very reluctant to give it up if provision was made to meet the loss and they could be rid of the race; but they did not like to be coerced into emancipation, either by the direct action of the government or by indirection, as through the emancipation of slaves in this District, or the confiscation of Southern property as now threatened; and he thought before they would consent to consider this proposition they would require to be informed on these points. The President replied that, unless he was expelled by the act of God or the Confederate armies he should occupy that house for three years; and as long as he remained there Maryland had nothing to fear either for her institutions or her interests on the points referred to.
Mr. Crisfield immediately added: "Mr. President, if what you now say could be heard by the people of Maryland, they would consider your proposition with a much better feeling than I fear without it they will be inclined to do."
The President: "That [meaning a publication of what he said] will not do; it would force me into a quarrel before the proper time "; and, again intimating, as he had before done, that a quarrel with the "Greeley faction" was impending, he said he did not wish to encounter it before the proper time, nor at all if it could be avoided.
[The Greely faction wanted an immediate Emancipation Proclamation. D.W.]
Governor Wickliffe, of Kentucky, then asked him respecting the constitutionality of his scheme.
The President replied: "As you may suppose, I have considered that; and the proposition now submitted does not encounter any constitutional difficulty. It proposes simply to co-operate with any State by giving such State pecuniary aid"; and he thought that the resolution, as proposed by him, would be considered rather as the expression of a sentiment than as involving any constitutional question.
Mr. Hall, of Missouri, thought that if this proposition was adopted at all it should be by the votes of the free States, and come as a proposition from them to the slave States, affording them an inducement to put aside this subject of discord; that it ought not to be expected that members representing slaveholding constituencies should declare at once, and in advance of any proposition to them, for the emancipation of slavery.
The President said he saw and felt the force of the objection; it was a fearful responsibility, and every gentleman must do as he thought best; that he did not know how this scheme was received by the members from the free States; some of them had spoken to him and received it kindly; but for the most part they were as reserved and chary as we had been, and he could not tell how they would vote. And in reply to some expression of Mr. Hall as to his own opinion regarding slavery, he said he did not pretend to disguise his anti-slavery feeling; that he thought it was wrong, and should continue to think so; but that was not the question we had to deal with now. Slavery existed, and that, too, as well by the act of the North as of the South; and in any scheme to get rid of it the North as well as the South was morally bound to do its full and equal share. He thought the institution wrong and ought never to have existed; but yet he recognized the rights of property which had grown out of it, and would respect those rights as fully as similar rights in any other property; that property can exist and does legally exist. He thought such a law wrong, but the rights of property resulting must be respected; he would get rid of the odious law, not by violating the rights, but by encouraging the proposition and offering inducements to give it up.
Here the interview, so far as this subject is concerned, terminated by Mr. Crittenden's assuring the President that, whatever might be our final action, we all thought him solely moved by a high patriotism and sincere devotion to the happiness and glory of his country; and with that conviction we should consider respectfully the important suggestions he had made.
After some conversation on the current war news, we retired, and I immediately proceeded to my room and wrote out this paper. J. W. CRISFIELD.
We were present at the interview described in the foregoing paper of Mr. Crisfield, and we certify that the substance of what passed on the occasion is in this paper faithfully and fully given.
J. W. MENZIES, J. J. CRITTENDEN, R. MALLORY.
March 10, 1862.
Major-General McClellan having personally taken the field at the head of the Army of the Potomac, until otherwise ordered he is relieved from the command of the other military departments, he retaining command of the Department of the Potomac.
Ordered further, That the departments now under the respective commands of Generals Halleck and Hunter, together with so much of that under General Buell as lies west of a north and south line indefinitely drawn through Knoxville, Tenn., be consolidated and designated the Department of the Mississippi, and that until otherwise ordered Major General Halleck have command of said department.
Ordered also, That the country west of the Department of the Potomac and east of the Department of the Mississippi be a military department, to be called the Mountain Department, and that the same be commanded by Major-General Fremont.
That all the commanders of departments, after the receipt of this order by them, respectively report severally and directly to the Secretary of War, and that prompt, full, and frequent reports will be expected of all and each of them.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. MCCLELLAN:
The President, having considered the plan of operations agreed upon by yourself and the commanders of army corps, makes no objection to the same but gives the following directions as to its execution:
1. Leave such force at Manassas Junction as shall make it entirely certain that the enemy shall no repossess himself of that position and line of communication.
2. Leave Washington entirely secure.
3. Move the remainder of the force down the Potomac, choosing a new base at Fortress Monroe or anywhere between here and there, or, at all events, move such remainder of the army at once in pursuit of the enemy by some route.
EDWARD M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
I thank you, Mr. Train, for your kindness in presenting me with this truly elegant and highly creditable specimen of the handiwork of the mechanics of your State of Massachusetts, and I beg of you to express my hearty thanks to the donors. It displays a perfection of workmanship which I really wish I had time to acknowledge in more fitting words, and I might then follow your idea that it is suggestive, for it is evidently expected that a good deal of whipping is to be done. But as we meet here socially let us not think only of whipping rebels, or of those who seem to think only of whipping negroes, but of those pleasant days, which it is to be hoped are in store for us, when seated behind a good pair of horses we can crack our whips and drive through a peaceful, happy, and prosperous land. With this idea, gentlemen, I must leave you for my business duties. [It was likely a Buggy-Whip D.W.]
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
The third section of the "Act further to promote the efficiency of the Navy," approved December 21, 1861, provides:
"That the President of the United States, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate, shall have the authority to detail from the retired list of the navy for the command of squadrons and single ships such officers as he may believe the good of the service requires to be thus placed in command; and such officers may, if upon the recommendation of the President of the United States they shall receive a vote of thanks cf Congress for their services and gallantry in action against an enemy, be restored to the active list, and not otherwise."
In conformity with this law, Captain Samuel F. Du Pont, of the navy, was nominated to the Senate for continuance as the flag-officer in command of the squadron which recently rendered such important service to the Union in the expedition to the coasts of South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida.
Believing that no occasion could arise which would more fully correspond with the intention of the law or be more pregnant with happy influence as an example, I cordially recommend that Captain Samuel F. Du Pont receive a vote of thanks of Congress for his service and gallantry displayed in the capture since the 21st December, 1861, of various ports on the coasts of Georgia and Florida, particularly Brunswick, Cumberland Island and Sound, Amelia Island, the towns of St. Mary's, St. Augustine, and Jacksonville and Fernandina.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN.
MY DEAR SIR:-This morning I felt constrained to order Blenker's division to Fremont, and I write this to assure you I did so with great pain, understanding that you would wish it otherwise. If you could know the full pressure of the case, I am confident that you would justify it, even beyond a mere acknowledgment that the commander-in-chief may order what he pleases.
Yours very truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, April 2, 1862.
MY DEAR SIR:-Allow me to thank you in behalf of my little son for your present of white rabbits. He is very much pleased with them.
Yours truly,
The Secretary of War will order that one or the other of the corps of General McDowell and General Sumner remain in front of Washington until further orders from the department, to operate at or in the direction of Manassas Junction, or otherwise, as occasion may require; that the other Corps not so ordered to remain go forward to General McClellan as speedily as possible; that General McClellan commence his forward movements from his new base at once, and that such incidental modifications as the foregoing may render proper be also made. A. LINCOLN.
GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN:
Yours of 11 A. M. today received. Secretary of War informs me that the forwarding of transportation, ammunition, and Woodbury's brigade, under your orders, is not, and will not be, interfered with. You now have over one hundred thousand troops with you, independent of General Wool's command. I think you better break the enemy's line from Yorktown to Warwick River at once. This will probably use time as advantageously as you can.
A. LINCOLN, President
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN.
MY DEAR SIR+—Your despatches, complaining that you are not properly sustained, while they do not offend me, do pain me very much.
Blenker's division was withdrawn from you before you left here, and you knew the pressure under which I did it, and, as I thought, acquiesced in it certainly not without reluctance.
After you left I ascertained that less than 20,000 unorganized men, without a single field battery, were all you designed to be left for the defense of Washington and Manassas Junction, and part of this even to go to General Hooker's old position; General Banks's corps, once designed for Manassas Junction, was divided and tied up on the line of Winchester and Strasburg, and could not leave it without again exposing the upper Potomac and the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. This presented (or would present when McDowell and Sumner should be gone) a great temptation to the enemy to turn back from the Rappahannock and sack Washington. My explicit order that Washington should, by the judgment of all the Commanders of corps, be left entirely secure, had been neglected. It was precisely this that drove me to detain McDowell.
I do not forget that I was satisfied with your arrangement to leave Banks at Manassas Junction; but when that arrangement was broken up and nothing substituted for it, of course I was not satisfied. I was constrained to substitute something for it myself.
And now allow me to ask, do you really think I should permit the line from Richmond via Manaasas Junction to this city to be entirely open, except what resistance could be presented by less than 20,000 unorganized troops? This is a question which the country will not allow me to evade.
There is a curious mystery about the number of the troops now with you. When I telegraphed you on the 6th, saying you had over 100,000 with you, I had just obtained from the Secretary of War a statement, taken as he said from your own returns, making 108,000 then with you and en route to you. You now say you will have but 85,000 when all enroute to you shall have reached you. How can this discrepancy of 23,000 be accounted for?
As to General Wool's command, I understand it is doing for you precisely what a like number of your own would have to do if that command was away. I suppose the whole force which has gone forward to you is with you by this time; and if so, I think it is the precise time for you to strike a blow. By delay the enemy will relatively gain upon you—that is, he will gain faster by fortifications and reinforcements than you can by reinforcements alone.
And once more let me tell you it is indispensable to you that you strike a blow. I am powerless to help this. You will do me the justice to remember I always insisted that going down the bay in search of a field, instead of fighting at or near Manassas, was only shifting and not surmounting a difficulty; that we would find the same enemy and the same or equal entrenchments at either place. The country will not fail to note—is noting now—that the present hesitation to move upon an entrenched enemy is but the story of Manassas repeated.
I beg to assure you that I have never written you or spoken to you in greater kindness of feeling than now, nor with a fuller purpose to sustain you, so far as in my most anxious judgment I consistently can; but you must act.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Saint Louis, Mo.: If the rigor of the confinement of Magoffin (Governor of Kentucky) at Alton is endangering his life, or materially impairing his health, I wish it mitigated as far as it can be consistently with his safe detention.
A. LINCOLN.
Please send above, by order of the President. JOHN HAY.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation
It has pleased Almighty God to vouchsafe signal victories to the land and naval forces engaged in suppressing, an internal rebellion, and at the same time to avert from our country the dangers of foreign intervention and invasion.
It is therefore recommended to the people of the United States that at their next weekly assemblages in their accustomed places of public worship which shall occur after notice of this proclamation shall have been received, they especially acknowledge and render thanks to our Heavenly Father for these inestimable blessings, that they then and there implore spiritual consolation in behalf of all who have been brought into affliction by the casualties and calamities of sedition and civil war, and that they reverently invoke the divine guidance for our national counsels, to the end that they may speedily result in the restoration of peace, harmony, and unity throughout our borders and hasten the establishment of fraternal relations among all the countries of the earth.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this tenth day of April, A.D. 1862, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-sixth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES: The act entitled "An act for the relief of certain persons held to service or labor in the District of Columbia" has this day been approved and signed.
I have never doubted the constitutional authority of Congress to abolish slavery in this District, and I have ever desired to see the national capital freed from the institution in some satisfactory way. Hence there has never been in my mind any question on the subject except the one of expediency, arising in view of all the circumstances. If there be matters within and about this act which might have taken a course or shape more satisfactory to my judgment, I do not attempt to specify them. I am gratified that the two principles of compensation and colonization are both recognized and practically applied in the act.
In the matter of compensation, it is provided that claims may be presented within ninety days from the passage of the act, "but not thereafter"; and there is no saving for minors, femmes covert, insane or absent persons. I presume this is an omission by mere oversight, and I recommend that it be supplied by an amendatory or supplemental act.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch of the 19th was received that day. Fredericksburg is evacuated and the bridges destroyed by the enemy, and a small part of McDowell's command occupies this side of the Rappahannock, opposite the town. He purposes moving his whole force to that point.
A. LINCOLN. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, April 24, 1862.
Hon. POSTMASTER-GENERAL.
MY DEAR SIR:—The member of Congress from the district including Tiffin, O., calls on me about the postmaster at that place. I believe I turned over a despatch to you from some persons there, asking a suspension, so as for them to be heard, or something of the sort. If nothing, or nothing amounting to anything, has been done, I think the suspension might now be suspended, and the commission go forward.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Would it derange or embarrass your operations if I were to appoint Captain Charles Griffin a brigadier-general of volunteers? Please answer.
In answer to the resolution of the Senate [of April 22] in relation to Brigadier-General Stone, I have the honor to state that he was arrested and imprisoned under my general authority, and upon evidence which whether he be guilty or innocent, required, as appears to me, such proceedings to be had against him for the public safety. I deem it incompatible with the public interest, as also, perhaps, unjust to General Stone, to make a more particular statement of the evidence.
He has not been tried because, in the state of military operations at the time of his arrest and since, the officers to constitute a court martial and for witnesses could not be withdrawn from duty without serious injury to the service. He will be allowed a trial without any unnecessary delay; the charges and specifications will be furnished him in due season, and every facility for his defense will be afforded him by the War Department.
A. LINCOLN, WASHINGTON, MAY 1, 1862
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your call for Parrott guns from Washington alarms me, chiefly because it argues indefinite procrastination. Is anything to be done?
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Pittsburgh Landing, Tennessee:
I am pressed by the Missouri members of Congress to give General Schofield independent command in Missouri. They insist that for want of this their local troubles gradually grow worse. I have forborne, so far, for fear of interfering with and embarrassing your operations. Please answer telling me whether anything, and what, I can do for them without injuriously interfering with you.
GENTLEMEN:—I welcome here the representatives of the Evangelical Lutherans of the United States. I accept with gratitude their assurances of the sympathy and support of that enlightened, influential, and loyal class of my fellow citizens in an important crisis which involves, in my judgment, not only the civil and religious liberties of our own dear land, but in a large degree the civil and religious liberties of mankind in many countries and through many ages. You well know, gentlemen, and the world knows, how reluctantly I accepted this issue of battle forced upon me on my advent to this place by the internal enemies of our country. You all know, the world knows, the forces and the resources the public agents have brought into employment to sustain a government against which there has been brought not one complaint of real injury committed against society at home or abroad. You all may recollect that in taking up the sword thus forced into our hands this government appealed to the prayers of the pious and the good, and declared that it placed its whole dependence on the favor of God. I now humbly and reverently, in your presence, reiterate the acknowledgment of that dependence, not doubting that, if it shall please the Divine Being who determines the destinies of nations, this shall remain a united people, and that they will, humbly seeking the divine guidance, make their prolonged national existence a source of new benefits to themselves and their successors, and to all classes and conditions of mankind.
FLAG-OFFICER GOLDSBOROUGH.
SIR:—Major-General McClellan telegraphs that he has ascertained by a reconnaissance that the battery at Jamestown has been abandoned, and he again requests that gunboats may be sent up the James River.
If you have tolerable confidence that you can successfully contend with the Merrimac without the help of the Galena and two accompanying gunboats, send the Galena and two gunboats up the James River at once. Please report your action on this to me at once. I shall be found either at General Wool's headquarters or on board the Miami.
Your obedient servant,
FORT MONROE, VIRGINIA, May 9, 1862
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
MY DEAR SIR:—I have just assisted the Secretary of War in framing part of a despatch to you relating to army corps, which despatch, of course, will have reached you long before this will. I wish to say a few words to you privately on this subject. I ordered the army corps organization not only on the unanimous opinion of the twelve generals whom you had selected and assigned as generals of divisions, but also on the unanimous opinion of every military man I could get an opinion from, and every modern military book, yourself only excepted. Of course, I did not on my own judgment pretend to understand the subject. I now think it indispensable for you to know how your struggle against it is received in quarters which we cannot entirely disregard. It is looked upon as merely an effort to pamper one or two pets, and to persecute and degrade their supposed rivals. I have had no word from Sumner, Heintzleman, or Keyes the commanders of these corps are, of course, the three highest officers with you; but I am constantly told that you have no consultation or communication with them; that you consult and communicate with nobody but General Fitz John Porter, and perhaps General Franklin. I do not say these complaints are true or just; but at all events, it is proper you should know of their existence. Do the commanders of corps disobey your orders in anything?
When you relieved General Hamilton of his command the other day, you thereby lost the confidence of at least one of your best friends in the Senate. And here let me say, not as applicable to you personally, that Senators and Representatives speak of me in their places without question, and that officers of the army must cease addressing insulting letters to them for taking no greater liberty with them.
But to return. Are you strong enough—are you strong enough even with my help—to set your foot upon the necks of Sumner, Heintzelman, and Keyes all at once? This is a practical and very serious question to you?
The success of your army and the cause of the country are the same, and, of course, I only desire the good of the cause.
Yours truly,
FLAG-OFFICER GOLDSBOROUGH.
MY DEAR SIR:—I send you this copy of your report of yesterday for the purpose of saying to you in writing that you are quite right in supposing the movement made by you and therein reported was made in accordance with my wishes verbally expressed to you in advance. I avail myself of the occasion to thank you for your courtesy and all your conduct, so far as known to me, during my brief visit here.
Yours very truly,
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas, by my proclamation of the 19th of April, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-one, it was declared that the ports of certain States, including those of Beaufort, in the State of North Carolina, Port Royal, in the State of South Carolina, and New Orleans, in the State of Louisiana, were, for reasons therein set forth, intended to be placed under blockade; and whereas the said ports of Beaufort, Port Royal, and New Orleans have since been blockaded; but as the blockade of the same ports may now be safely relaxed with advantage to the interests of commerce:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, pursuant to the authority in me vested by the fifth section of the act of Congress approved on the 13th of July last, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," do hereby declare that the blockade of the said ports of Beaufort, Port Royal, and New Orleans shall so far cease and determine, from and after the first day of June next, that commercial intercourse with those ports, except as to persons, things, and information contraband of war, may from that time be carried on, subject to the laws of the United States, and to the limitations and in pursuance of the regulations which are prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury in his order of this date, which is appended to this proclamation.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twelfth day of May, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-two, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-sixth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
THE WRITINGS OF A. LINCOLN, Volume Six, 1862-1863
RECOMMENDATION OF NAVAL OFFICERS
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
SPEECH TO THE 12TH INDIANA REGIMENT, MAY [15?] 1862
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
MEMORANDUM OF PROPOSED ADDITIONS TO INSTRUCTIONS OF ABOVE DATE
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
PROCLAMATION REVOKING GENERAL HUNTER'S ORDER OF MILITARY EMANCIPATION,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. E. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL RUFUS SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL D. S. MILES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. W. GEARY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER TAKING MILITARY POSSESSION OF RAILROADS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. SAXTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
HISTORY OF CONSPIRACY OF REBELLION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GOVERNOR ANDREW.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL FREMONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT.
TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT. WASHINGTON, June 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL N. P. BANKS.
SPEECH AT JERSEY CITY, JUNE 24, 1862.
ORDER CONSTITUTING THE ARMY OF VIRGINIA.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAMS TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
WAR DEPARTMENT, June, 28, 1862
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO FLAG-OFFICER L. M. GOLDSBOROUGH.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD. WAR DEPARTMENT, June 30, 1862.
CALL FOR TROOPS. NEW YORK, June 30, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAMS TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
WASHINGTON, D.C., June 30, 1862.
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, JULY 1, 1862.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July 1, 1862
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING TAXES IN REBELLIOUS STATES, JULY 1, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, JULY 1, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
CIRCULAR LETTER TO THE GOVERNORS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MEMORANDUM OF AN INTERVIEW BETWEEN THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL McCLELLAN
ORDER MAKING HALLECK GENERAL-IN-CHIEF.
ORDER CONCERNING THE SOUTHWEST BRANCH OF THE PACIFIC RAILROAD.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. WAR DEPARTMENT, July 11, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK. WAR DEPARTMENT, July 11, 1862.
APPEAL TO BORDER-STATES IN FAVOR OF COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
ACT OF COMPENSATED EMANCIPATION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. July 17, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. July 17, 1862.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER IN REGARD TO BEHAVIOR OF ALIENS
ORDER AUTHORIZING EMPLOYMENT OF "CONTRABANDS."
HOLD MY HAND WHILST THE ENEMY STABS ME
SPEECH AT A WAR MEETING, WASHINGTON, AUGUST 6, 1862
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR ANDREW. August 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR CURTIN. August 12, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. R. CURTIS. August 12, 1862.
ADDRESS ON COLONIZATION TO A DEPUTATION OF COLORED MEN.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER AT CAMP CHASE, OHIO.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BURNSIDE OR GENERAL PARKE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
ORDER TO GENERAL H. W. HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. E. WOOL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B, McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. C. BUELL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TO GOVERNOR CURTIN. September 11, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL C. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
REPLY TO REQUEST THE PRESIDENT ISSUE A PROCLAMATION OF EMANCIPATION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. G. WRIGHT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO J. K. DUBOIS. WASHINGTON, D.C.,
PRELIMINARY EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION, SEPTEMBER 22, 1862.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
REPLY TO SERENADE, SEPTEMBER 24, 1862.
RECORD EXPLAINING THE DISMISSAL OF MAJOR JOHN J. KEY
REMARKS TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC AT FREDERICK, MARYLAND,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. T. BOYLE.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PIERPOINT.
EXECUTIVE ORDER ESTABLISHING A PROVISIONAL COURT IN LOUISIANA.
GENERAL McCLELLAN'S TIRED HORSES
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN.
ORDER RELIEVING GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN
ORDER CONCERNING THE CONFISCATION ACT.
GENERAL ORDER RESPECTING THE OBSERVANCE OF THE SABBATH DAY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
ORDER PROHIBITING THE EXPORT OF ARMS AND MUNITIONS OF WAR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
ANNUAL MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, DECEMBER 1, 1862.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. December 8, 1862.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL H. H. SIBLEY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TO SECRETARIES SEWARD AND CHASE.
CONGRATULATIONS TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION, JANUARY 1, 1863.
TO CALEB RUSSELL AND SALLIE A. FENTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
CORRESPONDENCE WITH GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE, JANUARY 8, 1863.
HEADQUARTERS OF THE ARMY, WASHINGTON, January 7, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. R. CURTIS.
INSTRUCTION TO THE JUDGE-ADVOCATE-GENERAL.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES. JANUARY 14, 1863.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF MANCHESTER, ENGLAND.
FITZ-JOHN PORTER COURT-MARTIAL.
FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
ORDER RELIEVING GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE AND MAKING OTHER CHANGES.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF LONDON, ENGLAND.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHENCK. [Cipher.] WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C.,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
PROCLAMATION CONVENING THE SENATE, FEBRUARY 28, 1863
PROCLAMATION RECALLING SOLDIERS TO THEIR REGIMENTS, MARCH 10, 1863
GRANT'S EXCLUSION OF A NEWSPAPER REPORTER
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. A. HURLBUT.
QUESTION OF RAISING NEGRO TROOPS
PROCLAMATION APPOINTING A NATIONAL FAST-DAY.
LICENSE OF COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE.
PROCLAMATION ABOUT COMMERCIAL INTERCOURSE, APRIL 2, 1863
TELEGRAM TO THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT NASHVILLE.
TELEGRAM TO ADMIRAL S. P. DUPONT.
TO GENERAL D. HUNTER AND ADMIRAL S. F. DUPONT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. HOOKER.
STATEHOOD FOR WEST VIRGINIA, APRIL 20, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. BUTTERFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL R. INGALLS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. A. DIX.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTTERFIELD.
ORDERS SENDING C. L. VALLANDIGHAM BEYOND MILITARY LINES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. A. HURLBUT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BUCKINGHAM.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER. [Cipher.] EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTTERFIELD.
TO ERASTUS CORNING AND OTHERS.
TO THE SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
RESPONSE TO A "BESIEGED" GENERAL
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
NEEDS NEW TIRES ON HIS CARRIAGE
CALL FOR 100,000 MILITIA TO SERVE FOR SIX MONTHS, JUNE 15, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO P. KAPP AND OTHERS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. HOOKER.
FURTHER DEMOCRATIC PARTY CRITICISM
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL COUCH. [Cipher] WASHINGTON CITY, June 30, 1863. 3.23
ANNOUNCEMENT OF NEWS FROM GETTYSBURG.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL FRENCH. [Cipher] WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C.,
CONTINUED FAILURE TO PURSUE ENEMY
SURRENDER OF VICKSBURG TO GENERAL GRANT
TELEGRAM FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL G. C. MEADE.
NEWS OF GRANT'S CAPTURE OF VICKSBURG
TELEGRAM TO L. SWETT AND P. F. LOWE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
SON IN COLLEGE DOES NOT WRITE HIS PARENTS
INTIMATION OF ARMISTICE PROPOSALS
PROCLAMATION FOR THANKSGIVING, JULY 15, 1863
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD
To GENERAL G. G. MEADE. (Private.)
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. B. BURNSIDE.
TELEGRAM FROM GOVERNOR SEYMOUR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
TELEGRAM TO F. C. SHERMAN AND J. S. HAYES.
POLITICAL MOTIVATED MISQUOTATION IN NEWSPAPER
ORDER CONCERNING COMMERCIAL REGULATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO F. C. SHERMAN AND J. S. HAYES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS, SEPTEMBER 15, 1863.
REQUEST TO SUGGEST NAME FOR A BABY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO O. M. HATCH AND J. K. DUBOIS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
PROCLAMATION OPENING THE PORT OF ALEXANDRIA, VIRGINIA,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
MRS. LINCOLN'S REBEL BROTHER-IN-LAW KILLED
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. M. SCHOFIELD.
PROCLAMATION FOR THANKSGIVING, OCTOBER 3, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL J. M. SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
THE CASE OF DR. DAVID M. WRIGHT
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
AID TO MRS. HELM, MRS. LINCOLN'S SISTER
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, OCTOBER 17, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO J. WILLIAMS AND N. G. TAYLOR.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL R. C. SCHENCK.
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 14, 1862.
TO SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
The third section of the "Act further to promote the efficiency of the Navy," approved 21st of December, 1861, provides:
"That the President of the United States by and with the advice and consent of the Senate, shall have the authority to detail from the retired list of the navy for the command of squadrons and single ships such officers as he may believe that the good of the service requires to be thus placed in command; and such officers may, if upon the recommendation of the President of the United States they shall receive a vote of thanks of Congress for their services and gallantry in action against an enemy, be restored to the active list, and not otherwise."
In conformity with this law, Captain David G. Farragut was nominated to the Senate for continuance as the flag-officer in command of the squadron which recently rendered such important service to the Union by his successful operations on the lower Mississippi and capture of New Orleans.
Believing that no occasion could arise which would more fully correspond with the intention of the law or be more pregnant with happy influence as an example, I cordially recommend that Captain D. G. Farragut receive a vote of thanks of Congress for his services and gallantry displayed in the capture since 21st December, 1861, of Forts Jackson and St. Philip, city of New Orleans, and the destruction of various rebel gunboats, rams, etc.....
I submit herewith a list of naval officers who commanded vessels engaged in the recent brilliant operations of the squadron commanded by Flag-officer Farragut which led to the capture of Forts Jackson and St. Philip, city of New Orleans, and the destruction of rebel gunboats, rams, etc., in April 1862. For their services and gallantry on those occasions I cordially recommend that they should, by name, receive a vote of thanks of Congress:
LIST:
Captain Theodorus Bailey.
Captain Henry W. Morris.
Captain Thomas T. Craven.
Commander Henry H. Bell.
Commander Samuel Phillips Lee.
Commander Samuel Swartwout.
Commander Melancton Smith.
Commander Charles Stewart Boggs
Commander John De Camp
Commander James Alden.
Commander David D. Porter.
Commander Richard Wainwright.
Commander William B. Renshaw.
Lieutenant Commanding Abram D. Harrell.
Lieutenant Commanding Edward Donaldson.
Lieutenant Commanding George H. Preble.
Lieutenant Commanding Edward T. Nichols.
Lieutenant Commanding Jonathan M. Wainwright.
Lieutenant Commanding John Guest.
Lieutenant Commanding Charles H. B. Caldwell.
Lieutenant Commanding Napoleon B. Harrison.
Lieutenant Commanding Albert N. Smith.
Lieutenant Commanding Pierce Crosby.
Lieutenant Commanding George M. Ransom.
Lieutenant Commanding Watson Smith.
Lieutenant Commanding John H. Russell.
Lieutenant Commanding Walter W. Queen.
Lieutenant Commanding K. Randolph Breese.
Acting Lieutenant Commanding Sellin E. Woolworth.
Acting Lieutenant Commanding Charles H. Baldwin.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 14, 1862
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Cumberland, Virginia:
Your long despatch of yesterday is just received. I will answer more fully soon. Will say now that all your despatches to the Secretary of War have been promptly shown to me. Have done and shall do all I could and can to sustain you. Hoped that the opening of James River and putting Wool and Burnside in communication, with an open road to Richmond, or to you, had effected something in that direction. I am still unwilling to take all our force off the direct line between Richmond and here.
It has not been customary heretofore, nor will it be hereafter, for me to say something to every regiment passing in review. It occurs too frequently for me to have speeches ready on all occasions. As you have paid such a mark of respect to the chief magistrate, it appears that I should say a word or two in reply. Your colonel has thought fit, on his own account and in your name, to say that you are satisfied with the manner in which I have performed my part in the difficulties which have surrounded the nation. For your kind expressions I am extremely grateful, but on the other hand I assure you that the nation is more indebted to you, and such as you, than to me. It is upon the brave hearts and strong arms of the people of the country that our reliance has been placed in support of free government and free institutions.
For the part which you and the brave army of which you are a part have, under Providence, performed in this great struggle, I tender more thanks especially to this regiment, which has been the subject of good report. The thanks of the nation will follow you, and may God's blessing rest upon you now and forever. I hope that upon your return to your homes you will find your friends and loved ones well and happy. I bid you farewell.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL:
What is the strength of your force now actually with you?
May 17, 1862. You will retain the separate command of the forces taken with you; but while co-operating with General McClellan you will obey his orders, except that you are to judge, and are not to allow your force to be disposed otherwise than so as to give the greatest protection to this capital which may be possible from that distance.
[Indorsement.]
TO THE SECRETARY OF WAR:
The President having shown this to me, I suggested that it is dangerous to direct a subordinate not to obey the orders of his superior in any case, and that to give instructions to General McClellan to this same end and furnish General McDowell with a copy thereof would effect the object desired by the President. He desired me to say that the sketch of instructions to General McClellan herewith he thought made this addition unnecessary.
Respectfully, M. C. M.
INDORSEMENT RELATING TO GENERAL DAVID HUNTER'S ORDER OF MILITARY EMANCIPATION,
MAY 17, 1862
No commanding general shall do such a thing upon my responsibility without consulting me.
GENERAL: Your despatch to the President, asking reinforcements, has been received and carefully considered.
The President is not willing to uncover the capital entirely; and it is believed that, even if this were prudent, it would require more time to effect a junction between your army and that of the Rappahannock by the way of the Potomac and York rivers than by a land march. In order, therefore, to increase the strength of the attack upon Richmond at the earliest moment, General McDowell has been ordered to march upon that city by the shortest route. He is ordered, keeping himself always in position to save the capital from all possible attack, so to operate as to put his left wing in communication with your right wing, and you are instructed to co-operate so as to establish this communication as soon as possible by extending your right-wing to the north of Richmond.
It is believed that this communication can be safely established either north or south of the Pamunkey River.
In any event, you will be able to prevent the main body of the enemy's forces from leaving Richmond and falling in overwhelming force upon General McDowell. He will move with between thirty-five and forty thousand men.
A copy of the instructions to General McDowell are with this. The specific task assigned to his command has been to provide against any danger to the capital of the nation.
At your earnest call for reinforcements, he is sent forward to co-operate in the reduction of Richmond, but charged, in attempting this, not to uncover the city of Washington; and you will give no order, either before or after your junction, which can put him out of position to cover this city. You and he will communicate with each other by telegraph or otherwise as frequently as may be necessary for efficient cooperation. When General McDowell is in position on your right, his supplies must be drawn from West Point, and you will instruct your staff-officers to be prepared to supply him by that route.
The President desires that General McDowell retain the command of the Department of the Rappahannock and of the forces with which he moves forward.
By order of the President: EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN, Commanding Army of the Potomac, before Richmond.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation
Whereas there appears in the public prints what purports to be a proclamation of Major general Hunter, in the words and figures following, to wit:
(General Orders No. 11) HEADQUARTERS DEPARTMENT OF THE SOUTH, HILTON HEAD, PORT ROYAL, S. C., May 9, 1862.
"The three States of Georgia, Florida, and South Carolina, comprising the military department of the South, having deliberately declared themselves no longer under the protection of the United States of America, and having taken up arms against the said United States, it became a military necessity to declare martial law. This was accordingly done on the 25th day of April, 1862. Slavery and martial law in a free country are altogether incompatible. The persons in these three States: Georgia Florida, and South Carolina—heretofore held as slaves are therefore declared forever free.
"By command of Major-General D. Hunter: "(Official.)ED. W. SMITH, "Acting Assistant Adjutant-General."
And whereas the same is producing some excitement and misunderstanding: therefore,
I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, proclaim and declare that the Government of the United States, had no knowledge, information, or belief of an intention on the part of General Hunter to issue such a proclamation; nor has it yet any authentic information that the document is genuine. And further, that neither General Hunter nor any other commander or person has been authorized by the Government of the United States to make a proclamation declaring the slaves of any State free; and that the supposed proclamation now in question, whether genuine or false, is altogether void so far as respects such a declaration.
I further make known that whether it be competent for me, as commander-in-chief of the army and navy, to declare the slaves of any State or States free, and whether, at any time, in any case, it shall have become a necessity indispensable to the maintenance of the government to exercise such supposed power, are questions which under my responsibility I reserve to myself, and which I cannot feel justified in leaving to the decision of commanders in the field.
These are totally different questions from those of police regulations in armies and camps.
On the sixth day of March last, by special message, I recommended to Congress the adoption of a joint resolution, to be substantially as follows:
Resolved, That the United States ought to co-operate with any State which may adopt gradual abolishment of slavery, giving to such State pecuniary aid, to be used by such State, in its discretion, to compensate for the inconvenience, public and private, produced by such change of system.
The resolution in the language above quoted was adopted by large majorities in both branches of Congress, and now stands an authentic, definite, and solemn proposal of the nation to the States and people most immediately interested in the subject-matter. To the people of those States I now earnestly appeal. I do not argue—I beseech you to make arguments for yourselves. You cannot, if you would, be blind to the signs of the times. I beg of you a calm and enlarged consideration of them, ranging, if it may be, far above personal and partisan politics. This proposal makes common cause for a common object, casting no reproaches upon any. It acts not the Pharisee. The change it contemplates would come gently as the dews of heaven, not rending or wrecking anything. Will you not embrace it? So much good has not been done, by one effort, in all past time, as in the providence of God it is now your high privilege to do. May the vast future not have to lament that you have neglected it.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this nineteenth day of May, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-two, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-sixth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I have just been waited on by a large committee who present a petition signed by twenty-three senators and eighty-four representatives asking me to restore General Hamilton to his division. I wish to do this, and yet I do not wish to be understood as rebuking you. Please answer at once.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your long despatch of yesterday just received. You will have just such control of General McDowell and his forces as you therein indicate. McDowell can reach you by land sooner than he could get aboard of boats, if the boats were ready at Fredericksburg, unless his march shall be resisted, in which case the force resisting him will certainly not be confronting you at Richmond. By land he can reach you in five days after starting, whereas by water he would not reach you in two weeks, judging by past experience. Franklin's single division did not reach you in ten days after I ordered it.
A. LINCOLN,
President United States.
MAJOR-GENERAL G. B. McCLELLAN:
In consequence of General Banks's critical position, I have been compelled to suspend General McDowell's movements to join you. The enemy are making a desperate push upon Harper's Ferry, and we are trying to throw General Fremont's force and part of General McDowell's in their rear.
A. LINCOLN, President.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
I left General McDowell's camp at dark last evening. Shields's command is there, but it is so worn that he cannot move before Monday morning, the 26th. We have so thinned our line to get troops for other places that it was broken yesterday at Front Royal, with a probable loss to us of one regiment infantry, two Companies cavalry, putting General Banks in some peril.
The enemy's forces under General Anderson now opposing General McDowell's advance have as their line of supply and retreat the road to Richmond.
If, in conjunction with McDowell's movement against Anderson, you could send a force from your right to cut off the enemy's supplies from Richmond, preserve the railroad bridges across the two forks of the Pamunkey, and intercept the enemy's retreat, you will prevent the army now opposed to you from receiving an accession of numbers of nearly 15,000 men; and if you succeed in saving the bridges you will secure a line of railroad for supplies in addition to the one you now have. Can you not do this almost as well as not while you are building the Chickahominy bridges? McDowell and Shields both say they can, and positively will, move Monday morning. I wish you to move cautiously and safely.
You will have command of McDowell, after he joins you, precisely as you indicated in your long despatch to us of the 21st.
GENERAL SAXTON:
Geary reports Jackson with 20,000 moving from Ashby's Gap by the Little River turnpike, through Aldie, toward Centreville. This he says is reliable. He is also informed of large forces south of him. We know a force of some 15,000 broke up Saturday night from in front of Fredericksburg and went we know not where. Please inform us, if possible, what has become of the force which pursued Banks yesterday; also any other information you have.
COLONEL MILES, Harper's Ferry, Virginia
Could you not send scouts from Winchester who would tell whether enemy are north of Banks, moving on Winchester? What is the latest you have?
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Franklin:
You are authorized to purchase the 400 horses, or take them wherever or however you can get them. The exposed condition of General Banks makes his immediate relief a point of paramount importance. You are therefore directed by the President to move against Jackson at Harrisonburg and operate against the enemy in such way as to relieve Banks. This movement must be made immediately. You will acknowledge the receipt of this order, and specify the hour it is received by you.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Franklin, Virginia:
Many thanks for the promptness with which you have answered that you will execute the order. Much—perhaps all—depends upon the celerity with which you can execute it. Put the utmost speed into it. Do not lose a minute.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, near Corinth, Mississippi:
Several despatches from Assistant Secretary Scott and one from Governor Morton asking reinforcements for you have been received. I beg you to be assured we do the best we can. I mean to cast no blame where I tell you each of our commanders along our line from Richmond to Corinth supposes himself to be confronted by numbers superior to his own. Under this pressure We thinned the line on the upper Potomac, until yesterday it was broken with heavy loss to us, and General Banks put in great peril, out of which he is not yet extricated, and may be actually captured. We need men to repair this breach, and have them not at hand. My dear General, I feel justified to rely very much on you. I believe you and the brave officers and men with you can and will get the victory at Corinth.
A. LINCOLN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL I. McDOWELL
WAR DEPARTMENT, May 24, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Fredricksburg:
General Fremont has been ordered by telegraph to move from Franklin on Harrisonburg to relieve General Banks, and capture or destroy Jackson's and Ewell's forces. You are instructed, laying aside for the present the movement on Richmond, to put 20,000 men in motion at once for the Shenandoah, moving on the line or in advance of the line of the Manassas Gap railroad. Your object will be to capture the forces of Jackson and Ewell, either in co-operation with General Fremont, or, in case want of supplies or of transportation, interferes with his movements, it is believed that the force which you move will be sufficient to accomplish this object alone. The information thus far received here makes it probable that if the enemy operate actively against General Banks, you will not be able to count upon much assistance from him, but may even have to release him. Reports received this moment are that Banks is fighting with Ewell eight miles from Winchester.
MAJOR-GENERAL I. McDOWELL:
I am highly gratified by your alacrity in obeying my order. The change was as painful to me as it can possibly be to you or to any one. Everything now depends upon the celerity and vigor of your movement.
GENERAL GEARY, White Plains:
Please give us your best present impression as to the number of the enemy's forces north of Strasburg and Front Royal. Are the forces still moving north through the gap at Front Royal and between you and there?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
The enemy is moving north in sufficient force to drive General Banks before him—precisely in what force we cannot tell. He is also threatening Leesburg and Geary, on the Manassas Gap railroad, from both north and south—in precisely what force we cannot tell. I think the movement is a general and concerted one, such as would not be if he was acting upon the purpose of a very desperate defense of Richmond. I think the time is near when you must either attack Richmond or give up the job and come to the defense of Washington. Let me hear from you instantly.
A. LINCOLN, President.
Ordered: By virtue of the authority vested by act of Congress, the President takes military possession of all the railroads in the United States from and after this date until further order, and directs that the respective railroad companies, their officers and servants, shall hold themselves in readiness for the transportation of such troops and munitions of war as may be ordered by the military authorities, to the exclusion of all other business.
By order of the Secretary of War.
SECRETARY CHASE, Fredericksburg, Virginia:
It now appears that Banks got safely into Winchester last night, and is this morning retreating on Harper's Ferry. This justifies the inference that he is pressed by numbers superior to his own. I think it not improbable that Ewell, Jackson, and Johnson are pouring through the gap they made day before yesterday at Front Royal, making a dash northward. It will be a very valuable and very honorable service for General McDowell to cut them off. I hope he will put all possible energy and speed into the effort.
GENERAL SAXTON, Harper's Ferry:
If Banks reaches Martinsburg, is he any the better for it? Will not the enemy cut him from thence to Harper's Ferry? Have you sent anything to meet him and assist him at Martinsburg? This is an inquiry, not an order.
GENERAL SAXTON, Harper's Ferry:
One good six-gun battery, complete in its men and appointments, is now on its way to you from Baltimore. Eleven other guns, of different sorts, are on their way to you from here. Hope they will all reach you before morning. As you have but 2500 men at Harper's Ferry, where are the rest which were in that vicinity and which we have sent forward? Have any of them been cut off?
GENERAL SAXTON, Harper's Ferry:
I fear you have mistaken me. I did not mean to question the correctness of your conduct; on the contrary! I approve what you have done. As the 2500 reported by you seemed small to me, I feared some had got to Banks and been cut off with him. Please tell me the exact number you now have in hand.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, D. C., May 25,1862. 8.30 P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch received. General Banks was at Strasburg, with about 6,000 men, Shields having been taken from him to swell a column for McDowell to aid you at Richmond, and the rest of his force scattered at various places. On the 23d a rebel force of 7000 to 10,000 fell upon one regiment and two companies guarding the bridge at Front Royal, destroying it entirely; crossed the Shenandoah, and on the 24th (yesterday) pushed to get north of Banks, on the road to Winchester. Banks ran a race with them, beating them into Winchester yesterday evening. This morning a battle ensued between the two forces, in which Banks was beaten back into full retreat toward Martinsburg, and probably is broken up into a total rout. Geary, on the Manassas Gap railroad, just now reports that Jackson is now near Front Royal, With 10,000, following up and supporting, as I understand, the forces now pursuing Banks, also that another force of 10,000 is near Orleans, following on in the same direction. Stripped here, as we are here, it will be all we can do to prevent them crossing the Potomac at Harper's Ferry or above. We have about 20,000 of McDowell's force moving back to the vicinity of Front Royal, and General Fremont, who was at Franklin, is moving to Harrisonburg; both these movements intended to get in the enemy's rear.
One more of McDowell's brigades is ordered through here to Harper's Ferry; the rest of his force remains for the present at Fredericksburg. We are sending such regiments and dribs from here and Baltimore as we can spare to Harper's Ferry, supplying their places in some sort by calling in militia from the adjacent States. We also have eighteen cannon on the road to Harper's Ferry, of which arm there is not a single one yet at that point. This is now our situation.
If McDowell's force was now beyond our reach, we should be utterly helpless. Apprehension of something like this, and no unwillingness to sustain you, has always been my reason for withholding McDowell's force from you. Please understand this, and do the best you can with the force you have.
MAY 16, 1862 TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
The insurrection which is yet existing in the United States and aims at the overthrow of the Federal Constitution and the Union, was clandestinely prepared during the Winter of 1860 and 1861, and assumed an open organization in the form of a treasonable provisional government at Montgomery, in Alabama on the 18th day of February, 1861. On the 12th day of April, 1861, the insurgents committed the flagrant act of civil war by the bombardment and the capture of Fort Sumter, Which cut off the hope of immediate conciliation. Immediately afterward all the roads and avenues to this city were obstructed, and the capital was put into the condition of a siege. The mails in every direction were stopped and the lines of telegraph cut off by the insurgents, and military and naval forces which had been called out by the government for the defense of Washington were prevented from reaching the city by organized and combined treasonable resistance in the State of Maryland. There was no adequate and effective organization for the public defense. Congress had indefinitely adjourned. There was no time to convene them. It became necessary for me to choose whether, using only the existing means, agencies, and processes which Congress had provided, I should let the government fall at once into ruin or whether, availing myself of the broader powers conferred by the Constitution in cases of insurrection, I would make an effort to save it, with all its blessings, for the present age and for posterity.
I thereupon summoned my constitutional advisers, the heads of all the departments, to meet on Sunday, the 20th day of April, 1861, at the office of the Navy Department, and then and there, with their unanimous concurrence, I directed that an armed revenue cutter should proceed to sea to afford protection to the commercial marine, and especially the California treasure ships then on their way to this coast. I also directed the commandant of the navy-yard at Boston to purchase or charter and arm as quickly as possible five steamships for purposes of public defense. I directed the commandant of the navy-yard at Philadelphia to purchase or charter and arm an equal number for the same purpose. I directed the commandant at New York to purchase or charter and arm an equal number. I directed Commander Gillis to purchase or charter and arm and put to sea two other vessels. Similar directions were given to Commodore Dupont, with a view to the opening of passages by water to and from the capital. I directed the several officers to take the advice and obtain the aid and efficient services, in the matter, of his Excellency Edwin D. Morgan, the Governor of New York, or in his absence George D. Morgan, William M. Evarts, R. M. Blatchford, and Moses H. Grinnell, who were by my directions especially empowered by the Secretary of the Navy to act for his department in that crisis in matters pertaining to the forwarding of troops and supplies for the public defense.
The several departments of the government at that time contained so large a number of disloyal persons that it would have been impossible to provide safely through official agents only for the performance of the duties thus confided to citizens favorably known for their ability, loyalty, and patriotism.
The several orders issued upon these occurrences were transmitted by private messengers, who pursued a circuitous way to the seaboard cities, inland across the States of Pennsylvania and Ohio and the northern lakes. I believe by these and other similar measures taken in that crisis, some of which were without any authority of law, the government was saved from overthrow. I am not aware that a dollar of the public funds thus confided without authority of law to unofficial persons was either lost or wasted, although apprehensions of such misdirection occurred to me as objections to those extraordinary proceedings, and were necessarily overruled.
I recall these transactions now because my attention has been directed to a resolution which was passed by the House of Representatives on the 30th day of last month, which is in these words:
"Resolved, That Simon Cameron, late Secretary of War by investing Alexander Cummings with the control of large sums of the public money and authority to purchase military supplies without restriction, without requiring from him any guaranty for the faithful performance of his duties, when the services of competent public officers were available, and by involving the government in a vast number of contracts with persons not legitimately engaged in the business pertaining to the subject-matter of such contracts, especially in the purchase of arms for future delivery, has adopted a policy highly injurious to the public service, and deserves the censure of the House."
Congress will see that I should be wanting equally in candor and in justice if I should leave the censure expressed in this resolution to rest exclusively or chiefly upon Mr. Cameron. The same sentiment is unanimously entertained by the heads of department who participated in the proceedings which the House of Representatives have censured. It is due to Mr. Cameron to say that although he fully approved the proceedings they were not moved nor suggested by himself, and that not only the President, but all the other heads of departments, were at least equally responsible with him for whatever error, wrong, or fault was committed in the premises.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
We have General Banks's official report. He has saved his army and baggage, and has made a safe retreat to the river, and is probably safe at Williamsport. He reports the attacking force at 15,000.
A. LINCOLN, President.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Falmouth, Virginia:
Despatches from Geary just received have been sent you. Should not the remainder of your forces, except sufficient to hold the point at Fredericksburg, move this way—to Manassas Junction or Alexandria? As commander of this department, should you not be here? I ask these questions.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
Can you not cut the Alula Creek railroad? Also, what impression have you as to intrenched works for you to contend with in front of Richmond? Can you get near enough to throw shells into the city?
A. LINCOLN, President.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
I see that you are at Moorefield. You were expressly ordered to march to Harrisonburg. What does this mean?
GOVERNOR ANDREW, Boston:
The President directs that the militia be relieved, and the enlistments made for three years, or during the war. This, I think, will practically not be longer than for a year. The latest intelligence from General Banks states that he has saved nearly his whole command with small loss.
Concentrations of our force have been made, which it is hoped will capture the enemy.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Moorefield
The President directs you to halt at Moorefield and await orders, unless you hear of the enemy being in the general direction of Rodney, in which case you will move upon him. Acknowledge the receipt of this order, and the hour it is received.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
GENERAL McDOWELL, Manassas Junction:
General McClellan at 6.30 P.M. yesterday telegraphed that Fitz-John Porter's division had fought and driven 13,000 of the enemy, under General Branch, from Hanover Court-House, and was driving them from a stand they had made on the railroad at the time the messenger left. Two hours later he telegraphed that Stoneman had captured an engine and six cars on the Virginia Central, which he at once sent to communicate with Porter. Nothing further from McClellan.
If Porter effects a lodgment on both railroads near Hanover Court-House, consider whether your forces in front of Fredericksburg should not push through and join him.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
What of F.J. Porter's expedition? Please answer.
GENERAL McDOWELL, Manassas Junction:
You say General Geary's scouts report that they find no enemy this side of the Blue Ridge. Neither do I. Have they been to the Blue Ridge looking for them.
GENERAL McDOWELL, Manassas Junction:
I think the evidence now preponderates that Ewell and Jackson are still about Winchester. Assuming this, it is for you a question of legs. Put in all the speed you can. I have told Fremont as much, and directed him to drive at them as fast as possible. By the way, I suppose you know Fremont has got up to Moorefield, instead of going into Harrisonburg.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I am very glad of General F. J. Porter's victory. Still, if it was a total rout of the enemy, I am puzzled to know why the Richmond and Fredericksburg railroad was not seized again, as you say you have all the railroads but the Richmond and Fredericksburg. I am puzzled to see how, lacking that, you can have any, except the scrap from Richmond to West Point. The scrap of the Virginia Central from Richmond to Hanover Junction, without more, is simply nothing. That the whole of the enemy is concentrating on Richmond, I think cannot be certainly known to you or me. Saxton, at Harper's Ferry informs us that large forces, supposed to be Jackson's and Ewells, forced his advance from Charlestown today. General King telegraphs us from Fredericksburg that contrabands give certain information that 15,000 left Hanover Junction Monday morning to reinforce Jackson. I am painfully impressed with the importance of the struggle before you, and shall aid you all I can consistently with my view of due regard to all points.
MAJOR-GENERAL JOHN C. FREMONT, Moorefield:
The order to remain at Moorefield was based on the supposition that it would find you there.
Upon subsequent information that the enemy were still operating in the vicinity of Winchester and Martinsburg, you were directed to move against the enemy.
The President now again directs you to move against the enemy without delay. Please acknowledge the receipt of this, and the time received.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
GENERAL R. B. MARCY, McClellan's Headquarters:
Yours just received. I think it cannot be certainly known whether the force which fought General Porter is the same which recently confronted McDowell. Another item of evidence bearing on it is that General Branch commanded against Porter, while it was General Anderson who was in front of McDowell. He and McDowell were in correspondence about prisoners.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I think we shall be able within three days to tell you certainly whether any considerable force of the enemy—Jackson or any one else—is moving on to Harper's Ferry or vicinity. Take this expected development into your calculations.
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS, Williamsport, Maryland:
General McDowell's advance should, and probably will, be at or near Front Royal at twelve (noon) tomorrow. General Fremont will be at or near Strasburg as soon. Please watch the enemy closely, and follow and harass and detain him if he attempts to retire. I mean this for General Saxton's force as well as that immediately with you.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Moorefield, Virginia:
General McDowell's advance, if not checked by the enemy, should, and probably will, be at Front Royal by twelve (noon) to-morrow. His force, when up, will be about 20,000. Please have your force at Strasburg, or, if the route you are moving on does not lead to that point, as near Strasburg as the enemy may be by the same time. Your despatch No.30 received and satisfactory.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Manassas Junction:
General Fremont's force should, and probably will, be at or near Strasburg by twelve (noon) tomorrow. Try to have your force, or the advance of it, at Front Royal as soon.
GENERAL R. B. MARCY:
Your despatch as to the South Anna and Ashland being seized by our forces this morning is received. Understanding these points to be on the Richmond and Fredericksburg railroad, I heartily congratulate the country, and thank General McClellan and his army for their seizure.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Manassas Junction:
I somewhat apprehend that Fremont's force, in its present condition, may not be quite strong enough in case it comes in collision with the enemy. For this additional reason I wish you to push forward your column as rapidly as possible. Tell me what number your force reaching Front Royal will amount to.
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS,
Williamsport, Maryland, via Harper's Ferry:
If the enemy in force is in or about Martinsburg, Charlestown, and Winchester, Or any or all of them, he may come in collision with Fremont, in which case I am anxious that your force, with you and at Harper's Ferry, should so operate as to assist Fremont if possible; the same if the enemy should engage McDowell. This was the meaning of my despatch yesterday.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Rectortown:
Your despatch of to-day received and is satisfactory. Fremont has nominally 22,000, really about 17,000. Blenker's division is part of it. I have a despatch from Fremont this morning, not telling me where he is; but he says:
"Scouts and men from Winchester represent Jackson's force variously at 30,000 to 60,000. With him Generals Ewell and Longstreet."
The high figures erroneous, of course. Do you know where Longstreet is? Corinth is evacuated and occupied by us.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Moorefield, Virginia:
Yours, saying you will reach Strasburg or vicinity at 5 P.M. Saturday, has been received and sent to General McDowell, and he directed to act in view of it. You must be up to the time you promised, if possible.
Corinth was evacuated last night, and is occupied by our troops to-day; the enemy gone south to Okolotia, on the railroad to Mobile.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Rectortown, Va.:
I send you a despatch just received from Saxton at Harper's Ferry: "The rebels are in line of battle in front of our lines. They have nine pieces of artillery, and in position, and cavalry. I shelled the woods in which they were, and they in return threw a large number of shells into the lines and tents from which I moved last night to take up a stronger position. I expect a great deal from the battery on the mountain, having three 9 inch Dahlgren bearing directly on the enemy's approaches. The enemy appeared this morning and then retired, with the intention of drawing us on. I shall act on the defensive, as my position is a strong one. In a skirmish which took place this afternoon I lost one horse, The enemy lost two men killed and seven wounded.
"R. SAXTON, Brigadier General."
It seems the game is before you. Have sent a copy to General Fremont.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
A circle whose circumference shall pass through Harper's Ferry, Front Royal, and Strasburg, and whose center shall be a little northeast of Winchester, almost certainly has within it this morning the forces of Jackson, Ewell, and Edward Johnson. Quite certainly they were within it two days ago. Some part of their forces attacked Harper's Ferry at dark last evening, and are still in sight this morning. Shields, with McDowell's advance, retook Front Royal at 11 A.M. yesterday, with a dozen of our own prisoners taken there a week ago, 150 of the enemy, two locomotives, and eleven cars, some other property and stores, and saved the bridge.
General Fremont, from the direction of Moorefield, promises to be at or near Strasburg at 5 P.M. to-day. General Banks at Williamsport, with his old force and his new force at Harper's Ferry, is directed to co-operate. Shields at Front Royal reports a rumor of still an additional force of the enemy, supposed to be Anderson's, having entered the valley of Virginia. This last may or may not be true. Corinth is certainly in the hands of General Halleck.
GENERAL McCALL:
The President directs me to say to you that there can be nothing to justify a panic at Fredericksburg. He expects you to maintain your position there as becomes a soldier and a general.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
You are probably engaged with the enemy. I suppose he made the attack. Stand well on your guard, hold all your ground, or yield any only inch by inch and in good order. This morning we merge General Wool's department into yours, giving you command of the whole, and sending General Dix to Port Monroe and General Wool to Fort McHenry. We also send General Sigel to report to you for duty.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
With these continuous rains I am very anxious about the Chickahominy so close in your rear and crossing your line of communication. Please look to it.
A. LINCOLN, President.
MAJOR-GENERAL McDOWELL, Front Royal, Virginia:
Anxious to know whether Shields can head or flank Jackson. Please tell about where Shields and Jackson, respectively, are at the time this reaches you.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth:
Your despatch of to-day to Secretary of War received. Thanks for the good news it brings.
Have you anything from Memphis or other parts of the Mississippi River? Please answer.
WASHINGTON, June 4, 1862.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tennessee:
Do you really wish to have control of the question of releasing rebel prisoners so far as they may be Tennesseeans? If you do, please tell us so. Your answer not to be made public.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D.C., June 7, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch about Chattanooga and Dalton was duly received and sent to General Halleck. I have just received the following answer from him:
We have Fort Pillow, Randolph, and Memphis.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
We are changing one of the departmental lines, so as to give you all of Kentucky and Tennessee. In your movement upon Chattanooga I think it probable that you include some combination of the force near Cumberland Gap under General Morgan.
Do you?
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS, Winchester:
We are arranging a general plan for the valley of the Shenandoah, and in accordance with this you will move your main force to the Shenandoah at or opposite Front Royal as soon as possible.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
Halt at Harrisonburg, pursuing Jackson no farther. Get your force well in hand and stand on the defensive, guarding against a movement of the enemy either back toward Strasburg or toward Franklin, and await further orders, which will soon be sent you.
WASHINGTON, June 9, 1862.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, 'Tennessee:
Your despatch about seizing seventy rebels to exchange for a like number of Union men was duly received. I certainly do not disapprove the proposition.
Accounts, which we do not credit, represent that Jackson is largely reinforced and turning upon you. Get your forces well in hand and keep us well and frequently advised; and if you find yourself really pressed by a superior force of the enemy, fall back cautiously toward or to Winchester, and we will have in due time Banks in position to sustain you. Do not fall back upon Harrisonburg unless upon tolerably clear necessity. We understand Jackson is on the other side of the Shenandoah from you, and hence cannot in any event press you into any necessity of a precipitate withdrawal.
A. LINCOLN.
P.S.—Yours, preferring Mount Jackson to Harrisonburg, is just received. On this point use your discretion, remembering that our object is to give such protection as you can to western Virginia. Many thanks to yourself, officers, and men for the gallant battle of last Sunday. A. L.
June 13, 1862.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES: I herewith transmit a memorial addressed and presented to me in behalf of the State of New York in favor of enlarging the locks of the Erie and Oswego Canal. While I have not given nor have leisure to give the subject a careful examination, its great importance is obvious and unquestionable. The large amount of valuable statistical information which is collated and presented in the memorial will greatly facilitate the mature consideration of the subject, which I respectfully ask for it at your hands.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
We cannot afford to keep your force and Banks's and McDowell's engaged in keeping Jackson south of Strasburg and Front Royal. You fought Jackson alone and worsted him. He can have no substantial reinforcements so long as a battle is pending at Richmond. Surely you and Banks in supporting distance are capable of keeping him from returning to Winchester. But if Sigel be sent forward to you, and McDowell (as he must) be put to other work, Jackson will break through at Front Royal again. He is already on the right side of the Shenandoah to do it, and on the wrong side of it to attack you. The orders already sent you and Banks place you and him in the proper positions for the work assigned you. Jackson cannot move his whole force on either of you before the other can learn of it and go to his assistance. He cannot divide his force, sending part against each of you, because he will be too weak for either. Please do as I directed in the order of the 8th and my despatch of yesterday, the 12th, and neither you nor Banks will be overwhelmed by Jackson. By proper scout lookouts, and beacons of smoke by day and fires by night you can always have timely notice of the enemy's approach. I know not as to you, but by some this has been too much neglected.
A. LINCOLN. TO GENERAL J. C. FREMONT
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, D. C., June 15, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT:
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter of the 12th by Colonel Zagonyi is just received. In answer to the principal part of it, I repeat the substance of an order of the 8th and one or two telegraphic despatches sent you since.
We have no definite power of sending reinforcements; so that we are compelled rather to consider the proper disposal of the forces we have than of those we could wish to have. We may be able to send you some dribs by degrees, but I do not believe we can do more. As you alone beat Jackson last Sunday, I argue that you are stronger than he is to-day, unless he has been reinforced; and that he cannot have been materially reinforced, because such reinforcement could only have come from Richmond, and he is much more likely to go to Richmond than Richmond is to come to him. Neither is very likely. I think Jackson's game—his assigned work—now is to magnify the accounts of his numbers and reports of his movements, and thus by constant alarms keep three or four times as many of our troops away from Richmond as his own force amounts to. Thus he helps his friends at Richmond three or four times as much as if he were there. Our game is not to allow this. Accordingly, by the order of the 8th, I directed you to halt at Harrisonburg, rest your force, and get it well in hand, the objects being to guard against Jackson's returning by the same route to the upper Potomac over which you have just driven him out, and at the same time give some protection against a raid into West Virginia.
Already I have given you discretion to occupy Mount Jackson instead, if, on full consideration, you think best. I do not believe Jackson will attack you, but certainly he cannot attack you by surprise; and if he comes upon you in superior force, you have but to notify us, fall back cautiously, and Banks will join you in due time. But while we know not whether Jackson will move at all, or by what route, we cannot safely put you and Banks both on the Strasburg line, and leave no force on the Front Royal line—the very line upon which he prosecuted his late raid. The true policy is to place one of you on one line and the other on the other in such positions that you can unite once you actually find Jackson moving upon it. And this is precisely what we are doing. This protects that part of our frontier, so to speak, and liberates McDowell to go to the assistance of McClellan. I have arranged this, and am very unwilling to have it deranged. While you have only asked for Sigel, I have spoken only of Banks, and this because Sigel's force is now the principal part of Bank's force.
About transferring General Schenck's commands, the purchase of supplies, and the promotion and appointment of officers, mentioned in your letter, I will consult with the Secretary of War to-morrow.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL FREMONT, Mount Jackson, Virginia:
Your despatch of yesterday, reminding me of a supposed understanding that I would furnish you a corps of 35,000 men, and asking of me the "fulfilment of this understanding," is received. I am ready to come to a fair settlement of accounts with you on the fulfilment of understandings.
Early in March last, when I assigned you to the command of the Mountain Department, I did tell you I would give you all the force I could, and that I hoped to make it reach 35,000. You at the same time told me that within a reasonable time you would seize the railroad at or east of Knoxville, Tenn., if you could. There was then in the department a force supposed to be 25,000, the exact number as well known to you as to me. After looking about two or three days, you called and distinctly told me that if I would add the Blenker division to the force already in the department, you would undertake the job. The Blenker division contained 10,000, and at the expense of great dissatisfaction to General McClellan I took it from his army and gave it to you. My promise was literally fulfilled. I have given you all I could, and I have given you very nearly, if not quite, 35,000.
Now for yours. On the 23d of May, largely over two months afterward, you were at Franklin, Va., not within 300 miles of Knoxville, nor within 80 miles of any part of the railroad east of it, and not moving forward, but telegraphing here that you could not move for lack of everything. Now, do not misunderstand me. I do not say you have not done all you could. I presume you met unexpected difficulties; and I beg you to believe that as surely as you have done your best, so have I. I have not the power now to fill up your Corps to 35,000. I am not demanding of you to do the work of 35,000. I am only asking of you to stand cautiously on the defensive, get your force in order, and give such protection as you can to the valley of the Shenandoah and to western Virginia.
Have you received the orders, and will you act upon them?
BRIGADIER-GENERAL SCHURZ, Mount Jackson, Virginia:
Your long letter is received. The information you give is valuable. You say it is fortunate that Fremont did not intercept Jackson; that Jackson had the superior force, and would have overwhelmed him. If this is so, how happened it that Fremont fairly fought and routed him on the 8th? Or is the account that he did fight and rout him false and fabricated? Both General Fremont and you speak of Jackson having beaten Shields. By our accounts he did not beat Shields. He had no engagement with Shields. He did meet and drive back with disaster about 2000 of Shields's advance till they were met by an additional brigade of Shields's, when Jackson himself turned and retreated. Shields himself and more than half his force were not nearer than twenty miles to any of it.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
It would be of both interest and value to us here to know how the expedition toward East Tennessee is progressing, if in your judgment you can give us the information with safety.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Yours of to-day, making it probable that Jackson has been reinforced by about 10,000 from Richmond, is corroborated by a despatch from General King at Fredericksburg, saying a Frenchman, just arrived from Richmond by way of Gordonsville, met 10,000 to 15,000 passing through the latter place to join Jackson.
If this is true, it is as good as a reinforcement to you of an equal force. I could better dispose of things if I could know about what day you can attack Richmond, and would be glad to be informed, if you think you can inform me with safety.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Yours of last night just received, and for which I thank you.
If large reinforcements are going from Richmond to Jackson, it proves one of two things: either they are very strong at Richmond, or do not mean to defend the place desperately.
On reflection, I do not see how reinforcements from Richmond to Jackson could be in Gordonsville, as reported by the Frenchman and your deserters. Have not all been sent to deceive?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
In regard to the contemplated execution of Captains Spriggs and Triplett the government has no information whatever, but will inquire and advise you.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
We have this morning sent you a despatch of General Sigel corroborative of the proposition that Jackson is being reinforced from Richmond. This may be reality, and yet may only be contrivance for deception, and to determine which is perplexing. If we knew it was not true, we could send you some more force; but as the case stands we do not think we safely can. Still, we will watch the signs and do so if possible.
In regard to a contemplated execution of Captains Spriggs and Triplett the government has no information whatever, but will inquire and advise you.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
Your despatch of yesterday (2 P. M.) was received this morning. If it would not divert too much of your time and attention from the army under your immediate command, I would be glad to have your views as to the present state of military affairs throughout the whole country, as you say you would be glad to give them. I would rather it should be by letter than by telegraph, because of the better chance of secrecy. As to the numbers and positions of the troops not under your command in Virginia and elsewhere, even if I could do it with accuracy, which I cannot, I would rather not transmit either by telegraph or by letter, because of the chances of its reaching the enemy. I would be very glad to talk with you, but you cannot leave your camp, and I cannot well leave here.
A. LINCOLN, President
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS, Middletown:
I am very glad you are looking well to the west for a movement of the enemy in that direction. You know my anxiety on that point.
All was quiet at General McClellan's headquarters at two o'clock to-day.
WASHINGTON, June 23, 1862.
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
On the 7th day of December, 1861, I submitted to the Senate the project of a treaty between the United States and Mexico which had been proposed to me by Mr. Corwin, our minister to Mexico, and respectfully requested the advice of the Senate thereupon.
On the 25th day of February last a resolution was adopted by the Senate to the effect:
"That it is not advisable to negotiate a treaty that will require the United States to assume any portion of the principal or interest of the debt of Mexico, or that will require the concurrence of European powers."
This resolution having been duly communicated to me, notice thereof was immediately given by the Secretary of State to Mr. Corwin, and he was informed that he was to consider his instructions upon the subject referred to modified by this resolution and would govern his course accordingly. That despatch failed to reach Mr. Corwin, by reason of the disturbed condition of Mexico, until a very recent date, Mr. Corwin being without instructions, or thus practically left without instructions, to negotiate further with Mexico.
In view of the very important events Occurring there, he has thought that the interests of the United States would be promoted by the conclusion of two treaties which should provide for a loan to that republic. He has therefore signed such treaties, and they having been duly ratified by the Government of Mexico, he has transmitted them to me for my consideration. The action of the Senate is of course conclusive against an acceptance of the treaties On my part. I have, nevertheless, thought it just to our excellent minister in Mexico and respectful to the Government of that republic to lay the treaties before the Senate, together with the correspondence which has occurred in relation to them. In performing this duty I have only to add that the importance of the subject thus submitted to the Senate, can not be over estimated, and I shall cheerfully receive and consider with the highest respect any further advice the Senate may think proper to give upon the subject.
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
The bill which has passed the House of Representatives and the Senate, entitled "An act to repeal that part of an act of Congress which prohibits the circulation of bank-notes of a less denomination than five dollars in the District of Columbia," has received my attentive consideration, and I now return it to the Senate, in which it originated, with the following objections:
1. The bill proposes to repeal the existing legislation prohibiting the circulation of bank-notes of a less denomination than five dollars within the District of Columbia, without permitting the issuing of such bills by banks not now legally authorized to issue them. In my judgment, it will be found impracticable, in the present condition of the currency, to make such a discrimination. The banks have generally suspended specie payments, and a legal sanction given to the circulation of the irredeemable notes of one class of them will almost certainly be so extended, in practical operation, as to include those of all classes, whether authorized or unauthorized. If this view be correct, the currency of the District, should this act become a law, will certainly and greatly deteriorate, to the serious injury of honest trade and honest labor.
2. This bill seems to contemplate no end which cannot be otherwise more certainly and beneficially attained. During the existing war it is peculiarly the duty of the National Government to secure to the people a sound circulating medium. This duty has been, under existing circumstances, satisfactorily performed, in part at least, by authorizing the issue of United States notes, receivable for all government dues except customs, and made a legal tender for all debts, public and private, except interest on public debt. The object of the bill submitted to me—namely, that of providing a small note currency during the present suspension—can be fully accomplished by authorizing the issue, as part of any new emission of United States notes made necessary by the circumstances of the country, of notes of a similar character, but of less denomination than five dollars. Such an issue would answer all the beneficial purposes of the bill, would save a considerable amount to the treasury in interest, would greatly facilitate payments to soldiers and other creditors of small sums, and would furnish; to the people a currency as safe as their own government.
Entertaining these objections to the bill, I feel myself constrained to withhold from it my approval and return it for the further consideration and action of Congress.
When birds and animals are looked at through a fog, they are seen to disadvantage, and so it might be with you if I were to attempt to tell you why I went to see General Scott. I can only say that my visit to West Point did not have the importance which has been attached to it; but it concerned matters that you understand quite as well as if I were to tell you all about them. Now, I can only remark that it had nothing whatever to do with making or unmaking any general in the country. The Secretary of War, you know, holds a pretty tight rein on the press, so that they shall not tell more than they ought to; and I 'm afraid that if I blab too much, he might draw a tight rein on me.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your three despatches of yesterday in relation to the affair, ending with the statement that you completely succeeded in making your point, are very gratifying.
The later one of 6.15 P.M., suggesting the probability of your being overwhelmed by two hundred thousand, and talking of where the responsibility will belong, pains me very much. I give you all I can, and act on the presumption that you will do the best you can with what you have, while you continue, ungenerously I think, to assume that I could give you more if I would. I have omitted, and shall omit, no opportunity to send you reinforcements whenever I possibly can.
A. LINCOLN.
P. S. General Pope thinks if you fall back it would be much better towards York River than towards the James. As Pope now has charge of the capital, please confer with him through the telegraph.
Ordered: 1st. The forces under Major-Generals Fremont, Banks, and McDowell, including the troops now under Brigadier-General Sturgis at Washington, shall be consolidated and form one army, to be called the Army of Virginia.
2d. The command of the Army of Virginia is specially assigned to Major-General John Pope, as commanding general. The troops of the Mountain Department, heretofore under command of General Fremont, shall constitute the First Army Corps, under the command of General Fremont; the troops of the Shenandoah Department, now under General Banks, shall constitute the Second Army Corps, and be commanded by him; the troops under the command of General McDowell, except those within the fortifications and city of Washington, shall form the Third Army Corps, and be under his command.
3d. The Army of Virginia shall operate in such manner as, while protecting western Virginia and the national capital from danger or insult, it shall in the speediest manner attack and overcome the rebel forces under Jackson and Ewell, threaten the enemy in the direction of Charlottesville, and render the most effective aid to relieve General McClellan and capture Richmond.
4th. When the Army of the Potomac and the Army of Virginia shall be in position to communicate and directly co-operate at or before Richmond, the chief command, while so operating together, shall be governed, as in like cases, by the Rules and Articles of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
The enemy have concentrated in such force at Richmond as to render it absolutely necessary, in the opinion of the President, for you immediately to detach 25,000 of your force and forward it by the nearest and quickest route by way of Baltimore and Washington to Richmond. It is believed that the quickest route would be by way of Columbus, Ky., and up the Ohio River. But in detaching your force the President directs that it be done in such a way as to enable you to hold your ground and not interfere with the movement against Chattanooga and East Tennessee. This condition being observed, the forces to be detached and the routes they are to be sent are left to your own judgment.
The direction to send these forces immediately is rendered imperative by a serious reverse suffered by General McClellan before Richmond yesterday, the full extent of which is not yet known.
You will acknowledge the receipt of this despatch, stating the day and hour it is received, and inform me what your action will be, so that we may take measures to aid in river and railroad transportation.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
GENERAL BURNSIDE:
I think you had better go, with any reinforcements you can spare, to General McClellan.
We have intelligence that General McClellan has been attacked in large force and compelled to fall back toward the James River. We are not advised of his exact condition, but the President directs that you shall send him all the reinforcements from your command to the James River that you can safely do without abandoning your own position. Let it be infantry entirely, as he said yesterday that he had cavalry enough.
EDWIN M. STANTON,
Secretary of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Save your army, at all events. Will send reinforcements as fast as we can. Of course they cannot reach you to-day, to-morrow, or next day. I have not said you were ungenerous for saying you needed reinforcements. I thought you were ungenerous in assuming that I did not send them as fast as I could. I feel any misfortune to you and your army quite as keenly as you feel it yourself. If you have had a drawn battle, or a repulse, it is the price we pay for the enemy not being in Washington. We protected Washington, and the enemy concentrated on you. Had we stripped Washington, he would have been upon us before the troops could have gotten to you. Less than a week ago you notified us that reinforcements were leaving Richmond to come in front of us. It is the nature of the case, and neither you nor the government is to blame. Please tell at once the present condition and aspect of things.
HON. W. H. SEWARD.
MY DEAR SIR:—My view of the present condition of the war is about as follows:
The evacuation of Corinth and our delay by the flood in the Chickahominy have enabled the enemy to concentrate too much force in Richmond for McClellan to successfully attack. In fact there soon will be no substantial rebel force anywhere else. But if we send all the force from here to McClellan, the enemy will, before we can know of it, send a force from Richmond and take Washington. Or if a large part of the western army be brought here to McClellan, they will let us have Richmond, and retake Tennessee, Kentucky, Missouri, etc. What should be done is to hold what we have in the West, open the Mississippi, and take Chattanooga and East Tennessee without more. A reasonable force should in every event be kept about Washington for its protection. Then let the country give us a hundred thousand new troops in the shortest possible time, which, added to McClellan directly or indirectly, will take Richmond without endangering any other place which we now hold, and will substantially end the war. I expect to maintain this contest until successful, or till I die, or am conquered, or my term expires, or Congress or the country forsake me; and I would publicly appeal to the country for this new force were it not that I fear a general panic and stampede would follow, so hard it is to have a thing understood as it really is. I think the new force should be all, or nearly all, infantry, principally because such can be raised most cheaply and quickly.
Yours very truly,
GENERAL DIX:
Communication with McClellan by White House is cut off. Strain every nerve to open communication with him by James River, or any other way you can. Report to me.
FLAG-OFFICER GOLDS BOROUGH, Fort Monroe:
Enemy has cut McClellan's communication with White House, and is driving Stoneman back on that point. Do what you can for him with gunboats at or near that place. McClellan's main force is between the Chickahominy and the James. Also do what you can to communicate with him and support him there.
GOVERNOR O. P. MORTON, Indianapolis, Ind:
Your despatch of to-day is just received. I have no recollection of either John R. Cravens or Cyrus M. Allen having been named to me for appointment under the tax law. The latter particularly has been my friend, and I am sorry to learn that he is not yours. No appointment has been or will be made by me for the purpose of stabbing you.
HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Astor House, New York:
Not much more than when you left. Fulton of Baltimore American is now with us. He left White House at 11 A.M. yesterday. He conversed fully with a paymaster who was with Porter's force during the fight of Friday and fell back to nearer McClellan's quarters just a little sooner than Porter did, seeing the whole of it; stayed on the Richmond side of the Chickahominy over night, and left for White House at 5 A.M. Saturday. He says Porter retired in perfect order under protection of the guns arranged for the purpose, under orders and not from necessity; and with all other of our forces, except what was left on purpose to go to White House, was safely in pontoons over the Chickahominy before morning, and that there was heavy firing on the Richmond side, begun at 5 and ceased at 7 A.M. Saturday. On the whole, I think we have had the better of it up to that point of time. What has happened since we still know not, as we have no communication with General McClellan. A despatch from Colonel Ingalls shows that he thinks McClellan is fighting with the enemy at Richmond to-day, and will be to-morrow. We have no means of knowing upon what Colonel Ingalls founds his opinion. Confirmed about saving all property. Not a single unwounded straggler came back to White House from the field, and the number of wounded reaching there up to 11 A.M. Saturday was not large.
A. LINCOLN.
To what the President has above stated I will only add one or two points that may be satisfactory for you to know.
First. All the sick and wounded were safely removed
Second. A despatch from Burnside shows that he is from White House; not a man left behind in condition to afford efficient support, and is probably doing so.
Third. The despatch from Colonel Ingalls impresses me with the conviction that the movement was made by General McClellan to concentrate on Richmond, and was successful to the latest point of which we have any information.
Fourth. Mr. Fulton says that on Friday night, between twelve and one o'clock, General McClellan telegraphed Commodore Goldsborough that the result of the movement was satisfactory to him.
Fifth. From these and the facts stated by the President, my inference is that General McClellan will probably be in Richmond within two days.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
[Unfortunately McClellan did not do any of the things he was ordered, and that it was very likely possible to do. It is still some mystery what he was doing all these days other than hiding in the woods and staying out of communication so he would not receive any more uncomfortable orders. This was another place where the North was close to wining the war and did not. D.W.]
We are yet without communication with General McClellan, and this absence of news is our point of anxiety. Up to the latest point to which we are posted he effected everything in such exact accordance with his plan, contingently announced to us before the battle began, that we feel justified to hope that he has not failed since. He had a severe engagement in getting the part of his army on this side of the Chickahominy over to the other side, in which the enemy lost certainly as much as we did. We are not dissatisfied with this, only that the loss of enemies does not compensate for the loss of friends. The enemy cannot come below White House; certainly is not there now, and probably has abandoned the whole line. Dix's pickets are at New Kent Court-House.
The capture of New Orleans, Norfolk, and Corinth by the national forces has enabled the insurgents to concentrate a large force at and about Richmond, which place we must take with the least possible delay; in fact, there will soon be no formidable insurgent force except at Richmond. With so large an army there, the enemy can threaten us on the Potomac and elsewhere. Until we have re-established the national authority, all these places must be held, and we must keep a respectable force in front of WASHINGTON. But this, from the diminished strength of our army by sickness and casualties, renders an addition to it necessary in order to close the struggle which has been prosecuted for the last three months with energy and success. Rather than hazard the misapprehension of our military condition and of groundless alarm by a call for troops by proclamation, I have deemed it best to address you in this form. To accomplish the object stated we require without delay 150,000 men, including those recently called for by the Secretary of War. Thus reinforced our gallant army will be enabled to realize the hopes and expectations of the government and the people.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe:
Is it not probable that the enemy has abandoned the line between White House and McClellan's rear? He could have but little object to maintain it, and nothing to subsist upon. Would not Stoneman better move up and see about it? I think a telegraphic communication can at once be opened to White House from Williamsburg. The wires must be up still.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth:
Your telegram of this date just received. The Chattanooga expedition must not on any account be given up. The President regards that and the movement against East Tennessee as one of the most important movements of the war, and its occupation nearly as important as the capture of Richmond. He is not pleased with the tardiness of the movement toward Chattanooga, and directs that no force be sent here if you cannot do it without breaking up the operations against that point and East Tennessee. Infantry only are needed; our cavalry and artillery are strong enough. The first reports from Richmond were more discouraging than the truth warranted. If the advantage is not on our side, it is balanced. General McClellan has moved his whole force on the line of the James River, and is supported there by our gunboats; but he must be largely strengthened before advancing, and hence the call on you, which I am glad you answered so promptly. Let me know to what point on the river you will send your forces, so as to provide immediately for transportation.
EDWIN M. STANTON,
Secretary of War.
Would be very glad of 25,000 infantry; no artillery or cavalry; but please do not send a man if it endangers any place you deem important to hold, or if it forces you to give up or weaken or delay the expedition against Chattanooga. To take and hold the railroad at or east of Cleveland, in East Tennessee, I think fully as important as the taking and holding of Richmond.
The undersigned, governors of States of the Union, impressed with the belief that the citizens of the States which they respectively represent are of one accord in the hearty desire that the recent successes of the Federal arms may be followed up by measures which must insure the speedy restoration of the Union, and believing that, in view of the present state of the important military movements now in progress, and the reduced condition of our effective forces in the field, resulting from the usual and unavoidable casualties in the service, the time has arrived for prompt and vigorous measures to be adopted by the people in support of the great interests committed to your charge, respectfully request, if it meets with your entire approval, that you at once call upon the several States for such number of men as may be required to fill up all military organizations now in the field, and add to the armies heretofore organized such additional number of men as may, in your judgment, be necessary to garrison and hold all the numerous cities and military positions that have been captured by our armies, and to speedily crush the rebellion that still exists in several of the Southern States, thus practically restoring to the civilized world our great and good government. All believe that the decisive moment is near at hand, and to that end the people of the United States are desirous to aid promptly in furnishing all reinforcements that you may deem needful to sustain our government.
ISRAEL WASHBURN, JR., Governor of Maine.
H. S. BERRY, Governor of New Hampshire.
FREDERICK HOLBROOK, Governor of Vermont.
WILLIAM A. BUCKINGHAM, Governor of Connecticut.
E. D. MORGAN, Governor of New York.
CHARLES S. OLDEN, Governor of New Jersey.
A. G. CURTIN, Governor of Pennsylvania.
A. W. BRADFORD, Governor of Maryland.
F. H. PIERPOINT, Governor of Virginia.
AUSTIN BLAIR, Governor of Michigan.
J. B. TEMPLE, President Military Board of Kentucky.
ANDREW JOHNSON, Governor of Tennessee.
H. R. GAMBLE, Governor of Missouri.
O. P. MORTON, Governor of Indiana.
DAVID TODD, Governor of Ohio.
ALEXANDER RAMSEY, Governor of Minnesota.
RICHARD YATES, Governor of Illinois.
EDWARD SALOMON, Governor of Wisconsin.
GENTLEMEN:—Fully concurring in the wisdom of the views expressed to me in so patriotic a manner by you, in the communication of the twenty-eighth day of June, I have decided to call into the service an additional force of 300,000 men. I suggest and recommend that the troops should be chiefly of infantry. The quota of your State would be ———. I trust that they may be enrolled without delay, so as to bring this unnecessary and injurious civil war to a speedy and satisfactory conclusion. An order fixing the quotas of the respective States will be issued by the War Department to-morrow.
A Proclamation.
Whereas in and by the second section of an act of Congress passed on the 7th day of June, A. D. 1862, entitled "An act for the collection of direct taxes in insurrectionary districts within the United States, and for other purposes," it is made the duty of the President to declare, on or before the first day of July then next following, by his proclamation, in what States and parts of States insurrection exists:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, do hereby declare and proclaim that the States of South Carolina, Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Louisiana, Texas, Mississippi, Arkansas, Tennessee, North Carolina, and the State of Virginia except the following counties-Hancock, Brooke, Ohio, Marshall, Wetzel, Marion, Monongalia, Preston, Taylor, Pleasants, Tyler, Ritchie, Doddridge, Harrison, Wood, Jackson, Wirt, Roane, Calhoun, Gilmer, Barbour, Tucker, Lewis, Braxton, Upsbur, Randolph, Mason, Putnam, Kanawha, Clay, Nicholas, Cabell, Wayne, Boone, Logan, Wyoming, Webster, Fayette, and Raleigh-are now in insurrection and rebellion, and by reason thereof the civil authority of the United States is obstructed so that the provisions of the "Act to provide increased revenue from imports, to pay the interest on the public debt, and for other purposes," approved August 5, 1861, can not be peaceably executed; and that the taxes legally chargeable upon real estate under the act last aforesaid lying within the States and parts of States as aforesaid, together with a penalty of 50 per centum of said taxes, shall be a lien upon the tracts or lots of the same, severally charged, till paid.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed..............
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: F. W. SEWARD, Acting Secretary of State.
I most cordially recommend that Captain Andrew H. Foote, of the United States Navy, receive a vote of thanks of Congress for his eminent services in Organizing the flotilla on the western Waters, and for his gallantry at Fort Henry, Fort Donelson, Island Number Ten, and at various other places, whilst in command of the naval forces, embracing a period of nearly ten months.
A. LINCOLN.
WASHINGTON, D. C. July 1, 1862
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
It is impossible to reinforce you for your present emergency. If we had a million of men, We could not get them to you in time. We have not the men to send. If you are not strong enough to face the enemy, you must find a place of security, and wait, rest, and repair. Maintain your ground if you can, but save the army at all events, even if you fall back to Fort Monroe. We still have strength enough in the country, and will bring it out.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch of Tuesday morning induces me to hope your army is having some rest. In this hope allow me to reason with you a moment. When you ask for 50,000 men to be promptly sent you, you surely labor under some gross mistake of fact. Recently you sent papers showing your disposal of forces made last spring for the defense of WASHINGTON, and advising a return to that plan. I find it included in and about WASHINGTON 75,000 men. Now, please be assured I have not men enough to fill that very plan by 15,000. All of Fremont's in the valley, all of Banks's, all of McDowell's not with you, and all in WASHINGTON, taken together, do not exceed, if they reach, 60,000. With Wool and Dix added to those mentioned, I have not, outside of your army, 75,000 men east of the mountains. Thus the idea of sending you 50,000, or any other considerable force, promptly, is simply absurd. If, in your frequent mention of responsibility, you have the impression that I blame you for not doing more than you can, please be relieved of such impression. I only beg that in like manner you will not ask impossibilities of me. If you think you are not strong enough to take Richmond just now, I do not ask you to try just now. Save the army, material and personal, and I will strengthen it for the offensive again as fast as I can. The governors of eighteen States offer me a new levy of 300,000, which I accept.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
Your several despatches of yesterday to Secretary of War and myself received. I did say, and now repeat, I would be exceedingly glad for some reinforcements from you. Still do not send a man if in your judgment it will endanger any point you deem important to hold, or will force you to give up or weaken or delay the Chattanooga expedition.
Please tell me could you not make me a flying visit for consultation without endangering the Service in your department.
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
I herewith return to your honorable body, in which it originated, an act entitled "An act to provide for additional medical officers of the volunteer service," without my approval.
My reason for so doing is that I have approved an act of the same title passed by Congress after the passage of the one first mentioned for the express purpose of correcting errors in and superseding the same, as I am informed.
WAR DEPARTMENT, July 3, 1862.10.30 A.M.
GOVERNOR WASHBURN, Maine [and other governors] I should not want the half of 300,000 new troops if I could have them now. If I had 50,000 additional troops here now, I believe I could substantially close the war in two weeks. But time is everything, and if I get 50,000 new men in a month, I shall have lost 20,000 old ones during the same month, having gained only 30,000, with the difference between old and new troops still against me. The quicker you send, the fewer you will have to send. Time is everything. Please act in view of this. The enemy having given up Corinth, it is not wonderful that he is thereby enabled to check us for a time at Richmond.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
Yours of 5.30 yesterday is just received. I am satisfied that yourself, officers, and men have done the best you could. All accounts say better fighting was never done. Ten thousand thanks for it.
On the 28th we sent General Burnside an order to send all the force he could spare to you. We then learned that you had requested him to go to Goldsborough; upon which we said to him our order was intended for your benefit, and we did not wish to be in conflict with your views.
We hope you will have help from him soon. Today we have ordered General Hunter to send you all he can spare. At last advices General Halleck thinks he cannot send reinforcements without endangering all he has gained.
A. LINCOLN, President
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I understand your position as stated in your letter and by General Marcy. To reinforce you so as to enable you to resume the offensive within a month, or even six weeks, is impossible. In addition to that arrived and now arriving from the Potomac (about 10,000 men, I suppose), and about 10,000 I hope you will have from Burnside very soon, and about 5000 from Hunter a little later, I do not see how I can send you another man within a month. Under these circumstances the defensive for the present must be your only care. Save the army first, where you are, if you can; secondly, by removal, if you must. You, on the ground, must be the judge as to which you will attempt, and of the means for effecting it. I but give it as my opinion that with the aid of the gunboats and the reinforcements mentioned above you can hold your present position—provided, and so long as, you can keep the James River open below you. If you are not tolerably confident you can keep the James River open, you had better remove as soon as possible. I do not remember that you have expressed any apprehension as to the danger of having your communication cut on the river below you, yet I do not suppose it can have escaped your attention.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
P.S.—If at any time you feel able to take the offensive, you are not restrained from doing so. A.L.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
You do not know how much you would oblige us if, without abandoning any of your positions or plans, you could promptly send us even 10,000 infantry. Can you not? Some part of the Corinth army is certainly fighting McClellan in front of Richmond. Prisoners are in our hands from the late Corinth army.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe:
Send forward the despatch to Colonel Hawkins and this also. Our order and General McClellan's to General Burnside being the same, of course we wish it executed as promptly as possible.
MAJOR-GENERAL GEORGE B. McCLELLAN:
A thousand thanks for the relief your two despatches of 12 and 1 P.M. yesterday gave me. Be assured the heroism and skill of yourself and officers and men is, and forever will be, appreciated.
If you can hold your present position, we shall have the enemy yet.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi.
MY DEAR SIR:—This introduces Governor William Sprague, of Rhode Island. He is now Governor for the third time, and senator-elect of the United States.
I know the object of his visit to you. He has my cheerful consent to go, but not my direction. He wishes to get you and part of your force, one or both, to come here. You already know I should be exceedingly glad of this if, in your judgment, it could be without endangering positions and operations in the southwest; and I now repeat what I have more than once said by telegraph: "Do not come or send a man if, in your judgment, it will endanger any point you deem important to hold, or endangers or delays the Chattanooga expedition."
Still, please give my friend, Governor Sprague, a full and fair hearing.
Yours very truly,
AND OTHER OFFICERS DURING A VISIT TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC AT HARRISON'S LANDING, VIRGINIA.
July 9, 1862.
THE PRESIDENT: What amount of force have you now?
GENERAL McCLELLAN: About 80,000, can't vary much, certainly 75,000.
THE PRESIDENT:[to the corps commanders] What is the whole amount of your corps with you now.
GENERAL SUMNER: About 15,000.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: 15,000 for duty.
GENERAL KEYES: About 12,500.
GENERAL PORTER: About 23,000—fully 20,000 fit for duty.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: About 15,000.
THE PRESIDENT: What is likely to be your condition as to health in this camp?
GENERAL McCLELLAN: Better than in any encampment since landing at Fortress Monroe.
PRESIDENT LINCOLN:[to the corps commanders] In your present encampment what is the present and prospective condition as to health?
GENERAL SUMNER: As good as any part of Western Virginia.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: Excellent for health, and present health improving.
GENERAL KEYES: A little improved, but think camp is getting worse.
GENERAL PORTER: Very good.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: Not good.
THE PRESIDENT: Where is the enemy now?
GENERAL McCLELLAN: From four to five miles from us on all the roads—I think nearly the whole army—both Hills, Longstreet, Jackson, Magruder, Huger.
THE PRESIDENT: [to the corps commanders] Where and in what condition do you believe the enemy to be now?
GENERAL SUMNER: I think they have retired from our front; were very much damaged, especially in their best troops, in the late actions, from superiority of arms.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: Don't think they are in force in our vicinity.
GENERAL KEYES: Think he has withdrawn, and think preparing to go to WASHINGTON.
GENERAL PORTER: Believe he is mainly near Richmond. He feels he dare not attack us here.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: I learn he has withdrawn from our front and think that is probable.
THE PRESIDENT: [to the corps commanders] What is the aggregate of your killed, wounded, and missing from the attack on the 26th ultimo till now?
GENERAL SUMNER: 1175.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: Not large 745.
GENERAL KEYES: Less than 500.
GENERAL PORTER: Over 5000.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: Not over 3000.
THE PRESIDENT: If you desired could you remove the army safely?
GENERAL McCLELLAN: It would be a delicate and very difficult matter.
THE PRESIDENT: [to the corps commanders] If it were desired to get the army away, could it be safely effected?
GENERAL SUMNER: I think we could, but I think we give up the cause if we do.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: Perhaps we could, but I think it would be ruinous to the country.
GENERAL KEYES: I think it could if done quickly.
GENERAL PORTER: Impossible—move the army and ruin the country.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: I think we could, and that we had better—think Rappahannock the true line.
THE PRESIDENT: [to the corps commanders] Is the army secure in its present position?
GENERAL SUMNER: Perfectly so, in my judgment.
GENERAL HEINTZELMAN: I think it is safe.
GENERAL KEYES: With help of General B. [Burnside] can hold position.
GENERAL PORTER: Perfectly so. Not only, but we are ready to begin
moving forward.
GENERAL FRANKLIN: Unless river can be closed it is.
Ordered, That Major-General Henry W. Halleck be assigned to command the whole land forces of the United States, as general-in-chief, and that he repair to this capital so soon as he can with safety to the positions and operations within the department now under his charge.
Whereas, in the judgment of the President, the public safety does require that the railroad line called and known as the Southwest Branch of the Pacific Railroad in the State of Missouri be repaired, extended, and completed from Rolla to Lebanon, in the direction to Springfield, in the said State, the same being necessary to the successful and economical conduct of the war and to the maintenance of the authority of the government in the Southwest:
Therefore, under and in virtue of the act of Congress entitled "An act to authorize the President of the United States in certain cases to take possession of railroad and telegraph lines, and for other purposes," approved January 31, 1862, it is ordered, That the portion of the said railroad line which reaches from Rolla to Lebanon be repaired, extended, and completed, so as to be made available for the military uses of the government, as speedily as may be. And, inasmuch as upon the part of the said line from Rolla to the stream called Little Piney a considerable portion of the necessary work has already been done by the railroad company, and the road to this extent may be completed at comparatively small cost, it is ordered that the said line from Rolla to and across Little Piney be first completed, and as soon as possible.
The Secretary of War is charged with the execution of this order. And to facilitate the speedy execution of the work, he is directed, at his discretion, to take possession and control of the whole or such part of the said railroad line, and the whole or such part of the rolling stock, offices, shops, buildings, and all their appendages and appurtenances, as he may judge necessary or convenient for the early completion of the road from Rolla to Lebanon.
Done at the city of WASHINGTON, July 11, 1862.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I recommend that the thanks of Congress be given to the following officers of the United States Navy:
Captain James L. Lardner, for meritorious conduct at the battle of Port Royal and distinguished services on the coast of the United States against the enemy.
Captain Charles Henry Davis, for distinguished services in conflict with the enemy at Fort Pillow, at Memphis, and for successful operations at other points in the waters of the Mississippi River.
Commander John A. Dahlgren, for distinguished services in the line of his profession, improvements in ordnance, and zealous and efficient labors in the ordnance branch of the service.
Commander Stephen C. Rowan, for distinguished services in the waters of North Carolina, and particularly in the capture of Newbern, being in chief command of the naval forces.
Commander David D. Porter, for distinguished services in the conception and preparation of the means used for the capture of the forts below New Orleans, and for highly meritorious conduct in the management of the mortar flotilla during the bombardment of Forts Jackson and St. Philip.
Captain Silas H. Stringharn, now on the retired list, for distinguished services in the capture of Forts Hatteras and Clark.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of yesterday is received. Do you not, my good friend, perceive that what you ask is simply to put you in command in the West? I do not suppose you desire this. You only wish to control in your own localities; but this you must know may derange all other posts. Can you not, and will you not, have a full conference with General Halleck? Telegraph him, and meet him at such place as he and you can agree upon. I telegraph him to meet you and confer fully with you.
Governor Johnson, at Nashville, is in great trouble and anxiety about a raid into Kentucky. The governor is a true and valuable man—indispensable to us in Tennessee. Will you please get in communication with him, and have a full conference with him before you leave for here? I have telegraphed him on the subject.
GENTLEMEN:—After the adjournment of Congress now very near, I shall have no opportunity of seeing you for several months. Believing that you of the border States hold more power for good than any other equal number of members, I feel it a duty which I cannot justifiably waive to make this appeal to you. I intend no reproach or complaint when I assure you that, in my opinion, if you all had voted for the resolution in the gradual-emancipation message of last March, the war would now be substantially ended. And the plan therein proposed is yet one of the most potent and swift means of ending it. Let the States which are in rebellion see definitely and certainly that in no event will the States you represent ever join their proposed confederacy, and they cannot much longer maintain the contest. But you cannot divest them of their hope to ultimately have you with them so long as you show a determination to perpetuate the institution within your own States. Beat them at elections, as you have overwhelmingly done, and, nothing daunted, they still claim you as their own. You and I know what the lever of their power is. Break that lever before their faces, and they can shake you no more forever. Most of you have treated me with kindness and consideration and I trust you will not now think I improperly touch what is exclusively your own, when, for the sake of the whole country, I ask, Can you, for your States, do better than to take the course I urge? Discarding punctilio and maxims adapted to more manageable times, and looking only to the unprecedentedly stern facts of our case, can you do better in any possible event? You prefer that the constitutional relation of the States to the nation shall be practically restored without disturbance of the institution; and if this were done, my whole duty in this respect, under the Constitution and my oath of office, would be performed. But it is not done, and we are trying to accomplish it by war. The incidents of the war cannot be avoided. If the war continues long, as it must if the object be not sooner attained, the institution in your States will be extinguished by mere friction and abrasion—by the mere incidents of the war. It will be gone, and you will have nothing valuable in lieu of it. Much of its value is gone already. How much better for you and for your people to take the step which at once shortens the war and secures substantial compensation for that which is sure to be wholly lost in any other event! How much better to thus save the money which else we sink forever in war! How much better to do it while we can, lest the war ere long render us pecuniarily unable to do it! How much better for you as seller, and the nation as buyer, to sell out and buy out that without which the war could never have been, than to sink both the thing to be sold and the price of it in cutting one another's throats! I do not speak of emancipation at once, but of a decision at once to emancipate gradually. Room in South America for colonization can be obtained cheaply and in abundance, and when numbers shall be large enough to be company and encouragement for one another, the freed people will not be so reluctant to go.
I am pressed with a difficulty not yet mentioned—one which threatens division among those who, united, are none too strong. An instance of it is known to you. General Hunter is an honest man. He was, and I hope still is, my friend. I valued him none the less for his agreeing with me in the general wish that all men everywhere could be free. He proclaimed all men free within certain States, and I repudiated the proclamation. He expected more good and less harm from the measure than I could believe would follow. Yet, in repudiating it, I gave dissatisfaction, if not offence, to many whose support the country cannot afford to lose. And this is not the end of it. The pressure in this direction is still upon me, and is increasing. By conceding what I now ask you can relieve me, and, much more, can relieve the country in this important point.
Upon these considerations, I have again begged your attention to the message of March last. Before leaving the Capital, consider and discuss it among yourselves. You are patriots and statesmen, and as such I pray you consider this proposition; and, at the least, commend it to the consideration of your States and people. As you would perpetuate popular government for the best people in the world, I beseech you that you do in nowise omit this. Our common country is in great peril, demanding the loftiest views and boldest action to bring a speedy relief. Once relieved, its form of government is saved to the world; its beloved history and cherished memories are vindicated, and its happy future fully assured and rendered inconceivably grand. To you, more than to any others, the privilege is given to assure that happiness and swell that grandeur, and to link your own names therewith forever.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
MY DEAR SIR:—I am told that over 160,000 men have gone into your army on the Peninsula. When I was with you the other day we made out 86,500 remaining, leaving 73,500 to be accounted for. I believe 23,500 will cover all the killed, wounded, and missing in all your battles and skirmishes, leaving 50,000 who have left otherwise. No more than 5000 of these have died, leaving 45,000 of your army still alive and not with it. I believe half or two-thirds of them are fit for duty to-day. Have you any more perfect knowledge of this than I have? If I am right, and you had these men with you, you could go into Richmond in the next three days. How can they be got to you, and how can they be prevented from getting away in such numbers for the future?
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
They are having a stampede in Kentucky. Please look to it.
GENERAL J. T. BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
Your several despatches received. You should call on General Halleck. Telegraph him at once. I have telegraphed him that you are in trouble.
GENERAL J. T. BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
We cannot venture to order troops from General Buell. We know not what condition he is in. He maybe attacked himself. You must call on General Halleck, who commands, and whose business it is to understand and care for the whole field If you cannot telegraph to him, send a messenger to him. A dispatch has this moment come from Halleck at Tuscombia, Alabama.
July 4, 1862.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
Herewith is the draft of the bill to compensate any State which may abolish slavery within its limits, the passage of which, substantially as presented, I respectfully and earnestly recommend.
A. LINCOLN.
Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled:—That whenever the President of the United States shall be satisfied that any State shall have lawfully abolished slavery within and through-out such State, either immediately or gradually, it shall be the duty of the President, assisted by the Secretary of the Treasury, to prepare and deliver to each State an amount of six per cent. interest-bearing bonds of the United States equal to the aggregate value at ——— dollars per head of all the slaves within such State, as reported by the census of 1860; the whole amount for any one State to be delivered at once if the abolishment be immediate, or in equal annual instalments if it be gradual, interest to begin running on each bond at the time of delivery, and not before.
And be it further enacted, That if any State, having so received any such bonds, shall at any time afterwards by law reintroduce or tolerate slavery within its limits, contrary to the act of abolishment upon which such bonds shall have been received, said bonds so received by said State shall at once be null and void, in whosesoever hands they may be, and such State shall refund to the United States all interest which may have been paid on such bonds.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Corinth, Mississippi:
I am very anxious—almost impatient—to have you here. Have due regard to what you leave behind. When can you reach here?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
General Burnside's force is at Newport News, ready to move, on short notice, one way or the other, when ordered.
HON. SOLOMON FOOT, President pro tempore of the Senate.
SIR:—Please inform the Senate that I shall be obliged if they will postpone the adjournment at least one day beyond the time which I understand to be now fixed for it.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
[The same message was addressed to Hon. Galusha A. Grow Speaker of the House of Representatives.]
I have inadvertently omitted so long to inform you that in March last Mr. Cornelius Vanderbilt, of New York, gratuitously presented to the United States the ocean steamer Vanderbilt, by many esteemed the finest merchant ship in the world. She has ever since been and still is doing valuable service to the government. For the patriotic act of making this magnificent and valuable present to the country I recommend that some suitable acknowledgment be made.
Considering the bill for "An act to suppress insurrection, to punish treason and rebellion, to seize and confiscate the property of rebels, and for other purposes," and the joint resolution explanatory of said act as being substantially one, I have approved and signed both.
Before I was informed of the passage of the resolution I had prepared the draft of a message stating objections to the bill becoming a law, a copy of which draft is herewith transmitted.
I herewith return to your honorable body, in which it originated, the bill for an act entitled "An act to suppress treason and rebellion, to seize and confiscate the property of rebels, and for other purposes," together with my objections to its becoming a law.
There is much in the bill to which I perceive no objection. It is wholly prospective, and touches neither person nor property of any loyal citizen, in which particulars it is just and proper. The first and second sections provide for the conviction and punishment of persons Who shall be guilty of treason and persons who shall "incite, set on foot, assist, or engage in any rebellion or insurrection against the authority of the United States or the laws thereof, or shall give aid and comfort thereto, or shall engage in or give aid and comfort to any such existing rebellion or insurrection." By fair construction persons within these sections are not to be punished without regular trials in duly constituted courts, under the forms and all the substantial provisions of law and of the Constitution applicable to their several cases. To this I perceive no objection, especially as such persons would be within the general pardoning power and also the special provision for pardon and amnesty contained in this act.
It is also provided that the slaves of persons convicted under these sections shall be free. I think there is an unfortunate form of expression rather than a substantial objection in this. It is startling to say that Congress can free a slave within a State, and yet if it were said the ownership of the slave had first been transferred to the nation and that Congress had then liberated him the difficulty would at once vanish. And this is the real case. The traitor against the General Government forfeits his slave at least as justly as he does any other property, and he forfeits both to the government against which be offends. The government, so far as there can be ownership, thus owns the forfeited slaves, and the question for Congress in regard to them is, "Shall they be made free or be sold to new masters?" I perceive no objection to Congress deciding in advance that they shall be free. To the high honor of Kentucky, as I am informed, she is the owner of some slaves by escheat, and has sold none, but liberated all. I hope the same is true of some other States. Indeed, I do not believe it will be physically possible for the General Government to return persons so circumstanced to actual slavery. I believe there would be physical resistance to it which could neither be turned aside by argument nor driven away by force. In this view I have no objection to this feature of the bill. Another matter involved in these two sections, and running through other parts of the act, will be noticed hereafter.
I perceive no objection to the third or fourth sections.
So far as I wish to notice the fifth and sixth sections, they may be considered together. That the enforcement of these sections would do no injustice to the persons embraced within them, is clear. That those who make a causeless war should be compelled to pay the cost of it, is too obviously just to be called in question. To give governmental protection to the property of persons who have abandoned it, and gone on a crusade to overthrow the same government, is absurd, if considered in the mere light of justice. The severest justice may not always be the best policy. The principle of seizing and appropriating the property of the persons embraced within these sections is certainly not very objectionable, but a justly discriminating application of it would be very difficult and, to a great extent, impossible. And would it not be wise to place a power of remission somewhere, so that these persons may know they have something to lose by persisting and something to gain by desisting?
[A man without hope is a most dangerous man—he has nothing to lose!]
I am not sure whether such power of remission is or is not in section thirteen. Without any special act of Congress, I think our military commanders, when—in military phrase, "they are within the enemy's country," should, in an orderly manner, seize and use whatever of real or personal property may be necessary or convenient for their commands; at the same time preserving, in some way, the evidence of what they do.
What I have said in regard to slaves, while commenting on the first and second sections, is applicable to the ninth, with the difference that no provision is made in the whole act for determining whether a particular individual slave does or does not fall within the classes defined in that section. He is to be free upon certain conditions but whether those conditions do or do not pertain to him no mode of ascertaining is provided. This could be easily supplied.
To the tenth section I make no objection. The oath therein required seems to be proper, and the remainder of the section is substantially identical with a law already existing.
The eleventh section simply assumes to confer discretionary power upon the executive. Without the law, I have no hesitation to go as far in the direction indicated as I may at any time deem expedient. And I am ready to say now—I think it is proper for our military commanders to employ, as laborers, as many persons of African descent as can be used to advantage.
The twelfth and thirteenth sections are something better than unobjectionable; and the fourteenth is entirely proper, if all other parts of the act shall stand.
That to which I chiefly object pervades most parts of the act, but more distinctly appears in the first, second, seventh, and eighth sections. It is the sum of those provisions which results in the divesting of title forever.
For the causes of treason and ingredients of treason, not amounting to the full crime, it declares forfeiture extending beyond the lives of the guilty parties; whereas the Constitution of the United States declares that "no attainder of treason shall work corruption of blood or forfeiture except during the life of the person attainted." True, there is to be no formal attainder in this case; still, I think the greater punishment cannot be constitutionally inflicted, in a different form, for the same offence.
With great respect I am constrained to say I think this feature of the act is unconstitutional. It would not be difficult to modify it.
I may remark that the provision of the Constitution, put in language borrowed from Great Britain, applies only in this country, as I understand, to real or landed estate.
Again, this act in rem forfeits property for the ingredients of treason without a conviction of the supposed criminal, or a personal hearing given him in any proceeding. That we may not touch property lying within our reach, because we cannot give personal notice to an owner who is absent endeavoring to destroy the government, is certainly not satisfactory. Still, the owner may not be thus engaged; and I think a reasonable time should be provided for such parties to appear and have personal hearings. Similar provisions are not uncommon in connection with proceedings in rem.
For the reasons stated, I return the bill to the House in which it originated.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
This is Monday. I hope to be able to tell you on Thursday what is to be done with Burnside.
WASHINGTON, July 21, 1862.
The following order has been received from the President of the United States:
Representations have been made to the President by the ministers of various foreign powers in amity with the United States that subjects of such powers have during the present insurrection been obliged or required by military authorities to take an oath of general or qualified allegiance to this government. It is the duty of all aliens residing in the United States to submit to and obey the laws and respect the authority of the government. For any proceeding or conduct inconsistent with this obligation and subversive of that authority they may rightfully be subjected to military restraints when this may be necessary. But they cannot be required to take an oath of allegiance to this government, because it conflicts with the duty they owe to their own sovereigns. All such obligations heretofore taken are therefore remitted and annulled. Military commanders will abstain from imposing similar obligations in future, and will in lieu thereof adopt such other restraints of the character indicated as they shall find necessary, convenient, and effectual for the public safety. It is further directed that whenever any order shall be made affecting the personal liberty of an alien reports of the same and of the causes thereof shall be made to the War Department for the consideration of the Department of State.
By order of the Secretary of War:
L. THOMAS, Adjutant-General.
Ordered:
1. That military commanders within the States of Virginia, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas in an orderly manner seize and use any property, real or personal, which may be necessary or convenient for their several commands as supplies or for other military purposes; and that while property may be destroyed for proper military objects, none shall be destroyed in wantonness or malice.
2. That military and naval commanders shall employ as laborers within and from said States so many persons of African descent as can be advantageously used for military or naval purposes, giving them reasonable wages for their labor.
3. That as to both property and persons of African descent accounts shall be kept sufficiently accurate and in detail to show quantities and amounts and from whom both property and such persons shall have come, as a basis upon which compensation can be made in proper cases; and the several departments of this government shall attend to and perform their appropriate parts toward the execution of these orders.
By order of the President: EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
In pursuance of the sixth section of the act of Congress entitled "An act to suppress insurrection and to punish treason and rebellion, to seize and confiscate property of rebels, and for other purposes," approved July 17, 1862, and which act and the joint resolution explanatory thereof are herewith published, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby proclaim to and warn all persons within the contemplation of said sixth section to cease participating in, aiding, countenancing, or abetting the existing rebellion or any rebellion against the Government of the United States and to return to their proper allegiance to the United States, on pain of the forfeitures and seizures as within and by said sixth section provided.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twenty-fifth day of July, A.D. 1862, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
(Private.)
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July 26, 1862.
HON. REVERDY JOHNSON.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 16th is received...........
You are ready to say I apply to friends what is due only to enemies. I distrust the wisdom if not the sincerity of friends who would hold my hands while my enemies stab me. This appeal of professed friends has paralyzed me more in this struggle than any other one thing. You remember telling me, the day after the Baltimore mob in April, 1861, that it would crush all Union feeling in Maryland for me to attempt bringing troops over Maryland soil to Washington. I brought the troops notwithstanding, and yet there was Union feeling enough left to elect a Legislature the next autumn, which in turn elected a very excellent Union United States senator! I am a patient man—always willing to forgive on the Christian terms of repentance, and also to give ample time for repentance. Still, I must save this government, if possible. What I cannot do, of course, I will not do; but it may as well be understood, once for all, that I shall not surrender this game leaving any available card unplayed.
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, D. C., July 28, 1862.
CUTHBERT BULLITT, Esq., New Orleans, Louisiana.
SIR:—The copy of a letter addressed to yourself by Mr. Thomas J. Durant has been shown to me. The writer appears to be an able, a dispassionate, and an entirely sincere man. The first part of the letter is devoted to an effort to show that the secession ordinance of Louisiana was adopted against the will of a majority of the people. This is probably true, and in that fact may be found some instruction. Why did they allow the ordinance to go into effect? Why did they not assert themselves? Why stand passive and allow themselves to be trodden down by minority? Why did they not hold popular meetings and have a convention of their own to express and enforce the true sentiment of the State? If preorganization was against them then, why not do this now that the United States army is present to protect them? The paralysis—the dead palsy—of the government in this whole struggle is that this class of men will do nothing for the government, nothing for themselves, except demanding that the government shall not strike its open enemies, lest they be struck by accident!
Mr. Durant complains that in various ways the relation of master and slave is disturbed by the presence of our army, and he considers it particularly vexatious that this, in part, is done under cover of an act of Congress, while constitutional guaranties are suspended on the plea of military necessity. The truth is, that what is done and omitted about slaves is done and omitted on the same military necessity. It is a military necessity to have men and money; and we can get neither in sufficient numbers or amounts if we keep from or drive from our lines slaves coming to them. Mr. Durant cannot be ignorant of the pressure in this direction, nor of my efforts to hold it within bounds till he and such as he shall have time to help themselves.
I am not posted to speak understandingly on all the police regulations of which Mr. Durant complains. If experience shows any one of them to be wrong, let them be set right. I think I can perceive in the freedom of trade which Mr. Durant urges that he would relieve both friends and enemies from the pressure of the blockade. By this he would serve the enemy more effectively than the enemy is able to serve himself. I do not say or believe that to serve the enemy is the purpose, of Mr. Durant, or that he is conscious of any purpose other than national and patriotic ones. Still, if there were a class of men who, having no choice of sides in the contest, were anxious only to have quiet and comfort for themselves while it rages, and to fall in with the victorious side at the end of it without loss to themselves, their advice as to the mode of conducting the contest would be precisely such as his is. He speaks of no duty—apparently thinks of none—resting upon Union men. He even thinks it injurious to the Union cause that they should be restrained in trade and passage without taking sides. They are to touch neither a sail nor a pump, but to be merely passengers—deadheads at that—to be carried snug and dry throughout the storm, and safely landed right side up. Nay, more: even a mutineer is to go untouched, lest these sacred passengers receive an accidental wound. Of course the rebellion will never be suppressed in Louisiana if the professed Union men there will neither help to do it nor permit the government to do it without their help. Now, I think the true remedy is very different from what is suggested by Mr. Durant. It does not lie in rounding the rough angles of the war, but in removing the necessity for the war. The people of Louisiana who wish protection to person and property have but to reach forth their hands and take it. Let them in good faith reinaugurate the national authority, and set up a State government conforming thereto under the Constitution. They know how to do it and can have the protection of the army while doing it. The army will be withdrawn so soon as such State government can dispense with its presence; and the people of the State can then, upon the old constitutional terms, govern themselves to their own liking. This is very simple and easy.
If they will not do this—if they prefer to hazard all for the sake of destroying the government—it is for them to consider whether it is probable I will surrender the government to save them from losing all. If they decline what I suggest, you scarcely need to ask what I will do. What would you do in my position? Would you drop the war where it is? Or would you prosecute it in future with elder-stalk squirts charged with rose water? Would you deal lighter blows rather than heavier ones? Would you give up the contest, leaving any available means unapplied? I am in no boastful mood. I shall not do more than I can, and I shall do all I can, to save the government, which is my sworn duty as well as my personal inclination. I shall do nothing in malice. What I deal with is too vast for malicious dealing.
Yours truly,
July 28, 1862.
GOVERNORS OF ALL LOYAL STATES:
It would be of great service here for us to know, as fully as you can tell, what progress is made and making in recruiting for old regiments in your State. Also about what day the first regiments can move with you, what the second, what the third, and so on. This information is important to us in making calculations. Please give it as promptly and accurately as you call.
July 31, 1862.
Broken eggs cannot be mended; but Louisiana has nothing to do now but to take her place in the Union as it was, barring the already broken eggs. The sooner she does so, the smaller will be the amount of that which will be past mending. This government cannot much longer play a game in which it stakes all, and its enemies stake nothing. Those enemies must understand that they cannot experiment for ten years trying to destroy the government, and if they fail, still come back into the Union unhurt. If they expect in any contingency to ever have the Union as it was, I join with the writer in saying, "Now is the time."
How much better it would have been for the writer to have gone at this, under the protection of the army at New Orleans, than to have sat down in a closet writing complaining letters northward!
Yours truly,
August 4, 1863.
TO COUNT A. DE GASPARIN.
DEAR SIR—Your very acceptable letter, dated Orbe, Canton de Vaud, Switzerland, 18th of July, 1862, is received. The moral effect was the worst of the affair before Richmond, and that has run its course downward. We are now at a stand, and shall soon be rising again, as we hope. I believe it is true that, in men and material, the enemy suffered more than we in that series of conflicts, while it is certain that he is less able to bear it.
With us every soldier is a man of character, and must be treated with more consideration than is customary in Europe. Hence our great army, for slighter causes than could have prevailed there, has dwindled rapidly, bringing the necessity for a new call earlier than was anticipated. We shall easily obtain the new levy, however. Be not alarmed if you shall learn that we shall have resorted to a draft for part of this. It seems strange even to me, but it is true, that the government is now pressed to this course by a popular demand. Thousands who wish not to personally enter the service are nevertheless anxious to pay and send substitutes, provided they can have assurance that unwilling persons, similarly situated, will be compelled to do likewise. Besides this, volunteers mostly choose to enter newly forming regiments, while drafted men can be sent to fill up the old ones, wherein man for man they are quite doubly as valuable.
You ask, "Why is it that the North with her great armies so often is found with inferiority of numbers face to face with the armies of the South?" While I painfully know the fact, a military man, which I am not, would better answer the question. The fact I know has not been overlooked, and I suppose the cause of its continuance lies mainly in the other facts that the enemy holds the interior and we the exterior lines, and that we operate where the people convey information to the enemy, while he operates where they convey none to us.
I have received the volume and letter which you did me the honor of addressing to me, and for which please accept my sincere thanks. You are much admired in America for the ability of your writings, and much loved for your generosity to us and your devotion to liberal principles generally.
You are quite right as to the importance to us, for its bearing upon Europe, that we should achieve military successes, and the same is true for us at home as well as abroad. Yet it seems unreasonable that a series of successes, extending through half a year, and clearing more than 100,000 square miles of country, should help us so little, while a single half-defeat should hurt us so much. But let us be patient.
I am very happy to know that my course has not conflicted with your judgment of propriety and policy I can only say that I have acted upon my best convictions, without selfishness or malice, and that by the help of God I shall continue to do so.
Please be assured of my highest respect and esteem.
FELLOW CITIZENS: I believe there is no precedent for my appearing before you on this occasion, but it is also true that there is no precedent for your being here yourselves, and I offer in justification of myself and of you that, upon examination, I have found nothing in the Constitution against it. I, however, have an impression that; there are younger gentlemen who will entertain you better and better address your understanding than I will or could, and therefore I propose but to detain you a moment longer. I am very little inclined on any occasion to say anything unless I hope to produce some good by it. The only thing I think of just now not likely to be better said by some one else is a matter in which we have heard some other persons blamed for what I did myself There has been a very widespread attempt to have a quarrel between General McClellan and the Secretary of War Now, I occupy a position that enables me to believe that these two gentlemen are not nearly so deep in the quarrel as some presuming to be their friends. General McClellan's attitude is such that in the very selfishness of his nature he cannot but wish to be successful—and I hope he will—and the Secretary of War is precisely in the same situation. If the military commanders in the field cannot be successful, not only the Secretary of War, but myself, for the time being the master of both, cannot but be failures. I know General McClellan wishes to be successful, and I know he does not wish it any more than the Secretary of War for him, and both of them together no more than I wish it. Sometimes we have a dispute about how many men General McClellan has had, and those who would disparage him say he has had a very large number, and those who would disparage the Secretary of War insist that General McClellan has had a very small number. The basis for this is, there is always a wide difference, and on this occasion perhaps a wider one, between the grand total on McClellan's rolls and the men actually fit for duty; and those who would disparage him talk of the grand total on paper, and those who would disparage the Secretary of War talk of those at present fit for duty. General McClellan has sometimes asked for things that the Secretary of War did not give him. General McClellan is not to blame for asking for what he wanted and needed, and the Secretary of War is not to blame for not giving when he had none to give. And I say here, so far as I know, the Secretary of War has withheld no one thing at any time in my power to give him. I have no accusation against him. I believe he is a brave and able man, and I stand here, as justice requires me to do, to take upon myself what has been charged on the Secretary of War as withholding from him. I have talked longer than I expected to do, and now I avail myself of my privilege of saying no more.
GOVERNOR ANDREW, Boston, Mass.:
Your despatch saying "I can't get those regiments off because I can't get quick work out of the V. S. disbursing officer and the paymaster" is received. Please say to these gentlemen that if they do not work quickly I will make quick work with them. In the name of all that is reasonable, how long does it take to pay a couple of regiments? We were never more in need of the arrival of regiments than now—even to-day.
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg, Penn.:
It is very important for some regiments to arrive here at once. What lack you from us? What can we do to expedite matters? Answer.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, St. Louis, Missouri:
Would the completion of the railroad some distance farther in the direction of Springfield, Mo., be of any military advantage to you? Please answer.
This afternoon the President of the United States gave an audience to a committee of colored men at the White House. They were introduced by Rev. J. Mitchell, Commissioner of Emigration, E. M. Thomas, the chairman, remarked that they were there by invitation to hear what the Executive had to say to them.
Having all been seated, the President, after a few preliminary observations, informed them that a sum of money had been appropriated by Congress, and placed at his disposition, for the purpose of aiding the colonization, in some country, of the people, or a portion of them, of African descent, thereby making it his duty, as it had for a long time been his inclination, to favor that cause. And why, he asked, should the people of your race be colonized, and where? Why should they leave this country? This is, perhaps, the first question for proper consideration. You and we are different races. We have between us a broader difference than exists between almost any other two races. Whether it is right or wrong I need not discuss; but this physical difference is a great disadvantage to us both, as I think. Your race suffer very greatly, many of them, by living among us, while ours suffer from your presence. In a word, we suffer on each side. If this is admitted, it affords a reason, at least, why we should be separated. You here are free men, I suppose.
[A voice—"Yes, sir!"]
Perhaps you have long been free, or all your lives. Your race are suffering, in my judgment, the greatest wrong inflicted on any people. But even when you cease to be slaves, you are yet far removed from being placed on an equality with the white race. You are cut off from many of the advantages which the other race enjoys. The aspiration of men is to enjoy equality with the best when free, but on this broad continent not a single man of your race is made the equal of a single man of ours. Go where you are treated the best, and the ban is still upon you. I do not propose to discuss this, but to present it as a fact, with which we have to deal. I cannot alter it if I would. It is a fact about which we all think and feel alike, I and you. We look to our condition. Owing to the existence of the two races on this continent, I need not recount to you the effects upon white men, growing out of the institution of slavery.
I believe in its general evil effects on the white race. See our present condition—the country engaged in war—white men cutting one another's throats—none knowing how far it will extend—and then consider what we know to be the truth: But for your race among us there could not be war, although many men engaged on either side do not care for you one way or the other. Nevertheless I repeat, without the institution of slavery and the colored race as a basis, the war could not have an existence. It is better for us both, therefore, to be separated. I know that there are free men among you, who, even if they could better their condition, are not as much inclined to go out of the country as those who, being slaves, could obtain their freedom on this condition. I suppose one of the principal difficulties in the way of colonization is that the free colored man cannot see that his comfort would be advanced by it. You may believe that you can live in WASHINGTON, or elsewhere in the United States, the remainder of your life, as easily, perhaps more so, than you can in any foreign Country; and hence you may come to the conclusion that you have nothing to do with the idea of going to a foreign country.
This is (I speak in no unkind sense) an extremely selfish view of the case. You ought to do something to help those who are not so fortunate as yourselves. There is an unwillingness on the part of our people, harsh as it may be, for you free colored people to remain with us. Now, if you could give a start to the white people, you would open a wide door for many to be made free. If we deal with those who are not free at the beginning, and whose intellects are clouded by slavery, we have very poor material to start with. If intelligent colored men, such as are before me, would move in this matter, much might be accomplished.
It is exceedingly important that we have men at the beginning capable of thinking as white men, and not those who have been systematically oppressed. There is much to encourage you. For the sake of your race you should sacrifice something of your present comfort for the purpose of being as grand in that respect as the white people. It is a cheering thought throughout life that something can be done to ameliorate the condition of those who have been subject to the hard usages of the world. It is difficult to make a man miserable while he feels he is worthy of himself and claims kindred to the great God who made him. In the American Revolutionary war sacrifices were made by men engaged in it, but they were cheered by the future. General WASHINGTON himself endured greater physical hardships than if he had remained a British subject, yet he was a happy man because he had engaged in benefiting his race, in doing something for the children of his neighbors, having none of his own.
The colony of Liberia has been in existence a long time. In a certain sense it is a success. The old President of Liberia, Roberts, has just been with me—the first time I ever saw him. He says they have within the bounds of that colony between three and four hundred thousand people, or more than in some of our old States, such as Rhode Island or Delaware, or in some of our newer States, and less than in some of our larger ones. They are not all American colonists or their descendants. Something less than 12,000 have been sent thither from this country. Many of the original settlers have died; yet, like people else-where, their offspring outnumber those deceased. The question is, if the colored people are persuaded to go anywhere, why not there?
One reason for unwillingness to do so is that some of you would rather remain within reach of the country of your nativity. I do not know how much attachment you may have toward our race. It does not strike me that you have the greatest reason to love them. But still you are attached to them, at all events.
The place I am thinking about for a colony is in Central America. It is nearer to us than Liberia not much more than one fourth as far as Liberia, and within seven days' run by steamers. Unlike Liberia, it is a great line of travel—it is a highway. The country is a very excellent one for any people, and with great natural resources and advantages, and especially because of the similarity of climate with your native soil, thus being suited to your physical condition. The particular place I have in view is to be a great highway from the Atlantic or Caribbean Sea to the Pacific Ocean, and this particular place has all the advantages for a colony. On both sides there are harbors—among the finest in the world. Again, there is evidence of very rich coal-mines. A certain amount of coal is valuable in any country. Why I attach so much importance to coal is, it will afford an opportunity to the inhabitants for immediate employment till they get ready to settle permanently in their homes. If you take colonists where there is no good landing, there is a bad show; and so where there is nothing to cultivate and of which to make a farm. But if something is started so that you can get your daily bread as soon as reach you there, it is a great advantage. Coal land is the best thing I know of with which to commence an enterprise. To return—you have been talked to upon this subject, and told that a speculation is intended by gentlemen who have an interest in the country, including the coal-mines. We have been mistaken all our lives if we do not know whites, as well as blacks, look to their self-interest. Unless among those deficient of intellect, everybody you trade with makes something. You meet with these things here and everywhere. If such persons have what will be an advantage to them, the question is whether it cannot be made of advantage to you. You are intelligent, and know that success does not so much depend on external help as on self-reliance. Much, therefore, depends upon yourselves. As to the coal-mines, I think I see the means available for your self-reliance. I shall, if I get a sufficient number of you engaged, have provision made that you shall not be wronged. If you will engage in the enterprise, I will spend some of the money intrusted to me. I am not sure you will succeed. The government may lose the money; but we cannot succeed unless we try, and we think with care we can succeed. The political affairs in Central America are not in quite as satisfactory a condition as I wish. There are contending factions in that quarter, but it is true all the factions are agreed alike on the subject of colonization, and want it, and are more generous than we are here.
To your colored race they have no objection I would endeavor to have you made the equals, and have the best assurance that you should be the equals, of the best.
The practical thing I want to ascertain is whether I can get a number of able-bodied men, with their wives and children, who are willing to go when I present evidence of encouragement and protection. Could I get a hundred tolerably intelligent men, with their wives and children, and able to "cut their own fodder," so to speak? Can I have fifty? If I could find twenty-five able-bodied men, with a mixture of women and children—good things in the family relation, I think,—I could make a successful commencement. I want you to let me know whether this can be done or not. This is the practical part of my wish to see you. These are subjects of very great importance, worthy of a month's study, instead of a speech delivered in an hour. I ask you, then, to consider seriously, not pertaining to yourselves merely, nor for your race and ours for the present time, but as one of the things, if successfully managed, the good of mankind—not confined to the present generation, but as
"From age to age descends the lay To millions yet to be, Till far its echoes roll away Into eternity."
The above is merely given as the substance of the President's remarks.
The chairman of the delegation briefly replied that they would hold a consultation, and in a short time give an answer.
The President said: Take your full time-no hurry at all.
The delegation then withdrew.
OFFICER in charge of Confederate prisoners at Camp Chase, Ohio:
It is believed that a Dr. J. J. Williams is a prisoner in your charge, and if so tell him his wife is here and allow him to telegraph to her.
HON. HIRAM BARNEY, New York:
Mrs. L. has $1000 for the benefit of the hospitals and she will be obliged, and send the pay, if you will be so good as to select and send her $200 worth of good lemons and $100 worth of good oranges.
The Secretary of the Treasury and the Commissioner of Internal Revenue will please see Mr. Talcott, one of the best men there is, and, if any difference, one they would like better than they do me.
August 18, 1862
A. LINCOLN TELEGRAM TO S. B. MOODY
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON August 18, 1862
S. B. MOODY, Springfield, Ill.:
Which do you prefer—commissary or quartermaster? If appointed it must be without conditions.
A. LINCOLN.
Operator please send above for President. JOHN HAY
Mrs. MARGARET PRESTON, Lexington, Ky.:
Your despatch to Mrs. L. received yesterday. She is not well. Owing to her early and strong friendship for you, I would gladly oblige you, but I cannot absolutely do it. If General Boyle and Hon. James Guthrie, one or both, in their discretion see fit to give you the passes, this is my authority to them for doing so.
TO GENERAL BURNSIDE OR GENERAL PARKE:
What news about arrival of troops?
GILLET F. WATSON, Williamsburg, Va.:
Your telegram in regard to the lunatic asylum has been received. It is certainly a case of difficulty, but if you cannot remain, I cannot conceive who under my authority can. Remain as long as you safely can and provide as well as you can for the poor inmates of the institution.
HON. HORACE GREELEY.
DEAR SIR:—I have just read yours of the 19th, addressed to myself through the New York Tribune. If there be in it any statements or assumptions of fact which I may know to be erroneous, I do not now and here controvert them. If there be in it any inferences which I may believe to be falsely drawn, I do not now and here argue against them. If there be perceptible in it an impatient and dictatorial tone, I waive it in deference to an old friend, whose heart I have always supposed to be right.
As to the policy I "seem to be pursuing," as you say, I have not meant to leave any one in doubt.
I would save the Union. I would save it the shortest way under the Constitution. The sooner the national authority can be restored, the nearer the Union will be, "the Union as it was." If there be those who would not save the Union unless they could at the same time save slavery, I do not agree with them. If there be those who would not save the Union unless they could at the same time destroy slavery, I do not agree with them. My paramount object in this struggle is to save the Union, and is not either to save or destroy slavery. If I could save the Union without freeing any slave, I would do it; and if I could save it by freeing all the slaves, I would do it; and if I could do it by freeing some and leaving others alone, I would also do that. What I do about slavery and the colored race, I do because I believe it helps to save this Union; and what I forbear, I forbear because I do not believe it would help to save the Union. I shall do less whenever I shall believe what I am doing hurts the cause, and I shall do more whenever I shall believe doing more will help the cause. I shall try to correct errors when shown to be errors; and I shall adopt new views so fast as they shall appear to be true views. I have here stated my purpose according to my view of official duty, and I intend no modification of my oft expressed personal wish that all men, everywhere, could be free.
Yours,
HON. R. YATES, Springfield, Ill.:
I am pained to hear that you reject the service of an officer we sent to assist in organizing and getting off troops. Pennsylvania and Indiana accepted such officers kindly, and they now have more than twice as many new troops in the field as all the other States together. If Illinois had got forward as many troops as Indiana, Cumberland Gap would soon be relieved from its present peril. Please do not ruin us on punctilio.
GOVERNOR RAMSEY, St. Paul, Minnesota:
Yours received. Attend to the Indians. If the draft cannot proceed, of course it will not proceed. Necessity knows no law. The government cannot extend the time.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Alexandria, Virginia:
What news from the front?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Falmouth, Virginia:
Do you hear anything from Pope?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Falmouth, Virginia:
Any news from General Pope?
COLONEL HAUPT, Alexandria, Virginia:
Yours received. How do you learn that the rebel forces at Manassas are large and commanded by several of their best generals?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Falmouth, Virginia:
Any further news? Does Colonel Devon mean that sound of firing was heard in direction of Warrenton, as stated, or in direction of Warrenton Junction?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN
What news from direction of Manassas Junction? What generally?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN: Yours of to-day just received. I think your first alternative—to wit, "to concentrate all our available forces to open communication with Pope"—is the right one, but I wish not to control. That I now leave to General Halleck, aided by your counsels.
COLONEL HAUPT Alexandria, Virginia:
What news?
WAR DEPARTMENT, August 30, 1862. 3.50 P.M. COLONEL HAUPT, Alexandria, Virginia
Please send me the latest news.
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS, Manassas Junction, Virginia:
Please tell me what news.
GENERAL BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
What force, and what the numbers of it, which General Nelson had in the engagement near Richmond yesterday?
Ordered, That the general-in-chief, Major-General Halleck, immediately commence, and proceed with all possible despatch; to organize an army, for active operations, from all the material within and coming within his control, independent of the forces he may deem necessary for the defense of Washington when such active army shall take the field.
By order of the President:
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
[Indorsement.]
Copy delivered to Major-General Halleck, September 3, 1862, at 10 p.m.
E. D. TOWNSEND, Assistant-Adjutant General.
GENERAL WRIGHT, Cincinnati, Ohio:
Do you know to any certainty where General Bragg is? May he not be in Virginia?
GENERAL BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
Where is General Bragg? What do you know on the subject?
September 7, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL Wool, Baltimore:
What about Harper's Ferry? Do you know anything about it? How certain is your information about Bragg being in the valley of the Shenandoah?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Rockville, Maryland:
How does it look now?
GENERAL BUELL:
What degree of certainty have you that Bragg, with his command, is not now in the valley of the Shenandoah, Virginia?
THOMAS WEBSTER, Philadelphia:
Your despatch received, and referred to General Halleck, who must control the questions presented. While I am not surprised at your anxiety, I do not think you are in any danger. If half our troops were in Philadelphia, the enemy could take it, because he would not fear to leave the other half in his rear; but with the whole of them here, he dares not leave them in his rear.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Rockville, Maryland:
How does it look now?
HIS EXCELLENCY ANDREW G. CURTIN, Governor of Pennsylvania, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.
SIR:—The application made to me by your adjutant general for authority to call out the militia of the State of Pennsylvania has received careful consideration. It is my anxious desire to afford, as far as possible, the means and power of the Federal Government to protect the State of Pennsylvania from invasion by the rebel forces; and since, in your judgment, the militia of the State are required, and have been called upon by you, to organize for home defense and protection, I sanction the call that you have made, and will receive them into the service and pay of the United States to the extent they can be armed, equipped, and usefully employed. The arms and equipments now belonging to the General Government will be needed for the troops called out for the national armies, so that arms can only be furnished for the quota of militia furnished by the draft of nine months' men, heretofore ordered. But as arms may be supplied by the militia under your call, these, with the 30,000 in your arsenal, will probably be sufficient for the purpose contemplated by your call. You will be authorized to provide such equipments as may be required, according to the regulations of the United States service, which, upon being turned over to the United States Quartermaster's Department, will be paid for at regulation prices, or the rates allowed by the department for such articles. Railroad transportation will also be paid for, as in other cases. Such general officers will be supplied as the exigencies of the service will permit.
Yours truly,
HON. ANDREW G. CURTIN:
Please tell me at once what is your latest news from or toward Hagerstown, or of the enemy's movement in any direction.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
This is explanatory. If Porter, Heintzelman, and Sigel were sent you, it would sweep everything from the other side of the river, because the new troops have been distributed among them, as I understand. Porter reports himself 21,000 strong, which can only be by the addition of new troops. He is ordered tonight to join you as quickly as possible. I am for sending you all that can be spared, and I hope others can follow Porter very soon,
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Clarksburg, Maryland:
How does it look now?
HON. ANDREW G. CURTIN, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania:
Your despatch asking for 80,000 disciplined troops to be sent to Pennsylvania is received. Please consider we have not to exceed 80,000 disciplined troops, properly so called, this side of the mountains; and most of them, with many of the new regiments, are now close in the rear of the enemy supposed to be invading Pennsylvania. Start half of them to Harrisburg, and the enemy will turn upon and beat the remaining half, and then reach Harrisburg before the part going there, and beat it too when it comes. The best possible security for Pennsylvania is putting the strongest force possible in rear of the enemy.
MAJOR-GENERAL WRIGHT, Cincinnati, Ohio:
I am being appealed to from Louisville against your withdrawing troops from that place. While I cannot pretend to judge of the propriety of what you are doing, you would much oblige me by furnishing me a rational answer to make to the governor and others at Louisville.
MAJOR-GENERAL BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
Your despatch of last evening received. Where is the enemy which you dread in Louisville? How near to you? What is General Gilbert's opinion? With all possible respect for you, I must think General Wright's military opinion is the better. He is as much responsible for Louisville as for Cincinnati. General Halleck telegraphed him on this very subject yesterday, and I telegraph him now; but for us here to control him there on the ground would be a babel of confusion which would be utterly ruinous. Where do you understand Buell to be, and what is he doing?
HON. ALEXANDER HENRY, Philadelphia:
Yours of to-day received. General Halleck has made the best provision he can for generals in Pennsylvania. Please do not be offended when I assure you that in my confident belief Philadelphia is in no danger. Governor Curtin has just telegraphed me: "I have advices that Jackson is crossing the Potomac at Williamsport, and probably the whole rebel army will be drawn from Maryland." At all events, Philadelphia is more than 150 miles from Hagerstown, and could not be reached by the rebel army in ten days, if no hindrance was interposed.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Governor Curtin telegraphs me:
"I have advices that Jackson is crossing the Potomac at Williamsport, and probably the whole rebel army will be down from Maryland."
Receiving nothing from Harper's Ferry or Martinsburg to-day, and positive information from Wheeling that the line is cut, corroborates the idea that the enemy is crossing the Potomac. Please do not let him get off without being hurt.
A. LINCOLN.
[But he did! D.W.]
September 13,1862.
The subject presented in the memorial is one upon which I have thought much for weeks past, and I may even say for months. I am approached with the most opposite opinions and advice, and that by religious men, who are equally certain that they represent the Divine will. I am sure that either the one or the other class is mistaken in that belief, and perhaps in some respects both. I hope it will not be irreverent for me to say that if it is probable that God would reveal his will to others, on a point so connected with my duty, it might be supposed he would reveal it directly to me; for, unless I am more deceived in myself than I often am, it is my earnest desire to know the will of Providence in this matter. And if I can learn what it is I will do it! These are not, however, the days of miracles, and I suppose it will be granted that I am not to expect a direct revelation. I must study the plain physical facts of the case, ascertain what is possible, and learn what appears to be wise and right.
The subject is difficult, and good men do not agree. For instance, the other day, four gentlemen of standing and intelligence from New York called as a delegation on business connected with the war; but before leaving two of them earnestly besought me to proclaim general emancipation, upon which the other two at once attacked them. You know also that the last session of Congress had a decided majority of antislavery men, yet they could not unite on this policy. And the same is true of the religious people. Why, the rebel soldiers are praying with a great deal more earnestness, I fear, than our own troops, and expecting God to favor their side: for one of our soldiers who had been taken prisoner told Senator Wilson a few days since that he met nothing so discouraging as the evident sincerity of those he was among in their prayers. But we will talk over the merits of the case.
What good would a proclamation of emancipation from me do, especially as we are now situated? I do not want to issue a document that the whole world will see must necessarily be inoperative, like the Pope's bull against the comet! Would my word free the slaves, when I cannot even enforce the Constitution in the rebel States? Is there a single court, or magistrate or individual that would be influenced by it there? And what reason is there to think it would have any greater effect upon the slaves than the late law of Congress, which I approved, and which offers protection and freedom to the slaves of rebel masters who come within our lines? Yet I cannot learn that that law has caused a single slave to come over to us. And suppose they could be induced by a proclamation of freedom from me to throw themselves upon us, what should we do with them? How can we feed and care for such a multitude? General Butler wrote me a few days since that he was issuing more rations to the slaves who have rushed to him than to all the white troops under his command. They eat, and that is all; though it is true General Butler is feeding the whites also by the thousand; for it nearly amounts to a famine there. If, now, the pressure of the war should call off our forces from New Orleans to defend some other point, what is to prevent the masters from reducing the blacks to slavery again? for I am told that whenever the rebels take any black prisoners, free or slave, they immediately auction them off. They did so with those they took from a boat that was aground in the Tennessee River a few days ago. And then I am very ungenerously attacked for it! For instance, when, after the late battles at and near Bull Run, an expedition went out from Washington under a flag of truce to bury the dead and bring in the wounded, and the rebels seized the blacks who went along to help, and sent them into slavery, Horace Greeley said in his paper that the government would probably do nothing about it. What could I do?
Now, then, tell me, if you please, what possible result of good would follow the issuing of such a proclamation as you desire? Understand, I raise no objections against it on legal or constitutional grounds; for, as commander-in-chief of the army and navy, in time of war I suppose I have a right to take any measure which may best subdue the enemy; nor do I urge objections of a moral nature, in view of possible consequences of insurrection and massacre at the South. I view this matter as a practical war measure, to be decided on according to the advantages or disadvantages it may offer to the suppression of the rebellion.
I admit that slavery is the root of the rebellion, or at least its sine qua non. The ambition of politicians may have instigated them to act, but they would have been impotent without slavery as their instrument. I will also concede that emancipation would help us in Europe, and convince them that we are incited by something more than ambition. I grant, further, that it would help somewhat at the North, though not so much, I fear, as you and those you represent imagine. Still, some additional strength would be added in that way to the war, and then, unquestionably, it would weaken the rebels by drawing off their laborers, which is of great importance; but I am not so sure we could do much with the blacks. If we were to arm them, I fear that in a few weeks the arms would be in the hands of the rebels; and, indeed, thus far we have not had arms enough to equip our white troops. I will mention another thing, though it meet only your scorn and contempt. There are fifty thousand bayonets in the Union armies from the border slave States. It would be a serious matter if, in consequence of a proclamation such as you desire, they should go over to the rebels. I do not think they all would—not so many, indeed, as a year ago, or as six months ago—not so many to-day as yesterday. Every day increases their Union feeling. They are also getting their pride enlisted, and want to beat the rebels. Let me say one thing more: I think you should admit that we already have an important principle to rally and unite the people, in the fact that constitutional government is at stake. This is a fundamental idea going down about as deep as anything.
Do not misunderstand me because I have mentioned these objections. They indicate the difficulties that have thus far prevented my action in some such way as you desire. I have not decided against a proclamation of liberty to the slaves, but hold the matter under advisement; and I can assure you that the subject is on my mind, by day and night, more than any other. Whatever shall appear to be God's will, I will do. I trust that in the freedom with which I have canvassed your views I have not in any respect injured your feelings.
GENERAL WRIGHT, Cincinnati, Ohio:
Thanks for your despatch. Can you not pursue the retreating enemy, and relieve Cumberland Gap?
September 15, 1862. 2.45 P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch of to-day received. God bless you, and all with you. Destroy the rebel army if possible.
HON. K. DUBOIS, Springfield, Illinois:
I now consider it safe to say that General McClellan has gained a great victory over the great rebel army in Maryland, between Fredericktown and Hagerstown. He is now pursuing the flying foe.
A. LINCOLN.
[But not very fast—and he did not catch them! D.W.]
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg:
What do you hear from General McClellan's army? We have nothing from him to-day.
GOVERNOR O. P. MORTON, Indianapolis, Indiana:
I have received your despatch in regard to recommendations of General Wright. I have received no such despatch from him, at least not that I can remember. I refer yours for General Halleck's consideration.
GENERAL KETCHUM, Springfield, Illinois:
How many regiments are there in Illinois, ready for service but for want of arms? How many arms have you there ready for distribution?
A Proclamation.
I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America and Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy thereof, do hereby proclaim and declare that hereafter, as heretofore, the war will be prosecuted for the object of practically restoring the constitutional relation between the United States and each of the States and the people thereof in which States that relation is or may be suspended or disturbed.
That it is my purpose, upon the next meeting of Congress, to again recommend the adoption of a practical measure tendering pecuniary aid to the free acceptance or rejection of all slave States, so called, the people whereof may not then be in rebellion against the United States, and which States may then have voluntarily adopted, or thereafter may voluntarily adopt, immediate or gradual abolishment of slavery within their respective limits; and that the effort to colonize persons of African descent with their consent upon this continent or elsewhere, with the previously obtained consent of the governments existing there, will be continued.
That on the 1st day of January, A.D. 1863, all persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free; and the executive government of the United States, including the military and naval authority thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of such persons and will do no act or acts to repress such persons, or any of them, in any efforts they may make for their actual freedom.
That the Executive will on the 1st day of January aforesaid, by proclamation, designate the States and parts of States, if any, in which the people thereof, respectively, shall then be in rebellion against the United States; and the fact that any State or the people thereof shall on that day be in good faith represented in the Congress of the United States by members chosen thereto at elections wherein a majority of the qualified voters of such State shall have participated shall, in the absence of strong countervailing testimony, be deemed conclusive evidence that such State and the people thereof are not then in rebellion against the United States.
That attention is hereby called to an act of Congress entitled "An act to make an additional article of war," approved March 13, 1862, and which act is in the words and figure following:
"Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled, That hereafter the following shall be promulgated as an additional article of war for the government of the Army of the United States and shall be obeyed and observed as such.
"ART. All officers or persons in the military or naval service of the United States are prohibited from employing any of the forces under their respective commands for the purpose of returning fugitives from service or labor who may have escaped from any person, to whom such service or labor is claimed to be due, and any officer who shall be found guilty by a court-martial of violating this article shall be dismissed from the service.
"SEC. 2. And be it further enacted, That this act shall take effect from and after its passage."
Also to the ninth and tenth sections of an act entitled "An act to suppress insurrection, to punish treason and rebellion, to seize and confiscate the property of rebels, and for other purposes," approved July 17, 1862, and which sections are in the words and figures following:
"SEC. 9. And be it further enacted, That all slaves of persons who shall hereafter be engaged in rebellion against the Government of the United States, or who shall in any way give aid or comfort thereto, escaping from such persons and taking refuge within the lines of the army, and all slaves captured from such persons or deserted by them and coming under the control of the Government of the United States, and all slaves of such persons found on (or) being within any place occupied by rebel forces and afterwards occupied by the forces of the United States, shall be deemed captives of war and shall be forever free of their servitude and not again held as slaves.
"SEC. 9. And be it further enacted, That no slave escaping into any State, Territory, or the District of Columbia from any other State shall be delivered up or in any way impeded or hindered of his liberty, except for crime, or some offence against the laws, unless the person claiming said fugitive shall first make oath that the person to whom the labor or service of such fugitive is alleged to be due is his lawful owner, and has not borne arms against the United States in the present rebellion, nor in any way given aid and comfort thereto; and no person engaged in the military or naval service of the United States shall, under any pretense whatever, assume to decide on the validity of the claim of any person to the service or labor of any other person, or surrender up any such person to the claimant, on pain of being dismissed from the service."
And I do hereby enjoin upon and order all persons engaged in the military and naval service of the United States to observe, obey, and enforce, within their respective spheres of service, the act and sections above recited.
And the Executive will in due time recommend that all citizens of the United States who shall have remained loyal thereto throughout the rebellion shall (upon the restoration of the constitutional relation between the United States and their respective States and people, if that relation shall have been suspended or disturbed) be compensated for all losses by acts of the United States, including the loss of slaves.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the City of Washington, this twenty-second day of September, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-two, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
A Proclamation
Whereas it has become necessary to call into service not only volunteers, but also portions of the militia of the States by draft, in order to suppress the insurrection existing in the United States, and disloyal persons are not adequately restrained by the ordinary processes of law from hindering this measure, and from giving aid and comfort in various ways to the insurrection:
Now, therefore, be it ordered
First. That during the existing insurrection, and as a necessary measure for suppressing the same, all rebels and insurgents, their aiders and abettors within the United States, and all persons discouraging volunteer enlistments, resisting militia drafts, or guilty of any disloyal practice affording aid and comfort to rebels against the authority of the United States, shall be subject to martial law, and liable to trial and punishment by courts-martial or military commissions.
Second. That the writ of habeas corpus is suspended in respect to all persons arrested, or who are now, or hereafter during the rebellion shall be, imprisoned in any fort camp, arsenal, military prison or other place of confinement by any military authority or by the sentence of any court-martial or military commission.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of WASHINGTON, this twenty-fourth day of September. A.D. eighteen hundred and sixty-two, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
I appear before you to do little more than acknowledge the courtesy you pay me, and to thank you for it. I have not been distinctly informed why it is that on this occasion you appear to do me this honor, though I suppose it is because of the proclamation. What I did, I did after a very full deliberation, and under a very heavy and solemn sense of responsibility. I can only trust in God I have made no mistake. I shall make no attempt on this occasion to sustain what I have done or said by any comment. It is now for the country and the world to pass judgment and, maybe, take action upon it.
I will say no more upon this subject. In my position I am environed with difficulties. Yet they are scarcely so great as the difficulties of those who upon the battle-field are endeavoring to purchase with their blood and their lives the future happiness and prosperity of this country. Let us never forget them. On the fourteenth and seventeenth days of this present month there have been battles bravely, skillfully, and successfully fought. We do not yet know the particulars. Let us be sure that, in giving praise to certain individuals, we do no injustice to others. I only ask you, at the conclusion of these few remarks, to give three hearty cheers for all good and brave officers and men who fought those successful battles.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
September 26, 1862.
MAJOR JOHN J. KEY:
I am informed that, in answer to the question, "Why was not the rebel army bagged immediately after the battle near Sharpsburg?" propounded to you by Major Levi C. Turner, Judge Advocate, etc., you said: "That is not the game. The object is, that neither army shall get much advantage of the other; that both shall be kept in the field till they are exhausted, when we will make a compromise and save slavery."
I shall be very happy if you will, within twenty-four hours from the receipt of this, prove to me by Major Turner that you did not, either literally or in substance, make the answer stated.
[Above delivered to Major Key at 10.25 a.m. September 27th.]
At about 11 o'clock A.M., September 27, 1862, Major Key and Major Turner appeared before me. Major Turner says:
"As I remember it, the conversation was: 'Why did we not bag them after the battle of Sharpsburg?' Major Key's reply was: 'That was not the game; that we should tire the rebels out and ourselves; that that was the only way the Union could be preserved, we come together fraternally, and slavery be saved.'"
On cross-examination, Major Turner says he has frequently heard Major Key converse in regard to the present troubles, and never heard him utter a sentiment unfavorable to the maintenance of the Union. He has never uttered anything which he, Major T., would call disloyalty. The particular conversation detailed was a private one.
[Indorsement on the above.]
In my view, it is wholly inadmissible for any gentleman holding a military commission from the United States to utter such sentiments as Major Key is within proved to have done. Therefore, let Major John J. Key be forthwith dismissed from the military service of the United States.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
September 28, 1862.
HON. HANNIBAL HAMLIN.
MY DEAR SIR: Your kind letter of the 25th is just received. It is known to some that, while I hope something from the proclamation, my expectations are not as sanguine as are those of some friends. The time for its effect southward has not come; but northward the effect should be instantaneous. It is six days old, and, while commendation in newspapers and by distinguished individuals is all that a vain man could wish, the stocks have declined, and troops come forward more slowly than ever. This, looked soberly in the face, is not very satisfactory. We have fewer troops in the field at the end of the six days than we had at the beginning—the attrition among the old outnumbering the addition by the new. The North responds to the proclamation sufficiently in breath; but breath alone kills no rebels.
I wish I could write more cheerfully; nor do I thank you the less for the kindness of your letter.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
General Stuart, of the rebel army, has sent in a few of our prisoners under a flag of truce, paroled with terms to prevent their fighting the Indians, and evidently seeking to commit us to their right to parole prisoners in that way. My inclination is to send the prisoners back with a definite notice that we will recognize no paroles given to our prisoners by the rebels as extending beyond a prohibition against fighting them, though I wish your opinion upon it, based both upon the general law and our cartel. I wish to avoid violations of the law and bad faith. Answer as quickly as possible, as the thing, if done at all, should be done at once.
A. LINCOLN, President
I am surrounded by soldiers and a little farther off by the citizens of this good City of Frederick. Nevertheless I can only say, as I did five minutes ago, it is not proper for me to make speeches in my present position. I return thanks to our soldiers for the good services they have rendered, the energy they have shown, the hardships they have endured, and the blood they have shed for this Union of ours; and I also return thanks, not only to the soldiers, but to the good citizens of Frederick, and to the good men, women, and children in this land of ours, for their devotion to this glorious cause; and I say this with no malice in my heart towards those who have done otherwise. May our children and children's children, for a thousand generations, continue to enjoy the benefits conferred upon us by a united country, and have cause yet to rejoice under these glorious institutions, bequeathed to us by WASHINGTON and his compeers. Now, my friends, soldiers and citizens, I can only say once more-farewell.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I am instructed to telegraph you as follows: The President directs that you cross the Potomac and give battle to the enemy, or drive him south. Your army must move now, while the roads are good. If you cross the river between the enemy and Washington, and cover the latter by your operation, you can be reinforced by thirty thousand men. If you move up the valley of the Shenandoah, not more than twelve or fifteen thousand can be sent you. The President advises the interior line between Washington and the enemy, but does not order it. He is very desirous that your army move as soon as possible. You will immediately report what line you adopt, and when you intend to cross the river; also to what point the reinforcements are to be sent. It is necessary that the plan of your operations be positively determined on, before orders are given for building bridges and repairing railroads. I am directed to add that the Secretary of War and the General-in-chief fully concur with the President in these directions.
H. W. HALLECK, General-in-Chief.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN, Hdqs. Army of the Potomac:
You wish to see your family and I wish to oblige you. It might be left to your own discretion; certainly so, if Mrs. M. could meet you here at Washington.
THOMAS H. CLAY, Cincinnati, Ohio:
You cannot have reflected seriously when you ask that I shall order General Morgan's command to Kentucky as a favor because they have marched from Cumberland Gap. The precedent established by it would evidently break up the whole army. Buell's old troops, now in pursuit of Bragg, have done more hard marching recently; and, in fact, if you include marching and fighting, there are scarcely any old troops east or west of the mountains that have not done as hard service. I sincerely wish war was an easier and pleasanter business than it is; but it does not admit of holidays. On Morgan's command, where it is now sent, as I understand, depends the question whether the enemy will get to the Ohio River in another place.
MAJOR-GENERAL GRANT:
I congratulate you and all concerned in your recent battles and victories. How does it all sum up? I especially regret the death of General Hackleman, and am very anxious to know the condition of General Oglesby, who is an intimate personal friend.
GENERAL BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
Please send any news you have from General Buell to-day.
GENERAL BOYLE, Louisville, Kentucky:
We are anxious to hear from General Buell's army. We have heard nothing since day before yesterday. Have you anything?
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, Saint Louis, Missouri:
Would the completion of the railroad some distance further in the direction of Springfield, Mo., be of any military advantage to you? Please answer.
MY DEAR SIR—You remember my speaking to you of what I called your over-cautiousness. Are you not over-cautious when you assume that you cannot do what the enemy is constantly doing? Should you not claim to be at least his equal in prowess, and act upon the claim?
As I understand, you telegraphed General Halleck that you cannot subsist your army at Winchester unless the railroad from Harper's Ferry to that point be put in working order. But the enemy does now subsist his army at Winchester, at a distance nearly twice as great from railroad transportation as you would have to do, without the railroad last named. He now wagons from Culpepper Court-House, which is just about twice as far as you would have to do from Harper's Ferry. He is certainly not more than half as well provided with wagons as you are. I certainly should be pleased for you to have the advantage of the railroad from Harper's Perry to Winchester; but it wastes an the remainder of autumn to give it to you, and, in fact, ignores the question of time, which cannot and must not be ignored.
Again, one of the standard maxims of war, as you know, is "to operate upon the enemy's communications as much as possible, without exposing your own." You seem to act as if this applies against you, but cannot apply in your favor. Change positions with the enemy, and think you not he would break your communication with Richmond within the next twenty-four hours? You dread his going into Pennsylvania. But if he does so in full force, he gives up his communications to you absolutely, and you have nothing to do but to follow and ruin him; if he does so with less than full force, fall upon and beat what is left behind all the easier.
Exclusive of the water line, you are now nearer to Richmond than the enemy is, by the route that you can and he must take. Why can you not reach there before him, unless you admit that he is more than your equal on a march? His route is the arc of a circle, while yours is the chord. The roads are as good on yours as on his.
You know I desired, but did not order, you to cross the Potomac below instead of above the Shenandoah and Blue Ridge. My idea was, that this would at once menace the enemy's communications, which I would seize if he would permit. If he should move northward, I would follow him closely, holding his communications. If he should prevent our seizing his communications, and move toward Richmond, I would press closely to him, fight him if a favorable opportunity should present, and at least try to beat him to Richmond on the inside track. I say "try;" if we never try, we shall never succeed. If he makes a stand at Winchester, moving neither north or south, I would fight him there, on the idea that if we cannot beat him when he bears the wastage of coming to us, we never can when we bear the wastage of going to him. This proposition is a simple truth, and is too important to be lost sight of for a moment. In coming to us he tenders us an advantage which we should not waive. We should not so operate as to merely drive him away. As we must beat him somewhere or fail finally, we can do it, if at all, easier near to us than far away. If we cannot beat the enemy where he now is, we never can, he again being within the entrenchments of Richmond.
[And, indeed, the enemy was let back into Richmond and it took another two years and thousands of dead for McClelland cowardice—if that was all that it was. I still suspect, and I think the evidence is overwhelming that he was, either secretly a supporter of the South, or, what is more likely, a politician readying for a different campaign: that of the Presidency of the United States.]
Recurring to the idea of going to Richmond on the inside track, the facility of supplying from the side away from the enemy is remarkable, as it were, by the different spokes of a wheel extending from the hub toward the rim, and this whether you move directly by the chord or on the inside arc, hugging the Blue Ridge more closely. The chord line, as you see, carries you by Aldie, Hay Market, and Fredericksburg; and you see how turnpikes, railroads, and finally the Potomac, by Aquia Creek, meet you at all points from WASHINGTON; the same, only the lines lengthened a little, if you press closer to the Blue Ridge part of the way.
The gaps through the Blue Ridge I understand to be about the following distances from Harper's Ferry, to wit: Vestal's, 5 miles; Gregory's, 13; Snicker's, 18; Ashby's, 28; Manassas, 38; Chester, 45; and Thornton's, 53. I should think it preferable to take the route nearest the enemy, disabling him to make an important move without your knowledge, and compelling him to keep his forces together for dread of you. The gaps would enable you to attack if you should wish. For a great part of the way you would be practically between the enemy and both WASHINGTON and Richmond, enabling us to spare you the greatest number of troops from here. When at length running for Richmond ahead of him enables him to move this way, if he does so, turn and attack him in rear. But I think he should be engaged long before such a point is reached. It is all easy if our troops march as well as the enemy, and it is unmanly to say they cannot do it. This letter is in no sense an order.
Yours truly,
GOVERNOR PIERPOINT, Wheeling, Virginia:
Your despatch of to-day received. I am very sorry to have offended you. I appointed the collector, as I thought, on your written recommendation, and the assessor also with your testimony of worthiness, although I know you preferred a different man. I will examine to-morrow whether I am mistaken in this.
October 20, 1862.
The insurrection which has for some time prevailed in several of the States of this Union, including Louisiana, having temporarily subverted and swept away the civil institutions of that State, including the judiciary and the judicial authorities of the Union, so that it has become necessary to hold the State in military Occupation, and it being indispensably necessary that there shall be some judicial tribunal existing there capable of administering justice, I have therefore thought it proper to appoint, and I do hereby constitute, a provisional court, which shall be a court of record, for the State of Louisiana; and I do hereby appoint Charles A Peabody, of New York, to be a provisional judge to hold said court, with authority to hear, try, and determine all causes, civil and criminal, including causes in law, equity, revenue, and admiralty, and particularly all such powers and jurisdiction as belong to the district and circuit courts of the United States, conforming his proceedings so far as possible to the course of proceedings and practice which has been customary in the courts of the United States and Louisiana, his judgment to be final and conclusive. And I do hereby authorize and empower the said judge to make and establish such rules and regulations as may be necessary for the exercise of his jurisdiction, and empower the said judge to appoint a prosecuting attorney, marshal, and clerk of the said court, who shall perform the functions of attorney, marshal, and clerk according to such proceedings and practice as before mentioned and such rules and regulations as may be made and established by said judge. These appointments are to continue during the pleasure of the President, not extending beyond the military occupation of the city of New Orleans or the restoration of the civil authority in that city and in the State of Louisiana. These officers shall be paid, out of the contingent fund of the War Department, compensation as follows:
The judge at the rate of $3500 per annum; the prosecuting attorney, including the fees, at the rate of $3000 per annum; the marshal, including the fees, at the rate of $3000 per annum; and the clerk, including the fees, at the rate of $2500 per annum; such compensations to be certified by the Secretary of War. A copy of this order, certified by the Secretary of War and delivered to such judge, shall be deemed and held to be a sufficient commission.
A. LINCOLN,
President of the United States.
October 21, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL U. S. GRANT:
The bearer of this, Thomas R. Smith, a citizen of Tennessee, goes to that State seeking to have such of the people thereof as desire to avoid the unsatisfactory prospect before them, and to have peace again upon the old terms, under the Constitution of the United States, to manifest such desire by elections of members to the Congress of the United States particularly, and perhaps a Legislature, State officers, and a United States senator friendly to their object.
I shall be glad for you and each of you to aid him, and all others acting for this object, as much as possible. In all available ways give the people a show to express their wishes at these elections.
Follow law, and forms of law, as far as convenient, but at all events get the expression of the largest number of the people possible. All see how such action will connect with and affect the proclamation of September 22. Of course the men elected should be gentlemen of character, willing to swear support to the Constitution as of old, and known to be above reasonable suspicion of duplicity.
Yours very respectfully,
GENERAL JAMESON, Upper Stillwater, Me.:
How is your health now? Do you or not wish Lieut. R. P. Crawford to be restored to his office?
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, October 24 [25?], 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
I have just read your despatch about sore-tongued and fatigued horses. Will you pardon me for asking what the horses of your army have done since the battle of Antietam that fatigues anything?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Yours, in reply to mine about horses, received. Of course you know the facts better than I; still two considerations remain: Stuart's cavalry outmarched ours, having certainly done more marked service on the Peninsula and everywhere since. Secondly, will not a movement of our army be a relief to the cavalry, compelling the enemy to concentrate instead of foraging in squads everywhere? But I am so rejoiced to learn from your despatch to General Halleck that you begin crossing the river this morning.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON October 26, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe, Virginia:
Your despatch to Mr. Stanton, of which the enclosed is a copy, has been handed me by him. It would be dangerous for me now to begin construing and making specific applications of the proclamation.
It is obvious to all that I therein intended to give time and opportunity. Also, it is seen I left myself at liberty to exempt parts of States. Without saying more, I shall be very glad if any Congressional district will, in good faith, do as your despatch contemplates.
Could you give me the facts which prompted you to telegraph?
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Yours of yesterday received. Most certainly I intend no injustice to any, and if I have done any I deeply regret it. To be told, after more than five weeks' total inaction of the army, and during which period we have sent to the army every fresh horse we possibly could, amounting in the whole to 7918, that the cavalry horses were too much fatigued to move, presents a very cheerless, almost hopeless, prospect for the future, and it may have forced something of impatience in my despatch. If not recruited and rested then, when could they ever be? I suppose the river is rising, and I am glad to believe you are crossing.
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatch of 3 P.M. to-day, in regard to filling up old regiments with drafted men, is received, and the request therein shall be complied with as far as practicable.
And now I ask a distinct answer to the question, Is it your purpose not to go into action again until the men now being drafted in the States are incorporated into the old regiments?
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLELLAN:
Your despatches of night before last, yesterday, and last night all received. I am much pleased with the movement of the army. When you get entirely across the river let me know. What do you know of the enemy?
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg:
By some means I have not seen your despatch of the 27th about order No.154 until this moment. I now learn, what I knew nothing of before, that the history of the order is as follows:
When General McClellan telegraphed asking General Halleck to have the order made, General Halleck went to the Secretary of War with it, stating his approval of the plan. The Secretary assented and General Halleck wrote the order. It was a military question, which the Secretary supposed the General understood better than he.
I wish I could see Governor Curtin.
GOV. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn., via Louisville, Ky.:
Yours of the 29th received. I shall take it to General Halleck, but I already know it will be inconvenient to take General Morgan's command from where it now is. I am glad to hear you speak hopefully of Tennessee. I sincerely hope Rosecrans may find it possible to do something for her. David Nelson, son of the M. C. of your State, regrets his father's final defection, and asks me for a situation. Do you know him? Could he be of service to you or to Tennessee in any capacity in which I could send him?
November 1, 1862.
TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN: Captain Derrickson, with his company, has been for some time keeping guard at my residence, now at the Soldiers' Retreat. He and his company are very agreeable to me, and while it is deemed proper for any guard to remain, none would be more satisfactory than Captain Derrickson and his company.
EXECUTIVE MANSION WASHINGTON, November 5, 1862.
By direction of the President, it is ordered that Major-General McClellan be relieved from the command of the Army of the Potomac, and that Major-General Burnside take the command of that army. Also that Major-General Hunter take command of the corps in said army which is now commanded by General Burnside. That Major-General Fitz. John Porter be relieved from command of the corps he now commands in said army, and that Major-General Hooker take command of said corps.
The general-in-chief is authorized, in [his] discretion, to issue an order substantially as the above forthwith, or so soon as he may deem proper.
HON. M. F. ODELL, Brooklyn, New York:
You are re-elected. I wish to see you at once will you come? Please answer.
COL. W. W. LOWE, Fort Henry, Tennessee:
Yours of yesterday received. Governor Johnson, Mr. Ethridge, and others are looking after the very thing you telegraphed about.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Paul, Minnesota:
Your despatch giving the names of 300 Indians condemned to death is received. Please forward as soon as possible the full and complete record of their convictions; and if the record does not fully indicate the more guilty and influential of the culprits, please have a careful statement made on these points and forwarded to me. Send all by mail.
COMMODORE FARRAGUT:
DEAR SIR:—This will introduce Major-General Banks. He is in command of a considerable land force for operating in the South, and I shall be glad for you to co-Operate with him and give him such assistance as you can consistently with your orders from the Navy Department.
Your obedient servant,
Ordered, First: that clearances issued by the Treasury Department for vessels or merchandise bound for the port of Norfolk, for the military necessities of the department, certified by the military commandant at Fort Monroe, shall be allowed to enter said port.
Second: that vessels and domestic produce from Norfolk, permitted by the military commandant at Fort Monroe for the military purposes of his command, shall on his permit be allowed to pass from said port to their destination in any port not blockaded by the United States.
Ordered, by the President of the United States, That the Attorney-General be charged with the superintendence and direction of all proceedings to be had under the act of Congress of the 17th of July, 1862, entitled "An act to suppress insurrection, to punish treason and rebellion, to seize and confiscate the property of rebels, and for other purposes," in so far as may concern the seizure, prosecution, and condemnation of the estate, property, and effects of rebels and traitors, as mentioned and provided for in the fifth, sixth, and seventh sections of the said act of Congress. And the Attorney-General is authorized and required to give to the attorneys and marshals of the United States such instructions and directions as he may find needful and convenient touching all such seizures, prosecutions, and condemnations, and, moreover, to authorize all such attorneys and marshals, whenever there may be reasonable ground to fear any forcible resistance to them in the discharge of their respective duties in this behalf, to call upon any military officer in command of the forces of the United States to give to them such aid, protection, and support as may be necessary to enable them safely and efficiently to discharge their respective duties; and all such commanding officers are required promptly to obey such call, and to render the necessary service as far as may be in their power consistently with their other duties.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: EDWARD BATES, Attorney-General
GOV. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tennessee:
Your despatch of the 4th, about returning troops from western Virginia to Tennessee, is just received, and I have been to General Halleck with it. He says an order has already been made by which those troops have already moved, or soon will move, to Tennessee.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 15, 1862.
The President, Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy, desires and enjoins the orderly observance of the Sabbath by the officers and men in the military and naval service. The importance for man and beast of the prescribed weekly rest, the sacred rights of Christian soldiers and sailors, a becoming deference to the best sentiment of a Christian people, and a due regard for the divine will demand that Sunday labor in the army and navy be reduced to the measure of strict necessity.
The discipline and character of the national forces should not suffer nor the cause they defend be imperilled by the profanation of the day or name of the Most High. "At this time of public distress," adopting the words of Washington in 1776, "men may find enough to do in the service of God and their country without abandoning themselves to vice and immorality." The first general order issued by the Father of his Country after the Declaration of Independence indicates the spirit in which our institutions were founded and should ever be defended:
"The General hopes and trusts that every officer and man will endeavor to live and act as becomes a Christian soldier defending the dearest rights and liberties of his country."
HON. F. P. BLAIR:
Your brother says you are solicitous to be ordered to join General McLernand. I suppose you are ordered to Helena; this means that you are to form part of McLernand's expedition as it moves down the river; and General McLernand is so informed. I will see General Halleck as to whether the additional force you mention can go with you.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe:
Please give me your best opinion as to the number of the enemy now at Richmond and also at Petersburg.
HON. G. F. SHEPLEY.
DEAR SIR:—Dr. Kennedy, bearer of this, has some apprehension that Federal officers not citizens of Louisiana may be set up as candidates for Congress in that State. In my view there could be no possible object in such an election. We do not particularly need members of Congress from there to enable us to get along with legislation here. What we do want is the conclusive evidence that respectable citizens of Louisiana are willing to be members of Congress and to swear support to the Constitution, and that other respectable citizens there are willing to vote for them and send them. To send a parcel of Northern men here as representatives, elected, as would be understood (and perhaps really so), at the point of the bayonet, would be disgusting and outrageous; and were I a member of Congress here, I would vote against admitting any such man to a seat.
Yours very truly,
November 21, 1862.
Ordered, That no arms, ammunition, or munitions of war be cleared or allowed to be exported from the United States until further orders. That any clearance for arms, ammunition, or munitions of war issued heretofore by the Treasury Department be vacated, if the articles have not passed without the United States, and the articles stopped. That the Secretary of War hold possession of the arms, etc., recently seized by his order at Rouse's Point, bound for Canada.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 22, 1862.
MY DEAR GENERAL BANKS:—Early last week you left me in high hope with your assurance that you would be off with your expedition at the end of that week, or early in this. It is now the end of this, and I have just been overwhelmed and confounded with the sight of a requisition made by you which, I am assured, cannot be filled and got off within an hour short of two months. I enclose you a copy of the requisition, in some hope that it is not genuine—that you have never seen it. My dear General, this expanding and piling up of impedimenta has been, so far, almost our ruin, and will be our final ruin if it is not abandoned. If you had the articles of this requisition upon the wharf, with the necessary animals to make them of any use, and forage for the animals, you could not get vessels together in two weeks to carry the whole, to say nothing of your twenty thousand men; and, having the vessels, you could not put the cargoes aboard in two weeks more. And, after all, where you are going you have no use for them. When you parted with me you had no such ideas in your mind. I know you had not, or you could not have expected to be off so soon as you said. You must get back to something like the plan you had then, or your expedition is a failure before you start. You must be off before Congress meets. You would be better off anywhere, and especially where you are going, for not having a thousand wagons doing nothing but hauling forage to feed the animals that draw them, and taking at least two thousand men to care for the wagons and animals, who otherwise might be two thousand good soldiers. Now, dear General, do not think this is an ill-natured letter; it is the very reverse. The simple publication of this requisition would ruin you.
Very truly your friend,
GENERAL CARL SCHURZ.
MY DEAR SIR—I have just received and read your letter of the 20th. The purport of it is that we lost the late elections and the administration is failing because the war is unsuccessful, and that I must not flatter myself that I am not justly to blame for it. I certainly know that if the war fails the administration fails, and that I will be blamed for it, whether I deserve it or not. And I ought to be blamed if I could do better. You think I could do better; therefore you blame me already. I think I could not do better; therefore I blame you for blaming me. I understand you now to be willing to accept the help of men who are not Republicans, provided they have "heart in it." Agreed. I want no others. But who is to be the judge of hearts, or of "heart in it"? If I must discard my own judgment and take yours, I must also take that of others and by the time I should reject all I should be advised to reject, I should have none left, Republicans or others not even yourself. For be assured, my dear sir, there are men who have "heart in it" that think you are performing your part as poorly as you think I am performing mine. I certainly have been dissatisfied with the slowness of Buell and McClellan; but before I relieved them I had great fears I should not find successors to them who would do better; and I am sorry to add that I have seen little since to relieve those fears.
I do not see clearly the prospect of any more rapid movements. I fear we shall at last find out that the difficulty is in our case rather than in particular generals. I wish to disparage no one certainly not those who sympathize with me; but I must say I need success more than I need sympathy, and that I have not seen the so much greater evidence of getting success from my sympathizers than from those who are denounced as the contrary. It does seem to me that in the field the two classes have been very much alike in what they have done and what they have failed to do. In sealing their faith with their blood, Baker and Lyon and Bohien and Richardson, Republicans, did all that men could do; but did they any more than Kearny and Stevens and Reno and Mansfield, none of whom were Republicans, and some at least of whom have been bitterly and repeatedly denounced to me as secession sympathizers? I will not perform the ungrateful task of comparing cases of failure.
In answer to your question, "Has it not been publicly stated in the newspapers, and apparently proved as a fact, that from the commencement of the war the enemy was continually supplied with information by some of the confidential subordinates of as important an officer as Adjutant-General Thomas?" I must say "No," as far as my knowledge extends. And I add that if you can give any tangible evidence upon the subject, I will thank you to come to this city and do so.
Very truly your friend,
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Falmouth, Virginia:
If I should be in boat off Aquia Creek at dark tomorrow (Wednesday) evening, could you, without inconvenience, meet me and pass an hour or two with me?
November 29, 1862.
HON. ATTORNEY-GENERAL.
MY DEAR SIR:—Few things perplex me more than this question between Governor Gamble and the War Department, as to whether the peculiar force organized by the former in Missouri are State troops or United States troops. Now, this is either an immaterial or a mischievous question. First, if no more is desired than to have it settled what name the force is to be called by, it is immaterial. Secondly, if it is desired for more than the fixing a name, it can only be to get a position from which to draw practical inferences; then it is mischievous. Instead of settling one dispute by deciding the question, I should merely furnish a nest-full of eggs for hatching new disputes. I believe the force is not strictly either "State troops" or "United States troops." It is of mixed character. I therefore think it is safer, when a practical question arises, to decide that question directly, and not indirectly by deciding a general abstraction supposed to include it, and also including a great deal more. Without dispute Governor Gamble appoints the officers of this force, and fills vacancies when they occur. The question now practically in dispute is: Can Governor Gamble make a vacancy by removing an officer or accepting a resignation? Now, while it is proper that this question shall be settled, I do not perceive why either Governor Gamble or the government here should care which way it is settled. I am perplexed with it only because there seems to be pertinacity about it. It seems to me that it might be either way without injury to the service; or that the offer of the Secretary of War to let Governor Gamble make vacancies, and he (the Secretary) to ratify the making of them, ought to be satisfactory.
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, November 30, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, Saint Louis, Missouri:
Frank Blair wants Manter's Thirty-second, Curly's Twenty seventh, Boyd's Twenty-fourth and the Ninth and Tenth Cavalry to go with him down the river. I understand it is with you to decide whether he shall have them and if so, and if also it is consistent with the public service, you will oblige me a good deal by letting him have them.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December 1, 1862.
JUDGE-ADVOCATE-GENERAL.
SIR:—Three hundred Indians have been sentenced to death in Minnesota by a military commission, and execution only awaits my action. I wish your legal opinion whether if I should conclude to execute only a part of them, I must myself designate which, or could I leave the designation to some officer on the ground?
Yours very truly,
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES—Since your last annual assembling another year of health and bountiful harvests has passed; and while it has not pleased the Almighty to bless us with a return of peace, we can but press on, guided by the best light he gives us, trusting that in his own good time and wise way all will yet be well.
The correspondence touching foreign affairs which has taken place during the last year is herewith submitted, in virtual compliance with a request to that effect, made by the House of Representatives near the close of the last session of Congress.
If the condition of our relations with other nations is less gratifying than it has usually been at former periods, it is certainly more satisfactory than a nation so unhappily distracted as we are might reasonably have apprehended. In the month of June last there were some grounds to expect that the maritime powers which, at the beginning of our domestic difficulties, so unwisely and unnecessarily, as we think, recognized the insurgents as a belligerent, would soon recede from that position, which has proved only less injurious to themselves than to our own country. But the temporary reverses which afterward befell the national arms, and which were exaggerated by our own disloyal citizens abroad, have hitherto delayed that act of simple justice.
The civil war, which has so radically changed, for the moment, the occupations and habits of the American people, has necessarily disturbed the social condition, and affected very deeply the prosperity, of the nations with which we have carried on a commerce that has been steadily increasing throughout a period of half a century. It has, at the same time, excited political ambitions and apprehensions which have produced a profound agitation throughout the civilized world. In this unusual agitation we have forborne from taking part in any controversy between foreign states, and between parties or factions in such states. We have attempted no propagandism and acknowledged no revolution, but we have left to every nation the exclusive conduct and management of its own affairs. Our struggle has been, of course, contemplated by foreign nations with reference less to its own merits than to its supposed and often exaggerated effects and consequences resulting to those nations themselves, nevertheless, complaint on the part of this government, even if it were just, would certainly be unwise.
The treaty with Great Britain for the suppression of the slave trade has been put into operation with a good prospect of complete success. It is an occasion of special pleasure to acknowledge that the execution of it on the part of her Majesty's government has been marked with a jealous respect for the authority of the United States and the rights of their moral and loyal citizens.
The convention with Hanover for the abolition of the state dues has been carried into full effect under the act of Congress for that purpose.
A blockade of 3000 miles of seacoast could not be established and vigorously enforced in a season of great commercial activity like the present without committing occasional mistakes and inflicting unintentional injuries upon foreign nations and their subjects.
A civil war occurring in a country where foreigners reside and carry on trade under treaty stipulations is necessarily fruitful of complaints of the violation of neutral rights. All such collisions tend to excite misapprehensions, and possibly to produce mutual reclamations between nations which have a common interest in preserving peace and friendship. In clear cases of these kinds I have so far as possible heard and redressed complaints which have been presented by friendly powers. There is still, however, a large and an augmenting number of doubtful cases upon which the government is unable to agree with the governments whose protection is demanded by the claimants. There are, moreover, many cases in which the United States or their citizens suffer wrongs from the naval or military authorities of foreign nations which the governments of those states are not at once prepared to redress. I have proposed to some of the foreign states thus interested mutual conventions to examine and adjust such complaints. This proposition has been made especially to Great Britain, to France, to Spain, and to Prussia. In each case it has been kindly received, but has not yet been formally adopted.
I deem it my duty to recommend an appropriation in behalf of the owners of the Norwegian bark Admiral P. Tordenskiold, which vessel was in May, 1861, prevented by the commander of the blockading force off Charleston from leaving that port with cargo, notwithstanding a similar privilege had shortly before been granted to an English vessel. I have directed the Secretary of State to cause the papers in the case to be communicated to the proper committees.
Applications have been made to me by many free Americans of African descent to favor their emigration, with a view to such colonization as was contemplated in recent acts of Congress, Other parties, at home and abroad—some from interested motives, others upon patriotic considerations, and still others influenced by philanthropic sentiments—have suggested similar measures, while, on the other hand, several of the Spanish American republics have protested against the sending of such colonies to their respective territories. Under these circumstances I have declined to move any such colony to any state without first obtaining the consent of its government, with an agreement on its part to receive and protect such emigrants in all the rights of freemen; and I have at the same time offered to the several states situated within the Tropics, or having colonies there, to negotiate with them, subject to the advice and consent of the Senate, to favor the voluntary emigration of persons of that class to their respective territories, upon conditions which shall be equal, just, and humane. Liberia and Haiti are as yet the only countries to which colonists of African descent from here could go with certainty of being received and adopted as citizens; and I regret to say such persons contemplating colonization do not seem so willing to migrate to those countries as to some others, nor so willing as I think their interest demands. I believe, however, opinion among them in this respect is improving, and that ere long there will be an augmented and considerable migration to both these countries from the United States.
The new commercial treaty between the United States and the Sultan of Turkey has been carried into execution.
A commercial and consular treaty has been negotiated, subject to the Senate's consent, with Liberia, and a similar negotiation is now pending with the Republic of Haiti. A considerable improvement of the national commerce is expected to result from these measures.
Our relations with Great Britain, France, Spain, Portugal, Russia, Prussia, Denmark, Sweden, Austria, the Netherlands, Italy, Rome, and the other European states remain undisturbed. Very favorable relations also continue to be maintained with Turkey, Morocco, China, and Japan.
During the last year there has not only been no change of our previous relations with the independent states of our own continent, but more friendly sentiments than have heretofore existed are believed to be entertained by these neighbors, whose safety and progress are so intimately connected with our own. This statement especially applies to Mexico, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Honduras, Peru, and Chile.
The commission under the convention with the Republic of New Granada closed its session without having audited and passed upon all the claims which were submitted to it. A proposition is pending to revive the convention, that it may be able to do more complete justice. The joint commission between the United States and the Republic of Costa Rica has completed its labors and submitted its report.
I have favored the project for connecting the United States with Europe by an Atlantic telegraph, and a similar project to extend the telegraph from San Francisco to connect by a Pacific telegraph with the line which is being extended across the Russian Empire.
The Territories of the United States, with unimportant exceptions, have remained undisturbed by the civil war; and they are exhibiting such evidence of prosperity as justifies an expectation that some of them will soon be in a condition to be organized as States and be constitutionally admitted into the Federal Union.
The immense mineral resources of some of those Territories ought to be developed as rapidly as possible. Every step in that direction would have a tendency to improve the revenues of the government and diminish the burdens of the people. It is worthy of your serious consideration whether some extraordinary measures to promote that end cannot be adopted. The means which suggests itself as most likely to be effective is a scientific exploration of the mineral regions in those Territories with a view to the publication of its results at home and in foreign countries—results which cannot fail to be auspicious.
The condition of the finances win claim your most diligent consideration. The vast expenditures incident to the military and naval operations required for the suppression of the rebellion have hitherto been met with a promptitude and certainty unusual in similar circumstances, and the public credit has been fully maintained. The continuance of the war, however, and the increased disbursements made necessary by the augmented forces now in the field demand your best reflections as to the best modes of providing the necessary revenue without injury to business and with the least possible burdens upon labor.
The suspension of specie payments by the banks soon after the commencement of your last session made large issues of United States notes unavoidable. In no other way could the payment of troops and the satisfaction of other just demands be so economically or so well provided for. The judicious legislation of Congress, securing the receivability of these notes for loans and internal duties and making them a legal tender for other debts, has made them an universal currency, and has satisfied, partially at least, and for the time, the long-felt want of an uniform circulating medium, saving thereby to the people immense sums in discounts and exchanges.
A return to specie payments, however, at the earliest period compatible with due regard to all interests concerned should ever be kept in view. Fluctuations in the value of currency are always injurious, and to reduce these fluctuations to the lowest possible point will always be a leading purpose in wise legislation. Convertibility, prompt and certain convertibility, into coin is generally acknowledged to be the best and surest safeguard against them; and it is extremely doubtful whether a circulation of United States notes payable in coin and sufficiently large for the wants of the people can be permanently, usefully, and safely maintained.
Is there, then, any other mode in which the necessary provision for the public wants can be made and the great advantages of a safe and uniform currency secured?
I know of none which promises so certain results and is at the same time so unobjectionable as the organization of banking associations, under a general act of Congress, well guarded in its provisions. To such associations the government might furnish circulating notes, on the security of United States bonds deposited in the treasury. These notes, prepared under the supervision of proper officers, being uniform in appearance and security and convertible always into coin, would at once protect labor against the evils of a vicious currency and facilitate commerce by cheap and safe exchanges.
A moderate reservation from the interest on the bonds would compensate the United States for the preparation and distribution of the notes and a general supervision of the system, and would lighten the burden of that part of the public debt employed as securities. The public credit, moreover, would be greatly improved and the negotiation of new loans greatly facilitated by the steady market demand for government bonds which the adoption of the proposed system would create.
It is an additional recommendation of the measure, of considerable weight, in my judgment, that it would reconcile as far as possible all existing interests by the opportunity offered to existing institutions to reorganize under the act, substituting only the secured uniform national circulation for the local and various circulation, secured and unsecured, now issued by them.
The receipts into the treasury from all sources, including loans and balance from the preceding year, for the fiscal year ending on the 30th June, 1862, were $583,885,247.06, of which sum $49,056,397.62 were derived from customs; $1,795,331.73 from the direct tax; from public lands, $152,203.77; from miscellaneous sources, $931,787.64; from loans in all forms, $529,692,460.50. The remainder, $2,257,065.80, was the balance from last year.
The disbursements during the same period were: For congressional, executive, and judicial purposes, $5,939,009.29; for foreign intercourse, $1,339,710.35; for miscellaneous expenses, including the mints, loans, post-office deficiencies, collection of revenue, and other like charges, $14,129,771.50; for expenses under the Interior Department, $3,102,985.52; under the War Department, $394,368,407.36; under the Navy Department, $42,674,569.69; for interest on public debt, $13,190,324.45; and for payment of public debt, including reimbursement of temporary loan and redemptions, $96,096,922.09; making an aggregate of $570,841,700.25, and leaving a balance in the treasury on the 1st day of July, 1862, of $13,043,546.81.
It should be observed that the sum of $96,096,922.09, expended for reimbursements and redemption of public debt, being included also in the loans made, may be properly deducted both from receipts and expenditures, leaving the actual receipts for the year $487,788,324.97, and the expenditures $474,744,778.16.
Other information on the subject of the finances will be found in the report of the Secretary of the Treasury, to whose statements and views I invite your most candid and considerate attention.
The reports of the Secretaries of War and of the Navy are herewith transmitted. These reports, though lengthy, are scarcely more than brief abstracts of the very numerous and extensive transactions and operations conducted through those departments. Nor could I give a summary of them here upon any principle which would admit of its being much shorter than the reports themselves. I therefore content myself with laying the reports before you and asking your attention to them.
It gives me pleasure to report a decided improvement in the financial condition of the Post-Office Department as compared with several preceding years. The receipts for the fiscal year 1861 amounted to $8,349,296.40, which embraced the revenue from all the States of the Union for three quarters of that year. Notwithstanding the cessation of revenue from the so-called seceded States during the last fiscal year, the increase of the correspondence of the loyal States has been sufficient to produce a revenue during the same year of $8,299,820.90, being only $50,000 less than was derived from all the States of the Union during the previous year. The expenditures show a still more favorable result. The amount expended in 1861 was $13,606,759.11. For the last year the amount has been reduced to $11,125,364.13, showing a decrease of about $2,481,000 in the expenditures as compared with the preceding year, and about $3,750,000 as compared with the fiscal year 1860. The deficiency in the department for the previous year was $4,551,966.98. For the last fiscal year it was reduced to $2,112,814.57. These favorable results are in part owing to the cessation of mail service in the insurrectionary States and in part to a careful review of all expenditures in that department in the interest of economy. The efficiency of the postal service, it is believed, has also been much improved. The Postmaster-General has also opened a correspondence through the Department of State with foreign governments proposing a convention of postal representatives for the purpose of simplifying the rates of foreign postage and to expedite the foreign mails. This proposition, equally important to our adopted citizens and to the commercial interests of this country, has been favorably entertained and agreed to by all the governments from whom replies have been received.
I ask the attention of Congress to the suggestions of the Postmaster-General in his report respecting the further legislation required, in his opinion, for the benefit of the postal service.
The Secretary of the Interior reports as follows in regard to the public lands:
"The public lands have ceased to be a source of revenue. From the 1st July, 1861, to the 30th September, 1862, the entire cash receipts from the sale of lands were $137,476.2—a sum much less than the expenses of our land system during the same period. The homestead law, which will take effect on the 1st of January next, offers such inducements to settlers that sales for cash cannot be expected to an extent sufficient to meet the expenses of the General Land Office and the cost of surveying and bringing the land into market."
The discrepancy between the sum here stated as arising from the sales of the public lands and the sum derived from the same source as reported from the Treasury Department arises, as I understand, from the fact that the periods of time, though apparently were not really coincident at the beginning point, the Treasury report including a considerable sum now which had previously been reported from the Interior, sufficiently large to greatly overreach the sum derived from the three months now reported upon by the Interior and not by the Treasury.
The Indian tribes upon our frontiers have during the past year manifested a spirit of insubordination, and at several points have engaged in open hostilities against the white settlements in their vicinity. The tribes occupying the Indian country south of Kansas renounced their allegiance to the United States and entered into treaties with the insurgents. Those who remained loyal to the United States were driven from the country. The chief of the Cherokees has visited this city for the purpose of restoring the former relations of the tribe with the United States. He alleges that they were constrained by superior force to enter into treaties with the insurgents, and that the United States neglected to furnish the protection which their treaty stipulations required.
In the month of August last the Sioux Indians in Minnesota attacked the settlements in their vicinity with extreme ferocity, killing indiscriminately men, women, and children. This attack was wholly unexpected, and therefore no means of defense had been provided. It is estimated that not less than 800 persons were killed by the Indians, and a large amount of property was destroyed. How this outbreak was induced is not definitely known, and suspicions, which may be unjust, need not to be stated. Information was received by the Indian Bureau from different sources about the time hostilities were commenced that a simultaneous attack was to be made upon white settlements by all the tribes between the Mississippi River and the Rocky Mountains. The State of Minnesota has suffered great injury from this Indian war. A large portion of her territory has been depopulated, and a severe loss has been sustained by the destruction of property. The people of that State manifest much anxiety for the removal of the tribes beyond the limits of the State as a guaranty against future hostilities. The Commissioner of Indian Affairs will furnish full details. I submit for your especial consideration whether our Indian system shall not be remodeled. Many wise and good men have impressed me with the belief that this can be profitably done.
I submit a statement of the proceedings of commissioners, which shows the progress that has been made in the enterprise of constructing the Pacific Railroad. And this suggests the earliest completion of this road, and also the favorable action of Congress upon the projects now pending before them for enlarging the capacities of the great canals in New York and Illinois, as being of vital and rapidly increasing importance to the whole nation, and especially to the vast interior region hereinafter to be noticed at some greater length. I purpose having prepared and laid before you at an early day some interesting and valuable statistical information upon this subject. The military and commercial importance of enlarging the Illinois and Michigan Canal and improving the Illinois River is presented in the report of Colonel Webster to the Secretary of War, and now transmitted to Congress. I respectfully ask attention to it.
To carry out the provisions of the act of Congress of the 15th of May last, I have caused the Department of Agriculture of the United States to be organized.
The Commissioner informs me that within the period of a few months this department has established an extensive system of correspondence and exchanges, both at home and abroad, which promises to effect highly beneficial results in the development of a correct knowledge of recent improvements in agriculture, in the introduction of new products, and in the collection of the agricultural statistics of the different States.
Also, that it will soon be prepared to distribute largely seeds, cereals, plants, and cuttings, and has already published and liberally diffused much valuable information in anticipation of a more elaborate report, which will in due time be furnished, embracing some valuable tests in chemical science now in progress in the laboratory.
The creation of this department was for the more immediate benefit of a large class of our most valuable citizens, and I trust that the liberal basis upon which it has been organized will not only meet your approbation, but that it will realize at no distant day all the fondest anticipations of its most sanguine friends and become the fruitful source of advantage to all our people.
On the 22d day of September last a proclamation was issued by the Executive, a copy of which is herewith submitted.
In accordance with the purpose expressed in the second paragraph of that paper, I now respectfully recall your attention to what may be called "compensated emancipation."
A nation may be said to consist of its territory, its people, and its laws. The territory is the only part which is of certain durability. "One generation passeth away and another generation cometh, but the earth abideth forever." It is of the first importance to duly consider and estimate this ever enduring part. That portion of the earth's surface which is owned and inhabited by the people of the United States is well adapted to be the home of one national family, and it is not well adapted for two or more. Its vast extent and its variety of climate and productions are of advantage in this age for one people, whatever they might have been in former ages. Steam, telegraphs, and intelligence have brought these to be an advantageous combination for one united people.
In the inaugural address I briefly pointed out the total inadequacy of disunion as a remedy for the differences between the people of the two sections. I did so in language which I cannot improve, and which, therefore, I beg to repeat:
"One section of our country believes slavery is right and ought to be extended, while the other believes it is wrong and ought not to be extended. This is the only substantial dispute. The fugitive-slave clause of the Constitution and the laws for the suppression of the foreign slave trade are each as well enforced, perhaps, as any law can ever be in a community where the moral Sense of the people imperfectly supports the law itself. The great body of the people abide by the dry legal obligation in both cases, and a few break over in each. This, I think, cannot be perfectly cured, and it would be worse in both cases after the separation of the sections than before. The foreign slave trade, now imperfectly suppressed, would be ultimately revived without restriction in one section, while fugitive slaves, now only partially surrendered, would not be surrendered at all by the other.
"Physically speaking, we can not separate. We can not remove our respective sections from each other nor build an impassable wall between them. A husband and wife may be divorced and go out of the presence and beyond the reach of each other, but the different parts of our country cannot do this. They cannot but remain face to face, and intercourse, either amicable or hostile, must continue between them. Is it possible, then, to make that intercourse more advantageous or more satisfactory after separation than before? Can aliens make treaties easier than friends can make laws? Can treaties be more faithfully enforced between aliens than laws can among friends? Suppose you go to war, you cannot fight always; and when, after much loss on both sides and no gain on either, you cease fighting, the identical old questions, as to terms of intercourse, are again upon you."
There is no line, straight or crooked, suitable for a national boundary upon which to divide. Trace through, from east to west, upon the line between the free and slave country, and we shall find a little more than one third of its length are rivers, easy to be crossed, and populated, or soon to be populated, thickly upon both sides; while nearly all its remaining length are merely surveyors' lines, over which people may walk back and forth without any consciousness of their presence. No part of this line can be made any more difficult to pass by writing it down on paper or parchment as a national boundary. The fact of separation, if it comes, gives up on the part of the seceding section the fugitive-slave clause along with all other constitutional obligations upon the section seceded from, while I should expect no treaty stipulation would ever be made to take its place.
But there is another difficulty. The great interior region bounded east by the Alleghenies, north by the British dominions, west by the Rocky Mountains, and south by the line along which the culture of corn and cotton meets, and which includes part of Virginia, part of Tennessee, all of Kentucky, Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Iowa, Minnesota, and the Territories of Dakota, Nebraska, and part of Colorado, already has above 10,000,000 people, and will have 50,000,000 within fifty years if not prevented by any political folly or mistake. It contains more than one third of the country owned by the United States—certainly more than 1,000,000 square miles. Once half as populous as Massachusetts already is, it would have more than 75,000,000 people. A glance at the map shows that, territorially speaking, it is the great body of the Republic. The other parts are but marginal borders to it, the magnificent region sloping west from the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific being the deepest and also the richest in undeveloped resources. In the production of provisions, grains, grasses, and all which proceed from them this great interior region is naturally one of the most important in the world. Ascertain from statistics the small proportion of the region which has yet been brought into cultivation, and also the large and rapidly increasing amount of products, and we shall be overwhelmed with the magnitude of the prospect presented. And yet this region has no seacoast—touches no ocean anywhere. As part of one nation, its people now find, and may forever find, their way to Europe by New York, to South America and Africa by New Orleans, and to Asia by San Francisco; but separate our common country into two nations, as designed by the present rebellion, and every man of this great interior region is thereby cut off from some one or more of these outlets, not perhaps by a physical barrier, but by embarrassing and onerous trade regulations.
And this is true, wherever a dividing or boundary line may be fixed. Place it between the now free and slave country, or place it south of Kentucky or north of Ohio, and still the truth remains that none south of it can trade to any port or place north of it, and none north of it can trade to any port or place south of it, except upon terms dictated by a government foreign to them. These outlets, east, west, and south, are indispensable to the well-being of the people inhabiting and to inhabit this vast interior region. Which of the three may be the best is no proper question. All are better than either, and all of right belong to that people and to their successors forever. True to themselves, they will not ask where a line of separation shall be, but will vow rather that there shall be no such line.
Nor are the marginal regions less interested in these communications to and through them to the great outside world. They, too, and each of them, must have access to this Egypt of the West without paying toll at the crossing of any national boundary.
Our national strife springs not from our permanent part; not from the land we inhabit; not from our national homestead. There is no possible severing of this but would multiply and not mitigate evils among us. In all its adaptations and aptitudes it demands union and abhors separation. In fact, it would ere long force reunion, however much of blood and treasure the separation might have cost.
Our strife pertains to ourselves—to the passing generations of men—and it can without convulsion be hushed forever with the passing of one generation.
In this view I recommend the adoption of the following resolution and articles amendatory to the Constitution of the United States:
Resolved by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America, in Congress assembled, (two thirds of both Houses concurring), That the following articles be proposed to the Legislatures (or conventions) of the several States as amendments to the Constitution of the United States, all or any of which articles, when ratified by three fourths of the said Legislatures (or conventions), to be valid as part or parts of the said Constitution, viz.
ART.—Every State wherein slavery now exists which shall abolish the same therein at any time or times before the 1st day of January, A.D. 1900, shall receive compensation from the United States as follows, to wit:
The President of the United States shall deliver to every such State bonds of the United States bearing interest at the rate of — per cent. per annum to an amount equal to the aggregate sum of ——— for each slave shown to have been therein by the Eighth Census of the United States, said bonds to be delivered to such State by instalments or in one parcel at the completion of the abolishment, accordingly as the same shall have been gradual or at one time within such State; and interest shall begin to run upon any such bond only from the proper time of its delivery as aforesaid. Any State having received bonds as aforesaid and afterwards reintroducing or tolerating slavery therein shall refund to the United States the bonds so received, or the value thereof, and all interest paid thereon.
ART.—All slaves who shall have enjoyed actual freedom by the chances of the war at any time before the end of the rebellion shall be forever free; but all owners of such who shall not have been disloyal shall be compensated for them at the same rates as is provided for States adopting abolishment of slavery, but in such way that no slave shall be twice accounted for.
ART.—Congress may appropriate money and otherwise provide for colonizing free colored persons with their own consent at any place or places without the United States.
I beg indulgence to discuss these proposed articles at some length. Without slavery the rebellion could never have existed; without slavery it could not continue.
Among the friends of the Union there is great diversity of sentiment and of policy in regard to slavery and the African race amongst us. Some would perpetuate slavery; some would abolish it suddenly and without compensation; some would abolish it gradually and with compensation; some would remove the freed people from us, and some would retain them with us; and there are yet other minor diversities. Because of these diversities we waste much strength in struggles among ourselves. By mutual concession we should harmonize and act together. This would be compromise, but it would be compromise among the friends and not with the enemies of the Union. These articles are intended to embody a plan of such mutual concessions. If the plan shall be adopted, it is assumed that emancipation will follow, at least in several of the States.
As to the first article, the main points are, first, the emancipation; secondly, the length of time for consummating it (thirty-seven years); and, thirdly, the compensation.
The emancipation will be unsatisfactory to the advocates of perpetual slavery, but the length of time should greatly mitigate their dissatisfaction. The time spares both races from the evils of sudden derangement—in fact, from the necessity of any derangement—while most of those whose habitual course of thought will be disturbed by the measure will have passed away before its consummation. They will never see it. Another class will hail the prospect of emancipation, but will deprecate the length of time. They will feel that it gives too little to the now living slaves. But it really gives them much. It saves them from the vagrant destitution which must largely attend immediate emancipation in localities where their numbers are very great, and it gives the inspiring assurance that their posterity shall be free forever. The plan leaves to each State choosing to act under it to abolish slavery now or at the end of the century, or at any intermediate tune, or by degrees extending over the whole or any part of the period, and it obliges no two States to proceed alike. It also provides for compensation, and generally the mode of making it. This, it would seem, must further mitigate the dissatisfaction of those who favor perpetual slavery, and especially of those who are to receive the compensation. Doubtless some of those who are to pay and not to receive will object. Yet the measure is both just and economical. In a certain sense the liberation of slaves is the destruction of property—property acquired by descent or by purchase, the same as any other property. It is no less true for having been often said that the people of the South are not more responsible for the original introduction of this property than are the people of the North; and when it is remembered how unhesitatingly we all use cotton and sugar and share the profits of dealing in them, it may not be quite safe to say that the South has been more responsible than the North for its continuance. If, then, for a common object this property is to be sacrificed, is it not just that it be done at a common charge?
And if with less money, or money more easily paid, we can preserve the benefits of the Union by this means than we can by the war alone, is it not also economical to do it? Let us consider it, then. Let us ascertain the sum we have expended in the war Since compensated emancipation was proposed last March, and consider whether if that measure had been promptly accepted by even some of the slave States the same sum would not have done more to close the war than has been otherwise done. If so, the measure would save money, and in that view would be a prudent and economical measure. Certainly it is not so easy to pay something as it is to pay nothing, but it is easier to pay a large sum than it is to pay a larger one. And it is easier to pay any sum when we are able than it is to pay it before we are able. The war requires large sums, and requires them at once. The aggregate sum necessary for compensated emancipation of course would be large. But it would require no ready cash, nor the bonds even any faster than the emancipation progresses. This might not, and probably would not, close before the end of the thirty-seven years. At that time we shall probably have a hundred millions of people to share the burden, instead of thirty-one millions as now. And not only so, but the increase of our population may be expected to continue for a long time after that period as rapidly as before, because our territory will not have become full. I do not state this inconsiderately. At the same ratio of increase which we have maintained, on an average, from our first national census, in 1790, until that of 1860, we should in 1900 have a population of 103,208,415. And why may we not continue that ratio far beyond that period? Our abundant room, our broad national homestead, is our ample resource. Were our territory as limited as are the British Isles, very certainly our population could not expand as stated. Instead of receiving the foreign born as now, we should be compelled to send part of the native born away. But such is not our condition. We have 2,963,000 square miles. Europe has 3,800,000, with a population averaging 73 persons to the square mile. Why may not our country at some time average as many? Is it less fertile? Has it more waste surface by mountains, rivers, lakes, deserts, or other causes? Is it inferior to Europe in any natural advantage? If, then, we are at some time to be as populous as Europe, how soon? As to when this may be, we can judge by the past and the present; as to when it will be, if ever, depends much on whether we maintain the Union...............
[a page of tables of projected statistics]
These figures show that our country may be as populous as Europe now is at some point between 1920 and 1930, say about 1925—our territory, at 73 persons to the square mile, being of capacity to contain 217,186,000.
And we will reach this, too, if we do not ourselves relinquish the chance by the folly and evils of disunion or by long and exhausting war springing from the only great element of national discord among us. While it cannot be foreseen exactly how much one huge example of secession, breeding lesser ones indefinitely, would retard population, civilization, and prosperity, no one can doubt that the extent of it would be very great and injurious.
The proposed emancipation would shorten the war, perpetuate peace, insure this increase of population, and proportionately the wealth of the country. With these we should pay all the emancipation would cost, together with our other debt, easier than we should pay our other debt without it. If we had allowed our old national debt to run at six per cent. per annum, simple interest, from the end of our revolutionary struggle until to-day, without paying anything on either principal or interest, each man of us would owe less upon that debt now than each man owed upon it then; and this because our increase of men through the whole period has been greater than six per cent.—has run faster than the interest upon the debt. Thus time alone relieves a debtor nation, so long as its population increases faster than unpaid interest accumulates on its debt.
This fact would be no excuse for delaying payment of what is justly due, but it shows the great importance of time in this connection—the great advantage of a policy by which we shall not have to pay until we number 100,000,000 what by a different policy we would have to pay now, when we number but 31,000,000. In a word, it shows that a dollar will be much harder to pay for the war than will be a dollar for emancipation on the proposed plan. And then the latter will cost no blood, no precious life. It will be a saving of both.
As to the second article, I think it would be impracticable to return to bondage the class of persons therein contemplated. Some of them, doubtless, in the property sense belong to loyal owners, and hence Provision is made in this article for compensating such.
The third article relates to the future of the freed people. It does not oblige, but merely authorizes Congress to aid in colonizing such as may consent. This ought nut to be regarded as objectionable on the one hand or on the other, insomuch as it comes to nothing unless by the mutual consent of the people to be deported and the American voters through their representatives in Congress.
I cannot make it better known than it already is that I strongly favor colonization; and yet I wish to say there is an objection urged against free colored persons remaining in the country which is largely imaginary, if not sometimes malicious.
It is insisted that their presence would injure and displace white labor and white laborers. If there ever could be a proper time for mere catch arguments that time surely is not now. In times like the present men should utter nothing for which they would not willingly be responsible through time and in eternity. Is it true, then, that colored people can displace any more white labor by being free than by remaining slaves? If they stay in their old places, they jostle no white laborers; if they leave their old places, they leave them open to white laborers. Logically, there is neither more nor less of it. Emancipation, even without deportation, would probably enhance the wages of white labor, and very surely would not reduce them. Thus the customary amount of labor would still have to be performed. The freed people would surely not do more than their old proportion of it, and very probably for a time would do less, leaving an increased part to white laborers, bringing their labor into greater demand, and consequently enhancing the wages of it. With deportation, even to a limited extent, enhanced wages to white labor is mathematically certain. Labor is like any other commodity in the market-increase the demand for it and you increase the price of it. Reduce the supply of black labor by colonizing the black laborer out of the country, and by precisely so much you increase the demand for and wages of white labor.
But it is dreaded that the freed people will swarm forth and cover the whole land. Are they not already in the land? Will liberation make them any more numerous? Equally distributed among the whites of the whole country, and there would be but one colored to seven whites. Could the one in any way greatly disturb the seven? There are many communities now having more than one free colored person to seven whites, and this without any apparent consciousness of evil from it. The District of Columbia and the States of Maryland and Delaware are all in this condition. The District has more than one free colored to six whites, and yet in its frequent petitions to Congress I believe it has never presented the presence of free colored persons as one of its grievances. But why should emancipation South send the free people North? People of any color seldom run unless there be something to run from. Heretofore colored people to some extent have fled North from bondage, and now, perhaps, from both bondage and destitution. But if gradual emancipation and deportation be adopted, they will have neither to flee from. Their old masters will give them wages at least until new laborers can be procured, and the freedmen in turn will gladly give their labor for the wages till new homes can be found for them in congenial climes and with people of their own blood and race. This proposition can be trusted on the mutual interests involved. And in any event, cannot the North decide for itself whether to receive them?
Again, as practice proves more than theory in any case, has there been any irruption of colored people northward because of the abolishment of slavery in this District last spring?
What I have said of the proportion of free colored persons to the whites in the District is from the census of 1860, having no reference to persons called contrabands nor to those made free by the act of Congress abolishing slavery here.
The plan consisting of these articles is recommended, not but that a restoration of the national authority would be accepted without its adoption.
Nor will the war nor proceedings under the proclamation of September 22, 1862, be stayed because of the recommendation of this plan. Its timely adoption, I doubt not, would bring restoration, and thereby stay both.
And notwithstanding this plan, the recommendation that Congress provide by law for compensating any State which may adopt emancipation before this plan shall have been acted upon is hereby earnestly renewed. Such would be only an advance part of the plan, and the same arguments apply to both.
This plan is recommended as a means, not in exclusion of, but additional to, all others for restoring and preserving the national authority throughout the Union. The subject is presented exclusively in its economical aspect. The plan would, I am confident, secure peace more speedily and maintain it more permanently than can be done by force alone, while all it would cost, considering amounts and manner of payment and times of payment, would be easier paid than will be the additional cost of the war if we rely solely upon force. It is much, very much, that it would cost no blood at all.
The plan is proposed as permanent constitutional law. It cannot become such without the concurrence of, first, two thirds of Congress, and afterwards three fourths of the States. The requisite three fourths of the States will necessarily include seven of the slave States. Their concurrence, if obtained, will give assurance of their severally adopting emancipation at no very distant day upon the new constitutional terms. This assurance would end the struggle now and save the Union forever.
I do not forget the gravity which should characterize a paper addressed to the Congress of the nation by the chief magistrate of the nation, nor do I forget that some of you are my seniors, nor that many of you have more experience than I in the conduct of public affairs. Yet I trust that in view of the great responsibility resting upon me you will perceive no want of respect to yourselves in any undue earnestness I may seem to display.
Is it doubted, then, that the plan I propose, if adopted, would shorten the war, and thus lessen its expenditure of money and of blood? Is it doubted that it would restore the national authority and national prosperity and perpetuate both indefinitely? Is it doubted that we here—Congress and executive—can secure its adoption? Will not the good people respond to a united and earnest appeal from us? Can we, can they, by any other means so certainly or so speedily assure these vital objects? We can succeed only by concert. It is not "Can any of us imagine better?" but "Can we all do better?" Object whatsoever is possible, still the question recurs, "Can we do better?" The dogmas of the quiet past are inadequate to the stormy present. The occasion is piled high with difficulty, and we must rise with the occasion. As our case is new, so we must think anew and act anew. We must disenthrall ourselves, and then we shall save our country.
Fellow-citizens, we can not escape history. We of this Congress and this administration will be remembered in spite of ourselves. No personal significance or insignificance can spare one or another of us. The fiery trial through which we pass will light us down in honor or dishonor to the latest generation. We say we are for the Union. The world will not forget that we say this. We know how to save the Union. The world knows we do know how to save it. We, even we here, hold the power and bear the responsibility. In giving freedom to the slave we assure freedom to the free—honorable alike in what we give and what we preserve. We shall nobly save or meanly lose the last, best hope of earth. Other means may succeed; this could not fail. The way is plain, peaceful, generous, just—a way which if followed the world will forever applaud and God must forever bless.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
On the 3d of November, 1861, a collision took place off the coast of Cuba between the United States war steamer San Jacinto and the French brig Jules et Marie, resulting in serious damage to the latter. The obligation of this Government to make amends therefor could not be questioned if the injury resulted from any fault On the part of the San Jacinto. With a view to ascertain this, the subject was referred to a commission of the United States and French naval officers at New York, with a naval officer of Italy as an arbiter. The conclusion arrived at was that the collision was occasioned by the failure of the San Jacinto seasonably to reverse her engine. It then became necessary to ascertain the amount of indemnification due to the injured party. The United States consul-general at Havana was consequently instructed to confer with the consul of France on this point, and they have determined that the sum of $9,500 is an equitable allowance under the circumstances.
I recommend an appropriation of this sum for the benefit of the owners of the Jules et Marie.
A copy of the letter of Mr. Shufeldt, the consul-general of the United States at Havana, to the Secretary of State on the subject is herewith transmitted.
December 7, 1862.
Hon. H. J. RAYMOND, Times Office, New York:
Yours of November 25 reached me only yesterday. Thank you for it. I shall consider and remember your suggestions.
HON. B. GRATZ BROWN, Saint Louis, Missouri:
Yours of the 3d received yesterday. Have already done what I can in the premises.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December 8, 1862. GOVERNOR ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn.:
Jesse H. Strickland is here asking authority to raise a regiment of Tennesseeans. Would you advise that the authority be given him?
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In conformity to the law of July 16, 1862, I most cordially recommend, that Commander John L. Worden, United States Navy, receive a vote of thanks of Congress for the eminent skill and gallantry exhibited by him in the late remarkable battle between the United States ironclad steamer Monitor, under his command, and the rebel ironclad steamer Merrimac, in March last.
The thanks of Congress for his services on the occasion referred to were tendered by a resolution approved July 11, 1862, but the recommendation is now specially made in order to comply with the requirements of the ninth section of the act of July 16, 1862, which is in the following words, viz.:
"That any line officer of the navy or marine corps may be advanced one grade if upon recommendation of the President by name he receives the thanks of Congress for highly distinguished conduct in conflict with the enemy or for extraordinary heroism in the line of his profession."
December 10, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, St. Louis, Missouri:
Please suspend, until further order, all proceeding on the order made by General Schofield, on the twenty-eighth day of August last, for assessing and collecting from secessionists and Southern sympathizers the sum of five hundred thousand dollars, etc., and in the meantime make out and send me a statement of facts pertinent to the question, together with your opinion upon it.
December 10, 1862.
Hon. J. K. DuBois.
MY DEAR SIR:—In the summer of 1859, when Mr. Freeman visited Springfield, Illinois, in relation to the McCallister and Stebbins bonds I promised him that, upon certain conditions, I would ask members of the Legislature to give him a full and fair hearing of his case. I do not now remember, nor have I time to recall, exactly what the conditions were, nor whether they were completely performed; but there can be in no case any harm [in] his having a full and fair hearing, and I sincerely wish it may be given him.
Yours truly,
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
In compliance with your resolution of December 5, 1862, requesting the President "to furnish the Senate with all information in his possession touching the late Indian barbarities in the State of Minnesota, and also the evidence in his possession upon which some of the principal actors and head men were tried and condemned to death," I have the honor to state that on receipt of said resolution, I transmitted the same to the Secretary of the Interior, accompanied by a note, a copy of which is herewith inclosed, marked A, and in response to which I received, through that department, a letter of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, a copy of which is herewith inclosed, marked B.
I further state that on the eighth day of November last I received a long telegraphic despatch from Major-General Pope, at St. Paul, Minnesota, simply announcing the names of the persons sentenced to be hanged. I immediately telegraphed to have transcripts of the records in all cases forwarded to me, which transcripts, however, did not reach me until two or three days before the present meeting of Congress. Meantime I received, through telegraphic despatches and otherwise, appeals in behalf of the condemned, appeals for their execution, and expressions of opinion as to the proper policy in regard to them and to the Indians generally in that vicinity, none of which, as I understand, falls within the scope of your inquiry. After the arrival of the transcripts of records, but before I had sufficient opportunity to examine them, I received a joint letter from one of the senators and two of the representatives from Minnesota, which contains some statements of fact not found in the records of the trials, and for which reason I herewith transmit a copy, marked C. I also, for the same reason, inclose a printed memorial of the citizens of St. Paul, addressed to me, and forwarded with the letter aforesaid.
Anxious to not act with so much clemency as to encourage another outbreak on the one hand, nor with so much severity as to be real cruelty on the other, I caused a careful examination of the records of trials to be made, in view of first ordering the execution of such as had been proved guilty of violating females. Contrary to my expectation, only two of this class were found. I then directed a further examination and a classification of all who were proven to have participated in massacres, as distinguished from participation in battles. This class numbered forty, and included the two convicted of female violation. One of the number is strongly recommended, by the commission which tried them, for commutation to ten years imprisonment I have ordered the other thirty-nine to be executed on Friday the 19th instant. The order was despatched from here on Monday, the 8th instant, by a messenger to General Sibley, and a copy of which order is herewith transmitted, marked D.
An abstract of the evidence as to the forty is herewith inclosed, marked E.
To avoid the immense amount of copying, I lay before the Senate the original transcripts of the records of trials, as received by me.
This is as full and complete a response to the resolution as it is in my power to make.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I have in my possession three valuable swords, formerly the property of General David E. Twiggs, which I now place at the disposal of Congress. They are forwarded to me from New Orleans by Major-General Benjamin F. Butler. If they or any of them shall be by Congress disposed of in reward or compliment of military service, I think General Butler is entitled to the first consideration. A copy of the General's letter to me accompanying the swords is herewith transmitted.
HON. FERNANDO WOOD.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter of the 8th, with the accompanying note of same date, was received yesterday. The most important paragraph in the letter, as I consider, is in these words:
"On the 25th of November last I was advised by an authority which I deemed likely to be well informed, as well as reliable and truthful, that the Southern States would send representatives to the next Congress, provided that a full and general amnesty should permit them to do so. No guarantee or terms were asked for other than the amnesty referred to."
I strongly suspect your information will prove to be groundless; nevertheless, I thank you for communicating it to me. Understanding the phrase in the paragraph just quoted—"the Southern States would send representatives to the next Congress"—to be substantially the same as that "the people of the Southern States would cease resistance, and would reinaugurate, submit to, and maintain the national authority within the limits of such States, under the Constitution of the United States," I say that in such case the war would cease on the part of the United States; and that if within a reasonable time "a full and general amnesty" were necessary to such end, it would not be withheld.
I do not think it would be proper now to communicate this, formally or informally, to the people of the Southern States. My belief is that they already know it; and when they choose, if ever, they can communicate with me unequivocally. Nor do I think it proper now to suspend military operations to try any experiment of negotiation.
I should nevertheless receive with great pleasure the exact information you now have, and also such other as you may in any way obtain. Such information might be more valuable before the 1st of January than afterwards.
While there is nothing in this letter which I shall dread to see in history, it is, perhaps, better for the present that its existence should not become public. I therefore have to request that you will regard it as confidential.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, St. Louis, Missouri:
If my friend Dr. William Fithian, of Danville, Ill., should call on YOU, please give him such facilities as you consistently can about recovering the remains of a step-son, and matters connected therewith.
BRIG. GEN. H. H. SIBLEY, Saint Paul, Minn.:
As you suggest, let the executions fixed for Friday the 19th instant be postponed to, and be done on, Friday the 26th instant.
A. LINCOLN. (Private.) Operator please send this very carefully and accurately. A. L.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, Saint Louis, Missouri:
N. W. Watkins, of Jackson, Mo., (who is half brother to Henry Clay), writes me that a colonel of ours has driven him from his home at Jackson. Will you please look into the case and restore the old man to his home if the public interest will admit?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Falmouth:
Your despatch about General Stahel is received. Please ascertain from General Sigel and his old corps whether Stahel or Schurz is preferable and telegraph the result, and I will act immediately. After all I shall be governed by your preference.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS:
Could the civil authority be reintroduced into Missouri in lieu of the military to any extent, with advantage and safety?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE
George Patten says he was a classmate of yours and was in the same regiment of artillery. Have you a place you would like to put him in? And if so what is it?
GOVERNOR GAMBLE, Saint Louis, MO.:
It is represented to me that the enrolled militia alone would now maintain law and order in all the counties of your State north of the Missouri River. If so all other forces there might be removed south of the river, or out of the State. Please post yourself and give me your opinion upon the subject.
December 19, 1862.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Hon. W. A. Hall, member of Congress here, tells me, and Governor Gamble telegraphs me; that quiet can be maintained in all the counties north of the Missouri River by the enrolled militia. Confer with Governor Gamble and telegraph me.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE:
Come, of course, if in your own judgment it is safe to do so.
December 20, 1862.
HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD AND HON. SALMON P. CHASE.
GENTLEMEN:—You have respectively tendered me your resignations as Secretary of State and Secretary of the Treasury of the United States. I am apprised of the circumstances which may render this course personally desirable to each of you; but after most anxious consideration my deliberate judgment is that the public interest does not admit of it. I therefore have to request that you will resume the duties of your departments respectively.
Your obedient servant,
GOVERNOR ANDREW, Boston, Mass.:
Neither the Secretary of War nor I know anything except what you tell us about the "published official document" you mention.
HON. T. J. HENDERSON.
DEAR SIR:-Your letter of the 8th to Hon. William Kellogg has just been shown me. You can scarcely overestimate the pleasure it would give me to oblige you, but nothing is operating so ruinously upon us everywhere as "absenteeism." It positively will not do for me to grant leaves of absence in cases not sufficient to procure them under the regular rules.
It would astonish you to know the extent of the evil of "absenteeism." We scarcely have more than half the men we are paying on the spot for service anywhere.
Yours very truly,
December 22, 1862.
TO THE ARMY OF THE POTOMAC:
I have just read your general's report of the battle of Fredericksburg. Although you were not successful, the attempt was not an error, nor the failure other than accident. The courage with which you, in an open field, maintained the contest against an intrenched foe, and the consummate skill and success with which you crossed and recrossed the river in the face of the enemy, show that you possess all the qualities of a great army, which will yet give victory to the cause of the country and of popular government.
Condoling with the mourners for the dead, and sympathizing with the severely wounded, I congratulate you that the number of both is comparatively so small.
I tender to you, officers and soldiers, the thanks of the nation.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December, 23, 1862.
DEAR FANNY:—It is with deep regret that I learn of the death of your kind and brave father, and especially that it is affecting your young heart beyond what is common in such cases. In this sad world of ours sorrow comes to all, and to the young it comes with bittered agony because it takes them unawares.
The older have learned ever to expect it. I am anxious to afford some alleviation of your present distress, perfect relief is not possible, except with time. You cannot now realize that you will ever feel better. Is not this so? And yet it is a mistake. You are sure to be happy again. To know this, which is certainly true, will make you some less miserable now. I have had experience enough to know what I say, and you need only to believe it to feel better at once. The memory of your dear father, instead of an agony, will yet be a sad, sweet feeling in your heart, of a purer and holier sort than you have known before.
Please present my kind regards to your afflicted mother.
Your sincere friend,
HONORABLE SECRETARY OF WAR.
Sir:—Two Ohio regiments and one Illinois regiment which were captured at Hartsville have been paroled and are now at Columbus, Ohio. This brings the Ohio regiments substantially to their homes. I am strongly impressed with the belief that the Illinois regiment better be sent to Illinois, where it will be recruited and put in good condition by the time they are exchanged so as to re-enter the service. They did not misbehave, as I am satisfied, so that they should receive no treatment nor have anything withheld from them by way of punishment.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Let the order in regard to Dr. McPheeters and family be suspended until you hear from me.
HIS EXCELLENCY GOVERNOR GAMBLE:
I do not wish to leave the country north of the Missouri to the care of the enrolled militia except upon the concurrent judgment of yourself and General Curtis. His I have not yet obtained. Confer with him, and I shall be glad to act when you and he agree.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE:
I have good reason for saying you must not make a general movement of the army without letting me know.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe, Va.:
I hear not a word about the Congressional election of which you and I corresponded. Time clearly up.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December 31, 1862.
HON. H. J. RAYMOND:
The proclamation cannot be telegraphed to you until during the day to-morrow.
JNO. G. NICOLAY.
[Same to Horace Greeley]
A Proclamation.
Whereas on the 22d day of September, A.D. 1862, a proclamation was issued by the President of the United States, containing, among other things, the following, to wit:
"That on the 1st day of January, A.D., 1863, all persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free; and the executive government of the United States, including the military and naval authority thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of such persons and will do no act or acts to repress such persons, or any of them, in any efforts they may make for their actual freedom.
"That the executive will on the 1st day of January aforesaid, by proclamation, designate the States and parts of States, if any, in which the people thereof, respectively, shall then be in rebellion against the United States; and the fact that any State or the people thereof shall on that day be in good faith represented in the Congress of the United States by members chosen thereto at elections wherein a majority of the qualified voters of such States shall have participated shall, in the absence of strong countervailing testimony, be deemed conclusive evidence that such State and the people thereof are not then in rebellion against the United States."
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, by virtue of the power in me vested as Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States in time of actual armed rebellion against the authority and government of the United States, and as a fit and necessary war measure for suppressing said rebellion, do, on this 1st day of January, A. D. 1863, and in accordance with my purpose so to do, publicly proclaimed for the full period of one hundred days from the first day above mentioned, order and designate as the States and parts of States wherein the people thereof, respectively, are this day in rebellion against the United States the following, to wit:
Arkansas, Texas, Louisiana (except the parishes of St. Bernard, Plaquemines, Jefferson, St. John, St. Charles, St. James, Ascension, Assumption, Terre Bonne, Lafourche, St. Mary, St. Martin, and Orleans, including the city of New Orleans), Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia (except the forty-eight counties designated as West Virginia, and also the counties of Berkeley, Accomac, Northampton, Elizabeth City, York, Princess Anne, and Norfolk, including the cities of Norfolk and Portsmouth), and which excepted parts are for the present left precisely as if this proclamation were not issued.
And by virtue of the power and for the purpose aforesaid, I do order and declare that all persons held as slaves within said designated States and parts of States are, and henceforward shall be, free; and that the Executive Government of the United States, including the military and naval authorities thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of said persons.
And I hereby enjoin upon the people so declared to be free to abstain from all violence, unless in necessary self-defense; and I recommend to them that, in all cases when allowed, they labor faithfully for reasonable wages.
And I further declare and make known that such persons of suitable condition will be received into the armed service of the United States to garrison forts, positions, stations, and other places, and to man vessels of all sorts in said service.
And upon this act, sincerely believed to be an act of justice, warranted by the Constitution upon military necessity, I invoke the considerate judgment of mankind and the gracious favor of Almighty God.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this first day of January, A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK.
DEAR SIR:—General Burnside wishes to cross the Rappahannock with his army, but his grand division commanders all oppose the movement. If in such a difficulty as this you do not help, you fail me precisely in the point for which I sought your assistance You know what General Burnside's plan is, and it is my wish that you go with him to the ground, examine it as far as practicable, confer with the officers, getting their judgment, and ascertaining their temper—in a word, gather all the elements for forming a judgment of your own, and then tell General Burnside that you do approve or that you do not approve his plan. Your military skill is useless to me if you will not do this.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN
[Indorsement]
January 1, 1863 Withdrawn, because considered harsh by General Halleck.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I submit to Congress the expediency of extending to other departments of the government the authority conferred on the President by the eighth section of the act of the 8th of May, 1792, to appoint a person to temporarily discharge the duties of Secretary of State, Secretary of the Treasury, and Secretary of War, in case of the death, absence from the seat of government, or sickness of either of those officers.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of December 29 by the hand of Mr. Strong is just received. The day I telegraphed you suspending the order in relation to Dr. McPheeters, he, with Mr. Bates, the Attorney-General, appeared before me and left with me a copy of the order mentioned. The doctor also showed me the Copy of an oath which he said he had taken, which is indeed very strong and specific. He also verbally assured me that he had constantly prayed in church for the President and government, as he had always done before the present war. In looking over the recitals in your order, I do not see that this matter of the prayer, as he states it, is negatived, nor that any violation of his oath is charged nor, in fact, that anything specific is alleged against him. The charges are all general: that he has a rebel wife and rebel relations, that he sympathies with rebels, and that he exercises rebel influence. Now, after talking with him, I tell you frankly I believe he does sympathize with the rebels, but the question remains whether such a man, of unquestioned good moral character, who has taken such an oath as he has, and cannot even be charged with violating it, and who can be charged with no other specific act or omission, can, with safety to the government, be exiled upon the suspicion of his secret sympathies. But I agree that this must be left to you, who are on the spot; and if, after all, you think the public good requires his removal, my suspension of the order is withdrawn, only with this qualification, that the time during the suspension is not to be counted against him. I have promised him this. But I must add that the United States Government must not, as by this order, undertake to run the churches. When an individual in a church or out of it becomes dangerous to the public interest, he must be checked; but let the churches, as such, take care of themselves. It will not do for the United States to appoint trustees, supervisors, or other agents for the churches.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—The committee composed of Messrs. Yeatman and Filley (Mr. Broadhead not attending) has presented your letter and the memorial of sundry citizens. On the whole subject embraced exercise your best judgment, with a sole view to the public interest, and I will not interfere without hearing you.
A. LINCOLN., January 3, 1863.
HON. GIDEON WELLES, Secretary of the Navy.
DEAR SIR:—As many persons who come well recommended for loyalty and service to the Union cause, and who are refugees from rebel oppression in the State of Virginia, make application to me for authority and permission to remove their families and property to protection within the Union lines, by means of our armed gunboats on the Potomac River and Chesapeake Bay, you are hereby requested to hear and consider all such applications, and to grant such assistance to this class of persons as in your judgment their merits may render proper, and as may in each case be consistent with the perfect and complete efficiency of the naval service and with military expediency.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am having a good deal of trouble with Missouri matters, and I now sit down to write you particularly about it. One class of friends believe in greater severity and another in greater leniency in regard to arrests, banishments, and assessments. As usual in such cases, each questions the other's motives. On the one hand, it is insisted that Governor Gamble's unionism, at most, is not better than a secondary spring of action; that hunkerism and a wish for political influence stand before Unionism with him. On the other hand, it is urged that arrests, banishments, and assessments are made more for private malice, revenge, and pecuniary interest than for the public good. This morning I was told, by a gentleman who I have no doubt believes what he says, that in one case of assessments for $10,000 the different persons who paid compared receipts, and found they had paid $30,000. If this be true, the inference is that the collecting agents pocketed the odd $20,000. And true or not in the instance, nothing but the sternest necessity can justify the making and maintaining of a system so liable to such abuses. Doubtless the necessity for the making of the system in Missouri did exist, and whether it continues for the maintenance of it is now a practical and very important question. Some days ago Governor Gamble telegraphed me, asking that the assessments outside of St. Louis County might be suspended, as they already have been within it, and this morning all the members of Congress here from Missouri but one laid a paper before me asking the same thing. Now, my belief is that Governor Gamble is an honest and true man, not less so than yourself; that you and he could confer together on this and other Missouri questions with great advantage to the public; that each knows something which the other does not; and that acting together you could about double your stock of pertinent information. May I not hope that you and he will attempt this? I could at once safely do (or you could safely do without me) whatever you and he agree upon. There is absolutely no reason why you should not agree.
Yours as ever,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—I forgot to say that Hon. James S. Rollins, member of Congress from one of the Missouri districts, wishes that, upon his personal responsibility, Rev. John M. Robinson, of Columbia, Missouri; James L. Matthews, of Boone County, Missouri; and James L. Stephens, also of Boone County, Missouri, may be allowed to return to their respective homes. Major Rollins leaves with me very strong papers from the neighbors of these men, whom he says he knows to be true men. He also says he has many constituents who he thinks are rightly exiled, but that he thinks these three should be allowed to return. Please look into the case, and oblige Major Rollins if you consistently can.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
[Copy sent to Governor Gamble.]
MY GOOD FRIENDS: The Honorable Senator Harlan has just placed in my hands your letter of the 27th of December, which I have read with pleasure and gratitude.
It is most cheering and encouraging for me to know that in the efforts which I have made and am making for the restoration of a righteous peace to our country, I am upheld and sustained by the good wishes and prayers of God's people. No one is more deeply than myself aware that without His favor our highest wisdom is but as foolishness and that our most strenuous efforts would avail nothing in the shadow of His displeasure.
I am conscious of no desire for my country's welfare that is not in consonance with His will, and of no plan upon which we may not ask His blessing. It seems to me that if there be one subject upon which all good men may unitedly agree, it is imploring the gracious favor of the God of Nations upon the struggles our people are making for the preservation of their precious birthright of civil and religious liberty.
Very truly your friend;
MAJOR-GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn.: Your despatch announcing retreat of enemy has just reached here. God bless you and all with you! Please tender to all, and accept for yourself, the nation's gratitude for your and their skill, endurance, and dauntless courage.
MAJOR-GENERAL DIX, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Do Richmond papers of 6th say nothing about Vicksburg, or if anything, what?
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK.
MY DEAR SIR:—What think you of forming a reserve cavalry corps of, say, 6000 for the Army of the Potomac? Might not such a corps be constituted from the cavalry of Sigel's and Slocum's corps, with scraps we could pick up here and there?
Yours truly,
HON. B. GRATZ BROWN, Jefferson City, Mo.:
Yours of to-day just received. The administration takes no part between its friends in Missouri, of whom I, at least, consider you one; and I have never before had an intimation that appointees there were interfering, or were inclined to interfere.
HEADQUARTERS ARMY OF THE POTOMAC January 5, 1863.
HIS EXCELLENCY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES:
Since my return to the army I have become more than ever convinced that the general officers of this command are almost unanimously opposed to another crossing of the river; but I am still of the opinion that the crossing should be attempted, and I have accordingly issued orders to the engineers and artillery to prepare for it. There is much hazard in it, as there always is in the majority of military movements, and I cannot begin the movement without giving you notice of it, particularly as I know so little of the effect that it may have upon other movements of distant armies.
The influence of your telegram the other day is still upon me, and has impressed me with the idea that there are many parts of the problem which influence you that are not known to me.
In order to relieve you from all embarrassment in my case, I inclose with this my resignation of my commission as major-general of volunteers, which you can have accepted if my movement is not in accordance with the views of yourself and your military advisers.
I have taken the liberty to write to you personally upon this subject, because it was necessary, as I learned from General Halleck, for you to approve of my general plan, written at Warrenton, before I could commence the movement; and I think it quite as necessary that you should know of the important movement I am about to make, particularly as it will have to be made in opposition to the views of nearly all my general officers, and after the receipt of a despatch from you informing me of the opinion of some of them who had visited you.
In conversation with you on New Year's morning I was led to express some opinions which I afterward felt it my duty to place on paper, and to express them verbally to the gentleman of whom we were speaking, which I did in your presence, after handing you the letter. You were not disposed then, as I saw, to retain the letter, and I took it back, but I now return it to you for record if you wish it.
I beg leave to say that my resignation is not sent in in any spirit of insubordination, but, as I before said, simply to relieve you from any embarrassment in changing commanders where lack of confidence may have rendered it necessary.
The bearer of this will bring me any answer, or I should be glad to hear from you by telegraph in cipher.
I have the honor to be, very respectfully, your obedient servant,
A. E. BURNSIDE,
Major-General, Commanding Army of the Potomac.
GENERAL:—Your communication of the 5th was delivered to me by your aide-de-camp at 12 M. to-day.
In all my communications and interviews with you since you took command of the Army of the Potomac I have advised a forward movement across the Rappahannock. At our interview at Warrenton I urged that you should cross by the fords above Fredericksburg rather than to fall down to that place; and when I left you at Warrenton it was understood that at least a considerable part of your army would cross by the fords, and I so represented to the President. It was this modification of the plan proposed by you that I telegraphed you had received his approval. When the attempt at Fredericksburg was abandoned, I advised you to renew the attempt at some other point, either in whole or in part, to turn the enemy's works, or to threaten their wings or communications; in other words, to keep the enemy occupied till a favorable opportunity offered to strike a decisive blow. I particularly advised you to use your cavalry and light artillery upon his communications, and attempt to cut off his supplies and engage him at an advantage.
In all our interviews I have urged that our first object was, not Richmond, but the defeat or scattering of Lee's army, which threatened Washington and the line of the upper Potomac. I now recur to these things simply to remind you of the general views which I have expressed, and which I still hold.
The circumstances of the case, however, have somewhat changed since the early part of November. The chances of an extended line of operations are now, on account of the advanced season, much less than then. But the chances are still in our favor to meet and defeat the enemy on the Rappahannock, if we can effect a crossing in a position where we can meet the enemy on favorable or even equal terms. I therefore still advise a movement against him. The character of that movement, however, must depend upon circumstances which may change any day and almost any hour. If the enemy should concentrate his forces at the place you have selected for a crossing, make it a feint and try another place. Again, the circumstances at the time may be such as to render an attempt to cross the entire army not advisable. In that case, theory suggests that, while the enemy concentrates at that point, advantages can be gained by crossing smaller forces at other points to cut off his lines, destroy his communication, and capture his rear-guards, outposts, etc. The great object is to occupy the enemy to prevent his making large detachments or distant raids, and to injure him all you can with the least injury to yourself. If this can be best accomplished by feints of a general crossing and detached real crossings, take that course; if by an actual general crossing, with feints on other points, adopt that course. There seem to me to be many reasons why a crossing at some point should be attempted. It will not do to keep your large army inactive. As you yourself admit, it devolves on you to decide upon the time, place, and character of the crossing which you may attempt. I can only advise that an attempt be made, and as early as possible.
Very respectfully, your obedient servant,
H. W. HALLECK, General-in-Chief.
[Indorsement.]
January 8, 1863.
GENERAL BURNSIDE:
I understand General Halleck has sent you a letter of which this is a copy. I approve this letter. I deplore the want of concurrence with you in opinion by your general officers, but I do not see the remedy. Be cautious, and do not understand that the government or country is driving you. I do not yet see how I could profit by changing the command of the Army of the Potomac; and if I did, I should not wish to do it by accepting the resignation of your commission.
GOVERNOR JOHNSON, Nashville Tenn.:
A dispatch of yesterday from Nashville says the body of Captain Todd, of the Sixth Kentucky, was brought in to-day.
Please tell me what was his Christian name, and whether he was in our service or that of the enemy. I shall also be glad to have your impression as to the effect the late operations about Murfreesborough will have on the prospects of Tennessee.
MAJOR-GENERAL CURTIS, St. Louis, MO.:
I understand there is considerable trouble with the slaves in Missouri. Please do your best to keep peace on the question for two or three weeks, by which time we hope to do something here toward settling the question in Missouri.
GOVERNOR JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn.:
Yours received. I presume the remains of Captain Todd are in the hands of his family and friends, and I wish to give no order on the subject; but I do wish your opinion of the effects of the late battles about Murfreesborough upon the prospects of Tennessee.
The Judge-Advocate-General is instructed to revise the proceedings of the court-martial in the case of Major-General Fitz-John Porter, and to report fully upon any legal questions that may have arisen in them, and upon the bearing of the testimony in reference to the charges and specifications exhibited against the accused, and upon which he was tried.
TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES: The Secretary of State has submitted to me a resolution of the House of Representatives of the 5th instant, which has been delivered to him, and which is in the following words:
"Resolved, That the Secretary of State be requested to communicate to this House, if not, in his judgment, incompatible with the public interest, why our Minister in New Granada has not presented his credentials to the actual government of that country; also the reasons for which Senor Murillo is not recognized by the United States as the diplomatic representative of the Mosquera government of that country; also, what negotiations have been had, if any, with General Herran as the representative of Ospina's government in New Granada since it went into existence."
On the 12th day of December, 1846, a treaty of amity, peace, and concord was concluded between the United States of America and the Republic of New Granada, which is still in force. On the 7th day of December, 1847, General Pedro Alcantara Herran, who had been duly accredited, was received here as the envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary of that, republic. On the 30th day of August, 1849, Senor Don Rafael Rivas was received by this government as charge d'affaires of the same republic. On the 5th day of December, 1851, a consular convention was concluded between that republic and the United States, which treaty was signed on behalf of the Republic of Granada by the same Senor Rivas. This treaty is still in force. On the 27th of April, 1852, Senor Don Victoriano de Diego Paredes was received as charge d'affaires of the Republic of New Granada. On the 20th of June, 1855, General Pedro Alcantara Herran was again received as envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary, duly accredited by the Republic of New Granada, and he has ever since remained, under the same credentials, as the representative of that republic near the Government of the United States. On the 10th of September, 1857, a claims convention was concluded between the United States and the Republic of Granada. This convention is still in force, and has in part been executed. In May, 1858, the constitution of the republic was remodelled; and the nation assumed the political title of "The Granadian Confederacy." This fact was formally announced to this Government, but without any change in their representative here. Previously to the 4th day of March, 1861, a revolutionary war against the Republic of New Granada, which had thus been recognized and treated with by the United States, broke out in New Granada, assuming to set up a new government under the name of "United States of Colombia." This war has had various vicissitudes, sometimes favorable, sometimes adverse, to the revolutionary movements. The revolutionary organization has hitherto been simply a military provisionary power, and no definitive constitution of government has yet been established in New Granada in place of that organized by the constitution of 1858. The minister of the United States to the Granadian Confederacy, who was appointed on the 29th day of May, 1861, was directed, in view of the occupation of the capital by the revolutionary party and of the uncertainty of the civil war, not to present his credentials to either the government of the Granadian Confederacy or to the provisional military government, but to conduct his affairs informally, as is customary in such cases, and to report the progress of events and await the instructions of this Government. The advices which have been received from him have not hitherto, been sufficiently conclusive to determine me to recognize the revolutionary government. General Herran being here, with full authority from the Government of New Canada, which has been so long recognized by the United States, I have not received any representative from the revolutionary government, which has not yet been recognized, because such a proceeding would be in itself an act of recognition.
Official communications have been had on various incidental and occasional questions with General Herran as the minister plenipotentiary and envoy extraordinary of the Granadian Confederacy, but in no other character. No definitive measure or proceeding has resulted from these communications, and a communication of them at present would not, in my judgment, be compatible with the public interest.
SECRETARY OF WAR:
Please see Mr. Stafford, who wants to assist in raising colored troops in Missouri.
January 17, 1863.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I have signed the joint resolution to provide for the immediate payment of the army and navy of the United States, passed by the House of Representatives on the 14th and by the Senate on the 15th instant.
The joint resolution is a simple authority, amounting, however, under existing circumstances, to a direction, to the Secretary of the Treasury to make an additional issue of $100,000,000 in United States notes, if so much money is needed, for the payment of the army and navy.
My approval is given in order that every possible facility may be afforded for the prompt discharge of all arrears of pay due to our soldiers and our sailors.
While giving this approval, however, I think it my duty to express my sincere regret that it has been found necessary to authorize so large an additional issue of United States notes, when this circulation and that of the suspended banks together have become already so redundant as to increase prices beyond real values, thereby augmenting the cost of living to the injury of labor, and the cost of supplies to the injury of the whole country.
It seems very plain that continued issues of United States notes without any check to the issues of suspended banks, and without adequate provision for the raising of money by loans and for funding the issues so as to keep them within due limits, must soon produce disastrous consequences; and this matter appears to me so important that I feel bound to avail myself of this occasion to ask the special attention of Congress to it.
That Congress has power to regulate the currency of the country can hardly admit of doubt, and that a judicious measure to prevent the deterioration of this currency, by a seasonable taxation of bank circulation or otherwise, is needed seems equally clear. Independently of this general consideration, it would be unjust to the people at large to exempt banks enjoying the special privilege of circulation from their just proportion of the public burdens.
In order to raise money by way of loans most easily and cheaply, it is clearly necessary to give every possible support to the public credit. To that end a uniform currency, in which taxes, subscriptions to loans, and all other ordinary public dues as well as all private dues may be paid, is almost if not quite indispensable. Such a currency can be furnished by banking associations organized under a general act of Congress, as suggested in my message at the beginning of the present session. The securing of this circulation by the pledge of United States bonds, as therein suggested, would still further facilitate loans, by increasing the present and causing a future demand for such bonds.
In view of the actual financial embarrassments of the government, and of the greater embarrassment sure to come if the necessary means of relief be not afforded, I feel that I should not perform my duty by a simple announcement of my approval of the joint resolution, which proposes relief only by increased circulation, without expressing my earnest desire that measures such in substance as those I have just referred to may receive the early sanction of Congress. By such measures, in my opinion, will payment be most certainly secured, not only to the army and navy, but to all honest creditors of the government, and satisfactory provision made for future demands on the treasury.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF MANCHESTER:
I have the honor to acknowledge the receipt of the address and resolutions which you sent me on the eve of the new year. When I came, on the 4th of March, 1861, through a free and constitutional election to fireside in the Government of the United States, the country was found at the verge of civil war. Whatever might have been the cause, or whosesoever the fault, one duty, paramount to all others, was before me, namely, to maintain and preserve at once the Constitution and the integrity of the Federal Republic. A conscientious purpose to perform this duty is the key to all the measures of administration which have been and to all which will hereafter be pursued. Under our frame of government and my official oath, I could not depart from this purpose if I would. It is not always in the power of governments to enlarge or restrict the scope of moral results which follow the policies that they may deem it necessary for the public safety from time to time to adopt.
I have understood well that the duty of self-preservation rests solely with the American people; but I have at the same time been aware that favor or disfavor of foreign nations might have a material influence in enlarging or prolonging the struggle with disloyal men in which the country is engaged. A fair examination of history has served to authorize a belief that the past actions and influences of the United States were generally regarded as having been beneficial toward mankind. I have, therefore, reckoned upon the forbearance of nations. Circumstances—to some of which you kindly allude—induce me especially to expect that if justice and good faith should be practised by the United States, they would encounter no hostile influence on the part of Great Britain. It is now a pleasant duty to acknowledge the demonstration you have given of your desire that a spirit of amity and peace toward this country may prevail in the councils of your Queen, who is respected and esteemed in your own country only more than she is by the kindred nation which has its home on this side of the Atlantic.
I know and deeply deplore the sufferings which the workingmen at Manchester, and in all Europe, are called to endure in this crisis. It has been often and studiously represented that the attempt to overthrow this government, which was built upon the foundation of human rights, and to substitute for it one which should rest exclusively on the basis of human slavery, was likely to obtain the favor of Europe. Through the action of our disloyal citizens, the working-men of Europe have been subjected to severe trials, for the purpose of forcing their sanction to that attempt. Under the circumstance, I cannot but regard your decisive utterances upon the question as an instance of sublime Christian heroism which has not been surpassed in any age or in any country. It is indeed an energetic and inspiring assurance of the inherent power of truth and of the ultimate and universal triumph of justice, humanity, and freedom. I do not doubt that the sentiments, you have expressed will be sustained by your great nation; and, on the other hand, I have no hesitation in assuring you that they will excite admiration, esteem, and the most reciprocal feelings of friendship among the American people.
I hail this interchange of sentiment, therefore, as an augury that whatever else may happen, whatever misfortune may befall your country or my own, the peace and friendship which now exist between the two nations will be, as it shall be my desire to make them, perpetual.
GENTLEMEN OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
I submit herewith for your consideration the joint resolutions of the corporate authorities of the city of Washington, adopted September a 7, 1862, and a memorial of the same under date of October 28, 1862, both relating to and urging the construction of certain railroads concentrating upon the city of Washington.
In presenting this memorial and the joint resolutions to you, I am not prepared to say more than that the subject is one of great practical importance, and that I hope it will receive the attention of Congress.
HEADQUARTERS OF THE ARMY, WASHINGTON,
January 13, 1863.
In compliance with the Sixty-fifth Article of War, these whole proceedings are transmitted to the Secretary of War, to be laid before the President of the United States.
H. W. HALLECK,
General-in-Chief.
January 21, 1863.
The foregoing proceedings, findings, and sentence in the foregoing case of Major-General Fitz-John Porter are approved and confirmed, and it is ordered that the said Fitz-John Porter be, and he hereby is, cashiered and dismissed from the service of the United States as a major-general of volunteers, and as colonel and brevet brigadier-general in the regular service of the United States, and forever disqualified from holding any office of trust or profit under the Government of the United States.
January 21, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL GRANT, Memphis.
GENERAL:—The President has directed that so much of Arkansas as you may desire to control be temporarily attached to your department. This will give you control of both banks of the river.
In your operations down the Mississippi you must not rely too confidently upon any direct co-operation of General Banks and the lower flotilla, as it is possible that they may not be able to pass or reduce Port Hudson. They, however, will do everything in their power to form a junction with you at Vicksburg. If they should not be able to effect this, they will at least occupy a portion of the enemy's forces, and prevent them from reinforcing Vicksburg. I hope, however, that they will do still better and be able to join you.
It may be proper to give you some explanation of the revocation of your order expelling all Jews from your department. The President has no objection to your expelling traitors and Jew peddlers, which, I suppose, was the object of your order; but as it in terms proscribed an entire religious class, some of whom are fighting in our ranks, the President deemed it necessary to revoke it.
Very respectfully, your obedient servant,
H. W. HALLECK, General-in-Chief.
GENERAL BURNSIDE:
Will see you any moment when you come.
WAR DEPARTMENT, ADJUTANT-GENERAL'S OFFICE, WASHINGTON, D.C. JANUARY 25, 1863.
I. The President of the United States has directed:
1st. That Major-General A. E. Burnside, at his own request, be relieved from the command of the Army of the Potomac.
2d. That Major-General E. V. Sumner, at his own request, be relieved from duty in the Army of the Potomac.
3d. That Major-General W. B. Franklin be relieved from duty in the Army of the Potomac.
4th. That Major-General J. Hooker be assigned to the command of the Army of the Potomac.
II. The officers relieved as above will report in person to the adjutant-general of the army.
By order of the Secretary of War: D. TOWNSEND, Assistant Adjutant-General
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER.
GENERAL:—I have placed you at the head of the Army of the Potomac. Of course I have done this upon what appear to me to be sufficient reasons, and yet I think it best for you to know that there are some things in regard to which I am not quite satisfied with you. I believe you to be a brave and skillful soldier, which of course I like. I also believe you do not mix politics with your profession, in which you are right. You have confidence in yourself, which is a valuable if not an indispensable quality. You are ambitious, which within reasonable bounds does good rather than harm; but I think that during General Burnside's command of the army you have taken counsel of your ambition and thwarted him as much as you could, in which you did a great wrong to the country and to a most meritorious and honorable brother officer. I have heard, in such a way as to believe it, of your recently saying that both the army and the government needed a dictator. Of course it was not for this, but in spite of it, that I have given you the command. Only those generals who gain successes can set up dictators. What I now ask of you is military success, and I will risk the dictatorship. The government will support you to the utmost of its ability, which is neither more nor less than it has done and will do for all commanders. I much fear that the spirit that you have aided to infuse into the army, of criticizing their commander and withholding confidence from him, will now turn upon you. I shall assist you as far as I can to put it down. Neither you nor Napoleon, if he were alive again, could get any good out of an army while such a spirit prevails in it. And now beware of rashness. Beware of rashness, but with energy and sleepless vigilance go forward and give us victories.
Yours very truly,
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In conformity to the law of July 16, 1862, I most cordially recommend that Commander David D. Porter, United States Navy, acting rear-admiral, commanding the Mississippi Squadron, receive a vote of thanks of Congress for the bravery and skill displayed in the attack on the post of Arkansas, which surrendered to the combined military and naval forces on the 10th instant.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Lowell, Mass.:
Please come here immediately. Telegraph me about what time you will arrive.
MAJOR-GENERAL DIx, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Do Richmond papers have anything from Vicksburg?
HON. THURLOW WEED.
DEAR SIR:—Your valedictory to the patrons of the Albany Evening journal brings me a good deal of uneasiness. What does it mean?
Truly Yours,
January 30, 1863. 5.45 P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe, Va.:
What iron-clads, if any, have gone out of Hampton Roads within the last two days?
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe, Va.: Corcoran's and Pryor's battle terminated. Have you any news through Richmond papers or otherwise?
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
I do not take jurisdiction of the pass question. Exercise your own discretion as to whether Judge Pettis shall have a pass.
TO THE WORKING-MEN OF LONDON:
I have received the New Year's address which you have sent me, with a sincere appreciation of the exalted and humane sentiments by which it was inspired.
As these sentiments are manifestly the enduring support of the free institutions of England, so I am sure also that they constitute the only reliable basis for free institutions throughout the world.
The resources, advantages, and powers of the American people are very great, and they have consequently succeeded to equally great responsibilities. It seems to have devolved upon them to test whether a government established on the principles of human freedom can be maintained against an effort to build one upon the exclusive foundation of human bondage. They will rejoice with me in the new evidences which your proceedings furnish that the magnanimity they are exhibiting is justly estimated by the true friends of freedom and humanity in foreign countries.
Accept my best wishes for your individual welfare, and for the welfare and happiness of the whole British people.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
I hear of some difficulty in the streets of Baltimore yesterday. What is the amount of it?
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
On the 4th of September, 1862, Commander George Henry Preble, United States Navy, then senior officer in command of the naval force off the harbor of Mobile, was guilty of inexcusable neglect in permitting the armed steamer Oreto in open daylight to run the blockade. For his omission to perform his whole duty on that occasion, and the injury thereby inflicted on the service and the country, his name was stricken from the list of naval officers and he was dismissed [from] the service.
Since his dismissal earnest application has been made for his restoration to his former position by senators and naval officers, on the ground that his fault was an error of judgment, and that the example in his case has already had its effect in preventing a repetition of similar neglect.
I therefore on this application and representation, and in consideration of his previous fair record, do hereby nominate George Henry Preble to be a commander in the navy from the 16th July, 1862, to take rank on the active list next after Commander Edward Donaldson, and to fill a vacancy occasioned by the death of Commander J. M. Wainwright.
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES:
On the 24th August, 1861, Commander Roger Perry, United. States Navy, was dismissed from the service under a misapprehension in regard to his loyalty to the Government, from the circumstance that several oaths were transmitted to him and the Navy Department failed to receive any recognition of them. After his dismissal, and upon his assurance that the oath failed to reach him and his readiness to execute it, he was recommissioned to his original position on the 4th September following. On the same day, 4th September, he was ordered to command the sloop of war Vandalia; on the 22d this order was revoked and he was ordered to duty in the Mississippi Squadron, and on the 23d January, 1862, was detached sick, and has since remained unemployed. The advisory board under the act of 16th July, 1862, did not recommend him for further promotion.
This last commission, having been issued during the recess of the Senate, expired at the end of the succeeding session, 17th July, 1862, from which date, not having been nominated to the Senate, he ceased to be a commander in the navy.
To correct the omission to nominate this officer to the Senate at its last session, I now nominate Commander Roger Perry to be a commander in the navy from the 14th September, 1855, to take his relative position on the list of commanders not recommended for further promotion.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn.:
Your despatch about "river patrolling" received. I have called the Secretary of the Navy, Secretary of War, and General-in-Chief together, and submitted it to them, who promise to do their very best in the case. I cannot take it into my own hands without producing inextricable confusion.
HON. SIMON CAMERON, Harrisburg, Pa.: General Clay is here and I suppose the matter we spoke of will have to be definitely settled now. Please answer.
REV. ALEXANDER REED. MY DEAR SIR:—Your note, by which you, as General Superintendent of the United States Christian Commission, invite me to preside at a meeting to be held this day at the hall of the House of Representatives in this city, is received.
While, for reasons which I deem sufficient, I must decline to preside, I cannot withhold my approval of the meeting and its worthy objects.
Whatever shall be, sincerely and in God's name, devised for the good of the soldiers and seamen in their hard spheres of duty, can scarcely fail to be blessed; and whatever shall tend to turn our thoughts from the unreasoning and uncharitable passions, prejudices, and jealousies incident to a great national trouble such as ours, and to fix them on the vast and long enduring consequences, for weal or for woe, which are to result from the struggle, and especially to strengthen our reliance on the Supreme Being for the final triumph of the right, cannot but be well for us all.
The birthday of Washington and the Christian Sabbath coinciding this year, and suggesting together the highest interests of this life and of that to come, is most propitious for the meeting proposed.
Your obedient servant,
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C. February 26,1863.
HON. J. K. DuBois, Springfield, Ill.: General Rosecrans respectfully urges the appointment of William P. Caslin as a brigadier-general, What say you?
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
If it will be no detriment to the service I will be obliged for Capt. Henry A. Marchant, of Company I, Twenty-third Pennsylvania Volunteers, to come here and remain four or five days.
A Proclamation.
Whereas objects of interest to the United States require that the Senate should be convened at 12 o'clock on the 4th of March next to receive and act upon such communications as may be made to it on the part of the Executive:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, have considered it to be my duty to issue this my proclamation, declaring that an extraordinary occasion requires the Senate of the United States to convene for the transaction of business at the Capitol, in the city of Washington, on the 4th day of March next, at 12 o'clock at noon on that day, of which all who shall at that time be entitled to act as members of that body are hereby required to take notice.
Given under my hand and the seal of the United States, at Washington, the twenty eighth day of February A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States of America, the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary o f State.
Mr. M. is now with me on the question of the Honolulu Commissioner. It pains me some that this tilt for the place of Colonel Baker's friend grows so fierce, now that the Colonel is no longer alive to defend him. I presume, however, we shall have no rest from it. In self-defense I am disposed to say, "Make a selection and send it to me."
GOVERNOR DAVID TOD, Columbus, Ohio:
I think your advice with that of others would be valuable in the selection of provost-marshals for Ohio.
A Proclamation
In pursuance of the twenty-sixth section of the act of Congress entitled "An act for enrolling and calling out the national forces, and for other purposes," approved on the 3d day of March, 1863, I, Abraham Lincoln, President and Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States, do hereby order and command that all soldiers enlisted or drafted in the service of the United States now absent from their regiments without leave shall forthwith return to their respective regiments.
And I do hereby declare and proclaim that all soldiers now absent from their respective regiments without leave who shall, on or before the first day of April, 1863, report themselves at any rendezvous designated by the general orders of the War Department No. 58, hereto annexed, may be restored to their respective regiments without punishment, except the forfeiture of pay and allowances during their absence; and all who do not return within the time above specified shall be arrested as deserters and punished as the law provides; and
Whereas evil-disposed and disloyal persons at sundry places have enticed and procured soldiers to desert and absent themselves from their regiments, thereby weakening the strength of the armies and prolonging the war, giving aid and comfort to the enemy, and cruelly exposing the gallant and faithful soldiers remaining in the ranks to increased hardships and danger:
I do therefore call upon all patriotic and faithful citizens to oppose and resist the aforementioned dangerous and treasonable crimes, and to aid in restoring to their regiments all soldiers absent without leave, and to assist in the execution of the act of Congress "for enrolling and calling out the national forces, and for other purposes," and to support the proper authorities in the prosecution and punishment of offenders against said act and in suppressing the insurrection and rebellion.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand. Done at the city of Washington, this tenth day of March, A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
General Stahel wishes to be assigned to General Heintzelman and General Heintzelman also desires it. I would like to oblige both if it would not injure the service in your army, or incommode you. What say you?
I am very glad of your note saying "recent despatches from him are able, judicious, and loyal," and that if I agree; we will leave him there. I am glad to agree, so long as the public interest does not seem to require his removal.
HON. J. O. MORTON, Joliet, Ill.: William Chumasero is proposed for provost-marshal of your district. What think you of it? I understand he is a good man.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, March 20, 1863.
WHOM IT MAY CONCERN:—Whereas, it appears to my satisfaction that Thomas W. Knox, a correspondent of the New York Herald, has been by the sentence of a court-martial excluded from the military department under command of Major-General Grant, and also that General Thayer, president of the court-martial which rendered the sentence, and Major-General McClernand, in command of a corps of that department, and many other respectable persons, are of opinion that Mr. Knox's offense was technical rather than wilfully wrong, and that the sentence should be revoked: now, therefore, said sentence is hereby so far revoked as to allow Mr. Knox to return to General Grant's headquarters, and to remain if General Grant shall give his express assent, and to again leave the department if General Grant shall refuse such assent.
Mr. BENJAMIN GRATZ, Lexington, Ky.:
Show this to whom it may concern as your authority for allowing Mrs. Selby to remain at your house, so long as you choose to be responsible for what she may do.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn.:
Your dispatches about General Davis and General Mitchell are received. General Davis' case is not particular, being simply one of a great many recommended and not nominated because they would transcend the number allowed by law. General Mitchell (was) nominated and rejected by the Senate and I do not think it proper for me to renominate him without a change of circumstances such as the performance of additional service, or an expressed change of purpose on the part of at least some senators who opposed him.
MAJOR-GENERAL HURLBUT, Memphis:
What news have you? What from Vicksburg? What from Yazoo Pass? What from Lake Providence? What generally?
(Private.)
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON March 26, 1863.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am told you have at least thought of raising a negro military force. In my opinion the country now needs no specific thing so much as some man of your ability and position to go to this work. When I speak of your position, I mean that of an eminent citizen of a slave State and himself a slaveholder. The colored population is the great available and yet unavailed of force for restoring the Union. The bare sight of fifty thousand armed and drilled black soldiers upon the banks of the Mississippi would end the rebellion at once; and who doubts that we can present that sight if we but take hold in earnest? If you have been thinking of it, please do not dismiss the thought.
Yours very truly,
A Proclamation.
March 30, 1863.
Whereas the Senate of the United States, devoutly recognizing the supreme authority and just government of Almighty God in all the affairs of men and of nations, has by a resolution requested the President to designate and set apart a day for national prayer and humiliation:
And whereas it is the duty of nations as well as men to own their dependence upon the overruling power of God; to confess their sins and transgressions in humble sorrow, yet with assured hope that genuine repentance will lead to mercy and pardon; and to recognize the sublime truth, announced in the Holy Scriptures and proven by all history, that those nations only are blessed whose God is the Lord:
And insomuch as we know that by His divine law nations, like individuals, are subjected to punishments and chastisements in this world, may we not justly fear that the awful calamity of civil war which now desolates the land may be but a punishment inflicted upon us for our presumptuous sins, to the needful end of our national reformation as a whole people? We have been the recipients of the choicest bounties of Heaven. We have been preserved, these many years, in peace and prosperity. We have grown in numbers, wealth, and power as no other nation has ever grown; but we have forgotten God. We have forgotten the gracious hand which preserved us in peace, and multiplied and enriched and strengthened us; and we have vainly imagined, in the deceitfulness of our hearts, that all these blessings were produced by some superior wisdom and virtue of our own. Intoxicated with unbroken success, we have become too self-sufficient to feel the necessity of redeeming and preserving grace, too proud to pray to the God that made us:
It behooves us, then, to humble ourselves before the offended Power, to confess our national sins, and to pray for clemency and forgiveness:
Now, therefore, in compliance with the request, and fully concurring in the views, of the Senate, I do by this my proclamation designate and set apart Thursday, the 30th day of April, 1863, as a day of national humiliation, fasting, and prayer. And I do hereby request all the people to abstain on that day from their ordinary secular pursuits, and to unite at their several places of public worship and their respective homes in keeping the day holy to the Lord, and devoted to the humble discharge of the religious duties proper to that solemn occasion. All this being done in sincerity and truth, let us then rest humbly in the hope, authorized by the divine teachings, that the united cry of the nation will be heard on high, and answered with blessings no less than the pardon of our national sins, and the restoration of our now divided and suffering country to its former happy condition of unity and peace.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this thirtieth day of March, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
Whereas by the act of Congress approved July 13, 1861, entitled "An act to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," all commercial intercourse between the inhabitants of such States as should by proclamation be declared in insurrection against the United States and the citizens of the rest of the United States was prohibited so long as such condition of hostility should continue, except as the same shall be licensed and permitted by the President to be conducted and carried on only in pursuance of rules and regulations prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury; and:
Whereas it appears that a partial restoration of such intercourse between the inhabitants of sundry places and sections heretofore declared in insurrection in pursuance of said act and the citizens of the rest of the United States will favorably affect the public interests:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, exercising the authority and discretion confided to me by the said act of Congress, do hereby license and permit such commercial intercourse between the citizens of loyal States and the inhabitants of such insurrectionary States in the cases and under the restrictions described and expressed in the regulations prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury bearing even date with these presents, or in such other regulations as he may hereafter, with my approval, prescribe.
MAJOR-GENERAL HUNTER.
MY DEAR SIR:—I am glad to see the accounts of your colored force at Jacksonville, Florida. I see the enemy are driving at them fiercely, as is to be expected. It is important to the enemy that such a force shall not take shape and grow and thrive in the South, and in precisely the same proportion it is important to us that it shall. Hence the utmost caution and vigilance is necessary on our part. The enemy will make extra efforts to destroy them, and we should do the same to preserve and increase them.
Yours truly,
A Proclamation.
Whereas, in pursuance of the act of Congress approved July 13, 1861, I did, by proclamation dated August 16, 1861, declare that the inhabitants of the States of Georgia, South Carolina, Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama, Louisiana, Texas, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Florida (except the inhabitants of that part of Virginia lying west of the Alleghany Mountains, and of such other parts of that State and the other States hereinbefore named as might maintain a legal adhesion to the Union and the Constitution or might be from time to time occupied and controlled by forces of the United States engaged in the dispersion of said insurgents) were in a state of insurrection against the United States, and that all commercial intercourse between the same and the inhabitants thereof, with the exceptions aforesaid, and the citizens of other States and other parts of the United States was unlawful and would remain unlawful until such insurrection should cease or be suppressed, and that all goods and chattels, wares and merchandise, coming from any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, into other parts of the United States without the license and permission of the President, through the Secretary of the Treasury, or proceeding to any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, by land or water, together with the vessel or vehicle conveying the same to or from said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, would be forfeited to the United States, and:
Whereas experience has shown that the exceptions made in and by said proclamation embarrass the due enforcement of said act of July 13, 1861, and the proper regulation of the commercial intercourse authorized by said act with the loyal citizens of said States:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby revoke the said exceptions, and declare that the inhabitants of the States of Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama, Louisiana, Texas, Arkansas, Mississippi, Florida, and Virginia (except the forty-eight counties of Virginia designated as West Virginia, and except also the ports of New Orleans, Key West; Port Royal, and Beaufort in North Carolina) are in a state of insurrection against the United States, and that all commercial intercourse not licensed and conducted as provided in said act between the said States and the inhabitants thereof, with the exceptions aforesaid, and the citizens of other States and other parts of the United States is unlawful and will remain unlawful until such insurrection shall cease or has been suppressed and notice thereof has been duly given by proclamation; and all cotton, tobacco, and other products, and all other goods and chattels, wares and merchandise, coming from any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, into other parts of the United States, or proceeding to any of said States, with the exceptions aforesaid, without the license and permission of the President, through the Secretary of the Treasury, will together with the vessel or vehicle conveying the same, be forfeited to the United States.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this second day of April, A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Our plan is to pass Saturday night on the boat, go over from Aquia Creek to your camp Sunday morning, remain with you till Tuesday morning, and then return. Our party will probably not exceed six persons of all sorts.
On this general subject I respectfully refer Mr.———__ to the Secretaries of War and Navy for conference and consultation. I have a single idea of my own about harbor defense. It is a steam ram, built so as to sacrifice nearly all capacity for carrying to those of speed and strength, so as to be able to split any vessel having hollow enough in her to carry supplies for a voyage of any distance. Such ram, of course, could not herself carry supplies for a voyage of considerable distance, and her business would be to guard a particular harbor as a bulldog guards his master's door.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE NAVY:
Richmond Whig of the 8th has no telegraphic despatches from Charleston, but has the following as editorial:
"All thoughts are now centred upon Charleston. Official intelligence was made public early yesterday morning that the enemy's iron-clad fleet had attempted to cross the bar and failed, but later in the day it was announced that the gunboats and transports had succeeded in crossing and were at anchor. Our iron-clads lay between the forts quietly awaiting the attack. Further intelligence is looked for with eager anxiety. The Yankees have made no secret of this vast preparation for an attack on Charleston, and we may well anticipate a desperate conflict. At last the hour of trial has come for Charleston, the hour of deliverance or destruction, for no one believes the other alternative, surrender, possible. The heart of the whole country yearns toward the beleaguered city with intense solicitude, yet with hopes amounting to confidence. Charleston knows what is expected of her, and which is due to her fame, and to the relation she sustains to the cause. The devoted, the heroic, the great-hearted Beauregard is there, and he, too, knows what is expected of him and will not disappoint that expectation. We predict a Saragossa defense, and that if Charleston is taken it will be only a heap of ruins."
The rebel pickets are reported as calling over to our pickets today that we had taken some rebel fort. This is not very intelligible, and I think is entirely unreliable.
OFFICER IN COMMAND at Nashville, Tenn: Is there a soldier by the name of John R. Minnick of Wynkoop's cavalry under sentence of death, by a court-martial or military commission, in Nashville? And if so what was his offense, and when is he to be executed?
A. LINCOLN.
If necessary let the execution be staid till I can be heard from again.
A. LINCOLN.
[President Lincoln sent many telegrams similar in form to
this one in order to avoid tiresome repetition the editor
has omitted all those without especial interest. Hardly a
day went by that there were not people in the White House
begging mercy for a sentenced soldier. A mother one day,
pleaded with Lincoln to remit the sentence of execution on
her son. "Well, I don't think it will do him a bit of good"
said Mr. Lincoln—"Pardoned." D.W.]
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Your letter by the hand of General Butterfield is received, and will be conformed to. The thing you dispense with would have been ready by mid-day to-morrow.
ADMIRAL DUPONT:
Hold your position inside the bar near Charleston; or, if you shall have left it, return to it, and hold it until further orders. Do not allow the enemy to erect new batteries or defenses on Morris Island. If he has begun it, drive him out. I do not herein order you to renew the general attack. That is to depend on your own discretion or a further order.
GENERAL HUNTER AND ADMIRAL DUPONT:
This is intended to clear up an apparent inconsistency between the recent order to continue operations before Charleston and the former one to remove to another point in a certain contingency. No censure upon you, or either of you, is intended. We still hope that by cordial and judicious co-operation you can take the batteries on Morris Island and Sullivan's Island and Fort Sumter. But whether you can or not, we wish the demonstration kept up for a time, for a collateral and very important object. We wish the attempt to be a real one, though not a desperate one, if it affords any considerable chance of success. But if prosecuted as a demonstration only, this must not become public, or the whole effect will be lost. Once again before Charleston, do not leave until further orders from here. Of course this is not intended to force you to leave unduly exposed Hilton Head or other near points in your charge.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—Whoever receives this first, please send a copy to the other immediately. A.L.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
It is now 10.15 P.M. An hour ago I received your letter of this morning, and a few moments later your despatch of this evening. The latter gives me considerable uneasiness. The rain and mud of course were to be calculated upon. General S. is not moving rapidly enough to make the expedition come to anything. He has now been out three days, two of which were unusually fair weather, and all three without hindrance from the enemy, and yet he is not twenty-five miles from where he started. To reach his point he still has sixty to go, another river (the Rapidan) to cross, and will be hindered by the enemy. By arithmetic, how many days will it take him to do it? I do not know that any better can be done, but I greatly fear it is another failure already. Write me often. I am very anxious.
Yours truly,
APRIL 16, 1863. A. LINCOLN, PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, TO ALL TO WHOM THESE PRESENTS SHALL COME, GREETING:
Know ye that, whereas a paper bearing date the 3rd day of December last, purporting to be an agreement between the United States and one Bernard Kock for immigration of persons of African extraction to a dependency of the Republic of Haiti, was signed by me on behalf of the party of the first part; but whereas the said instrument was and has since remained incomplete in consequence of the seal of the United States not having been thereunto affixed; and whereas I have been moved by considerations by me deemed sufficient to withhold my authority for affixing the said seal:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby authorize the Secretary of State to cancel my signature to the instrument aforesaid.
Done at Washington, this sixteenth day of April, A.D. 1863.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas by the act of Congress approved the 31st day of December last the State of West Virginia was declared to be one of the United States of America, and was admitted into the Union on an equal footing with the original States in all respects whatever, upon the condition that certain changes should be duly made in the proposed constitution for that State; and
Whereas proof of a compliance with that condition, as required by the second section of the act aforesaid, has been submitted to me:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby, in pursuance of the act of Congress aforesaid, declare and proclaim that the said act shall take effect and be in force from and after sixty days from the date hereof.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twentieth day of April, A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn.:
Your despatch of the 21st received. I really cannot say that I have heard any complaint of you. I have heard complaint of a police corps at Nashville, but your name was not mentioned in connection with it, so far as I remember. It may be that by inference you are connected with it, but my attention has never been drawn to it in that light.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
How does it look now?
HON. A. O. CURTIN, Harrisburg, Penn.:
I do not think the people of Pennsylvania should be uneasy about an invasion. Doubtless a small force of the enemy is flourishing about in the northern part of Virginia, on the "skewhorn" principle, on purpose to divert us in another quarter. I believe it is nothing more. We think we have adequate force close after them.
HON. W. A. NEWELL, Allentown, N.J.:
I have some trouble about provost-marshal in your first district. Please procure HON. Mr. Starr to come with you and see me, or come to an agreement with him and telegraph me the result.
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg, Penn.:
The whole disposable force at Baltimore and else where in reach have already been sent after the enemy which alarms you. The worst thing the enemy could do for himself would be to weaken himself before Hooker, and therefore it is safe to believe he is not doing it; and the best thing he could do for himself would be to get us so scared as to bring part of Hooker's force away, and that is just what he is trying to do. I will telegraph you in the morning about calling out the militia.
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg, Penn.:
General Halleck tells me he has a despatch from General Schenck this morning, informing him that our forces have joined, and that the enemy menacing Pennsylvania will have to fight or run today. I hope I am not less anxious to do my duty to Pennsylvania than yourself, but I really do not yet see the justification for incurring the trouble and expense of calling out the militia. I shall keep watch, and try to do my duty.
A. LINCOLN P. S.—Our forces are exactly between the enemy and Pennsylvania.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTTERFIELD, Chief of Staff:
The President thanks you for your telegrams, and hopes you will keep him advised as rapidly as any information reaches you.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
WASHINGTON, D. C., May 3, 1863. 4.35 P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTTERFIELD:
Where is General Hooker? Where is Sedgwick Where is Stoneman?
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
We have news here that the enemy has reoccupied heights above Fredericksburg. Is that so?
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, O.:
Our friend General Sigel claims that you owe him a letter. If you so remember please write him at once. He is here.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
We have through General Dix the contents of Richmond papers of the 5th. General Dix's despatch in full is going to you by Captain Fox of the navy. The substance is General Lee's despatch of the 3d (Sunday), claiming that he had beaten you and that you were then retreating across the Rappahannock, distinctly stating that two of Longstreet's divisions fought you on Saturday, and that General [E. F.] Paxton was killed, Stonewall Jackson severely wounded, and Generals Heth and A. P. Hill slightly wounded. The Richmond papers also stated, upon what authority not mentioned, that our cavalry have been at Ashland, Hanover Court-House, and other points, destroying several locomotives and a good deal of other property, and all the railroad bridges to within five miles of Richmond.
Just as I telegraphed you contents of Richmond papers showing that our cavalry has not failed, I received General Butterfield's of 11 A.M. yesterday. This, with the great rain of yesterday and last night securing your right flank, I think puts a new face upon your case; but you must be the judge.
COLONEL INGALLS:
News has gone to General Hooker which may change his plans. Act in view of such contingency.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER.
MY DEAR SIR:—The recent movement of your army is ended without effecting its object, except, perhaps, some important breakings of the enemy's communications. What next? If possible, I would be very glad of another movement early enough to give us some benefit from the fact of the enemy's communication being broken; but neither for this reason nor any other do I wish anything done in desperation or rashness. An early movement would also help to supersede the bad moral effect of there certain, which is said to be considerably injurious. Have you already in your mind a plan wholly or partially formed? If you have, prosecute it without interference from me. If you have not, please inform me, so that I, incompetent as I may be, can try and assist in the formation of some plan for the army.
Yours as ever,
MAY 8, 1863. BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation
Whereas the Congress of the United States, at its last session, enacted a law entitled "An act for enrolling and calling out the national forces and for other purposes," which was approved on the 3d day of March last; and
Whereas it is recited in the said act that there now exists in the United States an insurrection and rebellion against the authority thereof, and it is, under the Constitution of the United States, the duty of the government to suppress insurrection and rebellion, to guarantee to each State a republican form of government, and to preserve the public tranquillity; and
Whereas for these high purposes a military force is indispensable, to raise and support which all persons Ought willingly to contribute; and
Whereas no service can be more praiseworthy and honorable than that which is rendered for the maintenance of the Constitution and the Union, and the consequent preservation of free government; and
Whereas, for the reasons thus recited, it was enacted by the said statute that all able-bodied male citizens of the United States, and persons of foreign birth who shall have declared on oath their intention to become citizens under and in pursuance of the laws thereof, between the ages of twenty and forty-five years (with certain exceptions not necessary to be here mentioned), are declared to constitute the national forces, and shall be liable to perform military duty in the service of the United States when called out by the President for that purpose; and
Whereas it is claimed by and in behalf of persons of foreign birth within the ages specified in said act, who have heretofore declared on oath their intentions to become citizens under and in pursuance of the laws of the United States, and who have not exercised the right of suffrage or any other political franchise under the laws of the United States, or of any of the States thereof, that they are not absolutely concluded by their aforesaid declaration of intention from renouncing their purpose to become citizens, and that, on the contrary, such persons under treaties or the law of nations retain a right to renounce that purpose and to forego the privileges of citizenship and residence within the United States under the obligations imposed by the aforesaid act of Congress:
Now, therefore, to avoid all misapprehensions concerning the liability of persons concerned to perform the service required by such enactment, and to give it full effect, I do hereby order and proclaim that no plea of alienage will be received or allowed to exempt from the obligations imposed by the aforesaid act of Congress any person of foreign birth who shall have declared on oath his intention to become a citizen of the United States under the laws thereof, and who shall be found within the United States at any time during the continuance of the present insurrection and rebellion, at or after the expiration of the period of sixty-five days from the date of this proclamation; nor shall any such plea of alienage be allowed in favor of any such person who has so, as aforesaid, declared his intention to become a citizen of the United States, and shall have exercised at any time the right of suffrage, or any other political franchise, within the United States, under the laws thereof, or under the laws of any of the several States.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed. Done at the city of Washington, this eighth day of May, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-seventh.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
The news is here of the capture by our forces of Grand Gulf—a large and very important thing. General Willich, an exchanged prisoner just from Richmond, has talked with me this morning. He was there when our cavalry cut the roads in that vicinity. He says there was not a sound pair of legs in Richmond, and that our men, had they known it, could have safely gone in and burned everything and brought in Jeff Davis. We captured and paroled 300 or 400 men. He says as he came to City Point there was an army three miles long (Longstreet's, he thought) moving toward Richmond.
Muroy has captured a despatch of General Lee, in which he says his loss was fearful in his last battle with you.
MAJOR-GENERAL DIX:
It is very important for Hooker to know exactly what damage is done to the railroads at all points between Fredericksburg and Richmond. As yet we have no word as to whether the crossings of the North and South Anna, or any of them, have been touched. There are four of these Crossings; that is, one on each road on each stream. You readily perceive why this information is desired. I suppose Kilpatrick or Davis can tell. Please ascertain fully what was done, and what is the present condition, as near as you can, and advise me at once.
I believe Mr. L. is a good man, but two things need to be remembered.
1st. Mr. R.'s rival was a relative of Mr. L.
2d. I hear of nobody calling Mr. R. a "Copperhead," but Mr. L. However, let us watch.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
DEAR SIR:—I have again concluded to relieve General Curtis. I see no other way to avoid the worst consequences there. I think of General Schofield as his successor, but I do not wish to take the matter of a successor out of the hands of yourself and General Halleck.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL DIX:
Do the Richmond papers have anything about Grand Gulf or Vicksburg?
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, May 11, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTTERFIELD:
About what distance is it from the observatory we stopped at last Thursday to the line of enemies' works you ranged the glass upon for me?
GOVERNOR SEYMOUR, Albany, N.Y.:
Dr. Swinburne and Mr. Gillett are here, having been refused, as they say, by the War Department, permission to go to the Army of the Potomac. They now appeal to me, saying you wish them to go. I suppose they have been excluded by a rule which experience has induced the department to deem proper; still they shall have leave to go, if you say you desire it. Please answer.
Dr. A. G. HENRY, Metropolitan Hotel, New York:
Governor Chase's feelings were hurt by my action in his absence. Smith is removed, but Governor Chase wishes to name his successor, and asks a day or two to make the designation.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER, Commanding.
MY DEAR SIR:—When I wrote on the 7th, I had an impression that possibly by an early movement you could get some advantage from the supposed facts that the enemy's communications were disturbed and that he was somewhat deranged in position. That idea has now passed away, the enemy having re-established his communications, regained his positions, and actually received reinforcements. It does not now appear probable to me that you can gain anything by an early renewal of the attempt to cross the Rappahannock. I therefore shall not complain if you do no more for a time than to keep the enemy at bay and out of other mischief by menaces and occasional cavalry raids, if practicable, and to put your own army in good condition again. Still, if in your own clear judgment you can renew the attack successfully, I do not mean to restrain you. Bearing upon this last point, I must tell you that I have some painful intimations that some of your corps and division commanders are not giving you their entire confidence. This would be ruinous, if true, and you should therefore, first of all, ascertain the real facts beyond all possibility of doubt.
Yours truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 15, 1863.
HON. H. T. BLOW, C. D. DRAKE, AND OTHERS, St. Louis, Mo.:
Your despatch of to-day is just received. It is very painful to me that you in Missouri cannot or will not settle your factional quarrel among yourselves. I have been tormented with it beyond endurance for months by both sides. Neither side pays the least respect to my appeals to your reason. I am now compelled to take hold of the case.
HON. JAMES GUTHRIE, Louisville, Ky.:
Your despatch of to-day is received. I personally know nothing of Colonel Churchill, but months ago and more than once he has been represented to me as exerting a mischievous influence at Saint Louis, for which reason I am unwilling to force his continuance there against the judgment of our friends on the ground; but if it will oblige you, he may come to and remain at Louisville upon taking the oath of allegiance, and your pledge for his good behavior.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—The commander of the Department at St. Louis has ordered several persons south of our military lines, which order is not disapproved by me. Yet at the special request of the HON. James Guthrie I have consented to one of the number, Samuel Churchill, remaining at Louisville, Ky., upon condition of his taking the oath of allegiance and Mr. Gutlirie's word of honor for his good behavior.
Yours truly,
UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH, May 10, 1863. By telegraph from Washington, 9.40 PM, 1863
TO MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Commanding Department of Ohio.
SIR:—The President directs that without delay you send C. L. Vallandigham under secure guard to the Headquarters of General Rosecrans, to be put by him beyond our military lines; and in case of his return within our lines, he be arrested and kept in close custody for the term specified in his sentence.
By order of the President: E. R. S. CANBY, Assistant Adjutant-General.
MAJOR-GENERAL A. B. BURNSIDE, Commanding Department of Ohio, Cincinnati, O.
Your despatch of three o'clock this afternoon to the Secretary of War has been received and shown to the President. He thinks the best disposition to be made of Vallandigham is to put him beyond the lines, as directed in the order transmitted to you last evening, and directs that you execute that order by sending him forward under secure guard without delay to General Rosecrans.
By order of the President: ED. R. S. CANBY, Brigadier-General
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS:
Yours of yesterday in regard to Colonel Haggard is received. I am anxious that you shall not misunderstand me. In no case have I intended to censure you or to question your ability. In Colonel Haggard's case I meant no more than to suggest that possibly you might have been mistaken in a point that could [be] corrected. I frequently make mistakes myself in the many things I am compelled to do hastily.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS:
For certain reasons it is thought best for Rev. Dr. Jaquess not to come here.
Present my respects to him, and ask him to write me fully on the subject he has in contemplation.
MAJOR-GENERAL HURLBUT, Memphis, Tenn.:
We have news here in the Richmond newspapers of 20th and 21st, including a despatch from General Joe Johnston himself, that on the 15th or 16th—a little confusion as to the day—Grant beat Pemberton and [W. W.] Loring near Edwards Station, at the end of a nine hours' fight, driving Pemberton over the Big Black and cutting Loring off and driving him south to Crystal Springs, twenty-five miles below Jackson. Joe Johnston telegraphed all this, except about Loring, from his camp between Brownsville and Lexington, on the 18th. Another despatch indicates that Grant was moving against Johnston on the 18th.
ANSON STAGER, Cleveland, O.:
Late last night Fuller telegraphed you, as you say, that "the Stars and Stripes float over Vicksburg and the victory is complete." Did he know what he said, or did he say it without knowing it? Your despatch of this afternoon throws doubt upon it.
COLONEL HAGGARD, Nashville, Tenn.:
Your despatch to Green Adams has just been shown me. General Rosecrans knows better than we can know here who should be in charge of the Fifth Cavalry.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, O.:
Your despatch about Campbell, Lyle, and others received and postponement ordered by you approved. I will consider and telegraph you again in a few days.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
Let the execution of William B. Compton be respited or suspended till further order from me, holding him in safe custody meanwhile. On receiving this notify me.
GOVERNOR BUCKINGHAM, Hartford, Conn.:
The execution of Warren Whitemarch is hereby respited or suspended until further order from me, he to be held in safe custody meanwhile. On receiving this notify me.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn.:
Have you anything from Grant? Where is Forrest's headquarters?
GENERAL JOHN M. SCHOFIELD.
MY DEAR SIR:—Having relieved General Curtis and assigned you to the command of the Department of the Missouri, I think it may be of some advantage for me to state why I did it. I did not relieve General Curtis because of any full conviction that he had done wrong by commission or omission. I did it because of a conviction in my mind that the Union men of Missouri, constituting, when united, a vast majority of the whole people, have entered into a pestilent factional quarrel among themselves—General Curtis, perhaps not of choice, being the head of one faction and Governor Gamble that of the other. After months of labor to reconcile the difficulty, it seemed to grow worse and worse, until I felt it my duty to break it up somehow; and as I could not remove Governor Gamble, I had to remove General Curtis. Now that you are in the position, I wish you to undo nothing merely because General Curtis or Governor Gamble did it, but to exercise your own judgment, and do right for the public interest. Let your military measures be strong enough to repel the invader and keep the peace, and not so strong as to unnecessarily harass and persecute the people. It is a difficult role, and so much greater will be the honor if you perform it well. If both factions, or neither, shall abuse you, you will probably be about right. Beware of being assailed by one and praised by the other.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Have you Richmond papers of this morning? If so, what news?
HON. ERASTUS CORNING, Albany, N.Y.:
The letter of yourself and others dated the 19th and inclosing the resolutions of a public meeting held at Albany on the 16th, was received night before last. I shall give the resolutions the consideration you ask, and shall try to find time and make a respectful response.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Murfreesborough, Tenn..
I would not push you to any rashness, but I am very anxious that you do your utmost, short of rashness, to keep Bragg from getting off to help Johnston against Grant.
GOVERNOR ANDREW JOHNSON, Louisville, Ky.:
General Burnside has been frequently informed lately that the division under General Getty cannot be spared. I am sorry to have to tell you this, but it is true, and cannot be helped.
MESSRS. JESSE K. DUBOIS, O. M. HATCH, JOHN WILLIAMS, JACOB BUNN, JOHN BUNN, GEORGE R. WEBER, WILLIAM YATES, S. M. CULLOM, CHARLES W. MATHENY, WILLIAM F. ELKIN, FRANCIS SPRINGER, B. A. WATSON, ELIPHALET HAWLEY, AND JAMES CAMPBELL.
GENTLEMEN:—Agree among yourselves upon any two of your own number—one of whom to be quartermaster and the other to be commissary to serve at Springfield, Illinois, and send me their names, and I will appoint them.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, O.:
Your despatch of to-day received. When I shall wish to supersede you I will let you know. All the Cabinet regretted the necessity of arresting, for instance, Vallandigham, some perhaps doubting there was a real necessity for it; but, being done, all were for seeing you through with it.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 1, 1863.
COLONEL LUDLOW, Fort Monroe:
Richardson and Brown, correspondents of the Tribune captured at Vicksburg, are detained at Richmond. Please ascertain why they are detained, and get them off if you can.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
It is said that Philip Margraf, in your army, is under sentence to be shot on Friday the 5th instant as a deserter. If so please send me up the record of his case at once.
MAJOR-GENERAL GRANT, Vicksburg, via Memphis:
Are you in communication with General Banks? Is he coming toward you or going farther off? Is there or has there been anything to hinder his coming directly to you by water from Alexandria?
June 4,1863.
Let execution of sentences in the cases of Daily, Margraf, and Harrington be respited till further orders from me, they remaining in close custody meanwhile.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTTERFIELD:
The news you send me from the Richmond Sentinel of the 3d must be greatly if not wholly incorrect. The Thursday mentioned was the 28th, and we have despatches here directly from Vicksburg of the 28th, 29th, 30th, and 31st; and, while they speak of the siege progressing, they speak of no assault or general fighting whatever, and in fact they so speak as to almost exclude the idea that there can have been any since Monday the 25th, which was not very heavy. Neither do they mention any demand made by Grant upon Pemberton for a surrender. They speak of our troops as being in good health, condition, and spirits. Some of them do say that Banks has Port Hudson invested.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have received additional despatches, which, with former ones, induce me to believe we should revoke or suspend the order suspending the Chicago Times; and if you concur in opinion, please have it done.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Yours of to-day was received an hour ago. So much of professional military skill is requisite to answer it that I have turned the task over to General Halleck. He promises to perform it with his utmost care. I have but one idea which I think worth suggesting to you, and that is, in case you find Lee coming to the north of the Rappahannock, I would by no means cross to the south of it. If he should leave a rear force at Fredericksburg, tempting you to fall upon it, it would fight in entrenchments and have you at advantage, and so, man for man, worst you at that point, While his main force would in some way be getting an advantage of you northward. In one word, I would not take any risk of being entangled up on the river like an ox jumped half over a fence and liable to be torn by dogs front and rear without a fair chance to gore one way or to kick the other.
If Lee would come to my side of the river I would keep on the same side and fight him, or act on the defensive, according as might be my estimate of his strength relatively to my own. But these are mere suggestions, which I desire to be controlled by the judgment of yourself and General Halleck.
Mrs. ELIZABETH J. GRIMSLEY, Springfield, Ill.:
Is your John ready to enter the naval school? If he is, telegraph me his full name.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe, Va.:
By noticing the news you send from the Richmond Dispatch of this morning you will see one of the very latest despatches says they have nothing reliable from Vicksburg since Sunday. Now we here have a despatch from there Sunday and others of almost every day preceding since the investment, and while they show the siege progressing they do not show any general fighting since the 21st and 22d. We have nothing from Port Hudson later than the 29th when things looked reasonably well for us. I have thought this might be of some interest to you.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe:
We have despatches from Vicksburg of the 3d. Siege progressing. No general fighting recently. All well. Nothing new from Port Hudson.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Fort Monroe:
The substance of news sent of the fighting at Port Hudson on the 27th we have had here three or four days, and I supposed you had it also, when I said this morning, "No news from Port Hudson." We knew that General Sherman was wounded, but we hoped not so dangerously as your despatch represents. We still have nothing of that Richmond newspaper story of Kirby Smith crossing and of Banks losing an arm.
HON. JOHN P. HALE, Dover, N. H.:
I believe that it was upon your recommendation that B. B. Bunker was appointed attorney for Nevada Territory. I am pressed to remove him on the ground that he does not attend to the office, nor in fact pass much time in the Territory. Do you wish to say anything on the subject?
MRS. LINCOLN, Philadelphia, Pa.:
Think you had better put "Tad's" pistol away. I had an ugly dream about him.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
I am told there are 50 incendiary shells here at the arsenal made to fit the 100 pounder Parrott gun now with you. If this be true would you like to have the shells sent to you?
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Your long despatch of to-day is just received. If left to me, I would not go south of the Rappahannock upon Lee's moving north of it. If you had Richmond invested to-day you would not be able to take it in twenty days; meanwhile your communications, and with them your army, would be ruined. I think Lee's army, and not Richmond, is your true objective point. If he comes towards the upper Potomac, follow on his flank, and on the inside track, shortening your lines while he lengthens his. Fight him, too, when opportunity offers. If he stay where he is, fret him and fret him.
MRS. LINCOLN, Philadelphia:
Your three despatches received. I am very well and am glad to know that you and "Tad" are so.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, JUNE 12, 1863. MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
If you can show me a trial of the incendiary shells on Saturday night, I will try to join you at 5 P.M. that day Answer.
HON. ERASTUS CORNING AND OTHERS.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter of May 19, inclosing the resolutions of a public meeting held at Albany, New York, on the 16th of the same month, was received several days ago.
The resolutions, as I understand them, are resolvable into two propositions—first, the expression of a purpose to sustain the cause of the Union, to secure peace through victory, and to support the administration in every constitutional and lawful measure to suppress the rebellion; and, secondly, a declaration of censure upon the administration for supposed unconstitutional action, such as the making of military arrests. And from the two propositions a third is deduced, which is that the gentlemen composing the meeting are resolved on doing their part to maintain our common government and country, despite the folly or wickedness, as they may conceive, of any administration. This position is eminently patriotic, and as such I thank the meeting, and congratulate the nation for it. My own purpose is the same; so that the meeting and myself have a common object, and can have no difference, except in the choice of means or measures for effecting that object.
And here I ought to close this paper, and would close it, if there were no apprehension that more injurious consequences than any merely personal to myself might follow the censures systematically cast upon me for doing what, in my view of duty, I could not forbear. The resolutions promise to support me in every constitutional and lawful measure to suppress the rebellion; and I have not knowingly employed, nor shall knowingly employ, any other. But the meeting, by their resolutions, assert and argue that certain military arrests, and proceedings following them, for which I am ultimately responsible, are unconstitutional. I think they are not. The resolutions quote from the Constitution the definition of treason, and also the limiting safeguards and guarantees therein provided for the citizen on trial for treason, and on his being held to answer for capital or otherwise infamous crimes, and in criminal prosecutions his right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury. They proceed to resolve "that these safeguards of the rights of the citizen against the pretensions of arbitrary power were intended more especially for his protection in times of civil commotion." And, apparently to demonstrate the proposition, the resolutions proceed: "They were secured substantially to the English people after years of protracted civil war, and were adopted into our Constitution at the close of the Revolution." Would not the demonstration have been better if it could have been truly said that these safeguards had been adopted and applied during the civil wars and during our Revolution, instead of after the one and at the close of the other? I too am devotedly for them after civil war, and before Civil war, and at all times, "except when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require" their suspension. The resolutions proceed to tell us that these safeguards "have stood the test of seventy-six years of trial under our republican system, under circumstances which show that, while they constitute the foundation of all free government, they are the elements of the enduring stability of the republic." No one denies that they have so stood the test up to the beginning of the present rebellion, if we except a certain occurrence at New Orleans hereafter to be mentioned; nor does any one question that they will stand the same test much longer after the rebellion closes. But these provisions of the Constitution have no application to the case we have in hand, because the arrests complained of were not made for treason—that is, not for the treason defined in the Constitution, and upon the conviction of which the punishment is death—nor yet were they made to hold persons to answer for any capital or otherwise infamous crimes; nor were the proceedings following, in any constitutional or legal sense, "criminal prosecutions." The arrests were made on totally different grounds, and the proceedings following accorded with the grounds of the arrests. Let us consider the real case with which we are dealing, and apply to it the parts of the Constitution plainly made for such cases.
Prior to my installation here it had been inculcated that any State had a lawful right to secede from the national Union, and that it would be expedient to exercise the right whenever the devotees of the doctrine should fail to elect a president to their own liking. I was elected contrary to their liking; and accordingly, so far as it was legally possible, they had taken seven States out of the Union, had seized many of the United States forts, and had fired upon the United States flag, all before I was inaugurated, and, of course, before I had done any official act whatever. The rebellion thus begun soon ran into the present civil war; and, in certain respects, it began on very unequal terms between the parties. The insurgents had been preparing for it more than thirty years, while the government had taken no steps to resist them. The former had carefully considered all the means which could be turned to their account. It undoubtedly was a well-pondered reliance with them that in their own unrestricted effort to destroy Union, Constitution and law, all together, the government would, in great degree, be restrained by the same Constitution and law from arresting their progress. Their sympathizers invaded all departments of the government and nearly all communities of the people. From this material, under cover of "liberty of speech," "liberty of the press," and "habeas corpus," they hoped to keep on foot amongst us a most efficient corps of spies, informers, suppliers, and aiders and abettors of their cause in a thousand ways. They knew that in times such as they were inaugurating, by the Constitution itself the "habeas corpus" might be suspended; but they also knew they had friends who would make a question as to who was to suspend it; meanwhile their spies and others might remain at large to help on their cause. Or if, as has happened, the Executive should suspend the writ without ruinous waste of time, instances of arresting innocent persons might occur, as are always likely to occur in such cases; and then a clamor could be raised in regard to this, which might be at least of some service to the insurgent cause. It needed no very keen perception to discover this part of the enemies program, so soon as by open hostilities their machinery was fairly put in motion. Yet, thoroughly imbued with a reverence for the guaranteed rights of individuals, I was slow to adopt the strong measures which by degrees I have been forced to regard as being within the exceptions of the Constitution, and as indispensable to the public safety. Nothing is better known to history than that courts of justice are utterly incompetent to such cases. Civil courts are organized chiefly for trials of individuals—or, at most, a few individuals acting in concert, and this in quiet times, and on charges of crimes well defined in the law. Even in times of peace bands of horse-thieves and robbers frequently grow too numerous and powerful for the ordinary courts of justice. But what comparison, in numbers have such bands ever borne to the insurgent sympathizers even in many of the loyal States? Again, a jury too frequently has at least one member more ready to hang the panel than to hang the traitor. And yet again, he who dissuades one man from volunteering, or induces one soldier to desert, weakens the Union cause as much as he who kills a Union soldier in battle. Yet this dissuasion or inducement may be so conducted as to be no defined crime of which any civil court would take cognizance.
Ours is a case of rebellion—so called by the resolutions before me—in fact, a clear, flagrant, and gigantic case of rebellion; and the provision of the Constitution that "the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus shall not be suspended unless when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require it," is the provision which specially applies to our present case. This provision plainly attests the understanding of those who made the Constitution that ordinary courts of justice are inadequate to "cases of rebellion"—attests their purpose that, in such cases, men may be held in custody whom the courts, acting on ordinary rules, would discharge. Habeas corpus does not discharge men who are proved to be guilty of defined crime, and its suspension is allowed by the Constitution on purpose that men may be arrested and held who can not be proved to be guilty of defined crime, "when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require it."
This is precisely our present case—a case of rebellion wherein the public safety does require the suspension—Indeed, arrests by process of courts and arrests in cases of rebellion do not proceed altogether upon the same basis. The former is directed at the small percentage of ordinary and continuous perpetration of crime, while the latter is directed at sudden and extensive uprisings against the government, which, at most, will succeed or fail in no great length of time. In the latter case arrests are made not so much for what has been done as for what probably would be done. The latter is more for the preventive and less for the vindictive than the former. In such cases the purposes of men are much more easily understood than in cases of ordinary crime. The man who stands by and says nothing when the peril of his government is discussed, cannot be misunderstood. If not hindered, he is sure to help the enemy; much more if he talks ambiguously—talks for his country with "buts," and "ifs," and "ands." Of how little value the constitutional provision I have quoted will be rendered if arrests shall never be made until defined crimes shall have been committed, may be illustrated by a few notable examples: General John C. Breckinridge, General Robert E. Lee, General Joseph E. Johnston, General John B. Magruder, General William B. Preston, General Simon B. Buckner, and Commodore Franklin Buchanan, now occupying the very highest places in the rebel war service, were all within the power of the government since the rebellion began, and were nearly as well known to be traitors then as now. Unquestionably if we had seized and had them the insurgent cause would be much weaker. But no one of them had then committed any crime defined in the law. Every one of them, if arrested, would have been discharged on habeas corpus were the writ allowed to operate. In view of these and similar cases, I think the time not unlikely to come when I shall be blamed for having made too few arrests rather than too many.
By the third resolution the meeting indicate their opinion that military arrests may be constitutional in localities where rebellion actually exists, but that such arrests are unconstitutional in localities where rebellion or insurrection does not actually exist. They insist that such arrests shall not be made "outside of the lines of necessary military occupation and the scenes of insurrection." Inasmuch, however, as the Constitution itself makes no such distinction, I am unable to believe that there is any such constitutional distinction. I concede that the class of arrests complained of can be constitutional only when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require them; and I insist that in such cases—they are constitutional wherever the public safety does require them, as well in places to which they may prevent the rebellion extending, as in those where it may be already prevailing; as well where they may restrain mischievous interference with the raising and supplying of armies to suppress the rebellion as where the rebellion may actually be; as well where they may restrain the enticing men out of the army as where they would prevent mutiny in the army; equally constitutional at all places where they will conduce to the public safety as against the dangers of rebellion or invasion. Take the particular case mentioned by the meeting. It is asserted in substance that Mr. Vallandigham was, by a military commander, seized and tried "for no other reason than words addressed to a public meeting in criticism of the course of the administration, and in condemnation of the military orders of the general." Now, if there be no mistake about this, if this assertion is the truth, and the whole truth, if there were no other reason for the arrest, then I concede that the arrest was wrong. But the arrest, as I understand, was made for a very different reason. Mr. Vallandigham avows his hostility to the war on the part of the Union; and his arrest was made because he was laboring, with some effect, to prevent the raising of troops, to encourage desertions from the army, and to leave the rebellion without an adequate military force to suppress it. He was not arrested because he was damaging the political prospects of the administration or the personal interests of the commanding general, but because he was damaging the army, upon the existence and vigor of which the life of the nation depends. He was warring upon the military, and thus gave the military constitutional jurisdiction to lay hands upon him. If Mr. Vallandigham was not damaging the military power of the country, then his arrest was made on mistake of fact, which I would be glad to correct on reasonably satisfactory evidence.
I understand the meeting whose resolutions I am considering to be in favor of suppressing the rebellion by military force—by armies. Long experience has shown that armies cannot be maintained unless desertion shall be punished by the severe penalty of death. The case requires, and the law and the Constitution sanction, this punishment. Must I shoot a simple-minded boy and not touch a hair of a wily agitator who induced him to desert. This is none the less injurious when effected by getting a father, or brother, or friend into a public meeting, and there working upon his feelings till he is persuaded to write the soldier boy that he is fighting in a bad cause, for a wicked administration of a contemptible government, too weak to arrest and punish him if he shall desert. I think that, in such a case, to silence the agitator and save the boy is not only constitutional, but withal a great mercy.
If I be wrong on this question of constitutional power, my error lies in believing that certain proceedings are constitutional when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety requires them, which would not be constitutional when, in absence of rebellion or invasion, the public safety does not require them: in other words, that the Constitution is not in its application in all respects the same in cases of rebellion or invasion involving the public safety as it is in times of profound peace and public security. The Constitution itself makes the distinction, and I can no more be persuaded that the government can constitutionally take no strong measures in time of rebellion, because it can be shown that the same could not be lawfully taken in times of peace, than I can be persuaded that a particular drug is not good medicine for a sick man because it can be shown to not be good food for a well one. Nor am I able to appreciate the danger apprehended by the meeting, that the American people will by means of military arrests during the rebellion lose the right of public discussion, the liberty of speech and the press, the law of evidence, trial by jury, and habeas corpus throughout the indefinite peaceful future which I trust lies before them, any more than I am able to believe that a man could contract so strong an appetite for emetics during temporary illness as to persist in feeding upon them during the remainder of his healthful life.
In giving the resolutions that earnest consideration which you request of me, I cannot overlook the fact that the meeting speak as "Democrats." Nor can I, with full respect for their known intelligence, and the fairly presumed deliberation with which they prepared their resolutions, be permitted to suppose that this occurred by accident, or in any way other than that they preferred to designate themselves "Democrats" rather than "American citizens." In this time of national peril I would have preferred to meet you upon a level one step higher than any party platform, because I am sure that from such more elevated position we could do better battle for the country we all love than we possibly can from those lower ones where, from the force of habit, the prejudices of the past, and selfish hopes of the future, we are sure to expend much of our ingenuity and strength in finding fault with and aiming blows at each other. But since you have denied me this I will yet be thankful for the country's sake that not all Democrats have done so. He on whose discretionary judgment Mr. Vallandigham was arrested and tried is a Democrat, having no old party affinity with me, and the judge who rejected the constitutional view expressed in these resolutions, by refusing to discharge Mr. Vallandigham on habeas corpus is a Democrat of better days than these, having received his judicial mantle at the hands of President Jackson. And still more: of all those Democrats who are nobly exposing their lives and shedding their blood on the battle-field, I have learned that many approve the course taken with Mr. Vallandigham, while I have not heard of a single one condemning it. I cannot assert that there are none such. And the name of President Jackson recalls an instance of pertinent history. After the battle of New Orleans, and while the fact that the treaty of peace had been concluded was well known in the city, but before official knowledge of it had arrived, General Jackson still maintained martial or military law. Now that it could be said that the war was over, the clamor against martial law, which had existed from the first, grew more furious. Among other things, a Mr. Louaillier published a denunciatory newspaper article. General Jackson arrested him. A lawyer by the name of Morel procured the United States Judge Hall to order a writ of habeas corpus to release Mr. Louaillier. General Jackson arrested both the lawyer and the judge. A Mr. Hollander ventured to say of some part of the matter that "it was a dirty trick." General Jackson arrested him. When the officer undertook to serve the writ of habeas corpus, General Jackson took it from him, and sent him away with a copy. Holding the judge in custody a few days, the general sent him beyond the limits of his encampment, and set him at liberty with an order to remain till the ratification of peace should be regularly announced, or until the British should have left the southern coast. A day or two more elapsed, the ratification of the treaty of peace was regularly announced, and the judge and others were fully liberated. A few days more, and the judge called General Jackson into court and fined him $1000 for having arrested him and the others named. The General paid the fine, and then the matter rested for nearly thirty years, when Congress refunded principal and interest. The late Senator Douglas, then in the House of Representatives, took a leading part in the debates, in which the constitutional question was much discussed. I am not prepared to say whom the journals would show to have voted for the measure.
It may be remarked—first, that we had the same Constitution then as now; secondly, that we then had a case of invasion, and now we have a case of rebellion; and, thirdly, that the permanent right of the people to public discussion, the liberty of speech and of the press, the trial by jury, the law of evidence, and the habeas corpus suffered no detriment whatever by that conduct of General Jackson, or its subsequent approval by the American Congress.
And yet, let me say that, in my own discretion, I do not know whether I would have ordered the arrest of Mr. Vallandigham. While I cannot shift the responsibility from myself, I hold that, as a general rule, the commander in the field is the better judge of the necessity in any particular case. Of course I must practice a general directory and revisory power in the matter.
One of the resolutions expresses the opinion of the meeting that arbitrary arrests will have the effect to divide and distract those who should be united in suppressing the rebellion, and I am specifically called on to discharge Mr. Vallandigham. I regard this as, at least, a fair appeal to me on the expediency of exercising a constitutional power which I think exists. In response to such appeal I have to say, it gave me pain when I learned that Mr. Vallandigham had been arrested (that is, I was pained that there should have seemed to be a necessity for arresting him), and that it will afford me great pleasure to discharge him so soon as I can by any means believe the public safety will not suffer by it.
I further say that, as the war progresses, it appears to me, opinion and action, which were in great confusion at first, take shape and fall into more regular channels, so that the necessity for strong dealing with them gradually decreases. I have every reason to desire that it should cease altogether, and far from the least is my regard for the opinions and wishes of those who, like the meeting at Albany, declare their purpose to sustain the government in every constitutional and lawful measure to suppress the rebellion. Still, I must continue to do so much as may seem to be required by the public safety.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
SIR:—Your note of this morning is received. You will co-operate by the revenue cutters under your direction with the navy in arresting rebel depredations on American commerce and transportation and in capturing rebels engaged therein.
GENERAL TYLER, Martinsburg: Is Milroy invested so that he cannot fall back to Harper's Ferry?
WAR DEPARTMENT, June 14, 1863.
GENERAL TYLER, Martinsburg:
If you are besieged, how do you despatch me? Why did you not leave before being besieged?
MAJOR-GENERAL KELLEY, Harper's Ferry:
Are the forces at Winchester and Martinsburg making any effort to get to you?
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
So far as we can make out here, the enemy have Muroy surrounded at Winchester, and Tyler at Martinsburg. If they could hold out a few days, could you help them? If the head of Lee's army is at Martinsburg and the tail of it on the plank-road between Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville, the animal must be very slim somewhere; could you not break him?
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK:
Get General Milroy from Winchester to Harper's Ferry, if possible. He will be "gobbled up" if he remains, if he is not already past salvation.
A. LINCOLN, President, United States.
WAR DEPARTMENT, June 15, 1863.
MRS. LINCOLN, Philadelphia, Pa.:
Tolerably well. Have not rode out much yet, but have at last got new tires on the carriage wheels and perhaps shall ride out soon.
A Proclamation
Whereas the armed insurrectionary combinations now existing in several of the States are threatening to make inroads into the States of Maryland, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Ohio, requiring immediately an additional military force for the service of the United States:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States and Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy thereof and of the militia of the several States when called into actual service, do hereby call into the service of the United States 100,000 militia from the States following, namely:
From the State of Maryland, 10,000; from the State of Pennsylvania, 50,000; from the State of Ohio, 30,000; from the State of West Virginia, 10,000—to be mustered into the service of the United States forthwith and to serve for a period of six months from the date of such muster into said service, unless sooner discharged; to be mustered in as infantry, artillery, and cavalry, in proportions which will be made known through the War Department, which Department will also designate the several places of rendezvous. These militia to be organized according to the rules and regulations of the volunteer service and such orders as may hereafter be issued. The States aforesaid will be respectively credited under the enrollment act for the militia services entered under this proclamation. In testimony whereof...............
FREDERICK KAPP AND OTHERS, New York:
The Governor of New York promises to send us troops, and if he wishes the assistance of General Fremont and General Sigel, one or both, he can have it. If he does not wish them it would but breed confusion for us to set them to work independently of him.
GENERAL T. FRANCIS MEAGHER, New York:
Your despatch received. Shall be very glad for you to raise 3000 Irish troops if done by the consent of and in concert with Governor Seymour.
MRS. LINCOLN, Philadelphia:
It is a matter of choice with yourself whether you come home. There is no reason why you should not, that did not exist when you went away. As bearing on the question of your coming home, I do not think the raid into Pennsylvania amounts to anything at all.
COL. WILLIAM S. BLISS, New York Hotel:
Your despatch asking whether I will accept "the Loyal Brigade of the North" is received. I never heard of that brigade by name and do not know where it is; yet, presuming it is in New York, I say I will gladly accept it, if tendered by and with the consent and approbation of the Governor of that State. Otherwise not.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
To remove all misunderstanding, I now place you in the strict military relation to General Halleck of a commander of one of the armies to the general-in-chief of all the armies. I have not intended differently, but as it seems to be differently understood I shall direct him to give you orders and you to obey them.
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Mr. Eckert, superintendent in the telegraph office, assures me that he has sent and will send you everything that comes to the office.
JOSHUA TEVIS, Esq., U. S. Attorney, Frankfort, Ky.:
A Mr. Burkner is here shoving a record and asking to be discharged from a suit in San Francisco, as bail for one Thompson. Unless the record shown me is defectively made out I think it can be successfully defended against. Please examine the case carefully and, if you shall be of opinion it cannot be sustained, dismiss it and relieve me from all trouble about it. Please answer.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON,
June 18, 1863.
GOVERNOR D. TOD, Columbus, O.:
Yours received. I deeply regret that you were not renominated, not that I have aught against Mr. Brough. On the contrary, like yourself, I say hurrah for him.
GENERAL A. DINGMAN, Belleville, C. W.:
Thanks for your offer of the Fifteenth Battalion. I do not think Washington is in danger.
MESSRS. B. B. MALHIOT, BRADISH JOHNSON, AND THOMAS COTTMAN.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter, which follows, has been received and Considered.
"The undersigned, a committee appointed by the planters of the State of Louisiana, respectfully represent that they have been delegated to seek of the General Government a full recognition of all the rights of the State as they existed previous to the passage of an act of secession, upon the principle of the existence of the State constitution unimpaired, and no legal act having transpired that could in any way deprive them of the advantages conferred by that constitution. Under this constitution the State wishes to return to its full allegiance, in the enjoyment of all rights and privileges exercised by the other States under the Federal Constitution. With the view of accomplishing the desired object, we further request that your Excellency will, as commander-in-chief of the army of the United States, direct the Military Governor of Louisiana to order an election, in conformity with the constitution and laws of the State, on the first Monday of November next, for all State and Federal officers.
"With high consideration and resect, we have the honor to subscribe ourselves,
"Your obedient servants,
"E. E. MALHIOT.
"BRADISH JOHNSON.
"THOMAS COTTMAN."
Since receiving the letter, reliable information has reached me that a respectable portion of the Louisiana people desire to amend their State constitution, and contemplate holding a State convention for that object. This fact alone, as it seems to me, is a sufficient reason why the General Government should not give the committal you seek to the existing State constitution. I may add that, while I do not perceive how such committal could facilitate our military operations in Louisiana, I really apprehend it might be so used as to embarrass them.
As to an election to be held next November, there is abundant time without any order or proclamation from me just now. The people of Louisiana shall not lack an opportunity for a fair election for both Federal and State officers by want of anything within my power to give them.
Your obedient servant,
June 22, 1863.
GENERAL JOHN M. SCHOFIELD. MY DEAR SIR:—Your despatch, asking in substance whether, in case Missouri shall adopt gradual emancipation, the General Government will protect slave owners in that species of property during the short time it shall be permitted by the State to exist within it, has been received. Desirous as I am that emancipation shall be adopted by Missouri, and believing as I do that gradual can be made better than immediate for both black and white, except when military necessity changes the case, my impulse is to say that such protection would be given. I cannot know exactly what shape an act of emancipation may take. If the period from the initiation to the final end should be comparatively short, and the act should prevent persons being sold during that period into more lasting slavery, the whole would be easier. I do not wish to pledge the General Government to the affirmative support of even temporary slavery beyond what can be fairly claimed under the Constitution. I suppose, however, this is not desired, but that it is desired for the military force of the United States, while in Missouri, to not be used in subverting the temporarily reserved legal rights in slaves during the progress of emancipation. This I would desire also. I have very earnestly urged the slave States to adopt emancipation; and it ought to be, and is, an object with me not to overthrow or thwart what any of them may in good faith do to that end. You are therefore authorized to act in the spirit of this letter in conjunction with what may appear to be the military necessities of your department. Although this letter will become public at some time, it is not intended to be made so now.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
Operator at Leesburg just now says: "I heard very little firing this A.M. about daylight, but it seems to have stopped now. It was in about the same direction as yesterday, but farther off."
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR:
You remember that Hon. W. D. Kelly and others are engaged in raising or trying to raise some colored regiments in Philadelphia. The bearer of this, Wilton M. Huput, is a friend of Judge Kelly, as appears by the letter of the latter. He is a private in the 112th Penn. and has been disappointed in a reasonable expectation of one of the smaller offices. He now wants to be a lieutenant in one of the colored regiments. If Judge Kelly will say in writing he wishes to so have him, I am willing for him to be discharged from his present position, and be so appointed. If you approve, so indorse and let him carry the letter to Kelly.
Yours truly,
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., June 23, 1863.
MAJOR VAN VLIET, New York:
Have you any idea what the news is in the despatch of General Banks to General Halleck?
MAJOR-GENERAL COUCH, Harrisburg, Pa.:
Have you any reports of the enemy moving into Pennsylvania? And if any, what?
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, Yorktown, Va.:
We have a despatch from General Grant of the 19th. Don't think Kirby Smith took Milliken's Bend since, allowing time to get the news to Joe Johnston and from him to Richmond. But it is not absolutely impossible. Also have news from Banks to the 16th, I think. He had not run away then, nor thought of it.
GENERAL PECK, Suffolk, Va.:
Colonel Derrom, of the Twenty-fifth New Jersey Volunteers, now mustered out, says there is a man in your hands under conviction for desertion, who formerly belonged to the above named regiment, and whose name is Templeton—Isaac F. Templeton, I believe. The Colonel and others appeal to me for him. Please telegraph to me what is the condition of the case, and if he has not been executed send me the record of the trial and conviction.
MAJOR-GENERAL SLOCUM, Leesburg, Va.:
Was William Gruvier, Company A, Forty-sixth, Pennsylvania, one of the men executed as a deserter last Friday?
MAJOR-GENERAL HOOKER:
It did not come from the newspapers, nor did I believe it, but I wished to be entirely sure it was a falsehood.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, O.:
There is nothing going on in Kentucky on the subject of which you telegraph, except an enrolment. Before anything is done beyond this, I will take care to understand the case better than I now do.
GOVERNOR J. T. BOYLE, Cincinnati, O.:
There is nothing going on in Kentucky on the subject of which you telegraph, except an enrolment. Before anything is done beyond this, I will take care to understand the case better than I now do.
MAJOR GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
Every place in the Naval school subject to my appointment is full, and I have one unredeemed promise of more than half a year's standing.
WASHINGTON, D. C., June 29,1863.
MESSRS. M. BIRCHARD, DAVID A. HOUK, et al:
GENTLEMEN:—The resolutions of the Ohio Democratic State convention, which you present me, together with your introductory and closing remarks, being in position and argument mainly the same as the resolutions of the Democratic meeting at Albany, New York, I refer you to my response to the latter as meeting most of the points in the former.
This response you evidently used in preparing your remarks, and I desire no more than that it be used with accuracy. In a single reading of your remarks, I only discovered one inaccuracy in matter, which I suppose you took from that paper. It is where you say: "The undersigned are unable to agree with you in the opinion you have expressed that the Constitution is different in time of insurrection or invasion from what it is in time of peace and public security."
A recurrence to the paper will show you that I have not expressed the opinion you suppose. I expressed the opinion that the Constitution is different in its application in cases of rebellion or invasion, involving the public safety, from what it is in times of profound peace and public security; and this opinion I adhere to, simply because, by the Constitution itself, things may be done in the one case which may not be done in the other.
I dislike to waste a word on a merely personal point, but I must respectfully assure you that you will find yourselves at fault should you ever seek for evidence to prove your assumption that I "opposed in discussions before the people the policy of the Mexican war."
You say: "Expunge from the Constitution this limitation upon the power of Congress to suspend the writ of habeas corpus, and yet the other guarantees of personal liberty would remain unchanged." Doubtless, if this clause of the Constitution, improperly called, as I think, a limitation upon the power of Congress, were expunged, the other guarantees would remain the same; but the question is not how those guarantees would stand with that clause out of the Constitution, but how they stand with that clause remaining in it, in case of rebellion or invasion involving the public safety. If the liberty could be indulged of expunging that clause, letter and spirit, I really think the constitutional argument would be with you.
My general view on this question was stated in the Albany response, and hence I do not state it now. I only add that, as seems to me, the benefit of the writ of habeas corpus is the great means through which the guarantees of personal liberty are conserved and made available in the last resort; and corroborative of this view is the fact that Mr. Vallandigham, in the very case in question, under the advice of able lawyers, saw not where else to go but to the habeas corpus. But by the Constitution the benefit of the writ of habeas corpus itself may be suspended when, in case of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require it.
You ask, in substance, whether I really claim that I may override all the guaranteed rights of individuals, on the plea of conserving the public safety when I may choose to say the public safety requires it. This question, divested of the phraseology calculated to represent me as struggling for an arbitrary personal prerogative, is either simply a question who shall decide, or an affirmation that nobody shall decide, what the public safety does require in cases of rebellion or invasion.
The Constitution contemplates the question as likely to occur for decision, but it does not expressly declare who is to decide it. By necessary implication, when rebellion or invasion comes, the decision is to be made from time to time; and I think the man whom, for the time, the people have, under the Constitution, made the commander-in-chief of their army and navy, is the man who holds the power and bears the responsibility of making it. If he uses the power justly, the same people will probably justify him; if he abuses it, he is in their hands to be dealt with by all the modes they have reserved to themselves in the Constitution.
The earnestness with which you insist that persons can only, in times of rebellion, be lawfully dealt with in accordance with the rules for criminal trials and punishments in times of peace, induces me to add a word to what I said on that point in the Albany response.
You claim that men may, if they choose, embarrass those whose duty it is to combat a giant rebellion, and then be dealt with in turn only as if there were no rebellion. The Constitution itself rejects this view. The military arrests and detentions which have been made, including those of Mr. Vallandigham, which are not different in principle from the others, have been for prevention, and not for punishment—as injunctions to stay injury, as proceedings to keep the peace; and hence, like proceedings in such cases and for like reasons, they have not been accompanied with indictments, or trials by juries, nor in a single case by any punishment whatever, beyond what is purely incidental to the prevention. The original sentence of imprisonment in Mr. Vallandigham's case was to prevent injury to the military service only, and the modification of it was made as a less disagreeable mode to him of securing the same prevention.
I am unable to perceive an insult to Ohio in the case of Mr. Vallandigham. Quite surely nothing of the sort was or is intended. I was wholly unaware that Mr. Vallandigham was, at the time of his arrest, a candidate for the Democratic nomination for governor until so informed by your reading to me the resolutions of the convention. I am grateful to the State of Ohio for many things, especially for the brave soldiers and officers she has given in the present national trial to the armies of the Union.
You claim, as I understand, that according to my own position in the Albany response, Mr. Vallandigham should be released; and this because, as you claim, he has not damaged the military service by discouraging enlistments, encouraging desertions, or otherwise; and that if he had, he should have been turned over to the civil authorities under the recent acts of Congress. I certainly do not know that Mr. Vallandigham has specifically and by direct language advised against enlistments and in favor of desertion and resistance to drafting.
We all know that combinations, armed in some instances, to resist the arrest of deserters began several months ago; that more recently the like has appeared in resistance to the enrolment preparatory to a draft; and that quite a number of assassinations have occurred from the same animus. These had to be met by military force, and this again has led to bloodshed and death. And now, under a sense of responsibility more weighty and enduring than any which is merely official, I solemnly declare my belief that this hindrance of the military, including maiming and murder, is due to the course in which Mr. Vallandigham has been engaged in a greater degree than to any other cause; and it is due to him personally in a greater degree than to any other one man.
These things have been notorious, known to all, and of course known to Mr. Vallandigham. Perhaps I would not be wrong to say they originated with his special friends and adherents. With perfect knowledge of them, he has frequently if not constantly made speeches in Congress and before popular assemblies; and if it can be shown that, with these things staring him in the face he has ever uttered a word of rebuke or counsel against them, it will be a fact greatly in his favor with me, and one of which as yet I am totally ignorant. When it is known that the whole burden of his speeches has been to stir up men against the prosecution of the war, and that in the midst of resistance to it he has not been known in any instance to counsel against such resistance, it is next to impossible to repel the inference that he has counseled directly in favor of it.
With all this before their eyes, the convention you represent have nominated Mr. Vallandigham for governor of Ohio, and both they and you have declared the purpose to sustain the national Union by all constitutional means. But of course they and you in common reserve to yourselves to decide what are constitutional means; and, unlike the Albany meeting, you omit to state or intimate that in your opinion an army is a constitutional means of saving the Union against a rebellion, or even to intimate that you are conscious of an existing rebellion being in progress with the avowed object of destroying that very Union. At the same time your nominee for governor, in whose behalf you appeal, is known to you and to the world to declare against the use of an army to suppress the rebellion. Your own attitude, therefore, encourages desertion, resistance to the draft, and the like, because it teaches those who incline to desert and to escape the draft to believe it is your purpose to protect them, and to hope that you will become strong enough to do so.
After a short personal intercourse with you, gentlemen of the committee, I cannot say I think you desire this effect to follow your attitude; but I assure your that both friends and enemies of the Union look upon it in this light. It is a substantial hope, and by consequence a real strength to the enemy. If it is a false hope, and one which you would willingly dispel, I will make the way exceedingly easy.
I send you duplicates of this letter in order that you, or a majority of you, may, if you choose, indorse your names upon one of them and return it thus indorsed to me with the understanding that those signing are thereby committed to the following propositions and to nothing else:
1. That there is now a rebellion in the United States, the object and tendency of which is to destroy the National Union; and that, in your opinion, an army and navy are constitutional means for suppressing that rebellion;
2. That no one of you will do anything which, in his own judgment, will tend to hinder the increase, or favor the decrease, or lessen the efficiency of the army or navy while engaged in the effort to suppress that rebellion; and
3. That each of you will, in his sphere, do all he can to have the officers, soldiers, and seamen of the army and navy, while engaged in the effort to suppress the rebellion, paid, fed, clad, and otherwise well provided for and supported.
And with the further understanding that upon receiving the letter and names thus indorsed, I will cause them to be published, which publication shall be, within itself, a revocation of the order in relation to Mr. Vallandigham. It will not escape observation that I consent to the release of Mr. Vallandigham upon terms not embracing any pledge from him or from others as to what he will or will not do. I do this because he is not present to speak for himself, or to authorize others to speak for him; and because I should expect that on his returning he would not put himself practically in antagonism with the position of his friends. But I do it chiefly because I thereby prevail on other influential gentlemen of Ohio to so define their position as to be of immense value to the army—thus more than compensating for the consequences of any mistake in allowing Mr. Vallandigham to return; so that, on the whole, the public safety will not have suffered by it. Still, in regard to Mr. Vallandigham and all others, I must hereafter, as heretofore, do so much as the public safety may seem to require.
I have the honor to be respectfully yours, etc.,
GOVERNOR PARKER, Trenton, N.J.:
Your despatch of yesterday received. I really think the attitude of the enemy's army in Pennsylvania presents us the best opportunity we have had since the war began. I think you will not see the foe in New Jersey. I beg you to be assured that no one out of my position can know so well as if he were in it the difficulties and involvements of replacing General McClellan in command, and this aside from any imputations upon him.
Please accept my sincere thanks for what you have done and are doing to get troops forward.
A. K. McCLURE, Philadelphia:
Do we gain anything by opening one leak to stop another? Do we gain anything by quieting one merely to open another, and probably a larger one?
P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL COUCH, Harrisburg, Pa.:
I judge by absence of news that the enemy is not crossing or pressing up to the Susquehanna. Please tell me what you know of his movements.
MAJOR-GENERAL HUNTER.
MY DEAR GENERAL:—I have just received your letter of the 25th of June.
I assure you, and you may feel authorized in stating, that the recent change of commanders in the Department of the South was made for no reasons which convey any imputation upon your known energy, efficiency, and patriotism; but for causes which seemed sufficient, while they were in no degree incompatible with the respect and esteem in which I have always held you as a man and an officer.
I cannot, by giving my consent to a publication of whose details I know nothing, assume the responsibility of whatever you may write. In this matter your own sense of military propriety must be your guide, and the regulations of the service your rule of conduct.
I am very truly your friend,
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, Ohio:
Private Downey, of the Twentieth or Twenty-sixth Kentucky Infantry, is said to have been sentenced to be shot for desertion to-day. If so, respite the execution until I can see the record.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July 3,1863.
ROBERT T. LINCOLN, Esq., Cambridge, Mass.:
Don't be uneasy. Your mother very slightly hurt by her fall.
A.L.
Please send at once.
July 4, 10.30 A.M.
The President announces to the country that news from the Army of the Potomac, up to 10 P.M. of the 3d, is such as to cover that army with the highest honor, to promise a great success to the cause of the Union, and to claim the condolence of all for the many gallant fallen; and that for this he especially desires that on this day He whose will, not ours, should ever be done be everywhere remembered and reverenced with profoundest gratitude.
July 5, 1863.
I see your despatch about destruction of pontoons. Cannot the enemy ford the river?
SOLDIERS' HOME, WASHINGTON, JULY 6 1863.7 P.M., MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
I left the telegraph office a good deal dissatisfied. You know I did not like the phrase—in Orders, No. 68, I believe—"Drive the invaders from our soil." Since that, I see a despatch from General French, saying the enemy is crossing his wounded over the river in flats, without saying why he does not stop it, or even intimating a thought that it ought to be stopped. Still later, another despatch from General Pleasonton, by direction of General Meade, to General French, stating that the main army is halted because it is believed the rebels are concentrating "on the road towards Hagerstown, beyond Fairfield," and is not to move until it is ascertained that the rebels intend to evacuate Cumberland Valley.
These things appear to me to be connected with a purpose to cover Baltimore and Washington and to get the enemy across the river again without a further collision, and they do not appear connected with a purpose to prevent his crossing and to destroy him. I do fear the former purpose is acted upon and the latter rejected.
If you are satisfied the latter purpose is entertained, and is judiciously pursued, I am content. If you are not so satisfied, please look to it.
Yours truly,
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I am very glad indeed to see you to-night, and yet I will not say I thank you for this call; but I do most sincerely thank Almighty God for the occasion on which you have called. How long ago is it Eighty-odd years since, on the Fourth of July, for the first time in the history of the world, a nation, by its representatives, assembled and declared as a self-evident truth "that all men are created equal." That was the birthday of the United States of America. Since then the Fourth of July has had several very peculiar recognitions. The two men most distinguished in the framing and support of the Declaration were Thomas Jefferson and John Adams, the one having penned it, and the other sustained it the most forcibly in debate—the only two of the fifty-five who signed it and were elected Presidents of the United States. Precisely fifty years after they put their hands to the paper, it pleased Almighty God to take both from this stage of action. This was indeed an extraordinary and remarkable event in our history. Another President, five years after, was called from this stage of existence on the same day and month of the year; and now on this last Fourth of July just passed, when we have a gigantic rebellion, at the bottom of which is an effort to overthrow the principle that all men were created equal, we have the surrender of a most powerful position and army on that very day. And not only so, but in the succession of battles in Pennsylvania, near to us, through three days, so rapidly fought that they might be called one great battle, on the first, second, and third of the month of July; and on the fourth the cohorts of those who opposed the Declaration that all men are created equal, "turned tail" and run.
Gentlemen, this is a glorious theme, and the occasion for a speech, but I am not prepared to make one worthy of the occasion. I would like to speak in terms of praise due to the many brave officers and soldiers who have fought in the cause of the Union and liberties of their country from the beginning of the war. These are trying occasions, not only in success, but for the want of success. I dislike to mention the name of one single officer, lest I might do wrong to those I might forget. Recent events bring up glorious names, and particularly prominent ones; but these I will not mention. Having said this much, I will now take the music.
WASHINGTON, D.C., July 7, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of the Potomac:
I have received from the President the following note, which I respectfully communicate:
"We have certain information that Vicksburg surrendered to General Grant on the Fourth of July. Now if General Meade can complete his work, so gloriously prosecuted this far, by the literal or substantial destruction of Lee's army, the rebellion will be over.
"Yours truly,
"A. LINCOLN."
H. W. HALLECK. General-in-Chief.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Frederick, Md.:
There is reliable information that the enemy is crossing at Williamsport. The opportunity to attack his divided forces should not be lost. The President is urgent and anxious that your army should move against him by forced marches.
H. W. HALLECK, General-in-Chief
GENERAL LORENZO THOMAS, Harrisburg, Pa.:
Your despatch of this morning to the Secretary of War is before me. The forces you speak of will be of no imaginable service if they cannot go forward with a little more expedition. Lee is now passing the Potomac faster than the forces you mention are passing Carlisle. Forces now beyond Carlisle to be joined by regiments still at Harrisburg, and the united force again to join Pierce somewhere, and the whole to move down the Cumberland Valley, will in my unprofessional opinion be quite as likely to capture the "man in the moon" as any part of Lee's army.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D.C., July 8, 1863.
E. DELAFIELD SMITH, New York:
Your kind despatch in behalf of self and friends is gratefully received. Capture of Vicksburg confirmed by despatch from General Grant himself.
HON. F. F. LOWE, San Francisco, Cal.:
There is no doubt that General Meade, now commanding the Army of the Potomac, beat Lee at Gettysburg, Pa., at the end of a three days' battle, and that the latter is now crossing the Potomac at Williamsport over the swollen stream and with poor means of crossing, and closely pressed by Meade. We also have despatches rendering it entirely certain that Vicksburg surrendered to General Grant on the glorious old 4th.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, D.C., July 9, 1863.
HON. LEONARD SWETT, HON. F. F. LOWE, San Francisco, Cal.:
Consult together and do not have a riot, or great difficulty about delivering possession.
HON. J. K. DUBOIS, Springfield, Ill.:
It is certain that, after three days' fighting at Gettysburg, Lee withdrew and made for the Potomac, that he found the river so swollen as to prevent his crossing; that he is still this side, near Hagerstown and Williamsport, preparing to defend himself; and that Meade is close upon him, and preparing to attack him, heavy skirmishing having occurred nearly all day yesterday.
I am more than satisfied with what has happened north of the Potomac so far, and am anxious and hopeful for what is to come.
A. LINCOLN.
[Nothing came! Lee was allowed to escape again and the war
went on for another two years. D.W.]
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, July 11, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
How many rebel prisoners captured within Maryland and Pennsylvania have reached Baltimore within this month of July?
MAJOR-GENERAL GRANT:
MY DEAR GENERAL:—I do not remember that you and I ever met personally. I write this now as a grateful acknowledgment of the almost inestimable service you have done the Country. I write to say a word further. When you first reached the vicinity of Vicksburg, I thought you should do what you finally did—march the troops across the neck, run the batteries with the transports, and thus go below; and I never had any faith except a general hope that you knew better than I, that the Yazoo Pass expedition and the like could succeed. When you dropped below, and took Port Gibson, Grand Gulf, and vicinity, I thought you should go down the river and join General Banks; and when you turned northward, east of the Big Black, I feared it was a mistake. I now wish to make the personal acknowledgment that you were right and I was wrong.
Yours very truly,
GENERAL SCHOFIELD. St. Louis, Mo.:
I regret to learn of the arrest of the Democrat editor. I fear this loses you the middle position I desired you to occupy. I have not learned which of the two letters I wrote you it was that the Democrat published, but I care very little for the publication of any letter I have written. Please spare me the trouble this is likely to bring.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON D.C., July 14, 1863.
ROBERT T. LINCOLN: New York, Fifth Avenue Hotel:
Why do I hear no more of you?
WITH THE PRESIDENT'S INDORSEMENT. PRESIDENT'S ROOM, WHITE HOUSE, WASHINGTON,
July [15?] 1864.
HIS EXCELLENCY ZEBULON B. VANCE.
MY DEAR SIR:—My former business partner, Mr. Frederic Kidder, of Boston, has forwarded to me a letter he has recently received from his brother, Edward Kidder, of Wilmington, in which (Edward Kidder) says that he has had an interview with you in which you expressed an anxiety for any peace compatible with honor; that you regard slavery as already dead, and the establishment of the Confederacy as hopeless; and that you should exert all your influence to bring about any reunion that would admit the South on terms of perfect equality with the North.
On receipt of this letter I lost no time in laying it before the President of the United States, who expressed great gratification at hearing such sentiments from you, one of the most influential and honored of the Southern governors, and he desires me to say that he fully shares your anxiety for the restoration of peace between the States and for a reunion of all the States on the basis of the abolition of slavery—the bone we are fighting over—and the full reinstatement of every Confederate citizen in all the rights of citizenship in our common country. These points conceded, the President authorizes me to say that he will be glad to receive overtures from any man, or body of men, who have authority to control the armies of the Confederacy; and that he and the United States Congress will be found very liberal on all collateral points that may come up in the settlement.
His views on the collateral points that may naturally arise, the President desires me to say he will communicate to you through me if you should suggest the personal interview that Mr. Edward Kidder recommends in his letter to his brother. In that case you will please forward to me, through Mr. Kidder, your official permit, as Governor of North Carolina, to enter and leave the State, and to remain in it in safety during the pendency of these negotiations, which, I suppose, should be conducted in entire secrecy until they assume an official character. With high consideration, I am,
Sincerely yours,
JAMES R. GILMORE.
[Indorsement.]
This letter has been written in my presence, has been read by me, and has my entire approval. A.L.
A Proclamation.
It has pleased Almighty God to hearken to the supplications and prayers of an afflicted people, and to vouchsafe to the army and navy of the United States victories on land and on the sea so signal and so effective as to furnish reasonable grounds for augmented confidence that the Union of these States will be maintained, their Constitution preserved, and their peace and prosperity permanently restored. But these victories have been accorded not without sacrifices of life, limb, health, and liberty, incurred by brave, loyal, and patriotic citizens. Domestic affliction in every part of the country follows in the train of these fearful bereavements. It is meet and right to recognize and confess the presence of the Almighty Father, and the power of His hand equally in these triumphs and in these sorrows.
Now, therefore, be it known that I do set apart Thursday, the 6th day of August next, to be observed as a day for national thanksgiving, praise, and prayer, and I invite the people of the United States to assemble on that occasion in their customary places of worship, and, in the forms approved by their own consciences, render the homage due to the Divine Majesty for the wonderful things He has done in the nation's behalf, and invoke the influence of His Holy Spirit to subdue the anger which has produced and so long sustained a needless and cruel rebellion, to change the hearts of the insurgents, to guide the counsels of the Government with wisdom adequate to so great a national emergency, and to visit with tender care and consolation throughout the length and breadth of our land all those who, through the vicissitudes of marches, voyages, battles, and sieges have been, brought to suffer in mind, body, or estate, and finally to lead the whole nation through the paths of repentance and submission to the Divine Will back to the perfect enjoyment of union and fraternal peace.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this fifteenth day of July, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By, the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, July 15, 1863.
HON. L SWETT, San Francisco, Cal.:
Many persons are telegraphing me from California, begging me for the peace of the State to suspend the military enforcement of the writ of possession in the Almaden case, while you are the single one who urges the contrary. You know I would like to oblige you, but it seems to me my duty in this case is the other way.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, JULY 15, 1863.
HON. SIMON CAMERON, Harrisburg, Pa.:
Your despatch of yesterday received. Lee was already across the river when you sent it. I would give much to be relieved of the impression that Meade, Couch, Smith, and all since the battle at Gettysburg, have striven only to get Lee over the river without another fight. Please tell me, if you know, who was the one corps commander who was for fighting in the council of war on Sunday night.
J. O. BROADHEAD, St. Louis, Mo.:
The effect on political position of McKee's arrest will not be relieved any by its not having been made with that purpose.
HON. S. H. LANE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Governor Carney has not asked to [have] General Blunt removed, or interfered with, in his military operations. He has asked that he, the Governor, be allowed to commission officers for troops raised in Kansas, as other governors of loyal States do; and I think he is right in this.
He has asked that General Blunt shall not take persons charged with civil crimes out of the hands of the courts and turn them over to mobs to be hung; and I think he is right in this also. He has asked that General Ewing's department be extended to include all Kansas; and I have not determined whether this is right or not.
Yours truly,
GOVERNOR O. P. MORTON, Indianapolis:
What do you remember about the case of John O. Brown, convicted of mutinous conduct and sentenced to death? What do you desire about it?
July 20, 1863.
HIS EXCELLENCY JOEL PARKER, Governor of New Jersey.
DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 15th has been received, and considered by the Secretary of War and myself. I was pained to be informed this morning by the Provost-Marshal-General that New Jersey is now behind twelve thousand, irrespective of the draft. I did not have time to ascertain by what rules this was made out; and I shall be very glad if it shall, by any means, prove to be incorrect. He also tells me that eight thousand will be about the quota of New Jersey on the first draft; and the Secretary of War says the first draft in that State would not be made for some time in any event. As every man obtained otherwise lessens the draft so much, and this may supersede it altogether, I hope you will push forward your volunteer regiments as fast as possible.
It is a very delicate matter to postpone the draft in one State, because of the argument it furnishes others to have postponement also. If we could have a reason in one case which would be good if presented in all cases, we could act upon it.
I will thank you, therefore, to inform me, if you can, by what day, at the earliest, you can promise to have ready to be mustered into the United States service the eight thousand men.
If you can make a reliable promise (I mean one which you can rely on yourself) of this sort, it will be of great value, if the day is not too remote.
I beg you to be assured I wish to avoid the difficulties you dread as much as yourself.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR GENERAL JOHN M. SCHOFIELD.
MY DEAR GENERAL:—I have received and read your letter of the 14th of July.
I think the suggestion you make, of discontinuing proceedings against Mr. McKee, a very proper one. While I admit that there is an apparent impropriety in the publication of the letter mentioned, without my consent or yours, it is still a case where no evil could result, and which I am entirely willing to overlook.
Yours truly,
MAJOR GENERAL SCHOFIELD, St. Louis, Mo.:
The following despatch has been placed in my hands. Please look to the subject of it.
LEXINGTON, Mo., JULY 21, 1863 HON. S C. POMEROY: Under Orders No.63 the sheriff is arresting slaves of rebels inside our lines, and returning them in great numbers. Can he do it? Answer. GOULD.
JULY 24, 1863. HON. POSTMASTER-GENERAL
SIR:-Yesterday little indorsements of mine went to you in two cases of postmasterships sought for widows whose husbands have fallen in the battles of this war. These cases occurring on the same day brought me to reflect more attentively than I had before done, as to what is fairly due from us herein the dispensing of patronage toward the men who, by fighting our battles, bear the chief burden of serving our country. My conclusion is that, other claims and qualifications being equal, they have the better right and this is especially applicable to the disabled and the soldier, deceased soldier's family.
Your obedient servant,
HON. SECRETARY OF THE NAVY.
SIR:—Certain matters have come to my notice, and considered by me, which induce me to believe that it will conduce to the public interest for you to add to the general instructions given to our naval commanders in relation to contraband trade propositions substantially as follows, to wit:
First. You will avoid the reality, and as far as possible the appearance, of using any neutral port to watch neutral vessels and then to dart out and seize them on their departure.
NOTE.—Complaint is made that this has been practiced at the port of St Thomas, which practice, if it exists, is disapproved and must cease.
Second. You will not in any case detain the crew of a captured neutral vessel or any other subject of a neutral power on board such vessel, as prisoners of war or otherwise, except the small number necessary as witnesses in the prize court.
NOTE.-The practice here forbidden is also charged to exist, which, if true, is disapproved and must cease.
My dear sir, it is not intended to be insinuated that you have been remiss in the performance of the arduous and responsible duties of your department, which, I take pleasure in affirming, has in your hands been conducted with admirable success. Yet, while your subordinates are almost of necessity brought into angry collision with the subjects of foreign states, the representatives of those states and yourself do not come into immediate contact for the purpose of keeping the peace, in spite of such collisions. At that point there is an ultimate and heavy responsibility upon me.
What I propose is in strict accordance with international law, and is therefore unobjectionable; whilst, if it does no other good, it will contribute to sustain a considerable portion of the present British ministry in their places, who, if displaced, are sure to be replaced by others more unfavorable to us.
Your obedient servant,
July 25, 1863.
HIS EXCELLENCY GOVERNOR JOEL PARKER.
SIR:—Yours of the 21st is received, and I have taken time and considered and discussed the subject with the Secretary of War and Provost-Marshal General, in order, if possible, to make you a more favorable answer than I finally find myself able to do.
It is a vital point with us to not have a special stipulation with the governor of any one State, because it would breed trouble in many, if not all, other States; and my idea was when I wrote you, as it still is, to get a point of time to which we could wait, on the reason that we were not ready ourselves to proceed, and which might enable you to raise the quota of your State, in whole, or in large part, without the draft. The points of time you fix are much farther off than I had hoped. We might have got along in the way I have indicated for twenty, or possibly thirty, days. As it stands, the best I can say is that every volunteer you will present us within thirty days from this date, fit and ready to be mustered into the United States service, on the usual terms, shall be pro tanto an abatement of your quota of the draft. That quota I can now state at eight thousand seven hundred and eighty-three (8783). No draft from New Jersey, other than for the above quota, will be made before an additional draft, common to [all] the States, shall be required; and I may add that if we get well through with this draft, I entertain a strong hope that any further one may never be needed. This expression of hope, however, must not be construed into a promise.
As to conducting the draft by townships, I find it would require such a waste of labor already done, and such an additional amount of it, and such a loss of time, as to make it, I fear, inadmissible.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—Since writing the above, getting additional information, I am enabled to say that the draft may be made in subdistricts, as the enrolment has been made, or is in process of making. This will amount practically to drafting by townships, as the enrollment subdistricts are generally about the extent of townships. A.L.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE:
I have not thrown General Hooker away; and therefore I would like to know whether it would be agreeable to you, all things considered, for him to take a corps under you, if he himself is willing to do so. Write me in perfect freedom, with the assurance that I will not subject you to any embarrassment by making your letter or its contents known to any one. I wish to know your wishes before I decide whether to break the subject to him. Do not lean a hair's breadth against your own feelings, or your judgment of the public service, on the idea of gratifying me.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cincinnati, O.:
Let me explain. In General Grant's first despatch after the fall of Vicksburg, he said, among other things, he would send the Ninth Corps to you. Thinking it would be pleasant to you, I asked the Secretary of War to telegraph you the news. For some reasons never mentioned to us by General Grant, they have not been sent, though we have seen outside intimations that they took part in the expedition against Jackson. General Grant is a copious worker and fighter, but a very meager writer or telegrapher. No doubt he changed his purpose in regard to the Ninth Corps for some sufficient reason, but has forgotten to notify us of it.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
Seeing General Meade's despatch of yesterday to yourself causes me to fear that he supposes the Government here is demanding of him to bring on a general engagement with Lee as soon as possible. I am claiming no such thing of him. In fact, my judgment is against it; which judgment, of course, I will yield if yours and his are the contrary. If he could not safely engage Lee at Williamsport, it seems absurd to suppose he can safely engage him now, when he has scarcely more than two thirds of the force he had at Williamsport, while it must be that Lee has been reinforced. True, I desired General Meade to pursue Lee across the Potomac, hoping, as has proved true, that he would thereby clear the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, and get some advantages by harassing him on his retreat. These being past, I am unwilling he should now get into a general engagement on the impression that we here are pressing him, and I shall be glad for you to so inform him, unless your own judgment is against it.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
H. W. HALLECK, General-in-Chief.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
SIR:—Can we not renew the effort to organize a force to go to western Texas?
Please consult with the general-in-chief on the subject.
If the Governor of New Jersey shall furnish any new regiments, might not they be put into such an expedition? Please think of it.
I believe no local object is now more desirable.
Yours truly,
It is the duty of every government to give protection to its citizens, of whatever class, color, or condition, and especially to those who are duly organized as soldiers in the public service. The law of nations and the usages and customs of war, as carried on by civilized powers, permit no distinction as to color in the treatment of prisoners of war as public enemies. To sell or enslave any captured person, on account of his color and for no offense against the laws of war, is a relapse into barbarism, and a crime against the civilization of the age.
The Government of the United States will give the same protection to all its soldiers; and if the enemy shall sell or enslave any one because of his color, the offense shall be punished by retaliation upon the enemy's prisoners in our possession.
It is therefore ordered that for every soldier of the United States killed in violation of the laws of war, a rebel soldier shall be executed; and for every one enslaved by the enemy or sold into slavery, a rebel soldier shall be placed at hard labor on the public works, and continued at such labor until the other shall be released and receive the treatment due to a prisoner of war.
MY DEAR GENERAL HURLBUT:
Your letter by Mr. Dana was duly received. I now learn that your resignation has reached the War Department. I also learn that an active command has been assigned you by General Grant. The Secretary of War and General Halleck are very partial to you, as you know I also am. We all wish you to reconsider the question of resigning; not that we would wish to retain you greatly against your wish and interest, but that your decision may be at least a very well-considered one.
I understand that Senator [William K.] Sebastian, of Arkansas, thinks of offering to resume his place in the Senate. Of course the Senate, and not I, would decide whether to admit or reject him. Still I should feel great interest in the question. It may be so presented as to be one of the very greatest national importance; and it may be otherwise so presented as to be of no more than temporary personal consequence to him.
The Emancipation Proclamation applies to Arkansas. I think it is valid in law, and will be so held by the courts. I think I shall not retract or repudiate it. Those who shall have tasted actual freedom I believe can never be slaves or quasi-slaves again. For the rest, I believe some plan substantially being gradual emancipation would be better for both white and black. The Missouri plan recently adopted, I do not object to on account of the time for ending the institution; but I am sorry the beginning should have been postponed for seven years, leaving all that time to agitate for the repeal of the whole thing. It should begin at once, giving at least the new-born a vested interest in freedom which could not be taken away. If Senator Sebastian could come with something of this sort from Arkansas, I, at least, should take great interest in his case; and I believe a single individual will have scarcely done the world so great a service. See him if you can, and read this to him; but charge him not to make it public for the present. Write me again.
Yours very truly,
TO THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES:
I ask that the draft be suspended in this State until I can send you a communication I am preparing.
HIS EXCELLENCY GOVERNOR SEYMOUR, Albany, N.Y.:
By what day may I expect your communication to reach me? Are you anxious about any part except the city and vicinity?
MAJOR-GENERAL FOSTER (or whoever may be in command of the military department with headquarters at Fort Monroe, Va.):
If Dr. Wright, on trial at Norfolk, has been or shall be convicted, send me a transcript of his trial and conviction, and do not let execution be done upon him until my further order.
MY DEAR GENERAL BANKS:
While I very well know what I would be glad for Louisiana to do, it is quite a different thing for me to assume direction of the matter. I would be glad for her to make a new constitution, recognizing the emancipation proclamation, and adopting emancipation in those parts of the State to which the proclamation does not apply. And while she is at it, I think it would not be objectionable for her to adopt some practical system by which the two races could gradually live themselves out of their old relation to each other, and both come out better prepared for the new. Education for young blacks should be included in the plan. After all, the power or element of "contract" may be sufficient for this probationary period, and by its simplicity and flexibility may be the better.
As an antislavery man, I have a motive to desire emancipation which proslavery men do not have but even they have strong enough reason to thus place themselves again under the shield of the Union, and to thus perpetually hedge against the recurrence of the scenes through which we are now passing.
Governor Shepley has informed me that Mr. Durant is now taking a registry, with a view to the election of a constitutional convention in Louisiana. This, to me, appears proper. If such convention were to ask my views, I could present little else than what I now say to you. I think the thing should be pushed forward, so that, if possible, its mature work may reach here by the meeting of Congress.
For my own part, I think I shall not, in any event, retract the emancipation proclamation: nor, as executive, ever return to slavery any person who is free by the terms of that proclamation, or by any of the acts of Congress.
If Louisiana shall send members to Congress, their admission to seats will depend, as you know, upon the respective Houses, and not upon the President.
Yours very truly,
HIS EXCELLENCY HORATIO SEYMOUR, Governor of New York:
Your communication of the 3rd instant has been received and attentively considered.
I cannot consent to suspend the draft in New York, as you request, because, among other reasons, time is too important.
By the figures you send, which I presume are correct, the twelve districts represented fall into two classes of eight and four respectively. The disparity of the quotas for the draft in these two classes is certainly very striking, being the difference between an average of 2200 in one class and 4864 in the other. Assuming that the districts are equal one to another in entire population, as required by the plan on which they were made, this disparity is such as to require attention. Much of it, however, I suppose will be accounted for by the fact that so many more persons fit for soldiers are in the city than are in the country who have too recently arrived from other parts of the United States and from Europe to be either included in the census of 1860, or to have voted in 1862. Still, making due allowance for this, I am yet unwilling to stand upon it as an entirely sufficient explanation of the great disparity.
I shall direct the draft to proceed in all the districts, drawing, however, at first from each of the four districts—to wit, the Second, Fourth, Sixth, and Eighth—only, 2200 being the average quota of the other class. After this drawing, these four districts, and also the Seventeenth and Twenty-ninth, shall be carefully re-enrolled; and, if you please, agents of yours may witness every step of the process. Any deficiency which may appear by the new enrolment will be supplied by a special draft for that object, allowing due credit for volunteers who may be obtained from these districts respectively during the interval; and at all points, so far as consistent with practical convenience, due credits shall be given for volunteers, and your Excellency shall be notified of the time fixed for commencing the draft in each district.
I do not object to abide a decision of the United States Supreme Court, or of the judges thereof, on the constitutionality of the draft law. In fact, I should be willing to facilitate the obtaining of it. But I cannot consent to lose the time while it is being obtained. We are contending with an enemy who, as I understand, drives every able-bodied man he can reach into his ranks, very much as a butcher drives bullocks into the slaughter-pen. No time is wasted, no argument is used. This produces an army which will soon turn upon our now victorious soldiers already in the field, if they shall not be sustained by recruits as they should be. It produces an army with a rapidity not to be matched on our side if we first waste time to re-experiment with the volunteer system, already deemed by Congress, and palpably, in fact, so far exhausted as to be inadequate; and then more time to obtain a court decision as to whether a law is constitutional, which requires a part of those not now in the service to go to the aid of those who are already in it; and still more time to determine with absolute certainty that we get those who are to go in the precisely legal proportion to those who are not to go. My purpose is to be in my action just and constitutional, and yet practical, in performing the important duty with which I am charged, of maintaining the unity and the free principles of our common country.
Your obedient servant,
MY DEAR GENERAL GRANT:
I see by a despatch of yours that you incline quite strongly toward an expedition against Mobile. This would appear tempting to me also, were it not that in view of recent events in Mexico I am greatly impressed with the importance of re-establishing the national authority in western Texas as soon as possible. I am not making an order, however; that I leave, for the present at least, to the general-in-chief.
A word upon another subject: General Thomas has gone again to the Mississippi Valley, with the view of raising colored troops. I have no reason to doubt that you are doing what you reasonably can upon the same subject. I believe it is a resource which if vigorously applied now will soon close the contest. It works doubly, weakening the enemy and strengthening us. We were not fully ripe for it until the river was opened. Now, I think at least one hundred thousand can and ought to be rapidly organized along its shores, relieving all white troops to serve elsewhere. Mr. Dana understands you as believing that the Emancipation Proclamation has helped some in your military operations. I am very glad if this is so.
Did you receive a short letter from me dated the 13th of July?
Yours very truly,
MY DEAR GENERAL ROSECRANS:
Yours of the 1st was received two days ago. I think you must have inferred more than General Halleck has intended, as to any dissatisfaction of mine with you. I am sure you, as a reasonable man, would not have been wounded could you have heard all my words and seen all my thoughts in regard to you. I have not abated in my kind feeling for and confidence in you. I have seen most of your despatches to General Halleck—probably all of them. After Grant invested Vicksburg I was very anxious lest Johnston should overwhelm him from the outside, and when it appeared certain that part of Bragg's force had gone and was going to Johnston, it did seem to me it was exactly the proper time for you to attack Bragg with what force he had left. In all kindness let me say it so seems to me yet. Finding from your despatches to General Halleck that your judgment was different, and being very anxious for Grant, I, on one occasion, told General Halleck I thought he should direct you to decide at once to immediately attack Bragg or to stand on the defensive and send part of your force to Grant. He replied he had already so directed in substance. Soon after, despatches from Grant abated my anxiety for him, and in proportion abated my anxiety about any movement of yours. When afterward, however, I saw a despatch of yours arguing that the right time for you to attack Bragg was not before, but would be after, the fall of Vicksburg, it impressed me very strangely, and I think I so stated to the Secretary of War and General Halleck. It seemed no other than the proposition that you could better fight Bragg when Johnston should be at liberty to return and assist him than you could before he could so return to his assistance.
Since Grant has been entirely relieved by the fall of Vicksburg, by which Johnston is also relieved, it has seemed to me that your chance for a stroke has been considerably diminished, and I have not been pressing you directly or indirectly. True, I am very anxious for East Tennessee to be occupied by us; but I see and appreciate the difficulties you mention. The question occurs, Can the thing be done at all? Does preparation advance at all? Do you not consume supplies as fast as you get them forward? Have you more animals to-day than you had at the battle of Stone's River? And yet have not more been furnished you since then than your entire present stock? I ask the same questions as to your mounted force.
Do not misunderstand: I am not casting blame upon you; I rather think by great exertion you can get to East Tennessee; but a very important question is, Can you stay there? I make no order in the case—that I leave to General Halleck and yourself.
And now be assured once more that I think of you in all kindness and confidence, and that I am not watching you with an evil eye.
Yours very truly,
HIS EXCELLENCY HORATIO SEYMOUR, Governor of New York:
Yours of the 8th, with Judge-Advocate-General Waterbury's report, was received to-day.
Asking you to remember that I consider time as being very important, both to the general cause of the country and to the soldiers in the field, I beg to remind you that I waited, at your request, from the 1st until the 6th inst., to receive your communication dated the 3d. In view of its great length, and the known time and apparent care taken in its preparation, I did not doubt that it contained your full case as you desired to present it. It contained the figures for twelve districts, omitting the other nineteen, as I suppose, because you found nothing to complain of as to them. I answered accordingly. In doing so I laid down the principle to which I purpose adhering, which is to proceed with the draft, at the same time employing infallible means to avoid any great wrong. With the communication received to-day you send figures for twenty-eight districts, including the twelve sent before, and still omitting three, for which I suppose the enrolments are not yet received. In looking over the fuller list of twenty-eight districts, I find that the quotas for sixteen of them are above 2000 and below 2700, while, of the rest, six are above 2700 and six are below 2000. Applying the principle to these new facts, the Fifth and Seventh districts must be added to the four in which the quotas have already been reduced to 2200 for the first draft; and with these four others just be added to those to be re-enrolled. The correct case will then stand: the quotas of the Second, Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, Seventh, and Eighth districts fixed at 2200 for the first draft. The Provost-Marshal-General informs me that the drawing is already completed in the Sixteenth, Seventeenth, Eighteenth, Twenty-second, Twenty-fourth, Twenty-sixth, Twenty-seventh, Twenty-eighth, Twenty-ninth, and Thirtieth districts. In the others, except the three outstanding, the drawing will be made upon the quotas as now fixed. After the first draft, the Second, Fourth, Fifth, Sixth, Seventh, Eighth, Sixteenth, Seventeenth, Twenty-first, Twenty-fifth, Twenty-ninth, and Thirty-first will be enrolled for the purpose and in the manner stated in my letter of the 7th inst. The same principle will be applied to the now outstanding districts when they shall come in. No part of my former letter is repudiated by reason of not being restated in this, or for any other cause.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL McCLERNAND.
MY DEAR SIR:—Our friend William G. Greene has just presented a kind letter in regard to yourself, addressed to me by our other friends Yates, Hatch, and Dubois.
I doubt whether your present position is more painful to you than to myself. Grateful for the patriotic stand so early taken by you in this life-and-death struggle of the nation, I have done whatever has appeared practicable to advance you and the public interest together. No charges, with a view to a trial, have been preferred against you by any one; nor do I suppose any will be. All there is, so far as I have heard, is General Grant's statement of his reasons for relieving you. And even this I have not seen or sought to see; because it is a case, as appears to me, in which I could do nothing without doing harm. General Grant and yourself have been conspicuous in our most important successes; and for me to interfere and thus magnify a breach between you could not but be of evil effect. Better leave it where the law of the case has placed it. For me to force you back upon General Grant would be forcing him to resign. I cannot give you a new command, because we have no forces except such as already have commanders.
I am constantly pressed by those who scold before they think, or without thinking at all, to give commands respectively to Fremont, McClellan, Butler, Sigel, Curtis, Hunter, Hooker, and perhaps others, when, all else out of the way, I have no commands to give them. This is now your case; which, as I have said, pains me not less than it does you. My belief is that the permanent estimate of what a general does in the field is fixed by the "cloud of witnesses" who have been with him in the field, and that, relying on these, he who has the right needs not to fear.
Your friend as ever,
GOVERNOR SEYMOUR, New York:
Your despatch of this morning is just received, and I fear I do not perfectly understand it.
My view of the principle is that every soldier obtained voluntarily leaves one less to be obtained by draft. The only difficulty is in applying the principle properly. Looking to time, as heretofore, I am unwilling to give up a drafted man now, even for the certainty, much less for the mere chance, of getting a volunteer hereafter. Again, after the draft in any district, would it not make trouble to take any drafted man out and put a volunteer in—for how shall it be determined which drafted man is to have the privilege of thus going out, to the exclusion of all the others? And even before the draft in any district the quota must be fixed; and the draft must be postponed indefinitely if every time a volunteer is offered the officers must stop and reconstruct the quota. At least I fear there might be this difficulty; but, at all events, let credits for volunteers be given up to the last moment which will not produce confusion or delay. That the principle of giving credits for volunteers shall be applied by districts seems fair and proper, though I do not know how far by present statistics it is practicable. When for any cause a fair credit is not given at one time, it should be given as soon thereafter as practicable. My purpose is to be just and fair, and yet to not lose time.
JAMES H. HACKETT, Esq.
MY DEAR SIR:—Months ago I should have acknowledged the receipt of your book and accompanying kind note; and I now have to beg your pardon for not having done so.
For one of my age I have seen very little of the drama. The first presentation of Falstaff I ever saw was yours here, last winter or spring. Perhaps the best compliment I can pay is to say, as I truly can, I am very anxious to see it again. Some of Shakespeare's plays I have never read, while others I have gone over perhaps as frequently as any un-professional reader. Among the latter are Lear, Richard III., Henry VIII., Hamlet, and especially Macbeth. I think nothing equals Macbeth. It is wonderful.
Unlike you gentlemen of the profession, I think the soliloquy in Hamlet commencing "Oh, my offense is rank," surpasses that commencing "To be or not to be." But pardon this small attempt at criticism. I should like to hear you pronounce the opening speech of Richard III. Will you not soon visit Washington again? If you do, please call and let me make your personal acquaintance.
Yours truly,
HON. P. F. LOWE, San Francisco, Cal.:
There seems to be considerable misunderstanding about the recent movement to take possession of the "New Almaden" mine. It has no reference to any other mine or mines.
In regard to mines and miners generally, no change of policy by the Government has been decided on, or even thought of, so far as I know.
The "New Almaden" mine was peculiar in this: that its occupants claimed to be the legal owners of it on a Mexican grant, and went into court on that claim. The case found its way into the Supreme Court of the United States, and last term, in and by that court, the claim of the occupants was decided to be utterly fraudulent. Thereupon it was considered the duty of the Government by the Secretary of the Interior, the Attorney-General, and myself to take possession of the premises; and the Attorney-General carefully made out the writ and I signed it. It was not obtained surreptitiously, although I suppose General Halleck thought it had been, when he telegraphed, simply because he thought possession was about being taken by a military order, while he knew no such order had passed through his hands as general-in-chief.
The writ was suspended, upon urgent representations from California, simply to keep the peace. It never had any direct or indirect reference to any mine, place, or person, except the "New Almaden" mine and the persons connected with it.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Warrenton, Va.:
At this late moment I am appealed to in behalf of William Thompson of Company K, Third Maryland Volunteers, in Twelfth Army Corps, said to be at Kelly's Ford, under sentence to be shot to-day as a deserter. He is represented to me to be very young, with symptoms of insanity. Please postpone the execution till further order.
GENERAL SCHOFIELD, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Please send me if you can a transcript of the record in the case of McQuin and Bell, convicted of murder by a military commission. I telegraphed General Strong for it, but he does not answer.
MRS. ELIZABETH J. GRIMSLEY, Springfield, Ill.:
I mail the papers to you to-day appointing Johnny to the Naval school.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, August 26, 1863.
HON. JAMES C. CONKLING.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter inviting me to attend a mass meeting of unconditional Union men, to be held at the capital of Illinois, on the 3d day of September, has been received. It would be very agreeable for me thus to meet my old friends at my own home, but I cannot just now be absent from here so long as a visit there would require.
The meeting is to be of all those who maintain unconditional devotion to the Union, and I am sure that my old political friends will thank me for tendering, as I do, the nation's gratitude to those other noble men whom no partisan malice or partisan hope can make false to the nation's life.
There are those who are dissatisfied with me. To such I would say: You desire peace, and you blame me that we do not have it. But how can we obtain it? There are but three conceivable ways:
First—to suppress the rebellion by force of arms. This I am trying to do. Are you for it? If you are, so far we are agreed. If you are not for it, a second way is to give up the Union. I am against this. Are you for it? If you are you should say so plainly. If you are not for force nor yet for dissolution, there only remains some imaginable compromise.
I do not believe that any compromise embracing the maintenance of the Union is now possible. All that I learn leads to a directly opposite belief. The strength of the rebellion is its military, its army. That army dominates all the country and all the people within its range. Any offer of terms made by any man or men within that range, in opposition to that army, is simply nothing for the present; because such man or men have no power whatever to enforce their side of a compromise, if one were made with them.
To illustrate: Suppose refugees from the South and peace men of the North get together in convention, and frame and proclaim a compromise embracing a restoration of the Union. In what way can that compromise be used to keep Lee's army out of Pennsylvania? Meade's army can keep Lee's army out of Pennsylvania, and, I think, can ultimately drive it out of existence. But no paper compromise to which the controllers of Lee's army are not agreed can at all affect that army. In an effort at such compromise we would waste time, which the enemy would improve to our disadvantage; and that would be all.
A compromise, to be effective, must be made either with those who control the rebel army, or with the people, first liberated from the domination of that army by the success of our own army. Now allow me to assure you that no word or intimation from that rebel army, or from any of the men controlling it, in relation to any peace compromise, has ever come to my knowledge or belief. All charges and insinuations to the contrary are deceptive and groundless. And I promise you that if any such proposition shall hereafter come, it shall not be rejected and kept a secret from you. I freely acknowledge myself to be the servant of the people, according to the bond of service, the United States Constitution, and that, as such, I am responsible to them.
But, to be plain: You are dissatisfied with me about the negro. Quite likely there is a difference of opinion between you and myself upon that subject. I certainly wish that all men could be free, while you, I suppose, do not. Yet, I have neither adopted nor proposed any measure which is not consistent with even your view, provided you are for the Union. I suggested compensated emancipation; to which you replied you wished not to be taxed to buy negroes. But I had not asked you to be taxed to buy negroes, except in such way as to save you from greater taxation to save the Union exclusively by other means.
You dislike the Emancipation Proclamation, and perhaps would have it retracted. You say it is unconstitutional. I think differently. I think the Constitution invests its commander-in-chief with the law of war in time of war. The most that can be said, if so much, is, that slaves are property. Is there, has there ever been, any question that by the law of war, property, both of enemies and friends, may be taken when needed? And is it not needed whenever it helps us and hurts the enemy? Armies, the world over, destroy enemies' property when they cannot use it, and even destroy their own to keep it from the enemy. Civilized belligerents do all in their power to help themselves or hurt the enemy, except a few things regarded as barbarous or cruel. Among the exceptions are the massacre of vanquished foes and non-combatants, male and female.
But the proclamation, as law, either is valid or is not valid. If it is not valid it needs no retraction. If it is valid it cannot be retracted, any more than the dead can be brought to life. Some of you profess to think its retraction would operate favorably for the Union, why better after the retraction than before the issue? There was more than a year and a half of trial to suppress the rebellion before the proclamation was issued, the last one hundred days of which passed under an explicit notice that it was coming, unless averted by those in revolt returning to their allegiance. The war has certainly progressed as favorably for us since the issue of the proclamation as before.
I know, as fully as one can know the opinions of others, that some of the commanders of our armies in the field, who have given us our most important victories, believe the emancipation policy and the use of colored troops constitute the heaviest blows yet dealt to the rebellion, and that at least one of those important successes could not have been achieved when it was but for the aid of black soldiers.
Among the commanders who hold these views are some who have never had any affinity with what is called "Abolitionism," or with "Republican Party politics," but who hold them purely as military opinions. I submit their opinions are entitled to some weight against the objections often urged that emancipation and arming the blacks are unwise as military measures, and were not adopted as such in good faith.
You say that you will not fight to free negroes. Some of them seem willing to fight for you; but no matter. Fight you, then, exclusively, to save the Union. I issued the proclamation on purpose to aid you in saving the Union. Whenever you shall have conquered all resistance to the Union, if I shall urge you to continue fighting, it will be an apt time then for you to declare you will not fight to free negroes. I thought that in your struggle for the Union, to whatever extent the negroes should cease helping the enemy, to that extent it weakened the enemy in his resistance to you. Do you think differently? I thought that whatever negroes can be got to do as soldiers, leaves just so much less for white soldiers to do in saving the Union. Does it appear otherwise to you? But negroes, like other people, act upon motives. Why should they do anything for us if we will do nothing for them? If they stake their lives for us they must be prompted by the strongest motive, even the promise of freedom. And the promise, being made, must be kept.
The signs look better. The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea. Thanks to the great Northwest for it; nor yet wholly to them. Three hundred miles up they met New England, Empire, Keystone, and Jersey, hewing their way right and left. The sunny South, too, in more colors than one, also lent a helping hand. On the spot, their part of the history was jotted down in black and white. The job was a great national one, and let none be slighted who bore an honorable part in it And while those who have cleared the great river may well be proud, even that is not all. It is hard to say that anything has been more bravely and well done than at Antietam, Murfreesboro, Gettysburg, and on many fields of less note. Nor must Uncle Sam's web-feet be forgotten. At all the watery margins they have been present; not only on the deep sea, the broad bay, and the rapid river, but also up the narrow, muddy bayou, and wherever the ground was a little damp, they have been and made their tracks. Thanks to all. For the great Republic—for the principle it lives by and keeps alive—for man's vast future—thanks to all.
Peace does not appear so distant as it did. I hope it will come soon, and come to stay, and so come as to be worth the keeping in all future time. It will then have been proved that among freemen there can be no successful appeal from the ballot to the bullet, and that they who take such appeal are sure to lose their case and pay the cost. And there will be some black men who can remember that with silent tongue, and clinched teeth, and steady eye, and well-poised bayonet, they have helped mankind on to this great consummation; while I fear there will be some white ones unable to forget that with malignant heart and deceitful speech they have striven to hinder it.
Still, let us not be over-sanguine of a speedy, final triumph. Let us be quite sober. Let us diligently apply the means, never doubting that a just God, in His own good time, will give us the rightful result.
Yours very truly,
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, D. C., August 27.1863.
HON. JAMES CONKLING.
MY DEAR CONKLING:—I cannot leave here now. Herewith is a letter instead. You are one of the best public readers. I have but one suggestion—read it very slowly. And now God bless you, and all good Union men.
Yours as ever,
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR SIR:-In my correspondence with Governor Seymour in relation to the draft, I have said to him, substantially, that credits shall be given for volunteers up to the latest moment, before drawing in any district, that can be done without producing confusion or delay. In order to do this, let our mustering officers in New York and elsewhere be at, once instructed that whenever they muster into our service any number of volunteers, to at once make return to the War Department, both by telegraph and mail, the date of the muster, the number mustered, and the Congressional or enrolment district or districts, of their residences, giving the numbers separately for each district. Keep these returns diligently posted, and by them give full credit on the quotas, if possible, on the last day before the draft begins in any district.
Again, I have informed Governor Seymour that he shall be notified of the time when the draft is to commence in each district in his State. This is equally proper for all the States. In order to carry it out, I propose that so soon as the day for commencing the draft in any district is definitely determined, the governor of the State, including the district, be notified thereof, both by telegraph and mail, in form about as follows:
———————————————
———————————— 1863.
Governor of ———————————————
——————————————————
You are notified that the draft will commence in the ————————— —— district, at ——— on the ——— day —————— 1863, at ——— A.M. of said day.
Please acknowledge receipt of this by telegraph and mail.
————————————
————————————
This notice may be given by the Provost-Marshal-General here, the sub-provost-marshal-generals in the States, or perhaps by the district provost-marshals.
Whenever we shall have so far proceeded in New York as to make the re-enrolment specially promised there practicable, I wish that also to go forward, and I wish Governor Seymour notified of it; so that if he choose, he can place agents of his with ours to see the work fairly done.
Yours truly,
HIS EXCELLENCY HORATIO SEYMOUR,
Governor of New York:
Yours of the 21st, with exhibits, was received on the 24th.
In the midst of pressing duties I have been unable to answer it sooner. In the meantime the Provost Marshal-General has had access to yours, and has addressed a communication in relation to it to the Secretary of War, a copy of which communication I herewith enclose to you.
Independently of this, I addressed a letter on the same subject to the Secretary of War, a copy of which I also enclose to you. The Secretary has sent my letter to the Provost-Marshal General, with direction that he adopt and follow the course therein pointed out. It will, of course, overrule any conflicting view of the Provost-Marshal-General, if there be such.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.-I do not mean to say that if the Provost-Marshal-General can find it practicable to give credits by subdistricts, I overrule him in that. On the contrary, I shall be glad of it; but I will not take the risk of over-burdening him by ordering him to do it. A. L.
Abraham Lincoln
GENERAL SCHOFIELD, St. LOUIS:
I have just received the despatch which follows, from two very influential citizens of Kansas, whose names I omit. The severe blow they have received naturally enough makes them intemperate even without there being any just cause for blame. Please do your utmost to give them future security and to punish their invaders.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Warrenton, Va.:
Walter, Rionese, Folancy, Lai, and Kuhn appealed to me for mercy, without giving any ground for it whatever. I understand these are very flagrant cases, and that you deem their punishment as being indispensable to the service. If I am not mistaken in this, please let them know at once that their appeal is denied.
F. C. SHERMAN, Mayor, J. S. HAVES, Comptroller, Chicago, Ill.:
Yours of the 24th, in relation to the draft, is received. It seems to me the Government here will be overwhelmed if it undertakes to conduct these matters with the authorities of cities and counties. They must be conducted with the governors of States, who will, of course, represent their cities and counties. Meanwhile you need not be uneasy until you again hear from here.
MAJOR-GENERAL FOSTER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Please notify, if you can, Senator Bowden, Mr. Segar, and Mr. Chandler, all or any of them, that I now have the record in Dr. Wright's case, and am ready to hear them. When you shall have got the notice to them, please let me know.
GENERAL CRAWFORD, Rappahannock Station, Va.:
I regret that I cannot be present to witness the presentation of a sword by the gallant Pennsylvania Reserve Corps to one so worthy to receive it as General Meade.
HON. L. SWETT, San Francisco, Cal.: If the Government's rights are reserved, the Government will be satisfied, and at all events it will consider.
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Manchester, N. H.:
All quite well. Fort Sumter is certainly battered down and utterly useless to the enemy, and it is believed here, but not entirely certain, that both Sumter and Fort Wagner are occupied by our forces. It is also certain that General Gilmore has thrown some shot into the city of Charleston.
August 31, 1863.
HON. JAMES C. CONKLING, Springfield, Ill.:
In my letter of the 26th insert between the sentence ending "since the issue of the Emancipation Proclamation as before" and the next, commencing "You say you will not fight, etc.," what follows below my signature hereto.
A. LINCOLN.
"I know as fully as one can know the opinions of others that some of the commanders of our armies in the field, who have given us our most important successes, believe the emancipation policy and the use of colored troops constitute the heaviest blow yet dealt to the rebellion, and that at least one of those important successes could not have been achieved when it was, but for the aid of black soldiers. Among the commanders holding these views are some who have never had any affinity with what is called abolitionism, or with Republican party politics, but who hold them purely as military opinions. I submit these opinions as being entitled to some weight against the objections, often urged, that emancipation and arming the blacks are unwise as military measures and were not adopted as such in good faith."
MY DEAR GENERAL ROSECRANS:
Yours of the 22d was received yesterday. When I wrote you before, I did not intend, nor do I now, to engage in an argument with you on military questions. You had informed me you were impressed through General Halleck that I was dissatisfied with you, and I could not bluntly deny that I was without unjustly implicating him. I therefore concluded to tell you the plain truth, being satisfied the matter would thus appear much smaller than it would if seen by mere glimpses. I repeat that my appreciation of you has not abated. I can never forget whilst I remember anything, that about the end of last year and the beginning of this, you gave us a hard-earned victory, which, had there been a defeat instead, the nation could hardly have lived over. Neither can I forget the check you so opportunely gave to a dangerous sentiment which was spreading in the North.
Yours, as ever,
It is not improbable that retaliation for the recent great outrage at Lawrence, in Kansas, may extend to indiscriminate slaughter on the Missouri border, unless averted by very judicious action. I shall be obliged if the general-in-chief can make any suggestions to General Schofield upon the subject.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, September 3, 1863.
HON. JAMES C. CONKLING, Springfield, Ill.:
I am mortified this morning to find the letter to you botched up in the Eastern papers, telegraphed from Chicago. How did this happen?
Ordered, That the executive order dated November 21, 1862, prohibiting the exportation from the United States of arms, ammunition, or munitions of war, under which the commandants of departments were, by order of the Secretary of War dated May 13, 1863, directed to prohibit the purchase and sale, for exportation from the United States, of all horses and mules within their respective commands, and to take and appropriate for the use of the United States any horses, mules, and live stock designed for exportation, be so far modified that any arms heretofore imported into the United States may be re-exported to the place of original shipment, and that any live stock raised in any State or Territory bounded by the Pacific Ocean may be exported from, any port of such State or Territory.
HON. JOSEPH SEGAR, Fort Monroe, Va.:
I have just seen your despatch to the Secretary of War, who is absent. I also send a despatch from Major Hayner of the 3d showing that he had notice of my order, and stating that the people were jubilant over it, as a victory over the Government extorted by fear, and that he had already collected about $4000 of the money. If he has proceeded since, I shall hold him accountable for his contumacy. On the contrary, no dollar shall be refunded by my order until it shall appear that my act in the case has been accepted in the right spirit.
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Manchester, Vt.:
All well and no news except that General Burnside has Knoxville, Ten.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR, Bedford, Pa.:
Burnside has Kingston and Knoxville, and drove the enemy across the river at Loudon, the enemy destroying the bridge there; captured some stores and one or two trains; very little fighting; few wounded and none killed. No other news of consequence.
Yours of August 29 just received. I suppose it was intended by Congress that this government should execute the act in question without dependence upon any other government, State, city, or county. It is, however, within the range of practical convenience to confer with the governments of States, while it is quite beyond that range to have correspondence on the subject with counties and cities. They are too numerous. As instances, I have corresponded with Governor Seymour, but Not with Mayor Opdyke; with Governor Curtin, but not with Mayor Henry.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn.:
Despatch of yesterday just received. I shall try to find the paper you mention and carefully consider it. In the meantime let me urge that you do your utmost to get every man you can, black and white, under arms at the very earliest moment, to guard roads, bridges, and trains, allowing all the better trained soldiers to go forward to Rosecrans. Of course I mean for you to act in co-operation with and not independently of, the military authorities.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Warrenton, Va.:
It would be a generous thing to give General Wheaton a leave of absence for ten or fifteen days, and if you can do so without injury to the service, please do it.
GENERAL WHEATON, Army of Potomac:
Yesterday at the instance of Mr. Blair, senator, I telegraphed General Meade asking him to grant you a leave of absence, to which he replied that you had not applied for such leave, and that you can have it when you do apply. I suppose it is proper for you to know this.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON.
MY DEAR SIR:—All Tennessee is now clear of armed insurrectionists. You need not to be reminded that it is the nick of time for reinaugurating a loyal State government. Not a moment should be lost. You and the co-operating friends there can better judge of the ways and means than can be judged by any here. I only offer a few suggestions. The reinauguration must not be such as to give control of the State and its representation in Congress to the enemies of the Union, driving its friends there into political exile. The whole struggle for Tennessee will have been profitless to both State and nation if it so ends that Governor Johnson is put down and Governor Harris put up. It must not be so. You must have it otherwise. Let the reconstruction be the work of such men only as can be trusted for the Union. Exclude all others, and trust that your government so organized will be recognized here as being the one of republican form to be guaranteed to the State, and to be protected against invasion and domestic violence. It is something on the question of time to remember that it cannot be known who is next to occupy the position I now hold, nor what he will do. I see that you have declared in favor of emancipation in Tennessee, for which may God bless you. Get emancipation into your new State government constitution and there will be no such word as fail for your cause. The raising of colored troops, I think, will greatly help every way.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Cumberland Gap:
Yours received. A thousand thanks for the late successes you have given us. We cannot allow you to resign until things shall be a little more settled in East Tennessee. If then, purely on your own account, you wish to resign, we will not further refuse you.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Warrenton, Va.:
It is represented to me that Thomas Edds, in your army, is under sentence of death for desertion, to be executed next Monday. It is also said his supposed desertion is comprised in an absence commencing with his falling behind last winter, being captured and paroled by the enemy, and then going home. If this be near the truth, please suspend the execution till further order and send in the record of the trial.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEAD, Warrenton, Va.:
The name is "Thomas Edds" not "Eddies" as in your despatch. The papers left with me do not designate the regiment to which he belongs. The man who gave me the papers, I do not know how to find again. He only told me that Edds is in the Army of the Potomac, and that he fell out of the ranks during Burnside's mud march last winter. If I get further information I will telegraph again.
Dr. WILLIAM H. H. SCOTT, Danville, Ill.:
Your niece, Mrs. Kate Sharp, can now have no difficulty in going to Knoxville, Tenn., as that place is within our military lines.
J. G. BLAINE, Augusta, Me.: Thanks both for the good news you send and for the sending of it.
A Proclamation.
Whereas the Constitution of the United States has ordained that the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus shall not be suspended unless when, in cases of rebellion or invasion, the public safety may require it; and:
Whereas a rebellion was existing on the third day of March, 1863, which rebellion is still existing; and:
Whereas by a statute which was approved on that day it was enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States in Congress assembled that during the present insurrection the President of the United States, whenever in his judgment the public safety may require, is authorized to suspend the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus in any case throughout the United States or any part thereof; and:
Whereas, in the judgment of the President, the public safety does require that the privilege of the said writ shall new be suspended throughout the United States in the cases where, by the authority of the President of the United States, military, naval, and civil officers of the United States, or any of them, hold persons under their command or in their custody, either as prisoners of war, spies, or aiders or abettors of the enemy, or officers, soldiers, or seamen enrolled or drafted or mustered or enlisted in or belonging to the land or naval forces of the United States, or as deserters therefrom, or otherwise amenable to military law or the rules and articles of war or the rules or regulations prescribed for the military or naval services by authority of the President of the United States, or for resisting a draft, or for any other offense against the military or naval service.
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby proclaim and make known to all whom it may concern that the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus is suspended throughout the United States in the several cases before mentioned, and that this suspension will continue throughout the duration of the said rebellion or until this proclamation shall, by a subsequent one to be issued by the President of the United States, be modified or revoked. And I do hereby require all magistrates, attorneys, and other civil officers within the United States and all officers and others in the military and naval services of the United States to take distinct notice of this suspension and to give it full effect, and all citizens of the United States to conduct and govern themselves accordingly and in conformity with the Constitution of the United States and the laws of Congress in such case made and provided.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed, this fifteenth day of September, A.D. 1863, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
If I did not misunderstand General Meade's last despatch, he posts you on facts as well as he can, and desires your views and those of the Government as to what he shall do. My opinion is that he should move upon Lee at once in manner of general attack, leaving to developments whether he will make it a real attack. I think this would develop Lee's real condition and purposes better than the cavalry alone can do. Of course my opinion is not to control you and General Meade.
Yours truly,
MRS. J. F. SPEED, Louisville, Ky.:
Mr. Holman will not be jostled from his place with my knowledge and consent.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Warrenton, Va.:
Is Albert Jones of Company K, Third Maryland Volunteers, to be shot on Friday next? If so please state to me the general features of the case.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
Major Haynor left here several days ago under a promise to put down in writing, in detail, the facts in relation to the misconduct of the people on the eastern shore of Virginia. He has not returned. Please send him over.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Headquarters Army of Potomac:
Yours in relation to Albert Jones is received. I am appealed to in behalf of Richard M. Abrams of Company A, Sixth New Jersey Volunteers, by Governor Parker, Attorney-General Frelinghuysen, Governor Newell, Hon. Mr. Middleton, M. C., of the district, and the marshal who arrested him. I am also appealed to in behalf of Joseph S. Smith, of Company A, Eleventh New Jersey Volunteers, by Governor Parker, Attorney-General Frelinghuysen, and Hon. Marcus C. Ward. Please state the circumstances of their cases to me.
WASHINGTON, D. C., September 18, 1863.
C.M. SMITH, Esq., Springfield, Ill.:
Why not name him for the general you fancy most? This is my suggestion.
MRS. HANNAH ARMSTRONG, Petersburg, Ill.:
I have just ordered the discharge of your boy William, as you say, now at Louisville, Ky.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., September 19.1863.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON.
MY DEAR SIR:—Herewith I send you a paper, substantially the same as the one drawn up by yourself and mentioned in your despatch, but slightly changed in two particulars: First, yours was so drawn as that I authorized you to carry into effect the fourth section, etc., whereas I so modify it as to authorize you to so act as to require the United States to carry into effect that section.
Secondly, you had a clause committing me in some sort to the State constitution of Tennessee, which I feared might embarrass you in making a new constitution, if you desire; so I dropped that clause.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
[Inclosure.]
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C.,
September 19, 1863.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Military Governor of Tennessee:
In addition to the matters contained in the orders and instructions given you by the Secretary of War, you are hereby authorized to exercise such powers as may be necessary and proper to enable the loyal people of Tennessee to present such a republican form of State government as will entitle the State to the guaranty of the United States therefor, and to be protected under such State government by the United States against invasion and domestic violence, all according to the fourth Section of the fourth article of the Constitution of the United States.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON D.C. September 19, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
By General Meade's despatch to you of yesterday it appears that he desires your views and those of the government as to whether he shall advance upon the enemy. I am not prepared to order, or even advise, an advance in this case, wherein I know so little of particulars, and wherein he, in the field, thinks the risk is so great and the promise of advantage so small.
And yet the case presents matter for very serious consideration in another aspect. These two armies confront each other across a small river, substantially midway between the two capitals, each defending its own capital, and menacing the other. General Meade estimates the enemy's infantry in front of him at not less than 40,000. Suppose we add fifty per cent. to this for cavalry, artillery, and extra-duty men stretching as far as Richmond, making the whole force of the enemy 60,000.
General Meade, as shown by the returns, has with him, and between him and Washington, of the same classes, of well men, over 90,000. Neither can bring the whole of his men into a battle; but each can bring as large a percentage in as the other. For a battle, then, General Meade has three men to General Lee's two. Yet, it having been determined that choosing ground and standing on the defensive gives so great advantage that the three cannot safely attack the two, the three are left simply standing on the defensive also.
If the enemy's 60,000 are sufficient to keep our 90,000 away from Richmond, why, by the same rule, may not 40,000 of ours keep their 60,000 away from Washington, leaving us 50,000 to put to some other use? Having practically come to the mere defensive, it seems to be no economy at all to employ twice as many men for that object as are needed. With no object, certainly, to mislead myself, I can perceive no fault in this statement, unless we admit we are not the equal of the enemy, man for man. I hope you will consider it.
To avoid misunderstanding, let me say that to attempt to fight the enemy slowly back into his entrenchments at Richmond, and then to capture him, is an idea I have been trying to repudiate for quite a year.
My judgment is so clear against it that I would scarcely allow the attempt to be made if the general in command should desire to make it. My last attempt upon Richmond was to get McClellan, when he was nearer there than the enemy was, to run in ahead of him. Since then I have constantly desired the Army of the Potomac to make Lee's army, and not Richmond, its objective point. If our army cannot fall upon the enemy and hurt him where he is, it is plain to me it can gain nothing by attempting to follow him over a succession of intrenched lines into a fortified city.
Yours truly,
MRS. A. LINCOLN, New York:
I neither see nor hear anything of sickness here now, though there may be much without my knowing it. I wish you to stay or come just as is most agreeable to yourself.
MRS. A. LINCOLN. Fifth Avenue Hotel. New York:
The air is so clear and cool and apparently healthy that I would be glad for you to come. Nothing very particular, but I would be glad to see you and Tad.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
I think it very important for General Rosecrans to hold his position at or about Chattanooga, because if held from that place to Cleveland, both inclusive, it keeps all Tennessee clear of the enemy, and also breaks one of his most important railroad lines. To prevent these consequences is so vital to his cause that he cannot give up the effort to dislodge us from the position, thus bringing him to us and saving us the labor, expense, and hazard of going farther to find him, and also giving us the advantage of choosing our own ground and preparing it to fight him upon. The details must, of course, be left to General Rosecrans, while we must furnish him the means to the utmost of our ability. If you concur, I think he would better be informed that we are not pushing him beyond this position; and that, in fact, our judgment is rather against his going beyond it. If he can only maintain this position, without more, this rebellion can only eke out a short and feeble existence, as an animal sometimes may with a thorn in its vitals.
Yours truly,
GENERAL BURNSIDE, Greenville, Tenn.:
If you are to do any good to Rosecrans it will not do to waste time with Jonesboro. It is already too late to do the most good that might have been done, but I hope it will still do some good. Please do not lose a moment.
GENERAL BURNSIDE, Knoxville, Tenn.:
Go to Rosecrans with your force without a moment's delay.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga:
Be of good cheer. We have unabated confidence in you, and in your soldiers and officers. In the main you must be the judge as to what is to be done. If I were to suggest, I would say, save your army by taking strong positions until Burnside joins you, when, I hope, you can turn the tide. I think you had better send a courier to Burnside to hurry him up. We cannot reach him by telegraph. We suppose some force is going to you from Corinth, but for want of communication we do not know how they are getting along. We shall do our utmost to assist you. Send us your present positions.
WAR DEPARTMENT, September 22, 1863.8.30 A.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Tenn.:
We have not a word here as to the whereabouts or condition of your army up to a later hour than sunset, Sunday, the 20th. Your despatches to me of 9 A.M., and to General Halleck of 2 P. M., yesterday, tell us nothing later on those points. Please relieve my anxiety as to the position and condition of your army up to the latest moment.
HON. O. M. HATCH, HON. J. K. DUBOIS, Springfield, Ill.:
Your letter is just received. The particular form of my despatch was jocular, which I supposed you gentlemen knew me well enough to understand. General Allen is considered here as a very faithful and capable officer, and one who would be at least thought of for quartermaster-general if that office were vacant.
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Fifth Avenue House, New York:—Did you receive my despatch of yesterday? Mrs. Cuthbert did not correctly understand me. I directed her to tell you to use your own pleasure whether to stay or come, and I did not say it is sickly and that you should on no account come. So far as I see or know, it was never healthier, and I really wish to see you. Answer this on receipt.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Tenn:
Below is Bragg's despatch as found in the Richmond papers. You see he does not claim so many prisoners or captured guns as you were inclined to concede. He also confesses to heavy loss. An exchanged general of ours leaving Richmond yesterday says two of Longstreet's divisions and his entire artillery and two of Pickett's brigades and Wise's legion have gone to Tennessee. He mentions no other.
"CHICAMAUGA RIVER, SEPTEMBER 20.
"GENERAL COOPER, Adjutant-General:
"After two days' hard fighting we have driven the enemy, after a desperate resistance, from several positions, and now hold the field; but he still confronts us. The loses are heavy on both sides, especially in our officers....
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas, in my proclamation of the twenty-seventh of April, 1861, the ports of the States of Virginia and North Carolina were, for reasons therein set forth, placed under blockade; and whereas the port of Alexandria, Virginia, has since been blockaded, but as the blockade of said port may now be safely relaxed with advantage to the interests of commerce:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United Sates, pursuant to the authority in me vested by the fifth section of the act of Congress, approved on the 13th of July, 1861, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," do hereby declare that the blockade of the said port of Alexandria shall so far cease and determine, from and after this date, that commercial intercourse with said port, except as to persons, things, and information contraband of war, may from this date be carried on, subject to the laws of the United States, and to the limitations and in pursuance of the regulations which are prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury in his order which is appended to my proclamation of the 12th of May, 1862.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twenty-fourth day of September in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Term.:
Last night we received the rebel accounts, through Richmond papers, of your late battle. They give Major-General Hood as mortally wounded, and Brigadiers Preston Smith, Wofford, Walthall, Helm of Kentucky, and DesMer killed, and Major-Generals Preston, Cleburne, and Gregg, and Brigadier-Generals Benning, Adams, Burm, Brown, and John [B. H.] Helm wounded. By confusion the two Helms may be the same man, and Bunn and Brown may be the same man. With Burnside, Sherman, and from elsewhere we shall get to you from forty to sixty thousand additional men.
WAR DEPARTMENT, SEPTEMBER 24, 1863
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Fifth Avenue Hotel, New York:
We now have a tolerably accurate summing up of the late battle between Rosecrans and Braag. The result is that we are worsted, if at all, only in the fact that we, after the main fighting was over, yielded the ground, thus leaving considerable of our artillery and wounded to fall into the enemy's hands., for which we got nothing in turn. We lost in general officers one killed and three or four wounded, all brigadiers, while, according to the rebel accounts which we have, they lost six killed and eight wounded: of the killed one major-general and five brigadiers including your brother-in-law, Helm; and of the wounded three major-generals and five brigadiers. This list may be reduced two in number by corrections of confusion in names. At 11.40 A.M. yesterday General Rosecrans telegraphed from Chattanooga: "We hold this point, and I cannot be dislodged except by very superior numbers and after a great battle." A despatch leaving there after night yesterday says, "No fight to-day."
GENERAL McCALLUM, Alexandria, Va.:
I have sent to General Meade, by telegraph, to suspend the execution of Daniel Sullivan of Company F, Thirteenth Massachusetts, which was to be to-day, but understanding there is an interruption on the line, may I beg you to send this to him by the quickest mode in your power?
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
Owing to the press in behalf of Daniel Sullivan, Company E, Thirteenth Massachusetts, and the doubt; though small, which you express of his guilty intention, I have concluded to say let his execution be suspended till further order, and copy of record sent me.
MY DEAR GENERAL ROSECRANS:
We are sending you two small corps, one under General Howard and one under General Slocum, and the whole under General Hooker.
Unfortunately the relations between Generals Hooker and Slocum are not such as to promise good, if their present relative positions remain. Therefore, let me beg—almost enjoin upon you—that on their reaching you, you will make a transposition by which General Slocum with his Corps, may pass from under the command of General Hooker, and General Hooker, in turn receive some other equal force. It is important for this to be done, though we could not well arrange it here. Please do it.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga., Tenn.:
You can perhaps communicate with General Burnside more rapidly by sending telegrams directly to him at Knoxville. Think of it. I send a like despatch to him.
GENERAL SCHOFIELD, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Following despatch just received:
"Union Men Driven out of Missouri."
"Leavenworth, September 29, 1863.
"Governor Gamble having authorized Colonel Moss, of Liberty, Missouri, to arm the men in Platte and Clinton Counties, he has armed mostly the returned rebel soldiers and men wider bonds. Moss's men are now driving the Union men out of Missouri. Over one hundred families crossed the river to-day. Many of the wives of our Union soldiers have been compelled to leave. Four or five Union men have been murdered by Colonel Moss's men."
Please look to this and, if true, in main or part, put a stop to it.
HON. FRANCIS S. CORKRAN, Baltimore, Md.: MRS. L. is now at home and would be pleased to see you any time. If the grape time has not passed away, she would be pleased to join in the enterprise you mention.
Yours truly,
GENERAL TYLER, Baltimore:
Take care of colored troops in your charge, but do nothing further about that branch of affairs until further orders. Particularly do nothing about General Vickers of Kent County.
A. LINCOLN.
Send a copy to Colonel Birney. A. L.
OCTOBER 1, 1863 GENERAL JOHN M. SCHOFIELD:
There is no organized military force in avowed opposition to the General Government now in Missouri, and if any shall reappear, your duty in regard to it will be too plain to require any special instruction. Still, the condition of things, both there and elsewhere, is such as to render it indispensable to maintain, for a time, the United States military establishment in that State, as well as to rely upon it for a fair contribution of support to that establishment generally. Your immediate duty in regard to Missouri now is to advance the efficiency of that establishment, and to so use it, as far as practicable, to compel the excited people there to let one another alone.
Under your recent order, which I have approved, you will only arrest individuals, and suppress assemblies or newspapers, when they may be working palpable injury to the military in your charge; and in no other case will you interfere with the expression of opinion in any form, or allow it to be interfered with violently by others. In this you have a discretion to exercise with great caution, calmness, and forbearance.
With the matter of removing the inhabitants of certain counties en masse, and of removing certain individuals from time to time, who are supposed to be mischievous, I am not now interfering, but am leaving to your own discretion.
Nor am I interfering with what may still seem to you to be necessary restrictions upon trade and intercourse. I think proper, however, to enjoin upon you the following: Allow no part of the military under your command to be engaged in either returning fugitive slaves or in forcing or enticing slaves from their homes; and, so far as practicable, enforce the same forbearance upon the people.
Report to me your opinion upon the availability for good of the enrolled militia of the State. Allow no one to enlist colored troops, except upon orders from you, or from here through you.
Allow no one to assume the functions of confiscating property, under the law of Congress, or otherwise, except upon orders from here.
At elections see that those, and only those, are allowed to vote who are entitled to do so by the laws of Missouri, including as of those laws the restrictions laid by the Missouri convention upon those who may have participated in the rebellion.
So far as practicable, you will, by means of your military force, expel guerrillas, marauders, and murderers, and all who are known to harbor, aid, or abet them. But in like manner you will repress assumptions of unauthorized individuals to perform the same service, because under pretense of doing this they become marauders and murderers themselves.
To now restore peace, let the military obey orders, and those not of the military leave each other alone, thus not breaking the peace themselves.
In giving the above directions, it is not intended to restrain you in other expedient and necessary matters not falling within their range.
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHOFIELD:
I have just seen your despatch to Halleck about Major-General Blunt. If possible, you better allow me to get through with a certain matter here, before adding to the difficulties of it. Meantime supply me the particulars of Major-General Blunt's case.
A. LINCOLN.
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL BIRNEY. [Cipher.] WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D.C., October 3, 1863.
COLONEL BIRNEY, Baltimore, Md.:
Please give me, as near as you can, the number of slaves you have recruited in Maryland. Of course the number is not to include the free colored.
A Proclamation.
The year that is drawing towards its close has been filled with the blessings of fruitful fields and healthful skies. To these bounties, which are so constantly enjoyed that we are prone to forget the source from which they come, others have been added which are of so extraordinary a nature that they cannot fail to penetrate and soften even the heart which is habitually insensible to the ever-watchful providence of Almighty God. In the midst of a civil war of unequalled magnitude and severity which has sometimes seemed to invite and provoke the aggressions of foreign states; peace has been preserved with all nations, order has been maintained, the laws have been respected and obeyed, and harmony has prevailed everywhere except in the theatre of military conflict; while that theatre has been greatly contracted by the advancing armies and navies of the Union. The needful diversion of wealth and strength from the fields of peaceful industry, to the national defense has not arrested the plough, the shuttle, or the ship: The axe has enlarged the borders of our settlements, and the mines, as well of, iron and coal as of the precious metals, have yielded even more abundantly than heretofore. Population has steadily increased, notwithstanding the waste that has been made in the camp, the siege, and the battle-field; and the country, rejoicing in the consciousness of augmented strength and vigor, is permitted to expect a continuance of years, with large increase of freedom.
No human counsel hath devised, nor hath any mortal hand worked out these great things. They are the gracious gifts of the Most High God, who, while dealing with us in anger for our sins, hath nevertheless remembered mercy.
It has seemed to me fit and proper that they should be reverently, solemnly, and gratefully acknowledged, as with one heart and voice, by the whole American people. I do, therefore, invite my fellow-citizens in every part of the United States, and also those who are at sea, and those who are sojourning in foreign lands, to set apart and observe the last Thursday of November next as a day of thanksgiving and prayer to our beneficent Father who dwelleth in the heavens. And I recommend to them that, while offering up the ascriptions justly due to Him for such singular deliverances and blessings, they do also, with humble penitence for our national perverseness and disobedience, commend to His tender care all those who have become widows, orphans, mourners, or sufferers in the lamentable civil strife in which we are unavoidably engaged, and fervently implore the interposition of the Almighty hand to heal the wounds of the nation, and to restore it, as soon as may be consistent with divine purposes, to the full enjoyment of peace, harmony, tranquillity, and union.
In testimony whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this third day of October, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHOFIELD, St. Louis, Mo.:
I think you will not have just cause to complain of my action.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Tenn.:
Yours of yesterday received. If we can hold Chattanooga and East Tennessee, I think the rebellion must dwindle and die. I think you and Burnside can do this, and hence doing so is your main object. Of course to greatly damage or destroy the enemy in your front would be a greater object, because it would include the former and more, but it is not so certainly within your power. I understand the main body of the enemy is very near you, so near that you could "board at home," so to speak, and menace or attack him any day. Would not the doing of this be your best mode of counteracting his raid on your communications? But this is not an order. I intend doing something like what you suggest whenever the case shall appear ripe enough to have it accepted in the true understanding rather than as a confession of weakness and fear.
HON. CHARLES D. DRAKE AND OTHERS, Committee.
GENTLEMEN:-Your original address, presented on the 30th ult., and the four supplementary ones presented on the 3d inst., have been carefully considered. I hope you will regard the other duties claiming my attention, together with the great length and importance of these documents, as constituting a sufficient apology for not having responded sooner.
These papers, framed for a common object, consist of the things demanded and the reasons for demanding them.
The things demanded are
First. That General Schofield shall be relieved, and General Butler be appointed as Commander of the Military Department of Missouri.
Second. That the system of enrolled militia in Missouri may be broken up, and national forces he substituted for it; and
Third. That at elections persons may not be allowed to vote who are not entitled by law to do so.
Among the reasons given, enough of suffering and wrong to Union men is certainly, and I suppose truly, stated. Yet the whole case, as presented, fails to convince me that General Schofield, or the enrolled militia, is responsible for that suffering and wrong. The whole can be explained on a more charitable, and, as I think, a more rational hypothesis.
We are in a civil war. In such cases there always is a main question, but in this case that question is a perplexing compound—Union and slavery. It thus becomes a question not of two sides merely, but of at least four sides, even among those who are for the Union, saying nothing of those who are against it. Thus, those who are for the Union with, but not without slavery; those for it without, but not with; those for it with or without, but prefer it with; and those for it with or without, but prefer it without.
Among these, again, is a subdivision of those who are for gradual, but not for immediate, and those who are for immediate, but not for gradual extinction of slavery.
It is easy to conceive that all these shades of opinion, and even more, may be sincerely entertained by honest and truthful men. Yet, all being for the Union, by reason of these differences each will prefer a different way of sustaining the Union. At once, sincerity is questioned, and motives are assailed. Actual war comming, blood grows hot and blood is spilled. Thought is forced from old channels into confusion. Deception breeds and thrives. Confidence dies, and universal suspicion reigns. Each man feels an impulse to kill his neighbor, lest he be killed by him. Revenge and retaliation follow. And all this, as before said, may be among honest men only. But this is not all. Every foul bird comes abroad, and every dirty reptile rises up. These add crime to confusion. Strong measures deemed indispensable, but harsh at best, such men make worse by maladministration. Murders for old grudges, and murders for self, proceed under any cloak that will best serve for the occasion.
These causes amply account for what has occurred in Missouri, without ascribing it to the weakness or wickedness of any general. The newspaper files, those chroniclers of current events, will show that the evils now complained of were quite as prevalent under Fremont, Hunter, Halleck, and Curtis, as under Schofield. If the former had greater force opposed to them, they also had greater force with which to meet it. When the organized rebel army left the State, the main Federal force had to go also, leaving the department commander at home relatively no stronger than before. Without disparaging any, I affirm with confidence that no commander of that department has, in proportion to his means, done better than General Schofield.
The first specific charge against General Schofield is, that the enrolled militia was placed under his command, whereas it had not been placed under the command of General Curtis. The fact is, I believe, true; but you do not point out, nor can I conceive, how that did, or could, injure loyal men or the Union cause.
You charge that, General Curtis being superseded by General Schofield, Franklin A. Dick was superseded by James O. Broadhead as Provost-Marshal General. No very specific showing is made as to how this did or could injure the Union cause. It recalls, however, the condition of things, as presented to me, which led to a change of commander of that department.
To restrain contraband intelligence and trade, a system of searches, seizures, permits, and passes, had been introduced, I think, by General Fremont. When General Halleck came, he found and continued the system, and added an order, applicable to some parts of the State, to levy and collect contributions from noted rebels, to compensate losses and relieve destitution caused by the rebellion. The action of General Fremont and General Halleck, as stated, constituted a sort of system which General Curtis found in full operation when he took command of the department. That there was a necessity for something of the sort was clear; but that it could only be justified by stern necessity, and that it was liable to great abuse in administration, was equally clear. Agents to execute it, contrary to the great prayer, were led into temptation. Some might, while others would not, resist that temptation. It was not possible to hold any to a very strict accountability; and those yielding to the temptation would sell permits and passes to those who would pay most and most readily for them, and would seize property and collect levies in the aptest way to fill their own pockets. Money being the object, the man having money, whether loyal or disloyal, would be a victim. This practice doubtless existed to some extent, and it was, a real additional evil that it could be, and was, plausibly charged to exist in greater extent than it did.
When General Curtis took command of the department, Mr. Dick, against whom I never knew anything to allege, had general charge of this system. A controversy in regard to it rapidly grew into almost unmanageable proportions. One side ignored the necessity and magnified the evils of the system, while the other ignored the evils and magnified the necessity; and each bitterly assailed the other. I could not fail to see that the controversy enlarged in the same proportion as the professed Union men there distinctly took sides in two opposing political parties. I exhausted my wits, and very nearly my patience also, in efforts to convince both that the evils they charged on each other were inherent in the case, and could not be cured by giving either party a victory over the other.
Plainly, the irritating system was not to be perpetual; and it was plausibly urged that it could be modified at once with advantage. The case could scarcely be worse, and whether it could be made better could only be determined by a trial. In this view, and not to ban or brand General Curtis, or to give a victory to any party, I made the change of commander for the department. I now learn that soon after this change Mr. Dick was removed, and that Mr. Broadhead, a gentleman of no less good character, was put in the place. The mere fact of this change is more distinctly complained of than is any conduct of the new officer, or other consequence of the change.
I gave the new commander no instructions as to the administration of the system mentioned, beyond what is contained in the private letter afterwards surreptitiously published, in which I directed him to act solely for the public good, and independently of both parties. Neither any thing you have presented me, nor anything I have otherwise learned, has convinced me that he has been unfaithful to this charge.
Imbecility is urged as one cause for removing General Schofield; and the late massacre at Lawrence, Kansas, is pressed as evidence of that imbecility. To my mind that fact scarcely tends to prove the proposition. That massacre is only an example of what Grierson, John Morgan, and many others might have repeatedly done on their respective raids, had they chosen to incur the personal hazard, and possessed the fiendish hearts to do it.
The charge is made that General Schofield, on purpose to protect the Lawrence murderers, would not allow them to be pursued into Missouri. While no punishment could be too sudden or too severe for those murderers, I am well satisfied that the preventing of the threatened remedial raid into Missouri was the only way to avoid an indiscriminate massacre there, including probably more innocent than guilty. Instead of condemning, I therefore approve what I understand General Schofield did in that respect.
The charges that General Schofield has purposely withheld protection from loyal people and purposely facilitated the objects of the disloyal are altogether beyond my power of belief. I do not arraign the veracity of gentlemen as to the facts complained of, but I do more than question the judgment which would infer that those facts occurred in accordance with the purposes of General Schofield.
With my present views, I must decline to remove General Schofield. In this I decide nothing against General Butler. I sincerely wish it were convenient to assign him a suitable command. In order to meet some existing evils I have addressed a letter of instructions to General Schofield, a copy of which I enclose to you.
As to the enrolled militia, I shall endeavor to ascertain better than I now know what is its exact value. Let me say now, however, that your proposal to substitute national forces for the enrolled militia implies that in your judgment the latter is doing something which needs to be done; and if so, the proposition to throw that force away and to supply its place by bringing other forces from the field where they are urgently needed seems to me very extraordinary. Whence shall they come? Shall they be withdrawn from Banks, or Grant, or Steele, or Rosecrans? Few things have been so grateful to my anxious feelings as when, in June last, the local force in Missouri aided General Schofield to so promptly send a large general force to the relief of General Grant, then investing Vicksburg and menaced from without by General Johnston. Was this all wrong? Should the enrolled militia then have been broken up and General Herron kept from Grant to police Missouri? So far from finding cause to object, I confess to a sympathy for whatever relieves our general force in Missouri and allows it to serve elsewhere. I therefore, as at present advised, cannot attempt the destruction of the enrolled militia of Missouri. I may add that, the force being under the national military control, it is also within the proclamation in regard to the habeas corpus.
I concur in the propriety of your request in regard to elections, and have, as you see, directed General Schofield accordingly. I do not feel justified to enter upon the broad field you present in regard to the political differences between Radicals and Conservatives. From time to time I have done and said what appeared to me proper to do and say. The public knows it all. It obliges nobody to follow me, and I trust it obliges me to follow nobody. The Radicals and Conservatives each agree with me in some things and disagree in others. I could wish both to agree with me in all things, for then they would agree with each other, and would be too strong for any foe from any quarter. They, however, choose to do otherwise; and I do not question their right. I too shall do what seems to be my duty. I hold whoever commands in Missouri or elsewhere responsible to me and not to either Radicals or Conservatives. It is my duty to hear all, but at last I must, within my sphere, judge what to do and what to forbear.
Your obedient servant,
WAR DEPARTMENT, ADJUTANT-GENERALS OFFICE,
WASHINGTON, October 8, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL J. G. FOSTER, Commanding Department of Virginia and North Carolina, Fort Monroe, Va.
SIR:—The proceedings of the military commission instituted for the trial of David Wright, of Norfolk, in Special Orders Nos. 195, 196, and 197, of 1863, from headquarters Department of Virginia, have been submitted to the President of the United States. The following are his remarks on the case:
Upon the presentation of the record in this case and the examination thereof, aided by the report thereon of the Judge-Advocate-General, and on full hearing of counsel for the accused, being specified that no proper question remained open except as to the sanity of the accused, I caused a very full examination to be made on that question, upon a great amount of evidence, including all effort by the counsel for accused, by an expert of high reputation in that professional department, who thereon reports to me, as his opinion, that the accused, Dr. David M. Wright, was not insane prior to or on the 11th day of July, 1863, the date of the homicide of Lieutenant Sanborn; that he has not been insane since, and is not insane now (Oct. 7, 1863). I therefore approve the finding and sentence of the military commission, and direct that the major-general in command of the department including the place of trial, and wherein the convict is now in custody, appoint a time and place and carry such sentence into execution.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
I am appealed to in behalf of August Blittersdorf, at Mitchell's Station, Va., to be shot to-morrow as a deserter. I am unwilling for any boy under eighteen to be shot, and his father affirms that he is yet under sixteen. Please answer. His regiment or company not given me.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
The boy telegraphs from Mitchell's Station, Va. The father thinks he is in the One hundred and nineteenth Pennsylvania Volunteers. The father signs the name "Blittersdorf." I can tell no more.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
The father and mother of John Murphy, of the One hundred and nineteenth Pennsylvania Volunteers, have filed their own affidavits that he was born June 22, 1846, and also the affidavits of three other persons who all swear that they remembered the circumstances of his birth and that it was in the year 1846, though they do not remember the particular day. I therefore, on account of his tender age, have concluded to pardon him, and to leave it to yourself whether to discharge him or continue him in the service.
WAR DEPARTMENT, October 12, 1863.8.35 A.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Term.:
As I understand, Burnside is menaced from the west, and so cannot go to you without surrendering East Tennessee. I now think the enemy will not attack Chattanooga, and I think you will have to look out for his making a concentrated drive at Burnside. You and Burnside now have him by the throat, and he must break your hold or perish I therefore think you better try to hold the road up to Kingston, leaving Burnside to what is above there. Sherman is coming to you, though gaps in the telegraph prevent our knowing how far he is advanced. He and Hooker will so support you on the west and northwest as to enable you to look east and northeast. This is not an order. General Halleck will give his views.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE: What news this morning? A despatch from Rosecrans, leaving him at 7.30 P.M. yesterday, says:
"Rebel rumors that head of Ewell's column reached Dalton yesterday."
I send this for what it is worth.
McVEIGH, Philadelphia:
The enemy some days ago made a movement, apparently to turn General Meade's right. This led to a maneuvering of the two armies and to pretty heavy skirmishing on Saturday, Sunday, and Monday. We have frequent despatches from General Meade and up to 10 o'clock last night nothing had happened giving either side any marked advantage. Our army reported to be in excellent condition. The telegraph is open to General Meade's camp this morning, but we have not troubled him for a despatch.
HON. THURLOW WEED.
DEAR SIR:—I have been brought to fear recently that somehow, by commission or omission, I have caused you some degree of pain. I have never entertained an unkind feeling or a disparaging thought toward you; and if I have said or done anything which has been construed into such unkindness or disparagement, it has been misconstrued. I am sure if we could meet we would not part with any unpleasant impression On either side.
Yours as ever,
L. B. TODD, Lexington, Ky.:
I send the following pass to your care.
To WHOM IT MAY CONCERN:
Allow MRS. Robert S. Todd, widow, to go south and bring her daughter, MRS. General B. Hardin Helm, with her children, north to Kentucky.
MAJOR-GENERAL FOSTER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Postpone the execution of Dr. Wright to Friday the 23d instant (October). This is intended for his preparation and is final.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
On the 4th instant you telegraphed me that Private Daniel Hanson, of Ninety-seventh New York Volunteers, had not yet been tried. When he shall be, please notify me of the result, with a brief statement of his case, if he be convicted. Gustave Blittersdorf, who you say is enlisted in the One hundred and nineteenth Pennsylvania Volunteers as William Fox, is proven to me to be only fifteen years old last January. I pardon him, and you will discharge him or put him in the ranks at your discretion. Mathias Brown, of Nineteenth Pennsylvania Volunteers, is proven to me to be eighteen last May, and his friends say he is convicted on an enlistment and for a desertion both before that time. If this last be true he is pardoned, to be kept or discharged as you please. If not true suspend his execution and report the facts of his case. Did you receive my despatch of 12th pardoning John Murphy?
A. LINCOLN.
[The Lincoln papers during this time have a suspended execution on almost every other page, I have omitted most of these D.W.]
THOMAS W. SWEENEY, Continental, Philadelphia:
Tad is teasing me to have you forward his pistol to him.
T. C. DURANT, New York:
I remember receiving nothing from you of the 10th, and I do not comprehend your despatch of to-day. In fact I do not remember, if I ever knew, who you are, and I have very little conception as to what you are telegraphing about.
DEAR SIR: On the point of leaving I am told, by a gentleman to whose statements I attach credit, that the opposition policy for the Presidential campaign will be to "abstain from voting." J.
[Comment.]
More likely to abstain from stopping, once they get at it, until they shall have voted several times each.
October 16. A. L.
MAJOR GENERAL HALLECK:
I do not believe Lee can have over 60,000 effective men.
Longstreet's corps would not be sent away to bring an equal force back upon the same road; and there is no other direction for them to have come from.
Doubtless, in making the present movement, Lee gathered in all available scraps, and added them to Hill's and Ewell's corps; but that is all, and he made the movement in the belief that four corps had left General Meade; and General Meade's apparently avoiding a collision with him has confirmed him in that belief. If General Meade can now attack him on a field no worse than equal for us, and will do so now with all the skill and courage which he, his officers, and men possess, the honor will be his if he succeeds, and the blame may be mine if he fails.
Yours truly,
A Proclamation.
Whereas the term of service of a part of the Volunteer forces of the United States will expire during the coming year; and whereas, in addition to the men raised by the present draft, it is deemed expedient to call out three hundred thousand volunteers to serve for three years or during the war, not, however, exceeding three years:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, and Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy thereof, and of the militia of the several States when called into actual service, do issue this my proclamation, calling upon the governors of the different States to raise, and have enlisted into the United States service, for the various companies and regiments in the field from their respective States, the quotas of three hundred thousand men.
I further proclaim that all the volunteers thus called out and duly enlisted shall receive advance pay, premium, and bounty, as heretofore communicated to the governors of States by the War Department through the Provost-Marshal-General's office, by special letters.
I further proclaim that all volunteers received under this call, as well as all others not heretofore credited, shall be duly credited and deducted from the quotas established for the next draft.
I further proclaim that if any State shall fail to raise the quota assigned to it by the War Department under this call, then a draft for the deficiency in said quota shall be made in said State, or in the districts of said State, for their due proportion of said quota, and the said draft shall commence on the 5th day of January, 1864.
And I further proclaim that nothing in this proclamation shall interfere with existing orders, or with those which may be issued for the present draft in the States where it is now in progress, or where it has not yet been commenced.
The quotas of the States and districts will be assigned by the War Department through the Provost-Marshal-General's office, due regard being had for the men heretofore furnished, whether by volunteering or drafting; and the recruiting will be conducted in accordance with such instructions as have been or may be issued by that department.
In issuing this proclamation, I address myself not only to the governors of the several States, but also to the good and loyal people thereof, invoking them to lend their cheerful, willing, and effective aid to the measures thus adopted, with a view to reinforce our victorious army now in the field, and bring our needful military operations to a prosperous end, thus closing forever the fountains of sedition and civil war.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.....................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL FOSTER, Port Monroe, Va.:
It would be useless for Mrs. Dr. Wright to come here. The subject is a very painful one, but the case is settled.
HON. WILLIAM B. THOMAS, Philadelphia, Pa.
I am grateful for your offer of 100,000 men, but as at present advised I do not consider that Washington is in danger, or that there is any emergency requiring 60 or 90 days men.
JOHN WILLIAMS AND N G. TAYLOR, Knoxville, Tenn.:
You do not estimate the holding of East Tennessee more highly than I do. There is no absolute purpose of withdrawing our forces from it, and only a contingent one to withdraw them temporarily for the purpose of not losing the position permanently. I am in great hope of not finding it necessary to withdraw them at all, particularly if you raise new troops rapidly for us there.
T. C. DURANT, New York:
As I do with others, so I will try to see you when you come.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Chattanooga, Tenn:
There has been no battle recently at Bull Run. I suppose what you have heard a rumor of was not a general battle, but an "affair" at Bristow Station on the railroad, a few miles beyond Manassas Junction toward the Rappahannock, on Wednesday, the 14th. It began by an attack of the enemy upon General Warren, and ended in the enemy being repulsed with a loss of four cannon and from four to seven hundred prisoners.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
A delegation is here saying that our armed colored troops are at many, if not all, the landings on the Patuxent River, and by their presence with arms in their hands are frightening quiet people and producing great confusion. Have they been sent there by any order, and if so, for what reason?
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHENCK, Baltimore, Md.:
Please come over here. The fact of one of our officers being killed on the Patuxent is a specimen of what I would avoid. It seems to me we could send white men to recruit better than to send negroes and thus inaugurate homicides on punctilio.
Please come over.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
Taking all our information together, I think it probable that Ewell's corps has started for East Tennessee by way of Abingdon, marching last Monday, say from Meade's front directly to the railroad at Charlottesville.
First, the object of Lee's recent movement against Meade; his destruction of the Alexandria and Orange Railroad, and subsequent withdrawal without more motive, not otherwise apparent, would be explained by this hypothesis.
Secondly, the direct statement of Sharpe's men that Ewell has gone to Tennessee.
Thirdly, the Irishman's [Northern Spy in Richmond] statement that he has not gone through Richmond, and his further statement of an appeal made to the people at Richmond to go and protect their salt, which could only refer to the works near Abingdon.
Fourthly, Graham's statement from Martinsburg that Imboden is in retreat for Harrisonburg. This last matches with the idea that Lee has retained his cavalry, sending Imboden and perhaps other scraps to join Ewell. Upon this probability what is to be done?
If you have a plan matured, I have nothing to say. If you have not, then I suggest that, with all possible expedition, the Army of the Potomac get ready to attack Lee, and that in the meantime a raid shall, at all hazards, break the railroad at or near Lynchburg.
Yours truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, October 26, 1863.
HON. E. B. WASHBURNE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of the 12th has been in my hands several days. Inclosed I send the leave of absence for your brother, in as good form as I think I can safely put it. Without knowing whether he would accept it. I have tendered the collectorship at Portland, Maine, to your other brother, the governor.
Thanks to both you and our friend Campbell for your kind words and intentions. A second term would be a great honor and a great labor, which, together, perhaps I would not decline if tendered.
Yours truly,
HON. SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
MY DEAR SIR:—The writer of the accompanying letter is one of Mrs. Lincoln's numerous cousins. He is a grandson of "Milliken's Bend," near Vicksburg—that is, a grandson of the man who gave name to Milliken's Bend. His father was a brother to MRS. Lincoln's mother. I know not a thing about his loyalty beyond what he says. Supposing he is loyal, can any of his requests be granted, and if any, which of them?
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
|
VOLUME ONE VOLUME TWO VOLUME THREE VOLUME FOUR VOLUME FIVE VOLUME SIX VOLUME SEVEN |
CONTENTS
THE WRITINGS OF A. LINCOLN, Volume Seven, 1863-1865
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 3, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL A. E. BURNSIDE. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, November
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. G. MEADE.
ORDER CONCERNING THE EXPORT OF TOBACCO PURCHASED BY FOREIGN NATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SCHOFIELD.
TELEGRAM to E. H. AND E. JAMESON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS.
ANNOUNCEMENT OF UNION SUCCESS IN EAST TENNESSEE.
PROCLAMATION OF AMNESTY AND RECONSTRUCTION. DECEMBER 8, 1863.
ANNUAL MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, DECEMBER 8, 1863.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS. WASHINGTON D. C., December 8, 1863.
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE. WASHINGTON, D. C., December 8, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING DISCRIMINATING DUTIES, DECEMBER 16, 1863.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO MILITARY COMMANDER AT POINT LOOKOUT.
TELEGRAM TO MILITARY COMMANDER AT POINT LOOKOUT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PIERPOINT.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BROUGH. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January 15,
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, JANUARY 20, 1864
ORDER APPROVING TRADE REGULATIONS.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE.
ORDER FOR A DRAFT OF FIVE HUNDRED THOUSAND MEN.
THE STORY OF THE EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING BLOCKADE, FEBRUARY 18, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
DESERTERS DEATH SENTENCES REMITTED
ORDER IN REGARD TO THE EXPORTATION OF TOBACCO BELONGING TO THE FRENCH
TELEGRAM TO UNITED STATES MARSHAL, LOUISVILLE.
ORDER ASSIGNING U. S. GRANT COMMAND OF THE ARMIES OF THE UNITED STATES.
CALL FOR TWO HUNDRED THOUSAND MEN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PASS FOR GENERAL D. E. SICKLES.
REMARKS AT A FAIR IN THE PATENT OFFICE,
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE FROM THE WORKINGMEN'S ASSOCIATION OF NEW YORK,
CORRESPONDENCE WITH GENERAL C. SCHURZ.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER COMMANDING AT FORT WARREN.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER COMMANDING AT FORT WARREN.
INDORSEMENT ON OFFER OF TROOPS, APRIL 23, 1864.
MESSAGE TO CONGRESS, APRIL 28, 1864.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES,
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS.
RECOMMENDATION OF THANKSGIVING.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL LEW WALLACE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS,
RESPONSE TO A METHODIST DELEGATION, MAY 14, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR YATES. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 18, 1864.
ARREST AND IMPRISONMENT OF IRRESPONSIBLE NEWSPAPER REPORTERS AND EDITORS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. P. BUTLER.
ORDER CONCERNING THE EXEMPTION OF AMERICAN CONSULS FROM MILITARY SERVICE
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR MORTON AND OTHERS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, May 21, 1864
TELEGRAM TO CHRISTIANA A. SACK. WAR DEPARTMENT WASHINGTON, D. C., May 21,
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BROUGH. WASHINGTON CITY, May 24, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 25,1864.
MEMORANDUM CONCERNING THE TRANSPORTATION OF THE NEW YORK NAVAL BRIGADE.
INDORSEMENT ON A LETTER TOUCHING THE REPUBLICAN NATIONAL CONVENTION.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL MEADE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 6, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS. WASHINGTON, June 8, 1864.
REPLY TO THE COMMITTEE NOTIFYING PRESIDENT LINCOLN OF HIS RENOMINATION,
PLATFORM OF THE UNION NATIONAL CONVENTION HELD IN BALTIMORE, MD., JUNE 7
REPLY TO A DELEGATION FROM THE NATIONAL UNION LEAGUE,
REPLY TO A DELEGATION FROM OHIO,
ADDRESS TO THE ENVOY FROM THE HAWAIIAN ISLANDS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL L. THOMAS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 13,
TELEGRAM TO THOMAS WEBSTER. WASHINGTON, D. C., June 13, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, June 15, 1864. 7 A.M.
ADDRESS AT A SANITARY FAIR IN PHILADELPHIA,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. ROSECRANS. WASHINGTON, June 24, 1864.
LETTER ACCEPTING THE NOMINATION FOR PRESIDENT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL GRANT. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, June 29, 1864.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GOVERNOR SEYMOUR.
PROCLAMATION SUSPENDING THE WRIT OF HABEAS CORPUS,
PROCLAMATION FOR A DAY OF PRAYER, JULY 7, 1864.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING A BILL "TO GUARANTEE TO CERTAIN STATES,
TELEGRAM TO J. W. GARRETT. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 9, 1864
TELEGRAM FROM GENERAL HALLECK TO GENERAL WALLACE.
TELEGRAM TO T. SWAN AND OTHERS. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 10, 1864. 9.20
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON CITY, July TO, 1864.2 P.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, July 11, 1864. 8 A.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., July 12, 1864. 11.30
TELEGRAM AND LETTER TO HORACE GREELEY. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, July
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, JULY 15, 1864.
SAFE CONDUCT FOR CLEMENT C. CLAY AND OTHERS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. [WASHINGTON] July 17. 1864. 11.25 A.M.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. HUNTER WASHINGTON JULY 17, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
ANNOUNCEMENT CONCERNING TERMS OF PEACE.
PROCLAMATION CALLING FOR FIVE HUNDRED THOUSAND VOLUNTEERS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL D. HUNTER. (Cipher.)
TO GOVERNOR CURTIN, ENCLOSING A LETTER TO WILLIAM O. SNIDER.
FROM JOHN HAY TO J. C. WELLING.
TO COLONEL, FIRST N. Y. VETERAN CAVALRY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL HALLECK.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. WASHINGTON, July 27, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U, S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN.
ENDORSEMENT OF APPLICATION FOR EMPLOYMENT, AUGUST 15, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING COMMERCIAL REGULATIONS, AUGUST 18, 1864.
INDORSEMENT CONCERNING AN EXCHANGE OF PRISONERS, AUGUST 18, 1864.
ADDRESS TO THE 164TH OHIO REGIMENT,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BUTLER. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., August
ADDRESS TO THE 166TH OHIO REGIMENT,
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR JOHNSON. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, August 26,
TELEGRAM TO B. H. BREWSTER. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., August
ORDERS OF GRATITUDE AND REJOICING.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, September 3, 1864.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, September 3, 1864.
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE OF COLORED PEOPLE FROM BALTIMORE
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR PICKERING.
ORDER OF THANKS TO HUNDRED-DAY TROOPS FROM OHIO.
TELEGRAM TO JAMES G. BLAINE. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., September
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN. WASHINGTON, D. C., September 17,1864.
INDORSEMENT CONCERNING AN EXCHANGE OF PRISONERS, SEPTEMBER 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL P. SHERIDAN. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, September
ORDER CONCERNING THE PURCHASE OF PRODUCTS IN INSURRECTIONARY STATES.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. T. SHERMAN. WASHINGTON, D. C., September 27, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D.C., September 29,1864.
ORDER RETURNING THANKS TO THE VOLUNTEERS FOR ONE HUNDRED DAYS
INDORSEMENT ON A MEMORANDUM BY GENERAL McDOWELL, OCTOBER 7, 1864
TELEGRAM TO ROBERT T. LINCOLN, Cambridge, Mass.:
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 12, 1864.
PROCLAMATION OF THANKSGIVING, OCTOBER 20, 1864.
TELEGRAM To J. G. NICOLAY. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 21, 1864. 9.45 P.M.
TO WILLIAM B. CAMPBELL AND OTHERS.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. H. THOMAS. WASHINGTON, D. C., October 23, 1864 5
TELEGRAM TO T. T. DAVIS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D.C., October 31,
PROCLAMATION ADMITTING NEVADA INTO THE UNION
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL BURBRIDGE.
TELEGRAM TO NAVAL OFFICER AT MOBILE BAY.
TELEGRAM TO SAILORS' FAIR, BOSTON, MASSACHUSETTS.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD. WASHINGTON, November 8, 1864.
RESPONSE TO A SERENADE, NOVEMBER 9, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO H. W. HOFFMAN. WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C. November 10,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL S. O. BURBRIDGE. WASHINGTON, D.C., November 10, 1864.
WASHINGTON, D.C., November 10, 1864. GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE, Frankfort, Ky.:
REPLY TO MARYLAND UNION COMMITTEE, NOVEMBER 17, 1864.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING BLOCKADE, NOVEMBER 19, 1864
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE. WASHINGTON, D. C. NOVEMBER 22, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO GOVERNOR CURTIN, WASHINGTON, D.C., NOVEMBER 25, 1864
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON D.C., NOV.
ORDER CONCERNING THE STEAMER "FUNAYMA SOLACE."
RESPONSE TO A SERENADE, DECEMBER 6, 1864.
ORDER APPOINTING COMMISSIONERS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G, H. THOMAS. WASHINGTON, D.C., December 16, 1864.
ORIGIN OF THE "GREENBACK" CURRENCY
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT CHATTANOOGA. EXECUTIVE MANSION,
CALL FOR 300,000 VOLUNTEERS, DECEMBER 19, 1864.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT LEXINGTON.
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT NASHVILLE.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
MESSAGE TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES.
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING COMMERCE, JANUARY 10, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. F. BUTLER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL B. F. BUTLER.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. M. DODGE. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January
FIRST OVERTURES FOR SURRENDER FROM DAVIS
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. M. DODGE.
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE, JANUARY 24, 1865.
EARLY CONSULTATIONS WITH REBELS
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY OF WAR TO GENERAL ORD.
INDORSEMENT ON A LETTER FROM J. M. ASHLEY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
INSTRUCTIONS TO SECRETARY SEWARD.
CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT FOR THE ABOLISHING OF SLAVERY
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, February 1, 1865
TELEGRAM TO MAJOR ECKERT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 1, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865.
ORDER TO MAKE CORRECTIONS IN THE DRAFT.
TELEGRAM TO LIEUTENANT-COLONEL GLENN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, February
CHRONOLOGIC REVIEW OF PEACE PROPOSALS
Afterwards Mr. Blair dictated for and authorized me to make an entry on
Afterwards the Secretary of War placed in my hands the following telegram,
MESSAGE TO THE SENATE. WASHINGTON, February 10, 1865
TO THE COMMANDING OFFICERS IN WEST TENNESSEE
PROCLAMATION CONVENING THE SENATE IN EXTRA SESSION,
TELEGRAM TO OFFICER IN COMMAND AT HARPER'S FERRY.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, February 25, 1865
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., February 27, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., March 2, 1865.
TELEGRAM FROM SECRETARY STANTON TO GENERAL GRANT.
SECOND INAUGURAL ADDRESS, MARCH 4, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL JOHN POPE.
TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. WASHINGTON, D. C., March 8, 1865.
PROCLAMATION OFFERING PARDON TO DESERTERS,
TELEGRAM TO COLONEL ROUGH AND OTHERS.
ADDRESS TO AN INDIANA REGIMENT,
PROCLAMATION CONCERNING INDIANS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL W. S. HANCOCK.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U.S. GRANT. CITY POINT, April 1, 1865.
TELEGRAMS TO SECRETARY STANTON. CITY POINT, VIRGINIA, April 2, 1865. 8.30
TELEGRAM TO MRS. LINCOLN. CITY POINT, VA., April 1, 1865.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL U. S. GRANT.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL.
TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY STANTON.
NOTE ON A CARD TO SECRETARY STANTON.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. H. GORDON.
PROCLAMATION CLOSING CERTAIN PORTS, APRIL 11, 1865.
PROCLAMATION OPENING THE PORT OF KEY WEST,
PROCLAMATION CLAIMING EQUALITY OF RIGHTS WITH ALL MARITIME NATIONS,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL G. WEITZEL. WASHINGTON, D.C., April 12, 1865.
INTERVIEW WITH SCHUYLER COLFAX ON THE MORNING OF APRIL 14, 1865.
OPINION ON THE LOSS OF GENERAL R. H. MILROY'S DIVISION.
October 27, 1863.
In June last a division was substantially lost at or near Winchester, Va. At the time, it was under General Milroy as immediate commander in the field, General Schenck as department commander at Baltimore, and General Halleck as general-in-chief at Washington.
General Milroy, as immediate commander, was put in arrest, and subsequently a court of inquiry examined chiefly with reference to disobedience of orders, and reported the evidence.
The foregoing is a synoptical statement of the evidence, together with the judge-advocate-general's conclusions. The disaster, when it came, was a surprise to all. It was very well known to Generals Shenck and Milroy for some time before, that General Halleck thought the division was in great danger of a surprise at Winchester; that it was of no service commensurate with the risk it incurred, and that it ought to be withdrawn; but, although he more than once advised its withdrawal, he never positively ordered it. General Schenck, on the contrary, believed the service of the force at Winchester was worth the hazard, and so did not positively order its withdrawal until it was so late that the enemy cut the wire and prevented the order reaching General Milroy.
General Milroy seems to have concurred with General Schenck in the opinion that the force should be kept at Winchester at least until the approach of danger, but he disobeyed no order upon the subject.
Some question can be made whether some of General Halleck's dispatches to General Schenk should not have been construed to be orders to withdraw the force, and obeyed accordingly; but no such question can be made against General Milroy. In fact, the last order he received was to be prepared to withdraw, but not to actually withdraw until further order, which further order never reached him.
Serious blame is not necessarily due to any serious disaster, and I cannot say that in this case any of the officers are deserving of serious blame. No court-martial is deemed necessary or proper in the case.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, October 28, 1863.
GENERAL JOHN M. SCHOFIELD:
There have recently reached the War Department, and thence been laid before me, from Missouri, three communications, all similar in import and identical in object. One of them, addressed to nobody, and without place or date, but having the signature of (apparently) the writer, is a letter of eight closely written foolscap pages. The other two are written by a different person, at St. Joseph, Mo., and of the dates, respectively, October 12 and 13, 1863, and each inclosing a large number of affidavits. The general statements of the whole are that the Federal and State authorities are arming the disloyal and disarming the loyal, and that the latter will all be killed or driven out of the State unless there shall be a change. In particular, no loyal man who has been disarmed is named, but the affidavits show by name forty-two persons as disloyal who have been armed. They are as follows: [The names are omitted.]
A majority of these are shown to have been in the rebel service. I believe it could be shown that the government here has deliberately armed more than ten times as many captured at Gettysburg, to say nothing of similar operations in East Tennessee. These papers contain altogether thirty—one manuscript pages, and one newspaper in extenso, and yet I do not find it anywhere charged in them that any loyal man has been harmed by reason of being disarmed, or that any disloyal one has harmed anybody by reason of being armed by the Federal or State Government. Of course, I have not had time to carefully examine all; but I have had most of them examined and briefed by others, and the result is as stated. The remarkable fact that the actual evil is yet only anticipated—inferred—induces me to suppose I understand the case; but I do not state my impression, because I might be mistaken, and because your duty and mine is plain in any event. The locality of nearly all this seems to be St. Joseph and Buchanan County. I wish you to give special attention to this region, particularly on election day. Prevent violence from whatever quarter, and see that the soldiers themselves do no wrong.
Yours truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., October 28, 1863.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn.: If not too inconvenient, please come at once and have a personal conversation with me.
AN ACT TO REGULATE THE DUTIES OF THE CLERK OF THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES IN PREPARING FOR THE ORGANIZATION OF THE HOUSE.
Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled, that, before the first meeting of the next Congress, and of every subsequent Congress, the clerk of the next preceding House of Representatives shall make a roll of the Representatives elect, and place thereon the names of all persons, and of such persons only, whose credentials show that they were regularly elected in accordance with the laws of their States respectively, or the laws of the United States.
Approved March 3, 1863.
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 29, 1863.
HON. JAMES W. GRIMES.
MY DEAR SIR:—The above act of Congress was passed, as I suppose, for the purpose of shutting out improper applicants for seats in the House of Representatives; and I fear there is some danger that it will be used to shut out proper ones. Iowa, having an entire Union delegation, will be one of the States the attempt will be made, if upon any. The Governor doubtless has made out the certificates, and they are already in the hands of the members. I suggest that they come on with them; but that, for greater caution, you, and perhaps Mr. Harlan with you, consult with the Governor, and have an additional set made out according to the form on the other half of this sheet; and still another set, if you can, by studying the law, think of a form that in your judgment, promises additional security, and quietly bring the whole on with you, to be used in case of necessity. Let what you do be kept still.
Yours truly,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., October 30, 1863.
HON. F. F. LOWE, San Francisco, Cal.:
Below is an act of Congress, passed last session, intended to exclude applicants not entitled to seats, but which, there is reason to fear, will be used to exclude some who are entitled. Please get with the Governor and one or two other discreet friends, study the act carefully, and make certificates in two or three forms, according to your best judgement, and have them sent to me, so as to multiply the chances of the delegation getting their seats. Let it be done without publicity. Below is a form which may answer for one. If you could procure the same to be done for the Oregon member it might be well.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
Much obliged for the information about deserters contained in your dispatch of yesterday, while I have to beg your pardon for troubling you in regard to some of them, when, as it appears by yours, I had the means of answering my own questions.
The Provost-Marshal-General has issued no proclamation at all. He has in no form announced anything recently in regard to troops in New York, except in his letter to Governor Seymour of October 21, which has been published in the newspapers of that State. It has not been announced or decided in any form by the Provost-Marshal-General, or any one else in authority of the Government, that every citizen who has paid his three hundred dollars commutation is liable to be immediately drafted again, or that towns that have just raised the money to pay their quotas will have again to be subject to similar taxation or suffer the operations of the new conscription, nor it is probable that the like of them ever will be announced or decided.
HON. W. H. SEWARD, Auburn, N.Y.:
No important news. Details of Hooker's night fight do great credit to his command, and particularly to the Eleventh Corps and Geary's part of the Twelfth. No discredit on any.
WASHINGTON, November 2, 1863.
HON. MONTGOMERY BLAIR.
MY DEAR SIR:—Some days ago I understood you to say that your brother, General Frank Blair, desires to be guided by my wishes as to whether he will occupy his seat in Congress or remain in the field. My wish, then, is compounded of what I believe will be best for the country; and it is that he will come here, put his military commission in my hands, take his seat, go into caucus with our friends, abide the nominations, help elect the nominees, and thus aid to organize a House of Representatives which will really support the Government in the war. If the result shall be the election of himself as Speaker, let him serve in that position. If not, let him retake his commission and return to the army for the benefit of the country.
This will heal a dangerous schism for him. It will relieve him from a dangerous position or a misunderstanding, as I think he is in danger of being permanently separated from those with whom only he can ever have a real sympathy—the sincere opponents of slavery.
It will be a mistake if he shall allow the provocations offered him by insincere time-servers to drive him from the house of his own building. He is young yet. He has abundant talents—quite enough to occupy all his time without devoting any to temper.
He is rising in military skill and usefulness. His recent appointment to the command of a corps, by one so competent to judge as General Sherman, proves this. In that line he can serve both the country and himself more profitably than he could as a member of Congress upon the floor.
The foregoing is what I would say if Frank Blair was my brother instead of yours.
Yours truly,
His EXCELLENCY A. W. BRADFORD, Governor of Maryland.
SIR:—Yours of the 31st ult. was received yesterday about noon, and since then I have been giving most earnest attention to the subject-matter of it. At my call General Schenck has attended, and he assures me it is almost certain that violence will be used at some of the voting places on election day unless prevented by his provost-guards. He says that at some of those places Union voters will not attend at all, or run a ticket, unless they have some assurance of protection. This makes the Missouri case, of my action in regard to which you express your approval.
The remaining point of your letter is a protest against any person offering to vote being put to any test not found in the laws of Maryland. This brings us to a difference between Missouri and Maryland. With the same reason in both States, Missouri has, by law, provided a test for the voter with reference to the present rebellion, while Maryland has not. For example, General Trimble, captured fighting us at Gettysburg, is, without recanting his treason, a legal voter by the laws of Maryland. Even General Schenck's order admits him to vote, if he recants upon oath. I think that is cheap enough. My order in Missouri, which you approve, and General Scherick's order here, reach precisely the same end. Bach assures the right of voting to all loyal men, and whether a man is loyal, each allows that man to fix by his own oath. Your suggestion that nearly all the candidates are loyal, I do not think quite meets the case. In this struggle for the nation's life, I cannot so confidently rely on those whose elections may have depended upon disloyal votes. Such men, when elected, may prove true; but such votes are given them in the expectation that they will prove false.
Nor do I think that to keep the peace at the polls, and to prevent the persistently disloyal from voting, constitutes just cause of offense to Maryland. I think she has her own example for it. If I mistake not, it is precisely what General Dix did when your Excellency was elected Governor.
I revoke the first of the three propositions in General Schenek's General Order No. 53; not that it is wrong in principle, but because the military, being of necessity exclusive judges as to who shall be arrested, the provision is too liable to abuse. For the revoked part I substitute the following:
That, all provost-marshals and other military officers do prevent all disturbance and violence at or about the polls, whether offered by such persons as above described, or by any other person or persons whomsoever.
The other two propositions of the order I allow to stand. General Schenek is fully determined, and has my strict orders besides, that all loyal men may vote, and vote for whom they please.
Your obedient servant,
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 2, 1863.
JAMES H. HACKETT.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of October 22d is received, as also was, in due course, that of October 3d. I look forward with pleasure to the fulfillment of the promise made in the former to visit Washington the following winter and to "call."
Give yourself no uneasiness on the subject mentioned in that of the 22d. My note to you I certainly did not expect to see in print, yet I have not been much shocked by the newspaper comments upon it.
Those comments constitute a fair specimen of what has occurred to me through life. I have endured a great deal of ridicule, without much malice; and have received a great deal of kindness not quite free from ridicule. I am used to it.
HON. W. H. SEWARD, Auburn, N. Y.:
Nothing new. Dispatches up to 12 last night from Chattanooga show all quiet and doing well. How is your son?
Samuel Wellers, private in Company B, Forty-ninth Pennsylvania Volunteers, writes that he is to be shot for desertion on the 6th instant. His own story is rather a bad one, and yet he tells it so frankly, that I am somewhat interested in him. Has he been a good soldier except the desertion? About how old is he?
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
Please suspend the execution of Samuel Wellers, Forty-ninth Pennsylvania Volunteers, until further orders.
9, 1863.4 P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Knoxville, Tenn.:
Have seen dispatch from General Grant about your loss at Rogersville. Per contra, about the same time, Averell and Duffle got considerable advantage of the enemy at and about Lewisburg, Virginia: and on Saturday, the seventh, Meade drove the enemy from Rappahannock Station and Kelly's Ford, capturing eight battle-flags, four guns, and over 1800 prisoners, with very little loss to himself. Let me hear from you.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE:
I have seen your dispatches about operations on the Rappahannock on Saturday, and I wish to say, "Well done!" Do the 1500 prisoners reported by General Sedgwick include the 400 taken by General French, or do the Whole amount to 1900?
WASHINGTON, November 10, 1863.
In consideration of the peculiar circumstances and pursuant to the comity deemed to be due to friendly powers, any tobacco in the United States belonging to the government either of France, Austria, or any other state with which this country is at peace, and which tobacco was purchased and paid for by such government prior to the 4th day of March, 1861, may be exported from any port of the United States under the supervision and upon the responsibility of naval officers of such governments and in conformity to such regulations as may be presented by the Secretary of State of the United States, and not otherwise.
GENERAL SCHOFIELD, Saint Louis, Mo.:
I see a dispatch here from Saint Louis, which is a little difficult for me to understand. It says "General Schofield has refused leave of absence to members in military service to attend the legislature. All such are radical and administration men. The election of two Senators from this place on Thursday will probably turn upon this thing." what does this mean? Of course members of the legislation must be allowed to attend its sessions. But how is there a session before the recent election returns are in? And how is it to be at "this place"—and that is Saint Louis? Please inform me.
GENERAL SCHOFIELD, Saint Louis, Mo.:
I believe the Secretary of War has telegraphed you about members of the legislation. At all events, allow those in the service to attend the session, and we can afterward decide whether they can stay through the entire session.
[Cipher.]
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., November 11, 1863.
HON. HIRAM BARNEY, New York; I would like an interview with you. Can you not come?
WASHINGTON, D. C., November 11, 1863.
JOHN MILDERBORGER, Peru, Ind.:
I cannot comprehend the object of your dispatch. I do not often decline seeing people who call upon me, and probably will see you if you call.
WASHINGTON, D. C., November 13, 1863.
E. H. and E. JAMESON, Jefferson City, Mo.:
Yours saying Brown and Henderson are elected Senators is received. I understand this is one and one. If so it is knocking heads together to some.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Cincinnati, Ohio:
I have received and considered your dispatch of yesterday. Of the reports you mention, I have not the means of seeing any except your own. Besides this, the publication might be improper in view of the court of inquiry which has been ordered. With every disposition, not merely to do justice, but to oblige you, I feel constrained to say I think the publications better not be made now.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURNSIDE, Knoxville, Tenn.:
What is the news?
HON. SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
MY DEAR SIR:—I expected to see you here at Cabinet meeting, and to say something about going to Gettysburg. There will be a train to take and return us. The time for starting is not yet fixed, but when it shall be I will notify you.
Yours truly,
Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battle-field of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this.
But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate—we can not consecrate—we can not hallow—this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
If there is a man by the name of King under sentence to be shot, please suspend execution till further order, and send record.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
An intelligent woman in deep distress, called this morning, saying her husband, a lieutenant in the Army of Potomac, was to be shot next Monday for desertion, and putting a letter in my hand, upon which I relied for particulars, she left without mentioning a name or other particular by which to identify the case. On opening the letter I found it equally vague, having nothing to identify by, except her own signature, which seems to be "Mrs. Anna S. King." I could not again find her. If you have a case which you shall think is probably the one intended, please apply my dispatch of this morning to it.
E. P. EVANS, West Union, Adams County, Ohio:
Yours to Governor Chase in behalf of John A Welch is before me. Can there be a worse case than to desert and with letters persuading others to desert? I cannot interpose without a better showing than you make. When did he desert? when did he write the letters?
MY DEAR SIR:—Two despatches since I saw you; one not quite so late on firing as we had before, but giving the points that Burnside thinks he can hold the place, that he is not closely invested, and that he forages across the river. The other brings the firing up to 11 A.M. yesterday, being twenty-three hours later than we had before.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL U.S. GRANT:
Your despatches as to fighting on Monday and Tuesday are here. Well done! Many thanks to all. Remember Burnside.
CHARLES P. KIRKLAND, ESQ., New York:
I have just received and have read your published letter to the HON. Benjamin R. Curtis. Under the circumstances I may not be the most competent judge, but it appears to me to be a paper of great ability, and for the country's sake more than for my own I thank you for it.
Yours very truly,
Reliable information being received that the insurgent force is retreating from East Tennessee, under circumstances rendering it probable that the Union forces cannot hereafter be dislodged from that important position; and esteeming this to be of high national consequence, I recommend that all loyal people do, on receipt of this information, assemble at their places of worship, and render special homage and gratitude to Almighty God for this great advancement of the national cause.
A Proclamation.
Whereas in and by the Constitution of the United States it is provided that the President "shall have power to grant reprieves and pardons for offenses against the United States, except in cases of impeachment;" and,
Whereas a rebellion now exists whereby the loyal State governments of several States have for a long time been subverted, and many persons have committed and are now guilty of treason against the United States; and
Whereas, with reference to said rebellion and treason, laws have been enacted by Congress declaring forfeitures and confiscation of property and liberation of slaves, all upon terms and conditions therein stated, and also declaring that the President was thereby authorized at any time thereafter, by proclamation, to extend to persons who may have participated in the existing rebellion in any State or part thereof pardon and amnesty, with such exceptions and at such times and on such conditions as he may deem expedient for the public welfare; and
Whereas the Congressional declaration for limited and conditional pardon accords with well-established judicial exposition of the pardoning power; and
Whereas, with reference to said rebellion, the President of the United States has issued several proclamations with provisions in regard to the liberation of slaves; and
Whereas it is now desired by some persons heretofore engaged in said rebellion to resume their allegiance to the United States and to reinaugurate loyal State governments within and for their respective States:
Therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do proclaim, declare, and make known to all persons who have, directly or by implication, participated in the existing rebellion, except as hereinafter excepted, that a full pardon is hereby granted to them and each of them, with restoration of all rights of property, except as to slaves and in property cases where rights of third parties shall have intervened, and upon the condition that every such person shall take and subscribe an oath and thenceforward keep and maintain said oath inviolate, and which oath shall be registered for permanent preservation and shall be of the tenor and effect following, to wit:
"I, ———, do solemnly swear, in presence of Almighty God, that I will henceforth faithfully support, protect, and defend the Constitution of the United States and the Union of the States thereunder; and that I will in like manner abide by and faithfully support all acts of Congress passed during the existing rebellion with reference to slaves, so long and so far as not repealed, modified, or held void by Congress or by decision of the Supreme Court; and that I will in like manner abide by and faithfully support all proclamations of the President made during the existing rebellion having reference to slaves, so long and so far as not modified or declared void by decision of the Supreme Court. So help me God."
The persons excepted from the benefits of the foregoing provisions are all who are or shall have been civil or diplomatic officers or agents of the so-called Confederate Government; all who have left judicial stations under the United States to aid the rebellion; all who are or shall have been military or naval officers of said so-called Confederate Government above the rank of colonel in the army or of lieutenant in the navy; all who left seats in the United States Congress to aid the rebellion; all who resigned commissions in the Army or Navy of the United States and afterwards aided the rebellion; and all who have engaged in any way in treating colored persons, or white persons in charge of such, otherwise than lawfully as prisoners of war, and which persons may have been found in the United States service as soldiers, seamen, or in any other capacity.
And I do further proclaim, declare, and make known that whenever, in any of the States of Arkansas, Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Tennessee, Alabama, Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, a number of persons, not less than one-tenth in number of the votes cast in such State at the Presidential election of the year A.D. 1860, each having taken oath aforesaid, and not having since violated it, and being a qualified voter by the election law of the State existing immediately before the so-called act of secession, and excluding all others, shall reestablish a State government which shall be republican and in nowise contravening said oath, such shall be recognized as the true government of the State, and the State shall receive thereunder the benefits of the constitutional provision which declares that "the United States shall guarantee to every State in this Union a republican form of government and shall protect each of them against invasion, and, on application of the legislature, or the EXECUTIVE (when the legislature can not be convened), against domestic violence."
And I do further proclaim, declare, and make known that any provision which may be adopted by such State government in relation to the freed people of such State which shall recognize and declare their permanent freedom, provide for their education, and which may yet be consistent as a temporary arrangement with their present condition as a laboring, landless, and homeless class, will not be objected to by the National EXECUTIVE.
And it is suggested as not improper that in constructing a loyal State government in any State the name of the State, the boundary, the subdivisions, the constitution, and the general code of laws as before the rebellion be maintained, subject only to the modifications made necessary by the conditions hereinbefore stated, and such others, if any, not contravening said co and which may be deemed expedient by those framing the new State government.
To avoid misunderstanding, it may be proper to say that this proclamation, so far as it relates to State governments, has no reference to States wherein loyal State governments have all the while been maintained. And for the same reason it may be proper to further say that whether members sent to Congress from any State shall be admitted to seats constitutionally rests exclusively with the respective Houses, and not to any extent with the EXECUTIVE. And, still further, that this proclamation is intended to present the people of the States wherein the national authority has been suspended and loyal State governments have been subverted a mode in and by which the national authority and loyal State governments may be re-established within said States or in any of them; and while the mode presented is the best the EXECUTIVE can suggest, with his present impressions, it must not be understood that no other possible mode would be acceptable.
Given under my hand at the city of WASHINGTON, the 8th day of December, A. D. 1863, and of the Independence of the United States of America the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:—
Another year of health, and of sufficiently abundant harvests, has passed. For these, and especially for the improved condition cf our national affairs, our renewed and profoundest gratitude to God is due.
We remain in peace and friendship with foreign powers.
The efforts of disloyal citizens of the United States to involve us in foreign wars, to aid an inexcusable insurrection, have been unavailing. Her Britannic Majesty's government, as was justly expected, have exercised their authority to prevent the departure of new hostile expeditions from British ports. The Emperor of France has, by a like proceeding, promptly vindicated the neutrality which he proclaimed at the beginning of the contest. Questions of great intricacy and importance have arisen out of the blockade, and other belligerent operations, between the Government and several of the maritime powers, but they have been discussed, and, as far as was possible, accommodated, in a spirit of frankness, justice, and mutual good-will. It is especially gratifying that our prize courts, by the impartiality of their adjudications, have commanded the respect and confidence of maritime powers.
The supplemental treaty between the United States and Great Britain for the suppression of the African slave-trade, made on the 17th day of February last, has been duly ratified and carried into execution. It is believed that, so far as American ports and American citizens are concerned, that inhuman and odious traffic has been brought to an end.
I shall submit, for the consideration of the Senate, a convention for the adjustment of possessory claims in Washington Territory, arising out of the treaty of the 15th of June, 1846, between the United States and Great Britain, and which have been the source of some disquiet among the citizens of that now rapidly improving part of the country.
A novel and important question, involving the extent of the maritime jurisdiction of Spain in the waters which surround the island of Cuba, has been debated without reaching an agreement, and it is proposed, in an amicable spirit, to refer it to the arbitrament of a friendly power. A convention for that purpose will be submitted to the Senate.
I have thought it proper, subject to the approval of the Senate, to concur with the interested commercial powers in an arrangement for the liquidation of the Scheldt dues upon the principles which have been heretofore adopted in regard to the imposts upon navigation in the waters of Denmark.
The long-pending controversy between this government and that of Chile touching the seizure at Sitana, in Peru, by Chilean officers, of a large amount in treasure belonging to citizens of the United States has been brought to a close by the award of His Majesty the King of the Belgians, to whose arbitration the question was referred by the parties. The subject was thoroughly and patiently examined by that justly respected magistrate, and although the sum awarded to the claimants may not have been as large as they expected there is no reason to distrust the wisdom of His Majesty's decision. That decision was promptly complied with by Chile when intelligence in regard to it reached that country.
The joint commission under the act of the last session of carrying into effect the convention with Peru on the subject of claims has been organized at Lima, and is engaged in the business intrusted to it.
Difficulties concerning interoceanic transit through Nicaragua are in course of amicable adjustment.
In conformity with principles set forth in my last annual message, I have received a representative from the United States of Colombia, and have accredited a minister to that Republic.
Incidents occurring in the progress of our civil war have forced upon my attention the uncertain state of international questions touching the rights of foreigners in this country and of United States citizens abroad. In regard to some governments these rights are at least partially defined by treaties. In no instance, however, is it expressly stipulated that in the event of civil war a foreigner residing in this country within the lines of the insurgents is to be exempted from the rule which classes him as a belligerent, in whose behalf the government of his country can not expect any privileges or immunities distinct from that character. I regret to say, however, that such claims have been put forward, and in some instances in behalf of foreigners who have lived in the United States the greater part of their lives.
There is reason to believe that many persons born in foreign countries who have declared their intention to become citizens, or who have been fully naturalized have evaded the military duty required of them by denying the fact and thereby throwing upon the Government the burden of proof. It has been found difficult or impracticable to obtain this proof from the want of guides to the proper sources of information. These might be supplied by requiring clerks of courts where declarations of intention may be made or naturalizations effected to send periodically lists of the names of the persons naturalized or declaring their intention to become citizens to the Secretary of the Interior, in whose Department those names might be arranged and printed for general information.
There is also reason to believe that foreigners frequently become citizens of the United States for the sole purpose of evading duties imposed by the laws of their native countries, to which on becoming naturalized here they at once repair, and though never returning to the United States they still claim the interposition of this government as citizens. Many altercations and great prejudices have heretofore arisen out of this abuse. It is therefore submitted to your serious consideration. It might be advisable to fix a limit beyond which no citizen of the United States residing abroad may claim the interposition of his government.
The right of suffrage has often been assumed and exercised by aliens under pretenses of naturalization, which they have disavowed when drafted into the military service. I submit the expediency of such an amendment of the law as will make the fact of voting an estoppe against any plea of exemption from military service or other civil obligation on the ground of alienage.
In common with other Western powers, our relations with Japan have been brought into serious jeopardy through the perverse opposition of the hereditary aristocracy of the Empire to the enlightened and liberal policy of the Tycoon, designed to bring the country into the society of nations. It is hoped, although not with entire confidence, that these difficulties may be peacefully overcome. I ask your attention to the claim of the minister residing there for the damages he sustained in the destruction by fire of the residence of the legation at Yedo.
Satisfactory arrangements have been made with the Emperor of Russia, which, it is believed, will result in effecting a continuous line of telegraph through that Empire from our Pacific coast.
I recommend to your favorable consideration the subject of an international telegraph across the Atlantic Ocean, and also of a telegraph between this capital and the national forts along the Atlantic seaboard and the Gulf of Mexico. Such communications, established with any reasonable outlay, would be economical as well as effective aids to the diplomatic, military, and naval service.
The consular system of the United States, under the enactments of the last Congress, begins to be self-sustaining, and there is reason to hope that it may become entirely so with the increase of trade which will ensue whenever peace is restored. Our ministers abroad have been faithful in defending American rights. In protecting commercial interests our consuls have necessarily had to encounter increased labors and responsibilities growing out of the war. These they have for the most part met and discharged with zeal and efficiency. This acknowledgment justly includes those consuls who, residing in Morocco, Egypt, Turkey, Japan, China, and other Oriental countries, are charged with complex functions and extraordinary powers.
The condition of the several organized Territories is generally satisfactory, although Indian disturbances in New Mexico have not been entirely suppressed. The mineral resources of Colorado, Nevada, Idaho, New Mexico, and Arizona are proving far richer than has been heretofore understood. I lay before you a communication on this subject from the Governor of New Mexico. I again submit to your consideration the expediency of establishing a system for the encouragement of immigration. Although this source of national wealth and strength is again flowing with greater freedom than for several years before the insurrection occurred, there is still a great deficiency of laborers in every field of industry, especially in agriculture and in our mines, as well of iron and coal as of the precious metals. While the demand for labor is much increased here, tens of thousands of persons, destitute of remunerative occupation, are thronging our foreign consulates and offering to emigrate to the United States if essential, but very cheap, assistance can be afforded them. It is easy to see that under the sharp discipline of civil war the nation is beginning a new life. This noble effort demands the aid and ought to receive the attention and support of the Government.
Injuries unforeseen by the Government and unintended may in some cases have been inflicted on the subjects or citizens of foreign countries, both at sea and on land, by persons in the service of the United States. As this government expects redress from other powers when similar injuries are inflicted by persons in their service upon citizens of the United States, we must be prepared to do justice to foreigners. If the existing judicial tribunals are inadequate to this purpose, a special court may be authorized, with power to hear and decide such claims of the character referred to as may have arisen under treaties and the public law. Conventions for adjusting the claims by joint commission have been proposed to some governments, but no definitive answer to the proposition has yet been received from any.
In the course of the session I shall probably have occasion to request you to provide indemnification to claimants where decrees of restitution have been rendered and damages awarded by admiralty courts, and in other cases where this government may be acknowledged to be liable in principle and where the amount of that liability has been ascertained by an informal arbitration.
The proper officers of the Treasury have deemed themselves required by the law of the United States upon the subject to demand a tax upon the incomes of foreign consuls in this country. While such a demand may not in strictness be in derogation of public law, or perhaps of any existing treaty between the United States and a foreign country, the expediency of so far modifying the act as to exempt from tax the income of such consuls as are not citizens of the United States, derived from the emoluments of their office or from property not situated in the United States, is submitted to your serious consideration. I make this suggestion upon the ground that a comity which ought to be reciprocated exempts our consuls in all other countries from taxation to the extent thus indicated. The United States, I think, ought not to be exceptionally illiberal to international trade and commerce.
The operations of the Treasury during the last year have been successfully conducted. The enactment by Congress of a national banking law has proved a valuable support of the public credit, and the general legislation in relation to loans has fully answered the expectations of its favorers. Some amendments may be required to perfect existing laws, but no change in their principles or general scope is believed to be needed.
Since these measures have been in operation all demands on the Treasury, including the pay of the Army and Navy, have been promptly met and fully satisfied. No considerable body of troops, it is believed, were ever more amply provided and more liberally and punctually paid, and it may be added that by no people were the burdens incident to a great war ever more cheerfully borne.
The receipts during the year from all sources, including loans and balance in the Treasury at its commencement, were $901,125,674.86, and the aggregate disbursements $895,796,630.65, leaving a balance on the 1st of July, 1863, of $5,329,044.21. Of the receipts there were derived from customs $69,059,642.40, from internal revenue $37,640,787.95, from direct tax $1,485,103.61, from lands $167,617.17, from miscellaneous sources $3,046,615.35, and from loans $776,682,361.57, making the aggregate $901,125,674.86. Of the disbursements there were for the civil service $23,253,922.08, for pensions and Indians $4,216,520.79, for interest on public debt $24,729,846.51, for the War Department $599,298,600.83, for the Navy Department $63,211,105.27, for payment of funded and temporary debt $181,086,635.07, making the aggregate $895,796,630.65 and leaving the balance of $5,329,044.21. But the payment of funded and temporary debt, having been made from moneys borrowed during the year, must be regarded as merely nominal payments and the moneys borrowed to make them as merely nominal receipts, and their amount, $181,086,635.07, should therefore be deducted both from receipts and disbursements. This being done there remains as actual receipts $720,039,039.79 and the actual disbursements $714,709,995.58, leaving the balance as already stated.
The actual receipts and disbursements for the first quarter and the estimated receipts and disbursements for the remaining three-quarters of the current fiscal year (1864) will be shown in detail by the report of the Secretary of the Treasury, to which I invite your attention. It is sufficient to say here that it is not believed that actual results will exhibit a state of the finances less favorable to the country than the estimates of that officer heretofore submitted while it is confidently expected that at the close of the year both disbursements and debt will be found very considerably less than has been anticipated.
The report of the Secretary of War is a document of great interest. It consists of:
1. The military operations of the year, detailed in the report of the General in Chief.
2. The organization of colored persons into the war service.
3. The exchange of prisoners, fully set forth in the letter of General Hitchcock.
4. The operations under the act for enrolling and calling out the national forces, detailed in the report of the Provost Marshal General.
5. The organization of the invalid corps, and
6. The operation of the several departments of the Quartermaster-General, Commissary-General, Paymaster-General, Chief of Engineers, Chief of Ordnance, and Surgeon-General.
It has appeared impossible to make a valuable summary of this report, except such as would be too extended for this place, and hence I content myself by asking your careful attention to the report itself.
The duties devolving on the naval branch of the service during the year and throughout the whole of this unhappy contest have been discharged with fidelity and eminent success. The extensive blockade has been constantly increasing in efficiency as the Navy has expanded, yet on so long a line it has so far been impossible to entirely suppress illicit trade. From returns received at the Navy Department it appears that more than 1,000 vessels have been captured since the blockade was instituted? and that the value of prizes already sent in for adjudication amounts to over $13,000,000.
The naval force of the United States consists at this time of five hundred and eighty-eight vessels completed and in the course of completion, and of these seventy-five are ironclad or armored steamers. The events of the war give an increased interest and importance to the Navy which will probably extend beyond the war itself.
The armored vessels in our Navy completed and in service, or which are under contract and approaching completion, are believed to exceed in number those of any other power; but while these may be relied upon for harbor defense and coast service, others of greater strength and capacity will be necessary for cruising purposes and to maintain our rightful position on the ocean.
The change that has taken place in naval vessels and naval warfare since the introduction of steam as a motive power for ships of war demands either a corresponding change in some of our existing navy yards or the establishment of new ones for the construction and necessary repair of modern naval vessels. No inconsiderable embarrassment, delay, and public injury have been experienced from the want of such governmental establishments. The necessity of such a navy-yard, so furnished, at some suitable place upon the Atlantic seaboard has on repeated occasions been brought to the attention of Congress by the Navy Department, and is again presented in the report of the Secretary which accompanies this communication. I think it my duty to invite your special attention to this subject, and also to that of establishing a yard and depot for naval purposes upon one of the Western rivers. A naval force has been created on those interior waters, and under many disadvantages, within little more than two years, exceeding in numbers the whole naval force of the country at the commencement of the present Administration. Satisfactory and important as have been the performances of the heroic men of the Navy at this interesting period, they are scarcely more wonderful than the success of our mechanics and artisans in the production of war vessels, which has created a new form of naval power.
Our country has advantages superior to any other nation in our resources of iron and timber, with inexhaustible quantities of fuel in the immediate vicinity of both, and all available and in close proximity to navigable waters. Without the advantage of public works, the resources of the nation have been developed and its power displayed in the construction of a Navy of such magnitude, which has at the very period of its creation rendered signal service to the Union.
The increase of the number of seamen in the public service from 7,500 men in the spring of 1861 to about 34,000 at the present time has been accomplished without special legislation or extraordinary bounties to promote that increase. It has been found, however, that the operation of the draft, with the high bounties paid for army recruits, is beginning to affect injuriously the naval service, and will, if not corrected, be likely to impair its efficiency by detaching seamen from their proper vocation and inducing them to enter the Army. I therefore respectfully suggest that Congress might aid both the army and naval services by a definite provision on this subject which would at the same time be equitable to the communities more especially interested.
I commend to your consideration the suggestions of the Secretary of the Navy in regard to the policy of fostering and training seamen and also the education of officers and engineers for the naval service. The Naval Academy is rendering signal service in preparing midshipmen for the highly responsible duties which in after life they will be required to perform. In order that the country should not be deprived of the proper quota of educated officers, for which legal provision has been made at the naval school, the vacancies caused by the neglect or omission to make nominations from the States in insurrection have been filled by the Secretary of the Navy. The school is now more full and complete than at any former period, and in every respect entitled to the favorable consideration of Congress.
During the past fiscal year the financial condition of the Post-Office Department has been one of increasing prosperity, and I am gratified in being able to state that the actual postal revenue has nearly equaled the entire expenditures, the latter amounting to $11,314,206.84 and the former to $11,163,789.59, leaving a deficiency of but $150,417.25. In 1860, the year immediately preceding the rebellion, the deficiency amounted to $5,656,705.49, the postal receipts of that year being $2,645,722.19 less that those of 1863. The decrease since 1860 in the annual amount of transportation has been only about twenty-five per cent, but the annual expenditure on account of the same has been reduced thirty-five per cent. It is manifest, therefore, that the Post-Office Department may become self-sustaining in a few years, even with the restoration of the whole service.
The international conference of postal delegates from the principal countries of Europe and America, which was called at the suggestion of the Postmaster-General, met at Paris on the 11th of May last and concluded its deliberations on the 8th of June. The principles established by the conference as best adapted to facilitate postal intercourse between nations and as the basis of future postal conventions inaugurate a general system of uniform international charges at reduced rates of postage, and can not fail to produce beneficial results.
I refer you to the report of the Secretary of the Interior, which is herewith laid before you, for useful and varied information in relation to the public lands, Indian affairs, patents, pensions, and other matters of public concern pertaining to his Department.
The quantity of land disposed of during the last and the first quarter of the present fiscal years was 3,841,549 acres, of which 161,911 acres were sold for cash, 1,456,514 acres were taken up under the homestead law, and the residue disposed of under laws granting lands for military bounties, for railroad and other purposes. It also appears that the sale of the public lands is largely on the increase.
It has long been a cherished opinion of some of our wisest statesmen that the people of the United States had a higher and more enduring interest in the early settlement and substantial cultivation of the public lands than in the amount of direct revenue to be derived from the sale of them. This opinion has had a controlling influence in shaping legislation upon the subject of our national domain. I may cite as evidence of this the liberal measures adopted in reference to actual settlers; the grant to the States of the overflowed lands within their limits, in order to their being reclaimed and rendered fit for cultivation; the grants to railway companies of alternate sections of land upon the contemplated lines of their roads, which when completed will so largely multiply the facilities for reaching our distant possessions. This policy has received its most signal and beneficent illustration in the recent enactment granting homesteads to actual settlers. Since the 1st day of January last the before-mentioned quantity of 1,456,514 acres of land have been taken up under its provisions. This fact and the amount of sales furnish gratifying evidence of increasing settlement upon the public lands, notwithstanding the great struggle in which the energies of the nation have been engaged, and which has required so large a withdrawal of our citizens from their accustomed pursuits. I cordially concur in the recommendation of the Secretary of the Interior suggesting a modification of the act in favor of those engaged in the military and naval service of the United States. I doubt not that Congress will cheerfully adopt such measures as will, without essentially changing the general features of the system, secure to the greatest practicable extent its benefits to those who have left their homes in the defense of the country in this arduous crisis.
I invite your attention to the views of the Secretary as to the propriety of raising by appropriate legislation a revenue from the mineral lands of the United States.
The measures provided at your last session for the removal of certain Indian tribes have been carried into effect. Sundry treaties have been negotiated, which will in due time be submitted for the constitutional action of the Senate. They contain stipulations for extinguishing the possessory rights of the Indians to large and valuable tracts of lands. It is hoped that the effect of these treaties will result in the establishment of permanent friendly relations with such of these tribes as have been brought into frequent and bloody collision with our outlying settlements and emigrants. Sound policy and our imperative duty to these wards of the Government demand our anxious and constant attention to their material well-being, to their progress in the arts of civilization, and, above all, to that moral training which under the blessing of Divine Providence will confer upon them the elevated and sanctifying influences, the hopes and consolations, of the Christian faith.
I suggested in my last annual message the propriety of remodeling our Indian system. Subsequent events have satisfied me of its necessity. The details set forth in the report of the Secretary evince the urgent need for immediate legislative action.
I commend the benevolent institutions established or patronized by the Government in this District to your generous and fostering care.
The attention of Congress during the last session was engaged to some extent with a proposition for enlarging the water communication between the Mississippi River and the northeastern seaboard, which proposition, however, failed for the time. Since then, upon a call of the greatest respectability, a convention has been held at Chicago upon the same subject, a summary of whose views is contained in a memorial addressed to the President and Congress, and which I now have the honor to lay before you. That this interest is one which ere long will force its own way I do not entertain a doubt, while it is submitted entirely to your wisdom as to what can be done now. Augmented interest is given to this subject by the actual commencement of work upon the Pacific Railroad, under auspices so favorable to rapid progress and completion. The enlarged navigation becomes a palpable need to the great road.
I transmit the second annual report of the Commissioner of the Department of Agriculture, asking your attention to the developments in that vital interest of the nation.
When Congress assembled a year ago, the war had already lasted nearly twenty months, and there had been many conflicts on both land and sea, with varying results; the rebellion had been pressed back into reduced limits; yet the tone of public feeling and opinion, at home and abroad, was not satisfactory. With other signs, the popular elections then just past indicated uneasiness among ourselves, while, amid much that was cold and menacing, the kindest words coming from Europe were uttered in accents of pity that we are too blind to surrender a hopeless cause. Our commerce was suffering greatly by a few armed vessels built upon and furnished from foreign shores, and we were threatened with such additions from the same quarter as would sweep our trade from the sea and raise our blockade. We had failed to elicit from European governments anything hopeful upon this subject. The preliminary emancipation proclamation, issued in September, was running its assigned period to the beginning of the new year. A month later the final proclamation came, including the announcement that colored men of suitable condition would be received into the war service. The policy of emancipation and of employing black soldiers gave to the future a new aspect, about which hope and fear and doubt contended in uncertain conflict. According to our political system, as a matter of civil administration, the General Government had no lawful power to effect emancipation in any State, and for a long time it had been hoped that the rebellion could be suppressed without resorting to it as a military measure. It was all the while deemed possible that the necessity for it might come, and that if it should the crisis of the contest would then be presented. It came, and, as was anticipated, it was followed by dark and doubtful days. Eleven months having now passed, we are permitted to take another review. The rebel borders are pressed still farther back, and by the complete opening of the Mississippi the country dominated by the rebellion is divided into distinct parts, with no practical communication between them. Tennessee and Arkansas have been substantially cleared of insurgent control, and influential citizens in each, owners of slaves and advocates of slavery at the beginning of the rebellion, now declare openly for emancipation in their respective States. Of those States not included in the emancipation proclamation, Maryland and Missouri, neither of which three years ago would tolerate any restraint upon the extension of slavery into new Territories, dispute now only as to the best mode of removing it within their own limits.
Of those who were slaves at the beginning of the rebellion full 100,000 are now in the United States military service, about one-half of which number actually bear arms in the ranks, thus giving the double advantage of taking so much labor from the insurgent cause and supplying the places which otherwise must be filled with so many white men. So far as tested, it is difficult to say they are not as good soldiers as any. No servile insurrection or tendency to violence or cruelty has marked the measures of emancipation and arming the blacks. These measures have been much discussed in foreign countries, and, contemporary with such discussion, the tone of public sentiment there is much improved. At home the same measures have been fully discussed, supported, criticized, and denounced, and the annual elections following are highly encouraging to those whose official duty it is to bear the country through this great trial. Thus we have the new reckoning. The crisis which threatened to divide the friends of the Union is past.
Looking now to the present and future, and with reference to a resumption of the national authority within the States wherein that authority has been suspended, I have thought fit to issue a proclamation, a copy of which is herewith transmitted. On examination of this proclamation it will appear, as is believed, that nothing will be attempted beyond what is amply justified by the Constitution. True, the form of an oath is given, but no man is coerced to take it. The man is promised a pardon only in case he voluntarily takes the oath. The Constitution authorizes the Executive to grant or withhold the pardon at his own absolute discretion, and this includes the power to grant on terms, as is fully established by judicial and other authorities.
It is also proffered that if in any of the States named a State government shall be in the mode prescribed set up, such government shall be recognized and guaranteed by the United States, and that under it the State shall, on the constitutional conditions, be protected against invasion and domestic violence. The constitutional obligation of the United States to guarantee to every State in the Union a republican form of government and to protect the State in the cases stated is explicit and full. But why tender the benefits of this provision only to a State government set up in this particular way? This section of the Constitution contemplates a case wherein the element within a State favorable to republican government in the Union may be too feeble for an opposite and hostile element external to or even within the State, and such are precisely the cases with which we are now dealing.
An attempt to guarantee and protect a revived State government, constructed in whole or in preponderating part from the very element against whose hostility and violence it is to be protected, is simply absurd. There must be a test by which to separate the opposing elements, so as to build only from the sound; and that test is a sufficiently liberal one which accepts as sound whoever will make a sworn recantation of his former unsoundness.
But if it be proper to require as a test of admission to the political body an oath of allegiance to the Constitution of the United States and to the Union under it, why also to the laws and proclamations in regard to slavery? Those laws and proclamations were enacted and put forth for the purpose of aiding in the suppression of the rebellion. To give them their fullest effect there had to be a pledge for their maintenance. In my judgment, they have aided and will further aid the cause for which they were intended. To now abandon them would be not only to relinquish a lever of power, but would also be a cruel and an astounding breach of faith. I may add at this point that while I remain in my present position I shall not attempt to retract or modify the emancipation proclamation, nor shall I return to slavery any person who is free by the terms of that proclamation or by any of the acts of Congress. For these and other reasons it is thought best that support of these measures shall be included in the oath, and it is believed the Executive may lawfully claim it in return for pardon and restoration of forfeited rights, which he has clear constitutional power to withhold altogether or grant upon the terms which he shall deem wisest for the public interest. It should be observed also that this part of the oath is subject to the modifying and abrogating power of legislation and supreme judicial decision.
The proposed acquiescence of the National Executive in any reasonable temporary State arrangement for the freed people is made with the view of possibly modifying the confusion and destitution which must at best attend all classes by a total revolution of labor throughout whole States. It is hoped that the already deeply afflicted people in those States may be somewhat more ready to give up the cause of their affliction if to this extent this vital matter be left to themselves, while no power of the National Executive to prevent an abuse is abridged by the proposition.
The suggestion in the proclamation as to maintaining the political framework of the States on what is called reconstruction is made in the hope that it may do good without danger of harm. It will save labor and avoid great confusion.
But why any proclamation now upon this subject? This question is beset with the conflicting views that the step might be delayed too long or be taken too soon. In some States the elements for resumption seem ready for action, but remain inactive apparently for want of a rallying point—a plan of action. Why shall A adopt the plan of B rather than B that of A? And if A and B should agree, how can they know but that the General Government here will reject their plan? By the proclamation a plan is presented which may be accepted by them as a rallying point, and which they are assured in advance will not be rejected here. This may bring them to act sooner than they otherwise would.
The objections to a premature presentation of a plan by the National Executive consist in the danger of committals on points which could be more safely left to further developments. Care has been taken to so shape the document as to avoid embarrassments from this source. Saying that on certain terms certain classes will be pardoned with rights restored, it is not said that other classes or other terms will never be included. Saying that reconstruction will be accepted if presented in a specified way, it is not said it will never be accepted in any other way.
The movements by State action for emancipation in several of the States not included in the emancipation proclamation are matters of profound gratulation. And while I do not repeat in detail what I have heretofore so earnestly urged upon this subject my general views and feelings remain unchanged and I trust that Congress will omit no fair opportunity of aiding these important steps to a great consummation.
In the midst of other cares, however important we must not lose sight of the fact that the war power is still our main reliance. To that power alone we look yet for a time to give confidence to the people in the contested regions that the insurgent power will not again overrun them. Until that confidence shall be established little can be done anywhere what is called reconstruction. Hence our chiefest care must still be directed to the Army and Navy who have thus far borne their harder part so nobly and well; and it may be esteemed fortunate that giving the greatest efficiency to these indispensable arms we do also honorably recognize the gallant men, from commander to sentinel, who compose them, and to whom more than to others the world must stand indebted for the home of freedom disenthralled, regenerated, enlarged, and perpetuated.
In conformity to the law of July 16, 1862, I most cordially recommend that Captain John Rogers United States Navy, receive a vote of thanks from Congress for the eminent skill and gallantry exhibited by him in the engagement with the rebel armed ironclad steamer Fingal, alias Atlanta, whilst in command of the United States ironclad steamer Weehawken, which led to her capture on the 17th June, 1863, and also for the zeal, bravery, and general good conduct shown by this officer on many occasions.
This recommendation is specially made in order to comply with the requirements of the ninth section of the aforesaid act, which is in the following words, viz:
That any line officer of the Navy or Marine Corps may be advanced one grade if upon recommendation of the President by name he receives the thanks of Congress for highly distinguished conduct in conflict with the enemy or for extraordinary heroism in the line of his profession.
Congress, on my recommendation, passed a resolution, approved 7th February, 1863, tendering its thanks to Commander D. D. Porter "for the bravery and skill displayed in the attack on the post of Arkansas on the 10th January, 1863," and in consideration of those services, together with his efficient labors and vigilance subsequently displayed in thwarting the efforts of the rebels to obstruct the Mississippi and its tributaries and the important part rendered by the squadron under his command, which led to the surrender of Vicksburg.
I do therefore, in conformity to the seventh section of the act approved 16th July, 1862, nominate Commander D. D. Porter to be a rear-admiral in the Navy on the active list from the 4th July, 1863, to fill an existing vacancy.
MAJOR-GENERAL GRANT:
Understanding that your lodgment at Chattanooga and Knoxville is now secure, I wish to tender you, and all under your command, my more than thanks, my profoundest gratitude, for the skill, courage, and perseverance with which you and they, over so great difficulties, have effected that important object. God bless you all!
HIS EXCELLENCY A. G. CURTIN,
Governor of Pennsylvania.
DEAR SIR:—I have to urge my illness, and the preparation of the message, in excuse for not having sooner transmitted you the inclosed from the Secretary of War and Provost Marshal General in response to yours in relation to recruiting in Pennsylvania. Though not quite as you desire, I hope the grounds taken will be reasonably satisfactory to you. Allow me to exchange congratulations with you on the organization of the House of Representatives, and especially on recent military events in Georgia and Tennessee.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Please suspend execution in any and all sentences of death in your department until further order.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of the Potomac:
Lieut. Col. James B. Knox, Tenth Regiment Pennsylvania Reserves, offers his resignation under circumstances inducing me to wish to accept it. But I prefer to know your pleasure upon the subject. Please answer.
HON. OGDEN HOFFMAN, U. S. District Judge, San Francisco, Cal.:
The oath in the proclamation of December 8 is intended for those who may voluntarily take it, and not for those who may be constrained to take it in order to escape actual imprisonment or punishment. It is intended that the latter class shall abide the granting or withholding of the pardoning power in the ordinary way.
MOTHER MARY GONYEAG, Superior, Academy of Visitation, Keokuk, Iowa:
The President has no authority as to whether you may raffle for the benevolent object you mention. If there is no objection in the Iowa laws, there is none here.
A Proclamation.
Whereas by an act of the Congress of the United States of the 24th of May, 1828, entitled "An act in addition to an act entitled 'An act concerning discriminating duties of tonnage and impost' and to equalize the duties on Prussian vessels and their cargoes," it is provided that upon satisfactory evidence being given to the President of the United States by the government of any foreign nation that no discriminating duties of tonnage or impost are imposed or levied in the ports of the said nation upon vessels wholly belonging to citizens of the United States or upon the produce, manufactures, or merchandise imported in the same from the United States or from any foreign country, the President is thereby authorized to issue his proclamation declaring that the foreign discriminating duties of tonnage and impost within the United States are and shall be suspended and discontinued so far as respects the vessels of the said foreign nation and the produce, manufactures, or merchandise imported into the United States in the same from the said foreign nation or from any other foreign country, the said suspension to take effect from the time of such notification being given to the President of the United States and to continue so long as the reciprocal exemption of vessels belonging to citizens of the United States and their cargoes, as aforesaid, shall be continued, and no longer; and
Whereas satisfactory evidence has lately been received by me through an official communication of Senor Don Luis Molina, Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of the Republic of Nicaragua, under date of the 28th of November, 1863, that no other or higher duties of tonnage and impost have been imposed or levied since the second day of August, 1838, in the ports of Nicaragua, upon vessels wholly belonging to citizens of the United States, and upon the produce, manufactures, or merchandise imported in the same from the United States, and from any foreign country whatever, than are levied on Nicaraguan ships and their cargoes in the same ports under like circumstances:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, do hereby declare and proclaim that so much of the several acts imposing discriminating duties of tonnage and impost within the United States are, and shall be, suspended and discontinued so far as respects the vessels of Nicaragua, and the produce, manufactures, and the merchandise imported into the United States in the same from the dominions of Nicaragua, and from any other foreign country whatever; the said suspension to take effect from the day above mentioned, and to continue thenceforward so long as the reciprocal exemption of the vessels of the United States, and the produce, manufactures, and merchandise imported into the dominions of Nicaragua in the same, as aforesaid, shall be continued on the part of the government of Nicaragua.
Given under my hand at the city of Washington, the sixteenth day of December, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and the eighty-eighth of the Independence of the United States.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES OF THE UNITED STATES:
Herewith I lay before you a letter addressed to myself by a committee of gentlemen representing the freedmen's aid societies in Boston, New York, Philadelphia, and Cincinnati. The subject of the letter, as indicated above, is one of great magnitude and importance, and one which these gentlemen, of known ability and high character, seem to have considered with great attention and care. Not having the time to form a mature judgment of my own as to whether the plan they suggest is the best, I submit the whole subject to Congress, deeming that their attention thereto is almost imperatively demanded.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., December 17, 1863.
MAJOR-GENERAL HURLBUT, Memphis, Tenn.:
I understand you have under sentence of death, a tall old man, by the name of Henry F. Luckett. I personally knew him, and did not think him a bad man. Please do not let him be executed unless upon further order from me, and in the meantime send me a transcript of the record.
GENERAL GRANT, Chattanooga, Tennessee:
The Indiana delegation in Congress, or at least a large part of them, are very anxious that General Milroy shall enter active service again, and I share in this feeling. He is not a difficult man to satisfy, sincerity and courage being his strong traits. Believing in our cause, and wanting to fight for it, is the whole matter with him. Could you, without embarrassment, assign him a place, if directed to report to you?
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C., December 21, 1863.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—Sending a note to the Secretary of the Navy, as I promised, he called over and said that the strikes in the ship-yards had thrown the completion of vessels back so much that he thought General Gilimore's proposition entirely proper. He only wishes (and in which I concur) that General Gillmore will courteously confer with, and explain to, Admiral Dahlgren.
In regard to the Western matter, I believe the program will have to stand substantially as I first put it. Henderson, and especially Brown, believe that the social influence of St. Louis would inevitably tell injuriously upon General Pope in the particular difficulty existing there, and I think there is some force in that view.
As to retaining General Schofield temporarily, if this should be done, I believe I should scarcely be able to get his nomination through the Senate. Send me over his nomination, which, however, I am not quite ready to send to the Senate.
Yours as ever,
O. D. FILLEY, ST. Louis, Missouri:
I have just looked over a petition signed by some three dozen citizens of St. Louis, and three accompanying letters, one by yourself, one by a Mr. Nathan Ranney, and one by a Mr. John D. Coalter, the whole relating to the Rev. Dr. McPheeters. The petition prays, in the name of justice and mercy, that I will restore Dr. McPheeters to all his ecclesiastical rights. This gives no intimation as to what ecclesiastical rights are withheld.
Your letter states that Provost-Marshal Dick, about a year ago, ordered the arrest of Dr. McPheeters, pastor of the Vine Street Church, prohibited him from officiating, and placed the management of the affairs of the church out of the control of its chosen trustees; and near the close you state that a certain course "would insure his release." Mr. Ranney's letter says: "Dr. Samuel S. McPheeters is enjoying all the rights of a civilian, but cannot preach the Gospel!!!!" Mr. Coalter, in his letter, asks: "Is it not a strange illustration of the condition of things, that the question of who shall be allowed to preach in a church in St. Louis shall be decided by the President of the United States?"
Now, all this sounds very strangely; and, withal, a little as if you gentlemen making the application do not understand the case alike; one affirming that the doctor is enjoying all the rights of a civilian, and another pointing out to me what will secure his release! On the second day of January last, I wrote to General Curtis in relation to Mr. Dick's order upon Dr. McPheeters; and, as I suppose the doctor is enjoying all the rights of a civilian, I only quote that part of my letter which relates to the church. It is as follows: "But I must add that the United States Government must not, as by this order, undertake to run the churches. When an individual, in a church or out of it, becomes dangerous to the public interest, he must be checked; but the churches, as such, must take care of themselves. It will not do for the United States to appoint trustees, supervisors, or other agents for the churches."
This letter going to General Curtis, then in command there, I supposed, of course, it was obeyed, especially as I heard no further complaint from Dr. McPheeters or his friends for nearly an entire year. I have never interfered, nor thought of interfering, as to who shall or shall not preach in any church; nor have I knowingly or believingly tolerated any one else to so interfere by my authority. If any one is so interfering by color of my authority, I would like to have it specifically made known to me. If, after all, what is now sought is to have me put Dr. McPheeters back over the heads of a majority of his own congregation, that, too, will be declined. I will not have control of any church on any side.
Yours respectfully,
MILITARY COMMANDER, Point Lookout, Md.:
If you have a prisoner by the name Linder—Daniel Linder, I think, and certainly the son of U. F. Linder, of Illinois, please send him to me by an officer.
MILITARY COMMANDER, Point Lookout, Md.:
If you send Linder to me as directed a day or two ago, also send Edwin C. Claybrook, of Ninth Virginia rebel cavalry.
HON. U. F. LINDER, Chicago, Ill.: Your son Dan has just left me with my order to the Secretary of War, to administer to him the oath of allegiance, discharge him and send him to you.
MAJOR-GENERAL BANKS:
Yours of the sixteenth is received, and I send you, as covering the ground of it, a copy of my answer to yours of the sixth, it being possible the original may not reach you. I intend you to be master in every controversy made with you.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Jacob Bowers is fully pardoned for past offence, upon condition that he returns to duty and re-enlists for three years or during the war.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
SIR:—Please fix up the department to which Curtis is to go, without waiting to wind up the Missouri matter. Lane is very anxious to have Fort Smith in it, and I am willing, unless there be decided military reasons to the contrary, in which case of course, I am not for it. It will oblige me to have the Curtis department fixed at once.
Yours truly,
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL SULLIVAN.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D.C., January 1, 1864. 3.30 p.m.
GENERAL SULLIVAN, Harper's Ferry:
Have you anything new from Winchester, Martinsburg or thereabouts?
GOVERNOR PIERPOINT, Alexandria, Va.:
Please call and see me to-day if not too inconvenient.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER.
SIR:—The Secretary of War and myself have concluded to discharge of the prisoners at Point Lookout the following classes: First, those who will take the oath prescribed in the proclamation of December 8, and issued by the consent of General Marston, will enlist in our service. Second, those who will take the oath and be discharged and whose homes lie safely within our military lines.
I send by Mr. Hay this letter and a blank-book and some other blanks, the way of using which I propose for him to explain verbally better than I can in writing.
Yours, very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE:
If not inconsistent with the service, please allow General William Harrow as long a leave of absence as the rules permit with the understanding that I may lengthen it if I see fit. He is an acquaintance and friend of mine, and his family matters very urgently require his presence.
GENTLEMEN OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
By a joint resolution of your honorable bodies approved December 23, 1863, the paying of bounties to veteran volunteers, as now practiced by the War Department, is, to the extent of three hundred dollars in each case, prohibited after this 5th day of the present month. I transmit for your consideration a communication from the Secretary of War, accompanied by one from the Provost-Marshal General to him, both relating to the subject above mentioned. I earnestly recommend that the law be so modified as to allow bounties to be paid as they now are, at least until the ensuing 1st day of February.
I am not without anxiety lest I appear to be importunate in thus recalling your attention to a subject upon which you have so recently acted, and nothing but a deep conviction that the public interest demands it could induce me to incur the hazard of being misunderstood on this point. The Executive approval was given by me to the resolution mentioned, and it is now by a closer attention and a fuller knowledge of facts that I feel constrained to recommend a reconsideration of the subject.
GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE, Frankfort, Kentucky:
Yours of yesterday received. Nothing is known here about General Foster's order, of which you complain, beyond the fair presumption that it comes from General Grant, and that it has an object which, if you understood, you would be loath to frustrate. True, these troops are, in strict law, only to be removed by my order; but General Grant's judgment would be the highest incentive to me to make such order. Nor can I understand how doing so is bad faith and dishonor, nor yet how it so exposes Kentucky to ruin. Military men here do not perceive how it exposes Kentucky, and I am sure Grant would not permit it if it so appeared to him.
MAJOR-GENERAL GILLMORE:
I understand an effort is being made by some worthy gentlemen to reconstruct a legal State government in Florida. Florida is in your Department, and it is not unlikely you may be there in person. I have given Mr. Hay a commission of major, and sent him to you, with some blank-books and other blanks, to aid in the reconstruction. He will explain as to the manner of using the blanks, and also my general views on the subject. It is desirable for all to co-operate, but if irreconcilable differences of opinion shall arise, you are master. I wish the thing done in the most speedy way, so that when done it be within the range of the late proclamation on the subject. The detail labor will, of course, have to be done by others; but I will be greatly obliged if you will give it such general supervision as you can find consistent with your more strictly military duties.
1864.
GOVERNOR BROUGH, Columbus, Ohio:
If Private William G. Toles, of Fifty-ninth Ohio Volunteers, returns to his regiment and faithfully serves out his term, he is fully pardoned for all military offenses prior to this.
MESSRS. CROSBY AND NICHOLS.
GENTLEMEN: The number for this month and year of the North American Review was duly received, and for which please accept my thanks. Of course I am not the most impartial judge; yet, with due allowance for this, I venture to hope that the article entitled "The President's Policy" will be of value to the country. I fear I am not worthy of all which is therein kindly said of me personally.
The sentence of twelve lines, commencing at the top of page 252, I could wish to be not exactly what it is. In what is there expressed, the writer has not correctly understood me. I have never had a theory that secession could absolve States or people from their obligations. Precisely the contrary is asserted in the inaugural address; and it was because of my belief in the continuation of those obligations that I was puzzled, for a time, as to denying the legal rights of those citizens who remained individually innocent of treason or rebellion. But I mean no more now than to merely call attention to this point.
Yours respectfully,
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE:
Sundry citizens of the State of Arkansas petition me that an election may be held in that State, at which to elect a Governor; that it be assumed at that election, and thenceforward, that the constitution and laws of the State, as before the rebellion, are in full force, except that the constitution is so modified as to declare that there shall be neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except in the punishment of crimes whereof the party shall have been duly convicted; that the General Assembly may make such provisions for the freed people as shall recognize and declare their permanent freedom, and provide for their education, and which may yet be construed as a temporary arrangement suitable to their condition as a laboring, landless, and homeless class; that said election shall be held on the 28th of March, 1864, at all the usual places of the State, or all such as voters may attend for that purpose, that the voters attending at eight o'clock in the morning of said day may choose judges and clerks of election for such purpose; that all persons qualified by said constitution and laws, and taking the oath presented in the President's proclamation of December 8, 1863, either before or at the election, and none others, may be voters; that each set of judges and clerks may make returns directly to you on or before the —th day of —— next; that in all other respects said election may be conducted according to said constitution and laws: that on receipt of said returns, when five thousand four hundred and six votes shall have been cast, you can receive said votes, and ascertain all who shall thereby appear to have been elected; that on the —th day of ——— next, all persons so appearing to have been elected, who shall appear before you at Little Rock, and take the oath, to be by you severally administered, to support the Constitution of the United States and said modified Constitution of the State of Arkansas, may be declared by you qualified and empowered to enter immediately upon the duties of the offices to which they shall have been respectively elected.
You will please order an election to take place on the 28th of March, 1864, and returns to be made in fifteen days thereafter.
In accordance with a letter addressed by the Secretary of State, with my approval, to the Hon. Joseph A. Wright, of Indiana, that patriotic and distinguished gentleman repaired to Europe and attended the International Agricultural Exhibition, held at Hamburg last year, and has since his return made a report to me, which, it is believed, can not fail to be of general interest, and especially so to the agricultural community. I transmit for your consideration copies of the letters and report. While it appears by the letter that no reimbursement of expenses or compensation was promised him, I submit whether reasonable allowance should not be made him for them.
I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States having seen and considered the additional regulations of trade prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury, and numbered LI, LII, LIII, LIV, LV, and LVI, do hereby approve the same; and I further declare and order that all property brought in for sale, in good faith, and actually sold in pursuance of said Regulations LII, LIII, LIV, LV, and LVI, after the same shall have taken effect and come in force as provided in Regulation LVI, shall be exempt from confiscation or forfeiture to the United States.
MAJOR-GENERAL FOSTER, Knoxville, Tenn.:
Is a supposed correspondence between General Longstreet and yourself about the amnesty proclamation, which is now in the newspapers, genuine?
HON. EDWARD STANLEY, San Francisco, Cal.:
Yours of yesterday received. We have rumors similar to the dispatch received by you, but nothing very definite from North Carolina. Knowing Mr. Stanley to be an able man, and not doubting that he is a patriot, I should be glad for him to be with his old acquaintances south of Virginia, but I am unable to suggest anything definite upon the subject.
WASHINGTON, January 28, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK:
Some citizens of Missouri, vicinity of Kansas City, are apprehensive that there is special danger of renewed troubles in that neighborhood, and thence on the route toward New Mexico. I am not impressed that the danger is very great or imminent, but I will thank you to give Generals Rosecrans and Curtis, respectively, such orders as may turn their attention thereto and prevent as far as possible the apprehended disturbance.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL SICKLES, New York:
Could you, without it being inconvenient or disagreeable to yourself, immediately take a trip to Arkansas for me?
GOVERNOR BRAMLETTE, Frankfort, Ky.:
General Boyle's resignation is accepted, so that your Excellency can give him the appointment proposed.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, February 1, 1864
HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
SIR:-You are directed to have a transport (either a steam or sailing vessel, as may be deemed proper by the Quartermaster-General) sent to the colored colony established by the United States at the island of Vache, on the coast of San Domingo, to bring back to this country such of the colonists there as desire to return. You will have the transport furnished with suitable supplies for that purpose, and detail an officer of the Quartermaster's Department, who, under special instructions to be given, shall have charge of the business. The colonists will be brought to Washington, unless otherwise hereafter directed, and be employed and provided for at the camps for colored persons around that city. Those only will be brought from the island who desire to return, and their effects will be brought with them.
Ordered, That a draft of five hundred thousand (500,000) men, to serve for three years or during the war, be made on the tenth (10th) day of March next, for the military service of the United States, crediting and deducting therefrom so many as may have been enlisted or drafted into the service prior to the first (1st) day of March, and not before credited.
GOVERNOR YATES, Springfield, Ill.:
The United States Government lot in Springfield can be used for a soldiers' home, with the understanding that the Government does not incur any expense in the case.
GOVERNOR J. MURPHY:
My order to General Steele about an election was made in ignorance of the action your convention had taken or would take. A subsequent letter directs General Steele to aid you on your own plan, and not to thwart or hinder you. Show this to him.
FEBRUARY 6, 1864.
"It had got to be," said Mr. Lincoln, "midsummer, 1862. Things had gone on from bad to worse, until I felt that we had reached the end of our rope on the plan of operations we had been pursuing; that we had about played our last card, and must change our tactics, or lose the game. I now determined upon the adoption of the emancipation policy; and without consultation with, or the knowledge of, the Cabinet, I prepared the original draft of the proclamation, and, after much anxious thought, called a Cabinet meeting upon the subject. This was the last of July or the first part of the month of August, 1862. [The exact date was July 22, 1862.]... All were present excepting Mr. Blair, the Postmaster-General, who was absent at the opening of the discussion, but came in subsequently. I said to the Cabinet that I had resolved upon this step, and had not called them together to ask their advice, but to lay the subject-matter of a proclamation before them, suggestions as to which would be in order after they had heard it read. Mr. Lovejoy was in error when he informed you that it excited no comment excepting on the part of Secretary Seward. Various suggestions were offered. Secretary Chase wished the language stronger in reference to the arming of the blacks.
"Mr. Blair, after he came in, deprecated the policy on the ground that it would cost the administration the fall elections. Nothing, however, was offered that I had not already fully anticipated and settled in my mind, until Secretary Seward spoke. He said in substance, 'Mr. President, I approve of the proclamation, but I question the expediency of its issue at this juncture. The depression of the public mind, consequent upon our repeated reverses, is so great that I fear the effect of so important a step. It may be viewed as the last measure of an exhausted government, a cry for help; the government stretching forth its hands to Ethiopia, instead of Ethiopia stretching forth her hands to the government.' His idea," said the President, "was that it would be considered our last shriek on the retreat." [This was his precise expression.] 'Now,' continued Mr. Seward, 'while I approve the measure, I suggest, sir, that you postpone its issue until you can give it to the country supported by military success, instead of issuing it, as would be the case now, upon the greatest disasters of the war.' Mr. Lincoln continued "The wisdom of the view of the Secretary of State struck me with very great force. It was an aspect of the case that, in all my thought upon the subject, I had entirely overlooked. The result was that I put the draft of the proclamation aside, as you do your sketch for a picture, waiting for a victory.
"From time to time I added or changed a line, touching it up here and there, anxiously watching the process of events. Well, the next news we had was of Pope's disaster at Bull Run. Things looked darker than ever. Finally came the week of the battle of Antietam. I determined to wait no longer. The news came, I think, on Wednesday, that the advantage was on our side. I was then staying at the Soldiers' Home [three miles out of Washington]. Here I finished writing the second draft of the preliminary proclamation; came up on Saturday; called the Cabinet together to hear it, and it was published on the following Monday."
MAJOR-GENERAL SEDGWICK, Army of Potomac:
Unless there be some strong reason to the contrary, please send General Kilpatrick to us here, for two or three days.
HON. HORACE MAYNARD, Nashville, Tenn.:
Your letter of [the] second received. Of course Governor Johnson will proceed with reorganization as the exigencies of the case appear to him to require. I do not apprehend he will think it necessary to deviate from my views to any ruinous extent. On one hasty reading I see no such deviation in his program, which you send.
WILLIAM M. FISHBACK, Little Rock, Arkansas:
When I fixed a plan for an election in Arkansas I did it in ignorance that your convention was doing the same work. Since I learned the latter fact I have been constantly trying to yield my plan to them. I have sent two letters to General Steele, and three or four despatches to you and others, saying that he, General Steele, must be master, but that it will probably be best for him to merely help the convention on its own plan. Some single mind must be master, else there will be no agreement in anything, and General Steele, commanding the military and being on the ground, is the best man to be that master. Even now citizens are telegraphing me to postpone the election to a later day than either that fixed by the convention or by me. This discord must be silenced.
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE, Little Rock, Arkansas:
The day fixed by the convention for the election is probably the best, but you on the ground, and in consultation with gentlemen there, are to decide. I should have fixed no day for an election, presented no plan for reconstruction, had I known the convention was doing the same things. It is probably best that you merely assist the convention on their own plan, as to election day and all other matters I have already written and telegraphed this half a dozen times.
A. ROBINSON, Leroy, N. Y.:
The law only obliges us to keep accounts with States, or at most Congressional Districts, and it would overwhelm us to attempt in counties, cities and towns. Nevertheless we do what we can to oblige in particular cases. In this view I send your dispatch to the Provost-Marshal General, asking him to do the best he can for you.
A Proclamation.
Whereas, by my proclamation of the nineteenth of April, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-one, the ports of the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas were, for reasons therein set forth, placed under blockade; and whereas, the port of Brownsville, in the district of Brazos Santiago, in the State of Texas, has since been blockaded, but as the blockade of said port may now be safely relaxed with advantage to the interests of commerce:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, pursuant to the authority in me vested by the fifth section of the act of Congress approved on the 13th of July, 1861, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," do hereby declare that the blockade of the said port of Brownsville shall so far cease and determine from and after this date, that commercial intercourse with said port, except as to persons, things, and information hereinafter specified, may, from this date, be carried on, subject to the laws of the United States, to the regulations prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury, and, until the rebellion shall have been suppressed, to such orders as may be promulgated by the general commanding the department, or by an officer duly authorized by him and commanding at said port. This proclamation does not authorize or allow the shipment or conveyance of persons in, or intending to enter, the service of the insurgents, or of things or information intended for their use, or for their aid or comfort, nor, except upon the permission of the Secretary of War, or of some officer duly authorized by him, of the following prohibited articles, namely: cannon, mortars, firearms, pistols, bombs, grenades, powder, saltpeter, sulphur, balls, bullets, pikes, swords, boarding-caps (always excepting the quantity of the said articles which may be necessary for the defense of the ship and those who compose the crew), saddles, bridles, cartridge-bag material, percussion and other caps, clothing adapted for uniforms; sail-cloth of all kinds, hemp and cordage, intoxicating drinks other than beer and light native wines.
To vessels clearing from foreign ports and destined to the port of Brownsville, opened by this proclamation, licenses will be granted by consuls of the United States upon satisfactory evidence that the vessel so licensed will convey no persons, property, or information excepted or prohibited above, either to or from the said port; which licenses shall be exhibited to the collector of said port immediately on arrival, and, if required, to any officer in charge of the blockade, and on leaving said port every vessel will be required to have a clearance from the collector of the customs, according to law, showing no violation of the conditions of the license. Any violations of said conditions will involve the forfeiture and condemnation of the vessel and cargo, and the exclusion of all parties concerned from any further privilege of entering the United States during the war for any purpose whatever.
In all respects, except as herein specified, the existing blockade remains in full force and effect as hitherto established and maintained, nor is it relaxed by this proclamation except in regard to the port to which relaxation is or has been expressly applied.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed. Done at the city of Washington, this eighteenth day of February, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-four, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
COMMANDER GEORGE S. BLAKE, Commandant Naval Academy, Newport, R. I.:
I desire the case of Midshipman C. Lyon re-examined and if not clearly inconsistent I shall be much obliged to have the recommendation changed.
HON. W. H. SEWARD, Secretary of State, Washington, D.C.:
In county and State elections, must citizens of Tennessee take the oath prescribed by Governor Johnson, or will the President's oath of amnesty entitle them to vote? I have been appointed to hold the March election in Cheatham County, and wish to act understandingly.
WARREN JORDAN.
WASHINGTON, February 20, 1864.
WARREN JORDAN, NASHVILLE:
In county elections you had better stand by Governor Johnson's plan; otherwise you will have conflict and confusion. I have seen his plan.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Saint LOUIS, MO.:
Colonel Sanderson will be ordered to you to-day, a mere omission that it was not done before. The other questions in your despatch I am not yet prepared to answer.
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE, Little Rock, Ark.:
Yours of yesterday received. Your conference with citizens approved. Let the election be on the 14th of March as they agreed.
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE, Little Rock, Arkansas:
General Sickles is not going to Arkansas. He probably will make a tour down the Mississippi and home by the gulf and ocean, but he will not meddle in your affairs.
At one time I did intend to have him call on you and explain more fully than I could do by letter or telegraph, so as to avoid a difficulty coming of my having made a plan here, while the convention made one there, for reorganizing Arkansas; but even his doing that has been given up for more than two weeks. Please show this to Governor Murphy to save me telegraphing him.
WAR DEPARTMENT, ADJUTANT-GENERALS OFFICE,
WASHINGTON, February 26, 1864.
Sentence of Deserters.
The President directs that the sentences of all deserters who have been condemned by court-martial to death, and that have not been otherwise acted upon by him, be mitigated to imprisonment during the war at the Dry Tortugas, Florida, where they will be sent under suitable guards by orders from army commanders.
The commanding generals, who have power to act on proceedings of courts-martial in such cases, are authorized in special cases to restore to duty deserters under sentence, when in their judgment the service will be thereby benefited.
Copies of all orders issued under the foregoing instructions will be immediately forwarded to the Adjutant-General and to the Judge-Advocate General.
By order of the Secretary of War: B. D. TOWNSEND, Assistant Adjutant-General
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, February 26, 1864
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort. Monroe, Va.:
I cannot remember at whose request it was that I gave the pass to Mrs. Bulky. Of course detain her, if the evidence of her being a spy is strong against her.
HON. W. JAYNE.
DEAR SIR—I dislike to make changes in office so long as they can be avoided. It multiplies my embarrassments immensely. I dislike two appointments when one will do. Send me the name of some man not the present marshal, and I will nominate him to be Provost-Marshal for Dakota.
Yours truly,
HON. E. H: EAST, Secretary of State, Nashville, Tennessee
Your telegram of the twenty-sixth instant asking for a copy of my despatch to Warren Jordan, Esq., at Nashville Press office, has just been referred to me by Governor Johnson. In my reply to Mr. Jordan, which was brief and hurried, I intended to say that in the county and State elections of Tennessee, the oath prescribed in the proclamation of Governor Johnson on the twenty-sixth of January, 1864, ordering an election in Tennessee on the first Saturday in March next, is entirely satisfactory to me as a test of loyalty of all persons proposing or offering to vote in said elections; and coming from him would better be observed and followed. There is no conflict between the oath of amnesty in my proclamation of eighth December, 1863, and that prescribed by Governor Johnson in his proclamation of the twenty-sixth ultimo.
No person who has taken the oath of amnesty of eighth December, 1863, and obtained a pardon thereby, and who intends to observe the same in good faith, should have any objection to taking that prescribed by Governor Johnson as a test of loyalty.
I have seen and examined Governor Johnson's proclamation, and am entirely satisfied with his plan, which is to restore the State government and place it under the control of citizens truly loyal to the Government of the United States.
A. LINCOLN.
Please send above to Governor Johnson. A. L.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
SIR:—You ask some instructions from me in relation to the Report of Special Commission constituted by an order of the War Department, dated December 5, 1863, "to revise the enrolment and quotas of the City and State of New York, and report whether there be any, and what, errors or irregularities therein, and what corrections, if any, should be made."
In the correspondence between the Governor of New York and myself last summer, I understood him to complain that the enrolments in several of the districts of that State had been neither accurately nor honestly made; and in view of this, I, for the draft then immediately ensuing, ordered an arbitrary reduction of the quotas in several of the districts wherein they seemed too large, and said: "After this drawing, these four districts, and also the seventeenth and twenty-ninth, shall be carefully re-enrolled, and, if you please, agents of yours may witness every step of the process." In a subsequent letter I believe some additional districts were put into the list of those to be re-enrolled. My idea was to do the work over according to the law, in presence of the complaining party, and thereby to correct anything which might be found amiss. The commission, whose work I am considering, seem to have proceeded upon a totally different idea. Not going forth to find men at all, they have proceeded altogether upon paper examinations and mental processes. One of their conclusions, as I understand, is that, as the law stands, and attempting to follow it, the enrolling officers could not have made the enrolments much more accurately than they did. The report on this point might be useful to Congress. The commission conclude that the quotas for the draft should be based upon entire population, and they proceed upon this basis to give a table for the State of New York, in which some districts are reduced and some increased. For the now ensuing draft, let the quotas stand as made by the enrolling officers, in the districts wherein this table requires them to be increased; and let them be reduced according to the table in the others: this to be no precedent for subsequent action. But, as I think this report may, on full consideration, be shown to have much that is valuable in it, I suggest that such consideration be given it, and that it be especially considered whether its suggestions can be conformed to without an alteration of the law.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN. TELEGRAM TO GENERAL THOMAS.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, February 28, 1864.
GENERAL L. THOMAS, Louisville, Kentucky:
I see your despatch of yesterday to the Secretary of War.
I wish you would go to the Mississippi River at once, and take hold of and be master in the contraband and leasing business. You understand it better than any other man does. Mr. Miller's system doubtless is well intended, but from what I hear I fear that, if persisted in, it would fall dead within its own entangling details. Go there and be the judge. A Mr. Lewis will probably follow you with something from me on this subject, but do not wait for him. Nor is this to induce you to violate or neglect any military order from the General-in-Chief or Secretary of War.
HON. SECRETARY OF THE TREASURY.
MY DEAR SIR:—I would have taken time to answer yours of the 22d inst. sooner, only that I did not suppose any evil could result from the delay, especially as, by a note, I promptly acknowledged the receipt of yours, and promised a fuller answer. Now, on consideration I find there is really very little to say. My knowledge of Mr. Pomeroy's letter having been made public came to me only the day you wrote; but I had, in spite of myself, known of its existence several days before. I have not yet read it, and I think I shall not. I was not shocked or surprised by the appearance of the letter, because I had had knowledge of Mr. Pomeroy's committee, and of secret issues which, I supposed, came from it, and of secret agents who, I supposed, were sent out by it for several weeks. I have known just as little a these things as my friends have allowed me to know. They bring the documents to me, but I do not read them; they tell me what they think fit to tell me, but I do not inquire for more.
I fully concur with you that neither of us can justly be held responsible for what our respective friends may do without our instigation or countenance and I assure you, as you have assured me, that no assault has been made upon you by my instigation, or with my countenance.
Whether you shall remain at the head of the Treasury Department is a question which I will not allow myself to consider from any standpoint other than my judgment of the public service, and, in that view, I do not perceive occasion for a change.
Yours truly,
GENERAL L. THOMAS:
This introduces Mr. Lewis, mentioned in my despatch sent you at Louisville some days ago. I have but little personal acquaintance with him; but he has the confidence of several members of Congress here who seem to know him well. He hopes to be useful, without charge to the government, in facilitating the introduction of the free-labor system on the Mississippi plantations. He is acquainted with, and has access to, many of the planters who wish to adopt the system. He will show you two letters of mine on this subject, one somewhat General, and the other relating to named persons; they are not different in principle. He will also show you some suggestions coming from some of the planters themselves. I desire that all I promise in these letters, so far as practicable, may be in good faith carried out, and that suggestions from the planters may be heard and adopted, so far as they may not contravene the principles stated, nor justice, nor fairness, to laborers. I do not herein intend to overrule your own mature judgment on any point.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE, Little Rock, Ark.:
Yours including address to people of Arkansas is received. I approve the address and thank you for it. Yours in relation to William M. Randolph also received. Let him take the oath of December 8, and go to work for the new constitution, and on your notifying me of it, I will immediately issue the special pardon for him.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, March 4,1864. MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Admiral Dahlgren is here, and of course is very anxious about his son. Please send me at once all you know or can learn of his fate.
GOVERNMENT. EXECUTIVE MANSION,
WASHINGTON, March 7, 1864.
Whereas, by an Executive order of the 10th of November last permission was given to export certain tobacco belonging to the French government from insurgent territory, which tobacco was supposed to have been purchased and paid for prior to the 4th day of March, 1861; but whereas it was subsequently ascertained that a part at least of the said tobacco had been purchased subsequently to that date, which fact made it necessary to suspend the carrying into effect of the said order; but whereas, pursuant to mutual explanations, a satisfactory understanding upon the subject has now been reached, it is directed that the order aforesaid may be carried into effect, it being understood that the quantity of French tobacco so to be exported shall not exceed seven thousand hogsheads, and that it is the same tobacco respecting the exportation of which application Was originally made by the French government.
U.S. MARSHAL, Louisville, Ky.:
Until further order suspend sale of property and further proceedings in cases of the United States against Dr. John B. English, and S. S. English, qt al., sureties for John L. Hill. Also same against same sureties for Thomas A. Ireland.
A. LINCOLN.
MAJOR ECKERT: Please send the above dispatch. JNO. G. NICOLAY, Private Secretary
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
New York City votes ninety-five hundred majority for allowing soldiers to vote, and the rest of the State nearly all on the same side. Tell the soldiers.
TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES
In compliance with a resolution of the Senate of the 1st instant, respecting the points of commencement of the Union Pacific Railroad, on the one hundredth degree of west longitude, and of the branch road, from the western boundary of Iowa to the said one hundredth degree of longitude, I transmit the accompanying report from the Secretary of the Interior, containing the information called for.
I deem it proper to add that on the 17th day of November last an Executive order was made upon this subject and delivered to the vice-president of the Union Pacific Railroad Company, which fixed the point on the western boundary of the State of Iowa from which the company should construct their branch road to the one hundredth degree of west longitude, and declared it to be within the limits of the township in Iowa opposite the town of Omaha, in Nebraska. Since then the company has represented to me that upon actual surveys made it has determined upon the precise point of departure of their said branch road from the Missouri River, and located the same as described in the accompanying report of the Secretary of the Interior, which point is within the limits designated in the order of November last; and inasmuch as that order is not of record in any of the Executive Departments, and the company having desired a more definite one, I have made the order of which a copy is herewith, and caused the same to be filed in the Department of the Interior.
GENERAL GRANT:—The expression of the nation's approbation of what you have already done, and its reliance on you for what remains to do in the existing great struggle, is now presented with this commission constituting you Lieutenant-General of the Army of the United States.
With this high honor, devolves on you an additional responsibility. As the country herein trusts you, so, under God, it will sustain you. I scarcely need add, that with what I here speak for the country, goes my own hearty personal concurrence.
GENERAL GRANT'S REPLY.
Mr. PRESIDENT:—I accept this commission, with gratitude for the high honor conferred.
With the aid of the noble armies that have fought on so many fields for our common country, it will be my earnest endeavor not to disappoint your expectations.
I feel the full weight of the responsibilities now devolving on me, and I know that if they are met, it will be due to those armies; and above all, to the favor of that Providence which leads both nations and men.
Under the authority of an act of Congress to revive the grade of lieutenant-General in the United States Army, approved February 29, 1864, Lieutenant-General Ulysses S. Grant, United States Army, is assigned to the command of the Armies of the United States.
GOVERNOR MURPHY, Little Rock, Arkansas:
I am not appointing officers for Arkansas now, and I will try to remember your request. Do your best to get out the largest vote possible, and of course as much of it as possible on the right side.
HON. MICHAEL HAHN.
MY DEAR SIR:—I congratulate you on having fixed your name in history as the first free-state governor of Louisiana. Now, you are about to have a convention, which among other things will probably define the elective franchise. I barely suggest for your private consideration, whether some of the colored people may not be let in,—as, for instance, the very intelligent, and especially those who have fought gallantly in our ranks. They would probably help, in some trying time to come, to keep the jewel of liberty within the family of freedom. But this is only a suggestion,—not to the public, but to you alone.
Yours truly,
In order to supply the force required to be drafted for the Navy and to provide an adequate reserve force for all contingencies, in addition to the five hundred thousand men called for February 1, 1864, a call is hereby made and a draft ordered for two hundred thousand men for the military service (Army, Navy, and Marine Corps) of the United States.
The proportional quotas for the different wards, towns, townships, precincts, or election districts, or counties, will be made known through the Provost Marshal-General's Bureau, and account will be taken of the credits and deficiencies on former quotas.
The 15th day of April, 1864, is designated as the time up to which the numbers required from each ward of a city, town, etc., may be raised by voluntary enlistment, and drafts will be made in each ward of a city, town, etc., which shall not have filled the quota assigned to it within the time designated for the number required to fill said quotas. The drafts will be commenced as soon after the 15th of April as practicable.
The Government bounties as now paid continue until April I, 1864, at which time the additional bounties cease. On and after that date one hundred dollars bounty only will be paid, as provided by the act approved July 22, 1861.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, March 15, 1864
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, Nashville, Tenn.:
General McPherson having been assigned to the command of a department, could not General Frank Blair, without difficulty or detriment to the service, be assigned to command the Corps he commanded a while last autumn?
WHOM IT MAY CONCERN
Major-General Sickles is making a tour for me from here by way of Cairo, New Orleans, and returning by the gulf, and ocean, and all land and naval officers and, employees are directed to furnish reasonable transportation and other reasonable facilities to himself and personal staff not inconsistent with the public service.
HIS EXCELLENCY MICHAEL HAHN, Governor of Louisiana
Until further order, you are hereby invested with the powers exercised hitherto by the military governor of Louisiana.
Yours truly,
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:
I appear to say but a word. This extraordinary war in which we are engaged falls heavily upon all classes of people but the most heavily upon the soldier. For it has been said, "All that a man hath will he give for his life;" and while all contribute of their substance, the soldier puts his life at stake, and often yields it up in his country's cause. The highest merit, then, is due to the soldier.
In this extraordinary war, extraordinary developments have manifested themselves, such as have not been seen in former wars; and among these manifestations nothing has been more remarkable than these fairs for the relief of suffering soldiers and their families. And the chief agents of these fairs are the women of America.
I am not accustomed to the use of language of eulogy: I have never studied the art of paying compliments to women; but I must say, that if all that has been said by orators and poets since the creation of the world in praise of women were applied to the women of America, it would not do them justice for their conduct during this war. I will close by saying, God bless the women of America.
GENTLEMEN OF THE COMMITTEE:
The honorary membership in your association, as generously tendered, is gratefully accepted.
You comprehend, as your address shows, that the existing rebellion means more and tends to do more than the perpetuation of African slavery—that it is, in fact, a war upon the rights of all working people. Partly to show that this view has not escaped my attention, and partly that I cannot better express myself, I read a passage from the message to Congress in December, 1861:
"It continues to develop that the insurrection is largely, if not exclusively, a war upon the first principle of popular government, the rights of the people. Conclusive evidence of this is found in the most grave and maturely considered public documents, as well as in the General tone of the insurgents. In those documents we find the abridgment of the existing right of suffrage, and the denial to the people of all right to participate in the selection of public officers, except the legislature, boldly advocated, with labored argument to prove that large control of the people in government is the source of all political evil. Monarchy itself is sometimes hinted at as a possible refuge from the power of the people. In my present position I could scarcely be justified were I to omit raising a warning voice against this approach of returning despotism.
"It is not needed, nor fitting here, that a General argument should be made in favor of popular institutions; but there is one point, with its connections, not so hackneyed as most others, to which I ask a brief attention. It is the effort to place capital on an equal footing, if not above labor, in the structure of government. It is assumed that labor is available only in connection with capital; that nobody labors unless somebody else, owning capital, somehow by the use of it induces him to labor. This assumed, it is next considered whether it is best that capital shall hire laborers, and thus induce them to work by their own consent or buy them, and drive them to it without their consent. Having proceeded so it is naturally concluded that all laborers are either hired laborers, or what we call slaves. And, further, it is assumed that whoever is once a hired laborer, is fixed in that condition for life. Now there is no such relation between capital and labor as assumed, nor is there any such thing as a free man being fixed for life in the condition of a hired laborer. Both these assumptions are false, and all inferences from them are groundless.
"Labor is prior to, and independent of, capital. Capital is only the fruit of labor, and could never have existed if labor had not first existed. Labor is the superior of capital, and deserves much the higher consideration. Capital has its rights, which are as worthy of protection as any other rights. Nor is it denied that there is, and probably always will be, a relation between capital and labor, producing mutual benefits. The error is in assuming that the whole labor of a community exists within that relation. A few men own capital, and that few avoid labor themselves, and, with their capital, hire or buy another few to labor for them. A large majority belong to neither class—neither work for others, nor have others working for them. In most of the Southern States, a majority of the whole people, of all colors, are neither slaves nor masters; while in the Northern, a large majority are neither hirers nor hired. Men with their families, wives, sons, and daughters—work for themselves, on their farms, in their houses, and in their shops, taking the whole product to themselves, and asking no favors of capital on the one hand, nor of hired laborers or slaves on the other. It is not forgotten that a considerable number of persons mingle their own labor with capital; that is, they labor with their own hands, and also buy or hire others to labor for them, but this is only a mixed and not a distinct class. No principle stated is disturbed by the existence of this mixed class.
"Again, as has already been said, there is not, of necessity, any such thing as the free hired laborer being fixed to that condition for life. Many independent men everywhere in these States, a few years back in their lives, were hired laborers. The prudent penniless beginner in the world labors for wages a while, saves a surplus with which to buy tools or land for himself, then labors on his own account another while, and at length hires another new beginner to help him. This is the just and generous and prosperous system which opens the way to all—gives hope to all, and consequent energy and progress, and improvement of condition to all. No men living are more worthy to be trusted than those who toil up from poverty—none less inclined to touch or take aught which they have not honestly earned. Let them beware of surrendering a political power they already possess, and which, if surrendered, will surely be used to close the door of advancement against such as they, and to fix new disabilities and burdens upon them, till all of liberty shall be lost."
The views then expressed remain unchanged, nor have I much to add. None are so deeply interested to resist the present rebellion as the working people. Let them beware of prejudices, working division and hostility among themselves. The most notable feature of a disturbance in your city last summer was the hanging of some working people by other working people. It should never be so. The strongest bond of human sympathy, outside of the family relation, should be one uniting all working people, of all nations, and tongues, and kindreds. Nor should this lead to a war upon property, or the owners of property. Property is the fruit of labor; property is desirable; is a positive good in the world. That some should be rich shows that others may become rich, and, hence, is just encouragement to industry and enterprise. Let not him who is houseless pull down the house of another, but let him labor diligently and build one for himself, thus by example assuring that his own shall be safe from violence when built.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Hon. W. R. Morrison says he has requested you by letter to effect a special exchange of Lieut. Col. A. F. Rogers, of Eightieth Illinois Volunteers, now in Libby Prison, and I shall be glad if you can effect it.
WASHINGTON, March 13, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL SCHURZ.
MY DEAR SIR:—Yours of February 29 reached me only four days ago; but the delay was of little consequence, because I found, on feeling around, I could not invite you here without a difficulty which at least would be unpleasant, and perhaps would be detrimental to the public service. Allow me to suggest that if you wish to remain in the military service, it is very dangerous for you to get temporarily out of it; because, with a major-general once out, it is next to impossible for even the President to get him in again. With my appreciation of your ability and correct principle, of course I would be very glad to have your service for the country in the approaching political canvass; but I fear we cannot properly have it without separating you from the military.
Yours truly,
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas, it has become necessary to define the cases in which insurgent enemies are entitled to the benefits of the Proclamation of the President of the United States, which was made on the 8th day of December, 1863, and the manner in which they shall proceed to avail themselves of these benefits; and whereas the objects of that Proclamation were to suppress the insurrection and to restore the authority of the United States; and whereas the amnesty therein proposed by the President was offered with reference to these objects alone:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby proclaim and declare that the said Proclamation does not apply to the cases of persons who, at the time when they seek to obtain the benefits thereof by taking the oath thereby prescribed, are in military, naval, or civil confinement or custody, or under bonds, or on parole of the civil, military, or naval authorities, or agents of the United States, as prisoners of war, or persons detained for offences of any kind, either before or after conviction; and that on the contrary it does apply only to those persons who, being yet at large, and free from any arrest, confinement, or duress, shall voluntarily come forward and take the said oath, with the purpose of restoring peace, and establishing the national authority.
Persons excluded from the amnesty offered in the said Proclamation may apply to the President for clemency, like all other offenders, and their application will receive due consideration.
I do further declare and proclaim that the oath presented in the aforesaid proclamation of the 8th of December, 1863, may be taken and subscribed before any commissioned officer, civil, military, or naval, in the service of the United States, or any civil or military officer of a State or Territory not in insurrection, who, by the laws thereof, may be qualified for administering oaths.
All officers who receive such oaths are hereby authorized to give certificates thereof to the persons respectively by whom they are made, and such officers are hereby required to transmit the original records of such oaths, at as early a day as may be convenient, to the Department of State, where they will be deposited, and remain in the archives of the Government.
The Secretary of State will keep a registry thereof, and will, on application, in proper cases, issue certificates of such records in the customary form of official certificates.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed............
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR.
MY DEAR SIR:—The Governor of Kentucky is here, and desires to have the following points definitely fixed:
First. That the quotas of troops furnished, and to be furnished, by Kentucky may be adjusted upon the basis as actually reduced by able-bodied men of hers having gone into the rebel service; and that she be required to furnish no more than her just quotas upon fair adjustment upon such basis.
Second. To whatever extent the enlistment and drafting, one or both, of colored troops may be found necessary within the State, it may be conducted within the law of Congress; and, so far as practicable, free from collateral embarrassments, disorders, and provocations.
I think these requests of the Governor are reasonable; and I shall be obliged if you will give him a full hearing, and do the best you can to effect these objects.
Yours very truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE.
MY DEAR SIR:—Your letter to Colonel Townsend, inclosing a slip from the "Herald," and asking a court of inquiry, has been laid before me by the Secretary of War, with the request that I would consider it. It is quite natural that you should feel some sensibility on the subject; yet I am not impressed, nor do I think the country is impressed, with the belief that your honor demands, or the public interest demands, such an inquiry. The country knows that at all events you have done good service; and I believe it agrees with me that it is much better for you to be engaged in trying to do more, than to be diverted, as you necessarily would be, by a court of inquiry.
Yours truly,
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, Army of the Potomac:
Captain Kinney, of whom I spoke to you as desiring to go on your staff, is now in your camp, in company with Mrs. Senator Dixon. Mrs. Grant and I, and some others, agreed last night that I should, by this despatch, kindly call your attention to Captain Kinney.
A. G. HODGES, ESQ., Frankfort, Kentucky:
MY DEAR SIR:—You ask me to put in writing the substance of what I verbally said the other day, in your presence, to Governor Bramlette and Senator Dixon. It was about as follows:
"I am naturally anti-slavery. If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong. I cannot remember when I did not so think and feel, and yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act officially upon this judgment and feeling. It was in the oath I took that I would to the best of my ability preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution of the United States. I could not take the office without taking the oath. Nor was it my view that I might take an oath to get power, and break the oath in using the power. I understood, too, that in ordinary civil administration this oath even forbade me to practically indulge my primary abstract judgment on the moral question of slavery. I had publicly declared this many times, and in many ways. And I aver that, to this day, I have done no official act in mere deference to my abstract judgment and feeling on slavery. I did understand, however, that my oath to preserve the Constitution to the best of my ability, imposed upon me the duty of preserving, by every indispensable means, that government, that nation, of which that Constitution was the organic law. Was it possible to lose the nation and yet preserve the Constitution? By General law, life and limb must be protected; yet often a limb must be amputated to save a life; but a life is never wisely given to save a limb. I felt that measures, otherwise unconstitutional, might become lawful, by becoming indispensable to the preservation of the Constitution, through the preservation of the nation. Right or wrong, I assumed this ground, and now avow it. I could not feel that to the best of my ability I had even tried to preserve the Constitution, if, to save slavery, or any minor matter, I should permit the wreck of government, country, and Constitution, altogether. When, early in the war, General Fremont attempted military emancipation, I forbade it, because I did not then think it an indispensable necessity. When, a little later, General Cameron, then Secretary of War, suggested the arming of the blacks, I objected, because I did not yet think it an indispensable necessity. When, still later, General Hunter attempted military emancipation, I again forbade it, because I did not yet think the indispensable necessity had come. When, in March, and May, and July, 1862, I made earnest and successive appeals to the Border States to favor compensated emancipation, I believed the indispensable necessity for military emancipation and arming the blacks would come, unless averted by that measure. They declined the proposition, and I was, in my best judgment, driven to the alternative of either surrendering the Union, and with it the Constitution, or of laying strong hand upon the colored element. I chose the latter. In choosing it, I hoped for greater gain than loss, but of this I was not entirely confident. More than a year of trial now shows no loss by it in our foreign relations, none in our home popular sentiment, none in our white military force, no loss by it any how, or anywhere. On the contrary, it shows a gain of quite one hundred and thirty thousand soldiers, seamen, and laborers. These are palpable facts, about which, as facts, there can be no caviling. We have the men; and we could not have had them without the measure.
"And now let any Union man who complains of the measure test himself by writing down in one line that he is for subduing the rebellion by force of arms; and in the next, that he is for taking these hundred and thirty thousand men from the Union side, and placing them where they would be but for the measure he condemns. If he cannot face his case so stated, it is only because he cannot face the truth."
I add a word which was not in the verbal conversation. In telling this tale I attempt no compliment to my own sagacity. I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me. Now, at the end of three years' struggle, the nation's condition is not what either party, or any man, devised or expected. God alone can claim it. Whither it is tending seems plain. If God now wills the removal of a great wrong, and wills also that we of the North, as well as you of the South, shall pay fairly for our complicity in that wrong, impartial history will find therein new cause to attest and revere the justice and goodness of God.
Yours truly,
MRS HORACE MANN:
MADAM:—The petition of persons under eighteen, praying that I would free all slave children, and the heading of which petition it appears you wrote, was handed me a few days since by Senator Sumner. Please tell these little people I am very glad their young hearts are so full of just and generous sympathy, and that, while I have not the power to grant all they ask, I trust they will remember that God has, and that, as it seems, he wills to do it.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
I am pressed to get from Libby, by special exchange, Jacob C. Hagenbuek, first lieutenant, Company H, Sixty-seventh Pennsylvania Volunteers. Please do it if you can without detriment or embarrassment.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of the Potomac:
Private William Collins of Company B, of the Sixty-ninth New York Volunteers, has been convicted of desertion, and execution suspended as in numerous other cases. Now Captain O'Neill, commanding the regiment, and nearly all its other regimental and company officers, petition for his full pardon and restoration to his company. Is there any good objection?
APRIL 18, 1864.
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN:—Calling to mind that we are in Baltimore, we cannot fail to note that the world moves. Looking upon these many people assembled here to serve, as they best may, the soldiers of the Union, it occurs at once that three years ago the same soldiers could not so much as pass through Baltimore. The change from then till now is both great and gratifying. Blessings on the brave men who have wrought the change, and the fair women who strive to reward them for it!
But Baltimore suggests more than could happen within Baltimore. The change within Baltimore is part only of a far wider change. When the war began, three years ago, neither party, nor any man, expected it would last till now. Each looked for the end, in some way, long ere to-day. Neither did any anticipate that domestic slavery would be much affected by the war. But here we are; the war has not ended, and slavery has been much affected how much needs not now to be recounted. So true is it that man proposes and God disposes.
But we can see the past, though we may not claim to have directed it; and seeing it, in this case, we feel more hopeful and confident for the future.
The world has never had a good definition of the word liberty, and the American people, just now, are much in want of one. We all declare for liberty; but in using the same word we do not all mean the same thing. With some the word liberty may mean for each man to do as he pleases with himself, and the product of his labor; while with others the same word may mean for some men to do as they please with other men, and the product of other men's labor. Here are two, not only different, but incompatible things, called by the same name, liberty. And it follows that each of the things is, by the respective parties, called by two different and incompatible names—liberty and tyranny.
The shepherd drives the wolf from the sheep's throat, for which the sheep thanks the shepherd as his liberator, while the wolf denounces him for the same act, as the destroyer of liberty, especially as the sheep was a black one. Plainly, the sheep and the wolf are not agreed upon a definition of the word liberty; and precisely the same difference prevails to-day among us human creatures, even in the North, and all professing to love liberty. Hence we behold the process by which thousands are daily passing from under the yoke of bondage hailed by some as the advance of liberty, and bewailed by others as the destruction of all liberty. Recently, as it seems, the people of Maryland have been doing something to define liberty, and thanks to them that, in what they have done, the wolf's dictionary has been repudiated.
It is not very becoming for one in my position to make speeches at length; but there is another subject upon which I feel that I ought to say a word. A painful rumor, true, I fear, has reached us, of the massacre, by the rebel forces at Fort Pillow, in the west end of Tennessee, on the Mississippi River, of some three hundred colored soldiers and white officers [I believe it latter turned out to be 500], who had just been overpowered by their assailants [numbering 5000]. There seems to be some anxiety in the public mind whether the Government is doing its duty to the colored soldier, and to the service, at this point. At the beginning of the war, and for some time, the use of colored troops was not contemplated; and how the change of purpose was wrought I will not now take time to explain. Upon a clear conviction of duty I resolved to turn that element of strength to account; and I am responsible for it to the American people, to the Christian world, to history, and in my final account to God. Having determined to use the negro as a soldier, there is no way but to give him all the protection given to any other soldier. The difficulty is not in stating the principle, but in practically applying it. It is a mistake to suppose the Government is indifferent to this matter, or is not doing the best it can in regard to it. We do not to-day know that a colored soldier, or white officer commanding colored soldiers, has been massacred by the rebels when made a prisoner. We fear it, we believe it, I may say,—but we do not know it. To take the life of one of their prisoners on the assumption that they murder ours, when it is short of certainty that they do murder ours, might be too serious, too cruel, a mistake. We are having the Fort Pillow affair thoroughly investigated; and such investigation will probably show conclusively how the truth is. If after all that has been said it shall turn out that there has been no massacre at Fort Pillow, it will be almost safe to say there has been none, and will be none, elsewhere. If there has been the massacre of three hundred there, or even the tenth part of three hundred, it will be conclusively proved; and being so proved, the retribution shall as surely come. It will be matter of grave consideration in what exact course to apply the retribution; but in the supposed case it must come.
[There was a massacre of a black company and their officers at Fort Pillow—they were prisoners who later on, the day of their capture, were ordered executed. The black soldiers were tied alive to individual planks—then man and plank were cobbled up like cord wood and burned. The white officers were shot. D.W.]
CALVIN TRUESDALE, ESQ., Postmaster, Rock Island, Ill.:
Thomas J. Pickett, late agent of the Quartermaster 's Department for the island of Rock Island, has been removed or suspended from that position on a charge of having sold timber and stone from the island for his private benefit. Mr. Pickett is an old acquaintance and friend of mine, and I will thank you, if you will, to set a day or days and place on and at which to take testimony on the point. Notify Mr. Pickett and one J. B. Danforth (who, as I understand, makes the charge) to be present with their witnesses. Take the testimony in writing offered by both sides, and report it in full to me. Please do this for me.
Yours truly,
OFFICER IN MILITARY COMMAND, Fort Warren, Boston Harbor, Mass.:
If there is a man by the name of Charles Carpenter, under sentence of death for desertion, at Fort Warren, suspend execution until further order and send the record of his trial. If sentenced for any other offence, telegraph what it is and when he is to be executed. Answer at all events.
OFFICER IN COMMAND AT FORT WARREN, Boston Harbor, Mass.:
The order I sent yesterday in regard to Charles Carpenter is hereby withdrawn and you are to act as if it never existed.
MAJOR-GENERAL Dix, New York:
Yesterday I was induced to telegraph the officer in military command at Fort Warren, Boston Harbor, Massachusetts, suspending the execution of Charles Carpenter, to be executed tomorrow for desertion. Just now, on reaching your order in the case, I telegraphed the same officer withdrawing the suspension, and leave the case entirely with you. The man's friends are pressing me, but I refer them to you, intending to take no further action myself.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Senator Ten Eyck is very anxious to have a special exchange of Capt. Frank J. McLean, of Ninth Tennessee Cavalry now, or lately, at Johnson's Island, for Capt. T. Ten Eyck, Eighteenth U. S. Infantry, and now at Richmond. I would like to have it done. Can it be?
1. The Governors of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, and Wisconsin offer to the President infantry troops for the approaching campaign as follows: Ohio, thirty thousand; Indiana, twenty thousand; Illinois, twenty thousand; Iowa, ten thousand; Wisconsin, five thousand.
2. The term of service to be one hundred days, reckoned from the date of muster into the service of the United States, unless sooner discharged.
3. The troops to be mustered into the service of the United States by regiments, when the regiments are filled up, according to regulations, to the minimum strength—the regiments to be organized according to the regulations of the War Department. The whole number to be furnished within twenty days from date of notice of the acceptance of this proposition.
4. The troops to be clothed, armed, equipped, subsisted; transported, and paid as other United States infantry volunteers, and to serve in fortifications,—or wherever their services may be required, within or without their respective States.
5. No bounty to be paid the troops, nor the service charged or credited on any draft.
6. The draft for three years' service to go on in any State or district where the quota is not filled up; but if any officer or soldier in this special service should be drafted, he shall be credited for the service rendered.
JOHN BROUGH, Governor of Ohio. O. P. MORTON, Governor of Indiana. RICHARD PATES, Governor of Illinois. WILLIAM M. STONE, Governor of Iowa. JAMES T. LEWIS, Governor of Wisconsin
(Indorsement.)
April 23, 1864.
The foregoing proposition of the governors is accepted, and the Secretary of War is directed to carry it into execution.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR:
MY DEAR SIR:—According to our understanding with Major-General Frank P. Blair at the time he took his seat in Congress last winter, he now asks to withdraw his resignation as Major-General, then tendered, and be sent to the field. Let this be done. Let the order sending him be such as shown me to-day by the Adjutant-General, only dropping from it the names of Maguire and Tompkins.
Yours truly,
JOHN WILLIAMS, Springfield, Ill.:
Yours of the 15th is just received. Thanks for your kind remembrance. I would accept your offer at once, were it not that I fear there might be some impropriety in it, though I do not see that there would. I will think of it a while.
MAJOR-GENERAL MEADE, Army of Potomac:
A Mr. Corby brought you a note from me at the foot of a petition I believe, in the case of Dawson, to be executed to-day. The record has been examined here, and it shows too strong a case for a pardon or commutation, unless there is something in the poor man's favor outside of the record, which you on the ground may know, but I do not. My note to you only means that if you know of any such thing rendering a suspension of the execution proper, on your own judgment, you are at liberty to suspend it. Otherwise I do not interfere.
MAJOR-GENERAL THOMAS, Chattanooga, Term.:
Suspend execution of death sentence of young Perry, of Wisconsin, condemned for sleeping on his post, till further orders, and forward record for examination.
GOVERNOR MURPHY, Little Rock, Arkansas:
I am much gratified to learn that you got out so large a vote, so nearly all the right way, at the late election; and not less so that your State government including the legislature, is organized and in good working order. Whatever I can I will do to protect you; meanwhile you must do your utmost to protect yourselves. Present my greeting to all.
I have the honor to transmit herewith an address to the President of the United States, and through him to both Houses of Congress, on the condition and wants of the people of east Tennessee, and asking their attention to the necessity of some action on the part of the Government for their relief, and which address is presented by a committee of an organization called "The East Tennessee Relief Association."
Deeply commiserating the condition of these most loyal and suffering people, I am unprepared to make any specific recommendation for their relief. The military is doing and will continue to do the best for them within its power. Their address represents that the construction of direct railroad communication between Knoxville and Cincinnati by way of central Kentucky would be of great consequence in the present emergency. It may be remembered that in the annual message of December, 1861, such railroad construction was recommended. I now add that, with the hearty concurrence of Congress, I would yet be pleased to construct a road, both for the relief of these people and for its continuing military importance.
TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In obedience to the resolution of your honorable body, a copy of which is herewith returned, I have the honor to make the following brief statement, which is believed to contain the information sought:
Prior to and at the meeting of the present Congress, Robert C. Schenck, of Ohio, and Frank P. Blair, Jr., of Missouri, members elect thereto, by and with the consent of the Senate held commissions from the Executive as major-generals in the volunteer army. General Schenck tendered the resignation of his said commission, and took his seat in the House of Representatives, at the assembling thereof, upon the distinct verbal understanding with the Secretary of War and the Executive that he might, at any time during the session, at his own pleasure, withdraw said resignation and return to the field.
General Blair was, by temporary assignment of General Sherman, in command of a corps through the battles in front of Chattanooga, and in the march to the relief of Knoxville, which occurred in the latter days of November and early days of December last, and of course was not present at the assembling of Congress. When he subsequently arrived here, he sought, and was allowed by the Secretary of War and the Executive, the same conditions and promise as allowed and made to General Schenck.
General Schenck has not applied to withdraw his resignation; but when General Grant was made Lieutenant-General, producing some change of commanders, General Blair sought to be assigned to the command of a corps. This was made known to Generals Grant and Sherman, and assented to by them, and the particular corps for him designated.
This was all arranged and understood, as now remembered, so much as a month ago; but the formal withdrawal of General Blair's resignation, and making the order assigning him to the command of the corps, were not consummated at the War Department until last week, perhaps on the 23d of April instant. As a summary of the whole, it may be stated that General Blair holds no military commission or appointment other than as herein stated, and that it is believed he is now acting as major-General upon the assumed validity of the commission herein stated, in connection with the facts herein stated, and not otherwise. There are some letters, notes, telegrams, orders, entries, and perhaps other documents in connection with this subject, which it is believed would throw no additional light upon it, but which will be cheerfully furnished if desired.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Not expecting to see you before the spring campaign opens, I wish to express in this way my entire satisfaction with what you have done up to this time, so far as I understand it.
The particulars of your plans I neither know nor seek to know. You are vigilant and self-reliant; and, pleased with this, I wish not to obtrude any restraints or constraints upon you. While I am very anxious that any great disaster or capture of our men in great number shall be avoided, I know that these points are less likely to escape your attention than they would be mine. If there be anything wanting which is within my power to give, do not fail to let me know it.
And now, with a brave army and a just cause, may God sustain you.
Yours very truly,
TO THE HONORABLE THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In compliance with the request contained in your resolution of the 29th ultimo, a copy of which resolution is herewith returned, I have the honor to transmit the following:
[Correspondence and orders relating to the resignation and reinstatement of Major-General Frank P. Blair, Jr., of Missouri.]
The foregoing constitutes all sought by the resolution so far as is remembered or has been found upon diligent search.
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERMAN, Chattanooga, Tenn.:
I have an imploring appeal in behalf of the citizens who say your Order No.8 will compel them to go north of Nashville. This is in no sense an order, nor is it even a request that you will do anything which in the least shall be a drawback upon your military operations, but anything you can do consistently with those operations for those suffering people I shall be glad of.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Commanding, Saint Louis, Mo.:
The President directs me to inquire whether a day has yet been fixed for the execution of citizen Robert Louden, and if so what day?
JOHN HAY, Major and Assistant Adjutant-General.
MRS. SARAH B. McCONKEY, West Chester, Pa.:
MADAM:—Our mutual friend, Judge Lewis, tells me you do me the honor to inquire for my personal welfare. I have been very anxious for some days in regard to our armies in the field, but am considerably cheered, just now, by favorable news from them.
I am sure you will join me in the hope for their further success; while yourself, and other good mothers, wives, sisters, and daughters, do all you and they can, to relieve and comfort the gallant soldiers who compose them.
Yours truly,
TO THE FRIENDS OF UNION AND LIBERTY:
Enough is known of army operations, within the last five days, to claim our special gratitude to God. While what remains undone demands our most sincere prayers to and reliance upon Him (without whom all effort is vain), I recommend that all patriots at their homes, in their places of public worship, and wherever they may be, unite in common thanksgiving and prayer to Almighty God.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I am very much obliged to you for the compliment of this call, though I apprehend it is owing more to the good news received to-day from the Army, than to a desire to see me. I am indeed very grateful to the brave men who have been struggling with the enemy in the field, to their noble commanders who have directed them, and especially to our Maker. Our commanders are following up their victories resolutely and successfully. I think, without knowing the particulars of the plans of General Grant, that what has been accomplished is of more importance than at first appears. I believe, I know (and am especially grateful to know) that General Grant has not been jostled in his purposes, that he has made all his points, and to-day he is on his line as he purposed before he moved his armies. I will volunteer to say that I am very glad at what has happened, but there is a great deal still to be done. While we are grateful to all the brave men and officers for the events of the past few days, we should, above all, be very grateful to Almighty God, who gives us victory.
There is enough yet before us requiring all loyal men and patriots to perform their share of the labor and follow the example of the modest General at the head of our armies, and sink all personal consideration for the sake of the country. I commend you to keep yourselves in the same tranquil mood that is characteristic of that brave and loyal man. I have said more than I expected when I came before you. Repeating my thanks for this call, I bid you good-bye.
MAJOR-GENERAL WALLACE, Baltimore:
Please tell me what is the trouble with Dr. Hawks. Also please ask Bishop Whittington to give me his view of the case.
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, St. Louis, Missouri:
Complaints are coming to me of disturbances in Canoll, Platte, and Buchanan counties. Please ascertain the truth, correct what is found wrong, and telegraph me.
F. B. LOOMIS, ESQ.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have the honor to acknowledge the receipt of your communication of the 28th April, in which you offer to replace the present garrison at Port Trumbull with volunteers, which you propose to raise at your own expense. While it seems inexpedient at this time to accept this proposition on account of the special duties now devolving upon the garrison mentioned, I cannot pass unnoticed such a meritorious instance of individual patriotism. Permit me, for the Government, to express my cordial thanks to you for this generous and public-spirited offer, which is worthy of note among the many called forth in these times of national trial.
I am very truly, your obedient servant,
GENTLEMEN:-In response to your address, allow me to attest the accuracy of its historical statements, indorse the sentiments it expresses, and thank you in the nation's name for the sure promise it gives. Nobly sustained, as the Government has been, by all the churches, I would utter nothing which might in the least appear invidious against any. Yet without this, it may fairly be said, that the Methodist Episcopal Church, not less devoted than the best, is by its greatest numbers the most important of all. It is no fault in others that the Methodist Church sends more soldiers to the field, more nurses to the hospitals, and more prayers to Heaven than—any other. God bless the Methodist Church Bless all the churches; and blessed be God, who in this our great trial giveth us the churches.
If any such proclamation has appeared, it is a forgery.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, May 18, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL JOHN A. DIX, Commanding at New York:
Whereas there has been wickedly and traitorously printed and published this morning in the New York World and New York Journal of Commerce, newspapers printed and published in the city of New York, a false and spurious proclamation purporting to be signed by the President and to be countersigned by the Secretary of State, which publication is of a treasonable nature, designed to give aid and comfort to the enemies of the United States and to the rebels now at war against the Government and their aiders and abettors, you are therefore hereby commanded forthwith to arrest and imprison in any fort or military prison in your command, the editors, proprietors, and publishers of the aforesaid newspapers, and all such persons as, after public notice has been given of the falsehood of said publication, print and publish the same with intent to give aid and comfort to the enemy; and you will hold the persons so arrested in close custody until they can be brought to trial before a military commission for their offense. You will also take possession by military force of the printing establishments of the New York World and Journal of Commerce, and hold the same until further orders, and prohibit any further publication therefrom.
A. LINCOLN.
[On the morning of May 18, 3864, a forged proclamation was published in the World, and Journal of Commerce, of New York. The proclamation named a day for fasting and prayer, called for 400,000 fresh troops, and purposed to raise by an "immediate and peremptory draft," whatever quotas were not furnished on the day specified. Ed.]
WASHINGTON, D. C., May 18, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Bermuda Hundred, Va.:
Until receiving your dispatch of yesterday, the idea of commissions in the volunteers expiring at the end of three years had not occurred to me. I think no trouble will come of it; and, at all events, I shall take care of it so far as in me lies. As to the major-generalships in the regular army, I think I shall not dispose of another, at least until the combined operations now in progress, under direction of General Grant, and within which yourself and command are included, shall be terminated.
Meanwhile, on behalf of yourself, officers, and men, please accept my hearty thanks for what you and they have so far done.
It is officially announced by the State Department that citizens of the United States holding commissions and recognized as Consuls of foreign powers, are not by law exempt from military service if drafted:
Therefore the mere enrolment of a citizen holding a foreign consulate will not be held to vacate his commission, but if he shall be drafted his exequatur will be revoked unless he shall have previously resigned in order that another Consul may be received.
An exequatur bearing date the 3d day of May, 1858, having been issued to Charles Hunt, a citizen of the United States, recognizing him as a Consul of Belgium for St. Louis, Missouri, and declaring him free to exercise and enjoy such functions, powers, and privileges as are allowed to the Consuls of the most favored nations in the United States, and the said Hunt having sought to screen himself from his military duty to his country, in consequence of thus being invested with the consular functions of a foreign power in the United States, it is deemed advisable that the said Charles Hunt should no longer be permitted to continue in the exercise of said functions, powers, and privileges.
These are therefore to declare that I no longer recognize the said Hunt as Consul of Belgium, for St. Louis, Missouri, and will not permit him to exercise or enjoy any of the functions, powers or privileges allowed to consuls of that nation, and that I do hereby wholly revoke and annul the said exequatur heretofore given, and do declare the same to be absolutely null and void from this day forward.
In testimony whereof, I have caused these letters to be made patent, and the seal of the United States of America to be hereunto affixed................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
The getting forward of hundred-day troops to sustain General Sherman's lengthening lines promises much good. Please put your best efforts into the work.
A. LINCOLN.
Same to Governor Yates, Springfield, Illinois; Governor Stone, Davenport, Iowa; Governor Lewis, Madison, Wisconsin.
1864
CHRISTIANA A. SACK, Baltimore, Md.:
I cannot postpone the execution of a convicted spy on a mere telegraphic despatch signed with a name I never heard before. General Wallace may give you a pass to see him if he chooses.
Yours to Secretary of War [received] asking for something cheering. We have nothing bad from anywhere. I have just seen a despatch of Grant, of 11 P.M., May 23, on the North Anna and partly across it, which ends as follows: "Everything looks exceedingly favorable for us." We have nothing later from him.
Mr. J. C. Swift wishes a pass from me to follow your army to pick up rags and cast-off clothing. I will give it to him if you say so, otherwise not.
A. LINCOLN.
["No job to big or too small" for this president—not even a request from a Rag Picker. D.W.]
WHOM IT MAY CONCERN:
I am again pressed with the claim of Mr. Marshall O. Roberts, for transportation of what was called the Naval Brigade from New York to Fortress Monroe. This force was a special organization got up by one Bartlett, in pretended pursuance of written authority from me, but in fact, pursuing the authority in scarcely anything whatever. The credit given him by Mr. Roberts, was given in the teeth of the express declaration that the Government would not be responsible for the class of expenses to which it belonged. After all some part of the transportation became useful to the Government, and equitably should be paid for; but I have neither time nor means to ascertain this equitable amount, or any appropriation to pay it with if ascertained. If the Quartermaster at New York can ascertain what would compensate for so much of the transportation as did result usefully to the Government, it might be a step towards reaching justice. I write this from memory, but I believe it is substantially correct.
WASHINGTON, June 3, 1864.
HON. F. A. CONKLING AND OTHERS.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter, inviting me to be present at a mass meeting of loyal citizens, to be held at New York on the 4th instant, for the purpose of expressing gratitude to Lieutenant-General Grant for his signal services, was received yesterday. It is impossible for me to attend. I approve, nevertheless, of whatever may tend to strengthen and sustain General Grant and the noble armies now under his direction. My previous high estimate of General Grant has been maintained and heightened by what has occurred in the remarkable campaign he is now conducting, while the magnitude and difficulty of the task before him does not prove less than I expected. He and his brave soldiers are now in the midst of their great trial, and I trust that at your meeting you will so shape your good words that they may turn to men and guns, moving to his and their support.
Yours truly,
(Indorsement.)
Swett is unquestionably all right. Mr. Holt is a good man, but I had not heard or thought of him for Vice-President. Wish not to interfere about Vice-President. Cannot interfere about platform. Convention must judge for itself.
Private James McCarthy, of the One-hundred and fortieth New York Volunteers, is here under sentence to the Dry Tortugas for an attempt to desert. His friends appeal to me and if his colonel and you consent, I will send him to his regiment. Please answer.
Yours of to-day received. I am unable to conceive how a message can be less safe by the express than by a staff-officer. If you send a verbal message, the messenger is one additional person let into the secret.
Mr. CHAIRMAN AND GENTLEMEN OF THE COMMITTEE:
I will neither conceal my gratification nor restrain the expression of my gratitude that the Union people, through their convention, in their continued effort to save and advance the nation, have deemed me not unworthy to remain in my present position. I know no reason to doubt that I shall accept the nomination tendered; and yet perhaps I should not declare definitely before reading and considering what is called the platform. I will say now, however, I approve the declaration in favor of so amending the Constitution as to prohibit slavery throughout the nation. When the people in revolt, with a hundred days of explicit notice that they could within those days resume their allegiance without the overthrow of their institution, and that they could not so resume it afterward, elected to stand out, such amendment of the Constitution as now proposed became a fitting and necessary conclusion to the final success of the Union cause. Such alone can meet and cover all cavils. Now the unconditional Union men, North and South, perceive its importance and embrace it. In the joint names of Liberty and Union, let us labor to give it legal form and practical effect.
AND 8, 1864.
1. Resolved, That it is the highest duty of every American citizen to maintain against all their enemies the integrity of the Union and the paramount authority of the Constitution and laws of the United States; and that, laying aside all differences of political opinion, we pledge ourselves, as Union men, animated by a common sentiment and aiming at a common object, to do everything in our power to aid the Government in quelling by force of arms the rebellion now raging against its authority, and in bringing to the punishment due to their crimes the rebels and traitors arrayed against it.
2. Resolved, That we approve the determination of the Government of the United States not to compromise with rebels, or to offer them any terms of peace, except such as may be based upon an unconditional surrender of their hostility and a return to their just allegiance to the Constitution and laws of the United States, and that we call upon the Government to maintain this position, and to prosecute the war with the utmost possible vigor to the complete suppression of the rebellion, in full reliance upon the self-sacrificing patriotism, the heroic valor, and the undying devotion of the American people to their Country and its free institutions.
3. Resolved, That as slavery was the cause, and now constitutes the strength, of this rebellion, and as it must be, always and everywhere, hostile to the principles of republican government, justice and the national safety demand its utter and complete extirpation from the soil of the republic; and that while we uphold and maintain the acts and proclamations by which the Government, in its own defense, has aimed a death-blow at this gigantic evil, we are in favor, furthermore, of such an amendment to the Constitution, to be made by the people in conformity with its provisions, as shall terminate and forever prohibit the existence of slavery within the limits or the jurisdiction of the United States.
4. Resolved, That the thanks of the American people are due to the soldiers and sailors of the Army and Navy, who have periled their lives in defense of their country and in vindication of the honor of its flag; that the nation owes to them some permanent recognition of their patriotism and their valor, and ample and permanent provision for those of their survivors who have received disabling and honorable wounds in the service of the country; and that the memories of those who have fallen in its defense shall be held in grateful and everlasting remembrance.
5. Resolved, That we approve and applaud the practical wisdom, the unselfish patriotism, and the unswerving fidelity to the Constitution and the principles of American liberty, with which Abraham Lincoln has discharged under circumstances of unparalleled difficulty the great duties and responsibilities of the Presidential office; that we approve and indorse as demanded by the emergency and essential to the preservation of the nation, and as within the provisions of the Constitution, the measures and acts which he has adopted to defend the nation against its open and secret foes; that we approve, especially, the Proclamation of Emancipation, and the employment as Union soldiers of men heretofore held in slavery; and that we have full confidence in his determination to carry these and all other constitutional measures essential to the salvation of the country into full and complete effect.
6. Resolved, That we deem it essential to the General welfare that harmony should prevail in the national councils, and we regard as worthy of public confidence and official trust those only who cordially indorse the principles proclaimed in these resolutions, and which should characterize the administration of the Government.
7. Resolved, That the Government owes to all men employed in its armies, without regard to distinction of color, the full protection of the laws of war, and that any violation of these laws, or of the usages of civilized nations in time of war, by the rebels now in arms, should be made the subject of prompt and full redress.
8. Resolved, That foreign immigration, which in the past has added so much to the wealth, development of resources, and increase of power to this nation, the asylum of the oppressed of all nations, should be fostered and encouraged by a liberal and just policy.
9. Resolved, That we are in favor of the speedy construction of the railroad to the Pacific coast.
10. Resolved, That the national faith, pledged for the redemption of the public debt, must be kept inviolate, and that for this purpose we recommend economy and rigid responsibility in the public expenditures, and a vigorous and just system of taxation: and that it is the duty of every loyal State to sustain the credit and promote the use of the national currency.
11. Resolved, That we approve the position taken by the Government that the people of the United States can never regard with indifference the attempt of any European power to overthrow by force or to supplant by fraud the institutions of any republican government on the Western Continent, and that they will view with extreme jealousy, as menacing to the peace and independence of their own country, the efforts of any such power to obtain new footholds for monarchical governments, sustained by foreign military force, in near proximity to the United States.
GENTLEMEN—I can only say in response to the remarks of your chairman, that I am very grateful for the renewed confidence which has been accorded to me, both by the convention and by the National League. I am not insensible at all to the personal compliment there is in this, yet I do not allow myself to believe that any but a small portion of it is to be appropriated as a personal compliment to me. The convention and the nation, I am assured, are alike animated by a higher view of the interests of the country, for the present and the great future, and the part I am entitled to appropriate as a compliment is only that part which I may lay hold of as being the opinion of the convention and of the League, that I am not entirely unworthy to be intrusted with the place I have occupied for the last three years. I have not permitted myself, gentlemen, to conclude that I am the best man in the country; but I am reminded in this connection of a story of an old Dutch farmer, who remarked to a companion once that "it was not best to swap horses when crossing a stream."
GENTLEMEN:—I am very much obliged to you for this compliment. I have just been saying, and will repeat it, that the hardest of all speeches I have to answer is a serenade. I never know what to say on these occasions. I suppose that you have done me this kindness in connection with the action of the Baltimore convention, which has recently taken place, and with which, of course, I am very well satisfied. What we want still more than Baltimore conventions, or Presidential elections, is success under General Grant. I propose that you constantly bear in mind that the support you owe to the brave officers and soldiers in the field is of the very first importance, and we should therefore bend all our energies to that point. Now without detaining you any longer, I propose that you help me to close up what I am now saying with three rousing cheers for General Grant and the officers and soldiers under his command.
SIR:—In every light in which the State of the Hawaiian Islands can be contemplated, it is an object of profound interest for the United States. Virtually it was once a colony. It is now a near and intimate neighbor. It is a haven of shelter and refreshment for our merchants, fishermen, seamen, and other citizens, when on their lawful occasions they are navigating the eastern seas and oceans. Its people are free, and its laws, language, and religion are largely the fruit of our own teaching and example. The distinguished part which you, Mr. Minister, have acted in the history of that interesting country, is well known here. It gives me pleasure to assure you of my sincere desire to do what I can to render now your sojourn in the United States agreeable to yourself, satisfactory to your sovereign, and beneficial to the Hawaiian people.
Soldiers! I understand you have just come from Ohio; come to help us in this the nation's day of trial, and also of its hopes. I thank you for your promptness in responding to the call for troops. Your services were never needed more than now. I know not where you are going. You may stay here and take the places of those who will be sent to the front, or you may go there yourselves. Wherever you go I know you will do your best. Again I thank you. Good-by.
1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL THOMAS, Louisville, Kentucky:
Complaint is made to me that in the vicinity of Henderson, our militia is seizing negroes and carrying them off without their own consent, and according to no rules whatever, except those of absolute violence. I wish you would look into this and inform me, and see that the making soldiers of negroes is done according to the rules you are acting upon, so that unnecessary provocation and irritation be avoided.
Will try to leave here Wednesday afternoon, say at 4 P.M., remain till Thursday afternoon and then return. This subject to events.
I have just received your dispatch of 1 P.M. yesterday. I begin to see it: you will succeed. God bless you all.
I suppose that this toast is intended to open the way for me to say something. War at the best is terrible, and this of ours in its magnitude and duration is one of the most terrible the world has ever known. It has deranged business totally in many places, and perhaps in all. It has destroyed property, destroyed life, and ruined homes. It has produced a national debt and a degree of taxation unprecedented in the history of this country. It has caused mourning among us until the heavens may almost be said to be hung in black. And yet it continues. It has had accompaniments not before known in the history of the world. I mean the Sanitary and Christian Commissions, with their labors for the relief of the soldiers, and the Volunteer Refreshment Saloons, understood better by those who hear me than by myself, and these fairs, first begun at Chicago and next held in Boston, Cincinnati, and other cities. The motive and object that lie at the bottom of them are worthy of the most that we can do for the soldier who goes to fight the battles of his country. From the fair and tender hand of women is much, very much, done for the soldier, continually reminding him of the care and thought for him at home. The knowledge that he is not forgotten is grateful to his heart. Another view of these institutions is worthy of thought. They are voluntary contributions, giving proof that the national resources are not at all exhausted, and that the national patriotism will sustain us through all. It is a pertinent question, When is this war to end? I do not wish to name the day when it will end, lest the end should not come at the given time. We accepted this war, and did not begin it. We accepted it for an object, and when that object is accomplished the war will end, and I hope to God that it will never end until that object is accomplished. We are going through with our task, so far as I am concerned, if it takes us three years longer. I have not been in the habit of making predictions, but I am almost tempted now to hazard one. I will. It is, that Grant is this evening in a position, with Meade and Hancock, of Pennsylvania, whence he can never be dislodged by the enemy until Richmond is taken. If I shall discover that General Grant may be greatly facilitated in the capture of Richmond by rapidly pouring to him a large number of armed men at the briefest notice, will you go? Will you march on with him? [Cries of "Yes, yes."] Then I shall call upon you when it is necessary.
HONORABLE ATTORNEY-GENERAL.
SIR:—By authority of the Constitution, and moved thereto by the fourth section of the act of Congress, entitled "An act making appropriations for the support of the army for the year ending the thirtieth of June, eighteen hundred and sixty-five, and for other purposes, approved June is, 1864," I require your opinion in writing as to what pay, bounty, and clothing are allowed by law to persons of color who were free on the nineteenth day of April, 1861, and who have been enlisted and mustered into the military service of the United States between the month of December, 1862, and the sixteenth of June, 1864.
Please answer as you would do, on my requirement, if the act of June 15, 1864, had not been passed, and I will so use your opinion as to satisfy that act.
Your obedient servant,
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Boston, Massachusetts:
All well and very warm. Tad and I have been to General Grant's army. Returned yesterday safe and sound.
Complaint is made to me that General Brown does not do his best to suppress bushwhackers. Please ascertain and report to me.
HON. WILLIAM DENNISON AND OTHERS, a Committee of the Union National Convention.
GENTLEMEN:—Your letter of the 14th inst.., formally notifying me that I have been nominated by the convention you represent for the Presidency of the United States for four years from the 4th of March next, has been received. The nomination is gratefully accepted, as the resolutions of the convention, called the platform, are heartily approved.
While the resolution in regard to the supplanting of republican government upon the Western Continent is fully concurred in, there might be misunderstanding were I not to say that the position of the Government in relation to the action of France in Mexico, as assumed through the State Department and indorsed by the convention among the measures and acts of the Executive, will be faithfully maintained so long as the state of facts shall leave that position pertinent and applicable.
I am especially gratified that the soldier and seaman were not forgotten by the convention, as they forever must and will be remembered by the grateful country for whose salvation they devote their lives.
Thanking you for the kind and complimentary terms in which you have communicated the nomination and other proceedings of the convention, I subscribe myself,
Your obedient servant,
MAJOR-GENERAL STEELE:
I understand that Congress declines to admit to seats the persons sent as Senators and Representatives from Arkansas. These persons apprehend that, in consequence, you may not support the new State government there as you otherwise would. My wish is that you give that government and the people there the same support and protection that you would if the members had been admitted, because in no event, nor in any view of the case, can this do any harm, while it will be the best you can do toward suppressing the rebellion.
Yours truly,
Dr. Worster wishes to visit you with a view of getting your permission to introduce into the army "Harmon's Sandal Sock." Shall I give him a pass for that object?
HON. DAVID TOD, Youngstown, Ohio: I have nominated you to be Secretary of the Treasury, in place of Governor Chase, who has resigned. Please come without a moment's delay.
To JOHN L. SCRIPPS, ESQ.
DEAR SIR:—Complaint is made to me that you are using your official power to defeat Mr. Arnold's nomination to Congress. I am well satisfied with Mr. Arnold as a member of Congress, and I do not know that the man who might supplant him would be as satisfactory; but the correct principle, I think, is that all our friends should have absolute freedom of choice among our friends. My wish, therefore, is that you will do just as you think fit with your own suffrage in the case, and not constrain any of your subordinates to [do] other than [as] he thinks fit with his. This is precisely the rule I inculcated and adhered to on my part, when a certain other nomination, now recently made, was being canvassed for.
Yours very truly,
A. LINCOLN.
TELEGRAM TO J. W. GARRETT. WASHINGTON, July 5, 1864.
J. W. GARRETT, President [B. & 0. R. R.], Camden Station:
You say telegraphic communication is re-established with Sandy Hook. Well, what does Sandy Hook say about operations of enemy and of Sigel during to-day?
HIS EXCELLENCY HORATIO SEYMOUR, Governor of New York, Albany:
The President directs me to inform you that a rebel force, variously estimated at from fifteen to twenty thousand men, have invaded the State of Maryland, and have taken Martinsburg and Harper's Ferry, and are threatening other points; that the public safety requires him to call upon the State executives for a militia force to repel this invasion. He therefore directs me to call on you for a militia force of twelve thousand men from your State to serve not more than one hundred days, and to request that you will with the utmost despatch forward the troops to Washington by rail or steamboat as may be most expeditious.
Please favor me with an answer at your earliest convenience.
EDWIN M. STANTON,
Secretary of War.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES:
A Proclamation.
Whereas, by a proclamation which was issued on the 15th day of April, 1861, the President of the United States announced and declared that the laws of the United States had been for some time past, and then were, opposed and the execution thereof obstructed in certain States therein mentioned, by combinations too powerful to be suppressed by the ordinary course of judicial proceedings or by the power vested in the marshals by law; and
Whereas, immediately after the issuing of the said proclamation the land and naval forces of the United States were put into activity to suppress the said insurrections and rebellion; and
Whereas, the Congress of the United States, by an act approved on the third day of March, 1863, did enact that during the said rebellion the President of the United States, whenever in his judgment the public safety may require it, is authorized to suspend the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus in any case throughout the United States, or any part thereof; and
Whereas, the said insurrection and rebellion still continue, endangering the existence of the Constitution and Government of the United States; and
Whereas, the military forces of the United States are now actively engaged in suppressing the said insurrection and rebellion in various parts of the States where the said rebellion has been successful in obstructing the laws and public authorities, especially in the States of Virginia and Georgia; and
Whereas, on the fifteenth day of September last, the President of the United States duly issued his proclamation, wherein he declared that the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus should be suspended throughout the United States, in Cases whereby the authority of the President of the United States, the military, naval, and civil officers of the United States, or any of them, hold persons under their command or in their custody, either as prisoners of war, spies, or aiders or abettors of the enemy, or officers, soldiers, or seamen enrolled or drafted, or mustered, or enlisted in, or belonging to the land or naval forces of the United States, or as deserters therefrom, or otherwise amenable to military law, or the rules and articles of war, or the rules and regulations prescribed for the military and naval service by authority of the President of the United States, or for resisting a draft, or for any other offence against the military or naval service; and
Whereas, many citizens of the State of Kentucky have joined the forces of the insurgents, who have on several occasions entered the said State of Kentucky in large force and not without aid and comfort furnished by disaffected and disloyal citizens of the United States residing therein, have not only greatly disturbed the public peace but have overborne the civil authorities and made flagrant civil war, destroying property and life in various parts of the State; and
Whereas, it has been made known to the President of the United States, by the officers commanding the National armies, that combinations have been formed in the said State of Kentucky, with a purpose of inciting the rebel forces to renew the said operations of civil war within the said State, and thereby to embarrass the United States armies now operating in the said States of Virginia and Georgia, and even to endanger their safety.
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, by virtue of the authority vested in me by the Constitution and laws, do hereby declare that in my judgment the public safety especially requires that the suspension of the privilege of the writ of habeas corpus so proclaimed in the said proclamation of the 15th of September, 1863, be made effectual and be duly enforced in and throughout the said State of Kentucky, and that martial law be for the present declared therein. I do therefore hereby require of the military officers of the said State that the privilege of the habeas corpus be effectually suspended within the said State, according to the aforesaid proclamation, and that martial law be established therein to take effect from the date of this proclamation, the said suspension and establishment of martial law to continue until this proclamation shall be revoked or modified, but not beyond the period when the said rebellion shall have been suppressed or come to an end. And I do hereby require and command, as well as military officers, all civil officers and authorities existing or found within the said State of Kentucky, to take notice of this proclamation and to give full effect to the same. The martial laws herein proclaimed and the things in that respect herein ordered will not be deemed or taken to interfere with the holding of lawful elections, or with the proceedings of the constitutional Legislature of Kentucky, or with the administration of justice in the courts of law existing therein between citizens of the United States in suits or proceedings which do not affect the military operations or the constituted authorities of the government of the United States.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the City of Washington this 5th day of July, in the year of our Lord 1864, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-eighth.
A. LINCOLN. By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
A Proclamation.
Whereas, the Senate and House of Representatives at their last session adopted a concurrent resolution, which was approved on the second day of July instant, and which `was in the words following, namely:
That the President of the United States be requested to appoint a day of humiliation and prayer by the people of the United States, that he request his constitutional advisers at the head of the Executive Departments to unite with him, as Chief Magistrate of the nation, at the City of Washington, and the members of Congress, and all magistrates, all civil, military, and naval officers, all soldiers, sailors, and marines, with all loyal and law-abiding people, to convene at their usual places of worship, or wherever they may be, to confess and to repent of their manifold sins, to implore the compassion and forgiveness of the Almighty, that, if consistent with His will, the existing rebellion may be speedily suppressed, and the supremacy of the Constitution and laws of the United States may be established throughout all the States; to implore Him, as the Supreme Ruler of the world, not to destroy us as a people, nor suffer us to be destroyed by the hostility or connivance of other nations, or by obstinate adhesion to our own counsels which may be in conflict with His eternal, purposes, and to implore Him to enlighten the mind of the nation to know and do His will, humbly believing that it is in accordance with His will that our place should be maintained as a united people among the family of nations; to implore Him to grant to our armed defenders, and the masses of the people, that courage, power of resistance, and endurance necessary to secure that result; to implore Him in His infinite goodness to soften the hearts, enlighten the minds, and quicken the conscience of those in rebellion, that they may lay down their arms, and speedily return to their allegiance to the United States, that they may not be utterly destroyed, that the effusion of blood may be stayed, and that unity and fraternity may be restored, and peace established throughout all our borders.
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the `United States, cordially concurring with the Congress of the United States, in the penitential and pious sentiments expressed in the aforesaid resolutions, and heartily approving of the devotional design and purpose thereof, do hereby appoint the first Thursday of August next to be observed by the people of the United States as a day of national humiliation and prayer.
I do hereby further invite and request the heads of the Executive Departments of this Government, together with all legislators, all judges and magistrates, and all other persons exercising authority in the land, whether civil, military, or naval, and all soldiers, seamen, and marines in the national service, and all other loyal and law-abiding people of the United States, to assemble in their preferred places of public worship on that day, and there to render to the Almighty and merciful Ruler of the Universe, such homage and such confessions, and to offer to Him such supplications as the Congress of the United States have, in their aforesaid resolution, so solemnly, so earnestly, and so reverently recommended.
In testimony whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed. Done at the city of Washington this seventh day of July, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-four, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
WHOSE GOVERNMENTS HAVE BEEN USURPED OR OVERTHROWN, A REPUBLICAN FORM OF GOVERNMENT," AND CONCERNING RECONSTRUCTION,
JULY 8, 1864. BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES:
A Proclamation.
Whereas at the late session Congress passed a bill "to guarantee to certain states whose governments have been usurped or overthrown a republican form of government," a copy of which is hereunto annexed; and
Whereas, the said bill was presented to the President of the United States for his approval less than one hour before the sine die adjournment of said session, and was not signed by him; and
Whereas the said bill contains, among other things, a plan for restoring the States in rebellion to their proper practical relation in the Union, which plan expresses the sense of Congress upon that subject, and which plan it is now thought fit to lay before the people for their consideration:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do proclaim, declare, and make known that while I am (as I was in December last, when, by proclamation, I propounded a plan for restoration) unprepared by a formal approval of this bill to be inflexibly committed to any single plan of restoration, and while I am also unprepared to declare that the free State constitutions and governments already adopted and installed in Arkansas and Louisiana shall be set aside and held for naught, thereby repelling and discouraging the loyal citizens who have set up the same as to further effort, or to declare a constitutional competency in Congress to abolish slavery in States, but am at the same time sincerely hoping and expecting that a constitutional amendment abolishing slavery throughout the nation may be adopted, nevertheless I am fully satisfied with the system for restoration contained in the bill as one very proper plan for the loyal people of any State choosing to adopt it, and that I am and at all times shall be prepared to give the Executive aid and assistance to any such people so soon as the military resistance to the United States shall have been suppressed in any such States and the people thereof shall have sufficiently returned to their obedience to the Constitution and the laws of the United States, in which cases militia-governors will be appointed with directions to proceed according to the bill.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed..............
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
HON. HORACE GREELEY.
DEAR SIR:—Your letter of the 7th, with inclosures, received.
If you can find any person, anywhere, professing to have any proposition of Jefferson Davis in writing, for peace, embracing the restoration of the Union and abandonment of slavery, whatever else it embraces, say to him he may come to me with you; and that if he really brings such proposition, he shall at the least have safe conduct with the paper (and without publicity, if he chooses) to the point where you shall have to meet him. The same if there be two or more persons.
Yours truly,
What have you heard about a battle at Monocacy to-day? We have nothing about it here except what you say.
MAJOR-GENERAL L. WALLACE, Commanding Middle Department:
I am directed by the President to say that you will rally your forces and make every possible effort to retard the enemy's march on Baltimore.
H. W. HALLECK, Major-General and Chief of Staff.
A.M.
THOMAS SWAN AND OTHERS, Baltimore, Maryland:
Yours of last night received. I have not a single soldier but whom is being disposed by the military for the best protection of all. By latest accounts the enemy is moving on Washington. They cannot fly to either place. Let us be vigilant, but keep cool. I hope neither Baltimore nor Washington will be sacked.
Your dispatch to General Halleck, referring to what I may think in the present emergency, is shown me. General Halleck says we have absolutely no force here fit to go to the field. He thinks that with the hundred-day men and invalids we have here we can defend Washington, and, scarcely, Baltimore. Besides these there are about eight thousand, not very reliable, under Howe, at Harper's Ferry with Hunter approaching that point very slowly, with what number I suppose you know better than I. Wallace, with some odds and ends, and part of what came up with Ricketts, was so badly beaten yesterday at Monocacy, that what is left can attempt no more than to defend Baltimore. What we shall get in from Pennsylvania and New York will scarcely be worth counting, I fear. Now, what I think is, that you should provide to retain your hold where you are, certainly, and bring the rest with you personally, and make a vigorous effort to destroy the enemy's forces in this vicinity. I think there is really a fair chance to do this, if the movement is prompt. This is what I think upon your suggestion, and is not an order.
Yours of 10.30 P.M. yesterday received, and very satisfactory. The enemy will learn of Wright's arrival, and then the difficulty will be to unite Wright and Hunter south of the enemy before he will recross the Potomac. Some firing between Rockville and here now.
AM.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Vague rumors have been reaching us for two or three days that Longstreet's corps is also on its way [to] this vicinity. Look out for its absence from your front.
12, 1864.
HON. HORACE GREELEY, New York:
I suppose you received my letter of the 9th. I have just received yours of the 13th, and am disappointed by it. I was not expecting you to send me a letter, but to bring me a man, or men. Mr. Hay goes to you with my answer to yours of the 13th.
A. LINCOLN.
[Carried by Major John Hay.]
MY DEAR SIR:-Yours of the 13th is just received, and I am disappointed that you have not already reached here with those commissioners, if they would consent to come on being shown my letter to you of the 9th instant. Show that and this to them, and if they will come on the terms stated in the former, bring them. I not only intend a sincere effort for peace, but I intend that you shall be a personal witness that it is made.
Yours truly,
The President of the United States directs that the four persons whose names follow, to wit, HON. Clement C. Clay, HON. Jacob Thompson, Professor James P. Holcombe, George N. Sanders, shall have safe conduct to the city of Washington in company with the HON. HORACE GREELEY, and shall be exempt from arrest or annoyance of any kind from any officer of the United States during their journey to the said city of Washington.
By order of the President: JOHN HAY, Major and Assistant Adjutant-General
In your dispatch of yesterday to General Sherman, I find the following, to wit:
"I shall make a desperate effort to get a position here, which will hold the enemy without the necessity of so many men."
Pressed as we are by lapse of time I am glad to hear you say this; and yet I do hope you may find a way that the effort shall not be desperate in the sense of great loss of life.
A. LINCOLN, President.
Yours of this morning received. You misconceive. The order you complain of was only nominally mine, and was framed by those who really made it with no thought of making you a scapegoat. It seemed to be General Grant's wish that the forces under General Wright and those under you should join and drive at the enemy under General Wright. Wright had the larger part of the force, but you had the rank. It was thought that you would prefer Crook's commanding your part to your serving in person under Wright. That is all of it. General Grant wishes you to remain in command of the department, and I do not wish to order otherwise.
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERMAN, Chattahoochee River, Georgia:
I have seen your despatches objecting to agents of Northern States opening recruiting stations near your camps. An act of Congress authorizes this, giving the appointment of agents to the States, and not to the Executive Government. It is not for the War Department, or myself, to restrain or modify the law, in its execution, further than actual necessity may require. To be candid, I was for the passage of the law, not apprehending at the time that it would produce such inconvenience to the armies in the field as you now cause me to fear. Many of the States were very anxious for it, and I hoped that, with their State bounties, and active exertions, they would get out substantial additions to our colored forces, which, unlike white recruits, help us where they come from, as well as where they go to. I still hope advantage from the law; and being a law, it must be treated as such by all of us. We here will do what we consistently can to save you from difficulties arising out of it. May I ask, therefore, that you will give your hearty co-operation.
WASHINGTON, July 18, 1864.
TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN:
Any proposition which embraces the restoration of peace, the integrity of the whole Union, and the abandonment of slavery, and which comes by and with an authority that can control the armies now at war against the United States, will be received and considered by the Executive Government of the United States, and will be met by liberal terms on other substantial and collateral points; and the bearer or bearers thereof shall have safe conduct both ways.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas by the act approved July 4, 1864, entitled "An act further to regulate and provide for the enrolling and calling out the national forces and for other purposes," it is provided that the President of the United States may, "at his discretion, at any time hereafter, call for any number of men, as volunteers for the respective terms of one, two, and three years for military service," and "that in case the quota or any part thereof of any town, township, ward of a city, precinct, or election district, or of a county not so subdivided, shall not be filled within the space of fifty days after such call, then the President shall immediately order a draft for one year to fill such quota or any part thereof which may be unfilled;" and
Whereas the new enrolment heretofore ordered is so far completed as that the aforementioned act of Congress may now be put in operation for recruiting and keeping up the strength of the armies in the field, for garrisons, and such military operations as may be required for the purpose of suppressing the rebellion and restoring the authority of the United States Government in the insurgent States:
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do issue this my last call for five hundred thousand volunteers for the military service: Provided, nevertheless, That this call shall be reduced by all credits which may be established under section eight of the aforesaid act on account of persons who have entered the naval service during the present rebellion and by credits for men furnished to the military service in excess of calls heretofore made. Volunteers will be accepted under this call for one, two, or three years, as they may elect, and will be entitled to the bounty provided by the law for the period of services for which they enlist.
And I hereby proclaim, order, and direct that immediately after the 5th day of September, 1864, being fifty days from the date of this call, a draft for troops to serve for one year shall be had in every town, township, ward of a city, precinct, or election district, or county not so subdivided, to fill the quota which shall be assigned to it under this call or any part thereof which may be unfilled by volunteers on the said 5th day of September, 1864.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the City of Washington, this 18th day of July, A.D. 1864, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Yours of yesterday, about a call for three hundred thousand, is received. I suppose you had not seen the call for five hundred thousand, made the day before, and which, I suppose, covers the case. Always glad to have your suggestions.
J. L. WRIGHT, Indianapolis, Ind.:
All a mistake. Mr. Stanton has not resigned.
MAJOR-GENERAL HUNTER, Harper's Ferry, West Va.
Are you able to take care of the enemy, when he turns back upon you, as he probably will on finding that Wright has left?
GOVERNOR CURTIN:
Herewith is the manuscript letter for the gentleman who sent me a cane through your hands. For my life I cannot make out his name; and therefore I cut it from his letter and pasted it on, as you see. I suppose [sic] will remember who he is, and I will thank you to forward him the letter. He dates his letter at Philadelphia.
Yours truly,
WILLIAM O. SNIDER:
The cane you did me the honor to present through Governor Curtin was duly placed in my hand by him. Please accept my thanks; and, at the same time, pardon me for not having sooner found time to tender them. Your obedient servant,
J. C. WELLING, ESQ.
SIR:—According to the request contained in your note, I have placed Mr. Gibson's letter of resignation in the hands of the President. He has read the letter, and says he accepts the resignation, as he will be glad to do with any other, which may be tendered, as this is, for the purpose of taking an attitude of hostility against him.
He says he was not aware that he was so much indebted to Mr. Gibson for having accepted the office at first, not remembering that he ever pressed him to do so, or that he gave it otherwise than as was usual, upon request made on behalf of Mr. Gibson.
He thanks Mr. Gibson for his acknowledgment that he has been treated with personal kindness and consideration, and says he knows of but two small drawbacks upon Mr. Gibson's right to still receive such treatment, one of which is that he never could learn of his giving much attention to the duties of his office, and the other is this studied attempt of Mr. Gibson's to stab him.
I am very truly,
Your obedient servant,
Thomas Connor, a private in the First Veteran New York Cavalry, is now imprisoned at hard labor for desertion. If the Colonel of said Regiment will say in writing on this sheets that he is willing to receive him back to the Regiment, I will pardon, and send him.
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERMAN, near Atlanta:
I have just seen yours complaining of the appointment of Hovey and Osterhaus. The point you make is unquestionably a good one, and yet please hear a word from us. My recollection is that both General Grant and yourself recommended both H [ovey] and O [sterhaus] for promotion, and these, with other strong recommendations, drew committals from us which we could neither honorably or safely disregard. We blamed H [ovey] for coming away in the manner in which he did, but he knew he had apparent reason to feel disappointed and mortified, and we felt it was not best to crush one who certainly had been a good soldier. As to [Osterhaus], we did not know of his leaving at the time we made the appointment, and do not now know the terms on which he left. Not to have appointed him, as the case appeared to us at the time, would have been almost, if not quite, a violation of our word. The word was given on what we thought was high merit and somewhat on his nationality. I beg you to believe we do not act in a spirit of disregarding merit. We expect to await your programme for further changes and promotions in your army. My profoundest thanks to you and your whole army for the present campaign so far.
MAJOR-GENERAL HALLECK, Chief of Staff of the Army:
GENERAL:—Lieutenant-General Grant having signified that, owing to the difficulties and delay of communication between his headquarters and Washington, it is necessary that in the present emergency military orders must be issued directly from Washington, the President directs me to instruct you that all the military operations for the defense of the Middle Department, the Department of the Susquehanna, the Department of Washington, and the Department of West Virginia, and all the forces in those departments, are placed under your general command, and that you will be expected to take all military measures necessary for defense against any attack of the enemy and for his capture and destruction. You will issue from time to time such orders to the commanders of the respective departments and to the military authorities therein as may be proper.
Your obedient servant,
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Yours in relation to General A. C. Gillam just received. Will look after the matter to-day.
I also received yours about General Carl Schurz. I appreciate him certainly, as highly as you do; but you can never know until you have the trial, how difficult it is to find a place for an officer of so high rank when there is no place seeking him.
Mrs. ANNE WILLIAMSON.
MADAM:—The plaid you send me is just now placed in my hands. I thank you for that pretty and useful present, but still more for those good wishes for myself and our country, which prompted you to present it.
Your obedient servant,
A. LINCOLN. INDORSEMENT, AUGUST 3, 1864.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, August 2, 1864.
MR. PRESIDENT:—This note will introduce to you Mr. Schley of Baltimore, who desires to appeal to you for the revocation of an order of General Hunter, removing some persons, citizens of Frederick, beyond his lines, and imprisoning others. This Department has no information of the reasons or proofs on which General Hunter acts, and I do not therefore feel at liberty to suspend or interfere with his action except under your direction.
Yours truly,
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
[Indorsement.]
August 3, 1864.
The Secretary of War will suspend the order of General Hunter mentioned within, until further order and direct him to send to the Department a brief report of what is known against each one proposed to be dealt with.
WASHINGTON, D. C.. August 3, 1864
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
I have seen your despatch in which you say, "I want Sheridan put in command of all the troops in the field, with instructions to put himself south of the enemy, and follow him to the death. Wherever the enemy goes, let our troops go also."
This, I think, is exactly right as to how our forces should move; but please look over the despatches you may have received from here, ever since you made that order, and discover, if you can, that there is any idea in the head of any one here of "putting our army south of the enemy," or of following him to the "death," in any direction. I repeat to you, it will neither be done nor attempted, unless you watch it every day and hour, and force it.
A. LINCOLN.
[Here the President was mistaken in thinking that Sherman,
Sheridan, and Grant had the same inability of most of his
previous general officers. No one needed to watch Grant or
Sherman or Sheridan, they only needed to get out of their
way. D.W.]
HON. HORACE GREELEY, New York:
Yours to Major Hay about publication of our correspondence received. With the suppression of a few passages in your letters in regard to which I think you and I would not disagree, I should be glad of the publication. Please come over and see me.
HON. HORACE GREELEY, New York:
I telegraphed you Saturday. Did you receive the despatch? Please answer.
WASHINGTON, D. C., August 8, 1864
MAJOR-GENERAL BURBRIDGE, Lexington, Ky.:
Last December Mrs. Emily T. Helm, half-sister of Mrs. Lincoln, and widow of the rebel general, Ben Hardin Helm, stopped here on her way from Georgia to Kentucky, and I gave her a paper, as I remember, to protect her against the mere fact of her being General Helm's widow. I hear a rumor to-day that you recently sought to arrest her, but were prevented by her presenting the paper from me. I do not intend to protect her against the consequences of disloyal words or acts, spoken or done by her since her return to Kentucky, and if the paper given her by me can be construed to give her protection for such words and acts, it is hereby revoked pro tanto. Deal with her for current conduct just as you would with any other.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
The Secretary of War and I concur that you had better confer with General Lee, and stipulate for a mutual discontinuance of house-burning and other destruction of private property. The time and manner of conference and particulars of stipulation we leave, on our part, to your convenience and judgment.
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERMAN, near Atlanta, Ga.:
If the Government should purchase, on its own account, cotton northward of you, and on the line of your communications, would it be an inconvenience to you, or detriment to the military service, for it to come to the north on the railroad?
"Mr. President," said Governor Randall, "why can't you seek seclusion, and play hermit for a fortnight? It would reinvigorate you."
"Ah," said the President, "two or three weeks would do me no good. I cannot fly from my thoughts—my solicitude for this great country follows me wherever I go. I do not think it is personal vanity or ambition, though I am not free from these infirmities, but I cannot but feel that the weal or woe of this great nation will be decided in November. There is no program offered by any wing of the Democratic party but that must result in the permanent destruction of the Union."
"But, Mr. President, General McClellan is in favor of crushing out this rebellion by force. He will be the Chicago candidate."
"Sir, the slightest knowledge of arithmetic will prove to any man that the rebel armies cannot be destroyed by Democratic strategy. It would sacrifice all the white men of the North to do it. There are now in the service of the United States nearly one hundred and fifty thousand able-bodied colored men, most of them under arms, defending and acquiring Union territory. The Democratic strategy demands that these forces be disbanded, and that the masters be conciliated by restoring them to slavery. The black men who now assist Union prisoners to escape are to be converted into our enemies, in the vain hope of gaining the good-will of their masters. We shall have to fight two nations instead of one.
"You cannot conciliate the South if you guarantee to them ultimate success; and the experience of the present war proves their success is inevitable if you fling the compulsory labor of millions of black men into their side of the scale. Will you give our enemies such military advantages as insure success, and then depend on coaxing, flattery, and concession to get them back into the Union? Abandon all the posts now garrisoned by black men, take one hundred and fifty thousand men from our side and put them in the battle-field or corn-field against us, and we would be compelled to abandon the war in three weeks.
"We have to hold territory in inclement and sickly places; where are the Democrats to do this? It was a free fight, and the field was open to the war Democrats to put down this rebellion by fighting against both master and slave, long before the present policy was inaugurated.
"There have been men base enough to propose to me to return to slavery the black warriors of Port Hudson and Olustee, and thus win the respect of the masters they fought. Should I do so, I should deserve to be damned in time and eternity. Come what will, I will keep my faith with friend and foe. My enemies pretend I am now carrying on this war for the sole purpose of abolition. So long as I am President, it shall be carried on for the sole purpose of restoring the Union. But no human power can subdue this rebellion without the use of the emancipation policy, and every other policy calculated to weaken the moral and physical forces of the rebellion.
"Freedom has given us one hundred and fifty thousand men, raised on Southern soil. It will give us more yet. Just so much it has subtracted from the enemy, and, instead of alienating the South, there are now evidences of a fraternal feeling growing up between our men and the rank and file of the rebel soldiers. Let my enemies prove to the country that the destruction of slavery is not necessary to a restoration of the Union. I will abide the issue."
I am always for the man who wishes to work; and I shall be glad for this man to get suitable employment at Cavalry Depot, or elsewhere.
HON. HENRY J. RAYMOND.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have proposed to Mr. Greeley that the Niagara correspondence be published, suppressing only the parts of his letters over which the red pencil is drawn in the copy which I herewith send. He declines giving his consent to the publication of his letters unless these parts be published with the rest. I have concluded that it is better for me to submit, for the time, to the consequences of the false position in which I consider he has placed me, than to subject the country to the consequences of publishing these discouraging and injurious parts. I send you this, and the accompanying copy, not for publication, but merely to explain to you, and that you may preserve them until their proper time shall come.
Yours truly,
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
I have seen your despatch expressing your unwillingness to break your hold where you are. Neither am I willing. Hold on with a bulldog grip, and chew and choke as much as possible.
A Proclamation.
Whereas the act of Congress of the 28th of September, 1850, entitled "An act to create additional collection districts in the State of California, and to change the existing districts therein, and to modify the existing collection districts in the United States," extends to merchandise warehoused under bond the privilege of being exported to the British North American provinces adjoining the United States, in the manner prescribed in the act of Congress of the 3d of March, 1845, which designates certain frontier ports through which merchandise may be exported, and further provides "that such other ports, situated on the frontiers of the United States adjoining the British North American provinces, as may hereafter be found expedient, may have extended to them the like privileges, on the recommendation of the Secretary of the Treasury, and proclamation duly made by the President of the United States, specially designating the ports to which the aforesaid privileges are to be extended."
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, in accordance with the recommendation of the Secretary of the Treasury, do hereby declare and proclaim that the port of Newport, in the State of Vermont, is and shall be entitled to all the privileges in regard to the exportation of merchandise in bond to the British North American provinces adjoining the United States, which are extended to the ports enumerated in the seventh section of the act of Congress of the 3d of March, 1845, aforesaid, from and after the date of this proclamation.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed. Done at the city of Washington, this eighteenth day of August, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-four, and of the independence of the United States of America, the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
If General Hitchcock can effect a special exchange of Thomas D. Armesy, now under conviction as a spy, or something of the sort, and in prison at for Major Nathan Goff, made a prisoner of war, and now in prison at Richmond, let it be done.
SOLDIERS:—You are about to return to your homes and your friends, after having, as I learn, performed in camp a comparatively short term of duty in this great contest. I am greatly obliged to you, and to all who have come forward at the call of their country. I wish it might be more generally and universally understood what the country is now engaged in. We have, as all will agree, a free government, where every man has a right to be equal with every other man. In this great struggle, this form of government and every form of human right is endangered if our enemies succeed. There is more involved in this contest than is realized by every one. There is involved in this struggle, the question whether your children and my children shall enjoy the privileges we have enjoyed. I say this, in order to impress upon you, if you are not already so impressed, that no small matter should divert us from our great purpose.
There may be some inequalities in the practical application of our system. It is fair that each man shall pay taxes in exact proportion to the value of his property; but if we should wait, before collecting a tax, to adjust the taxes upon each man in exact proportion with every other man, we should never collect any tax at all. There may be mistakes made sometimes; and things may be done wrong, while the officers of the Government do all they can to prevent mistakes. But I beg of you, as citizens of this great Republic, not to let your minds be carried off from the great work we have before us. This struggle is too large for you to be diverted from it by any small matter. When you return to your homes, rise up to the height of a generation of men worthy of a free government, and we will carry out the great work we have commenced. I return to you my sincere thanks, soldiers, for the honor you have done me this afternoon.
20, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Bermuda Hundred, Va.:
Please allow Judge Snead to go to his family on Eastern Shore, or give me some good reason why not.
SOLDIERS—I suppose you are going home to see your families and friends. For the services you have done in this great struggle in which we are engaged, I present you sincere thanks for myself and the country.
I almost always feel inclined, when I say anything to soldiers, to impress upon them, in a few brief remarks, the importance of success in this contest. It is not merely for the day, but for all time to come, that we should perpetuate for our children's children that great and free government which we have enjoyed all our lives. I beg you to remember this, not merely for my sake, but for yours. I happen, temporarily, to occupy this big White House. I am a living witness that any one of your children may look to come here as my father's child has. It is in order that each one of you may have, through this free government which we have enjoyed, an open field, and a fair chance for your industry, enterprise, and intelligence; that you may all have equal privileges in the race of life with all its desirable human aspirations—it is for this that the struggle should be maintained, that we may not lose our birthrights—not only for one, but for two or three years, if necessary. The nation is worth fighting for, to secure such an inestimable jewel.
This morning, as for some days past, it seems exceedingly probable that this administration will not be re-elected. Then it will be my duty to so co-operate with the President-elect as to save the Union between the election and the inauguration; as he will have secured his election on such ground that he cannot possibly save it afterward.
1864.
GOVERNOR JOHNSON, Nashville, Tenn.:
Thanks to General Gillam for making the news and also to you for sending it. Does Joe Heiskell's "walking to meet us" mean any more than that "Joe" was scared and wanted to save his skin?
30,1864.
HON. B. H. BREWSTER, Astor House, New York:
Your letter of yesterday received. Thank you for it. Please have no fears.
Any person or persons engaged in bringing out cotton, in strict conformity with authority given by W. P. Fessenden, Secretary of the United States Treasury, must not be hindered by the War, Navy, or any other Department of the Government, or any person engaged under any of said Departments.
COLONEL H. C. HUIDEKOPER, Meadville, Penn.
SIR: It is represented to me that there are at Rock Island, Illinois, as rebel prisoners of war, many persons of Northern and foreign birth who are unwilling to be exchanged and sent South, but who wish to take the oath of allegiance and enter the military service of the Union. Colonel Huidekoper, on behalf of the people of some parts of Pennsylvania, wishes to pay the bounties the Government would have to pay to proper persons of this class, have them enter the service of the United States, and be credited to the localities furnishing the bounty money. He will therefore proceed to Rock Island, ascertain the names of such persons (not including any who have attractions Southward), and telegraph them to the Provost-Marshal-General here, whereupon direction will be given to discharge the persons named upon their taking the oath of allegiance; and then upon the official evidence being furnished that they shall have been duly received and mustered into the service of the United States, their number will be credited as may be directed by Colonel Huidekoper.
The signal success that Divine Providence has recently vouchsafed to the operations of the United States fleet and army in the harbor of Mobile, and the reduction of Fort Powell, Fort Gaines, and Fort Morgan, and the glorious achievements of the army under Major-General Sherman, in the State of Georgia, resulting in the capture of the city of Atlanta, call for devout acknowledgment to the Supreme Being in whose hands are the destinies of nations. It is therefore requested that on next Sunday, in all places of worship in the United States, thanksgivings be offered to Him for His mercy in preserve our national existence against the insurgent rebels who have been waging a cruel war against the Government of the United States for its overthrow, and also that prayer be made for Divine protection to our brave soldiers and their leaders in the field who have so often and so gallantly periled their lives in battling with the enemy, and for blessings and comfort from the Father of mercies to the sick, wounded, and prisoners, and to the orphans and widows of those who have fallen in the service of their country, and that He will continue to uphold the Government of the United States against all the efforts of public enemies and secret foes.
The national thanks are tendered by the President to Admiral Farragut and Major-General Canby, for the skill and harmony with which the recent operations in Mobile Harbor and against Fort Powell, Fort Gaines, and Fort Morgan were planned and carried into execution. Also to Admiral Farragut and Major-General Granger, under whose immediate command they were conducted, and to the gallant commanders on sea and land, and to the sailors and soldiers engaged in the operations, for their energy and courage, which, under the blessing of Providence, have been crowned with brilliant success, and have won for them the applause and thanks of the nation.
The national thanks are tendered by the President to Major-General William T. Sherman and the gallant officers and soldiers of his command before Atlanta, for the distinguished ability, courage, and perseverance displayed in the campaign in Georgia, which under Divine power resulted in the capture of the city of Atlanta. The marches, battles, sieges, and other military operations that have signalized this campaign must render it famous in the annals of war, and have entitled those who have participated therein to the applause and thanks of the nation.
Ordered: First, That on Monday, the fifth day of September, commencing at the hour of twelve o'clock noon, there shall be given a salute of one hundred guns at the arsenal and navy-yard, at Washington, and on Tuesday, the 6th of September, or on the day after the receipt of this order, at each arsenal and navy-yard in the United States, for the recent brilliant achievements of the fleet and land forces of the United States in the harbor of Mobile, and in the reduction of Fort Powell, Fort Gaines, and Fort Morgan. The Secretary of War and the Secretary of the Navy will issue the necessary directions in their respective departments for the execution of this order.
Second, That on Wednesday, the 7th of September, commencing at the hour of twelve o'clock noon, there shall be fired a salute of one hundred guns at the arsenal at Washington, and at New York, Boston, Philadelphia, Baltimore, Pittsburg, Newport (Ky.), and St. Louis, and New Orleans, Mobile, and Pensacola, Hilton Head, and Newbern, the day after the receipt of this order, for the brilliant achievements of the army under command of Major-General Sherman, in the State of Georgia, and for the capture of Atlanta. The Secretary of War will issue directions for the execution of this order.
A. LINCOLN, President Of the United States.
ELIZA P. GURNEY.
MY ESTEEMED FRIEND:—I have not forgotten probably never shall forget the very impressive occasion when yourself and friends visited me on a Sabbath forenoon two years ago—nor has your kind letter, written nearly a year later, even been for gotten. In all, it has been your purpose to strengthen my reliance on God. I am much indebted to the good Christian people of the country for their constant prayer and consolations; and to no one of them, more than to yourself. The purposes of the Almighty are perfect, and must prevail, though we erring mortals may fail to accurately perceive them in advance. We hoped for a happy termination of this terrible war long before this; but God knows best, and has ruled otherwise. We shall yet acknowledge His wisdom, and our own error therein. Mean while we must work earnestly in the best light He gives us, trusting that so working still conduces to the great ends He ordains. Surely He intends some great good to follow this mighty convulsion, which no mortal could make, and no mortal could stay.
Your people—the Friends—have had, and are having, a very great trial. On principle, and faith, opposed to both war and oppression, they can only practically oppose oppression by war. For those appealing to me on conscientious grounds, I have done, and shall do, the best I could and can, in my own conscience, under my oath to the law. That you believe this I doubt not, and believing it, I shall still receive, for our country and myself your earnest prayers to our Father in Heaven.
Your sincere friend,
SEPTEMBER 7, 1864.
I can only say now, as I have often said before, it has always been a sentiment with me, that all mankind should be free. So far as I have been able, so far as came within my sphere, I have always acted as I believed was just and right, and done all I could for the good of mankind. I have, in letters sent forth from this office, expressed myself better than I can now.
In regard to the great Book, I have only to say it is the best gift which God has ever given to man. All the good from the Saviour of the world is communicated to us through this book. But for that Book, we could not know right from wrong. All those things desirable to man are contained in it. I return you sincere thanks for this very elegant copy of this great Book of God which you present.
GOVERNOR PICKERING, Olympia, W. T.:
Your patriotic despatch of yesterday received and will be published.
The term of one hundred days for which the National Guard of Ohio volunteered having expired, the President directs an official acknowledgment to be made of their patriotic and valuable services during the recent campaigns. The term of service of their enlistment was short, but distinguished by memorable events. In the Valley of the Shenandoah, on the Peninsula, in the operations on the James River, around Petersburg and Richmond, in the battle of Monocacy, and in the intrenchments of Washington, and in other important service, the National Guard of Ohio performed with alacrity the duty of patriotic volunteers, for which they are entitled to and are hereby tendered, through the Governor of their State, the national thanks.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Sheridan and Early are facing each other at a dead-lock. Could we not pick up a regiment here and there, to the number of say ten thousand men, and quietly but suddenly concentrate them at Sheridan's camp and enable him to make a strike?
This is but a suggestion.
Yours truly,
13, 1864.
HON. J. G. BLAINE, Augusta, Me.: On behalf of the Union, thanks to Maine. Thanks to you personally for sending the news.
A. LINCOLN.
P. S.—Send same to L. B. Smith and M. A. Blanchard, Portland, Me. A. L.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL ROSECRANS. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, September 13, 1864
MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS, Saint Louis:
Postpone the execution of S. H. Anderson for two weeks. Hear what his friends can say in mitigation and report to me.
A. LINCOLN.
MAJOR ECKERT: Please send the above telegram.
JNO. G. NICOLAY, Private Secretary.
GENERAL SLOUGH, Alexandria, Va.:
On the 14th I commuted the sentence of Conley, but fearing you may not have received notice I send this. Do not execute him.
I feel great interest in the subjects of your despatch mentioning corn and sorghum, and the contemplated visit to you.
A. LINCOLN, President of the United States.
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERMAN:
The State election of Indiana occurs on the 11th of October, and the loss of it to the friends of the Government would go far towards losing the whole Union cause. The bad effect upon the November election, and especially the giving the State government to those who will oppose the war in every possible way, are too much to risk if it can be avoided. The draft proceeds, notwithstanding its strong tendency to lose us the State. Indiana is the only important State voting in October whose soldiers cannot vote in the field. Anything you can safely do to let her soldiers or any part of them go home and vote at the State election will be greatly in point. They need not remain for the Presidential election, but may return to you at once. This is in no sense an order, but is merely intended to impress you with the importance to the Army itself of your doing all you safely can, yourself being the judge of what you can safely do.
Yours truly,
The writer of this, who appeals for his brother, is our minister to Ecuador, and whom, if at all compatible, I would like to have obliged by a special exchange of his brother.
20, 1864
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERIDAN, Winchester, Va.:
Have just heard of your great victory. God bless you all, officers and men. Strongly inclined to come up and See you.
GENERAL HITCHCOCK:
Please see the bearer, Mr. Broadwell, on a question about a mutual supplying of clothes to prisoners.
Yours truly,
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
I send this as an explanation to you, and to do justice to the Secretary of War. I was induced, upon pressing application, to authorize the agents of one of the districts of Pennsylvania to recruit in one of the prison depots in Illinois; and the thing went so far before it came to the knowledge of the Secretary that, in my judgment, it could not be abandoned without greater evil than would follow its going through. I did not know at the time that you had protested against that class of thing being done; and I now say that while this particular job must be completed, no other of the sort will be authorized, without an understanding with you, if at all. The Secretary of War is wholly free of any part in this blunder.
Yours truly,
HON. MONTGOMERY BLAIR.
MY DEAR SIR:—You have generously said to me, more than once, that whenever your resignation could be a relief to me, it was at my disposal. The time has come. You very well know that this proceeds from no dissatisfaction of mine with you personally or officially. Your uniform kindness has been unsurpassed by that of any other friend, and while it is true that the war does not so greatly add to the difficulties of your department as to those of some others, it is yet much to say, as I most truly can, that in the three years and a half during which you have administered the General Post-Office, I remember no single complaint against you in connection therewith.
Yours, as ever,
I. Congress having authorized the purchase for the United States of the products of States declared in insurrection, and the Secretary of the Treasury having designated New Orleans, Memphis, Nashville, Pensacola, Port Royal, Beaufort (North Carolina), and Norfolk, as places of purchase, and, with my approval, appointed agents and made regulations under which said products may be purchased, therefore:
II. All persons except such as may be in the civil, military, or naval service of the government, having in their possession any products of States or parts of States declared in insurrection, which said agents are authorized to purchase; and all persons owning or controlling such products therein are authorized to convey such products to either of the places which have been hereby or may hereafter be designated as places of purchase, and such products so destined shall not be liable to detention, seizure, or forfeiture while in transitu, or in store waiting transportation.
III. Any person having the certificate of a purchasing agent, as prescribed by Treasury Regulation VIII, is authorized to pass with the necessary means of transportation to the points named in said certificate, and to return therefrom with the products required for the fulfilment of the stipulations set forth in said certificate.
IV. Any person having sold and delivered to a purchasing agent any products of an insurrectionary State in accordance with the regulations in relation thereto, and having in his possession a certificate setting forth the fact of such purchase and sale; the character and quantity of products, and the aggregate amount paid therefor, as prescribed by Regulation I, shall be permitted by the military authority commanding at the place of sale to purchase from any authorized dealer at such place merchandise and other articles not contraband of war nor prohibited by order of the War Department, nor coin, bullion, or foreign exchange, to an amount not exceeding in value one-third of the aggregate value of the products sold by him as certified by the agents purchasing, and the merchandise and other articles so purchased may be transported by the same route, and to the same place, from and by which the products sold and delivered reached the purchasing agent, as set forth in the certificate, and such merchandise and other articles shall have safe conduct, and shall not be subject to detention, seizure, or forfeiture while being transported to the places and by the routes set forth in the said certificate.
V. Generals commanding military districts, and commandants of military posts and detachments, and officers commanding fleets, flotillas, and gunboats, will give safe conduct to persons and products, merchandise, and other articles duly authorized as aforesaid, and not contraband of war, or prohibited by order of the War Department, or of the order of such generals commanding, or other duly authorized military or naval officer, made in pursuance hereof, and all persons hindering or preventing such safe conduct of persons or property will, be deemed guilty of a military offense and punished accordingly.
VI. Any person transporting or attempting to transport any merchandise or other articles except in pursuance of regulations of the Secretary of the Treasury, dated July 29, 1864, or in pursuance of this order, or transporting or attempting to transport any merchandise or other articles contraband of war or forbidden by any order of the War Department, will be deemed guilty of a military offense and punished accordingly; and all products of insurrectionary States found in transitu to any other person or than a purchasing agent and a designated of purchase shall be seized and forfeited to the States, except such as may be moving to a loyal state under duly authorized permits of a proper officer of the Treasury Department, as prescribed by Regulation XXXVIII, concerning commercial intercourse, dated July 29, 1864, or such as may have been found abandoned, or have been captured and are moving in pursuance of the act of March 12, 1864.
VII. No military or naval officer of the United States, or person in the military or naval service, nor any civil officer, except such as are appointed for that purpose, shall engage in trade or traffic in the products of the insurrectionary States, or furnish transportation therefor under pain of being deemed guilty of unlawful trading with the enemy and punished accordingly.
VIII. The Secretary of War will make such general orders or regulations as will insure the proper observance and execution of,, this order, and the Secretary of the Navy will give instructions to officers commanding fleets, flotillas, and gunboats in conformity therewith.
You say Jefferson Davis is on a visit to Hood. I judge that Brown and Stephens are the objects of his visit.
I hope it will have no constraint on you, nor do harm any way, for me to say I am a little afraid lest Lee sends reinforcements to Early, and thus enables him to turn upon Sheridan.
I think the bearer of this, Second Lieutenant Albee, deserves a hearing. Will the Secretary of War please accord it to him?
EXECUTIVE MANSION,
WASHINGTON, October 1, 1864.
The term of one hundred days for which volunteers from the States of Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, and Wisconsin volunteered, under the call of their respective governors, in the months of May and June, to aid in the campaign of General Sherman, having expired; the President directs an official acknowledgment to be made of their patriotic service. It was their good fortune to render efficient service in the brilliant operations in the Southwest and to contribute to the victories of the national arms over the rebel forces in Georgia under command of Johnston and Hood. On all occasions and in every service to which they were assigned their duty as patriotic volunteers was performed with alacrity and courage, for which they are entitled to and are hereby tendered the national thanks through the governors of their respective States.
The Secretary of War is directed to transmit a copy of this order to the governors of Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, and Wisconsin and to cause a certificate of their honorable service to be delivered to the officers and soldiers of the States above named who recently served in the military force of the United States as volunteers for one hundred days.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
I inclose you a copy of a correspondence in regard to a contemplated exchange of naval prisoners through your lines, and not very distant from your headquarters. It only came to the knowledge of the War Department and of myself yesterday, and it gives us some uneasiness. I therefore send it to you with the statement that, as the numbers to be exchanged under it are small, and so much has already been done to effect the exchange, I hope you may find it consistent to let it go forward under the general supervision of General Butler, and particularly in reference to the points he holds vital in exchanges. Still, you are at liberty to arrest the whole operation if in your judgment the public good requires it.
Yours truly,
I well remember the meetings herein narrated. See nothing for me to object to in the narrative as being made by General McDowell, except the phrase attributed to me "of the Jacobinism of Congress",
[This memorandum describes the private discussions that
preceded the transfer of McClellan's army from the Potomac,
where it had confronted the Confederates at Manassas. See H.
J. Raymond: Life of Lincoln, p. 772]
which phrase I do not remember using literally or in substance, and which I wish not to be published in any event.
HON. HENRY W. HOFFMAN.
MY DEAR SIR:—A convention of Maryland has framed a new constitution for the State; a public meeting is called for this evening at Baltimore to aid in securing its ratification by the people, and you ask a word from me for the occasion. I presume the only feature of the instrument about which there is serious controversy is that which provides for the extinction of slavery. It needs not to be a secret and I presume it is no secret, that I wish success to this provision. I desire it on every consideration. I wish all men to be free. I wish the material prosperity of the already free, which I feel sure the extinction of slavery would bring. I wish to see in process of disappearing that only thing which ever could bring this nation to civil war. I attempt no argument. Argument upon the question is already exhausted by the abler, better informed, and more immediately interested sons of Maryland herself. I only add that I shall be gratified exceedingly if the good people of the State shall, by their votes, ratify the new constitution.
Yours truly,
GOVERNOR CURTIN, Harrisburg, Pa.:
Yours of to-day just this moment received, and the Secretary having left it is impossible for me to answer to-day. I have not received your letter from Erie.
Your letter makes us a little uneasy about your health. Telegraph us how you are. If you think it would help you, make us a visit.
Secretary of War not being in, I answer yours about election. Pennsylvania very close, and still in doubt on home vote. Ohio largely for us, with all the members of Congress but two or three. Indiana largely for us,—Governor, it is said, by fifteen thousand, and eight of the eleven members of Congress. Send us what you may know of your army vote.
FRIENDS AND FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I am notified that this is a compliment paid me by the loyal Marylanders resident in this District. I infer that the adoption of the new constitution for the State furnishes the occasion, and that in your view the extirpation of slavery constitutes the chief merit of the new constitution. Most heartily do I congratulate you, and Maryland, and the nation, and the world, upon this event. I regret that it did not occur two years sooner, which, I am sure, would have saved the nation more money than would have met all the private loss incident to the measure; but it has come at last, and I sincerely hope its friends may fully realize all their anticipations of good from it, and that its opponents may by its effects be agreeably and profitably disappointed.
A word upon another subject. Something said by the Secretary of State in his recent speech at Auburn, has been construed by some into a threat, that if I shall be beaten at the election, I will, between then and the end of my constitutional term, do what I may be able to ruin the Government.
Others regard the fact that the Chicago Convention adjourned, not sine die, but to meet again, if called to do so by a particular individual, as the intimation of a purpose that if their nominee shall be elected he will at once seize control of the Government. I hope the good people will permit themselves to suffer no uneasiness on either point. I am struggling to maintain the Government, not to overthrow it. I am struggling especially to prevent others from overthrowing it. I therefore say, that if I live, I shall remain President until the 4th of next March, and that whoever shall be constitutionally elected, in November, shall be duly installed as President on the 4th of March, and in the interval I shall do my utmost that whoever is to hold the helm for the next voyage shall start with the best possible chance of saving the ship. This is due to the people, both on principle and under the Constitution. Their will, constitutionally expressed, is the ultimate law for all. If they should deliberately resolve to have immediate peace, even at the loss of their country and their liberties, I know not the power or the right to resist them. It is their own business, and they must do as they please with their own. I believe, however, they are still resolved to preserve their country and their liberties; and in this, in office or out of it, I am resolved to stand by them. I may add, that in this purpose to save the country and its liberties, no classes of people seem so nearly unanimous as the soldiers in the field and the sailors afloat. Do they not have the hardest of it? Who should quail while they do not? God bless the soldiers and seamen, with all their brave commanders.
A Proclamation.
It has pleased Almighty God to prolong our national life another year, defending us with his guardian care against unfriendly designs from abroad, and vouchsafing to us in His mercy many and signal victories over the enemy, who is of our own household. It has also pleased our Heavenly Father to favor as well our citizens in their homes as our soldiers in their camps, and our sailors on the rivers and seas, with unusual health. He has largely augmented our free population by emancipation and by immigration, while he has opened to us new: sources of wealth, and has crowned the labor of our working-men in every department of industry with abundant rewards. Moreover, he has been pleased to animate and inspire our minds and hearts with fortitude, courage, and resolution sufficient for the great trial of civil war into which we have been brought by our adherence as a nation to the cause of freedom and humanity, and to afford to us reasonable hopes of an ultimate and happy deliverance from all our dangers and afflictions.
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby appoint and set apart the last Thursday in November next as a day which I desire to be observed by all my fellow-citizens, wherever they may be then, as a day of thanksgiving and praise to Almighty God, the beneficent Creator and Ruler of the Universe. And I do further recommend to my fellow-citizens aforesaid, that on that occasion they do reverently humble themselves in the dust, and from thence offer up penitent and fervent prayers and supplications to the great Disposer of events for a return of the inestimable blessings of peace, union, and harmony throughout the, land which it has pleased him to assign as a dwelling-place for ourselves and for our posterity throughout all generations.
In testimony whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this twentieth day of October, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-four, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
While Curtis is fighting Price, have you any idea where the force under Rosecrans is, or what it is doing?
MESSRS WILLIAM B. CAMPBELL, THOMAS A. R. NELSON, JAMES T. P. CARTER, JOHN WILLIAMS, A. BLIZZARD, HENRY COOPER, BAILLIE PEYTON, JOHN LELLYET, EMERSON ETHERIDGE, and JOHN D. PERRYMAN.
GENTLEMEN:—On the 15th day of this month, as I remember, a printed paper manuscript, with a few manuscript interlineations, called a protest, with your names appended thereto, and accompanied by another printed paper, purporting to be a proclamation by Andrew Johnson, Military Governor of Tennessee, and also a manuscript paper, purporting to be extracts from the Code of Tennessee, were laid before me.
The protest, proclamation, and extracts are respectively as follows:
[The protest is here recited, and also the proclamation of Governor Johnson, dated September 30, to which it refers, together with a list of the counties in East, Middle, and West Tennessee; also extracts from the Code of Tennessee in relation to electors of President and Vice-President, qualifications of voters for members of the General Assembly, places of holding elections, and officers of popular elections.]
At the time these papers were presented, as before stated, I had never seen either of them, nor heard of the subject to which they related, except in a general way one day previously.
Up to the present moment, nothing whatever upon the subject has passed between Governor Johnson, or any one else, connected with the proclamation, and myself.
Since receiving the papers, as stated, I have given the subject such brief consideration as I have been able to do, in the midst of so many pressing public duties.
My conclusion is, that I can have nothing to do with the matter, either to sustain the plan as the convention and Governor Johnson have initiated it, or to revoke or modify it as you demand.
By the Constitution and laws, the President is charged with no duty in the presidential election in any State, nor do I in this case perceive any military reason for his interference in the matter.
The movement set on foot by the convention and Governor Johnson does not, as seems to be assumed by you, emanate from the National Executive.
In no proper sense can it be considered other than an independent movement of, at least, a portion of the loyal people of Tennessee.
I do not perceive in the plan any menace, or violence, or coercion towards any one.
Governor Johnson, like any other loyal citizen of Tennessee, has the right to favor any political plan he chooses, and, as military governor, it is his duty to keep peace among and for the loyal people of the State.
I cannot discern that by this plan he purposes any more. But you object to the plan.
Leaving it alone will be your perfect security against it. It is not proposed to force you into it. Do as you please, on your own account, peaceably and loyally, and Governor Johnson will not molest you, but will protect you against violence as far as in his power.
I presume that the conducting of a presidential election in Tennessee in strict accordance with the old Code of the State, is not now a possibility.
It is scarcely necessary to add, that if any election shall be held and any votes shall be cast in the State of Tennessee for President and Vice-President of the United States, it will belong, not to the military agents, nor yet to the Executive Department, but exclusively to another department of the Government, to determine whether they are entitled to be counted in conformity with the Constitution and laws of the United States.
Except it be to give protection against violence, I decline to interfere in any way with any presidential election.
A. LINCOLN.
TELEGRAM TO GENERAL P. H. SHERIDAN. EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, October 22, 1864
MAJOR-GENERAL SHERIDAN:
With great pleasure I tender to you and your brave army the thanks of the nation, and my own personal admiration and gratitude, for the month's operations in the Shenandoah Valley; and especially for the splendid work of October 19, 1864.
Your obedient servant,
P.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL THOMAS, Nashville, Tennessee:
I have received information to-day, having great appearance of authenticity, that there is to be a rebel raid into Western Kentucky; that it is to consist of four thousand infantry and three thousand cavalry, and is to start from Corinth, Mississippi, On the fourth day of November.
A. LINCOLN, President.
Send copy to General Washburn at Memphis. A. L.
1864.
HON. THOMAS T. DAVIS, Syracuse, N.Y.:
I have ordered that Milton D. Norton be discharged on taking the oath. Please notify his mother.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation
Whereas the Congress of the United States passed an act, which was approved on the 21st day of March last, entitled "An act to enable the people of Nevada to form a constitution and State government, and for the admission of such State into the Union on an equal footing with the original States;" and,
Whereas the said constitution and State government have been formed, pursuant to the conditions prescribed by the fifth section of the act of Congress aforesaid, and the certificate required by the said act and also a copy of the constitution and ordinances have been submitted to the President of the United States:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, in accordance with the duty imposed upon me by the act of Congress aforesaid, do hereby declare and proclaim that the said State of Nevada is admitted into the Union on an equal footing with the original States.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed..........
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL BURBRIDGE, Lexington, Ky.
Suspend execution of all the deserters ordered to be executed on Sunday at Louisville, until further order, and send me the records in the cases. Acknowledge receipt.
MAJOR-GENERAL CANBY, New Orleans, La.:
Please forward with all possible despatch to the naval officer commanding at Mobile Bay the following order.
A. LINCOLN.
(Inclosure.)
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 6, 1864.
NAVAL OFFICER IN COMMAND AT MOBILE BAY
Do not on any account, or on any showing of authority whatever, from whomsoever purporting to come, allow the blockade to be violated.
TO THE MANAGING COMMITTEE OF THE SAILORS' FAIR, Boston, Massachusetts
Allow me to wish you a great success. With the old fame of the Navy made brighter in the present war you cannot fail. I name none lest I wrong others by omission. To all, from rear-admiral to honest Jack, I tender the nation's admiration and gratitude.
HON. A. H. RICE, Boston, Massachusetts:
Yours received. I have no other notice that the ox is mine. If it be really so, I present it to the Sailors' Fair as a contribution.
News from Grant, Sherman, Thomas and Rosecrans satisfactory, but not important. Pirate Florida captured by the Wachusett October 7, on the coast of Brazil. The information is certain.
FRIENDS AND FELLOW-CITIZENS:—Even before I had been informed by you that this compliment was paid me by loyal citizens of Pennsylvania, friendly to me, I had inferred that you were of that portion of my countrymen who think that the best interests of the nation are to be subserved by the support of the present administration. I do not pretend to say that you, who think so, embrace all the patriotism and loyalty of the country, but I do believe, and I trust without personal interest, that the welfare of the country does require that such support and indorsement should be given.
I earnestly believe that the consequences of this day's work, if it be as you assume, and as now seems probable, will be to the lasting advantage, if not to the very salvation, of the country. I cannot at this hour say what has been the result of the election. But, whatever it may be, I have no desire to modify this opinion: that all who have labored to-day in behalf of the Union have wrought for the best interests of the country and the world; not only for the present, but for all future ages.
I am thankful to God for this approval of the people; but, while deeply grateful for this mark of their confidence in me, if I know my heart, my gratitude is free from any taint of personal triumph. I do not impugn the motives of any one opposed to me. It is no pleasure to me to triumph over any one, but I give thanks to the Almighty for this evidence of the people's resolution to stand by free government and the rights of humanity.
1864.
H. HOFFMAN, Baltimore, Md.:
The Maryland soldiers in the Army of the Potomac cast a total vote of fourteen hundred and twenty-eight, out of which we get eleven hundred and sixty majority. This is directly from General Meade and General Grant.
It has long been a grave question whether any government, not too strong for the liberties of its people, can be strong enough to maintain its existence in great emergencies. On this point the present rebellion brought our government to a severe test, and a presidential election occurring in regular course during the rebellion, added not a little to the strain.
If the loyal people united were put to the utmost of their strength by the rebellion, must they not fail when divided and partially paralyzed by a political war among themselves? But the election was a necessity. We cannot have free government without elections; and if the election could force us to forego or postpone a national election, it might fairly claim to have already conquered and ruined us. The strife of the election is but human nature practically applied to the facts of the case. What has occurred in this case must ever recur in similar cases. Human nature will not change. In any future great national trial, compared with the men of this, we will have as weak and as strong, as silly and as wise, as bad and as good. Let us, therefore, study the incidents of this as philosophy to learn wisdom from, and none of them as wrongs to be revenged.
But the election, along with its incidental and undesirable strife, has done good, too. It has demonstrated that a people's government can sustain a national election in the midst of a great civil war. Until now, it has not been known to the world that this was a possibility. It shows, also, how sound and strong we still are. It shows that even among the candidates of the same party, he who is most devoted to the Union and most opposed to treason can receive most of the people's votes. It shows, also, to the extent yet known, that we have more men now than we had when the war began. Gold is good in its place; but living, brave, and patriotic men are better than gold.
But the rebellion continues, and, now that the election is over, may not all have a common interest to reunite in a common effort to save our common country? For my own part, I have striven and shall strive to avoid placing any obstacle in the way. So long as I have been here, I have not willingly planted a thorn in any man's bosom. While I am duly sensible to the high compliment of a re-election, and duly grateful, as I trust, to Almighty God, for having directed my countrymen to a right conclusion, as I think, for their good, it adds nothing to my satisfaction that any other man may be disappointed by the result.
May I ask those who have not differed with me to join with me in this same spirit towards those who have? And now, let me close by asking three hearty cheers for our brave soldiers and seamen, and their gallant and skillful commanders.
I have just received a telegram from Governor Bramlette saying: "General John B. Houston, a loyal man and prominent citizen, was arrested, and yesterday, started off by General Burbridge, to be sent beyond our lines by way of Catlettsburg, for no other offense than opposition to your re-election," and I have answered him as follows below, of which please take notice and report to me.
Yours of yesterday received. I can scarcely believe that General John B. Houston has been arrested "for no other offense than opposition to my re-election;" for, if that had been deemed sufficient cause of arrest, I should have heard of more than one arrest in Kentucky on election day. If, however, General Houston has been arrested for no other cause than opposition to my re-election, General Burbridge will discharge him at once, I sending him a copy of this as an order to that effect.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 14, 1864.
MAJOR-GENERAL HURLBUT:
Few things since I have been here have impressed me more painfully than what, for four or five months past, has appeared a bitter military opposition to the new State government of Louisiana. I still indulged some hope that I was mistaken in the fact; but copies of a correspondence on the subject between General Canby and yourself, and shown me to-day, dispel that hope. A very fair proportion of the people of Louisiana have inaugurated a new State government, making an excellent new constitution—better for the poor black man than we have in Illinois. This was done under military protection, directed by me, in the belief, still sincerely entertained, that with such a nucleus around which to build we could get the State into position again sooner than otherwise. In this belief a general promise of protection and support, applicable alike to Louisiana and other States, was given in the last annual message. During the formation of the new government and constitution they were supported by nearly every loyal person, and opposed by every secessionist. And this support and this opposition, from the respective standpoints of the parties, was perfectly consistent and logical. Every Unionist ought to wish the new government to succeed; and every disunionist must desire it to fail. Its failure would gladden the heart of Slidell in Europe, and of every enemy of the old flag in the world. Every advocate of slavery naturally desires to see blasted and crushed the liberty promised the black man by the new constitution. But why General Canby and General Hurlbut should join on the same side is to me incomprehensible.
Of course, in the condition of things at New Orleans, the military must not be thwarted by the civil authority; but when the Constitutional Convention, for what it deems a breach of privilege, arrests an editor in no way connected with the military, the military necessity for insulting the convention and forcibly discharging the editor is difficult to perceive. Neither is the military necessity for protecting the people against paying large salaries fixed by a legislature of their own choosing very apparent. Equally difficult to perceive is the military necessity for forcibly interposing to prevent a bank from loaning its own money to the State. These things, if they have occurred, are, at the best, no better than gratuitous hostility. I wish I could hope that they may be shown not to have occurred. To make assurance against misunderstanding, I repeat that in the existing condition of things in Louisiana, the military must not be thwarted by the civil authority; and I add that on points of difference the commanding general must be judge and master. But I also add that in the exercise of this judgment and control, a purpose, obvious, and scarcely unavowed, to transcend all military necessity, in order to crush out the civil government, will not be overlooked.
Yours truly,
The President, in reply, said that he had to confess he had been duly notified of the intention to make this friendly call some days ago, and in this he had had a fair opportunity afforded to be ready with a set speech; but he had not prepared one, being too busy for that purpose. He would say, however, that he was gratified with the result of the presidential election. He had kept as near as he could to the exercise of his best judgment for the interest of the whole country, and to have the seal of approbation stamped on the course he had pursued was exceedingly grateful to his feelings. He thought he could say, in as large a sense as any other man, that his pleasure consisted in belief that the policy he had pursued was the best, if not the only one, for the safety of the country.
He had said before, and now repeated, that he indulged in no feeling of triumph over any man who thought or acted differently from himself. He had no such feeling toward any living man. When he thought of Maryland, in particular, he was of the opinion that she had more than double her share in what had occurred in the recent elections. The adoption of a free-State constitution was a greater thing than the part taken by the people of the State in the presidential election. He would any day have stipulated to lose Maryland in the presidential election to save it by the adoption of a free-State constitution, because the presidential election comes every four years, while that is a thing which, being done, cannot be undone. He therefore thought that in that they had a victory for the right worth a great deal more than their part in the presidential election, though of the latter he thought highly. He had once before said, but would say again, that those who have differed with us and opposed us will see that the result of the presidential election is better for their own good than if they had been successful.
Thanking the committee for their compliment, he brought his brief speech to a close.
A Proclamation.
Whereas by my proclamation of the 19th of April, 1861, it was declared that the ports of certain States, including those of Norfolk, in the State of Virginia, Fernandina and Pensacola, in the State of Florida, were, for reasons therein set forth, intended to be placed under blockade; and:
Whereas the said ports were subsequently blockaded accordingly, but having for some time past been in the military possession of the United States, it is deeemd advisable that they should be opened to domestic and foreign commerce:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, pursuant to the authority in me vested by the fifth section of the act of Congress approved on the 13th of July, 1861, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," do hereby declare that the blockade of the said ports of Norfolk, Fernandina, and Pensacola shall so far cease and determine, from and after the first day of December next, that commercial intercourse with those ports, except as to persons, things, and information contraband of war, may, from that time, be carried on, subject to the laws of the United States, to the limitations and in pursuance of the regulations which may be prescribed by the Secretary of the Treasury, and to such military and naval regulations as are now in force, or may hereafter be found necessary.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed. Done at the city of Washington, this nineteenth day of November, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-four, and of the independence of the United States the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, November 21, 1864.
MRS. BIXBY, Boston, Massachusetts.
DEAR MADAM:—I have been shown in the files of the War Department a statement of the Adjutant-General of Massachusetts that you are the mother of five sons who have died gloriously on the field of battle. I feel how weak and fruitless must be any words of mine which should attempt to beguile you from the grief of a loss so overwhelming. But I cannot refrain from tendering to you the consolation that may be found in the thanks of the Republic they died to save. I pray that our Heavenly Father may assuage the anguish of your bereavement, and leave you only the cherished memory of the loved and lost, and the solemn pride that must be yours to have laid so costly a sacrifice upon the altar of freedom.
Yours very sincerely and respectfully,
DEACON JOHN PHILLIPS.
MY DEAR SIR:—I have heard of the incident at the polls in your town, in which you acted so honorable a part, and I take the liberty of writing to you to express my personal gratitude for the compliment paid me by the suffrage of a citizen so venerable.
The example of such devotion to civic duties in one whose days have already been extended an average lifetime beyond the Psalmist's limit, cannot but be valuable and fruitful. It is not for myself only, but for the country which you have in your sphere served so long and so well, that I thank you.
Your friend and servant,
Yours of to-day received. It seems that Lieutenant-Governor Jacobs and Colonel Wolford are stationary now. General Sudarth and Mr. Hodges are here, and the Secretary of War and myself are trying to devise means of pacification and harmony for Kentucky, which we hope to effect soon, now that the passion-exciting subject of the election is past.
I have no knowledge, information, or belief, that three States—or any States, offer to resume allegiance.
26, 1864 MAJOR-GENERAL ROSECRANS:
Please telegraph me briefly on what charge and evidence Mrs. Anna B. Martin has been sent to the penitentiary at Alton.
On Thursday of last week, two ladies from Tennessee came before the President, asking the release of their husbands held as prisoners of war at Johnson's Island. They were put off until Friday, when they came again, and were again put off until Saturday. At each of the interviews one of the ladies urged that her husband was a religious man, and on Saturday the President ordered the release of the prisoners, when he said to this lady: "You say your husband is a religious man; tell him when you meet him, that I say I am not much of a judge of religion, but that, in my opinion, the religion that sets men to rebel and fight against their own government, because, as they think, that government does not sufficiently help some men to eat their bread in the sweat of other men's faces, is not the sort of religion upon which people can get to heaven."
A war steamer, called the Funayma Solace, having been built in this country, for the Japanese government and at the instance of that government, it is deemed to comport with the public interest, in view of the unsettled condition of the relations of the United States with that Empire, that the steamer should not be allowed to proceed to Japan. If, however, the Secretary of the Navy should ascertain that the steamer is adapted to our service, he is authorized to purchase her, but the purchase money will be held in trust toward satisfying any valid claims which may be presented by the Japanese on account of the construction of the steamer and the failure to deliver the same, as above set forth.
A. LINCOLN. MESSAGE TO CONGRESS.
WASHINGTON CITY, December 5, 1864
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In conformity to the law of July 16, 1862, I most cordially recommend that Captain John A. Winslow, United States Navy, receive a vote of thanks from Congress for the skill and gallantry exhibited by him in the brilliant action whilst in command of the United States steamer Keaysarge, which led to the total destruction of the piratical craft Alabama, on the 19th of June, 1864., a vessel superior in tonnage, superior in number of guns, and superior in number of crew.
This recommendation is specially made in order to comply with the requirements of the ninth section of the aforesaid act, which is in the following words, viz:
That any line officer of the navy or marine corps may be advanced one grade, if, upon recommendation by the President by name he receives the thanks of Congress for highly distinguished conduct in conflict with the enemy, or far extraordinary heroism in the line of his profession.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In conformity to the law of July 16, 1862, I most cordially recommend that Lieutenant William B. Gushing, United States Navy, receive a vote of thanks from Congress for his important, gallant, and perilous achievement in destroying the rebel ironclad steamer Albemarle on the night of the 27th of October, 1864., at Plymouth, N. C.
The destruction of so formidable a vessel, which had resisted the continued attacks of a number of our vessels on former occasions, is an important event touching our future naval and military operations, and would reflect honor on any officer, and redounds to the credit of this young officer and the few brave comrades who assisted in this successful and daring undertaking.
This recommendation is specially made in order to comply with the requirements of the ninth section of the Aforesaid act, which is in the following words, namely:
That any line officer of the navy or marine corps may be advanced one grade if upon recommendation of the President by name he receives the thanks of Congress for highly distinguished conduct in conflict with the enemy, or for extraordinary heroism in the line of his profession.
FELLOW-CITIZENS OF THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
Again the blessings of health and abundant harvests claim our profoundest gratitude to Almighty God.
The condition of our foreign affairs is reasonably satisfactory.
Mexico continues to be a theater of civil war. While our political relations with that country have undergone no change, we have at the same time strictly maintained neutrality between the belligerents.
At the request of the States of Costa Rica and Nicaragua, a competent engineer has been authorized to make a survey of the river San Juan and the port of San Juan. It is a source of much satisfaction that the difficulties which for a moment excited some political apprehensions and caused a closing of the interoceanic transit route have been amicably adjusted, and that there is a good prospect that the route will soon be reopened with an increase of capacity and adaptation. We could not exaggerate either the commercial or the political importance of that great improvement.
It would be doing injustice to an important South American State not to acknowledge the directness, frankness, and cordiality with which the United States of Colombia have entered into intimate relations with this government. A claims convention has been constituted to complete the unfinished work of the one which closed its session in 1861.
The new liberal constitution of Venezuela having gone into effect with the universal acquiescence of the people, the government under it has been recognized and diplomatic intercourse with it has opened in a cordial and friendly spirit. The long-deferred Aves Island claim has been satisfactorily paid and discharged.
Mutual payments have been made of the claims awarded by the late joint commission for the settlement of claims between the United States and Peru. An earnest and cordial friendship continues to exist between the two countries, and such efforts as were in my power have been used to remove misunderstanding, and avert a threatened war between Peru and Spain.
Our relations are of the most friendly nature with Chile, the Argentine Republic, Bolivia, Costa Rica, Paraguay, San Salvador, and Haiti.
During the past year no differences of any kind have arisen with any of these republics, and on the other hand, their sympathies with the United States are constantly expressed with cordiality and earnestness.
The claim arising from the seizure of the cargo of the brig Macedonian in 1821 has been paid in full by the Government of Chile.
Civil war continues in the Spanish part of San Domingo, apparently without prospect of an early close.
Official correspondence has been freely opened with Liberia, and it gives us a pleasing view of social and political progress in that republic. It may be expected to derive new vigor from American influence improved by the rapid disappearance of slavery in the United States.
I solicit your authority to furnish to the republic a gunboat, at moderate cost, to be reimbursed to the United States by instalments. Such a vessel is needed for the safety of that state against the native African races, and in Liberian hands it would be more effective in arresting the African slave-trade than a squadron in our own hands. The possession of the least organized naval force would stimulate a generous ambition in the republic, and the confidence which we should manifest by furnishing it would win forbearance and favor toward the colony from all civilized nations.
The proposed overland telegraph between America and Europe, by the way of Bering Straits and Asiatic Russia, which was sanctioned by Congress at the last session, has been undertaken, under very favorable circumstances, by an association of American citizens, with the cordial good-will and support as well of this Government as of those of Great Britain and Russia. Assurances have been received from most of the South American States of their high appreciation of the enterprise and their readiness to co-operate in constructing lines tributary to that world-encircling communication. I learn with much satisfaction that the noble design of a telegraphic communication between the eastern coast of America and Great Britain has been renewed, with full expectation of its early accomplishment.
Thus it is hoped that with the return of domestic peace the country will be able to resume with energy and advantage its former high career of commerce and civilization.
Our very popular and estimable representative in Egypt died in April last. An unpleasant altercation which arose between the temporary incumbent of the office and the Government of the Pasha resulted in a suspension of intercourse. The evil was promptly corrected on the arrival of the successor in the consulate, and our relations with Egypt, as well as our relations with the Barbary Powers, are entirely satisfactory.
The rebellion which has so long been flagrant in China has at last been suppressed, with the co-operating good offices of this Government and of the other Western commercial States. The judicial consular establishment there has become very difficult and onerous, and it will need legislative revision to adapt it to the extension of our commerce and to the more intimate intercourse which has been instituted with the Government and people of that vast Empire. China seems to be accepting with hearty good-will the conventional laws which regulate commercial and social intercourse among the Western nations.
Owing to the peculiar situation of Japan and the anomalous form of its Government, the action of that empire in performing treaty stipulations is inconstant and capricious. Nevertheless, good progress has been effected by the Western powers, moving with enlightened concert. Our own pecuniary claims have been allowed or put in course of settlement, and the inland sea has been reopened to commerce. There is reason also to believe that these proceedings have increased rather than diminished the friendship of Japan toward the United States.
The ports of Norfolk, Fernandina, and Pensacola have been opened by proclamation. It is hoped that foreign merchants will now consider whether it is not safer and more profitable to themselves, as well as just to the United States, to resort to these and other open ports than it is to pursue, through many hazards and at vast cost, a contraband trade with other ports which are closed, if not by actual military occupation, at least by a lawful and effective blockade.
For myself, I have no doubt of the power and duty of the Executive, under the law of nations, to exclude enemies of the human race from an asylum in the United States. If Congress should think that proceedings in such cases lack the authority of law, or ought to be further regulated by it, I recommend that provision be made for effectually preventing foreign slave traders from acquiring domicile and facilities for their criminal occupation in our country.
It is possible that if it were a new and open question the maritime powers, with the lights they now enjoy, would not concede the privileges of a naval belligerent to the insurgents of the United States, destitute, as they are, and always have been, equally of ships of war and of ports and harbors. Disloyal emissaries have been neither assiduous nor more successful during the last year than they were before that time in their efforts, under favor of that privilege, to embroil our country in foreign wars. The desire and determination of the governments of the maritime states to defeat that design are believed to be as sincere as and can not be more earnest than our own. Nevertheless, unforeseen political difficulties have arisen, especially in Brazilian and British ports and on the northern boundary of the United States, which have required, and are likely to continue to require, the practice of constant vigilance and a just and conciliatory spirit on the part of the United States, as well as of the nations concerned and their governments.
Commissioners have been appointed under the treaty with Great Britain on the adjustment of the claims of the Hudson Bay and Puget Sound Agricultural Companies, in Oregon, and are now proceeding to the execution of the trust assigned to them.
In view of the insecurity of life and property in the region adjacent to the Canadian border, by reason of recent assaults and depredations committed by inimical and desperate persons who are harbored there, it has been thought proper to give notice that after the expiration of six months, the period conditionally stipulated in the existing arrangement with Great Britain, the United States must hold themselves at liberty to increase their naval armament upon the Lakes if they shall find that proceeding necessary. The condition of the border will necessarily come into consideration in connection with the question of continuing or modifying the rights of transit from Canada through the United States, as well as the regulation of imposts, which were temporarily established by the reciprocity treaty of the 5th June, 1854.
I desire, however, to be understood while making this statement that the colonial authorities of Canada are not deemed to be intentionally unjust or unfriendly toward the United States, but, on the contrary, there is every reason to expect that, with the approval of the Imperial Government, they will take the necessary measures to prevent new incursions across the border.
The act passed at the last session for the encouragement of immigration has so far as was possible been put into operation. It seems to need amendment which will enable the officers of the Government to prevent the practice of frauds against the immigrants while on their way and on their arrival in the ports, so as to secure them here a free choice of avocations and places of settlement. A liberal disposition toward this great national policy is manifested by most of the European States, and ought to be reciprocated on our part by giving the immigrants effective national protection. I regard our immigrants as one of the principal replenishing streams which are appointed by Providence to repair the ravages of internal war and its wastes of national strength and health. All that is necessary is to secure the flow of that stream in its present fullness, and to that end the Government must in every way make it manifest that it neither needs nor designs to impose involuntary military service upon those who come from other lands to cast their lot in our country. The financial affairs of the Government have been successfully administered during the last year. The legislation of the last session of Congress has beneficially affected the revenues, although sufficient time has not yet elapsed to experience the full effect of several of the provisions of the acts of Congress imposing increased taxation.
The receipts during the year from all sources, upon the basis of warrants signed by the Secretary of the Treasury, including loans and the balance in the Treasury on the 1st day of July, 1863, were $1,394,196,007.62, and the aggregate disbursements, upon the same basis, were $1,298,056,101.89, leaving a balance in the Treasury, as shown by warrants, of $96,739,905.73.
Deduct from these amounts the amount of the principal of the public debt redeemed and the amount of issues in substitution therefor, and the actual cash operations of the Treasury were: receipts, $884,076,646.57; disbursements, $865,234,087.86; which leaves a cash balance in the Treasury of $18,842,558.71.
Of the receipts there were derived from customs $102,316,152.99, from lands $588,333.29, from direct taxes $475,648.96, from internal revenue $109,741,134.10, from miscellaneous sources $47,511,448.10, and from loans applied to actual expenditures, including former balance, $623,443,929.13.
There were disbursed for the civil service $27,505,599.46, for pensions and Indians $7,517,930.97, for the War Department $690,791,842.97, for the Navy Department $85,733,292.77, for interest on the public debt $53,685,421.69, making an aggregate of $865,234,087.86, and leaving a balance in the Treasury of $18,842,558.71, as before stated.
For the actual receipts and disbursements for the first quarter and the estimated receipts and disbursements for the three remaining quarters of the current fiscal year, and the general operations of the Treasury in detail, I refer you to the report of the Secretary of the Treasury. I concur with him in the opinion that the proportion of moneys required to meet the expenses consequent upon the war derived from taxation should be still further increased; and I earnestly invite your attention to this subject to the end that there be such additional legislation as shall be required to meet the just expectations of the Secretary.
The public debt on the first day of July last, as appears by the books of the Treasury, amounted to $1,740,690,489.49. Probably, should the war continue for another year, that amount may be increased by not far from $500,000,000. Held, as it is, for the most part by our own people, it has become a substantial branch of national, though private, property. For obvious reasons the more nearly this property can be distributed among all the people the better. To favor such general distribution, greater inducements to become owners might, perhaps, with good effect and without injury be presented to persons of limited means. With this view I suggest whether it might not be both competent and expedient for Congress to provide that a limited amount of some future issue of public securities might be held by any bona fide purchaser exempt from taxation and from seizure for debt, under such restrictions and limitations as might be necessary to guard against abuse of so important a privilege. This would enable every prudent person to set aside a small annuity against a possible day of want.
Privileges like these would render the possession of such securities to the amount limited most desirable to every person of small means who might be able to save enough for the purpose. The great advantage of citizens being creditors as well as debtors with relation to the public debt is obvious. Men readily perceive that they can not be much oppressed by a debt which they owe to themselves.
The public debt on the first day of July last, although somewhat exceeding the estimate of the Secretary of the Treasury made to Congress at the commencement of the last session, falls short of the estimate of that officer made in the preceding December as to its probable amount at the beginning of this year by the sum of $3,995,097.31. This fact exhibits a satisfactory condition and conduct of the operations of the Treasury.
The national banking system is proving to be acceptable to capitalists and to the people. On the twenty-fifth day of November five hundred and eighty-four national banks had been organized, a considerable number of which were conversions from State banks. Changes from State systems to the national system are rapidly taking place, and it is hoped that very soon there will be in the United States no banks of issue not authorized by Congress and no bank-note circulation not secured by the Government. That the Government and the people will derive great benefit from this change in the banking systems of the country can hardly be questioned. The national system will create a reliable and permanent influence in support of the national credit and protect the people against losses in the use of paper money. Whether or not any further legislation is advisable for the suppression of State-bank issues, it will be for Congress to determine. It seems quite clear that the Treasury can not be satisfactorily conducted unless the Government can exercise a restraining power over the bank-note circulation of the country.
The report of the Secretary of War and the accompanying documents will detail the campaigns of the armies in the field since the date of the last annual message, and also the operations of the several administrative bureaus of the War Department during the last year. It will also specify the measures deemed essential for the national defense and to keep up and supply the requisite military force.
The report of the Secretary of the Navy presents a comprehensive and satisfactory exhibit of the affairs of that Department and of the naval service. It is a subject of congratulation and laudable pride to our countrymen that a Navy of such vast proportions has been organized in so brief a period and conducted with so much efficiency and success.
The general exhibit of the Navy, including vessels under construction on the first of December, 1864, shows a total of 671 vessels, carrying 4610 guns, and of 510,396 tons, being an actual increase during the year, over and above all losses by shipwreck or in battle, of 83 vessels, 167 guns, and 42,427 tons.
The total number of men at this time in the naval service, including officers, is about 51,000.
There have been captured by the Navy during the year 324 vessels, and the whole number of naval captures since hostilities commenced is 1379, of which 267 are steamers.
The gross proceeds arising from the sale of condemned prize property thus far reported amount to $14,369,250.51. A large amount of such proceeds is still under adjudication and yet to be reported.
The total expenditure of the Navy Department of every description, including the cost of the immense squadrons that have been called into existence from the fourth of March, 1861, to the first of November, 1864, is $238,647,262.35.
Your favorable consideration is invited to the various recommendations of the Secretary of the Navy, especially in regard to a navy-yard and suitable establishment for the construction and repair of iron vessels and the machinery and armature for our ships, to which reference was made in my last annual message.
Your attention is also invited to the views expressed in the report in relation to the legislation of Congress at its last session in respect to prize on our inland waters.
I cordially concur in the recommendation of the Secretary as to the propriety of creating the new rank of vice-admiral in our naval service.
Your attention is invited to the report of the Postmaster-General for a detailed account of the operations and financial condition of the Post-Office Department.
The postal revenues for the year ending June 30, 1864, amounted to $12,438,253.78, and the expenditures to $12,644,786.20, the excess of expenditures over receipts being $206,532.42.
The views presented by the Postmaster-General on the subject of special grants by the Government in aid of the establishment of new lines of ocean mail steamships and the policy he recommends for the development of increased commercial intercourse with adjacent and neighboring countries should receive the careful consideration of Congress.
It is of noteworthy interest that the steady expansion of population, improvement, and governmental institutions over the new and unoccupied portions of our country have scarcely been checked, much less impeded or destroyed, by our great civil war, which at first glance would seem to have absorbed almost the entire energies of the nation.
The organization and admission of the State of Nevada has been completed in conformity with law, and thus our excellent system is firmly established in the mountains, which once seemed a barren and uninhabitable waste between the Atlantic States and those which have grown up on the coast of the Pacific Ocean.
The Territories of the Union are generally in a condition of prosperity and rapid growth. Idaho and Montana, by reason of their great distance and the interruption of communication with them by Indian hostilities, have been only partially organized; but it is understood that these difficulties are about to disappear, which will permit their governments, like those of the others, to go into speedy and full operation.
As intimately connected with and promotive of this material growth of the nation, I ask the attention of Congress to the valuable information and important recommendations relating to the public lands, Indian affairs, the Pacific Railroad, and mineral discoveries contained in the report of the Secretary of the Interior which is herewith transmitted, and which report also embraces the subjects of patents, pensions, and other topics of public interest pertaining to his Department.
The quantity of public land disposed of during the five quarters ending on the thirtieth of September last was 4,221,342 acres, of which 1,538,614 acres were entered under the homestead law. The remainder was located with military land warrants, agricultural scrip certified to States for railroads, and sold for cash. The cash received from sales and location fees was $1,019,446.
The income from sales during the fiscal year ending June 30, 1864, was $678,007.21, against $136,077.95 received during the preceding year. The aggregate number of acres surveyed during the year has been equal to the quantity disposed of, and there is open to settlement about 133,000,000 acres of surveyed land.
The great enterprise of connecting the Atlantic with the Pacific States by railways and telegraph lines has been entered upon with a vigor that gives assurance of success, notwithstanding the embarrassments arising from the prevailing high prices of materials and labor. The route of the main line of the road has been definitely located for one hundred miles westward from the initial point at Omaha City, Nebraska, and a preliminary location of the Pacific Railroad of California has been made from Sacramento eastward to the great bend of the Truckee River in Nevada.
Numerous discoveries of gold, silver, and cinnabar mines have been added to the many heretofore known, and the country occupied by the Sierra Nevada and Rocky mountains and the subordinate ranges now teems with enterprising labor, which is richly remunerative. It is believed that the produce of the mines of precious metals in that region has during the year reached, if not exceeded, $100,000,000 in value.
It was recommended in my last annual message that our Indian system be remodeled. Congress at its last session, acting upon the recommendation, did provide for reorganizing the system in California, and it is believed that under the present organization the management of the Indians there will be attended with reasonable success. Much yet remains to be done to provide for the proper government of the Indians in other parts of the country, to render it secure for the advancing settler, and to provide for the welfare of the Indian. The Secretary reiterates his recommendations, and to them the attention of Congress is invited.
The liberal provisions made by Congress for paying pensions to invalid soldiers and sailors of the Republic and to the widows, orphans, and dependent mothers of those who have fallen in battle or died of disease contracted or of wounds received in the service of their country have been diligently administered. There have been added to the pension rolls during the year ending the 30th day of June last the names of 16,770 invalid soldiers and of 271 disabled seamen, making the present number of army invalid pensioners 22,767 and of navy invalid pensioners 712.
Of widows, orphans, and mothers 22,198 have been placed on the army pension rolls and 248 on the navy rolls. The present number of army pensioners of this class is 25,433 and of navy pensioners 793. At the beginning of the year the number of Revolutionary pensioners was 1430. Only twelve of them were soldiers, of whom seven have since died. The remainder are those who under the law receive pensions because of relationship to Revolutionary soldiers. During the year ending the thirtieth of June, 1864, $4,504,616.92 have been paid to pensioners of all classes.
I cheerfully commend to your continued patronage the benevolent institutions of the District of Columbia which have hitherto been established or fostered by Congress, and respectfully refer for information concerning them and in relation to the Washington Aqueduct, the Capitol, and other matters of local interest to the report of the Secretary.
The Agricultural Department, under the supervision of its present energetic and faithful head, is rapidly commending itself to the great and vital interest it was created to advance. It is peculiarly the people's department, in which they feel more directly concerned than in any other. I commend it to the continued attention and fostering care of Congress.
The war continues. Since the last annual message all the important lines and positions then occupied by our forces have been maintained and our arms have steadily advanced, thus liberating the regions left in rear, so that Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, and parts of other States have again produced reasonably fair crops.
The most remarkable feature in the military operations of the year is General Sherman's attempted march of three hundred miles directly through the insurgent region. It tends to show a great increase of our relative strength that our General-in-Chief should feel able to confront and hold in check every active force of the enemy, and yet to detach a well-appointed large army to move on such an expedition. The result not yet being known, conjecture in regard to it is not here indulged.
Important movements have also occurred during the year to the effect of molding society for durability in the Union. Although short of complete success, it is much in the right direction that twelve thousand citizens in each of the States of Arkansas and Louisiana have organized loyal State governments, with free constitutions, and are earnestly struggling to maintain and administer them. The movements in the same direction more extensive though less definite in Missouri, Kentucky, and Tennessee, should not be overlooked. But Maryland presents the example of complete success. Maryland is secure to liberty and union for all the future. The genius of rebellion will no more claim Maryland. Like another foul spirit being driven out, it may seek to tear her, but it will woo her no more.
At the last session of Congress a proposed amendment of the Constitution abolishing slavery throughout the United States passed the Senate, but failed for lack of the requisite two-thirds vote in the House of Representatives. Although the present is the same Congress and nearly the same members, and without questioning the wisdom or patriotism of those who stood in opposition, I venture to recommend the reconsideration and passage of the measure at the present session. Of course the abstract question is not changed; but an intervening election shows almost certainly that the next Congress will pass the measure if this does not. Hence there is only a question of time as to when the proposed amendment will go to the States for their action. And as it is to so go at all events, may we not agree that the sooner the better? It is not claimed that the election has imposed a duty on members to change their views or their votes any further than, as an additional element to be considered, their judgment may be affected by it. It is the voice of the people now for the first time heard upon the question. In a great national crisis like ours, unanimity of action among those seeking a common end is very desirable, almost indispensable. And yet no approach to such unanimity is attainable unless some deference shall be paid to the will of the majority simply because it is the will of the majority. In this case the common end is the maintenance of the Union, and among the means to secure that end such will, through the election, is most clearly declared in favor of such Constitutional amendment.
The most reliable indication of public purpose in this country is derived through our popular elections. Judging by the recent canvass and its result, the purpose of the people within the loyal States to maintain the integrity of the Union was never more firm nor more nearly unanimous than now. The extraordinary calmness and good order with which the millions of voters met and mingled at the polls give strong assurance of this. Not only all those who supported the Union ticket, so called, but a great majority of the opposing party also may be fairly claimed to entertain and to be actuated by the same purpose. It is an unanswerable argument to this effect that no candidate for any office whatever, high or low, has ventured to seek votes on the avowal that he was for giving up the Union. There have been much impugning of motives and much heated controversy as to the proper means and best mode of advancing the Union cause, but on the distinct issue of Union or no Union the politicians have shown their instinctive knowledge that there is no diversity among the people. In affording the people the fair opportunity of showing one to another and to the world this firmness and unanimity of purpose, the election has been of vast value to the national cause.
The election has exhibited another fact not less valuable to be known—the fact that we do not approach exhaustion in the most important branch of national resources, that of living men. While it is melancholy to reflect that the war has filled so many graves and carried mourning to so many hearts, it is some relief to know that, compared with the surviving, the fallen have been so few. While corps and divisions and brigades and regiments have formed and fought and dwindled and gone out of existence, a great majority of the men who composed them are still living. The same is true of the naval service. The election returns prove this. So many voters could not else be found. The States regularly holding elections, both now and four years ago, to wit, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wisconsin, cast 3,982,011 votes now, against 3,870,222 cast then, showing an aggregate now of 3,982,011. To this is to be added 33,762 cast now in the new States of Kansas and Nevada, which States did not vote in 1860, thus swelling the aggregate to 4,015,773 and the net increase during the three years and a half of war to 145,551. A table is appended showing particulars. To this again should be added the number of all soldiers in the field from Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Delaware, Indiana, Illinois, and California, who by the laws of those States could not vote away from their homes, and which number can not be less than 90,000. Nor yet is this all. The number in organized Territories is triple now what it was four years ago—while thousands, white and black, join us as the national arms press back the insurgent lines. So much is shown, affirmatively and negatively, by the election. It is not material to inquire how the increase has been produced or to show that it would have been greater but for the war, which is probably true. The important fact remains demonstrated that we have more men now than we had when the war began; that we are not exhausted nor in process of exhaustion; that we are gaining strength and may if need be maintain the contest indefinitely. [This sentence recognizes the concern of a guerilla war after the main war finished.]This as to men. Material resources are now more complete and abundant than ever.
The national resources, then, are unexhausted, and, as we believe, inexhaustible. The public purpose to re-establish and maintain the national authority is unchanged, and, as we believe, unchangeable. The manner of continuing the effort remains to choose. On careful consideration of all the evidence accessible it seems to me that no attempt at negotiation with the insurgent leader could result in any good. He would accept nothing short of severance of the Union, precisely what we will not and can not give. His declarations to this effect are explicit and oft repeated. He does not attempt to deceive us. He affords us no excuse to deceive ourselves. He can not voluntarily reaccept the Union; we can not voluntarily yield it. Between him and us the issue is distinct, simple, and inflexible. It is an issue which can only be tried by war and decided by victory. If we yield, we are beaten; if the Southern people fail him, he is beaten. Either way it would be the victory and defeat following war. What is true, however, of him who heads the insurgent cause is not necessarily true of those who follow. Although he can not reaccept the Union, they can. Some of them, we know, already desire peace and reunion. The number of such may increase. They can at any moment have peace simply by laying down their arms and submitting to the national authority under the Constitution. After so much the Government could not, if it would, maintain war against them. The loyal people would not sustain or allow it. If questions should remain, we would adjust them by the peaceful means of legislation, conference, courts, and votes, operating only in Constitutional and lawful channels. Some certain, and other possible, questions are and would be beyond the Executive power to adjust; as, for instance, the admission of members into Congress and whatever might require the appropriation of money. The Executive power itself would be greatly diminished by the cessation of actual war. Pardons and remissions of forfeitures, however, would still be within Executive control. In what spirit and temper this control would be exercised can be fairly judged of by the past.
A year ago general pardon and amnesty, upon specified terms, were offered to all except certain designated classes, and it was at the same time made known that the excepted classes were still within contemplation of special clemency. During the year many availed themselves of the general provision, and many more would, only that the signs of bad faith in some led to such precautionary measures as rendered the practical process less easy and certain. During the same time also special pardons have been granted to individuals of the excepted classes, and no voluntary application has been denied. Thus practically the door has been for a full year open to all except such as were not in condition to make free choice; that is, such as were in custody or under constraint. It is still so open to all. But the time may come, probably will come, when public duty shall demand that it be closed and that in lieu more rigorous measures than heretofore shall be adopted.
In presenting the abandonment of armed resistance to the national authority on the part of the insurgents as the only indispensable condition to ending the war on the part of the Government, I retract nothing heretofore said as to slavery. I repeat the declaration made a year ago, that "while I remain in my present position I shall not attempt to retract or modify the emancipation proclamation, nor shall I return to slavery any person who is free by the terms of that proclamation or by any of the acts of Congress." If the people should, by whatever mode or means, make it an Executive duty to re-enslave such persons, another, and not I, must be their instrument to perform it.
In stating a single condition of peace I mean simply to say that the war will cease on the part of the Government whenever it shall have ceased on the part of those who began it.
FRIENDS AND FELLOW-CITIZENS:—I believe I shall never be old enough to speak without embarrassment when I have nothing to talk about. I have no good news to tell you, and yet I have no bad news to tell. We have talked of elections until there is nothing more to say about them. The most interesting news now we have is from Sherman. We all know where he went in at, but I can't tell where he will come out at. I will now close by proposing three cheers for General Sherman and his army.
GOVERNOR HALL, Jefferson City, Mo.:
Complaint is made to me of the doings of a man at Hannibal, Mo., by the name of Haywood, who, as I am told, has charge of some militia force, and is not in the United States service. Please inquire into the matter and correct anything you may find amiss if in your power.
COLONEL FASLEIGH, Louisville, Ky.:
I am appealed to in behalf of a man by the name of Frank Fairbairns, said to have been for a long time and still in prison, without any definite ground stated. How is it?
EXECUTIVE MANSION, December 10, 1864.
ORDERED, First, that Major-General William P. Smith and the Hon. Henry Stanbery be, and they are hereby, appointed special commissioners to investigate and report, for the information of the President; upon the civil and military administration in the military division bordering upon and west of the Mississippi, under such instructions as shall be issued by authority of the President and the War Department.
Second, said commissioners shall have power to examine witnesses upon oath, and to take such proofs orally or in writing, upon the subject-matters of investigation as they may deem expedient, and return the same together with their report.
Third, all officers and persons in the military, naval and revenue services, or in any branch of the public service under the authority of the United States Government, are required, upon subpoena issued by direction of the said commissioners, to appear before them at such time and place as may be designated in said subpoena and to give testimony on oath touching such matters as may be inquired of by the commissioners, and to produce such books, papers, writings, and documents as they may be notified or required to produce by the commissioners, and as may be in their possession.
Fourth, said special commissioners shall also investigate and report upon any other matters that may hereafter be directed by the Secretary of War, and shall with all convenient dispatch make report to him in writing of their investigation, and shall also from time to time make special reports to the Secretary of War upon such matters as they may deem of importance to the public interests.
Fifth, the Secretary of War shall assign to the said commissioners such aid and assistance as may be required for the performance of their duties, and make such just and reasonable allowances and compensation for the said commissioners and for the persons employed by them as he may deem proper.
Please accept for yourself, officers, and men, the nation's thanks for your good work of yesterday. You made a magnificent beginning; a grand consummation is within your easy reach. Do not let it slip.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December [16?], 1864.
DEAR COLONEL DICK:—I have long determined to make public the origin of the greenback and tell the world that it is Dick Taylor's creation. You had always been friendly to me, and when troublous times fell on us, and my shoulders, though broad and willing, were weak, and myself surrounded by such circumstances and such people that I knew not whom to trust, then I said in my extremity: "I will send for Colonel Taylor; he will know what to do." I think it was in January, 1862, on or about the 16th, that I did so. You came, and I said to you:
"What can we do?" Said you, "Why, issue Treasury notes bearing no interest, printed on the best banking paper. Issue enough to pay off the Army expenses and declare it legal tender."
Chase thought it a hazardous thing, but we finally accomplished it, and gave the people of this Republic the greatest blessing they ever had—their own paper to pay their own debts.
It is due to you, the father of the present greenback, that the people should know it, and I take great pleasure in making it known. How many times have I laughed at you telling me plainly that I was too lazy to be anything but a lawyer.
Yours truly,
WASHINGTON, December 16, 1864
It is said that Harry Walters, a private in the Anderson cavalry, is now and for a long time has been in prison at Chattanooga. Please report to me what is his condition, and for what he is imprisoned.
A Proclamation
Whereas, by the act approved July 4, 1864, entitled "An act further to regulate and provide for the enrolling and calling out the national forces, and for other purposes," it is provided that the President of the United States may, "at his discretion, at any time hereafter, call for any number of men, as volunteers for the respective terms of one, two, and three years for military service," and "that in case the quota or any part thereof of any town, township, ward of a city, precinct, or election district, or of any country not so subdivided, shall not be filled within the space of fifty days after such call, then the President shall immediately order a draft for one year to fill such quota or any part thereof which may be unfilled;" and
Whereas, by the credits allowed in accordance with the act of Congress on the call for 500,000 men, made July 18, 1864, the number of men to be obtained under that call was reduced to 280,000; and
Whereas, the operations of the enemy in certain States have rendered it impracticable to procure from them their full quotas of troops under said call; and
Whereas, from the foregoing causes but 240,000 men have been put into the Army, Navy, and Marine Corps under the said call of July 18, 1864, leaving a deficiency on that call of two hundred and sixty thousand (260,000):
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, in order to supply the aforesaid deficiency and to provide for casualties in the military and naval service of the United States, do issue this my call for three hundred thousand (300,000) volunteers to serve for one, two, or three years. The quotas of the States, districts, and subdistricts under this call will be assigned by the War Department through the bureau of the Provost-Marshal General of the United States, and "in case the quota or any part thereof of any town, township, ward of a city, precinct, or election district, or of any county not so subdivided, shall not be filled" before the fifteenth of February, 1865, then a draft shall be made to fill such quota or any part thereof under this call which may be unfilled on said fifteenth day of February, 1865.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed..........
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, December 26, 1864
MY DEAR GENERAL SHERMAN:—Many, many thanks for your Christmas gift, the capture of Savannah.
When you were about leaving Atlanta for the Atlantic coast, I was anxious, if not fearful; but feeling that you were the better judge, and remembering that "nothing risked, nothing gained," I did not interfere. Now, the undertaking being a success, the honor is all yours; for I believe none of us went further than to acquiesce.
And taking the work of General Thomas into the count, as it should be taken, it is indeed a great success. Not only does it afford the obvious and immediate military advantages; but in showing to the world that your army could be divided, putting the stronger part to an important new service, and yet leaving enough to vanquish the old opposing force of the whole,—Hood's army,—it brings those who sat in darkness to see a great light. But what next?
I suppose it will be safe if I leave General Grant and yourself to decide.
Please make my grateful acknowledgments to your whole army of officers and men.
Yours very truly,
OFFICER IN COMMAND at Lexington, Ky.:
If within your power send me the particulars of the causes for which Lieutenant-Governor Jacob was arrested and sent away.
Dr. JOHN MACLEAN:
MY DEAR SIR:—I have the honor to acknowledge the reception of your note of the twentieth of December, conveying the announcement that the Trustees of the College of New Jersey had conferred upon me the degree of Doctor of Laws.
The assurance conveyed by this high compliment, that the course of the Government which I represent, has received the approval of a body of gentlemen of such character and intelligence, in this time of public trial, is most grateful to me.
Thoughtful men must feel that the fate of civilization upon this continent is involved in the issue of our contest. Among the most gratifying proofs of this conviction is the hearty devotion everywhere exhibited by our schools and colleges to the national cause.
I am most thankful if my labors have seemed to conduct to the preservation of those institutions, under which alone we can expect good government and in its train sound learning, and the progress of the liberal arts.
I am, sir, very truly, your obedient servant,
OFFICER IN COMMAND at Nashville, Tenn.:
Suspend execution of James R. Mallory, for six weeks from Friday the thirtieth of this month, which time I have given his friends to make proof, if they can, upon certain points.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
If there be no objection, please tell me what you now understand of the Wilmington expedition, present and prospective.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER:
There is a man in Company I, Eleventh Connecticut Volunteers, First Brigade, Third Division, Twenty-fourth Army Corps, at Chapin's Farm, Va.; under the assumed name of William Stanley, but whose real name is Frank R. Judd, and who is under arrest, and probably about to be tried for desertion. He is the son of our present minister to Prussia, who is a close personal friend of Senator Trumbull and myself. We are not willing for the boy to be shot, but we think it as well that his trial go regularly on, suspending execution until further order from me and reporting to me.
COLONEL WARNER, Indianapolis, Ind.:
It is said that you were on the court-martial that tried John Lennon, and that you are disposed to advise his being pardoned and sent to his regiment. If this be true, telegraph me to that effect at once.
JOHN WILLIAMS, Springfield, Ill.:
Let Trumbo's substitute be regularly mustered in, send me the evidence that it is done and I will then discharge Trumbo.
TO THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES OF THE UNITED STATES:
I herewith return to your honorable body, in which it originated, a "joint resolution to correct certain clerical errors in the internal revenue act," without my approval.
My reason for so doing is that I am informed that this joint resolution was prepared during the last moments of the last session of Congress for the purpose of correcting certain errors of reference in the internal revenue act, which were discovered on an examination of an official copy procured from the State Department a few hours only before the adjournment. It passed the House and went to the Senate, where a vote was taken upon it, but by some accident it was not presented to the President of the Senate for his signature.
Since the adjournment of the last session of Congress, other errors of a kind similar to those which this resolution was designed to correct, have been discovered in the law, and it is now thought most expedient to include all the necessary corrections in one act or resolution.
The attention of the proper committee of the House has, I am informed, been already directed to the preparation of a bill for this purpose.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Richard T. Jacob, Lieutenant-Governor of Kentucky, is at the Spotswood House, in Richmond, under an order of General Burbridge not to return to Kentucky. Please communicate leave to him to pass our lines, and come to me here at Washington.
WASHINGTON, January 6, 1865, LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point:
If there is a man at City Point by the name of Waterman Thornton who is in trouble about desertion, please have his case briefly stated to me and do not let him be executed meantime.
TO THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES: I transmit to Congress a copy of two treaties between the United States and Belgium, for the extinguishment of the Scheldt dues, etc., concluded on the twentieth of May, 1863, and twentieth of July, 1863, respectively, the ratifications of which were exchanged at Brussels on the twenty-fourth of June last; and I recommend an appropriation to carry into effect the provisions thereof relative to the payment of the proportion of the United States toward the capitalization of the said dues.
HON. SCHUYLER COLFAX, Speaker of the House of Representatives.
SIR:—I transmit herewith the letter of the Secretary of War, with accompanying report of the Adjutant-General, in reply to the resolution of the House of Representatives, dated December 7, 1864, requesting me "to communicate to the House the report made by Col. Thomas M. Key of an interview between himself and General Howell Cobb on the fourteenth [15th] day of June, 1862, on the banks of the Chickahominy, on the subject of the exchange of prisoners of war."
I am, sir, very respectfully, your obedient servant,
A Proclamation.
Whereas the act of Congress of the twenty-eighth of September, 1850, entitled "An act to create additional collection districts in the State of California, and to change the existing districts therein, and to modify the existing collection districts in the United States," extends to merchandise warehoused under bond the privilege of being exported to the British North American provinces adjoining the United States, in the manner prescribed in the act of Congress of the third of March, 1845, which designates certain frontier ports through which merchandise may be exported, and further provides "that such other ports situated on the frontiers of the United States, adjoining the British North American provinces, as may hereafter be found expedient, may have extended to them the like privileges on the recommendation of the Secretary of the Treasury, and proclamation duly made by the President of the United States, specially designating the ports to which the aforesaid privileges are to be extended;"
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, in accordance with the recommendation of the Secretary of the Treasury, do hereby declare and proclaim that the port of St. Albans, in the State of Vermont, is, and shall be, entitled to all the privileges in regard to the exportation of merchandise in bond to the British North American provinces adjoining the United States, which are extended to the ports enumerated in the seventh section of the act of Congress of the third of March, 1845, aforesaid, from and after the date of this proclamation.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this tenth day of January, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred-and sixty-five, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
No principal report of yours on the Wilmington expedition has ever reached the War Department, as I am informed there. A preliminary report did reach here, but was returned to General Grant at his request. Of course, leave to publish cannot be given without inspection of the paper, and not then if it should be deemed to be detrimental to the public service.
MAJOR-GENERAL BUTLER, Fort Monroe, Va.:
Yours asking leave to come to Washington is received. You have been summoned by the Committee on the Conduct of the War to attend here, which, of course, you will do.
GOVERNOR JOHNSON, Nashville, Tennessee:
Yours announcing ordinance of emancipation received. Thanks to the convention and to you. When do you expect to be here? Would be glad to have your suggestion as to supplying your place of military governor.
15, 1865.
MAJOR-GENERAL DODGE, St. Louis, Missouri:
It is represented to me that there is so much irregular violence in northern Missouri as to be driving away the people and almost depopulating it. Please gather information, and consider whether an appeal to the people there to go to their homes and let one another alone recognizing as a full right of protection for each that he lets others alone, and banning only him who refuses to let others alone may not enable you to withdraw the troops, their presence itself [being] a cause of irritation and constant apprehension, and thus restore peace and quiet, and returning prosperity. Please consider this and telegraph or write me.
WASHINGTON, January 18, 1865.
F. P. BLAIR, ESQ.
SIR:-You having shown me Mr. Davis's letter to you of the twelfth instant, you may say to him that I have constantly been, am now, and shall continue, ready to receive any agent whom he or any other influential person now resisting the national authority may informally send to me with the view of securing peace to the people of our one common country.
Yours, etc.,
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Please read and answer this letter as though I was not President, but only a friend. My son, now in his twenty-second year, having graduated at Harvard, wishes to see something of the war before it ends. I do not wish to put him in the ranks, nor yet to give him a commission, to which those who have already served long are better entitled and better qualified to hold. Could he, without embarrassment to you, or detriment to the service, go into your military family with some nominal rank, I, and not the public, furnishing his necessary means? If no, say so without the least hesitation, because I am as anxious and as deeply interested that you shall not be encumbered as you can be yourself.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL DODGE, Saint Louis, Mo.:
If Mrs. Beattie, alias Mrs. Wolff, shall be sentenced to death, notify me, and postpone the execution till further order.
MAJOR-GENERAL ORD:
You have a man in arrest for desertion passing by the name of Stanley. William Stanley, I think, but whose real name is different. He is the son of so close a friend of mine that I must not let him be executed. Please let me know what is his present and prospective condition.
MAJOR-GENERAL DODGE, St. Louis, Mo.:
It is said an old lady in Clay County, Missouri, by name Mrs. Winifred B. Price, is about being sent South. If she is not misbehaving let her remain.
HON. ANDREW JOHNSON, Nashville, Tennessee:
Several members of the Cabinet, with myself, considered the question, to-day, as to the time of your coming on here. While we fully appreciate your wish to remain in Tennessee until her State government shall be completely reinaugurated, it is our unanimous conclusion that it is unsafe for you to not be here on the 4th of March. Be sure to reach here by that time.
I accept with emotions of profoundest gratitude, the beautiful gift you have been pleased to present to me. You will, of course, expect that I acknowledge it. So much has been said about Gettysburg and so well, that for me to attempt to say more may perhaps only serve to weaken the force of that which has already been said. A most graceful and eloquent tribute was paid to the patriotism and self-denying labors of the American ladies, on the occasion of the consecration of the National Cemetery at Gettysburg, by our illustrious friend, Edward Everett, now, alas! departed from earth. His life was a truly great one, and I think the greatest part of it was that which crowned its closing years, I wish you to read, if you have not already done so, the eloquent and truthful words which he then spoke of the women of America. Truly, the services they have rendered to the defenders of our country in this perilous time, and are yet rendering, can never be estimated as they ought to be. For your kind wishes to me personally, I beg leave to render you likewise my sincerest thanks. I assure you they are reciprocated. And now, gentlemen and ladies, may God bless you all.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point
If Newell W. Root, of First Connecticut Heavy Artillery, is under sentence of death, please telegraph me briefly the circumstances.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Having received the report in the case of Newell W. Root, I do not interfere further in the case.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January 30, 1865.
MAJOR T. T. ECKERT.
SIR:-You will proceed with the documents placed in your hands, and on reaching General Ord will deliver him the letter addressed to him by the Secretary of War. Then, by General Ord's assistance procure an interview with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, or any of them, deliver to him or them the paper on which your own letter is written. Note on the copy which you retain the time of delivery and to whom delivered. Receive their answer in writing, waiting a reasonable time for it, and which, if it contain their decision to come through without further condition, will be your warrant to ask General Ord to pass them through as directed in the letter of the Secretary of War to him. If by their answer they decline to come, or propose other terms, do not have them pass through. And this being your whole duty, return and report to me.
Yours truly,
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., January 30, 1865.
MAJOR-GENERAL ORD, Headquarters Army of the James:
By direction of the President you are instructed to inform the three gentlemen, Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, that a messenger will be dispatched to them at or near where they now are, without unnecessary delay.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
DEAR SIR:—The report is in circulation in the House that Peace Commissioners are on their way or in the city, and is being used against us. If it is true, I fear we shall lose the bill. Please authorize me to contradict it, if it is not true.
Respectfully, J. M. ASHLEY.
To the President.
(Indorsement.)
So far as I know there are no Peace Commissioners in the city or likely to be in it.
A. LINCOLN. January 31, 1865
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
A messenger is coming to you on the business contained in your despatch. Detain the gentlemen in comfortable quarters until he arrives, and then act upon the message he brings, as far as applicable, it having been made up to pass through General Ord's hands, and when the gentlemen were supposed to be beyond our lines.
HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State
You will proceed to Fortress Monroe, Virginia, there to meet and informally confer with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, on the basis of my letter to F. P. Blair, Esq., of January 18, 1865, a copy of which you have. You will make known to them that three things are indispensable to wit:
1. The restoration of the national authority throughout all the States.
2. No receding by the Executive of the United States on the slavery question from the position assumed thereon in the late annual message to Congress, and in preceding documents.
3. No cessation of hostilities short of an end of the war and the disbanding of all forces hostile to the Government.
You will inform them that all propositions of theirs, not inconsistent with the above, will be considered and passed upon in a spirit of sincere liberality. You will hear all they may choose to say and report it to me. You will not assume to definitely consummate anything.
Yours, etc.,
PASSAGE THROUGH CONGRESS OF THE CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT FOR THE ABOLISHING OF SLAVERY
RESPONSE TO A SERENADE, JANUARY 31, 1865.
He supposed the passage through Congress of the Constitutional amendment for the abolishing of slavery throughout the United States was the occasion to which he was indebted for the honor of this call.
The occasion was one of congratulation to the country, and to the whole world. But there is a task yet before us—to go forward and consummate by the votes of the States that which Congress so nobly began yesterday. He had the honor to inform those present that Illinois had already done the work. Maryland was about half through, but he felt proud that Illinois was a little ahead.
He thought this measure was a very fitting if not an indispensable adjunct to the winding up of the great difficulty. He wished the reunion of all the States perfected, and so effected as to remove all causes of disturbance in the future; and, to attain this end, it was necessary that the original disturbing cause should, if possible, be rooted out. He thought all would bear him witness that he had never shirked from doing all that he could to eradicate slavery, by issuing an Emancipation Proclamation. But that proclamation falls short of what the amendment will be when fully consummated. A question might be raised whether the proclamation was legally valid. It might be added, that it only aided those who came into our lines, and that it was inoperative as to those who did not give themselves up; or that it would have no effect upon the children of the slaves born hereafter; in fact, it would be urged that it did not meet the evil. But this amendment is a king's cure for all evils. It winds the whole thing up. He would repeat, that it was the fitting if not the indispensable adjunct to the consummation of the great game we are playing. He could not but congratulate all present—himself, the country, and the whole world upon this great moral victory.
Let nothing which is transpiring change, hinder, or delay your military movements or plans.
Call at Fortress Monroe, and put yourself under direction of Mr. Seward, whom you will find there.
Say to the gentlemen I will meet them personally at Fortress Monroe as soon as I can get there.
Induced by a despatch of General Grant, I join you at Fort Monroe, as soon as I can come.
Whereas complaints are made in some localities respecting the assignments of quotas and credits allowed for the pending call of troops to fill up the armies: Now, in order to determine all controversies in respect thereto, and to avoid any delay in filling up the armies, it is ordered,
1. That the Attorney-General, Brigadier-General Richard Delafield, and Colonel C. W. Foster, be, and they are hereby constituted, a board to examine into the proper quotas and credits of the respective States and districts under the call of December 19, 1864, with directions, if any errors be found therein, to make such corrections as the law and facts may require, and report their determination to the Provost-Marshal-General. The determination of said board to be final and conclusive, and the draft to be made in conformity therewith.
2. The Provost-Marshal-General is ordered to make the draft in the respective districts as speedily as the same can be done after the fifteenth of this month.
PROVOST-MARSHAL-GENERAL:
These gentlemen distinctly say to me this morning that what they want is the means from your office of showing their people that the quota assigned to them is right. They think it will take but little time—two hours, they say. Please give there double the time and every facility you can.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
February 6, 1865.
The Provost-Marshal brings this letter back to me and says he cannot give the facility required without detriment to the service, and thereupon he is excused from doing it.
LIEUTENANT-COLONEL GLENN, Commanding Post at Henderson, Ky.:
Complaint is made to me that you are forcing negroes into the military service, and even torturing them—riding them on rails and the like to extort their consent. I hope this may be a mistake. The like must not be done by you, or any one under you. You must not force negroes any more than white men. Answer me on this.
HIS EXCELLENCY GOVERNOR SMITH, of Vermont:
Complaint is made to me, by Vermont, that the assignment of her quota for the draft on the pending call is intrinsically unjust, and also in bad faith of the Government's promise to fairly allow credits for men previously furnished. To illustrate, a supposed case is stated as follows:
Vermont and New Hampshire must between them furnish six thousand men on the pending call; and being equal, each must furnish as many as the other in the long run. But the Government finds that on former calls Vermont furnished a surplus of five hundred, and New Hampshire a surplus, of fifteen hundred. These two surpluses making two thousand and added to the six thousand, making eight thousand to be furnished by the two States, or four thousand each less, by fair credits. Then subtract Vermont's surplus of five hundred from her four thousand, leaves three thousand five hundred as her quota on the pending call; and likewise subtract New Hampshire's surplus of fifteen hundred from her four thousand, leaves two thousand five hundred as her quota on the pending call. These three thousand five hundred and two thousand five hundred make precisely six thousand, which the supposed case requires from the two States, and it is just equal for Vermont to furnish one thousand more now than New Hampshire, because New Hampshire has heretofore furnished one thousand more than Vermont, which equalizes the burdens of the two in the long run. And this result, so far from being bad faith to Vermont, is indispensable to keeping good faith with New Hampshire. By no other result can the six thousand men be obtained from the two States, and, at the same time deal justly and keep faith with both, and we do but confuse ourselves in questioning the process by which the right result is reached. The supposed case is perfect as an illustration.
The pending call is not for three hundred thousand men subject to fair credits, but is for three hundred thousand remaining after all fair credits have been deducted, and it is impossible to concede what Vermont asks without coming out short of three hundred thousand men, or making other localities pay for the partiality shown her.
This upon the case stated. If there be different reasons for making an allowance to Vermont, let them be presented and considered.
Yours truly,
TO THE HONORABLE THE SENATE AND HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
The joint resolution entitled "Joint resolution declaring certain States not entitled to representation in the electoral college" has been signed by the Executive in deference to the view of Congress implied in its passage and presentation to him. In his own view, however, the two Houses of Congress, convened under the twelfth article of the Constitution, have complete power to exclude from counting all electoral votes deemed by them to be illegal, and it is not competent for the Executive to defeat or obstruct that power by a veto, as would be the case if his action were at all essential in the matter. He disclaims all right of the Executive to interfere in any way in the matter of canvassing or counting electoral votes, and he also disclaims that by signing said resolution he has expressed any opinion on the recitals of the preamble or any judgment of his own upon the subject of the resolution.
8, 1865
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point. Va.:
I am called on by the House of Representatives to give an account of my interview with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, and it is very desirable to me to put your despatch of February 1, to the Secretary of War, in which, among other things, you say: "I fear now their going back without any expression from any one in authority will have a bad influence." I think the despatch does you credit, while I do not see that it can embarrass you. May I use it?
REPLY TO A COMMITTEE OF CONGRESS, REPORTING THE RESULT OF THE ELECTORAL COUNT,
FEBRUARY 9, 1865.
With deep gratitude to my countrymen for this mark of their confidence; with a distrust of my own ability to perform the duty required under the most favorable circumstances, and now rendered doubly difficult by existing national perils; yet with a firm reliance on the strength of our free government, and the eventual loyalty of the people to the just principles upon which it is founded, and above all with an unshaken faith in the Supreme Ruler of nations, I accept this trust. Be pleased to signify this to the respective Houses of Congress.
EXECUTIVE MANSION, February 10, 1865
TO THE HONORABLE THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES:
In response to your resolution of the eighth instant, requesting information in relation to a conference recently held in Hampton Roads, I have the honor to state that on the day of the date I gave Francis P. Blair, Sr., a card, written on as follows, to wit:
December 28, 1864.
Allow the bearer, F. P. Blair, Sr., to pass our lines, go South, and return.
A. LINCOLN.
That at the time I was informed that Mr. Blair sought the card as a means of getting to Richmond, Va., but he was given no authority to speak or act for the Government, nor was I informed of anything he would say or do on his own account or otherwise. Afterwards Mr. Blair told me that he had been to Richmond and had seen Mr. Jefferson Davis; and he (Mr. B.) at the same time left with me a manuscript letter, as follows, to wit:
RICHMOND, VA., January 12, 1865. F. P. BLAIR, ESQ.
SIR: I have deemed it proper, and probably desirable to you, to give you in this for in the substance of remarks made by me, to be repeated by you to President Lincoln, etc., etc.
I have no disposition to find obstacles in forms, and am willing, now as heretofore, to enter into negotiations for the restoration of peace, and am ready to send a commission whenever I have reason to suppose it will be received, or to receive a commission if the United States Government shall choose to send one. That notwithstanding the rejection of our former offers, I would, if you could promise that a commissioner, minister, or other agent would be received, appoint one immediately, and renew the effort to enter into conference with a view to secure peace to the two countries.
Yours, etc., JEFFERSON DAVIS.
Afterwards, and with the view that it should be shown to Mr. Davis, I wrote and delivered to Mr. Blair a letter, as follows, to wit:
WASHINGTON, January 18, 1865.
P. P. BLAIR, ESQ.
SIR:—Your having shown me Mr. Davis's letter to you of the twelfth instant, you may say to him that I have constantly been, am now, and shall continue ready to receive any agent whom he or any other influential person now resisting the national authority may informally send to me with the view of securing peace to the people of our one common country.
Yours, etc.,
the back of my retained copy of the letter last above recited, which entry is as follows:
To-day Mr. Blair tells me that on the twenty-first instant he delivered to Mr. Davis the original of which the within is a copy, and left it with him; that at the time of delivering it Mr. Davis read it over twice in Mr. Blair's presence, at the close of which he (Mr. Blair) remarked that the part about "our one common country" related to the part of Mr. Davis' letter about "the two countries," to which Mr. Davis replied that he so understood it.
indorsed by him, as appears:
OFFICE UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH WAR DEPARTMENT. The following telegram received at Washington January 29, 1865, from headquarters Army of James,
6.30 P.M., January 29, 1865:
"HON. EDWIN M. STANTON," Secretary of War:
"The following despatch just received from Major-General Parke, who refers it to me for my action. I refer it to you in Lieutenant-General Grant's absence:
"E. O. C. ORD, Major-General, Commanding. HEADQUARTERS ARMY OF POTOMAC, January 29, 1863. 4 P.M." 'MAJOR-GENERAL E. O. C. ORD, 'Headquarters Army of James: 'The following despatch is forwarded to you for your action. Since I have no knowledge of General Grant's having had any understanding of this kind, I refer the matter to you as the ranking officer present in the two armies. 'JNO. G. PARKE, Major-General, Commanding.'
"'FROM HEADQUARTERS NINTH ARMY Cos, 29th. 'MAJOR-GENERAL JNO. G. PARKE, 'Headquarters Army of Potomac: 'Alexander H. Stephens, R. M. T. Hunter, and J. A. Campbell desire to cross my lines, in accordance with an understanding claimed to exist with Lieutenant-General Grant, on their way to Washington as peace commissioners. Shall they be admitted? They desire an early answer, to come through immediately. Would like to reach City Point tonight if they can. If they can not do this, they would like to come through at 10 A.M. to-morrow morning. 'O. B. WILCOX, 'Major-General, Commanding Ninth Corps.'
"January 29, 8.30 P.M. "Respectfully referred to the President for such instructions as he may be pleased to give. "EDWIN M. STANTON, "Secretary of War."
It appears that about the time of placing the foregoing telegram in my hands the Secretary of War dispatched General Ord as follows, to wit:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON CITY, January 29, 1865. 10 P.M. (Sent at 2 A.M., 30th.) MAJOR-GENERAL ORD.
SIR:—This Department has no knowledge of any understanding by General Grant to allow any person to come within his lines as commissioner of any sort. You will therefore allow no one to come into your lines under such character or profession until you receive the President's instructions, to whom your telegraph will be submitted for his directions.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Afterwards, by my direction, the Secretary of War telegraphed General Ord as follows, to wit:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D.C., January 30. 10.30 A.M.
MAJOR-GENERAL E. O. C. ORD, Headquarters Army of the James.
SIR:—By direction of the President, you are instructed to inform the three gentlemen, Messrs. Stephens, Hunter and Campbell, that a messenger will be dispatched to them at or near where they now are without unnecessary delay.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Afterwards I prepared and put into the hands of Major Thomas T. Eckert the following instructions and message:
EXECUTIVE MANSION,
MAJOR T. T. ECKERT. WASHINGTON, January 30, 1865
SIR:—You will proceed with the documents placed in your hands, and on reaching General Ord will deliver him the letter addressed to him by the Secretary of War; then, by General Ord's assistance, procure an interview with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, or any of them. Deliver to him or them the paper on which your own letter is written. Note on the copy which you retain the time of delivery and to whom delivered. Receive their answer in writing, waiting a reasonable time for it, and which, if it contain their decision to come through without further condition, will be your warrant to ask General Ord to pass them through, as directed in the letter of the Secretary of War to him. If by their answer they decline to come, or propose other terms, do not have them pass through. And this being your whole duty, return and report to me.
A. LINCOLN.
CITY POINT, VA.. February 1, 1865.
MESSRS. ALEXANDER H. STEPHENS, J. A. CAMPBELL AND R. M. T. HUNTER.
GENTLEMEN:—I am instructed by the President of the United States to place this paper in your hands, with the information that if you pass through the United States military lines it will be understood that you do so for the purpose of an informal conference on the basis of the letter a copy of which is on the reverse side of this sheet, and that if you choose to pass on such understanding, and so notify me in writing, I will procure the commanding general to pass you through the lines and to Fortress Monroe under such military precautions as he may deem prudent, and at which place you will be met in due time by some person or persons for the purpose of such informal conference; and, further, that you shall have protection, safe conduct, and safe return in all events.
THOMAS T. ECKERT, Major and Aide-de-Camp.
WASHINGTON, January 18, 1865. F. P. BLAIR, ESQ.
SIR:—Your having shown me Mr. Davis's letter to you of the twelfth instant, you may say to him that I have constantly been, am now, and shall continue ready to receive any agent whom he or any other influential person now resisting the national authority may informally send to me with the view of securing peace to the people of our one common country.
Yours, etc.,
A. LINCOLN.
Afterwards, but before Major Eckert had departed, the following dispatch was received from General Grant:
OFFICE UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH, WAR DEPARTMENT.
The following telegram received at Washington January 30, 1865, from City Point, Va., 10.30 A.M., January 30, 1865:
"His EXCELLENCY A. LINCOLN, President of the United States: "The following communication was received here last evening: "'PETERSBURG, VA., January 30, 1865. 'LIEUTENANT-GENERAL U.S. GRANT, Commanding Armies United States. 'SIR: We desire to pass your lines under safe conduct, and to proceed to Washington to hold a conference with President Lincoln upon the subject of the existing war, and with a view of ascertaining upon what terms it may be terminated, in pursuance of the course indicated by him in his letter to Mr. Blair of January 18, 1865, of which we presume you have a copy; and if not, we wish to see you in person, if convenient, and to confer with you upon the subject. 'Very respectfully, yours, 'ALEXANDER H. STEPHENS. 'J. A. CAMPBELL. 'R. M. T. HUNTER.'"
"I have sent directions to receive these gentlemen, and expect to have them at my quarters this evening, awaiting your instructions. U.S. GRANT, Lieutenant-General, Commanding Armies United States."
This, it will be perceived, transferred General Ord's agency in the matter to General Grant. I resolved, however, to send Major Eckert forward with his message, and accordingly telegraphed General Grant as follows, to wit:
EXECUTIVE MANSION WASHINGTON, January 13, 1865 (Sent at 1.30 P.M.)
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
A messenger is coming to you on the business contained in your despatch. Detain the gentlemen in comfortable quarters until he arrives, and then act upon the message he brings as far as applicable, it having been made up to pass through General Ord's hands, and when the gentlemen were supposed to be beyond our lines.
A. LINCOLN.
When Major Eckert departed, he bore with him a letter of the Secretary of War to General Grant, as follows, to wit:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., January 30, 1865.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, Commanding, etc.
GENERAL:—The President desires that you will please procure for the bearer, Major Thomas T. Eckert, an interview with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, and if on his return to you he requests it pass them through our lines to Fortress Monroe by such route and under such military precautions as you may deem prudent, giving them protection and comfortable quarters while there, and that you let none of this have any effect upon your movements or plans.
By order of the President: EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Supposing the proper point to be then reached, I dispatched the Secretary of State with the following instructions, Major Eckert, however, going ahead of him:
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, January 31, 1865.
HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State:
You will proceed to Fortress Monroe, Va., there to meet and informally confer with Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell on the basis of my letter to F. P. Blair, Esq., of January 18, 1865, a copy of which you have.
You will make known to them that three things are indispensable, to Wit:
1. The restoration of the national authority throughout all the States.
2. No receding by the Executive of the United States on the slavery question from the position assumed thereon in the late annual message to Congress and in preceding documents.
3. No cessation of hostilities short of an end of the war and the disbanding of all forces hostile to the Government.
You will inform them that all propositions of theirs not inconsistent with the above will be considered and passed upon in a spirit of sincere liberality. You will hear all they may choose to say and report it to me.
You will not assume to definitely consummate anything.
Yours, etc.,
A. LINCOLN.
On the day of its date the following telegram was sent to General Grant:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 1,1865 (Sent at 9.30 A.M.)
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Let nothing which is transpiring change, hinder, or delay your military movements or plans.
A. LINCOLN.
Afterwards the following despatch was received from General Grant:
OFFICE UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH WAR DEPARTMENT. The following telegram received at Washington, 2.30 P.M., February 1, 1865, from City Point, Va., February 1, 12.30 PM., 1865:
"His EXCELLENCY A. LINCOLN, President United States:
"Your despatch received. There will be no armistice in consequence of the presence of Mr. Stephens and others within our lines. The troops are kept in readiness to move at the shortest notice if occasion should justify it.
"U.S. GRANT, Lieutenant-General."
To notify Major Eckert that the Secretary of State would be at Fortress Monroe, and to put them in communication, the following despatch was sent:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 1, 1865.
MAJOR T. T. ECKERT, Care of General Grant, City Point, Va.:
Call at Fortress Monroe and put yourself under direction of Mr. S., whom you will find there.
A. LINCOLN.
On the morning of the 2d instant the following telegrams were received by me respectively from the Secretary of State and Major Eckert:
FORT MONROE, VA., February 1,1865. 11.30 PM.
THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES:
Arrived at 10 this evening. Richmond party not here. I remain here.
WILLIAM H. SEWARD.
CITY POINT, VA., February 1, 1865. 10 P.M.
HIS EXCELLENCY A. LINCOLN, President of the United States: I have the honor to report the delivery of your communication and my letter at 4.15 this afternoon, to which I received a reply at 6 P.M., but not satisfactory.
At 8 P.M. the following note, addressed to General Grant, was received:
CITY POINT, VA., February 1, 1865
"LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT.
"SIR:—We desire to go to Washington City to confer informally with the President personally in reference to the matters mentioned in his letter to Mr. Blair of the 18th January ultimo, without any personal compromise on any question in the letter. We have the permission to do so from the authorities in Richmond.
Very respectfully yours,
ALEX. H. STEPHENS R. M. T. HUNTER. J. A. CAMPBELL."
At 9.30 P.M. I notified them that they could not proceed further unless they complied with the terms expressed in my letter. The point of meeting designated in the above note would not, in my opinion, be insisted upon. Think Fort Monroe would be acceptable. Having complied with my instructions, I will return to Washington to-morrow unless otherwise ordered.
THOS. T. ECKERT, Major, etc.
On reading this despatch of Major Eckert I was about to recall him and the Secretary of State, when the following telegram of General Grant to the Secretary of War was shown me:
OFFICE UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH, WAR DEPARTMENT.
The following telegram received at Washington 4.35 A.M., February 2, 1865, from City Point, Va., February 1, 10.30 P.M., 1865:
"HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, "Secretary of War:
"Now that the interview between Major Eckert, under his written instructions, and Mr. Stephens and party has ended, I will state confidentially, but not officially to become a matter of record, that I am convinced upon conversation with Messrs. Stephens and Hunter that their intentions are good and their desire sincere to restore peace and union. I have not felt myself at liberty to express even views of my own or to account for my reticency. This has placed me in an awkward position, which I could have avoided by not seeing them in the first instance. I fear now their going back without any expression from anyone in authority will have a bad influence. At the same time, I recognize the difficulties in the way of receiving these informal commissioners at this time, and do not know what to recommend. I am sorry, however, that Mr. Lincoln can not have an interview with the two named in this despatch, if not all three now within our lines. Their letter to me was all that the President's instructions contemplated to secure their safe conduct if they had used the same language to Major Eckert.
"U.S. GRANT "Lieutenant-General."
This despatch of General Grant changed my purpose, and accordingly I telegraphed him and the Secretary of State, respectively, as follows:
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865. (Sent at 9 A.M.)
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.:
Say to the gentlemen I will meet them personally at Fortress Monroe as soon as I can get there.
A. LINCOLN.
WAR DEPARTMENT, WASHINGTON, D. C., February 2, 1865. (Sent at 9 A.M.)
HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Fortress Monroe, Va.:
Induced by a despatch from General Grant, I join you at Fort Monroe as soon as I can come.
A. LINCOLN.
Before starting, the following despatch was shown me. I proceeded, nevertheless:
OFFICE UNITED STATES MILITARY TELEGRAPH, WAR DEPARTMENT.
The following telegram received at Washington, February 2, 1865, from City Point, Va., 9 A.M., February 2, 1865:
"HON. WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State, Fort Monroe:
"The gentlemen here have accepted the proposed terms, and will leave for Fort Monroe at 9.30 A.M.
"U. S. GRANT, Lieutenant-General."
(Copy to HON. Edwin M. Stanton, Secretary of War, Washington.)
On the night of the 2nd I reached Hampton Roads, found the Secretary of State and Major Eckert on a steamer anchored offshore, and learned of them that the Richmond gentlemen were on another steamer also anchored offshore, in the Roads, and that the Secretary of State had not yet seen or communicated with them. I ascertained that Major Eckert had literally complied with his instructions, and I saw for the first time the answer of the Richmond gentlemen to him, which in his despatch to me of the 1st he characterizes as "not satisfactory." That answer is as follows, to wit:
CITY POINT, VA., February 1, 1865. THOMAS T. ECKERT, Major and Aid-de-Camp. MAJOR:-Your note, delivered by yourself this day, has been considered. In reply we have to say that we were furnished with a copy of the letter of President Lincoln to Francis P. Blair, Esq., of the 18th of January ultimo, another copy of which is appended to your note. Our instructions are contained in a letter of which the following is a copy:
"RICHMOND, January 28, 1865. "In conformity with the letter of Mr. Lincoln, of which the foregoing is a copy, you are to proceed to Washington City for informal conference with him upon the issues involved in the existing war, and for the purpose of securing peace to the two countries. "With great respect, your obedient servant, "JEFFERSON DAVIS."
The substantial object to be obtained by the informal conference is to ascertain upon what terms the existing war can be terminated honorably.
Our instructions contemplate a personal interview between President Lincoln and ourselves at Washington City, but with this explanation we are ready to meet any person or persons that President Lincoln may appoint at such place as he may designate.
Our earnest desire is that a just and honorable peace may be agreed upon, and we are prepared to receive or to submit propositions which may possibly lead to the attainment of that end.
Very respectfully, yours,
ALEXANDER H. STEPHENS.
R. M. T. HUNTER.
JOHN A. CAMPBELL.
A note of these gentlemen, subsequently addressed to General Grant, has already been given in Major Eckert's despatch of the 1st instant.
I also here saw, for the first time, the following note, addressed by the Richmond gentlemen to Major Eckert:
CITY POINT, VA., February 2, 1865. THOMAS T. ECKERT, Major and Aid-de-Camp. MAJOR:—In reply to your verbal statement that your instructions did not allow you to alter the conditions upon which a passport could be given to us, we say that we are willing to proceed to Fortress Monroe and there to have an informal conference with any person or persons that President Lincoln may appoint on the basis of his letter to Francis P. Blair of the 18th of January ultimo, or upon any other terms or conditions that he may hereafter propose not inconsistent with the essential principles of self-government and popular rights, upon which our institutions are founded.
It is our earnest wish to ascertain, after a free interchange of ideas and information, upon what principles and terms, if any, a just and honorable peace can be established without the further effusion of blood, and to contribute our utmost efforts to accomplish such a result.
We think it better to add that in accepting your passport we are not to be understood as committing ourselves to anything but to carry to this informal conference the views and feelings above expressed.
Very respectfully, yours, etc.,
ALEXANDER H. STEPHENS, J. A. CAMPBELL, R. M. T. HUNTER.
Note.-The above communication was delivered to me at Fort Monroe at 4.30 P.M. February 2 by Lieutenant-Colonel Babcock, of General Grant's staff.
THOMAS T. ECKERT Major and Aid-de-Camp.
On the morning of the third the three gentlemen, Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell, came aboard of our steamer and had an interview with the Secretary of State and myself of several hours' duration. No question of preliminaries to the meeting was then and there made or mentioned; no other person was present; no papers were exchanged or produced; and it was in advance agreed that the conversation was to be informal and verbal merely. On our part the whole substance of the instructions to the Secretary of State hereinbefore recited was stated and insisted upon, and nothing was said inconsistent therewith; while by the other party it was not said that in any event or on any condition they ever would consent to reunion, and yet they equally omitted to declare that they never would consent. They seemed to desire a postponement of that question and the adoption of some other course first, which, as some of them seemed to argue, might or might not lead to reunion, but which course we thought would amount to an indefinite postponement. The conference ended without result.
The foregoing, containing, as is believed, all the information sought is respectfully submitted.
In answer to the resolution of the Senate of the eighth instant, requesting information concerning recent conversations or communications with insurgents, under executive sanction, I transmit a report from the Secretary of State, to whom the resolution was referred.
A. LINCOLN. TO THE PRESIDENT:
The Secretary of State, to whom was referred a resolution of the Senate of the 8th instant, requesting "the President of the United States, if, in his opinion, not incompatible with the public interests, to furnish to the Senate any information in his possession concerning recent conversations or communications with certain rebels, said to have taken place under executive sanction, including communications with the rebel Jefferson Davis, and any correspondence relating thereto," has the honor to report that the Senate may properly be referred to a special message of the President bearing upon the subject of the resolution, and transmitted to the House this day. Appended to this report is a copy of an instruction which has been addressed to Charles Francis Adams, Esq., envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary of the United States at London, and which is the only correspondence found in this department touching the subject referred to in the resolution.
Respectfully submitted,
WILLIAM H. SEWARD.
DEPARTMENT OF STATE, WASHINGTON, February 10, 1865.
DEPARTMENT OF STATE, WASHINGTON, February 7,1865
On the morning of the 3d, the President, attended by the Secretary, received Messrs. Stephens, Hunter, and Campbell on board the United States steam transport River Queen in Hampton Roads. The conference was altogether informal. There was no attendance of secretaries, clerks, or other witnesses. Nothing was written or read. The conversation, although earnest and free, was calm, and courteous, and kind on both sides. The Richmond party approached the discussion rather indirectly, and at no time did they either make categorical demands, or tender formal stipulations or absolute refusals. Nevertheless, during the conference, which lasted four hours, the several points at issue between the Government and the insurgents were distinctly raised, and discussed fully, intelligently, and in an amicable spirit. What the insurgent party seemed chiefly to favor was a postponement of the question of separation, upon which the war is waged, and a mutual direction of efforts of the Government, as well as those of the insurgents, to some extrinsic policy or scheme for a season during which passions might be expected to subside, and the armies be reduced, and trade and intercourse between the people of both sections resumed. It was suggested by them that through such postponement we might now have immediate peace, with some not very certain prospect of an ultimate satisfactory adjustment of political relations between this Government and the States, section, or people now engaged in conflict with it.
This suggestion, though deliberately considered, was nevertheless regarded by the President as one of armistice or truce, and he announced that we can agree to no cessation or suspension of hostilities, except on the basis of the disbandment of the insurgent forces, and the restoration of the national authority throughout all the States in the Union. Collaterally, and in subordination to the proposition which was thus announced, the antislavery policy of the United States was reviewed in all its bearings, and the President announced that he must not be expected to depart from the positions he had heretofore assumed in his proclamation of emancipation and other documents, as these positions were reiterated in his last annual message. It was further declared by the President that the complete restoration of the national authority was an indispensable condition of any assent on our part to whatever form of peace might be proposed. The President assured the other party that, while he must adhere to these positions, he would be prepared, so far as power is lodged with the Executive, to exercise liberality. His power, however, is limited by the Constitution; and when peace should be made, Congress must necessarily act in regard to appropriations of money and to the admission of representatives from the insurrectionary States. The Richmond party were then informed that Congress had, on the 31st ultimo, adopted by a constitutional majority a joint resolution submitting to the several States the proposition to abolish slavery throughout the Union, and that there is every reason to expect that it will be soon accepted by three fourths of the States, so as to become a part of the national organic law.
The conference came to an end by mutual acquiescence, without producing an agreement of views upon the several matters discussed, or any of them. Nevertheless, it is perhaps of some importance that we have been able to submit our opinions and views directly to prominent insurgents, and to hear them in answer in a courteous and not unfriendly manner.
I am, sir, your obedient servant,
REAR-ADMIRAL DAVID D. PORTER, Commanding North Atlantic Squadron, Hampton Roads, Va.
SIR:—It is made my agreeable duty to enclose herewith the joint resolution approved 24th January, 1865, tendering the thanks of Congress to yourself, the officers and men under your command for their gallantry and good conduct in the capture of Fort Fisher, and through you to all who participated in that brilliant and decisive victory under your command.
Very respectfully,
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Louis, Missouri:
I understand that provost-marshals in different parts of Missouri are assuming to decide that the conditions of bonds are forfeited, and therefore are seizing and selling property to pay damages. This, if true, is both outrageous and ridiculous. Do not allow it. The courts, and not provost-marshals, are to decide such questions unless when military necessity makes an exception. Also excuse John Eaton, of Clay County, and Wesley Martin, of Platte, from being sent South, and let them go East if anywhere.
TO THE MILITARY OFFICERS COMMANDING IN WEST TENNESSEE:
While I cannot order as within requested, allow me to say that it is my wish for you to relieve the people from all burdens, harassments, and oppressions, so far as is possible consistently with your military necessities; that the object of the war being to restore and maintain the blessings of peace and good government, I desire you to help, and not hinder, every advance in that direction.
Of your military necessities you must judge and execute, but please do so in the spirit and with the purpose above indicated.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Louis, Missouri:
Yours of yesterday about provost-marshal system received. As part of the same subject, let me say I am now pressed in regard to a pending assessment in St. Louis County. Please examine and satisfy yourself whether this assessment should proceed or be abandoned; and if you decide that it is to proceed, please examine as to the propriety of its application to a gentleman by the name of Charles McLaran.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Louis, Missouri:
Please ascertain whether General Fisk's administration is as good as it might be, and answer me.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation
Whereas objects of interest to the United States require that the Senate should be convened at twelve o'clock on the fourth of March next to receive and act upon such communications as may be made to it on the part of the Executive;
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, have considered it to be my duty to issue this, my proclamation, declaring that an extraordinary occasion requires the Senate of the United States to convene for the transaction of business at the Capitol, in the city of Washington, on the fourth day of March next, at twelve o'clock at noon on that day, of which all who shall at that time be entitled to act as members of that body are hereby required to take notice.
Given under my hand and the seal of the United States, at Washington...............
A. LINCOLN. By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
OFFICER IN COMMAND AT HARPER'S FERRY:
Chaplain Fitzgibbon yesterday sent me a despatch invoking Clemency for Jackson, Stewart, and Randall, who are to be shot to-day. The despatch is so vague that there is no means here of ascertaining whether or not the execution of sentence of one or more of them may not already have been ordered. If not suspend execution of sentence m their cases until further orders and forward records of trials for examination.
A. LINCOLN
MAJOR ECKERT: Please send above telegram JNO. G. NICOLAY.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Virginia:
I am in a little perplexity. I was induced to authorize a gentleman to bring Roger A. Pryor here with a view of effecting an exchange of him; but since then I have seen a despatch of yours showing that you specially object to his exchange. Meantime he has reached here and reported to me. It is an ungracious thing for me to send him back to prison, and yet inadmissible for him to remain here long. Cannot you help me out with it? I can conceive that there may be difference to you in days, and I can keep him a few days to accommodate on that point. I have not heard of my son's reaching you.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Please inquire and report to me whether there is any propriety of longer keeping in Gratiott Street Prison a man said to be there by the name of Riley Whiting.
General Sheridan's despatch to you, of to-day, in which he says he "will be off on Monday," and that he "will leave behind about two thousand men," causes the Secretary of War and myself considerable anxiety. Have you well considered whether you do not again leave open the Shenandoah Valley entrance to Maryland and Pennsylvania, or, at least, to the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad?
Subsequent reflection, conference with General Halleck, your despatch, and one from General Sheridan, have relieved my anxiety; and so I beg that you will dismiss any concern you may have on my account, in the matter of my last despatch.
MR. THOMAS W. CONWAY, General Superintendent Freedmen, Department of the Gulf.
SIR:—Your statement to Major-General Hurlbut of the condition of the freedmen of your department, and of your success in the work of their moral and physical elevation, has reached me and given me much pleasure.
That we shall be entirely successful in our efforts I firmly believe.
The blessing of God and the efforts of good and faithful men will bring us an earlier and happier consummation than the most sanguine friends of the freedmen could reasonably expect.
Yours,
You have not sent contents of Richmond papers for Tuesday or Wednesday. Did you not receive them? If not, does it indicate anything?
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
The President directs me to say to you that he wishes you to have no conference with General Lee unless it be for the capitulation of General Lee's army, or on some minor and purely military matter. He instructs me to say that you are not to decide, discuss, or confer upon any political question. Such questions the President holds in his own hands, and will submit them to no military conferences or conventions. Meantime you are to press to the utmost your military advantages.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
FELLOW-COUNTRYMEN:—At this second appearing to take the oath of the presidential office there is less occasion for an extended address than there was at the first. Then a statement somewhat in detail of a course to be pursued seemed fitting and proper. Now, at the expiration of four years, during which public declarations have been constantly called forth on every point and phase of the great contest which still absorbs the attention and engrosses the energies of the nation, little that is new could be presented. The progress of our arms, upon which all else chiefly depends, is as well known to the public as to myself, and it is, I trust, reasonably satisfactory and encouraging to all. With high hope for the future, no prediction in regard to it is ventured.
On the occasion corresponding to this four years ago all thoughts were anxiously directed to an impending civil war. All dreaded it, all sought to avert it. While the inaugural address was being delivered from this place, devoted altogether to saving the Union without war, insurgent agents were in the city seeking to destroy it without war seeking to dissolve the Union and divide effects by negotiation. Both parties deprecated war, but one of them would make war rather than let the nation survive, and the other would accept war rather than let it perish, and the war came.
One eighth of the whole population was colored slaves, not distributed generally over the Union, but localized in the southern part of it. These slaves constituted a peculiar and powerful interest. All knew that this interest was somehow the cause of the war. To strengthen, perpetuate, and extend this interest was the object for which the insurgents would rend the Union even by war, while the Government claimed no right to do more than to restrict the territorial enlargement of it. Neither party expected for the war the magnitude or the duration which it has already attained. Neither anticipated that the cause of the conflict might cease with or even before the conflict itself should cease. Each looked for an easier triumph, and a result less fundamental and astounding. Both read the same Bible and pray to the same God, and each invokes His aid against the other. It may seem strange that any men should dare to ask a just God's assistance in wringing their bread from the sweat of other men's faces, but let us judge not, that we be not judged. The prayers of both could not be answered. That of neither has been answered fully. The Almighty has His own purposes. "Woe unto the world because of offenses; for it must needs be that offenses come, but woe to that man by whom the offense cometh." If we shall suppose that American slavery is one of those offenses which, in the providence of God, must needs come, but which, having continued through His appointed time, He now wills to remove, and that He gives to both North and South this terrible war as the woe due to those by whom the offense came, shall we discern therein any departure from those divine attributes which the believers in a living God always ascribe to Him? Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsman's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said, "The judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether."
With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation's wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Louis, Missouri:
Please state briefly, by telegraph, what you concluded about the assessments in St. Louis County. Early in the war one Samuel B. Churchill was sent from St. Louis to Louisville, where I have quite satisfactory evidence that he has not misbehaved. Still I am told his property at St. Louis is subjected to the assessment, which I think it ought not to be. Still I wish to know what you think.
Your two despatches to the Secretary of War, one relating to supplies for the enemy going by the Blackwater, and the other to General Singleton and Judge Hughes, have been laid before me by him. As to Singleton and Hughes, I think they are not in Richmond by any authority, unless it be from you. I remember nothing from me which could aid them in getting there, except a letter to you, as follows, to wit:
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON CITY, February 7, 1865. LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, City Point, Va.: General Singleton, who bears you this, claims that he already has arrangements made, if you consent, to bring a large amount of Southern produce through your lines. For its bearing on our finances, I would be glad for this to be done, if it can be, without injuriously disturbing your military operations, or supplying the enemy. I wish you to be judge and master on these points. Please see and hear him fully, and decide whether anything, and, if anything, what, can be done in the premises. Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN.
I believe I gave Hughes a card putting him with Singleton on the same letter. However this may be, I now authorize you to get Singleton and Hughes away from Richmond, if you choose, and can. I also authorize you, by an order, or in what form you choose, to suspend all operations on the Treasury trade permits, in all places southeastward of the Alleghenies. If you make such order, notify me of it, giving a copy, so that I can give corresponding direction to the Navy.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
A Proclamation
Whereas, the twenty-first section of the act of Congress, approved on the 3d instant, entitled "An Act to amend the several acts heretofore passed to provide for the enrolling and calling out the national forces and for other purposes," requires that in addition to the other lawful penalties of the crime of desertion from the military or naval service, all persons who have deserted the military or naval service of the United States who shall not return to said service or report themselves to a provost-marshal within sixty days after the proclamation hereinafter mentioned, shall be deemed and taken to have voluntarily relinquished and forfeited their citizenship and their right to become citizens, and such deserters shall be forever incapable of holding any office of trust or profit under the United States, or of exercising any rights of citizens thereof; and all persons who shall hereafter desert the military or naval service, and all persons who, being duly enrolled, shall depart the jurisdiction of the district in which they are enrolled, or go beyond the limits of the United States with intent to avoid any draft into the military or naval service duly ordered, shall be liable to the penalties of this section; and the President is hereby authorized and required forthwith, on the passage of this act, to issue his proclamation setting forth the provisions of this section, in which proclamation the President is requested to notify all deserters returning within sixty days as aforesaid that they shall be pardoned on condition of returning to their regiments and companies, or to such other organizations as they may be assigned to, until they shall have served for a period of time equal to their original term of enlistment:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do issue this my proclamation as required by said act, ordering and requiring all deserters to return to their proper posts; and I do hereby notify them that all deserters who shall within sixty days from the date of this proclamation, viz., on or before the 10th day of May, 1865, return to service or report themselves to a provost-marshal, shall be pardoned on condition that they return to their regiments or companies or to such other organization as they may be assigned to, and serve the remainder of their original terms of enlistment, and in addition thereto a period equal to the time lost by desertion.
In testimony whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed...............
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State
HON. HENRY T. BLOW, Saint Louis, Mo.:
A Miss E. Snodgrass, who was banished from Saint Louis in May,1863, wishes to take the oath and return home. What say you?
EXECUTIVE MANSION, WASHINGTON, D. C.
DEAR Mr. WEED:
Every one likes a compliment. Thank you for yours on my little notification speech and on the recent inaugural address. I expect the latter to wear as well as perhaps better than—anything I have produced; but I believe it is not immediately popular. Men are not flattered by being shown that there has been a difference of purpose between the Almighty and them. To deny it, however, in this case, is to deny that there is a God governing the world. It is a truth which I thought needed to be told, and, as whatever of humiliation there is in it falls most directly on myself, I thought others might afford for me to tell it.
Truly yours,
COL. R. M. ROUGH AND OTHERS, Chicago, Ill.:
Yours received. The best I can do with it is, to refer it to the War Department. The Rock Island case referred to, was my individual enterprise; and it caused so much difficulty in so many ways that I promised to never undertake another.
FELLOW-CITIZENS:—It will be but a very few words that I shall undertake to say. I was born in Kentucky, raised in Indiana, and lived in Illinois; and now I am here, where it is my business to care equally for the good people of all the States. I am glad to see an Indiana regiment on this day able to present the captured flag to the Governor of Indiana. I am not disposed, in saying this, to make a distinction between the States, for all have done equally well.
There are but few views or aspects of this great war upon which I have not said or written something whereby my own opinions might be known. But there is one—the recent attempt of our erring brethren, as they are sometimes called, to employ the negro to fight for them. I have neither written nor made a speech on that subject, because that was their business, not mine, and if I had a wish on the subject, I had not the power to introduce it, or make it effective. The great question with them was whether the negro, being put into the army, will fight for them. I do not know, and therefore cannot decide. They ought to know better than me. I have in my lifetime heard many arguments why the negroes ought to be slaves; but if they fight for those who would keep them in slavery, it will be a better argument than any I have yet heard. He who will fight for that, ought to be a slave. They have concluded, at last, to take one out of four of the slaves and put them in the army, and that one out of the four who will fight to keep the others in slavery, ought to be a slave himself, unless he is killed in a fight. While I have often said that all men ought to be free, yet would I allow those colored persons to be slaves who want to be, and next to them those white people who argue in favor of making other people slaves. I am in favor of giving an appointment to such white men to try it on for these slaves. I will say one thing in regard to the negroes being employed to fight for them. I do know he cannot fight and stay at home and make bread too. And as one is about as important as the other to them, I don't care which they do. I am rather in favor of having them try them as soldiers. They lack one vote of doing that, and I wish I could send my vote over the river so that I might cast it in favor of allowing the negro to fight. But they cannot fight and work both. We must now see the bottom of the enemy's resources. They will stand out as long as they can, and if the negro will fight for them they must allow him to fight. They have drawn upon their last branch of resources, and we can now see the bottom. I am glad to see the end so near at hand. I have said now more than I intended, and will therefore bid you good-by.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas reliable information has been received that hostile Indians, within the limits of the United States, have been furnished with arms and munitions of war by persons dwelling in conterminous foreign territory, and are thereby enabled to prosecute their savage warfare upon the exposed and sparse settlements of the frontier;
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States of America, do hereby proclaim and direct that all persons detected in that nefarious traffic shall be arrested and tried by court-martial at the nearest military post, and if convicted, shall receive the punishment due to their deserts.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed...................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
MARCH 18, 1865.
I am unwilling for the sentence to stand, and be executed, to any extent in this case. In the absence of a more adequate motive than the evidence discloses, I am wholly unable to believe in the existence of criminal or fraudulent intent on the part of men of such well established good character. If the evidence went as far to establish a guilty profit of one or two hundred thousand dollars, as it does of one or two hundred dollars, the case would, on the question of guilt, bear a far different aspect. That on this contract, involving some twelve hundred thousand dollars, the contractors would plan, and attempt to execute a fraud which, at the most, could profit them only one or two hundred, or even one thousand dollars, is to my mind beyond the power of rational belief. That they did not, in such a case, make far greater gains, proves that they did not, with guilty or fraudulent intent, make at all. The judgment and sentence are disapproved, and declared null, and the defendants are fully discharged.
A. LINCOLN March 18, 1865.
MAJOR-GENERAL POPE, St. Louis, Missouri:
Understanding that the plan of action for Missouri contained in your letter to the Governor of that State, and your other letter to me, is concurred in by the Governor, it is approved by me, and you will be sustained in proceeding upon it.
MAJOR-GENERAL ORD, Army of the James
Is it true that George W. Lane is detained at Norfolk without any charge against him? And if so why is it done?
WASHINGTON, March 21, 1865.
HON. WALTER B. SCATES, Centralia, Illinois:
If you choose to go to New Mexico and reside, I will appoint you chief justice there. What say you? Please answer.
Seeing your despatch about General Crook, and fearing that through misapprehension something unpleasant may occur, I send you below two despatches of General Grant, which I suppose will fully explain General Crook's movements.
GENERAL DODGE, Commanding, &c, Saint Louis, Mo.:
Allow Mrs. R. S. Ewell the benefit of my amnesty proclamation on her taking the oath.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR, Washington, D. C.:
Arrived here all safe about 9 P.M. yesterday. No war news. General Grant does not seem to know very much about Yeatman, but thinks very well of him so far as he does know.
I like Mr. Whiting very much, and hence would wish him to remain or resign as best suits himself. Hearing this much from me, do as you think best in the matter. General Lee has sent the Russell letter back, concluding, as I understand from Grant, that their dignity does not admit of their receiving the document from us. Robert just now tells me there was a little rumpus up the line this morning, ending about where it began.
HEADQUARTERS ARMY OF THE POTOMAC, March 25, 1865. (Received 5 P.M.)
HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War:
I am here within five miles of the scene of this morning's action. I have nothing to add to what General Meade reports except that I have seen the prisoners myself and they look like there might be the number he states—1600.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR:
I approve your Fort Sumter programme. Grant don't seem to know Yeatman very well, but thinks very well of him so far as he knows. Thinks it probable that Y. is here now, for the place. I told you this yesterday as well as that you should do as you think best about Mr. Whiting's resignation, but I suppose you did not receive the dispatch. I am on the boat and have no later war news than went to you last night.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR, Washington, D.C.:
Yours inclosing Fort Sumter order received. I think of but one suggestion. I feel quite confident that Sumter fell on the 13th, and not on the 14th of April, as you have it. It fell on Saturday, the 13th; the first call for troops on our part was got up on Sunday, the 14th, and given date and issued on Monday, the 15th. Look up the old almanac and other data, and see if I am not right.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR, Washington, D.C.: After your explanation, I think it is little or no difference whether the Fort Sumter ceremony takes place on the 13th or 14th.
General Sherman tells me he is well acquainted with James Yeatman, and that he thinks him almost the best man in the country for anything he will undertake.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR:
I begin to feel that I ought to be at home and yet I dislike to leave without seeing nearer to the end of General Grant's present movement. He has now been out since yesterday morning and although he has not been diverted from his programme no considerable effort has yet been produced so far as we know here. Last night at 10.15 P. M. when it was dark as a rainy night without a moon could be, a furious cannonade soon joined in by a heavy musketry fire opened near Petersburg and lasted about two hours. The sound was very distinct here as also were the flashes of the guns up the clouds. It seemed to me a great battle, but the older hands here scarcely noticed it and sure enough this morning it was found that very little had been done.
SECRETARY STANTON:
At 12.30 P.M. to-day General Grant telegraphed me as follows: "There has been much hard fighting this morning. The enemy drove our left from near Dabney's house back well toward the Boydton plank road. We are now about to take the offensive at that point, and I hope will more than recover the lost ground."
Later he telegraphed again as follows:
"Our troops, after being driven back to the Boydton plank road, turned and drove the enemy in turn, and took the White Oak road, which we now have. This gives us the ground occupied by the enemy this morning. I will send you a rebel flag captured by our troops in driving the enemy back. There have been four flags captured to-day."
Judging by the two points from which General Grant telegraphs, I infer that he moved his headquarters about one mile since he sent the first of the two despatches.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Yours to Colonel Bowers about the Secretary of War is shown to me. He is not here, nor have I any notice that he is coming. I presume the mistake comes of the fact that the Secretary of State was here. He started back to Washington this morning. I have your two despatches of this morning, and am anxious to hear from Sheridan.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR, Washington, D.C.:
I have had two despatches from General Grant since my last to you, but they contain little additional, except that Sheridan also had pretty hot work yesterday, that infantry was sent to his support during the night, and that he (Grant) has not since heard from Sheridan.
Mrs. Lincoln has started home, and I will thank you to see that our coachman is at the Arsenal wharf at eight o'clock to-morrow morning, there to wait until she arrives.
A. LINCOLN. TELEGRAM TO SECRETARY SEWARD.
CITY POINT, VA., April, 1865. 5.30?.M.
HON. W. H. SEWARD, Secretary of State, Fort Monroe:
Despatch just received, showing that Sheridan, aided by Warren, had, at 2 P.M., pushed the enemy back, so as to retake the Five Forks and bring his own headquarters up to J. Boisseau's. The Five Forks were barricaded by the enemy and carried by Devin's division of cavalry. This part of the enemy seem to now be trying to work along the White Oak road, to join the main force in front of Grant, while Sheridan and Warren are pressing them as closely as possible.
Yours showing Sheridan's success of to-day is just received and highly appreciated. Having no great deal to do here, I am still sending the substance of your despatches to the Secretary of War.
MRS. A. LINCOLN, Executive Mansion:
Last night General Grant telegraphed that General Sheridan with his cavalry and the Fifth Corps had captured three brigades of infantry, a train of wagons, and several batteries, prisoners amounting to several thousand. This morning General Grant having ordered an attack along the whole line telegraphs as follows.
Robert yesterday wrote a little cheerful note to Captain Penrose, which is all he has heard of him since you left.
A.M.
HON. E. M. STANTON, Secretary of War:
Last night General Grant telegraphed that General Sheridan, with his cavalry and the Fifth Corps, had captured three brigades of infantry, a train of wagons, and several batteries; the prisoners amounting to several thousand.
This morning General Grant, having ordered an attack along the whole line, telegraphs as follows:
"Both Wright and Parke got through the enemy's lines. The battle now rages furiously. General Sheridan, with his cavalry, the Fifth corps, and Miles's Division of the Second Corps, which was sent to him this morning, is now sweeping down from the west.
"All now looks highly favorable. General Ord is engaged, but I have not yet heard the result in his front."
A. LINCOLN.
CITY POINT, April 1. 11.00 A.M.
Despatches are frequently coming in. All is going on finely. Generals Parke, Wright, and Ord's lines are extending from the Appomattox to Hatcher's Run. They have all broken through the enemy's intrenched lines, taking some forts, guns, and prisoners. Sheridan, with his own cavalry, the Fifth Corps, and part of the Second, is coming in from the west on the enemy's flank. Wright is already tearing up the Southside Railroad.
A. LINCOLN
CITY POINT, VIRGINIA, April 2. 2 P.M.
At 10.45 A.M. General Grant telegraphs as follows:
"Everything has been carried from the left of the Ninth Corps. The Sixth Corps alone captured more than three thousand prisoners. The Second and Twenty-fourth Corps captured forts, guns, and prisoners from the enemy, but I cannot tell the numbers. We are now closing around the works of the line immediately enveloping Petersburg. All looks remarkably well. I have not yet heard from Sheridan. His headquarters have been moved up to Banks's house, near the Boydton road, about three miles southwest of Petersburg."
A. LINCOLN.
CITY POINT, VIRGINIA, April 2. 8.30 P.M.
At 4.30 P.M. to-day General Grant telegraphs as follows:
"We are now up and have a continuous line of troops, and in a few hours will be intrenched from the Appomattox below Petersburg to the river above. The whole captures since the army started out will not amount to less than twelve thousand men, and probably fifty pieces of artillery. I do not know the number of men and guns accurately, however. A portion of Foster's Division, Twenty Fourth Corps, made a most gallant charge this afternoon, and captured a very important fort from the enemy, with its entire garrison. All seems well with us, and everything is quiet just now."
At 4.30 P.M. to-day General Grant telegraphs that he has Petersburg completely enveloped from river below to river above, and has captured, since he started last Wednesday, about twelve thousand prisoners and fifty guns. He suggests that I shall go out and see him in the morning, which I think I will do. Tad and I are both well, and will be glad to see you and your party here at the time you name.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Allow me to tender to you and all with you the nation's grateful thanks for this additional and magnificent success. At your kind suggestion I think I will meet you to-morrow.
HON. E. M. STANTON, Secretary of War:
This morning Lieutenant-General Grant reports Petersburg evacuated, and he is confident that Richmond also is. He is pushing forward to cut off, if possible, the retreating rebel army.
HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War:
Yours received. Thanks for your caution, but I have already been to Petersburg. Staid with General Grant an hour and a half and returned here. It is certain now that Richmond is in our hands, and I think I will go there to-morrow. I will take care of myself.
HON. EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War:
General Weitzel telegraphs from Richmond that of railroad stock he found there twenty-eight locomotives, forty-four passenger and baggage cars, and one hundred and six freight cars. At 3.30 this evening General Grant, from Sutherland's Station, ten miles from Petersburg toward Burkevllle, telegraphs as follows:
"General Sheridan picked up twelve hundred prisoners to-day, and from three hundred to five hundred more have been gathered by other troops. The majority of the arms that were left in the hands of the remnant of Lee's army are now scattered between Richmond and where his troops are. The country is also full of stragglers; the line of retreat marked with artillery, ammunition, burned or charred wagons, caissons, ambulances, etc."
HON. SECRETARY OF STATE:
Yours of to-day received. I think there is no probability of my remaining here more than two days longer. If that is too long come down. I passed last night at Richmond and have just returned.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT, in the Field:
Secretary Seward was thrown from his carriage yesterday and seriously injured. This, with other matters, will take me to Washington soon. I was at Richmond yesterday and the day before, when and where Judge Campbell, who was with Messrs. Hunter and Stephens in February, called on me, and made such representations as induced me to put in his hands an informal paper, repeating the propositions in my letter of instructions to Mr. Seward, which you remember, and adding that if the war be now further persisted in by the rebels, confiscated property shall at the least bear the additional cost, and that confiscation shall be remitted to the people of any State which will now promptly and in good faith withdraw its troops and other support from resistance to the Government.
Judge Campbell thought it not impossible that the rebel legislature of Virginia would do the latter if permitted; and accordingly I addressed a private letter to General Weitzel, with permission to Judge Campbell to see it, telling him (General Weitzel) that if they attempt this, to permit and protect them, unless they attempt something hostile to the United States, in which case to give them notice and time to leave, and to arrest any remaining after such time.
I do not think it very probable that anything win come of this, but I have thought best to notify you so that if you should see signs you may understand them.
From your recent despatches it seems that you are pretty effectually withdrawing the Virginia troops from opposition to the Government. Nothing that I have done, or probably shall do, is to delay, hinder, or interfere with your work.
Yours truly,
MAJOR-GENERAL WEITZEL, Richmond, Va.:
It has been intimated to me that the gentlemen who have acted as the legislature of Virginia in support of the rebellion may now desire to assemble at Richmond and take measures to withdraw the Virginia troops and other support from resistance to the General Government. If they attempt it, give them permission and protection, until, if at all, they attempt some action hostile to the United States, in which case you will notify them, give them reasonable time to leave, and at the end of which time arrest any who remain. Allow Judge Campbell to see this, but do not make it public.
HON. SECRETARY OF WAR:
At 11.15 P.M. yesterday at Burkesville Station, General Grant sends me the following from General Sheridan:
"April 6, 11.15 P.M.
"LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
I have the honor to report that the enemy made a stand at the intersection of the Burks Station road with the road upon which they were retreating. I attacked them with two divisions of the Sixth Army Corps and routed them handsomely, making a connection with the cavalry. I am still pressing on with both cavalry and infantry. Up to the present time we have captured Generals Ewell, Kershaw, Button, Corse, DeBare, and Custis Lee, several thousand prisoners, fourteen pieces of artillery with caissons and a large number of wagons. If the thing is pressed I think Lee will surrender.
"P. H. SHERIDAN,
"Major-General, Commanding."
HEADQUARTERS ARMIES OF THE UNITED STATES,
CITY POINT, April 7, 11 A.M., 1865.
LIEUTENANT-GENERAL GRANT:
Gen. Sheridan says:
"If the thing is pressed I think that Lee will surrender."
Let the thing be pressed.
Tad wants some flags—can he be accommodated?
If the company had assembled by appointment, some mistake had crept in their understanding. He had appeared before a larger audience than this one to-day, and he would repeat what he then said, namely, he supposed owing to the great, good news, there would be some demonstration. He would prefer to-morrow evening, when he should be quite willing, and he hoped ready, to say something. He desired to be particular, because every thing he said got into print. Occupying the position he did, a mistake would produce harm, and therefore he wanted to be careful not to make a mistake.
BRIG. GEN. G. H. GORDON, Norfolk, Va.:
Send to me at once a full statement as to the cause or causes for which, and by authority of what tribunal George W. Lane, Charles Whitlock, Ezra Baler, J. M. Renshaw, and others are restrained of their liberty. Do this promptly and fully.
A Proclamation.
Whereas by my proclamations of the 19th and 27th days of April, A.D. 1861, the ports of the United States in the States of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas were declared to be subject to blockade; but
Whereas the said blockade has, in consequence of actual military occupation by this Government, since been conditionally set aside or relaxed in respect to the ports of Norfolk and Alexandria, in the State of Virginia; Beaufort, in the State of North Carolina; Port Royal, in the State of South Carolina; Pensacola and Fernandina, in the State of Florida; and New Orleans, in the State of Louisiana; and
Whereas by the fourth section of the act of Congress approved on the 13th of July, 1861, entitled "An act further to provide for the collection of duties on imports, and for other purposes," the President, for the reasons therein set forth, is authorized to close certain ports of entry:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln. President of the United States, do hereby proclaim that the ports of Richmond, Tappahannock, Cherrystone, Yorktown, and Petersburg, in Virginia; of Camden (Elizabeth City), Edenton, Plymouth, Washington, Newbern, Ocracoke, and Wilmington in North Carolina; of Charleston, Georgetown, and Beaufort, in South Carolina; of Savannah, St. Marys, and Brunswick (Darien), in Georgia; of Mobile, in Alabama; of Pearl River (Shieldsboro), Natchez and Vicksburg, in Mississippi; of St. Augustine, Key West, St. Marks (Port Leon), St. Johns (Jacksonville), and Apalachicola, in Florida; of Teche (Franklin), in Louisiana; of Galveston, La Salle, Brazos de Santiago (Point Isabel), and Brownsville, in Texas, are hereby closed, and all right of importation, warehousing, and other privileges shall, in respect to the ports aforesaid, cease until they shall have again been opened by order of the President; and if while said parts are so closed any ship or vessel from beyond the United States or having on board any articles subject to duties shall attempt to enter any such port, the same, together with its tackle, apparel, furniture, and cargo, shall be forfeited to the United States.
In witness whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this eleventh day of April, A.D., 1865, and of the independence of the United States of America, the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas by my proclamation of this date the port of Key West, in the State of Florida, was inadvertently included among those which are not open to commerce:
Now, therefore, be it known that I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby declare and make known that the said port of Key West is and shall remain open to foreign and domestic commerce upon the same conditions by which that commerce has there hitherto been governed.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto set my hand and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the city of Washington, this eleventh day of April, A.D. 1865, and of the independence of the United States of America the eighty-ninth.
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
BY THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA:
A Proclamation.
Whereas for some time past vessels of war of the United States have been refused in certain foreign ports, privileges and immunities to which they were entitled by treaty, public law, or the community of nations, at the same time that vessels of war of the country wherein the said privileges and immunities have been withheld have enjoyed them fully and uninterruptedly in ports of the United States, which condition of things has not always been forcibly resisted by the United States, although, on the other hand, they have not at any time failed to protest against and declare their dissatisfaction with the same. In the view of the United States, no condition any longer exists which can be claimed to justify the denial to them by any one of such nations of customary naval rights as has heretofore been so unnecessarily persisted in.......
Now, therefore, I, Abraham Lincoln, President of the United States, do hereby make known that if, after a reasonable time shall have elapsed for intelligence of this proclamation to have reached any foreign country in whose ports the said privileges and immunities shall have been refused as aforesaid, they shall continue to be so refused, then and thenceforth the same privileges and immunities shall be refused to the vessels of war of that country in the ports of the United States, and this refusal shall continue until war vessels of the United States shall have been placed upon an entire equality in the foreign ports aforesaid with similar vessels of other countries. The United States, whatever claim or pretense may have existed heretofore, are now, at least, entitled to claim and concede an entire and friendly equality of rights and hospitalities with all maritime nations.
In witness whereof, I have hereunto set my hand, and caused the seal of the United States to be affixed..................
A. LINCOLN.
By the President: WILLIAM H. SEWARD, Secretary of State.
FELLOW-CITIZENS—We meet this evening not in sorrow, but in gladness of heart. The evacuation of Petersburg and Richmond, and the surrender of the principal insurgent army, give hope of a righteous and speedy peace, whose joyous expression cannot be restrained. In the midst of this, however, He from whom blessings flow must not be forgotten.
A call for a national thanksgiving is being prepared, and will be duly promulgated. Nor must those whose harder part gives us the cause of rejoicing be overlooked. Their honors must not be parceled out with others. I myself was near the front, and had the pleasure of transmitting much of the good news to you. But no part of the honor for plan or execution is mine. To General Grant, his skillful officers, and brave men, all belongs. The gallant navy stood ready, but was not in reach to take active part. By these recent successes, the reinauguration of the national authority—reconstruction which has had a large share of thought from the first, is pressed much more closely upon our attention. It is fraught with great difficulty. Unlike a case of war between independent nations, there is no authorized organ for us to treat with—no one man has authority to give up the rebellion for any other man. We simply must begin with and mould from disorganized and discordant elements. Nor is it a small additional embarrassment that we, the loyal people, differ among ourselves as to the mode, manner, and measure of reconstruction. As a general rule, I abstain from reading the reports of attacks upon myself, Wishing not to be provoked by that to which I cannot properly offer an answer. In spite of this precaution, however, it comes to my knowledge that I am much censured for some supposed agency in setting up and seeking to sustain the new State government of Louisiana. In this I have done just so much and no more than the public knows. In the Annual Message of December, 1863, and the accompanying proclamation, I presented a plan of reconstruction, as the phrase goes, which I promised, if adopted by any State, would be acceptable to and sustained by the Executive Government of the nation. I distinctly stated that this was not the only plan that might possibly be acceptable, and I also distinctly protested that the Executive claimed no right to say when or whether members should be admitted to seats in Congress from such States. This plan was in advance submitted to the then Cabinet, and approved by every member of it. One of them suggested that I should then and in that connection apply the Emancipation Proclamation to the theretofore excepted parts of Virginia and Louisiana; that I should drop the suggestion about apprenticeship for freed people, and that I should omit the protest against my own power in regard to the admission of members of Congress. But even he approved every part and parcel of the plan which has since been employed or touched by the action of Louisiana. The new constitution of Louisiana, declaring emancipation for the whole State, practically applies the proclamation to the part previously excepted. It does not adopt apprenticeship for freed people, and is silent, as it could not well be otherwise, about the admission of members to Congress. So that, as it applied to Louisiana, every member of the Cabinet fully approved the plan. The message went to Congress, and I received many commendations of the plan, written and verbal, and not a single objection to it from any professed emancipationist came to my knowledge until after the news reached Washington that the people of Louisiana had begun to move in accordance with it. From about July, 1862, I had corresponded with different persons supposed to be interested in seeking a reconstruction of a State government for Louisiana. When the message of 1863, with the plan before mentioned, reached New Orleans, General Banks wrote me that he was confident that the people, with his military co-operation, would reconstruct substantially on that plan. I wrote to him and some of them to try it. They tried it, and the result is known. Such has been my only agency in getting up the Louisiana government. As to sustaining it my promise is out, as before stated. But, as bad promises are better broken than kept, I shall treat this as a bad promise and break it, whenever I shall be convinced that keeping it is adverse to the public interest; but I have not yet been so convinced. I have been shown a letter on this subject, supposed to be an able one, in which the writer expresses regret that my mind has not seemed to be definitely fixed upon the question whether the seceded States, so called, are in the Union or out of it. It would perhaps add astonishment to his regret were he to learn that since I have found professed Union men endeavoring to answer that question, I have purposely forborne any public expression upon it. As appears to me, that question has not been nor yet is a practically material one, and that any discussion of it, while it thus remains practically immaterial, could have no effect other than the mischievous one of dividing our friends. As yet, whatever it may become, that question is bad as the basis of a controversy, and good for nothing at all—a merely pernicious abstraction. We all agree that the seceded States, so called, are out of their proper practical relation with the Union, and that the sole object of the Government, civil and military, in regard to those States, is to again get them into their proper practical relation. I believe that it is not only possible, but in fact easier, to do this without deciding or even considering whether those States have ever been out of the Union, than with it. Finding themselves safely at home, it would be utterly immaterial whether they had been abroad. Let us all join in doing the acts necessary to restore the proper practical relations between these States and the Union, and each forever after innocently indulge his own opinion whether, in doing the acts he brought the States from without into the Union, or only gave them proper assistance, they never having been out of it. The amount of constituency, so to speak, on which the Louisiana government rests, would be more satisfactory to all if it contained fifty thousand, or thirty thousand, or even twenty thousand, instead of twelve thousand, as it does. It is also unsatisfactory to some that the elective franchise is not given to the colored man. I would myself prefer that it were now conferred on the very intelligent, and on those who serve our cause as soldiers. Still, the question is not whether the Louisiana government, as it stands, is quite all that is desirable. The question is, Will it be wiser to take it as it is and help to improve it, or to reject and disperse? Can Louisiana be brought into proper practical relation with the Union sooner by sustaining or by discarding her new State government? Some twelve thousand voters in the heretofore Slave State of Louisiana have sworn allegiance to the Union, assumed to be the rightful political power of the State, held elections, organized a State government, adopted a Free State constitution, giving the benefit of public schools equally to black and white, and empowering the Legislature to confer the elective franchise upon the colored man. This Legislature has already voted to ratify the Constitutional Amendment recently passed by Congress, abolishing slavery throughout the nation. These twelve thousand persons are thus fully committed to the Union and to perpetuate freedom in the State—committed to the very things, and nearly all things, the nation wants—and they ask the nation's recognition and its assistance to make good this committal. Now, if we reject and spurn them, we do our utmost to disorganize and disperse them. We, in fact, say to the white man: You are worthless or worse; we will neither help you nor be helped by you. To the blacks we say: This cup of liberty which these, your old masters, held to your lips, we will dash from you, and leave you to the chances of gathering the spilled and scattered contents in some vague and undefined when, where, and how. If this course, discouraging and paralyzing both white and black, has any tendency to bring Louisiana into proper practical relations with the Union, I have so far been unable to perceive it. If, on the contrary, we recognize and sustain the new government of Louisiana, the converse of all this is made true. We encourage the hearts and nerve the arms of twelve thousand to adhere to their work, and argue for it, and proselyte for it, and fight for it, and feed it, and grow it, and ripen it to a complete success. The colored man, too, in seeing all united for him, is inspired with vigilance, and energy, and daring to the same end. Grant that he desires the elective franchise, will he not attain it sooner by saving the already advanced steps towards it, than by running backward over them? Concede that the new government of Louisiana is only to what it should be as the egg is to the fowl, we shall sooner have the fowl by hatching the egg than by smashing it. Again, if we reject Louisiana, we also reject one vote in favor of the proposed amendment to the National Constitution. To meet this proposition, it has been argued that no more than three fourths of those States which have not attempted secession are necessary to validly ratify the amendment. I do not commit myself against this, further than to say that such a ratification would be questionable, and sure to be persistently questioned, while a ratification by three fourths of all the States would be unquestioned and unquestionable. I repeat the question, Can Louisiana be brought into proper practical relation with the Union sooner by sustaining or by discarding her new State government? What has been said of Louisiana will apply to other States. And yet so great peculiarities pertain to each State, and such important and sudden changes occur in the same State, and withal so new and unprecedented is the whole case, that no exclusive and inflexible plan can safely be prescribed as to details and collaterals. Such exclusive and inflexible plan would surely become a new entanglement. Important principles may and must be inflexible. In the present situation as the phrase goes, it may be my duty to make some new announcement to the people of the South. I am considering, and shall not fail to act, when satisfied that action will be proper.
I have seen your despatch to Colonel Hardie about the matter of prayers. I do not remember hearing prayers spoken of while I was in Richmond; but I have no doubt you have acted in what appeared to you to be the spirit and temper manifested by me while there. Is there any sign of the rebel legislature coming together on the understanding of my letter to you? If there is any such sign, inform me what it is; if there is no such sign, you may withdraw the offer.
I have just seen Judge Campbell's letter to you of the 7th. He assumes, as appears to me, that I have called the insurgent legislature of Virginia together, as the rightful legislature of the State, to settle all differences with the United States. I have done no such thing. I spoke of them, not as a legislature, but as "the gentlemen who have acted as the legislature of Virginia in support of the rebellion." I did this on purpose to exclude the assumption that I was recognizing them as a rightful body. I deal with them as men having power de facto to do a specific thing, to wit: "To withdraw the Virginia troops and other support from resistance to the General Government," for which, in the paper handed Judge Campbell, I promised a specific equivalent, to wit: a remission to the people of the State, except in certain cases, of the confiscation of their property. I meant this, and no more. Inasmuch, however, as Judge Campbell misconstrues this, and is still pressing for an armistice, contrary to the explicit statement of the paper I gave him, and particularly as General Grant has since captured the Virginia troops, so that giving a consideration for their withdrawal is no longer applicable, let my letter to you and the paper to Judge Campbell both be withdrawn, or countermanded, and he be notified of it. Do not now allow them to assemble, but if any have come, allow them safe return to their homes.
Mr. Colfax, I want you to take a message from me to the miners whom you visit. I have very large ideas of the mineral wealth of our nation. I believe it practically inexhaustible. It abounds all over the Western country, from the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific, and its development has scarcely commenced. During the war, when we were adding a couple of millions of dollars every day to our national debt, I did not care about encouraging the increase in the volume of our precious metals. We had the country to save first. But now that the rebellion is overthrown, and we know pretty nearly the amount of our national debt, the more gold and silver we mine, we make the payment of that debt so much the easier. "Now," said he, speaking with more emphasis, "I am going to encourage that in every possible way. We shall have hundreds of thousands of disbanded soldiers, and many have feared that their return home in such great numbers might paralyze industry, by furnishing, suddenly, a greater supply of labor than there will be demand for. I am going to try to attract them to the hidden wealth of our mountain ranges, where there is room enough for all. Immigration, which even the war has not stopped, will land upon our shores hundreds of thousands more per year from overcrowded Europe. I intend to point them to the gold and silver that wait for them in the West. Tell the miners for me, that I shall promote their interests to the utmost of my ability; because their prosperity is the prosperity of the nation; and," said he, his eye kindling with enthusiasm, "we shall prove, in a very few years, that we are indeed the treasury of the world."
GENERAL VAN ALLEN:
I intend to adopt the advice of my friends and use due precaution.... I thank you for the assurance you give me that I shall be supported by conservative men like yourself, in the efforts I may make to restore the Union, so as to make it, to use your language, a Union of hearts and hands as well as of States.
Yours truly,
A. LINCOLN. April 14, 1865



ABRAHAM LINCOLN, the Great Story Telling President, whose Emancipation Proclamation freed more than four million slaves, was a keen politician, profound statesman, shrewd diplomatist, a thorough judge of men and possessed of an intuitive knowledge of affairs. He was the first Chief Executive to die at the hands of an assassin. Without school education he rose to power by sheer merit and will-power. Born in a Kentucky log cabin in 1809, his surroundings being squalid, his chances for advancement were apparently hopeless. President Lincoln died April 15th, 1865, having been shot by J. Wilkes Booth the night before.
CONTENTS OF YARNS AND STORIES
LINCOLN’S NAME AROUSES AN AUDIENCE
“ABE” LINCOLN’S YARNS AND STORIES.
HIS KNOWLEDGE OF HUMAN NATURE.
LINCOLN’S STORY TO PEACE COMMISSIONERS.
IT DEPENDED UPON HIS CONDITION.
“HONEST ABE” SWALLOWS HIS ENEMIES.
A JOB FOR THE NEW CABINETMAKER.
WANTED TO BURN HIM DOWN TO THE STUMP.
THE CASE OF BETSY ANN DOUGHERTY.
“ABE” STIRRING THE “BLACK” COALS.
LOST HIS CERTIFICATE OF CHARACTER.
JEFF DAVIS AND CHARLES THE FIRST.
REMINDED HIM OF “A LITTLE STORY.”
MAKE SOMETHING OUT OF IT, ANYWAY.
VICIOUS OXEN HAVE SHORT HORNS.
LINCOLN’S NAME FOR “WEEPING WATER.”
PETER CARTWRIGHT’S DESCRIPTION OF LINCOLN.
“DON’T KILL HIM WITH YOUR FIST.”
LINCOLN ADOPTED THE SUGGESTION.
GREELEY CARRIES LINCOLN TO THE LUNATIC ASYLUM.
SAFE AS LONG AS THEY WERE GOOD.
“SMELT NO ROYALTY IN OUR CARRIAGE.”
HELL A MILE FROM THE WHITE HOUSE.
ORIGIN OF THE “INFLUENCE” STORY.
PAT WAS “FORNINST THE GOVERNMENT.”
HARDTACK BETTER THAN GENERALS.
MR. BULL DIDN’T GET HIS COTTON.
“AND YOU DON’T WEAR HOOPSKIRTS.”
LIEUTENANT TAD LINCOLN’S SENTINELS.
“ABE, YOU CAN’T PLAY THAT ON ME.”
LINCOLN CALLS MEDILL A COWARD.
“MRS. NORTH AND HER ATTORNEY.”
“WEBSTER COULDN’T HAVE DONE MORE.”
REMINDED “ABE” OF A LITTLE JOKE.
LINCOLN PROTECTED CURRENCY ISSUES.
“THE BAD BIRD AND THE MUDSILL.”
PRESIDENT LINCOLN’S LAST PUBLIC ADDRESS.
MOST VALUABLE POLITICAL ATTRIBUTE.
OFFICE SEEKERS WORSE THAN WAR.
DIDN’T KNOW GRANT’S PREFERENCE.
HOW “FIGHTING JOE” WAS APPOINTED.
A FORTUNE-TELLER’S PREDICTION.
SHOULD HAVE FOUGHT ANOTHER BATTLE.
WHEN LINCOLN AND GRANT CLASHED.
WON JAMES GORDON BENNETT’S SUPPORT.
DIDN’T WANT A MILITARY REPUTATION.
LINCOLN’S REJECTED MANUSCRIPT.
LINCOLN’S IDEAS ON CROSSING A RIVER WHEN HE GOT TO IT.
“CONSIDER THE SYMPATHY OF LINCOLN.”
HIS PASSES TO RICHMOND NOT HONORED.
“PUBLIC HANGMAN” FOR THE UNITED STATES.
LINCOLN A MAN OF SIMPLE HABITS.
FORGOT EVERYTHING HE KNEW BEFORE.
LINCOLN BELIEVED IN EDUCATION.
LINCOLN ON THE DRED SCOTT DECISION.
LINCOLN MADE MANY NOTABLE SPEECHES.
CALLED BLESSINGS ON THE AMERICAN WOMEN.
TALKED TO THE NEGROES OF RICHMOND.
ANGELS COULDN’T SWEAR IT RIGHT.
LINCOLN WASN’T BUYING NOMINATIONS.
HE ENVIED THE SOLDIER AT THE FRONT.
THE PRESIDENT HAD KNOWLEDGE OF HIM.
HOW STANTON GOT INTO THE CABINET.
WHY HE WAS CALLED “HONEST ABE.”
“ABE’S” NAME REMAINED ON THE SIGN.
HE PROPOSED TO SAVE THE UNION.
WOULD NOT RECALL A SINGLE WORD.
WOULDN’T HOLD TITLE AGAINST HIM.
COULDN’T LOCATE HIS BIRTHPLACE.
“ABE” OFFERS A SPEECH FOR SOMETHING TO EAT.
“BUTCHER-KNIFE BOYS” AT THE POLLS.
NO “SECOND COMING” FOR SPRINGFIELD.
GAVE THE SOLDIER THE PREFERENCE.
JEFF. DAVIS’ REPLY TO LINCOLN.
DESERTER’S SINS WASHED OUT IN BLOOD.
LINCOLN DEFENDS FIFTEEN MRS. NATIONS.
AVOIDED EVEN APPEARANCE OF EVIL
LINCOLN PAID HOMAGE TO WASHINGTON.
ETERNAL FIDELITY TO THE CAUSE OF LIBERTY.
WROTE “PIECES” WHEN VERY YOUNG.
“THE ‘RAIL-SPUTTER’ REPAIRING THE UNION.”
“GOVERNMENT RESTS IN PUBLIC OPINION.”
LINCOLN WOULD HAVE PREFERRED DEATH.
“PUNCH” AND HIS LITTLE PICTURE.
THE FIVE POINTS SUNDAY SCHOOL.
THOUGHT GOD WOULD HAVE TOLD HIM.
NAUGHTY BOY HAD TO TAKE HIS MEDICINE.
LINCOLN’S MEN WERE “HUSTLERS.”
DODGING “BROWSING PRESIDENTS.”
SCALPING IN THE BLACK HAWK WAR.
HOW THE TOWN OF LINCOLN, ILL., WAS NAMED.
PRESIDENT AND CABINET JOINED IN PRAYER.
LINCOLN WISHED TO SEE RICHMOND.
“LINCOLN GOES IN WHEN THE QUAKERS ARE OUT”
“ABE WANTED NO SNEAKIN’ ‘ROUND.”
“HOW DO YOU GET OUT OF THIS PLACE?”
“TAD” INTRODUCES “OUR FRIENDS.”
“LONG ABE’S” FEET “PROTRUDED OVER.”
COULD LICK ANY MAN IN THE CROWD.
“LEFT IT THE WOMEN TO HOWL ABOUT ME.”
HE’D RUIN ALL THE OTHER CONVICTS.
“FIXED UP” A BIT FOR THE “CITY FOLKS.”
EVEN REBELS OUGHT TO BE SAVED.
“HOLDING A CANDLE TO THE CZAR.”
NASHVILLE WAS NOT SURRENDERED.
HE COULDN’T WAIT FOR THE COLONEL.
LINCOLN PRONOUNCED THIS STORY FUNNY.
“I’D A BEEN MISSED BY MYSE’F.”
IT ALL “DEPENDED” UPON THE EFFECT.
TOO SWIFT TO STAY IN THE ARMY.
WISHED THE ARMY CHARGED LIKE THAT.
“UNCLE ABRAHAM” HAD EVERYTHING READY.
“NEVER REGRET WHAT YOU DON’T WRITE.”
ASSISTANT PILOT ON A STEAMBOAT.
“CAPTAIN LINCOLN” PLEASED HIM.
SURVEYOR WITH NO STRINGS ON HIM.
DEFEATS PETER CARTWRIGHT FOR CONGRESS.
MAKES SPEECHES FOR “OLD ZACH.”
TELLING STORIES ON THE CIRCUIT.
THE LION IS AROUSED TO ACTION.
HELPS TO ORGANIZE THE REPUBLICAN PARTY.
THE RAIL-SPLITTER vs. THE LITTLE GIANT.
FIRST NOMINATION FOR PRESIDENT.
FORMATION OF THE SOUTHERN CONFEDERACY.
THE “SECRET PASSAGE” TO WASHINGTON.
HIS ELOQUENT INAUGURAL ADDRESS.
FOLLOWS PRECEDENT OF WASHINGTON.
REASONS FOB FREEING THE SLAVES.
A FUN-LOVING AND HUMOR-LOVING MAN.
BOOTH BRANDISHES HIS DAGGER AND ESCAPES.
Dean Swift said that the man who makes two blades of grass grow where one grew before serves well of his kind. Considering how much grass there is in the world and comparatively how little fun, we think that a still more deserving person is the man who makes many laughs grow where none grew before.
Sometimes it happens that the biggest crop of laugh is produced by a man who ranks among the greatest and wisest. Such a man was Abraham Lincoln whose wholesome fun mixed with true philosophy made thousands laugh and think at the same time. He was a firm believer in the saying, “Laugh and the world laughs with you.”
Whenever Abraham Lincoln wanted to make a strong point he usually began by saying, “Now, that reminds me of a story.” And when he had told a story every one saw the point and was put into a good humor.
The ancients had Aesop and his fables. The moderns had Abraham Lincoln and his stories.
Aesop’s Fables have been printed in book form in almost every language and millions have read them with pleasure and profit. Lincoln’s stories were scattered in the recollections of thousands of people in various parts of the country. The historians who wrote histories of Lincoln’s life remembered only a few of them, but the most of Lincoln’s stories and the best of them remained unwritten. More than five years ago the author of this book conceived the idea of collecting all the yarns and stories, the droll sayings, and witty and humorous anecdotes of Abraham Lincoln into one large book, and this volume is the result of that idea.
Before Lincoln was ever heard of as a lawyer or politician, he was famous as a story teller. As a politician, he always had a story to fit the other side; as a lawyer, he won many cases by telling the jury a story which showed them the justice of his side better than any argument could have done.
While nearly all of Lincoln’s stories have a humorous side, they also contain a moral, which every good story should have.
They contain lessons that could be taught so well in no other way. Every one of them is a sermon. Lincoln, like the Man of Galilee, spoke to the people in parables.
Nothing that can be written about Lincoln can show his character in such a true light as the yarns and stories he was so fond of telling, and at which he would laugh as heartily as anyone.
For a man whose life was so full of great responsibilities, Lincoln had many hours of laughter when the humorous, fun-loving side of his great nature asserted itself.
Every person to keep healthy ought to have one good hearty laugh every day. Lincoln did, and the author hopes that the stories at which he laughed will continue to furnish laughter to all who appreciate good humor, with a moral point and spiced with that true philosophy bred in those who live close to nature and to the people around them.
In producing this new Lincoln book, the publishers have followed an entirely new and novel method of illustrating it. The old shop-worn pictures that are to be seen in every “History of Lincoln,” and in every other book written about him, such as “A Flatboat on the Sangamon River,” “State Capitol at Springfield,” “Old Log Cabin,” etc., have all been left out and in place of them the best special artists that could be employed have supplied original drawings illustrating the “point” of Lincoln’s stories.
These illustrations are not copies of other pictures, but are original drawings made from the author’s original text expressly for this book.
In these high-class outline pictures the artists have caught the true spirit of Lincoln’s humor, and while showing the laughable side of many incidents in his career, they are true to life in the scenes and characters they portray.
In addition to these new and original pictures, the book contains many rare and valuable photograph portraits, together with biographies, of the famous men of Lincoln’s day, whose lives formed a part of his own life history.
No Lincoln book heretofore published has ever been so profusely, so artistically and expensively illustrated.
The parables, yarns, stories, anecdotes and sayings of the “Immortal Abe” deserve a place beside Aesop’s Fables, Bunyan’s Pilgrim’s Progress and all other books that have added to the happiness and wisdom of mankind.
Lincoln’s stories are like Lincoln himself. The more we know of them the better we like them.
BY COLONEL ALEXANDER K. McCLURE.
While Lincoln would have been great among the greatest of the land as a statesman and politician if like Washington, Jefferson and Jackson, he had never told a humorous story, his sense of humor was the most fascinating feature of his personal qualities.
He was the most exquisite humorist I have ever known in my life. His humor was always spontaneous, and that gave it a zest and elegance that the professional humorist never attains.
As a rule, the men who have become conspicuous in the country as humorists have excelled in nothing else. S. S. Cox, Proctor Knott, John P. Hale and others were humorists in Congress. When they arose to speak if they failed to be humorous they utterly failed, and they rarely strove to be anything but humorous. Such men often fail, for the professional humorist, however gifted, cannot always be at his best, and when not at his best he is grievously disappointing.
I remember Corwin, of Ohio, who was a great statesman as well as a great humorist, but whose humor predominated in his public speeches in Senate and House, warning a number of the younger Senators and Representatives on a social occasion when he had returned to Congress in his old age, against seeking to acquire the reputation of humorists. He said it was the mistake of his life. He loved it as did his hearers, but the temptation to be humorous was always uppermost, and while his speech on the Mexican War was the greatest ever delivered in the Senate, excepting Webster’s reply to Hayne, he regretted that he was more known as a humorist than as a statesman.
His first great achievement in the House was delivered in 1840 in reply to General Crary, of Michigan, who had attacked General Harrison’s military career. Corwin’s reply in defense of Harrison is universally accepted as the most brilliant combination of humor and invective ever delivered in that body. The venerable John Quincy Adams a day or two after Corwin’s speech, referred to Crary as “the late General Crary,” and the justice of the remark from the “Old Man Eloquent” was accepted by all. Mr. Lincoln differed from the celebrated humorists of the country in the important fact that his humor was unstudied. He was not in any sense a professional humorist, but I have never in all my intercourse with public men, known one who was so apt in humorous illustration us Mr. Lincoln, and I have known him many times to silence controversy by a humorous story with pointed application to the issue.
His face was the saddest in repose that I have ever seen among accomplished and intellectual men, and his sympathies for the people, for the untold thousands who were suffering bereavement from the war, often made him speak with his heart upon his sleeve, about the sorrows which shadowed the homes of the land and for which his heart was freely bleeding.
I have many times seen him discussing in the most serious and heartfelt manner the sorrows and bereavements of the country, and when it would seem as though the tension was so strained that the brittle cord of life must break, his face would suddenly brighten like the sun escaping from behind the cloud to throw its effulgence upon the earth, and he would tell an appropriate story, and much as his stories were enjoyed by his hearers none enjoyed them more than Mr. Lincoln himself.
I have often known him within the space of a few minutes to be transformed from the saddest face I have ever looked upon to one of the brightest and most mirthful. It was well known that he had his great fountain of humor as a safety valve; as an escape and entire relief from the fearful exactions his endless duties put upon him. In the gravest consultations of the cabinet where he was usually a listener rather than a speaker, he would often end dispute by telling a story and none misunderstood it; and often when he was pressed to give expression on particular subjects, and his always abundant caution was baffled, he many times ended the interview by a story that needed no elaboration.
I recall an interview with Mr. Lincoln at the White House in the spring of 1865, just before Lee retreated from Petersburg. It was well understood that the military power of the Confederacy was broken, and that the question of reconstruction would soon be upon us.
Colonel Forney and I had called upon the President simply to pay our respects, and while pleasantly chatting with him General Benjamin F. Butler entered. Forney was a great enthusiast, and had intense hatred of the Southern leaders who had hindered his advancement when Buchanan was elected President, and he was bubbling over with resentment against them. He introduced the subject to the President of the treatment to be awarded to the leaders of the rebellion when its powers should be confessedly broken, and he was earnest in demanding that Davis and other conspicuous leaders of the Confederacy should be tried, condemned and executed as traitors.
General Butler joined Colonel Forney in demanding that treason must be made odious by the execution of those who had wantonly plunged the country into civil war. Lincoln heard them patiently, as he usually heard all, and none could tell, however carefully they scanned his countenance what impression the appeal made upon him.
I said to General Butler that, as a lawyer pre-eminent in his profession, he must know that the leaders of a government that had beleaguered our capital for four years, and was openly recognized as a belligerent power not only by our government but by all the leading governments of the world, could not be held to answer to the law for the crime of treason.
Butler was vehement in declaring that the rebellious leaders must be tried and executed. Lincoln listened to the discussion for half an hour or more and finally ended it by telling the story of a common drunkard out in Illinois who had been induced by his friends time and again to join the temperance society, but had always broken away. He was finally gathered up again and given notice that if he violated his pledge once more they would abandon him as an utterly hopeless vagrant. He made an earnest struggle to maintain his promise, and finally he called for lemonade and said to the man who was preparing it: “Couldn’t you put just a drop of the cratur in unbeknownst to me?”
After telling the story Lincoln simply added: “If these men could get away from the country unbeknownst to us, it might save a world of trouble.” All understood precisely what Lincoln meant, although he had given expression in the most cautious manner possible and the controversy was ended.
Lincoln differed from professional humorists in the fact that he never knew when he was going to be humorous. It bubbled up on the most unexpected occasions, and often unsettled the most carefully studied arguments. I have many times been with him when he gave no sign of humor, and those who saw him under such conditions would naturally suppose that he was incapable of a humorous expression. At other times he would effervesce with humor and always of the most exquisite and impressive nature. His humor was never strained; his stories never stale, and even if old, the application he made of them gave them the freshness of originality.
I recall sitting beside him in the White House one day when a message was brought to him telling of the capture of several brigadier-generals and a number of horses somewhere out in Virginia. He read the dispatch and then in an apparently soliloquizing mood, said: “Sorry for the horses; I can make brigadier-generals.”
There are many who believe that Mr. Lincoln loved to tell obscene or profane stories, but they do great injustice to one of the purest and best men I have ever known. His humor must be judged by the environment that aided in its creation.
As a prominent lawyer who traveled the circuit in Illinois, he was much in the company of his fellow lawyers, who spent their evenings in the rude taverns of what was then almost frontier life. The Western people thus thrown together with but limited sources of culture and enjoyment, logically cultivated the story teller, and Lincoln proved to be the most accomplished in that line of all the members of the Illinois bar. They had no private rooms for study, and the evenings were always spent in the common barroom of the tavern, where Western wit, often vulgar or profane, was freely indulged in, and the best of them at times told stories which were somewhat “broad;” but even while thus indulging in humor that would grate harshly upon severely refined hearers, they despised the vulgarian; none despised vulgarity more than Lincoln.
I have heard him tell at one time or another almost or quite all of the stories he told during his Presidential term, and there were very few of them which might not have been repeated in a parlor and none descended to obscene, vulgar or profane expressions. I have never known a man of purer instincts than Abraham Lincoln, and his appreciation of all that was beautiful and good was of the highest order.
It was fortunate for Mr. Lincoln that he frequently sought relief from the fearfully oppressive duties which bore so heavily upon him. He had immediately about him a circle of men with whom he could be “at home” in the White House any evening as he was with his old time friends on the Illinois circuit.
David Davis was one upon whom he most relied as an adviser, and Leonard Swett was probably one of his closest friends, while Ward Lamon, whom he made Marshal of the District of Columbia to have him by his side, was one with whom he felt entirely “at home.” Davis was of a more sober order but loved Lincoln’s humor, although utterly incapable of a humorous expression himself. Swett was ready with Lincoln to give and take in storyland, as was Lamon, and either of them, and sometimes all of them, often dropped in upon Lincoln and gave him an hour’s diversion from his exacting cares. They knew that he needed it and they sought him for the purpose of diverting him from what they feared was an excessive strain.
His devotion to Lamon was beautiful. I well remember at Harrisburg on the night of February 22, 1861, when at a dinner given by Governor Curtin to Mr. Lincoln, then on his way to Washington, we decided, against the protest of Lincoln, that he must change his route to Washington and make the memorable midnight journey to the capital. It was thought to be best that but one man should accompany him, and he was asked to choose. There were present of his suite Colonel Sumner, afterwards one of the heroic generals of the war, Norman B. Judd, who was chairman of the Republican State Committee of Illinois, Colonel Lamon and others, and he promptly chose Colonel Lamon, who alone accompanied him on his journey from Harrisburg to Philadelphia and thence to Washington.
Before leaving the room Governor Curtin asked Colonel Lamon whether he was armed, and he answered by exhibiting a brace of fine pistols, a huge bowie knife, a black jack, and a pair of brass knuckles. Curtin answered: “You’ll do,” and they were started on their journey after all the telegraph wires had been cut. We awaited through what seemed almost an endless night, until the east was purpled with the coming of another day, when Colonel Scott, who had managed the whole scheme, reunited the wires and soon received from Colonel Lamon this dispatch: “Plums delivered nuts safely,” which gave us the intensely gratifying information that Lincoln had arrived in Washington.
Of all the Presidents of the United States, and indeed of all the great statesmen who have made their indelible impress upon the policy of the Republic, Abraham Lincoln stands out single and alone in his individual qualities. He had little experience in statesmanship when he was called to the Presidency. He had only a few years of service in the State Legislature of Illinois, and a single term in Congress ending twelve years before he became President, but he had to grapple with the gravest problems ever presented to the statesmanship of the nation for solution, and he met each and all of them in turn with the most consistent mastery, and settled them so successfully that all have stood unquestioned until the present time, and are certain to endure while the Republic lives.
In this he surprised not only his own cabinet and the leaders of his party who had little confidence in him when he first became President, but equally surprised the country and the world.
He was patient, tireless and usually silent when great conflicts raged about him to solve the appalling problems which were presented at various stages of the war for determination, and when he reached his conclusion he was inexorable. The wrangles of faction and the jostling of ambition were compelled to bow when Lincoln had determined upon his line of duty.
He was much more than a statesman; he was one of the most sagacious politicians I have ever known, although he was entirely unschooled in the machinery by which political results are achieved. His judgment of men was next to unerring, and when results were to be attained he knew the men who should be assigned to the task, and he rarely made a mistake.
I remember one occasion when he summoned Colonel Forney and myself to confer on some political problem, he opened the conversation by saying: “You know that I never was much of a conniver; I don’t know the methods of political management, and I can only trust to the wisdom of leaders to accomplish what is needed.”
Lincoln’s public acts are familiar to every schoolboy of the nation, but his personal attributes, which are so strangely distinguished from the attributes of other great men, are now the most interesting study of young and old throughout our land, and I can conceive of no more acceptable presentation to the public than a compilation of anecdotes and incidents pertaining to the life of the greatest of all our Presidents.
A.K. McClure
When I have had to address a fagged and listless audience, I have found that nothing was so certain to arouse them as to introduce the name of Abraham Lincoln.
REVERE WASHINGTON AND LOVE LINCOLN, REV. DR. THEODORE L. CUYLER.
No other name has such electric power on every true heart, from Maine to Mexico, as the name of Lincoln. If Washington is the most revered, Lincoln is the best loved man that ever trod this continent.
GREATEST CHARACTER SINCE CHRIST BY JOHN HAY, Former Private Secretary to President Lincoln, and Later Secretary of State in President McKinley’s Cabinet.
As, in spite of some rudeness, republicanism is the sole hope of a sick world, so Lincoln, with all his foibles, is the greatest character since Christ.
STORIES INFORM THE COMMON PEOPLE, BY CHAUNCEY M. DEPEW, United States Senator from New York.
Mr. Lincoln said to me once: “They say I tell a great many stories; I reckon I do, but I have found in the course of a long experience that common people, take them as they run, are more easily informed through the medium of a broad illustration than in any other way, and as to what the hypercritical few may think, I don’t care.”
HUMOR A PASSPORT TO THE HEART BY GEO. S. BOUTWELL, Former Secretary of the United States Treasury.
Mr. Lincoln’s wit and mirth will give him a passport to the thoughts and hearts of millions who would take no interest in the sterner and more practical parts of his character.
DROLL, ORIGINAL AND APPROPRIATE. BY ELIHU B. WASHBURNE, Former United States Minister to France.
Mr. Lincoln’s anecdotes were all so droll, so original, so appropriate and so illustrative of passing incidents, that one never wearied.
LINCOLN’S HUMOR A SPARKLING SPRING, BY DAVID R. LOCKE (PETROLEUM V. NASBY), Lincoln’s Favorite Humorist.
Mr. Lincoln’s flow of humor was a sparkling spring, gushing out of a rock—the flashing water had a somber background which made it all the brighter.
LIKE AESOP’S FABLES, BY HUGH McCULLOCH, Former Secretary of the United States Treasury.
Many of Mr. Lincoln’s stories were as apt and instructive as the best of Aesop’s Fables.
FULL OF FUN, BY GENERAL JAMES B. FRY, Former Adjutant-General United States Army.
Mr. Lincoln was a humorist so full of fun that he could not keep it all in.
INEXHAUSTIBLE FUND OF STORIES, BY LAWRENCE WELDON, Judge United States Court of Claims.
Mr. Lincoln’s resources as a story-teller were inexhaustible, and no condition could arise in a case beyond his capacity to furnish an illustration with an appropriate anecdote.
CHAMPION STORY-TELLER, BY BEN. PERLEY POORE, Former Editor of The Congressional Record.
Mr. Lincoln was recognized as the champion story-teller of the Capitol.
LINCOLN CHRONOLOGY.
1806—Marriage of Thomas Lincoln and Nancy Hanks, June 12th,
Washington County, Kentucky.
1809—Born February 12th, Hardin (now La Rue County), Kentucky.
1816—Family Removed to Perry County, Indiana.
1818—Death of Abraham’s Mother, Nancy Hanks Lincoln.
1819—Second Marriage Thomas Lincoln; Married Sally Bush
Johnston, December 2nd, at Elizabethtown, Kentucky.
1830—Lincoln Family Removed to Illinois, Locating in Macon County.
1831—Abraham Located at New Salem.
1832—Abraham a Captain in the Black Hawk War.
1833—Appointed Postmaster at New Salem.
1834—Abraham as a Surveyor. First Election to the Legislature.
1835—Love Romance with Anne Rutledge.
1836—Second Election to the Legislature.
1837—Licensed to Practice Law.
1838—Third Election to the Legislature.
1840—Presidential Elector on Harrison Ticket.
Fourth Election to the Legislature.
1842—Married November 4th, to Mary Todd. “Duel” with General Shields.
1843—Birth of Robert Todd Lincoln, August 1st.
1846—Elected to Congress. Birth of Edward Baker Lincoln, March 10th.
1848—Delegate to the Philadelphia National Convention.
1850—Birth of William Wallace Lincoln, December 2nd.
1853—Birth of Thomas Lincoln, April 4th.
1856—Assists in Formation Republican Party.
1858—Joint Debater with Stephen A. Douglas. Defeated for the
United States Senate.
1860—Nominated and Elected to the Presidency.
1861—Inaugurated as President, March 4th. 1863-Issued
Emancipation Proclamation. 1864-Re-elected to the Presidency.
1865—Assassinated by J. Wilkes Booth, April 14th. Died April
15th. Remains Interred at Springfield, Illinois, May 4th.


Colonel Alexander K. McClure, the editorial director of the Philadelphia Times, which he founded in 1875, began his forceful career as a tanner’s apprentice in the mountains of Pennsylvania threescore years ago. He tanned hides all day, and read exchanges nights in the neighboring weekly newspaper office. The learned tanner’s boy also became the aptest Inner in the county, and the editor testified his admiration for young McClure’s attainments by sending him to edit a new weekly paper which the exigencies of politics called into being in an adjoining county.
The lad was over six feet high, had the thews of Ajax and the voice of Boanerges, and knew enough about shoe-leather not to be afraid of any man that stood in it. He made his paper a success, went into politics, and made that a success, studied law with William McLellan, and made that a success, and actually went into the army—and made that a success, by an interesting accident which brought him into close personal relations with Abraham Lincoln, whom he had helped to nominate, serving as chairman of the Republican State Committee of Pennsylvania through the campaign.
In 1862 the government needed troops badly, and in each Pennsylvania county Republicans and Democrats were appointed to assist in the enrollment, under the State laws. McClure, working day and night at Harrisburg, saw conscripts coming in at the rate of a thousand a day, only to fret in idleness against the army red-tape which held them there instead of sending a regiment a day to the front, as McClure demanded should be done. The military officer continued to dispatch two companies a day—leaving the mass of the conscripts to be fed by the contractors.
McClure went to Washington and said to the President, “You must send a mustering officer to Harrisburg who will do as I say; I can’t stay there any longer under existing conditions.”
Lincoln sent into another room for Adjutant-General Thomas. “General,” said he, “what is the highest rank of military officer at Harrisburg?” “Captain, sir,” said Thomas. “Bring me a commission for an Assistant Adjutant-General of the United States Army,” said Lincoln.
So Adjutant-General McClure was mustered in, and after that a regiment a day of boys in blue left Harrisburg for the front. Colonel McClure is one of the group of great Celt-American editors, which included Medill, McCullagh and McLean.
Lincoln was, naturally enough, much surprised one day, when a man of rather forbidding countenance drew a revolver and thrust the weapon almost into his face. In such circumstances “Abe” at once concluded that any attempt at debate or argument was a waste of time and words.
“What seems to be the matter?” inquired Lincoln with all the calmness and self-possession he could muster.
“Well,” replied the stranger, who did not appear at all excited, “some years ago I swore an oath that if I ever came across an uglier man than myself I’d shoot him on the spot.”
A feeling of relief evidently took possession of Lincoln at this rejoinder, as the expression upon his countenance lost all suggestion of anxiety.
“Shoot me,” he said to the stranger; “for if I am an uglier man than you I don’t want to live.”
Thurlow Weed, the veteran journalist and politician, once related how, when he was opposing the claims of Montgomery Blair, who aspired to a Cabinet appointment, that Mr. Lincoln inquired of Mr. Weed whom he would recommend, “Henry Winter Davis,” was the response.
“David Davis, I see, has been posting you up on this question,” retorted Lincoln. “He has Davis on the brain. I think Maryland must be a good State to move from.”
The President then told a story of a witness in court in a neighboring county, who, on being asked his age, replied, “Sixty.” Being satisfied he was much older the question was repeated, and on receiving the same answer the court admonished the witness, saying, “The court knows you to be much older than sixty.”
“Oh, I understand now,” was the rejoinder, “you’re thinking of those ten years I spent on the eastern share of Maryland; that was so much time lost, and didn’t count.”
Blair was made Postmaster-General.
Riding at one time in a stage with an old Kentuckian who was returning from Missouri, Lincoln excited the old gentleman’s surprise by refusing to accept either of tobacco or French brandy.
When they separated that afternoon—the Kentuckian to take another stage bound for Louisville—he shook hands warmly with Lincoln, and said, good-humoredly:
“See here, stranger, you’re a clever but strange companion. I may never see you again, and I don’t want to offend you, but I want to say this: My experience has taught me that a man who has no vices has d——d few virtues. Good-day.”
Miss Todd (afterwards Mrs. Lincoln) had a keen sense of the ridiculous, and wrote several articles in the Springfield (Ill.) “Journal” reflecting severely upon General James Shields (who won fame in the Mexican and Civil Wars, and was United States Senator from three states), then Auditor of State.
Lincoln assumed the authorship, and was challenged by Shields to meet him on the “field of honor.” Meanwhile Miss Todd increased Shields’ ire by writing another letter to the paper, in which she said: “I hear the way of these fire-eaters is to give the challenged party the choice of weapons, which being the case, I’ll tell you in confidence that I never fight with anything but broom-sticks, or hot water, or a shovelful of coals, the former of which, being somewhat like a shillalah, may not be objectionable to him.”


Lincoln accepted the challenge, and selected broadswords as the weapons. Judge Herndon (Lincoln’s law partner) gives the closing of this affair as follows:
“The laws of Illinois prohibited dueling, and Lincoln demanded that the meeting should be outside the state. Shields undoubtedly knew that Lincoln was opposed to fighting a duel—that his moral sense would revolt at the thought, and that he would not be likely to break the law by fighting in the state. Possibly he thought Lincoln would make a humble apology. Shields was brave, but foolish, and would not listen to overtures for explanation. It was arranged that the meeting should be in Missouri, opposite Alton. They proceeded to the place selected, but friends interfered, and there was no duel. There is little doubt that the man who had swung a beetle and driven iron wedges into gnarled hickory logs could have cleft the skull of his antagonist, but he had no such intention. He repeatedly said to the friends of Shields that in writing the first article he had no thought of anything personal. The Auditor’s vanity had been sorely wounded by the second letter, in regard to which Lincoln could not make any explanation except that he had had no hand in writing it. The affair set all Springfield to laughing at Shields.”
A country meeting-house, that was used once a month, was quite a distance from any other house.
The preacher, an old-line Baptist, was dressed in coarse linen pantaloons, and shirt of the same material. The pants, manufactured after the old fashion, with baggy legs, and a flap in the front, were made to attach to his frame without the aid of suspenders.
A single button held his shirt in position, and that was at the collar. He rose up in the pulpit, and with a loud voice announced his text thus: “I am the Christ whom I shall represent to-day.”
About this time a little blue lizard ran up his roomy pantaloons. The old preacher, not wishing to interrupt the steady flow of his sermon, slapped away on his leg, expecting to arrest the intruder, but his efforts were unavailing, and the little fellow kept on ascending higher and higher.
Continuing the sermon, the preacher loosened the central button which graced the waistband of his pantaloons, and with a kick off came that easy-fitting garment.
But, meanwhile, Mr. Lizard had passed the equatorial line of the waistband, and was calmly exploring that part of the preacher’s anatomy which lay underneath the back of his shirt.
Things were now growing interesting, but the sermon was still grinding on. The next movement on the preacher’s part was for the collar button, and with one sweep of his arm off came the tow linen shirt.
The congregation sat for an instant as if dazed; at length one old lady in the rear part of the room rose up, and, glancing at the excited object in the pulpit, shouted at the top of her voice: “If you represent Christ, then I’m done with the Bible.”
Once, when Lincoln was pleading a case, the opposing lawyer had all the advantage of the law; the weather was warm, and his opponent, as was admissible in frontier courts, pulled off his coat and vest as he grew warm in the argument.
At that time, shirts with buttons behind were unusual. Lincoln took in the situation at once. Knowing the prejudices of the primitive people against pretension of all sorts, or any affectation of superior social rank, arising, he said: “Gentlemen of the jury, having justice on my side, I don’t think you will be at all influenced by the gentleman’s pretended knowledge of the law, when you see he does not even know which side of his shirt should be in front.” There was a general laugh, and Lincoln’s case was won.
President Lincoln once told the following story of Colonel W., who had been elected to the Legislature, and had also been judge of the County Court. His elevation, however, had made him somewhat pompous, and he became very fond of using big words. On his farm he had a very large and mischievous ox, called “Big Brindle,” which very frequently broke down his neighbors’ fences, and committed other depredations, much to the Colonel’s annoyance.
One morning after breakfast, in the presence of Lincoln, who had stayed with him over night, and who was on his way to town, he called his overseer and said to him:
“Mr. Allen, I desire you to impound ‘Big Brindle,’ in order that I may hear no animadversions on his eternal depredations.”
Allen bowed and walked off, sorely puzzled to know what the Colonel wanted him to do. After Colonel W. left for town, he went to his wife and asked her what the Colonel meant by telling him to impound the ox.
“Why, he meant to tell you to put him in a pen,” said she.
Allen left to perform the feat, for it was no inconsiderable one, as the animal was wild and vicious, but, after a great deal of trouble and vexation, succeeded.
“Well,” said he, wiping the perspiration from his brow and soliloquizing, “this is impounding, is it? Now, I am dead sure that the Colonel will ask me if I impounded ‘Big Brindle,’ and I’ll bet I puzzle him as he did me.”
The next day the Colonel gave a dinner party, and as he was not aristocratic, Allen, the overseer, sat down with the company. After the second or third glass was discussed, the Colonel turned to the overseer and said:
“Eh, Mr. Allen, did you impound ‘Big Brindle,’ sir?”
Allen straightened himself, and looking around at the company, replied:
“Yes, I did, sir; but ‘Old Brindle’ transcended the impanel of the impound, and scatterlophisticated all over the equanimity of the forest.”
The company burst into an immoderate fit of laughter, while the Colonel’s face reddened with discomfiture.
“What do you mean by that, sir?” demanded the Colonel.
“Why, I mean, Colonel,” replied Allen, “that ‘Old Brindle,’ being prognosticated with an idea of the cholera, ripped and teared, snorted and pawed dirt, jumped the fence, tuck to the woods, and would not be impounded nohow.”
This was too much; the company roared again, the Colonel being forced to join in the laughter, and in the midst of the jollity Allen left the table, saying to himself as he went, “I reckon the Colonel won’t ask me to impound any more oxen.”
Some of Mr. Lincoln’s intimate friends once called his attention to a certain member of his Cabinet who was quietly working to secure a nomination for the Presidency, although knowing that Mr. Lincoln was to be a candidate for re-election. His friends insisted that the Cabinet officer ought to be made to give up his Presidential aspirations or be removed from office. The situation reminded Mr. Lincoln of a story:
“My brother and I,” he said, “were once plowing corn, I driving the horse and he holding the plow. The horse was lazy, but on one occasion he rushed across the field so that I, with my long legs, could scarcely keep pace with him. On reaching the end of the furrow, I found an enormous chin-fly fastened upon him, and knocked him off. My brother asked me what I did that for. I told him I didn’t want the old horse bitten in that way. ‘Why,’ said my brother, ‘that’s all that made him go.’ Now,” said Mr. Lincoln, “if Mr.—— has a Presidential chin-fly biting him, I’m not going to knock him off, if it will only make his department go.”
Mr. T. W. S. Kidd, of Springfield, says that he once heard a lawyer opposed to Lincoln trying to convince a jury that precedent was superior to law, and that custom made things legal in all cases. When Lincoln arose to answer him he told the jury he would argue his case in the same way.
“Old ‘Squire Bagly, from Menard, came into my office and said, ‘Lincoln, I want your advice as a lawyer. Has a man what’s been elected justice of the peace a right to issue a marriage license?’ I told him he had not; when the old ‘squire threw himself back in his chair very indignantly, and said, ‘Lincoln, I thought you was a lawyer. Now Bob Thomas and me had a bet on this thing, and we agreed to let you decide; but if this is your opinion I don’t want it, for I know a thunderin’ sight better, for I have been ‘squire now for eight years and have done it all the time.’”
When the President, early in the War, was anxious about the defenses of Washington, he told a story illustrating his feelings in the case. General Scott, then Commander-in-Chief of the United States Army, had but 1,500 men, two guns and an old sloop of war, the latter anchored in the Potomac, with which to protect the National Capital, and the President was uneasy.
To one of his queries as to the safety of Washington, General Scott had replied, “It has been ordained, Mr. President, that the city shall not be captured by the Confederates.”
“But we ought to have more men and guns here,” was the Chief Executive’s answer. “The Confederates are not such fools as to let a good chance to capture Washington go by, and even if it has been ordained that the city is safe, I’d feel easier if it were better protected. All this reminds me of the old trapper out in the West who had been assured by some ‘city folks’ who had hired him as a guide that all matters regarding life and death were prearranged.
“‘It is ordained,’ said one of the party to the old trapper, ‘that you are to die at a certain time, and no one can kill you before that time. If you met a thousand Indians, and your death had not been ordained for that day, you would certainly escape.’
“‘I don’t exactly understand this “ordained” business,’ was the trapper’s reply. ‘I don’t care to run no risks. I always have my gun with me, so that if I come across some reds I can feel sure that I won’t cross the Jordan ‘thout taking some of ‘em with me. Now, for instance, if I met an Indian in the woods; he drew a bead on me—sayin’, too, that he wasn’t more’n ten feet away—an’ I didn’t have nothing to protect myself; say it was as bad as that, the redskin bein’ dead ready to kill me; now, even if it had been ordained that the Indian (sayin’ he was a good shot), was to die that very minute, an’ I wasn’t, what would I do ‘thout my gun?’
“There you are,” the President remarked; “even if it has been ordained that the city of Washington will never be taken by the Southerners, what would we do in case they made an attack upon the place, without men and heavy guns?”

Judge T. Lyle Dickey of Illinois related that when the excitement over the Kansas Nebraska bill first broke out, he was with Lincoln and several friends attending court. One evening several persons, including himself and Lincoln, were discussing the slavery question. Judge Dickey contended that slavery was an institution which the Constitution recognized, and which could not be disturbed. Lincoln argued that ultimately slavery must become extinct. “After awhile,” said Judge Dickey, “we went upstairs to bed. There were two beds in our room, and I remember that Lincoln sat up in his night shirt on the edge of the bed arguing the point with me. At last we went to sleep. Early in the morning I woke up and there was Lincoln half sitting up in bed. ‘Dickey,’ said he, ‘I tell you this nation cannot exist half slave and half free.’ ‘Oh, Lincoln,’ said I, ‘go to sleep.”’
President Lincoln, while eager that the United States troops should be supplied with the most modern and serviceable weapons, often took occasion to put his foot down upon the mania for experimenting with which some of his generals were afflicted. While engaged in these experiments much valuable time was wasted, the enemy was left to do as he thought best, no battles were fought, and opportunities for winning victories allowed to pass.
The President was an exceedingly practical man, and when an invention, idea or discovery was submitted to him, his first step was to ascertain how any or all of them could be applied in a way to be of benefit to the army. As to experimenting with “contrivances” which, to his mind, could never be put to practical use, he had little patience.
“Some of these generals,” said he, “experiment so long and so much with newfangled, fancy notions that when they are finally brought to a head they are useless. Either the time to use them has gone by, or the machine, when put in operation, kills more than it cures.
“One of these generals, who has a scheme for ‘condensing’ rations, is willing to swear his life away that his idea, when carried to perfection, will reduce the cost of feeding the Union troops to almost nothing, while the soldiers themselves will get so fat that they’ll ‘bust out’ of their uniforms. Of course, uniforms cost nothing, and real fat men are more active and vigorous than lean, skinny ones, but that is getting away from my story.
“There was once an Irishman—a cabman—who had a notion that he could induce his horse to live entirely on shavings. The latter he could get for nothing, while corn and oats were pretty high-priced. So he daily lessened the amount of food to the horse, substituting shavings for the corn and oats abstracted, so that the horse wouldn’t know his rations were being cut down.
“However, just as he had achieved success in his experiment, and the horse had been taught to live without other food than shavings, the ungrateful animal ‘up and died,’ and he had to buy another.
“So far as this general referred to is concerned, I’m afraid the soldiers will all be dead at the time when his experiment is demonstrated as thoroughly successful.”
Speed, who was a prosperous young merchant of Springfield, reports that Lincoln’s personal effects consisted of a pair of saddle-bags, containing two or three lawbooks, and a few pieces of clothing. Riding on a borrowed horse, he thus made his appearance in Springfield. When he discovered that a single bedstead would cost seventeen dollars he said, “It is probably cheap enough, but I have not enough money to pay for it.” When Speed offered to trust him, he said: “If I fail here as a lawyer, I will probably never pay you at all.” Then Speed offered to share large double bed with him.

“Where is your room?” Lincoln asked.
“Upstairs,” said Speed, pointing from the store leading to his room.
Without saying a word, he took his saddle-bags on his arm, went upstairs, set them down on the floor, came down again, and with a face beaming with pleasure and smiles, exclaimed: “Well, Speed, I’m moved.”
“By the way,” remarked President Lincoln one day to Colonel Cannon, a close personal friend, “I can tell you a good story about my hair. When I was nominated at Chicago, an enterprising fellow thought that a great many people would like to see how ‘Abe’ Lincoln looked, and, as I had not long before sat for a photograph, the fellow, having seen it, rushed over and bought the negative.
“He at once got no end of wood-cuts, and so active was their circulation they were soon selling in all parts of the country.
“Soon after they reached Springfield, I heard a boy crying them for sale on the streets. ‘Here’s your likeness of “Abe” Lincoln!’ he shouted. ‘Buy one; price only two shillings! Will look a great deal better when he gets his hair combed!”’
Secretary of State Seward was bothered considerably regarding the complication into which Spain had involved the United States government in connection with San Domingo, and related his troubles to the President. Negotiations were not proceeding satisfactorily, and things were mixed generally. We wished to conciliate Spain, while the negroes had appealed against Spanish oppression.
The President did not, to all appearances, look at the matter seriously, but, instead of treating the situation as a grave one, remarked that Seward’s dilemma reminded him of an interview between two negroes in Tennessee.
One was a preacher, who, with the crude and strange notions of his ignorant race, was endeavoring to admonish and enlighten his brother African of the importance of religion and the danger of the future.
“Dar are,” said Josh, the preacher, “two roads befo’ you, Joe; be ca’ful which ob dese you take. Narrow am de way dat leads straight to destruction; but broad am de way dat leads right to damnation.”
Joe opened his eyes with affright, and under the spell of the awful danger before him, exclaimed, “Josh, take which road you please; I shall go troo de woods.”
“I am not willing,” concluded the President, “to assume any new troubles or responsibilities at this time, and shall therefore avoid going to the one place with Spain, or with the negro to the other, but shall ‘take to the woods.’ We will maintain an honest and strict neutrality.”
“My first strong impression of Mr. Lincoln,” says a lady of Springfield, “was made by one of his kind deeds. I was going with a little friend for my first trip alone on the railroad cars. It was an epoch of my life. I had planned for it and dreamed of it for weeks. The day I was to go came, but as the hour of the train approached, the hackman, through some neglect, failed to call for my trunk. As the minutes went on, I realized, in a panic of grief, that I should miss the train. I was standing by the gate, my hat and gloves on, sobbing as if my heart would break, when Mr. Lincoln came by.
“‘Why, what’s the matter?’ he asked, and I poured out all my story.
“‘How big’s the trunk? There’s still time, if it isn’t too big.’ And he pushed through the gate and up to the door. My mother and I took him up to my room, where my little old-fashioned trunk stood, locked and tied. ‘Oh, ho,’ he cried, ‘wipe your eyes and come on quick.’ And before I knew what he was going to do, he had shouldered the trunk, was down stairs, and striding out of the yard. Down the street he went fast as his long legs could carry him, I trotting behind, drying my tears as I went. We reached the station in time. Mr. Lincoln put me on the train, kissed me good-bye, and told me to have a good time. It was just like him.”
Lincoln never failed to take part in all political campaigns in Illinois, as his reputation as a speaker caused his services to be in great demand. As was natural, he was often the target at which many of the “Smart Alecks” of that period shot their feeble bolts, but Lincoln was so ready with his answers that few of them cared to engage him a second time.
In one campaign Lincoln was frequently annoyed by a young man who entertained the idea that he was a born orator. He had a loud voice, was full of language, and so conceited that he could not understand why the people did not recognize and appreciate his abilities.
This callow politician delighted in interrupting public speakers, and at last Lincoln determined to squelch him. One night while addressing a large meeting at Springfield, the fellow became so offensive that “Abe” dropped the threads of his speech and turned his attention to the tormentor.
“I don’t object,” said Lincoln, “to being interrupted with sensible questions, but I must say that my boisterous friend does not always make inquiries which properly come under that head. He says he is afflicted with headaches, at which I don’t wonder, as it is a well-known fact that nature abhors a vacuum, and takes her own way of demonstrating it.
“This noisy friend reminds me of a certain steamboat that used to run on the Illinois river. It was an energetic boat, was always busy. When they built it, however, they made one serious mistake, this error being in the relative sizes of the boiler and the whistle. The latter was usually busy, too, and people were aware that it was in existence.
“This particular boiler to which I have reference was a six-foot one, and did all that was required of it in the way of pushing the boat along; but as the builders of the vessel had made the whistle a six-foot one, the consequence was that every time the whistle blew the boat had to stop.”
President Lincoln one day remarked to a number of personal friends who had called upon him at the White House:
“General McClellan’s tardiness and unwillingness to fight the enemy or follow up advantages gained, reminds me of a man back in Illinois who knew a few law phrases but whose lawyer lacked aggressiveness. The man finally lost all patience and springing to his feet vociferated, ‘Why don’t you go at him with a fi. fa., a demurrer, a capias, a surrebutter, or a ne exeat, or something; or a nundam pactum or a non est?’
“I wish McClellan would go at the enemy with something—I don’t care what. General McClellan is a pleasant and scholarly gentleman. He is an admirable engineer, but he seems to have a special talent for a stationary engine.”
One of the last, if not the very last story told by President Lincoln, was to one of his Cabinet who came to see him, to ask if it would be proper to permit “Jake” Thompson to slip through Maine in disguise and embark for Portland.
The President, as usual, was disposed to be merciful, and to permit the arch-rebel to pass unmolested, but Secretary Stanton urged that he should be arrested as a traitor.
“By permitting him to escape the penalties of treason,” persisted the War Secretary, “you sanction it.”
“Well,” replied Mr. Lincoln, “let me tell you a story. There was an Irish soldier here last summer, who wanted something to drink stronger than water, and stopped at a drug-shop, where he espied a soda-fountain. ‘Mr. Doctor,’ said he, ‘give me, plase, a glass of soda-wather, an’ if yez can put in a few drops of whiskey unbeknown to any one, I’ll be obleeged.’ Now,” continued Mr. Lincoln, “if ‘Jake’ Thompson is permitted to go through Maine unbeknown to any one, what’s the harm? So don’t have him arrested.”
The President was bothered to death by those persons who boisterously demanded that the War be pushed vigorously; also, those who shouted their advice and opinions into his weary ears, but who never suggested anything practical. These fellows were not in the army, nor did they ever take any interest, in a personal way, in military matters, except when engaged in dodging drafts.
“That reminds me,” remarked Mr. Lincoln one day, “of a farmer who lost his way on the Western frontier. Night came on, and the embarrassments of his position were increased by a furious tempest which suddenly burst upon him. To add to his discomfort, his horse had given out, leaving him exposed to all the dangers of the pitiless storm.
“The peals of thunder were terrific, the frequent flashes of lightning affording the only guide on the road as he resolutely trudged onward, leading his jaded steed. The earth seemed fairly to tremble beneath him in the war of elements. One bolt threw him suddenly upon his knees.
“Our traveler was not a prayerful man, but finding himself involuntarily brought to an attitude of devotion, he addressed himself to the Throne of Grace in the following prayer for his deliverance:
“‘O God! hear my prayer this time, for Thou knowest it is not often that I call upon Thee. And, O Lord! if it is all the same to Thee, give us a little more light and a little less noise.’
“I wish,” the President said, sadly, “there was a stronger disposition manifested on the part of our civilian warriors to unite in suppressing the rebellion, and a little less noise as to how and by whom the chief executive office shall be administered.”
Lincoln made the best of everything, and if he couldn’t get what he wanted he took what he could get. In matters of policy, while President he acted according to this rule. He would take perilous chances, even when the result was, to the minds of his friends, not worth the risk he had run.
One day at a meeting of the Cabinet, it being at the time when it seemed as though war with England and France could not be avoided, Secretary of State Seward and Secretary of War Stanton warmly advocated that the United States maintain an attitude, the result of which would have been a declaration of hostilities by the European Powers mentioned.
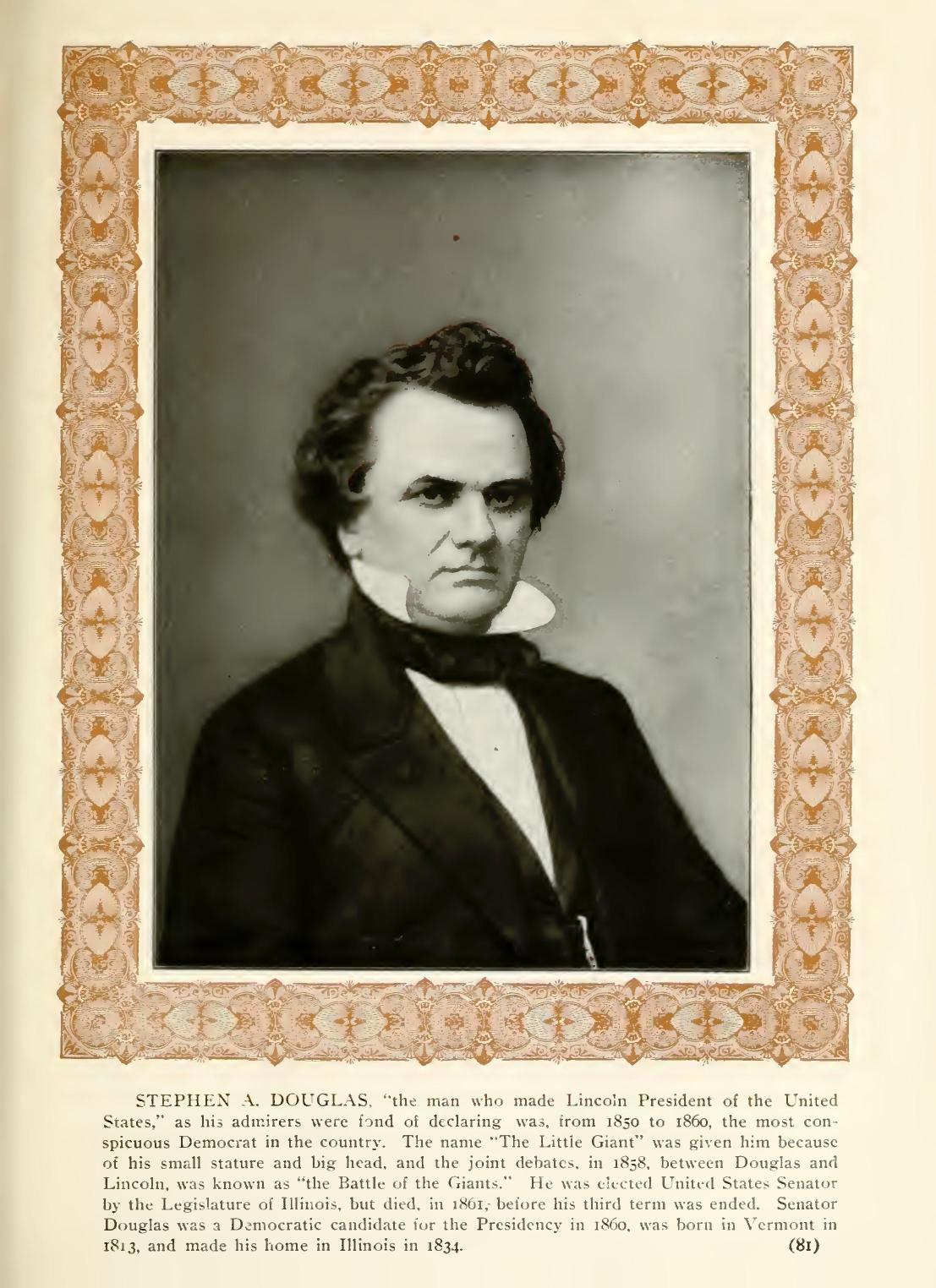




“Why take any more chances than are absolutely necessary?” asked the President.
“We must maintain our honor at any cost,” insisted Secretary Seward.
“We would be branded as cowards before the entire world,” Secretary Stanton said.
“But why run the greater risk when we can take a smaller one?” queried the President calmly. “The less risk we run the better for us. That reminds me of a story I heard a day or two ago, the hero of which was on the firing line during a recent battle, where the bullets were flying thick.
“Finally his courage gave way entirely, and throwing down his gun, he ran for dear life.
“As he was flying along at top speed he came across an officer who drew his revolver and shouted, ‘Go back to your regiment at once or I will shoot you!’
“‘Shoot and be hanged,’ the racer exclaimed. ‘What’s one bullet to a whole hatful?’”
Among the reminiscences of Lincoln left by Editor Henry J. Raymond, is the following:
Among the stories told by Lincoln, which is freshest in my mind, one which he related to me shortly after its occurrence, belongs to the history of the famous interview on board the River Queen, at Hampton Roads, between himself and Secretary Seward and the rebel Peace Commissioners. It was reported at the time that the President told a “little story” on that occasion, and the inquiry went around among the newspapers, “What was it?”
The New York Herald published what purported to be a version of it, but the “point” was entirely lost, and it attracted no attention. Being in Washington a few days subsequent to the interview with the Commissioners (my previous sojourn there having terminated about the first of last August), I asked Mr. Lincoln one day if it was true that he told Stephens, Hunter and Campbell a story.
“Why, yes,” he replied, manifesting some surprise, “but has it leaked out? I was in hopes nothing would be said about it, lest some over-sensitive people should imagine there was a degree of levity in the intercourse between us.” He then went on to relate the circumstances which called it out.
“You see,” said he, “we had reached and were discussing the slavery question. Mr. Hunter said, substantially, that the slaves, always accustomed to an overseer, and to work upon compulsion, suddenly freed, as they would be if the South should consent to peace on the basis of the ‘Emancipation Proclamation,’ would precipitate not only themselves, but the entire Southern society, into irremediable ruin. No work would be done, nothing would be cultivated, and both blacks and whites would starve!”
Said the President: “I waited for Seward to answer that argument, but as he was silent, I at length said: ‘Mr. Hunter, you ought to know a great deal better about this argument than I, for you have always lived under the slave system. I can only say, in reply to your statement of the case, that it reminds me of a man out in Illinois, by the name of Case, who undertook, a few years ago, to raise a very large herd of hogs. It was a great trouble to feed them, and how to get around this was a puzzle to him. At length he hit on the plan of planting an immense field of potatoes, and, when they were sufficiently grown, he turned the whole herd into the field, and let them have full swing, thus saving not only the labor of feeding the hogs, but also that of digging the potatoes. Charmed with his sagacity, he stood one day leaning against the fence, counting his hogs, when a neighbor came along.
“‘Well, well,’ said he, ‘Mr. Case, this is all very fine. Your hogs are doing very well just now, but you know out here in Illinois the frost comes early, and the ground freezes for a foot deep. Then what you going to do?’
“This was a view of the matter which Mr. Case had not taken into account. Butchering time for hogs was ‘way on in December or January! He scratched his head, and at length stammered: ‘Well, it may come pretty hard on their snouts, but I don’t see but that it will be “root, hog, or die.”’”
When Lincoln was a young lawyer in Illinois, he and a certain Judge once got to bantering one another about trading horses; and it was agreed that the next morning at nine o’clock they should make a trade, the horses to be unseen up to that hour, and no backing out, under a forfeiture of $25. At the hour appointed, the Judge came up, leading the sorriest-looking specimen of a horse ever seen in those parts. In a few minutes Mr. Lincoln was seen approaching with a wooden saw-horse upon his shoulders.


Great were the shouts and laughter of the crowd, and both were greatly increased when Lincoln, on surveying the Judge’s animal, set down his saw-horse, and exclaimed:
“Well, Judge, this is the first time I ever got the worst of it in a horse trade.”
The President had made arrangements to visit New York, and was told that President Garrett, of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, would be glad to furnish a special train.
“I don’t doubt it a bit,” remarked the President, “for I know Mr. Garrett, and like him very well, and if I believed—which I don’t, by any means—all the things some people say about his ‘secesh’ principles, he might say to you as was said by the Superintendent of a certain railroad to a son of one my predecessors in office. Some two years after the death of President Harrison, the son of his successor in this office wanted to take his father on an excursion somewhere or other, and went to the Superintendent’s office to order a special train.
“This Superintendent was a Whig of the most uncompromising sort, who hated a Democrat more than all other things on the earth, and promptly refused the young man’s request, his language being to the effect that this particular railroad was not running special trains for the accommodation of Presidents of the United States just at that season.
“The son of the President was much surprised and exceedingly annoyed. ‘Why,’ he said, ‘you have run special Presidential trains, and I know it. Didn’t you furnish a special train for the funeral of President Harrison?’
“‘Certainly we did,’ calmly replied the Superintendent, with no relaxation of his features, ‘and if you will only bring your father here in the same shape as General Harrison was, you shall have the best train on the road.”’
When the laughter had subsided, the President said: “I shall take pleasure in accepting Mr. Garrett’s offer, as I have no doubts whatever as to his loyalty to the United States government or his respect for the occupant of the Presidential office.”
A. B. Chandler, chief of the telegraph office at the War Department, occupied three rooms, one of which was called “the President’s room,” so much of his time did Mr. Lincoln spend there. Here he would read over the telegrams received for the several heads of departments. Three copies of all messages received were made—one for the President, one for the War Department records and one for Secretary Stanton.
Mr. Chandler told a story as to the manner in which the President read the despatches:
“President Lincoln’s copies were kept in what we called the ‘President’s drawer’ of the ‘cipher desk.’ He would come in at any time of the night or day, and go at once to this drawer, and take out a file of telegrams, and begin at the top to read them. His position in running over these telegrams was sometimes very curious.
“He had a habit of sitting frequently on the edge of his chair, with his right knee dragged down to the floor. I remember a curious expression of his when he got to the bottom of the new telegrams and began on those that he had read before. It was, ‘Well, I guess I have got down to the raisins.’
“The first two or three times he said this he made no explanation, and I did not ask one. But one day, after he had made the remark, he looked up under his eyebrows at me with a funny twinkle in his eyes, and said: ‘I used to know a little girl out West who sometimes was inclined to eat too much. One day she ate a good many more raisins than she ought to, and followed them up with a quantity of other goodies. They made her very sick. After a time the raisins began to come.
“She gasped and looked at her mother and said: ‘Well, I will be better now I guess, for I have got down to the raisins.’”


“‘Honest Abe’ Taking Them on the Half-Shell” was one of the cartoons published in 1860 by one of the illustrated periodicals. As may be seen, it represents Lincoln in a “Political Oyster House,” preparing to swallow two of his Democratic opponents for the Presidency—Douglas and Breckinridge. He performed the feat at the November election. The Democratic party was hopelessly split in 1860 The Northern wing nominated Stephen A. Douglas, of Illinois, as their candidate, the Southern wing naming John C. Breckinridge, of Kentucky; the Constitutional Unionists (the old American of Know-Nothing party) placed John Bell, of Tennessee, in the field, and against these was put Abraham Lincoln, who received the support of the Abolitionists.
Lincoln made short work of his antagonists when the election came around. He received a large majority in the Electoral College, while nearly every Northern State voted majorities for him at the polls. Douglas had but twelve votes in the Electoral College, while Bell had thirty-nine. The votes of the Southern States, then preparing to secede, were, for the most part, thrown for Breckinridge. The popular vote was: Lincoln, 1,857,610; Douglas, 1,365,976; Breckinridge, 847,953; Bell, 590,631; total vote, 4,662,170. In the Electoral College Lincoln received 180; Douglas, 12; Breckinridge, 72; Bell, 39; Lincoln’s majority over all, 57.
Judge H. W. Beckwith of Danville, Ill., said that soon after the Ottawa debate between Lincoln and Douglas he passed the Chenery House, then the principal hotel in Springfield. The lobby was crowded with partisan leaders from various sections of the state, and Mr. Lincoln, from his greater height, was seen above the surging mass that clung about him like a swarm of bees to their ruler. The day was warm, and at the first chance he broke away and came out for a little fresh air, wiping the sweat from his face.
“As he passed the door he saw me,” said Judge Beckwith, “and, taking my hand, inquired for the health and views of his ‘friends over in Vermillion county.’ He was assured they were wide awake, and further told that they looked forward to the debate between him and Senator Douglas with deep concern. From the shadow that went quickly over his face, the pained look that came to give way quickly to a blaze of eyes and quiver of lips, I felt that Mr. Lincoln had gone beneath my mere words and caught my inner and current fears as to the result. And then, in a forgiving, jocular way peculiar to him, he said: ‘Sit down; I have a moment to spare, and will tell you a story.’ Having been on his feet for some time, he sat on the end of the stone step leading into the hotel door, while I stood closely fronting him.
“‘You have,’ he continued, ‘seen two men about to fight?’
“‘Yes, many times.’
“‘Well, one of them brags about what he means to do. He jumps high in the air, cracking his heels together, smites his fists, and wastes his wreath trying to scare somebody. You see the other fellow, he says not a word,’—here Mr. Lincoln’s voice and manner changed to great earnestness, and repeating—‘you see the other man says not a word. His arms are at his sides, his fists are closely doubled up, his head is drawn to the shoulder, and his teeth are set firm together. He is saving his wind for the fight, and as sure as it comes off he will win it, or die a-trying.’”
Where men bred in courts, accustomed to the world, or versed in diplomacy, would use some subterfuge, or would make a polite speech, or give a shrug of the shoulders, as the means of getting out of an embarrassing position, Lincoln raised a laugh by some bold west-country anecdote, and moved off in the cloud of merriment produced by the joke.
When Attorney-General Bates was remonstrating apparently against the appointment of some indifferent lawyer to a place of judicial importance, the President interposed with: “Come now, Bates, he’s not half as bad as you think. Besides that, I must tell you, he did me a good turn long ago. When I took to the law, I was going to court one morning, with some ten or twelve miles of bad road before me, and I had no horse.
“The judge overtook me in his carriage.
“‘Hallo, Lincoln! are you not going to the court-house? Come in and I will give you a seat!’
“Well, I got in, and the Judge went on reading his papers. Presently the carriage struck a stump on one side of the road, then it hopped off to the other. I looked out, and I saw the driver was jerking from side to side in his seat, so I says:
“‘Judge, I think your coachman has been taking a little too much this morning.’
“‘Well, I declare, Lincoln,’ said he, ‘I should not much wonder if you were right, for he has nearly upset me half a dozen times since starting.’
“So, putting his head out of the window, he shouted, ‘Why, you infernal scoundrel, you are drunk!’
“Upon which, pulling up his horses, and turning round with great gravity, the coachman said:
“‘Begorra! that’s the first rightful decision that you have given for the last twelvemonth.’”
While the company were laughing, the President beat a quiet retreat from the neighborhood.
After the War was well on, and several battles had been fought, a lady from Alexandria asked the President for an order to release a certain church which had been taken for a Federal hospital. The President said he could do nothing, as the post surgeon at Alexandria was immovable, and then asked the lady why she did not donate money to build a hospital.
“We have been very much embarrassed by the war,” she replied, “and our estates are much hampered.”
“You are not ruined?” asked the President.
“No, sir, but we do not feel that we should give up anything we have left.”
The President, after some reflection, then said: “There are more battles yet to be fought, and I think God would prefer that your church be devoted to the care and alleviation of the sufferings of our poor fellows. So, madam, you will excuse me. I can do nothing for you.”
Afterward, in speaking of this incident, President Lincoln said that the lady, as a representative of her class in Alexandria, reminded him of the story of the young man who had an aged father and mother owning considerable property. The young man being an only son, and believing that the old people had outlived their usefulness, assassinated them both. He was accused, tried and convicted of the murder. When the judge came to pass sentence upon him, and called upon him to give any reason he might have why the sentence of death should not be passed upon him, he with great promptness replied that he hoped the court would be lenient upon him because he was a poor orphan!
It is true that Lincoln did not drink, never swore, was a stranger to smoking and lived a moral life generally, but he did like horse-racing and chicken fighting. New Salem, Illinois, where Lincoln was “clerking,” was known the neighborhood around as a “fast” town, and the average young man made no very desperate resistance when tempted to join in the drinking and gambling bouts.
“Bap.” McNabb was famous for his ability in both the raising and the purchase of roosters of prime fighting quality, and when his birds fought the attendance was large. It was because of the “flunking” of one of “Bap.‘s” roosters that Lincoln was enabled to make a point when criticising McClellan’s unreadiness and lack of energy.
One night there was a fight on the schedule, one of “Bap.” McNabb’s birds being a contestant. “Bap.” brought a little red rooster, whose fighting qualities had been well advertised for days in advance, and much interest was manifested in the outcome. As the result of these contests was generally a quarrel, in which each man, charging foul play, seized his victim, they chose Lincoln umpire, relying not only on his fairness but his ability to enforce his decisions. Judge Herndon, in his “Abraham Lincoln,” says of this notable event:
“I cannot improve on the description furnished me in February, 1865, by one who was present.
“They formed a ring, and the time having arrived, Lincoln, with one hand on each hip and in a squatting position, cried, ‘Ready.’ Into the ring they toss their fowls, ‘Bap.‘s’ red rooster along with the rest. But no sooner had the little beauty discovered what was to be done than he dropped his tail and ran.
“The crowd cheered, while ‘Bap.,’ in disappointment, picked him up and started away, losing his quarter (entrance fee) and carrying home his dishonored fowl. Once arrived at the latter place he threw his pet down with a feeling of indignation and chagrin.
“The little fellow, out of sight of all rivals, mounted a woodpile and proudly flirting out his feathers, crowed with all his might. ‘Bap.’ looked on in disgust.
“‘Yes, you little cuss,’ he exclaimed, irreverently, ‘you’re great on dress parade, but not worth a darn in a fight.”’
It is said, according to Judge Herndon, that Lincoln considered McClellan as “great on dress parade,” but not so much in a fight.
When Lincoln was a candidate of the Know Nothings for the State Legislature, the party was over-confident, and the Democrats pursued a still-hunt. Lincoln was defeated. He compared the situation to one of the camp-followers of General Taylor’s army, who had secured a barrel of cider, erected a tent, and commenced selling it to the thirsty soldiers at twenty-five cents a drink, but he had sold but little before another sharp one set up a tent at his back, and tapped the barrel so as to flow on his side, and peddled out No. 1 cider at five cents a drink, of course, getting the latter’s entire trade on the borrowed capital.
“The Democrats,” said Mr. Lincoln, “had played Knownothing on a cheaper scale than had the real devotees of Sam, and had raked down his pile with his own cider!”
Judge H. W. Beckwith, of Danville, Ill., in his “Personal Recollections of Lincoln,” tells a story which is a good example of Lincoln’s way of condensing the law and the facts of an issue in a story: “A man, by vile words, first provoked and then made a bodily attack upon another. The latter, in defending himself, gave the other much the worst of the encounter. The aggressor, to get even, had the one who thrashed him tried in our Circuit Court on a charge of an assault and battery. Mr. Lincoln defended, and told the jury that his client was in the fix of a man who, in going along the highway with a pitchfork on his shoulder, was attacked by a fierce dog that ran out at him from a farmer’s dooryard. In parrying off the brute with the fork, its prongs stuck into the brute and killed him.
“‘What made you kill my dog?’ said the farmer.
“‘What made him try to bite me?’
“‘But why did you not go at him with the other end of the pitchfork?’
“‘Why did he not come after me with his other end?’
“At this Mr. Lincoln whirled about in his long arms an imaginary dog, and pushed its tail end toward the jury. This was the defensive plea of ‘son assault demesne’—loosely, that ‘the other fellow brought on the fight,’—quickly told, and in a way the dullest mind would grasp and retain.”
The President had decided to select a new War Minister, and the Leading Republican Senators thought the occasion was opportune to change the whole seven Cabinet ministers. They, therefore, earnestly advised him to make a clean sweep, and select seven new men, and so restore the waning confidence of the country.
The President listened with patient courtesy, and when the Senators had concluded, he said, with a characteristic gleam of humor in his eye:
“Gentlemen, your request for a change of the whole Cabinet because I have made one change reminds me of a story I once heard in Illinois, of a farmer who was much troubled by skunks. His wife insisted on his trying to get rid of them.
“He loaded his shotgun one moonlight night and awaited developments. After some time the wife heard the shotgun go off, and in a few minutes the farmer entered the house.
“‘What luck have you?’ asked she.
“‘I hid myself behind the wood-pile,’ said the old man, ‘with the shotgun pointed towards the hen roost, and before long there appeared not one skunk, but seven. I took aim, blazed away, killed one, and he raised such a fearful smell that I concluded it was best to let the other six go.”’
The Senators laughed and retired.
The following story was told by Mr. Lincoln to Mr. A. J. Conant, the artist, who painted his portrait in Springfield in 1860:
“One day a man who was migrating to the West drove up in front of my store with a wagon which contained his family and household plunder. He asked me if I would buy an old barrel for which he had no room in his wagon, and which he said contained nothing of special value. I did not want it, but to oblige him I bought it, and paid him, I think, half a dollar for it. Without further examination, I put it away in the store and forgot all about it. Some time after, in overhauling things, I came upon the barrel, and, emptying it upon the floor to see what it contained, I found at the bottom of the rubbish a complete edition of Blackstone’s Commentaries. I began to read those famous works, and I had plenty of time; for during the long summer days, when the farmers were busy with their crops, my customers were few and far between. The more I read”—this he said with unusual emphasis—“the more intensely interested I became. Never in my whole life was my mind so thoroughly absorbed. I read until I devoured them.”
This cartoon, labeled “A Job for the New Cabinetmaker,” was printed in “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” on February 2d, 1861, a month and two days before Abraham Lincoln was inaugurated President of the United States. The Southern states had seceded from the Union, the Confederacy was established, with Jefferson Davis as its President, the Union had been split in two, and the task Lincoln had before him was to glue the two parts of the Republic together. In his famous speech, delivered a short time before his nomination for the Presidency by the Republican National Convention at Chicago, in 1860, Lincoln had said: “A house divided against itself cannot stand; this nation cannot exist half slave and half free.” After his inauguration as President, Mr. Lincoln went to work to glue the two pieces together, and after four years of bloody war, and at immense cost, the job was finished; the house of the Great American Republic was no longer divided; the severed sections—the North and the South—were cemented tightly; the slaves were freed, peace was firmly established, and the Union of states was glued together so well that the nation is stronger now than ever before. Lincoln was just the man for that job, and the work he did will last for all time. “The New Cabinetmaker” knew his business thoroughly, and finished his task of glueing in a workmanlike manner. At the very moment of its completion, five days after the surrender of Lee to Grant at Appomattox, the Martyr President fell at the hands of the assassin, J. Wilkes Booth.
United States Senator Benjamin Wade, of Ohio, Henry Winter Davis, of Maryland, and Wendell Phillips were strongly opposed to President Lincoln’s re-election, and Wade and Davis issued a manifesto. Phillips made several warm speeches against Lincoln and his policy.
When asked if he had read the manifesto or any of Phillips’ speeches, the President replied:
“I have not seen them, nor do I care to see them. I have seen enough to satisfy me that I am a failure, not only in the opinion of the people in rebellion, but of many distinguished politicians of my own party. But time will show whether I am right or they are right, and I am content to abide its decision.
“I have enough to look after without giving much of my time to the consideration of the subject of who shall be my successor in office. The position is not an easy one; and the occupant, whoever he may be, for the next four years, will have little leisure to pluck a thorn or plant a rose in his own pathway.”
It was urged that this opposition must be embarrassing to his Administration, as well as damaging to the party. He replied: “Yes, that is true; but our friends, Wade, Davis, Phillips, and others are hard to please. I am not capable of doing so. I cannot please them without wantonly violating not only my oath, but the most vital principles upon which our government was founded.
“As to those who, like Wade and the rest, see fit to depreciate my policy and cavil at my official acts, I shall not complain of them. I accord them the utmost freedom of speech and liberty of the press, but shall not change the policy I have adopted in the full belief that I am right.
“I feel on this subject as an old Illinois farmer once expressed himself while eating cheese. He was interrupted in the midst of his repast by the entrance of his son, who exclaimed, ‘Hold on, dad! there’s skippers in that cheese you’re eating!’
“‘Never mind, Tom,’ said he, as he kept on munching his cheese, ‘if they can stand it I can.’”
President Lincoln was compelled to acknowledge that he made at least one mistake in “sizing up” men. One day a very dignified man called at the White House, and Lincoln’s heart fell when his visitor approached. The latter was portly, his face was full of apparent anxiety, and Lincoln was willing to wager a year’s salary that he represented some Society for the Easy and Speedy Repression of Rebellions.

The caller talked fluently, but at no time did he give advice or suggest a way to put down the Confederacy. He was full of humor, told a clever story or two, and was entirely self-possessed.
At length the President inquired, “You are a clergyman, are you not, sir?”
“Not by a jug full,” returned the stranger heartily.
Grasping him by the hand Lincoln shook it until the visitor squirmed. “You must lunch with us. I am glad to see you. I was afraid you were a preacher.”
“I went to the Chicago Convention,” the caller said, “as a friend of Mr. Seward. I have watched you narrowly ever since your inauguration, and I called merely to pay my respects. What I want to say is this: I think you are doing everything for the good of the country that is in the power of man to do. You are on the right track. As one of your constituents I now say to you, do in future as you d—— please, and I will support you!”
This was spoken with tremendous effect.
“Why,” said Mr. Lincoln in great astonishment, “I took you to be a preacher. I thought you had come here to tell me how to take Richmond,” and he again grasped the hand of his strange visitor.
Accurate and penetrating as Mr. Lincoln’s judgment was concerning men, for once he had been wholly mistaken. The scene was comical in the extreme. The two men stood gazing at each other. A smile broke from the lips of the solemn wag and rippled over the wide expanse of his homely face like sunlight overspreading a continent, and Mr. Lincoln was convulsed with laughter.
He stayed to lunch.




President Lincoln, while entertaining a few friends, is said to have related the following anecdote of a man who knew too much:
During the administration of President Jackson there was a singular young gentleman employed in the Public Postoffice in Washington.
His name was G.; he was from Tennessee, the son of a widow, a neighbor of the President, on which account the old hero had a kind feeling for him, and always got him out of difficulties with some of the higher officials, to whom his singular interference was distasteful.
Among other things, it is said of him that while employed in the General Postoffice, on one occasion he had to copy a letter to Major H., a high official, in answer to an application made by an old gentleman in Virginia or Pennsylvania, for the establishment of a new postoffice.
The writer of the letter said the application could not be granted, in consequence of the applicant’s “proximity” to another office.
When the letter came into G.‘s hand to copy, being a great stickler for plainness, he altered “proximity” to “nearness to.”
Major H. observed it, and asked G. why he altered his letter.
“Why,” replied G., “because I don’t think the man would understand what you mean by proximity.”
“Well,” said Major H., “try him; put in the ‘proximity’ again.”
In a few days a letter was received from the applicant, in which he very indignantly said that his father had fought for liberty in the second war for independence, and he should like to have the name of the scoundrel who brought the charge of proximity or anything else wrong against him.
“There,” said G., “did I not say so?”
G. carried his improvements so far that Mr. Berry, the Postmaster-General, said to him: “I don’t want you any longer; you know too much.”
Poor G. went out, but his old friend got him another place.
This time G.‘s ideas underwent a change. He was one day very busy writing, when a stranger called in and asked him where the Patent Office was.
“I don’t know,” said G.
“Can you tell me where the Treasury Department is?” said the stranger.
“No,” said G.
“Nor the President’s house?”
“No.”
The stranger finally asked him if he knew where the Capitol was.
“No,” replied G.
“Do you live in Washington, sir.”
“Yes, sir,” said G.
“Good Lord! and don’t you know where the Patent Office, Treasury, President’s House and Capitol are?”
“Stranger,” said G., “I was turned out of the postoffice for knowing too much. I don’t mean to offend in that way again.
“I am paid for keeping this book.
“I believe I know that much; but if you find me knowing anything more you may take my head.”
“Good morning,” said the stranger.
Judge Breese, of the Supreme bench, one of the most distinguished of American jurists, and a man of great personal dignity, was about to open court at Springfield, when Lincoln called out in his hearty way: “Hold on, Breese! Don’t open court yet! Here’s Bob Blackwell just going to tell a story!” The judge passed on without replying, evidently regarding it as beneath the dignity of the Supreme Court to delay proceedings for the sake of a story.
In an argument against the opposite political party at one time during a campaign, Lincoln said: “My opponent uses a figurative expression to the effect that ‘the Democrats are vulnerable in the heel, but they are sound in the heart and head.’ The first branch of the figure—that is the Democrats are vulnerable in the heel—I admit is not merely figuratively but literally true. Who that looks but for a moment at their hundreds of officials scampering away with the public money to Texas, to Europe, and to every spot of the earth where a villain may hope to find refuge from justice, can at all doubt that they are most distressingly affected in their heels with a species of running itch?
“It seems that this malady of their heels operates on the sound-headed and honest-hearted creatures very much as the cork leg in the comic song did on its owner, which, when he once got started on it, the more he tried to stop it, the more it would run away.
“At the hazard of wearing this point threadbare, I will relate an anecdote the situation calls to my mind, which seems to be too strikingly in point to be omitted. A witty Irish soldier, who was always boasting of his bravery when no danger was near, but who invariably retreated without orders at the first charge of the engagement, being asked by his captain why he did so, replied, ‘Captain, I have as brave a heart as Julius Caesar ever had, but somehow or other, whenever danger approaches, my cowardly legs will run away with it.’
“So with the opposite party—they take the public money into their hands for the most laudable purpose that wise heads and honest hearts can dictate; but before they can possibly get it out again, their rascally, vulnerable heels will run away with them.”
Preston King once introduced A. J. Bleeker to the President, and the latter, being an applicant for office, was about to hand Mr. Lincoln his vouchers, when he was asked to read them. Bleeker had not read very far when the President disconcerted him by the exclamation, “Stop a minute! You remind me exactly of the man who killed the dog; in fact, you are just like him.”
“In what respect?” asked Bleeker, not feeling he had received a compliment.
“Well,” replied the President, “this man had made up his mind to kill his dog, an ugly brute, and proceeded to knock out his brains with a club. He continued striking the dog after the latter was dead until a friend protested, exclaiming, ‘You needn’t strike him any more; the dog is dead; you killed him at the first blow.’
“‘Oh, yes,’ said he, ‘I know that; but I believe in punishment after death.’ So, I see, you do.”
Bleeker acknowledged it was possible to overdo a good thing, and then came back at the President with an anecdote of a good priest who converted an Indian from heathenism to Christianity; the only difficulty he had with him was to get him to pray for his enemies. “This Indian had been taught to overcome and destroy all his friends he didn’t like,” said Bleeker, “but the priest told him that while that might be the Indian method, it was not the doctrine of Christianity or the Bible. ‘Saint Paul distinctly says,’ the priest told him, ‘If thine enemy hunger, feed him; if he thirst, give him drink.’
“The Indian shook his head at this, but when the priest added, ‘For in so doing thou shalt heap coals of fire on his head,’ Poor Lo was overcome with emotion, fell on his knees, and with outstretched hands and uplifted eyes invoked all sorts of blessings on the heads of all his enemies, supplicating for pleasant hunting-grounds, a large supply of squaws, lots of papooses, and all other Indian comforts.
“Finally the good priest interrupted him (as you did me, Mr. President), exclaiming, ‘Stop, my son! You have discharged your Christian duty, and have done more than enough.’
“‘Oh, no, father,’ replied the Indian; ‘let me pray! I want to burn him down to the stump!”
During the war, one of the Northern Governors, who was able, earnest and untiring in aiding the administration, but always complaining, sent dispatch after dispatch to the War Office, protesting against the methods used in raising troops. After reading all his papers, the President said, in a cheerful and reassuring tone to the Adjutant-General:
“Never mind, never mind; those dispatches don’t mean anything. Just go right ahead. The Governor is like a boy I once saw at a launching. When everything was ready, they picked out a boy and sent him under the ship to knock away the trigger and let her go.
“At the critical moment everything depended on the boy. He had to do the job well by a direct, vigorous blow, and then lie flat and keep still while the boat slid over him.
“The boy did everything right, but he yelled as if he were being murdered from the time he got under the keel until he got out. I thought the hide was all scraped off his back, but he wasn’t hurt at all.
“The master of the yard told me that this boy was always chosen for that job; that he did his work well; that he never had been hurt, but that he always squealed in that way.
“That’s just the way with Governor—. Make up your mind that he is not hurt, and that he is doing the work right, and pay no attention to his squealing. He only wants to make you understand how hard his task is, and that he is on hand performing it.”
Many requests and petitions made to Mr. Lincoln when he was President were ludicrous and trifling, but he always entered into them with that humor-loving spirit that was such a relief from the grave duties of his great office.
Once a party of Southerners called on him in behalf of one Betsy Ann Dougherty. The spokesman, who was an ex-Governor, said:
“Mr. President, Betsy Ann Dougherty is a good woman. She lived in my county and did my washing for a long time. Her husband went off and joined the rebel army, and I wish you would give her a protection paper.” The solemnity of this appeal struck Mr. Lincoln as uncommonly ridiculous.
The two men looked at each other—the Governor desperately earnest, and the President masking his humor behind the gravest exterior. At last Mr. Lincoln asked, with inimitable gravity, “Was Betsy Ann a good washerwoman?” “Oh, yes, sir, she was, indeed.”
“Was your Betsy Ann an obliging woman?” “Yes, she was certainly very kind,” responded the Governor, soberly. “Could she do other things than wash?” continued Mr. Lincoln with the same portentous gravity.
“Oh, yes; she was very kind—very.”
“Where is Betsy Ann?”
“She is now in New York, and wants to come back to Missouri, but she is afraid of banishment.”
“Is anybody meddling with her?”
“No; but she is afraid to come back unless you will give her a protection paper.”
Thereupon Mr. Lincoln wrote on a visiting card the following:
“Let Betsy Ann Dougherty alone as long as she behaves herself.
“A. LINCOLN.”
He handed this card to her advocate, saying, “Give this to Betsy Ann.”
“But, Mr. President, couldn’t you write a few words to the officers that would insure her protection?”
“No,” said Mr. Lincoln, “officers have no time now to read letters. Tell Betsy Ann to put a string in this card and hang it around her neck. When the officers see this, they will keep their hands off your Betsy Ann.”
Captain “Abe” Lincoln and his company (in the Black Hawk War) were without any sort of military knowledge, and both were forced to acquire such knowledge by attempts at drilling. Which was the more awkward, the “squad” or the commander, it would have been difficult to decide.
In one of Lincoln’s earliest military problems was involved the process of getting his company “endwise” through a gate. Finally he shouted, “This company is dismissed for two minutes, when it will fall in again on the other side of the gate!”
Lincoln was one of the first of his company to be arraigned for unmilitary conduct. Contrary to the rules he fired a gun “within the limits,” and had his sword taken from him. The next infringement of rules was by some of the men, who stole a quantity of liquor, drank it, and became unfit for duty, straggling out of the ranks the next day, and not getting together again until late at night.
For allowing this lawlessness the captain was condemned to wear a wooden sword for two days. These were merely interesting but trivial incidents of the campaign. Lincoln was from the very first popular with his men, although one of them told him to “go to the devil.”
Under the caption, “The American Difficulty,” “Punch” printed on May 11th, 1861, the cartoon reproduced here. The following text was placed beneath the illustration: PRESIDENT ABE: “What a nice White House this would be, if it were not for the blacks!” It was the idea in England, and, in fact, in all the countries on the European continent, that the War of the Rebellion was fought to secure the freedom of the negro slaves. Such was not the case. The freedom of the slaves was one of the necessary consequences of the Civil War, but not the cause of that bloody four years’ conflict. The War was the result of the secession of the states of the South from the Union, and President “Abe’s” main aim was to compel the seceding states to resume their places in the Federal Union of states.
The blacks did not bother President “Abe” in the least as he knew he would be enabled to give them their freedom when the proper time came. He had the project of freeing them in his mind long before he issued his Emancipation Proclamation, the delay in promulgating that document being due to the fact that he did not wish to estrange the hundreds of thousands of patriots of the border states who were fighting for the preservation of the Union, and not for the freedom of the negro slaves. President “Abe” had patience, and everything came out all right in the end.
Charles A. Dana, who was Assistant Secretary of War under Mr. Stanton, relates the following: A certain Thompson had been giving the government considerable trouble. Dana received information that Thompson was about to escape to Liverpool.
Calling upon Stanton, Dana was referred to Mr. Lincoln.
“The President was at the White House, business hours were over, Lincoln was washing his hands. ‘Hallo, Dana,’ said he, as I opened the door, ‘what is it now?’ ‘Well, sir,’ I said, ‘here is the Provost Marshal of Portland, who reports that Jacob Thompson is to be in town to-night, and inquires what orders we have to give.’ ‘What does Stanton say?’ he asked. ‘Arrest him,’ I replied. ‘Well,’ he continued, drawling his words, ‘I rather guess not. When you have an elephant on your hands, and he wants to run away, better let him run.’”
The nearest Lincoln ever came to a fight was when he was in the vicinity of the skirmish at Kellogg’s Grove, in the Black Hawk War. The rangers arrived at the spot after the engagement and helped bury the five men who were killed.
Lincoln told Noah Brooks, one of his biographers, that he “remembered just how those men looked as we rode up the little hill where their camp was. The red light of the morning sun was streaming upon them as they lay, heads toward us, on the ground. And every man had a round, red spot on the top of his head about as big as a dollar, where the redskins had taken his scalp. It was frightful, but it was grotesque; and the red sunlight seemed to paint everything all over.”
Lincoln paused, as if recalling the vivid picture, and added, somewhat irrelevantly, “I remember that one man had on buckskin breeches.”
Always indifferent in matters of dress, Lincoln cut but small figure in social circles, even in the earliest days of Illinois. His trousers were too short, his hat too small, and, as a rule, the buttons on the back of his coat were nearer his shoulder blades than his waist.
No man was richer than his fellows, and there was no aristocracy; the women wore linsey-woolsey of home manufacture, and dyed them in accordance with the tastes of the wearers; calico was rarely seen, and a woman wearing a dress of that material was the envy of her sisters.
There being no shoemakers the women wore moccasins, and the men made their own boots. A hunting shirt, leggins made of skins, buckskin breeches, dyed green, constituted an apparel no maiden could withstand.
One man who knew Lincoln at New Salem, says the first time he saw him he was lying on a trundle-bed covered with books and papers and rocking a cradle with his foot.
The whole scene was entirely characteristic—Lincoln reading and studying, and at the same time helping his landlady by quieting her child.
A gentleman who knew Mr. Lincoln well in early manhood says: “Lincoln at this period had nothing but plenty of friends.”
After the customary hand-shaking on one occasion in the White House at Washington several gentlemen came forward and asked the President for his autograph. One of them gave his name as “Cruikshank.” “That reminds me,” said Mr. Lincoln, “of what I used to be called when a young man—‘Long-shanks!’”
“I suppose you found it necessary to make large concessions to him, as he returned from you perfectly satisfied,” suggested a friend.
“Oh, no,” the President replied, “I did not concede anything. You have heard how that Illinois farmer got rid of a big log that was too big to haul out, too knotty to split, and too wet and soggy to burn.
“‘Well, now,’ said he, in response to the inquiries of his neighbors one Sunday, as to how he got rid of it, ‘well, now, boys, if you won’t divulge the secret, I’ll tell you how I got rid of it—I ploughed around it.’
“Now,” remarked Lincoln, in conclusion, “don’t tell anybody, but that’s the way I got rid of Governor Blank. I ploughed all round him, but it took me three mortal hours to do it, and I was afraid every minute he’d see what I was at.”
During a public “reception,” a farmer from one of the border counties of Virginia told the President that the Union soldiers, in passing his farm, had helped themselves not only to hay, but his horse, and he hoped the President would urge the proper officer to consider his claim immediately.
Mr. Lincoln said that this reminded him of an old acquaintance of his, “Jack” Chase, a lumberman on the Illinois, a steady, sober man, and the best raftsman on the river. It was quite a trick to take the logs over the rapids; but he was skilful with a raft, and always kept her straight in the channel. Finally a steamer was put on, and “Jack” was made captain of her. He always used to take the wheel, going through the rapids. One day when the boat was plunging and wallowing along the boiling current, and “Jack’s” utmost vigilance was being exercised to keep her in the narrow channel, a boy pulled his coat-tail and hailed him with:
“Say, Mister Captain! I wish you would just stop your boat a minute—I’ve lost my apple overboard!”
Mr. Lincoln prepared his first inaugural address in a room over a store in Springfield. His only reference works were Henry Clay’s great compromise speech of 1850, Andrew Jackson’s Proclamation against Nullification, Webster’s great reply to Hayne, and a copy of the Constitution.
When Mr. Lincoln started for Washington, to be inaugurated, the inaugural address was placed in a special satchel and guarded with special care. At Harrisburg the satchel was given in charge of Robert T. Lincoln, who accompanied his father. Before the train started from Harrisburg the precious satchel was missing. Robert thought he had given it to a waiter at the hotel, but a long search failed to reveal the missing satchel with its precious document. Lincoln was annoyed, angry, and finally in despair. He felt certain that the address was lost beyond recovery, and, as it only lacked ten days until the inauguration, he had no time to prepare another. He had not even preserved the notes from which the original copy had been written.
Mr. Lincoln went to Ward Lamon, his former law partner, then one of his bodyguards, and informed him of the loss in the following words:
“Lamon, I guess I have lost my certificate of moral character, written by myself. Bob has lost my gripsack containing my inaugural address.” Of course, the misfortune reminded him of a story.
“I feel,” said Mr. Lincoln, “a good deal as the old member of the Methodist Church did when he lost his wife at the camp meeting, and went up to an old elder of the church and asked him if he could tell him whereabouts in h—l his wife was. In fact, I am in a worse fix than my Methodist friend, for if it were only a wife that were missing, mine would be sure to bob up somewhere.”
The clerk at the hotel told Mr. Lincoln that he would probably find his missing satchel in the baggage-room. Arriving there, Mr. Lincoln saw a satchel which he thought was his, and it was passed out to him. His key fitted the lock, but alas! when it was opened the satchel contained only a soiled shirt, some paper collars, a pack of cards and a bottle of whisky. A few minutes later the satchel containing the inaugural address was found among the pile of baggage.
The recovery of the address also reminded Mr. Lincoln of a story, which is thus narrated by Ward Lamon in his “Recollections of Abraham Lincoln”:
The loss of the address and the search for it was the subject of a great deal of amusement. Mr. Lincoln said many funny things in connection with the incident. One of them was that he knew a fellow once who had saved up fifteen hundred dollars, and had placed it in a private banking establishment. The bank soon failed, and he afterward received ten per cent of his investment. He then took his one hundred and fifty dollars and deposited it in a savings bank, where he was sure it would be safe. In a short time this bank also failed, and he received at the final settlement ten per cent on the amount deposited. When the fifteen dollars was paid over to him, he held it in his hand and looked at it thoughtfully; then he said, “Now, darn you, I have got you reduced to a portable shape, so I’ll put you in my pocket.” Suiting the action to the word, Mr. Lincoln took his address from the bag and carefully placed it in the inside pocket of his vest, but held on to the satchel with as much interest as if it still contained his “certificate of moral character.”
The great English funny paper, London “Punch,” printed this cartoon on September 27th, 1862. It is intended to convey the idea that Lincoln, having asserted that the war would be over in ninety days, had not redeemed his word: The text under the Cartoon in Punch was:
MR. SOUTH TO MR. NORTH: “Your ‘ninety-day’ promissory note isn’t taken up yet, sirree!”
The tone of the cartoon is decidedly unfriendly. The North finally took up the note, but the South had to pay it. “Punch” was not pleased with the result, but “Mr. North” did not care particularly what this periodical thought about it. The United States, since then, has been prepared to take up all of its obligations when due, but it must be acknowledged that at the time this cartoon was published the outlook was rather dark and gloomy. Lincoln did not despair, however; but although business was in rather bad shape for a time, the financial skies finally cleared, business was resumed at the old stand, and Uncle Sam’s credit is now as good, or better, than other nations’ cash in hand.
Lincoln could not sympathize with those Union generals who were prone to indulge in high-sounding promises, but whose performances did not by any means come up to their predictions as to what they would do if they ever met the enemy face to face. He said one day, just after one of these braggarts had been soundly thrashed by the Confederates:
“These fellows remind me of the fellow who owned a dog which, so he said, just hungered and thirsted to combat and eat up wolves. It was a difficult matter, so the owner declared, to keep that dog from devoting the entire twenty-four hours of each day to the destruction of his enemies. He just ‘hankered’ to get at them.
“One day a party of this dog-owner’s friends thought to have some sport. These friends heartily disliked wolves, and were anxious to see the dog eat up a few thousand. So they organized a hunting party and invited the dog-owner and the dog to go with them. They desired to be personally present when the wolf-killing was in progress.
“It was noticed that the dog-owner was not over-enthusiastic in the matter; he pleaded a ‘business engagement,’ but as he was the most notorious and torpid of the town loafers, and wouldn’t have recognized a ‘business engagement’ had he met it face to face, his excuse was treated with contempt. Therefore he had to go.
“The dog, however, was glad enough to go, and so the party started out. Wolves were in plenty, and soon a pack was discovered, but when the ‘wolf-hound’ saw the ferocious animals he lost heart, and, putting his tail between his legs, endeavored to slink away. At last—after many trials—he was enticed into the small growth of underbrush where the wolves had secreted themselves, and yelps of terror betrayed the fact that the battle was on.
“Away flew the wolves, the dog among them, the hunting party following on horseback. The wolves seemed frightened, and the dog was restored to public favor. It really looked as if he had the savage creatures on the run, as he was fighting heroically when last sighted.
“Wolves and dog soon disappeared, and it was not until the party arrived at a distant farmhouse that news of the combatants was gleaned.
“‘Have you seen anything of a wolf-dog and a pack of wolves around here?’ was the question anxiously put to the male occupant of the house, who stood idly leaning upon the gate.
“‘Yep,’ was the short answer.
“‘How were they going?’
“‘Purty fast.’
“‘What was their position when you saw them?’
“‘Well,’ replied the farmer, in a most exasperatingly deliberate way, ‘the dog was a leetle bit ahead.’
“Now, gentlemen,” concluded the President, “that’s the position in which you’ll find most of these bragging generals when they get into a fight with the enemy. That’s why I don’t like military orators.”


When Lincoln was nineteen years of age, he went to work for a Mr. Gentry, and, in company with Gentry’s son, took a flatboat load of provisions to New Orleans. At a plantation six miles below Baton Rouge, while the boat was tied up to the shore in the dead hours of the night, and Abe and Allen were fast asleep in the bed, they were startled by footsteps on board. They knew instantly that it was a gang of negroes come to rob and perhaps murder them. Allen, thinking to frighten the negroes, called out, “Bring guns, Lincoln, and shoot them!” Abe came without the guns, but fell among the negroes with a huge bludgeon and belabored them most cruelly, following them onto the bank. They rushed back to their boat and hastily put out into the stream. It is said that Lincoln received a scar in this tussle which he carried with him to his grave. It was on this trip that he saw the workings of slavery for the first time. The sight of New Orleans was like a wonderful panorama to his eyes, for never before had he seen wealth, beauty, fashion and culture. He returned home with new and larger ideas and stronger opinions of right and justice.
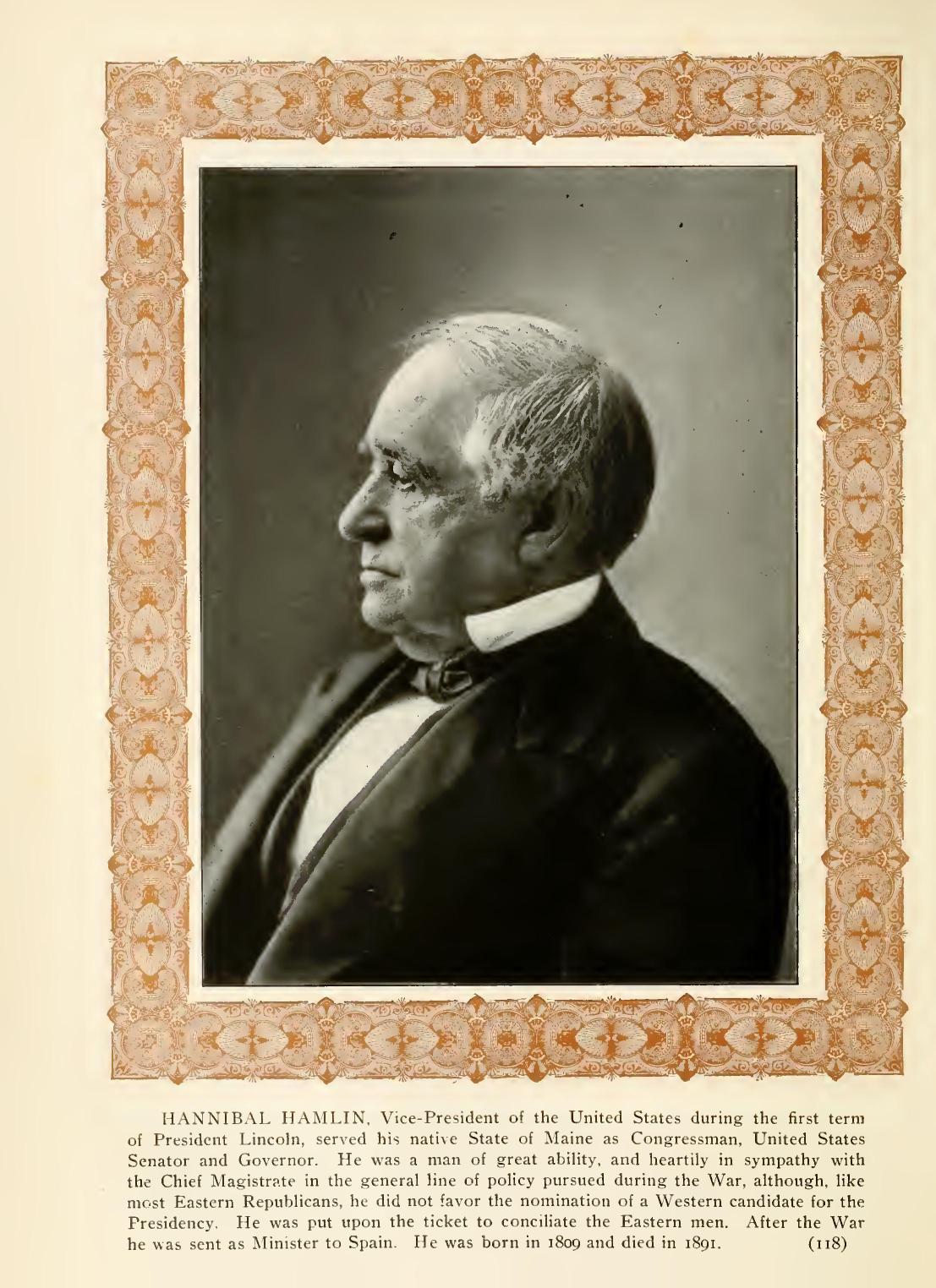




“Every man has his own peculiar and particular way of getting at and doing things,” said President Lincoln one day, “and he is often criticised because that way is not the one adopted by others. The great idea is to accomplish what you set out to do. When a man is successful in whatever he attempts, he has many imitators, and the methods used are not so closely scrutinized, although no man who is of good intent will resort to mean, underhanded, scurvy tricks.
“That reminds me of a fellow out in Illinois, who had better luck in getting prairie chickens than any one in the neighborhood. He had a rusty old gun no other man dared to handle; he never seemed to exert himself, being listless and indifferent when out after game, but he always brought home all the chickens he could carry, while some of the others, with their finely trained dogs and latest improved fowling-pieces, came home alone.
“‘How is it, Jake?’ inquired one sportsman, who, although a good shot, and knew something about hunting, was often unfortunate, ‘that you never come home without a lot of birds?’
“Jake grinned, half closed his eyes, and replied: ‘Oh, I don’t know that there’s anything queer about it. I jes’ go ahead an’ git ‘em.’
“‘Yes, I know you do; but how do you do it?’
“‘You’ll tell.’
“‘Honest, Jake, I won’t say a word. Hope to drop dead this minute.’
“‘Never say nothing, if I tell you?’
“‘Cross my heart three times.’
“This reassured Jake, who put his mouth close to the ear of his eager questioner, and said, in a whisper:
“‘All you got to do is jes’ to hide in a fence corner an’ make a noise like a turnip. That’ll bring the chickens every time.’”
When Lincoln was a candidate for re-election to the Illinois Legislature in 1836, a meeting was advertised to be held in the court-house in Springfield, at which candidates of opposing parties were to speak. This gave men of spirit and capacity a fine opportunity to show the stuff of which they were made.
George Forquer was one of the most prominent citizens; he had been a Whig, but became a Democrat—possibly for the reason that by means of the change he secured the position of Government land register, from President Andrew Jackson. He had the largest and finest house in the city, and there was a new and striking appendage to it, called a lightning-rod! The meeting was very large. Seven Whig and seven Democratic candidates spoke.
Lincoln closed the discussion. A Kentuckian (Joshua F. Speed), who had heard Henry Clay and other distinguished Kentucky orators, stood near Lincoln, and stated afterward that he “never heard a more effective speaker;... the crowd seemed to be swayed by him as he pleased.” What occurred during the closing portion of this meeting must be given in full, from Judge Arnold’s book:
“Forquer, although not a candidate, asked to be heard for the Democrats, in reply to Lincoln. He was a good speaker, and well known throughout the county. His special task that day was to attack and ridicule the young countryman from Salem.
“Turning to Lincoln, who stood within a few feet of him, he said: ‘This young man must be taken down, and I am truly sorry that the task devolves upon me.’ He then proceeded, in a very overbearing way, and with an assumption of great superiority, to attack Lincoln and his speech. He was fluent and ready with the rough sarcasm of the stump, and he went on to ridicule the person, dress and arguments of Lincoln with so much success that Lincoln’s friends feared that he would be embarrassed and overthrown.”
“The Clary’s Grove boys were present, and were restrained with difficulty from ‘getting up a fight’ in behalf of their favorite (Lincoln), they and all his friends feeling that the attack was ungenerous and unmanly.
“Lincoln, however, stood calm, but his flashing eye and pale cheek indicated his indignation. As soon as Forquer had closed he took the stand, and first answered his opponent’s arguments fully and triumphantly. So impressive were his words and manner that a hearer (Joshua F. Speed) believes that he can remember to this day and repeat some of the expressions.
“Among other things he said: ‘The gentleman commenced his speech by saying that “this young man,” alluding to me, “must be taken down.” I am not so young in years as I am in the tricks and the trades of a politician, but,’ said he, pointing to Forquer, ‘live long or die young, I would rather die now than, like the gentleman, change my politics, and with the change receive an office worth $3,000 a year, and then,’ continued he, ‘feel obliged to erect a lightning-rod over my house, to protect a guilty conscience from an offended God!’”
Jefferson Davis insisted on being recognized by his official title as commander or President in the regular negotiation with the Government. This Mr. Lincoln would not consent to.
Mr. Hunter thereupon referred to the correspondence between King Charles the First and his Parliament as a precedent for a negotiation between a constitutional ruler and rebels. Mr. Lincoln’s face then wore that indescribable expression which generally preceded his hardest hits, and he remarked: “Upon questions of history, I must refer you to Mr. Seward, for he is posted in such things, and I don’t profess to be; but my only distinct recollection of the matter is, that Charles lost his head.”
Lincoln loved anything that savored of wit or humor among the soldiers. He used to relate two stories to show, he said, that neither death nor danger could quench the grim humor of the American soldier:
“A soldier of the Army of the Potomac was being carried to the rear of battle with both legs shot off, who, seeing a pie-woman, called out, ‘Say, old lady, are them pies sewed or pegged?’
“And there was another one of the soldiers at the battle of Chancellorsville, whose regiment, waiting to be called into the fight, was taking coffee. The hero of the story put to his lips a crockery mug which he had carried with care through several campaigns. A stray bullet, just missing the tinker’s head, dashed the mug into fragments and left only the handle on his finger. Turning his head in that direction, he scowled, ‘Johnny, you can’t do that again!’”
Captain T. W. S. Kidd of Springfield was the crier of the court in the days when Mr. Lincoln used to ride the circuit.
“I was younger than he,” says Captain Kidd, “but he had a sort of admiration for me, and never failed to get me into his stories. I was a story-teller myself in those days, and he used to laugh very heartily at some of the stories I told him.
“Now and then he got me into a good deal of trouble. I was a Democrat, and was in politics more or less. A good many of our Democratic voters at that time were Irishmen. They came to Illinois in the days of the old canal, and did their honest share in making that piece of internal improvement an accomplished fact.
“One time Mr. Lincoln told the story of one of those important young fellows—not an Irishman—who lived in every town, and have the cares of state on their shoulders. This young fellow met an Irishman on the street, and called to him, officiously: ‘Oh, Mike, I’m awful glad I met you. We’ve got to do something to wake up the boys. The campaign is coming on, and we’ve got to get out voters. We’ve just had a meeting up here, and we’re going to have the biggest barbecue that ever was heard of in Illinois. We are going to roast two whole oxen, and we’re going to have Douglas and Governor Cass and some one from Kentucky, and all the big Democratic guns, and we’re going to have a great big time.’
“‘By dad, that’s good!’ says the Irishman. ‘The byes need stirrin’ up.’
“‘Yes, and you’re on one of the committees, and you want to hustle around and get them waked up, Mike.’
“‘When is the barbecue to be?’ asked Mike.
“‘Friday, two weeks.’
“‘Friday, is it? Well, I’ll make a nice committeeman, settin’ the barbecue on a day with half of the Dimocratic party of Sangamon county can’t ate a bite of mate. Go on wid ye.’
“Lincoln told that story in one of his political speeches, and when the laugh was over he said: ‘Now, gentlemen, I know that story is true, for Tom Kidd told it to me.’ And then the Democrats would make trouble for me for a week afterward, and I’d have to explain.”
About two years before Lincoln was nominated for the Presidency he went to Bloomington, Illinois, to try a case of some importance. His opponent—who afterward reached a high place in his profession—was a young man of ability, sensible but sensitive, and one to whom the loss of a case was a great blow. He therefore studied hard and made much preparation.
This particular case was submitted to the jury late at night, and, although anticipating a favorable verdict, the young attorney spent a sleepless night in anxiety. Early next morning he learned, to his great chagrin, that he had lost the case.
Lincoln met him at the court-house some time after the jury had come in, and asked him what had become of his case.
With lugubrious countenance and in a melancholy tone the young man replied, “It’s gone to hell.”
“Oh, well,” replied Lincoln, “then you will see it again.”
When arguing a case in court, Mr. Lincoln never used a word which the dullest juryman could not understand. Rarely, if ever, did a Latin term creep into his arguments. A lawyer, quoting a legal maxim one day in court, turned to Lincoln, and said: “That is so, is it not, Mr. Lincoln?”
“If that’s Latin.” Lincoln replied, “you had better call another witness.”
Mr. Carpenter, the artist, relates the following incident: “Some photographers came up to the White House to make some stereoscopic studies for me of the President’s office. They requested a dark closet in which to develop the pictures, and, without a thought that I was infringing upon anybody’s rights, I took them to an unoccupied room of which little ‘Tad’ had taken possession a few days before, and, with the aid of a couple of servants, had fitted up a miniature theater, with stage, curtains, orchestra, stalls, parquette and all. Knowing that the use required would interfere with none of his arrangements, I led the way to this apartment.
“Everything went on well, and one or two pictures had been taken, when suddenly there was an uproar. The operator came back to the office and said that ‘Tad’ had taken great offense at the occupation of his room without his consent, and had locked the door, refusing all admission.
“The chemicals had been taken inside, and there was no way of getting at them, he having carried off the key. In the midst of this conversation ‘Tad’ burst in, in a fearful passion. He laid all the blame upon me—said that I had no right to use his room, and the men should not go in even to get their things. He had locked the door and they should not go there again—‘they had no business in his room!’
“Mr. Lincoln was sitting for a photograph, and was still in the chair. He said, very mildly, ‘Tad, go and unlock the door.’ Tad went off muttering into his mother’s room, refusing to obey. I followed him into the passage, but no coaxing would pacify him. Upon my return to the President, I found him still patiently in the chair, from which he had not risen. He said: ‘Has not the boy opened the door?’ I replied that we could do nothing with him—he had gone off in a great pet. Mr. Lincoln’s lips came together firmly, and then, suddenly rising, he strode across the passage with the air of one bent on punishment, and disappeared in the domestic apartments. Directly he returned with the key to the theater, which he unlocked himself.
“‘Tad,’ said he, half apologetically, ‘is a peculiar child. He was violently excited when I went to him. I said, “Tad, do you know that you are making your father a great deal of trouble?” He burst into tears, instantly giving me up the key.’”
When Lincoln’s attention was called to the fact that, at one time in his boyhood, he had spelled the name of the Deity with a small “g,” he replied:
“That reminds me of a little story. It came about that a lot of Confederate mail was captured by the Union forces, and, while it was not exactly the proper thing to do, some of our soldiers opened several letters written by the Southerners at the front to their people at home.
“In one of these missives the writer, in a postscript, jotted down this assertion:
“‘We’ll lick the Yanks termorrer, if goddlemity (God Almighty) spares our lives.’
“That fellow was in earnest, too, as the letter was written the day before the second battle of Manassas.”
“The first time I ever remember seeing ‘Abe’ Lincoln,” is the testimony of one of his neighbors, “was when I was a small boy and had gone with my father to attend some kind of an election. One of the neighbors, James Larkins, was there.
“Larkins was a great hand to brag on anything he owned. This time it was his horse. He stepped up before ‘Abe,’ who was in a crowd, and commenced talking to him, boasting all the while of his animal.
“‘I have got the best horse in the country,’ he shouted to his young listener. ‘I ran him nine miles in exactly three minutes, and he never fetched a long breath.’
“‘I presume,’ said ‘Abe,’ rather dryly, ‘he fetched a good many short ones, though.’”
On May 3rd, 1862, “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” printed this cartoon, over the title of “Sandbag Lincoln and the Old Man of the Sea, Secretary of the Navy Welles.” It was intended to demonstrate that the head of the Navy Department was incompetent to manage the affairs of the Navy; also that the Navy was not doing as good work as it might.
When this cartoon was published, the United States Navy had cleared and had under control the Mississippi River as far south as Memphis; had blockaded all the cotton ports of the South; had assisted in the reduction of a number of Confederate forts; had aided Grant at Fort Donelson and the battle of Shiloh; the Monitor had whipped the ironclad terror, Merrimac (the Confederates called her the Virginia); Admiral Farragut’s fleet had compelled the surrender of the city of New Orleans, the great forts which had defended it, and the Federal Government obtained control of the lower Mississippi.
“The Old Man of the Sea” was therefore, not a drag or a weight upon President Lincoln, and the Navy was not so far behind in making a good record as the picture would have the people of the world believe. It was not long after the Monitor’s victory that the United States Navy was the finest that ever plowed the seas. The building of the Monitor also revolutionized naval warfare.
About a week after the Chicago Convention, a gentleman from New York called upon the President, in company with the Assistant Secretary of War, Mr. Dana.
In the course of conversation, the gentleman said: “What do you think, Mr. President, is the reason General McClellan does not reply to the letter from the Chicago Convention?”
“Oh!” replied Mr. Lincoln, with a characteristic twinkle of the eye, “he is intrenching!”
From the day of his nomination by the Chicago convention, gifts poured in upon Lincoln. Many of these came in the form of wearing apparel. Mr. George Lincoln, of Brooklyn, who brought to Springfield, in January, 1861, a handsome silk hat to the President-elect, the gift of a New York hatter, told some friends that in receiving the hat Lincoln laughed heartily over the gifts of clothing, and remarked to Mrs. Lincoln: “Well, wife, if nothing else comes out of this scrape, we are going to have some new clothes, are we not?”
In speaking of the many mean and petty acts of certain members of Congress, the President, while talking on the subject one day with friends, said:
“I have great sympathy for these men, because of their temper and their weakness; but I am thankful that the good Lord has given to the vicious ox short horns, for if their physical courage were equal to their vicious disposition, some of us in this neck of the woods would get hurt.”
“I was speaking one time to Mr. Lincoln,” said Governor Saunders, “of Nebraska, of a little Nebraskan settlement on the Weeping Water, a stream in our State.”
“‘Weeping Water!’ said he.
“Then with a twinkle in his eye, he continued.
“‘I suppose the Indians out there call Minneboohoo, don’t they? They ought to, if Laughing Water is Minnehaha in their language.’”
Peter Cartwright, the famous and eccentric old Methodist preacher, who used to ride a church circuit, as Mr. Lincoln and others did the court circuit, did not like Lincoln very well, probably because Mr. Lincoln was not a member of his flock, and once defeated the preacher for Congress. This was Cartwright’s description of Lincoln: “This Lincoln is a man six feet four inches tall, but so angular that if you should drop a plummet from the center of his head it would cut him three times before it touched his feet.”
A gentleman was relating to the President how a friend of his had been driven away from New Orleans as a Unionist, and how, on his expulsion, when he asked to see the writ by which he was expelled, the deputation which called on him told him the Government would do nothing illegal, and so they had issued no illegal writs, and simply meant to make him go of his own free will.
“Well,” said Mr. Lincoln, “that reminds me of a hotel-keeper down at St. Louis, who boasted that he never had a death in his hotel, for whenever a guest was dying in his house he carried him out to die in the gutter.”
The day following the adjournment of the Baltimore Convention, at which President Lincoln was renominated, various political organizations called to pay their respects to the President. While the Philadelphia delegation was being presented, the chairman of that body, in introducing one of the members, said:
“Mr. President, this is Mr. S., of the second district of our State,—a most active and earnest friend of yours and the cause. He has, among other things, been good enough to paint, and present to our league rooms, a most beautiful portrait of yourself.”
President Lincoln took the gentleman’s hand in his, and shaking it cordially said, with a merry voice, “I presume, sir, in painting your beautiful portrait, you took your idea of me from my principles and not from my person.”
Lincoln was married—he balked at the first date set for the ceremony and did not show up at all—November 4, 1842, under most happy auspices. The officiating clergyman, the Rev. Mr. Dresser, used the Episcopal church service for marriage. Lincoln placed the ring upon the bride’s finger, and said, “With this ring I now thee wed, and with all my worldly goods I thee endow.”
Judge Thomas C. Browne, who was present, exclaimed, “Good gracious, Lincoln! the statute fixes all that!”
“Oh, well,” drawled Lincoln, “I just thought I’d add a little dignity to the statute.”
The joint debates between Lincoln and Douglas were attended by crowds of people, and the arrival of both at the places of speaking were in the nature of a triumphal procession. In these processions there were many banners bearing catch-phrases and mottoes expressing the sentiment of the people on the candidates and the issues.
The following were some of the mottoes on the Lincoln banners:
| Westward the star of empire takes its way; |
| The girls link on to Lincoln, their mothers were for Clay. |
| Abe, the Giant-Killer. |
| Edgar County for the Tall Sucker. |
| Free Territories and Free Men, |
| Free Pulpits and Free Preachers, |
| Free Press and a Free Pen, |
| Free Schools and Free Teachers. |
Between the first election and inauguration of Mr. Lincoln the disunion sentiment grew rapidly in the South, and President Buchanan’s failure to stop the open acts of secession grieved Mr. Lincoln sorely. Mr. Lincoln had a long talk with his friend, Judge Gillespie, over the state of affairs. One incident of the conversation is thus narrated by the Judge:
“When I retired, it was the master of the house and chosen ruler of the country who saw me to my room. ‘Joe,’ he said, as he was about to leave me, ‘I am reminded and I suppose you will never forget that trial down in Montgomery county, where the lawyer associated with you gave away the whole case in his opening speech. I saw you signaling to him, but you couldn’t stop him.
“‘Now, that’s just the way with me and Buchanan. He is giving away the case, and I have nothing to say, and can’t stop him. Good-night.’”
Mr. Leonard Volk, the artist, relates that, being in Springfield when Lincoln’s nomination for President was announced, he called upon Mr. Lincoln, whom he found looking smiling and happy. “I exclaimed, ‘I am the first man from Chicago, I believe, who has had the honor of congratulating you on your nomination for President.’ Then those two great hands took both of mine with a grasp never to be forgotten, and while shaking, I said, ‘Now that you will doubtless be the next President of the United States, I want to make a statue of you, and shall try my best to do you justice.’
“Said he, ‘I don’t doubt it, for I have come to the conclusion that you are an honest man,’ and with that greeting, I thought my hands in a fair way of being crushed.
“On the Sunday following, by agreement, I called to make a cast of Mr. Lincoln’s hands. I asked him to hold something in his hands, and told him a stick would do. Thereupon he went to the woodshed, and I heard the saw go, and he soon returned to the dining-room, whittling off the end of a piece of broom handle. I remarked to him that he need not whittle off the edges. ‘Oh, well,’ said he, ‘I thought I would like to have it nice.’”
During Lincoln’s first and only term in Congress—he was elected in 1846—he formed quite a cordial friendship with Stephen A. Douglas, a member of the United States Senate from Illinois, and the beaten one in the contest as to who should secure the hand of Miss Mary Todd. Lincoln was the winner; Douglas afterwards beat him for the United States Senate, but Lincoln went to the White House.
During all of the time that they were rivals in love and in politics they remained the best of friends personally. They were always glad to see each other, and were frequently together. The disparity in their size was always the more noticeable upon such occasions, and they well deserved their nicknames of “Long Abe” and the “Little Giant.” Lincoln was the tallest man in the National House of Representatives, and Douglas the shortest (and perhaps broadest) man the Senate, and when they appeared on the streets together much merriment was created. Lincoln, when joked about the matter, replied, in a very serious tone, “Yes, that’s about the length and breadth of it.”
Lincoln couldn’t sing, and he also lacked the faculty of musical adaptation. He had a liking for certain ballads and songs, and while he memorized and recited their lines, someone else did the singing. Lincoln often recited for the delectation of his friends, the following, the authorship of which is unknown:
| The first factional fight in old Ireland, they say, |
| Was all on account of St. Patrick’s birthday; |
| It was somewhere about midnight without any doubt, |
| And certain it is, it made a great rout. |
| On the eighth day of March, as some people say, |
| St. Patrick at midnight he first saw the day; |
| While others assert ‘twas the ninth he was born— |
| ‘Twas all a mistake—between midnight and morn. |
| Some blamed the baby, some blamed the clock; |
| Some blamed the doctor, some the crowing cock. |
| With all these close questions sure no one could know, |
| Whether the babe was too fast or the clock was too slow. |
| Some fought for the eighth, for the ninth some would die; |
| He who wouldn’t see right would have a black eye. |
| At length these two factions so positive grew, |
| They each had a birthday, and Pat he had two. |
| Till Father Mulcahay who showed them their sins, |
| He said none could have two birthdays but as twins. |
| “Now boys, don’t be fighting for the eight or the nine; |
| Don’t quarrel so always, now why not combine.” |
| Combine eight with nine. It is the mark; |
| Let that be the birthday. Amen! said the clerk. |
| So all got blind drunk, which completed their bliss, |
| And they’ve kept up the practice from that day to this. |
Senator John Sherman, of Ohio, introduced his brother, William T. Sherman (then a civilian) to President Lincoln in March, 1861. Sherman had offered his services, but, as in the case of Grant, they had been refused.
After the Senator had transacted his business with the President, he said: “Mr. President, this is my brother, Colonel Sherman, who is just up from Louisiana; he may give you some information you want.”
To this Lincoln replied, as reported by Senator Sherman himself: “Ah! How are they getting along down there?”
Sherman answered: “They think they are getting along swimmingly; they are prepared for war.”
To which Lincoln responded: “Oh, well, I guess we’ll manage to keep the house.”
“Tecump,” whose temper was not the mildest, broke out on “Brother John” as soon as they were out of the White House, cursed the politicians roundly, and wound up with, “You have got things in a h—l of a fix, and you may get out as best you can.”
Sherman was one of the very few generals who gave Lincoln little or no worry.
“Just after receiving my commission as lieutenant-general the President called me aside to speak to me privately. After a brief reference to the military situation, he said he thought he could illustrate what he wanted to say by a story. Said he:
“‘At one time there was a great war among the animals, and one side had great difficulty in getting a commander who had sufficient confidence in himself. Finally they found a monkey by the name of Jocko, who said he thought he could command their army if his tail could be made a little longer. So they got more tail and spliced it on to his caudal appendage.
“‘He looked at it admiringly, and then said he thought he ought to have still more tail. This was added, and again he called for more. The splicing process was repeated many times until they had coiled Jocko’s tail around the room, filling all the space.
“‘Still he called for more tail, and, there being no other place to coil it, they began wrapping it around his shoulders. He continued his call for more, and they kept on winding the additional tail around him until its weight broke him down.’
“I saw the point, and, rising from my chair, replied, ‘Mr. President, I will not call for any more assistance unless I find it impossible to do with what I already have.’”
Ward Lamon, Marshal of the District of Columbia during Lincoln’s time in Washington, was a powerful man; his strength was phenomenal, and a blow from his fist was like unto that coming from the business end of a sledge.
Lamon tells this story, the hero of which is not mentioned by name, but in all probability his identity can be guessed:
“On one occasion, when the fears of the loyal element of the city (Washington) were excited to fever-heat, a free fight near the old National Theatre occurred about eleven o’clock one night. An officer, in passing the place, observed what was going on, and seeing the great number of persons engaged, he felt it to be his duty to command the peace.
“The imperative tone of his voice stopped the fighting for a moment, but the leader, a great bully, roughly pushed back the officer and told him to go away or he would whip him. The officer again advanced and said, ‘I arrest you,’ attempting to place his hand on the man’s shoulder, when the bully struck a fearful blow at the officer’s face.
“This was parried, and instantly followed by a blow from the fist of the officer, striking the fellow under the chin and knocking him senseless. Blood issued from his mouth, nose and ears. It was believed that the man’s neck was broken. A surgeon was called, who pronounced the case a critical one, and the wounded man was hurried away on a litter to the hospital.
“There the physicians said there was concussion of the brain, and that the man would die. All the medical skill that the officer could procure was employed in the hope of saving the life of the man. His conscience smote him for having, as he believed, taken the life of a fellow-creature, and he was inconsolable.
“Being on terms of intimacy with the President, about two o’clock that night the officer went to the White House, woke up Mr. Lincoln, and requested him to come into his office, where he told him his story. Mr. Lincoln listened with great interest until the narrative was completed, and then asked a few questions, after which he remarked:
“‘I am sorry you had to kill the man, but these are times of war, and a great many men deserve killing. This one, according to your story, is one of them; so give yourself no uneasiness about the matter. I will stand by you.’
“‘That is not why I came to you. I knew I did my duty, and had no fears of your disapproval of what I did,’ replied the officer; and then he added: ‘Why I came to you was, I felt great grief over the unfortunate affair, and I wanted to talk to you about it.’
“Mr. Lincoln then said, with a smile, placing his hand on the officer’ shoulder: ‘You go home now and get some sleep; but let me give you this piece of advice—hereafter, when you have occasion to strike a man, don’t hit him with your fist; strike him with a club, a crowbar, or with something that won’t kill him.’”
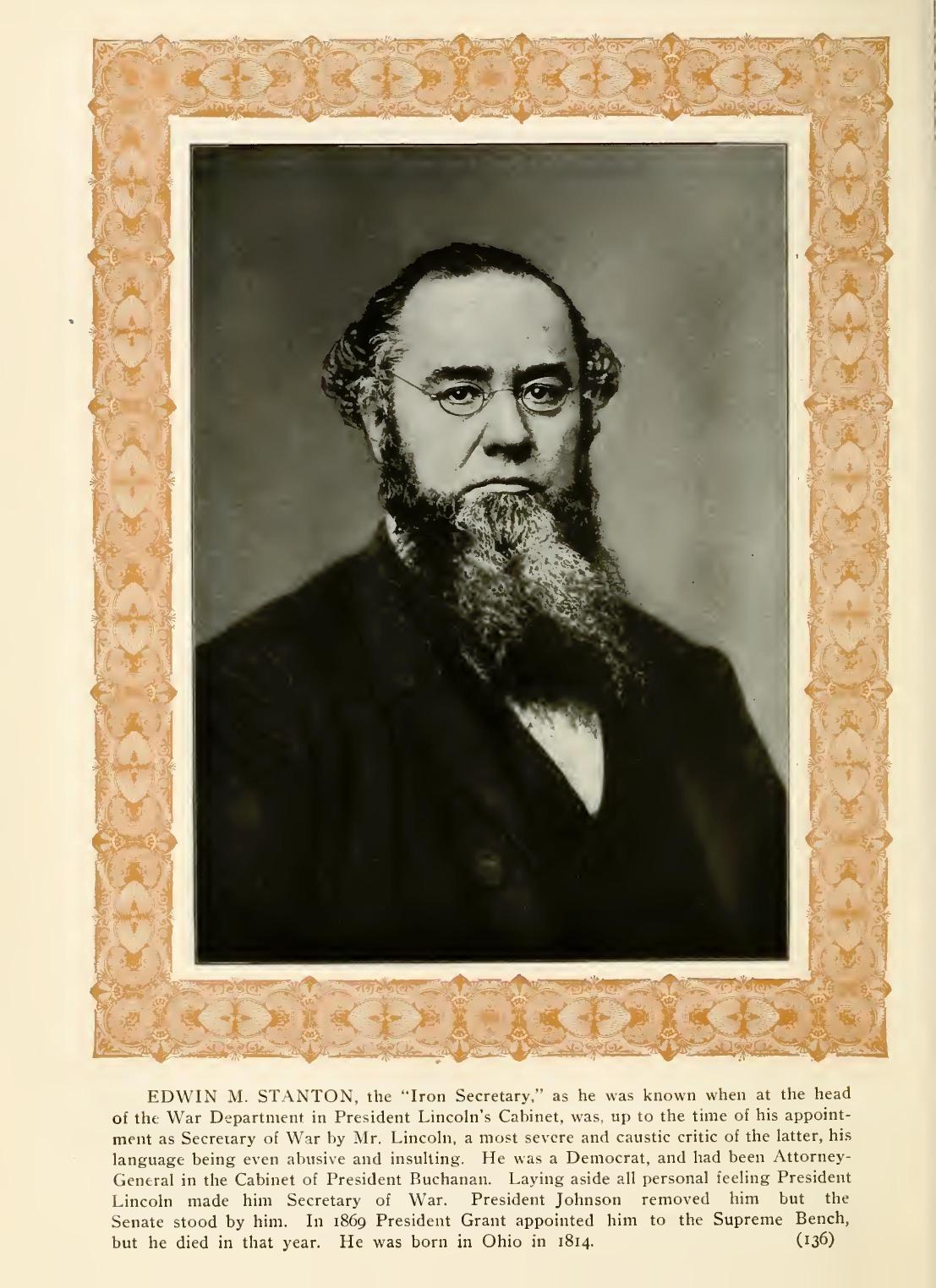




Lincoln could be arbitrary when occasion required. This is the letter he wrote to one of the Department heads:
“You must make a job of it, and provide a place for the bearer of this, Elias Wampole. Make a job of it with the collector and have it done. You can do it for me, and you must.”
There was no delay in taking action in this matter. Mr. Wampole, or “Eli,” as he was thereafter known, “got there.”
Many amusing stories are told of President Lincoln and his gloves. At about the time of his third reception he had on a tight-fitting pair of white kids, which he had with difficulty got on. He saw approaching in the distance an old Illinois friend named Simpson, whom he welcomed with a genuine Sangamon county (Illeenoy) shake, which resulted in bursting his white kid glove, with an audible sound. Then, raising his brawny hand up before him, looking at it with an indescribable expression, he said, while the whole procession was checked, witnessing this scene:
“Well, my old friend, this is a general bustification. You and I were never intended to wear these things. If they were stronger they might do well enough to keep out the cold, but they are a failure to shake hands with between old friends like us. Stand aside, Captain, and I’ll see you shortly.”
Simpson stood aside, and after the unwelcome ceremony was terminated he rejoined his old Illinois friend in familiar intercourse.
H. C. Whitney wrote in 1866: “I was in Washington in the Indian service for a few days before August, 1861, and I merely said to President Lincoln one day: ‘Everything is drifting into the war, and I guess you will have to put me in the army.’
“The President looked up from his work and said, good-humoredly: ‘I’m making generals now; in a few days I will be making quartermasters, and then I’ll fix you.’”
“Mr. Lincoln walked into the corridor with us; and, as he bade us good-by and thanked Blank for what he had told him, he again brightened up for a moment and asked him in an abrupt kind of way, laying his hand as he spoke with a queer but not uncivil familiarity on his shoulder, ‘You haven’t such a thing as a postmaster in your pocket, have you?’
“Blank stared at him in astonishment, and I thought a little in alarm, as if he suspected a sudden attack of insanity; then Mr. Lincoln went on:
‘You see it seems to me kind of unnatural that you shouldn’t have at least a postmaster in your pocket. Everybody I’ve seen for days past has had foreign ministers and collectors, and all kinds, and I thought you couldn’t have got in here without having at least a postmaster get into your pocket!’”


When a surveyor, Mr. Lincoln first platted the town of Petersburg, Ill. Some twenty or thirty years afterward the property-owners along one of the outlying streets had trouble in fixing their boundaries. They consulted the official plat and got no relief. A committee was sent to Springfield to consult the distinguished surveyor, but he failed to recall anything that would give them aid, and could only refer them to the record. The dispute therefore went into the courts. While the trial was pending, an old Irishman named McGuire, who had worked for some farmer during the summer, returned to town for the winter. The case being mentioned in his presence, he promptly said: “I can tell you all about it. I helped carry the chain when Abe Lincoln laid out this town. Over there where they are quarreling about the lines, when he was locating the street, he straightened up from his instrument and said: ‘If I run that street right through, it will cut three or four feet off the end of ——‘s house. It’s all he’s got in the world and he never could get another. I reckon it won’t hurt anything out here if I skew the line a little and miss him.”’
The line was “skewed,” and hence the trouble, and more testimony furnished as to Lincoln’s abounding kindness of heart, that would not willingly harm any human being.
One of the most celebrated courts-martial during the War was that of Franklin W. Smith and his brother, charged with defrauding the government. These men bore a high character for integrity. At this time, however, courts-martial were seldom invoked for any other purpose than to convict the accused, and the Smiths shared the usual fate of persons whose cases were submitted to such arbitrament. They were kept in prison, their papers seized, their business destroyed, and their reputations ruined, all of which was followed by a conviction.
The finding of the court was submitted to the President, who, after a careful investigation, disapproved the judgment, and wrote the following endorsement upon the papers:
“Whereas, Franklin W. Smith had transactions with the Navy Department to the amount of a million and a quarter of dollars; and:
“Whereas, he had a chance to steal at least a quarter of a million and was only charged with stealing twenty-two hundred dollars, and the question now is about his stealing one hundred, I don’t believe he stole anything at all.
“Therefore, the record and the findings are disapproved, declared null and void, and the defendants are fully discharged.”
President Lincoln, after listening to the arguments and appeals of a committee which called upon him at the White House not long before the Emancipation Proclamation was issued, said:
“I do not want to issue a document that the whole world will see must necessarily be inoperative, like the Pope’s bull against the comet.”
A “high” private of the One Hundred and Fortieth Infantry Regiment, Pennsylvania Volunteers, wounded at Chancellorsville, was taken to Washington. One day, as he was becoming convalescent, a whisper ran down the long row of cots that the President was in the building and would soon pass by. Instantly every boy in blue who was able arose, stood erect, hands to the side, ready to salute his Commander-in-Chief.
The Pennsylvanian stood six feet seven inches in his stockings. Lincoln was six feet four. As the President approached this giant towering above him, he stopped in amazement, and casting his eyes from head to foot and from foot to head, as if contemplating the immense distance from one extremity to the other, he stood for a moment speechless.
At length, extending his hand, he exclaimed, “Hello, comrade, do you know when your feet get cold?”
“Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” of March 2nd, 1861, two days previous to the inauguration of President-elect Lincoln, contained the caricature reproduced here. It was intended to convey the idea that the National Administration would thereafter depend upon the support of bayonets to uphold it, and the text underneath the picture ran as follows:
OLD ABE: “Oh, it’s all well enough to say that I must support the dignity of my high office by force—but it’s darned uncomfortable sitting, I can tell yer.”
This journal was not entirely friendly to the new Chief Magistrate, but it could not see into the future. Many of the leading publications of the East, among them some of those which condemned slavery and were opposed to secession, did not believe Lincoln was the man for the emergency, but instead of doing what they could do to help him along, they attacked him most viciously. No man, save Washington, was more brutally lied about than Lincoln, but he bore all the slurs and thrusts, not to mention the open, cruel antagonism of those who should have been his warmest friends, with a fortitude and patience few men have ever shown. He was on the right road, and awaited the time when his course should receive the approval it merited.
General James B. Fry told a good one on Secretary of War Stanton, who was worsted in a contention with the President. Several brigadier-generals were to be selected, and Lincoln maintained that “something must be done in the interest of the Dutch.” Many complaints had come from prominent men, born in the Fatherland, but who were fighting for the Union.
“Now, I want Schimmelpfennig given one of those brigadierships.”
Stanton was stubborn and headstrong, as usual, but his manner and tone indicated that the President would have his own way in the end. However, he was not to be beaten without having made a fight.
“But, Mr. President,” insisted the Iron War Secretary, “it may be that this Mr. Schim—what’s-his-name—has no recommendations showing his fitness. Perhaps he can’t speak English.”
“That doesn’t matter a bit, Stanton,” retorted Lincoln, “he may be deaf and dumb for all I know, but whatever language he speaks, if any, we can furnish troops who will understand what he says. That name of his will make up for any differences in religion, politics or understanding, and I’ll take the risk of his coming out all right.”
Then, slamming his great hand upon the Secretary’s desk, he said, “Schim-mel-fen-nig must be appointed.”
And he was, there and then.
“Do you know General A—?” queried the President one day to a friend who had “dropped in” at the White House.
“Certainly; but you are not wasting any time thinking about him, are you?” was the rejoinder.
“You wrong him,” responded the President, “he is a really great man, a philosopher.”
“How do you make that out? He isn’t worth the powder and ball necessary to kill him so I have heard military men say,” the friend remarked.
“He is a mighty thinker,” the President returned, “because he has mastered that ancient and wise admonition, ‘Know thyself;’ he has formed an intimate acquaintance with himself, knows as well for what he is fitted and unfitted as any man living. Without doubt he is a remarkable man. This War has not produced another like him.”
“How is it you are so highly pleased with General A—— all at once?”
“For the reason,” replied Mr. Lincoln, with a merry twinkle of the eye, “greatly to my relief, and to the interests of the country, he has resigned. The country should express its gratitude in some substantial way.”
There was no member of the Cabinet from the South when Attorney-General Bates handed in his resignation, and President Lincoln had a great deal of trouble in making a selection. Finally Titian F. Coffey consented to fill the vacant place for a time, and did so until the appointment of Mr. Speed.
In conversation with Mr. Coffey the President quaintly remarked:
“My Cabinet has shrunk up North, and I must find a Southern man. I suppose if the twelve Apostles were to be chosen nowadays, the shrieks of locality would have to be heeded.”
It is not generally known that President Lincoln adopted a suggestion made by Secretary of the Treasury Salmon P. Chase in regard to the Emancipation Proclamation, and incorporated it in that famous document.
After the President had read it to the members of the Cabinet he asked if he had omitted anything which should be added or inserted to strengthen it. It will be remembered that the closing paragraph of the Proclamation reads in this way:
“And upon this act, sincerely believed to be an act of justice warranted by the Constitution, I invoke the considerate judgment of mankind, and the gracious favor of Almighty God!” President Lincoln’s draft of the paper ended with the word “mankind,” and the words, “and the gracious favor of Almighty God,” were those suggested by Secretary Chase.
It was the President’s overweening desire to accommodate all persons who came to him soliciting favors, but the opportunity was never offered until an untimely and unthinking disease, which possessed many of the characteristics of one of the most dreaded maladies, confined him to his bed at the White House.
The rumor spread that the President was afflicted with this disease, while the truth was that it was merely a very mild attack of varioloid. The office-seekers didn’t know the facts, and for once the Executive Mansion was clear of them.
One day, a man from the West, who didn’t read the papers, but wanted the postoffice in his town, called at the White House. The President, being then practically a well man, saw him. The caller was engaged in a voluble endeavor to put his capabilities in the most favorable light, when the President interrupted him with the remark that he would be compelled to make the interview short, as his doctor was due.
“Why, Mr. President, are you sick?” queried the visitor.
“Oh, nothing much,” replied Mr. Lincoln, “but the physician says he fears the worst.”
“What worst, may I ask?”
“Smallpox,” was the answer; “but you needn’t be scared. I’m only in the first stages now.”
The visitor grabbed his hat, sprang from his chair, and without a word bolted for the door.
“Don’t be in a hurry,” said the President placidly; “sit down and talk awhile.”
“Thank you, sir; I’ll call again,” shouted the Westerner, as he disappeared through the opening in the wall.
“Now, that’s the way with people,” the President said, when relating the story afterward. “When I can’t give them what they want, they’re dissatisfied, and say harsh things about me; but when I’ve something to give to everybody they scamper off.”
An applicant for a sutlership in the army relates this story: “In the winter of 1864, after serving three years in the Union Army, and being honorably discharged, I made application for the post sutlership at Point Lookout. My father being interested, we made application to Mr. Stanton, the Secretary of War. We obtained an audience, and were ushered into the presence of the most pompous man I ever met. As I entered he waved his hand for me to stop at a given distance from him, and then put these questions, viz.:
“‘Did you serve three years in the army?’
“‘I did, sir.’
“‘Were you honorably discharged?’
“‘I was, sir.’
“‘Let me see your discharge.’
“I gave it to him. He looked it over, then said:
‘Were you ever wounded?’ I told him yes, at the battle of Williamsburg, May 5, 1861.
“He then said: ‘I think we can give this position to a soldier who has lost an arm or leg, he being more deserving; and he then said I looked hearty and healthy enough to serve three years more. He would not give me a chance to argue my case.
“The audience was at an end. He waved his hand to me. I was then dismissed from the august presence of the Honorable Secretary of War.
“My father was waiting for me in the hallway, who saw by my countenance that I was not successful. I said to my father:
“‘Let us go over to Mr. Lincoln; he may give us more satisfaction.’
“He said it would do me no good, but we went over. Mr. Lincoln’s reception room was full of ladies and gentlemen when we entered.
“My turn soon came. Lincoln turned to my father and said:
“‘Now, gentlemen, be pleased to be as quick as possible with your business, as it is growing late.’
“My father then stepped up to Lincoln and introduced me to him. Lincoln then said:
“‘Take a seat, gentlemen, and state your business as quickly as possible.’
“There was but one chair by Lincoln, so he motioned my father to sit, while I stood. My father stated the business to him as stated above. He then said:
“‘Have you seen Mr. Stanton?’
“We told him yes, that he had refused. He (Mr. Lincoln) then said:
“‘Gentlemen, this is Mr. Stanton’s business; I cannot interfere with him; he attends to all these matters and I am sorry I cannot help you.’
“He saw that we were disappointed, and did his best to revive our spirits. He succeeded well with my father, who was a Lincoln man, and who was a staunch Republican.
“Mr. Lincoln then said:
“‘Now, gentlemen, I will tell you, what it is; I have thousands of applications like this every day, but we cannot satisfy all for this reason, that these positions are like office seekers—there are too many pigs for the teats.’
“The ladies who were listening to the conversation placed their handkerchiefs to their faces and turned away. But the joke of ‘Old Abe’ put us all in a good humor. We then left the presence of the greatest and most just man who ever lived to fill the Presidential chair.’”
No sooner was Abraham Lincoln made the candidate for the Presidency of the Republican Party, in 1860, than the opposition began to lampoon and caricature him. In the cartoon here reproduced, which is given the title of:
“The Republican Party Going to the Right House,” Lincoln is represented as entering the Lunatic Asylum, riding on a rail, carried by Horace Greeley, the great Abolitionist; Lincoln, followed by his “fellow-cranks,” is assuring the latter that the millennium is “going to begin,” and that all requests will be granted.


Lincoln’s followers are depicted as those men and women composing the “free love” element; those who want religion abolished; negroes, who want it understood that the white man has no rights his black brother is bound to respect; women suffragists, who demand that men be made subject to female authority; tramps, who insist upon free lodging-houses; criminals, who demand the right to steal from all they meet; and toughs, who want the police forces abolished, so that “the b’hoys” can “run wid de masheen,” and have “a muss” whenever they feel like it, without interference by the authorities.
Speaking of his last meeting with Judge Douglas, Mr. Lincoln said: “One day Douglas came rushing in and said he had just got a telegraph dispatch from some friends in Illinois urging him to come out and help set things right in Egypt, and that he would go, or stay in Washington, just where I thought he could do the most good.
“I told him to do as he chose, but that probably he could do best in Illinois. Upon that he shook hands with me, and hurried away to catch the next train. I never saw him again.”
Lincoln was one of the attorneys in a case of considerable importance, court being held in a very small and dilapidated schoolhouse out in the country; Lincoln was compelled to stoop very much in order to enter the door, and the seats were so low that he doubled up his legs like a jackknife.
Lincoln was obliged to sit upon a school bench, and just in front of him was another, making the distance between him and the seat in front of him very narrow and uncomfortable.
His position was almost unbearable, and in order to carry out his preference which he secured as often as possible, and that was “to sit as near to the jury as convenient,” he took advantage of his discomfort and finally said to the Judge on the “bench”:
“Your Honor, with your permission, I’ll sit up nearer to the gentlemen of the jury, for it hurts my legs less to rub my calves against the bench than it does to skin my shins.”
When Mr. Lincoln had prepared his brief letter accepting the Presidential nomination he took it to Dr. Newton Bateman, the State Superintendent of Education.
“Mr. Schoolmaster,” he said, “here is my letter of acceptance. I am not very strong on grammar and I wish you to see if it is all right. I wouldn’t like to have any mistakes in it.”.
The doctor took the letter and after reading it, said:
“There is only one change I should suggest, Mr. Lincoln, you have written ‘It shall be my care to not violate or disregard it in any part,’ you should have written ‘not to violate.’ Never split an infinitive, is the rule.”
Mr. Lincoln took the manuscript, regarding it a moment with a puzzled air, “So you think I better put those two little fellows end to end, do you?” he said as he made the change.
Reuben and Charles Grigsby were married in Spencer county, Indiana, on the same day to Elizabeth Ray and Matilda Hawkins, respectively. They met the next day at the home of Reuben Grigsby, Sr., and held a double infare, to which most of the county was invited, with the exception of the Lincolns. This Abraham duly resented, and it resulted in his first attempt at satirical writing, which he called “The Chronicles of Reuben.”
The manuscript was lost, and not recovered until 1865, when a house belonging to one of the Grigsbys was torn down. In the loft a boy found a roll of musty old papers, and was intently reading them, when he was asked what he was doing.
“Reading a portion of the Scriptures that haven’t been revealed yet,” was the response. This was Lincoln’s “Chronicles,” which is herewith given:
“THE CHRONICLES OF REUBEN.”
“Now, there was a man whose name was Reuben, and the same was very great in substance, in horses and cattle and swine, and a very great household.
“It came to pass when the sons of Reuben grew up that they were desirous of taking to themselves wives, and, being too well known as to honor in their own country, they took a journey into a far country and there procured for themselves wives.
“It came to pass also that when they were about to make the return home they sent a messenger before them to bear the tidings to their parents.
“These, inquiring of the messenger what time their sons and wives would come, made a great feast and called all their kinsmen and neighbors in, and made great preparation.
“When the time drew nigh, they sent out two men to meet the grooms and their brides, with a trumpet to welcome them, and to accompany them.
“When they came near unto the house of Reuben, the father, the messenger came before them and gave a shout, and the whole multitude ran out with shouts of joy and music, playing on all kinds of instruments.
“Some were playing on harps, some on viols, and some blowing on rams’ horns.
“Some also were casting dust and ashes toward Heaven, and chief among them all was Josiah, blowing his bugle and making sounds so great the neighboring hills and valleys echoed with the resounding acclamation.
“When they had played and their harps had sounded till the grooms and brides approached the gates, Reuben, the father, met them and welcomed them to his house.
“The wedding feast being now ready, they were all invited to sit down and eat, placing the bridegrooms and their brides at each end of the table.
“Waiters were then appointed to serve and wait on the guests. When all had eaten and were full and merry, they went out again and played and sung till night.
“And when they had made an end of feasting and rejoicing the multitude dispersed, each going to his own home.
“The family then took seats with their waiters to converse while preparations were being made in two upper chambers for the brides and grooms.
“This being done, the waiters took the two brides upstairs, placing one in a room at the right hand of the stairs and the other on the left.
“The waiters came down, and Nancy, the mother, then gave directions to the waiters of the bridegrooms, and they took them upstairs, but placed them in the wrong rooms.
“The waiters then all came downstairs.
“But the mother, being fearful of a mistake, made inquiry of the waiters, and learning the true facts, took the light and sprang upstairs.
“It came to pass she ran to one of the rooms and exclaimed, ‘O Lord, Reuben, you are with the wrong wife.’
“The young men, both alarmed at this, ran out with such violence against each other, they came near knocking each other down.
“The tumult gave evidence to those below that the mistake was certain.
“At last they all came down and had a long conversation about who made the mistake, but it could not be decided.
“So ended the chapter.”
The original manuscript of “The Chronicles of Reuben” was last in the possession of Redmond Grigsby, of Rockport, Indiana. A newspaper which had obtained a copy of the “Chronicles,” sent a reporter to interview Elizabeth Grigsby, or Aunt Betsy, as she was called, and asked her about the famous manuscript and the mistake made at the double wedding.
“Yes, they did have a joke on us,” said Aunt Betsy. “They said my man got into the wrong room and Charles got into my room. But it wasn’t so. Lincoln just wrote that for mischief. Abe and my man often laughed about that.”
An officer, having had some trouble with General Sherman, being very angry, presented himself before Mr. Lincoln, who was visiting the camp, and said, “Mr. President, I have a cause of grievance. This morning I went to General Sherman and he threatened to shoot me.”
“Threatened to shoot you?” asked Mr. Lincoln. “Well, (in a stage whisper) if I were you I would keep away from him; if he threatens to shoot, I would not trust him, for I believe he would do it.”
Early in the Presidential campaign of 1864, President Lincoln said one night to a late caller at the White House:
“We have met the enemy and they are ‘ourn!’ I think the cabal of obstructionists ‘am busted.’ I feel certain that, if I live, I am going to be re-elected. Whether I deserve to be or not, it is not for me to say; but on the score even of remunerative chances for speculative service, I now am inspired with the hope that our disturbed country further requires the valuable services of your humble servant. ‘Jordan has been a hard road to travel,’ but I feel now that, notwithstanding the enemies I have made and the faults I have committed, I’ll be dumped on the right side of that stream.
“I hope, however, that I may never have another four years of such anxiety, tribulation and abuse. My only ambition is and has been to put down the rebellion and restore peace, after which I want to resign my office, go abroad, take some rest, study foreign governments, see something of foreign life, and in my old age die in peace with all of the good of God’s creatures.”
An old acquaintance of the President visited him in Washington. Lincoln desired to give him a place. Thus encouraged, the visitor, who was an honest man, but wholly inexperienced in public affairs or business, asked for a high office, Superintendent of the Mint.
The President was aghast, and said: “Good gracious! Why didn’t he ask to be Secretary of the Treasury, and have done with it?”
Afterward, he said: “Well, now, I never thought Mr.—— had anything more than average ability, when we were young men together. But, then, I suppose he thought the same thing about me, and—here I am!”
At the celebrated Peace Conference, whereat there was much “pow-wow” and no result, President Lincoln, in response to certain remarks by the Confederate commissioners, commented with some severity upon the conduct of the Confederate leaders, saying they had plainly forfeited all right to immunity from punishment for their treason.
Being positive and unequivocal in stating his views concerning individual treason, his words were of ominous import. There was a pause, during which Commissioner Hunter regarded the speaker with a steady, searching look. At length, carefully measuring his words, Mr. Hunter said:
“Then, Mr. President, if we understand you correctly, you think that we of the Confederacy have committed treason; are traitors to your Government; have forfeited our rights, and are proper subjects for the hangman. Is not that about what your words imply?”
“Yes,” replied President Lincoln, “you have stated the proposition better than I did. That is about the size of it!”
Another pause, and a painful one succeeded, and then Hunter, with a pleasant smile remarked:
“Well, Mr. Lincoln, we have about concluded that we shall not be hanged as long as you are President—if we behave ourselves.”
And Hunter meant what he said.
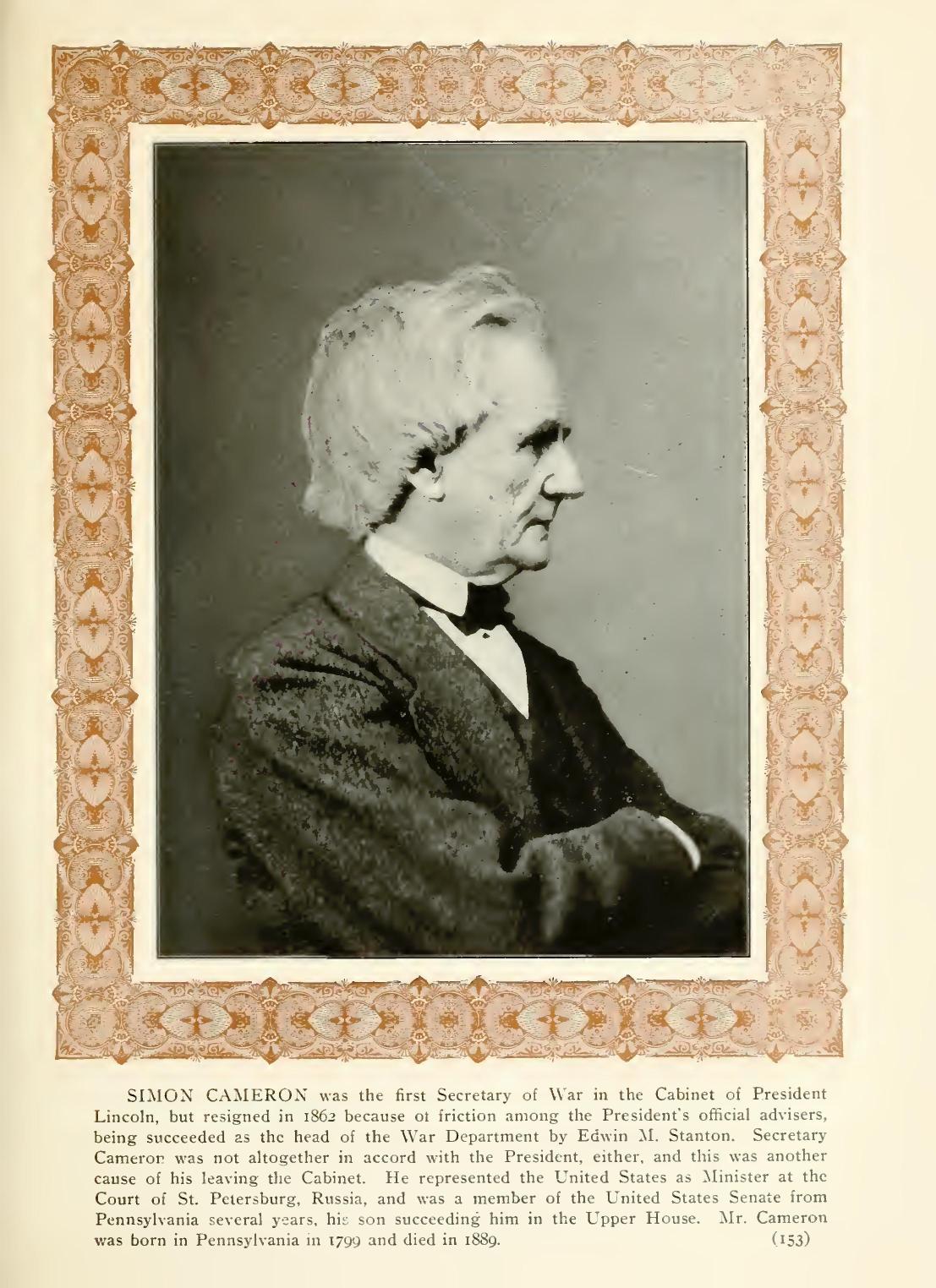
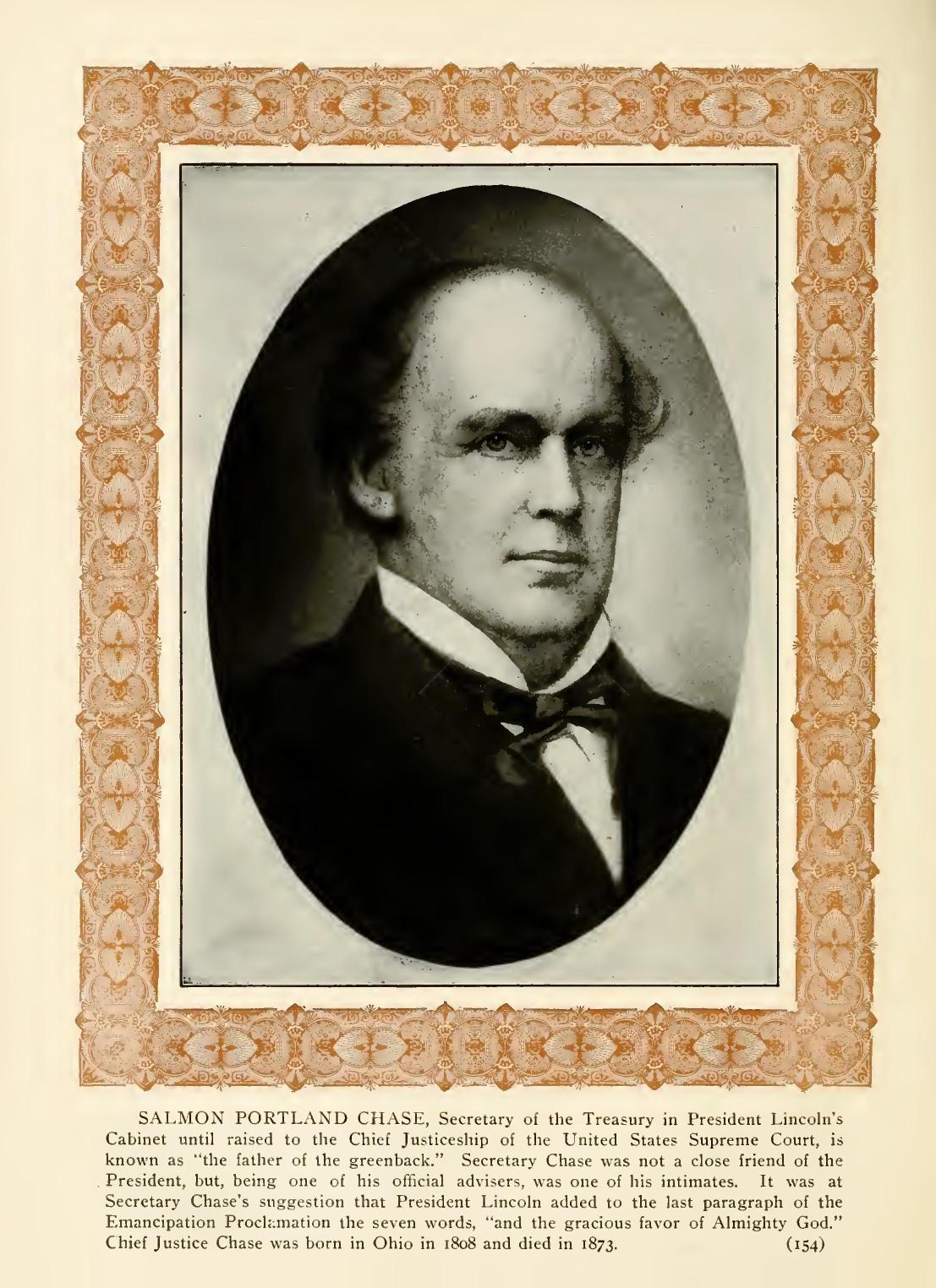




On one occasion, in going to meet an appointment in the southern part of the Sucker State—that section of Illinois called Egypt—Lincoln, with other friends, was traveling in the “caboose” of a freight train, when the freight was switched off the main track to allow a special train to pass.
Lincoln’s more aristocratic rival (Stephen A. Douglas) was being conveyed to the same town in this special. The passing train was decorated with banners and flags, and carried a band of music, which was playing “Hail to the Chief.”
As the train whistled past, Lincoln broke out in a fit of laughter, and said: “Boys, the gentleman in that car evidently smelt no royalty in our carriage.”
Ward Lamon told this story of President Lincoln, whom he found one day in a particularly gloomy frame of mind. Lamon said:
“The President remarked, as I came in, ‘I fear I have made Senator Wade, of Ohio, my enemy for life.’
“‘How?’ I asked.
“‘Well,’ continued the President, ‘Wade was here just now urging me to dismiss Grant, and, in response to something he said, I remarked, “Senator, that reminds me of a story.”’
“‘What did Wade say?’ I inquired of the President.
“‘He said, in a petulant way,’ the President responded, ‘“It is with you, sir, all story, story! You are the father of every military blunder that has been made during the war. You are on your road to hell, sir, with this government, by your obstinacy, and you are not a mile off this minute.”’
“‘What did you say then?’
“I good-naturedly said to him,’ the President replied, ‘“Senator, that is just about from here to the Capitol, is it not?” He was very angry, grabbed up his hat and cane, and went away.’”
President Lincoln had not been in the White House very long before Mrs. Lincoln became seized with the idea that a fine new barouche was about the proper thing for “the first lady in the land.” The President did not care particularly about it one way or the other, and told his wife to order whatever she wanted.
Lincoln forgot all about the new vehicle, and was overcome with astonishment one afternoon when, having acceded to Mrs. Lincoln’s desire to go driving, he found a beautiful barouche standing in front of the door of the White House.
His wife watched him with an amused smile, but the only remark he made was, “Well, Mary, that’s about the slickest ‘glass hack’ in town, isn’t it?”
Lincoln, in the days of his youth, was often unfaithful to his Quaker traditions. On the day of election in 1840, word came to him that one Radford, a Democratic contractor, had taken possession of one of the polling places with his workmen, and was preventing the Whigs from voting. Lincoln started off at a gait which showed his interest in the matter in hand.
He went up to Radford and persuaded him to leave the polls, remarking at the same time: “Radford, you’ll spoil and blow, if you live much longer.”
Radford’s prudence prevented an actual collision, which, it is said, Lincoln regretted. He told his friend Speed he wanted Radford to show fight so that he might “knock him down and leave him kicking.”
President Lincoln was at all times an advocate of peace, provided it could be obtained honorably and with credit to the United States. As to the cause of the Civil War, which side of Mason and Dixon’s line was responsible for it, who fired the first shots, who were the aggressors, etc., Lincoln did not seem to bother about; he wanted to preserve the Union, above all things. Slavery, he was assured, was dead, but he thought the former slaveholders should be recompensed.
To illustrate his feelings in the matter he told this story:
“Some of the supporters of the Union cause are opposed to accommodate or yield to the South in any manner or way because the Confederates began the war; were determined to take their States out of the Union, and, consequently, should be held responsible to the last stage for whatever may come in the future. Now this reminds me of a good story I heard once, when I lived in Illinois.
“A vicious bull in a pasture took after everybody who tried to cross the lot, and one day a neighbor of the owner was the victim. This man was a speedy fellow and got to a friendly tree ahead of the bull, but not in time to climb the tree. So he led the enraged animal a merry race around the tree, finally succeeding in seizing the bull by the tail.
“The bull, being at a disadvantage, not able to either catch the man or release his tail, was mad enough to eat nails; he dug up the earth with his feet, scattered gravel all around, bellowed until you could hear him for two miles or more, and at length broke into a dead run, the man hanging onto his tail all the time.
“While the bull, much out of temper, was legging it to the best of his ability, his tormentor, still clinging to the tail, asked, ‘Darn you, who commenced this fuss?’
“It’s our duty to settle this fuss at the earliest possible moment, no matter who commenced it. That’s my idea of it.”
When General W. T. Sherman, November 12th, 1864, severed all communication with the North and started for Savannah with his magnificent army of sixty thousand men, there was much anxiety for a month as to his whereabouts. President Lincoln, in response to an inquiry, said: “I know what hole Sherman went in at, but I don’t know what hole he’ll come out at.”
Colonel McClure had been in consultation with the President one day, about two weeks after Sherman’s disappearance, and in this connection related this incident:
“I was leaving the room, and just as I reached the door the President turned around, and, with a merry twinkling of the eye, inquired, ‘McClure, wouldn’t you like to hear something from Sherman?’
“The inquiry electrified me at the instant, as it seemed to imply that Lincoln had some information on the subject. I immediately answered, ‘Yes, most of all, I should like to hear from Sherman.’
“To this President Lincoln answered, with a hearty laugh: ‘Well, I’ll be hanged if I wouldn’t myself.’”
Although himself a most polished, even a fastidious, gentleman, Senator Sumner never allowed Lincoln’s homely ways to hide his great qualities. He gave him a respect and esteem at the start which others accorded only after experience. The Senator was most tactful, too, in his dealings with Mrs. Lincoln, and soon had a firm footing in the household. That he was proud of this, perhaps a little boastful, there is no doubt.
Lincoln himself appreciated this. “Sumner thinks he runs me,” he said, with an amused twinkle, one day.
When Hood’s army had been scattered into fragments, President Lincoln, elated by the defeat of what had so long been a menacing force on the borders of Tennessee was reminded by its collapse of the fate of a savage dog belonging to one of his neighbors in the frontier settlements in which he lived in his youth. “The dog,” he said, “was the terror of the neighborhood, and its owner, a churlish and quarrelsome fellow, took pleasure in the brute’s forcible attitude.
“Finally, all other means having failed to subdue the creature, a man loaded a lump of meat with a charge of powder, to which was attached a slow fuse; this was dropped where the dreaded dog would find it, and the animal gulped down the tempting bait.
“There was a dull rumbling, a muffled explosion, and fragments of the dog were seen flying in every direction. The grieved owner, picking up the shattered remains of his cruel favorite, said: ‘He was a good dog, but as a dog, his days of usefulness are over.’ Hood’s army was a good army,” said Lincoln, by way of comment, “and we were all afraid of it, but as an army, its usefulness is gone.”
Judge Baldwin, of California, being in Washington, called one day on General Halleck, then Commander-in-Chief of the Union forces, and, presuming upon a familiar acquaintance in California a few years since, solicited a pass outside of our lines to see a brother in Virginia, not thinking that he would meet with a refusal, as both his brother and himself were good Union men.
“We have been deceived too often,” said General Halleck, “and I regret I can’t grant it.”
Judge B. then went to Stanton, and was very briefly disposed of with the same result. Finally, he obtained an interview with Mr. Lincoln, and stated his case.
“Have you applied to General Halleck?” inquired the President.
“Yes, and met with a flat refusal,” said Judge B.
“Then you must see Stanton,” continued the President.
“I have, and with the same result,” was the reply.
“Well, then,” said Mr. Lincoln, with a smile, “I can do nothing; for you must know that I have very little influence with this Administration, although I hope to have more with the next.”
Many ladies attended the famous debates between Lincoln and Douglas, and they were the most unprejudiced listeners. “I can recall only one fact of the debates,” says Mrs. William Crotty, of Seneca, Illinois, “that I felt so sorry for Lincoln while Douglas was speaking, and then to my surprise I felt so sorry for Douglas when Lincoln replied.”
The disinterested to whom it was an intellectual game, felt the power and charm of both men.
“What made the deepest impression upon you?” inquired a friend one day, “when you stood in the presence of the Falls of Niagara, the greatest of natural wonders?”
“The thing that struck me most forcibly when I saw the Falls,” Lincoln responded, with characteristic deliberation, “was, where in the world did all that water come from?”
The second election of Abraham Lincoln to the Presidency of the United States was the reward of his courage and genius bestowed upon him by the people of the Union States. General George B. McClellan was his opponent in 1864 upon the platform that “the War is a failure,” and carried but three States—New Jersey, Delaware and Kentucky. The States which did not think the War was a failure were those in New England, New York, Pennsylvania, all the Western commonwealths, West Virginia, Tennessee, Louisiana, Arkansas and the new State of Nevada, admitted into the Union on October 31st. President Lincoln’s popular majority over McClellan, who never did much toward making the War a success, was more than four hundred thousand. Underneath the cartoon reproduced here, from “Harper’s Weekly” of November 26th, 1864, were the words, “Long Abraham Lincoln a Little Longer.”
But the beloved President’s time upon earth was not to be much longer, as he was assassinated just one month and ten days after his second inauguration. Indeed, the words, “a little longer,” printed below the cartoon, were strangely prophetic, although not intended to be such.
The people of the United States had learned to love “Long Abe,” their affection being of a purely personal nature, in the main. No other Chief Executive was regarded as so sincerely the friend of the great mass of the inhabitants of the Republic as Lincoln. He was, in truth, one of “the common people,” having been born among them, and lived as one of them.
Lincoln’s great height made him an easy subject for the cartoonist, and they used it in his favor as well as against him.
A Commissioner to the Hawaiian Islands was to be appointed, and eight applicants had filed their papers, when a delegation from the South appeared at the White House on behalf of a ninth. Not only was their man fit—so the delegation urged—but was also in bad health, and a residence in that balmy climate would be of great benefit to him.
The President was rather impatient that day, and before the members of the delegation had fairly started in, suddenly closed the interview with this remark:
“Gentlemen, I am sorry to say that there are eight other applicants for that place, and they are all ‘sicker’n’ your man.”
An officer of low volunteer rank persisted in telling and re-telling his troubles to the President on a summer afternoon when Lincoln was tired and careworn.
After listening patiently, he finally turned upon the man, and, looking wearily out upon the broad Potomac in the distance, said in a peremptory tone that ended the interview:
“Now, my man, go away, go away. I cannot meddle in your case. I could as easily bail out the Potomac River with a teaspoon as attend to all the details of the army.”
When the Emancipation Proclamation was taken to Mr. Lincoln by Secretary Seward, for the President’s signature, Mr. Lincoln took a pen, dipped it in the ink, moved his hand to the place for the signature, held it a moment, then removed his hand and dropped the pen. After a little hesitation, he again took up the pen and went through the same movement as before. Mr. Lincoln then turned to Mr. Seward and said:
“I have been shaking hands since nine o’clock this morning, and my right arm is almost paralyzed. If my name ever goes into history, it will be for this act, and my whole soul is in it. If my hand trembles when I sign the Proclamation, all who examine the document hereafter will say, ‘He hesitated.’”
He then turned to the table, took up the pen again, and slowly, firmly wrote “Abraham Lincoln,” with which the whole world is now familiar.
He then looked up, smiled, and said, “That will do.”
Mr. Lovejoy, heading a committee of Western men, discussed an important scheme with the President, and the gentlemen were then directed to explain it to Secretary of War Stanton.
Upon presenting themselves to the Secretary, and showing the President’s order, the Secretary said: “Did Lincoln give you an order of that kind?”
“He did, sir.”
“Then he is a d—d fool,” said the angry Secretary.
“Do you mean to say that the President is a d—d fool?” asked Lovejoy, in amazement.
“Yes, sir, if he gave you such an order as that.”
The bewildered Illinoisan betook himself at once to the President and related the result of the conference.
“Did Stanton say I was a d—d fool?” asked Lincoln at the close of the recital.
“He did, sir, and repeated it.”
After a moment’s pause, and looking up, the President said: “If Stanton said I was a d—d fool, then I must be one, for he is nearly always right, and generally says what he means. I will slip over and see him.”
A good story is told of how Mrs. Lincoln made a little surprise for her husband.
In the early days it was customary for lawyers to go from one county to another on horseback, a journey which often required several weeks. On returning from one of these trips, late one night, Mr. Lincoln dismounted from his horse at the familiar corner and then turned to go into the house, but stopped; a perfectly unknown structure was before him. Surprised, and thinking there must be some mistake, he went across the way and knocked at a neighbor’s door. The family had retired, and so called out:
“Who’s there?”
“Abe Lincoln,” was the reply. “I am looking for my house. I thought it was across the way, but when I went away a few weeks ago there was only a one-story house there and now there is a two-story house in its place. I think I must be lost.”
The neighbors then explained that Mrs. Lincoln had added another story during his absence. And Mr. Lincoln laughed and went to his remodeled house.
The persistence of office-seekers nearly drove President Lincoln wild. They slipped in through the half-opened doors of the Executive Mansion; they dogged his steps if he walked; they edged their way through the crowds and thrust their papers in his hands when he rode; and, taking it all in all, they well-nigh worried him to death.
He once said that if the Government passed through the Rebellion without dismemberment there was the strongest danger of its falling a prey to the rapacity of the office-seeking class.
“This human struggle and scramble for office, for a way to live without work, will finally test the strength of our institutions,” were the words he used.
On April 20th a delegation from Baltimore appeared at the White House and begged the President that troops for Washington be sent around and not through Baltimore.
President Lincoln replied, laughingly: “If I grant this concession, you will be back tomorrow asking that no troops be marched ‘around’ it.”
The President was right. That afternoon, and again on Sunday and Monday, committees sought him, protesting that Maryland soil should not be “polluted” by the feet of soldiers marching against the South.
The President had but one reply: “We must have troops, and as they can neither crawl under Maryland nor fly over it, they must come across it.”
The Governor-General of Canada, with some of his principal officers, visited President Lincoln in the summer of 1864.
They had been very troublesome in harboring blockade runners, and they were said to have carried on a large trade from their ports with the Confederates. Lincoln treated his guests with great courtesy.
After a pleasant interview, the Governor, alluding to the coming Presidential election said, jokingly, but with a grain of sarcasm: “I understand Mr. President, that everybody votes in this country. If we remain until November, can we vote?”
“You remind me,” replied the President, “of a countryman of yours, a green emigrant from Ireland. Pat arrived on election day, and perhaps was as eager as your Excellency to vote, and to vote early, and late and often.
“So, upon landing at Castle Garden, he hastened to the nearest voting place, and as he approached, the judge who received the ballots inquired, ‘Who do you want to vote for? On which side are you?’ Poor Pat was embarrassed; he did not know who were the candidates. He stopped, scratched his head, then, with the readiness of his countrymen, he said:
“‘I am forninst the Government, anyhow. Tell me, if your Honor plase: which is the rebellion side, and I’ll tell you haw I want to vote. In ould Ireland, I was always on the rebellion side, and, by Saint Patrick, I’ll do that same in America.’ Your Excellency,” said Mr. Lincoln, “would, I should think, not be at all at a loss on which side to vote!”
One night, about eleven o’clock, Colonel A. K. McClure, whose intimacy with President Lincoln was so great that he could obtain admittance to the Executive Mansion at any and all hours, called at the White House to urge Mr. Lincoln to remove General Grant from command.
After listening patiently for a long time, the President, gathering himself up in his chair, said, with the utmost earnestness:
“I can’t spare this man; he fights!”
In relating the particulars of this interview, Colonel McClure said:
“That was all he said, but I knew that it was enough, and that Grant was safe in Lincoln’s hands against his countless hosts of enemies. The only man in all the nation who had the power to save Grant was Lincoln, and he had decided to do it. He was not influenced by any personal partiality for Grant, for they had never met.
“It was not until after the battle of Shiloh, fought on the 6th and 7th of April, 1862, that Lincoln was placed in a position to exercise a controlling influence in shaping the destiny of Grant. The first reports from the Shiloh battle-field created profound alarm throughout the entire country, and the wildest exaggerations were spread in a floodtide of vituperation against Grant.
“The few of to-day who can recall the inflamed condition of public sentiment against Grant caused by the disastrous first day’s battle at Shiloh will remember that he was denounced as incompetent for his command by the public journals of all parties in the North, and with almost entire unanimity by Senators and Congressmen, regardless of political affinities.
“I appealed to Lincoln for his own sake to remove Grant at once, and in giving my reasons for it I simply voiced the admittedly overwhelming protest from the loyal people of the land against Grant’s continuance in command.
“I did not forget that Lincoln was the one man who never allowed himself to appear as wantonly defying public sentiment. It seemed to me impossible for him to save Grant without taking a crushing load of condemnation upon himself; but Lincoln was wiser than all those around him, and he not only saved Grant, but he saved him by such well-concerted effort that he soon won popular applause from those who were most violent in demanding Grant’s dismissal.”
During the Lincoln-Douglas joint debates of 1858, the latter accused Lincoln of having, when in Congress, voted against the appropriation for supplies to be sent the United States soldiers in Mexico. In reply, Lincoln said: “This is a perversion of the facts. I was opposed to the policy of the administration in declaring war against Mexico; but when war was declared I never failed to vote for the support of any proposition looking to the comfort of our poor fellows who were maintaining the dignity of our flag in a war that I thought unnecessary and unjust.”
He gradually became more and more excited; his voice thrilled and his whole frame shook. Sitting on the stand was O. B. Ficklin, who had served in Congress with Lincoln in 1847. Lincoln reached back, took Ficklin by the coat-collar, back of his neck, and in no gentle manner lifted him from his seat as if he had been a kitten, and roared: “Fellow-citizens, here is Ficklin, who was at that time in Congress with me, and he knows it is a lie.”
He shook Ficklin until his teeth chattered. Fearing he would shake Ficklin’s head off, Ward Lamon grasped Lincoln’s hand and broke his grip.
After the speaking was over, Ficklin, who had warm personal friendship with him, said: “Lincoln, you nearly shook all the Democracy out of me to-day.”
President Lincoln was censured for appointing one that had zealously opposed his second term.
He replied: “Well, I suppose Judge E., having been disappointed before, did behave pretty ugly, but that wouldn’t make him any less fit for the place; and I think I have Scriptural authority for appointing him.
“You remember when the Lord was on Mount Sinai getting out a commission for Aaron, that same Aaron was at the foot of the mountain making a false god for the people to worship. Yet Aaron got his commission, you know.”
At the time of Lincoln’s nomination, at Chicago, Mr. Newton Bateman, Superintendent of Public Instruction for the State of Illinois, occupied a room adjoining and opening into the Executive Chamber at Springfield. Frequently this door was open during Mr. Lincoln’s receptions, and throughout the seven months or more of his occupation he saw him nearly every day. Often, when Mr. Lincoln was tired, he closed the door against all intruders, and called Mr. Bateman into his room for a quiet talk. On one of these occasions, Mr. Lincoln took up a book containing canvass of the city of Springfield, in which he lived, showing the candidate for whom each citizen had declared it his intention to vote in the approaching election. Mr. Lincoln’s friends had, doubtless at his own request, placed the result of the canvass in his hands. This was towards the close of October, and only a few days before election. Calling Mr. Bateman to a seat by his side, having previously locked all the doors, he said:
“Let us look over this book; I wish particularly to see how the ministers if Springfield are going to vote.” The leaves were turned, one by one, and as the names were examined Mr. Lincoln frequently asked if this one and that one was not a minister, or an elder, or a member of such and such a church, and sadly expressed his surprise on receiving an affirmative answer. In that manner he went through the book, and then he closed it, and sat silently for some minutes regarding a memorandum in pencil which lay before him. At length he turned to Mr. Bateman, with a face full of sadness, and said:
“Here are twenty-three ministers of different denominations, and all of them are against me but three, and here are a great many prominent members of churches, a very large majority are against me. Mr. Bateman, I am not a Christian—God knows I would be one—but I have carefully read the Bible, and I do not so understand this book,” and he drew forth a pocket New Testament.
“These men well know,” he continued, “that I am for freedom in the Territories, freedom everywhere, as free as the Constitution and the laws will permit, and that my opponents are for slavery. They know this, and yet, with this book in their hands, in the light of which human bondage cannot live a moment, they are going to vote against me; I do not understand it at all.”
Here Mr. Lincoln paused—paused for long minutes, his features surcharged with emotion. Then he rose and walked up and down the reception-room in the effort to retain or regain his self-possession. Stopping at last, he said, with a trembling voice and cheeks wet with tears:
“I know there is a God, and that He hates injustice and slavery. I see the storm coming, and I know that His hand is in it. If He has a place and work for me, and I think He has, I believe I am ready. I am nothing, but Truth is everything. I know I am right, because I know that liberty is right, for Christ teaches it, and Christ is God. I have told them that a house divided against itself cannot stand; and Christ and Reason say the same, and they will find it so.
“Douglas doesn’t care whether slavery is voted up or down, but God cares, and humanity cares, and I care; and with God’s help I shall not fail. I may not see the end, but it will come, and I shall be vindicated; and these men will find they have not read their Bible right.”
Much of this was uttered as if he were speaking to himself, and with a sad, earnest solemnity of manner impossible to be described. After a pause he resumed:
“Doesn’t it seem strange that men can ignore the moral aspect of this contest? No revelation could make it plainer to me that slavery or the Government must be destroyed. The future would be something awful, as I look at it, but for this rock on which I stand” (alluding to the Testament which he still held in his hand), “especially with the knowledge of how these ministers are going to vote. It seems as if God had borne with this thing (slavery) until the teachers of religion have come to defend it from the Bible, and to claim for it a divine character and sanction; and now the cup of iniquity is full, and the vials of wrath will be poured out.”
Everything he said was of a peculiarly deep, tender, and religious tone, and all was tinged with a touching melancholy. He repeatedly referred to his conviction that the day of wrath was at hand, and that he was to be an actor in the terrible struggle which would issue in the overthrow of slavery, although he might not live to see the end.
After further reference to a belief in the Divine Providence and the fact of God in history, the conversation turned upon prayer. He freely stated his belief in the duty, privilege, and efficacy of prayer, and intimated, in no unmistakable terms, that he had sought in that way Divine guidance and favor. The effect of this conversation upon the mind of Mr. Bateman, a Christian gentleman whom Mr. Lincoln profoundly respected, was to convince him that Mr. Lincoln had, in a quiet way, found a path to the Christian standpoint—that he had found God, and rested on the eternal truth of God. As the two men were about to separate, Mr. Bateman remarked:
“I have not supposed that you were accustomed to think so much upon this class of subjects; certainly your friends generally are ignorant of the sentiments you have expressed to me.”
He replied quickly: “I know they are, but I think more on these subjects than upon all others, and I have done so for years; and I am willing you should know it.”




Secretary of War Stanton told the President the following story, which greatly amused the latter, as he was especially fond of a joke at the expense of some high military or civil dignitary.
Stanton had little or no sense of humor.
When Secretary Stanton was making a trip up the Broad River in North Carolina, in a tugboat, a Federal picket yelled out, “What have you got on board of that tug?”
The severe and dignified answer was, “The Secretary of War and Major-General Foster.”
Instantly the picket roared back, “We’ve got Major-Generals enough up here. Why don’t you bring us up some hardtack?”
A story told by a Cabinet member tended to show how accurately Lincoln could calculate political results in advance—a faculty which remained with him all his life.
“A friend, who was a Democrat, had come to him early in the canvass and told him he wanted to see him elected, but did not like to vote against his party; still he would vote for him, if the contest was to be so close that every vote was needed.
“A short time before the election Lincoln said to him: ‘I have got the preacher, and I don’t want your vote.’”
When General Halleck was Commander-in-Chief of the Union forces, with headquarters at Washington, President Lincoln unconsciously played a big practical joke upon that dignified officer. The President had spent the night at the Soldiers’ Home, and the next morning asked Captain Derickson, commanding the company of Pennsylvania soldiers, which was the Presidential guard at the White House and the Home—wherever the President happened to be—to go to town with him.
Captain Derickson told the story in a most entertaining way:
“When we entered the city, Mr. Lincoln said he would call at General Halleck’s headquarters and get what news had been received from the army during the night. I informed him that General Cullum, chief aid to General Halleck, was raised in Meadville, and that I knew him when I was a boy.
“He replied, ‘Then we must see both the gentlemen.’ When the carriage stopped, he requested me to remain seated, and said he would bring the gentlemen down to see me, the office being on the second floor. In a short time the President came down, followed by the other gentlemen. When he introduced them to me, General Cullum recognized and seemed pleased to see me.
“In General Halleck I thought I discovered a kind of quizzical look, as much as to say, ‘Isn’t this rather a big joke to ask the Commander-in-Chief of the army down to the street to be introduced to a country captain?’”
A gentleman, visiting a hospital at Washington, heard an occupant of one of the beds laughing and talking about the President, who had been there a short time before and gladdened the wounded with some of his stories. The soldier seemed in such good spirits that the gentleman inquired:
“You must be very slightly wounded?”
“Yes,” replied the brave fellow, “very slightly—I have only lost one leg, and I’d be glad enough to lose the other, if I could hear some more of ‘Old Abe’s’ stories.”
William B. Wilson, employed in the telegraph office at the War Department, ran over to the White House one day to summon Mr. Lincoln. He described the trip back to the War Department in this manner:
“Calling one of his two younger boys to join him, we then started from the White House, between stately trees, along a gravel path which led to the rear of the old War Department building. It was a warm day, and Mr. Lincoln wore as part of his costume a faded gray linen duster which hung loosely around his long gaunt frame; his kindly eye was beaming with good nature, and his ever-thoughtful brow was unruffled.
“We had barely reached the gravel walk before he stooped over, picked up a round smooth pebble, and shooting it off his thumb, challenged us to a game of ‘followings,’ which we accepted. Each in turn tried to hit the outlying stone, which was being constantly projected onward by the President. The game was short, but exciting; the cheerfulness of childhood, the ambition of young manhood, and the gravity of the statesman were all injected into it.
“The game was not won until the steps of the War Department were reached. Every inch of progression was toughly contested, and when the President was declared victor, it was only by a hand span. He appeared to be as much pleased as if he had won a battle.”
Because of the blockade, by the Union fleets, of the Southern cotton ports, England was deprived of her supply of cotton, and scores of thousands of British operatives were thrown out of employment by the closing of the cotton mills at Manchester and other cities in Great Britain. England (John Bull) felt so badly about this that the British wanted to go to war on account of it, but when the United States eagle ruffled up its wings the English thought over the business and concluded not to fight.
“Harper’s Weekly” of May 16th, 1863, contained the cartoon we reproduce, which shows John Bull as manifesting much anxiety regarding the cotton he had bought from the Southern planters, but which the latter could not deliver. Beneath the cartoon is this bit of dialogue between John Bull and President Lincoln: MR. BULL (confiding creature): “Hi want my cotton, bought at fi’pence a pound.”
MR. LINCOLN: “Don’t know anything about it, my dear sir. Your friends, the rebels, are burning all the cotton they can find, and I confiscate the rest. Good-morning, John!”
As President Lincoln has a big fifteen-inch gun at his side, the black muzzle of which is pressed tightly against Mr. Bull’s waistcoat, the President, to all appearances, has the best of the argument “by a long shot.” Anyhow, Mr. Bull had nothing more to say, but gave the cotton matter up as a bad piece of business, and pocketed the loss.
President Lincoln’s first conclusion (that Mason and Slidell should be released) was the real ground on which the Administration submitted. “We must stick to American principles concerning the rights of neutrals.” It was to many, as Secretary of the Treasury Chase declared it was to him, “gall and wormwood.” James Russell Lowell’s verse expressed best the popular feeling:
We give the critters back, John, Cos Abram thought ‘twas right; It warn’t your bullyin’ clack, John, Provokin’ us to fight.
The decision raised Mr. Lincoln immeasurably in the view of thoughtful men, especially in England.
General John C. Fremont, with headquarters at St. Louis, astonished the country by issuing a proclamation declaring, among other things, that the property, real and personal, of all the persons in the State of Missouri who should take up arms against the United States, or who should be directly proved to have taken an active part with its enemies in the field, would be confiscated to public use and their slaves, if they had any, declared freemen.
The President was dismayed; he modified that part of the proclamation referring to slaves, and finally replaced Fremont with General Hunter.
Mrs. Fremont (daughter of Senator T. H. Benton), her husband’s real chief of staff, flew to Washington and sought Mr. Lincoln. It was midnight, but the President gave her an audience. Without waiting for an explanation, she violently charged him with sending an enemy to Missouri to look into Fremont’s case, and threatening that if Fremont desired to he could set up a government for himself.
“I had to exercise all the rude tact I have to avoid quarreling with her,” said Mr. Lincoln afterwards.
Lincoln’s attempt to make a lawyer of himself under adverse and unpromising circumstances—he was a bare-footed farm-hand—excited comment. And it was not to be wondered. One old man, who was yet alive as late as 1901, had often employed Lincoln to do farm work for him, and was surprised to find him one day sitting barefoot on the summit of a woodpile and attentively reading a book.
“This being an unusual thing for farm-hands in that early day to do,” said the old man, when relating the story, “I asked him what he was reading.
“‘I’m not reading,’ he answered. ‘I’m studying.’
“‘Studying what?’ I inquired.
“‘Law, sir,’ was the emphatic response.
“It was really too much for me, as I looked at him sitting there proud as Cicero. ‘Great God Almighty!’ I exclaimed, and passed on.” Lincoln merely laughed and resumed his “studies.”
In a political campaign, Lincoln once replied to Colonel Richard Taylor, a self-conceited, dandified man, who wore a gold chain and ruffled shirt. His party at that time was posing as the hard-working bone and sinew of the land, while the Whigs were stigmatized as aristocrats, ruffled-shirt gentry. Taylor making a sweeping gesture, his overcoat became torn open, displaying his finery. Lincoln in reply said, laying his hand on his jeans-clad breast:
“Here is your aristocrat, one of your silk-stocking gentry, at your service.” Then, spreading out his hands, bronzed and gaunt with toil: “Here is your rag-basin with lily-white hands. Yes, I suppose, according to my friend Taylor, I am a bloated aristocrat.”
Soon after hostilities broke out between the North and South, Congress appointed a Committee on the Conduct of the War. This committee beset Mr. Lincoln and urged all sorts of measures. Its members were aggressive and patriotic, and one thing they determined upon was that the Army of the Potomac should move. But it was not until March that they became convinced that anything would be done.
One day early in that month, Senator Chandler, of Michigan, a member of the committee, met George W. Julian. He was in high glee. “‘Old’ Abe is mad,” said Julian, “and the War will now go on.”
During one of the periods when things were at a standstill, the Washington authorities, being unable to force General McClellan to assume an aggressive attitude, President Lincoln went to the general’s headquarters to have a talk with him, but for some reason he was unable to get an audience.
Mr. Lincoln returned to the White House much disturbed at his failure to see the commander of the Union forces, and immediately sent for two general officers, to have a consultation. On their arrival, he told them he must have some one to talk to about the situation, and as he had failed to see General McClellan, he wished their views as to the possibility or probability of commencing active operations with the Army of the Potomac.
“Something’s got to be done,” said the President, emphatically, “and done right away, or the bottom will fall out of the whole thing. Now, if McClellan doesn’t want to use the army for awhile, I’d like to borrow it from him and see if I can’t do something or other with it.
“If McClellan can’t fish, he ought at least to be cutting bait at a time like this.”
After Mr. Lincoln’s nomination for the Presidency, the Executive Chamber, a large, fine room in the State House at Springfield, was set apart for him, where he met the public until after his election.
As illustrative of the nature of many of his calls, the following incident was related by Mr. Holland, an eye-witness: “Mr. Lincoln being in conversation with a gentleman one day, two raw, plainly-dressed young ‘Suckers’ entered the room, and bashfully lingered near the door. As soon as he observed them, and saw their embarrassment, he rose and walked to them, saying: ‘How do you do, my good fellows? What can I do for you? Will you sit down?’ The spokesman of the pair, the shorter of the two, declined to sit, and explained the object of the call thus: He had had a talk about the relative height of Mr. Lincoln and his companion, and had asserted his belief that they were of exactly the same height. He had come in to verify his judgment. Mr. Lincoln smiled, went and got his cane, and, placing the end of it upon the wall, said” ‘Here, young man, come under here.’ “The young man came under the cane as Mr. Lincoln held it, and when it was perfectly adjusted to his height, Mr. Lincoln said:
“‘Now, come out, and hold the cane.’
“This he did, while Mr. Lincoln stood under. Rubbing his head back and forth to see that it worked easily under the measurement, he stepped out, and declared to the sagacious fellow who was curiously looking on, that he had guessed with remarkable accuracy—that he and the young man were exactly the same height. Then he shook hands with them and sent them on their way. Mr. Lincoln would just as soon have thought of cutting off his right hand as he would have thought of turning those boys away with the impression that they had in any way insulted his dignity.”
An Ohio Senator had an appointment with President Lincoln at six o’clock, and as he entered the vestibule of the White House his attention was attracted toward a poorly clad young woman, who was violently sobbing. He asked her the cause of her distress. She said she had been ordered away by the servants, after vainly waiting many hours to see the President about her only brother, who had been condemned to death. Her story was this:
She and her brother were foreigners, and orphans. They had been in this country several years. Her brother enlisted in the army, but, through bad influences, was induced to desert. He was captured, tried and sentenced to be shot—the old story.
The poor girl had obtained the signatures of some persons who had formerly known him, to a petition for a pardon, and alone had come to Washington to lay the case before the President. Thronged as the waiting-rooms always were, she had passed the long hours of two days trying in vain to get an audience, and had at length been ordered away.
The gentleman’s feelings were touched. He said to her that he had come to see the President, but did not know as he should succeed. He told her, however, to follow him upstairs, and he would see what could be done for her.
Just before reaching the door, Mr. Lincoln came out, and, meeting his friend, said good-humoredly, “Are you not ahead of time?” The gentleman showed him his watch, with the hand upon the hour of six.
“Well,” returned Mr. Lincoln, “I have been so busy to-day that I have not had time to get a lunch. Go in and sit down; I will be back directly.”
The gentleman made the young woman accompany him into the office, and when they were seated, said to her: “Now, my good girl, I want you to muster all the courage you have in the world. When the President comes back, he will sit down in that armchair. I shall get up to speak to him, and as I do so you must force yourself between us, and insist upon his examination of your papers, telling him it is a case of life and death, and admits of no delay.” These instructions were carried out to the letter. Mr. Lincoln was at first somewhat surprised at the apparent forwardness of the young woman, but observing her distressed appearance, he ceased conversation with his friend, and commenced an examination of the document she had placed in his hands.
Glancing from it to the face of the petitioner, whose tears had broken forth afresh, he studied its expression for a moment, and then his eye fell upon her scanty but neat dress. Instantly his face lighted up.
“My poor girl,” said he, “you have come here with no Governor, or Senator, or member of Congress to plead your cause. You seem honest and truthful; and you don’t wear hoopskirts—and I will be whipped but I will pardon your brother.” And he did.
President Lincoln’s favorite son, Tad, having been sportively commissioned a lieutenant in the United States Army by Secretary Stanton, procured several muskets and drilled the men-servants of the house in the manual of arms without attracting the attention of his father. And one night, to his consternation, he put them all on duty, and relieved the regular sentries, who, seeing the lad in full uniform, or perhaps appreciating the joke, gladly went to their quarters. His brother objected; but Tad insisted upon his rights as an officer. The President laughed but declined to interfere, but when the lad had lost his little authority in his boyish sleep, the Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy of the United States went down and personally discharged the sentries his son had put on the post.
When Mr. Lincoln delivered his first inaugural he was introduced by his friend, United States Senator E. D. Baker, of Oregon. He carried a cane and a little roll—the manuscript of his inaugural address. There was moment’s pause after the introduction, as he vainly looked for a spot where he might place his high silk hat.
Stephen A. Douglas, the political antagonist of his whole public life, the man who had pressed him hardest in the campaign of 1860, was seated just behind him. Douglas stepped forward quickly, and took the hat which Mr. Lincoln held helplessly in his hand.
“If I can’t be President,” Douglas whispered smilingly to Mrs. Brown, a cousin of Mrs. Lincoln and a member of the President’s party, “I at least can hold his hat.”
Mr. Lincoln once said in a speech: “Fellow-citizens, my friend, Mr. Douglas, made the startling announcement to-day that the Whigs are all dead.
“If that be so, fellow-citizens, you will now experience the novelty of hearing a speech from a dead man; and I suppose you might properly say, in the language of the old hymn:
“‘Hark! from the tombs a doleful sound.’”
President Lincoln—as he himself put it in conversation one day with a friend—“fairly ached” for his generals to “get down to business.” These slow generals he termed “snails.”
Grant, Sherman and Sheridan were his favorites, for they were aggressive. They did not wait for the enemy to attack. Too many of the others were “lingerers,” as Lincoln called them. They were magnificent in defense, and stubborn and brave, but their names figured too much on the “waiting list.”
The greatest fault Lincoln found with so many of the commanders on the Union side was their unwillingness to move until everything was exactly to their liking.
Lincoln could not understand why these leaders of Northern armies hesitated.
When the Union forces were routed in the first battle of Bull Run, there were many civilians present, who had gone out from Washington to witness the battle. Among the number were several Congressmen. One of these was a tall, long-legged fellow, who wore a long-tailed coat and a high plug hat. When the retreat began, this Congressman was in the lead of the entire crowd fleeing toward Washington. He outran all the rest, and was the first man to arrive in the city. No person ever made such good use of long legs as this Congressman. His immense stride carried him yards at every bound. He went over ditches and gullies at a single leap, and cleared a six-foot fence with a foot to spare. As he went over the fence his plug hat blew off, but he did not pause. With his long coat-tails flying in the wind, he continued straight ahead for Washington.
Many of those behind him were scared almost to death, but the flying Congressman was such a comical figure that they had to laugh in spite of their terror.
Mr. Lincoln enjoyed the description of how this Congressman led the race from Bull’s Run, and laughed at it heartily.
“I never knew but one fellow who could run like that,” he said, “and he was a young man out in Illinois. He had been sparking a girl, much against the wishes of her father. In fact, the old man took such a dislike to him that he threatened to shoot him if he ever caught him around his premises again.
“One evening the young man learned that the girl’s father had gone to the city, and he ventured out to the house. He was sitting in the parlor, with his arm around Betsy’s waist, when he suddenly spied the old man coming around the corner of the house with a shotgun. Leaping through a window into the garden, he started down a path at the top of his speed. He was a long-legged fellow, and could run like greased lightning. Just then a jack-rabbit jumped up in the path in front of him. In about two leaps he overtook the rabbit. Giving it a kick that sent it high in the air, he exclaimed: ‘Git out of the road, gosh dern you, and let somebody run that knows how.’
“I reckon,” said Mr. Lincoln, “that the long-legged Congressman, when he saw the rebel muskets, must have felt a good deal like that young fellow did when he saw the old man’s shot-gun.”
Lincoln was a strong believer in the virtue of dealing honestly with the people.
“If you once forfeit the confidence of your fellow-citizens,” he said to a caller at the White House, “you can never regain their respect and esteem.
“It is true that you may fool all the people some of the time; you can even fool some of the people all the time; but you can’t fool all of the people all the time.”
The night President-elect Lincoln arrived at Washington, one man was observed watching Lincoln very closely as he walked out of the railroad station. Standing a little to one side, the man looked very sharply at Lincoln, and, as the latter passed, seized hold of his hand, and said in a loud tone of voice, “Abe, you can’t play that on me!”
Ward Lamon and the others with Lincoln were instantly alarmed, and would have struck the stranger had not Lincoln hastily said, “Don’t strike him! It is Washburne. Don’t you know him?”
Mr. Seward had given Congressman Washburne a hint of the time the train would arrive, and he had the right to be at the station when the train steamed in, but his indiscreet manner of loudly addressing the President-elect might have led to serious consequences to the latter.
Mrs. Rose Linder Wilkinson, who often accompanied her father, Judge Linder, in the days when he rode circuit with Mr. Lincoln, tells the following story:
“At night, as a rule, the lawyers spent awhile in the parlor, and permitted the women who happened to be along to sit with them. But after half an hour or so we would notice it was time for us to leave them. I remember traveling the circuit one season when the young wife of one of the lawyers was with him. The place was so crowded that she and I were made to sleep together. When the time came for banishing us from the parlor, we went up to our room and sat there till bed-time, listening to the roars that followed each ether swiftly while those lawyers down-stairs told stories and laughed till the rafters rang.
“In the morning Mr. Lincoln said to me: ‘Rose, did we disturb your sleep last night?’ I answered, ‘No, I had no sleep’—which was not entirely true but the retort amused him. Then the young lawyer’s wife complained to him that we were not fairly used. We came along with them, young women, and when they were having the best time we were sent away like children to go to bed in the dark.
“‘But, Madame,’ said Mr. Lincoln, ‘you would not enjoy the things we laugh at.’ And then he entered into a discussion on what have been termed his ‘broad’ stories. He deplored the fact that men seemed to remember them longer and with less effort than any others.
“My father said: ‘But, Lincoln, I don’t remember the “broad” part of your stories so much as I do the moral that is in them,’ and it was a thing in which they were all agreed.”
When President Lincoln heard of the Confederate raid at Fairfax, in which a brigadier-general and a number of valuable horses were captured, he gravely observed:
“Well, I am sorry for the horses.”
“Sorry for the horses, Mr. President!” exclaimed the Secretary of War, raising his spectacles and throwing himself back in his chair in astonishment.
“Yes,” replied Mr., Lincoln, “I can make a brigadier-general in five minutes, but it is not easy to replace a hundred and ten horses.”
Dr. Jerome Walker, of Brooklyn, told how Mr. Lincoln once administered to him a mild rebuke. The doctor was showing Mr. Lincoln through the hospital at City Point.
“Finally, after visiting the wards occupied by our invalid and convalescing soldiers,” said Dr. Walker, “we came to three wards occupied by sick and wounded Southern prisoners. With a feeling of patriotic duty, I said: ‘Mr. President, you won’t want to go in there; they are only rebels.’
“I will never forget how he stopped and gently laid his large hand upon my shoulder and quietly answered, ‘You mean Confederates!’ And I have meant Confederates ever since.
“There was nothing left for me to do after the President’s remark but to go with him through these three wards; and I could not see but that he was just as kind, his hand-shakings just as hearty, his interest just as real for the welfare of the men, as when he was among our own soldiers.”
“Old Pap,” as the soldiers called General George H. Thomas, was aggravatingly slow at a time when the President wanted him to “get a move on”; in fact, the gallant “Rock of Chickamauga” was evidently entered in a snail-race.
“Some of my generals are so slow,” regretfully remarked Lincoln one day, “that molasses in the coldest days of winter is a race horse compared to them.
“They’re brave enough, but somehow or other they get fastened in a fence corner, and can’t figure their way out.”
Joseph Medill, for many years editor of the Chicago Tribune, not long before his death, told the following story regarding the “talking to” President Lincoln gave himself and two other Chicago gentlemen who went to Washington to see about reducing Chicago’s quota of troops after the call for extra men was made by the President in 1864:
“In 1864, when the call for extra troops came, Chicago revolted. She had already sent 22,000 troops up to that time, and was drained. When the call came there were no young men to go, and no aliens except what were bought. The citizens held a mass meeting and appointed three persons, of whom I was one, to go to Washington and ask Stanton to give Cook County a new enrollment. On reaching Washington, we went to Stanton with our statement. He refused entirely to give us the desired aid. Then we went to Lincoln. ‘I cannot do it,’ he said, ‘but I will go with you to the War Department, and Stanton and I will hear both sides.’
“So we all went over to the War Department together. Stanton and General Frye were there, and they, of course, contended that the quota should not be changed. The argument went on for some time, and was finally referred to Lincoln, who had been sitting silently listening.
“I shall never forget how he suddenly lifted his head and turned on us a black and frowning face.
“‘Gentlemen,’ he said, in a voice full of bitterness, ‘after Boston, Chicago has been the chief instrument in bringing war on this country. The Northwest has opposed the South as New England has opposed the South. It is you who are largely responsible for making blood flow as it has.
“‘You called for war until we had it. You called for Emancipation, and I have given it to you. Whatever you have asked, you have had. Now you come here begging to be let off from the call for men, which I have made to carry out the war which you demanded. You ought to be ashamed of yourselves. I have a right to expect better things of you.
“‘Go home and raise your six thousand extra men. And you, Medill, you are acting like a coward. You and your Tribune have had more influence than any paper in the Northwest in making this war. You can influence great masses, and yet you cry to be spared at a moment when your cause is suffering. Go home and send us those men!’
“I couldn’t say anything. It was the first time I ever was whipped, and I didn’t have an answer. We all got up and went out, and when the door closed one of my colleagues said:
“‘Well, gentlemen, the old man is right. We ought to be ashamed of ourselves. Let us never say anything about this, but go home and raise the men.’
“And we did—six thousand men—making twenty-eight thousand in the War from a city of one hundred and fifty-six thousand. But there might have been crape on every door, almost, in Chicago, for every family had lost a son or a husband. I lost two brothers. It was hard for the mothers.”
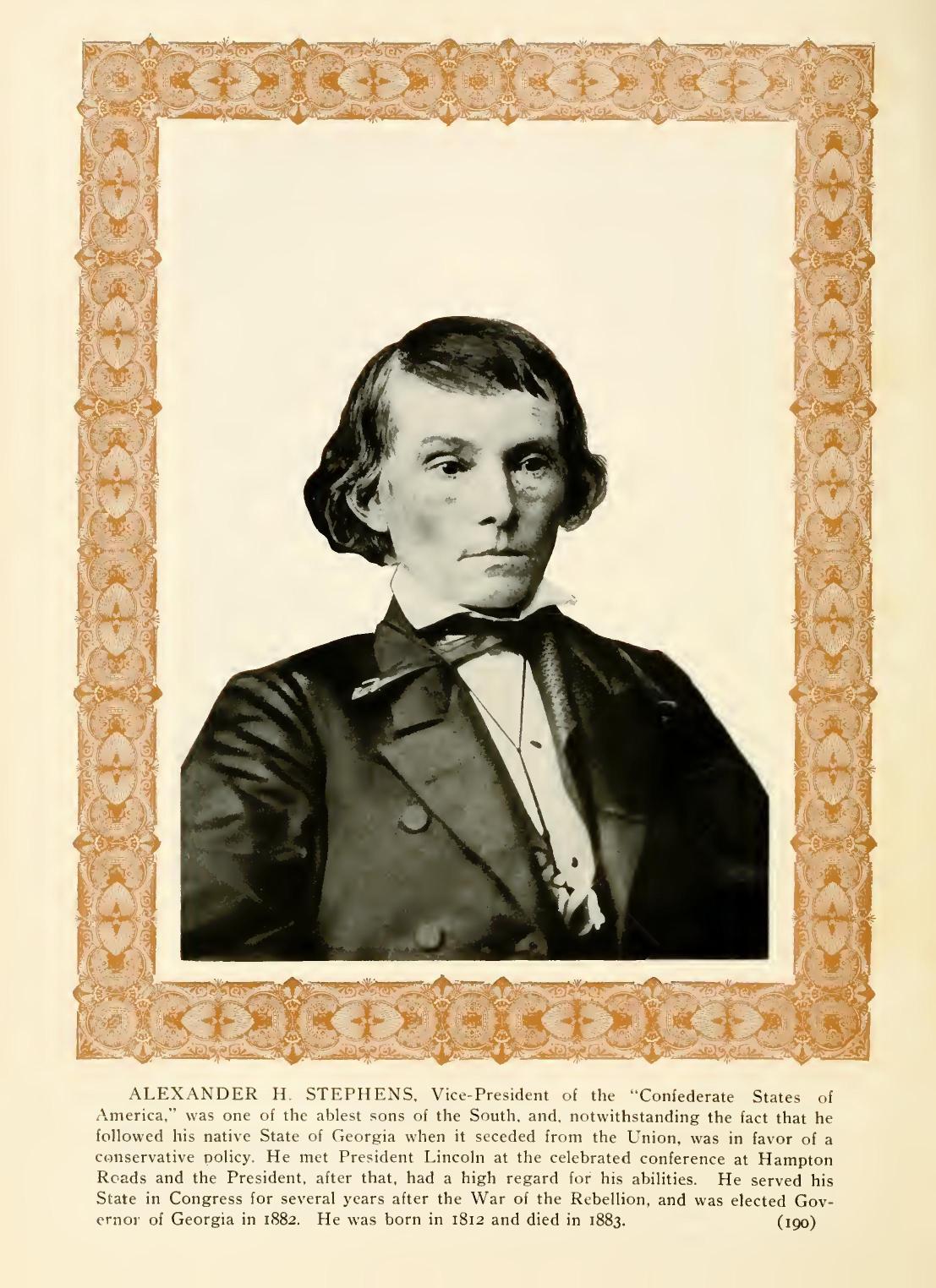




In 1862 a delegation of New York millionaires waited upon President Lincoln to request that he furnish a gunboat for the protection of New York harbor.
Mr. Lincoln, after listening patiently, said: “Gentlemen, the credit of the Government is at a very low ebb; greenbacks are not worth more than forty or fifty cents on the dollar; it is impossible for me, in the present condition of things, to furnish you a gunboat, and, in this condition of things, if I was worth half as much as you, gentlemen, are represented to be, and as badly frightened as you seem to be, I would build a gunboat and give it to the Government.”
President Lincoln’s sense of duty to the country, together with his keen judgment of men, often led to the appointment of persons unfriendly to him. Some of these appointees were, as well, not loyal to the National Government, for that matter.
Regarding Secretary of War Stanton’s attitude toward Lincoln, Colonel A. K. McClure, who was very close to President Lincoln, said:
“After Stanton’s retirement from the Buchanan Cabinet when Lincoln was inaugurated, he maintained the closest confidential relations with Buchanan, and wrote him many letters expressing the utmost contempt for Lincoln, the Cabinet, the Republican Congress, and the general policy of the Administration.
“These letters speak freely of the ‘painful imbecility of Lincoln,’ of the ‘venality and corruption’ which ran riot in the government, and expressed the belief that no better condition of things was possible ‘until Jeff Davis turns out the whole concern.’
“He was firmly impressed for some weeks after the battle of Bull Run that the government was utterly overthrown, as he repeatedly refers to the coming of Davis into the National Capital.
“In one letter he says that ‘in less than thirty days Davis will be in possession of Washington;’ and it is an open secret that Stanton advised the revolutionary overthrow of the Lincoln government, to be replaced by General McClellan as military dictator. These letters, bad as they are, are not the worst letters written by Stanton to Buchanan. Some of them were so violent in their expressions against Lincoln and the administration that they have been charitably withheld from the public, but they remain in the possession of the surviving relatives of President Buchanan.
“Of course, Lincoln had no knowledge of the bitterness exhibited by Stanton to himself personally and to his administration, but if he had known the worst that Stanton ever said or wrote about him, I doubt not that he would have called him to the Cabinet in January, 1862. The disasters the army suffered made Lincoln forgetful of everything but the single duty of suppressing the rebellion.
“Lincoln was not long in discovering that in his new Secretary of War he had an invaluable but most troublesome Cabinet officer, but he saw only the great and good offices that Stanton was performing for the imperilled Republic.
“Confidence was restored in financial circles by the appointment of Stanton, and his name as War Minister did more to strengthen the faith of the people in the government credit than would have been probable from the appointment of any other man of that day.
“He was a terror to all the hordes of jobbers and speculators and camp-followers whose appetites had been whetted by a great war, and he enforced the strictest discipline throughout our armies.
“He was seldom capable of being civil to any officer away from the army on leave of absence unless he had been summoned by the government for conference or special duty, and he issued the strictest orders from time to time to drive the throng of military idlers from the capital and keep them at their posts. He was stern to savagery in his enforcement of military law. The wearied sentinel who slept at his post found no mercy in the heart of Stanton, and many times did Lincoln’s humanity overrule his fiery minister.
“Any neglect of military duty was sure of the swiftest punishment, and seldom did he make even just allowance for inevitable military disaster. He had profound, unfaltering faith in the Union cause, and, above all, he had unfaltering faith in himself.
“He believed that he was in all things except in name Commander-in-Chief of the armies and the navy of the nation, and it was with unconcealed reluctance that he at times deferred to the authority of the President.”
In one of his political speeches, Judge Douglas made use of the following figure of speech: “As between the crocodile and the negro, I take the side of the negro; but as between the negro and the white man—I would go for the white man every time.”
Lincoln, at home, noted that; and afterwards, when he had occasion to refer to the remark, he said: “I believe that this is a sort of proposition in proportion, which may be stated thus: ‘As the negro is to the white man, so is the crocodile to the negro; and as the negro may rightfully treat the crocodile as a beast or reptile, so the white man may rightfully treat the negro as a beast or reptile.’”
On one occasion, Colonel Baker was speaking in a court-house, which had been a storehouse, and, on making some remarks that were offensive to certain political rowdies in the crowd, they cried: “Take him off the stand!”
Immediate confusion followed, and there was an attempt to carry the demand into execution. Directly over the speaker’s head was an old skylight, at which it appeared Mr. Lincoln had been listening to the speech. In an instant, Mr. Lincoln’s feet came through the skylight, followed by his tall and sinewy frame, and he was standing by Colonel Baker’s side. He raised his hand and the assembly subsided into silence. “Gentlemen,” said Mr. Lincoln, “let us not disgrace the age and country in which we live. This is a land where freedom of speech is guaranteed. Mr. Baker has a right to speak, and ought to be permitted to do so. I am here to protect him, and no man shall take him from this stand if I can prevent it.” The suddenness of his appearance, his perfect calmness and fairness, and the knowledge that he would do what he had promised to do, quieted all disturbance, and the speaker concluded his remarks without difficulty.
Two young men called on the President from Springfield, Illinois. Lincoln shook hands with them, and asked about the crops, the weather, etc.
Finally one of the young men said, “Mother is not well, and she sent me up to inquire of you how the suit about the Wells property is getting on.”
Lincoln, in the same even tone with which he had asked the question, said: “Give my best wishes and respects to your mother, and tell her I have so many outside matters to attend to now that I have put that case, and others, in the hands of a lawyer friend of mine, and if you will call on him (giving name and address) he will give you the information you want.”
After they had gone, a friend, who was present, said: “Mr. Lincoln, you did not seem to know the young men?”
He laughed and replied: “No, I had never seen them before, and I had to beat around the bush until I found who they were. It was up-hill work, but I topped it at last.”
President Lincoln wrote to General Hooker on June 5, 1863, warning Hooker not to run any risk of being entangled on the Rappahannock “like an ox jumped half over a fence and liable to be torn by dogs, front and rear, without a fair chance to give one way or kick the other.” On the 10th he warned Hooker not to go south of the Rappahannock upon Lee’s moving north of it. “I think Lee’s army and not Richmond is your true objective power. If he comes toward the upper Potomac, follow on his flank, and on the inside track, shortening your lines while he lengthens his. Fight him, too, when opportunity offers. If he stay where he is, fret him, and fret him.”
On the 14th again he says: “So far as we can make out here, the enemy have Milroy surrounded at Winchester, and Tyler at Martinsburg. If they could hold out for a few days, could you help them? If the head of Lee’s army is at Martinsburg, and the tail of it on the flank road between Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville, the animal must be very slim somewhere; could you not break him?”


In the issue of London “Punch” of September 24th, 1864, President Lincoln is pictured as sitting at a table in his law office, while in a chair to his right is a client, Mrs. North. The latter is a fine client for any attorney to have on his list, being wealthy and liberal, but as the lady is giving her counsel, who has represented her in a legal way for four years, notice that she proposes to put her legal business in the hands of another lawyer, the dejected look upon the face of Attorney Lincoln is easily accounted for. “Punch” puts these words in the lady’s mouth:
MRS. NORTH: “You see, Mr. Lincoln, we have failed utterly in our course of action; I want peace, and so, if you cannot effect an amicable arrangement, I must put the case into other hands.”
In this cartoon, “Punch” merely reflected the idea, or sentiment, current in England in 1864, that the North was much dissatisfied with the War policy of President Lincoln; and would surely elect General McClellan to succeed the Westerner in the White House. At the election McClellan carried but one Northern State—New Jersey, where he was born—President Lincoln sweeping the country like a prairie fire.
“Punch” had evidently been deceived by some bold, bad man, who wanted a little spending money, and sold the prediction to the funny journal with a certificate of character attached, written by—possibly—a member of the Horse Marines. “Punch,” was very much disgusted to find that its credulity and faith in mankind had been so imposed upon, especially when the election returns showed that “the-War-is-a-failure” candidate ran so slowly that Lincoln passed him as easily as though the Democratic nominee was tied to a post.
In the far-away days when “Abe” went to school in Indiana, they had exercises, exhibitions and speaking-meetings in the schoolhouse or the church, and “Abe” was the “star.” His father was a Democrat, and at that time “Abe” agreed with his parent. He would frequently make political and other speeches to the boys and explain tangled questions.
Booneville was the county seat of Warrick county, situated about fifteen miles from Gentryville. Thither “Abe” walked to be present at the sittings of the court, and listened attentively to the trials and the speeches of the lawyers.
One of the trials was that of a murderer. He was defended by Mr. John Breckinridge, and at the conclusion of his speech “Abe” was so enthusiastic that he ventured to compliment him. Breckinridge looked at the shabby boy, thanked him, and passed on his way.
Many years afterwards, in 1862, Breckinridge called on the President, and he was told, “It was the best speech that I, up to that time, had ever heard. If I could, as I then thought, make as good a speech as that, my soul would be satisfied.”
Mr. Alcott, of Elgin, Ill., tells of seeing Mr. Lincoln coming away from church unusually early one Sunday morning. “The sermon could not have been more than half way through,” says Mr. Alcott. “‘Tad’ was slung across his left arm like a pair of saddlebags, and Mr. Lincoln was striding along with long, deliberate steps toward his home. On one of the street corners he encountered a group of his fellow-townsmen. Mr. Lincoln anticipated the question which was about to be put by the group, and, taking his figure of speech from practices with which they were only too familiar, said: ‘Gentlemen, I entered this colt, but he kicked around so I had to withdraw him.”’
No matter who was with the President, or how intently absorbed, his little son “Tad” was always welcome. He almost always accompanied his father.
Once, on the way to Fortress Monroe, he became very troublesome. The President was much engaged in conversation with the party who accompanied him, and he at length said:
“‘Tad,’ if you will be a good boy, and not disturb me any more until we get to Fortress Monroe, I will give you a dollar.”
The hope of reward was effectual for awhile in securing silence, but, boylike, “Tad” soon forgot his promise, and was as noisy as ever. Upon reaching their destination, however, he said, very promptly: “Father, I want my dollar.” Mr. Lincoln looked at him half-reproachfully for an instant, and then, taking from his pocketbook a dollar note, he said “Well, my son, at any rate, I will keep my part of the bargain.”
Henry J. Raymond, the famous New York editor, thus tells of Mr. Lincoln’s fondness for the Nasby letters:
“It has been well said by a profound critic of Shakespeare, and it occurs to me as very appropriate in this connection, that the spirit which held the woe of Lear and the tragedy of “Hamlet” would have broken had it not also had the humor of the “Merry Wives of Windsor” and the merriment of the “Midsummer Night’s Dream.”
“This is as true of Mr. Lincoln as it was of Shakespeare. The capacity to tell and enjoy a good anecdote no doubt prolonged his life.
“The Saturday evening before he left Washington to go to the front, just previous to the capture of Richmond, I was with him from seven o’clock till nearly twelve. It had been one of his most trying days. The pressure of office-seekers was greater at this juncture than I ever knew it to be, and he was almost worn out.
“Among the callers that evening was a party composed of two Senators, a Representative, an ex-Lieutenant-Governor of a Western State, and several private citizens. They had business of great importance, involving the necessity of the President’s examination of voluminous documents. Pushing everything aside, he said to one of the party:
“‘Have you seen the Nasby papers?’
“‘No, I have not,’ was the reply; ‘who is Nasby?’
“‘There is a chap out in Ohio,’ returned the President, ‘who has been writing a series of letters in the newspapers over the signature of Petroleum V. Nasby. Some one sent me a pamphlet collection of them the other day. I am going to write to “Petroleum” to come down here, and I intend to tell him if he will communicate his talent to me, I will swap places with him!’
“Thereupon he arose, went to a drawer in his desk, and, taking out the ‘Letters,’ sat down and read one to the company, finding in their enjoyment of it the temporary excitement and relief which another man would have found in a glass of wine. The instant he had ceased, the book was thrown aside, his countenance relapsed into its habitual serious expression, and the business was entered upon with the utmost earnestness.”
On the occasion of a serenade, the President was called for by the crowd assembled. He appeared at a window with his wife (who was somewhat below the medium height), and made the following “brief remarks”:
“Here I am, and here is Mrs. Lincoln. That’s the long and the short of it.”
Some gentlemen were once finding fault with the President because certain generals were not given commands.
“The fact is,” replied President Lincoln, “I have got more pegs than I have holes to put them in.”
Lincoln “got even” with the Illinois Central Railroad Company, in 1855, in a most substantial way, at the same time secured sweet revenge for an insult, unwarranted in every way, put upon him by one of the officials of that corporation.
Lincoln and Herndon defended the Illinois Central Railroad in an action brought by McLean County, Illinois, in August, 1853, to recover taxes alleged to be due the county from the road. The Legislature had granted the road immunity from taxation, and this was a case intended to test the constitutionality of the law. The road sent a retainer fee of $250.
In the lower court the case was decided in favor of the railroad. An appeal to the Supreme Court followed, was argued twice, and finally decided in favor of the road. This last decision was rendered some time in 1855. Lincoln then went to Chicago and presented the bill for legal services. Lincoln and Herndon only asked for $2,000 more.
The official to whom he was referred, after looking at the bill, expressed great surprise.
“Why, sir,” he exclaimed, “this is as much as Daniel Webster himself would have charged. We cannot allow such a claim.”
“Why not?” asked Lincoln.
“We could have hired first-class lawyers at that figure,” was the response.
“We won the case, didn’t we?” queried Lincoln.
“Certainly,” replied the official.
“Daniel Webster, then,” retorted Lincoln in no amiable tone, “couldn’t have done more,” and “Abe” walked out of the official’s office.
Lincoln withdrew the bill, and started for home. On the way he stopped at Bloomington, where he met Grant Goodrich, Archibald Williams, Norman B. Judd, O. H. Browning, and other attorneys, who, on learning of his modest charge for the valuable services rendered the railroad, induced him to increase the demand to $5,000, and to bring suit for that sum.
This was done at once. On the trial six lawyers certified that the bill was reasonable, and judgment for that sum went by default; the judgment was promptly paid, and, of course, his partner, Herndon, got “your half Billy,” without delay.
When a member of Congress, Lincoln went to Lexington, Kentucky, to hear Henry Clay speak. The Westerner, a Kentuckian by birth, and destined to reach the great goal Clay had so often sought, wanted to meet the “Millboy of the Slashes.” The address was a tame affair, as was the personal greeting when Lincoln made himself known. Clay was courteous, but cold. He may never have heard of the man, then in his presence, who was to secure, without solicitation, the prize which he for many years had unsuccessfully sought. Lincoln was disenchanted; his ideal was shattered. One reason why Clay had not realized his ambition had become apparent.
Clay was cool and dignified; Lincoln was cordial and hearty. Clay’s hand was bloodless and frosty, with no vigorous grip in it; Lincoln’s was warm, and its clasp was expressive of kindliness and sympathy.
President Lincoln had a little joke at the expense of General George B. McClellan, the Democratic candidate for the Presidency in opposition to the Westerner in 1864. McClellan was nominated by the Democratic National Convention, which assembled at Chicago, but after he had been named, and also during the campaign, the military candidate was characteristically slow in coming to the front.
President Lincoln had his eye upon every move made by General McClellan during the campaign, and when reference was made one day, in his presence, to the deliberation and caution of the New Jerseyite, Mr. Lincoln remarked, with a twinkle in his eye, “Perhaps he is intrenching.”
The cartoon we reproduce appeared in “Harper’s Weekly,” September 17th, 1864, and shows General McClellan, with his little spade in hand, being subjected to the scrutiny of the President—the man who gave McClellan, when the latter was Commander-in-Chief of the Union forces, every opportunity in the world to distinguish himself. There is a smile on the face of “Honest Abe,” which shows conclusively that he does not regard his political opponent as likely to prove formidable in any way. President Lincoln “sized up” McClellan in 1861-2, and knew, to a fraction, how much of a man he was, what he could do, and how he went about doing it. McClellan was no politician, while the President was the shrewdest of political diplomats.
When Washington had become an armed camp, and full of soldiers, President Lincoln and his Cabinet officers drove daily to one or another of these camps. Very often his outing for the day was attending some ceremony incident to camp life: a military funeral, a camp wedding, a review, a flag-raising. He did not often make speeches. “I have made a great many poor speeches,” he said one day, in excusing himself, “and I now feel relieved that my dignity does not permit me to be a public speaker.”
Judge Kelly, of Pennsylvania, who was one of the committee to advise Lincoln of his nomination, and who was himself a great many feet high, had been eyeing Lincoln’s lofty form with a mixture of admiration and possibly jealousy.
This had not escaped Lincoln, and as he shook hands with the judge he inquired, “What is your height?”
“Six feet three. What is yours, Mr. Lincoln?”
“Six feet four.”
“Then,” said the judge, “Pennsylvania bows to Illinois. My dear man, for years my heart has been aching for a President that I could look up to, and I’ve at last found him.”
Mr. Jeriah Bonham, in describing a visit he paid Lincoln at his room in the State House at Springfield, where he found him quite alone, except that two of his children, one of whom was “Tad,” were with him.
“The door was open.
“We walked in and were at once recognized and seated—the two boys still continuing their play about the room. “Tad” was spinning his top; and Lincoln, as we entered, had just finished adjusting the string for him so as to give the top the greatest degree of force. He remarked that he was having a little fun with the boys.”
At another time, at Lincoln’s residence, “Tad” came into the room, and, putting his hand to his mouth, and his mouth to his father’s ear, said, in a boy’s whisper: “Ma says come to supper.”
All heard the announcement; and Lincoln, perceiving this, said: “You have heard, gentlemen, the announcement concerning the interesting state of things in the dining-room. It will never do for me, if elected, to make this young man a member of my Cabinet, for it is plain he cannot be trusted with secrets of state.”
A Union general, operating with his command in West Virginia, allowed himself and his men to be trapped, and it was feared his force would be captured by the Confederates. The President heard the report read by the operator, as it came over the wire, and remarked:
“Once there was a man out West who was ‘heading’ a barrel, as they used to call it. He worked like a good fellow in driving down the hoops, but just about the time he thought he had the job done, the head would fall in. Then he had to do the work all over again.
“All at once a bright idea entered his brain, and he wondered how it was he hadn’t figured it out before. His boy, a bright, smart lad, was standing by, very much interested in the business, and, lifting the young one up, he put him inside the barrel, telling him to hold the head in its proper place, while he pounded down the hoops on the sides. This worked like a charm, and he soon had the ‘heading’ done.
“Then he realized that his boy was inside the barrel, and how to get him out he couldn’t for his life figure out. General Blank is now inside the barrel, ‘headed in,’ and the job now is to get him out.”
Government Printer Defrees, when one of the President’s messages was being printed, was a good deal disturbed by the use of the term “sugar-coated,” and finally went to Mr. Lincoln about it.
Their relations to each other being of the most intimate character, he told the President frankly that he ought to remember that a message to Congress was a different affair from a speech at a mass meeting in Illinois; that the messages became a part of history, and should be written accordingly.
“What is the matter now?” inquired the President.
“Why,” said Defrees, “you have used an undignified expression in the message”; and, reading the paragraph aloud, he added, “I would alter the structure of that, if I were you.”
“Defrees,” replied the President, “that word expresses exactly my idea, and I am not going to change it. The time will never come in this country when people won’t know exactly what ‘sugar-coated’ means.”
When a grocery clerk at New Salem, the annual election came around. A Mr. Graham was clerk, but his assistant was absent, and it was necessary to find a man to fill his place. Lincoln, a “tall young man,” had already concentrated on himself the attention of the people of the town, and Graham easily discovered him. Asking him if he could write, “Abe” modestly replied, “I can make a few rabbit-tracks.” His rabbit-tracks proving to be legible and even graceful, he was employed.
The voters soon discovered that the new assistant clerk was honest and fair, and performed his duties satisfactorily, and when, the work done, he began to “entertain them with stories,” they found that their town had made a valuable personal and social acquisition.
Marshal Ward Lamon was in President Lincoln’s office in the White House one day, and casually asked the President if he knew how the currency of the country was made. Greenbacks were then under full headway of circulation, these bits of paper being the representatives of United State money.
“Our currency,” was the President’s answer, “is made, as the lawyers would put it, in their legal way, in the following manner, to-wit: The official engraver strikes off the sheets, passes them over to the Register of the Currency, who, after placing his earmarks upon them, signs the same; the Register turns them over to old Father Spinner, who proceeds to embellish them with his wonderful signature at the bottom; Father Spinner sends them to Secretary of the Treasury Chase, and he, as a final act in the matter, issues them to the public as money—and may the good Lord help any fellow that doesn’t take all he can honestly get of them!”
Taking from his pocket a $5 greenback, with a twinkle in his eye, the President then said: “Look at Spinner’s signature! Was there ever anything like it on earth? Yet it is unmistakable; no one will ever be able to counterfeit it!”
Lamon then goes on to say:
“‘But,’ I said, ‘you certainly don’t suppose that Spinner actually wrote his name on that bill, do you?’
“‘Certainly, I do; why not?’ queried Mr. Lincoln.
“I then asked, ‘How much of this currency have we afloat?’
“He remained thoughtful for a moment, and then stated the amount.
“I continued: ‘How many times do you think a man can write a signature like Spinner’s in the course of twenty-four hours?’
“The beam of hilarity left the countenance of the President at once. He put the greenback into his vest pocket, and walked the floor; after awhile he stopped, heaved a long breath and said: ‘This thing frightens me!’ He then rang for a messenger and told him to ask the Secretary of the Treasury to please come over to see him.
“Mr. Chase soon put in an appearance; President Lincoln stated the cause of his alarm, and asked Mr. Chase to explain in detail the operations, methods, system of checks, etc., in his office, and a lengthy discussion followed, President Lincoln contending there were not sufficient safeguards afforded in any degree in the money-making department, and Secretary Chase insisting that every protection was afforded he could devise.”
Afterward the President called the attention of Congress to this important question, and devices were adopted whereby a check was put upon the issue of greenbacks that no spurious ones ever came out of the Treasury Department, at least. Counterfeiters were busy, though, but this was not the fault of the Treasury.
“General Grant is a copious worker and fighter,” President Lincoln wrote to General Burnside in July, 1863, “but a meagre writer or telegrapher.”
Grant never wrote a report until the battle was over.
President Lincoln wrote a letter to General Grant on July 13th, 1863, which indicated the strength of the hold the successful fighter had upon the man in the White House.
It ran as follows:
“I do not remember that you and I ever met personally.
“I write this now as a grateful acknowledgment for the almost inestimable service you have done the country.
“I write to say a word further.
“When you first reached the vicinity of Vicksburg, I thought you should do what you finally did—march the troops across the neck, run the batteries with the transports, and thus go below; and I never had any faith, except a general hope, that you knew better than I, that the Yazoo Pass expedition, and the like, could succeed.
“When you got below and took Port Gibson, Grand Gulf and vicinity, I thought you should go down the river and join General Banks; and when you turned northward, east of Big Black, I feared it was a mistake.
“I now wish to make the personal acknowledgment that you were right and I was wrong.”
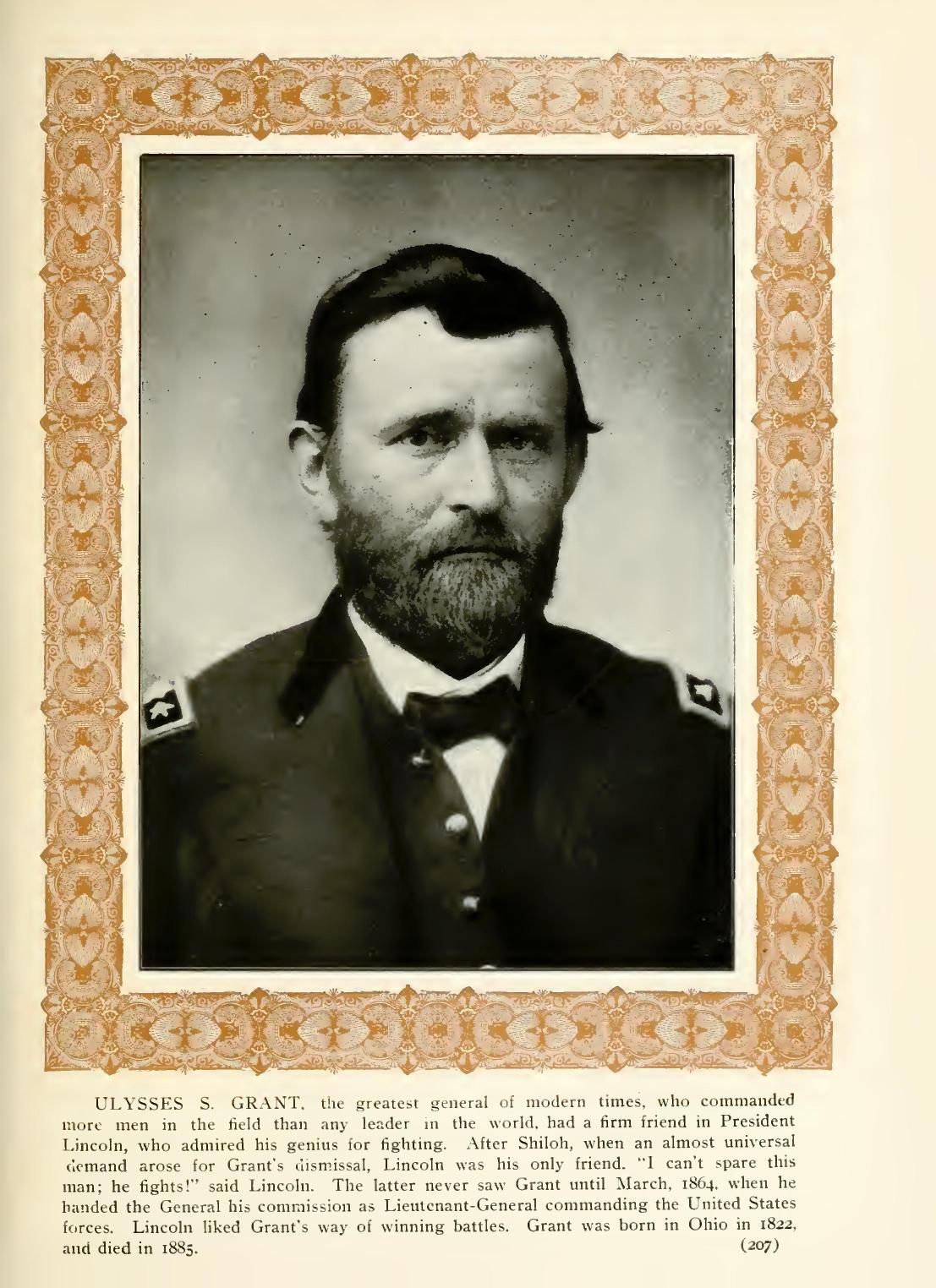
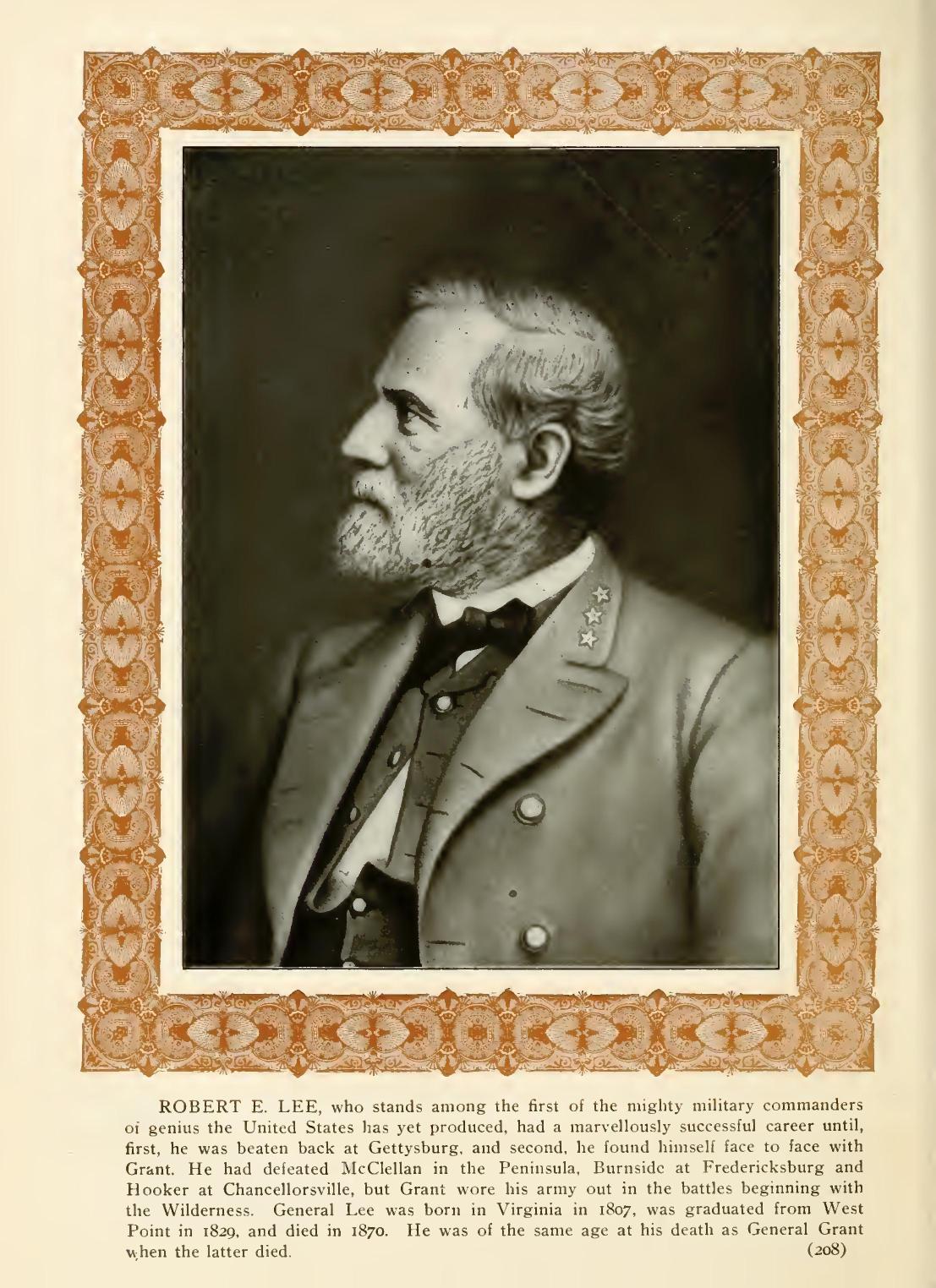




Lincoln never used profanity, except when he quoted it to illustrate a point in a story. His favorite expressions when he spoke with emphasis were “By dear!” and “By jing!”
Just preceding the Civil War he sent Ward Lamon on a ticklish mission to South Carolina.
When the proposed trip was mentioned to Secretary Seward, he opposed it, saying, “Mr. President, I fear you are sending Lamon to his grave. I am afraid they will kill him in Charleston, where the people are excited and desperate. We can’t spare Lamon, and we shall feel badly if anything happens to him.”
Mr. Lincoln said in reply: “I have known Lamon to be in many a close place, and he has never, been in one that he didn’t get out of, somehow. By jing! I’ll risk him. Go ahead, Lamon, and God bless you! If you can’t bring back any good news, bring a palmetto.” Lamon brought back a palmetto branch, but no promise of peace.
Lincoln had been in the telegraph office at Springfield during the casting of the first and second ballots in the Republican National Convention at Chicago, and then left and went over to the office of the State Journal, where he was sitting conversing with friends while the third ballot was being taken.
In a few moments came across the wires the announcement of the result. The superintendent of the telegraph company wrote on a scrap of paper: “Mr. Lincoln, you are nominated on the third ballot,” and a boy ran with the message to Lincoln.
He looked at it in silence, amid the shouts of those around him; then rising and putting it in his pocket, he said quietly: “There’s a little woman down at our house would like to hear this; I’ll go down and tell her.”
After Lincoln had finished that celebrated speech in “Egypt” (as a section of Southern Illinois was formerly designated), in the course of which he seized Congressman Ficklin by the coat collar and shook him fiercely, he apologized. In return, Ficklin said Lincoln had “nearly shaken the Democracy out of him.” To this Lincoln replied:
“That reminds me of what Paul said to Agrippa, which, in language and substance, was about this: ‘I would to God that such Democracy as you folks here in Egypt have were not only almost, but altogether, shaken out of, not only you, but all that heard me this day, and that you would all join in assisting in shaking off the shackles of the bondmen by all legitimate means, so that this country may be made free as the good Lord intended it.’”
Said Ficklin in rejoinder: “Lincoln, I remember of reading somewhere in the same book from which you get your Agrippa story, that Paul, whom you seem to desire to personate, admonished all servants (slaves) to be obedient to them that are their masters according to the flesh, in fear and trembling.
“It would seem that neither our Savior nor Paul saw the iniquity of slavery as you and your party do. But you must not think that where you fail by argument to convince an old friend like myself and win him over to your heterodox abolition opinions, you are justified in resorting to violence such as you practiced on me to-day.
“Why, I never had such a shaking up in the whole course of my life. Recollect that that good old book that you quote from somewhere says in effect this: ‘Woe be unto him who goeth to Egypt for help, for he shall fall. The holpen shall fall, and they shall all fall together.’”
Lincoln’s quarrel with Shields was his last personal encounter. In later years it became his duty to give an official reprimand to a young officer who had been court-martialed for a quarrel with one of his associates. The reprimand is probably the gentlest on record:
“Quarrel not at all. No man resolved to make the most of himself can spare time for personal contention. Still less can he afford to take all the consequences, including the vitiating of his temper and the loss of self-control. Yield larger things to which you can show no more than equal right; and yield lesser ones, though clearly your own.
“Better give your path to a dog than be bitten by him in contesting for the right. Even killing the dog would not cure the bite.”
Some one came to the President with a story about a plot to accomplish some mischief in the Government. Lincoln listened to what was a very superficial and ill-formed story, and then said: “There is one thing that I have learned, and that you have not. It is only one word—‘thorough.’”
Then, bringing his hand down on the table with a thump to emphasize his meaning, he added, “thorough!”
Being in Washington one day, the Rev. Robert Collyer thought he’d take a look around. In passing through the grounds surrounding the White House, he cast a glance toward the Presidential residence, and was astonished to see three pairs of feet resting on the ledge of an open window in one of the apartments of the second story. The divine paused for a moment, calmly surveyed the unique spectacle, and then resumed his walk toward the War Department.
Seeing a laborer at work not far from the Executive Mansion, Mr. Collyer asked him what it all meant. To whom did the feet belong, and, particularly, the mammoth ones? “You old fool,” answered the workman, “that’s the Cabinet, which is a-settin’, an’ them thar big feet belongs to ‘Old Abe.’”
A soldier tells the following story of an attempt upon the life of Mr. Lincoln “One night I was doing sentinel duty at the entrance to the Soldiers’ Home. This was about the middle of August, 1864. About eleven o’clock I heard a rifle shot, in the direction of the city, and shortly afterwards I heard approaching hoof-beats. In two or three minutes a horse came dashing up. I recognized the belated President. The President was bareheaded. The President simply thought that his horse had taken fright at the discharge of the firearms.
“On going back to the place where the shot had been heard, we found the President’s hat. It was a plain silk hat, and upon examination we discovered a bullet hole through the crown.
“The next day, upon receiving the hat, the President remarked that it was made by some foolish marksman, and was not intended for him; but added that he wished nothing said about the matter.
“The President said, philosophically: ‘I long ago made up my mind that if anybody wants to kill me, he will do it. Besides, in this case, it seems to me, the man who would succeed me would be just as objectionable to my enemies—if I have any.’
“One dark night, as he was going out with a friend, he took along a heavy cane, remarking, good-naturedly: ‘Mother (Mrs. Lincoln) has got a notion into her head that I shall be assassinated, and to please her I take a cane when I go over to the War Department at night—when I don’t forget it.’”
Two ladies from Tennessee called at the White House one day and begged Mr. Lincoln to release their husbands, who were rebel prisoners at Johnson’s Island. One of the fair petitioners urged as a reason for the liberation of her husband that he was a very religious man, and rang the changes on this pious plea.
“Madam,” said Mr. Lincoln, “you say your husband is a religious man. Perhaps I am not a good judge of such matters, but in my opinion the religion that makes men rebel and fight against their government is not the genuine article; nor is the religion the right sort which reconciles them to the idea of eating their bread in the sweat of other men’s faces. It is not the kind to get to heaven on.”
Later, however, the order of release was made, President Lincoln remarking, with impressive solemnity, that he would expect the ladies to subdue the rebellious spirit of their husbands, and to that end he thought it would be well to reform their religion. “True patriotism,” said he, “is better than the wrong kind of piety.”
During the Presidential campaign of 1864 much ill-feeling was displayed by the opposition to President Lincoln. The Democratic managers issued posters of large dimensions, picturing the Washington Administration as one determined to rule or ruin the country, while the only salvation for the United States was the election of McClellan.
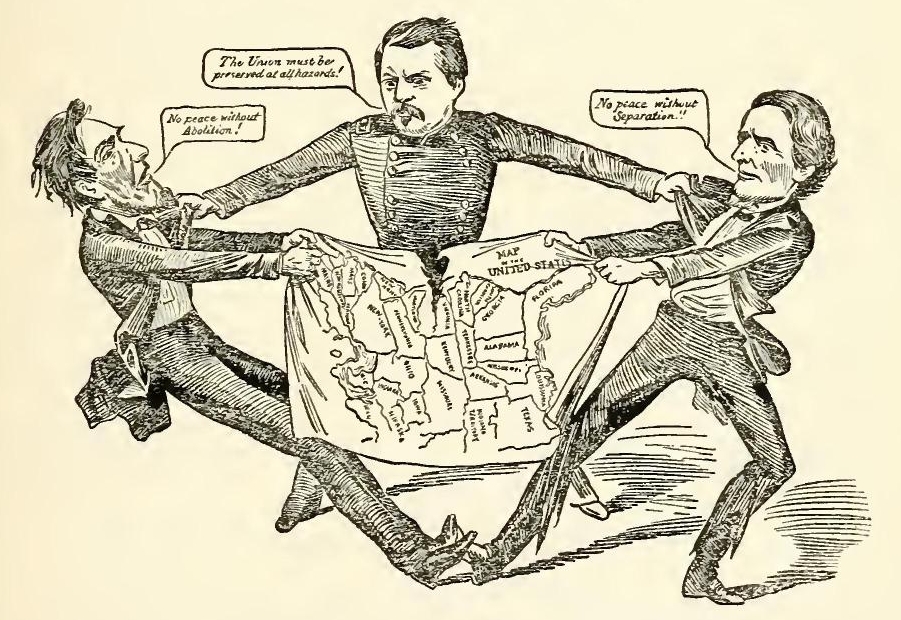

We reproduce one of these 1864 campaign posters on this page, the title of which is, “The True Issue; or ‘That’s What’s the Matter.’”
The dominant idea or purpose of the cartoon-poster was to demonstrate McClellan’s availability. Lincoln, the Abolitionist, and Davis, the Secessionist, are pictured as bigots of the worst sort, who were determined that peace should not be restored to the distracted country, except upon the lines laid down by them. McClellan, the patriotic peacemaker, is shown as the man who believed in the preservation of the Union above all things—a man who had no fads nor vagaries.
This peacemaker, McClellan, standing upon “the War-is-a-failure” platform, is portrayed as a military chieftain, who would stand no nonsense; who would compel Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Davis to cease their quarreling; who would order the soldiers on both sides to quit their blood-letting and send the combatants back to the farm, workshop and counting-house; and the man whose election would restore order out of chaos, and make everything bright and lovely.
One day when President Lincoln was receiving callers a buxom Irish woman came into the office, and, standing before the President, with her hands on her hips, said:
“Mr. Lincoln, can’t I sell apples on the railroad?”
President Lincoln replied: “Certainly, madam, you can sell all you wish.”
“But,” she said, “you must give me a pass, or the soldiers will not let me.”
President Lincoln then wrote a few lines and gave them to her.
“Thank you, sir; God bless you!” she exclaimed as she departed joyfully.
It was in the spring of 1830 that “Abe” Lincoln, “wearing a jean jacket, shrunken buckskin trousers, a coonskin cap, and driving an ox-team,” became a citizen of Illinois. He was physically and mentally equipped for pioneer work. His first desire was to obtain a new and decent suit of clothes, but, as he had no money, he was glad to arrange with Nancy Miller to make him a pair of trousers, he to split four hundred fence rails for each yard of cloth—fourteen hundred rails in all. “Abe” got the clothes after awhile.
It was three miles from his father’s cabin to her wood-lot, where he made the forest ring with the sound of his ax. “Abe” had helped his father plow fifteen acres of land, and split enough rails to fence it, and he then helped to plow fifty acres for another settler.
Whenever the people of Lincoln’s neighborhood engaged in dispute; whenever a bet was to be decided; when they differed on points of religion or politics; when they wanted to get out of trouble, or desired advice regarding anything on the earth, below it, above it, or under the sea, they went to “Abe.”
Two fellows, after a hot dispute lasting some hours, over the problem as to how long a man’s legs should be in proportion to the size of his body, stamped into Lincoln’s office one day and put the question to him.
Lincoln listened gravely to the arguments advanced by both contestants, spent some time in “reflecting” upon the matter, and then, turning around in his chair and facing the disputants, delivered his opinion with all the gravity of a judge sentencing a fellow-being to death.
“This question has been a source of controversy,” he said, slowly and deliberately, “for untold ages, and it is about time it should be definitely decided. It has led to bloodshed in the past, and there is no reason to suppose it will not lead to the same in the future.
“After much thought and consideration, not to mention mental worry and anxiety, it is my opinion, all side issues being swept aside, that a man’s lower limbs, in order to preserve harmony of proportion, should be at least long enough to reach from his body to the ground.”
“The first week I was with my command there were twenty-four deserters sentenced by court-martial to be shot, and the warrants for their execution were sent to the President to be signed. He refused.
“I went to Washington and had an interview. I said:
“‘Mr. President, unless these men are made an example of, the army itself is in danger. Mercy to the few is cruelty to the many.’
“He replied: ‘Mr. General, there are already too many weeping widows in the United States. For God’s sake, don’t ask me to add to the number, for I won’t do it.’”
In the early stages of the war, after several battles had been fought, Union troops seized a church in Alexandria, Va., and used it as a hospital.
A prominent lady of the congregation went to Washington to see Mr. Lincoln and try to get an order for its release.
“Have you applied to the surgeon in charge at Alexandria?” inquired Mr. Lincoln.
“Yes, sir, but I can do nothing with him,” was the reply.
“Well, madam,” said Mr. Lincoln, “that is an end of it, then. We put him there to attend to just such business, and it is reasonable to suppose that he knows better what should be done under the circumstances than I do.”
The lady’s face showed her keen disappointment. In order to learn her sentiment, Mr. Lincoln asked:
“How much would you be willing to subscribe toward building a hospital there?”
She said that the war had depreciated Southern property so much that she could afford to give but little.
“This war is not over yet,” said Mr. Lincoln, “and there will likely be another fight very soon. That church may be very useful in which to house our wounded soldiers. It is my candid opinion that God needs that church for our wounded fellows; so, madam, I can do nothing for you.”
An amusing instance of the President’s preoccupation of mind occurred at one of his levees, when he was shaking hands with a host of visitors passing him in a continuous stream.
An intimate acquaintance received the usual conventional hand-shake and salutation, but perceiving that he was not recognized, kept his ground instead of moving on, and spoke again, when the President, roused to a dim consciousness that something unusual had happened, perceived who stood before him, and, seizing his friend’s hand, shook it again heartily, saying:
“How do you do? How do you do? Excuse me for not noticing you. I was thinking of a man down South.”
“The man down South” was General W. T. Sherman, then on his march to the sea.
When Governor Custer of Pennsylvania described the terrible butchery at the battle of Fredericksburg, Mr. Lincoln was almost broken-hearted.
The Governor regretted that his description had so sadly affected the President. He remarked: “I would give all I possess to know how to rescue you from this terrible war.” Then Mr. Lincoln’s wonderful recuperative powers asserted themselves and this marvelous man was himself.
Lincoln’s whole aspect suddenly changed, and he relieved his mind by telling a story.
“This reminds me, Governor,” he said, “of an old farmer out in Illinois that I used to know.
“He took it into his head to go into hog-raising. He sent out to Europe and imported the finest breed of hogs he could buy.
“The prize hog was put in a pen, and the farmer’s two mischievous boys, James and John, were told to be sure not to let it out. But James, the worst of the two, let the brute out the next day. The hog went straight for the boys, and drove John up a tree, then the hog went for the seat of James’ trousers, and the only way the boy could save himself was by holding on to the hog’s tail.
“The hog would not give up his hunt, nor the boy his hold! After they had made a good many circles around the tree, the boy’s courage began to give out, and he shouted to his brother, ‘I say, John, come down, quick, and help me let go this hog!’
“Now, Governor, that is exactly my case. I wish some one would come and help me to let the hog go.”
Judge Joseph Gillespie, of Chicago, was a firm friend of Mr. Lincoln, and went to Springfield to see him shortly before his departure for the inauguration.
“It was,” said judge Gillespie, “Lincoln’s Gethsemane. He feared he was not the man for the great position and the great events which confronted him. Untried in national affairs, unversed in international diplomacy, unacquainted with the men who were foremost in the politics of the nation, he groaned when he saw the inevitable War of the Rebellion coming on. It was in humility of spirit that he told me he believed that the American people had made a mistake in selecting him.
“In the course of our conversation he told me if he could select his cabinet from the old bar that had traveled the circuit with him in the early days, he believed he could avoid war or settle it without a battle, even after the fact of secession.
“‘But, Mr. Lincoln,’ said I, ‘those old lawyers are all Democrats.’
“‘I know it,’ was his reply. ‘But I would rather have Democrats whom I know than Republicans I don’t know.’”
“I remember one day being in his room when Lincoln was sitting at his table with a large pile of papers before him, and after a pleasant talk he turned quite abruptly and said: ‘Get out of the way, Swett; to-morrow is butcher-day, and I must go through these papers and see if I cannot find some excuse to let these poor fellows off.’
“The pile of papers he had were the records of courts-martial of men who on the following day were to be shot.”
It took quite a long time, as well as the lives of thousands of men, to say nothing of the cost in money, to take Richmond, the Capital City of the Confederacy. In this cartoon, taken from “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper,” of February 21, 1863, Jeff Davis is sitting upon the Secession eggs in the “Richmond” nest, smiling down upon President Lincoln, who is up to his waist in the Mud of Difficulties.
The President finally waded through the morass, in which he had become immersed, got to the tree, climbed its trunk, reached the limb, upon which the “bad bird” had built its nest, threw the mother out, destroyed the eggs of Secession and then took the nest away with him, leaving the “bad bird” without any home at all.
The “bad bird” had its laugh first, but the last laugh belonged to the “mudsill,” as the cartoonist was pleased to call the President of the United States. It is true that the President got his clothes and hat all covered with mud, but as the job was a dirty one, as well as one that had to be done, the President didn’t care. He was able to get another suit of clothes, as well as another hat, but the “bad bird” couldn’t, and didn’t, get another nest.
The laugh was on the “bad bird” after all.
Once, when asked what he remembered about the war with Great Britain, Lincoln replied: “Nothing but this: I had been fishing one day and caught a little fish, which I was taking home. I met a soldier in the road, and, having been always told at home that we must be good to the soldiers, I gave him my fish.”
This must have been about 1814, when “Abe” was five years of age.
Lincoln was once associate counsel for a defendant in a murder case. He listened to the testimony given by witness after witness against his client, until his honest heart could stand it no longer; then, turning to his associate, he said: “The man is guilty; you defend him—I can’t,” and when his associate secured a verdict of acquittal, Lincoln refused to share the fee to the extent of one cent.
Lincoln would never advise clients to enter into unwise or unjust lawsuits, always preferring to refuse a retainer rather than be a party to a case which did not commend itself to his sense of justice.
General Creswell called at the White House to see the President the day of the latter’s assassination. An old friend, serving in the Confederate ranks, had been captured by the Union troops and sent to prison. He had drawn an affidavit setting forth what he knew about the man, particularly mentioning extenuating circumstances.
Creswell found the President very happy. He was greeted with: “Creswell, old fellow, everything is bright this morning. The War is over. It has been a tough time, but we have lived it out,—or some of us have,” and he dropped his voice a little on the last clause of the sentence. “But it is over; we are going to have good times now, and a united country.”
General Creswell told his story, read his affidavit, and said, “I know the man has acted like a fool, but he is my friend, and a good fellow; let him out; give him to me, and I will be responsible that he won’t have anything more to do with the rebs.”
“Creswell,” replied Mr. Lincoln, “you make me think of a lot of young folks who once started out Maying. To reach their destination, they had to cross a shallow stream, and did so by means of an old flatboat. When the time came to return, they found to their dismay that the old scow had disappeared. They were in sore trouble, and thought over all manner of devices for getting over the water, but without avail.
“After a time, one of the boys proposed that each fellow should pick up the girl he liked best and wade over with her. The masterly proposition was carried out, until all that were left upon the island was a little short chap and a great, long, gothic-built, elderly lady.
“Now, Creswell, you are trying to leave me in the same predicament. You fellows are all getting your own friends out of this scrape; and you will succeed in carrying off one after another, until nobody but Jeff Davis and myself will be left on the island, and then I won’t know what to do. How should I feel? How should I look, lugging him over?
“I guess the way to avoid such an embarrassing situation is to let them all out at once.”
He made a somewhat similar illustration at an informal Cabinet meeting, at which the disposition of Jefferson Davis and other prominent Confederates was discussed. Each member of the Cabinet gave his opinion; most of them were for hanging the traitors, or for some severe punishment. President Lincoln said nothing.
Finally, Joshua F. Speed, his old and confidential friend, who had been invited to the meeting, said, “I have heard the opinion of your Ministers, and would like to hear yours.”
“Well, Josh,” replied President Lincoln, “when I was a boy in Indiana, I went to a neighbor’s house one morning and found a boy of my own size holding a coon by a string. I asked him what he had and what he was doing.
“He says, ‘It’s a coon. Dad cotched six last night, and killed all but this poor little cuss. Dad told me to hold him until he came back, and I’m afraid he’s going to kill this one too; and oh, “Abe,” I do wish he would get away!’
“‘Well, why don’t you let him loose?’
“‘That wouldn’t be right; and if I let him go, Dad would give me h—. But if he got away himself, it would be all right.’
“Now,” said the President, “if Jeff Davis and those other fellows will only get away, it will be all right. But if we should catch them, and I should let them go, ‘Dad would give me h—!’”
Don Piatt, a noted journalist of Washington, told the story of the first proposition to President Lincoln to issue interest-bearing notes as currency, as follows:
“Amasa Walker, a distinguished financier of New England, suggested that notes issued directly from the Government to the people, as currency, should bear interest. This for the purpose, not only of making the notes popular, but for the purpose of preventing inflation, by inducing people to hoard the notes as an investment when the demands of trade would fail to call them into circulation as a currency.
“This idea struck David Taylor, of Ohio, with such force that he sought Mr. Lincoln and urged him to put the project into immediate execution. The President listened patiently, and at the end said, ‘That is a good idea, Taylor, but you must go to Chase. He is running that end of the machine, and has time to consider your proposition.’
“Taylor sought the Secretary of the Treasury, and laid before him Amasa Walker’s plan. Secretary Chase heard him through in a cold, unpleasant manner, and then said: ‘That is all very well, Mr. Taylor; but there is one little obstacle in the way that makes the plan impracticable, and that is the Constitution.’
“Saying this, he turned to his desk, as if dismissing both Mr. Taylor and his proposition at the same moment.
“The poor enthusiast felt rebuked and humiliated. He returned to the President, however, and reported his defeat. Mr. Lincoln looked at the would-be financier with the expression at times so peculiar to his homely face, that left one in doubt whether he was jesting or in earnest. ‘Taylor!’ he exclaimed, ‘go back to Chase and tell him not to bother himself about the Constitution. Say that I have that sacred instrument here at the White House, and I am guarding it with great care.’
“Taylor demurred to this, on the ground that Secretary Chase showed by his manner that he knew all about it, and didn’t wish to be bored by any suggestion.
“‘We’ll see about that,’ said the President, and taking a card from the table, he wrote upon it:
“‘The Secretary of the Treasury will please consider Mr. Taylor’s proposition. We must have money, and I think this a good way to get it.
Among the men whom Captain Lincoln met in the Black Hawk campaign were Lieutenant-Colonel Zachary Taylor, Lieutenant Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederacy, and Lieutenant Robert Anderson, all of the United States Army.
Judge Arnold, in his “Life of Abraham Lincoln,” relates that Lincoln and Anderson did not meet again until some time in 1861. After Anderson had evacuated Fort Sumter, on visiting Washington, he called at the White House to pay his respects to the President. Lincoln expressed his thanks to Anderson for his conduct at Fort Sumter, and then said:
“Major, do you remember of ever meeting me before?”
“No, Mr. President, I have no recollection of ever having had that pleasure.”
“My memory is better than yours,” said Lincoln; “you mustered me into the service of the United States in 1832, at Dixon’s Ferry, in the Black Hawk war.”
In February, 1860, not long before his nomination for the Presidency, Lincoln made several speeches in Eastern cities. To an Illinois acquaintance, whom he met at the Astor House, in New York, he said: “I have the cottage at Springfield, and about three thousand dollars in money. If they make me Vice-President with Seward, as some say they will, I hope I shall be able to increase it to twenty thousand, and that is as much as any man ought to want.”
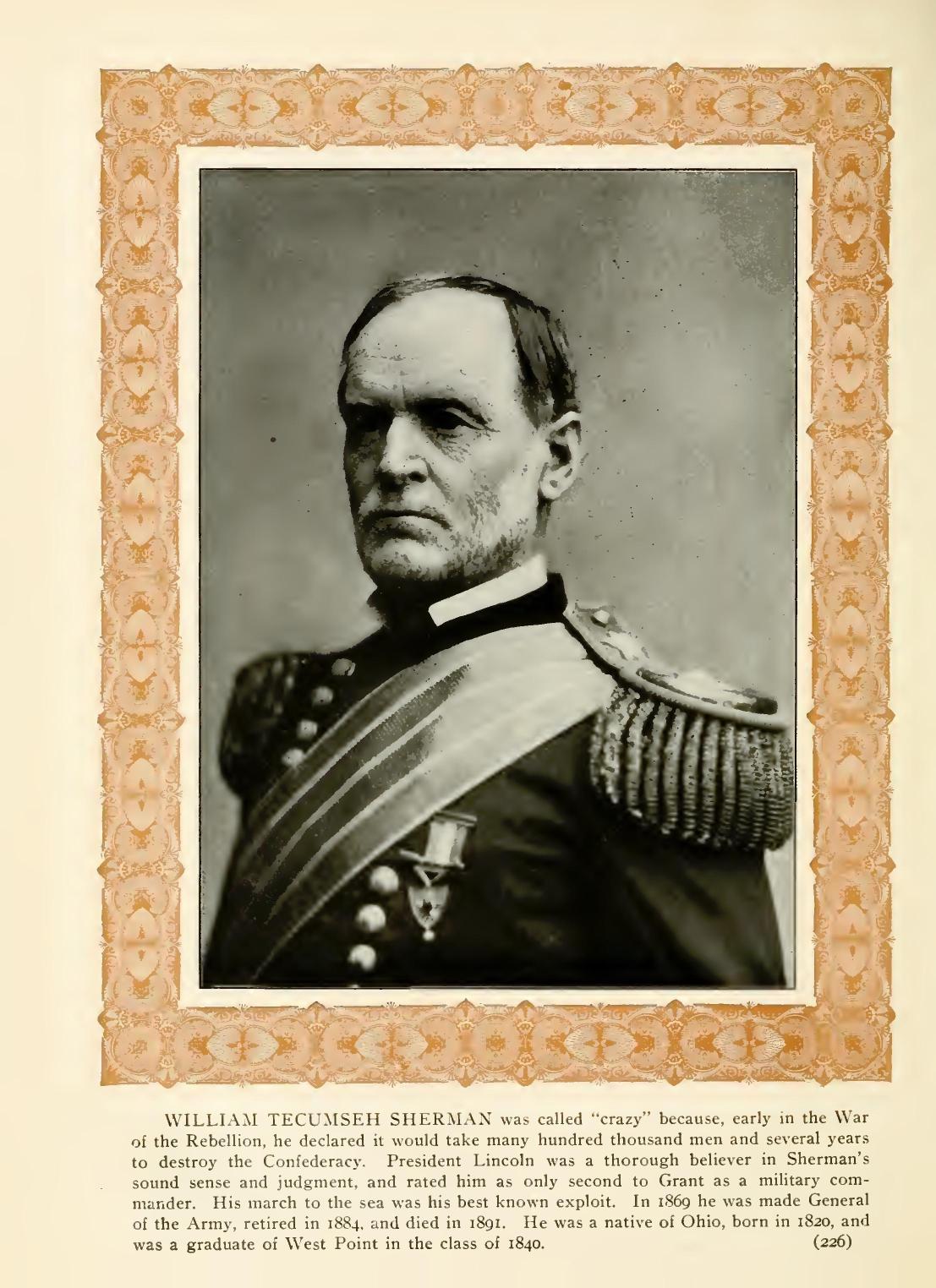




“A few days after the battle of Antietam, the President was driving over the field in an ambulance, accompanied by Marshal Lamon, General McClellan and another officer. Heavy details of men were engaged in the task of burying the dead. The ambulance had just reached the neighborhood of the old stone bridge, where the dead were piled highest, when Mr. Lincoln, suddenly slapping Marshal Lamon on the knee, exclaimed: ‘Come, Lamon, give us that song about “Picayune Butler”; McClellan has never heard it.’
“‘Not now, if you please,’ said General McClellan, with a shudder; ‘I would prefer to hear it some other place and time.’”
President Lincoln refused to pay any attention to the story, would not read the comments made upon it by the newspapers, and would permit neither denial nor explanation to be made. The National election was coming on, and the President’s friends appealed to him to settle the matter for once and all. Marshal Lamon was particularly insistent, but the President merely said:
“Let the thing alone. If I have not established character enough to give the lie to this charge, I can only say that I am mistaken in my own estimate of myself. In politics, every man must skin his own skunk. These fellows are welcome to the hide of this one. Its body has already given forth its unsavory odor.”
But Lamon would not “let the thing alone.” He submitted to Lincoln a draft of what he conceived to be a suitable explanation, after reading which the President said:
“Lamon, your ‘explanation’ is entirely too belligerent in tone for so grave a matter. There is a heap of ‘cussedness’ mixed up with your usual amiability, and you are at times too fond of a fight. If I were you, I would simply state the facts as they were. I would give the statement as you have here, without the pepper and salt. Let me try my hand at it.”
The President then took up a pen and wrote the following, which was copied and sent out as Marshal Lamon’s refutation of the shameless slander:
“The President has known me intimately for nearly twenty years, and has often heard me sing little ditties. The battle of Antietam was fought on the 17th day of September, 1862. On the first day of October, just two weeks after the battle, the President, with some others, including myself, started from Washington to visit the Army, reaching Harper’s Ferry at noon of that day.
“In a short while General McClellan came from his headquarters near the battleground, joined the President, and with him reviewed the troops at Bolivar Heights that afternoon, and at night returned to his headquarters, leaving the President at Harper’s Ferry.
“On the morning of the second, the President, with General Sumner, reviewed the troops respectively at Loudon Heights and Maryland Heights, and at about noon started to General McClellan’s headquarters, reaching there only in time to see very little before night.
“On the morning of the third all started on a review of the Third Corps and the cavalry, in the vicinity of the Antietam battle-ground. After getting through with General Burnside’s corps, at the suggestion of General McClellan, he and the President left their horses to be led, and went into an ambulance to go to General Fitz John Porter’s corps, which was two or three miles distant.
“I am not sure whether the President and General McClellan were in the same ambulance, or in different ones; but myself and some others were in the same with the President. On the way, and on no part of the battleground, and on what suggestions I do not remember, the President asked me to sing the little sad song that follows (“Twenty Years Ago, Tom”), which he had often heard me sing, and had always seemed to like very much.
“After it was over, some one of the party (I do not think it was the President) asked me to sing something else; and I sang two or three little comic things, of which ‘Picayune Butler’ was one. Porter’s corps was reached and reviewed; then the battle-ground was passed over, and the most noted parts examined; then, in succession, the cavalry and Franklin’s corps were reviewed, and the President and party returned to General McClellan’s headquarters at the end of a very hard, hot and dusty day’s work.
“Next day (the 4th), the President and General McClellan visited such of the wounded as still remained in the vicinity, including the now lamented General Richardson; then proceeded to and examined the South-Mountain battle-ground, at which point they parted, General McClellan returning to his camp, and the President returning to Washington, seeing, on the way, General Hartsoff, who lay wounded at Frederick Town.
“This is the whole story of the singing and its surroundings. Neither General McClellan nor any one else made any objections to the singing; the place was not on the battle-field; the time was sixteen days after the battle; no dead body was seen during the whole time the President was absent from Washington, nor even a grave that had not been rained on since the time it was made.”
Nothing in Lincoln’s entire career better illustrated the surprising resources of his mind than his manner of dealing with “The Trent Affair.” The readiness and ability with which he met this perilous emergency, in a field entirely new to his experience, was worthy the most accomplished diplomat and statesman. Admirable, also, was his cool courage and self-reliance in following a course radically opposed to the prevailing sentiment throughout the country and in Congress, and contrary to the advice of his own Cabinet.
Secretary of the Navy Welles hastened to approve officially the act of Captain Wilkes in apprehending the Confederate Commissioners Mason and Slidell, Secretary Stanton publicly applauded, and even Secretary of State Seward, whose long public career had made him especially conservative, stated that he was opposed to any concession or surrender of Mason and Slidell.
But Lincoln, with great sagacity, simply said, “One war at a time.”
The President made his last public address on the evening of April 11th, 1865, to a gathering at the White House. Said he:
“We meet this evening not in sorrow, but in gladness of heart.
“The evacuation of Petersburg and Richmond, and the surrender of the principal insurgent army, give hope of a righteous and speedy peace, whose joyous expression cannot be restrained.
“In the midst of this, however, He from whom all blessings flow must not be forgotten.
“Nor must those whose harder part gives us the cause of rejoicing be overlooked; their honors must not be parceled out with others.
“I myself was near the front, and had the high pleasure of transmitting the good news to you; but no part of the honor, for plan or execution, is mine.
“To General Grant, his skillful officers and brave men, all belongs.”
One day an old lady from the country called on President Lincoln, her tanned face peering up to his through a pair of spectacles. Her errand was to present Mr. Lincoln a pair of stockings of her own make a yard long. Kind tears came to his eyes as she spoke to him, and then, holding the stockings one in each hand, dangling wide apart for general inspection, he assured her that he should take them with him to Washington, where (and here his eyes twinkled) he was sure he should not be able to find any like them.
Quite a number of well-known men were in the room with the President when the old lady made her presentation. Among them was George S. Boutwell, who afterwards became Secretary of the Treasury.
The amusement of the company was not at all diminished by Mr. Boutwell’s remark, that the lady had evidently made a very correct estimate of Mr. Lincoln’s latitude and longitude.
Lincoln was appointed postmaster at New Salem by President Jackson. The office was given him because everybody liked him, and because he was the only man willing to take it who could make out the returns. Lincoln was pleased, because it gave him a chance to read every newspaper taken in the vicinity. He had never been able to get half the newspapers he wanted before.
Years after the postoffice had been discontinued and Lincoln had become a practicing lawyer at Springfield, an agent of the Postoffice Department entered his office and inquired if Abraham Lincoln was within. Lincoln responded to his name, and was informed that the agent had called to collect the balance due the Department since the discontinuance of the New Salem office.
A shade of perplexity passed over Lincoln’s face, which did not escape the notice of friends present. One of them said at once:
“Lincoln, if you are in want of money, let us help you.”
He made no reply, but suddenly rose, and pulled out from a pile of books a little old trunk, and, returning to the table, asked the agent how much the amount of his debt was.
The sum was named, and then Lincoln opened the trunk, pulled out a little package of coin wrapped in a cotton rag, and counted out the exact sum, amounting to more than seventeen dollars.
After the agent had left the room, he remarked quietly that he had never used any man’s money but his own. Although this sum had been in his hands during all those years, he had never regarded it as available, even for any temporary use of his own.
At a Saturday afternoon reception at the White House, many persons noticed three little girls, poorly dressed, the children of some mechanic or laboring man, who had followed the visitors into the White House to gratify their curiosity. They passed around from room to room, and were hastening through the reception-room, with some trepidation, when the President called to them:
“Little girls, are you going to pass me without shaking hands?”
Then he bent his tall, awkward form down, and shook each little girl warmly by the hand. Everybody in the apartment was spellbound by the incident, so simple in itself.


Uncle Sam was pretty well satisfied with his horse, “Old Abe,” and, as shown at the Presidential election of 1864, made up his mind to keep him, and not “swap” the tried and true animal for a strange one. “Harper’s Weekly” of November 12th, 1864, had a cartoon which illustrated how the people of the United States felt about the matter better than anything published at the time. We reproduce it on this page. Beneath the picture was this text:
JOHN BULL: “Why don’t you ride the other horse a bit? He’s the best animal.” (Pointing to McClellan in the bushes at the rear.)
BROTHER JONATHAN: “Well, that may be; but the fact is, OLD ABE is just where I can put my finger on him; and as for the other—though they say he’s some when out in the scrub yonder—I never know where to find him.”
“One time I remember I asked Mr. Lincoln what attribute he considered most valuable to the successful politician,” said Captain T. W. S. Kidd, of Springfield.
“He laid his hand on my shoulder and said, very earnestly:
“‘To be able to raise a cause which shall produce an effect, and then fight the effect.’
“The more you think about it, the more profound does it become.”
A cashiered officer, seeking to be restored through the power of the executive, became insolent, because the President, who believed the man guilty, would not accede to his repeated requests, at last said, “Well, Mr. President, I see you are fully determined not to do me justice!”
This was too aggravating even for Mr. Lincoln; rising he suddenly seized the disgraced officer by the coat collar, and marched him forcibly to the door, saying as he ejected him into the passage:
“Sir, I give you fair warning never to show your face in this room again. I can bear censure, but not insult. I never wish to see your face again.”
Salmon P. Chase, when Secretary of the Treasury, had a disagreement with other members of the Cabinet, and resigned.
The President was urged not to accept it, as “Secretary Chase is to-day a national necessity,” his advisers said.
“How mistaken you are!” Lincoln quietly observed. “Yet it is not strange; I used to have similar notions. No! If we should all be turned out to-morrow, and could come back here in a week, we should find our places filled by a lot of fellows doing just as well as we did, and in many instances better.
“Now, this reminds me of what the Irishman said. His verdict was that ‘in this country one man is as good as another; and, for the matter of that, very often a great deal better.’ No; this Government does not depend upon the life of any man.”
George B. Lincoln, a prominent merchant of Brooklyn, was traveling through the West in 1855-56, and found himself one night in a town on the Illinois River, by the name of Naples. The only tavern of the place had evidently been constructed with reference to business on a small scale. Poor as the prospect seemed, Mr. Lincoln had no alternative but to put up at the place.
The supper-room was also used as a lodging-room. Mr. Lincoln told his host that he thought he would “go to bed.”
“Bed!” echoed the landlord. “There is no bed for you in this house unless you sleep with that man yonder. He has the only one we have to spare.”
“Well,” returned Mr. Lincoln, “the gentleman has possession, and perhaps would not like a bed-fellow.”
Upon this a grizzly head appeared out of the pillows, and said:
“What is your name?”
“They call me Lincoln at home,” was the reply.
“Lincoln!” repeated the stranger; “any connection of our Illinois Abraham?”
“No,” replied Mr. Lincoln. “I fear not.”
“Well,” said the old gentleman, “I will let any man by the name of ‘Lincoln’ sleep with me, just for the sake of the name. You have heard of Abe?” he inquired.
“Oh, yes, very often,” replied Mr. Lincoln. “No man could travel far in this State without hearing of him, and I would be very glad to claim connection if I could do so honestly.”
“Well,” said the old gentleman, “my name is Simmons. ‘Abe’ and I used to live and work together when young men. Many a job of woodcutting and rail-splitting have I done up with him. Abe Lincoln was the likeliest boy in God’s world. He would work all day as hard as any of us and study by firelight in the log-house half the night; and in this way he made himself a thorough, practical surveyor. Once, during those days, I was in the upper part of the State, and I met General Ewing, whom President Jackson had sent to the Northwest to make surveys. I told him about Abe Lincoln, what a student he was, and that I wanted he should give him a job. He looked over his memorandum, and, holding out a paper, said:
“‘There is County must be surveyed; if your friend can do the work properly, I shall be glad to have him undertake it—the compensation will be six hundred dollars.’
“Pleased as I could be, I hastened to Abe, after I got home, with an account of what I had secured for him. He was sitting before the fire in the log-cabin when I told him; and what do you think was his answer? When I finished, he looked up very quietly, and said:
“‘Mr. Simmons, I thank you very sincerely for your kindness, but I don’t think I will undertake the job.’
“‘In the name of wonder,’ said I, ‘why? Six hundred does not grow upon every bush out here in Illinois.’
“‘I know that,’ said Abe, ‘and I need the money bad enough, Simmons, as you know; but I have never been under obligation to a Democratic Administration, and I never intend to be so long as I can get my living another way. General Ewing must find another man to do his work.’”
A friend related this story to the President one day, and asked him if it were true.
“Pollard Simmons!” said Lincoln. “Well do I remember him. It is correct about our working together, but the old man must have stretched the facts somewhat about the survey of the county. I think I should have been very glad of the job at the time, no matter what Administration was in power.”
President Lincoln said, long before the National political campaign of 1864 had opened:
“If the unworthy ambition of politicians and the jealousy that exists in the army could be repressed, and all unite in a common aim and a common endeavor, the rebellion would soon be crushed.”
The President once explained to a friend the theory of the Rebellion by the aid of the maps before him.
Running his long fore-finger down the map, he stopped at Virginia.
“We must drive them away from here” (Manassas Gap), he said, “and clear them out of this part of the State so that they cannot threaten us here (Washington) and get into Maryland.
“We must keep up a good and thorough blockade of their ports. We must march an army into East Tennessee and liberate the Union sentiment there. Finally we must rely on the people growing tired and saying to their leaders, ‘We have had enough of this thing, we will bear it no longer.’”
Such was President Lincoln’s plan for heading off the Rebellion in the summer of 1861. How it enlarged as the War progressed, from a call for seventy thousand volunteers to one for five hundred thousand men and $500,000,000 is a matter of well-known history.
Three or four days after the battle of Bull Run, some gentlemen who had been on the field called upon the President.
He inquired very minutely regarding all the circumstances of the affair, and, after listening with the utmost attention, said, with a touch of humor: “So it is your notion that we whipped the rebels and then ran away from them!”
Old Dennis Hanks was sent to Washington at one time by persons interested in securing the release from jail of several men accused of being copperheads. It was thought Old Dennis might have some influence with the President.
The latter heard Dennis’ story and then said: “I will send for Mr. Stanton. It is his business.”
Secretary Stanton came into the room, stormed up and down, and said the men ought to be punished more than they were. Mr. Lincoln sat quietly in his chair and waited for the tempest to subside, and then quietly said to Stanton he would like to have the papers next day.
When he had gone, Dennis said:
“‘Abe,’ if I was as big and as ugly as you are, I would take him over my knee and spank him.”
The President replied: “No, Stanton is an able and valuable man for this Nation, and I am glad to bear his anger for the service he can give the Nation.”
The quaint remark of the President to an applicant, “My dear sir, I have not much influence with the Administration,” was one of Lincoln’s little jokes.
Mr. Stanton, Secretary of War, once replied to an order from the President to give a colonel a commission in place of the resigning brigadier:
“I shan’t do it, sir! I shan’t do it! It isn’t the way to do it, sir, and I shan’t do it. I don’t propose to argue the question with you, sir.”
A few days after, the friend of the applicant who had presented the order to Secretary Stanton called upon the President and related his reception. A look of vexation came over the face of the President, and he seemed unwilling to talk of it, and desired the friend to see him another day. He did so, when he gave his visitor a positive order for the promotion. The latter told him he would not speak to Secretary Stanton again until he apologized.
“Oh,” said the President, “Stanton has gone to Fortress Monroe, and Dana is acting. He will attend to it for you.”
This he said with a manner of relief, as if it was a piece of good luck to find a man there who would obey his orders.
The nomination was sent to the Senate and confirmed.
Many applications reached Lincoln as he passed to and from the White House and the War Department. One day as he crossed the park he was stopped by a negro, who told him a pitiful story. The President wrote him out a check, which read. “Pay to colored man with one leg five dollars.”
When the Republican party came into power, Washington swarmed with office-seekers. They overran the White House and gave the President great annoyance. The incongruity of a man in his position, and with the very life of the country at stake, pausing to appoint postmasters, struck Mr. Lincoln forcibly. “What is the matter, Mr. Lincoln,” said a friend one day, when he saw him looking particularly grave and dispirited. “Has anything gone wrong at the front?” “No,” said the President, with a tired smile. “It isn’t the war; it’s the postoffice at Brownsville, Missouri.”
Immediately after Mr. Lincoln’s nomination for President at the Chicago Convention, a committee, of which Governor Morgan, of New York, was chairman, visited him in Springfield, Ill., where he was officially informed of his nomination.
After this ceremony had passed, Mr. Lincoln remarked to the company that as a fit ending to an interview so important and interesting as that which had just taken place, he supposed good manners would require that he should treat the committee with something to drink; and opening the door that led into the rear, he called out, “Mary! Mary!” A girl responded to the call, to whom Mr. Lincoln spoke a few words in an undertone, and, closing the door, returned again and talked with his guests. In a few minutes the maid entered, bearing a large waiter, containing several glass tumblers, and a large pitcher, and placed them upon the center-table. Mr. Lincoln arose, and, gravely addressing the company, said: “Gentlemen, we must pledge our mutual health in the most healthy beverage that God has given to man—it is the only beverage I have ever used or allowed my family to use, and I cannot conscientiously depart from it on the present occasion. It is pure Adam’s ale from the spring.” And, taking the tumbler, he touched it to his lips, and pledged them his highest respects in a cup of cold water. Of course, all his guests admired his consistency, and joined in his example.
A few days before the President’s death, Secretary Stanton tendered his resignation as Secretary of War. He accompanied the act with a most heartfelt tribute to Mr. Lincoln’s constant friendship and faithful devotion to the country, saying, also, that he, as Secretary, had accepted the position to hold it only until the war should end, and that now he felt his work was done, and his duty was to resign.
Mr. Lincoln was greatly moved by the Secretary’s words, and, tearing in pieces the paper containing the resignation, and throwing his arms about the Secretary, he said:
“Stanton, you have been a good friend and a faithful public servant, and it is not for you to say when you will no longer be needed here.”
Several friends of both parties were present on the occasion, and there was not a dry eye that witnessed the scene.
When the War was fairly on, many people were astonished to find that “Old Abe” was a fighter from “way back.” No one was the victim of greater amazement than Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America. Davis found out that “Abe” was not only a hard hitter, but had staying qualities of a high order. It was a fight to a “finish” with “Abe,” no compromises being accepted. Over the title, “North and South,” the issue of “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” of December 24th, 1864, contained the cartoon, see reproduce on this page. Underneath the picture were the lines:
“Now, Jeffy, when you think you have had enough of this, say so, and I’ll leave off.” (See President’s message.) In his message to Congress, December 6th,
President Lincoln said: “No attempt at negotiation with the insurgent leader could result in any good. He would accept of nothing short of the severance of the Union.”
Therefore, Father Abraham, getting “Jeffy’s” head “in chancery,” proceeded to change the appearance and size of the secessionist’s countenance, much to the grief and discomfort of the Southerner. It was Lincoln’s idea to re-establish the Union, and he carried out his purpose to the very letter. But he didn’t “leave off” until “Jeffy” cried “enough.”
In October, 1864, President Lincoln, while he knew his re-election to the White House was in no sense doubtful, knew that if he lost New York and with it Pennsylvania on the home vote, the moral effect of his triumph would be broken and his power to prosecute the war and make peace would be greatly impaired. Colonel A. K. McClure was with Lincoln a good deal of the time previous to the November election, and tells this story:
“His usually sad face was deeply shadowed with sorrow when I told him that I saw no reasonable prospect of carrying Pennsylvania on the home vote, although we had about held our own in the hand-to-hand conflict through which we were passing.
“‘Well, what is to be done?’ was Lincoln’s inquiry, after the whole situation had been presented to him. I answered that the solution of the problem was a very simple and easy one—that Grant was idle in front of Petersburg; that Sheridan had won all possible victories in the Valley; and that if five thousand Pennsylvania soldiers could be furloughed home from each army, the election could be carried without doubt.
“Lincoln’s face’ brightened instantly at the suggestion, and I saw that he was quite ready to execute it. I said to him: ‘Of course, you can trust want to make the suggestion to him to furlough five thousand Pennsylvania troops for two weeks?’
“‘To my surprise, Lincoln made no answer, and the bright face of a few moments before was instantly shadowed again. I was much disconcerted, as I supposed that Grant was the one man to whom Lincoln could turn with absolute confidence as his friend. I then said, with some earnestness: ‘Surely, Mr. President, you can trust Grant with a confidential suggestion to furlough Pennsylvania troops?’
“Lincoln remained silent and evidently distressed at the proposition I was pressing upon him. After a few moments, and speaking with emphasis, I said: ‘It can’t be possible that Grant is not your friend; he can’t be such an ingrate?’
“Lincoln hesitated for some time, and then answered in these words: ‘Well, McClure, I have no reason to believe that Grant prefers my election to that of McClellan.’
“I believe Lincoln was mistaken in his distrust of Grant.”
Lincoln was constantly bothered by members of delegations of “goody-goodies,” who knew all about running the War, but had no inside information as to what was going on. Yet, they poured out their advice in streams, until the President was heartily sick of the whole business, and wished the War would find some way to kill off these nuisances.
“How many men have the Confederates now in the field?” asked one of these bores one day.
“About one million two hundred thousand,” replied the President.
“Oh, my! Not so many as that, surely, Mr. Lincoln.”
“They have fully twelve hundred thousand, no doubt of it. You see, all of our generals when they get whipped say the enemy outnumbers them from three or five to one, and I must believe them. We have four hundred thousand men in the field, and three times four make twelve,—don’t you see it? It is as plain to be seen as the nose on a man’s face; and at the rate things are now going, with the great amount of speculation and the small crop of fighting, it will take a long time to overcome twelve hundred thousand rebels in arms.
“If they can get subsistence they have everything else, except a just cause. Yet it is said that ‘thrice is he armed that hath his quarrel just.’ I am willing, however, to risk our advantage of thrice in justice against their thrice in numbers.”
General McClellan had little or no conception of the greatness of Abraham Lincoln. As time went on, he began to show plainly his contempt of the President, frequently allowing him to wait in the ante-room of his house while he transacted business with others. This discourtesy was so open that McClellan’s staff noticed it, and newspaper correspondents commented on it. The President was too keen not to see the situation, but he was strong enough to ignore it. It was a battle he wanted from McClellan, not deference.
“I will hold McClellan’s horse, if he will only bring us success,” he said one day.
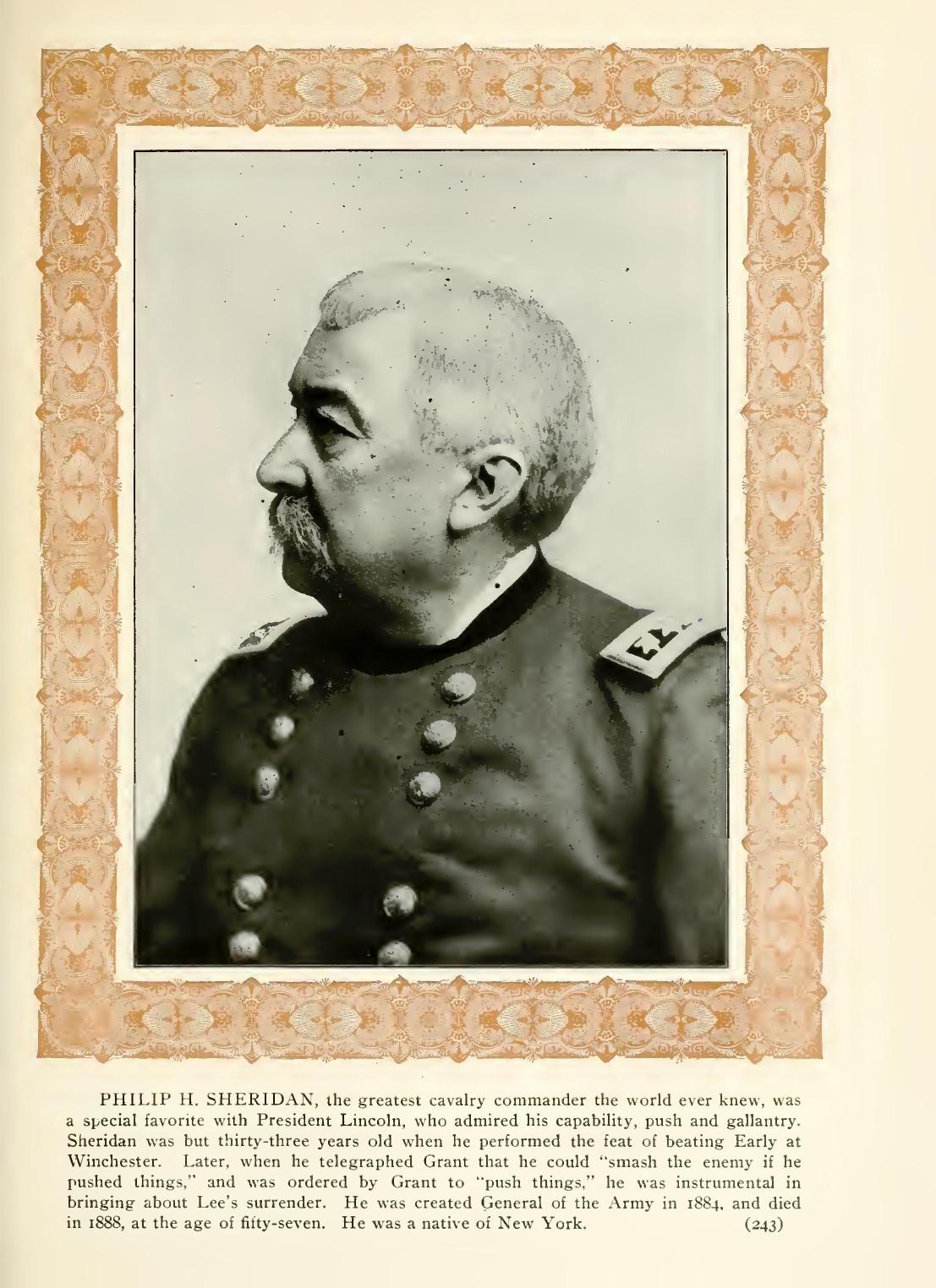
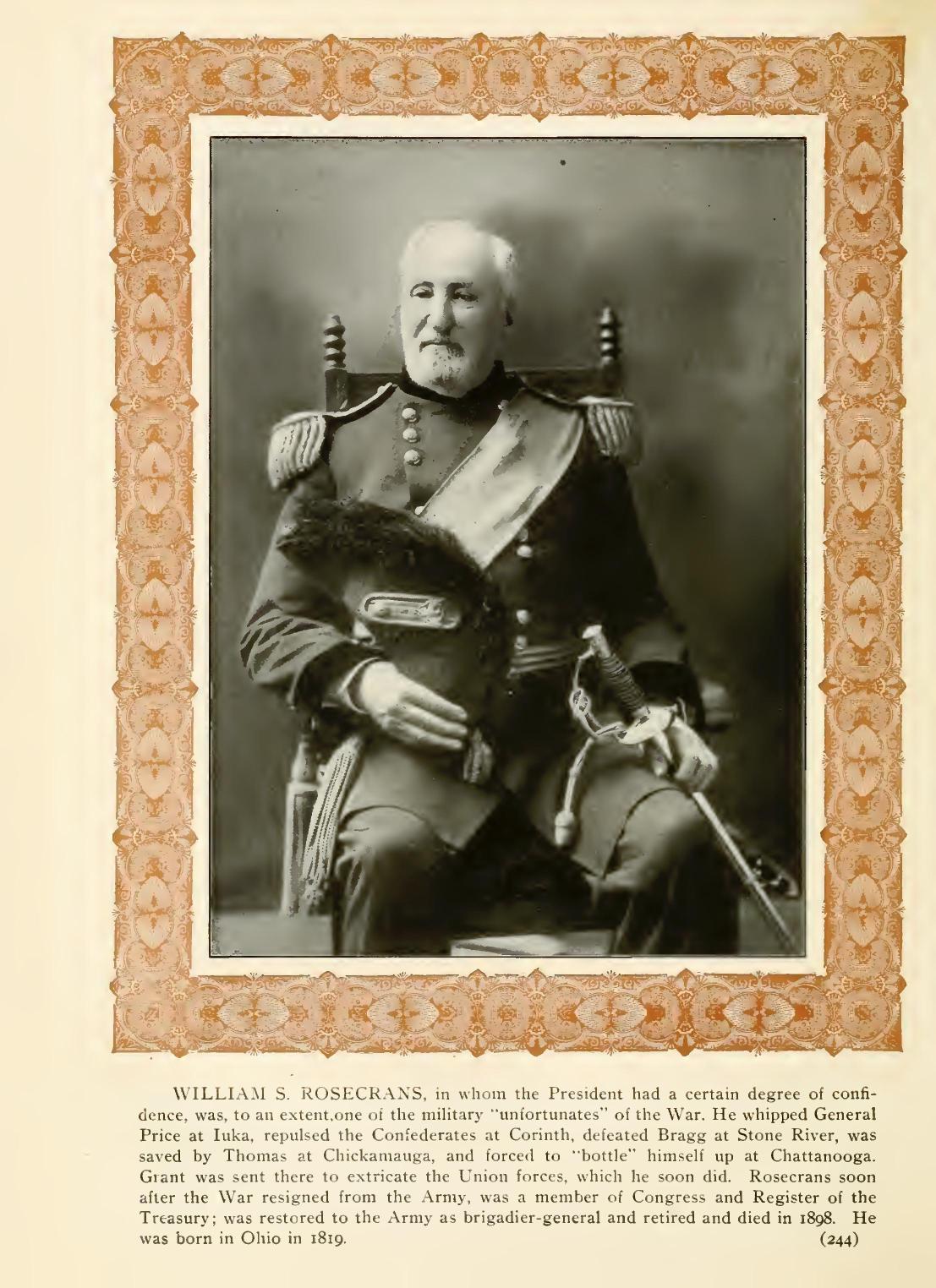




G. H. Giddings was selected as the bearer of a message from the President to Governor Sam Houston, of Texas. A conflict had arisen there between the Southern party and the Governor, Sam Houston, and on March 18 the latter had been deposed. When Mr. Lincoln heard of this, he decided to try to get a message to the Governor, offering United States support if he would put himself at the head of the Union party of the State.
Mr. Giddings thus told of his interview with the President:
“He said to me that the message was of such importance that, before handing it to me, he would read it to me. Before beginning to read he said, ‘This is a confidential and secret message. No one besides my Cabinet and myself knows anything about it, and we are all sworn to secrecy. I am going to swear you in as one of my Cabinet.’
“And then he said to me in a jocular way, ‘Hold up your right hand,’ which I did.
“‘Now,’ said he, consider yourself a member of my Cabinet.”’
With the possible exception of President Washington, whose political opponents did not hesitate to rob the vocabulary of vulgarity and wickedness whenever they desired to vilify the Chief Magistrate, Lincoln was the most and “best” abused man who ever held office in the United States. During the first half of his initial term there was no epithet which was not applied to him.
One newspaper in New York habitually characterized him as “that hideous baboon at the other end of the avenue,” and declared that “Barnum should buy and exhibit him as a zoological curiosity.”
Although the President did not, to all appearances, exhibit annoyance because of the various diatribes printed and spoken, yet the fact is that his life was so cruelly embittered by these and other expressions quite as virulent, that he often declared to those most intimate with him, “I would rather be dead than, as President, thus abused in the house of my friends.”
General “Joe” Hooker, the fourth commander of the noble but unfortunate Army of the Potomac, was appointed to that position by President Lincoln in January, 1863. General Scott, for some reason, disliked Hooker and would not appoint him. Hooker, after some months of discouraging waiting, decided to return to California, and called to pay his respects to President Lincoln. He was introduced as Captain Hooker, and to the surprise of the President began the following speech:
“Mr. President, my friend makes a mistake. I am not Captain Hooker, but was once Lieutenant-Colonel Hooker of the regular army. I was lately a farmer in California, but since the Rebellion broke out I have been trying to get into service, but I find I am not wanted.
“I am about to return home; but before going, I was anxious to pay my respects to you, and express my wishes for your personal welfare and success in quelling this Rebellion. And I want to say to you a word more.
“I was at Bull Run the other day, Mr. President, and it is no vanity in me to say, I am a darned sight better general than you had on the field.”
This was said, not in the tone of a braggart, but of a man who knew what he was talking about. Hooker did not return to California, but in a few weeks Captain Hooker received from the President a commission as Brigadier-General Hooker.
The President, like old King Saul, when his term was about to expire, was in a quandary concerning a further lease of the Presidential office. He consulted again the “prophetess” of Georgetown, immortalized by his patronage.
She retired to an inner chamber, and, after raising and consulting more than a dozen of distinguished spirits from Hades, she returned to the reception-parlor, where the chief magistrate awaited her, and declared that General Grant would capture Richmond, and that “Honest Old Abe” would be next President.
She, however, as the report goes, told him to beware of Chase.
Lincoln had been born and reared among people who were believers in premonitions and supernatural appearances all his life, and he once declared to his friends that he was “from boyhood superstitious.”
He at one time said to Judge Arnold that “the near approach of the important events of his life were indicated by a presentiment or a strange dream, or in some other mysterious way it was impressed upon him that something important was to occur.” This was earlier than 1850.
It is said that on his second visit to New Orleans, Lincoln and his companion, John Hanks, visited an old fortune-teller—a voodoo negress. Tradition says that “during the interview she became very much excited, and after various predictions, exclaimed: ‘You will be President, and all the negroes will be free.’”
That the old voodoo negress should have foretold that the visitor would be President is not at all incredible. She doubtless told this to many aspiring lads, but Lincoln, so it is avowed took the prophecy seriously.
So great was Lincoln’s anxiety for the success of the Union arms that he considered no labor on his part too arduous, and spent much of his time in looking after even the small details.
Admiral Dahlgren was sent for one morning by the President, who said “Well, captain, here’s a letter about some new powder.”
After reading the letter he showed the sample of powder, and remarked that he had burned some of it, and did not believe it was a good article—here was too much residuum.
“I will show you,” he said; and getting a small piece of paper, placed thereupon some of the powder, then went to the fire and with the tongs picked up a coal, which he blew, clapped it on the powder, and after the resulting explosion, added, “You see there is too much left there.”
McClellan was a thorn in Lincoln’s side—“always up in the air,” as the President put it—and yet he hesitated to remove him. “The Young Napoleon” was a good organizer, but no fighter. Lincoln sent him everything necessary in the way of men, ammunition, artillery and equipments, but he was forever unready.
Instead of making a forward movement at the time expected, he would notify the President that he must have more men. These were given him as rapidly as possible, and then would come a demand for more horses, more this and that, usually winding up with a demand for still “more men.”
Lincoln bore it all in patience for a long time, but one day, when he had received another request for more men, he made a vigorous protest.
“If I gave McClellan all the men he asks for,” said the President, “they couldn’t find room to lie down. They’d have to sleep standing up.”
General Meade, after the great victory at Gettysburg, was again face to face with General Lee shortly afterwards at Williamsport, and even the former’s warmest friends agree that he might have won in another battle, but he took no action. He was not a “pushing” man like Grant. It was this negligence on the part of Meade that lost him the rank of Lieutenant-General, conferred upon General Sheridan.
A friend of Meade’s, speaking to President Lincoln and intimating that Meade should have, after that battle, been made Commander-in-Chief of the Union Armies, received this reply from Lincoln:
“Now, don’t misunderstand me about General Meade. I am profoundly grateful down to the bottom of my boots for what he did at Gettysburg, but I think that if I had been General Meade I would have fought another battle.”
In one of his reminiscences of Lincoln, Ward Lamon tells how keenly the President-elect always regretted the “sneaking in act” when he made the celebrated “midnight ride,” which he took under protest, and landed him in Washington known to but a few. Lamon says:
“The President was convinced that he committed a grave mistake in listening to the solicitations of a ‘professional spy’ and of friends too easily alarmed, and frequently upbraided me for having aided him to degrade himself at the very moment in all his life when his behavior should have exhibited the utmost dignity and composure.
“Neither he nor the country generally then understood the true facts concerning the dangers to his life. It is now an acknowledged fact that there never was a moment from the day he crossed the Maryland line, up to the time of his assassination, that he was not in danger of death by violence, and that his life was spared until the night of the 14th of April, 1865, only through the ceaseless and watchful care of the guards thrown around him.”
President Lincoln was calm and unmoved when England and France were blustering and threatening war. At Lincoln’s instance Secretary of State Seward notified the English Cabinet and the French Emperor that as ours was merely a family quarrel of a strictly private and confidential nature, there was no call for meddling; also that they would have a war on their hands in a very few minutes if they didn’t keep their hands off.
Many of Seward’s notes were couched in decidedly peppery terms, some expressions being so tart that President Lincoln ran his pen through them.
General Farnsworth told the writer nearly twenty years ago that, being in the War Office one day, Secretary Stanton told him that at the last Cabinet meeting he had learned a lesson he should never forget, and thought he had obtained an insight into Mr. Lincoln’s wonderful power over the masses. The Secretary said a Cabinet meeting was called to consider our relations with England in regard to the Mason-Slidell affair. One after another of the Cabinet presented his views, and Mr. Seward read an elaborate diplomatic dispatch, which he had prepared.
Finally Mr. Lincoln read what he termed “a few brief remarks upon the subject,” and asked the opinions of his auditors. They unanimously agreed that our side of the question needed no more argument than was contained in the President’s “few brief remarks.”
Mr. Seward said he would be glad to adopt the remarks, and, giving them more of the phraseology usual in diplomatic circles, send them to Lord Palmerston, the British premier.
“Then,” said Secretary Stanton, “came the demonstration. The President, half wheeling in his seat, threw one leg over the chair-arm, and, holding the letter in his hand, said, ‘Seward, do you suppose Palmerston will understand our position from that letter, just as it is?’
“‘Certainly, Mr. President.’
“‘Do you suppose the London Times will?’
“‘Certainly.’
“‘Do you suppose the average Englishman of affairs will?’
“‘Certainly; it cannot be mistaken in England.’
“‘Do you suppose that a hackman out on his box (pointing to the street) will understand it?’
“‘Very readily, Mr. President.’
“‘Very well, Seward, I guess we’ll let her slide just as she is.’
“And the letter did ‘slide,’ and settled the whole business in a manner that was effective.”
One morning President Lincoln asked Major Eckert, on duty at the White House, “Who is that woman crying out in the hall? What is the matter with her?”
Eckert said it was a woman who had come a long distance expecting to go down to the army to see her husband. An order had gone out a short time before to allow no women in the army, except in special cases.
Mr. Lincoln sat moodily for a moment after hearing this story, and suddenly looking up, said, “Let’s send her down. You write the order, Major.”
Major Eckert hesitated a moment, and replied, “Would it not be better for Colonel Hardie to write the order?”
“Yes,” said Mr. Lincoln, “that is better; let Hardie write it.”
The major went out, and soon returned, saying, “Mr. President, would it not be better in this case to let the woman’s husband come to Washington?”
Mr. Lincoln’s face lighted up with pleasure. “Yes, yes,” was the President’s answer in a relieved tone; “that’s the best way; bring him up.”
The order was written, and the man was sent to Washington.
The President, although almost feminine in his kind-heartedness, knew not only this, but also that large bodies of soldiers in camp were at the mercy of diseases of every sort, the result being a heavy casualty list.
Of the (estimated) half-million men of the Union armies who gave up their lives in the War of the Rebellion—1861-65—fully seventy-five per cent died of disease. The soldiers killed upon the field of battle constituted a comparatively small proportion of the casualties.
London “Punch” caricatured President Lincoln in every possible way, holding him and the Union cause up to the ridicule of the world so far as it could. On August 23rd, 1862, its cartoon entitled “Lincoln’s Two Difficulties” had the text underneath: LINCOLN: “What? No money! No men!” “Punch” desired to create the impression that the Washington Government was in a bad way, lacking both money and men for the purpose of putting down the Rebellion; that the United States Treasury was bankrupt, and the people of the North so devoid of patriotism that they would not send men for the army to assist in destroying the Confederacy. The truth is, that when this cartoon was printed the North had five hundred thousand men in the field, and, before the War closed, had provided fully two million and a half troops. The report of the Secretary of the Treasury which showed the financial affairs and situation of the United States up to July, 1862. The receipts of the National Government for the year ending June 30th, 1862, were $10,000,000 in excess of the expenditures, although the War was costing the country $2,000,000 per day; the credit of the United States was good, and business matters were in a satisfactory state. The Navy, by August 23rd, 1862, had received eighteen thousand additional men, and was in fine shape; the people of the North stood ready to supply anything the Government needed, so that, all things taken together, the “Punch” cartoon was not exactly true, as the facts and figures abundantly proved.
An old and intimate friend from Springfield called on President Lincoln and found him much depressed.
The President was reclining on a sofa, but rising suddenly he said to his friend:
“You know better than any man living that from my boyhood up my ambition was to be President. I am President of one part of this divided country at least; but look at me! Oh, I wish I had never been born!
“I’ve a white elephant on my hands—one hard to manage. With a fire in my front and rear to contend with, the jealousies of the military commanders, and not receiving that cordial co-operative support from Congress that could reasonably be expected with an active and formidable enemy in the field threatening the very life-blood of the Government, my position is anything but a bed of roses.”
Ward Lamon, one of President Lincoln’s law partners, and his most intimate friend in Washington, has this to relate:
“I am not aware that there was ever a serious discord or misunderstanding between Mr. Lincoln and General Grant, except on a single occasion. From the commencement of the struggle, Lincoln’s policy was to break the backbone of the Confederacy by depriving it of its principal means of subsistence.
“Cotton was its vital aliment; deprive it of this, and the rebellion must necessarily collapse. The Hon. Elihu B. Washburne from the outset was opposed to any contraband traffic with the Confederates.
“Lincoln had given permits and passes through the lines to two persons—Mr. Joseph Mattox of Maryland and General Singleton of Illinois—to enable them to bring cotton and other Southern products from Virginia. Washburne heard of it, called immediately on Mr. Lincoln, and, after remonstrating with him on the impropriety of such a demarche, threatened to have General Grant countermand the permits if they were not revoked.
“Naturally, both became excited. Lincoln declared that he did not believe General Grant would take upon himself the responsibility of such an act. ‘I will show you, sir; I will show you whether Grant will do it or not,’ responded Mr. Washburne, as he abruptly withdrew.
“By the next boat, subsequent to this interview, the Congressman left Washington for the headquarters of General Grant. He returned shortly afterward to the city, and so likewise did Mattox and Singleton. Grant had countermanded the permits.
“Under all the circumstances, it was, naturally, a source of exultation to Mr. Washburne and his friends, and of corresponding surprise and mortification to the President. The latter, however, said nothing further than this:
“‘I wonder when General Grant changed his mind on this subject? He was the first man, after the commencement of this War, to grant a permit for the passage of cotton through the lines, and that to his own father.’
“The President, however, never showed any resentment toward General Grant.
“In referring afterwards to the subject, the President said: ‘It made me feel my insignificance keenly at the moment; but if my friends Washburne, Henry Wilson and others derive pleasure from so unworthy a victory over me, I leave them to its full enjoyment.’
“This ripple on the otherwise unruffled current of their intercourse did not disturb the personal relations between Lincoln and Grant; but there was little cordiality between the President and Messrs. Washburne and Wilson afterwards.”
The story as to how President Lincoln won the support of James Gordon Bennett, Sr., founder of the New York Herald, is a most interesting one. It was one of Lincoln’s shrewdest political acts, and was brought about by the tender, in an autograph letter, of the French Mission to Bennett.
The New York Times was the only paper in the metropolis which supported him heartily, and President Lincoln knew how important it was to have the support of the Herald. He therefore, according to the way Colonel McClure tells it, carefully studied how to bring its editor into close touch with himself.
The outlook for Lincoln’s re-election was not promising. Bennett had strongly advocated the nomination of General McClellan by the Democrats, and that was ominous of hostility to Lincoln; and when McClellan was nominated he was accepted on all sides as a most formidable candidate.
It was in this emergency that Lincoln’s political sagacity served him sufficiently to win the Herald to his cause, and it was done by the confidential tender of the French Mission. Bennett did not break over to Lincoln at once, but he went by gradual approaches.
His first step was to declare in favor of an entirely new candidate, which was an utter impossibility. He opened a “leader” in the Herald on the subject in this way: “Lincoln has proved a failure; McClellan has proved a failure; Fremont has proved a failure; let us have a new candidate.”
Lincoln, McClellan and Fremont were then all in the field as nominated candidates, and the Fremont defection was a serious threat to Lincoln. Of course, neither Lincoln nor McClellan declined, and the Herald, failing to get the new man it knew to be an impossibility, squarely advocated Lincoln’s re-election.
Without consulting any one, and without any public announcement: whatever, Lincoln wrote to Bennett, asking him to accept the mission to France. The offer was declined. Bennett valued the offer very much more than the office, and from that day until the day of the President’s death he was one of Lincoln’s most appreciative friends and hearty supporters on his own independent line.
Once, in reply to a delegation, which visited the White House, the members of which were unusually vociferous in their demands that the Silent Man (as General Grant was called) should be relieved from duty, the President remarked:
“What I want and what the people want is generals who will fight battles and win victories.
“Grant has done this, and I propose to stand by him.”
This declaration found its way into the newspapers, and Lincoln was upheld by the people of the North, who, also, wanted “generals who will fight battles and win victories.”
President Lincoln and Secretary of State Seward met Alexander H. Stephens, Vice-President of the Confederacy, on February 2nd, 1865, on the River Queen, at Fortress Monroe. Stephens was enveloped in overcoats and shawls, and had the appearance of a fair-sized man. He began to take off one wrapping after another, until the small, shriveled old man stood before them.


Lincoln quietly said to Seward: “This is the largest shucking for so small a nubbin that I ever saw.”
President Lincoln had a friendly conference, but presented his ultimatum that the one and only condition of peace was that Confederates “must cease their resistance.”
During the Civil War, Clement L. Vallandigham, of Ohio, had shown himself, in the National House of Representatives and elsewhere, one of the bitterest and most outspoken of all the men of that class which insisted that “the war was a failure.” He declared that it was the design of “those in power to establish a despotism,” and that they had “no intention of restoring the Union.” He denounced the conscription which had been ordered, and declared that men who submitted to be drafted into the army were “unworthy to be called free men.” He spoke of the President as “King Lincoln.”
Such utterances at this time, when the Government was exerting itself to the utmost to recruit the armies, were dangerous, and Vallandigham was arrested, tried by court-martial at Cincinnati, and sentenced to be placed in confinement during the war.
General Burnside, in command at Cincinnati, approved the sentence, and ordered that he be sent to Fort Warren, in Boston Harbor; but the President ordered that he be sent “beyond our lines into those of his friends.” He was therefore escorted to the Confederate lines in Tennessee, thence going to Richmond. He did not meet with a very cordial reception there, and finally sought refuge in Canada.
Vallandigham died in a most peculiar way some years after the close of the War, and it was thought by many that his death was the result of premeditation upon his part.
In August, 1864, the President called for five hundred thousand more men. The country was much depressed. The Confederates had, in comparatively small force, only a short time before, been to the very gates of Washington, and returned almost unharmed.
The Presidential election was impending. Many thought another call for men at such a time would insure, if not destroy, Mr. Lincoln’s chances for re-election. A friend said as much to him one day, after the President had told him of his purpose to make such a call.
“As to my re-election,” replied Mr. Lincoln, “it matters not. We must have the men. If I go down, I intend to go, like the Cumberland, with my colors flying!”
The cartoon reproduced below was published in “Harper’s Weekly” on January 31st, 1863, the explanatory text, underneath, reading in this way:
MANAGER LINCOLN: “Ladies and gentlemen, I regret to say that the tragedy entitled ‘The Army of the Potomac’ has been withdrawn on account of quarrels among the leading performers, and I have substituted three new and striking farces, or burlesques, one, entitled ‘The Repulse of Vicksburg,’ by the well-known favorite, E. M. Stanton, Esq., and the others, ‘The Loss of the Harriet Lane,’ and ‘The Exploits of the Alabama’—a very sweet thing in farces, I assure you—by the veteran composer, Gideon Welles. (Unbounded applause by the Copperheads).”
In July, after this cartoon appeared, the Army of the Potomac defeated Lee at Gettysburg, and sounded the death-knell of the Confederacy; General Hooker, with his corps from this Army opened the Tennessee River, thus affording some relief to the Union troops in Chattanooga; Hooker’s men also captured Lookout Mountain, and assisted in taking Missionary Ridge.
General Grant converted the farce “The Repulse of Vicksburg” into a tragedy for the Copperheads, taking that stronghold on July 4th, and Captain Winslow, with the Union man-of-war Kearsarge, meeting the Confederate privateer Alabama, off the coast of France, near Cherbourg, fought the famous ship to a finish and sunk her. Thus the tragedy of “The Army of the Potomac” was given after all, and Playwright Stanton and Composer Welles were vindicated, their compositions having been received by the public with great favor.
Secretary of State Seward did not appreciate President Lincoln’s ability until he had been associated with him for quite a time, but he was awakened to a full realization of the greatness of the Chief Executive “all of a sudden.”
Having submitted “Some Thoughts for the President’s Consideration”—a lengthy paper intended as an outline of the policy, both domestic and foreign, the Administration should pursue—he was not more surprised at the magnanimity and kindness of President Lincoln’s reply than the thorough mastery of the subject displayed by the President.
A few months later, when the Secretary had begun to understand Mr. Lincoln, he was quick and generous to acknowledge his power.
“Executive force and vigor are rare qualities,” he wrote to Mrs. Seward. “The President is the best of us.”
Superintendent Chandler, of the Telegraph Office in the War Department, once told how President Lincoln wrote telegrams. Said he:
“Mr. Lincoln frequently wrote telegrams in my office. His method of composition was slow and laborious. It was evident that he thought out what he was going to say before he touched his pen to the paper. He would sit looking out of the window, his left elbow on the table, his hand scratching his temple, his lips moving, and frequently he spoke the sentence aloud or in a half whisper.
“After he was satisfied that he had the proper expression, he would write it out. If one examines the originals of Mr. Lincoln’s telegrams and letters, he will find very few erasures and very little interlining. This was because he had them definitely in his mind before writing them.
“In this he was the exact opposite of Mr. Stanton, who wrote with feverish haste, often scratching out words, and interlining frequently. Sometimes he would seize a sheet which he had filled, and impatiently tear it into pieces.”
Several United States Senators urged President Lincoln to muster Southern slaves into the Union Army. Lincoln replied:
“Gentlemen, I have put thousands of muskets into the hands of loyal citizens of Tennessee, Kentucky, and Western North Carolina. They have said they could defend themselves, if they had guns. I have given them the guns. Now, these men do not believe in mustering-in the negro. If I do it, these thousands of muskets will be turned against us. We should lose more than we should gain.”
Being still further urged, President Lincoln gave them this answer:
“Gentlemen,” he said, “I can’t do it. I can’t see it as you do. You may be right, and I may be wrong; but I’ll tell you what I can do; I can resign in favor of Mr. Hamlin. Perhaps Mr. Hamlin could do it.”
The matter ended there, for the time being.
The President took a lively interest in all new firearm improvements and inventions, and it sometimes happened that, when an inventor could get nobody else in the Government to listen to him, the President would personally test his gun. A former clerk in the Navy Department tells an incident illustrative.
He had stayed late one night at his desk, when he heard some one striding up and down the hall muttering: “I do wonder if they have gone already and left the building all alone.” Looking out, the clerk was surprised to see the President.
“Good evening,” said Mr. Lincoln. “I was just looking for that man who goes shooting with me sometimes.”
The clerk knew Mr. Lincoln referred to a certain messenger of the Ordnance Department who had been accustomed to going with him to test weapons, but as this man had gone home, the clerk offered his services. Together they went to the lawn south of the White House, where Mr. Lincoln fixed up a target cut from a sheet of white Congressional notepaper.
“Then pacing off a distance of about eighty or a hundred feet,” writes the clerk, “he raised the rifle to a level, took a quick aim, and drove the round of seven shots in quick succession, the bullets shooting all around the target like a Gatling gun and one striking near the center.
“‘I believe I can make this gun shoot better,’ said Mr. Lincoln, after we had looked at the result of the first fire. With this he took from his vest pocket a small wooden sight which he had whittled from a pine stick, and adjusted it over the sight of the carbine. He then shot two rounds, and of the fourteen bullets nearly a dozen hit the paper!”
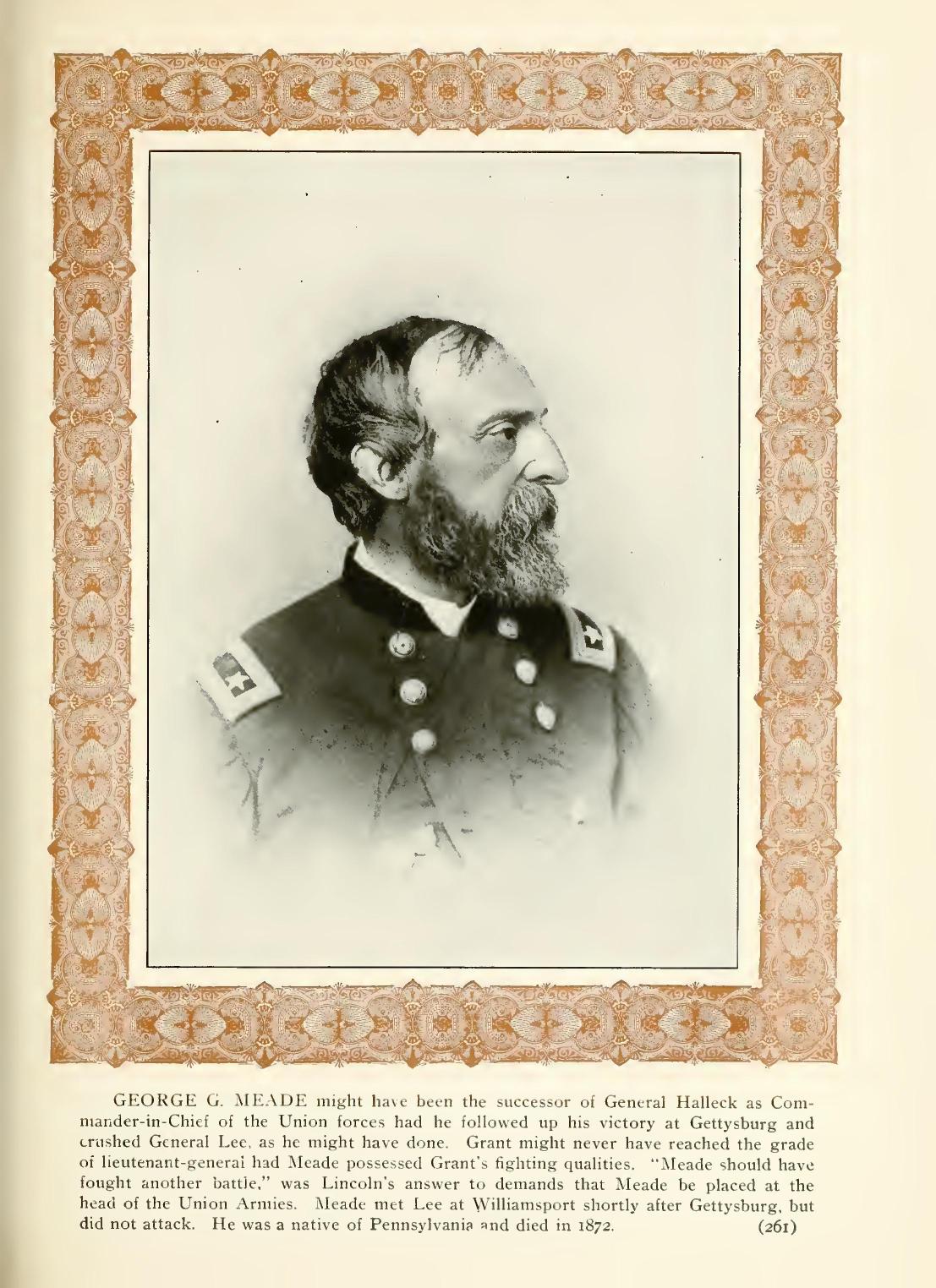
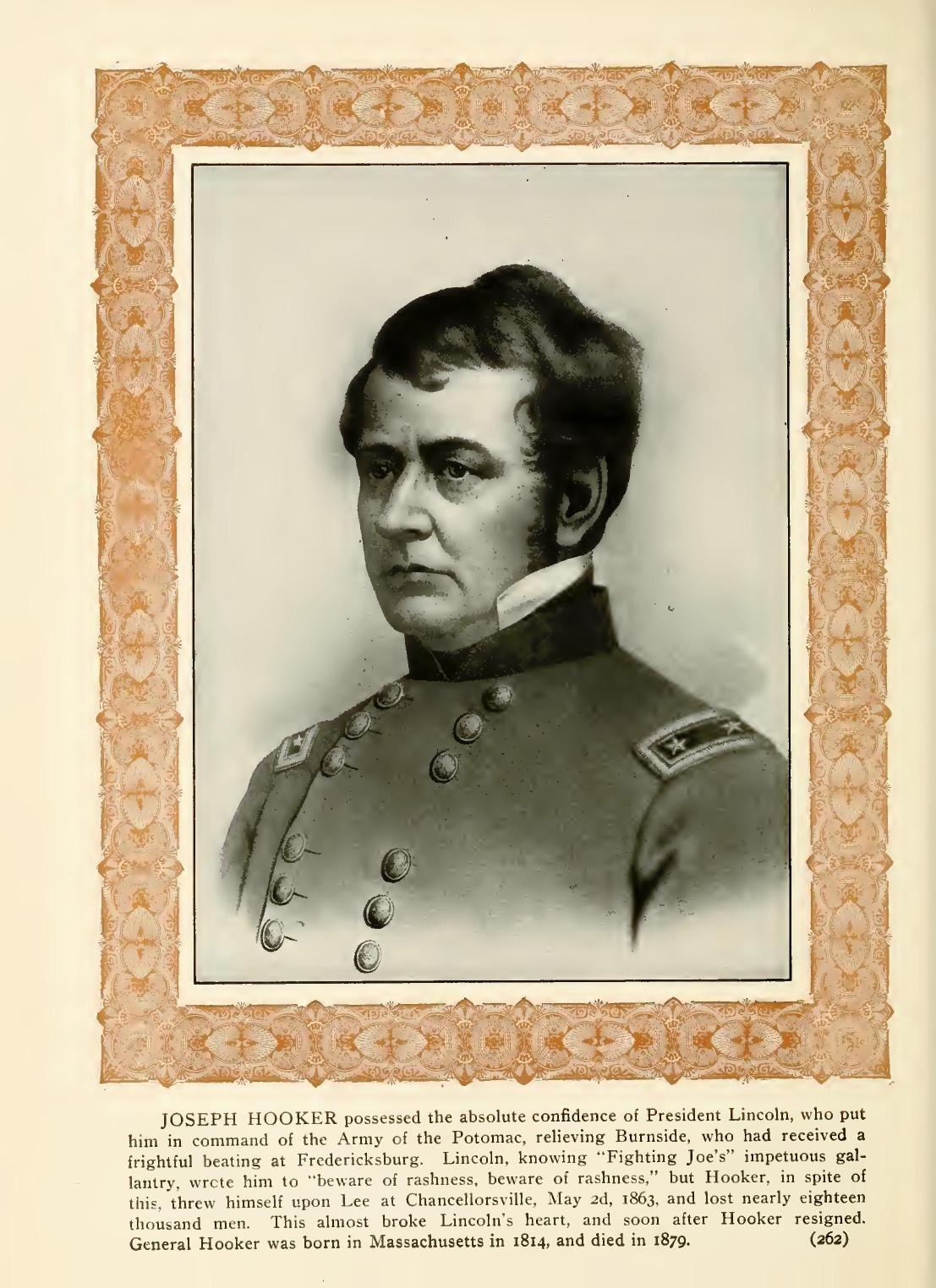




General McClellan, aside from his lack of aggressiveness, fretted the President greatly with his complaints about military matters, his obtrusive criticism regarding political matters, and especially at his insulting declaration to the Secretary of War, dated June 28th, 1862, just after his retreat to the James River.
General Halleck was made Commander-in-Chief of the Union forces in July, 1862, and September 1st McClellan was called to Washington. The day before he had written his wife that “as a matter of self-respect, I cannot go there.” President Lincoln and General Halleck called at McClellan’s house, and the President said: “As a favor to me, I wish you would take command of the fortifications of Washington and all the troops for the defense of the capital.”
Lincoln thought highly of McClellan’s ability as an organizer and his strength in defense, yet any other President would have had him court-martialed for using this language, which appeared in McClellan’s letter of June 28th:
“If I save this army now, I tell you plainly that I owe no thanks to you or to any other person in Washington. You have done your best to sacrifice this army.”
This letter, although addressed to the Secretary of War, distinctly embraced the President in the grave charge of conspiracy to defeat McClellan’s army and sacrifice thousands of the lives of his soldiers.
When General Cass was a candidate for the Presidency his friends sought to endow him with a military reputation.
Lincoln, at that time a representative in Congress, delivered a speech before the House, which, in its allusion to Mr. Cass, was exquisitely sarcastic and irresistibly humorous:
“By the way, Mr. Speaker,” said Lincoln, “do you know I am a military hero?
“Yes, sir, in the days of the Black Hawk War, I fought, bled, and came away.
“Speaking of General Cass’s career reminds me of my own.
“I was not at Stillman’s defeat, but I was about as near it as Cass to Hull’s surrender; and like him I saw the place very soon afterwards.
“It is quite certain I did not break my sword, for I had none to break, but I bent my musket pretty badly on one occasion.
“If General Cass went in advance of me picking whortleberries, I guess I surpassed him in charging upon the wild onion.
“If he saw any live, fighting Indians, it was more than I did, but I had a good many bloody struggles with the mosquitoes, and although I never fainted from loss of blood, I can truly say that I was often very hungry.”
Lincoln concluded by saying that if he ever turned Democrat and should run for the Presidency, he hoped they would not make fun of him by attempting to make him a military hero.
About March, 1862, General Benjamin F. Butler, in command at Fortress Monroe, advised President Lincoln that he had determined to regard all slaves coming into his camps as contraband of war, and to employ their labor under fair compensation, and Secretary of War Stanton replied to him, in behalf of the President, approving his course, and saying, “You are not to interfere between master and slave on the one hand, nor surrender slaves who may come within your lines.”
This was a significant milestone of progress to the great end that was thereafter to be reached.
Mr. Lincoln being found fault with for making another “call,” said that if the country required it, he would continue to do so until the matter stood as described by a Western provost marshal, who says:
“I listened a short time since to a butternut-clad individual, who succeeded in making good his escape, expatiate most eloquently on the rigidness with which the conscription was enforced south of the Tennessee River. His response to a question propounded by a citizen ran somewhat in this wise:
“‘Do they conscript close over the river?’
“‘Stranger, I should think they did! They take every man who hasn’t been dead more than two days!’
“If this is correct, the Confederacy has at least a ghost of a chance left.”
And of another, a Methodist minister in Kansas, living on a small salary, who was greatly troubled to get his quarterly instalment. He at last told the non-paying trustees that he must have his money, as he was suffering for the necessaries of life.
“Money!” replied the trustees; “you preach for money? We thought you preached for the good of souls!”
“Souls!” responded the reverend; “I can’t eat souls; and if I could it would take a thousand such as yours to make a meal!”
“That soul is the point, sir,” said the President.
On February 5th, 1865, President Lincoln formulated a message to Congress, proposing the payment of $400,000,000 to the South as compensation for slaves lost by emancipation, and submitted it to his Cabinet, only to be unanimously rejected.
Lincoln sadly accepted the decision, and filed away the manuscript message, together with this indorsement thereon, to which his signature was added: “February 5, 1865. To-day these papers, which explain themselves, were drawn up and submitted to the Cabinet unanimously disapproved by them.”
When the proposed message was disapproved, Lincoln soberly asked: “How long will the war last?”
To this none could make answer, and he added: “We are spending now, in carrying on the war, $3,000,000 a day, which will amount to all this money, besides all the lives.”
In his youth, Mr. Lincoln once got an idea for a thrilling, romantic story. One day, in Springfield, he was sitting with his feet on the window sill, chatting with an acquaintance, when he suddenly changed the drift of the conversation by saying: “Did you ever write out a story in your mind? I did when I was a little codger. One day a wagon with a lady and two girls and a man broke down near us, and while they were fixing up, they cooked in our kitchen. The woman had books and read us stories, and they were the first I had ever heard. I took a great fancy to one of the girls; and when they were gone I thought of her a great deal, and one day when I was sitting out in the sun by the house I wrote out a story in my mind. I thought I took my father’s horse and followed the wagon, and finally I found it, and they were surprised to see me. I talked with the girl, and persuaded her to elope with me; and that night I put her on my horse, and we started off across the prairie. After several hours we came to a camp; and when we rode up we found it was the one we had left a few hours before, and went in. The next night we tried again, and the same thing happened—the horse came back to the same place; and then we concluded that we ought not to elope. I stayed until I had persuaded her father to give her to me. I always meant to write that story out and publish it, and I began once; but I concluded that it was not much of a story. But I think that was the beginning of love with me.”
Lincoln’s reply to a Springfield (Illinois) clergyman, who asked him what was to be his policy on the slavery question was most apt:
“Well, your question is rather a cool one, but I will answer it by telling you a story:
“You know Father B., the old Methodist preacher? and you know Fox River and its freshets?
“Well, once in the presence of Father B., a young Methodist was worrying about Fox River, and expressing fears that he should be prevented from fulfilling some of his appointments by a freshet in the river.
“Father B. checked him in his gravest manner. Said he:
“‘Young man, I have always made it a rule in my life not to cross Fox River till I get to it.’
“And,” said the President, “I am not going to worry myself over the slavery question till I get to it.”
A few days afterward a Methodist minister called on the President, and on being presented to him, said, simply:
“Mr. President, I have come to tell you that I think we have got to Fox River!”
Lincoln thanked the clergyman, and laughed heartily.
The day of Lincoln’s second nomination for the Presidency he forgot all about the Republican National Convention, sitting at Baltimore, and wandered over to the War Department. While there, a telegram came announcing the nomination of Johnson as Vice-President.
“What,” said Lincoln to the operator, “do they nominate a Vice-President before they do a President?”
“Why,” replied the astonished official, “have you not heard of your own nomination? It was sent to the White House two hours ago.”
“It is all right,” replied the President; “I shall probably find it on my return.”
The illustrated newspapers of the United States and England had a good deal of fun, not only with President Lincoln, but the latter’s Cabinet officers and military commanders as well. It was said by these funny publications that the President had set up a guillotine in his “back-yard,” where all those who offended were beheaded with both neatness, and despatch. “Harper’s Weekly” of January 3rd, 1863, contained a cartoon labeled “Those Guillotines; a Little Incident at the White House,” the personages figuring in the “incident” being Secretary of War Stanton and a Union general who had been unfortunate enough to lose a battle to the Confederates. Beneath the cartoon was the following dialogue:
SERVANT: “If ye plase, sir, them Gilliteens has arrove.” MR. LINCOLN: “All right, Michael. Now, gentlemen, will you be kind enough to step out in the back-yard?”
The hair and whiskers of Secretary of War Stanton are ruffled and awry, and his features are not calm and undisturbed, indicating that he has an idea of what’s the matter in that back-yard; the countenance of the officer in the rear of the Secretary of War wears rather an anxious, or worried, look, and his hair isn’t combed smoothly, either.
President Lincoln’s frequent changes among army commanders—before he found Grant, Sherman and Sheridan—afforded an opportunity the caricaturists did not neglect, and some very clever cartoons were the consequence.
Consider the sympathy of Abraham Lincoln. Do you know the story of William Scott, private? He was a boy from a Vermont farm.
There had been a long march, and the night succeeding it he had stood on picket. The next day there had been another long march, and that night William Scott had volunteered to stand guard in the place of a sick comrade who had been drawn for the duty.
It was too much for William Scott. He was too tired. He had been found sleeping on his beat.
The army was at Chain Bridge. It was in a dangerous neighborhood. Discipline must be kept.
William Scott was apprehended, tried by court-martial, sentenced to be shot. News of the case was carried to Lincoln. William Scott was a prisoner in his tent, expecting to be shot next day.
But the flaps of his tent were parted, and Lincoln stood before him. Scott said:
“The President was the kindest man I had ever seen; I knew him at once by a Lincoln medal I had long worn.
“I was scared at first, for I had never before talked with a great man; but Mr. Lincoln was so easy with me, so gentle, that I soon forgot my fright.
“He asked me all about the people at home, the neighbors, the farm, and where I went to school, and who my schoolmates were. Then he asked me about mother and how she looked; and I was glad I could take her photograph from my bosom and show it to him.
“He said how thankful I ought to be that my mother still lived, and how, if he were in my place, he would try to make her a proud mother, and never cause her a sorrow or a tear.
“I cannot remember it all, but every word was so kind.
“He had said nothing yet about that dreadful next morning; I thought it must be that he was so kind-hearted that he didn’t like to speak of it.
“But why did he say so much about my mother, and my not causing her a sorrow or a tear, when I knew that I must die the next morning?
“But I supposed that was something that would have to go unexplained; and so I determined to brace up and tell him that I did not feel a bit guilty, and ask him wouldn’t he fix it so that the firing party would not be from our regiment.
“That was going to be the hardest of all—to die by the hands of my comrades.
“Just as I was going to ask him this favor, he stood up, and he says to me:
“‘My boy, stand up here and look me in the face.’
“I did as he bade me.
“‘My boy,’ he said, ‘you are not going to be shot to-morrow. I believe you when you tell me that you could not keep awake.
“‘I am going to trust you, and send you back to your regiment.
“‘But I have been put to a good deal of trouble on your account.
“‘I have had to come up here from Washington when I have got a great deal to do; and what I want to know is, how are you going to pay my bill?’
“There was a big lump in my throat; I could scarcely speak. I had expected to die, you see, and had kind of got used to thinking that way.
“To have it all changed in a minute! But I got it crowded down, and managed to say:
“‘I am grateful, Mr. Lincoln! I hope I am as grateful as ever a man can be to you for saving my life.
“‘But it comes upon me sudden and unexpected like. I didn’t lay out for it at all; but there is some way to pay you, and I will find it after a little.
“‘There is the bounty in the savings bank; I guess we could borrow some money on the mortgage of the farm.’
“‘There was my pay was something, and if he would wait until pay-day I was sure the boys would help; so I thought we could make it up if it wasn’t more than five or six hundred dollars.
“‘But it is a great deal more than that,’ he said.
“Then I said I didn’t just see how, but I was sure I would find some way—if I lived.
“Then Mr. Lincoln put his hands on my shoulders, and looked into my face as if he was sorry, and said; “‘My boy, my bill is a very large one. Your friends cannot pay it, nor your bounty, nor the farm, nor all your comrades!
“‘There is only one man in all the world who can pay it, and his name is William Scott!
“‘If from this day William Scott does his duty, so that, if I was there when he comes to die, he can look me in the face as he does now, and say, I have kept my promise, and I have done my duty as a soldier, then my debt will be paid.
“‘Will you make that promise and try to keep it?”
The promise was given. Thenceforward there never was such a soldier as William Scott.
This is the record of the end. It was after one of the awful battles of the Peninsula. He was shot all to pieces. He said:
“Boys, I shall never see another battle. I supposed this would be my last. I haven’t much to say.
“You all know what you can tell them at home about me.
“I have tried to do the right thing! If any of you ever have the chance I wish you would tell President Lincoln that I have never forgotten the kind words he said to me at the Chain Bridge; that I have tried to be a good soldier and true to the flag; that I should have paid my whole debt to him if I had lived; and that now, when I know that I am dying, I think of his kind face, and thank him again, because he gave me the chance to fall like a soldier in battle, and not like a coward, by the hands of my comrades.”
What wonder that Secretary Stanton said, as he gazed upon the tall form and kindly face as he lay there, smitten down by the assassin’s bullet, “There lies the most perfect ruler of men who ever lived.”
One day during the Black Hawk War a poor old Indian came into the camp with a paper of safe conduct from General Lewis Cass in his possession. The members of Lincoln’s company were greatly exasperated by late Indian barbarities, among them the horrible murder of a number of women and children, and were about to kill him; they said the safe-conduct paper was a forgery, and approached the old savage with muskets cocked to shoot him.
Lincoln rushed forward, struck up the weapons with his hands, and standing in front of the victim, declared to the Indian that he should not be killed. It was with great difficulty that the men could be kept from their purpose, but the courage and firmness of Lincoln thwarted them.
Lincoln was physically one of the bravest of men, as his company discovered.
Frank P. Blair, of Chicago, tells an incident, showing Mr. Lincoln’s love for children and how thoroughly he entered into all of their sports:
“During the war my grandfather, Francis P. Blair, Sr., lived at Silver Springs, north of Washington, seven miles from the White House. It was a magnificent place of four or five hundred acres, with an extensive lawn in the rear of the house. The grandchildren gathered there frequently.
“There were eight or ten of us, our ages ranging from eight to twelve years. Although I was but seven or eight years of age, Mr. Lincoln’s visits were of such importance to us boys as to leave a clear impression on my memory. He drove out to the place quite frequently. We boys, for hours at a time played ‘town ball’ on the vast lawn, and Mr. Lincoln would join ardently in the sport. I remember vividly how he ran with the children; how long were his strides, and how far his coat-tails stuck out behind, and how we tried to hit him with the ball, as he ran the bases. He entered into the spirit of the play as completely as any of us, and we invariably hailed his coming with delight.”
“Well,” said the President, “I would be very happy to oblige, if my passes were respected; but the fact is, sir, I have, within the past two years, given passes to two hundred and fifty thousand men to go to Richmond, and not one has got there yet.”
The applicant quietly and respectfully withdrew on his tiptoes.
A certain United States Senator, who believed that every man who believed in secession should be hanged, asked the President what he intended to do when the War was over.
“Reconstruct the machinery of this Government,” quickly replied Lincoln.
“You are certainly crazy,” was the Senator’s heated response. “You talk as if treason was not henceforth to be made odious, but that the traitors, cutthroats and authors of this War should not only go unpunished, but receive encouragement to repeat their treason with impunity! They should be hanged higher than Haman, sir! Yes, higher than any malefactor the world has ever known!”
The President was entirely unmoved, but, after a moment’s pause, put a question which all but drove his visitor insane.
“Now, Senator, suppose that when this hanging arrangement has been agreed upon, you accept the post of Chief Executioner. If you will take the office, I will make you a brigadier general and Public Hangman for the United States. That would just about suit you, wouldn’t it?”
“I am a gentleman, sir,” returned the Senator, “and I certainly thought you knew me better than to believe me capable of doing such dirty work. You are jesting, Mr. President.”
The President was extremely patient, exhibiting no signs of ire, and to this bit of temper on the part of the Senator responded:
“You speak of being a gentleman; yet you forget that in this free country all men are equal, the vagrant and the gentleman standing on the same ground when it comes to rights and duties, particularly in time of war. Therefore, being a gentleman, as you claim, and a law-abiding citizen, I trust, you are not exempt from doing even the dirty work at which your high spirit revolts.”
This was too much for the Senator, who quitted the room abruptly, and never again showed his face in the White House while Lincoln occupied it.
“He won’t bother me again,” was the President’s remark as he departed.
Lincoln was a very quiet man, and went about his business in a quiet way, making the least noise possible. He heartily disliked those boisterous people who were constantly deluging him with advice, and shouting at the tops of their voices whenever they appeared at the White House. “These noisy people create a great clamor,” said he one day, in conversation with some personal friends, “and remind me, by the way, of a good story I heard out in Illinois while I was practicing, or trying to practice, some law there. I will say, though, that I practiced more law than I ever got paid for.
“A fellow who lived just out of town, on the bank of a large marsh, conceived a big idea in the money-making line. He took it to a prominent merchant, and began to develop his plans and specifications. ‘There are at least ten million frogs in that marsh near me, an’ I’ll just arrest a couple of carloads of them and hand them over to you. You can send them to the big cities and make lots of money for both of us. Frogs’ legs are great delicacies in the big towns, an’ not very plentiful. It won’t take me more’n two or three days to pick ‘em. They make so much noise my family can’t sleep, and by this deal I’ll get rid of a nuisance and gather in some cash.’
“The merchant agreed to the proposition, promised the fellow he would pay him well for the two carloads. Two days passed, then three, and finally two weeks were gone before the fellow showed up again, carrying a small basket. He looked weary and ‘done up,’ and he wasn’t talkative a bit. He threw the basket on the counter with the remark, ‘There’s your frogs.’
“‘You haven’t two carloads in that basket, have you?’ inquired the merchant.
“‘No,’ was the reply, ‘and there ain’t no two carloads in all this blasted world.’
“‘I thought you said there were at least ten millions of ‘em in that marsh near you, according to the noise they made,’ observed the merchant. ‘Your people couldn’t sleep because of ‘em.’
“‘Well,’ said the fellow, ‘accordin’ to the noise they made, there was, I thought, a hundred million of ‘em, but when I had waded and swum that there marsh day and night fer two blessed weeks, I couldn’t harvest but six. There’s two or three left yet, an’ the marsh is as noisy as it uster be. We haven’t catched up on any of our lost sleep yet. Now, you can have these here six, an’ I won’t charge you a cent fer ‘em.’
“You can see by this little yarn,” remarked the President, “that these boisterous people make too much noise in proportion to their numbers.”
Being asked one time by an “anxious” visitor as to what he would do in certain contingencies—provided the rebellion was not subdued after three or four years of effort on the part of the Government?
“Oh,” replied the President, “there is no alternative but to keep ‘pegging’ away!”
After the issue of the Emancipation Proclamation, Governor Morgan, of New York, was at the White House one day, when the President said:
“I do not agree with those who say that slavery is dead. We are like whalers who have been long on a chase—we have at last got the harpoon into the monster, but we must now look how we steer, or, with one ‘flop’ of his tail, he will yet send us all into eternity!”
President Lincoln was depicted as a headsman in a cartoon printed in “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper,” on February 14, 1863, the title of the picture being “Lincoln’s Dreams; or, There’s a Good Time Coming.”


The cartoon, reproduced here, represents, on the right, the Union Generals who had been defeated by the Confederates in battle, and had suffered decapitation in consequence—McDowell, who lost at Bull Run; McClellan, who failed to take Richmond, when within twelve miles of that city and no opposition, comparatively; and Burnside, who was so badly whipped at Fredericksburg. To the left of the block, where the President is standing with the bloody axe in his hand, are shown the members of the Cabinet—Secretary of State Seward, Secretary of War Stanton, Secretary of the Navy Welles, and others—each awaiting his turn. This part of the “Dream” was never realized, however, as the President did not decapitate any of his Cabinet officers.
It was the idea of the cartoonist to hold Lincoln up as a man who would not countenance failure upon the part of subordinates, but visit the severest punishment upon those commanders who did not win victories. After Burnside’s defeat at Fredericksburg, he was relieved by Hooker, who suffered disaster at Chancellorsville; Hooker was relieved by Meade, who won at Gettysburg, but was refused promotion because he did not follow up and crush Lee; Rosecrans was all but defeated at Chickamauga, and gave way to Grant, who, of all the Union commanders, had never suffered defeat. Grant was Lincoln’s ideal fighting man, and the “Old Commander” was never superseded.
Dr. Hovey, of Dansville, New York, thought he would call and see the President.
Upon arriving at the White House he found the President on horseback, ready for a start.
Approaching him, he said:
“President Lincoln, I thought I would call and see you before leaving the city, and hear you tell a story.”
The President greeted him pleasantly, and asked where he was from.
“From Western New York.”
“Well, that’s a good enough country without stories,” replied the President, and off he rode.
Lincoln’s habits at the White House were as simple as they were at his old home in Illinois.
He never alluded to himself as “President,” or as occupying “the Presidency.”
His office he always designated as “the place.”
“Call me Lincoln,” said he to a friend; “Mr. President” had become so very tiresome to him.
“If you see a newsboy down the street, send him up this way,” said he to a passenger, as he stood waiting for the morning news at his gate.
Friends cautioned him about exposing himself so openly in the midst of enemies; but he never heeded them.
He frequently walked the streets at night, entirely unprotected; and felt any check upon his movements a great annoyance.
He delighted to see his familiar Western friends; and he gave them always a cordial welcome.
He met them on the old footing, and fell at once into the accustomed habits of talk and story-telling.
An old acquaintance, with his wife, visited Washington. Mr. and Mrs. Lincoln proposed to these friends a ride in the Presidential carriage.
It should be stated in advance that the two men had probably never seen each other with gloves on in their lives, unless when they were used as protection from the cold.
The question of each—Lincoln at the White House, and his friend at the hotel—was, whether he should wear gloves.
Of course the ladies urged gloves; but Lincoln only put his in his pocket, to be used or not, according to the circumstances.
When the Presidential party arrived at the hotel, to take in their friends, they found the gentleman, overcome by his wife’s persuasions, very handsomely gloved.
The moment he took his seat he began to draw off the clinging kids, while Lincoln began to draw his on!
“No! no! no!” protested his friend, tugging at his gloves. “It is none of my doings; put up your gloves, Mr. Lincoln.”
So the two old friends were on even and easy terms, and had their ride after their old fashion.
President Lincoln was reading the draft of a speech. Edward, the conservative but dignified butler of the White House, was seen struggling with Tad and trying to drag him back from the window from which was waving a Confederate flag, captured in some fight and given to the boy. Edward conquered and Tad, rushing to find his father, met him coming forward to make, as it proved, his last speech.
The speech began with these words, “We meet this evening, not in sorrow, but in gladness of heart.” Having his speech written in loose leaves, and being compelled to hold a candle in the other hand, he would let the loose leaves drop to the floor one by one. “Tad” picked them up as they fell, and impatiently called for more as they fell from his father’s hand.
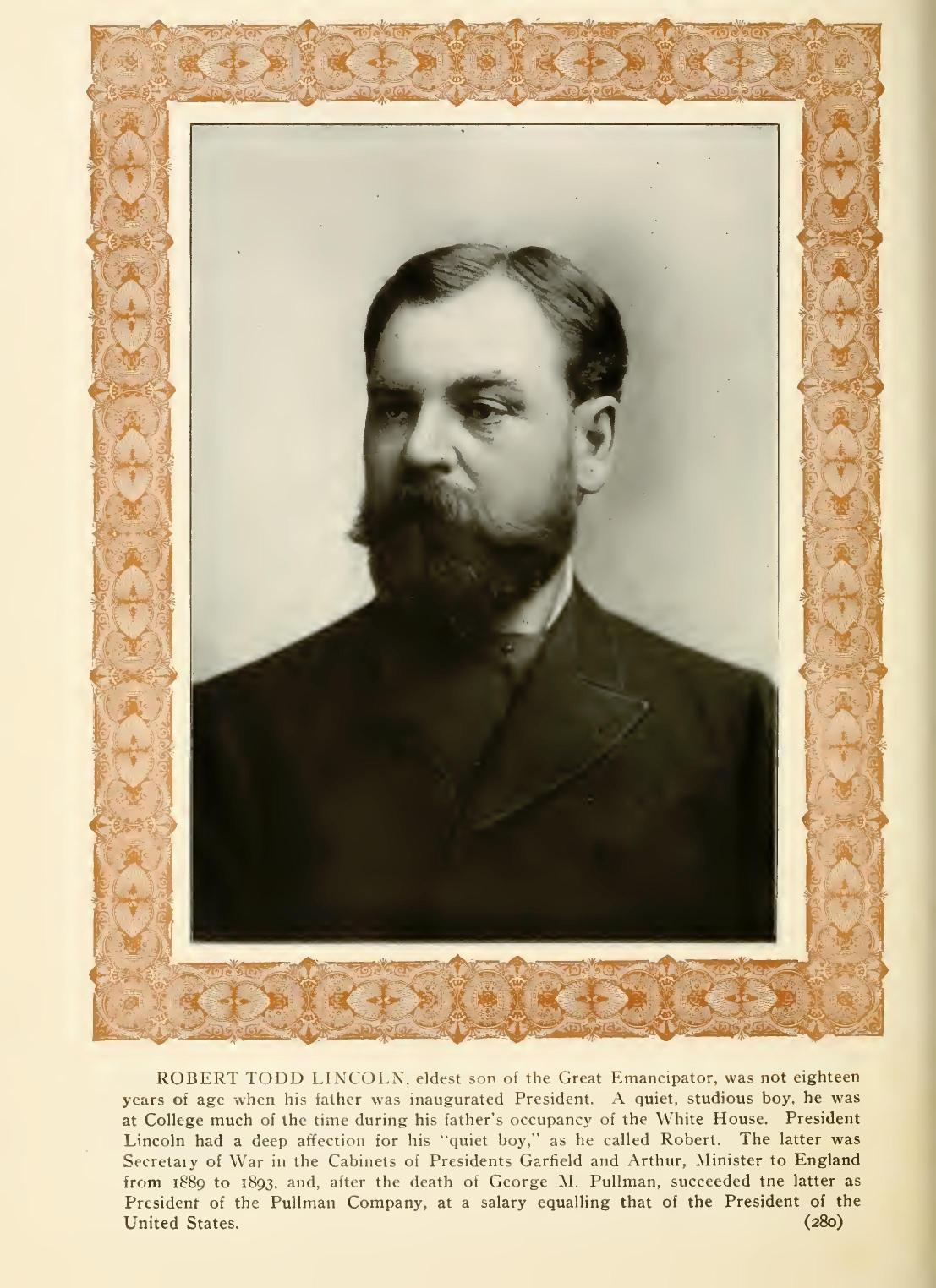




President Lincoln, while entertaining a few select friends, is said to have related the following anecdote of a man who knew too much:
He was a careful, painstaking fellow, who always wanted to be absolutely exact, and as a result he frequently got the ill-will of his less careful superiors.
During the administration of President Jackson there was a singular young gentleman employed in the Public Postoffice in Washington.
His name was G.; he was from Tennessee, the son of a widow, a neighbor of the President, on which account the old hero had a kind feeling for him, and always got him out of difficulties with some of the higher officials, to whom his singular interference was distasteful.
Among other things, it is said of him that while employed in the General Postoffice, on one occasion he had to copy a letter to Major H., a high official, in answer to an application made by an old gentleman in Virginia or Pennsylvania, for the establishment of a new postoffice.
The writer of the letter said the application could not be granted, in consequence of the applicant’s “proximity” to another office.
When the letter came into G.‘s hand to copy, being a great stickler for plainness, he altered “proximity” to “nearness to.”
Major H. observed it, and asked G. why he altered his letter.
“Why,” replied G., “because I don’t think the man would understand what you mean by proximity.”
“Well,” said Major H., “try him; put in the ‘proximity’ again.”
In a few days a letter was received from the applicant, in which he very indignantly said that his father had fought for liberty in the second war for independence, and he should like to have the name of the scoundrel who brought the charge of proximity or anything else wrong against him.
“There,” said G., “did I not say so?”
G. carried his improvements so far that Mr. Berry, the Postmaster-General, said to him: “I don’t want you any longer; you know too much.”
Poor G. went out, but his old friend got him another place.
This time G.‘s ideas underwent a change. He was one day very busy writing, when a stranger called in and asked him where the Patent Office was.
“I don’t know,” said G.
“Can you tell me where the Treasury Department is?” said the stranger.
“No,” said G.
“Nor the President’s house?”
“No.”
The stranger finally asked him if he knew where the Capitol was.
“No,” replied G.
“Do you live in Washington, sir?”
“Yes, sir,” said G.
“Good Lord! and don’t you know where the Patent Office, Treasury, President’s house and Capitol are?”
“Stranger,” said G., “I was turned out of the postoffice for knowing too much. I don’t mean to offend in that way again.
“I am paid for keeping this book.
“I believe I know that much; but if you find me knowing anything more you may take my head.”
“Good morning,” said the stranger.
“That every man may receive at least a moderate education, and thereby be enabled to read the histories of his own and other countries, by which he may duly appreciate the value of our free institutions, appears to be an object of vital importance; even on this account alone, to say nothing of the advantages and satisfaction to be derived from all being able to read the Scriptures and other works, both of a religious and moral nature, for themselves.
“For my part, I desire to see the time when education, by its means, morality, sobriety, enterprise and integrity, shall become much more general than at present, and should be gratified to have it in my power to contribute something to the advancement of any measure which might have a tendency to accelerate the happy period.”
In a speech at Springfield, Illinois, June 26th, 1857, Lincoln referred to the decision of Chief Justice Roger B. Taney, of the United States Supreme Court, in the Dred Scott case, in this manner:
“The Chief justice does not directly assert, but plainly assumes as a fact, that the public estimate of the black man is more favorable now than it was in the days of the Revolution.
“In those days, by common consent, the spread of the black man’s bondage in the new countries was prohibited; but now Congress decides that it will not continue the prohibition, and the Supreme Court decides that it could not if it would.
“In those days, our Declaration of Independence was held sacred by all, and thought to include all; but now, to aid in making the bondage of the negro universal and eternal, it is assailed and sneered at, and constructed and hawked at, and torn, till, if its framers could rise from their graves, they could not at all recognize it.
“All the powers of earth seem combining against the slave; Mammon is after him, ambition follows, philosophy follows, and the theology of the day is fast joining the cry.”
Abraham Lincoln made many notable addresses and speeches during his career previous to the time of his election to the Presidency.
However, beautiful in thought and expression as they were, they were not appreciated by those who heard and read them until after the people of the United States and the world had come to understand the man who delivered them.
Lincoln had the rare and valuable faculty of putting the most sublime feeling into his speeches; and he never found it necessary to incumber his wisest, wittiest and most famous sayings with a weakening mass of words.
He put his thoughts into the simplest language, so that all might comprehend, and he never said anything which was not full of the deepest meaning.
Mr. Roland Diller, who was one of Mr. Lincoln’s neighbors in Springfield, tells the following:
“I was called to the door one day by the cries of children in the street, and there was Mr. Lincoln, striding by with two of his boys, both of whom were wailing aloud. ‘Why, Mr. Lincoln, what’s the matter with the boys?’ I asked.
“‘Just what’s the matter with the whole world,’ Lincoln replied. ‘I’ve got three walnuts, and each wants two.’”
One of the prettiest incidents in the closing days of the Civil War occurred when the troops, ‘marching home again,’ passed in grand form, if with well-worn uniforms and tattered bunting, before the White House.
Naturally, an immense crowd had assembled on the streets, the lawns, porches, balconies, and windows, even those of the executive mansion itself being crowded to excess. A central figure was that of the President, Abraham Lincoln, who, with bared head, unfurled and waved our Nation’s flag in the midst of lusty cheers.
But suddenly there was an unexpected sight.
A small boy leaned forward and sent streaming to the air the banner of the boys in gray. It was an old flag which had been captured from the Confederates, and which the urchin, the President’s second son, Tad, had obtained possession of and considered an additional triumph to unfurl on this all-important day.
Vainly did the servant who had followed him to the window plead with him to desist. No, Master Tad, Pet of the White House, was not to be prevented from adding to the loyal demonstration of the hour.
To his surprise, however, the crowd viewed it differently. Had it floated from any other window in the capital that day, no doubt it would have been the target of contempt and abuse; but when the President, understanding what had happened, turned, with a smile on his grand, plain face, and showed his approval by a gesture and expression, cheer after cheer rent the air.
President Lincoln attended a Ladies’ Fair for the benefit of the Union soldiers, at Washington, March 16th, 1864.
In his remarks he said:
“I appear to say but a word.
“This extraordinary war in which we are engaged falls heavily upon all classes of people, but the most heavily upon the soldiers. For it has been said, ‘All that a man hath will he give for his life,’ and, while all contribute of their substance, the soldier puts his life at stake, and often yields it up in his country’s cause.
“The highest merit, then, is due the soldiers.
“In this extraordinary war extraordinary developments have manifested themselves such as have not been seen in former wars; and among these manifestations nothing has been more remarkable than these fairs for the relief of suffering soldiers and their families, and the chief agents in these fairs are the women of America!
“I am not accustomed to the use of language of eulogy; I have never studied the art of paying compliments to women; but I must say that if all that has been said by orators and poets since the creation of the world in praise of women were applied to the women of America, it would not do them justice for their conduct during the war.
“I will close by saying, God bless the women of America!”
After the United States had enlisted former negro slaves as soldiers to fight alongside the Northern troops for the maintenance of the integrity of the Union, so great was the indignation of the Confederate Government that President Davis declared he would not recognize blacks captured in battle and in uniform as prisoners of war. This meant that he would have them returned to their previous owners, have them flogged and fined for running away from their masters, or even shot if he felt like it. This attitude of the President of the Confederate States of America led to the promulgation of President Lincoln’s famous “Order No. 252,” which, in effect, was a notification to the commanding officers of the Southern forces that if negro prisoners of war were not treated as such, the Union commanders would retaliate. “Harper’s Weekly” of August 15th, 1863, contained a clever cartoon, which we reproduce, representing President Lincoln holding the South by the collar, while “Old Abe” shouts the following words of warning to Jeff Davis, who, cat-o’-nine-tails in hand, is in pursuit of a terrified little negro boy:
MR. LINCOLN: “Look here, Jeff Davis! If you lay a finger on that boy, to hurt him, I’ll lick this ugly cub of yours within an inch of his life!”
Much to the surprise of the Confederates, the negro soldiers fought valiantly; they were fearless when well led, obeyed orders without hesitation, were amenable to discipline, and were eager and anxious, at all times, to do their duty. In battle they were formidable opponents, and in using the bayonet were the equal of the best trained troops. The Southerners hated them beyond power of expression.
The President walked through the streets of Richmond—without a guard except a few seamen—in company with his son “Tad,” and Admiral Porter, on April 4th, 1865, the day following the evacuation of the city.
Colored people gathered about him on every side, eager to see and thank their liberator. Mr. Lincoln addressed the following remarks to one of these gatherings:
“My poor friends, you are free—free as air. You can cast off the name of slave and trample upon it; it will come to you no more.
“Liberty is your birthright. God gave it to you as He gave it to others, and it is a sin that you have been deprived of it for so many years.
“But you must try to deserve this priceless boon. Let the world see that you merit it, and are able to maintain it by your good work.
“Don’t let your joy carry you into excesses; learn the laws, and obey them. Obey God’s commandments, and thank Him for giving you liberty, for to Him you owe all things.
“There, now, let me pass on; I have but little time to spare.
“I want to see the Capitol, and must return at once to Washington to secure to you that liberty which you seem to prize so highly.”
Lincoln fell in love with Miss Mary S. Owens about 1833 or so, and, while she was attracted toward him she was not passionately fond of him.
Lincoln’s letter of proposal of marriage, sent by him to Miss Owens, while singular, unique, and decidedly unconventional, was certainly not very ardent. He, after the fashion of the lawyer, presented the matter very cautiously, and pleaded his own cause; then presented her side of the case, advised her not “to do it,” and agreed to abide by her decision.
Miss Owens respected Lincoln, but promptly rejected him—really very much to “Abe’s” relief.
Not far from New Salem, Illinois, at a place called Clary’s Grove, a gang of frontier ruffians had established headquarters, and the champion wrestler of “The Grove” was “Jack” Armstrong, a bully of the worst type.
Learning that Abraham was something of a wrestler himself, “Jack” sent him a challenge. At that time and in that community a refusal would have resulted in social and business ostracism, not to mention the stigma of cowardice which would attach.
It was a great day for New Salem and “The Grove” when Lincoln and Armstrong met. Settlers within a radius of fifty miles flocked to the scene, and the wagers laid were heavy and many. Armstrong proved a weakling in the hands of the powerful Kentuckian, and “Jack’s” adherents were about to mob Lincoln when the latter’s friends saved him from probable death by rushing to the rescue.
The President was once speaking about an attack made on him by the Congressional Committee on the Conduct of the War for a certain alleged blunder in the Southwest—the matter involved being one which had fallen directly under the observation of the army officer to whom he was talking, who possessed official evidence completely upsetting all the conclusions of the Committee.
“Might it not be well for me,” queried the officer, “to set this matter right in a letter to some paper, stating the facts as they actually transpired?”
“Oh, no,” replied the President, “at least, not now. If I were to try to read, much less answer, all the attacks made on me, this shop might as well be closed for any other business. I do the very best I know how the very best I can; and I mean to keep doing so until the end. If the end brings me out all right, what is said against me won’t amount to anything. If the end brings me out wrong, ten thousand angels swearing I was right would make no difference.”
Ward Hill Lamon was President Lincoln’s Cerberus, his watch dog, guardian, friend, companion and confidant. Some days before Lincoln’s departure for Washington to be inaugurated, he wrote to Lamon at Bloomington, that he desired to see him at once. He went to Springfield, and Lincoln said:
“Hill, on the 11th I go to Washington, and I want you to go along with me. Our friends have already asked me to send you as Consul to Paris. You know I would cheerfully give you anything for which our friends may ask or which you may desire, but it looks as if we might have war.
“In that case I want you with me. In fact, I must have you. So get yourself ready and come along. It will be handy to have you around. If there is to be a fight, I want you to help me to do my share of it, as you have done in times past. You must go, and go to stay.”
This is Lamon’s version of it.
To a party who wished to be empowered to negotiate reward for promises of influence in the Chicago Convention, 1860, Mr. Lincoln replied:
“No, gentlemen; I have not asked the nomination, and I will not now buy it with pledges.
“If I am nominated and elected, I shall not go into the Presidency as the tool of this man or that man, or as the property of any factor or clique.”
After some very bad news had come in from the army in the field, Lincoln remarked to Schuyler Colfax:
“How willingly would I exchange places to-day with the soldier who sleeps on the ground in the Army of the Potomac!”

In the campaign of 1852, Lincoln, in reply to Douglas’ speech, wherein he spoke of confidence in Providence, replied: “Let us stand by our candidate (General Scott) as faithfully as he has always stood by our country, and I much doubt if we do not perceive a slight abatement of Judge Douglas’ confidence in Providence as well as the people. I suspect that confidence is not more firmly fixed with the judge than it was with the old woman whose horse ran away with her in a buggy. She said she ‘trusted in Providence till the britchen broke,’ and then she ‘didn’t know what in airth to do.’”
Lincoln’s great generosity to his leaders was shown when, in January, 1863, he assigned “Fighting Joe” Hooker to the command of the Army of the Potomac. Hooker had believed in a military dictatorship, and it was an open secret that McClellan might have become such had he possessed the nerve. Lincoln, however, was not bothered by this prattle, as he did not think enough of it to relieve McClellan of his command. The President said to Hooker:
“I have heard, in such a way as to believe it, of your recently saying that both the army and the Government needed a dictator. Of course, it was not for this, but in spite of it, that I have given you the command. Only those generals who gain success can be dictators.
“What I now ask of you is military success, and I will risk the dictatorship.”
Lincoln also believed Hooker had not given cordial support to General Burnside when he was in command of the army. In Lincoln’s own peculiarly plain language, he told Hooker that he had done “a great wrong to the country and to a most meritorious and honorable brother officer.”
At one time the President had the appointment of a large additional number of brigadier and major generals. Among the immense number of applications, Mr. Lincoln came upon one wherein the claims of a certain worthy (not in the service at all), “for a generalship” were glowingly set forth. But the applicant didn’t specify whether he wanted to be brigadier or major general.
The President observed this difficulty, and solved it by a lucid indorsement. The clerk, on receiving the paper again, found written across its back, “Major General, I reckon. A. Lincoln.”
Judge Herndon, Lincoln’s law partner, said that he never saw Lincoln more cheerful than on the day previous to his departure from Springfield for Washington, and Judge Gillespie, who visited him a few days earlier, found him in excellent spirits.
“I told him that I believed it would do him good to get down to Washington,” said Herndon.
“I know it will,” Lincoln replied. “I only wish I could have got there to lock the door before the horse was stolen. But when I get to the spot, I can find the tracks.”
If all the days Lincoln attended school were added together, they would not make a single year’s time, and he never studied grammar or geography or any of the higher branches. His first teacher in Indiana was Hazel Dorsey, who opened a school in a log schoolhouse a mile and a half from the Lincoln cabin. The building had holes for windows, which were covered over with greased paper to admit light. The roof was just high enough for a man to stand erect. It did not take long to demonstrate that “Abe” was superior to any scholar in his class. His next teacher was Andrew Crawford, who taught in the winter of 1822-3, in the same little schoolhouse. “Abe” was an excellent speller, and it is said that he liked to show off his knowledge, especially if he could help out his less fortunate schoolmates. One day the teacher gave out the word “defied.” A large class was on the floor, but it seemed that no one would be able to spell it. The teacher declared he would keep the whole class in all day and night if “defied” was not spelled correctly.
When the word came around to Katy Roby, she was standing where she could see young “Abe.” She started, “d-e-f,” and while trying to decide whether to spell the word with an “i” or a “y,” she noticed that Abe had his finger on his eye and a smile on his face, and instantly took the hint. She spelled the word correctly and school was dismissed.
At one of the afternoon receptions at the White House a stranger shook hands with him, and, as he did so, remarked casually, that he was elected to Congress about the time Mr. Lincoln’s term as representative expired, which happened many years before.
“Yes,” said the President, “You are from—” (mentioning the State). “I remember reading of your election in a newspaper one morning on a steamboat going down to Mount Vernon.”
At another time a gentleman addressed him, saying, “I presume, Mr. President, you have forgotten me?”
“No,” was the prompt reply; “your name is Flood. I saw you last, twelve years ago, at—” (naming the place and the occasion).
“I am glad to see,” he continued, “that the Flood goes on.”
Subsequent to his re-election a deputation of bankers from various sections were introduced one day by the Secretary of the Treasury.
After a few moments of general conversation, Lincoln turned to one of them and said:
“Your district did not give me so strong a vote at the last election as it did in 1860.”
“I think, sir, that you must be mistaken,” replied the banker. “I have the impression that your majority was considerably increased at the last election.”
“No,” rejoined the President, “you fell off about six hundred votes.”
Then taking down from the bookcase the official canvass of 1860 and 1864, he referred to the vote of the district named, and proved to be quite right in his assertion.
As President Lincoln, arm in arm with ex-President Buchanan, entered the Capitol, and passed into the Senate Chamber, filled to overflowing with Senators, members of the Diplomatic Corps, and visitors, the contrast between the two men struck every observer.
“Mr. Buchanan was so withered and bowed with age,” wrote George W. Julian, of Indiana, who was among the spectators, “that in contrast with the towering form of Mr. Lincoln he seemed little more than half a man.”
As soon as the result of the Presidential election of 1864 was known, General Grant telegraphed from City Point his congratulations, and added that “the election having passed off quietly... is a victory worth more to the country than a battle won.”
London “Punch” persistently maintained throughout the War for the Union that the question of what to do with the blacks was the most bothersome of all the problems President Lincoln had to solve. “Punch” thought the Rebellion had its origin in an effort to determine whether there should or should not be slavery in the United States, and was fought with this as the main end in view. “Punch” of August 15th, 1863, contained the cartoon reproduced on this page, the title being “Brutus and Caesar.”
President Lincoln was pictured as Brutus, while the ghost of Caesar, which appeared in the tent of the American Brutus during the dark hours of the night, was represented in the shape of a husky and anything but ghost-like African, whose complexion would tend to make the blackest tar look like skimmed milk in comparison. This was the text below the cartoon: (From the American Edition of Shakespeare.) The Tent of Brutus (Lincoln). Night. Enter the Ghost of Caesar.
BRUTUS: “Wall, now! Do tell! Who’s you?”
CAESAR: “I am dy ebil genus, Massa Linking. Dis child am awful impressional!”
“Punch’s” cartoons were decidedly unfriendly in tone toward President Lincoln, some of them being not only objectionable in the display of bad taste, but offensive and vulgar. It is true that after the assassination of the President, “Punch,” in illustrations, paid marked and deserved tribute to the memory of the Great Emancipator, but it had little that was good to say of him while he was among the living and engaged in carrying out the great work for which he was destined to win eternal fame.
President Lincoln, well aware of Stanton’s unfriendliness, was surprised when Secretary of the Treasury Chase told him that Stanton had expressed the opinion that the arrest of the Confederate Commissioners, Mason and Slidell, was legal and justified by international law. The President asked Secretary Chase to invite Stanton to the White House, and Stanton came. Mr. Lincoln thanked him for the opinion he had expressed, and asked him to put it in writing.
Stanton complied, the President read it carefully, and, after putting it away, astounded Stanton by offering him the portfolio of War. Stanton was a Democrat, had been one of the President’s most persistent vilifiers, and could not realize, at first, that Lincoln meant what he said. He managed, however to say:
“I am both surprised and embarrassed, Mr. President, and would ask a couple of days to consider this most important matter.”
Lincoln fully understood what was going on in Stanton’s mind, and then said:
“This is a very critical period in the life of the nation, Mr. Stanton, as you are well aware, and I well know you are as much interested in sustaining the government as myself or any other man. This is no time to consider mere party issues. The life of the nation is in danger. I need the best counsellors around me. I have every confidence in your judgment, and have concluded to ask you to become one of my counsellors. The office of the Secretary of War will soon be vacant, and I am anxious to have you take Mr. Cameron’s place.”
Stanton decided to accept.
“Abe” Lincoln’s father was never at loss for an answer. An old neighbor of Thomas Lincoln—“Abe’s” father—was passing the Lincoln farm one day, when he saw “Abe’s” father grubbing up some hazelnut bushes, and said to him: “Why, Grandpap, I thought you wanted to sell your farm?”
“And so I do,” he replied, “but I ain’t goin’ to let my farm know it.”
“‘Abe’s’ jes’ like his father,” the old ones would say.
One of the most notable of Lincoln’s law cases was that in which he defended William D. Armstrong, charged with murder. The case was one which was watched during its progress with intense interest, and it had a most dramatic ending.
The defendant was the son of Jack and Hannah Armstrong. The father was dead, but Hannah, who had been very motherly and helpful to Lincoln during his life at New Salem, was still living, and asked Lincoln to defend him. Young Armstrong had been a wild lad, and was often in bad company.
The principal witness had sworn that he saw young Armstrong strike the fatal blow, the moon being very bright at the time.
Lincoln brought forward the almanac, which showed that at the time the murder was committed there was no moon at all. In his argument, Lincoln’s speech was so feelingly made that at its close all the men in the jury-box were in tears. It was just half an hour when the jury returned a verdict of acquittal.
Lincoln would accept no fee except the thanks of the anxious mother.
Lincoln’s reading in his early days embraced a wide range. He was particularly fond of all stories containing fun, wit and humor, and every one of these he came across he learned by heart, thus adding to his personal store.
He improved as a reciter and retailer of the stories he had read and heard, and as the reciter of tales of his own invention, and he had ready and eager auditors.
Judge Herndon, in his “Abraham Lincoln,” relates that as a mimic Lincoln was unequalled. An old neighbor said: “His laugh was striking. Such awkward gestures belonged to no other man. They attracted universal attention, from the old and sedate down to the schoolboy. Then, in a few moments, he was as calm and thoughtful as a judge on the bench, and as ready to give advice on the most important matters; fun and gravity grew on him alike.”
During the year Lincoln was in Denton Offutt’s store at New Salem, that gentleman, whose business was somewhat widely and unwisely spread about the country, ceased to prosper in his finances and finally failed. The store was shut up, the mill was closed, and Abraham Lincoln was out of business.
The year had been one of great advance, in many respects. He had made new and valuable acquaintances, read many books, mastered the grammar of his own tongue, won multitudes of friends, and became ready for a step still further in advance.
Those who could appreciate brains respected him, and those whose ideas of a man related to his muscles were devoted to him. It was while he was performing the work of the store that he acquired the sobriquet of “Honest Abe”—a characterization he never dishonored, and an abbreviation that he never outgrew.
He was judge, arbitrator, referee, umpire, authority, in all disputes, games and matches of man-flesh, horse-flesh, a pacificator in all quarrels; everybody’s friend; the best-natured, the most sensible, the best-informed, the most modest and unassuming, the kindest, gentlest, roughest, strongest, best fellow in all New Salem and the region round about.




Enduring friendship and love of old associations were prominent characteristics of President Lincoln. When about to leave Springfield for Washington, he went to the dingy little law office which had sheltered his saddest hours.
He sat down on the couch, and said to his law partner, Judge Herndon:
“Billy, you and I have been together for more than twenty years, and have never passed a word. Will you let my name stay on the old sign until I come back from Washington?”
The tears started to Herndon’s eyes. He put out his hand. “Mr. Lincoln,” said he, “I never will have any other partner while you live”; and to the day of assassination, all the doings of the firm were in the name of “Lincoln & Herndon.”
Early in January, 1861, Colonel Alex. K. McClure, of Philadelphia, received a telegram from President-elect Lincoln, asking him (McClure) to visit him at Springfield, Illinois. Colonel McClure described his disappointment at first sight of Lincoln in these words:
“I went directly from the depot to Lincoln’s house and rang the bell, which was answered by Lincoln himself opening the door. I doubt whether a wholly concealed my disappointment at meeting him.
“Tall, gaunt, ungainly, ill clad, with a homeliness of manner that was unique in itself, I confess that my heart sank within me as I remembered that this was the man chosen by a great nation to become its ruler in the gravest period of its history.
“I remember his dress as if it were but yesterday—snuff-colored and slouchy pantaloons, open black vest, held by a few brass buttons; straight or evening dresscoat, with tightly fitting sleeves to exaggerate his long, bony arms, and all supplemented by an awkwardness that was uncommon among men of intelligence.
“Such was the picture I met in the person of Abraham Lincoln. We sat down in his plainly furnished parlor, and were uninterrupted during the nearly four hours that I remained with him, and little by little, as his earnestness, sincerity and candor were developed in conversation, I forgot all the grotesque qualities which so confounded me when I first greeted him.”
“If a man is honest in his mind,” said Lincoln one day, long before he became President, “you are pretty safe in trusting him.”
“Abe’s” nephew—or one of them—related a story in connection with Lincoln’s first love (Anne Rutledge), and his subsequent marriage to Miss Mary Todd. This nephew was a plain, every-day farmer, and thought everything of his uncle, whose greatness he quite thoroughly appreciated, although he did not pose to any extreme as the relative of a President of the United States.
Said he one day, in telling his story:
“Us child’en, w’en we heerd Uncle ‘Abe’ wuz a-goin’ to be married, axed Gran’ma ef Uncle ‘Abe’ never hed hed a gal afore, an’ she says, sez she, ‘Well, “Abe” wuz never a han’ nohow to run ‘round visitin’ much, or go with the gals, neither, but he did fall in love with a Anne Rutledge, who lived out near Springfield, an’ after she died he’d come home an’ ev’ry time he’d talk ‘bout her, he cried dreadful. He never could talk of her nohow ‘thout he’d jes’ cry an’ cry, like a young feller.’
“Onct he tol’ Gran’ma they wuz goin’ ter be hitched, they havin’ promised each other, an’ thet is all we ever heered ‘bout it. But, so it wuz, that arter Uncle ‘Abe’ hed got over his mournin’, he wuz married ter a woman w’ich hed lived down in Kentuck.
“Uncle ‘Abe’ hisself tol’ us he wuz married the nex’ time he come up ter our place, an’ w’en we ast him why he didn’t bring his wife up to see us, he said: ‘She’s very busy and can’t come.’
“But we knowed better’n that. He wuz too proud to bring her up, ’cause nothin’ would suit her, nohow. She wuzn’t raised the way we wuz, an’ wuz different from us, and we heerd, tu, she wuz as proud as cud be.
“No, an’ he never brought none uv the child’en, neither.
“But then, Uncle ‘Abe,’ he wuzn’t to blame. We never thought he wuz stuck up.”
“My paramount object is to save the Union, and not either to save or to destroy slavery.
“If I could save the Union without freeing any slave, I would do it.
“If I could save it by freeing all the slaves, I would do it; and if I could do it by freeing some and leaving others alone, I would also do that.
“What I do about slavery and the colored race, I do because I believe it helps to save this Union; and what I forbear, I forbear because I do not believe it would help to save the Union.
“I shall do less whenever I shall believe what I am doing hurts the cause, and I shall do more whenever I believe doing more will help the cause.”
One of President Lincoln’s friends, visiting at the White House, was finding considerable fault with the constant agitation in Congress of the slavery question. He remarked that, after the adoption of the Emancipation policy, he had hoped for something new.
“There was a man down in Maine,” said the President, in reply, “who kept a grocery store, and a lot of fellows used to loaf around for their toddy. He only gave ‘em New England rum, and they drank pretty considerable of it. But after awhile they began to get tired of that, and kept asking for something new—something new—all the time. Well, one night, when the whole crowd were around, the grocer brought out his glasses, and says he, ‘I’ve got something New for you to drink, boys, now.’
“‘Honor bright?’ said they.
“‘Honor bright,’ says he, and with that he sets out a jug. ‘Thar’ says he, ‘that’s something new; it’s New England rum!’ says he.
“Now,” remarked the President, in conclusion, “I guess we’re a good deal like that crowd, and Congress is a good deal like that store-keeper!”
When Mr. Lincoln was quite a small boy he met with an accident that almost cost him his life. He was saved by Austin Gollaher, a young playmate. Mr. Gollaher lived to be more than ninety years of age, and to the day of his death related with great pride his boyhood association with Lincoln.
“Yes,” Mr. Gollaher once said, “the story that I once saved Abraham Lincoln’s life is true. He and I had been going to school together for a year or more, and had become greatly attached to each other. Then school disbanded on account of there being so few scholars, and we did not see each other much for a long while.
“One Sunday my mother visited the Lincolns, and I was taken along. ‘Abe’ and I played around all day. Finally, we concluded to cross the creek to hunt for some partridges young Lincoln had seen the day before. The creek was swollen by a recent rain, and, in crossing on the narrow footlog, ‘Abe’ fell in. Neither of us could swim. I got a long pole and held it out to ‘Abe,’ who grabbed it. Then I pulled him ashore.
“He was almost dead, and I was badly scared. I rolled and pounded him in good earnest. Then I got him by the arms and shook him, the water meanwhile pouring out of his mouth. By this means I succeeded in bringing him to, and he was soon all right.
“Then a new difficulty confronted us. If our mothers discovered our wet clothes they would whip us. This we dreaded from experience, and determined to avoid. It was June, the sun was very warm, and we soon dried our clothing by spreading it on the rocks about us. We promised never to tell the story, and I never did until after Lincoln’s tragic end.”
In conversation with some friends at the White House on New Year’s evening, 1863, President Lincoln said, concerning his Emancipation Proclamation:
“The signature looks a little tremulous, for my hand was tired, but my resolution was firm.
“I told them in September, if they did not return to their allegiance, and cease murdering our soldiers, I would strike at this pillar of their strength.
“And now the promise shall be kept, and not one word of it will I ever recall.”
During the time the enemies of General Grant were making their bitterest attacks upon him, and demanding that the President remove him from command, “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper,” of June 13, 1863, came out with the cartoon reproduced. The text printed under the picture was to the following effect:
OLD ABE: “Greeley be hanged! I want no more new brooms. I begin to think that the worst thing about my old ones was in not being handled right.”
The old broom the President holds in his right hand is labeled “Grant.” The latter had captured Fort Donelson, defeated the Confederates at Shiloh, Iuka, Port Gibson, and other places, and had Vicksburg in his iron grasp. When the demand was made that Lincoln depose Grant, the President answered, “I can’t spare this man; he fights!” Grant never lost a battle and when he found the enemy he always fought him. McClellan, Burnside, Pope and Hooker had been found wanting, so Lincoln pinned his faith to Grant. As noted in the cartoon, Horace Greeley, editor of the New York Tribune, Thurlow Weed, and others wanted Lincoln to try some other new brooms, but President Lincoln was wearied with defeats, and wanted a few victories to offset them. Therefore; he stood by Grant, who gave him victories.
| Abraham Lincoln |
| his hand and pen |
| he will be good |
| but god Knows When |
These lines were found written in young Lincoln’s own hand at the bottom of a page whereon he had been ciphering. Lincoln always wrote a clear, regular “fist.” In this instance he evidently did not appreciate the sacredness of the name of the Deity, when he used a little “g.”
Lincoln once said he did not remember the time when he could not write.
It was the custom in Sangamon for the “menfolks” to gather at noon and in the evening, when resting, in a convenient lane near the mill. They had rolled out a long peeled log, on which they lounged while they whittled and talked.
Lincoln had not been long in Sangamon before he joined this circle. At once he became a favorite by his jokes and good-humor. As soon as he appeared at the assembly ground the men would start him to story-telling. So irresistibly droll were his “yarns” that whenever he’d end up in his unexpected way the boys on the log would whoop and roll off. The result of the rolling off was to polish the log like a mirror. The men, recognizing Lincoln’s part in this polishing, christened their seat “Abe’s log.”
Long after Lincoln had disappeared from Sangamon, “Abe’s log” remained, and until it had rotted away people pointed it out, and repeated the droll stories of the stranger.
President Lincoln, in company with General Grant, was inspecting the Dutch Gap Canal at City Point. “Grant, do you know what this reminds me of? Out in Springfield, Ill., there was a blacksmith who, not having much to do, took a piece of soft iron and attempted to weld it into an agricultural implement, but discovered that the iron would not hold out; then he concluded it would make a claw hammer; but having too much iron, attempted to make an ax, but decided after working awhile that there was not enough iron left. Finally, becoming disgusted, he filled the forge full of coal and brought the iron to a white heat; then with his tongs he lifted it from the bed of coals, and thrusting it into a tub of water near by, exclaimed: ‘Well, if I can’t make anything else of you, I will make a fizzle, anyhow.’” “I was afraid that was about what we had done with the Dutch Gap Canal,” said General Grant.
When Lincoln was in the Black Hawk War as captain, the volunteer soldiers drank in with delight the jests and stories of the tall captain. Aesop’s Fables were given a new dress, and the tales of the wild adventures that he had brought from Kentucky and Indiana were many, but his inspiration was never stimulated by recourse to the whisky jug.
When his grateful and delighted auditors pressed this on him he had one reply: “Thank you, I never drink it.”
President Lincoln was passing down Pennsylvania avenue in Washington one day, when a man came running after him, hailed him, and thrust a bundle of papers in his hands.
It angered him not a little, and he pitched the papers back, saying, “I’m not going to open shop here.”
Lincoln delivered a remarkable speech at Springfield, Illinois, when but twenty-eight years of age, upon the liberty possessed by the people of the United States.
In part, he said:
“In the great journal of things happening under the sun, we, the American people, find our account running under date of the nineteenth century of the Christian era.
“We find ourselves in the peaceful possession of the fairest portion of the earth as regards extent of territory, fertility of soil, and salubrity of climate.
“We find ourselves under the government of a system of political institutions conducing more essentially to the ends of civil and religious liberty than any of which history of former times tells us.
“We, when mounting the stage of existence, found ourselves the legal inheritors of these fundamental blessings.
“We toiled not in the acquisition or establishment of them; they are a legacy bequeathed to us by a once hardy, brave, and patriotic, but now lamented and departed race of ancestors.
“Theirs was the task (and nobly did they perform it) to possess themselves, us, of this goodly land, to uprear upon its hills and valleys a political edifice of liberty and equal rights; ‘tis ours to transmit these—the former unprofaned by the foot of an intruder, the latter undecayed by the lapse of time and untorn by usurpation—to the generation that fate shall permit the world to know.
“This task, gratitude to our fathers, justice to ourselves, duty to posterity—all imperatively require us faithfully to perform.
“How, then, shall we perform it? At what point shall we expect the approach of danger?
“Shall we expect some trans-Atlantic military giant to step the ocean and crush us at a blow?
“Never! All the armies of Europe, Asia and Africa, combined, with all the treasures of the earth (our own excepted) in their military chest, with a Bonaparte for a commander, could not, by force, take a drink from the Ohio, or make a track on the Blue Ridge, in a trial of a thousand years.
“At what point, then, is this approach of danger to be expected?
“I answer, if ever it reach us, it must spring up amongst us. It cannot come from abroad.
“If destruction be our lot, we must ourselves be its author and finisher.
“As a nation of freemen, we must live through all time or die by suicide.
“I hope I am not over-wary; but, if I am not, there is even now something of ill-omen amongst us.
“I mean the increasing disregard for law which pervades the country, the disposition to substitute the wild and furious passions in lieu of the sober judgment of courts, and the worse than savage mobs for the executive ministers of justice.
“This disposition is awfully fearful in any community, and that it now exists in ours, though grating to our feelings to admit it, it would be a violation of truth and an insult to deny.
“Accounts of outrages committed by mobs form the every-day news of the times.
“They have pervaded the country from New England to Louisiana; they are neither peculiar to the eternal snows of the former, nor the burning sun of the latter.
“They are not the creatures of climate, neither are they confined to the slave-holding or non-slave-holding States.
“Alike they spring up among the pleasure-hunting Southerners and the order-loving citizens of the land of steady habits.
“Whatever, then, their cause may be, it is common to the whole country.
“Many great and good men, sufficiently qualified for any task they may undertake, may ever be found, whose ambition would aspire to nothing beyond a seat in Congress, a gubernatorial or Presidential chair; but such belong not to the family of the lion, or the tribe of the eagle.
“What! Think you these places would satisfy an Alexander, a Caesar, or a Napoleon? Never!
“Towering genius disdains a beaten path. It seeks regions hitherto unexplored.
“It seeks no distinction in adding story to story upon the monuments of fame, erected to the memory of others.
“It denies that it is glory enough to serve under any chief.
“It scorns to tread in the footpaths of any predecessor, however illustrious.
“It thirsts and burns for distinction, and, if possible, it will have it, whether at the expense of emancipating the slaves or enslaving freemen.
“Another reason which once was, but which to the same extent is now no more, has done much in maintaining our institutions thus far.
“I mean the powerful influence which the interesting scenes of the Revolution had upon the passions of the people, as distinguished from their judgment.
“But these histories are gone. They can be read no more forever. They were a fortress of strength.
“But what the invading foeman could never do, the silent artillery of time has done, the levelling of the walls.
“They were a forest of giant oaks, but the all-resisting hurricane swept over them and left only here and there a lone trunk, despoiled of its verdure, shorn of its foliage, unshading and unshaded, to murmur in a few more gentle breezes and to combat with its mutilated limbs a few more rude storms, then to sink and be no more.
“They were the pillars of the temple of liberty, and now that they have crumbled away, that temple must fall, unless we, the descendants, supply the places with pillars hewn from the same solid quarry of sober reason.
“Passion has helped us, but can do so no more. It will in future be our enemy.
“Reason—cold, calculating, unimpassioned reason—must furnish all the materials for our support and defense.
“Let those materials be molded into general intelligence, sound morality, and, in particular, a reverence for the Constitution and the laws; and then our country shall continue to improve, and our nation, revering his name, and permitting no hostile foot to pass or desecrate his resting-place, shall be the first to hear the last trump that shall awaken our Washington.
“Upon these let the proud fabric of freedom rest as the rock of its basis, and as truly as has been said of the only greater institution, ‘the gates of hell shall not prevail against it.’”
One of Mr. Lincoln’s warm friends was Dr. Robert Boal, of Lacon, Illinois. Telling of a visit he paid to the White House soon after Mr. Lincoln’s inauguration, he said: “I found him the same Lincoln as a struggling lawyer and politician that I did in Washington as President of the United States, yet there was a dignity and self-possession about him in his high official authority. I paid him a second call in the evening. He had thrown off his reserve somewhat, and would walk up and down the room with his hands to his sides and laugh at the joke he was telling, or at one that was told to him. I remember one story he told to me on this occasion.
“Tom Corwin, of Ohio, had been down to Alexandria, Va., that day and had come back and told Lincoln a story which pleased him so much that he broke out in a hearty laugh and said: ‘I must tell you Tom Corwin’s latest. Tom met an old man at Alexandria who knew George Washington, and he told Tom that George Washington often swore. Now, Corwin’s father had always held the father of our country up as a faultless person and told his son to follow in his footsteps.
“‘"Well,” said Corwin, “when I heard that George Washington was addicted to the vices and infirmities of man, I felt so relieved that I just shouted for joy.”’”
The lawyers on the circuit traveled by Lincoln got together one night and tried him on the charge of accepting fees which tended to lower the established rates. It was the understood rule that a lawyer should accept all the client could be induced to pay. The tribunal was known as “The Ogmathorial Court.”
Ward Lamon, his law partner at the time, tells about it:
“Lincoln was found guilty and fined for his awful crime against the pockets of his brethren of the bar. The fine he paid with great good humor, and then kept the crowd of lawyers in uproarious laughter until after midnight.
“He persisted in his revolt, however, declaring that with his consent his firm should never during its life, or after its dissolution, deserve the reputation enjoyed by those shining lights of the profession, ‘Catch ‘em and Cheat ‘em.’”
Lincoln had assisted in the prosecution of a man who had robbed his neighbor’s hen roosts. Jogging home along the highway with the foreman of the jury that had convicted the hen stealer, he was complimented by Lincoln on the zeal and ability of the prosecution, and remarked: “Why, when the country was young, and I was stronger than I am now, I didn’t mind packing off a sheep now and again, but stealing hens!” The good man’s scorn could not find words to express his opinion of a man who would steal hens.
A lawyer, who was a stranger to Mr. Lincoln, once expressed to General Linder the opinion that Mr. Lincoln’s practice of telling stories to the jury was a waste of time.
“Don’t lay that flattering unction to your soul,” Linder answered; “Lincoln is like Tansey’s horse, he ‘breaks to win.’”


On the 3rd of January, 1863, “Harper’s Weekly” appeared with a cartoon representing Columbia indignantly demanding of President Lincoln and Secretary of War Stanton that they restore to her those of her sons killed in battle. Below the picture is the reading matter:
COLUMBIA: “Where are my 15,000 sons—murdered at Fredericksburg?”
LINCOLN: “This reminds me of a little joke—”
COLUMBIA: “Go tell your joke at Springfield!!”
The battle of Fredericksburg was fought on December 13th, 1862, between General Burnside, commanding the Army of the Potomac, and General Lee’s force. The Union troops, time and again, assaulted the heights where the Confederates had taken position, but were driven back with frightful losses. The enemy, being behind breastworks, suffered comparatively little. At the beginning of the fight the Confederate line was broken, but the result of the engagement was disastrous to the Union cause. Burnside had one thousand one hundred and fifty-two killed, nine thousand one hundred and one wounded, and three thousand two hundred and thirty-four missing, a total of thirteen thousand seven hundred and seventy-one. General Lee’s losses, all told, were not much more than five thousand men.
Burnside had succeeded McClellan in command of the Army of the Potomac, mainly, it was said, through the influence of Secretary of War Stanton. Three months before, McClellan had defeated Lee at Antietam, the bloodiest battle of the War, Lee’s losses footing up more than thirteen thousand men. At Fredericksburg, Burnside had about one hundred and twenty thousand men; at Antietam, McClellan had about eighty thousand. It has been maintained that Burnside should not have fought this battle, the chances of success being so few.
“Abe’s” school teacher, Crawford, endeavored to teach his pupils some of the manners of the “polite society” of Indiana—1823 or so. This was a part of his system:
One of the pupils would retire, and then come in as a stranger, and another pupil would have to introduce him to all the members of the school n what was considered “good manners.”
As “Abe” wore a linsey-woolsey shirt, buckskin breeches which were too short and very tight, and low shoes, and was tall and awkward, he no doubt created considerable merriment when his turn came. He was growing at a fearful rate; he was fifteen years of age, and two years later attained his full height of six feet four inches.
Early in 1831, “Abe” was one of the guests of honor at a boat-launching, he and two others having built the craft. The affair was a notable one, people being present from the territory surrounding. A large party came from Springfield with an ample supply of whisky, to give the boat and its builders a send-off. It was a sort of bipartisan mass-meeting, but there was one prevailing spirit, that born of rye and corn. Speeches were made in the best of feeling, some in favor of Andrew Jackson and some in favor of Henry Clay. Abraham Lincoln, the cook, told a number of funny stories, and it is recorded that they were not of too refined a character to suit the taste of his audience. A sleight-of-hand performer was present, and among other tricks performed, he fried some eggs in Lincoln’s hat. Judge Herndon says, as explanatory to the delay in passing up the hat for the experiment, Lincoln drolly observed: “It was out of respect for the eggs, not care for my hat.”
William G. Greene, an old-time friend of Lincoln, was a student at Illinois College, and one summer brought home with him, on a vacation, Richard Yates (afterwards Governor of Illinois) and some other boys, and, in order to entertain them, took them up to see Lincoln.
He found him in his usual position and at his usual occupation—flat on his back, on a cellar door, reading a newspaper. This was the manner in which a President of the United States and a Governor of Illinois became acquainted with each other.
Greene says Lincoln repeated the whole of Burns, and a large quantity of Shakespeare for the entertainment of the college boys, and, in return, was invited to dine with them on bread and milk. How he managed to upset his bowl of milk is not a matter of history, but the fact is that he did so, as is the further fact that Greene’s mother, who loved Lincoln, tried to smooth over the accident and relieve the young man’s embarrassment.
Once “Abe” borrowed Weems’ “Life of Washington” from Joseph Crawford, a neighbor. “Abe” devoured it; read it and re-read it, and when asleep put it by him between the logs of the wall. One night a rain storm wet it through and ruined it.
“I’ve no money,” said “Abe,” when reporting the disaster to Crawford, “but I’ll work it out.”
“All right,” was Crawford’s response; “you pull fodder for three days, an’ the book is your’n.”
“Abe” pulled the fodder, but he never forgave Crawford for putting so much work upon him. He never lost an opportunity to crack a joke at his expense, and the name “Blue-nose Crawford” “Abe” applied to him stuck to him throughout his life.
When Mr. Lincoln was a candidate for the Legislature, it was the practice at that date in Illinois for two rival candidates to travel over the district together. The custom led to much good-natured raillery between them; and in such contests Lincoln was rarely, if ever, worsted. He could even turn the generosity of a rival to account by his whimsical treatment.
On one occasion, says Mr. Weir, a former resident of Sangamon county, he had driven out from Springfield in company with a political opponent to engage in joint debate. The carriage, it seems, belonged to his opponent. In addressing the gathering of farmers that met them, Lincoln was lavish in praise of the generosity of his friend.
“I am too poor to own a carriage,” he said, “but my friend has generously invited me to ride with him. I want you to vote for me if you will; but if not then vote for my opponent, for he is a fine man.”
His extravagant and persistent praise of his opponent appealed to the sense of humor in his rural audience, to whom his inability to own a carriage was by no means a disqualification.
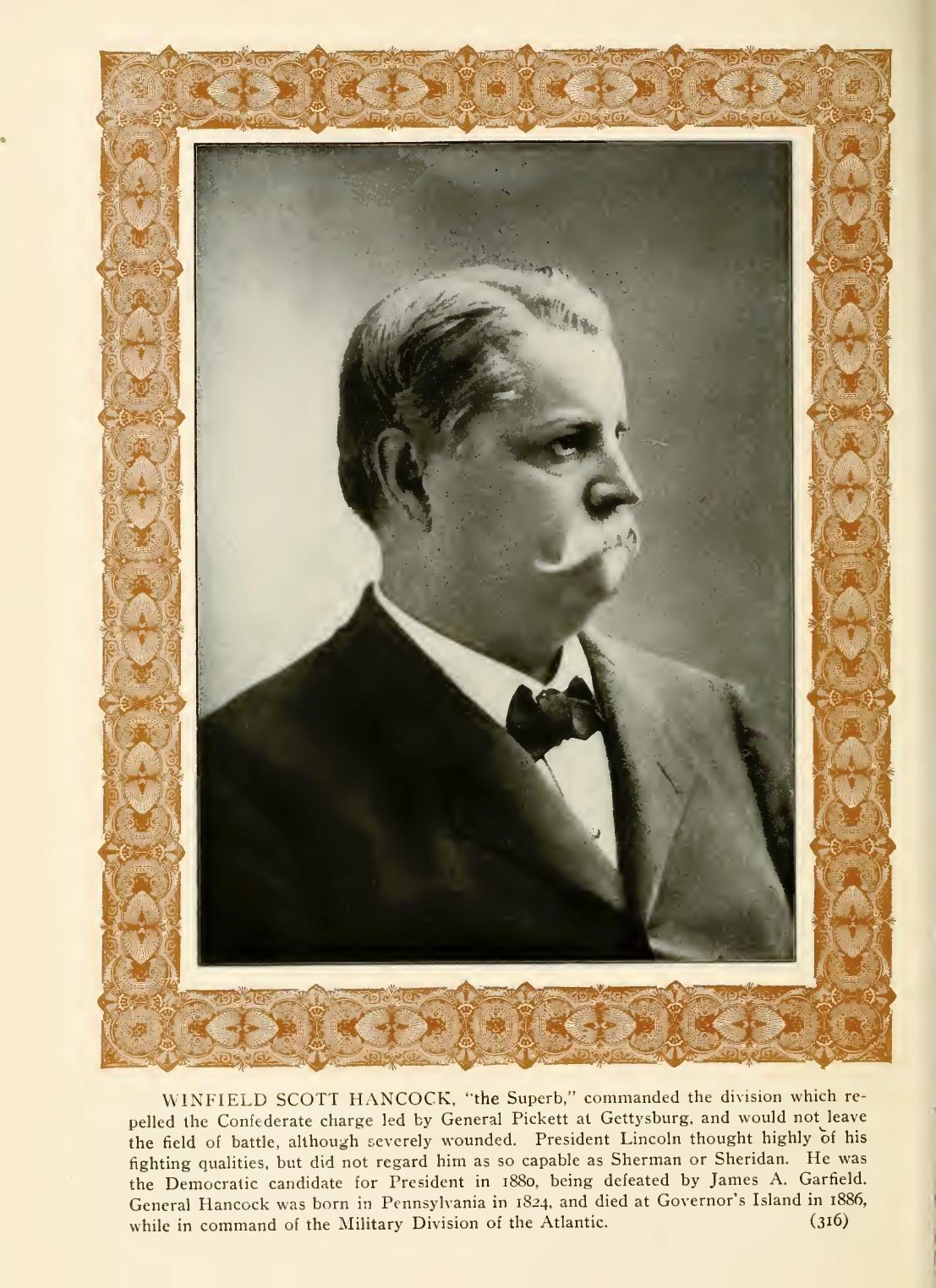




Lincoln admitted that he was not particularly energetic when it came to real hard work.
“My father,” said he one day, “taught me how to work, but not to love it. I never did like to work, and I don’t deny it. I’d rather read, tell stories, crack jokes, talk, laugh—anything but work.”
The opening of the year 1860 found Mr. Lincoln’s name freely mentioned in connection with the Republican nomination for the Presidency. To be classed with Seward, Chase, McLean, and other celebrities, was enough to stimulate any Illinois lawyer’s pride; but in Mr. Lincoln’s case, if it had any such effect, he was most artful in concealing it. Now and then, some ardent friend, an editor, for example, would run his name up to the masthead, but in all cases he discouraged the attempt.
“In regard to the matter you spoke of,” he answered one man who proposed his name, “I beg you will not give it a further mention. Seriously, I do not think I am fit for the Presidency.”
There was a “social” at Lincoln’s house in Springfield, and “Abe” introduced his wife to Ward Lamon, his law partner. Lamon tells the story in these words:
“After introducing me to Mrs. Lincoln, he left us in conversation. I remarked to her that her husband was a great favorite in the eastern part of the State, where I had been stopping.
“‘Yes,’ she replied, ‘he is a great favorite everywhere. He is to be President of the United States some day; if I had not thought so I never would have married him, for you can see he is not pretty.
“‘But look at him, doesn’t he look as if he would make a magnificent President?’”
The following article on Niagara Falls, in Mr. Lincoln’s handwriting, was found among his papers after his death:
“Niagara Falls! By what mysterious power is it that millions and millions are drawn from all parts of the world to gaze upon Niagara Falls? There is no mystery about the thing itself. Every effect is just as any intelligent man, knowing the causes, would anticipate without seeing it. If the water moving onward in a great river reaches a point where there is a perpendicular jog of a hundred feet in descent in the bottom of the river, it is plain the water will have a violent and continuous plunge at that point. It is also plain, the water, thus plunging, will foam and roar, and send up a mist continuously, in which last, during sunshine, there will be perpetual rainbows. The mere physical of Niagara Falls is only this. Yet this is really a very small part of that world’s wonder. Its power to excite reflection and emotion is its great charm. The geologist will demonstrate that the plunge, or fall, was once at Lake Ontario, and has worn its way back to its present position; he will ascertain how fast it is wearing now, and so get a basis for determining how long it has been wearing back from Lake Ontario, and finally demonstrate by it that this world is at least fourteen thousand years old. A philosopher of a slightly different turn will say, ‘Niagara Falls is only the lip of the basin out of which pours all the surplus water which rains down on two or three hundred thousand square miles of the earth’s surface.’ He will estimate with approximate accuracy that five hundred thousand tons of water fall with their full weight a distance of a hundred feet each minute—thus exerting a force equal to the lifting of the same weight, through the same space, in the same time.
“But still there is more. It calls up the indefinite past. When Columbus first sought this continent—when Christ suffered on the cross—when Moses led Israel through the Red Sea—nay, even when Adam first came from the hand of his Maker; then, as now, Niagara was roaring here. The eyes of that species of extinct giants whose bones fill the mounds of America have gazed on Niagara, as ours do now. Contemporary with the first race of men, and older than the first man, Niagara is strong and fresh to-day as ten thousand years ago. The Mammoth and Mastodon, so long dead that fragments of their monstrous bones alone testify that they ever lived, have gazed on Niagara—in that long, long time never still for a single moment (never dried), never froze, never slept, never rested.”
A lady relative, who lived for two years with the Lincolns, said that Mr. Lincoln was in the habit of lying on the floor with the back of a chair for a pillow when he read.
One evening, when in this position in the hall, a knock was heard at the front door, and, although in his shirtsleeves, he answered the call. Two ladies were at the door, whom he invited into the parlor, notifying them in his open, familiar way, that he would “trot the women folks out.”
Mrs. Lincoln, from an adjoining room, witnessed the ladies’ entrance, and, overhearing her husband’s jocose expression, her indignation was so instantaneous she made the situation exceedingly interesting for him, and he was glad to retreat from the house. He did not return till very late at night, and then slipped quietly in at a rear door.
During the rebellion the Austrian Minister to the United States Government introduced to the President a count, a subject of the Austrian government, who was desirous of obtaining a position in the American army.
Being introduced by the accredited Minister of Austria he required no further recommendation to secure the appointment; but, fearing that his importance might not be fully appreciated by the republican President, the count was particular in impressing the fact upon him that he bore that title, and that his family was ancient and highly respectable.
President Lincoln listened with attention, until this unnecessary commendation was mentioned; then, with a merry twinkle in his eye, he tapped the aristocratic sprig of hereditary nobility on the shoulder in the most fatherly way, as if the gentleman had made a confession of some unfortunate circumstance connected with his lineage, for which he was in no way responsible, and said:
“Never mind, you shall be treated with just as much consideration for all that. I will see to it that your bearing a title shan’t hurt you.”
A young man living in Kentucky had been enticed into the rebel army. After a few months he became disgusted, and managed to make his way back home. Soon after his arrival, the Union officer in command of the military stationed in the town had him arrested as a rebel spy, and, after a military trial he was condemned to be hanged.
President Lincoln was seen by one of his friends from Kentucky, who explained his errand and asked for mercy. “Oh, yes, I understand; some one has been crying, and worked upon your feelings, and you have come here to work on mine.”
His friend then went more into detail, and assured him of his belief in the truth of the story. After some deliberation, Mr. Lincoln, evidently scarcely more than half convinced, but still preferring to err on the side of mercy, replied:
“If a man had more than one life, I think a little hanging would not hurt this one; but after he is once dead we cannot bring him back, no matter how sorry we may be; so the boy shall be pardoned.”
And a reprieve was given on the spot.
While the celebrated artist, Hicks, was engaged in painting Mr. Lincoln’s portrait, just after the former’s first nomination for the Presidency, he asked the great statesman if he could point out the precise spot where he was born.
Lincoln thought the matter over for a day or two, and then gave the artist the following memorandum:
“Springfield, Ill., June 14, 1860
“I was born February 12, 1809, in then Hardin county, Kentucky, at a point within the now county of Larue, a mile or a mile and a half from where Rodgen’s mill now is. My parents being dead, and my own memory not serving, I know no means of identifying the precise locality. It was on Nolen Creek.
In his message to Congress in December, 1864, just after his re-election, President Lincoln, in his message of December 6th, let himself out, in plain, unmistakable terms, to the effect that the freedmen should never be placed in bondage again. “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” of December 24th, 1864, printed the cartoon we herewith reproduce, the text underneath running in this way:
UNCLE ABE: “Sambo, you are not handsome, any more than myself, but as to sending you back to your old master, I’m not the man to do it—and, what’s more, I won’t.” (Vice President’s message.)
Congress, at the previous sitting, had neglected to pass the resolution for the Constitutional amendment prohibiting slavery, but, on the 31st of January, 1865, the resolution was finally adopted, and the United States Constitution soon had the new feature as one of its clauses, the necessary number of State Legislatures approving it. President Lincoln regarded the passage of this resolution by Congress as most important, as the amendment, in his mind, covered whatever defects a rigid construction of the Constitution might find in his Emancipation Proclamation.
After the latter was issued, negroes were allowed to enlist in the Army, and they fought well and bravely. After the War, in the reorganization of the Regular Army, four regiments of colored men were provided for—the Ninth and Tenth Cavalry and the Twenty-fourth and Twenty-fifth Infantry. In the cartoon, Sambo has evidently been asking “Uncle Abe” as to the probability or possibility of his being again enslaved.
Some Lincoln enthusiast in Kansas, with much more pretensions than power, wrote him in March, 1860 proposing to furnish a Lincoln delegation from that State to the Chicago Convention, and suggesting that Lincoln should pay the legitimate expenses of organizing, electing, and taking to the convention the promised Lincoln delegates.
To this Lincoln replied that “in the main, the use of money is wrong, but for certain objects in a political contest the use of some is both right and indispensable.” And he added: “If you shall be appointed a delegate to Chicago, I will furnish $100 to bear the expenses of the trip.”
He heard nothing further from the Kansas man until he saw an announcement in the newspapers that Kansas had elected delegates and instructed them for Seward.
Lincoln’s military service in the Back Hawk war had increased his popularity at New Salem, and he was put up as a candidate for the Legislature.
A. Y. Ellis describes his personal appearance at this time as follows: “He wore a mixed jean coat, claw-hammer style, short in the sleeves and bob-tailed; in fact, it was so short in the tail that he could not sit on it; flax and tow linen pantaloons and a straw hat. I think he wore a vest, but do not remember how it looked; he wore pot-metal boots.”
A little girl, who had been told that the President was very homely, was taken by her father to see the President at the White House.
Lincoln took her upon his knee and chatted with her for a moment in his merry way, when she turned to her father and exclaimed:
“Oh, Pa! he isn’t ugly at all; he’s just beautiful!”
To a curiosity-seeker who desired a permit to pass the lines to visit the field of Bull Run, after the first battle, Lincoln made the following reply:
“A man in Cortlandt county raised a porker of such unusual size that strangers went out of their way to see it.
“One of them the other day met the old gentleman and inquired about the animal.
“‘Wall, yes,’ the old fellow said, ‘I’ve got such a critter, mi’ty big un; but I guess I’ll have to charge you about a shillin’ for lookin’ at him.’
“The stranger looked at the old man for a minute or so, pulled out the desired coin, handed it to him and started to go off. ‘Hold on,’ said the other, ‘don’t you want to see the hog?’
“‘No,’ said the stranger; ‘I have seen as big a hog as I want to see!’
“And you will find that fact the case with yourself, if you should happen to see a few live rebels there as well as dead ones.”
When Lincoln’s special train from Springfield to Washington reached the Illinois State line, there was a stop for dinner. There was such a crowd that Lincoln could scarcely reach the dining-room. “Gentlemen,” said he, as he surveyed the crowd, “if you will make me a little path, so that I can get through and get something to eat, I will make you a speech when I get back.”
When complaints were made to President Lincoln by victims of Secretary of War Stanton’s harshness, rudeness, and refusal to be obliging—particularly in cases where Secretary Stanton had refused to honor Lincoln’s passes through the lines—the President would often remark to this effect “I cannot always be sure that permits given by me ought to be granted. There is an understanding between myself and Stanton that when I send a request to him which cannot consistently be granted, he is to refuse to honor it. This he sometimes does.”
“There won’t be a tar barrel left in Illinois to-night,” said Senator Stephen A. Douglas, in Washington, to his Senatorial friends, who asked him, when the news of the nomination of Lincoln reached them, “Who is this man Lincoln, anyhow?”
Douglas was right. Not only the tar barrels, but half the fences of the State of Illinois went up in the fire of rejoicing.
In explanation of Lincoln’s great popularity, D. W. Bartlett, in his “Life and Speeches of Abraham Lincoln,” published in 1860 makes this statement of “Abe’s” efficient service to his neighbors in the “Great Snow” of 1830-31:
“The deep snow which occurred in 1830-31 was one of the chief troubles endured by the early settlers of central and southern Illinois. Its consequences lasted through several years. The people were ill-prepared to meet it, as the weather had been mild and pleasant—unprecedentedly so up to Christmas—when a snow-storm set in which lasted two days, something never before known even among the traditions of the Indians, and never approached in the weather of any winter since.
“The pioneers who came into the State (then a territory) in 1800 say the average depth of snow was never, previous to 1830, more than knee-deep to an ordinary man, while it was breast-high all that winter. It became crusted over, so as, in some cases, to bear teams. Cattle and horses perished, the winter wheat was killed, the meager stock of provisions ran out, and during the three months’ continuance of the snow, ice and continuous cold weather the most wealthy settlers came near starving, while some of the poor ones actually did. It was in the midst of such scenes that Abraham Lincoln attained his majority, and commenced his career of bold and manly independence.....
“Communication between house and house was often entirely obstructed for teams, so that the young and strong men had to do all the traveling on foot; carrying from one neighbor what of his store he could spare to another, and bringing back in return something of his store sorely needed. Men living five, ten, twenty and thirty miles apart were called ‘neighbors’ then. Young Lincoln was always ready to perform these acts of humanity, and was foremost in the counsels of the settlers when their troubles seemed gathering like a thick cloud about them.”
A certain rich man in Springfield, Illinois, sued a poor attorney for $2.50, and Lincoln was asked to prosecute the case. Lincoln urged the creditor to let the matter drop, adding, “You can make nothing out of him, and it will cost you a good deal more than the debt to bring suit.” The creditor was still determined to have his way, and threatened to seek some other attorney. Lincoln then said, “Well, if you are determined that suit should be brought, I will bring it; but my charge will be $10.”
The money was paid him, and peremptory orders were given that the suit be brought that day. After the client’s departure Lincoln went out of the office, returning in about an hour with an amused look on his face.
Asked what pleased him, he replied, “I brought suit against ——, and then hunted him up, told him what I had done, handed him half of the $10, and we went over to the squire’s office. He confessed judgment and paid the bill.”
Lincoln added that he didn’t see any other way to make things satisfactory for his client as well as the other.
Judge Thomas B. Bryan, of Chicago, a member of the Union Defense Committee during the War, related the following concerning the original copy of the Emancipation Proclamation:
“I asked Mr. Lincoln for the original draft of the Proclamation,” said Judge Bryan, “for the benefit of our Sanitary Fair, in 1865. He sent it and accompanied it with a note in which he said:
“‘I had intended to keep this paper, but if it will help the soldiers, I give it to you.’
“The paper was put up at auction and brought $3,000. The buyer afterward sold it again to friends of Mr. Lincoln at a greatly advanced price, and it was placed in the rooms of the Chicago Historical Society, where it was burned in the great fire of 1871.”
An elegantly dressed young Virginian assured Lincoln that he had done a great deal of hard manual labor in his time. Much amused at this solemn declaration, Lincoln said:
“Oh, yes; you Virginians shed barrels of perspiration while standing off at a distance and superintending the work your slaves do for you. It is different with us. Here it is every fellow for himself, or he doesn’t get there.”
When young Lincoln had fully demonstrated that he was the champion wrestler in the country surrounding New Salem, the men of “de gang” at Clary’s Grove, whose leader “Abe” had downed, were his sworn political friends and allies.
Their work at the polls was remarkably effective. When the “Butcherknife boys,” the “huge-pawed boys,” and the “half-horse-half-alligator men” declared for a candidate the latter was never defeated.
Soon after the opening of Congress in 1861, Mr. Shannon, from California, made the customary call at the White House. In the conversation that ensued, Mr Shannon said: “Mr. President, I met an old friend of yours in California last summer, a Mr. Campbell, who had a good deal to say of your Springfield life.”
“Ah!” returned Mr. Lincoln, “I am glad to hear of him. Campbell used to be a dry fellow in those days,” he continued. “For a time he was Secretary of State. One day during the legislative vacation, a meek, cadaverous-looking man, with a white neck-cloth, introduced himself to him at his office, and, stating that he had been informed that Mr. C. had the letting of the hall of representatives, he wished to secure it, if possible, for a course of lectures he desired to deliver in Springfield.
“‘May I ask,’ said the Secretary, ‘what is to be the subject of your lectures?’
“‘Certainly,’ was the reply, with a very solemn expression of countenance. ‘The course I wish to deliver is on the Second Coming of our Lord.’
“‘It is of no use,’ said C.; ‘if you will take my advice, you will not waste your time in this city. It is my private opinion that, if the Lord has been in Springfield once, He will never come the second time!’”
J. S. Moulton, of Chicago, a master in chancery and influential in public affairs, looked upon the candidacy of Mr. Lincoln for President as something in the nature of a joke. He did not rate the Illinois man in the same class with the giants of the East. In fact he had expressed himself as by no means friendly to the Lincoln cause.
Still he had been a good friend to Lincoln and had often met him when the Springfield lawyer came to Chicago. Mr. Lincoln heard of Moulton’s attitude, but did not see Moulton until after the election, when the President-elect came to Chicago and was tendered a reception at one of the big hotels.
Moulton went up in the line to pay his respects to the newly-elected chief magistrate, purely as a formality, he explained to his companions. As Moulton came along the line Mr. Lincoln grasped Moulton’s hand with his right, and with his left took the master of chancery by the shoulder and pulled him out of the line.
“You don’t belong in that line, Moulton,” said Mr. Lincoln. “You belong here by me.”
Everyone at the reception was a witness to the honoring of Moulton. From that hour every faculty that Moulton possessed was at the service of the President. A little act of kindness, skillfully bestowed, had won him; and he stayed on to the end.
If a client did not pay, Lincoln did not believe in suing for the fee. When a fee was paid him his custom was to divide the money into two equal parts, put one part into his pocket, and the other into an envelope labeled “Herndon’s share.”
It is recorded that when “Abe” was born, the household goods of his father consisted of a few cooking utensils, a little bedding, some carpenter tools, and four hundred gallons of the fierce product of the mountain still.


One of the cartoon-posters issued by the Democratic National Campaign Committee in the fall of 1864 is given here. It had the legend, “Running the Machine,” printed beneath; the “machine” was Secretary Chase’s “Greenback Mill,” and the mill was turning out paper money by the million to satisfy the demands of greedy contractors. “Uncle Abe” is pictured as about to tell one of his funny stories, of which the scene “reminds” him; Secretary of War Stanton is receiving a message from the front, describing a great victory, in which one prisoner and one gun were taken; Secretary of State Seward is handing an order to a messenger for the arrest of a man who had called him a “humbug,” the habeas corpus being suspended throughout the Union at that period; Secretary of the Navy Welles—the long-haired, long-bearded man at the head of the table—is figuring out a naval problem; at the side of the table, opposite “Uncle Abe,” are seated two Government contractors, shouting for “more greenbacks,” and at the extreme left is Secretary of the Treasury Fessenden (who succeeded Chase when the latter was made Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court), who complains that he cannot satisfy the greed of the contractors for “more greenbacks,” although he is grinding away at the mill day and night.
Lincoln was the actual head of the administration, and whenever he chose to do so he controlled Secretary of War Stanton as well as the other Cabinet ministers.
Secretary Stanton on one occasion said: “Now, Mr. President, those are the facts and you must see that your order cannot be executed.”
Lincoln replied in a somewhat positive tone: “Mr. Secretary, I reckon you’ll have to execute the order.”
Stanton replied with vigor: “Mr. President, I cannot do it. This order is an improper one, and I cannot execute it.”
Lincoln fixed his eyes upon Stanton, and, in a firm voice and accent that clearly showed his determination, said: “Mr. Secretary, it will have to be done.”
It was done.
Ward Lamon, once Lincoln’s law partner, relates a story which places Lincoln’s high sense of honor in a prominent light. In a certain case, Lincoln and Lamon being retained by a gentleman named Scott, Lamon put the fee at $250, and Scott agreed to pay it. Says Lamon:
“Scott expected a contest, but, to his surprise, the case was tried inside of twenty minutes; our success was complete. Scott was satisfied, and cheerfully paid over the money to me inside the bar, Lincoln looking on. Scott then went out, and Lincoln asked, ‘What did you charge that man?’
“I told him $250. Said he: ‘Lamon, that is all wrong. The service was not worth that sum. Give him back at least half of it.’
“I protested that the fee was fixed in advance; that Scott was perfectly satisfied, and had so expressed himself. ‘That may be,’ retorted Lincoln, with a look of distress and of undisguised displeasure, ‘but I am not satisfied. This is positively wrong. Go, call him back and return half the money at least, or I will not receive one cent of it for my share.’
“I did go, and Scott was astonished when I handed back half the fee.
“This conversation had attracted the attention of the lawyers and the court. Judge David Davis, then on our circuit bench (afterwards Associate Justice on the United States Supreme bench), called Lincoln to him. The Judge never could whisper, but in this instance he probably did his best. At all events, in attempting to whisper to Lincoln he trumpeted his rebuke in about these words, and in rasping tones that could be heard all over the court-room: ‘Lincoln, I have been watching you and Lamon. You are impoverishing this bar by your picayune charges of fees, and the lawyers have reason to complain of you. You are now almost as poor as Lazarus, and if you don’t make people pay you more for your services you will die as poor as Job’s turkey!’
“Judge O. L. Davis, the leading lawyer in that part of the State, promptly applauded this malediction from the bench; but Lincoln was immovable.
“‘That money,’ said he, ‘comes out of the pocket of a poor, demented girl, and I would rather starve than swindle her in this manner.’”
“Billy, don’t shoot too high—aim lower, and the common people will understand you,” Lincoln once said to a brother lawyer.
“They are the ones you want to reach—at least, they are the ones you ought to reach.
“The educated and refined people will understand you, anyway. If you aim too high, your idea will go over the heads of the masses, and only hit those who need no hitting.”
One who afterward became one of Lincoln’s most devoted friends and adherents tells this story regarding the manner in which Lincoln received him when they met for the first time:
“After a comical survey of my fashionable toggery,—my swallow-tail coat, white neck-cloth, and ruffled shirt (an astonishing outfit for a young limb of the law in that settlement), Lincoln said:
“‘Going to try your hand at the law, are you? I should know at a glance that you were a Virginian; but I don’t think you would succeed at splitting rails. That was my occupation at your age, and I don’t think I have taken as much pleasure in anything else from that day to this.’”
“Yesterday little indorsements of mine went to you in two cases of postmasterships, sought for widows whose husbands have fallen in the battles of this war.
“These cases, occurring on the same day, brought me to reflect more attentively than what I had before done as to what is fairly due from us here in dispensing of patronage toward the men who, by fighting our battles, bear the chief burden of saving our country.
“My conclusion is that, other claims and qualifications being equal, they have the right, and this is especially applicable to the disabled soldier and the deceased soldier’s family.”
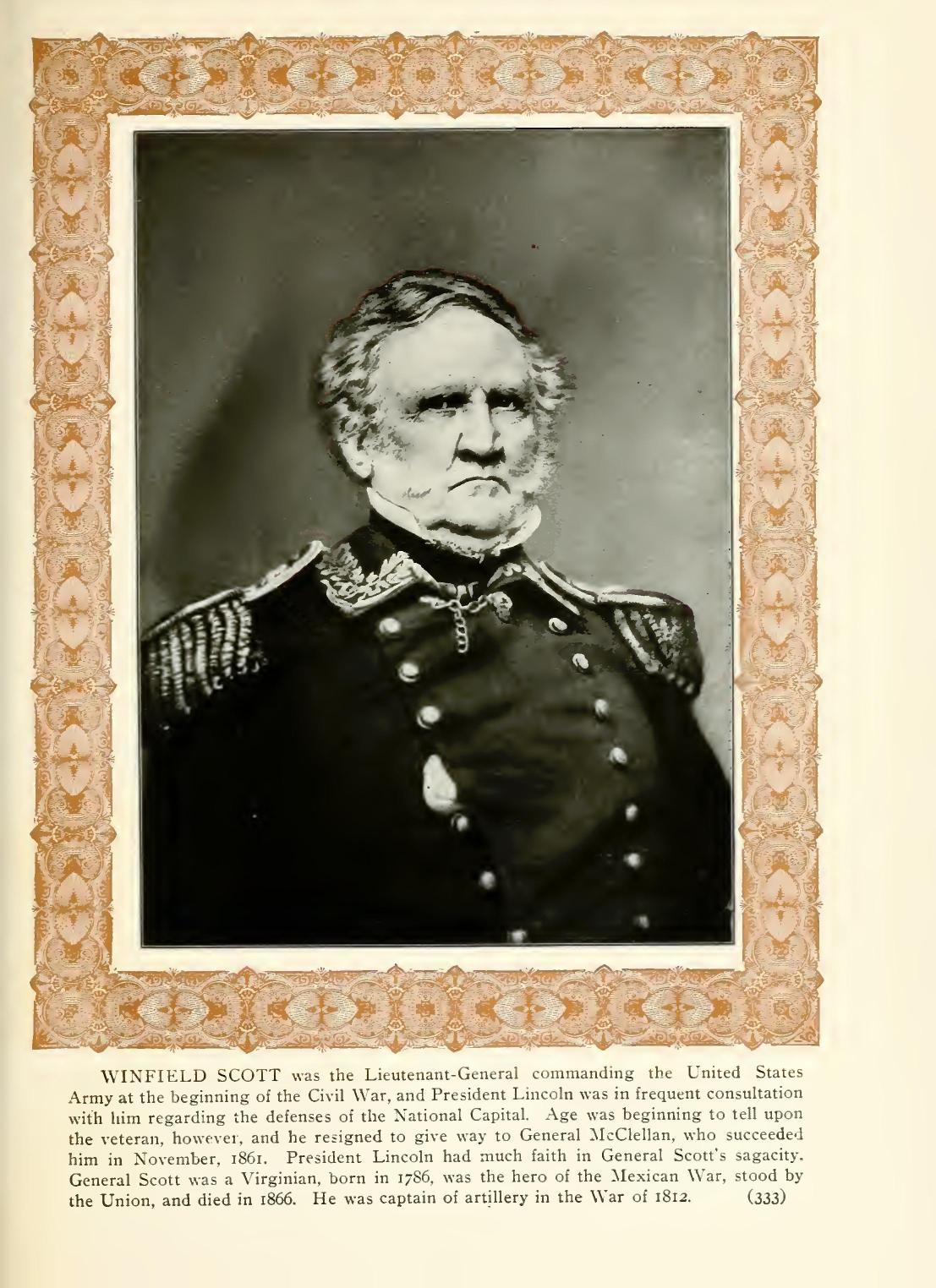
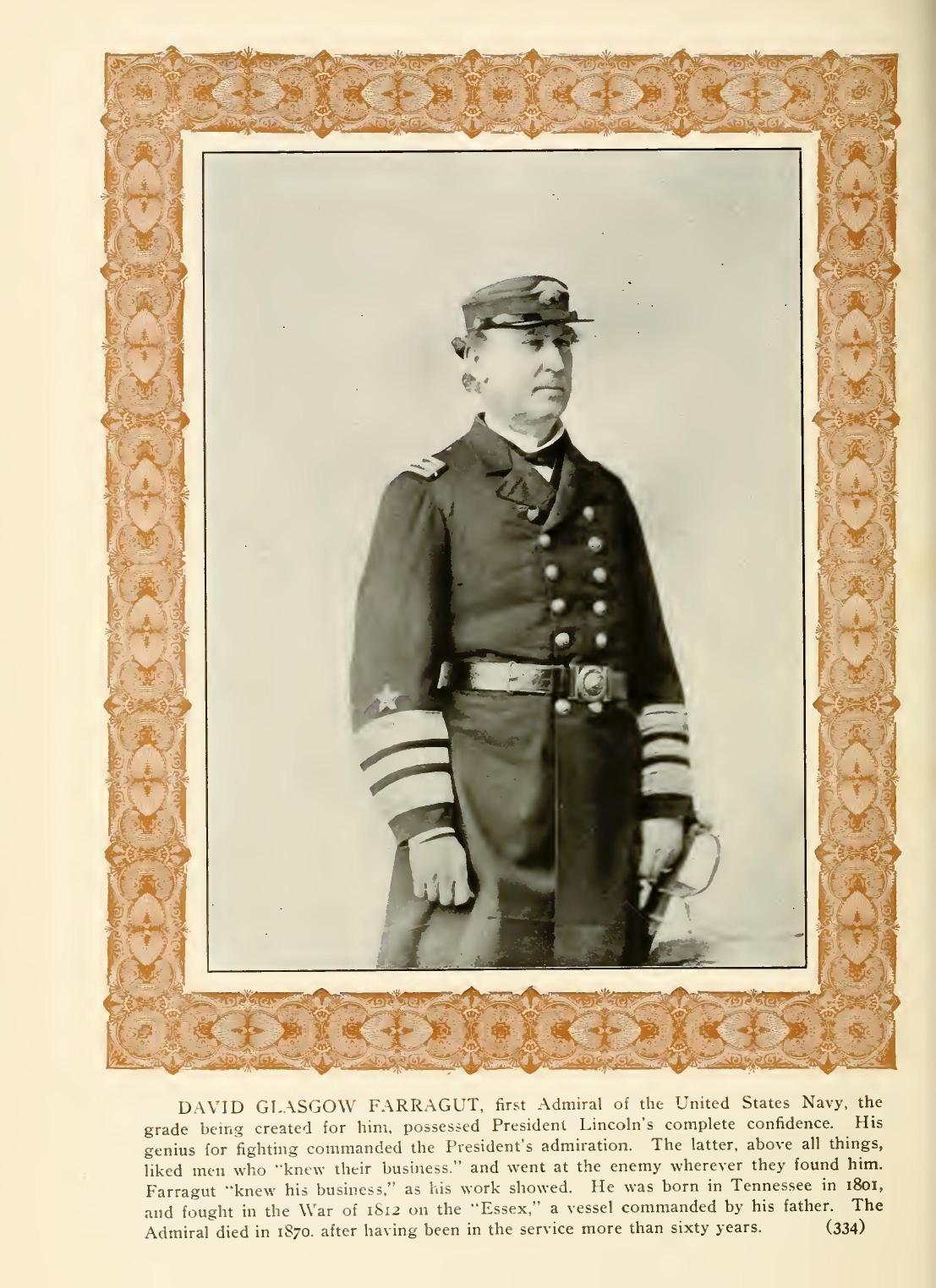




When told how uneasy all had been at his going to Richmond, Lincoln replied:
“Why, if any one else had been President and had gone to Richmond, I would have been alarmed; but I was not scared about myself a bit.”
On the 20th of July, 1864, Horace Greeley crossed into Canada to confer with refugee rebels at Niagara. He bore with him this paper from the President:
“To Whom It May Concern: Any proposition which embraces the restoration of peace, the integrity of the whole Union, and the abandonment of slavery, and which comes by and with an authority that can control the armies now at war with the United States, will be received and considered by the executive government of the United States, and will be met by liberal terms and other substantial and collateral points, and the bearer or bearers thereof shall have safe conduct both ways.”
To this Jefferson Davis replied: “We are not fighting for slavery; we are fighting for independence.”
Lincoln was compelled to contend with the results of the ill-judged zeal of politicians, who forced ahead his flatboat and rail-splitting record, with the homely surroundings of his earlier days, and thus, obscured for the time, the other fact that, always having the heart, he had long since acquired the manners of a true gentleman.
So, too, did he suffer from Eastern censors, who did not take those surroundings into account, and allowed nothing for his originality of character. One of these critics heard at Washington that Mr. Lincoln, in speaking at different times of some move or thing, said “it had petered out;” that some other one’s plan “wouldn’t gibe;” and being asked if the War and the cause of the Union were not a great care to him, replied:
“Yes, it is a heavy hog to hold.”
The first two phrases are so familiar here in the West that they need no explanation. Of the last and more pioneer one it may be said that it had a special force, and was peculiarly Lincoln-like in the way applied by him.
In the early times in Illinois, those having hogs, did their own killing, assisted by their neighbors. Stripped of its hair, one held the carcass nearly perpendicular in the air, head down, while others put one point of the gambrel-bar through a slit in its hock, then over the string-pole, and the other point through the other hock, and so swung the animal clear of the ground. While all this was being done, it took a good man to “hold the hog,” greasy, warmly moist, and weighing some two hundred pounds. And often those with the gambrel prolonged the strain, being provokingly slow, in hopes to make the holder drop his burden.
This latter thought is again expressed where President Lincoln, writing of the peace which he hoped would “come soon, to stay; and so come as to be worth the keeping in all future time,” added that while there would “be some black men who can remember that with silent tongue and clenched teeth and steady eye, and well-poised bayonet, they have helped mankind on to this great consummation,” he feared there would “be some white ones unable to forget that, with malignant heart and deceitful tongue, they had striven to hinder it.”
He had two seemingly opposite elements little understood by strangers, and which those in more intimate relations with him find difficult to explain; an open, boyish tongue when in a happy mood, and with this a reserve of power, a force of thought that impressed itself without words on observers in his presence. With the cares of the nation on his mind, he became more meditative, and lost much of his lively ways remembered “back in Illinois.”
One of the most beautiful traits of Mr. Lincoln’s character was his considerate regard for the poor and obscure relatives he had left, plodding along in their humble ways of life. Wherever upon his circuit he found them, he always went to their dwellings, ate with them, and, when convenient, made their houses his home. He never assumed in their presence the slightest superiority to them. He gave them money when they needed it and he had it. Countless times he was known to leave his companions at the village hotel, after a hard day’s work in the court-room, and spend the evening with these old friends and companions of his humbler days. On one occasion, when urged not to go, he replied, “Why, Aunt’s heart would be broken if I should leave town without calling upon her;” yet, he was obliged to walk several miles to make the call.
This was the reply made by Lincoln to an application for the pardon of a soldier who had shown himself brave in war, had been severely wounded, but afterward deserted:
“Did you say he was once badly wounded?
“Then, as the Scriptures say that in the shedding of blood is the remission of sins, I guess we’ll have to let him off this time.”
“Blair,” said the President, “did you ever know that fright has sometimes proven a cure for boils?” “No, Mr. President, how is that?” “I’ll tell you. Not long ago when a colonel, with his cavalry, was at the front, and the Rebs were making things rather lively for us, the colonel was ordered out to a reconnaissance. He was troubled at the time with a big boil where it made horseback riding decidedly uncomfortable. He finally dismounted and ordered the troops forward without him. Soon he was startled by the rapid reports of pistols and the helter-skelter approach of his troops in full retreat before a yelling rebel force. He forgot everything but the yells, sprang into his saddle, and made capital time over the fences and ditches till safe within the lines. The pain from his boil was gone, and the boil, too, and the colonel swore that there was no cure for boils so sure as fright from rebel yells.”
When President Lincoln issued a military order, it was usually expressive, as the following shows:
“War Department, Washington, July 22, ‘62.
“First: Ordered that military commanders within the States of Virginia, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas and Arkansas, in an orderly manner, seize and use any property, real or personal, which may be necessary or convenient for their several commands, for supplies, or for other military purposes; and that while property may be all stored for proper military objects, none shall be destroyed in wantonness or malice.
“Second: That military and naval commanders shall employ as laborers within and from said States, so many persons of African descent as can be advantageously used for military or naval purposes, giving them reasonable wages for their labor.
“Third: That as to both property and persons of African descent, accounts shall be kept sufficiently accurate and in detail to show quantities and amounts, and from whom both property and such persons shall have come, as a basis upon which compensation can be made in proper cases; and the several departments of this Government shall attend to and perform their appropriate parts towards the execution of these orders.
“By order of the President.”
Judge David Davis, Justice of the United States Supreme Court, and United States Senator from Illinois, was one of Lincoln’s most intimate friends. He told this story on “Abe”:
“Lincoln was very bashful when in the presence of ladies. I remember once we were invited to take tea at a friend’s house, and while in the parlor I was called to the front gate to see someone.
“When I returned, Lincoln, who had undertaken to entertain the ladies, was twisting and squirming in his chair, and as bashful as a schoolboy.”


There was much that was irritating and uncomfortable in the circuit-riding of the Illinois court, but there was more which was amusing to a temperament like Lincoln’s. The freedom, the long days in the open air, the unexpected if trivial adventures, the meeting with wayfarers and settlers—all was an entertainment to him. He found humor and human interest on the route where his companions saw nothing but commonplaces.
“He saw the ludicrous in an assemblage of fowls,” says H. C. Whitney, one of his fellow-itinerants, “in a man spading his garden, in a clothes-line full of clothes, in a group of boys, in a lot of pigs rooting at a mill door, in a mother duck teaching her brood to swim—in everything and anything.”
It was in the latter part of 1863 that Russia offered its friendship to the United States, and sent a strong fleet of warships, together with munitions of war, to this country to be used in any way the President might see fit. Russia was not friendly to England and France, these nations having defeated her in the Crimea a few years before. As Great Britain and the Emperor of the French were continually bothering him, President Lincoln used Russia’s kindly feeling and action as a means of keeping the other two powers named in a neutral state of mind. Underneath the cartoon we here reproduce, which was labeled “Drawing Things to a Head,” and appeared in the issue of “Harper’s Weekly,” of November 28, 1863, was this DR. LINCOLN (to smart boy of the shop): “Mild applications of Russian Salve for our friends over the way, and heavy doses—and plenty of it for our Southern patient!!”
Secretary of State Seward was the “smart boy” of the shop, and “our friend over the way” were England and France. The latter bothered President Lincoln no more, but it is a fact that the Confederate privateer Alabama was manned almost entirely by British seamen; also, that when the Alabama was sunk by the Kearsarge, in the summer of 1864, the Confederate seamen were picked up by an English vessel, taken to Southhampton, and set at liberty!
Lincoln was candor itself when conducting his side of a case in court. General Mason Brayman tells this story as an illustration:
“It is well understood by the profession that lawyers do not read authors favoring the opposite side. I once heard Mr. Lincoln, in the Supreme Court of Illinois, reading from a reported case some strong points in favor of his argument. Reading a little too far, and before becoming aware of it, plunged into an authority against himself.
“Pausing a moment, he drew up his shoulders in a comical way, and half laughing, went on, ‘There, there, may it please the court, I reckon I’ve scratched up a snake. But, as I’m in for it, I guess I’ll read it through.’
“Then, in his most ingenious and matchless manner, he went on with his argument, and won his case, convincing the court that it was not much of a snake after all.”
Lincoln was fond of going all by himself to any little show or concert. He would often slip away from his fellow-lawyers and spend the entire evening at a little magic lantern show intended for children.
A traveling concert company was always sure of drawing Lincoln. A Mrs. Hillis, a member of the “Newhall Family,” and a good singer, was the only woman who ever seemed to exhibit any liking for him—so Lincoln said. He attended a negro-minstrel show in Chicago, once, where he heard Dixie sung. It was entirely new, and pleased him greatly.
An Eastern newspaper writer told how Lincoln, after his first nomination, received callers, the majority of them at his law office:
“While talking to two or three gentlemen and standing up, a very hard looking customer rolled in and tumbled into the only vacant chair and the one lately occupied by Mr. Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln’s keen eye took in the fact, but gave no evidence of the notice.
“Turning around at last he spoke to the odd specimen, holding out his hand at such a distance that our friend had to vacate the chair if he accepted the proffered shake. Mr. Lincoln quietly resumed his chair.
“It was a small matter, yet one giving proof more positively than a larger event of that peculiar way the man has of mingling with a mixed crowd.”
Among the lawyers who traveled the circuit with Lincoln was Usher F. Linder, whose daughter, Rose Linder Wilkinson, has left many Lincoln reminiscences.
“One case in which Mr. Lincoln was interested concerned a member of my own family,” said Mrs. Wilkinson. “My brother, Dan, in the heat of a quarrel, shot a young man named Ben Boyle and was arrested. My father was seriously ill with inflammatory rheumatism at the time, and could scarcely move hand or foot. He certainly could not defend Dan. I was his secretary, and I remember it was but a day or so after the shooting till letters of sympathy began to pour in. In the first bundle which I picked up there was a big letter, the handwriting on which I recognized as that of Mr. Lincoln. The letter was very sympathetic.
“‘I know how you feel, Linder,’ it said. ‘I can understand your anger as a father, added to all the other sentiments. But may we not be in a measure to blame? We have talked about the defense of criminals before our children; about our success in defending them; have left the impression that the greater the crime, the greater the triumph of securing an acquittal. Dan knows your success as a criminal lawyer, and he depends on you, little knowing that of all cases you would be of least value in this.’
“He concluded by offering his services, an offer which touched my father to tears.
“Mr. Lincoln tried to have Dan released on bail, but Ben Boyle’s family and friends declared the wounded man would die, and feeling had grown so bitter that the judge would not grant any bail. So the case was changed to Marshall county, but as Ben finally recovered it was dismissed.”
Lincoln at one time thought seriously of learning the blacksmith’s trade. He was without means, and felt the immediate necessity of undertaking some business that would give him bread. While entertaining this project an event occurred which, in his undetermined state of mind, seemed to open a way to success in another quarter.
Reuben Radford, keeper of a small store in the village of New Salem, had incurred the displeasure of the “Clary Grove Boys,” who exercised their “regulating” prerogatives by irregularly breaking his windows. William G. Greene, a friend of young Lincoln, riding by Radford’s store soon afterward, was hailed by him, and told that he intended to sell out. Mr. Greene went into the store, and offered him at random $400 for his stock, which offer was immediately accepted.
Lincoln “happened in” the next day, and being familiar with the value of the goods, Mr. Greene proposed to him to take an inventory of the stock, to see what sort of a bargain he had made. This he did, and it was found that the goods were worth $600.
Lincoln then made an offer of $125 for his bargain, with the proposition that he and a man named Berry, as his partner, take over Greene’s notes given to Radford. Mr. Greene agreed to the arrangement, but Radford declined it, except on condition that Greene would be their security. Greene at last assented.
Lincoln was not afraid of the “Clary Grove Boys”; on the contrary, they had been his most ardent friends since the time he thrashed “Jack” Armstrong, champion bully of “The Grove”—but their custom was not heavy.
The business soon became a wreck; Greene had to not only assist in closing it up, but pay Radford’s notes as well. Lincoln afterwards spoke of these notes, which he finally made good to Greene, as “the National Debt.”
When Lincoln’s sympathies were enlisted in any cause, he worked like a giant to win. At one time (about 1855) he was in attendance upon court at the little town of Clinton, Ill., and one of the cases on the docket was where fifteen women from a neighboring village were defendants, they having been indicted for trespass. Their offense, as duly set forth in the indictment, was that of swooping down upon one Tanner, the keeper of a saloon in the village, and knocking in the heads of his barrels. Lincoln was not employed in the case, but sat watching the trial as it proceeded.
In defending the ladies, their attorney seemed to evince a little want of tact, and this prompted one of the former to invite Mr. Lincoln to add a few words to the jury, if he thought he could aid their cause. He was too gallant to refuse, and their attorney having consented, he made use of the following argument:
“In this case I would change the order of indictment and have it read The State vs. Mr. Whiskey, instead of The State vs. The Ladies; and touching these there are three laws: the law of self-protection; the law of the land, or statute law; and the moral law, or law of God.
“First the law of self-protection is a law of necessity, as evinced by our forefathers in casting the tea overboard and asserting their right to the pursuit of life, liberty and happiness: In this case it is the only defense the Ladies have, for Tanner neither feared God nor regarded man.
“Second, the law of the land, or statute law, and Tanner is recreant to both.
“Third, the moral law, or law of God, and this is probably a law for the violation of which the jury can fix no punishment.”
Lincoln gave some of his own observations on the ruinous effects of whiskey in society, and demanded its early suppression.
After he had concluded, the Court, without awaiting the return of the jury, dismissed the ladies, saying:
“Ladies, go home. I will require no bond of you, and if any fine is ever wanted of you, we will let you know.”
Frank W. Tracy, President of the First National Bank of Springfield, tells a story illustrative of two traits in Mr. Lincoln’s character. Shortly after the National banking law went into effect the First National of Springield was chartered, and Mr. Tracy wrote to Mr. Lincoln, with whom he was well acquainted in a business way, and tendered him an opportunity to subscribe for some of the stock.
In reply to the kindly offer Mr. Lincoln wrote, thanking Mr. Tracy, but at the same time declining to subscribe. He said he recognized that stock in a good National bank would be a good thing to hold, but he did not feel that he ought, as President, profit from a law which had been passed under his administration.
“He seemed to wish to avoid even the appearance of evil,” said Mr. Tracy, in telling of the incident. “And so the act proved both his unvarying probity and his unfailing policy.”
“I sincerely wish war was a pleasanter and easier business than it is, but it does not admit of holidays.”
Old John Bull got himself into a precious fine scrape when he went so far as to “play double” with the North, as well as the South, during the great American Civil War. In its issue of November 14th, 1863, London “Punch” printed a rather clever cartoon illustrating the predicament Bull had created for himself. John is being lectured by Mrs. North and Mrs. South—both good talkers and eminently able to hold their own in either social conversation, parliamentary debate or political argument—but he bears it with the best grace possible. This is the way the text underneath the picture runs:
MRS. NORTH. “How about the Alabama, you wicked old man?” MRS. SOUTH: “Where’s my rams? Take back your precious consols—there!!” “Punch” had a good deal of fun with old John before it was through with him, but, as the Confederate privateer Alabama was sent beneath the waves of the ocean at Cherbourg by the Kearsarge, and Mrs. South had no need for any more rams, John got out of the difficulty without personal injury. It was a tight squeeze, though, for Mrs. North was in a fighting humor, and prepared to scratch or pull hair. The fact that the privateer Alabama, built at an English shipyard and manned almost entirely by English sailors, had managed to do about $10,000,000 worth of damage to United States commerce, was enough to make any one angry.
After the war was well on, a patriot woman of the West urged President Lincoln to make hospitals at the North where the sick from the Army of the Mississippi could revive in a more bracing air. Among other reasons, she said, feelingly: “If you grant my petition, you will be glad as long as you live.”
With a look of sadness impossible to describe, the President said:
“I shall never be glad any more.”
Lincoln always regarded himself as the friend and protector of unfortunate clients, and such he would never press for pay for his services. A client named Cogdal was unfortunate in business, and gave a note in settlement of legal fees. Soon afterward he met with an accident by which he lost a hand. Meeting Lincoln some time after on the steps of the State-House, the kind lawyer asked him how he was getting along.
“Badly enough,” replied Cogdal; “I am both broken up in business and crippled.” Then he added, “I have been thinking about that note of yours.”
Lincoln, who had probably known all about Cogdal’s troubles, and had prepared himself for the meeting, took out his pocket-book, and saying, with a laugh, “Well, you needn’t think any more about it,” handed him the note.
Cogdal protesting, Lincoln said, “Even if you had the money, I would not take it,” and hurried away.
“I have seen your dispatch expressing your unwillingness to break your hold where you are. Neither am I willing.
“Hold on with a bulldog grip.”
As a student (if such a term could be applied to Lincoln), one who did not know him might have called him indolent. He would pick up a book and run rapidly over the pages, pausing here and there.
At the end of an hour—never more than two or three hours—he would close the book, stretch himself out on the office lounge, and then, with hands under his head and eyes shut, would digest the mental food he had just taken.

War Governor Richard Yates (he was elected Governor of Illinois in 1860, when Lincoln was first elected President) told a good story at Springfield (Ill.) about Lincoln.
One day the latter was in the Sangamon River with his trousers rolled up five feet—more or less—trying to pilot a flatboat over a mill-dam. The boat was so full of water that it was hard to manage. Lincoln got the prow over, and then, instead of waiting to bail the water out, bored a hole through the projecting part and let it run out, affording a forcible illustration of the ready ingenuity of the future President.
The Martyr President thus spoke of Washington in the course of an address:
“Washington is the mightiest name on earth—long since the mightiest in the cause of civil liberty, still mightiest in moral reformation.
“On that name a eulogy is expected. It cannot be.
“To add brightness to the sun or glory to the name of Washington is alike impossible.
“Let none attempt it.
“In solemn awe pronounce the name, and, in its naked, deathless splendor, leave it shining on.”
Lincoln’s influence upon his audiences was wonderful. He could sway people at will, and nothing better illustrates his extraordinary power than he manner in which he stirred up the newspaper reporters by his Bloomingon speech.
Joseph Medill, editor of the Chicago Tribune, told the story:
“It was my journalistic duty, though a delegate to the convention, to make a ‘longhand’ report of the speeches delivered for the Tribune. I did make a few paragraphs of what Lincoln said in the first eight or ten minutes, but I became so absorbed in his magnetic oratory that I forgot myself and ceased to take notes, and joined with the convention in cheering and stamping and clapping to the end of his speech.
“I well remember that after Lincoln sat down and calm had succeeded the tempest, I waked out of a sort of hypnotic trance, and then thought of my report for the paper. There was nothing written but an abbreviated introduction.
“It was some sort of satisfaction to find that I had not been ‘scooped,’ as all the newspaper men present had been equally carried away by the excitement caused by the wonderful oration and had made no report or sketch of the speech.”
When “Abe” was fourteen years of age, John Hanks journeyed from Kentucky to Indiana and lived with the Lincolns. He described “Abe’s” habits thus:
“When Lincoln and I returned to the house from work, he would go to the cupboard, snatch a piece of corn-bread, take down a book, sit down on a chair, cock his legs up as high as his head, and read.
“He and I worked barefooted, grubbed it, plowed, mowed, cradled together; plowed corn, gathered it, and shucked corn. ‘Abe’ read constantly when he had an opportunity.”
During the Harrison Presidential campaign of 1840, Lincoln said, in a speech at Springfield, Illinois:
“Many free countries have lost their liberty, and ours may lose hers; but if she shall, be it my proudest plume, not that I was last to desert, but that I never deserted her.
“I know that the great volcano at Washington, aroused and directed by the evil spirit that reigns there, is belching forth the lava of political corruption in a current broad and deep, which is sweeping with frightful velocity over the whole length and breadth of the land, bidding fair to leave unscathed no green spot or living thing.
“I cannot deny that all may be swept away. Broken by it, I, too, may be; bow to it I never will.
“The possibility that we may fail in the struggle ought not to deter us from the support of a cause which we believe to be just. It shall never deter me.
“If ever I feel the soul within me elevate and expand to those dimensions not wholly unworthy of its Almighty Architect, it is when I contemplate the cause of my country, deserted by all the world beside, and I standing up boldly alone, and hurling defiance at her victorious oppressors.
“Here, without contemplating consequences, before heaven, and in the face of the world, I swear eternal fidelity to the just cause, as I deem it, of the land of my life, my liberty, and my love; and who that thinks with me will not fearlessly adopt the oath that I take?
“Let none falter who thinks he is right, and we may succeed.
“But if, after all, we shall fail, be it so; we have the proud consolation of saying to our consciences, and to the departed shade of our country’s freedom, that the cause approved of our judgment, and, adorned of our hearts in disaster, in chains, in death, we never faltered in defending.”
Lincoln could not rest for as instant under the consciousness that, even unwittingly, he had defrauded anybody. On one occasion, while clerking in Offutt’s store, at New Salem, he sold a woman a little bale of goods, amounting, by the reckoning, to $2.20. He received the money, and the woman went away.
On adding the items of the bill again to make himself sure of correctness, he found that he had taken six and a quarter cents too much.
It was night, and, closing and locking the store, he started out on foot, a distance of two or three miles, for the house of his defrauded customer, and, delivering to her the sum whose possession had so much troubled him, went home satisfied.
On another occasion, just as he was closing the store for the night, a woman entered and asked for half a pound of tea. The tea was weighed out and paid for, and the store was left for the night.
The next morning Lincoln, when about to begin the duties of the day, discovered a four-ounce weight on the scales. He saw at once that he had made a mistake, and, shutting the store, he took a long walk before breakfast to deliver the remainder of the tea.
These are very humble incidents, but they illustrate the man’s perfect conscientiousness—his sensitive honesty—better, perhaps, than they would if they were of greater moment.




Leonard Swett, of Chicago, whose counsels were doubtless among the most welcome to Lincoln, in summing up Lincoln’s character, said:
“From the commencement of his life to its close I have sometimes doubted whether he ever asked anybody’s advice about anything. He would listen to everybody; he would hear everybody; but he rarely, if ever, asked for opinions.
“As a politician and as President he arrived at all his conclusions from his own reflections, and when his conclusions were once formed he never doubted but what they were right.
“One great public mistake of his (Lincoln’s) character, as generally received and acquiesced in, is that he is considered by the people of this country as a frank, guileless, and unsophisticated man. There never was a greater mistake.
“Beneath a smooth surface of candor and apparent declaration of all his thoughts and feelings he exercised the most exalted tact and wisest discrimination. He handled and moved men remotely as we do pieces upon a chess-board.
“He retained through life all the friends he ever had, and he made the wrath of his enemies to praise him. This was not by cunning or intrigue in the low acceptation of the term, but by far-seeing reason and discernment. He always told only enough of his plans and purposes to induce the belief that he had communicated all; yet he reserved enough to have communicated nothing.”
When the United States found that a war with Black Hawk could not be dodged, Governor Reynolds, of Illinois, issued a call for volunteers, and among the companies that immediately responded was one from Menard county, Illinois. Many of these volunteers were from New Salem and Clary’s Grove, and Lincoln, being out of business, was the first to enlist.
The company being full, the men held a meeting at Richland for the election of officers. Lincoln had won many hearts, and they told him that he must be their captain. It was an office to which he did not aspire, and for which he felt he had no special fitness; but he finally consented to be a candidate.
There was but one other candidate, a Mr. Kirkpatrick, who was one of the most influential men of the region. Previously, Kirkpatrick had been an employer of Lincoln, and was so overbearing in his treatment of the young man that the latter left him.
The simple mode of electing a captain adopted by the company was by placing the candidates apart, and telling the men to go and stand with the one they preferred. Lincoln and his competitor took their positions, and then the word was given. At least three out of every four went to Lincoln at once.
When it was seen by those who had arranged themselves with the other candidate that Lincoln was the choice of the majority of the company, they left their places, one by one, and came over to the successful side, until Lincoln’s opponent in the friendly strife was left standing almost alone.
“I felt badly to see him cut so,” says a witness of the scene.
Here was an opportunity for revenge. The humble laborer was his employer’s captain, but the opportunity was never improved. Mr. Lincoln frequently confessed that no subsequent success of his life had given him half the satisfaction that this election did.
In one of his many stories of Lincoln, his law partner, W. H. Herndon, told this as illustrating Lincoln’s shrewdness as a lawyer:
“I was with Lincoln once and listened to an oral argument by him in which he rehearsed an extended history of the law. It was a carefully prepared and masterly discourse, but, as I thought, entirely useless. After he was through and we were walking home, I asked him why he went so far back in the history of the law. I presumed the court knew enough history.
“‘That’s where you’re mistaken,’ was his instant rejoinder. ‘I dared not just the case on the presumption that the court knows everything—in fact I argued it on the presumption that the court didn’t know anything,’ a statement, which, when one reviews the decision of our appellate courts, is not so extravagant as one would at first suppose.”
One day Thaddeus Stevens called at the White House with an elderly woman, whose son had been in the army, but for some offense had been court-martialed and sentenced to death. There were some extenuating circumstances, and after a full hearing the President turned to Stevens and said: “Mr. Stevens, do you think this is a case which will warrant my interference?”
“With my knowledge of the facts and the parties,” was the reply, “I should have no hesitation in granting a pardon.”
“Then,” returned Mr. Lincoln, “I will pardon him,” and proceeded forthwith to execute the paper.
The gratitude of the mother was too deep for expression, save by her tears, and not a word was said between her and Stevens until they were half way down the stairs on their passage out, when she suddenly broke forth in an excited manner with the words:
“I knew it was a copperhead lie!”
“What do you refer to, madam?” asked Stevens.
“Why, they told me he was an ugly-looking man,” she replied, with vehemence. “He is the handsomest man I ever saw in my life.”
“Lincoln’s Last Warning” was the title of a cartoon which appeared in “Harper’s Weekly,” on October 11, 1862. Under the picture was the text:
“Now if you don’t come down I’ll cut the tree from under you.”
This illustration was peculiarly apt, as, on the 1st of January, 1863, President Lincoln issued his great Emancipation Proclamation, declaring all slaves in the United States forever free. “Old Abe” was a handy man with the axe, he having split many thousands of rails with its keen edge. As the “Slavery Coon” wouldn’t heed the warning, Lincoln did cut the tree from under him, and so he came down to the ground with a heavy thump.
This Act of Emancipation put an end to the notion of the Southern slave holders that involuntary servitude was one of the “sacred institutions” on the Continent of North America. It also demonstrated that Lincoln was thoroughly in earnest when he declared that he would not only save the Union, but that he meant what he said in the speech wherein he asserted, “This Nation cannot exist half slave and half free.”
At fifteen years of age “Abe” wrote “pieces,” or compositions, and even some doggerel rhyme, which he recited, to the great amusement of his playmates.
One of his first compositions was against cruelty to animals. He was very much annoyed and pained at the conduct of the boys, who were in the habit of catching terrapins and putting coals of fire on their backs, which thoroughly disgusted Abraham.
“He would chide us,” said “Nat” Grigsby, “tell us it was wrong, and would write against it.”
When eighteen years old, “Abe” wrote a “piece” on “National Politics,” and it so pleased a lawyer friend, named Pritchard, that the latter had it printed in an obscure paper, thereby adding much to the author’s pride. “Abe” did not conceal his satisfaction. In this “piece” he wrote, among other things:
“The American government is the best form of government for an intelligent people. It ought to be kept sound, and preserved forever, that general education should be fostered and carried all over the country; that the Constitution should be saved, the Union perpetuated and the laws revered, respected and enforced.”
John A. Logan and a friend of Illinois called upon Lincoln at Willard’s Hotel, Washington, February 23d, the morning of his arrival, and urged a vigorous, firm policy.
Patiently listening, Lincoln replied seriously but cheerfully:
“As the country has placed me at the helm of the ship, I’ll try to steer her through.”
Lincoln was a marked and peculiar young man. People talked about him. His studious habits, his greed for information, his thorough mastery of the difficulties of every new position in which he was placed, his intelligence on all matters of public concern, his unwearying good-nature, his skill in telling a story, his great athletic power, his quaint, odd ways, his uncouth appearance—all tended to bring him in sharp contrast with the dull mediocrity by which he was surrounded.
Denton Offutt, his old employer, said, after having had a conversation with Lincoln, that the young man “had talent enough in him to make a President.”
When Lincoln was on his way to the National Cemetery at Gettysburg, an old gentleman told him that his only son fell on Little Round Top at Gettysburg, and he was going to look at the spot. Mr. Lincoln replied: “You have been called on to make a terrible sacrifice for the Union, and a visit to that spot, I fear, will open your wounds afresh.
“But, oh, my dear sir, if we had reached the end of such sacrifices, and had nothing left for us to do but to place garlands on the graves of those who have already fallen, we could give thanks even amidst our tears; but when I think of the sacrifices of life yet to be offered, and the hearts and homes yet to be made desolate before this dreadful war is over, my heart is like lead within me, and I feel at times like hiding in deep darkness.” At one of the stopping places of the train, a very beautiful child, having a bunch of rosebuds in her hand, was lifted up to an open window of the President’s car. “Floweth for the President.” The President stepped to the window, took the rosebuds, bent down and kissed the child, saying, “You are a sweet little rosebud yourself. I hope your life will open into perpetual beauty and goodness.”
There was a rough gallantry among the young people; and Lincoln’s old comrades and friends in Indiana have left many tales of how he “went to see the girls,” of how he brought in the biggest back-log and made the brightest fire; of how the young people, sitting around it, watching the way the sparks flew, told their fortunes.
He helped pare apples, shell corn and crack nuts. He took the girls to meeting and to spelling school, though he was not often allowed to take part in the spelling-match, for the one who “chose first” always chose “Abe” Lincoln, and that was equivalent to winning, as the others knew that “he would stand up the longest.”
A lady reader or elocutionist came to Springfield in 1857. A large crowd greeted her. Among other things she recited “Nothing to Wear,” a piece in which is described the perplexities that beset “Miss Flora McFlimsy” in her efforts to appear fashionable.
In the midst of one stanza in which no effort is made to say anything particularly amusing, and during the reading of which the audience manifested the most respectful silence and attention, some one in the rear seats burst out with a loud, coarse laugh, a sudden and explosive guffaw.
It startled the speaker and audience, and kindled a storm of unsuppressed laughter and applause. Everybody looked back to ascertain the cause of the demonstration, and were greatly surprised to find that it was Mr. Lincoln.
He blushed and squirmed with the awkward diffidence of a schoolboy. What caused him to laugh, no one was able to explain. He was doubtless wrapped up in a brown study, and recalling some amusing episode, indulged in laughter without realizing his surroundings. The experience mortified him greatly.
Soon after Mr. Lincoln began to practice law at Springfield, he was engaged in a criminal case in which it was thought there was little chance of success. Throwing all his powers into it, he came off victorious, and promptly received for his services five hundred dollars. A legal friend, calling upon him the next morning, found him sitting before a table, upon which his money was spread out, counting it over and over.
“Look here, Judge,” said he. “See what a heap of money I’ve got from this case. Did you ever see anything like it? Why, I never had so much money in my life before, put it all together.” Then, crossing his arms upon the table, his manner sobering down, he added: “I have got just five hundred dollars; if it were only seven hundred and fifty, I would go directly and purchase a quarter section of land, and settle it upon my old step-mother.”
His friend said that if the deficiency was all he needed, he would loan him the amount, taking his note, to which Mr. Lincoln instantly acceded.
His friend then said:
“Lincoln, I would do just what you have indicated. Your step-mother is getting old, and will not probably live many years. I would settle the property upon her for her use during her lifetime, to revert to you upon her death.”
With much feeling, Mr. Lincoln replied:
“I shall do no such thing. It is a poor return at best for all the good woman’s devotion and fidelity to me, and there is not going to be any halfway business about it.” And so saying, he gathered up his money and proceeded forthwith to carry his long-cherished purpose into execution.
Lincoln believed in preventing unnecessary litigation, and carried out this in his practice. “Who was your guardian?” he asked a young man who came to him to complain that a part of the property left him had been withheld. “Enoch Kingsbury,” replied the young man.
“I know Mr. Kingsbury,” said Lincoln, “and he is not the man to have cheated you out of a cent, and I can’t take the case, and advise you to drop the subject.”
And it was dropped.
Edwin M. Stanton was one of the attorneys in the great “reaper patent” case heard in Cincinnati in 1855, Lincoln also having been retained. The latter was rather anxious to deliver the argument on the general propositions of law applicable to the case, but it being decided to have Mr. Stanton do this, the Westerner made no complaint.
Speaking of Stanton’s argument and the view Lincoln took of it, Ralph Emerson, a young lawyer who was present at the trial, said:
“The final summing up on our side was by Mr. Stanton, and though he took but about three hours in its delivery, he had devoted as many, if not more, weeks to its preparation. It was very able, and Mr. Lincoln was throughout the whole of it a rapt listener. Mr. Stanton closed his speech in a flight of impassioned eloquence.
“Then the court adjourned for the day, and Mr. Lincoln invited me to take a long walk with him. For block after block he walked rapidly forward, not saying a word, evidently deeply dejected.
“At last he turned suddenly to me, exclaiming, ‘Emerson, I am going home.’ A pause. ‘I am going home to study law.’
“‘Why,’ I exclaimed, ‘Mr. Lincoln, you stand at the head of the bar in Illinois now! What are you talking about?’
“‘Ah, yes,’ he said, ‘I do occupy a good position there, and I think that I can get along with the way things are done there now. But these college-trained men, who have devoted their whole lives to study, are coming West, don’t you see? And they study their cases as we never do. They have got as far as Cincinnati now. They will soon be in Illinois.’
“Another long pause; then stopping and turning toward me, his countenance suddenly assuming that look of strong determination which those who knew him best sometimes saw upon his face, he exclaimed, ‘I am going home to study law! I am as good as any, of them, and when they get out to Illinois, I will be ready for them.’”


The cartoon given here in facsimile was one of the posters which decorated the picturesque Presidential campaign of 1864, and assisted in making the period previous to the vote-casting a lively and memorable one. This poster was a lithograph, and, as the title, “The Rail-Splitter at Work Repairing the Union,” would indicate, the President is using the Vice-Presidential candidate on the Republican National ticket (Andrew Johnson) as an aid in the work. Johnson was, in early life, a tailor, and he is pictured as busily engaged in sewing up the rents made in the map of the Union by the secessionists.
Both men are thoroughly in earnest, and, as history relates, the torn places in the Union map were stitched together so nicely that no one could have told, by mere observation, that a tear had ever been made. Andrew Johnson, who succeeded Lincoln upon the assassination of the latter, was a remarkable man. Born in North Carolina, he removed to Tennessee when young, was Congressman, Governor, and United States Senator, being made military Governor of his State in 1862. A strong, stanch Union man, he was nominated for the Vice-Presidency on the Lincoln ticket to conciliate the War Democrats. After serving out his term as President, he was again elected United States Senator from Tennessee, but died shortly after taking his seat. But he was just the sort of a man to assist “Uncle Abe” in sewing up the torn places in the Union map, and as military Governor of Tennessee was a powerful factor in winning friends in the South to the Union cause.
“Several of us lawyers,” remarked one of his colleagues, “in the eastern end of the circuit, annoyed Lincoln once while he was holding court for Davis by attempting to defend against a note to which there were many makers. We had no legal, but a good moral defense, but what we wanted most of all was to stave it off till the next term of court by one expedient or another.
“We bothered ‘the court’ about it till late on Saturday, the day of adjournment. He adjourned for supper with nothing left but this case to dispose of. After supper he heard our twaddle for nearly an hour, and then made this odd entry.
“‘L. D. Chaddon vs. J. D. Beasley et al. April Term, 1856. Champaign county Court. Plea in abatement by B. Z. Green, a defendant not served, filed Saturday at 11 o’clock a. m., April 24, 1856, stricken from the files by order of court. Demurrer to declaration, if there ever was one, overruled. Defendants who are served now, at 8 o’clock p. m., of the last day of the term, ask to plead to the merits, which is denied by the court on the ground that the offer comes too late, and therefore, as by nil dicet, judgment is rendered for Pl’ff. Clerk assess damages. A. Lincoln, Judge pro tem.’
“The lawyer who reads this singular entry will appreciate its oddity if no one else does. After making it, one of the lawyers, on recovering from his astonishment, ventured to enquire: ‘Well, Lincoln, how can we get this case up again?’
“Lincoln eyed him quizzically for a moment, and then answered, ‘You have all been so mighty smart about this case, you can find out how to take it up again yourselves.”’
Mr. Lincoln, one day, was talking with the Rev. Dr. Sunderland about the Emancipation Proclamation and the future of the negro. Suddenly a ripple of amusement broke the solemn tone of his voice. “As for the negroes, Doctor, and what is going to become of them: I told Ben Wade the other day, that it made me think of a story I read in one of my first books, ‘Aesop’s Fables.’ It was an old edition, and had curious rough wood cuts, one of which showed three white men scrubbing a negro in a potash kettle filled with cold water. The text explained that the men thought that by scrubbing the negro they might make him white. Just about the time they thought they were succeeding, he took cold and died. Now, I am afraid that by the time we get through this War the negro will catch cold and die.”
Personal encounters were of frequent occurrence in Gentryville in early days, and the prestige of having thrashed an opponent gave the victor marked social distinction. Green B. Taylor, with whom “Abe” worked the greater part of one winter on a farm, furnished an account of the noted fight between John Johnston, “Abe’s” stepbrother, and William Grigsby, in which stirring drama “Abe” himself played an important role before the curtain was rung down.
Taylor’s father was the second for Johnston, and William Whitten officiated in a similar capacity for Grigsby. “They had a terrible fight,” related Taylor, “and it soon became apparent that Grigsby was too much for Lincoln’s man, Johnston. After they had fought a long time without interference, it having been agreed not to break the ring, ‘Abe’ burst through, caught Grigsby, threw him off and some feet away. There Grigsby stood, proud as Lucifer, and, swinging a bottle of liquor over his head, swore he was ‘the big buck of the lick.’
“‘If any one doubts it,’ he shouted, ‘he has only to come on and whet his horns.’”
A general engagement followed this challenge, but at the end of hostilities the field was cleared and the wounded retired amid the exultant shouts of their victors.
Lincoln delivered a speech at a Republican banquet at Chicago, December 10th, 1856, just after the Presidential campaign of that year, in which he said:
“Our government rests in public opinion. Whoever can change public opinion can change the government practically just so much.
“Public opinion, on any subject, always has a ‘central idea,’ from which all its minor thoughts radiate.
“That ‘central idea’ in our political public opinion at the beginning was, and until recently has continued to be, ‘the equality of man.’
“And although it has always submitted patiently to whatever of inequality there seemed to be as a matter of actual necessity, its constant working has been a steady progress toward the practical equality of all men.
“Let everyone who really believes, and is resolved, that free society is not and shall not be a failure, and who can conscientiously declare that in the past contest he has done only what he thought best—let every such one have charity to believe that every other one can say as much.
“Thus, let bygones be bygones; let party differences as nothing be, and with steady eye on the real issue, let us reinaugurate the good old ‘central ideas’ of the Republic.
“We can do it. The human heart is with us; God is with us.
“We shall never be able to declare that ‘all States as States are equal,’ nor yet that ‘all citizens are equal,’ but to renew the broader, better declaration, including both these and much more, that ‘all men are created equal.’”
Up to the very last moment of the life of the Confederacy, the London “Punch” had its fling at the United States. In a cartoon, printed February 18th, 1865, labeled “The Threatening Notice,” “Punch” intimates that Uncle Sam is in somewhat of a hurry to serve notice on John Bull regarding the contentions in connection with the northern border of the United States.
Lincoln, however, as attorney for his revered Uncle, advises caution. Accordingly, he tells his Uncle, according to the text under the picture:
ATTORNEY LINCOLN: “Now, Uncle Sam, you’re in a darned hurry to serve this here notice on John Bull. Now, it’s my duty, as your attorney, to tell you that you may drive him to go over to that cuss, Davis.” (Uncle Sam considers.) In this instance, President Lincoln is given credit for judgment and common sense, his advice to his Uncle Sam to be prudent being sound. There was trouble all along the Canadian border during the War, while Canada was the refuge of Northern conspirators and Southern spies, who, at times, crossed the line and inflicted great damage upon the States bordering on it. The plot to seize the great lake cities—Chicago, Milwaukee, Detroit, Cleveland, Buffalo and others—was figured out in Canada by the Southerners and Northern allies. President Lincoln, in his message to Congress in December, 1864, said the United States had given notice to England that, at the end of six months, this country would, if necessary, increase its naval armament upon the lakes. What Great Britain feared was the abrogation by the United States of all treaties regarding Canada. By previous stipulation, the United States and England were each to have but one war vessel on the Great Lakes.
This story cannot be repeated in Lincoln’s own language, although he told it often enough to intimate friends; but, as it was never taken down by a stenographer in the martyred President’s exact words, the reader must accept a simple narration of the strange occurrence.
It was not long after the first nomination of Lincoln for the Presidency, when he saw, or imagined he saw, the startling apparition. One day, feeling weary, he threw himself upon a lounge in one of the rooms of his house at Springfield to rest. Opposite the lounge upon which he was lying was a large, long mirror, and he could easily see the reflection of his form, full length.
Suddenly he saw, or imagined he saw, two Lincolns in the mirror, each lying full length upon the lounge, but they differed strangely in appearance. One was the natural Lincoln, full of life, vigor, energy and strength; the other was a dead Lincoln, the face white as marble, the limbs nerveless and lifeless, the body inert and still.
Lincoln was so impressed with this vision, which he considered merely an optical illusion, that he arose, put on his hat, and went out for a walk. Returning to the house, he determined to test the matter again—and the result was the same as before. He distinctly saw the two Lincolns—one living and the other dead.
He said nothing to his wife about this, she being, at that time, in a nervous condition, and apprehensive that some accident would surely befall her husband. She was particularly fearful that he might be the victim of an assassin. Lincoln always made light of her fears, but yet he was never easy in his mind afterwards.
To more thoroughly test the so-called “optical illusion,” and prove, beyond the shadow of a doubt, whether it was a mere fanciful creation of the brain or a reflection upon the broad face of the mirror which might be seen at any time, Lincoln made frequent experiments. Each and every time the result was the same. He could not get away from the two Lincolns—one living and the other dead.
Lincoln never saw this forbidding reflection while in the White House. Time after time he placed a couch in front of a mirror at a distance from the glass where he could view his entire length while lying down, but the looking-glass in the Executive Mansion was faithful to its trust, and only the living Lincoln was observable.
The late Ward Lamon, once a law partner of Lincoln, and Marshal of the District of Columbia during his first administration, tells, in his “Recollections of Abraham Lincoln,” of the dreams the President had—all foretelling death.
Lamon was Lincoln’s most intimate friend, being, practically, his bodyguard, and slept in the White House. In reference to Lincoln’s “death dreams,” he says:
“How, it may be asked, could he make life tolerable, burdened as he was with that portentous horror, which, though visionary, and of trifling import in our eyes, was by his interpretation a premonition of impending doom? I answer in a word: His sense of duty to his country; his belief that ‘the inevitable’ is right; and his innate and irrepressible humor.
“But the most startling incident in the life of Mr. Lincoln was a dream he had only a few days before his assassination. To him it was a thing of deadly import, and certainly no vision was ever fashioned more exactly like a dread reality. Coupled with other dreams, with the mirror-scene and with other incidents, there was something about it so amazingly real, so true to the actual tragedy which occurred soon after, that more than mortal strength and wisdom would have been required to let it pass without a shudder or a pang.
“After worrying over it for some days, Mr. Lincoln seemed no longer able to keep the secret. I give it as nearly in his own words as I can, from notes which I made immediately after its recital. There were only two or three persons present.
“The President was in a melancholy, meditative mood, and had been silent for some time. Mrs. Lincoln, who was present, rallied him on his solemn visage and want of spirit. This seemed to arouse him, and, without seeming to notice her sally, he said, in slow and measured tones:
“‘It seems strange how much there is in the Bible about dreams. There are, I think, some sixteen chapters in the Old Testament and four or five in the New, in which dreams are mentioned; and there are many other passages scattered throughout the book which refer to visions. In the old days, God and His angels came to men in their sleep and made themselves known in dreams.’
“Mrs. Lincoln here remarked, ‘Why, you look dreadfully solemn; do you believe in dreams?’
“‘I can’t say that I do,’ returned Mr. Lincoln; ‘but I had one the other night which has haunted me ever since. After it occurred the first time, I opened the Bible, and, strange as it may appear, it was at the twenty-eighth chapter of Genesis, which relates the wonderful dream Jacob had. I turned to other passages, and seemed to encounter a dream or a vision wherever I looked. I kept on turning the leaves of the old book, and everywhere my eyes fell upon passages recording matters strangely in keeping with my own thoughts—supernatural visitations, dreams, visions, etc.’
“He now looked so serious and disturbed that Mrs. Lincoln exclaimed ‘You frighten me! What is the matter?’
“‘I am afraid,’ said Mr. Lincoln, observing the effect his words had upon his wife, ‘that I have done wrong to mention the subject at all; but somehow the thing has got possession of me, and, like Banquo’s ghost, it will not down.’
“This only inflamed Mrs. Lincoln’s curiosity the more, and while bravely disclaiming any belief in dreams, she strongly urged him to tell the dream which seemed to have such a hold upon him, being seconded in this by another listener. Mr. Lincoln hesitated, but at length commenced very deliberately, his brow overcast with a shade of melancholy.
“‘About ten days ago,’ said he, ‘I retired very late. I had been up waiting for important dispatches from the front. I could not have been long in bed when I fell into a slumber, for I was weary. I soon began to dream. There seemed to be a deathlike stillness about me. Then I heard subdued sobs, as if a number of people were weeping.
“‘I thought I left my bed and wandered down-stairs. There the silence was broken by the same pitiful sobbing, but the mourners were invisible. I went from room to room; no living person was in sight, but the same mournful sounds of distress met me as I passed along. It was light in all the rooms; every object was familiar to me; but where were all the people who were grieving as if their hearts would break? I was puzzled and alarmed. What could be the meaning of all this?
“‘Determined to find the cause of a state of things so mysterious and so shocking, I kept on until I arrived at the East Room, which I entered. There I met with a sickening surprise. Before me was a catafalque, on which rested a corpse wrapped in funeral vestments. Around it were stationed soldiers who were acting as guards; and there was a throng of people, some gazing mournfully upon the corpse, whose face was covered, others weeping pitifully.
“‘"Who is dead in the White House?” I demanded of one of the soldiers.
“‘"The President,” was his answer; “he was killed by an assassin.”
“‘Then came a loud burst of grief from the crowd, which awoke me from my dream. I slept no more that night; and although it was only a dream, I have been strangely annoyed by it ever since.’
“‘That is horrid!’ said Mrs. Lincoln. ‘I wish you had not told it. I am glad I don’t believe in dreams, or I should be in terror from this time forth.’
“‘Well,’ responded Mr. Lincoln, thoughtfully, ‘it is only a dream, Mary. Let us say no more about it, and try to forget it.’
“This dream was so horrible, so real, and so in keeping with other dreams and threatening presentiments of his, that Mr. Lincoln was profoundly disturbed by it. During its recital he was grave, gloomy, and at times visibly pale, but perfectly calm. He spoke slowly, with measured accents and deep feeling.
“In conversations with me, he referred to it afterwards, closing one with this quotation from ‘Hamlet’: ‘To sleep; perchance to dream! ay, there’s the rub!’ with a strong accent upon the last three words.
“Once the President alluded to this terrible dream with some show of playful humor. ‘Hill,’ said he, ‘your apprehension of harm to me from some hidden enemy is downright foolishness. For a long time you have been trying to keep somebody-the Lord knows who—from killing me.
“‘Don’t you see how it will turn out? In this dream it was not me, but some other fellow, that was killed. It seems that this ghostly assassin tried his hand on some one else. And this reminds me of an old farmer in Illinois whose family were made sick by eating greens.
“‘Some poisonous herb had got into the mess, and members of the family were in danger of dying. There was a half-witted boy in the family called Jake; and always afterward when they had greens the old man would say, “Now, afore we risk these greens, let’s try ‘em on Jake. If he stands ‘em we’re all right.” Just so with me. As long as this imaginary assassin continues to exercise himself on others, I can stand it.’
“He then became serious and said: ‘Well, let it go. I think the Lord in His own good time and way will work this out all right. God knows what is best.’
“These words he spoke with a sigh, and rather in a tone of soliloquy, as if hardly noting my presence.
“Mr. Lincoln had another remarkable dream, which was repeated so frequently during his occupancy of the White House that he came to regard it is a welcome visitor. It was of a pleasing and promising character, having nothing in it of the horrible.
“It was always an omen of a Union victory, and came with unerring certainty just before every military or naval engagement where our arms were crowned with success. In this dream he saw a ship sailing away rapidly, badly damaged, and our victorious vessels in close pursuit.
“He saw, also, the close of a battle on land, the enemy routed, and our forces in possession of vantage ground of inestimable importance. Mr. Lincoln stated it as a fact that he had this dream just before the battles of Antietam, Gettysburg, and other signal engagements throughout the War.
“The last time Mr. Lincoln had this dream was the night before his assassination. On the morning of that lamentable day there was a Cabinet meeting, at which General Grant was present. During an interval of general discussion, the President asked General Grant if he had any news from General Sherman, who was then confronting Johnston. The reply was in the negative, but the general added that he was in hourly expectation of a dispatch announcing Johnston’s surrender.
“Mr. Lincoln then, with great impressiveness, said, ‘We shall hear very soon, and the news will be important.’
“General Grant asked him why he thought so.
“‘Because,’ said Mr. Lincoln, ‘I had a dream last night; and ever since this War began I have had the same dream just before every event of great national importance. It portends some important event which will happen very soon.’
“On the night of the fateful 14th of April, 1865, Mrs. Lincoln’s first exclamation, after the President was shot, was, ‘His dream was prophetic!’
“Lincoln was a believer in certain phases of the supernatural. Assured as he undoubtedly was by omens which, to his mind, were conclusive, that he would rise to greatness and power, he was as firmly convinced by the same tokens that he would be suddenly cut off at the height of his career and the fullness of his fame. He always believed that he would fall by the hand of an assassin.
“Mr. Lincoln had this further idea: Dreams, being natural occurrences, in the strictest sense, he held that their best interpreters are the common people; and this accounts, in great measure, for the profound respect he always had for the collective wisdom of plain people—‘the children of Nature,’ he called them—touching matters belonging to the domain of psychical mysteries. There was some basis of truth, he believed, for whatever obtained general credence among these ‘children of Nature.’
“Concerning presentiments and dreams, Mr. Lincoln had a philosophy of his own, which, strange as it may appear, was in perfect harmony with his character in all other respects. He was no dabbler in divination—astrology, horoscopy, prophecy, ghostly lore, or witcheries of any sort.”
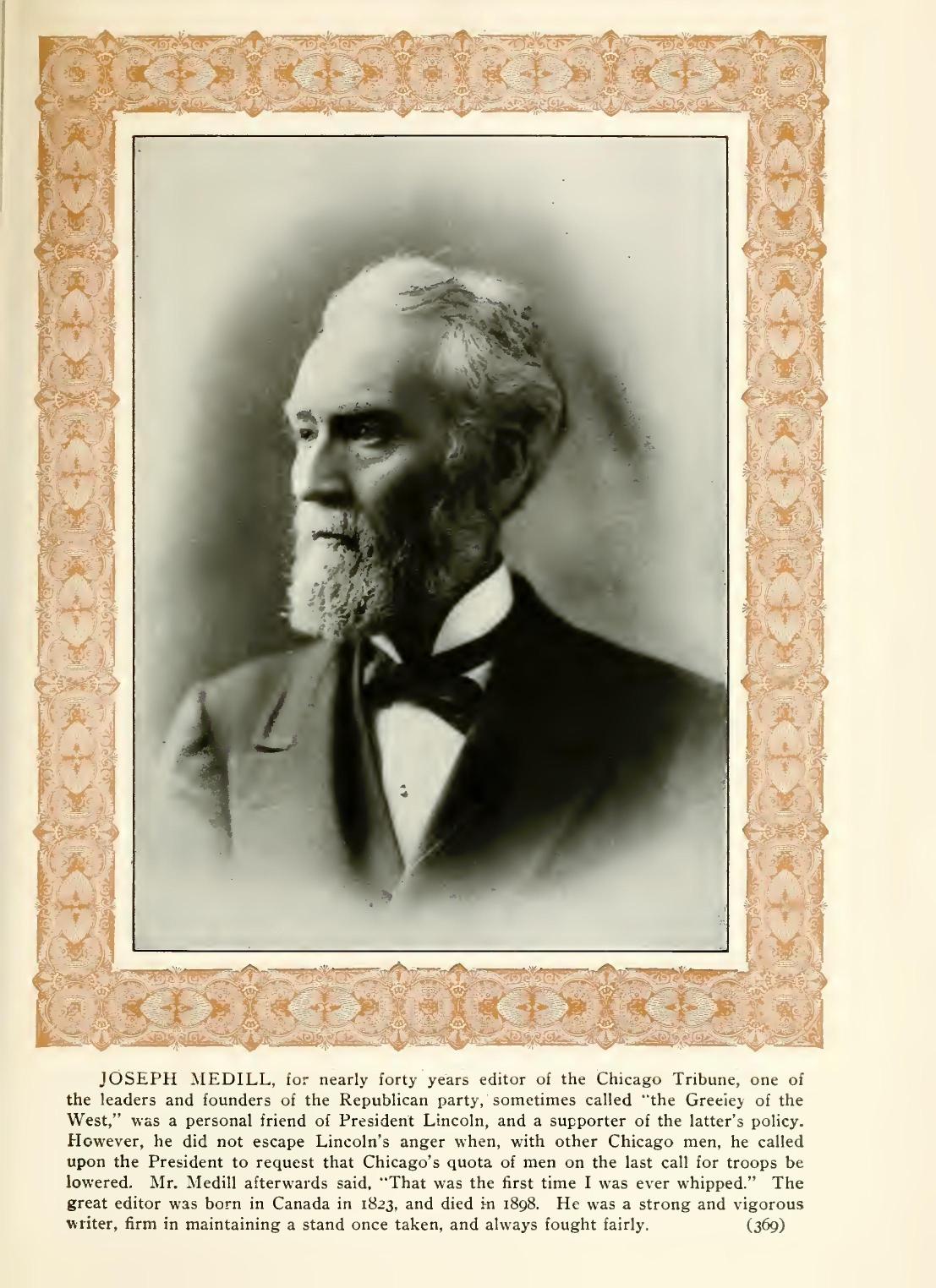




As the time drew near at which Mr. Lincoln said he would issue the Emancipation Proclamation, some clergymen, who feared the President might change his mind, called on him to urge him to keep his promise.

“We were ushered into the Cabinet room,” says Dr. Sunderland. “It was very dim, but one gas jet burning. As we entered, Mr. Lincoln was standing at the farther end of the long table, which filled the center of the room. As I stood by the door, I am so very short, that I was obliged to look up to see the President. Mr. Robbins introduced me, and I began at once by saying: ‘I have come, Mr. President, to anticipate the new year with my respects, and if I may, to say to you a word about the serious condition of this country.’
“‘Go ahead, Doctor,’ replied the President; ‘every little helps.’ But I was too much in earnest to laugh at his sally at my smallness.”
President Lincoln (at times) said he felt sure his life would end with the War. A correspondent of a Boston paper had an interview with him in July, 1864, and wrote regarding it:
“The President told me he was certain he should not outlast the rebellion. As will be remembered, there was dissension then among the Republican leaders. Many of his best friends had deserted him, and were talking of an opposition convention to nominate another candidate, and universal gloom was among the people.
“The North was tired of the War, and supposed an honorable peace attainable. Mr. Lincoln knew it was not—that any peace at that time would be only disunion. Speaking of it, he said: ‘I have faith in the people. They will not consent to disunion. The danger is, they are misled. Let them know the truth, and the country is safe.’
“He looked haggard and careworn; and further on in the interview I remarked on his appearance, ‘You are wearing yourself out with work.’
“‘I can’t work less,’ he answered; ‘but it isn’t that—work never troubled me. Things look badly, and I can’t avoid anxiety. Personally, I care nothing about a re-election, but if our divisions defeat us, I fear for the country.’
“When I suggested that right must eventually triumph, he replied, ‘I grant that, but I may never live to see it. I feel a presentiment that I shall not outlast the rebellion. When it is over, my work will be done.’
“He never intimated, however, that he expected to be assassinated.”
“After the Civil War began, Lincoln’s tenacity of purpose paralleled his former immobility; I believe he would have been nearly the last, if not the very last, man in America to recognize the Southern Confederacy had its armies been triumphant. He would have preferred death.”
London “Punch” was not satisfied with anything President Lincoln did. On December 3rd, 1864, after Mr. Lincoln’s re-election to the Presidency, a cartoon appeared in one of the pages of that genial publication, the reproduction being printed here, labeled “The Federal Phoenix.” It attracted great attention at the time, and was particularly pleasing to the enemies of the United States, as it showed Lincoln as the Phoenix arising from the ashes of the Federal Constitution, the Public Credit, the Freedom of the Press, State Rights and the Commerce of the North American Republic.
President Lincoln’s endorsement by the people of the United States meant that the Confederacy was to be crushed, no matter what the cost; that the Union of States was to be preserved, and that State Rights was a thing of the past. “Punch” wished to create the impression that President Lincoln’s re-election was a personal victory; that he would set up a despotism, with himself at its head, and trample upon the Constitution of the United States and all the rights the citizens of the Republic ever possessed.
The result showed that “Punch” was suffering from an acute attack of needless alarm.
Lincoln was particularly fascinated by the wonderful happenings recorded in history. He loved to read of those mighty events which had been foretold, and often brooded upon these subjects. His early convictions upon occult matters led him to read all books tending’ to strengthen these convictions.
The following lines, in Byron’s “Dream,” were frequently quoted by him:
| "Sleep hath its own world, |
| A boundary between the things misnamed |
| Death and existence: Sleep hath its own world |
| And a wide realm of wild reality. |
| And dreams in their development have breath, |
| And tears and tortures, and the touch of joy; |
| They leave a weight upon our waking thoughts, |
| They take a weight from off our waking toils, |
| They do divide our being.” |
Those with whom he was associated in his early youth and young manhood, and with whom he was always in cordial sympathy, were thorough believers in presentiments and dreams; and so Lincoln drifted on through years of toil and exceptional hardship—meditative, aspiring, certain of his star, but appalled at times by its malignant aspect. Many times prior to his first election to the Presidency he was both elated and alarmed by what seemed to him a rent in the veil which hides from mortal view what the future holds.
He saw, or thought he saw, a vision of glory and of blood, himself the central figure in a scene which his fancy transformed from giddy enchantment to the most appalling tragedy.
The suspense of the days when the capital was isolated, the expected troops not arriving, and an hourly attack feared, wore on Mr. Lincoln greatly.
“I begin to believe,” he said bitterly, one day, to some Massachusetts soldiers, “that there is no North. The Seventh Regiment is a myth. Rhode Island is another. You are the only real thing.”
And again, after pacing the floor of his deserted office for a half-hour, he was heard to exclaim to himself, in an anguished tone: “Why don’t they come! Why don’t they come!”
Lincoln was not a man of impulse, and did nothing upon the spur of the moment; action with him was the result of deliberation and study. He took nothing for granted; he judged men by their performances and not their speech.
If a general lost battles, Lincoln lost confidence in him; if a commander was successful, Lincoln put him where he would be of the most service to the country.
“Grant is a drunkard,” asserted powerful and influential politicians to the President at the White House time after time; “he is not himself half the time; he can’t be relied upon, and it is a shame to have such a man in command of an army.”
“So Grant gets drunk, does he?” queried Lincoln, addressing himself to one of the particularly active detractors of the soldier, who, at that period, was inflicting heavy damage upon the Confederates.
“Yes, he does, and I can prove it,” was the reply.
“Well,” returned Lincoln, with the faintest suspicion of a twinkle in his eye, “you needn’t waste your time getting proof; you just find out, to oblige me, what brand of whiskey Grant drinks, because I want to send a barrel of it to each one of my generals.”
That ended the crusade against Grant, so far as the question of drinking was concerned.
A New York firm applied to Abraham Lincoln, some years before he became President, for information as to the financial standing of one of his neighbors. Mr. Lincoln replied:
“I am well acquainted with Mr.—— and know his circumstances. First of all, he has a wife and baby; together they ought to be worth $50,000 to any man. Secondly, he has an office in which there is a table worth $1.50 and three chairs worth, say, $1. Last of all, there is in one corner a large rat hole, which will bear looking into. Respectfully, A. Lincoln.”
President Lincoln appointed as consul to a South American country a young man from Ohio who was a dandy. A wag met the new appointee on his way to the White House to thank the President. He was dressed in the most extravagant style. The wag horrified him by telling him that the country to which he was assigned was noted chiefly for the bugs that abounded there and made life unbearable.
“They’ll bore a hole clean through you before a week has passed,” was the comforting assurance of the wag as they parted at the White House steps. The new consul approached Lincoln with disappointment clearly written all over his face. Instead of joyously thanking the President, he told him the wag’s story of the bugs. “I am informed, Mr. President,” he said, “that the place is full of vermin and that they could eat me up in a week’s time.” “Well, young man,” replied Lincoln, “if that’s true, all I’ve got to say is that if such a thing happened they would leave a mighty good suit of clothes behind.”
A. W. Swan, of Albuquerque, New Mexico, told this story on Lincoln, being an eyewitness of the scene:
“One day President Lincoln was met in the park between the White House and the War Department by an irate private soldier, who was swearing in a high key, cursing the Government from the President down. Mr. Lincoln paused and asked him what was the matter. ‘Matter enough,’ was the reply. ‘I want my money. I have been discharged here, and can’t get my pay.’ Mr. Lincoln asked if he had his papers, saying that he used to practice law in a small way, and possibly could help him.
“My friend and I stepped behind some convenient shrubbery where we could watch the result. Mr. Lincoln took the papers from the hands of the crippled soldier, and sat down with him at the foot of a convenient tree, where he examined them carefully, and writing a line on the back, told the soldier to take them to Mr. Potts, Chief Clerk of the War Department, who would doubtless attend to the matter at once.
“After Mr. Lincoln had left the soldier, we stepped out and asked him if he knew whom he had been talking with. ‘Some ugly old fellow who pretends to be a lawyer,’ was the reply. My companion asked to see the papers, and on their being handed to him, pointed to the indorsement they had received: This indorsement read:
“‘Mr. Potts, attend to this man’s case at once and see that he gets his pay. A. L.’”
The following story illustrates the power of Mr. Lincoln’s memory of names and faces. When he was a comparatively young man, and a candidate for the Illinois Legislature, he made a personal canvass of the district. While “swinging around the circle” he stopped one day and took dinner with a farmer in Sangamon county.
Years afterward, when Mr. Lincoln had become President, a soldier came to call on him at the White House. At the first glance the Chief Executive said: “Yes, I remember; you used to live on the Danville road. I took dinner with you when I was running for the Legislature. I recollect that we stood talking out at the barnyard gate while I sharpened my jackknife.”
“Y-a-a-s,” drawled the soldier, “you did. But say, wherever did you put that whetstone? I looked for it a dozen times, but I never could find it after the day you used it. We allowed as how mabby you took it ‘long with you.”
“No,” said Lincoln, looking serious and pushing away a lot of documents of state from the desk in front of him. “No, I put it on top of that gatepost—that high one.”
“Well!” exclaimed the visitor, “mabby you did. Couldn’t anybody else have put it there, and none of us ever thought of looking there for it.”
The soldier was then on his way home, and when he got there the first thing he did was to look for the whetstone. And sure enough, there it was, just where Lincoln had laid it fifteen years before. The honest fellow wrote a letter to the Chief Magistrate, telling him that the whetstone had been found, and would never be lost again.
When Abe Lincoln used to be drifting around the country, practicing law in Fulton and Menard counties, Illinois, an old fellow met him going to Lewiston, riding a horse which, while it was a serviceable enough animal, was not of the kind to be truthfully called a fine saddler. It was a weatherbeaten nag, patient and plodding, and it toiled along with Abe—and Abe’s books, tucked away in saddle-bags, lay heavy on the horse’s flank.
“Hello, Uncle Tommy,” said Abe.
“Hello, Abe,” responded Uncle Tommy. “I’m powerful glad to see ye, Abe, fer I’m gwyne to have sumthin’ fer ye at Lewiston co’t, I reckon.”
“How’s that, Uncle Tommy?” said Abe.
“Well, Jim Adams, his land runs ‘long o’ mine, he’s pesterin’ me a heap an’ I got to get the law on Jim, I reckon.”
“Uncle Tommy, you haven’t had any fights with Jim, have you?”
“No.”
“He’s a fair to middling neighbor, isn’t he?”
“Only tollable, Abe.”
“He’s been a neighbor of yours for a long time, hasn’t he?”
“Nigh on to fifteen year.”
“Part of the time you get along all right, don’t you?”
“I reckon we do, Abe.”
“Well, now, Uncle Tommy, you see this horse of mine? He isn’t as good a horse as I could straddle, and I sometimes get out of patience with him, but I know his faults. He does fairly well as horses go, and it might take me a long time to get used to some other horse’s faults. For all horses have faults. You and Uncle Jimmy must put up with each other as I and my horse do with one another.”
“I reckon, Abe,” said Uncle Tommy, as he bit off about four ounces of Missouri plug. “I reckon you’re about right.”
And Abe Lincoln, with a smile on his gaunt face, rode on toward Lewiston.
When Mr. Lincoln visited New York in 1860, he felt a great interest in many of the institutions for reforming criminals and saving the young from a life of crime. Among others, he visited, unattended, the Five Points House of Industry, and the superintendent of the Sabbath school there gave the following account of the event:
“One Sunday morning I saw a tall, remarkable-looking man enter the room and take a seat among us. He listened with fixed attention to our exercises, and his countenance expressed such genuine interest that I approached him and suggested that he might be willing to say something to the children. He accepted the invitation with evident pleasure, and coming forward began a simple address, which at once fascinated every little hearer and hushed the room into silence. His language was strikingly beautiful, and his tones musical with intense feeling. The little faces would droop into sad conviction when he uttered sentences of warning, and would brighten into sunshine as he spoke cheerful words of promise. Once or twice he attempted to close his remarks, but the imperative shout of, ‘Go on! Oh, do go on!’ would compel him to resume.
“As I looked upon the gaunt and sinewy frame of the stranger, and marked his powerful head and determined features, now touched into softness by the impressions of the moment, I felt an irrepressible curiosity to learn something more about him, and while he was quietly leaving the room, I begged to know his name. He courteously replied: ‘It is Abraham Lincoln, from Illinois.’”
A slight variation of the traditional sentry story is related by C. C. Buel. It was a cold, blusterous winter night. Says Mr. Buel:
“Mr. Lincoln emerged from the front door, his lank figure bent over as he drew tightly about his shoulders the shawl which he employed for such protection; for he was on his way to the War Department, at the west corner of the grounds, where in times of battle he was wont to get the midnight dispatches from the field. As the blast struck him he thought of the numbness of the pacing sentry, and, turning to him, said: ‘Young man, you’ve got a cold job to-night; step inside, and stand guard there.’
“‘My orders keep me out here,’ the soldier replied.
“‘Yes,’ said the President, in his argumentative tone; ‘but your duty can be performed just as well inside as out here, and you’ll oblige me by going in.’
“‘I have been stationed outside,’ the soldier answered, and resumed his beat.
“‘Hold on there!’ said Mr. Lincoln, as he turned back again; ‘it occurs to me that I am Commander-in-Chief of the army, and I order you to go inside.’”
Perhaps the majority of people in the United States don’t know why Lincoln “growed” whiskers after his first nomination for the Presidency. Before that time his face was clean shaven.
In the beautiful village of Westfield, Chautauqua county, New York, there lived, in 1860, little Grace Bedell. During the campaign of that year she saw a portrait of Lincoln, for whom she felt the love and reverence that was common in Republican families, and his smooth, homely face rather disappointed her. She said to her mother: “I think, mother, that Mr. Lincoln would look better if he wore whiskers, and I mean to write and tell him so.”
The mother gave her permission.
Grace’s father was a Republican; her two brothers were Democrats. Grace wrote at once to the “Hon. Abraham Lincoln, Esq., Springfield, Illinois,” in which she told him how old she was, and where she lived; that she was a Republican; that she thought he would make a good President, but would look better if he would let his whiskers grow. If he would do so, she would try to coax her brothers to vote for him. She thought the rail fence around the picture of his cabin was very pretty. “If you have not time to answer my letter, will you allow your little girl to reply for you?”
Lincoln was much pleased with the letter, and decided to answer it, which he did at once, as follows:
“Springfield, Illinois, October 19, 1860.
“Miss Grace Bedell.
“My Dear Little Miss: Your very agreeable letter of the fifteenth is received. I regret the necessity of saying I have no daughter. I have three sons; one seventeen, one nine and one seven years of age. They, with their mother, constitute my whole family. As to the whiskers, having never worn any, do you not think people would call it a piece of silly affectation if I should begin it now? Your very sincere well-wisher, A. LINCOLN.”
When on the journey to Washington to be inaugurated, Lincoln’s train stopped at Westfield. He recollected his little correspondent and spoke of her to ex-Lieutenant Governor George W. Patterson, who called out and asked if Grace Bedell was present.
There was a large surging mass of people gathered about the train, but Grace was discovered at a distance; the crowd opened a pathway to the coach, and she came, timidly but gladly, to the President-elect, who told her that she might see that he had allowed his whiskers to grow at her request. Then, reaching out his long arms, he drew her up to him and kissed her. The act drew an enthusiastic demonstration of approval from the multitude.
Grace married a Kansas banker, and became Grace Bedell Billings.
Lincoln made his first appearance in society when he was first sent to Springfield, Ill., as a member of the State Legislature. It was not an imposing figure which he cut in a ballroom, but still he was occasionally to be found there. Miss Mary Todd, who afterward became his wife, was the magnet which drew the tall, awkward young man from his den. One evening Lincoln approached Miss Todd, and said, in his peculiar idiom:
“Miss Todd, I should like to dance with you the worst way.” The young woman accepted the inevitable, and hobbled around the room with him. When she returned to her seat, one of her companions asked mischievously:
“Well, Mary, did he dance with you the worst way.”
“Yes,” she answered, “the very worst.”
An instance of young Lincoln’s practical humanity at an early period of his life is recorded in this way:
One evening, while returning from a “raising” in his wide neighborhood, with a number of companions, he discovered a stray horse, with saddle and bridle upon him. The horse was recognized as belonging to a man who was accustomed to get drunk, and it was suspected at once that he was not far off. A short search only was necessary to confirm the belief.
The poor drunkard was found in a perfectly helpless condition, upon the chilly ground. Abraham’s companions urged the cowardly policy of leaving him to his fate, but young Lincoln would not hear to the proposition.
At his request, the miserable sot was lifted on his shoulders, and he actually carried him eighty rods to the nearest house.
Sending word to his father that he should not be back that night, with the reason for his absence, he attended and nursed the man until the morning, and had the pleasure of believing that he had saved his life.
On one occasion, exasperated at the discrepancy between the aggregate of troops forwarded to McClellan and the number that same general reported as having received, Lincoln exclaimed: “Sending men to that army is like shoveling fleas across a barnyard—half of them never get there.”
To a politician who had criticised his course, he wrote: “Would you have me drop the War where it is, or would you prosecute it in future with elder stalk squirts charged with rosewater?”
When, on his first arrival in Washington as President, he found himself besieged by office-seekers, while the War was breaking out, he said: “I feel like a man letting lodgings at one end of his house while the other end is on fire.”
Ward Lamon, Marshal of the District of Columbia during Lincoln’s time in Washington, accompanied the President everywhere. He was a good singer, and, when Lincoln was in one of his melancholy moods, would “fire a few rhythmic shots” at the President to cheer the latter. Lincoln keenly relished nonsense in the shape of witty or comic ditties. A parody of “A Life on the Ocean Wave” was always pleasing to him:
| “Oh, a life on the ocean wave, |
| And a home on the rolling deep! |
| With ratlins fried three times a day |
| And a leaky old berth for to sleep; |
| Where the gray-beard cockroach roams, |
| On thoughts of kind intent, |
| And the raving bedbug comes |
| The road the cockroach went.” |
Lincoln could not control his laughter when he heard songs of this sort.
He was fond of negro melodies, too, and “The Blue-Tailed Fly” was a great favorite with him. He often called for that buzzing ballad when he and Lamon were alone, and he wanted to throw off the weight of public and private cares. The ballad of “The Blue-Tailed Fly” contained two verses, which ran:
| “When I was young I used to wait |
| At massa’s table, ‘n’ hand de plate, |
| An’ pass de bottle when he was dry, |
| An’ brush away de blue-tailed fly. |
| “Ol’ Massa’s dead; oh, let him rest! |
| Dey say all things am for de best; |
| But I can’t forget until I die |
| Ol’ massa an’ de blue-tailed fly.” |
While humorous songs delighted the President, he also loved to listen to patriotic airs and ballads containing sentiment. He was fond of hearing “The Sword of Bunker Hill,” “Ben Bolt,” and “The Lament of the Irish Emigrant.” His preference of the verses in the latter was this:
| “I’m lonely now, Mary, |
| For the poor make no new friends; |
| But, oh, they love the better still |
| The few our Father sends! |
| And you were all I had, Mary, |
| My blessing and my pride; |
| There’s nothing left to care for now, |
| Since my poor Mary died.” |
Those who knew Lincoln were well aware he was incapable of so monstrous an act as that of wantonly insulting the dead, as was charged in the infamous libel which asserted that he listened to a comic song on the field of Antietam, before the dead were buried.
Mr. Lincoln once remarked to a friend that his religion was like that of an old man named Glenn, in Indiana, whom he heard speak at a church meeting, and who said: “When I do good, I feel good; when I do bad, I feel bad; and that’s my religion.”
Mrs. Lincoln herself has said that Mr. Lincoln had no faith—no faith, in the usual acceptance of those words. “He never joined a church; but still, as I believe, he was a religious man by nature. He first seemed to think about the subject when our boy Willie died, and then more than ever about the time he went to Gettysburg; but it was a kind of poetry in his nature, and he never was a technical Christian.”
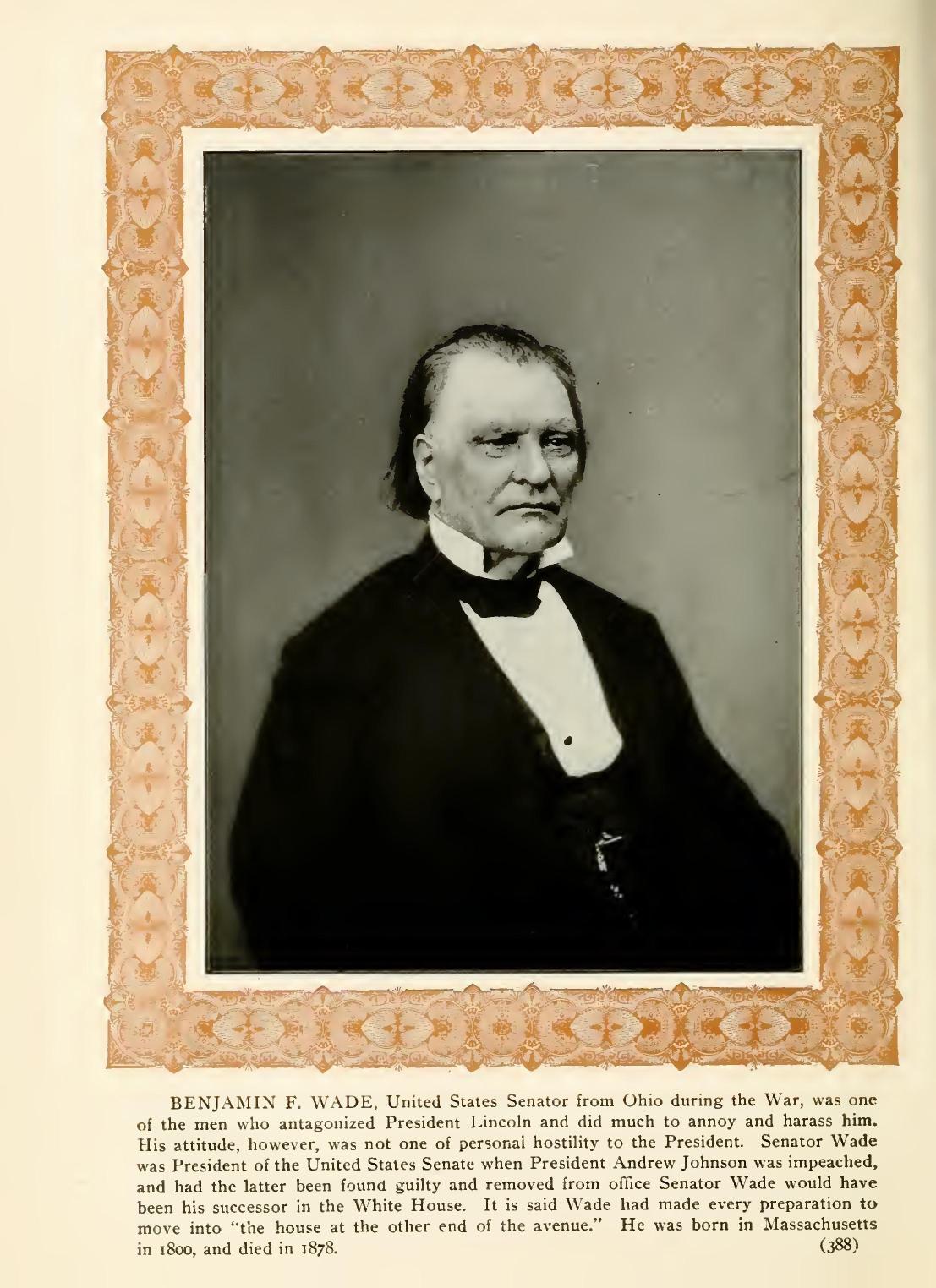




During the afternoon preceding his assassination the President signed a pardon for a soldier sentenced to be shot for desertion, remarking as he did so, “Well, I think the boy can do us more good above ground than under ground.”
He also approved an application for the discharge, on taking the oath of allegiance, of a rebel prisoner, in whose petition he wrote, “Let it be done.”
This act of mercy was his last official order.
The first corps of the army commanded by General Reynolds was once reviewed by the President on a beautiful plain at the north of Potomac Creek, about eight miles from Hooker’s headquarters. The party rode thither in an ambulance over a rough corduroy road, and as they passed over some of the more difficult portions of the jolting way the ambulance driver, who sat well in front, occasionally let fly a volley of suppressed oaths at his wild team of six mules.
Finally, Mr. Lincoln, leaning forward, touched the man on the shoulder and said,
“Excuse me, my friend, are you an Episcopalian?”
The man, greatly startled, looked around and replied:
“No, Mr. President; I am a Methodist.”
“Well,” said Lincoln, “I thought you must be an Episcopalian, because you swear just like Governor Seward, who is a church warder.”
The first night after the departure of President-elect Lincoln from Springfield, on his way to Washington, was spent in Indianapolis. Governor Yates, O. H. Browning, Jesse K. Dubois, O. M. Hatch, Josiah Allen, of Indiana, and others, after taking leave of Mr. Lincoln to return to their respective homes, took Ward Lamon into a room, locked the door, and proceeded in the most solemn and impressive manner to instruct him as to his duties as the special guardian of Mr. Lincoln’s person during the rest of his journey to Washington. Lamon tells the story as follows:
“The lesson was concluded by Uncle Jesse, as Mr. Dubois was commonly, called, who said:
“‘Now, Lamon, we have regarded you as the Tom Hyer of Illinois, with Morrissey attachment. We intrust the sacred life of Mr. Lincoln to your keeping; and if you don’t protect it, never return to Illinois, for we will murder you on sight.”’
Professor Jonathan Baldwin Turner was one of the few men to whom Mr. Lincoln confided his intention to issue the Proclamation of Emancipation.
Mr. Lincoln told his Illinois friend of the visit of a delegation to him who claimed to have a message from God that the War would not be successful without the freeing of the negroes, to whom Mr. Lincoln replied: “Is it not a little strange that He should tell this to you, who have so little to do with it, and should not have told me, who has a great deal to do with it?”
At the same time he informed Professor Turner he had his Proclamation in his pocket.
A writer who heard Mr. Lincoln’s famous speech delivered in New York after his nomination for President has left this record of the event:
“When Lincoln rose to speak, I was greatly disappointed. He was tall, tall, oh, so tall, and so angular and awkward that I had for an instant a feeling of pity for so ungainly a man. He began in a low tone of voice, as if he were used to speaking out of doors and was afraid of speaking too loud.
“He said ‘Mr. Cheerman,’ instead of ‘Mr. Chairman,’ and employed many other words with an old-fashioned pronunciation. I said to myself, ‘Old fellow, you won’t do; it is all very well for the Wild West, but this will never go down in New York.’ But pretty soon he began to get into the subject; he straightened up, made regular and graceful gestures; his face lighted as with an inward fire; the whole man was transfigured.
“I forgot the clothing, his personal appearance, and his individual peculiarities. Presently, forgetting myself, I was on my feet with the rest, yelling like a wild Indian, cheering the wonderful man. In the close parts of his argument you could hear the gentle sizzling of the gas burners.
“When he reached a climax the thunders of applause were terrific. It was a great speech. When I came out of the hall my face was glowing with excitement and my frame all a-quiver. A friend, with his eyes aglow, asked me what I thought of ‘Abe’ Lincoln, the rail-splitter. I said, ‘He’s the greatest man since St. Paul.’ And I think so yet.”
President Lincoln one day noticed a small, pale, delicate-looking boy, about thirteen years old, among the number in the White House antechamber.
The President saw him standing there, looking so feeble and faint, and said: “Come here, my boy, and tell me what you want.”
The boy advanced, placed his hand on the arm of the President’s chair, and, with a bowed head and timid accents, said: “Mr. President, I have been a drummer boy in a regiment for two years, and my colonel got angry with me and turned me off. I was taken sick and have been a long time in the hospital.”
The President discovered that the boy had no home, no father—he had died in the army—no mother.
“I have no father, no mother, no brothers, no sisters, and,” bursting into tears, “no friends—nobody cares for me.”
Lincoln’s eyes filled with tears, and the boy’s heart was soon made glad by a request to certain officials “to care for this poor boy.”
One of the most noted murder cases in which Lincoln defended the accused was tried in August, 1859. The victim, Crafton, was a student in his own law office, the defendant, “Peachy” Harrison, was a grandson of Rev. Peter Cartwright; both were connected with the best families in the county; they were brothers-in-law, and had always been friends.
Senator John M. Palmer and General John A. McClelland were on the side of the prosecution. Among those who represented the defendant were Lincoln and Senator Shelby M. Cullom. The two young men had engaged in a political quarrel, and Crafton was stabbed to death by Harrison. The tragic pathos of a case which involved the deepest affections of almost an entire community reached its climax in the appearance in court of the venerable Peter Cartwright. Lincoln had beaten him for Congress in 1846.
Eccentric and aggressive as he was, he was honored far and wide; and when he arose to take the witness stand, his white hair crowned with this cruel sorrow, the most indifferent spectator felt that his examination would be unbearable.
It fell to Lincoln to question Cartwright. With the rarest gentleness he began to put his questions.
“How long have you known the prisoner?”
Cartwright’s head dropped on his breast for a moment; then straightening himself, he passed his hand across his eyes and answered in a deep, quavering voice:
“I have known him since a babe, he laughed and cried on my knee.”
The examination ended by Lincoln drawing from the witness the story of how Crafton had said to him, just before his death: “I am dying; I will soon part with all I love on earth, and I want you to say to my slayer that I forgive him. I want to leave this earth with a forgiveness of all who have in any way injured me.”
This examination made a profound impression on the jury. Lincoln closed his argument by picturing the scene anew, appealing to the jury to practice the same forgiving spirit that the murdered man had shown on his death-bed. It was undoubtedly to his handling of the grandfather’s evidence that Harrison’s acquittal was due.
During the War Congress appropriated $10,000 to be expended by the President in defending United States Marshals in cases of arrests and seizures where the legality of their actions was tested in the courts. Previously the Marshals sought the assistance of the Attorney-General in defending them, but when they found that the President had a fund for that purpose they sought to control the money.
In speaking of these Marshals one day, Mr. Lincoln said:
“They are like a man in Illinois, whose cabin was burned down, and, according to the kindly custom of early days in the West, his neighbors all contributed something to start him again. In his case they had been so liberal that he soon found himself better off than before the fire, and he got proud. One day a neighbor brought him a bag of oats, but the fellow refused it with scorn.
“‘No,’ said he, ‘I’m not taking oats now. I take nothing but money.’”
The resistance to the military draft of 1863 by the City of New York, the result of which was the killing of several thousand persons, was illustrated on August 29th, 1863, by “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper,” over the title of “The Naughty Boy, Gotham, Who Would Not Take the Draft.” Beneath was also the text:
MAMMY LINCOLN: “There now, you bad boy, acting that way, when your little sister Penn (State of Pennsylvania) takes hers like a lady!”
Horatio Seymour was then Governor of New York, and a prominent “the War is a failure” advocate. He was in Albany, the State capital, when the riots broke out in the City of New York, July 13th, and after the mob had burned the Colored Orphan Asylum and killed several hundred negroes, came to the city. He had only soft words for the rioters, promising them that the draft should be suspended. Then the Government sent several regiments of veterans, fresh from the field of Gettysburg, where they had assisted in defeating Lee. These troops made short work of the brutal ruffians, shooting down three thousand or so of them, and the rioting was subdued. The “Naughty Boy Gotham” had to take his medicine, after all, but as the spirit of opposition to the War was still rampant, the President issued a proclamation suspending the writ of habeas corpus in all the States of the Union where the Government had control. This had a quieting effect upon those who were doing what they could in obstructing the Government.
Mr. Lincoln had advised Lieutenant-General Winfield Scott, commanding the United States Army, of the threats of violence on inauguration day, 1861. General Scott was sick in bed at Washington when Adjutant-General Thomas Mather, of Illinois, called upon him in President-elect Lincoln’s behalf, and the veteran commander was much wrought up. Said he to General Mather:
“Present my compliments to Mr. Lincoln when you return to Springfield, and tell him I expect him to come on to Washington as soon as he is ready; say to him that I will look after those Maryland and Virginia rangers myself. I will plant cannon at both ends of Pennsylvania avenue, and if any of them show their heads or raise a finger, I’ll blow them to h—-.”
One day, when the President was with the troops who were fighting at the front, the wounded, both Union and Confederate, began to pour in.
As one stretcher was passing Lincoln, he heard the voice of a lad calling to his mother in agonizing tones. His great heart filled. He forgot the crisis of the hour. Stopping the carriers, he knelt, and bending over him, asked: “What can I do for you, my poor child?”
“Oh, you will do nothing for me,” he replied. “You are a Yankee. I cannot hope that my message to my mother will ever reach her.”
Lincoln, in tears, his voice full of tenderest love, convinced the boy of his sincerity, and he gave his good-bye words without reserve.
The President directed them copied, and ordered that they be sent that night, with a flag of truce, into the enemy’s lines.
When Mr. Lincoln made his famous humorous speech in Congress ridiculing General Cass, he began to speak from notes, but, as he warmed up, he left his desk and his notes, to stride down the alley toward the Speaker’s chair.
Occasionally, as he would complete a sentence amid shouts of laughter, he would return up the alley to his desk, consult his notes, take a sip of water and start off again.
Mr. Lincoln received many congratulations at the close, Democrats joining the Whigs in their complimentary comments.
One Democrat, however (who had been nicknamed “Sausage” Sawyer), didn’t enthuse at all.
“Sawyer,” asked an Eastern Representative, “how did you like the lanky Illinoisan’s speech? Very able, wasn’t it?”
“Well,” replied Sawyer, “the speech was pretty good, but I hope he won’t charge mileage on his travels while delivering it.”
“John McNamer was buried last Sunday, near Petersburg, Menard county. A long while ago he was Assessor and Treasurer of the County for several successive terms. Mr. McNamer was an early settler in that section, and, before the town of Petersburg was laid out, in business in Old Salem, a village that existed many years ago two miles south of the present site of Petersburg.
“‘Abe’ Lincoln was then postmaster of the place and sold whisky to its inhabitants. There are old-timers yet living in Menard who bought many a jug of corn-juice from ‘Old Abe’ when he lived at Salem. It was here that Anne Rutledge dwelt, and in whose grave Lincoln wrote that his heart was buried.
“As the story runs, the fair and gentle Anne was originally John McNamer’s sweetheart, but ‘Abe’ took a ‘shine’ to the young lady, and succeeded in heading off McNamer and won her affections. But Anne Rutledge died, and Lincoln went to Springfield, where he some time afterwards married.
“It is related that during the War a lady belonging to a prominent Kentucky family visited Washington to beg for her son’s pardon, who was then in prison under sentence of death for belonging to a band of guerrillas who had committed many murders and outrages.
“With the mother was her daughter, a beautiful young lady, who was an accomplished musician. Mr. Lincoln received the visitors in his usual kind manner, and the mother made known the object of her visit, accompanying her plea with tears and sobs and all the customary romantic incidents.
“There were probably extenuating circumstances in favor of the young rebel prisoner, and while the President seemed to be deeply pondering the young lady moved to a piano near by and taking a seat commenced to sing ‘Gentle Annie,’ a very sweet and pathetic ballad which, before the War, was a familiar song in almost every household in the Union, and is not yet entirely forgotten, for that matter.
“It is to be presumed that the young lady sang the song with more plaintiveness and effect than ‘Old Abe’ had ever heard it in Springfield. During its rendition, he arose from his seat, crossed the room to a window in the westward, through which he gazed for several minutes with a ‘sad, far-away look,’ which has so often been noted as one of his peculiarities.
“His memory, no doubt, went back to the days of his humble life on the Sangamon, and with visions of Old Salem and its rustic people, who once gathered in his primitive store, came a picture of the ‘Gentle Annie’ of his youth, whose ashes had rested for many long years under the wild flowers and brambles of the old rural burying-ground, but whose spirit then, perhaps, guided him to the side of mercy.
“Be that as it may, President Lincoln drew a large red silk handkerchief from his coatpocket, with which he wiped his face vigorously. Then he turned, advanced quickly to his desk, wrote a brief note, which he handed to the lady, and informed her that it was the pardon she sought.
“The scene was no doubt touching in a great degree and proves that a nice song, well sung, has often a powerful influence in recalling tender recollections. It proves, also, that Abraham Lincoln was a man of fine feelings, and that, if the occurrence was a put-up job on the lady’s part, it accomplished the purpose all the same.”


Lincoln made a political speech at Pappsville, Illinois, when a candidate for the Legislature the first time. A free-for-all fight began soon after the opening of the meeting, and Lincoln, noticing one of his friends about to succumb to the energetic attack of an infuriated ruffian, edged his way through the crowd, and, seizing the bully by the neck and the seat of his trousers, threw him, by means of his strength and long arms, as one witness stoutly insists, “twelve feet away.” Returning to the stand, and throwing aside his hat, he inaugurated his campaign with the following brief but pertinent declaration:
“Fellow-citizens, I presume you all know who I am. I am humble Abraham Lincoln. I have been solicited by many friends to become a candidate for the Legislature. My politics are short and sweet, like the old woman’s dance. I am in favor of the national bank; I am in favor of the internal improvement system and a high protective tariff. These are my sentiments; if elected, I shall be thankful; if not, it will be all the same.”
One day, when President Lincoln was alone and busily engaged on an important subject, involving vexation and anxiety, he was disturbed by the unwarranted intrusion of three men, who, without apology, proceeded to lay their claim before him.
The spokesman of the three reminded the President that they were the owners of some torpedo or other warlike invention which, if the government would only adopt it, would soon crush the rebellion.
“Now,” said the spokesman, “we have been here to see you time and again; you have referred us to the Secretary of War, the Chief of Ordnance, and the General of the Army, and they give us no satisfaction. We have been kept here waiting, till money and patience are exhausted, and we now come to demand of you a final reply to our application.”
Mr. Lincoln listened to this insolent tirade, and at its close the old twinkle came into his eye.
“You three gentlemen remind me of a story I once heard,” said he, “of a poor little boy out West who had lost his mother. His father wanted to give him a religious education, and so placed him in the family of a clergyman, whom he directed to instruct the little fellow carefully in the Scriptures. Every day the boy had to commit to memory and recite one chapter of the Bible. Things proceeded smoothly until they reached that chapter which details the story of the trial of Shadrach, Meshach and Abednego in the fiery furnace. When asked to repeat these three names the boy said he had forgotten them.
“His teacher told him that he must learn them, and gave him another day to do so. The next day the boy again forgot them.
“‘Now,’ said the teacher, ‘you have again failed to remember those names and you can go no farther until you have learned them. I will give you another day on this lesson, and if you don’t repeat the names I will punish you.’
“A third time the boy came to recite, and got down to the stumbling block, when the clergyman said: ‘Now tell me the names of the men in the fiery furnace.’
“‘Oh,’ said the boy, ‘here come those three infernal bores! I wish the devil had them!’”
Having received their “final answer,” the three patriots retired, and at the Cabinet meeting which followed, the President, in high good humor, related how he had dismissed his unwelcome visitors.
In the Chicago Convention of 1860 the fight for Seward was maintained with desperate resolve until the final ballot was taken. Thurlow Weed was the Seward leader, and he was simply incomparable as a master in handling a convention. With him were Governor Morgan, Henry J. Raymond, of the New York Times, with William M. Evarts as chairman of the New York delegation, whose speech nominating Seward was the most impressive utterance of his life. The Bates men (Bates was afterwards Lincoln’s Attorney-General) were led by Frank Blair, the only Republican Congressman from a slave State, who was nothing if not heroic, aided by his brother Montgomery (afterwards Lincoln’s Postmaster General), who was a politician of uncommon cunning. With them was Horace Greeley, who was chairman of the delegation from the then almost inaccessible State of Oregon.
It was Lincoln’s friends, however, who were the “hustlers” of that battle. They had men for sober counsel like David Davis; men of supreme sagacity like Leonard Swett; men of tireless effort like Norman B. Judd; and they had what was more important than all—a seething multitude wild with enthusiasm for “Old Abe.”
On one occasion when Mr. Lincoln was going to attend a political convention one of his rivals, a liveryman, provided him with a slow horse, hoping that he would not reach his destination in time. Mr. Lincoln got there, however, and when he returned with the horse he said: “You keep this horse for funerals, don’t you?” “Oh, no,” replied the liveryman. “Well, I’m glad of that, for if you did you’d never get a corpse to the grave in time for the resurrection.”
General McClellan, after being put in command of the Army, resented any “interference” by the President. Lincoln, in his anxiety to know the details of the work in the army, went frequently to McClellan’s headquarters. That the President had a serious purpose in these visits McClellan did not see.
“I enclose a card just received from ‘A. Lincoln,’” he wrote to his wife one day; “it shows too much deference to be seen outside.”
In another letter to Mrs. McClellan he spoke of being “interrupted” by the President and Secretary Seward, “who had nothing in particular to say,” and again of concealing himself “to dodge all enemies in shape of ‘browsing’ Presidents,” etc.
“I am becoming daily more disgusted with this Administration—perfectly sick of it,” he wrote early in October; and a few days later, “I was obliged to attend a meeting of the Cabinet at 8 P. M., and was bored and annoyed. There are some of the greatest geese in the Cabinet I have ever seen—enough to tax the patience of Job.”
At a Cabinet meeting once, the advisability of putting a legend on greenbacks similar to the In God We Trust legend on the silver coins was discussed, and the President was asked what his view was. He replied: “If you are going to put a legend on the greenback, I would suggest that of Peter and Paul: ‘Silver and gold we have not, but what we have we’ll give you.’”
One of Mr. Lincoln’s notable religious utterances was his reply to a deputation of colored people at Baltimore who presented him a Bible. He said:
“In regard to the great book, I have only to say it is the best gift which God has ever given man. All the good from the Savior of the world is communicated to us through this book. But for this book we could not know right from wrong. All those things desirable to man are contained in it.”
When Lincoln was President he told this story of the Black Hawk War:
The only time he ever saw blood in this campaign, was one morning when, marching up a little valley that makes into the Rock River bottom, to reinforce a squad of outposts that were thought to be in danger, they came upon the tent occupied by the other party just at sunrise. The men had neglected to place any guard at night, and had been slaughtered in their sleep.
As the reinforcing party came up the slope on which the camp had been made, Lincoln saw them all lying with their heads towards the rising sun, and the round red spot that marked where they had been scalped gleamed more redly yet in the ruddy light of the sun. This scene years afterwards he recalled with a shudder.
For a while during the Civil War, General Fremont was without a command. One day in discussing Fremont’s case with George W. Julian, President Lincoln said he did not know where to place him, and that it reminds him of the old man who advised his son to take a wife, to which the young man responded: “All right; whose wife shall I take?”
On April 14, 1865, a few hours previous to his assassination, President Lincoln sent a message by Congressman Schuyler Colfax, Vice-President during General Grant’s first term, to the miners in the Rocky Mountains and the regions bounded by the Pacific ocean, in which he said:
“Now that the Rebellion is overthrown, and we know pretty nearly the amount of our National debt, the more gold and silver we mine, we make the payment of that debt so much easier.
“Now I am going to encourage that in every possible way. We shall have hundreds of thousands of disbanded soldiers, and many have feared that their return home in such great numbers might paralyze industry by furnishing, suddenly, a greater supply of labor than there will be demand for. I am going to try to attract them to the hidden wealth of our mountain ranges, where there is room enough for all. Immigration, which even the War has not stopped, will land upon our shores hundreds of thousands more per year from overcrowded Europe. I intend to point them to the gold and silver that wait for them in the West.
“Tell the miners for me that I shall promote their interests to the utmost of my ability; because their prosperity as the prosperity of the nation; and,” said he, his eye kindling with enthusiasm, “we shall prove, in a very few years, that we are indeed the treasury of the world.”
President Lincoln made a significant remark to a clergyman in the early days of the War.
“Let us have faith, Mr. President,” said the minister, “that the Lord is on our side in this great struggle.”
Mr. Lincoln quietly answered: “I am not at all concerned about that, for I know that the Lord is always on the side of the right; but it is my constant anxiety and prayer that I and this nation may be on the Lord’s side.”
It was Lincoln’s custom to hold an informal reception once a week, each caller taking his turn.
Upon one of these eventful days an old friend from Illinois stood in line for almost an hour. At last he was so near the President his voice could reach him, and, calling out to his old associate, he startled every one by exclaiming, “Hallo, ‘Abe’; how are ye? I’m in line and hev come for an orfice, too.”
Lincoln singled out the man with the stentorian voice, and recognizing a particularly old friend, one whose wife had befriended him at a peculiarly trying time, the President responded to his greeting in a cordial manner, and told him “to hang onto himself and not kick the traces. Keep in line and you’ll soon get here.”
They met and shook hands with the old fervor and renewed their friendship.
The informal reception over, Lincoln sent for his old friend, and the latter began to urge his claims.
After having given him some good advice, Lincoln kindly told him he was incapable of holding any such position as he asked for. The disappointment of the Illinois friend was plainly shown, and with a perceptible tremor in his voice he said, “Martha’s dead, the gal is married, and I’ve guv Jim the forty.”
Then looking at Lincoln he came a little nearer and almost whispered, “I knowed I wasn’t eddicated enough to git the place, but I kinder want to stay where I ken see ‘Abe’ Lincoln.”
He was given employment in the White House grounds.
Afterwards the President said, “These brief interviews, stripped of even the semblance of ceremony, give me a better insight into the real character of the person and his true reason for seeking one.”
William H. Seward, idol of the Republicans of the East, six months after Lincoln had made his “Divided House” speech, delivered an address at Rochester, New York, containing this famous sentence:
“It is an irrepressible conflict between opposing and enduring forces, and it means that the United States must, and will, sooner or later, become either entirely a slave-holding nation, or entirely a free-labor nation.”
Seward, who had simply followed in Lincoln’s steps, was defeated for the Presidential nomination at the Republican National Convention of 1860, because he was “too radical,” and Lincoln, who was still “radicaler,” was named.
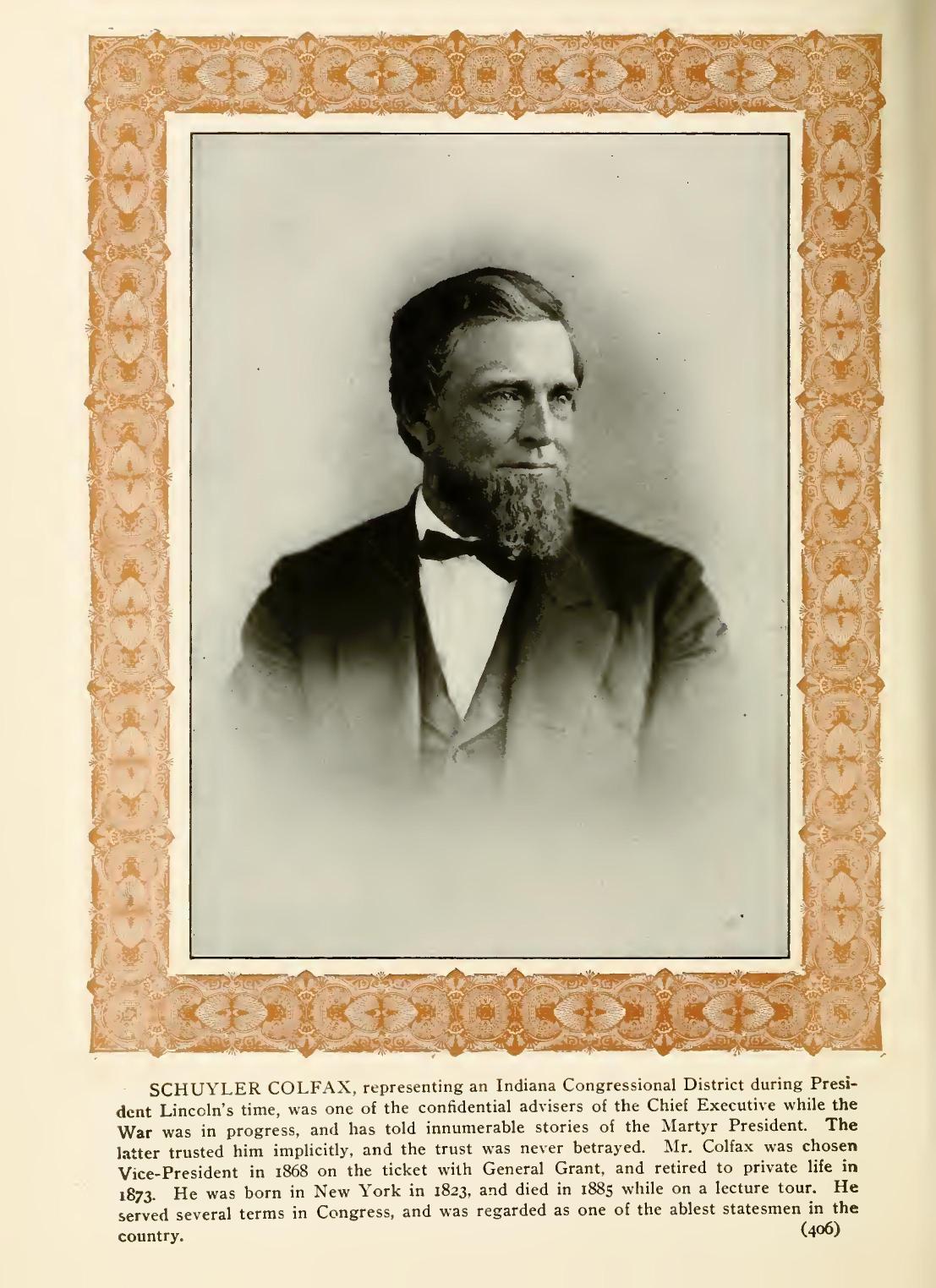




The chief interest of the Illinois campaign of 1843 lay in the race for Congress in the Capital district, which was between Hardin—fiery, eloquent, and impetuous Democrat—and Lincoln—plain, practical, and ennobled Whig. The world knows the result. Lincoln was elected.
It is not so much his election as the manner in which he secured his nomination with which we have to deal. Before that ever-memorable spring Lincoln vacillated between the courts of Springfield, rated as a plain, honest, logical Whig, with no ambition higher politically than to occupy some good home office.
Late in the fall of 1842 his name began to be mentioned in connection with Congressional aspirations, which fact greatly annoyed the leaders of his political party, who had already selected as the Whig candidate E. D. Baker, afterward the gallant Colonel who fell so bravely and died such an honorable death on the battlefield of Ball’s Bluff.
Despite all efforts of his opponents within his party, the name of the “gaunt rail-splitter” was hailed with acclaim by the masses, to whom he had endeared himself by his witticisms, honest tongue, and quaint philosophy when on the stump, or mingling with them in their homes.
The convention, which met in early spring, in the city of Springfield, was to be composed of the usual number of delegates. The contest for the nomination was spirited and exciting.
A few weeks before the meeting of the convention the fact was found by the leaders that the advantage lay with Lincoln, and that unless they pulled some very fine wires nothing could save Baker.
They attempted to play the game that has so often won, by “convincing” delegates under instructions for Lincoln to violate them, and vote for Baker. They had apparently succeeded.
“The best laid plans of mice and men gang aft agley.” So it was in this case. Two days before the convention Lincoln received an intimation of this, and, late at night, wrote the following letter.
The letter was addressed to Martin Morris, who resided at Petersburg, an intimate friend of his, and by him circulated among those who were instructed for him at the county convention.
It had the desired effect. The convention met, the scheme of the conspirators miscarried, Lincoln was nominated, made a vigorous canvass, and was triumphantly elected, thus paving the way for his more extended and brilliant conquests.
This letter, Lincoln had often told his friends, gave him ultimately the Chief Magistracy of the nation. He has also said, that, had he been beaten before the convention, he would have been forever obscured. The following is a verbatim copy of the epistle:
“April 14, 1843.
“Friend Morris: I have heard it intimated that Baker is trying to get you or Miles, or both of you, to violate the instructions of the meeting that appointed you, and to go for him. I have insisted, and still insist, that this cannot be true.
“Sure Baker would not do the like. As well might Hardin ask me to vote for him in the convention.
“Again, it is said there will be an attempt to get instructions in your county requiring you to go for Baker. This is all wrong. Upon the same rule, why might I not fly from the decision against me at Sangamon and get up instructions to their delegates to go for me. There are at least 1,200 Whigs in the county that took no part, and yet I would as soon stick my head in the fire as attempt it.
“Besides, if any one should get the nomination by such extraordinary means, all harmony in the district would inevitably be lost. Honest Whigs (and very nearly all of them are honest) would not quietly abide such enormities.
“I repeat, such an attempt on Baker’s part cannot be true. Write me at Springfield how the matter is. Don’t show or speak of this letter.
“A. LINCOLN.”
Mr. Morris did show the letter, and Mr. Lincoln always thanked his stars that he did.
Mr. Lincoln’s favorite poem was “Oh! Why Should the Spirit of Mortal Be Proud?” written by William Knox, a Scotchman, although Mr. Lincoln never knew the author’s name. He once said to a friend:
“This poem has been a great favorite with me for years. It was first shown to me, when a young man, by a friend. I afterward saw it and cut it from a newspaper and learned it by heart. I would give a great deal to know who wrote it, but I have never been able to ascertain.”
| “Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud?-- |
| Like a swift-fleeing meteor, a fast-flying cloud, |
| A flash of the lightning, a break of the wave, |
| He passeth from life to his rest in the grave. |
| “The leaves of the oak and the willow shall fade, |
| Be scattered around, and together be laid; |
| And the young and the old, and the low and the high, |
| Shall moulder to dust, and together shall lie. |
| “The infant a mother attended and loved; |
| The mother, that infant’s affection who proved, |
| The husband, that mother and infant who blessed |
| --Each, all, are away to their dwellings of rest. |
| “The maid on whose cheek, on whose brow, in whose eye, |
| Shone beauty and pleasure--her triumphs are by; |
| And the memory of those who loved her and praised, |
| Are alike from the minds of the living erased. |
| “The hand of the king, that the sceptre hath borne, |
| The brow of the priest, that the mitre hath worn, |
| The eye of the sage, and the heart of the brave, |
| Are hidden and lost in the depths of the grave. |
| “The peasant, whose lot was to sow and to reap, |
| The herdsman, who climbed with his goats up the steep; |
| The beggar, who wandered in search of his bread, |
| Have faded away like the grass that we tread. |
| “The saint, who enjoyed the communion of heaven, |
| The sinner, who dared to remain unforgiven; |
| The wise and the foolish, the guilty and just, |
| Have quietly mingled their bones in the dust. |
| “So the multitude goes--like the flower or the weed |
| That withers away to let others succeed; |
| So the multitude comes--even those we behold, |
| To repeat every tale that has often been told: |
| “For we are the same our fathers have been; |
| We see the same sights our fathers have seen; |
| We drink the same stream, we view the same sun, |
| And run the same course our fathers have run. |
| “The thoughts we are thinking, our fathers would think; |
| From the death we are shrinking, our fathers would shrink; |
| To the life we are clinging, they also would cling |
| --But it speeds from us all like a bird on the wing. |
| “They loved--but the story we cannot unfold; |
| They scorned--but the heart of the haughty is cold; |
| They grieved--but no wail from their slumber will come; |
| They joyed--but the tongue of their gladness is dumb. |
| “They died--aye, they died--and we things that are now, |
| That walk on the turf that lies o’er their brow, |
| And make in their dwellings a transient abode, |
| Meet the things that they met on their pilgrimage road. |
| “Yea! hope and despondency, pleasure and pain, |
| Are mingled together in sunshine and rain; |
| And the smile and the tear, the song and the dirge, |
| Still follow each other, like surge upon surge. |
| “‘Tis the wink of an eye,--’tis the draught of a breath; |
| --From the blossom of health to the paleness of death, |
| From the gilded saloon to the bier and the shroud: |
| --Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud?” |
President Lincoln had great doubt as to his right to emancipate the slaves under the War power. In discussing the question, he used to like the case to that of the boy who, when asked how many legs his calf would have if he called its tail a leg, replied, “five,” to which the prompt response was made that calling the tail a leg would not make it a leg.
The following is told by Thomas H. Nelson, of Terre Haute, Indiana, who was appointed minister to Chili by Lincoln:
Judge Abram Hammond, afterwards Governor of Indiana, and myself arranged to go from Terre Haute to Indianapolis in a stage-coach.
As we stepped in we discovered that the entire back seat was occupied by a long, lank individual, whose head seemed to protrude from one end of the coach and his feet from the other. He was the sole occupant, and was sleeping soundly. Hammond slapped him familiarly on the shoulder, and asked him if he had chartered the coach that day.
“Certainly not,” and he at once took the front seat, politely giving us the place of honor and comfort. An odd-looking fellow he was, with a twenty-five cent hat, without vest or cravat. Regarding him as a good subject for merriment, we perpetrated several jokes.
He took them all with utmost innocence and good nature, and joined in the laugh, although at his own expense.
After an astounding display of wordy pyrotechnics, the dazed and bewildered stranger asked, “What will be the upshot of this comet business?”
Late in the evening we reached Indianapolis, and hurried to Browning’s hotel, losing sight of the stranger altogether.
We retired to our room to brush our clothes. In a few minutes I descended to the portico, and there descried our long, gloomy fellow traveler in the center of an admiring group of lawyers, among whom were Judges McLean and Huntington, Albert S. White, and Richard W. Thompson, who seemed to be amused and interested in a story he was telling. I inquired of Browning, the landlord, who he was. “Abraham Lincoln, of Illinois, a member of Congress,” was his response.
I was thunderstruck at the announcement. I hastened upstairs and told Hammond the startling news, and together we emerged from the hotel by a back door, and went down an alley to another house, thus avoiding further contact with our distinguished fellow traveler.
Years afterward, when the President-elect was on his way to Washington, I was in the same hotel looking over the distinguished party, when a long arm reached to my shoulder, and a shrill voice exclaimed, “Hello, Nelson! do you think, after all, the whole world is going to follow the darned thing off?” The words were my own in answer to his question in the stage-coach. The speaker was Abraham Lincoln.
Lincoln had periods while “clerking” in the New Salem grocery store during which there was nothing for him to do, and was therefore in circumstances that made laziness almost inevitable. Had people come to him for goods, they would have found him willing to sell them. He sold all that he could, doubtless.
The store soon became the social center of the village. If the people did not care (or were unable) to buy goods, they liked to go where they could talk with their neighbors and listen to stories. These Lincoln gave them in abundance, and of a rare sort.
It was in these gatherings of the “Four Hundred” at the village store that Lincoln got his training as a debater. Public questions were discussed there daily and nightly, and Lincoln always took a prominent part in the discussions. Many of the debaters came to consider “Abe Linkin” as about the smartest man in the village.
Lincoln wanted men of level heads for important commands. Not infrequently he gave his generals advice.
He appreciated Hooker’s bravery, dash and activity, but was fearful of the results of what he denominated “swashing around.”
This was one of his telegrams to Hooker:
“And now, beware of rashness; beware of rashness, but, with energy and sleepless vigilance, go forward and give us victories.”
When the Confederate iron-clad Merrimac was sent against the Union vessels in Hampton Roads President Lincoln expressed his belief in the Monitor to Captain Fox, the adviser of Captain Ericsson, who constructed the Monitor. “We have three of the most effective vessels in Hampton Roads, and any number of small craft that will hang on the stern of the Merrimac like small dogs on the haunches of a bear. They may not be able to tear her down, but they will interfere with the comfort of her voyage. Her trial trip will not be a pleasure trip, I am certain.
“We have had a big share of bad luck already, but I do not believe the future has any such misfortunes in store for us as you anticipate.” Said Captain Fox: “If the Merrimac does not sink our ships, who is to prevent her from dropping her anchor in the Potomac, where that steamer lies,” pointing to a steamer at anchor below the long bridge, “and throwing her hundred-pound shells into this room, or battering down the walls of the Capitol?”
“The Almighty, Captain,” answered the President, excitedly, but without the least affectation. “I expect set-backs, defeats; we have had them and shall have them. They are common to all wars. But I have not the slightest fear of any result which shall fatally impair our military and naval strength, or give other powers any right to interfere in our quarrel. The destruction of the Capitol would do both.
“I do not fear it, for this is God’s fight, and He will win it in His own good time. He will take care that our enemies will not push us too far.
“Speaking of iron-clads,” said the President, “you do not seem to take the little Monitor into account. I believe in the Monitor and her commander. If Captain Worden does not give a good account of the Monitor and of himself, I shall have made a mistake in following my judgment for the first time since I have been here, Captain.
“I have not made a mistake in following my clear judgment of men since this War began. I followed that judgment when I gave Worden the command of the Monitor. I would make the appointment over again to-day. The Monitor should be in Hampton Roads now. She left New York eight days ago.”
After the captain had again presented what he considered the possibilities of failure the President replied, “No, no, Captain, I respect your judgments as you have reason to know, but this time you are all wrong.
“The Monitor was one of my inspirations; I believed in her firmly when that energetic contractor first showed me Ericsson’s plans. Captain Ericsson’s plain but rather enthusiastic demonstration made my conversion permanent. It was called a floating battery then; I called it a raft. I caught some of the inventor’s enthusiasm and it has been growing upon me. I thought then, and I am confident now, it is just what we want. I am sure that the Monitor is still afloat, and that she will yet give a good account of herself. Sometimes I think she may be the veritable sling with a stone that will yet smite the Merrimac Philistine in the forehead.”
Soon was the President’s judgment verified, for the “Fight of the Monitor and Merrimac” changed all the conditions of naval warfare.
After the victory was gained, the presiding Captain Fox and others went on board the Monitor, and Captain Worden was requested by the President to narrate the history of the encounter.
Captain Worden did so in a modest manner, and apologized for not being able better to provide for his guests. The President smilingly responded “Some charitable people say that old Bourbon is an indispensable element in the fighting qualities of some of our generals in the field, but, Captain, after the account that we have heard to-day, no one will say that any Dutch courage is needed on board the Monitor.”
“It never has been, sir,” modestly observed the captain.
Captain Fox then gave a description of what he saw of the engagement and described it as indescribably grand. Then, turning to the President, he continued, “Now standing here on the deck of this battle-scarred vessel, the first genuine iron-clad—the victor in the first fight of iron-clads—let me make a confession, and perform an act of simple justice.
“I never fully believed in armored vessels until I saw this battle.
“I know all the facts which united to give us the Monitor. I withhold no credit from Captain Ericsson, her inventor, but I know that the country is principally indebted for the construction of the vessel to President Lincoln, and for the success of her trial to Captain Worden, her commander.”
At one time a certain Major Hill charged Lincoln with making defamatory remarks regarding Mrs. Hill.
Hill was insulting in his language to Lincoln who never lost his temper.
When he saw his chance to edge a word in, Lincoln denied emphatically using the language or anything like that attributed to him.
He entertained, he insisted, a high regard for Mrs. Hill, and the only thing he knew to her discredit was the fact that she was Major Hill’s wife.
Among those who called to congratulate Mr. Lincoln upon his nomination for President was an old lady, very plainly dressed. She knew Mr. Lincoln, but Mr. Lincoln did not at first recognize her. Then she undertook to recall to his memory certain incidents connected with his ride upon the circuit—especially his dining at her house upon the road at different times. Then he remembered her and her home.
Having fixed her own place in his recollection, she tried to recall to him a certain scanty dinner of bread and milk that he once ate at her house. He could not remember it—on the contrary, he only remembered that he had always fared well at her house.
“Well,” she said, “one day you came along after we had got through dinner, and we had eaten up everything, and I could give you nothing but a bowl of bread and milk, and you ate it; and when you got up you said it was good enough for the President of the United States!”
The good woman had come in from the country, making a journey of eight or ten miles, to relate to Mr. Lincoln this incident, which, in her mind, had doubtless taken the form of a prophecy. Mr. Lincoln placed the honest creature at her ease, chatted with her of old times, and dismissed her in the most happy frame of mind.
The story of naming the town of Lincoln, the county seat of Logan county, Illinois, is thus given on good authority:
The first railroad had been built through the county, and a station was about to be located there. Lincoln, Virgil Hitchcock, Colonel R. B. Latham and several others were sitting on a pile of ties and talking about moving a county seat from Mount Pulaski. Mr. Lincoln rose and started to walk away, when Colonel Latham said: “Lincoln, if you will help us to get the county seat here, we will call the place Lincoln.”
“All right, Latham,” he replied.
Colonel Latham then deeded him a lot on the west side of the courthouse, and he owned it at the time he was elected President.
“Jeff” Davis had a large and threatening nightmare in November, 1864, and what he saw in his troubled dreams was the long and lanky figure of Abraham Lincoln, who had just been endorsed by the people of the United States for another term in the White House at Washington. The cartoon reproduced here is from the issue of “Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper” of December 3rd, 1864, it being entitled “Jeff Davis’ November Nightmare.”
Davis had been told that McClellan, “the War is a failure” candidate for the Presidency, would have no difficulty whatever in defeating Lincoln; that negotiations with the Confederate officials for the cessation of hostilities would be entered into as soon as McClellan was seated in the Chief Executive’s chair; that the Confederacy would, in all probability, be recognized as an independent government by the Washington Administration; that the “sacred institution” of slavery would continue to do business at the old stand; that the Confederacy would be one of the great nations of the world, and have all the “State Rights” and other things it wanted, with absolutely no interference whatever upon the part of the North.
Therefore, Lincoln’s re-election was a rough, rude shock to Davis, who had not prepared himself for such an event. Six months from the date of that nightmare-dream he was a prisoner in the hands of the Union forces, and the Confederacy was a thing of the past.
Probably the last official act of President Lincoln’s life was the signing of the commission reappointing Alvin Saunders Governor of Nebraska.
“I saw Mr. Lincoln regarding the matter,” said Governor Saunders, “and he told me to go home; that he would attend to it all right. I left Washington on the morning of the 14th, and while en route the news of the assassination on the evening of the same day reached me. I immediately wired back to find out what had become of my commission, and was told that the room had not been opened. When it was opened, the document was found lying on the desk.
“Mr. Lincoln signed it just before leaving for the theater that fatal evening, and left it lying there, unfolded.
“A note was found below the document as follows: ‘Rather a lengthy commission, bestowing upon Mr. Alvin Saunders the official authority of Governor of the Territory of Nebraska.’ Then came Lincoln’s signature, which, with one exception, that of a penciled message on the back of a card sent up by a friend as Mr. Lincoln was dressing for the theater, was the very last signature of the martyred President.”
A personal friend of President Lincoln is authority for this:
“I called on him one day in the early part of the War. He had just written a pardon for a young man who had been sentenced to be shot for sleeping at his post. He remarked as he read it to me:
“‘I could not think of going into eternity with the blood of the poor young man on my skirts.’ Then he added:
“‘It is not to be wondered at that a boy, raised on a farm, probably in the habit of going to bed at dark, should, when required to watch, fall asleep; and I cannot consent to shoot him for such an act.’”
By the Act of Emancipation President Lincoln built for himself forever the first place in the affections of the African race in this country. The love and reverence manifested for him by many of these people has, on some occasions, almost reached adoration. One day Colonel McKaye, of New York, who had been one of a committee to investigate the condition of the freedmen, upon his return from Hilton Head and Beaufort called upon the President, and in the course of the interview said that up to the time of the arrival among them in the South of the Union forces they had no knowledge of any other power. Their masters fled upon the approach of our soldiers, and this gave the slaves the conception of a power greater than their masters exercised. This power they called “Massa Linkum.”
Colonel McKaye said their place of worship was a large building they called “the praise house,” and the leader of the “meeting,” a venerable black man, was known as “the praise man.”
On a certain day, when there was quite a large gathering of the people, considerable confusion was created by different persons attempting to tell who and what “Massa Linkum” was. In the midst of the excitement the white-headed leader commanded silence. “Brederen,” said he, “you don’t know nosen’ what you’se talkin’ ‘bout. Now, you just listen to me. Massa Linkum, he ebery whar. He know ebery ting.”
Then, solemnly looking up, he added: “He walk de earf like de Lord!”
One of Lincoln’s most dearly loved friends, United States Senator Edward D. Baker, of Oregon, Colonel of the Seventy-first Pennsylvania, a former townsman of Mr. Lincoln, was killed at the battle of Ball’s Bluff, in October, 1861. The President went to General McClellan’s headquarters to hear the news, and a friend thus described the effect it had upon him:
“We could hear the click of the telegraph in the adjoining room and low conversation between the President and General McClellan, succeeded by silence, excepting the click, click of the instrument, which went on with its tale of disaster.
“Five minutes passed, and then Mr. Lincoln, unattended, with bowed head and tears rolling down his furrowed cheeks, his face pale and wan, his breast heaving with emotion, passed through the room. He almost fell as he stepped into the street. We sprang involuntarily from our seats to render assistance, but he did not fall.
“With both hands pressed upon his heart, he walked down the street, not returning the salute of the sentinel pacing his beat before the door.”
Lincoln never indulged in profanity, but confessed that when Lee was beaten at Malvern Hill, after seven days of fighting, and Richmond, but twelve miles away, was at McClellan’s mercy, he felt very much like swearing when he learned that the Union general had retired to Harrison’s Landing.
Lee was so confident his opponent would not go to Richmond that he took his army into Maryland—a move he would not have made had an energetic fighting man been in McClellan’s place.
It is true McClellan followed and defeated Lee in the bloodiest battle of the War—Antietam—afterwards following him into Virginia; but Lincoln could not bring himself to forgive the general’s inaction before Richmond.
President Lincoln said to General Sickles, just after the victory of Gettysburg: “The fact is, General, in the stress and pinch of the campaign there, I went to my room, and got down on my knees and prayed God Almighty for victory at Gettysburg. I told Him that this was His country, and the war was His war, but that we really couldn’t stand another Fredericksburg or Chancellorsville. And then and there I made a solemn vow with my Maker that if He would stand by you boys at Gettysburg I would stand by Him. And He did, and I will! And after this I felt that God Almighty had taken the whole thing into His hands.”
President Lincoln, having arranged to go to New York, was late for his train, much to the disgust of those who were to accompany him, and all were compelled to wait several hours until the next train steamed out of the station. President Lincoln was much amused at the dissatisfaction displayed, and then ventured the remark that the situation reminded him of “a little story.” Said he:
“Out in Illinois, a convict who had murdered his cellmate was sentenced to be hanged. On the day set for the execution, crowds lined the roads leading to the spot where the scaffold had been erected, and there was much jostling and excitement. The condemned man took matters coolly, and as one batch of perspiring, anxious men rushed past the cart in which he was riding, he called out, ‘Don’t be in a hurry, boys. You’ve got plenty of time. There won’t be any fun until I get there.’
“That’s the condition of things now,” concluded the President; “there won’t be any fun at New York until I get there.”
On the day the news of General Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Court-House was received, so an intimate friend of President Lincoln relates, the Cabinet meeting was held an hour earlier than usual. Neither the President nor any member of the Cabinet was able, for a time, to give utterance to his feelings. At the suggestion of Mr. Lincoln all dropped on their knees, and offered, in silence and in tears, their humble and heartfelt acknowledgments to the Almighty for the triumph He had granted to the National cause.
Mr. Lincoln was much impressed with the devotion and earnestness of purpose manifested by a certain lady of the “Christian Commission” during the War, and on one occasion, after she had discharged the object of her visit, said to her:
“Madam, I have formed a high opinion of your Christian character, and now, as we are alone, I have a mind to ask you to give me in brief your idea of what constitutes a true religious experience.”
The lady replied at some length, stating that, in her judgment, it consisted of a conviction of one’s own sinfulness and weakness, and a personal need of the Saviour for strength and support; that views of mere doctrine might and would differ, but when one was really brought to feel his need of divine help, and to seek the aid of the Holy Spirit for strength and guidance, it was satisfactory evidence of his having been born again. This was the substance of her reply.
When she had, concluded Mr. Lincoln was very thoughtful for a few moments. He at length said, very earnestly: “If what you have told me is really a correct view of this great subject I think I can say with sincerity that I hope I am a Christian. I had lived,” he continued, “until my boy Willie died without fully realizing these things. That blow overwhelmed me. It showed me my weakness as I had never felt it before, and if I can take what you have stated as a test I think I can safely say that I know something of that change of which you speak; and I will further add that it has been my intention for some time, at a suitable opportunity, to make a public religious profession.”
Mr. Lincoln once remarked to Mr. Noah Brooks, one of his most intimate personal friends: “I should be the most presumptuous blockhead upon this footstool if I for one day thought that I could discharge the duties which have come upon me, since I came to this place, without the aid and enlightenment of One who is stronger and wiser than all others.”
He said on another occasion: “I am very sure that if I do not go away from here a wiser man, I shall go away a better man, from having learned here what a very poor sort of a man I am.”
One night Schuyler Colfax left all other business to go to the White House to ask the President to respite the son of a constituent, who was sentenced to be shot, at Davenport, for desertion. Mr. Lincoln heard the story with his usual patience, though he was wearied out with incessant calls, and anxious for rest, and then replied:
“Some of our generals complain that I impair discipline and subordination in the army by my pardons and respites, but it makes me rested, after a hard day’s work, if I can find some good excuse for saving a man’s life, and I go to bed happy as I think how joyous the signing of my name will make him and his family and his friends.”
And with a happy smile beaming over that care-furrowed face, he signed that name that saved that life.
As the President and Mrs. Lincoln were leaving the White House, a few minutes before eight o’clock, on the evening of April 14th, 1865, Lincoln wrote this note:
“Allow Mr. Ashmun and friend to come to see me at 9 o’clock a. m., to-morrow, April 15th, 1865.”
One day during the War an attractively and handsomely dressed woman called on President Lincoln to procure the release from prison of a relation in whom she professed the deepest interest.
She was a good talker, and her winning ways seemed to make a deep impression on the President. After listening to her story, he wrote a few words on a card: “This woman, dear Stanton, is a little smarter than she looks to be,” enclosed it in an envelope and directed her to take it to the Secretary of War.
On the same day another woman called, more humble in appearance, more plainly clad. It was the old story.
Father and son both in the army, the former in prison. Could not the latter be discharged from the army and sent home to help his mother?
A few strokes of the pen, a gentle nod of the head, and the little woman, her eyes filling with tears and expressing a grateful acknowledgment her tongue, could not utter, passed out.
A lady so thankful for the release of her husband was in the act of kneeling in thankfulness. “Get up,” he said, “don’t kneel to me, but thank God and go.”
An old lady for the same reason came forward with tears in her eyes to express her gratitude. “Good-bye, Mr. Lincoln,” said she; “I shall probably never see you again till we meet in heaven.” She had the President’s hand in hers, and he was deeply moved. He instantly took her right hand in both of his, and, following her to the door, said, “I am afraid with all my troubles I shall never get to the resting-place you speak of; but if I do, I am sure I shall find you. That you wish me to get there is, I believe, the best wish you could make for me. Good-bye.”
Then the President remarked to a friend, “It is more than many can often say, that in doing right one has made two people happy in one day. Speed, die when I may, I want it said of me by those who know me best, that I have always plucked a thistle and planted a flower when I thought a flower would grow.”
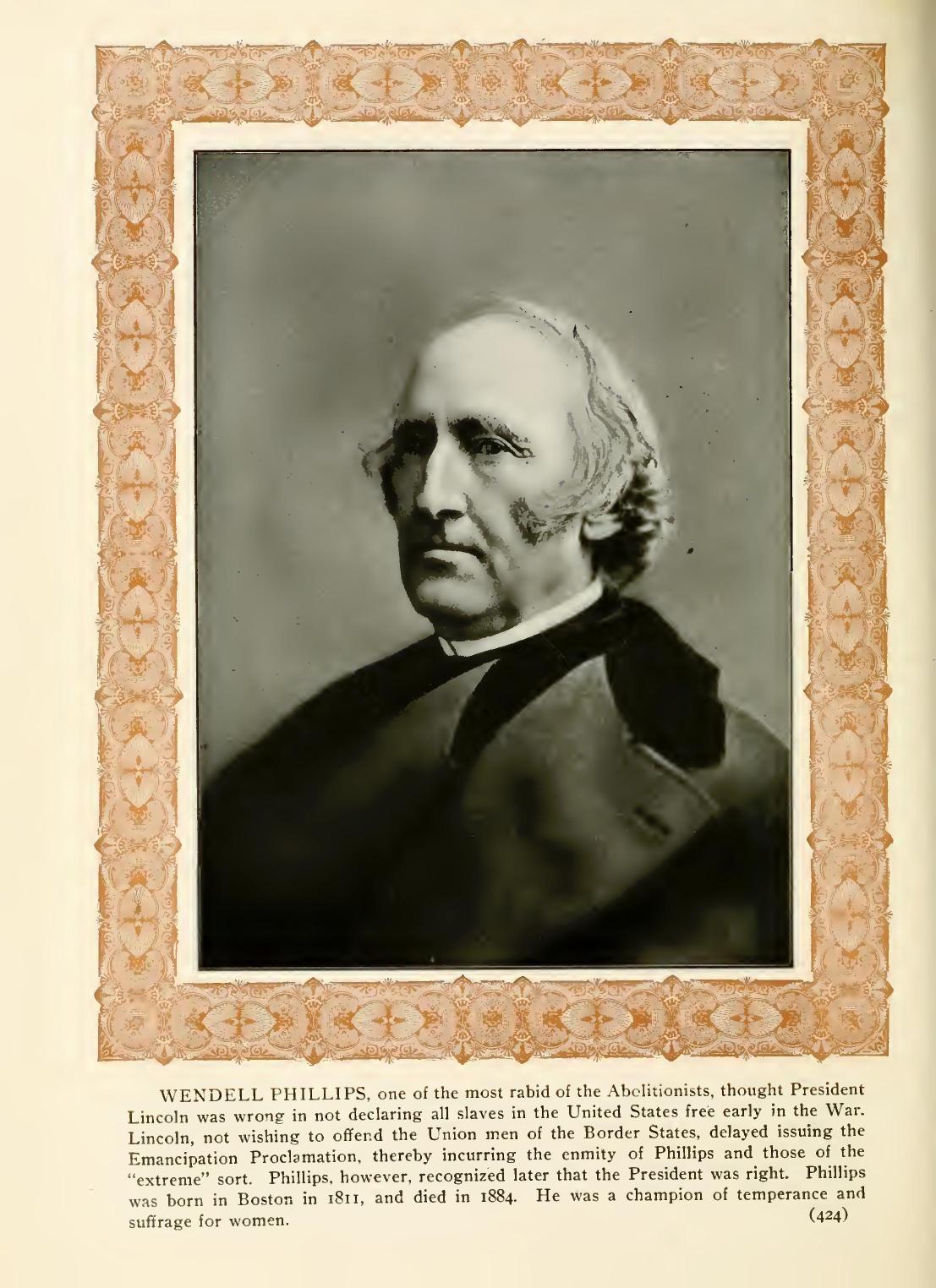




The President remarked to Admiral David D. Porter, while on board the flagship Malvern, on the James River, in front of Richmond, the day the city surrendered:
“Thank God that I have lived to see this!
“It seems to me that I have been dreaming a horrid dream for four years, and now the nightmare is gone.
“I wish to see Richmond.”
Frederick Douglass told, in these words, of his first interview with President Lincoln:
“I approached him with trepidation as to how this great man might receive me; but one word and look from him banished all my fears and set me perfectly at ease. I have often said since that meeting that it was much easier to see and converse with a great man than it was with a small man.
“On that occasion he said:
“‘Douglass, you need not tell me who you are. Mr. Seward has told me all about you.’
“I then saw that there was no reason to tell him my personal story, however interesting it might be to myself or others, so I told him at once the object of my visit. It was to get some expression from him upon three points:
“1. Equal pay to colored soldiers.
“2. Their promotion when they had earned it on the battle-field.
“3. Should they be taken prisoners and enslaved or hanged, as Jefferson Davis had threatened, an equal number of Confederate prisoners should be executed within our lines.
“A declaration to that effect I thought would prevent the execution of the rebel threat. To all but the last, President Lincoln assented. He argued, however, that neither equal pay nor promotion could be granted at once. He said that in view of existing prejudices it was a great step forward to employ colored troops at all; that it was necessary to avoid everything that would offend this prejudice and increase opposition to the measure.
“He detailed the steps by which white soldiers were reconciled to the employment of colored troops; how these were first employed as laborers; how it was thought they should not be armed or uniformed like white soldiers; how they should only be made to wear a peculiar uniform; how they should be employed to hold forts and arsenals in sickly locations, and not enter the field like other soldiers.
“With all these restrictions and limitations he easily made me see that much would be gained when the colored man loomed before the country as a full-fledged United States soldier to fight, flourish or fall in defense of the united republic. The great soul of Lincoln halted only when he came to the point of retaliation.
“The thought of hanging men in cold blood, even though the rebels should murder a few of the colored prisoners, was a horror from which he shrank.
“‘Oh, Douglass! I cannot do that. If I could get hold of the actual murderers of colored prisoners I would retaliate; but to hang those who have no hand in such murders, I cannot.’
“The contemplation of such an act brought to his countenance such an expression of sadness and pity that it made it hard for me to press my point, though I told him it would tend to save rather than destroy life. He, however, insisted that this work of blood, once begun, would be hard to stop—that such violence would beget violence. He argued more like a disciple of Christ than a commander-in-chief of the army and navy of a warlike nation already involved in a terrible war.
“How sad and strange the fate of this great and good man, the saviour of his country, the embodiment of human charity, whose heart, though strong, was as tender as a heart of childhood; who always tempered justice with mercy; who sought to supplant the sword with counsel of reason, to suppress passion by kindness and moderation; who had a sigh for every human grief and a tear for every human woe, should at last perish by the hand of a desperate assassin, against whom no thought of malice had ever entered his heart!”
One of the campaign songs of 1860 which will never be forgotten was Whittier’s “The Quakers Are Out:—”
| “Give the flags to the winds! |
| Set the hills all aflame! |
| Make way for the man with |
| The Patriarch’s name! |
| Away with misgivings—away |
| With all doubt, |
| For Lincoln goes in when the |
| Quakers are out!” |
Speaking of this song (with which he was greatly pleased) one day at the White House, the President said: “It reminds me of a little story I heard years ago out in Illinois. A political campaign was on, and the atmosphere was kept at a high temperature. Several fights had already occurred, many men having been seriously hurt, and the prospects were that the result would be close. One of the candidates was a professional politician with a huge wart on his nose, this disfigurement having earned for him the nickname of ‘Warty.’ His opponent was a young lawyer who wore ‘biled’ shirts, ‘was shaved by a barber, and had his clothes made to fit him.
“Now, ‘Warty’ was of Quaker stock, and around election time made a great parade of the fact. When there were no campaigns in progress he was anything but Quakerish in his language or actions. The young lawyer didn’t know what the inside of a meeting house looked like.
“Well, the night before election-day the two candidates came together at a joint debate, both being on the speakers’ platform. The young lawyer had to speak after ‘Warty,’ and his reputation suffered at the hands of the Quaker, who told the many Friends present what a wicked fellow the young man was—never went to church, swore, drank, smoked and gambled.
“After ‘Warty’ had finished the other arose and faced the audience. ‘I’m not a good man,’ said he, ‘and what my opponent has said about me is true enough, but I’m always the same. I don’t profess religion when I run for office, and then turn around and associate with bad people when the campaign’s over. I’m no hypocrite. I don’t sing many psalms. Neither does my opponent; and, talking about singing, I’d just like to hear my friend who is running against me sing the song—for the benefit of this audience—I heard him sing the night after he was nominated. I yield the floor to him:
“Of course ‘Warty’ refused, his Quaker supporters grew suspicious, and when they turned out at the polls the following day they voted for the wicked young lawyer.
“So, it’s true that when ‘the Quakers are out’ the man they support is apt to go in.”
“General Blank asks for more men,” said Secretary of War Stanton to the President one day, showing the latter a telegram from the commander named appealing for re-enforcements.
“I guess he’s killed off enough men, hasn’t he?” queried the President.
“I don’t mean Confederates—our own men. What’s the use in sending volunteers down to him if they’re only used to fill graves?”
“His dispatch seems to imply that, in his opinion, you have not the confidence in him he thinks he deserves,” the War Secretary went on to say, as he looked over the telegram again.
“Oh,” was the President’s reply, “he needn’t lose any of his sleep on that account. Just telegraph him to that effect; also, that I don’t propose to send him any more men.”
During the progress of a Cabinet meeting the subject of food for the men in the Army happened to come up. From that the conversation changed to the study of the Latin language.
“I studied Latin once,” said Mr. Lincoln, in a casual way.
“Were you interested in it?” asked Mr. Seward, the Secretary of State.
“Well, yes. I saw some very curious things,” was the President’s rejoinder.
“What?” asked Secretary Seward.
“Well, there’s the word hominy, for instance. We have just ordered a lot of that stuff for the troops. I see how the word originated. I notice it came from the Latin word homo—a man.
“When we decline homo, it is:
“‘Homo—a man.
“‘Hominis—of man.
“‘Homini—for man.’
“So you see, hominy, being ‘for man,’ comes from the Latin. I guess those soldiers who don’t know Latin will get along with it all right—though I won’t rest real easy until I hear from the Commissary Department on it.”
One day, while listening to one of the wise men who had called at the White House to unload a large cargo of advice, the President interjected a remark to the effect that he had a great reverence for learning.
“This is not,” President Lincoln explained, “because I am not an educated man. I feel the need of reading. It is a loss to a man not to have grown up among books.”
“Men of force,” the visitor answered, “can get on pretty well without books. They do their own thinking instead of adopting what other men think.”
“Yes,” said Mr. Lincoln, “but books serve to show a man that those original thoughts of his aren’t very new, after all.”
This was a point the caller was not willing to debate, and so he cut his call short.
Lincoln made his first speech when he was a mere boy, going barefoot, his trousers held up by one suspender, and his shock of hair sticking through a hole in the crown of his cheap straw hat.
“Abe,” in company with Dennis Hanks, attended a political meeting, which was addressed by a typical stump speaker—one of those loud-voiced fellows who shouted at the top of his voice and waved his arms wildly.
At the conclusion of the speech, which did not meet the views either of “Abe” or Dennis, the latter declared that “Abe” could make a better speech than that. Whereupon he got a dry-goods box and called on “Abe” to reply to the campaign orator.
Lincoln threw his old straw hat on the ground, and, mounting the dry-goods box, delivered a speech which held the attention of the crowd and won him considerable applause. Even the campaign orator admitted that it was a fine speech and answered every point in his own “oration.”
Dennis Hanks, who thought “Abe” was about the greatest man that ever lived, was delighted, and he often told how young “Abe” got the better of the trained campaign speaker.
It was in 1830, when “Abe” was just twenty-one years of age, that the Lincoln family moved from Gentryville, Indiana, to near Decatur, Illinois, their household goods being packed in a wagon drawn by four oxen driven by “Abe.”
The winter previous the latter had “worked” in a country store in Gentryville and before undertaking the journey he invested all the money he had—some thirty dollars—in notions, such as needles, pins, thread, buttons and other domestic necessities. These he sold to families along the route and made a profit of about one hundred per cent.
This mercantile adventure of his youth “reminded” the President of a very clever story while the members of the Cabinet were one day solemnly debating a rather serious international problem. The President was in the minority, as was frequently the case, and he was “in a hole,” as he afterwards expressed it. He didn’t want to argue the points raised, preferring to settle the matter in a hurry, and an apt story was his only salvation.
Suddenly the President’s fact brightened. “Gentlemen,” said he, addressing those seated at the Cabinet table, “the situation just now reminds me of a fix I got into some thirty years or so ago when I was peddling ‘notions’ on the way from Indiana to Illinois. I didn’t have a large stock, but I charged large prices, and I made money. Perhaps you don’t see what I am driving at?”
Secretary of State Seward was wearing a most gloomy expression of countenance; Secretary of War Stanton was savage and inclined to be morose; Secretary of the Treasury Chase was indifferent and cynical, while the others of the Presidential advisers resigned themselves to the hearing of the inevitable “story.”
“I don’t propose to argue this matter,” the President went on to say, “because arguments have no effect upon men whose opinions are fixed and whose minds are made up. But this little story of mine will make some things which now are in the dark show up more clearly.”
There was another pause, and the Cabinet officers, maintaining their previous silence, began wondering if the President himself really knew what he was “driving at.”
“Just before we left Indiana and crossed into Illinois,” continued Mr. Lincoln solemnly, speaking in a grave tone of voice, “we came across a small farmhouse full of nothing but children. These ranged in years from seventeen years to seventeen months, and all were in tears. The mother of the family was red-headed and red-faced, and the whip she held in her right hand led to the inference that she had been chastising her brood. The father of the family, a meek-looking, mild-mannered, tow-headed chap, was standing in the front door-way, awaiting—to all appearances—his turn to feel the thong.
“I thought there wasn’t much use in asking the head of that house if she wanted any ‘notions.’ She was too busy. It was evident an insurrection had been in progress, but it was pretty well quelled when I got there. The mother had about suppressed it with an iron hand, but she was not running any risks. She kept a keen and wary eye upon all the children, not forgetting an occasional glance at the ‘old man’ in the doorway.
“She saw me as I came up, and from her look I thought she was of the opinion that I intended to interfere. Advancing to the doorway, and roughly pushing her husband aside, she demanded my business.
“‘Nothing, madame,’ I answered as gently as possible; ‘I merely dropped in as I came along to see how things were going.’
“‘Well, you needn’t wait,’ was the reply in an irritated way; ‘there’s trouble here, an’ lots of it, too, but I kin manage my own affairs without the help of outsiders. This is jest a family row, but I’ll teach these brats their places ef I hev to lick the hide off ev’ry one of them. I don’t do much talkin’, but I run this house, an’ I don’t want no one sneakin’ round tryin’ to find out how I do it, either.’
“That’s the case here with us,” the President said in conclusion. “We must let the other nations know that we propose to settle our family row in our own way, and ‘teach these brats their places’ (the seceding States) if we have to ‘lick the hide off’ of each and every one of them. And, like the old woman, we don’t want any ‘sneakin’ ‘round’ by other countries who would like to find out how we are to do it, either.
“Now, Seward, you write some diplomatic notes to that effect.”
And the Cabinet session closed.
As the President considered it his duty to keep in touch with all the improvements in the armament of the vessels belonging to the United States Navy, he was necessarily interested in the various types of these floating fortresses. Not only was it required of the Navy Department to furnish seagoing warships, deep-draught vessels for the great rivers and the lakes, but this Department also found use for little gunboats which could creep along in the shallowest of water and attack the Confederates in by-places and swamps.
The consequence of the interest taken by Mr. Lincoln in the Navy was that he was besieged, day and night, by steamboat contractors, each one eager to sell his product to the Washington Government. All sorts of experiments were tried, some being dire failures, while others were more than fairly successful. More than once had these tiny war vessels proved themselves of great service, and the United States Government had a large number of them built.
There was one particular contractor who bothered the President more than all the others put together. He was constantly impressing upon Mr. Lincoln the great superiority of his boats, because they would run in such shallow water.
“Oh, yes,” replied the President, “I’ve no doubt they’ll run anywhere where the ground is a little moist!”
“It seems to me,” remarked the President one day while reading, over some of the appealing telegrams sent to the War Department by General McClellan, “that McClellan has been wandering around and has sort of got lost. He’s been hollering for help ever since he went South—wants somebody to come to his deliverance and get him out of the place he’s got into.
“He reminds me of the story of a man out in Illinois who, in company with a number of friends, visited the State penitentiary. They wandered all through the institution and saw everything, but just about the time to depart this particular man became separated from his friends and couldn’t find his way out.
“He roamed up and down one corridor after another, becoming more desperate all the time, when, at last, he came across a convict who was looking out from between the bars of his cell-door. Here was salvation at last. Hurrying up to the prisoner he hastily asked,
“‘Say! How do you get out of this place?”
President Lincoln often avoided interviews with delegations representing various States, especially when he knew the objects of their errands, and was aware he could not grant their requests. This was the case with several commissioners from Kentucky, who were put off from day to day.
They were about to give up in despair, and were leaving the White House lobby, their speech being interspersed with vehement and uncomplimentary terms concerning “Old Abe,” when “Tad” happened along. He caught at these words, and asked one of them if they wanted to see “Old Abe,” laughing at the same time.
“Yes,” he replied.
“Wait a minute,” said “Tad,” and rushed into his father’s office. Said he, “Papa, may I introduce some friends to you?”
His father, always indulgent and ready to make him happy, kindly said, “Yes, my son, I will see your friends.”
“Tad” went to the Kentuckians again, and asked a very dignified looking gentleman of the party his name. He was told his name. He then said, “Come, gentlemen,” and they followed him.
Leading them up to the President, “Tad,” with much dignity, said, “Papa, let me introduce to you Judge ——, of Kentucky;” and quickly added, “Now Judge, you introduce the other gentlemen.”
The introductions were gone through with, and they turned out to be the gentlemen Mr. Lincoln had been avoiding for a week. Mr. Lincoln reached for the boy, took him in his lap, kissed him, and told him it was all right, and that he had introduced his friend like a little gentleman as he was. Tad was eleven years old at this time.
The President was pleased with Tad’s diplomacy, and often laughed at the incident as he told others of it. One day while caressing the boy, he asked him why he called those gentlemen “his friends.” “Well,” said Tad, “I had seen them so often, and they looked so good and sorry, and said they were from Kentucky, that I thought they must be our friends.” “That is right, my son,” said Mr. Lincoln; “I would have the whole human race your friends and mine, if it were possible.”
The President told a story which most beautifully illustrated the muddled situation of affairs at the time McClellan’s fate was hanging in the balance. McClellan’s work was not satisfactory, but the President hesitated to remove him; the general was so slow that the Confederates marched all around him; and, to add to the dilemma, the President could not find a suitable man to take McClellan’s place.
The latter was a political, as well as a military, factor; his friends threatened that, if he was removed, many war Democrats would cast their influence with the South, etc. It was, altogether, a sad mix-up, and the President, for a time, was at his wits’ end. He was assailed on all sides with advice, but none of it was worth acting upon.
“This situation reminds me,” said the President at a Cabinet meeting one day not long before the appointment of General Halleck as McClellan’s successor in command of the Union forces, “of a Union man in Kentucky whose two sons enlisted in the Federal Army. His wife was of Confederate sympathies. His nearest neighbor was a Confederate in feeling, and his two sons were fighting under Lee. This neighbor’s wife was a Union woman and it nearly broke her heart to know that her sons were arrayed against the Union.
“Finally, the two men, after each had talked the matter over with his wife, agreed to obtain divorces; this they, did, and the Union man and Union woman were wedded, as were the Confederate man and the Confederate woman—the men swapped wives, in short. But this didn’t seem to help matters any, for the sons of the Union woman were still fighting for the South, and the sons of the Confederate woman continued in the Federal Army; the Union husband couldn’t get along with his Union wife, and the Confederate husband and his Confederate wife couldn’t agree upon anything, being forever fussing and quarreling.
“It’s the same thing with the Army. It doesn’t seem worth while to secure divorces and then marry the Army and McClellan to others, for they won’t get along any better than they do now, and there’ll only be a new set of heartaches started. I think we’d better wait; perhaps a real fighting general will come along some of these days, and then we’ll all be happy. If you go to mixing in a mix-up, you only make the muddle worse.”
George M. Pullman, the great sleeping-car builder, once told a joke in which Lincoln was the prominent figure. In fact, there wouldn’t have been any joke had it not been for “Long Abe.” At the time of the occurrence, which was the foundation for the joke—and Pullman admitted that the latter was on him—Pullman was the conductor of his only sleeping-car. The latter was an experiment, and Pullman was doing everything possible to get the railroads to take hold of it.
“One night,” said Pullman in telling the story, “as we were about going out of Chicago—this was long before Lincoln was what you might call a renowned man—a long, lean, ugly man, with a wart on his cheek, came into the depot. He paid me fifty cents, and half a berth was assigned him. Then he took off his coat and vest and hung them up, and they fitted the peg about as well as they fitted him. Then he kicked off his boots, which were of surprising length, turned into the berth, and, undoubtedly having an easy conscience, was sleeping like a healthy baby before the car left the depot.
“Pretty soon along came another passenger and paid his fifty cents. In two minutes he was back at me, angry as a wet hen.
“‘There’s a man in that berth of mine,’ said he, hotly, ‘and he’s about ten feet high. How am I going to sleep there, I’d like to know? Go and look at him.’
“In I went—mad, too. The tall, lank man’s knees were under his chin, his arms were stretched across the bed and his feet were stored comfortably—for him. I shook him until he awoke, and then told him if he wanted the whole berth he would have to pay $1.
“‘My dear sir,’ said the tall man, ‘a contract is a contract. I have paid you fifty cents for half this berth, and, as you see, I’m occupying it. There’s the other half,’ pointing to a strip about six inches wide. ‘Sell that and don’t disturb me again.’
“And so saying, the man with a wart on his face went to sleep again. He was Abraham Lincoln, and he never grew any shorter afterward. We became great friends, and often laughed over the incident.”
When the enemies of General Grant were bothering the President with emphatic and repeated demands that the “Silent Man” be removed from command, Mr. Lincoln remained firm. He would not consent to lose the services of so valuable a soldier. “Grant fights,” said he in response to the charges made that Grant was a butcher, a drunkard, an incompetent and a general who did not know his business.
“That reminds me of a story,” President Lincoln said one day to a delegation of the “Grant-is-no-good” style.
“Out in my State of Illinois there was a man nominated for sheriff of the county. He was a good man for the office, brave, determined and honest, but not much of an orator. In fact, he couldn’t talk at all; he couldn’t make a speech to save his life.
“His friends knew he was a man who would preserve the peace of the county and perform the duties devolving upon him all right, but the people of the county didn’t know it. They wanted him to come out boldly on the platform at political meetings and state his convictions and principles; they had been used to speeches from candidates, and were somewhat suspicious of a man who was afraid to open his mouth.
“At last the candidate consented to make a speech, and his friends were delighted. The candidate was on hand, and, when he was called upon, advanced to the front and faced the crowd. There was a glitter in his eye that wasn’t pleasing, and the way he walked out to the front of the stand showed that he knew just what he wanted to say.
“‘Feller Citizens,’ was his beginning, the words spoken quietly, ‘I’m not a speakin’ man; I ain’t no orator, an’ I never stood up before a lot of people in my life before; I’m not goin’ to make no speech, ‘xcept to say that I can lick any man in the crowd!’”

Charles E. Anthony’s one meeting with Mr. Lincoln presents an interesting contrast to those of the men who shared the emancipator’s interest in public affairs. It was in the latter part of the winter of 1861, a short time before Mr. Lincoln left for his inauguration at Washington. Judge Anthony went to the Sherman House, where the President-elect was stopping, and took with him his son, Charles, then but a little boy. Charles played about the room as a child will, looking at whatever interested him for the time, and when the interview with his father was over he was ready to go.
But Mr. Lincoln, ever interested in little children, called the lad to him and took him upon his great knee.
“My impression of him all the time I had been playing about the room,” said Mr. Anthony, “was that he was a terribly homely man. I was rather repelled. But no sooner did he speak to me than the expression of his face changed completely, or, rather, my view of it changed. It at once became kindly and attractive. He asked me some questions, seeming instantly to find in the turmoil of all the great questions that must have been heavy upon him, the very ones that would go to the thought of a child. I answered him without hesitation, and after a moment he patted my shoulder and said:
“‘Well, you’ll be a man before your mother yet,’ and put me down.
“I had never before heard the homely old expression, and it puzzled me for a time. After a moment I understood it, but he looked at me while I was puzzling over it, and seemed to be amused, as no doubt he was.”
The incident simply illustrates the ease and readiness with which Lincoln could turn from the mighty questions before the nation, give a moment’s interested attention to a child, and return at once to matters of state.
Donn Piatt, one of the brightest newspaper writers in the country, told a good story on the President in regard to the refusal of the latter to sanction the death penalty in cases of desertion from the Union Army.
“There was far more policy in this course,” said Piatt, “than kind feeling. To assert the contrary is to detract from Lincoln’s force of character, as well as intellect. Our War President was not lost in his high admiration of brigadiers and major-generals, and had a positive dislike for their methods and the despotism upon which an army is based. He knew that he was dependent upon volunteers for soldiers, and to force upon such men as those the stern discipline of the Regular Army was to render the service unpopular. And it pleased him to be the source of mercy, as well as the fountain of honor, in this direction.
“I was sitting with General Dan Tyler, of Connecticut, in the antechamber of the War Department, shortly after the adjournment of the Buell Court of Inquiry, of which we had been members, when President Lincoln came in from the room of Secretary Stanton. Seeing us, he said: ‘Well, gentlemen, have you any matter worth reporting?’
“‘I think so, Mr. President,’ replied General Tyler. ‘We had it proven that Bragg, with less than ten thousand men, drove your eighty-three thousand men under Buell back from before Chattanooga, down to the Ohio at Louisville, marched around us twice, then doubled us up at Perryville, and finally got out of the State of Kentucky with all his plunder.’
“‘Now, Tyler,’ returned the President, ‘what is the meaning of all this; what is the lesson? Don’t our men march as well, and fight as well, as these rebels? If not, there is a fault somewhere. We are all of the same family—same sort.’
“‘Yes, there is a lesson,’ replied General Tyler; ‘we are of the same sort, but subject to different handling. Bragg’s little force was superior to our larger number because he had it under control. If a man left his ranks, he was punished; if he deserted, he was shot. We had nothing of that sort. If we attempt to shoot a deserter you pardon him, and our army is without discipline.’
“The President looked perplexed. ‘Why do you interfere?’ continued General Tyler. ‘Congress has taken from you all responsibility.’
“‘Yes,’ answered the President impatiently, ‘Congress has taken the responsibility and left the women to howl all about me,’ and so he strode away.”
One of the droll stories brought into play by the President as an ally in support of his contention, proved most effective. Politics was rife among the generals of the Union Army, and there was more “wire-pulling” to prevent the advancement of fellow commanders than the laying of plans to defeat the Confederates in battle.
However, when it so happened that the name of a particularly unpopular general was sent to the Senate for confirmation, the protest against his promotion was almost unanimous. The nomination didn’t seem to please anyone. Generals who were enemies before conferred together for the purpose of bringing every possible influence to bear upon the Senate and securing the rejection of the hated leader’s name. The President was surprised. He had never known such unanimity before.
“You remind me,” said the President to a delegation of officers which called upon him one day to present a fresh protest to him regarding the nomination, “of a visit a certain Governor paid to the Penitentiary of his State. It had been announced that the Governor would hear the story of every inmate of the institution, and was prepared to rectify, either by commutation or pardon, any wrongs that had been done to any prisoner.
“One by one the convicts appeared before His Excellency, and each one maintained that he was an innocent man, who had been sent to prison because the police didn’t like him, or his friends and relatives wanted his property, or he was too popular, etc., etc. The last prisoner to appear was an individual who was not all prepossessing. His face was against him; his eyes were shifty; he didn’t have the appearance of an honest man, and he didn’t act like one.
“‘Well,’ asked the Governor, impatiently, ‘I suppose you’re innocent like the rest of these fellows?’
“‘No, Governor,’ was the unexpected answer; ‘I was guilty of the crime they charged against me, and I got just what I deserved.’
“When he had recovered from his astonishment, the Governor, looking the fellow squarely in the face, remarked with emphasis: ‘I’ll have to pardon you, because I don’t want to leave so bad a man as you are in the company of such innocent sufferers as I have discovered your fellow-convicts to be. You might corrupt them and teach them wicked tricks. As soon as I get back to the capital, I’ll have the papers made out.’
“You gentlemen,” continued the President, “ought to be glad that so bad a man, as you represent this officer to be, is to get his promotion, for then you won’t be forced to associate with him and suffer the contamination of his presence and influence. I will do all I can to have the Senate confirm him.”
And he was confirmed.
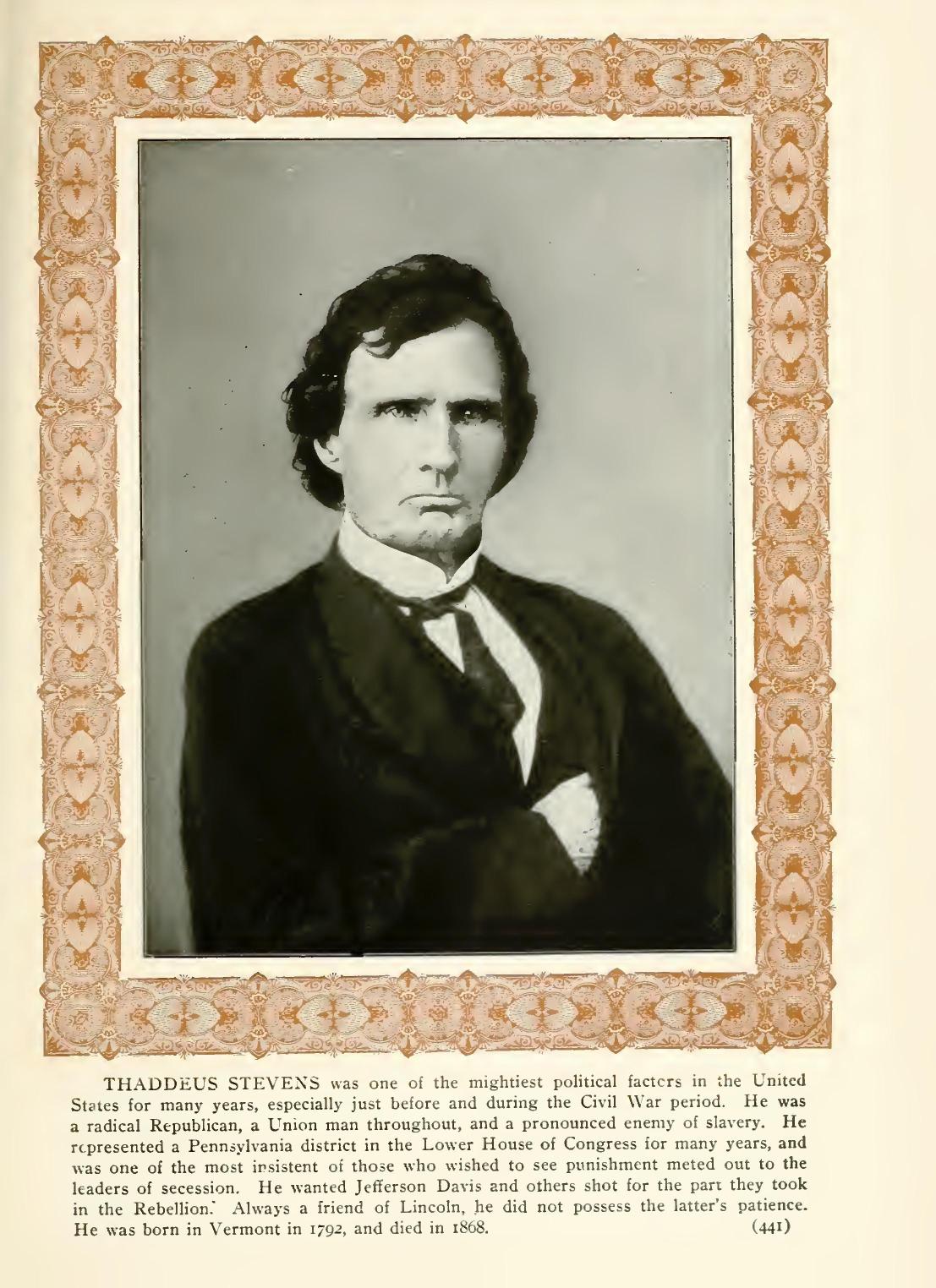
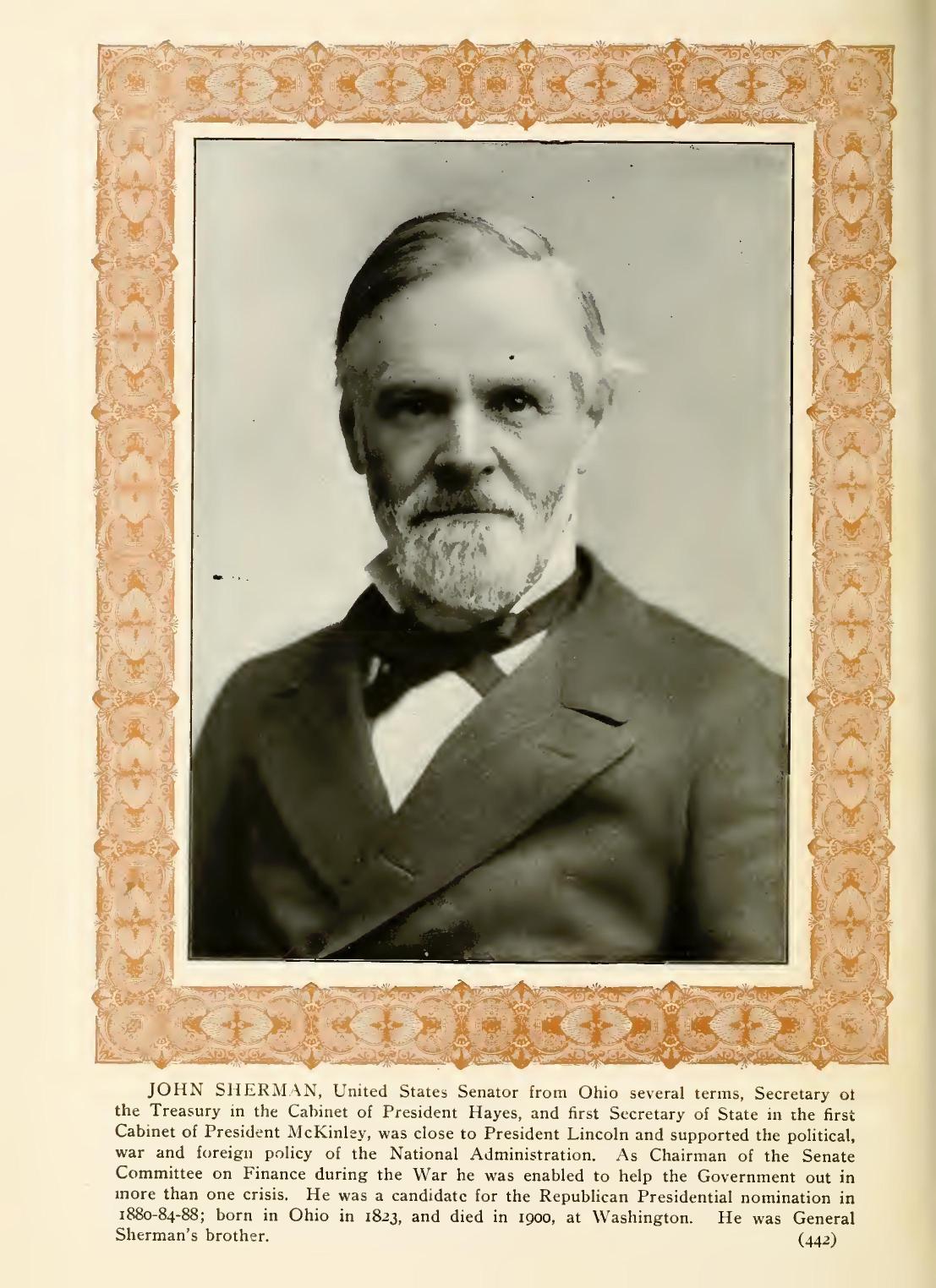




The President was often in opposition to the general public sentiment of the North upon certain questions of policy, but he bided his time, and things usually came out as he wanted them. It was Lincoln’s opinion, from the first, that apology and reparation to England must be made by the United States because of the arrest, upon the high seas, of the Confederate Commissioners, Mason and Slidell. The country, however (the Northern States), was wild for a conflict with England.
“One war at a time,” quietly remarked the President at a Cabinet meeting, where he found the majority of his advisers unfavorably disposed to “backing down.” But one member of the Cabinet was a really strong supporter of the President in his attitude.
“I am reminded,” the President said after the various arguments had been put forward by the members of the Cabinet, “of a fellow out in my State of Illinois who happened to stray into a church while a revival meeting was in progress. To be truthful, this individual was not entirely sober, and with that instinct which seems to impel all men in his condition to assume a prominent part in proceedings, he walked up the aisle to the very front pew.
“All noticed him, but he did not care; for awhile he joined audibly in the singing, said ‘Amen’ at the close of the prayers, but, drowsiness overcoming him, he went to sleep. Before the meeting closed, the pastor asked the usual question—‘Who are on the Lord’s side?’—and the congregation arose en masse. When he asked, ‘Who are on the side of the Devil?’ the sleeper was about waking up. He heard a portion of the interrogatory, and, seeing the minister on his feet, arose.
“‘I don’t exactly understand the question,’ he said, ‘but I’ll stand by you, parson, to the last. But it seems to me,’ he added, ‘that we’re in a hopeless minority.’
“I’m in a hopeless minority now,” said the President, “and I’ll have to admit it.”
John Morrissey, the noted prize fighter, was the “Boss” of Tammany Hall during the Civil War period. It pleased his fancy to go to Congress, and his obedient constituents sent him there. Morrissey was such an absolute despot that the New York City democracy could not make a move without his consent, and many of the Tammanyites were so afraid of him that they would not even enter into business ventures without consulting the autocrat.
President Lincoln had been seriously annoyed by some of his generals, who were afraid to make the slightest move before asking advice from Washington. One commander, in particular, was so cautious that he telegraphed the War Department upon the slightest pretext, the result being that his troops were lying in camp doing nothing, when they should have been in the field.
“This general reminds me,” the President said one day while talking to Secretary Stanton, at the War Department, “of a story I once heard about a Tammany man. He happened to meet a friend, also a member of Tammany, on the street, and in the course of the talk the friend, who was beaming with smiles and good nature, told the other Tammanyite that he was going to be married.
“This first Tammany man looked more serious than men usually do upon hearing of the impending happiness of a friend. In fact, his face seemed to take on a look of anxiety and worry.
“‘Ain’t you glad to know that I’m to get married?’ demanded the second Tammanyite, somewhat in a huff.
“‘Of course I am,’ was the reply; ‘but,’ putting his mouth close to the ear of the other, ‘have ye asked Morrissey yet?’
“Now, this general of whom we are speaking, wouldn’t dare order out the guard without asking Morrissey,” concluded the President.
At one time, when Lincoln and Douglas were “stumping” Illinois, they met at a certain town, and it was agreed that they would have a joint debate. Douglas was the first speaker, and in the course of his talk remarked that in early life, his father, who, he said, was an excellent cooper by trade, apprenticed him out to learn the cabinet business.
This was too good for Lincoln to let pass, so when his turn came to reply, he said:
“I had understood before that Mr. Douglas had been bound out to learn the cabinet-making business, which is all well enough, but I was not aware until now that his father was a cooper. I have no doubt, however, that he was one, and I am certain, also, that he was a very good one, for (here Lincoln gently bowed toward Douglas) he has made one of the best whiskey casks I have ever seen.”
As Douglas was a short heavy-set man, and occasionally imbibed, the pith of the joke was at once apparent, and most heartily enjoyed by all.
On another occasion, Douglas made a point against Lincoln by telling the crowd that when he first knew Lincoln he was a “grocery-keeper,” and sold whiskey, cigars, etc.
“Mr. L.,” he said, “was a very good bar-tender!” This brought the laugh on Lincoln, whose reply, however, soon came, and then the laugh was on the other side.
“What Mr. Douglas has said, gentlemen,” replied Lincoln, “is true enough; I did keep a grocery and I did sell cotton, candles and cigars, and sometimes whiskey; but I remember in those days that Mr. Douglas was one of my best customers.”
“I can also say this; that I have since left my side of the counter, while Mr. Douglas still sticks to his!”
This brought such a storm of cheers and laughter that Douglas was unable to reply.
Mrs. Lincoln knew her husband was not “pretty,” but she liked to have him presentable when he appeared before the public. Stephen Fiske, in “When Lincoln Was First Inaugurated,” tells of Mrs. Lincoln’s anxiety to have the President-elect “smoothed down” a little when receiving a delegation that was to greet them upon reaching New York City.
“The train stopped,” writes Mr. Fiske, “and through the windows immense crowds could be seen; the cheering drowning the blowing off of steam of the locomotive. Then Mrs. Lincoln opened her handbag and said:
“‘Abraham, I must fix you up a bit for these city folks.’
“Mr. Lincoln gently lifted her upon the seat before him; she parted, combed and brushed his hair and arranged his black necktie.
“‘Do I look nice now, mother?’ he affectionately asked.
“‘Well, you’ll do, Abraham,’ replied Mrs. Lincoln critically. So he kissed her and lifted her down from the seat, and turned to meet Mayor Wood, courtly and suave, and to have his hand shaken by the other New York officials.”
The Rev. Mr. Shrigley, of Philadelphia, a Universalist, had been nominated for hospital chaplain, and a protesting delegation went to Washington to see President Lincoln on the subject.
“We have called, Mr. President, to confer with you in regard to the appointment of Mr. Shrigley, of Philadelphia, as hospital chaplain.”
The President responded: “Oh, yes, gentlemen. I have sent his name to the Senate, and he will no doubt be confirmed at an early date.” One of the young men replied: “We have not come to ask for the appointment, but to solicit you to withdraw the nomination.”
“Ah!” said Lincoln, “that alters the case; but on what grounds do you wish the nomination withdrawn?”
The answer was: “Mr. Shrigley is not sound in his theological opinions.”
The President inquired: “On what question is the gentleman unsound?”
Response: “He does not believe in endless punishment; not only so, sir, but he believes that even the rebels themselves will be finally saved.”
“Is that so?” inquired the President.
The members of the committee responded, “Yes, yes.’
“Well, gentlemen, if that be so, and there is any way under Heaven whereby the rebels can be saved, then, for God’s sake and their sakes, let the man be appointed.”
The Rev. Mr. Shrigley was appointed, and served until the close of the war.
John M. Palmer, Major-General in the Volunteer Army, Governor of the State of Illinois, and United States Senator from the Sucker State, became acquainted with Lincoln in 1839, and the last time he saw the President was at the White House in February, 1865. Senator Palmer told the story of his interview as follows:
“I had come to Washington at the request of the Governor, to complain that Illinois had been credited with 18,000 too few troops. I saw Mr. Lincoln one afternoon, and he asked me to come again in the morning.
“Next morning I sat in the ante-room while several officers were relieved. At length I was told to enter the President’s room. Mr. Lincoln was in the hands of the barber.
“‘Come in, Palmer,’ he called out, ‘come in. You’re home folks. I can shave before you. I couldn’t before those others, and I have to do it some time.’
“We chatted about various matters, and at length I said:
“‘Well, Mr. Lincoln, if anybody had told me that in a great crisis like this the people were going out to a little one-horse town and pick out a one-horse lawyer for President I wouldn’t have believed it.’
“Mr. Lincoln whirled about in his chair, his face white with lather, a towel under his chin. At first I thought he was angry. Sweeping the barber away he leaned forward, and, placing one hand on my knee, said:
“‘Neither would I. But it was time when a man with a policy would have been fatal to the country. I have never had a policy. I have simply tried to do what seemed best each day, as each day came.’”
England was anything but pleased when the Czar Alexander, of Russia, showed his friendship for the United States by sending a strong fleet to this country with the accompanying suggestion that Uncle Sam, through his representative, President Lincoln, could do whatever he saw fit with the ironclads and the munitions of war they had stowed away in their holds.
London “Punch,” on November 7th, 1863, printed the cartoon shown on this page, the text under the picture reading in this way: “Holding a candle to the * * * * *.” (Much the same thing.)
Of course, this was a covert sneer, intended to convey the impression that President Lincoln, in order to secure the support and friendship of the Emperor of Russia as long as the War of the Rebellion lasted, was willing to do all sorts of menial offices, even to the extent of holding the candle and lighting His Most Gracious Majesty, the White Czar, to his imperial bed-chamber.
It is a somewhat remarkable fact that the Emperor Alexander, who tendered inestimable aid to the President of the United States, was the Lincoln of Russia, having given freedom to millions of serfs in his empire; and, further than that, he was, like Lincoln, the victim of assassination. He was literally blown to pieces by a bomb thrown under his carriage while riding through the streets near the Winter Palace at St. Petersburg.
“I was told a mighty good story,” said the President one day at a Cabinet meeting, “by Colonel Granville Moody, ‘the fighting Methodist parson,’ as they used to call him in Tennessee. I happened to meet Moody in Philadelphia, where he was attending a conference.
“The story was about ‘Andy’ Johnson and General Buell. Colonel Moody happened to be in Nashville the day it was reported that Buell had decided to evacuate the city. The rebels, strongly re-inforced, were said to be within two days’ march of the capital. Of course, the city was greatly excited. Moody said he went in search of Johnson at the edge of the evening and found him at his office closeted with two gentlemen, who were walking the floor with him, one on each side. As he entered they retired, leaving him alone with Johnson, who came up to him, manifesting intense feeling, and said:
“‘Moody, we are sold out. Buell is a traitor. He is going to evacuate the city, and in forty-eight hours we will all be in the hands of the rebels!’
“Then he commenced pacing the floor again, twisting his hands and chafing like a caged tiger, utterly insensible to his friend’s entreaties to become calm. Suddenly he turned and said:
“‘Moody, can you pray?’
“‘That is my business, sir, as a minister of the gospel,’ returned the colonel.
“‘Well, Moody, I wish you would pray,’ said Johnson, and instantly both went down upon their knees at opposite sides of the room.
“As the prayer waxed fervent, Johnson began to respond in true Methodist style. Presently he crawled over on his hands and knees to Moody’s side and put his arms over him, manifesting the deepest emotion.
“Closing the prayer with a hearty ‘amen’ from each, they arose.
“Johnson took a long breath, and said, with emphasis:
“‘Moody, I feel better.’
“Shortly afterward he asked:
“‘Will you stand by me?’
“‘Certainly I will,’ was the answer.
“‘Well, Moody, I can depend upon you; you are one in a hundred thousand.’
“He then commenced pacing the floor again. Suddenly he wheeled, the current of his thought having changed, and said:
“‘Oh, Moody, I don’t want you to think I have become a religious man because I asked you to pray. I am sorry to say it, I am not, and never pretended to be religious. No one knows this better than you, but, Moody, there is one thing about it, I do believe in Almighty God, and I believe also in the Bible, and I say, d—n me if Nashville shall be surrendered!’
“And Nashville was not surrendered!”
General Fisk, attending a reception at the White House, saw waiting in the ante-room a poor old man from Tennessee, and learned that he had been waiting three or four days to get an audience, on which probably depended the life of his son, under sentence of death for some military offense.
General Fisk wrote his case in outline on a card and sent it in, with a special request that the President would see the man. In a moment the order came; and past impatient senators, governors and generals, the old man went.
He showed his papers to Mr. Lincoln, who said he would look into the case and give him the result next day.
The old man, in an agony of apprehension, looked up into the President’s sympathetic face and actually cried out:
“To-morrow may be too late! My son is under sentence of death! It ought to be decided now!”
His streaming tears told how much he was moved.
“Come,” said Mr. Lincoln, “wait a bit and I’ll tell you a story;” and then he told the old man General Fisk’s story about the swearing driver, as follows:
“The general had begun his military life as a colonel, and when he raised his regiment in Missouri he proposed to his men that he should do all the swearing of the regiment. They assented; and for months no instance was known of the violation of the promise.
“The colonel had a teamster named John Todd, who, as roads were not always the best, had some difficulty in commanding his temper and his tongue.
“John happened to be driving a mule team through a series of mudholes a little worse than usual, when, unable to restrain himself any longer, he burst forth into a volley of energetic oaths.
“The colonel took notice of the offense and brought John to account.
“‘John,’ said he, ‘didn’t you promise to let me do all the swearing of the regiment?’
“‘Yes, I did, colonel,’ he replied, ‘but the fact was, the swearing had to be done then or not at all, and you weren’t there to do it.’”
As he told the story the old man forgot his boy, and both the President and his listener had a hearty laugh together at its conclusion.
Then he wrote a few words which the old man read, and in which he found new occasion for tears; but the tears were tears of joy, for the words saved the life of his son.
The President was heard to declare one day that the story given below was one of the funniest he ever heard.
One of General Fremont’s batteries of eight Parrott guns, supported by a squadron of horse commanded by Major Richards, was in sharp conflict with a battery of the enemy near at hand. Shells and shot were flying thick and fast, when the commander of the battery, a German, one of Fremont’s staff, rode suddenly up to the cavalry, exclaiming, in loud and excited terms, “Pring up de shackasses! Pring up de shackasses! For Cot’s sake, hurry up de shackasses, im-me-di-ate-ly!”
The necessity of this order, though not quite apparent, will be more obvious when it is remembered that “shackasses” are mules, carry mountain howitzers, which are fired from the backs of that much-abused but valuable animal; and the immediate occasion for the “shackasses” was that two regiments of rebel infantry were at that moment discovered ascending a hill immediately behind our batteries.
The “shackasses,” with the howitzers loaded with grape and canister, were soon on the ground.
The mules squared themselves, as they well knew how, for the shock.
A terrific volley was poured into the advancing column, which immediately broke and retreated.
Two hundred and seventy-eight dead bodies were found in the ravine next day, piled closely together as they fell, the effects of that volley from the backs of the “shackasses.”


Mr. Lincoln enjoyed a joke at his own expense. Said he: “In the days when I used to be in the circuit, I was accosted in the cars by a stranger, who said, ‘Excuse me, sir, but I have an article in my possession which belongs to you.’ ‘How is that?’ I asked, considerably astonished.
“The stranger took a jackknife from his pocket. ‘This knife,’ said he, ‘was placed in my hands some years ago, with the injunction that I was to keep it until I had found a man uglier than myself. I have carried it from that time to this. Allow me to say, sir, that I think you are fairly entitled to the property.’”
It so happened that an official of the War Department had escaped serious punishment for a rather flagrant offense, by showing where grosser irregularities existed in the management of a certain bureau of the Department. So valuable was the information furnished that the culprit who “gave the snap away” was not even discharged.
“That reminds me,” the President said, when the case was laid before him, “of a story about Daniel Webster, when the latter was a boy.
“When quite young, at school, Daniel was one day guilty of a gross violation of the rules. He was detected in the act, and called up by the teacher for punishment.
“This was to be the old-fashioned ‘feruling’ of the hand. His hands happened to be very dirty.
“Knowing this, on the way to the teacher’s desk, he spit upon the palm of his right hand, wiping it off upon the side of his pantaloons.
“‘Give me your hand, sir,’ said the teacher, very sternly.
“Out went the right hand, partly cleansed. The teacher looked at it a moment, and said:
“‘Daniel, if you will find another hand in this school-room as filthy as that, I will let you off this time!’
“Instantly from behind the back came the left hand.
“‘Here it is, sir,’ was the ready reply.
“‘That will do,’ said the teacher, ‘for this time; you can take your seat, sir.’”
The President did not consider that every soldier who ran away in battle, or did not stand firmly to receive a bayonet charge, was a coward. He was of opinion that self-preservation was the first law of Nature, but he didn’t want this statute construed too liberally by the troops.
At the same time he took occasion to illustrate a point he wished to make by a story in connection with a darky who was a member of the Ninth Illinois Infantry Regiment. This regiment was one of those engaged at the capture of Fort Donelson. It behaved gallantly, and lost as heavily as any.
“Upon the hurricane-deck of one of our gunboats,” said the President in telling the story, “I saw an elderly darky, with a very philosophical and retrospective cast of countenance, squatted upon his bundle, toasting his shins against the chimney, and apparently plunged into a state of profound meditation.
“As the negro rather interested me, I made some inquiries, and found that he had really been with the Ninth Illinois Infantry at Donelson. and began to ask him some questions about the capture of the place.
“‘Were you in the fight?’
“‘Had a little taste of it, sa.’
“‘Stood your ground, did you?’
“‘No, sa, I runs.’
“‘Run at the first fire, did you?
“‘Yes, sa, and would hab run soona, had I knowd it war comin’.”
“‘Why, that wasn’t very creditable to your courage.’
“‘Dat isn’t my line, sa—cookin’s my profeshun.’
“‘Well, but have you no regard for your reputation?’
“‘Reputation’s nuffin to me by de side ob life.’
“‘Do you consider your life worth more than other people’s?’
“‘It’s worth more to me, sa.’
“‘Then you must value it very highly?’
“‘Yes, sa, I does, more dan all dis wuld, more dan a million ob dollars, sa, for what would dat be wuth to a man wid de bref out ob him? Self-preserbation am de fust law wid me.’
“‘But why should you act upon a different rule from other men?’
“‘Different men set different values on their lives; mine is not in de market.’
“‘But if you lost it you would have the satisfaction of knowing that you died for your country.’
“‘Dat no satisfaction when feelin’s gone.’
“‘Then patriotism and honor are nothing to you?’
“‘Nufin whatever, sat—I regard them as among the vanities.’
“‘If our soldiers were like you, traitors might have broken up the government without resistance.’
“‘Yes, sa, dar would hab been no help for it. I wouldn’t put my life in de scale ‘g’inst any gobernment dat eber existed, for no gobernment could replace de loss to me.’
“‘Do you think any of your company would have missed you if you had been killed?’
“‘Maybe not, sa—a dead white man ain’t much to dese sogers, let alone a dead nigga—but I’d a missed myse’f, and dat was de p’int wid me.’
“I only tell this story,” concluded the President, “in order to illustrate the result of the tactics of some of the Union generals who would be sadly ‘missed’ by themselves, if no one else, if they ever got out of the Army.”
President Lincoln and some members of his Cabinet were with a part of the Army some distance south of the National Capital at one time, when Secretary of War Stanton remarked that just before he left Washington he had received a telegram from General Mitchell, in Alabama. General Mitchell asked instructions in regard to a certain emergency that had arisen.
The Secretary said he did not precisely understand the emergency as explained by General Mitchell, but had answered back, “All right; go ahead.”
“Now,” he said, as he turned to Mr. Lincoln, “Mr. President, if I have made an error in not understanding him correctly, I will have to get you to countermand the order.”
“Well,” exclaimed President Lincoln, “that is very much like the happening on the occasion of a certain horse sale I remember that took place at the cross-roads down in Kentucky, when I was a boy.
“A particularly fine horse was to be sold, and the people in large numbers had gathered together. They had a small boy to ride the horse up and down while the spectators examined the horse’s points.
“At last one man whispered to the boy as he went by: ‘Look here, boy, hain’t that horse got the splints?’
“The boy replied: ‘Mister, I don’t know what the splints is, but if it’s good for him, he has got it; if it ain’t good for him, he ain’t got it.’
“Now,” said President Lincoln, “if this was good for Mitchell, it was all right; but if it was not, I have got to countermand it.”
There were strange, queer, odd things and happenings in the Army at times, but, as a rule, the President did not allow them to worry him. He had enough to bother about.
A quartermaster having neglected to present his accounts in proper shape, and the matter being deemed of sufficient importance to bring it to the attention of the President, the latter remarked:
“Now this instance reminds me of a little story I heard only a short time ago. A certain general’s purse was getting low, and he said it was probable he might be obliged to draw on his banker for some money.
“‘How much do you want, father?’ asked his son, who had been with him a few days.
“‘I think I shall send for a couple of hundred,’ replied the general.
“Why, father,’ said his son, very quietly, ‘I can let you have it.’
“‘You can let me have it! Where did you get so much money?
“‘I won it playing draw-poker with your staff, sir!’ replied the youth.
“The earliest morning train bore the young man toward his home, and I’ve been wondering if that boy and that quartermaster had happened to meet at the same table.”
Governor Hoyt of Wisconsin tells a story of Mr. Lincoln’s great admiration for physical strength. Mr. Lincoln, in 1859, made a speech at the Wisconsin State Agricultural Fair. After the speech, in company with the Governor, he strolled about the grounds, looking at the exhibits. They came to a place where a professional “strong man” was tossing cannon balls in the air and catching them on his arms and juggling with them as though they were light as baseballs. Mr. Lincoln had never before seen such an exhibition, and he was greatly surprised and interested.
When the performance was over, Governor Hoyt, seeing Mr. Lincoln’s interest, asked him to go up and be introduced to the athlete. He did so, and, as he stood looking down musingly on the man, who was very short, and evidently wondering that one so much smaller than he could be so much stronger, he suddenly broke out with one of his quaint speeches. “Why,” he said, “why, I could lick salt off the top of your hat.”
A prominent volunteer officer who, early in the War, was on duty in Washington and often carried reports to Secretary Stanton at the War Department, told a characteristic story on President Lincoln. Said he:
“I was with several other young officers, also carrying reports to the War Department, and one morning we were late. In this instance we were in a desperate hurry to deliver the papers, in order to be able to catch the train returning to camp.
“On the winding, dark staircase of the old War Department, which many will remember, it was our misfortune, while taking about three stairs at a time, to run a certain head like a catapult into the body of the President, striking him in the region of the right lower vest pocket.
“The usual surprised and relaxed grunt of a man thus assailed came promptly.
“We quickly sent an apology in the direction of the dimly seen form, feeling that the ungracious shock was expensive, even to the humblest clerk in the department.
“A second glance revealed to us the President as the victim of the collision. Then followed a special tender of ‘ten thousand pardons,’ and the President’s reply:
“‘One’s enough; I wish the whole army would charge like that.’”
“You can’t do anything with them Southern fellows,” the old man at the table was saying.
“If they get whipped, they’ll retreat to them Southern swamps and bayous along with the fishes and crocodiles. You haven’t got the fish-nets made that’ll catch ‘em.”
“Look here, old gentleman,” remarked President Lincoln, who was sitting alongside, “we’ve got just the nets for traitors, in the bayous or anywhere.”
“Hey? What nets?”
“Bayou-nets!” and “Uncle Abraham” pointed his joke with his fork, spearing a fishball savagely.
Mr. Lincoln’s skill in parrying troublesome questions was wonderful. Once he received a call from Congressman John Ganson, of Buffalo, one of the ablest lawyers in New York, who, although a Democrat, supported all of Mr. Lincoln’s war measures. Mr. Ganson wanted explanations. Mr. Ganson was very bald with a perfectly smooth face. He had a most direct and aggressive way of stating his views or of demanding what he thought he was entitled to. He said: “Mr. Lincoln, I have supported all of your measures and think I am entitled to your confidence. We are voting and acting in the dark in Congress, and I demand to know—think I have the right to ask and to know—what is the present situation, and what are the prospects and conditions of the several campaigns and armies.”
Mr. Lincoln looked at him critically for a moment and then said: “Ganson, how clean you shave!”
Most men would have been offended, but Ganson was too broad and intelligent a man not to see the point and retire at once, satisfied, from the field.
Chauncey M. Depew says that Mr. Lincoln told him the following story, which he claimed was one of the best two things he ever originated: He was trying a case in Illinois where he appeared for a prisoner charged with aggravated assault and battery. The complainant had told a horrible story of the attack, which his appearance fully justified, when the District Attorney handed the witness over to Mr. Lincoln, for cross-examination. Mr. Lincoln said he had no testimony, and unless he could break down the complainant’s story he saw no way out. He had come to the conclusion that the witness was a bumptious man, who rather prided himself upon his smartness in repartee and, so, after looking at him for some minutes, he said:
“Well, my friend, how much ground did you and my client here fight over?”
The fellow answered: “About six acres.”
“Well,” said Mr. Lincoln, “don’t you think that this is an almighty small crop of fight to gather from such a big piece of ground?”
The jury laughed. The Court and District-Attorney and complainant all joined in, and the case was laughed out of court.
A simple remark one of the party might make would remind Mr. Lincoln of an apropos story.
Secretary of the Treasury Chase happened to remark, “Oh, I am so sorry that I did not write a letter to Mr. So-and-so before I left home!”
President Lincoln promptly responded:
“Chase, never regret what you don’t write; it is what you do write that you are often called upon to feel sorry for.”
In an interview between President Lincoln and Petroleum V. Nasby, the name came up of a recently deceased politician of Illinois whose merit was blemished by great vanity. His funeral was very largely attended.
“If General —— had known how big a funeral he would have had,” said Mr. Lincoln, “he would have died years ago.”
A Senator, who was calling upon Mr. Lincoln, mentioned the name of a most virulent and dishonest official; one, who, though very brilliant, was very bad.
“It’s a good thing for B——” said Mr. Lincoln, “that there is such a thing as a deathbed repentance.”
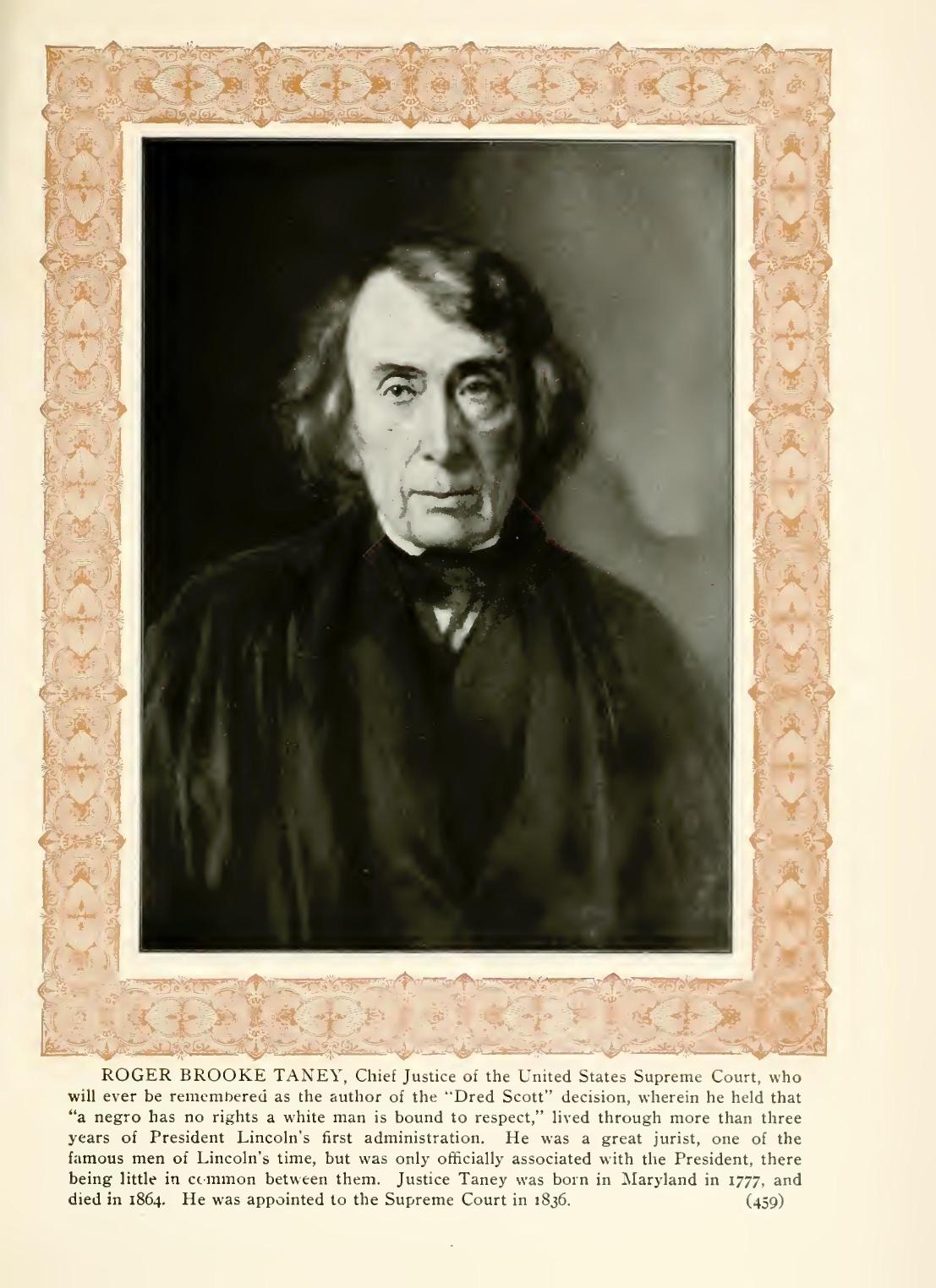




A member of Congress from Ohio came into Mr. Lincoln’s presence in a state of unutterable intoxication, and sinking into a chair, exclaimed in tones that welled up fuzzy through the gallon or more of whiskey that he contained, “Oh, ‘why should (hic) the spirit of mortal be proud?’”
“My dear sir,” said the President, regarding him closely, “I see no reason whatever.”
When Abraham Lincoln once was asked to tell the story of his life, he replied:
“It is contained in one line of Gray’s ‘Elegy in a Country Churchyard’:
“‘The short and simple annals of the poor.’”
That was true at the time he said it, as everything else he said was Truth, but he was then only at the beginning of a career that was to glorify him as one of the heroes of the world, and place his name forever beside the immortal name of the mighty Washington.
Many great men, particularly those of America, began life in humbleness and poverty, but none ever came from such depths or rose to such a height as Abraham Lincoln.
His birthplace, in Hardin county, Kentucky, was but a wilderness, and Spencer county, Indiana, to which the Lincoln family removed when Abraham was in his eighth year, was a wilder and still more uncivilized region.
The little red schoolhouse which now so thickly adorns the country hillside had not yet been built. There were scattered log schoolhouses, but they were few and far between. In several of these Mr. Lincoln got the rudiments of an education—an education that was never finished, for to the day of his death he was a student and a seeker after knowledge.
Some records of his schoolboy days are still left us. One is a book made and bound by Lincoln himself, in which he had written the table of weights and measures, and the sums to be worked out therefrom. This was his arithmetic, for he was too poor to own a printed copy.
On one of the pages of this quaint book he had written these four lines of schoolboy doggerel:
| “Abraham Lincoln, |
| His Hand and Pen, |
| He Will be Good, |
| But God knows when.” |
The poetic spirit was strong in the young scholar just then for on another page of the same book he had written these two verses, which are supposed to have been original with him:
| “Time, what an empty vapor ‘tis, |
| And days, how swift they are; |
| Swift as an Indian arrow |
| Fly on like a shooting star. |
| The present moment just is here, |
| Then slides away in haste, |
| That we can never say they’re ours, |
| But only say they’re past.” |
Another specimen of the poetical, or rhyming ability, is found in the following couplet, written by him for his friend, Joseph C. Richardson:
| “Good boys who to their books apply, |
| Will all be great men by and by.” |
In all, Lincoln’s “schooling” did not amount to a year’s time, but he was a constant student outside of the schoolhouse. He read all the books he could borrow, and it was his chief delight during the day to lie under the shade of some tree, or at night in front of an open fireplace, reading and studying. His favorite books were the Bible and Aesop’s fables, which he kept always within reach and read time and again.
The first law book he ever read was “The Statutes of Indiana,” and it was from this work that he derived his ambition to be a lawyer.
When he was but a barefoot boy he would often make political speeches to the boys in the neighborhood, and when he had reached young manhood and was engaged in the labor of chopping wood or splitting rails he continued this practice of speech-making with only the stumps and surrounding trees for hearers.
At the age of seventeen he had attained his full height of six feet four inches and it was at this time he engaged as a ferry boatman on the Ohio river, at thirty-seven cents a day.
That he was seriously beginning to think of public affairs even at this early age is shown by the fact that about this time he wrote a composition on the American Government, urging the necessity for preserving the Constitution and perpetuating the Union. A Rockport lawyer, by the name of Pickert, who read this composition, declared that “the world couldn’t beat it.”
When the dreaded disease, known as the “milk-sick” created such havoc in Indiana in 1829, the father of Abraham Lincoln, who was of a roving disposition, sought and found a new home in Illinois, locating near the town of Decatur, in Macon county, on a bluff overlooking the Sangamon river. A short time thereafter Abraham Lincoln came of age, and having done his duty to his father, began life on his own account.
His first employer was a man named Denton Offut, who engaged Lincoln, together with his step-brother and John Hanks, to take a boat-load of stock and provisions to New Orleans. Offut was so well pleased with the energy and skill that Lincoln displayed on this trip that he engaged him as clerk in a store which Offut opened a few months later at New Salem.
It was while clerking for Offut that Lincoln performed many of those marvelous feats of strength for which he was noted in his youth, and displayed his wonderful skill as a wrestler. In addition to being six feet four inches high he now weighed two hundred and fourteen pounds. And his strength and skill were so great combined that he could out-wrestle and out-lift any man in that section of the country.
During his clerkship in Offut’s store Lincoln continued to read and study and made considerable progress in grammar and mathematics. Offut failed in business and disappeared from the village. In the language of Lincoln he “petered out,” and his tall, muscular clerk had to seek other employment.
In his first public speech, which had already been delivered, Lincoln had contended that the Sangamon river was navigable, and it now fell to his lot to assist in giving practical proof of his argument. A steamboat had arrived at New Salem from Cincinnati, and Lincoln was hired as an assistant in piloting the vessel through the uncertain channel of the Sangamon river to the Illinois river. The way was obstructed by a milldam. Lincoln insisted to the owners of the dam that under the Federal Constitution and laws no one had a right to dam up or obstruct a navigable stream and as he had already proved that the Sangamon was navigable a portion of the dam was torn away and the boat passed safely through.
At this period in his career the Blackhawk War broke out, and Lincoln was one of the first to respond to Governor Reynold’s call for a thousand mounted volunteers to assist the United States troops in driving Blackhawk back across the Mississippi. Lincoln enlisted in the company from Sangamon county and was elected captain. He often remarked that this gave him greater pleasure than anything that had happened in his life up to this time. He had, however, no opportunities in this war to perform any distinguished service.
Upon his return from the Blackhawk War, in which, as he said afterward, in a humorous speech, when in Congress, that he “fought, bled and came away,” he was an unsuccessful candidate for the Legislature. This was the only time in his life, as he himself has said, that he was ever beaten by the people. Although defeated, in his own town of New Salem he received all of the two hundred and eight votes cast except three.
Lincoln’s next business venture was with William Berry in a general store, under the firm name of Lincoln & Berry, but did not take long to show that he was not adapted for a business career. The firm failed, Berry died and the debts of the firm fell entirely upon Lincoln. Many of these debts he might have escaped legally, but he assumed them all and it was not until fifteen years later that the last indebtedness of Lincoln & Berry was discharged. During his membership in this firm he had applied himself to the study of law, beginning at the beginning, that is with Blackstone. Now that he had nothing to do he spent much of his time lying under the shade of a tree poring over law books, borrowed from a comrade in the Blackhawk War, who was then a practicing lawyer at Springfield.


It was about this time, too, that Lincoln’s fame as a story-teller began to spread far and wide. His sayings and his jokes were repeated throughout that section of the country, and he was famous as a story-teller before anyone ever heard of him as a lawyer or a politician.
It required no little moral courage to resist the temptation that beset an idle young man on every hand at that time, for drinking and carousing were of daily and nightly occurrence. Lincoln never drank intoxicating liquors, nor did he at that time use tobacco, but in any sports that called for skill or muscle he took a lively interest, even in horse races and cock fights.
John Calhoun was at that time surveyor of Sangamon county. He had been a lawyer and had noticed the studious Lincoln. Needing an assistant he offered the place to Lincoln. The average young man without any regular employment and hard-pressed for means to pay his board as Lincoln was, would have jumped at the opportunity, but a question of principle was involved which had to be settled before Lincoln would accept. Calhoun was a Democrat and Lincoln was a Whig, therefore Lincoln said, “I will take the office if I can be perfectly free in my political actions, but if my sentiments or even expression of them are to be abridged in any way, I would not have it or any other office.”
With this understanding he accepted the office and began to study books on surveying, furnished him by his employer. He was not a natural mathematician, and in working out his most difficult problems he sought the assistance of Mentor Graham, a famous schoolmaster in those days, who had previously assisted Lincoln in his studies. He soon became a competent surveyor, however, and was noted for the accurate way in which he ran his lines and located his corners.
Surveying was not as profitable then as it has since become, and the young surveyor often had to take his pay in some article other than money. One old settler relates that for a survey made for him by Lincoln he paid two buckskins, which Hannah Armstrong “foxed” on his pants so that the briars would not wear them out.
About this time, 1833, he was made postmaster at New Salem, the first Federal office he ever held. Although the postoffice was located in a store, Lincoln usually carried the mail around in his hat and distributed it to people when he met them.
The following year Lincoln again ran for the Legislature, this time as an avowed Whig. Of the four successful candidates, Lincoln received the second highest number of votes.
When Lincoln went to take his seat in the Legislature at Vandalia he was so poor that he was obliged to borrow $200 to buy suitable clothes and uphold the dignity of his new position. He took little part in the proceedings, keeping in the background, but forming many lasting acquaintances and friendships.
Two years later, when he was again a candidate for the same office, there were more political issues to be met, and Lincoln met them with characteristic honesty and boldness. During the campaign he issued the following letter:
“New Salem, June 13, 1836.
“To the Editor of The Journal:
“In your paper of last Saturday I see a communication over the signature of ‘Many Voters’ in which the candidates who are announced in the journal are called upon to ‘show their hands.’ Agreed. Here’s mine:
“I go for all sharing the privileges of the government who assist in bearing its burdens. Consequently, I go for admitting all whites to the right of suffrage who pay taxes or bear arms (by no means excluding females).
“If elected, I shall consider the whole people of Sangamon my constituents, as well those that oppose as those that support me.
“While acting as their Representative, I shall be governed by their will on all subjects upon which I have the means of knowing what their will is; and upon all others I shall do what my own judgment teaches me will best advance their interests. Whether elected or not, I go for distributing the proceeds of the sales of public lands to the several States to enable our State, in common with others, to dig canals and construct railroads without borrowing money and paying the interest on it.
“If alive on the first Monday in November, I shall vote for Hugh L. White, for President.
“Very respectfully,
“A. LINCOLN.”
This was just the sort of letter to win the support of the plain-spoken voters of Sangamon county. Lincoln not only received more votes than any other candidate on the Legislative ticket, but the county which had always been Democratic was turned Whig.
The other candidates elected with Lincoln were Ninian W. Edwards, John Dawson, Andrew McCormick, “Dan” Stone, William F. Elkin, Robert L. Wilson, “Joe” Fletcher, and Archer G. Herndon. These were known as the “Long Nine.” Their average height was six feet, and average weight two hundred pounds.
This Legislature was one of the most famous that ever convened in Illinois. Bonds to the amount of $12,000,000 were voted to assist in building thirteen hundred miles of railroad, to widen and deepen all the streams in the State and to dig a canal from the Illinois river to Lake Michigan. Lincoln favored all these plans, but in justice to him it must be said that the people he represented were also in favor of them.
It was at this session that the State capital was changed from Vandalia to Springfield. Lincoln, as the leader of the “Long Nine,” had charge of the bill and after a long and bitter struggle succeeded in passing it.
At this early stage in his career Abraham Lincoln began his opposition to slavery which eventually resulted in his giving liberty to four million human beings. This Legislature passed the following resolutions on slavery:
“Resolved by the General Assembly, of the State of Illinois: That we highly disapprove of the formation of Abolition societies and of the doctrines promulgated by them.
“That the right of property in slaves is sacred to the slave-holding States by the Federal Constitution, and that they cannot be deprived of that right without their consent,
“That the General Government cannot abolish slavery in the District of Columbia against the consent of the citizens of said district without a manifest breach of good faith.”
Against this resolution Lincoln entered a protest, but only succeeded in getting one man in the Legislature to sign the protest with him.
The protest was as follows:
“Resolutions upon the subject of domestic slavery having passed both branches of the General Assembly at its present session, the undersigned hereby protest against the passage of the same.
“They believe that the institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy, but that the promulgation of abolition doctrines tends rather to increase than abate its evils.
“They believe that the Congress of the United States has no power under the Constitution to interfere with the institution of slavery in the different States.
“They believe that the Congress of the United States has the power under the Constitution to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, but that the power ought not to be exercised unless at the request of the people of the District.
“The difference between these opinions and those contained in the above resolutions is their reason for entering this protest.
“DAN STONE, “A. LINCOLN,
“Representatives from the county of Sangamon.”
At the end of this session of the Legislature, Mr. Lincoln decided to remove to Springfield and practice law. He entered the office of John T. Stuart, a former comrade in the Blackhawk War, and in March, 1837, was licensed to practice.
Stephen T. Logan was judge of the Circuit Court, and Stephen A. Douglas, who was destined to become Lincoln’s greatest political opponent, was prosecuting attorney. When Lincoln was not in his law office his headquarters were in the store of his friend Joshua F. Speed, in which gathered all the youthful orators and statesmen of that day, and where many exciting arguments and discussions were held. Lincoln and Douglas both took part in the discussion held in Speed’s store. Douglas was the acknowledged leader of the Democratic side and Lincoln was rapidly coming to the front as a leader among the Whig debaters. One evening in the midst of a heated argument Douglas, or “the Little Giant,” as he was called, exclaimed:
“This store is no place to talk politics.”
Arrangements were at once made for a joint debate between the leading Democrats and Whigs to take place in a local church. The Democrats were represented by Douglas, Calhoun, Lamborn and Thomas. The Whig speakers were Judge Logan, Colonel E. D. Baker, Mr. Browning and Lincoln. This discussion was the forerunner of the famous joint-debate between Lincoln and Douglas, which took place some years later and attracted the attention of the people throughout the United States. Although Mr. Lincoln was the last speaker in the first discussion held, his speech attracted more attention than any of the others and added much to his reputation as a public debater.
Mr. Lincoln’s last campaign for the Legislature was in 1840. In the same year he was made an elector on the Harrison presidential ticket, and in his canvass of the State frequently met the Democratic champion, Douglas, in debate. After 1840 Mr. Lincoln declined re-election to the Legislature, but he was a presidential elector on the Whig tickets of 1844 and 1852, and on the Republican ticket for the State at large in 1856.
Among the social belles of Springfield was Mary Todd, a handsome and cultivated girl of the illustrious descent which could be traced back to the sixth century, to whom Mr. Lincoln was married in 1842. Stephen A. Douglas was his competitor in love as well as in politics. He courted Mary Todd until it became evident that she preferred Mr. Lincoln.
Previous to his marriage Mr. Lincoln had two love affairs, one of them so serious that it left an impression upon his whole future life. One of the objects of his affection was Miss Mary Owen, of Green county, Kentucky, who decided that Mr. Lincoln “was deficient in those little links which make up the chain of woman’s happiness.” The affair ended without any damage to Mr. Lincoln’s heart or the heart of the lady.
Lincoln’s first love, however, had a sad termination. The object of his affections at that time was Anne Rutledge, whose father was one of the founders of New Salem. Like Miss Owen, Miss Rutledge was also born in Kentucky, and was gifted with the beauty and graces that distinguish many Southern women. At the time that Mr. Lincoln and Anne Rutledge were engaged to be married, he thought himself too poor to properly support a wife, and they decided to wait until such time as he could better his financial condition. A short time thereafter Miss Rutledge was attacked with a fatal illness, and her death was such a blow to her intended husband that for a long time his friends feared that he would lose his mind.
Just previous to his marriage with Mary Todd, Mr. Lincoln was challenged to fight a duel by James Shields, then Auditor of State. The challenge grew out of some humorous letters concerning Shields, published in a local paper. The first of these letters was written by Mr. Lincoln. The others by Mary Todd and her sister. Mr. Lincoln acknowledged the authorship of the letters without naming the ladies, and agreed to meet Shields on the field of honor. As he had the choice of weapons he named broadswords, and actually went to the place selected for the duel.
The duel was never fought. Mutual friends got together and patched up an understanding between Mr. Lincoln and the hot-headed Irishman.


Before this time Mr. Lincoln had dissolved partnership with Stuart and entered into a law partnership with Judge Logan. In 1843 both Lincoln and Logan were candidates for nomination for Congress and the personal ill-will caused by their rivalry resulted in the dissolution of the firm and the formation of a new law firm of Lincoln & Herndon, which continued, nominally at least, until Mr. Lincoln’s death.
The congressional nomination, however, went to Edward D. Baker, who was elected. Two years later the principal candidates for the Whig nomination for Congress were Mr. Lincoln and his former law partner, Judge Logan. Party sentiment was so strongly in favor of Lincoln that Judge Logan withdrew and Lincoln was nominated unanimously. The campaign that followed was one of the most memorable and interesting ever held in Illinois.
Mr. Lincoln’s opponent on the Democratic ticket was no less a person than old Peter Cartwright, the famous Methodist preacher and circuit rider. Cartwright had preached to almost every congregation in the district and had a strong following in all the churches. Mr. Lincoln did not underestimate the strength of his great rival. He abandoned his law business entirely and gave his whole attention to the canvass. This time Mr. Lincoln was victorious and was elected by a large majority.
When Lincoln took his seat in Congress, in 1847, he was the only Whig member from Illinois. His great political rival, Douglas, was in the Senate. The Mexican War had already broken out, which, in common with his party, he had opposed. Later in life he was charged with having opposed the voting of supplies to the American troops in Mexico, but this was a falsehood which he easily disproved. He was strongly opposed to the War, but after it was once begun he urged its vigorous prosecution and voted with the Democrats on all measures concerning the care and pay of the soldiers. His opposition to the War, however, cost him a re-election; it cost his party the congressional district, which was carried by the Democrats in 1848. Lincoln’s former law partner, Judge Logan, secured the Whig nomination that year and was defeated.
In the national convention at Philadelphia, in 1848, Mr. Lincoln was a delegate and advocated the nomination of General Taylor.
After the nomination of General Taylor, or “Old Zach,” or “rough and Ready,” as he was called, Mr. Lincoln made a tour of New York and several New England States, making speeches for his candidate.
Mr. Lincoln went to New England in this campaign on account of the great defection in the Whig party. General Taylor’s nomination was unsatisfactory to the free-soil element, and such leaders as Henry Wilson, Charles Francis Adams, Charles Allen, Charles Sumner, Stephen C. Phillips, Richard H. Dana, Jr., and Anson Burlingame, were in open revolt. Mr. Lincoln’s speeches were confined largely to a defense of General Taylor, but at the same time he denounced the free-soilers for helping to elect Cass. Among other things he said that the free-soilers had but one principle and that they reminded him of the Yankee peddler going to sell a pair of pantaloons and describing them as “large enough for any man, and small enough for any boy.”
It is an odd fact in history that the prominent Whigs of Massachusetts at that time became the opponents of Mr. Lincoln’s election to the presidency and the policy of his administration, while the free-soilers, whom he denounced, were among his strongest supporters, advisers and followers.
At the second session of Congress Mr. Lincoln’s one act of consequence was the introduction of a bill providing for the gradual emancipation of the slaves in the District of Columbia. Joshua R. Giddings, the great antislavery agitator, and one or two lesser lights supported it, but the bill was laid on the table.
After General Taylor’s election Mr. Lincoln had the distribution of Federal patronage in his own Congressional district, and this added much to his political importance, although it was a ceaseless source of worry to him.
Just before the close of his term in Congress Mr. Lincoln was an applicant for the office of Commissioner of the General Land Office, but was unsuccessful. He had been such a factor in General Taylor’s election that the administration thought something was due him, and after his return to Illinois he was called to Washington and offered the Governorship of the Territory of Oregon. It is likely he would have accepted this had not Mrs. Lincoln put her foot down with an emphatic no.
He declined a partnership with a well-known Chicago lawyer and returning to his Springfield home resumed the practice of law.
From this time until the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, which opened the way for the admission of slavery into the territories, Mr. Lincoln devoted himself more industriously than ever to the practice of law, and during those five years he was probably a greater student than he had ever been before. His partner, W. H. Herndon, has told of the changes that took place in the courts and in the methods of practice while Mr. Lincoln was away.
When he returned to active practice he saw at once that the courts had grown more learned and dignified and that the bar relied more upon method and system and a knowledge of the statute law than upon the stump speech method of early days.
Mr. Herndon tells us that Lincoln would lie in bed and read by candle light, sometimes until two o’clock in the morning, while his famous colleagues, Davis, Logan, Swett, Edwards and Herndon, were soundly and sometimes loudly sleeping. He read and reread the statutes and books of practice, devoured Shakespeare, who was always a favorite of his, and studied Euclid so diligently that he could easily demonstrate all the propositions contained in the six books.
Mr. Lincoln detested office work. He left all that to his partner. He disliked to draw up legal papers or to write letters. The firm of which he was a member kept no books. When either Lincoln or Herndon received a fee they divided the money then and there. If his partner were not in the office at the time Mr. Lincoln would wrap up half of the fee in a sheet of paper, on which he would write, “Herndon’s half,” giving the name of the case, and place it in his partner’s desk.
But in court, arguing a case, pleading to the jury and laying down the law, Lincoln was in his element. Even when he had a weak case he was a strong antagonist, and when he had right and justice on his side, as he nearly always had, no one could beat him.
He liked an outdoor life, hence he was fond of riding the circuit. He enjoyed the company of other men, liked discussion and argument, loved to tell stories and to hear them, laughing as heartily at his own stories as he did at those that were told to him.
The court circuit in those days was the scene of many a story-telling joust, in which Lincoln was always the chief. Frequently he would sit up until after midnight reeling off story after story, each one followed by roars of laughter that could be heard all over the country tavern, in which the story-telling group was gathered. Every type of character would be represented in these groups, from the learned judge on the bench down to the village loafer.
Lincoln’s favorite attitude was to sit with his long legs propped up on the rail of the stove, or with his feet against the wall, and thus he would sit for hours entertaining a crowd, or being entertained.
One circuit judge was so fond of Lincoln’s stories that he often would sit up until midnight listening to them, and then declare that he had laughed so much he believed his ribs were shaken loose.
The great success of Abraham Lincoln as a trial lawyer was due to a number of facts. He would not take a case if he believed that the law and justice were on the other side. When he addressed a jury he made them feel that he only wanted fair play and justice. He did not talk over their heads, but got right down to a friendly tone such as we use in ordinary conversation, and talked at them, appealing to their honesty and common sense.
And making his argument plain by telling a story or two that brought the matter clearly within their understanding.
When he did not know the law in a particular case he never pretended to know it. If there were no precedents to cover a case he would state his side plainly and fairly; he would tell the jury what he believed was right for them to do, and then conclude with his favorite expression, “it seems to me that this ought to be the law.”
Some time before the repeal of the Missouri Compromise a lawyer friend said to him: “Lincoln, the time is near at hand when we shall have to be all Abolitionists or all Democrats.”
“When that time comes my mind is made up,” he replied, “for I believe the slavery question never can be compromised.”
While Lincoln took a mild interest in politics, he was not a candidate for office, except as a presidential elector, from the time of leaving Congress until the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. This repeal Legislation was the work of Lincoln’s political antagonist, Stephen A. Douglas, and aroused Mr. Lincoln to action as the lion is roused by some foe worthy of his great strength and courage.
Mr. Douglas argued that the true intent and meaning of the act was not to legislate slavery into any territory or state, nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way.
“Douglas’ argument amounts to this,” said Mr. Lincoln, “that if any one man chooses to enslave another no third man shall be allowed to object.”
After the adjournment of Congress Mr. Douglas returned to Illinois and began to defend his action in the repeal of the Missouri Compromise. His most important speech was made at Springfield, and Mr. Lincoln was selected to answer it. That speech alone was sufficient to make Mr. Lincoln the leader of anti-Slavery sentiment in the West, and some of the men who heard it declared that it was the greatest speech he ever made.
With the repeal of the Missouri Compromise the Whig party began to break up, the majority of its members who were pronounced Abolitionists began to form the nucleus of the Republican party. Before this party was formed, however, Mr. Lincoln was induced to follow Douglas around the State and reply to him, but after one meeting at Peoria, where they both spoke, they entered into an agreement to return to their homes and make no more speeches during the campaign.
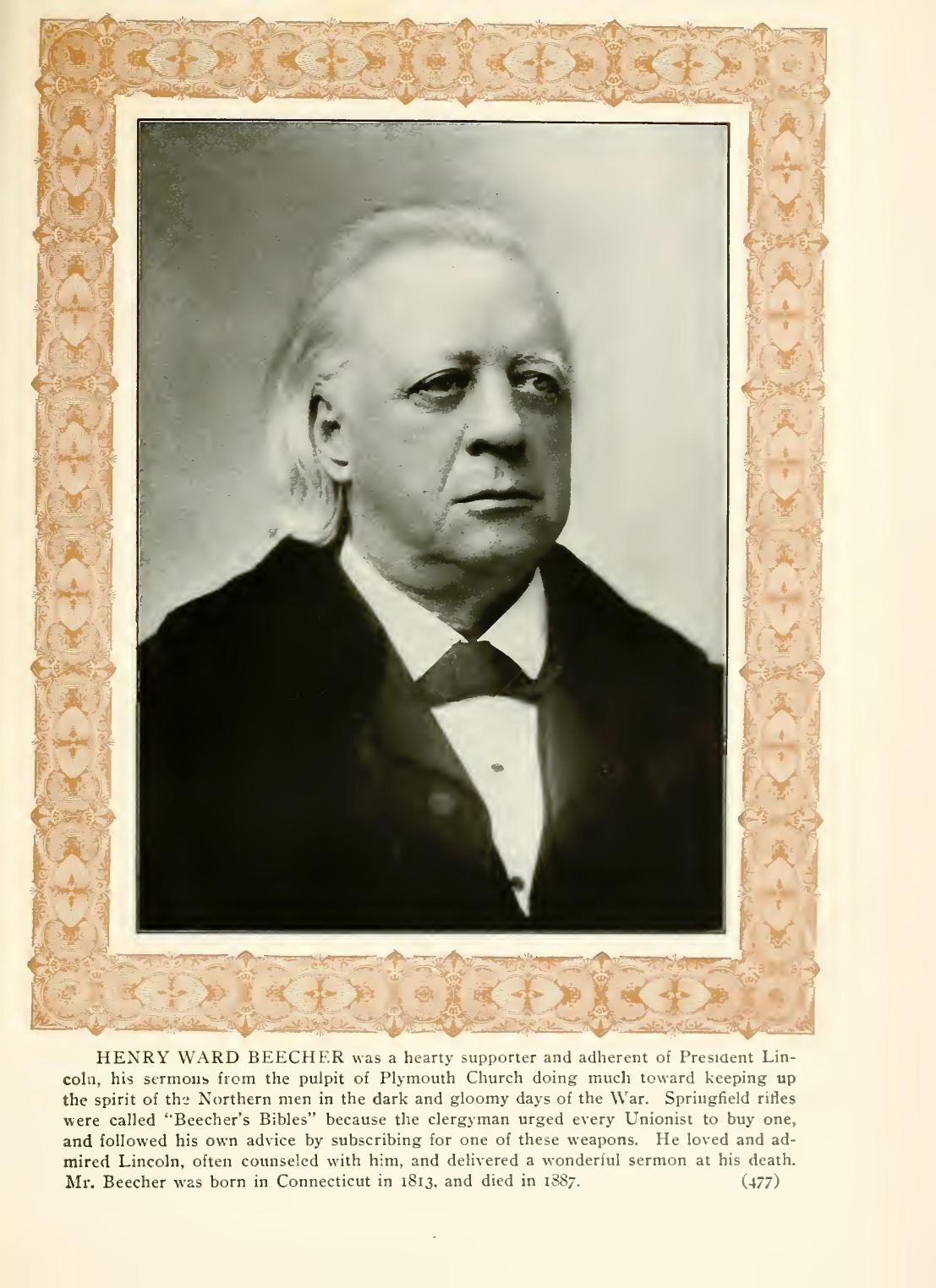
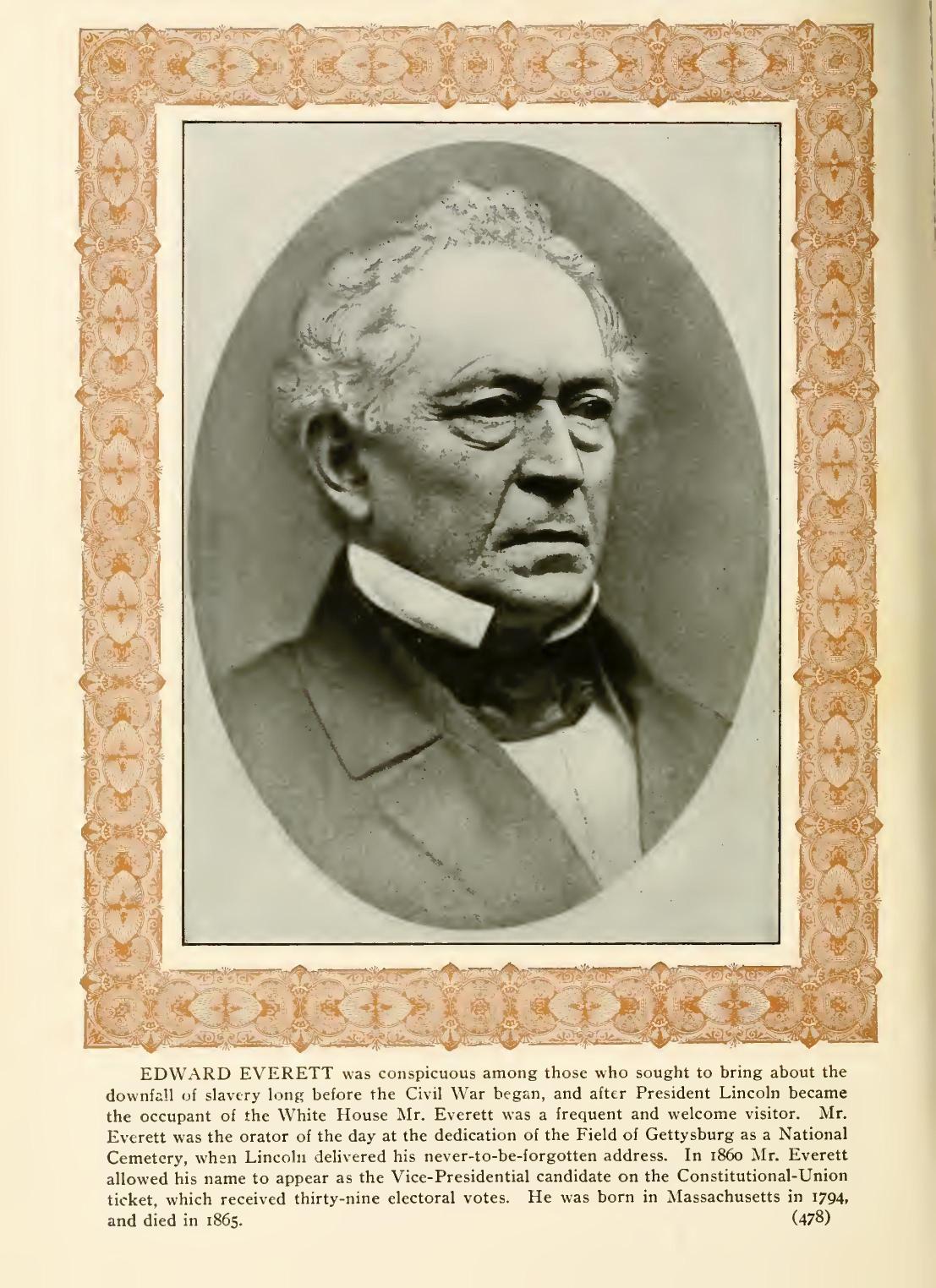




Mr. Lincoln made no secret at this time of his ambition to represent Illinois in the United States Senate. Against his protest he was nominated and elected to the Legislature, but resigned his seat. His old rival, James Shields, with whom he was once near to a duel, was then senator, and his term was to expire the following year.
A letter, written by Mr. Lincoln to a friend in Paris, Illinois, at this time is interesting and significant. He wrote:
“I have a suspicion that a Whig has been elected to the Legislature from Eagar. If this is not so, why, then, ‘nix cum arous;’ but if it is so, then could you not make a mark with him for me for United States senator? I really have some chance.”
Another candidate besides Mr. Lincoln was seeking the seat in the United States Senate, soon to be vacated by Mr. Shields. This was Lyman Trumbull, an anti-slavery Democrat. When the Legislature met it was found that Mr. Lincoln lacked five votes of an election, while Mr. Trumbull had but five supporters. After several ballots Mr. Lincoln feared that Trumbull’s votes would be given to a Democratic candidate and he determined to sacrifice himself for the principle at stake. Accordingly he instructed his friends in the Legislature to vote for Judge Trumbull, which they did, resulting in Trumbull’s election.
The Abolitionists in the West had become very radical in their views, and did not hesitate to talk of opposing the extension of slavery by the use of force if necessary. Mr. Lincoln, on the other hand, was conservative and counseled moderation. In the meantime many outrages, growing out of the extension of slavery, were being perpetrated on the borders of Kansas and Missouri, and they no doubt influenced Mr. Lincoln to take a more radical stand against the slavery question.
An incident occurred at this time which had great effect in this direction. The negro son of a colored woman in Springfield had gone South to work. He was born free, but did not have his free papers with him. He was arrested and would have been sold into slavery to pay his prison expenses, had not Mr. Lincoln and some friends purchased his liberty. Previous to this Mr. Lincoln had tried to secure the boy’s release through the Governor of Illinois, but the Governor informed him that nothing could be done.
Then it was that Mr. Lincoln rose to his full height and exclaimed:
“Governor, I’ll make the ground in this country too hot for the foot of a slave, whether you have the legal power to secure the release of this boy or not.”
The year after Mr. Trumbull’s election to the Senate the Republican party was formally organized. A state convention of that party was called to meet at Bloomington May 29, 1856. The call for this convention was signed by many Springfield Whigs, and among the names was that of Abraham Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln’s name had been signed to the call by his law partner, but when he was informed of this action he endorsed it fully. Among the famous men who took part in this convention were Abraham Lincoln, Lyman Trumbull, David Davis, Leonard Swett, Richard Yates, Norman, B. Judd and Owen Lovejoy, the Alton editor, whose life, like Lincoln’s, finally paid the penalty for his Abolition views. The party nominated for Governor, Wm. H. Bissell, a veteran of the Mexican War, and adopted a platform ringing with anti-slavery sentiment.
Mr. Lincoln was the greatest power in the campaign that followed. He was one of the Fremont Presidential electors, and he went to work with all his might to spread the new party gospel and make votes for the old “Path-Finder of the Rocky Mountains.”
An amusing incident followed close after the Bloomington convention. A meeting was called at Springfield to ratify the action at Bloomington. Only three persons attended—Mr. Lincoln, his law partner and a man named John Paine. Mr. Lincoln made a speech to his colleagues, in which, among other things, he said: “While all seems dead, the age itself is not. It liveth as sure as our Maker liveth.”
In this campaign Mr. Lincoln was in general demand not only in his own state, but in Indiana, Iowa and Wisconsin as well.
The result of that Presidential campaign was the election of Buchanan as President, Bissell as Governor, leaving Mr. Lincoln the undisputed leader of the new party. Hence it was that two years later he was the inevitable man to oppose Judge Douglas in the campaign for United States Senator.
No record of Abraham Lincoln’s career would be complete without the story of the memorable joint debates between the “Rail-Splitter of the Sangamon Valley” and the “Little Giant.” The opening lines in Mr. Lincoln’s speech to the Republican Convention were not only prophetic of the coming rebellion, but they clearly made the issue between the Republican and Democratic parties for two Presidential campaigns to follow. The memorable sentences were as follows:
“A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this Government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved; I do not expect the house to fall; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all the one thing or the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it becomes alike lawful in all the states, old as well as new, North as well as South.”
It is universally conceded that this speech contained the most important utterances of Mr. Lincoln’s life.
Previous to its delivery, the Democratic convention had endorsed Mr. Douglas for re-election to the Senate, and the Republican convention had resolved that “Abraham Lincoln is our first and only choice for United States Senator, to fill the vacancy about to be created by the expiration of Mr. Douglas’ term of office.”
Before Judge Douglas had made many speeches in this Senatorial campaign, Mr. Lincoln challenged him to a joint debate, which was accepted, and seven memorable meetings between these two great leaders followed. The places and dates were: Ottawa, August 21st; Freeport, August 27th; Jonesboro, September 15th; Charleston, September 18th; Galesburg, October 7th; Quincy, October 13th; and Alton, October 15th.
The debates not only attracted the attention of the people in the state of Illinois, but aroused an interest throughout the whole country equal to that of a Presidential election.
All the meetings of the joint debate were attended by immense crowds of people. They came in all sorts of vehicles, on horseback, and many walked weary miles on foot to hear these two great leaders discuss the issues of the campaign. There had never been political meetings held under such unusual conditions as these, and there probably never will be again. At every place the speakers were met by great crowds of their friends and escorted to the platforms in the open air where the debates were held. The processions that escorted the speakers were most unique. They carried flags and banners and were preceded by bands of music. The people discharged cannons when they had them, and, when they did not, blacksmiths’ anvils were made to take their places.
Oftentimes a part of the escort would be mounted, and in most of the processions were chariots containing young ladies representing the different states of the Union designated by banners they carried. Besides the bands, there was usually vocal music. Patriotic songs were the order of the day, the “Star-Spangled Banner” and “Hail Columbia” being great favorites.
So far as the crowds were concerned, these joint debates took on the appearance of a circus day, and this comparison was strengthened by the sale of lemonade, fruit, melons and confectionery on the outskirts of the gatherings.
At Ottawa, after his speech, Mr. Lincoln was carried around on the shoulders of his enthusiastic supporters, who did not put him down until they reached the place where he was to spend the night.
In the joint debates, each of the candidates asked the other a series of questions. Judge Douglas’ replies to Mr. Lincoln’s shrewd questions helped Douglas to win the Senatorial election, but they lost him the support of the South in the campaign for President two years thereafter. Mr. Lincoln was told when he framed his questions that if Douglas answered them in the way it was believed he would that the answers would make him Senator.
“That may be,” said Mr. Lincoln, “but if he takes that shoot he never can be President.”
The prophecy was correct. Mr. Douglas was elected Senator, but two years later only carried one state—Missouri—for President.
After the close of this canvass, Mr. Lincoln again devoted himself to the practice of his profession, but he was destined to remain but a short time in retirement. In the fall of 1859 Mr. Douglas went to Ohio to stump the state for his friend, Mr. Pugh, the Democratic candidate for Governor. The Ohio Republicans at once asked Mr. Lincoln to come to the state and reply to the “Little Giant.” He accepted the invitation and made two masterly speeches in the campaign. In one of them, delivered at Cincinnati, he prophesied the outcome of the rebellion if the Southern people attempted to divide the Union by force.
Addressing himself particularly to the Kentuckians in the audience, he said:
“I have told you what we mean to do. I want to know, now, when that thing takes place, what do you mean to do? I often hear it intimated that you mean to divide the Union whenever a Republican, or anything like it, is elected President of the United States. [A Voice—“That is so.”] ‘That is so,’ one of them says; I wonder if he is a Kentuckian? [A Voice—“He is a Douglas man.”] Well, then, I want to know what you are going to do with your half of it?
“Are you going to split the Ohio down through, and push your half off a piece? Or are you going to keep it right alongside of us outrageous fellows? Or are you going to build up a wall some way between your country, and ours, by which that movable property of yours can’t come over here any more, to the danger of your losing it? Do you think you can better yourselves on that subject by leaving us here under no obligation whatever to return those specimens of your movable property that come hither?
“You have divided the Union because we would not do right with you, as you think, upon that subject; when we cease to be under obligations to do anything for you, how much better off do you think you will be? Will you make war upon us and kill us all? Why, gentlemen, I think you are as gallant and as brave men as live; that you can fight as bravely in a good cause, man for man, as any other people living; that you have shown yourselves capable of this upon various occasions; but, man for man, you are not better than we are, and there are not so many of you as there are of us.
“You will never make much of a hand at whipping us. If we were fewer in numbers than you, I think that you could whip us; if we were equal, it would likely be a drawn battle; but, being inferior in numbers, you will make nothing by attempting to master us.
“But perhaps I have addressed myself as long, or longer, to the Kentuckians than I ought to have done, inasmuch as I have said that, whatever course you take, we intend in the end to beat you.”


Later in the year Mr. Lincoln also spoke in Kansas, where he was received with great enthusiasm, and in February of the following year he made his great speech in Cooper Union, New York, to an immense gathering, presided over by William Cullen Bryant, the poet, who was then editor of the New York Evening Post. There was great curiosity to see the Western rail-splitter who had so lately met the famous “Little Giant” of the West in debate, and Mr. Lincoln’s speech was listened to by many of the ablest men in the East.
This speech won for him many supporters in the Presidential campaign that followed, for his hearers at once recognized his wonderful ability to deal with the questions then uppermost in the public mind.
The Republican National Convention of 1860 met in Chicago, May 16, in an immense building called the “Wigwam.” The leading candidates for President were William H. Seward of New York and Abraham Lincoln of Illinois. Among others spoken of were Salmon P. Chase of Ohio and Simon Cameron of Pennsylvania.
On the first ballot for President, Mr. Seward received one hundred and seventy-three and one-half votes; Mr. Lincoln, one hundred and two votes, the others scattering. On the first ballot, Vermont had divided her vote, but on the second the chairman of the Vermont delegation announced: “Vermont casts her ten votes for the young giant of the West—Abraham Lincoln.”
This was the turning point in the convention toward Mr. Lincoln’s nomination. The second ballot resulted: Seward, one hundred and eighty-four and one-half; Lincoln, one hundred and eighty-one. On the third ballot, Mr. Lincoln received two hundred and thirty votes. One and one-half votes more would nominate him. Before the ballot was announced, Ohio made a change of four votes in favor of Mr. Lincoln, making him the nominee for President.
Other states tried to follow Ohio’s example, but it was a long time before any of the delegates could make themselves heard. Cannons planted on top of the wigwam were roaring and booming; the large crowd in the wigwam and the immense throng outside were cheering at the top of their lungs, while bands were playing victorious airs.
When order had been restored, it was announced that on the third ballot Abraham Lincoln of Illinois had received three hundred and fifty-four votes and was nominated by the Republican party to the office of President of the United States.
Mr. Lincoln heard the news of his nomination while sitting in a newspaper office in Springfield, and hurried home to tell his wife.
As Mr. Lincoln had predicted, Judge Douglas’ position on slavery in the territories lost him the support of the South, and when the Democratic convention met at Charleston, the slave-holding states forced the nomination of John C. Breckinridge. A considerable number of people who did not agree with either party nominated John Bell of Tennessee.
In the election which followed, Mr. Lincoln carried all of the free states, except New Jersey, which was divided between himself and Douglas; Breckinridge carried all the slave states, except Kentucky, Tennessee and Virginia, which went for Bell, and Missouri gave its vote to Douglas.
The election was scarcely over before it was evident that the Southern States did not intend to abide by the result, and that a conspiracy was on foot to divide the Union. Before the Presidential election even, the Secretary of War in President Buchanan’s Cabinet had removed one hundred and fifty thousand muskets from Government armories in the North and sent them to Government armories in the South.
Before Mr. Lincoln had prepared his inaugural address, South Carolina, which took the lead in the secession movement, had declared through her Legislature her separation from the Union. Before Mr. Lincoln took his seat, other Southern States had followed the example of South Carolina, and a convention had been held at Montgomery, Alabama, which had elected Jefferson Davis President of the new Confederacy, and Alexander H. Stevens, of Georgia, Vice-President.
Southern men in the Cabinet, Senate and House had resigned their seats and gone home, and Southern States were demanding that Southern forts and Government property in their section should be turned over to them.
Between his election and inauguration, Mr. Lincoln remained silent, reserving his opinions and a declaration of his policy for his inaugural address.
Before Mr. Lincoln’s departure from Springfield for Washington, threats had been freely made that he would never reach the capital alive, and, in fact, a conspiracy was then on foot to take his life in the city of Baltimore.
Mr. Lincoln left Springfield on February 11th, in company with his wife and three sons, his brother-in-law, Dr. W. S. Wallace; David Davis, Norman B. Judd, Elmer E. Elsworth, Ward H. Lamon, Colonel E. V. Sunder of the United States Army, and the President’s two secretaries.
Early in February, before leaving for Washington, Mr. Lincoln slipped away from Springfield and paid a visit to his aged step-mother in Coles county. He also paid a visit to the unmarked grave of his father and ordered a suitable stone to mark the spot.
Before leaving Springfield, he made an address to his fellow-townsmen, in which he displayed sincere sorrow at parting from them.
“Friends,” he said, “no one who has never been placed in a like position can understand my feelings at this hour, nor the oppressive sadness I feel at this parting. For more than a quarter of a century I have lived among you, and during all that time I have received nothing but kindness at your hands. Here I have lived from my youth until now I am an old man. Here the most sacred ties of earth were assumed. Here all my children were born, and here one of them lies buried.
“To you, dear friends, I owe all that I have, all that I am. All the strange, checkered past seems to crowd now upon my mind. To-day I leave you. I go to assume a task more difficult than that which devolved upon Washington. Unless the great God who assisted him shall be with and aid me, I must fail; but if the same omniscient mind and almighty arm that directed and protected him shall guide and support me, I shall not fail—I shall succeed. Let us all pray that the God of our fathers may not forsake us now.
“To Him I commend you all. Permit me to ask that with equal sincerity and faith you will invoke His wisdom and guidance for me. With these words I must leave you, for how long I know not. Friends, one and all, I must now bid you an affectionate farewell.”
The journey from Springfield to Philadelphia was a continuous ovation for Mr. Lincoln. Crowds assembled to meet him at the various places along the way, and he made them short speeches, full of humor and good feeling. At Harrisburg, Pa., the party was met by Allan Pinkerton, who knew of the plot in Baltimore to take the life of Mr. Lincoln.
Throughout his entire life, Abraham Lincoln’s physical courage was as great and superb as his moral courage. When Mr. Pinkerton and Mr. Judd urged the President-elect to leave for Washington that night, he positively refused to do it. He said he had made an engagement to assist at a flag raising in the forenoon of the next day and to show himself to the people of Harrisburg in the afternoon, and that he intended to keep both engagements.
At Philadelphia the Presidential party was met by Mr. Seward’s son, Frederick, who had been sent to warn Mr. Lincoln of the plot against his life. Mr. Judd, Mr. Pinkerton and Mr. Lamon figured out a plan to take Mr. Lincoln through Baltimore between midnight and daybreak, when the would-be assassins would not be expecting him, and this plan was carried out so thoroughly that even the conductor on the train did not know the President-elect was on board.
Mr. Lincoln was put into his berth and the curtains drawn. He was supposed to be a sick man. When the conductor came around, Mr. Pinkerton handed him the “sick man’s” ticket and he passed on without question.
When the train reached Baltimore, at half-past three o’clock in the morning, it was met by one of Mr. Pinkerton’s detectives, who reported that everything was “all right,” and in a short time the party was speeding on to the national capital, where rooms had been engaged for Mr. Lincoln and his guard at Willard’s Hotel.
Mr. Lincoln always regretted this “secret passage” to Washington, for it was repugnant to a man of his high courage. He had agreed to the plan simply because all of his friends urged it as the best thing to do.
Now that all the facts are known, it is assured that his friends were right, and that there never was a moment from the day he crossed the Maryland line until his assassination that his life was not in danger, and was only saved as long as it was by the constant vigilance of those who were guarding him.
The wonderful eloquence of Abraham Lincoln—clear, sincere, natural—found grand expression in his first inaugural address, in which he not only outlined his policy toward the States in rebellion, but made that beautiful and eloquent plea for conciliation. The closing sentences of Mr. Lincoln’s first inaugural address deservedly take rank with his Gettysburg speech:
“In your hands, my dissatisfied fellow-countrymen,” he said, “and not in mine, is the momentous issue of civil war. The Government will not assail you.
“You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors. You have no oath registered in heaven to destroy the Government, while I shall have the most solemn one to ‘preserve, protect and defend’ it.
“I am loath to close. We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies. Though passion may have strained, it must not break our bonds of affection.
“The mystic cord of memory, stretching from every battle-field and patriot grave to every living heart and hearthstone all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union, when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature.”
In selecting his Cabinet, Mr. Lincoln, consciously or unconsciously, followed a precedent established by Washington, of selecting men of almost opposite opinions. His Cabinet was composed of William H. Seward of New York, Secretary of State; Salmon P. Chase of Ohio, Secretary of the Treasury; Simon Cameron of Pennsylvania, Secretary of War; Gideon E. Welles of Connecticut, Secretary of the Navy; Caleb B. Smith of Indiana, Secretary of the Interior; Montgomery Blair of Maryland, Postmaster-General; Edward Bates of Missouri, Attorney-General.
Mr. Chase, although an anti-slavery leader, was a States-Rights Federal Republican, while Mr. Seward was a Whig, without having connected himself with the anti-slavery movement.
Mr. Chase and Mr. Seward, the leading men of Mr. Lincoln’s Cabinet, were as widely apart and antagonistic in their views as were Jefferson, the Democrat, and Hamilton, the Federalist, the two leaders in Washington’s Cabinet. But in bringing together these two strong men as his chief advisers, both of whom had been rival candidates for the Presidency, Mr. Lincoln gave another example of his own greatness and self-reliance, and put them both in a position to render greater service to the Government than they could have done, probably, as President.
Mr. Lincoln had been in office little more than five weeks when the War of the Rebellion began by the firing on Fort Sumter.
The War of the Rebellion revealed to the people—in fact, to the whole world—the many sides of Abraham Lincoln’s character. It showed him as a real ruler of men—not a ruler by the mere power of might, but by the power of a great brain. In his Cabinet were the ablest men in the country, yet they all knew that Lincoln was abler than any of them.
Mr. Seward, the Secretary of State, was a man famed in statesmanship and diplomacy. During the early stages of the Civil War, when France and England were seeking an excuse to interfere and help the Southern Confederacy, Mr. Seward wrote a letter to our minister in London, Charles Francis Adams, instructing him concerning the attitude of the Federal government on the question of interference, which would undoubtedly have brought about a war with England if Abraham Lincoln had not corrected and amended the letter. He did this, too, without yielding a point or sacrificing in any way his own dignity or that of the country.
Throughout the four years of war, Mr. Lincoln spent a great deal of time in the War Department, receiving news from the front and conferring with Secretary of War Stanton concerning military affairs.
Mr. Lincoln’s War Secretary, Edwin M. Stanton, who had succeeded Simon Cameron, was a man of wonderful personality and iron will. It is generally conceded that no other man could have managed the great War Secretary so well as Lincoln. Stanton had his way in most matters, but when there was an important difference of opinion he always found Lincoln was the master.
Although Mr. Lincoln’s communications to the generals in the field were oftener in the nature of suggestions than positive orders, every military leader recognized Mr. Lincoln’s ability in military operations. In the early stages of the war, Mr. Lincoln followed closely every plan and movement of McClellan, and the correspondence between them proves Mr. Lincoln to have been far the abler general of the two. He kept close watch of Burnside, too, and when he gave the command of the Army of the Potomac to “Fighting Joe” Hooker he also gave that general some fatherly counsel and advice which was of great benefit to him as a commander.
It was not until General Grant had been made Commander-in-Chief that President Lincoln felt he had at last found a general who did not need much advice. He was the first to recognize that Grant was a great military leader, and when he once felt sure of this fact nothing could shake his confidence in that general. Delegation after delegation called at the White House and asked for Grant’s removal from the head of the army. They accused him of being a butcher, a drunkard, a man without sense or feeling.
President Lincoln listened to all of these attacks, but he always had an apt answer to silence Grant’s enemies. Grant was doing what Lincoln wanted done from the first—he was fighting and winning victories, and victories are the only things that count in war.


The crowning act of Lincoln’s career as President was the emancipation of the slaves. All of his life he had believed in gradual emancipation, but all of his plans contemplated payment to the slaveholders. While he had always been opposed to slavery, he did not take any steps to use it as a war measure until about the middle of 1862. His chief object was to preserve the Union.
He wrote to Horace Greeley that if he could save the Union without freeing any of the slaves he would do it; that if he could save it by freeing some and leaving the others in slavery he would do that; that if it became necessary to free all the slaves in order to save the Union he would take that course.
The anti-slavery men were continually urging Mr. Lincoln to set the slaves free, but he paid no attention to their petitions and demands until he felt that emancipation would help him to preserve the Union of the States.
The outlook for the Union cause grew darker and darker in 1862, and Mr. Lincoln began to think, as he expressed it, that he must “change his tactics or lose the game.” Accordingly he decided to issue the Emancipation Proclamation as soon as the Union army won a substantial victory. The battle of Antietam, on September 17, gave him the opportunity he sought. He told Secretary Chase that he had made a solemn vow before God that if General Lee should be driven back from Pennsylvania he would crown the result by a declaration of freedom to the slaves.
On the twenty-second of that month he issued a proclamation stating that at the end of one hundred days he would issue another proclamation declaring all slaves within any State or Territory to be forever free, which was done in the form of the famous Emancipation Proclamation.
In the conduct of the war and in his purpose to maintain the Union, Abraham Lincoln exhibited a will of iron and determination that could not be shaken, but in his daily contact with the mothers, wives and daughters begging for the life of some soldier who had been condemned to death for desertion or sleeping on duty he was as gentle and weak as a woman.
It was a difficult matter for him to refuse a pardon if the slightest excuse could be found for granting it.
Secretary Stanton and the commanding generals were loud in declaring that Mr. Lincoln would destroy the discipline of the army by his wholesale pardoning of condemned soldiers, but when we come to examine the individual cases we find that Lincoln was nearly always right, and when he erred it was always on the side of humanity.
During the four years of the long struggle for the preservation of the Union, Mr. Lincoln kept “open shop,” as he expressed it, where the general public could always see him and make known their wants and complaints. Even the private soldier was not denied admittance to the President’s private office, and no request or complaint was too small or trivial to enlist his sympathy and interest.
It was once said of Shakespeare that the great mind that conceived the tragedies of “Hamlet,” “Macbeth,” etc., would have lost its reason if it had not found vent in the sparkling humor of such comedies as “The Merry Wives of Windsor” and “The Comedy of Errors.”
The great strain on the mind of Abraham Lincoln produced by four years of civil war might likewise have overcome his reason had it not found vent in the yarns and stories he constantly told. No more fun-loving or humor-loving man than Abraham Lincoln ever lived. He enjoyed a joke even when it was on himself, and probably, while he got his greatest enjoyment from telling stories, he had a keen appreciation of the humor in those that were told him.
His favorite humorous writer was David R. Locke, better known as “Petroleum V. Nasby,” whose political satires were quite famous in their day. Nearly every prominent man who has written his recollections of Lincoln has told how the President, in the middle of a conversation on some serious subject, would suddenly stop and ask his hearer if he ever read the Nasby letters.
Then he would take from his desk a pamphlet containing the letters and proceed to read them, laughing heartily at all the good points they contained. There is probably no better evidence of Mr. Lincoln’s love of humor and appreciation of it than his letter to Nasby, in which he said: “For the ability to write these things I would gladly trade places with you.”
Mr. Lincoln was re-elected President in 1864. His opponent on the Democratic ticket was General George B. McClellan, whose command of the Army of the Potomac had been so unsatisfactory at the beginning of the war. Mr. Lincoln’s election was almost unanimous, as McClellan carried but three States—Delaware, Kentucky and New Jersey.
General Grant, in a telegram of congratulation, said that it was “a victory worth more to the country than a battle won.”
The war was fast drawing to a close. The black war clouds were breaking and rolling away. Sherman had made his famous march to the sea. Through swamp and ravine, Grant was rapidly tightening the lines around Richmond. Thomas had won his title of the “Rock of Chickamauga.” Sheridan had won his spurs as the great modern cavalry commander, and had cleaned out the Shenandoah Valley. Sherman was coming back from his famous march to join Grant at Richmond.
The Confederacy was without a navy. The Kearsarge had sunk the Alabama, and Farragut had fought and won the famous victory in Mobile Bay. It was certain that Lee would soon have to evacuate Richmond only to fall into the hands of Grant.
Lincoln saw the dawn of peace. When he came to deliver his second inaugural address, it contained no note of victory, no exultation over a fallen foe. On the contrary, it breathed the spirit of brotherly love and of prayer for an early peace: “With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphans, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.”
Not long thereafter, General Lee evacuated Richmond with about half of his original army, closely pursued by Grant. The boys in blue overtook their brothers in gray at Appomattox Court House, and there, beneath the warm rays of an April sun, the great Confederate general made his final surrender. The war was over, the American flag was floated over all the territory of the United States, and peace was now a reality. Mr. Lincoln visited Richmond and the final scenes of the war and then returned to Washington to carry out his announced plan of “binding up the nation’s wounds.”
He had now reached the climax of his career and touched the highest point of his greatness. His great task was over, and the heavy burden that had so long worn upon his heart was lifted.
While the whole nation was rejoicing over the return of peace, the Saviour of the Union was stricken down by the hand of an assassin.
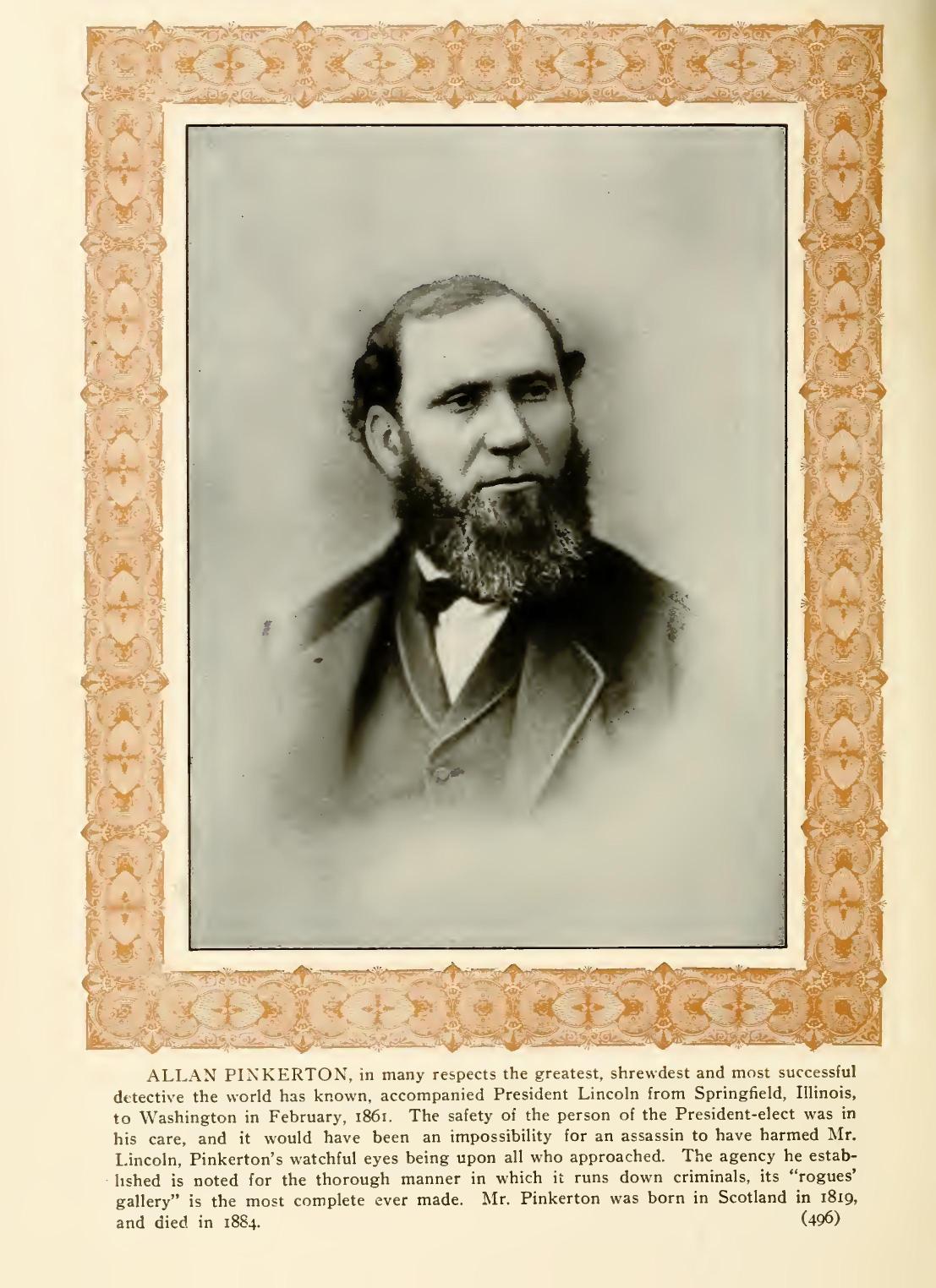




From early youth, Mr. Lincoln had presentiments that he would die a violent death, or, rather, that his final days would be marked by some great tragic event. From the time of his first election to the Presidency, his closest friends had tried to make him understand that he was in constant danger of assassination, but, notwithstanding his presentiments, he had such splendid courage that he only laughed at their fears.
During the summer months he lived at the Soldiers’ Home, some miles from Washington, and frequently made the trip between the White House and the Home without a guard or escort. Secretary of War Stanton and Ward Lamon, Marshal of the District, were almost constantly alarmed over Mr. Lincoln’s carelessness in exposing himself to the danger of assassination.
They warned him time and again, and provided suitable body-guards to attend him. But Mr. Lincoln would often give the guards the slip, and, mounting his favorite riding horse, “Old Abe,” would set out alone after dark from the White House for the Soldiers’ Home.
While riding to the Home one night, he was fired upon by some one in ambush, the bullet passing through his high hat. Mr. Lincoln would not admit that the man who fired the shot had tried to kill him. He always attributed it to an accident, and begged his friends to say nothing about it.
Now that all the circumstances of the assassination are known, it is plain that there was a deep-laid and well-conceived plot to kill Mr. Lincoln long before the crime was actually committed. When Mr. Lincoln was delivering his second inaugural address on the steps of the Capitol, an excited individual tried to force his way through the guards in the building to get on the platform with Mr. Lincoln.
It was afterward learned that this man was John Wilkes Booth, who afterwards assassinated Mr. Lincoln in Ford’s Theatre, on the night of the 14th of April.
The manager of the theatre had invited the President to witness a performance of a new play known as “Our American Cousin,” in which the famous actress, Laura Keane, was playing. Mr. Lincoln was particularly fond of the theatre. He loved Shakespeare’s plays above all others and never missed a chance to see the leading Shakespearean actors.
As “Our American Cousin” was a new play, the President did not care particularly to see it, but as Mrs. Lincoln was anxious to go, he consented and accepted the invitation.
General Grant was in Washington at the time, and as he was extremely anxious about the personal safety of the President, he reported every day regularly at the White House. Mr. Lincoln invited General Grant and his wife to accompany him and Mrs. Lincoln to the theatre on the night of the assassination, and the general accepted, but while they were talking he received a note from Mrs. Grant saying that she wished to leave Washington that evening to visit her daughter in Burlington. General Grant made his excuses to the President and left to accompany Mrs. Grant to the railway station. It afterwards became known that it was also a part of the plot to assassinate General Grant, and only Mrs. Grant’s departure from Washington that evening prevented the attempt from being made.
General Grant afterwards said that as he and Mrs. Grant were riding along Pennsylvania avenue to the railway station a horseman rode rapidly by at a gallop, and, wheeling his horse, rode back, peering into their carriage as he passed.
Mrs. Grant remarked to the general: “That is the very man who sat near us at luncheon to-day and tried to overhear our conversation. He was so rude, you remember, as to cause us to leave the dining-room. Here he is again, riding after us.”
General Grant attributed the action of the man to idle curiosity, but learned afterward that the horseman was John Wilkes Booth.
Probably one reason why Mr. Lincoln did not particularly care to go to the theatre that night was a sort of half promise he had made to his friend and bodyguard, Marshal Lamon. Two days previous he had sent Lamon to Richmond on business connected with a call of a convention for reconstruction. Before leaving, Mr. Lamon saw Mr. Usher, the Secretary of the Interior, and asked him to persuade Mr. Lincoln to use more caution about his personal safety, and to go out as little as possible while Lamon was absent. Together they went to see Mr. Lincoln, and Lamon asked the President if he would make him a promise.
“I think I can venture to say I will,” said Mr. Lincoln. “What is it?”
“Promise me that you will not go out after night while I am gone,” said Mr. Lamon, “particularly to the theatre.”
Mr. Lincoln turned to Mr. Usher and said: “Usher, this boy is a monomaniac on the subject of my safety. I can hear him or hear of his being around at all times in the night, to prevent somebody from murdering me. He thinks I shall be killed, and we think he is going crazy. What does any one want to assassinate me for? If any one wants to do so, he can do it any day or night if he is ready to give his life for mine. It is nonsense.”
Mr. Usher said to Mr. Lincoln that it was well to heed Lamon’s warning, as he was thrown among people from whom he had better opportunities to know about such matters than almost any one.
“Well,” said Mr. Lincoln to Lamon, “I promise to do the best I can toward it.”
The assassination of President Lincoln was most carefully planned, even to the smallest detail. The box set apart for the President’s party was a double one in the second tier at the left of the stage. The box had two doors with spring locks, but Booth had loosened the screws with which they were fastened so that it was impossible to secure them from the inside. In one door he had bored a hole with a gimlet, so that he could see what was going on inside the box.
An employee of the theatre by the name of Spangler, who was an accomplice of the assassin, had even arranged the seats in the box to suit the purposes of Booth.
On the fateful night the theatre was packed. The Presidential party arrived a few minutes after nine o’clock, and consisted of the President and Mrs. Lincoln, Miss Harris and Major Rathbone, daughter and stepson of Senator Harris of New York. The immense audience rose to its feet and cheered the President as he passed to his box.
Booth came into the theatre about ten o’clock. He had not only, planned to kill the President, but he had also planned to escape into Maryland, and a swift horse, saddled and ready for the journey, was tied in the rear of the theatre. For a few minutes he pretended to be interested in the performance, and then gradually made his way back to the door of the President’s box.
Before reaching there, however, he was confronted by one of the President’s messengers, who had been stationed at the end of the passage leading to the boxes to prevent any one from intruding. To this man Booth handed a card saying that the President had sent for him, and was permitted to enter.
Once inside the hallway leading to the boxes, he closed the hall door and fastened it by a bar prepared for the occasion, so that it was impossible to open it from without. Then he quickly entered the box through the right-hand door. The President was sitting in an easy armchair in the left-hand corner of the box nearest the audience. He was leaning on one hand and with the other had hold of a portion of the drapery. There was a smile on his face. The other members of the party were intently watching the performance on the stage.
The assassin carried in his right hand a small silver-mounted derringer pistol and in his left a long double-edged dagger. He placed the pistol just behind the President’s left ear and fired.
Mr. Lincoln bent slightly forward and his eyes closed, but in every other respect his attitude remained unchanged.
The report of the pistol startled Major Rathbone, who sprang to his feet. The murderer was then about six feet from the President, and Rathbone grappled with him, but was shaken off. Dropping his pistol, Booth struck at Rathbone with the dagger and inflicted a severe wound. The assassin then placed his left hand lightly on the railing of the box and jumped to the stage, eight or nine feet below.
The box was draped with the American flag, and, in jumping, Booth’s spurs caught in the folds, tearing down the flag, the assassin falling heavily to the stage and spraining his ankle. He arose, however, and walked theatrically across the stage, brandished his knife and shouted, “Sic semper tyrannis!” and then added, “The South is avenged.”
For the moment the audience was horrified and incapable of action. One man only, a lawyer named Stuart, had sufficient presence of mind to leap upon the stage and attempt to capture the assassin. Booth went to the rear door of the stage, where his horse was held in readiness for him, and, leaping into the saddle, dashed through the streets toward Virginia. Miss Keane rushed to the President’s box with water and stimulants, and medical aid was summoned.
By this time the audience realized the tragedy that had been enacted, and then followed a scene such as has never been witnessed in any public gathering in this country. Women wept, shrieked and fainted; men raved and swore, and horror was depicted on every face. Before the audience could be gotten out of the theatre, horsemen were dashing through the streets and the telegraph was carrying the terrible details of the tragedy throughout the nation.
Walt Whitman, the poet, has sketched in graphic language the scenes of that most eventful fourteenth of April. His account of the assassination has become historic, and is herewith given:
“The day (April 14, 1865) seems to have been a pleasant one throughout the whole land—the moral atmosphere pleasant, too—the long storm, so dark, so fratricidal, full of blood and doubt and gloom, over and ended at last by the sunrise of such an absolute national victory, and utter breaking down of secessionism—we almost doubted our senses! Lee had capitulated, beneath the apple tree at Appomattox. The other armies, the flanges of the revolt, swiftly followed.
“And could it really be, then? Out of all the affairs of this world of woe and passion, of failure and disorder and dismay, was there really come the confirmed, unerring sign of peace, like a shaft of pure light—of rightful rule—of God?
“But I must not dwell on accessories. The deed hastens. The popular afternoon paper, the little Evening Star, had scattered all over its third page, divided among the advertisements in a sensational manner in a hundred different places:
“‘The President and his lady will be at the theatre this evening.’
“Lincoln was fond of the theatre. I have myself seen him there several times. I remember thinking how funny it was that he, the leading actor in the greatest and stormiest drama known to real history’s stage, through centuries, should sit there and be so completely interested in those human jackstraws, moving about with their silly little gestures, foreign spirit, and flatulent text.
“So the day, as I say, was propitious. Early herbage, early flowers, were out. I remember where I was stopping at the time, the season being advanced, there were many lilacs in full bloom.
“By one of those caprices that enter and give tinge to events without being a part of them, I find myself always reminded of the great tragedy of this day by the sight and odor of these blossoms. It never fails.
“On this occasion the theatre was crowded, many ladies in rich and gay costumes, officers in their uniforms, many well-known citizens, young folks, the usual cluster of gas lights, the usual magnetism of so many people, cheerful with perfumes, music of violins and flutes—and over all, that saturating, that vast, vague wonder, Victory, the nation’s victory, the triumph of the Union, filling the air, the thought, the sense, with exhilaration more than all the perfumes.
“The President came betimes, and, with his wife, witnessed the play from the large stage boxes of the second tier, two thrown into one, and profusely draped with the national flag. The acts and scenes of the piece—one of those singularly witless compositions which have at the least the merit of giving entire relief to an audience engaged in mental action or business excitements and cares during the day, as it makes not the slightest call on either the moral, emotional, esthetic or spiritual nature—a piece in which among other characters, so called, a Yankee—certainly such a one as was never seen, or at least like it ever seen in North America, is introduced in England, with a varied fol-de-rol of talk, plot, scenery, and such phantasmagoria as goes to make up a modern popular drama—had progressed perhaps through a couple of its acts, when, in the midst of this comedy, or tragedy, or non-such, or whatever it is to be called, and to offset it, or finish it out, as if in Nature’s and the Great Muse’s mockery of these poor mimics, comes interpolated that scene, not really or exactly to be described at all (for on the many hundreds who were there it seems to this hour to have left little but a passing blur, a dream, a blotch)—and yet partially described as I now proceed to give it:
“There is a scene in the play, representing the modern parlor, in which two unprecedented ladies are informed by the unprecedented and impossible Yankee that he is not a man of fortune, and therefore undesirable for marriage-catching purposes; after which, the comments being finished, the dramatic trio make exit, leaving the stage clear for a moment.
“There was a pause, a hush, as it were. At this period came the death of Abraham Lincoln.
“Great as that was, with all its manifold train circling around it, and stretching into the future for many a century, in the politics, history, art, etc., of the New World, in point of fact, the main thing, the actual murder, transpired with the quiet and simplicity of any commonest occurrence—the bursting of a bud or pod in the growth of vegetation, for instance.
“Through the general hum following the stage pause, with the change of positions, etc., came the muffled sound of a pistol shot, which not one-hundredth part of the audience heard at the time—and yet a moment’s hush—somehow, surely a vague, startled thrill—and then, through the ornamented, draperied, starred and striped space-way of the President’s box, a sudden figure, a man, raises himself with hands and feet, stands a moment on the railing, leaps below to the stage, falls out of position, catching his boot heel in the copious drapery (the American flag), falls on one knee, quickly recovers himself, rises as if nothing had happened (he really sprains his ankle, unfelt then)—and the figure, Booth, the murderer, dressed in plain black broadcloth, bareheaded, with a full head of glossy, raven hair, and his eyes, like some mad animal’s, flashing with light and resolution, yet with a certain strange calmness holds aloft in one hand a large knife—walks along not much back of the footlights—turns fully towards the audience, his face of statuesque beauty, lit by those basilisk eyes, flashing with desperation, perhaps insanity—launches out in a firm and steady voice the words, ‘Sic semper tyrannis’—and then walks with neither slow nor very rapid pace diagonally across to the back of the stage, and disappears.
“(Had not all this terrible scene—making the mimic ones preposterous—had it not all been rehearsed, in blank, by Booth, beforehand?)
“A moment’s hush, incredulous—a scream—a cry of murder—Mrs. Lincoln leaning out of the box, with ashy cheeks and lips, with involuntary cry, pointing to the retreating figure, ‘He has killed the President!’
“And still a moment’s strange, incredulous suspense—and then the deluge!—then that mixture of horror, noises, uncertainty—the sound, somewhere back, of a horse’s hoofs clattering with speed—the people burst through chairs and railings, and break them up—that noise adds to the queerness of the scene—there is inextricable confusion and terror—women faint—quite feeble persons fall, and are trampled on—many cries of agony are heard—the broad stage suddenly fills to suffocation with a dense and motley crowd, like some horrible carnival—the audience rush generally upon it—at least the strong men do—the actors and actresses are there in their play costumes and painted faces, with mortal fright showing through the rouge—some trembling, some in tears—the screams and calls, confused talk—redoubled, trebled—two or three manage to pass up water from the stage to the President’s box, others try to clamber up, etc., etc.
“In the midst of all this the soldiers of the President’s Guard, with others, suddenly drawn to the scene, burst in—some two hundred altogether—they storm the house, through all the tiers, especially the upper ones—inflamed with fury, literally charging the audience with fixed bayonets, muskets and pistols, shouting, ‘Clear out! clear out!’
“Such a wild scene, or a suggestion of it, rather, inside the playhouse that night!
“Outside, too, in the atmosphere of shock and craze, crowds of people filled with frenzy, ready to seize any outlet for it, came near committing murder several times on innocent individuals.
“One such case was particularly exciting. The infuriated crowd, through some chance, got started against one man, either for words he uttered, or perhaps without any cause at all, and were proceeding to hang him at once to a neighboring lamp-post, when he was rescued by a few heroic policemen, who placed him in their midst and fought their way slowly and amid great peril toward the station-house.
“It was a fitting episode of the whole affair. The crowd rushing and eddying to and fro, the night, the yells, the pale faces, many frightened people trying in vain to extricate themselves, the attacked man, not yet freed from the jaws of death, looking like a corpse; the silent, resolute half-dozen policemen, with no weapons but their little clubs, yet stern and steady through all those eddying swarms, made, indeed, a fitting side scene to the grand tragedy of the murder. They gained the station-house with the protected man, whom they placed in security for the night, and discharged in the morning.
“And in the midst of that night pandemonium of senseless hate, infuriated soldiers, the audience and the crowd—the stage, and all its actors and actresses, its paint pots, spangles, gas-light—the life-blood from those veins, the best and sweetest of the land, drips slowly down, and death’s ooze already begins its little bubbles on the lips.
“Such, hurriedly sketched, were the accompaniments of the death of President Lincoln. So suddenly, and in murder and horror unsurpassed, he was taken from us. But his death was painless.”
The assassin’s bullet did not produce instant death, but the President never again became conscious. He was carried to a house opposite the theatre, where he died the next morning. In the meantime the authorities had become aware of the wide-reaching conspiracy, and the capital was in a state of terror.


On the night of the President’s assassination, Mr. Seward, Secretary of State, was attacked while in bed with a broken arm, by Booth’s fellow-conspirators, and badly wounded.
The conspirators had also planned to take the lives of Vice-President Johnson and Secretary Stanton. Booth had called on Vice-President Johnson the day before, and, not finding him in, left a card.
Secretary Stanton acted with his usual promptness and courage. During the period of excitement he acted as President, and directed the plans for the capture of Booth.
Among other things, he issued the following reward:
REWARD OFFERED BY SECRETARY STANTON. War Department, Washington, April 20, 1865. Major-General John A. Dix, New York:
The murderer of our late beloved President, Abraham Lincoln, is still at large. Fifty thousand dollars reward will be paid by this Department for his apprehension, in addition to any reward offered by municipal authorities or State Executives.
Twenty-five thousand dollars reward will be paid for the apprehension of G. W. Atzerodt, sometimes called “Port Tobacco,” one of Booth’s accomplices. Twenty-five thousand dollars reward will be paid for the apprehension of David C. Herold, another of Booth’s accomplices.
A liberal reward will be paid for any information that shall conduce to the arrest of either the above-named criminals or their accomplices.
All persons harboring or secreting the said persons, or either of them, or aiding or assisting their concealment or escape, will be treated as accomplices in the murder of the President and the attempted assassination of the Secretary of State, and shall be subject to trial before a military commission, and the punishment of death.
Let the stain of innocent blood be removed from the land by the arrest and punishment of the murderers.
All good citizens are exhorted to aid public justice on this occasion. Every man should consider his own conscience charged with this solemn duty, and rest neither night nor day until it be accomplished.
EDWIN M. STANTON, Secretary of War.
Booth, accompanied by David C. Herold, a fellow-conspirator, finally made his way into Maryland, where eleven days after the assassination the two were discovered in a barn on Garrett’s farm near Port Royal on the Rappahannock. The barn was surrounded by a squad of cavalrymen, who called upon the assassins to surrender. Herold gave himself up and was roundly cursed and abused by Booth, who declared that he would never be taken alive.
The cavalrymen then set fire to the barn and as the flames leaped up the figure of the assassin could be plainly seen, although the wall of fire prevented him from seeing the soldiers. Colonel Conger saw him standing upright upon a crutch with a carbine in his hands.
When the fire first blazed up Booth crept on his hands and knees to the spot, evidently for the purpose of shooting the man who had applied the torch, but the blaze prevented him from seeing anyone. Then it seemed as if he were preparing to extinguish the flames, but seeing the impossibility of this he started toward the door with his carbine held ready for action.
His eyes shone with the light of fever, but he was pale as death and his general appearance was haggard and unkempt. He had shaved off his mustache and his hair was closely cropped. Both he and Herold wore the uniforms of Confederate soldiers.
The last orders given to the squad pursuing Booth were: “Don’t shoot Booth, but take him alive.” Just as Booth started to the door of the barn this order was disobeyed by a sergeant named Boston Corbett, who fired through a crevice and shot Booth in the neck. The wounded man was carried out of the barn and died four hours afterward on the grass where they had laid him. Before he died he whispered to Lieutenant Baker, “Tell mother I died for my country; I thought I did for the best.” What became of Booth’s body has always been and probably always will be a mystery. Many different stories have been told concerning his final resting place, but all that is known positively is that the body was first taken to Washington and a post-mortem examination of it held on the Monitor Montauk. On the night of April 27th it was turned over to two men who took it in a rowboat and disposed of it secretly. How they disposed of it none but themselves know and they have never told.
The conspiracy to assassinate the President involved altogether twenty-five people. Among the number captured and tried were David C. Herold, G. W. Atzerodt, Louis Payne, Edward Spangler, Michael O’Loughlin, Samuel Arnold, Mrs. Surratt and Dr. Samuel Mudd, a physician, who set Booth’s leg, which was sprained by his fall from the stage box. Of these Herold, Atzerodt, Payne and Mrs. Surratt were hanged. Dr. Mudd was deported to the Dry Tortugas. While there an epidemic of yellow fever broke out and he rendered such good service that he was granted a pardon and died a number of years ago in Maryland.
John Surratt, the son of the woman who was hanged, made his escape to Italy, where he became one of the Papal guards in the Vatican at Rome. His presence there was discovered by Archbishop Hughes, and, although there were no extradition laws to cover his case, the Italian Government gave him up to the United States authorities.
He had two trials. At the first the jury disagreed; the long delay before his second trial allowed him to escape by pleading the statute of limitation. Spangler and O’Loughlin were sent to the Dry Tortugas and served their time.
Ford, the owner of the theatre in which the President was assassinated, was a Southern sympathizer, and when he attempted to re-open his theatre after the great national tragedy, Secretary Stanton refused to allow it. The Government afterward bought the theatre and turned it into a National museum.
President Lincoln was buried at Springfield, and on the day of his funeral there was universal grief.
No final words of that great life can be more fitly spoken than the eulogy pronounced by Henry Ward Beecher:
“And now the martyr is moving in triumphal march, mightier than when alive. The nation rises up at every stage of his coming. Cities and States are his pall-bearers, and the cannon speaks the hours with solemn progression. Dead, dead, dead, he yet speaketh.
“Is Washington dead? Is Hampden dead? Is any man that was ever fit to live dead? Disenthralled of flesh, risen to the unobstructed sphere where passion never comes, he begins his illimitable work. His life is now grafted upon the infinite, and will be fruitful as no earthly life can be.
“Pass on, thou that hast overcome. Ye people, behold the martyr whose blood, as so many articulate words, pleads for fidelity, for law, for liberty.”
Abraham Lincoln was married on November 4, 1842, to Miss Mary Todd, four sons being the issue of the union.
Robert Todd, born August 1, 1843, removed to Chicago after his father’s death, practiced law, and became wealthy; in 1881 he was appointed Secretary of War by President Garfield, and served through President Arthur’s term; was made Minister to England in 1889, and served four years; became counsel for the Pullman Palace Car Company, and succeeded to the presidency of that corporation upon the death of George M. Pullman.
Edward Baker, born March 10, 1846, died in infancy.
William Wallace, born December 21, 1850, died in the White House in February, 1862.
Thomas (known as “Tad”), born April 4, 1853, died in 1871.
Mrs. Lincoln died in her sixty-fourth year at the home of her sister, Mrs. Ninian W. Edwards, at Springfield, Illinois, in 1882. She was the daughter of Robert S. Todd, of Kentucky. Her great-uncle, John Todd, and her grandfather, Levi Todd, accompanied General George Rogers Clark to Illinois, and were present at the capture of Kaskaskia and Vincennes. In December, 1778, John Todd was appointed by Patrick Henry, Governor of Virginia, to be lieutenant of the County of Illinois, then a part of Virginia. Colonel John Todd was one of the original proprietors of the town of Lexington, Kentucky. While encamped on the site of the present city, he heard of the opening battle of the Revolution, and named his infant settlement in its honor.
Mrs. Lincoln was a proud, ambitious woman, well-educated, speaking French fluently, and familiar with the ways of the best society in Lexington, Kentucky, where she was born December 13, 1818. She was a pupil of Madame Mantelli, whose celebrated seminary in Lexington was directly opposite the residence of Henry Clay. The conversation at the seminary was carried on entirely in French.
She visited Springfield, Illinois, in 1837, remained three months and then returned to her native State. In 1839 she made Springfield her permanent home. She lived with her eldest sister, Elizabeth, wife of Ninian W. Edwards, Lincoln’s colleague in the Legislature, and it was not strange she and Lincoln should meet. Stephen A. Douglas was also a friend of the Edwards family, and a suitor for her hand, but she rejected him to accept the future President. She was one of the belles of the town.
She is thus described at the time she made her home in Springfield—1839:
“She was of the average height, weighing about a hundred and thirty pounds. She was rather compactly built, had a well rounded face, rich dark-brown hair, and bluish-gray eyes. In her bearing she was proud, but handsome and vivacious; she was a good conversationalist, using with equal fluency the French and English languages.
“When she used a pen, its point was sure to be sharp, and she wrote with wit and ability. She not only had a quick intellect but an intuitive judgment of men and their motives. Ordinarily she was affable and even charming in her manners; but when offended or antagonized she could be very bitter and sarcastic.
“In her figure and physical proportions, in education, bearing, temperament, history—in everything she was the exact reverse of Lincoln.”
That Mrs. Lincoln was very proud of her husband there is no doubt; and it is probable that she married him largely from motives of ambition. She knew Lincoln better than he knew himself; she instinctively felt that he would occupy a proud position some day, and it is a matter of record that she told Ward Lamon, her husband’s law partner, that “Mr. Lincoln will yet be President of the United States.”
Mrs. Lincoln was decidedly pro-slavery in her views, but this never disturbed Lincoln. In various ways they were unlike. Her fearless, witty, and austere nature had nothing in common with the calm, imperturbable, and simple ways of her thoughtful and absent-minded husband. She was bright and sparkling in conversation, and fit to grace any drawing-room. She well knew that to marry Lincoln meant not a life of luxury and ease, for Lincoln was not a man to accumulate wealth; but in him she saw position in society, prominence in the world, and the grandest social distinction. By that means her ambition was certainly satisfied, for nineteen years after her marriage she was “the first lady of the land,” and the mistress of the White House.
After his marriage, by dint of untiring efforts and the recognition of influential friends, the couple managed through rare frugality to move along.
In Lincoln’s struggles, both in the law and for political advancement, his wife shared his sacrifices. She was a plucky little woman, and in fact endowed with a more restless ambition than he. She was gifted with a rare insight into the motives that actuate mankind, and there is no doubt that much of Lincoln’s success was in a measure attributable to her acuteness and the stimulus of her influence.
His election to Congress within four years after their marriage afforded her extreme gratification. She loved power and prominence, and was inordinately proud of her tall and ungainly husband. She saw in him bright prospects ahead, and his every move was watched by her with the closest interest. If to other persons he seemed homely, to her he was the embodiment of noble manhood, and each succeeding day impressed upon her the wisdom of her choice of Lincoln over Douglas—if in reality she ever seriously accepted the latter’s attentions.
“Mr. Lincoln may not be as handsome a figure,” she said one day in Lincoln’s law office during her husband’s absence, when the conversation turned on Douglas, “but the people are perhaps not aware that his heart is as large as his arms are long.”
The remains of Abraham Lincoln rest beneath a magnificent monument in Oak Ridge Cemetery, Springfield, Ill. Before they were deposited in their final resting place they were moved many times.
On May 4, 1865, all that was mortal of Abraham Lincoln was deposited in the receiving vault at the cemetery, until a tomb could be built. In 1876 thieves made an unsuccessful attempt to steal the remains. From the tomb the body of the martyred President was removed later to the monument.
A flight of iron steps, commencing about fifty yards east of the vault, ascends in a curved line to the monument, an elevation of more than fifty feet.
Excavation for this monument commenced September 9, 1869. It is built of granite, from quarries at Biddeford, Maine. The rough ashlers were shipped to Quincy, Massachusetts, where they were dressed and numbered, thence shipped to Springfield. It is 721 feet from east to west, 119 1/2 feet from north to south, and 100 feet high. The total cost is about $230,000 to May 1, 1885. All the statuary is orange-colored bronze. The whole monument was designed by Larkin G. Mead; the statuary was modeled in plaster by him in Florence, Italy, and cast by the Ames Manufacturing Company, of Chicopee, Massachusetts. A statue of Lincoln and Coat of Arms were first placed on the monument; the statue was unveiled and the monument dedicated October 15, 1874. Infantry and Naval Groups were put on in September, 1877, an Artillery Group, April 13, 1882, and a Cavalry Group, March 13, 1883.
The principal front of the monument is on the south side, the statue of Lincoln being on that side of the obelisk, over Memorial Hall. On the east side are three tablets, upon which are the letters U. S. A. To the right of that, and beginning with Virginia, we find the abbreviations of the original thirteen States. Next comes Vermont, the first state admitted after the Union was perfected, the States following in the order they were admitted, ending with Nebraska on the east, thus forming the cordon of thirty-seven States composing the United States of America when the monument was erected. The new States admitted since the monument was built have been added.
The statue of Lincoln is just above the Coat of Arms of the United States. The grand climax is indicated by President Lincoln, with his left hand holding out as a golden scepter the emancipation Proclamation, while in his right he holds the pen with which he has just written it. The right hand is resting on another badge of authority, the American flag, thrown over the fasces. At the foot of the fasces lies a wreath of laurel, with which to crown the President as the victor over slavery and rebellion.
On March 10, 1900, President Lincoln’s body was removed to a temporary vault to permit of alterations to the monument. The shaft was made twenty feet higher, and other changes were made costing $100,000.
April 24, 1901. the body was again transferred to the monument without public ceremony.
The letters herein by Lincoln are so thoroughly characteristic of the man, and are in themselves so completely self-explanatory, that it requires no comment to enable the reader fully to understand and appreciate them. It will be observed that the philosophical admonitions in the letter to his brother, Johnston, were written on the same sheet with the letter to his father.
The promptness and decision with which Lincoln despatched the multitudinous affairs of his office during the most turbulent scenes of the Civil War are exemplified in his unequivocal order to the Attorney-General, indorsed on the back of the letter of Hon. Austin A. King, requesting a pardon for John B. Corner. The indorsement bears even date with the letter itself, and Corner was pardoned on the following day.
THE ORIGINALS FROM WHICH THE WITHIN FACSIMILES WERE MADE ARE IN THE COLLECTION OF MR. WILLIAM K. BIXBY, AND THROUGH HIS COURTESY THEY ARE REPRODUCED FOR MEMBERS OF THE BIBLIOPHILE SOCIETY
Your letter of the 7th was received night before last. I very cheerfully send you the twenty dollars, which sum you say is necessary to save your land from sale. It is singular that you should have forgotten a judgment against you; and it is more singular that the plaintiff should have let you forget it so long, particularly as I suppose you have always had property enough to satisfy a judgment of that amount. Before you pay it, it would be well to be sure you have not paid it; or, at least, that you can not prove you have paid it. Give my love to Mother, and all the connections.
Affectionately your son,
A. LINCOLN.
[Written on same page with above.]
Dear Johnston:—
Your request for eighty dollars, I do not think it best to comply with now. At the various times when I have helped you a little, you have said to me, "We can get along very well now," but in a very short time I find you in the same difficulty again. Now this can only happen by some defect in your conduct. What that defect is, I think I know. You are not lazy, and still you are an idler. I doubt whether since I saw you, you have done a good whole day's work, in any one day. You do not very much dislike to work, and still you do not work much, merely because it does not seem to you that you could get much for it. This habit of uselessly wasting time, is the whole difficulty; and it is vastly important to you, and still more so to your children, that you should break this habit. It is more important to them, because they have longer to live, and can keep out of an idle habit before they are in it easier than they can get out after they are in.
You are now in need of some ready money; and what I propose is, that you shall go to work, "tooth and nail," for somebody who will give you money for it. Let father and your boys take charge of things at home—prepare for a crop, and make the crop; and you go to work for the best money wages, or in discharge of any debt you owe, that you can get. And to secure you a fair reward for your labor, I now promise you that for every dollar you will, between this and the first of next May, get for your own labor either in money or in your own indebtedness, I will then give you one other dollar. By this, if you hire yourself at ten dollars a month, from me you will get ten more, making twenty dollars a month for your work. In this, I do not mean you shall go off to St. Louis, or the lead mines, or the gold mines, in California, but I mean for you to go at it for the best wages you can get close to home, in Coles County. Now if you will do this, you will soon be out of debt, and what is better, you will have a habit that will keep you from getting in debt again. But if I should now clear you out, next year you will be just as deep in as ever. You say you would almost give your place in Heaven for $70 or $80. Then you value your place in Heaven very cheaply, for I am sure you can with the offer I make you get the seventy or eighty dollars for four or five months' work. You say if I furnish you the money you will deed me the land, and if you don't pay the money back, you will deliver possession—Nonsense! If you can't now live with the land, how will you then live without it? You have always been kind to me, and I do not now mean to be unkind to you. On the contrary, if you will but follow my advice, you will find it worth more than eight times eighty dollars to you.
Affectionately your brother,
Lieutenant-General Grant,—
Not expecting to see you again before the spring campaign opens, I wish to express, in this way, my entire satisfaction with what you have done up to this time, so far as I understand it. The particulars of your plans I neither know, or seek to know. You are vigilant and self reliant; and, pleased with this, I wish not to obtrude any constraints or restraints upon you. While I am very anxious that any great disaster, or the capture of our men in great numbers, shall be avoided, I know these points are less likely to escape your attention than they would be mine. If there is anything wanting which is within my power to give, do not fail to let me know it.
And now with a brave Army, and a just cause, may God sustain you.
Yours very truly,
[Transcriber's Note: The letter from Austin A. King, requesting a pardon for John B. Corner is contained in files f_linc05.jpg and f_linc06.jpg. Lincoln's note approving the pardon is contained in file f_linc07.jpg. As these letters were not transcribed in the print book, they have not been transcribed here.]
TO THE MEN AND WOMEN OF AMERICA
WHO HAVE GROWN UP SINCE HIS TRAGIC DEATH, AND WHO HAVE YET TO LEARN THE STORY OF HIS LIFE, THIS RECORD OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN IS FAITHFULLY INSCRIBED
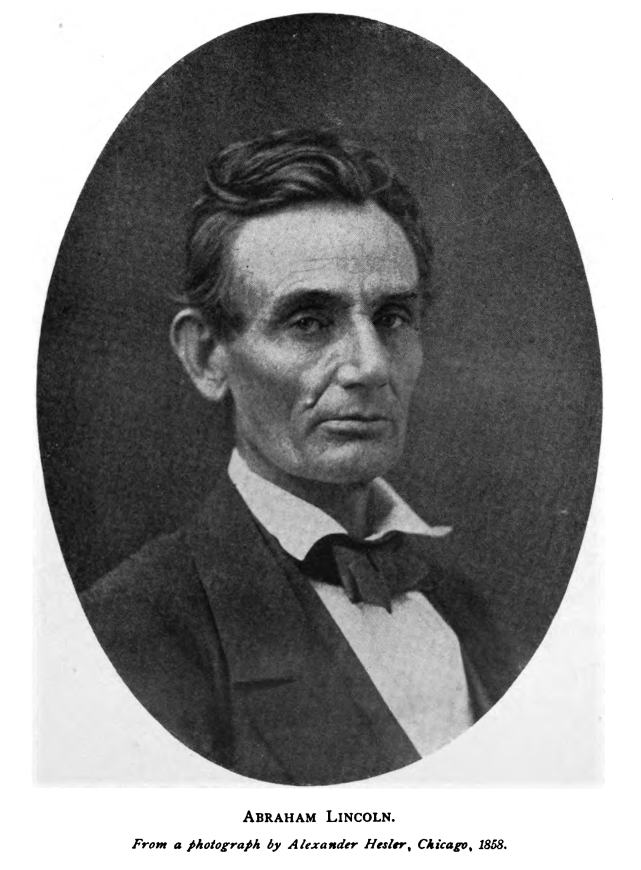

A quarter of a century has well-nigh rolled by since the tragic death of Abraham Lincoln. The prejudice and bitterness with which he was assailed have disappeared from the minds of men, and the world is now beginning to view him as a great historical character. Those who knew and walked with him are gradually passing away, and ere long the last man who ever heard his voice or grasped his hand will have gone from earth. With a view to throwing a light on some attributes of Lincoln's character heretofore obscure, and thus contributing to the great fund of history which goes down to posterity, these volumes are given to the world.
If Mr. Lincoln is destined to fill that exalted station in history or attain that high rank in the estimation of the coming generations which has been predicted of him, it is alike just to his memory and the proper legacy of mankind that the whole truth concerning him should be known. If the story of his life is truthfully and courageously told-nothing colored or suppressed; nothing false either written or suggested-the reader will see and feel the presence of the living man. He will, in fact, live with him and be moved to think and act with him. If, on the other hand, the story is colored or the facts in any degree suppressed, the reader will be not only misled, but imposed upon as well. At last the truth will come, and no man need hope to evade it.
"There is but one true history in the world," said one of Lincoln's closest friends to whom I confided the project of writing a history of his life several years ago, "and that is the Bible. It is often said of the old characters portrayed there that they were bad men. They are contrasted with other characters in history, and much to the detriment of the old worthies. The reason is, that the Biblical historian told the whole truth-the inner life. The heart and secret acts are brought to light and faithfully photographed. In other histories virtues are perpetuated and vices concealed. If the life of King David had been written by an ordinary historian the affair of Uriah would at most have been a quashed indictment with a denial of all the substantial facts. You should not forget there is a skeleton in every house. The finest character dug out thoroughly, photographed honestly, and judged by that standard of morality or excellence which we exact for other men is never perfect. Some men are cold, some lewd, some dishonest, some cruel, and many a combination of all. The trail of the serpent is over them all! Excellence consists, not in the absence of these attributes, but in the degree in which they are redeemed by the virtues and graces of life. Lincoln's character will, I am certain, bear close scrutiny. I am not afraid of you in this direction. Don't let anything deter you from digging to the bottom; yet don't forget that if Lincoln had some faults, Washington had more—few men have less. In drawing the portrait tell the world what the skeleton was with Lincoln. What gave him that peculiar melancholy? What cancer had he inside?"
Some persons will doubtless object to the narration of certain facts which appear here for the first time, and which they contend should have been consigned to the tomb. Their pretense is that no good can come from such ghastly exposures. To such over-sensitive souls, if any such exist, my answer is that these facts are indispensable to a full knowledge of Mr. Lincoln in all the walks of life. In order properly to comprehend him and the stirring, bloody times in which he lived, and in which he played such an important part, we must have all the facts—we must be prepared to take him as he was.
In determining Lincoln's title to greatness we must not only keep in mind the times in which he lived, but we must, to a certain extent, measure him with other men. Many of our great men and our statesmen, it is true, have been self-made, rising gradually through struggles to the topmost round of the ladder; but Lincoln rose from a lower depth than any of them. His origin was in that unknown and sunless bog in which history never made a foot-print. I should be remiss in my duty if I did not throw the light on this part of the picture, so that the world may realize what marvellous contrast one phase of his life presents to another.
The purpose of these volumes is to narrate facts, avoiding as much as possible any expression of opinion, and leaving the reader to form his own conclusions. Use has been made of the views and recollections of other persons, but only those known to be truthful and trustworthy. A thread of the narrative of Lincoln's life runs through the work, but an especial feature is an analysis of the man and a portrayal of his attributes and characteristics. The attempt to delineate his qualities, his nature and its manifestations, may occasion frequent repetitions of fact, but if truthfully done this can only augment the store of matter from which posterity is to learn what manner of man he was.
The object of this work is to deal with Mr. Lincoln individually and domestically; as lawyer, as citizen, as statesman. Especial attention is given to the history of his youth and early manhood; and while dwelling on this portion of his life the liberty is taken to insert many things which would be omitted or suppressed in other places, where the cast-iron rules that govern magazine-writing are allowed to prevail. Thus much is stated in advance, so that no one need be disappointed in the scope and extent of the work. The endeavor is to keep Lincoln in sight all the time; to cling close to his side all the way through—leaving to others the more comprehensive task of writing a history of his times. I have no theory of his life to establish or destroy. Mr. Lincoln was my warm, devoted friend.
I always loved him, and I revere his name to this day. My purpose to tell the truth about him need occasion no apprehension; for I know that "God's naked truth," as Carlyle puts it, can never injure the fame of Abraham Lincoln. It will stand that or any other test, and at last untarnished will reach the loftiest niche in American history.
My long personal association with Mr. Lincoln gave me special facilities in the direction of obtaining materials for these volumes. Such were our relations during all that portion of his life when he was rising to distinction, that I had only to exercise a moderate vigilance in order to gather and preserve the real data of his personal career. Being strongly drawn to the man, and believing in his destiny, I was not unobservant or careless in this respect. It thus happened that I became the personal depositary of the larger part of the most valuable Lincolniana in existence. Out of this store the major portion of the materials of the following volumes has been drawn. I take this, my first general opportunity, to return thanks to the scores of friends in Kentucky, Indiana, Illinois, and elsewhere for the information they have so generously furnished and the favors they have so kindly extended me. Their names are too numerous for separate mention, but the recompense of each one will be the consciousness of having contributed a share towards a true history of the "first American."
Over twenty years ago I began this book; but an active life at the bar has caused me to postpone the work of composition, until, now, being somewhat advanced in years, I find myself unable to carry out the undertaking. Within the past three years I have been assisted in the preparation of the book by Mr. Jesse W. Weik, of Greencastle, Ind., whose industry, patience, and literary zeal have not only lessened my labors, but have secured for him the approbation of Lincoln's friends and admirers. Mr. Weik has by his personal investigation greatly enlarged our common treasure of facts and information. He has for several years been indefatigable in exploring the course of Lincoln's life. In no particular has he been satisfied with anything taken at second hand. He has visited—as I also did in 1865—Lincoln's birthplace in Kentucky, his early homes in Indiana and Illinois, and together, so to speak, he and I have followed our hero continuously and attentively till he left Springfield in 1861 to be inaugurated President. We have retained the original MSS. in all cases, and they have never been out of our hands. In relating facts therefore, we refer to them in most cases, rather than to the statements of other biographers.
This brief preliminary statement is made so that posterity, in so far as posterity may be interested in the subject, may know that the vital matter of this narrative has been deduced directly from the consciousness, reminiscences, and collected data of
William H. Herndon.
Springfield, Ill.,
November 1, 1888.
CONTENTS
ILLUSTRATIONS
First Presbyterian in Springfield
Edwards Residence Where Lincoln Married
Court House, Springfield 1850-1860
I was called upon during the lifetime of Mr. Herndon to write for the second edition of this work a chapter on the Lincoln-Douglas campaign of 1858. After this had been done and the book had been revised for the press, I was requested by the publishers to add something in the nature of a character sketch of Mr. Lincoln as I knew him before his fame had spread much beyond the confines of Illinois, and to tell what were those qualities that made him so attractive then. Of course, they were the same qualities which made him attractive afterward on a wider scale. The popular judgment of him is, in the main, correct and unshakable. I say in the main, because there is in this judgment a tendency to apotheosis which, while pardonable, is not historical, and will not last.
At the time when he was preparing himself unconsciously to be the nation's leader in a great crisis the only means of gaining public attention was by public speech. The press did not exist for him, or for the people among whom he lived. The ambitious young men of the day must make their mark by oratory, or not at all. There was no division of labor between the speaker and the editor. If a man was to gain any popularity he must gain it by talking into the faces of the people. He must have a ready tongue, and must be prepared to meet all comers and to accept all challenges. Stump-speaking, wrestling, story-telling, and horse-racing were the only amusements of the people. In the first three of these Mr. Lincoln excelled. He grew up in this atmosphere, as did all his rivals. It was a school to develop all the debating powers that the community possessed, and to bring them to a high degree of perfection. Polish was not necessary to success, but plainness of diction was. The successful speaker was he who could make himself best understood by the common people, and in turn could best understand them.
Among the earliest accounts that we get of Mr. Lincoln we find him talking to other boys from some kind of a platform. He had a natural gift, and he exercised it as opportunity came to him. When he arrived at man's estate these opportunities came as often as could be desired. Other young men gifted in the same way were growing up around him. Douglas, Baker, Trumbull, Hardin, Browning, Yates, Archibald Williams, Josiah Lamborn, and Lisle Smith were among them. All these had the same kind of training for public preferment that Lincoln had; some of them had more book learning, but not much more. We have his own word for it that he was as ambitious of such preferment as Douglas was; and this was putting it in the superlative degree.
The popular conception of Mr. Lincoln as one not seeking public honors, but not avoiding public duties, is a post bellum growth, very wide of the mark. He was entirely human in this regard, but his desire for political preferment was hedged about by a sense of obligation to the truth which nothing could shake. This fidelity to truth was ingrained and unchangeable. In all the speeches I ever heard him make—and they were many—he never even insinuated an untruth, nor did he ever fail when stating his opponent's positions to state them fully and fairly. He often stated his opponent's position better than his opponent did or could. To say what was false, or even to leave his hearers under a wrong impression, was impossible to him. Within this high inclosure he was as ambitious of earthly honors as any man of his time. Furthermore, he was an adept at log-rolling or any political game that did not involve falsity. I was Secretary of the Republican State Committee of Illinois during some years when he was in active campaign work. He was often present at meetings of the committee, although not a member, and took part in the committee work. His judgment was very much deferred to in such matters. He was one of the shrewdest politicians of the State. Nobody had had more experience in that way, nobody knew better than he what was passing in the minds of the people. Nobody knew better how to turn things to advantage politically, and nobody was readier to take such advantage, provided it did not involve dishonorable means. He could not cheat people out of their votes any more than out of their money. The Abraham Lincoln that some people have pictured to themselves, sitting in his dingy law office, working over his cases till the voice of duty roused him, never existed. If this had been his type he never would have been called at all. It was precisely because he was up and stirring, and in hot, incessant competition with his fellows for earthly honors, that the public eye became fixed upon him and the public ear attuned to his words. Fortunate was it for all of us that he was no shrinking patriot, that he was moved as other men are moved, so that his fellows might take heed of him and know him as one of themselves, and as fit to be their leader in a crisis.
Let me repeat and emphasize what I have here said. Mr. Lincoln never gave his assent, so far as my knowledge goes, to any plan or project for getting votes that would not have borne the full light of day. At the same time, he had no objection to the getting of votes by the pledge of offices, nor was he too particular what kind of men got the offices. His preference was always for good men; but he could not resist pressure where persons were concerned, even though his conscience told him that he was doing wrong.
We have seen what kind of debating school Mr. Lincoln grew up in. It was the best possible school for him, and it was an advantage to him that he had able men for his competitors. Among them was Stephen A. Douglas, the most versatile, indomitable, and unscrupulous of all of them. He was Lincoln's rival, as is shown in these pages, for almost everything, from the hand of Mary Todd to the presidency of the United States. He had the strength and presence of a lion, with all the cunning of a fox. He possessed every quality which wins popular favor and high station except veracity, and I know of nothing in the pages of history more cheering to pious souls than the eventual triumph of Honest Abe over the Little Giant.
It was by restless competition and rough-and-tumble with Douglas and others that Mr. Lincoln acquired that rare power of expression, by mouth and pen, which drew to himself the attention of the State and afterward of the nation and the world. He rarely used ornament in his speeches. Although gifted with the power of humor to an extraordinary degree, he seldom employed it in his later years except in private circles. Thus it came about that this growing master of logic, this profound and earnest debater of the most serious questions of the day, was the most popular of tavern loungers, and could draw more people together and hold them longer by mere drollery and cameraderie than any other man I ever knew. Mr. Lincoln's nature was one of almost child-like sweetness. He did not "put you at your ease" when you came into his presence. You felt at your ease without being put there. He never assumed superiority over anybody in the ordinary intercourse of life.
A good test of this trait in his character was furnished in my own experience. When I was first thrown into his society I was just out of college, and was as callow and as self-confident as boys usually are at that time of life. Mr. Lincoln was at the maturity of his powers. I was often with him when he had no other companion. In our intercourse he always paid marked deference to my opinions, and if we differed he would argue the point with me as earnestly as though I had been the opposing counsel in a lawsuit. And this he would do with anybody, young or old, ignorant or learned. I never heard him express contempt for any man's honest errors, although he would sometimes make a droll remark or tell a funny story about them. Deference to other people's opinions was habitual to him. There was no calculation, no politics in it. It was part and parcel of his sense of equal rights. His democracy was of the unconscious kind—he did not know anything different from it. Coupled with this was a habit of unselfishness and kindly temper most engaging to all who knew him or had any dealings with him. At the same time he knew when he was imposed upon, and it was unsafe for anybody to presume upon his good nature or to take him for a flat.
But more than intellectual gifts, more than good-fellowship, did the sense of justice give him his hold on others. That was a magnetic field whose influences could not be escaped. He carried it as unconsciously as he carried his hair. The Athenians would never have ostracized him—indeed, they would never have called him the Just. They would have taken him as they took the bees on Hymettus—as one naturally searching after sweet things.
To say that Mr. Lincoln was a man who had the courage of his convictions would be rather an under-statement. This was part and parcel of his sense of justice. He wore it as he wore his clothes, except that it fitted him much better than his garments usually did. At the time I first knew him it was irksome to very many of his friends to be told that there ought to be an efficient fugitive slave law. But it was his conviction as a lawyer that there ought to be one, and he never failed to say so when interrogated, or when occasion required that that subject should be touched upon. And it is a fact that abolitionists like Lovejoy and Codding would take this from Lincoln without murmuring, when they would not take it from anybody else. He never would echo the popular cry, "No more slave States!" Whenever this subject was discussed he would say that if a Territory having the requisite population and belonging to us should apply for admission to the Union without fraud or constraint, yet with slavery, he could not see any other disposition to be made of her than to admit her. And when he had said this, even to an audience of radical antislavery men, there would be no protestations. Those who were not convinced would observe a respectful silence.
Mr. Lincoln's facial expression when in repose and when animated presented most remarkable contrasts. I have before me a photograph of him taken at Pittsfield, Illinois, during the campaign of 1858. It looks as I have seen him a hundred times, his lantern jaws and large mouth and solid nose firmly set, his sunken eyes looking at nothing yet not unexpressive, his wrinkled and retreating forehead cut off by a mass of tousled hair, with a shade of melancholy drawn like a veil over his whole face. Nothing more unlike this can be imagined than the same Lincoln when taking part in a conversation, or addressing an audience, or telling a story. The dull, listless features dropped like a mask. The melancholy shadow disappeared in a twinkling. The eye began to sparkle, the mouth to smile, the whole countenance was wreathed with animation, so that a stranger would have said: "Why, this man, so angular and somber a moment ago, is really handsome."
What more can be said of the qualities that first made Mr. Lincoln attractive to his contemporaries? These were debating power, honesty of purpose, a child-like temper, purity of life, and courage of conviction. All these traits will be seen in the following pages, rising, unfolding, expanding in a regular, orderly, human way as the young Lincoln grew to mature years.
What Mr. Lincoln was after he became President can be best understood by knowing what he was before. The world owes more to William H. Herndon for this particular knowledge than to all other persons taken together. It is no exaggeration to say that his death, which took place at his farm near Springfield, Illinois, March 18, 1891, removed from earth the person who, of all others, had most thoroughly searched the sources of Mr. Lincoln's biography and had most attentively, intelligently, and also lovingly studied his character. He was generous in imparting his information to others. Almost every life of Lincoln published since the tragedy at Ford's Theatre has been enriched by his labors. He was nine years the junior of Mr. Lincoln. Their partnership began in 1843, and it continued until it was dissolved by the death of the senior member. Between them there was never an unkind word or thought. When Mr. Lincoln became President, Mr. Herndon could have had his fortunes materially advanced under the new Administration by saying a word. He was a poor man then and always, but he chose to remain in his more humble station and to earn his bread by his daily labor.
Some six years ago Mr. Herndon conceived the project of writing a series of magazine articles intended to portray the youth and early manhood of Lincoln. Being somewhat infirm, he called Mr. Weik to his assistance, as he has explained in his preface. The magazine articles expanded insensibly to the present volumes. Lincolniana is increasing and is destined to increase. It has been enriched within recent years by the indispensable but too massive work of Nicolay and Hay, by the masterly essay of Schurz, and by the posthumous lecture of Greeley, which latter, being in reality if not in terms a hearty, ungrudging confession that he had underestimated Lincoln in his lifetime, is doubly welcome. As a portraiture of the man Lincoln—and this is what we look for above all things in a biography—I venture to think that Mr. Herndon's work will never be surpassed.
Horace White.
New York, February, 1892.

BEYOND the fact that he was born on the 12th day of February, 1809, in Hardin county, Kentucky, Mr. Lincoln usually had but little to say of himself, the lives of his parents, or the history of the family before their removal to Indiana. If he mentioned the subject at all, it was with great reluctance and significant reserve. There was something about his origin he never cared to dwell upon. His nomination for the Presidency in 1860, however, made the publication of his life a necessity, and attracted to Springfield an army of campaign biographers and newspaper men. They met him in his office, stopped him in his walks, and followed him to his house. Artists came to paint his picture, and sculptors to make his bust. His autographs were in demand, and people came long distances to shake him by the hand. This sudden elevation to national prominence found Mr. Lincoln unprepared in a great measure for the unaccustomed demonstrations that awaited him. While he was easy of approach and equally courteous to all, yet, as he said to me one evening after a long day of hand-shaking, he could not understand why people should make so much over him.
Among the earliest newspaper men to arrive in Springfield after the Chicago convention was the late J. L. Scripps of the Chicago Tribune, who proposed to prepare a history of his life. Mr. Lincoln deprecated the idea of writing even a campaign biography. "Why, Scripps," said he, "it is a great piece of folly to attempt to make anything out of me or my early life. It can all be condensed into a single sentence, and that sentence you will find in Gray's Elegy,
'The short and simple annals of the poor.'
That's my life, and that's all you or anyone else can make out of it."
He did, however, communicate some facts and meagre incidents of his early days, and, with the matter thus obtained, Mr. Scripps prepared his book. Soon after the death of Lincoln I received a letter from Scripps, in which, among other things, he recalled the meeting with Lincoln, and the view he took of the biography matter.
"Lincoln seemed to be painfully impressed," he wrote, "with the extreme poverty of his early surroundings, and the utter absence of all romantic and heroic elements. He communicated some facts to me concerning his ancestry, which he did not wish to have published then, and which I have never spoken of or alluded to before."
What the facts referred to by Mr. Scripps were we do not know; for he died several years ago without, so far as is known revealing them to anyone.
On the subject of his ancestry and origin I only remember one time when Mr. Lincoln ever referred to it. It was about 1850, when he and I were driving in his one-horse buggy to the court in Menard county, Illinois. The suit we were going to try was one in which we were likely, either directly or collaterally, to touch upon the subject of hereditary traits. During the ride he spoke, for the first time in my hearing, of his mother, dwelling on her characteristics, and mentioning or enumerating what qualities he inherited from her. He said, among other things, that she was the daughter of Lucy Hanks and a well-bred but obscure Virginia farmer or planter; and he argued that from this last source came his power of analysis, his logic, his mental activity, his ambition, and all the qualities that distinguished him from the other members and descendants of the Hanks family.
In only two instances did Mr. Lincoln over his own hand leave any record of his history or family descent. One of these was the modest bit of autobiography furnished to Jesse W. Fell, in 1859, in which, after stating that his parents were born in Virginia of "undistinguished or second families," he makes the brief mention of his mother, saying that she came "of a family of the name of Hanks."* The other record was the register of marriages, births, and deaths which he made in his father's Bible. The latter now lies before me. That portion of the page which probably contained the record of the marriage of his parents, Thomas Lincoln and Nancy Hanks, has been lost; but fortunately the records of Washington county, Kentucky, and the certificate of the minister who performed the marriage ceremony—the Rev. Jesse Head—fix the fact and date of the latter on the 12th day of June, 1806.
* If anyone will take the pains to read the Fell autobiography they will be struck with Lincoln's meagre reference to his mother. He even fails to give her maiden or Christian name, and devotes but three lines to her family. A history of the Lincolns occupies almost an entire page.
On the 10th day of February in the following year a daughter Sarah* was born, and two years later, on the 12th of February, the subject of these memoirs came into the world. After him came the last child, a boy—named Thomas after his father—who lived but a few days. No mention of his existence is found in the Bible record.
* Most biographers of Lincoln, in speaking of Mr. Lincoln's sister, call her Nancy, some—notably Nicolay and Hay— insisting that she was known by that name among her family and friends. In this they are in error. I have interviewed the different members of the Hanks and Lincoln families who survived the President, and her name was invariably given as Sarah. The mistake, I think, arises from the fact that, in the Bible record referred to, all that portion relating to the birth of "Sarah, daughter of Thomas and Nancy Lincoln," down to the word Nancy has been torn away, and the latter name has therefore been taken erroneously for that of the daughter. Reading the entry of Abraham's birth below satisfies one that it must refer to the mother.
Abraham Lincoln, the grandfather of the President, emigrated to Jefferson county, Kentucky, from Virginia, about 1780, and from that time forward the former State became an important one in the history of the family, for in it was destined to be born its most illustrious member. About five years before this, a handful of Virginians had started across the mountains for Kentucky, and in the company, besides their historian, William Calk,—whose diary recently came to light,—was one Abraham Hanks. They were evidently a crowd of jolly young men bent on adventure and fun, but their sport was attended with frequent disasters. Their journey began at "Mr. Priges' tavern on the Rapidan." When only a few days out "Hanks' Dog's leg got broke." Later in the course of the journey, Hanks and another companion became separated from the rest of the party and were lost in the mountains for two days; in crossing a stream "Abraham's saddle turned over and his load all fell in Indian creek"; finally they meet their brethren from whom they have been separated and then pursue their way without further interruption. Returning emigrants whom they meet, according to the journal of Calk, tell such "news of the indians" that certain members of the company are "afrade to go aney further." The following day more or less demoralization takes place among the members of this pioneer party when the announcement is made, as their chronicler so faithfully records it, that "Philip Drake Bakes bread without washing his hands." This was an unpardonable sin, and at it they revolted. A day later the record shows that "Abram turns Back." Beyond this we shall never know what became of Abraham Hanks, for no further mention of him is made in this or any other history. He may have returned to Virginia and become, for aught we know, one of the President's ancestors on the maternal side of the house; but if so his illustrious descendant was never able to establish the fact or trace his lineage satisfactorily beyond the first generation which preceded him. He never mentioned who his maternal grandfather was, if indeed he knew.
His paternal grandfather, Abraham Lincoln,* the pioneer from Virginia, met his death within two years after his settlement in Kentucky at the hands of the Indians; "not in battle," as his distinguished grandson tells us, "but by stealth, when he was laboring to open a farm in the forest." The story of his death in sight of his youngest son Thomas, then only six years old, is by no means a new one to the world. In fact I have often heard the President describe the tragedy as he had inherited the story from his father. The dead pioneer had three sons, Mordecai, Josiah, and Thomas, in the order named. When the father fell, Mordecai, having hastily sent Josiah to the neighboring fort after assistance, ran into the cabin, and pointing his rifle through a crack between the logs, prepared for defense. Presently an Indian came stealing up to the dead father's body. Beside the latter sat the little boy Thomas. Mordecai took deliberate aim at a silver crescent which hung suspended from the Indian's breast, and brought him to the ground. Josiah returned from the fort with the desired relief, and the savages were easily dispersed, leaving behind one dead and one wounded.
* "They [the Lincolns] were also called Linkhorns. The old settlers had a way of pronouncing names not as they were spelled, but rather, it seemed, as they pleased. Thus they called Medcalf 'Medcap,' and Kaster they pronounced 'Custard.'"—MS. letter, Charles Friend, March 19,1866.
The tragic death of his father filled Mordecai with an intense hatred of the Indians—a feeling from which he never recovered. It was ever with him like an avenging spirit. From Jefferson county he removed to Grayson, where he spent the remainder of his days. A correspondent* from there wrote me in 1865: "Old Mordecai was easily stirred up by the sight of an Indian. One time, hearing of a few Indians passing through the county, he mounted his horse, and taking his rifle on his shoulder, followed on after them and was gone two days. When he returned he said he left one lying in a sink hole. The Indians, he said, had killed his father, and he was determined before he died to have satisfaction." The youngest boy, Thomas, retained a vivid recollection of his father's death, which, together with other reminiscences of his boyhood, he was fond of relating later in life to his children to relieve the tedium of long winter evenings. Mordecai and Josiah,** both remaining in Kentucky, became the heads of good-sized families, and although never known or heard of outside the limits of the neighborhoods in which they lived, were intelligent, well-to-do men.
* W. T. Claggett, unpublished MS. ** "I knew Mordecai and Josiah Lincoln intimately. They were excellent men, plain, moderately educated, candid in their manners and intercourse, and looked upon as honorable as any men I have ever heard of. Mordecai was the oldest son, and his father having been killed by the Indians before the law of primogeniture was repealed, he inherited a very competent estate. The others were poor. Mordecai was celebrated for his bravery, and had been in the early campaigns of the West"-Henry Pirtle, letter, June 17,1865, MS.
In Thomas, roving and shiftless, to whom was "reserved the honor of an illustrious paternity," are we alone interested. He was, we are told, five feet ten inches high, weighed one hundred and ninety-five pounds, had a well-rounded face, dark hazel eyes, coarse black hair, and was slightly stoop-shouldered. His build was so compact that Dennis Hanks used to say he could not find the point of separation between his ribs. He was proverbially slow of movement, mentally and physically; was careless, inert, and dull; was sinewy, and gifted with great strength; was inoffensively quiet and peaceable, but when roused to resistance a dangerous antagonist. He had a liking for jokes and stories, which was one of the few traits he transmitted to his illustrious son; was fond of the chase, and had no marked aversion for the bottle, though in the latter case he indulged no more freely than the average Kentuckian of his day. At the time of his marriage to Nancy Hanks he could neither read nor write; but his wife, who was gifted with more education, and was otherwise his mental superior, taught him, it is said, to write his name and to read—at least, he was able in later years to spell his way slowly through the Bible. In his religious belief he first affiliated with the Free-Will Baptists. After his removal to Indiana he changed his adherence to the Presbyterians—or Predestinarians, as they were then called—and later united with the Christian—vulgarly called Campbellite Church, in which latter faith he is supposed to have died. He was a carpenter by trade, and essayed farming too; but in this, as in almost every other undertaking, he was singularly unsuccessful. He was placed in possession of several tracts of land at different times in his life, but was never able to pay for a single one of them. The farm on which he died was one his son purchased, providing a life estate therein for him and his wife. He never fell in with the routine of labor; was what some people would call unfortunate or unlucky in all his business ventures—if in reality he ever made one—and died near the village of Farmington in Coles county, Illinois, on the 17th day of January, 1851. His son, on account of sickness in his own family, was unable to be present at his father's bedside, or witness his death. To those who notified him of his probable demise he wrote: "I sincerely hope that father may yet recover his health; but at all events tell him to remember to call upon and confide in our great and good and merciful Maker, who will not turn away from him in any extremity. He notes the fall of a sparrow, and numbers the hairs of our heads; and He will not forget the dying man who puts his trust in him. Say to him that if we could meet now it is doubtful whether it would not be more painful than pleasant; but that if it be his lot to go now he will soon have a joyous meeting with the many loved ones gone before, and where the rest of us, through the help of God, hope ere long to join them." *
* MS. letter to John Johnston, Jan. 12, 1851.
Nancy Hanks, the mother of the President, at a very early age was taken from her mother Lucy—afterwards married to Henry Sparrow—and sent to live with her aunt and uncle, Thomas and Betsy Sparrow. Under this same roof the irrepressible and cheerful waif, Dennis Hanks*—whose name will be frequently seen in these pages—also found a shelter. At the time of her marriage to Thomas Lincoln, Nancy was in her twenty-third year. She was above the ordinary height in stature, weighed about 130 pounds, was slenderly built, and had much the appearance of one inclined to consumption. Her skin was dark; hair dark brown; eyes gray and small; forehead prominent; face sharp and angular, with a marked expression of melancholy which fixed itself in the memory of everyone who ever saw or knew her. Though her life was seemingly beclouded by a spirit of sadness, she was in disposition amiable and generally cheerful. Mr. Lincoln himself said to me in 1851, on receiving the news of his father's death, that whatever might be said of his parents, and however unpromising the early surroundings of his mother may have been, she was highly intellectual by nature, had a strong memory, acute judgment, and was cool and heroic. From a mental standpoint she no doubt rose above her surroundings, and had she lived, the stimulus of her nature would have accelerated her son's success, and she would have been a much more ambitious prompter than his father ever was.
* Dennis Hanks, still living at the age of ninety years in Illinois, was the son of another Nancy Hanks—the aunt of the President's mother. He furnished Mr. Weik and me with much interesting information, especially facts and incidents relating to early life in Indiana.
As a family the Hankses were peculiar to the civilization of early Kentucky. Illiterate and superstitious, they corresponded to that nomadic class still to be met with throughout the South, and known as "poor whites." They are happily and vividly depicted in the description of a camp-meeting held at Elizabethtown, Kentucky, in 1806, which was furnished me in August, 1865, by an eye-witness.*
* J. B. Helm, MS.
"The Hanks girls," narrates the latter, "were great at camp-meetings. I remember one in 1806. I will give you a scene, and if you will then read the books written on the subject you may find some apology for the superstition that was said to be in Abe Lincoln's character. It was at a camp-meeting, as before said, when a general shout was about to commence. Preparations were being made; a young lady invited me to stand on a bench by her side where we could see all over the altar. To the right a strong, athletic young man, about twenty-five years old, was being put in trim for the occasion, which was done by divesting him of all apparel except shirt and pants. On the left a young lady was being put in trim in much the same manner, so that her clothes would not be in the way, and so that, when her combs flew out, her hair would go into graceful braids. She, too, was young—not more than twenty perhaps. The performance commenced about the same time by the young man on the right and the young lady on the left. Slowly and gracefully they worked their way towards the centre, singing, shouting, hugging and kissing, generally their own sex, until at last nearer and nearer they came. The centre of the altar was reached, and the two closed, with their arms around each other, the man singing and shouting at the top of his voice,
"'I have my Jesus in my arms Sweet as honey, strong as bacon ham.'
"Just at this moment the young lady holding to my arm whispered, 'They are to be married next week; her name is Hanks.' There were very few who did not believe this true religion, inspired by the Holy Spirit, and the man who could not believe it, did well to keep it to himself. The Hankses were the finest singers and shouters in our country."
Here my informant stops, and on account of his death several years ago I failed to learn whether the young lady shouter who figured in the foregoing scene was the President's mother or not. The fact that Nancy Hanks did marry that year gives color to the belief that it was she. As to the probability of the young man being Thomas Lincoln it is difficult to say; such a performance as the one described must have required a little more emotion and enthusiasm than the tardy and inert carpenter was in the habit of manifesting.
Sarah, the sister of Abraham Lincoln, though in some respects like her brother, lacked his stature. She was thick-set, had dark-brown hair, deep-gray eyes, and an even disposition. In contact with others she was kind and considerate. Her nature was one of amiability, and God had endowed her with that invincible combination—modesty and good sense. Strange to say, Mr. Lincoln never said much about his sister in after years, and we are really indebted to the Hankses—Dennis and John—for the little we have learned about this rather unfortunate young woman. She was married to Aaron Grigsby, in Spencer county, Indiana, in the month of August, 1826, and died January 20, 1828. Her brother accompanied her to school while they lived in Kentucky, but as he was only seven, and as she had not yet finished her ninth year when their father removed with them to Indiana, it is to be presumed that neither made much progress in the matter of school education. Still it is authoritatively stated that they attended two schools during this short period. One of these was kept by Zachariah Riney, the other by Caleb Hazel. It is difficult at this late day to learn much of the boy Abraham's life during those seven years of residence in Kentucky. One man, * who was a clerk in the principal store in the village where the Lincolns purchased their family supplies, remembers him as a "small boy who came sometimes to the store with his mother. He would take his seat on a keg of nails, and I would give him a lump of sugar. He would sit there and eat it like any other boy; but these little acts of kindness," observes my informant, in an enthusiastic statement made in 1865, "so impressed his mind that I made a steadfast friend in a man whose power and influence have since been felt throughout the world." A school-mate** of Lincoln's at Hazel's school, speaking of the master, says: "He perhaps could teach spelling and reading and indifferent writing, and possibly could cipher to the rule of three; but he had no other qualification of a teacher, unless we accept large size and bodily strength. Abe was a mere spindle of a boy, had his due proportion of harmless mischief, but as we lived in a country abounding in hazel switches, in the virtue of which the master had great faith, Abe of course received his due allowance."
This part of the boy's history is painfully vague and dim, and even after arriving at man's estate Mr. Lincoln was significantly reserved when reference was made to it. It is barely mentioned in the autobiography furnished to Fell in 1859. John Duncan,*** afterwards a preacher of some prominence in Kentucky, relates how he and Abe on one occasion ran a ground-hog into a crevice between two rocks, and after working vainly almost two hours to get him out, "Abe ran off about a quarter of a mile to a blacksmith shop, and returned with an iron hook fastened to the end of a pole," and with this rude contrivance they virtually "hooked" the animal out of his retreat. Austin Gollaher of Hodgensville, claims to have saved Lincoln from drowning one day as they were trying to "coon it" across Knob creek on a log. The boys were in pursuit of birds, when young Lincoln fell into the water, and his vigilant companion, who still survives to narrate the thrilling story, fished him out with a sycamore branch.
* John B. Helm, June 20,1865. ** Samuel Haycraft, December 6,1866. *** Letter, February 21, 1867.
Meanwhile Thomas Lincoln was becoming daily more dissatisfied with his situation and surroundings. He had purchased, since his marriage, on the easy terms then prevalent, two farms or tracts of land in succession; no terms were easy enough for him, and the land, when the time for the payment of the purchase-money rolled around, reverted to its former owner. Kentucky, at that day, afforded few if any privileges, and possessed fewer advantages to allure the poor man; and no doubt so it seemed to Thomas Lincoln. The land he occupied was sterile and broken. A mere barren glade, and destitute of timber, it required a persistent effort to coax a living out of it; and to one of his easy-going disposition, life there was a never-ending struggle. Stories of vast stretches of rich and unoccupied lands in Indiana reaching his ears, and despairing of the prospect of any betterment in his condition so long as he remained in Kentucky, he resolved, at last, to leave the State and seek a more inviting lodgment beyond the Ohio. The assertion made by some of Mr. Lincoln's biographers, and so often repeated by sentimental writers, that his father left Kentucky to avoid the sight of or contact with slavery, lacks confirmation. In all Hardin county—at that time a large area of territory—there were not over fifty slaves; and it is doubtful if he saw enough of slavery to fill him with the righteous opposition to the institution with which he has so frequently been credited. Moreover, he never in later years manifested any especial aversion to it.
Having determined on emigrating to Indiana, he began preparations for removal in the fall of 1816 by building for his use a flat-boat. Loading it with his tools and other personal effects, including in the invoice, as we are told, four hundred gallons of whiskey, he launched his "crazy craft" on a tributary of Salt creek known as the Rolling Fork. Along with the current he floated down to the Ohio river, but his rudely-made vessel, either from the want of experience in its navigator, or because of its ill adaptation to withstand the force and caprices of the currents in the great river, capsized one day, and boat and cargo went to the bottom. The luckless boatman set to work however, and by dint of great patience and labor succeeded in recovering the tools and the bulk of the whiskey. Righting his boat, he continued down the river, landing at a point called Thompson's Ferry, in Perry county, on the Indiana side. Here he disposed of his vessel, and placing his goods in the care of a settler named Posey, he struck out through the interior in search of a location for his new home. Sixteen miles back from the river he found one that pleased his fancy, and he marked it off for himself. His next move in the order of business was a journey to Vincennes to purchase the tract at the Land Office—under the "two-dollar-an-acre law," as Dennis Hanks puts it—and a return to the land to identify it by blazing the trees and piling up brush on the corners to establish the proper boundary lines. Having secured a place for his home he trudged back to Kentucky—walking all the way—for his family. Two horses brought them and all their household effects to the Indiana shore. Posey kindly gave or hired them the use of a wagon, into which they packed not only their furniture and carpenter tools, but the liquor, which it is presumed had lain undisturbed in the former's cellar. Slowly and carefully picking their way through the dense woods, they at last reached their destination on the banks of Little Pigeon creek. There were some detentions on the way, but no serious mishaps.
The head of the household now set resolutely to work to build a shelter for his family.
The structure, when completed, was fourteen feet square, and was built of small unhewn logs. In the language of the day, it was called a "half-faced camp," being enclosed on all sides but one. It had neither floor, door, nor windows. In this forbidding hovel these doughty emigrants braved the exposure of the varying seasons for an entire year. At the end of that time Thomas and Betsy Sparrow followed, bringing with them Dennis Hanks; and to them Thomas Lincoln surrendered the "half-faced camp," while he moved into a more pretentious structure—a cabin enclosed on all sides. The country was thickly covered with forests of walnut, beech, oak, elm, maple, and an undergrowth of dog-wood, sumac, and wild grape-vine. In places where the growth was not so thick grass came up abundantly, and hogs found plenty of food in the unlimited quantity of mast the woods afforded. The country abounded in bear, deer, turkey, and other wild game, which not only satisfied the pioneer's love for sport, but furnished his table with its supply of meat.
Thomas Lincoln, with the aid of the Hankses and Sparrows, was for a time an attentive farmer. The implements of agriculture then in use were as rude as they were rare, and yet there is nothing to show that in spite of the slow methods then in vogue he did not make commendable speed. "We raised corn mostly"—relates Dennis—"and some wheat—enough for a cake Sunday morning. Hog and venison hams were a legal tender, and coon skins also. We raised sheep and cattle, but they did not bring much. Cows and calves were only worth six to eight dollars; corn ten cents, and wheat twenty-five cents, a bushel." So with all his application and frugality the head of this ill-assorted household made but little headway in the accumulation of the world's goods. We are told that he was indeed a poor man, and that during his entire stay in Indiana his land barely yielded him sufficient return to keep his larder supplied with the commonest necessaries of life. His skill as a hunter—though never brought into play unless at the angered demand of a stomach hungry for meat—in no slight degree made up for the lack of good management in the cultivation of his land. His son Abraham* never evinced the same fondness for hunting, although his cousin Dennis with much pride tells us how he could kill a wild turkey on the wing. "At that time," relates one of the latter's playmates** descanting on the abundance of wild game, "there were a great many deer-licks; and Abe and myself would go to these licks sometimes and watch of nights to kill deer, though Abe was not so fond of a gun or the sport as I was."***
* "Abe was a good boy—an affectionate one—a boy who loved his parents well and was obedient to their every wish. Although anything but an impudent or rude boy he was sometimes uncomfortably inquisitive. When strangers would ride along or pass by his father's fence he always—either through boyish pride or to tease his father—would be sure to ask the first question. His father would sometimes knock him over. When thus punished he never bellowed, but dropped a kind of silent, unwelcome tear as evidence of his sensitiveness or other feelings."—Dennis Hanks, MS., June 13,1865. ** David Turnham, MS. letter, June 10, 1866. *** Mr. Lincoln used to relate the following "coon" story: His father had at home a little yellow house-dog, which invariably gave the alarm if the boys undertook to slip away unobserved after night had set in—as they oftentimes did— to go coon hunting. One evening Abe and his step-brother, John Johnston, with the usual complement of boys required in a successful coon hunt, took the insignificant little cur with them. They located the coveted coon, killed him, and then in a sportive vein sewed the hide on the diminutive yellow dog. The latter struggled vigorously during the operation of sewing on, and being released from the hands of his captors made a bee-line for home. Other large and more important canines, on the way, scenting coon, tracked the little animal home, and possibly mistaking him for real coon, speedily demolished him. The next morning old Thomas Lincoln discovered lying in his yard the lifeless remains of yellow "Joe," with strong proof of coon-skin accompaniment. "Father was much incensed at his death," observed Mr. Lincoln, in relating the story, "but as John and I, scantily protected from the morning wind, stood shivering in the doorway, we felt assured little yellow Joe would never be able again to sound the call for another coon hunt."
The cabin to which the Lincoln family removed after leaving the little half-faced camp to the Sparrows was in some respects a pretentious structure. It was of hewed logs, and was eighteen feet square. It was high enough to admit of a loft, where Abe slept, and to which he ascended each night by means of pegs driven in the wall. The rude furniture was in keeping with the surroundings. Three-legged stools answered for chairs. The bedstead, made of poles fastened in the cracks of the logs on one side, and supported by a crotched stick driven in the ground floor on the other, was covered with skins, leaves, and old clothes. A table of the same finish as the stools, a few pewter dishes, a Dutch oven, and a skillet completed the household outfit. In this uninviting frontier structure the future President was destined to pass the greater part of his boyhood. Withal his spirits were light, and it cannot be denied that he must have enjoyed unrestrained pleasure in his surroundings. It is related that one day the only thing that graced the dinner-table was a dish of roasted potatoes. The elder Lincoln, true to the custom of the day, returned thanks for the blessing. The boy, realizing the scant proportions of the meal, looked up into his father's face and irreverently observed, "Dad, I call these"—meaning the potatoes—"mighty poor blessings." Among other children of a similar age he seemed unconsciously to take the lead, and it is no stretch of the truth to say that they, in turn, looked up to him. He may have been a little precocious—children sometimes are—but in view of the summary treatment received at the hands of his father it cannot truthfully be said he was a "spoiled child." One morning when his mother was at work he ran into the cabin from the outside to enquire, with a quizzical grin, "Who was the father of Zebedee's children?" As many another mother before and since has done, she brushed the mischievous young inquirer aside to attend to some more important detail of household concern.*
* Harriet Chapman, MS. letter.
The dull routine of chores and household errands in the boy's every-day life was brightened now and then by a visit to the mill. I often in later years heard Mr. Lincoln say that going to mill gave him the greatest pleasure of his boyhood days.
"We had to go seven miles to mill," relates David Turnham, the friend of his youth, "and then it was a hand-mill that would only grind from fifteen to twenty bushels of corn in a day. There was but little wheat grown at that time, and when we did have wheat we had to grind it in the mill described and use it without bolting, as there were no bolts in the country. Abe and I had to do the milling, frequently going twice to get one grist."
In his eleventh year he began that marvellous and rapid growth in stature for which he was so widely noted in the Pigeon creek settlement. "As he shot up," says Turnham, "he seemed to change in appearance and action. Although quick-witted and ready with an answer, he began to exhibit deep thoughtfulness, and was so often lost in studied reflection we could not help noticing the strange turn in his actions. He disclosed rare timidity and sensitiveness, especially in the presence of men and women, and although cheerful enough in the presence of the boys, he did not appear to seek our company as earnestly as before."* It was only the development we find in the history of every boy. Nature was a little abrupt in the case of Abraham Lincoln; she tossed him from the nimbleness of boyhood to the gravity of manhood in a single night.
* D. Turnham, MS. letter.
In the fall of 1818, the scantily settled region in the vicinity of Pigeon creek—where the Lincolns were then living—suffered a visitation of that dread disease common in the West in early days, and known in the vernacular of the frontier as "the milk-sick." It hovered like a spectre over the Pigeon creek settlement for over ten years, and its fatal visitation and inroads among the Lincolns, Hankses, and Sparrows finally drove that contingent into Illinois. To this day the medical profession has never agreed upon any definite cause for the malady, nor have they in all their scientific wrangling determined exactly what the disease itself is. A physician, who has in his practice met a number of cases, describes the symptoms to be "a whitish coat on the tongue, burning sensation of the stomach, severe vomiting, obstinate constipation of the bowels, coolness of the extremities, great restlessness and jactitation, pulse rather small, somewhat more frequent than natural, and slightly chorded. In the course of the disease the coat on the tongue becomes brownish and dark, the countenance dejected, and the prostration of the patient is great. A fatal termination may take place in sixty hours, or life may be prolonged for a period of fourteen days. These are the symptoms of the disease in an acute form. Sometimes it runs into the chronic form, or it may assume that form from the commencement, and after months or years the patient may finally die or recover only a partial degree of health."
When the disease broke out in the Pigeon creek region it not only took off the people, but it made sad havoc among the cattle. One man testifies that he "lost four milch cows and eleven calves in one week." This, in addition to the risk of losing his own life, was enough, he declared, to ruin him, and prompted him to leave for "points further west."
Early in October of the year 1818, Thomas and Betsy Sparrow fell ill of the disease and died within a few days of each other. Thomas Lincoln performed the services of undertaker. With his whipsaw he cut out the lumber, and with commendable promptness he nailed together the rude coffins to enclose the forms of the dead. The bodies were borne to a scantily cleared knoll in the midst of the forest, and there, without ceremony, quietly let down into the grave. Meanwhile Abe's mother had also fallen a victim to the insidious disease. Her sufferings, however, were destined to be of brief duration. Within a week she too rested from her labors. "She struggled on, day by day," says one of the household, "a good Christian woman, and died on the seventh day after she was taken sick. Abe and his sister Sarah waited on their mother, and did the little jobs and errands required of them. There was no physician nearer than thirty-five miles. The mother knew she was going to die, and called the children to her bedside. She was very weak, and the children leaned over while she gave her last message. Placing her feeble hand on little Abe's head she told him to be kind and good to his father and sister; to both she said, 'Be good to one another,' expressing a hope that they might live, as they had been taught by her, to love their kindred and worship God." Amid the miserable surroundings of a home in the wilderness Nancy Hanks passed across the dark river. Though of lowly birth, the victim of poverty and hard usage, she takes a place in history as the mother of a son who liberated a race of men. At her side stands another Mother whose son performed a similar service for all mankind eighteen hundred years before.
After the death of their mother little Abe and his sister Sarah began a dreary life—indeed, one more cheerless and less inviting seldom falls to the lot of any child. In a log-cabin without a floor, scantily protected from the severities of the weather, deprived of the comfort of a mother's love, they passed through a winter the most dismal either one ever experienced. Within a few months, and before the close of the winter, David Elkin, an itinerant preacher whom Mrs. Lincoln had known in Kentucky, happened into the settlement, and in response to the invitation from the family and friends, delivered a funeral sermon over her grave. No one is able now to 'remember the language of Parson Elkin's discourse, but it is recalled that he commemorated the virtues and good phases of character, and passed in silence the few shortcomings and frailties of the poor woman sleeping under the winter's snow. She had done her work in this world. Stoop-shouldered, thin-breasted, sad,—at times miserable,—groping through the perplexities of life, without prospect of any betterment in her condition, she passed from earth, little dreaming of the grand future that lay in store for the ragged, hapless little boy who stood at her bedside in the last days of her life.
Thomas Lincoln's widowerhood was brief. He had scarcely mourned the death of his first wife a year until he reappeared in Kentucky at Elizabethtown in search of another. His admiration had centred for a second time on Sally Bush, the widow of Daniel Johnston, the jailer of Hardin county, who had died several years before of a disease known as the "cold plague." The tradition still kept alive in the Kentucky neighborhood is that Lincoln had been a suitor for the hand of the lady before his marriage to Nancy Hanks, but that she had rejected him for the hand of the more fortunate Johnston. However that may have been, it is certain that he began his campaign in earnest this time, and after a brief siege won her heart. "He made a very short courtship," wrote Samuel Haycraft* to me in a letter, December 7, 1866. "He came to see her on the first day of December, 1819, and in a straightforward manner told her that they had known each other from childhood. 'Miss Johnston,' said he, 'I have no wife and you no husband. I came a-purpose to marry you. I knowed you from a gal and you knowed me from a boy. I've no time to lose; and if you're willin' let it be done straight off.' She replied that she could not marry him right off, as she had some little debts which she wanted to pay first. He replied, 'Give me a list of them.' He got the list and paid them that evening. Next morning I issued the license, and they were married within sixty yards of my house." Lincoln's brother-in-law, Ralph Krume, and his four horses and spacious wagon were again brought into requisition. With commendable generosity he transported the newly married pair and their household effects to their home in Indiana. The new Mrs. Lincoln was accompanied by her three children, John, Sarah, and Matilda. Her social status is fixed by the comparison of a neighbor, who observed that "life among the Hankses, the Lincolns, and the Enlows was a long ways below life among the Bushes."
* Clerk of the Court. MS.
In the eyes of her spouse she could not be regarded as a poor widow. She was the owner of a goodly stock of furniture and household goods; bringing with her among other things a walnut bureau valued at fifty dollars. What effect the new family, their collection of furniture, cooking utensils, and comfortable bedding must have had on the astonished and motherless pair who from the door of Thomas Lincoln's forlorn cabin watched the well-filled wagon as it came creaking through the woods can better be imagined than described. Surely Sarah and Abe, as the stores of supplies were rolled in through the doorless doorways, must have believed that a golden future awaited them. The presence and smile of a motherly face in the cheerless cabin radiated sunshine into every neglected corner. If the Lincoln mansion did not in every respect correspond to the representations made by its owner to the new Mrs. Lincoln before marriage, the latter gave no expression of disappointment or even surprise. With true womanly courage and zeal she set resolutely to work to make right that which seemed wrong. Her husband was made to put a floor in the cabin, as well as to supply doors and windows. The cracks between the logs were plastered up. A clothes-press filled the space between the chimney jamb and the wall, and the mat of corn husks and leaves on which the children had slept in the corner gave way to the comfortable luxuriance of a feather bed. She washed the two orphans, and fitted them out in clothes taken from the stores of her own. The work of renovation in and around the cabin continued until even Thomas Lincoln himself, under the general stimulus of the new wife's presence, caught the inspiration, and developed signs of intense activity. The advent of Sarah Bush was certainly a red-letter day for the Lincolns. She was not only industrious and thrifty, but gentle and affectionate; and her newly adopted children for the first time, perhaps, realized the benign influence of a mother's love. Of young Abe she was especially fond, and we have her testimony that her kindness and care for him were warmly and bountifully returned. Her granddaughter furnished me* in after years with this description of her:
* Harriet Chapman. MS.
"My grandmother is a very tall woman, straight as an Indian, of fair complexion, and was, when I first remember her, very handsome, sprightly, talkative, and proud. She wore her hair curled till gray; is kind-hearted and very charitable, and also very industrious." In September, 1865, I visited the old lady* and spent an entire day with her. She was then living on the farm her stepson had purchased and given her, eight miles south of the town of Charleston, in Illinois. She died on the 10th of April, 1869.
* During my interview with this old lady I was much and deeply impressed with the sincerity of her affection for her illustrious stepson. She declined to say much in answer to my questions about Nancy Hanks, her predecessor in the Lincoln household, but spoke feelingly of the latter's daughter and son. Describing Mr. Lincoln's last visit to her in February, 1861, she broke into tears and wupt bitterly. "I did not want Abe to run for President," she sobbed, "and did not want to see him elected. I was afraid that something would happen to him, and when he came down to see me, after he was elected President, I still felt, and my heart told me, that something would befall him, and that I should never see him again. Abe and his father are in heaven now, I am sure, and I expect soon to go there and meet them."
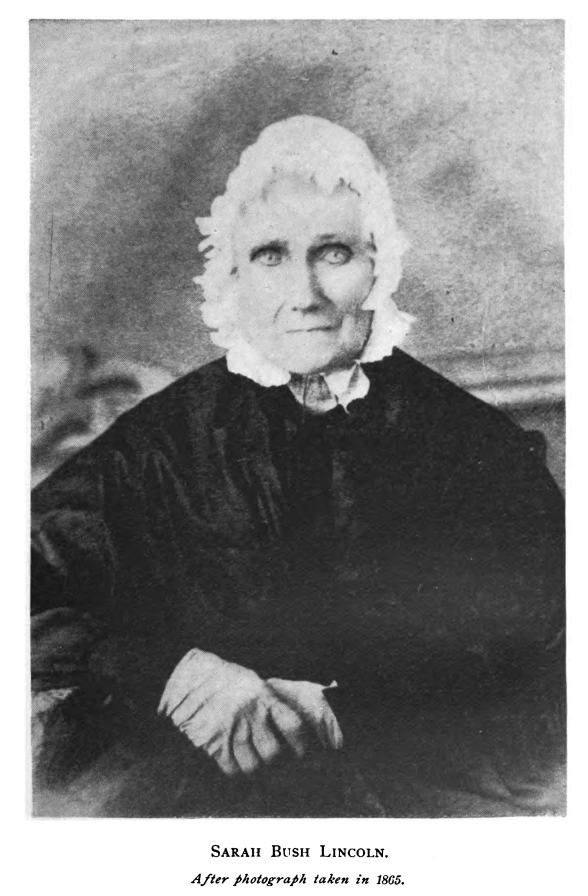

The two sets of children in the Lincoln household—to their credit be it said—lived together in perfect accord. Abe was in his tenth year, and his stepmother, awake to the importance of an education, made a way for him to attend school. To her he seemed full of promise; and although not so quick of comprehension as other boys, yet she believed in encouraging his every effort. He had had a few weeks of schooling under Riney and Hazel in Kentucky, but it is hardly probable that he could read; he certainly could not write. As illustrating his moral make-up, I diverge from the chronological order of the narrative long enough to relate an incident which occurred some years later. In the Lincoln family, Matilda Johnston, or Tilda, as her mother called her, was the youngest child. After Abe had reached the estate of manhood, she was still in her 'teens. It was Abe's habit each morning one fall, to leave the house early, his axe on his shoulder, to clear a piece of forest which lay some distance from home. He frequently carried his dinner with him, and remained all day. Several times the young and frolicsome 'Tilda sought to accompany him, but was each time restrained by her mother, who firmly forbade a repetition of the attempt. One morning the girl escaped maternal vigilance, and slyly followed after the young woodman, who had gone some distance from the house, and was already hidden from view behind the dense growth of trees and underbrush. Following a deer-path, he went singing along, little dreaming of the girl in close pursuit. The latter gained on him, and when within a few feet, darted forward and with a cat-like leap landed squarely on his back. With one hand on each shoulder, she planted her knee in the middle of his back, and dexterously brought the powerful frame of the rail-splitter to the ground. It was a trick familiar to every schoolboy. Abe, taken by surprise, was unable at first to turn around or learn who his assailant was. In the fall to the ground, the sharp edge of the axe imbedded itself in the young lady's ankle, inflicting a wound from which there came a generous effusion of blood. With sundry pieces of cloth torn from Abe's shirt and the young lady's dress, the flow of blood was stanched, and the wound rudely bound up. The girl's cries having lessened somewhat, her tall companion, looking at her in blank astonishment, knowing what an in-fraction the whole thing was of her mother's oft-repeated instructions, asked; "'Tilda, what are you going to tell mother about getting hurt?" "Tell her I did it with the axe," she sobbed. "That will be the truth, won't it?" To which last inquiry Abe manfully responded,
"Yes, that's the truth, but it's not all the truth. Tell the whole truth,'Tilda, and trust your good mother for the rest."
This incident was, many years afterward, related to me by'Tilda, who was then the mother of a devoted and interesting family herself.
Hazel Dorsey was Abe's first teacher in Indiana. He held forth a mile and a half from the Lincoln farm. The school-house was built of round logs, and was just high enough for a man to stand erect under the loft. The floor was of split logs, or what were called puncheons. The chimney was made of poles and clay; and the windows were made by cutting out parts of two logs, placing pieces of split boards a proper distance apart, and over the aperture thus formed pasting pieces of greased paper to admit light. At school Abe evinced ability enough to gain him a prominent place in the respect of the teacher and the affections of his fellow-scholars.*
* "He always appeared to be very quiet during playtime; never was rude; seemed to have a liking for solitude; was the one chosen in almost every case to adjust difficulties between boys of his age and size, and when appealed to, his decision was an end of the trouble. He was also rather noted for keeping his clothes clean longer than any of the others, and although considered a boy of courage, had few, if any, difficulties."—E. R. Burba, letter, March 31, 1866.
Elements of leadership in him seem to have manifested themselves already. Nathaniel Grigsby—whose brother, Aaron, afterwards married Abe's sister, Sarah—attended the same school. He certifies to Abe's proficiency and worth in glowing terms.
"He was always at school early," writes Grigsby, "and attended to his studies. He was always at the head of his class, and passed us rapidly in his studies. He lost no time at home, and when he was not at work was at his books. He kept up his studies on Sunday, and carried his books with him to work, so that he might read when he rested from labor." Now and then, the family exchequer running low, it would be found necessary for the young rail-splitter to stop school, and either work with his father on the farm, or render like service for the neighbors. These periods of work occurred so often and continued so long, that all his school days added together would not make a year in the aggregate. When he attended school, his sister Sarah usually accompanied him. "Sally was a quick-minded young woman," is the testimony of a school-mate. "She was more industrious than Abe, in my opinion. I can hear her good-humored laugh now. Like her brother, she could greet you kindly and put you at ease. She was really an intelligent woman." *
* Nat Grigsby, Sept. 12,1865, MS.
Abe's love for books, and his determined effort to obtain an education in spite of so many obstacles, induced the belief in his father's mind, that book-learning was absorbing a greater proportion of his energy and industry than the demands of the farm. The old gentleman had but little faith in the value of books or papers,* and hence the frequent drafts he made on the son to aid in the drudgery of daily toil. He undertook to teach him his own trade**—he was a carpenter and joiner—but Abe manifested such a striking want of interest that the effort to make a carpenter of him was soon abandoned.
* "I induced my husband to permit Abe to read and study at home as well as at school. At first he was not easily reconciled to it, but finally he too seemed willing to encourage him to a certain extent. Abe was a dutiful son to me always, and we took particular care when he was reading not to disturb him—would let him read on and on till he quit of his own accord."—Mrs. Thomas Lincoln, Sept. 8, 1865. ** A little walnut cabinet, two feet high, and containing two rows of neat drawers, now in the possession of Captain J. W. Wartmann, clerk of the United States Court in Evansville, Ind., is carefully preserved as a specimen of the joint work of Lincoln and his father at this time.
At Dorsey's school Abe was ten years old; at the next one, Andrew Crawford's, he was about fourteen; and at Swaney's he was in his seventeenth year. The last school required a walk of over four miles, and on account of the distance his attendance was not only irregular but brief. Schoolmaster Crawford introduced a new feature in his school, and we can imagine its effect on his pupils, whose training had been limited to the social requirements of the backwoods settlement. It was instruction in manners. One scholar was required to go outside, and re-enter the room as a lady or gentleman would enter a drawing-room or parlor. Another scholar would receive the first party at the door, and escort him or her about the room, making polite introductions to each person in the room. How the gaunt and clumsy Abe went through this performance we shall probably never know. If his awkward movements gave rise to any amusement, his school-mates never revealed it.
The books used at school were Webster's Spelling Book and the American Speller. All the scholars learned to cipher, and afterwards used Pike's Arithmetic. Mr. Lincoln told me in later years that Murray's English Reader was the best school-book ever put into the hands of an American youth. I conclude, therefore, he must have used that also. At Crawford's school Abe was credited with the authorship of several literary efforts—short dissertations in which he strove to correct some time-honored and wanton sport of the schoolboy. While in Indiana I met several persons who recalled a commendable and somewhat pretentious protest he wrote against cruelty to animals. The wholesome effects of a temperate life and the horrors of war were also subjects which claimed the services of his pen then, as they in later years demanded the devoted attention of his mind and heart.
He was now over six feet high and was growing at a tremendous rate, for he added two inches more before the close of his seventeenth year, thus reaching the limit of his stature. He weighed in the region of a hundred and sixty pounds; was wiry, vigorous, and strong. His feet and hands were large, arms and legs long and in striking contrast with his slender trunk and small head. "His skin was shrivelled and yellow," declares one of the girls* who attended Crawford's school. "His shoes, when he had any, were low. He wore buckskin breeches, linsey-woolsey shirt, and a cap made of the skin of a squirrel or coon. His breeches were baggy and lacked by several inches meeting the tops of his shoes, thereby exposing his shinbone, sharp, blue, and narrow." In one branch of school learning he was a great success; that was spelling. We are indebted to Kate Roby, a pretty miss of fifteen, for an incident which illustrates alike his proficiency in orthography and his natural inclination to help another out of the mire. The word "defied" had been given out by Schoolmaster Crawford, but had been misspelled several times when it came Miss Roby's turn. "Abe stood on the opposite side of the room" (related Miss Roby** to me in 1865) "and was watching me. I began d-e-f—and then I stopped, hesitating whether to proceed with an 'i' or a 'y.' Looking up I beheld Abe, a grin covering his face, and pointing with his index finger to his eye. I took the hint, spelled the word with an 'i,' and it went through all right."
* Kate Gentry. ** Miss Roby afterward married Allen Gentry.
There was more or less of an attachment between Miss Roby and Abe, although the lady took pains to assure me that they were never in love. She described with self-evident pleasure, however, the delightful experience of an evening's stroll down to the river with him, where they were wont to sit on the bank and watch the moon as it slowly rose over the neighboring hills. Dangling their youthful feet in the water, they gazed on the pale orb of night, as many a fond pair before them had done and will continue to do until the end of the world. One evening, when thus engaged, their conversation and thoughts turned on the movement of the planets. "I did not suppose that Abe, who had seen so little of the world, would know anything about it, but he proved to my satisfaction that the moon did not go down at all; that it only seemed to; that the earth, revolving from west to east, carried us under, as it were. 'We do the sinking,' he explained; 'while to us the moon is comparatively still. The moon's sinking is only an illusion.' I at once dubbed him a fool, but later developments convinced me that I was the fool, not he. He was well acquainted with the general laws of astronomy and the movements of the heavenly bodies, but where he could have learned so much, or how to put it so plainly, I never could understand."

Absalom Roby is authority for the statement that even at that early day Abe was a patient reader of a Louisville newspaper, which some one at Gentryville kindly furnished him. Among the books he read were the Bible, "Ã?sop's Fables," "Robinson Crusoe," Bunyan's "Pilgrim's Progress," a "History of the United States," and Weems' "Life of Washington." A little circumstance attended the reading of the last-named book, which only within recent years found its way into public print. The book was borrowed from a close-fisted neighbor, Josiah Crawford, and one night, while lying on a little shelf near a crack between two logs in the Lincoln cabin during a storm, the covers were damaged by rain. Crawford—not the schoolmaster, but old "Blue Nose," as Abe and others called him—assessed the damage to his book at seventy-five cents, and the unfortunate borrower was required to pull fodder for three days at twenty-five cents a day in settlement of the account. While at school it is doubtful if he was able to own an arithmetic. His stepmother was unable to remember his ever having owned one. She gave me, however, a few leaves from a book made and bound by Abe, in which he had entered, in a large, bold hand, the tables of weights and measures, and the "sums" to be worked out in illustration of each table. Where the arithmetic was obtained I could not learn. On one of the pages which the old lady gave me, and just underneath the table which tells how many pints there are in a bushel, the facetious young student had scrawled these four lines of schoolboy doggerel:
"Abraham Lincoln, His hand and pen, He will be good, But God knows when."
On another page were found, in his own hand, a few lines which it is also said he composed. Nothing indicates that they were borrowed, and I have always, therefore, believed that they were original with him. Although a little irregular in metre, the sentiment would, I think, do credit to an older head.
Time, what an empty vapor 'tis, And days how swift they are: Swift as an Indian arrow, Fly on like a shooting star. The present moment just is here, Then slides away in haste, That we can never say they're ours, But only say they're past."
His penmanship, after some practice, became so regular in form that it excited the admiration of other and younger boys. One of the latter, Joseph C. Richardson, said that "Abe Lincoln was the best penman in the neighborhood." At Richardson's request he made some copies for practice. During my visit to Indiana I met Richardson, who showed these two lines which Abe had prepared for him:
"Good boys who to their books apply Will all be great men by and by."
To comprehend Mr. Lincoln fully we must know in substance not only the facts of his origin, but also the manner of his development. It will always be a matter of wonder to the American people, I have no doubt—as it has been to me—that from such restricted and unpromising opportunities in early life, Mr. Lincoln grew into the great man he was. The foundation for his education was laid in Indiana and in the little town of New Salem in Illinois, and in both places he gave evidence of a nature and characteristics that distinguished him from every associate and surrounding he had. He was not peculiar or eccentric, and yet a shrewd observer would have seen that he was decidedly unique and original. Although imbued with a marked dislike for manual labor, it cannot be truthfully said of him that he was indolent. From a mental standpoint he was one of the most energetic young men of his day. He dwelt altogether in the land of thought. His deep meditation and abstraction easily induced the belief among his horny-handed companions that he was lazy. In fact, a neighbor, John Romine, makes that charge. "He worked for me," testifies the latter, "but was always reading and thinking. I used to get mad at him for it. I say he was awfully lazy. He would laugh and talk—crack his jokes and tell stories all the time; didn't love work half as much as his pay. He said to me one day that his father taught him to work, but he never taught him to love it." Verily there was but one Abraham Lincoln!
His chief delight during the day, if unmolested, was to lie down under the shade of some inviting tree to read and study. At night, lying on his stomach in front of the open fireplace, with a piece of charcoal he would cipher on a broad wooden shovel. When the latter was covered over on both sides he would take his father's drawing knife or plane and shave it off clean, ready for a fresh supply of inscriptions the next day. He often moved about the cabin with a piece of chalk, writing and ciphering on boards and the flat sides of hewn logs. When every bare wooden surface had been filled with his letters and ciphers he would erase them and begin anew. Thus it was always; and the boy whom dull old Thomas Lincoln and rustic John Romine conceived to be lazy was in reality the most tireless worker in all the region around Gentryvllle. His stepmother told me he devoured everything in the book line within his reach. If in his reading he came across anything that pleased his fancy, he entered it down in a copy-book—a sort of repository, in which he was wont to store everything worthy of preservation. "Frequently," related his stepmother, "he had no paper to write his pieces down on. Then he would put them with chalk on a board or plank, sometimes only making a few signs of what he intended to write. When he got paper he would copy them, always bringing them to me and reading them. He would ask my opinion of what he had read, and often explained things to me in his plain and simple language." How he contrived at the age of fourteen to absorb information is thus told by John Hanks: "When Abe and I returned to the house from work he would go to the cupboard, snatch a piece of corn bread, sit down, take a book, cock his legs up as high as his head, and read. We grubbed, plowed, mowed, and worked together barefooted in the field. Whenever Abe had a chance in the field while at work, or at the house, he would stop and read." He kept the Bible and "Ã?sop's Fables" always within reach, and read them over and over again. These two volumes furnished him with the many figures of speech and parables which he used with such happy effect in his later and public utterances.
Amid such restricted and unromantic environments the boy developed into the man. The intellectual fire burned slowly, but with a steady and intense glow. Although denied the requisite training of the school-room, he was none the less competent to cope with those who had undergone that discipline. No one had a more retentive memory. If he read or heard a good thing it never escaped him. His powers of concentration were intense, and in the ability through analysis to strip bare a proposition he was unexcelled. His thoughtful and investigating mind dug down after ideas, and never stopped till bottom facts were reached. With such a mental equipment the day was destined to come when the world would need the services of his intellect and heart. That he was equal to the great task when the demand came is but another striking proof of the grandeur of his character.
The first law book Lincoln ever read was "The Statutes of Indiana." He obtained the volume from his friend David Tumham, who testifies that he fairly devoured the book in his eager efforts to abstract the store of knowledge that lay between the lids. No doubt, as Tumham insists, the study of the statutes at this early day led Abe to think of the law as his calling in maturer years. At any rate he now began to evince no little zeal in the matter of public speaking—in compliance with the old notion, no doubt, that a lawyer can never succeed unless he has the elements of the orator or advocate in his construction—and even when at work in the field he could not resist the temptation to mount the nearest stump and practise on his fellow laborers. The latter would flock around him, and active operations would cease whenever he began. A cluster of tall and stately trees often made him a most dignified and apreciative audience during the delivery of these maiden forensic efforts. He was old enough to attend musters, log-rollings, and horse-races, and was rapidly becoming a favored as well as favorite character. "The first time I ever remember of seeing Abe Lincoln," is the testimony of one of his neighbors,* "was when I was a small boy and had gone with my father to attend some kind of an election. One of our neighbors, James Larkins, was there. Larkins was a great hand to brag on anything he owned. This time it was his horse. He stepped up before Abe, who was in the crowd, and commenced talking to him, boasting all the while of his animal.
"'I have got the best horse in the country'" he shouted to his young listener. "'I ran him three miles in exactly nine minutes, and he never fetched a long breath.'"
"'I presume,' said Abe, rather dryly, 'he fetched a good many short ones though.'"
* John W. Lamar, MS. letter, June 29, 1866.
With all his peaceful propensities Abe was not averse to a contest of strength, either for sport or in settlement—as in one memorable case—of grievances. Personal encounters were of frequent occurrence in Gentryville in those days, and the prestige of having thrashed an opponent gave the victor marked social distinction. Green B. Taylor, with whom Abe worked the greater part of one winter on a farm, furnished me with an account of the noted fight between John Johnston, Abe's stepbrother, and William Grigsby, in which stirring drama Abe himself played an important rôle before the curtain was rung down. Taylor's father was the second for Johnston, and William Whitten officiated in a similar capacity for Grigsby. "They had a terrible fight," relates Taylor, "and it soon became apparent that Grigsby was too much for Lincoln's man, Johnston. After they had fought a long time without interference, it having been agreed not to break the ring, Abe burst through, caught Grigsby, threw him off and some feet away. There he stood, proud as Lucifer, and swinging a bottle of liquor over his head swore he was 'the big buck of the lick.' 'If any one doubts it,' he shouted, 'he has only to come on and whet his horns.'" A general engagement followed this challenge, but at the end of hostilities the field was cleared and the wounded retired amid the exultant shouts of their victors.
Much of the latter end of Abe's boyhood would have been lost in the midst of tradition but for the store of information and recollections I was fortunate enough to secure from an interesting old lady whom I met in Indiana in 1865. She was the wife of Josiah Crawford*—"Blue Nose," as Abe had named him—and possessed rare accomplishments for a woman reared in the backwoods of Indiana. She was not only impressed with Abe's early efforts, but expressed great admiration for his sister Sarah, whom she often had with her at her own hospitable home and whom she described as a modest, industrious, and sensible sister of a humorous and equally sensible brother. From Mrs. Crawford I obtained the few specimens of Abe's early literary efforts and much of the matter that follows in this chapter. The introduction here of the literary feature as affording us a glimpse of Lincoln's boyhood days may to a certain extent grate harshly on over-refined ears; but still no apology is necessary, for, as intimated at the outset, I intend to keep close to Lincoln all the way through. Some writers would probably omit these songs and backwoods recitals as savoring too strongly of the Bacchanalian nature, but that would be a narrow view to take of history. If we expect to know Lincoln thoroughly we must be prepared to take him as he really was.
* In one of her conversations with me Mrs. Crawford told me of the exhibitions with which at school they often entertained the few persons who attended the closing day. Sometimes, in warm weather, the scholars made a platform of clean boards covered overhead with green boughs. Generally, however, these exhibitions took place in the school-room. The exercises consisted of the varieties offered at this day at the average seminary or school—declamations and dialogues or debates. The declamations were obtained principally from a book called "The Kentucky Preceptor," which volume Mrs. Crawford gave me as a souvenir of my visit. Lincoln had often used it himself, she said. The questions for discussion were characteristic of the day and age. The relative merits of the "Bee and the Ant," the difference in strength between "Wind and Water," taxed their knowledge of physical phenomena; and the all-important question "Which has the most right to complain, the Indian or the Negro?" called out their conceptions of a great moral or national wrong. In the discussion of all these grave subjects Lincoln took a deep interest.
In 1826 Abe's sister Sarah was married to Aaron Grigsby, and at the wedding the Lincoln family sang a song composed in honor of the event by Abe himself. It is a tiresome doggerel and full of painful rhymes. I reproduce it here from the manuscript furnished me by Mrs. Crawford. The author and composer called it "Adam and Eve's Wedding Song."
"When Adam was created He dwelt in Eden's shade, As Moses has recorded, And soon a bride was made. Ten thousand times ten thousand Of creatures swarmed around Before a bride was formed, And yet no mate was found. The Lord then was not willing That man should be alone, But caused a sleep upon him, And from him took a bone. Then Adam he rejoiced To see his loving bride A part of his own body, The product of his side. The woman was not taken From Adam's feet we see, So he must not abuse her, The meaning seems to be. The woman was not taken From Adam's head, we know, To show she must not rule him, 'Tis evidently so. The woman she was taken From under Adam's arm, So she must be protected From injuries and harm."
Poor Sarah, at whose wedding this song was sung, never lived to see the glory nor share in the honor that afterwards fell to the lot of her tall and angular brother. Within two years after her marriage she died in childbirth.
Although devoid of any natural ability as a singer Abe nevertheless made many efforts and had great appreciation of certain songs. In after years he told me he doubted if he really knew what the harmony of sound was. The songs in vogue then were principally of the sacred order. They were from Watts' and Dupuy's hymn-books. David Tumham furnished me with a list, marking as especial favorites the following: "Am I a Soldier of the Cross"; "How Tedious and Tasteless the Hours"; "There is a Fountain Filled with Blood," and, "Alas, and did my Saviour Bleed?" One song pleased Abe not a little. "I used to sing it for old Thomas Lincoln," relates Turnham, "at Abe's request. The old gentleman liked it and made me sing it often. I can only remember one couplet:
"'There was a Romish lady She was brought up in Popery.'"
Dennis Hanks insists that Abe used to try his hand and voice at "Poor old Ned," but never with any degree of success. "Rich, racy verses" were sung by the big boys in the country villages of that day with as keen a relish as they are to-day. There is no reason and less evidence for the belief that Abe did not partake of this forbidden fruit along with other boys of the same age and condition in life. Among what Dennis called "field songs" are a few lines from this one:
"The turbaned Turk that scorns the world And struts about with his whiskers curled, For no other man but himself to see."
Of another ballad we have this couplet:
"Hail Columbia, happy land, If you aint drunk then I'll be damned."
We can imagine the merry Dennis, hilarious with the exhilaration of deep potations at the village grocery, singing this "field song" as he and Abe wended their way homeward. A stanza from a campaign song which Abe was in the habit of rendering, according to Mrs. Crawford, attests his earliest political predilections:
"Let auld acquaintance be forgot And never brought to mind, May Jackson be our president, And Adams left behind."
A mournful and distressing ballad, "John Anderson's Lamentation," as rendered by Abe, was written out for me by Mrs. Crawford, but the first lines,
"Oh, sinners, poor sinners, take warning by me, The fruits of transgression behold now and see,"
will suffice to indicate how mournful the rest of it was.
The centre of wit and wisdom in the village of Gentryville was at the store. This place was in charge of one Jones, who soon after embarking in business seemed to take quite a fancy to Abe. He took the only newspaper—sent from Louisville—and at his place of business gathered Abe, Dennis Hanks, Baldwin the blacksmith, and other kindred spirits to discuss such topics as are the exclusive property of the store lounger. Abe's original and ridiculous stories not only amused the crowd, but the display of his unique faculties made him many friends. One who saw him at this time says:
"Lincoln would frequently make political speeches to the boys; he was always calm, logical, and clear. His jokes and stories were so odd, original, and witty all the people in town would gather around him. He would keep them till midnight. Abe was a good talker, a good reasoner, and a kind of newsboy." He attended all the trials before the "squire," as that important functionary was called, and frequently wandered off to Boonville, a town on the river, distant fifteen miles, and the county seat of Warrick County, to hear and see how the courts were conducted there. On one occasion, at the latter place, he remained during the trial of a murderer and attentively absorbed the proceedings. A lawyer named Breckenridge represented the defense, and his speech so pleased and thrilled his young listener that the latter could not refrain from approaching the eloquent advocate at the close of his address and congratulating him on his signal success. How Breckenridge accepted the felicitations of the awkward, hapless youth we shall probably never know. The story is told that during Lincoln's term as President, he was favored one day at the White House with a visit by this same Breckenridge, then a resident of Texas, who had called to pay his respects. In a conversation about early days in Indiana, the President, recalling Breckenridge's argument in the murder trial, remarked, "If I could, as I then thought, have made as good a speech as that, my soul would have been satisfied; for it was up to that time the best speech I had ever heard."
No feature of his backwoods life pleased Abe so well as going to mill. It released him from a day's work in the woods, besides affording him a much desired opportunity to watch the movement of the mill's primitive and cumbersome machinery. It was on many of these trips that David Tumham accompanied him. In later years Mr. Lincoln related the following reminiscence of his experience as a miller in Indiana; One day, taking a bag of corn, he mounted the old flea-bitten gray mare and rode leisurely to Gordon's mill. Arriving somewhat late, his turn did not come till almost sundown. In obedience to the custom requiring each man to furnish his own power he hitched the old mare to the arm, and as the animal moved round, the machinery responded with equal speed. Abe was mounted on the arm, and at frequent intervals made use of his whip to urge the animal on to better speed. With a careless "Get up, you old hussy," he applied the lash at each revolution of the arm. In the midst of the exclamation, or just as half of it had escaped through his teeth, the old jade, resenting the continued use of the goad, elevated her shoeless hoof and striking the young engineer in the forehead, sent him sprawling to the earth. Miller Gordon hurried in, picked up the bleeding, senseless boy, whom he took for dead, and at once sent for his father. Old Thomas Lincoln came—came as soon as embodied listlessness could moveloaded the lifeless boy in a wagon and drove home. Abe lay unconscious all night, but towards break of day the attendants noticed signs of returning consciousness. The blood beginning to flow normally, his tongue struggled to loosen itself, his frame jerked for an instant, and he awoke, blurting out the words "you old hussy," or the latter half of the sentence interrupted by the mare's heel at the mill.
Mr. Lincoln considered this one of the remarkable incidents of his life. He often referred to it, and we had many discussions in our law office over the psychological phenomena involved in the operation. Without expressing my own views I may say that his idea was that the latter half of the expression, "Get up, you old hussy," was cut off by a suspension of the normal flow of his mental energy, and that as soon as life's forces returned he unconsciously ended the sentence; or, as he in a plainer figure put it: "Just before I struck the old mare my will through the mind had set the muscles of my tongue to utter the expression, and when her heels came in contact with my head the whole thing stopped half-cocked, as it were, and was only fired off when mental energy or force returned."
By the time he had reached his seventeenth year he had attained the physical proportions of a full-grown man. He was employed to assist James Taylor in the management of a ferry-boat across the Ohio river near the mouth of Anderson's creek, but was not allowed a man's wages for the work. He received thirty-seven cents a day for what he afterwards told me was the roughest work a young man could be made to do. In the midst of whatever work he was engaged on he still found time to utilize his pen. He prepared a composition on the American Government, calling attention to the necessity of preserving the Constitution and perpetuating the Union, which with characteristic modesty he turned over to his friend and patron, William Woods, for safe-keeping and perusal. Through the instrumentality of Woods it attracted the attention of many persons, among them one Pitcher,* a lawyer at Rockport, who with faintly concealed enthusiasm declared "the world couldn't beat it." An article on Temperance was shown under similar circumstance to Aaron Farmer, a Baptist preacher of local renown, and by him furnished to an Ohio newspaper for publication. The thing, however, which gave him such prominence—a prominence too which could have been attained in no other way—was his remarkable physical strength, for he was becoming not only one of the longest, but one of the strongest men around Gentryville. He enjoyed the brief distinction his exhibitions of strength gave him more than the admiration of his friends for his literary or forensic efforts. Some of the feats attributed to him almost surpass belief. One witness declares he was equal to three men, having on a certain occasion carried a load of six hundred pounds At another time he walked away with a pair of logs which three robust men were skeptical of their ability to carry. "He could strike with a maul a heavier blow—could sink an axe deeper into wood than any man I ever saw," is the testimony of another witness.
* This gentleman, Judge John Pitcher, ninety-three years old, is still living in Mount Vernon, Indiana. He says that young Lincoln often called at his office and borrowed books to read at home during leisure hours. On one occasion he expressed a desire to study law with Pitcher, but explained that his parents were so poor that he could not be spared from the farm on which they lived. "He related to me in my office one day," says Pitcher, "an account of his payment to Crawford of the damage done to the latter's book—Weems' 'Life of Washington.' Lincoln said, "You see, I am tall and long-armed, and I went to work in earnest. At the end of the two days there was not a corn-blade left on a stalk in the field. I wanted to pay full damage for all the wetting the book got, and I made a clean sweep."
After he had passed his nineteenth year and was nearing his majority he began to chafe and grow restless under the restraints of home rule. Seeing no prospect of betterment in his condition, so long as his fortune was interwoven with that of his father, he at last endeavored to strike out into the broad world for himself. Having great faith in the judgment and influence of his fast friend Wood, he solicited from him a recommendation to the officers of some one of the boats plying up and down the river, hoping thereby to obtain employment more congenial than the dull, fatiguing work of the farm. To this project the judicious Wood was much opposed, and therefore suggested to the would-be boatman the moral duty that rested on him to remain with his father till the law released him from that obligation. With deep regret he retraced his steps to the paternal mansion, seriously determined not to evade the claim from which in a few weary months he would be finally released. Meanwhile occurred his first opportunity to see the world. In March, 1828, James Gentry, for whom he had been at work, had fitted out a boat with a stock of grain and meat for a trading expedition to New Orleans, and placed his son Allen in charge of the cargo for the voyage. Abe's desire to make a river trip was at last satisfied, and he accompanied the proprietor's son, serving as "bow hand." His pay was eight dollars a month and board. In due course of time the navigators returned from their expedition with the evidence of profitable results to gladden the heart of the owner. The only occurrence of interest they could relate of the voyage was the encounter with a party of marauding negroes at the plantation of Madame Duchesne, a few miles below Baton Rouge. Abe and Gentry, having tied up for the night, were fast asleep on their boat when aroused by the arrival of a crowd of negroes bent on plunder. They set to work with clubs, and not only drove off the intruders, but pursued them inland, then hastily returning to their quarters they cut loose their craft and floated down-stream till daylight.
Before passing on further it may not be amiss to glance for a moment at the social side of life as it existed in Gentryville in Abe's day. "We thought nothing," said an old lady whom I interviewed when in Indiana, "of going eight or ten miles to church. The ladies did not stop for the want of a shawl, cloak, or riding-dress in winter time, but would put on their husbands' old overcoats and wrap up their little ones and take one or two of them on their beasts. Their husbands would walk, and thus they would go to church, frequently remaining till the second day before they returned home."
The old men starting from the fields and out of the woods would carry their guns on their shoulders and go also. They dressed in deer-skin pants, moccasins, and coarse hunting shirts—the latter usually fastened with a rope or leather strap. Arriving at the house where services were to be held they would recite to each other thrilling stories of their hunting exploits, and smoke their pipes with the old ladies. They were treated, and treated each other, with the utmost kindness. A bottle of liquor, a pitcher of water, sugar, and glasses were set out for them; also a basket of apples or turnips, with, now and then, a pie or cakes. Thus they regaled themselves till the preacher found himself in a condition to begin. The latter, having also partaken freely of the refreshments provided, would "take his stand, draw his coat, open his shirt collar, read his text, and preach and pound till the sweat, produced alike by his exertions and the exhilarating effects of the toddy, rolled from his face in great drops. Shaking hands and singing ended the service."
The houses were scattered far apart, but the people travelled great distances to participate in the frolic and coarse fun of a log-rolling and sometimes a wedding. Unless in mid-winter the young ladies carried their shoes in their hands, and only put them on when the scene of the festivities was reached. The ladies of maturer years drank whiskey toddy, while the men took the whiskey straight. They all danced merrily, many of them barefooted, to the tune of a cracked fiddle the night through. We can imagine the gleeful and more hilarious swaggering home at daybreak to the tune of Dennis Hanks' festive lines:
"Hail Columbia, happy land, If you ain't drunk then I'll be damned."
Although gay, prosperous, and light-hearted, these people were brimming over with superstition. It was at once their food and drink. They believed in the baneful influence of witches, pinned their faith to the curative power of wizards in dealing with sick animals, and shot the image of a witch with a silver ball to break the spell she was supposed to have over human beings. They followed with religious minuteness the directions of the water-wizard, with his magic divining rod, and the faith doctor who wrought miraculous cures by strange sounds and signals to some mysterious agency. The flight of a bird in at the window, the breath of a horse on a child's head, the crossing by a dog of a hunter's path, all betokened evil luck in store for some one. The moon exercised greater influence on the actions of the people and the growth of vegetation than the sun and all the planetary system combined. Fence rails could only be cut in the light of the moon, and potatoes planted in the dark of the moon. Trees and plants which bore their fruit above ground could be planted when the moon shone full. Soap could only be made in the light of the moon, and it must only be stirred in one way and by one person. They had the horror of Friday which with many exists to this day. Nothing was to be begun on that unlucky day, for if the rule were violated an endless train of disasters was sure to follow.
Surrounded by people who believed in these things, Lincoln grew to manhood. With them he walked, talked, and labored, and from them he also absorbed whatever of superstition showed itself in him thereafter. His early Baptist training made him a fatalist up to the day of his death, and, listening in boyish wonder to the legends of some toothless old dame led him to believe in the significance of dreams and visions. His surroundings helped to create that unique character which in the eyes of a great portion of the American people was only less curious and amusing than it was august and noble.
The winter of 1829 was marked by another visitation of that dreaded disease, "the milk-sick." It was making the usual ravages among the cattle. Human victims were falling before it every day, and it caused the usual stampede in southern Indiana. Dennis Hanks, discouraged by the prospect and grieving over the loss of his stock, proposed a move further westward. Returning emigrants had brought encouraging news of the newly developed state of Illinois. Vast stretches of rich alluvial lands were to be had there on the easiest of terms.
Besides this, Indiana no longer afforded any inducements to the poor man. The proposition of Dennis met with the general assent of the Lincoln family, and especially suited the roving and migratory spirit of Thomas Lincoln. He had been induced to leave Kentucky for the hills of Indiana by the same rosy and alluring reports. He had moved four times since his marriage and in point of worldly goods was no better off than when he started in life. His land groaned under the weight of a long neglected incumbrance and, like many of his neighbors, he was ready for another change. Having disposed of his land to James Gentry, and his grain and stock to young David Turnham, he loaded his household effects into a wagon drawn by two yoke of oxen, and in March, 1830, started for Illinois. The two daughters of Mrs. Lincoln had meanwhile married Dennis Hanks and Levi Hall, and with these additions the party numbered thirteen in all. Abe had just passed his twenty-first birthday.
The journey was a long and tedious one; the streams were swollen and the roads were muddy almost to the point of impassability. The rude, heavy wagon, with its primitive wheels, creaked and groaned as it crawled through the woods and now and then stalled in the mud. Many were the delays, but none ever disturbed the equanimity of its passengers. They were cheerful in the face of all adversity, hopeful, and some of them determined; but none of them more so than the tall, ungainly youth in buckskin breeches and coon-skin cap who wielded the gad and urged the patient oxen forward. As these humble emigrants entered the new State little did the curious people in the towns through which they passed dream that the obscure and penniless driver who yelled his commands to the oxen would yet become Chief Magistrate of the greatest nation of modern times.*
* Mr. Lincoln once described this journey to me. He said the ground had not yet yielded up the frosts of winter; that daring the day the roads would thaw out on the surface and at night freeze over again, thus making travelling, especially with oxen, painfully slow and tiresome. There were, of course, no bridges, and the party were consequently driven to ford the streams, unless by a circuitous route they could avoid them. In the early part of the day the latter were also frozen slightly, and the oxen would break through a square yard of thin ice at every step. Among other things which the party brought with them was a pet dog, which trotted along after the wagon. One day the little fellow fell behind and failed to catch up till after they had crossed the stream. Missing him they looked back, and there, on the opposite bank, he stood, whining and jumping about in great distress. The water was running over the broken edges of the ice, and the poor animal was afraid to cross. It would not pay to turn the oxen and wagon back and ford the stream again in order to recover a dog, and so the majority, in their anxiety to move forward, decided to go on without him. "But I could not endure the idea of abandoning even a dog," related Lincoln. "Pulling off shoes and socks I waded across the stream and triumphantly returned with the shivering animal under my arm. His frantic leaps of joy and other evidences of a dog's gratitude amply repaid me for all the exposure I had undergone."

After a fortnight of rough and fatiguing travel the colony of Indiana emigrants reached a point in Illinois five miles north-west of the town of Decatur in Macon county. John Hanks, son of that Joseph Hanks in whose shop at Elizabethtown Thomas Lincoln had learned what he knew of the carpenter's art, met and sheltered them until they were safely housed on a piece of land which he had selected for them five miles further westward. He had preceded them over a year, and had in the meantime hewed out a few timbers to be used in the construction of their cabin. The place he had selected was on a bluff overlooking the Sangamon river,—for these early settlers must always be in sight of a running stream,—well supplied with timber. It was a charming and picturesque site, and all hands set resolutely to work to prepare the new abode. One felled the trees; one hewed the timbers for the cabin; while another cleared the ground of its accumulated growth of underbrush. All was bustle and activity. Even old Thomas Lincoln, infused with the spirit of the hour, was spurred to unwonted exertion. What part of the work fell to his lot our only chronicler, John Hanks, fails to note; but it is conjectured from the old gentleman's experience in the art of building that his services corresponded to those of the more modern supervising architect. With the aid of the oxen and a plow John and Abe broke up fifteen acres of sod, and "Abe and myself," observes Hanks in a matter-of-fact way, "split rails enough to fence the place in." As they swung their axes, or with wedge and maul split out the rails, how strange to them the thought would have seemed that those self-same rails were destined to make one of them immortal. If such a vision flashed before the mind of either he made no sign of it, but each kept steadily on in his simple, unromantic task.
Abe had now attained his majority and began to throw from his shoulders the vexations of parental restraint. He had done his duty to his father, and felt able to begin life on his own account. As he steps out into the broad and inviting world we take him up for consideration as a man. At the same time we dispense with further notice of his father, Thomas Lincoln. In the son are we alone interested. The remaining years of his life marked no change in the old gentleman's nature. He still listened to the glowing descriptions of prosperity in the adjoining counties, and before his death moved three times in search of better times and a healthy location. In 1851 we find him living on forty acres of land on Goose Nest prairie, in Coles county, Illinois. The land bore the usual incumbrance—a mortgage for two hundred dollars, which his son afterwards paid. On the 17th of January, after suffering for many weeks from a disorder of the kidneys, he passed away at the ripe old age—as his son tells us—of "seventy-three years and eleven days." For a long time after beginning life on his own account Abe remained in sight of the parental abode. He worked at odd jobs in the neighborhood, or wherever the demand for his services called him. As late as 1831 he was still in the same parts, and John Hanks is authority for the statement that he "made three thousand rails for Major Warnick" walking daily three miles to his work. During the intervals of leisure he read the few books obtainable, and continued the practice of extemporaneous speaking to the usual audience of undemonstrative stumps and voiceless trees. His first attempt at public speaking after landing in Illinois is thus described to me by John Hanks, whose language I incorporate: "After Abe got to Decatur, or rather to Macon county, a man by the name of Posey came into our neighborhood and made a speech. It was a bad one, and I said Abe could beat it. I turned down a box and Abe made his speech. The other man was a candidate—Abe wasn't. Abe beat him to death, his subject being the navigation of the Sangamon river. The man, after Abe's speech was through, took him aside and asked him where he had learned so much and how he could do so well. Abe replied, stating his manner and method of reading, and what he had read. The man encouraged him to persevere."
For the first time we are now favored with the appearance on the scene of a very important personage—one destined to exert no little influence in shaping Lincoln's fortunes. It is Denton Offut, a brisk and venturesome business man, whose operations extended up and down the Sangamon river for many miles. Having heard glowing reports of John Hanks' successful experience as a boatman in Kentucky he had come down the river to engage the latter's services to take a boatload of stock and provisions to New Orleans. "He wanted me to go badly," observes Hanks, "but I waited awhile before answering. I hunted up Abe, and I introduced him and John Johnston, his step-brother, to Offut. After some talk we at last made an engagement with Offut at fifty cents a day and sixty dollars to make the trip to New Orleans. Abe and I came down the Sangamon river in a canoe in March, 1831; landed at what is now called Jamestown, five miles east of Springfield, then known as Judy's Ferry." Here Johnston joined them, and, leaving their canoe in charge of one Uriah Mann, they walked to Springfield, where after some inquiry they found the genial and enterprising Offut regaling himself with the good cheer dispensed at "The Buckhorn" inn. This hostelry, kept by Andrew Elliot, was the leading place of its kind in the then unpretentious village of Springfield. The figure of a buck's head painted on a sign swinging in front of the house gave rise to its name. Offut had agreed with Hanks to have a boat ready for him and his two companions at the mouth of Spring creek on their arrival, but too many deep potations with the new-comers who daily thronged about the "Buckhorn" had interfered with the execution of his plans, and the boat still remained in the womb of the future. Offut met the three expectant navigators on their arrival, and deep were his regrets over his failure to provide the boat. The interview resulted in the trio engaging to make the boat themselves. From what was known as "Congress land" they obtained an abundance of timber, and by the aid of the machinery at Kirkpatrick's mill they soon had the requisite material for their vessel. While the work of construction was going on a shanty was built in which they were lodged. Lincoln was elected cook, a distinction he never underestimated for a moment. Within four weeks the boat was ready to launch. Offut was sent for, and was present when she slid into the water. It was the occasion of much political chat and buncombe, in which the Whig party and Jackson alike were, strangely enough, lauded to the skies. It is difficult to account for the unanimous approval of such strikingly antagonistic ideas, unless it be admitted that Offut must have brought with him some substantial reminder of the hospitality on draught at the "Buckhorn" inn. Many disputes arose, we are told, in which Lincoln took part and found a good field for practice and debate.
A travelling juggler halted long enough in Sangamontown, where the boat was launched, to give an exhibition of his art and dexterity in the loft of Jacob Carman's house. In Lincoln's low-crowned, broad-brimmed hat the magician cooked eggs. As explanatory of the delay in passing up his hat Lincoln drolly observed, "It was out of respect for the eggs, not care for my hat."
Having loaded the vessel with pork in barrels, corn, and hogs, these sturdy boatmen swung out into the stream. On April 19 they reached the town of New Salem, a place destined to be an important spot in the career of Lincoln. There they met with their first serious delay. The boat stranded on Rutledge's mill-dam and hung helplessly over it a day and a night. "We unloaded the boat," narrated one of the crew to explain how they obtained relief from their embarrassing situation; "that is, we transferred the goods from our boat to a borrowed one. We then rolled the barrels forward; Lincoln bored a hole in the end [projecting] over the dam; the water which had leaked in ran out and we slid over." Offut was profoundly impressed with this exhibition of Lincoln's ingenuity. In his enthusiasm he declared to the crowd who covered the hill and who had been watching Lincoln's operation that he would build a steamboat to plow up and down the Sangamon, and that Lincoln should be her Captain. She would have rollers for shoals and dams, runners for ice, and with Lincoln in charge, "By thunder, she'd have to go!"
After release from their embarrassing, not to say perilous, position the boat and her crew floated away from New Salem and passed on to a point known as Blue Banks, where as the historian of the voyage says: "We had to load some hogs bought of Squire Godbey. We tried to drive them aboard, but could not. They would run back past us. Lincoln then suggested that we sew their eyes shut. Thinking to try it, we caught them, Abe holding their heads and I their tails while Offut sewed up their eyes. Still they wouldn't drive. At last, becoming tired, we carried them to the boat. Abe received them and cut open their eyes, Johnston and I handing them to him." After thus disposing of the hog problem they again swung loose and floated down-stream. From the Sangamon they passed to the Illinois. At Beardstown their unique craft, with its "sails made of planks and cloth," excited the amusement and laughter of those who saw them from the shore. Once on the bosom of the broad Mississippi they glided past Alton, St. Louis, and Cairo in rapid succession, tied up for a day at Memphis, and made brief stops at Vicksburg and Natchez. Early in May they reached New Orleans, where they lingered a month, disposing of their cargo and viewing the sights which the Crescent City afforded.
In New Orleans, for the first time Lincoln beheld the true horrors of human slavery. He saw "negroes in chains—whipped and scourged." Against this inhumanity his sense of right and justice rebelled, and his mind and conscience were awakened to a realization of what he had often heard and read. No doubt, as one of his companions has said, "Slavery ran the iron into him then and there." One morning in their rambles over the city the trio passed a slave auction. A vigorous and comely mulatto girl was being sold. She underwent a thorough examination at the hands of the bidders; they pinched her flesh and made her trot up and down the room like a horse, to show how she moved, and in order, as the auctioneer said, that "bidders might satisfy themselves" whether the article they were offering to buy was sound or not. The whole thing was so revolting that Lincoln moved away from the scene with a deep feeling of "unconquerable hate." Bidding his companions follow him he said, "By God, boys, let's get away from this. If ever I get a chance to hit that thing [meaning slavery], I'll hit it hard." This incident was furnished me in 1865, by John Hanks. I have also heard Mr. Lincoln refer to it himself.
In June the entire party, including Offut, boarded a steamboat going up the river. At St. Louis they disembarked, Offut remaining behind while Lincoln, Hanks, and Johnston started across Illinois on foot. At Edwardsville they separated, Hanks going to Springfield, while Lincoln and his stepbrother followed the road to Coles county, to which point old Thomas Lincoln had meanwhile removed. Here Abe did not tarry long, probably not over a month, but long enough to dispose most effectually of one Daniel Needham, a famous wrestler who had challenged the returned boatman to a test of strength. The contest took place at a locality known as "Wabash Point." Abe threw his antagonist twice with comparative ease, and thereby demonstrated such marked strength and agility as to render him forever popular with the boys of that neighborhood.
In August the waters of the Sangamon river washed Lincoln in to New Salem. This once sprightly and thriving village is no longer in existence. Not a building, scarcely a stone, is left to mark the place where it once stood. To reach it now the traveller must ascend a bluff a hundred feet above the general level of the surrounding country. The brow of the ridge, two hundred and fifty feet broad where it overlooks the river, widens gradually as it extends westwardly to the forest and ultimately to broad pastures. Skirting the base of the bluff is the Sangamon river, which, coming around a sudden bend from the south-east, strikes the rocky hill and is turned abruptly north. Here is an old mill, driven by water-power, and reaching across the river is the mill-dam on which Offut's vessel hung stranded in April, 1831. As the river rolled her turbid waters over the dam, plunging them into the whirl and eddy beneath, the roar of waters, like low, continuous, distant thunder, could be distinctly heard through the village day and night.
The country in almost every direction is diversified by alternate stretches of hills and level lands, with streams between each struggling to reach the river. The hills are bearded with timber—oak, hickory, walnut, ash, and elm. Below them are stretches of rich alluvial bottom land, and the eye ranges over a vast expanse of foliage, the monotony of which is relieved by the alternating swells and depressions of the landscape. Between peak and peak, through its bed of limestone, sand, and clay, sometimes kissing the feet of one bluff and then hugging the other, rolls the Sangamon river. The village of New Salem, which once stood on the ridge, was laid out in 1828; it became a trading place, and in 1836 contained twenty houses and a hundred inhabitants. In the days of land offices and stage-coaches it was a sprightly village with a busy market. Its people were progressive and industrious. Propitious winds filled the sails of its commerce, prosperity smiled graciously on its every enterprise, and the outside world encouraged its social pretensions. It had its day of glory, but, singularly enough, cotemporaneous with the departure of Lincoln from its midst it went into a rapid decline. A few crumbling stones here and there are all that attest its former existence. "How it vanished," observes one writer, "like a mist in the morning, to what distant places its inhabitants dispersed, and what became of the abodes they left behind, shall be questions for the local historian."
Lincoln's return to New Salem in August, 1831, was, within a few days, contemporaneous with the reappearance of Offut, who made the gratifying announcement that he had purchased a stock of goods which were to follow him from Beardstown. He had again retained the services of Lincoln to assist him when his merchandise should come to hand. The tall stranger—destined to be a stranger in New Salem no longer—pending the arrival of his employer's goods, lounged about the village with nothing to do. Leisure never sat heavily on him. To him there was nothing uncongenial in it, and he might very properly have been dubbed at the time a "loafer." He assured those with whom he came in contact that he was a piece of floating driftwood; that after the winter of deep snow, he had come down the river with the freshet; borne along by the swelling waters, and aimlessly floating about, he had accidentally lodged at New Salem. Looking back over his history we are forced to conclude that Providence or chance, or whatever power is responsible for it, could not have assigned him to a more favorable refuge.
His introduction to the citizens of New Salem, as Mentor Graham* the school-teacher tells us, was in the capacity of clerk of an election board. Graham furnishes ample testimony of the facility, fairness, and honesty which characterized the new clerk's work, and both teacher and clerk were soon bound together by the warmest of ties. During the day, when votes were coming in slowly, Lincoln began to entertain the crowd at the polls with a few attempts at story-telling. My cousin, J. R. Herndon, was present and enjoyed this feature of the election with the keenest relish. He never forgot some of Lincoln's yarns, and was fond of repeating them in after years. The recital of a few stories by Lincoln easily established him in the good graces of all New Salem. Perhaps he did not know it at the time, but he had used the weapon nearest at hand and had won.
* Nicolay and Hay in the Century make the mistake of spelling this man's name "Menton" Graham. In all the letters and papers from him he signs himself "Mentor" in every case.—J. W. W. ** "In the afternoon, as things were dragging a little, Lincoln the new man, began to spin out a stock of Indiana yarns. One that amused me more than any other he called the lizard story. 'The meeting-house,'" he said, "was in the woods and quite a distance from any other house. It was only used once a month. The preacher—an old line Baptist—was dressed in coarse linen pantaloons, and shirt of the same material. The pants, manufactured after the old fashion, with, baggy legs and a flap in front, were made to attach to his frame without the aid of suspenders. A single button held his shirt in position, and that was at the collar. He rose up in the pulpit and with a loud voice announced his text thus: 'I am the Christ, whom I shall represent to-day.' About this time a little blue lizard ran up underneath his roomy pantaloons. The old preacher, not wishing to interrupt the steady flow of his sermon, slapped away on his legs, expecting to arrest the intruder; but his efforts were unavailing, and the little fellow kept on ascending higher and higher. Continuing the sermon, the preacher slyly loosened the central button which graced the waist-band of his pantaloons and with a kick off came that easy-fitting garment. But meanwhile Mr. Lizard had passed the equatorial line of waist-band and was calmly exploring that part of the preacher's anatomy which lay underneath the back of his shirt. Things were now growing interesting, but the sermon was still grinding on. The next movement on the preacher's part was for the collar button, and with one sweep of his arm off came the tow linen shirt. The congregation sat for an instant as if dazed; at length one old lady in the rear of the room rose up and glancing at the excited object in the pulpit, shouted at the top of her voice: 'If you represent Christ then I'm done with the Bible.'"—J. R. Herndon, MS., July 2, 1865.
A few days after the election Lincoln found employment with one Dr. Nelson, who after the style of dignitaries of later days started with his family and effects in his "private" conveyance—which in this instance was a flat-boat—for Texas. Lincoln was hired to pilot the vessel through to the Illinois river. Arriving at Beardstown the pilot was discharged, and returned on foot across the sand and hills to New Salem. In the meantime Offut's long expected goods had arrived, and Lincoln was placed in charge. Offut relied in no slight degree on the business capacity of his clerk. In his effusive way he praised him beyond reason. He boasted of his skill as a business man and his wonderful intellectual acquirements. As for physical strength and fearlessness of danger, he challenged New Salem and the entire world to produce his equal. In keeping with his widely known spirit of enterprise Offut rented the Rutledge and Cameron mill, which stood at the foot of the hill, and thus added another iron to keep company with the half-dozen already in the fire. As a further test of his business ability Lincoln was placed in charge of this also. William G. Greene was hired to assist him, and between the two a life-long friendship sprang up. They slept in the store, and so strong was the intimacy between them that "when one turned over the other had to do likewise." At the head of these varied enterprises was Offut, the most progressive man by all odds in the village. He was certainly an odd character, if we accept the judgment of his cotemporaries. By some he is given the character of a clear-headed, brisk man of affairs. By others he is variously described as "wild, noisy, and reckless," or "windy, rattle-brained, unsteady, and improvident." Despite the unenviable traits ascribed to him he was good at heart and a generous friend of Lincoln. His boast that the latter could outrun, whip, or throw down any man in Sangamon county was soon tested, as we shall presently see, for, as another has truthfully expressed it, "honors such as Offut accorded to Abe were to be won before they were worn at New Salem." In the neighborhood of the village, or rather a few miles to the south-west, lay a strip of timber called Clary's Grove. The boys who lived there were a terror to the entire region—seemingly a necessary product of frontier civilization. They were friendly and good-natured; they could trench a pond, dig a bog, build a house; they could pray and fight, make a village or create a state. They would do almost anything for sport or fun, love or necessity. Though rude and rough, though life's forces ran over the edge of the bowl, foaming and sparkling in pure deviltry for deviltry's sake, yet place before them a poor man who needed their aid, a lame or sick man, a defenceless woman, a widow, or an orphaned child, they melted into sympathy and charity at once. They gave all they had, and willingly toiled or played cards for more. Though there never was under the sun a more generous parcel of rowdies, a stranger's introduction was likely to be the most unpleasant part of his acquaintance with them. They conceded leadership to one Jack Armstrong, a hardy, strong, and well-developed specimen of physical manhood, and under him they were in the habit of "cleaning out" New Salem whenever his order went forth to do so. Offut and "Bill" Clary—the latter skeptical of Lincoln's strength and agility—ended a heated discussion in the store one day over the new clerk's ability to meet the tactics of Clary's Grove, by a bet of ten dollars that Jack Armstrong was, in the language of the day, "a better man than Lincoln." The new clerk strongly opposed this sort of an introduction, but after much entreaty from Offut, at last consented to make his bow to the social lions of the town in this unusual way. He was now six feet four inches high, and weighed, as his friend and confidant, William Greene, tells us with impressive precision, "two hundred and fourteen pounds." The contest was to be a friendly one and fairly conducted. All New Salem adjourned to the scene of the wrestle. Money, whiskey, knives, and all manner of property were staked on the result. It is unnecessary to go into the details of the encounter. Everyone knows how it ended; how at last the tall and angular rail-splitter, enraged at the suspicion of foul tactics, and profiting by his height and the length of his arms, fairly lifted the great bully by the throat and shook him like a rag; how by this act he established himself solidly in the esteem of all New Salem, and secured the respectful admiration and friendship of the very man whom he had so thoroughly vanquished.*
* Mr. Lincoln's remarkable strength resulted not so much from muscular power as from the toughness of his sinews. He could not only lift from the ground enormous weight, but could throw a cannon-ball or a maul farther than anyone else in New Salem. I heard him explain once how he was enabled thus to excel others. He did not attribute it to a greater proportion of physical strength, but contended that because of the unusual length of his arms the ball or projectile had a greater swing and therefore acquired more force and momentum than in the hands of an average man.
From this time forward Jack Armstrong, his wife Hannah, and all the other Armstrongs became his warm and trusted friends. None stood readier than they to rally to his support, none more willing to lend a helping hand. Lincoln appreciated their friendship and support, and in after years proved his gratitude by saving one member of the family from the gallows.
The business done over Offut's counter gave his clerk frequent intervals of rest, so that, if so inclined, an abundance of time for study was always at his disposal. Lincoln had long before realized the deficiencies of his education, and resolved, now that the conditions were favorable, to atone for early neglect by a course of study. Nothing was more apparent to him than his limited knowledge of language, and the proper way of expressing his ideas. Moreover, it may be said that he appreciated his inefficiency in a rhetorical sense, and therefore determined to overcome all these obstacles by mastering the intricacies of grammatical construction. Acting on the advice of Mentor Graham he hunted up one Vaner, who was the reputed owner of Kirkham's Grammar, and after a walk of several miles returned to the store with the coveted volume under his arm. With zealous perseverance he at once applied himself to the book. Sometimes he would stretch out at full length on the counter, his head propped up on a stack of calico prints, studying it; or he would steal away to the shade of some inviting tree, and there spend hours ar a time in a determined effort to fix in his mind the arbitrary rule that "adverbs qualify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs." From the vapidity of grammar it was now and then a great relaxation to turn to the more agreeable subject of mathematics; and he might often have been seen lying face downwards, stretched out over six feet of grass, figuring out on scraps of paper some problem given for solution by a quizzical store lounger, or endeavoring to prove that, "multiplying the denominator of a fraction divides it, while dividing the denominator multiplies it." Rather a poor prospect one is forced to admit for a successful man of business.
At this point in my narrative I am pained to drop from further notice our buoyant and effusive friend Offut. His business ventures failing to yield the extensive returns he predicted, and too many of his obligations maturing at the same time, he was forced to pay the penalty of commercial delinquency and went to the wall. He soon disappeared from the village, and the inhabitants thereof never knew whither he went. In the significant language of Lincoln he "petered out." As late as 1873 I received a letter from Dr. James Hall, a physician living at St. Dennis, near Baltimore, Maryland, who, referring to the disappearance of Offut, relates the following reminiscence: "Of what consequence to know or learn more of Offut I cannot imagine; but be assured he turned up after leaving New Salem. On meeting the name it seemed familiar, but I could not locate him. Finally I fished up from memory that some twenty-five years ago one "Denton Offut" appeared in Baltimore, hailing from Kentucky, advertising himself in the city papers as a veterinary surgeon and horse tamer, professing to have a secret to whisper in the horse's ear, or a secret manner of whispering in his ear, which he could communicate to others, and by which the most refractory and vicious horse could be quieted and controlled. For this secret he charged five dollars, binding the recipient by oath not to divulge it. I know several persons, young fancy horsemen, who paid for the trick. Offut advertised himself not only through the press, but by his strange attire. He appeared in the streets on horseback and on foot, in plain citizens' dress of black, but with a broad sash across his right shoulder, of various colored ribbons, crossed on his left hip under a large rosette of the same material, the whole rendering his appearance most ludicrously conspicuous. Having occasion to purchase a horse I encountered him at several of our stables and was strongly urged to avail myself of his secret. So much for Offut; but were he living in '61, I doubt not Mr. Lincoln would have heard of him."
The early spring of 1832 brought to Springfield and New Salem a most joyful announcement. It was the news of the coming of a steamboat down the Sangamon river—proof incontestable that the stream was navigable. The enterprise was undertaken and carried through by Captain Vincent Bogue, of Springfield, who had gone to Cincinnati to procure a vessel and thus settle the much-mooted question of the river's navigability. When, therefore, he notified the people of his town that the steamboat Talisman would put out from Cincinnati for Springfield, we can well imagine what great excitement and unbounded enthusiasm followed the announcement. Springfield, New Salem, and all the other towns along the now interesting Sangamon* were to be connected by water with the outside world.
*The final syllable of this name was then pronounced to rhyme with "raw." In later days the letter "n" was added— probably for euphony's sake.
Public meetings, with the accompaniment of long subscription lists, were held; the merchants of Springfield advertised the arrival of goods "direct from the East per steamer Talisman;" the mails were promised as often as once a week from the same direction; all the land adjoining each enterprising and aspiring village along the river was subdivided into town lots—in fact, the whole region began to feel the stimulating effects of what, in later days, would have been called a "boom." I remember the occasion well, for two reasons. It was my first sight of a steamboat, and also the first time I ever saw Mr. Lincoln—although I never became acquainted with him till his second race for the Legislature in 1834. In response to the suggestion of Captain Bogue, made from Cincinnati, a number of citizens—among the number Lincoln—had gone down the river to Beardstown to meet the vessel as she emerged from the Illinois. These were armed with axes having long handles, to cut away, as Bogue had recommended, "branches of trees hanging over from the banks." After having passed New Salem, I and other boys on horseback followed the boat, riding along the river's bank as far as Bogue's mill, where she tied up. There we went aboard, and lost in boyish wonder, feasted our eyes on the splendor of her interior decorations. The Sangamon Journal of that period contains numerous poetical efforts celebrating the Talisman's arrival. A few lines under date of April 5, 1832, unsigned, but supposed to have been the product of a local poet—one Oliphant*—were sung to the tune of "Clar de Kitchen." I cannot refrain from inflicting a stanza or two of this ode on the reader:
* E. P. Oliphant, a lawyer. "O, Captain Bogue he gave the load, And Captain Bogue he showed the road; And we came up with a right good will, And tied our boat up to his mill. Now we are up the Sangamo, And here we'll have a grand hurra, So fill your glasses to the brim, Of whiskey, brandy, wine, and gin. Illinois suckers, young and raw, Were strung along the Sangamo, To see a boat come up by steam They surely thought it was a dream."
On its arrival at Springfield, or as near Springfield as the river ran, the crew of the boat were given a reception and dance in the court-house. The cream of the town's society attended to pay their respects to the newly arrived guests. The captain in charge of the boat—not Captain Bogue, but a vainly dressed fellow from the East—was accompanied by a woman, more gaudily attired than himself, whom he introduced as his wife. Of course the most considerate attention was shown them both, until later in the evening, when it became apparent that the gallant officer and his fair partner had imbibed too freely—for in those days we had plenty of good cheer—and were becoming unpleasantly demonstrative in their actions. This breach of good manners openly offended the high-toned nature of Springfield's fair ladies; but not more than the lamentable fact, which they learned on the following day, that the captain's partner was not his wife after all, but a woman of doubtful reputation whom he had brought with him from some place further east. But to return to the Talisman. That now interesting vessel lay for a week longer at Bogue's mill, when the receding waters admonished her officers that unless they purposed spending the remainder of the year there they must head her down-stream. In this emergency recourse was had to my cousin Rowan Herndon, who had had no little experience as a boatman, and who recommended the employment of Lincoln as a skilful assistant. These two inland navigators undertook therefore the contract of piloting the vessel—which had now become elephantine in proportions—through the uncertain channel of the Sangamon to the Illinois river. The average speed was four miles a day. At New Salem safe passage over the mill-dam was deemed impossible unless the same could be lowered or a portion removed.*
* The affair at New Salem is thus described by Oliphant in the poem before referred to:
To this, Cameron and Rutledge, owners of the mill, entered their most strenuous protest. The boat's officers responded that under the Federal Constitution and laws no one had the right to dam up or in any way obstruct a navigable stream, and they argued that, as they had just demonstrated that the Sangamon was navigable (?), they proposed to remove enough of the obstruction to let the boat through. Rowan Herndon, describing it to me in 1865, said: "When we struck the dam she hung. We then backed off and threw the anchor over. We tore away part of the dam and raising steam ran her over on the first trial." The entire proceeding stirred up no little feeling, in which mill owners, boat officers, and passengers took part. The effect the return trip of the Talisman had on those who believed in the successful navigation of the Sangamon is shrewdly indicated by the pilot, who with laconic complacency adds: "As soon as she was over, the company that chartered her was done with her." Lincoln and Herndon, in charge of the vessel, piloted her through to Beardstown. There they were paid forty dollars each, according to contract, and bidding adieu to the Talisman's officers and crew, set out on foot for New Salem again. A few months later the Talisman caught fire at the wharf in St. Louis and went up in flames. The experiment of establishing a steamboat line to Springfield proved an unfortunate venture for its projector, Captain Bogue. Finding himself unable to meet his rapidly maturing obligations, incurred in aid of the enterprise, it is presumed that he left the country, for the Journal of that period is filled with notices of attachment proceedings brought by vigilant creditors who had levied on his goods.
"And when we came to Salem dam, Up we went against it jam: We tried to cross with all our might, But found we couldn't and staid all night."
The departure of the Talisman for deeper waters, the downfall of Denton Offut's varied enterprises and his disappearance from New Salem, followed in rapid succession, and before the spring of 1832 had merged into summer Lincoln found himself a piece of "floating driftwood" again. Where he might have lodged had not the Black Hawk war intervened can only be a matter of conjecture. A glance at this novel period in his life may not be out of keeping with the purpose of this book. The great Indian chief, Black Hawk, who on the 30th of June, 1831, had entered into an agreement, having all the solemnity of a treaty, with Governor Reynolds and General Gaines that none of his tribe should ever cross the Mississippi "to their usual place of residence, nor any part of their old hunting grounds east of the Mississippi, without permission of the President of the United States or the governor of the State of Illinois," had openly broken the compact. On the 6th of April, 1832, he recrossed the Mississippi and marched up Rock River Valley, accompanied by about five hundred warriors on horseback; while his women and children went up the river in canoes. The great chief was now sixty-seven years old, and believed that his plots were all ripe and his allies fast and true. Although warned by General Atkinson, then in command of Fort Armstrong, against this aggression, and ordered to return, he proudly refused, claiming that he had "come to plant corn." On being informed of the movement of Black Hawk Governor Reynolds called for a thousand mounted volunteers to co-operate with the United States forces under command of General Atkinson, and drive the wily Indian back across the Mississippi. The response to the governor's call was prompt and energetic. In the company from Sangamon county Lincoln enlisted, and now for the first time entered on the vicissitudinous and dangerous life of a soldier. That he in fact regarded the campaign after the Indians as a sort of holiday affair and chicken-stealing expedition is clearly shown in a speech he afterwards made in Congress in exposure of the military pretensions of General Cass. However, in grim, soldierly severity he marched with the Sangamon county contingent to Rushville,* in Schuyler county, where, much to his surprise, he was elected captain of the company over William Kirkpatrick. A recital of the campaign that followed, in the effort to drive the treacherous Indians back, or a description of the few engagements—none of which reached the dignity of a battle—which took place, have in no wise been overlooked by the historians of Illinois and of the Black Hawk war. With the exception of those things which relate to Lincoln alone I presume it would be needless to attempt to add anything to what has so thoroughly and truthfully been told.
* While at the rendezvous at Rushville and on the march to the front Lincoln of course drilled his men, and gave them such meager instruction in military tactics as he could impart. Some of the most grotesque things he ever related were descriptions of these drills. In marching one morning at the head of the company, who were following in lines of twenty abreast, it became necessary to pass through a gate much narrower than the lines. The captain could not remember the proper command to turn the company endwise, and the situation was becoming decidedly embarrassing, when one of those thoughts born of the depths of despair came to his rescue. Facing the lines, he shouted: "Halt! This company will break ranks for two minutes and form again on the other side of the gate." The manouvre was successfully executed.
On being elected captain, Lincoln replied in a brief response of modest and thankful acceptance. It was the first official trust ever turned over to his keeping, and he prized it and the distinction it gave him more than any which in after years fell to his lot. His company savored strongly of the Clary's Grove order, and though daring enough in the presence of danger, were difficult to bring down to the inflexibilities of military discipline. Each one seemed perfectly able and willing to care for himself, and while the captain's authority was respectfully observed, yet, as some have said, they were none the less a crowd of "generous ruffians." I heard Mr. Lincoln say once on the subject of his career as captain in this company and the discipline he exercised over his men, that to the first order given one of them he received the response, "Go to the devil, sir!" Notwithstanding the interchange of many such unsoldierlike civilities between the officer and his men, a strong bond of affection united them together, and if a contest had arisen over the conflict of orders between the United States authorities and those emanating from Captain Lincoln or some other Illinois officer—as at one time was threatened—we need not be told to which side the Sangamon county company to a man would have gone. A general order forbidding the discharge of firearms within fifty yards of the camp was disobeyed by Captain Lincoln himself. For this violation of rule he was placed under arrest and deprived of his sword for a day. But this and other punishments in no way humiliated him in the esteem of his men; if anything, they only clung the closer, and when Clary's Grove friendship asserted itself, it meant that firm and generous attachment found alone on the frontier—that bond, closer than the affinity of blood, which becomes stronger as danger approaches death.
A soldier of the Sangamon county company broke into the officers' quarters one night, and with the aid of a tomahawk and four buckets, obtained by stealth a good supply of wines and liquors, which he generously distributed to his appreciative comrades. The next morning at daybreak, when the army began to move, the Sangamon county company, much to their captain's astonishment, were unfit for the march. Their nocturnal expedition had been too much for them, and one by one they fell by the wayside, until but a mere handful remained to keep step with their gallant and astounded captain. Those who fell behind gradually overcame the effects of their carousal, but were hard pressed to overtake the command, and it was far into the night when the last one straggled into camp. The investigation which followed resulted only in the captain suffering the punishment for the more guilty men. For this infraction of military law he was put under arrest and made to carry a wooden sword for two days, "and this too," as one of his company has since assured me, "although he was entirely blameless in the matter."
Among the few incidents of Lincoln's career in the Black Hawk war that have found a place in history was his manly interference to protect an old Indian who strayed, hungry and helpless, into camp one day, and whom the soldiers were conspiring to kill on the ground that he was a spy. A letter from General Cass, recommending him for his past kind and faithful services to the whites, which the trembling old savage drew from beneath the folds of his blanket failed in any degree to appease the wrath of the men who confronted him. They had come out to fight the treacherous Indians, and here was one who had the temerity even to steal into their camp. "Make an example of him," they exclaimed. "The letter is a forgery and he is a spy." They might have put their threats into execution had not the tall form of their captain, his face "swarthy with resolution and rage," interposed itself between them and their defenseless victim. Lincoln's determined look and demand that "it must not be done" were enough. They sullenly desisted, and the Indian, unmolested, continued on his way.
Lincoln's famous wrestling match with the redoubtable Thompson, a soldier from Union county, who managed to throw him twice in succession, caused no diminution in the admiration and pride his men felt in their captain's muscle and prowess. They declared that unfair advantage had been taken of their champion, that Thompson had been guilty of foul tactics, and that, in the language of the sporting arena, it was a "dog-fall." Lincoln's magnanimous action, however, in according his opponent credit for fair dealing in the face of the wide-spread and adverse criticism that prevailed, only strengthened him in the esteem of all.*
* William L. Wilson, a survivor of the war, in a letter under date of February 3, 1882, after detailing reminiscences of Stillman's defeat, says: "I have during that time had much fun with the afterwards President of the United States, Abraham Lincoln. I remember one time of wrestling with him, two best in three, and ditched him. He was not satisfied, and we tried it in a foot-race for a five-dollar bill. I won the money, and 'tis spent long ago. And many more reminiscences could I give, but am of the Quaker persuasion, and not much given to writing."
At times the soldiers were hard pressed for food, but by a combination of ingenuity and labor in proportions known only to a volunteer soldier, they managed to avoid the unpleasant results of long-continued and unsatisfied hunger. "At an old Winnebago town called Turtle Village," narrates a member of the company, "after stretching our rations over nearly four days, one of our mess, an old acquaintance of Lincoln, G. B. Fanchier, shot a dove, and having a gill of flour left we made a gallon and a half of delicious soup in an old tin bucket that had been lost by Indians. This soup we divided among several messes that were hungrier than we were and our own mess, by pouring in each man's cup a portion of the esculent. Once more, at another time, in the extreme northern part of Illinois, we had been very hungry for two days, but suddenly came upon a new cabin at the edge of the prairie that the pioneer sovereign squatter family had vacated and 'skedaddled' from for fear of losing their scalps. There were plenty of chickens about the cabin, much hungrier than we ourselves were, if poverty is to test the matter, and the boys heard a voice saying 'Slay and eat.' They at once went to running, clubbing, and shooting them as long as they could be found. Whilst the killing was going on I climbed to the ridge-pole of the smoke-house to see distinctly what I saw obscurely from the ground, and behold! the cleanest, sweetest jole I ever saw—alone, half hid by boards and ridge-pole, stuck up no doubt for future use. By this time many of the chickens were on the fire, broiling, for want of grease or gravy to fry them in. Some practical fellow proposed to throw in with the fowls enough bacon to convert broiling into frying; the proposition was adopted, and they were soon fried. We began to eat the tough, dry chickens with alternating mouthfuls of the jole, when Lincoln came to the repast with the query, 'Eating chicken, boys?' 'Not much, sir,' I responded, for we had operated principally on the jole, it being sweeter and more palatable than the chickens. 'It is much like eating saddlebags,' he responded; 'but I think the stomach can accomplish much to-day; but what have you got therewith the skeletons, George? 'We did have a sweet jole of a hog, sir,' I answered, 'but you are nearly too late for your share,' at the same time making room for him to approach the elm-bark dish. He ate the bacon a moment, then commenced dividing by mouthfuls to the boys from other messes, who came to 'see what Abe was at,' and saying many quaint and funny things suited to the time and the jole." The captain, it will be seen, by his "freedom without familiarity" and his "courtesy without condescension," was fast making inroads on the respect of his rude but appreciative men. He was doubtless looking a long way ahead, when both their friendship and respect would be of avail, for as the chronicler last quoted from continues: "He was acquainted with everybody, and he had determined, as he told me, to become a candidate for the next Legislature. The mess immediately pitched on him as our standard-bearer, and he accepted."
The term for which the volunteers had enlisted had now expired, and the majority, tiring of the service, the novelty of which had worn off, and longing for the comforts and good cheer of their homes, refused either to re-enlist or render further service. They turned their faces homeward, each with his appetite for military glory well satiated. But the war was not over, and the mighty Black Hawk was still east of the Mississippi. A few remained and re-enlisted. Among them was Lincoln. This time, eschewing the responsibility of a captaincy, and to avoid the possible embarrassment of dragging about camp a wooden sword, he entered the company of Elijah Iles as a dignified private. It has pleased some of Mr. Lincoln's biographers to attribute this re-enlistment to pure patriotism on his part and a conscientious desire to serve his country. From the standpoint of sentiment that is a comfortable view to take of it; but I have strong reason to believe that Mr. Lincoln never entertained such serious notions of the campaign. In fact, I may say that my information comes from the best authority to be had in the matter—the soldier himself. Mr. Lincoln had no home; he had cut loose from his parents, from the Hankses and the Johnstons; he left behind him no anxious wife and children; and no chair before a warm fireside remained vacant for him. "I was out of work," he said to me once, "and there being no danger of more fighting, I could do nothing better than enlist again."
After his discharge from this last and brief period of service, along with the remainder of the Sangamon county soldiers, he departed from the scenes of recent hostilities for New Salem again. His soldier days had ended, and he returned now to enter upon a far different career. However much in later years he may have pretended to ridicule the disasters of the Black Hawk war, or the part he took in it, yet I believe he was rather proud of it after all. When Congress, along in the fifties, granted him a land warrant he was greatly pleased. He located it on some land in Iowa, and declared to me one day that he would die seized of that land, and although the tract never yielded him anything he never, so far as my knowledge extends parted with its ownership.*
* "In regard to the Bounty Land Warrants issued to Abraham Lincoln for military services during the Black Hawk war as Captain of 4th Illinois Volunteers, the first warrant, No. 52,076, for forty acres (Act of 1850), was issued to Abraham Lincoln, Captain, etc. on the 16th of April, 1852, and was located in his name by his duly appointed attorney, John P. Davis, at Dubuque, Iowa, July 21, 1854, on the north-west quarter of the south-west quarter of section 20, in Township 84, north of Range 39, west, Iowa. A patent as recorded in volume 280, page 21, was issued for this tract to Abraham Lincoln on the 1st of June, 1855, and transmitted the 26th October, 1855, to the Register of delivery. "Under the Act of 1855, another Land Warrant, No. 68,465, for 120 acres, was issued to Abraham Lincoln, Captain Illinois Militia, Black Hawk war, on the 22d April, 1856, and was located by himself at Springfield, Illinois, December 27, 1859, on the east half of the north-east quarter and the north-west quarter of the north-east quarter of section 18, in Township 84, north of Range 39, west; for which a patent, as recorded in volume 468, page 53, was issued September 10, 1860, and sent October 30, 1860, to the Register for delivery."—Letter Jos. S. Wilson Acting Commissioner Land Office, June 27, 1865.
The return of the Black Hawk warriors to New Salem occurred in the month of August, but a short time before the general election. A new Legislature was to be chosen, and as Lincoln had declared to his comrades in the army he would, and in obedience to the effusive declaration of principles which he had issued over his signature in March, before he went to the war, he presented himself to the people of his newly adopted county as a candidate for the Legislature. It is not necessary to enter into an account of the political conditions in Illinois at that time, or the effect had on the same by those who had in charge the governmental machinery. Lincoln's course is all that interests us. Though he may not have distinctly avowed himself a Whig, yet, as one of his friends asserted, "he stood openly on Whig principles." He favored a national bank, a liberal system of internal improvements, and a high protective tariff. The handbill or circular alluded to announcing his candidacy was a sort of literary fulmination, but on account of its length I deem it unnecessary to insert the whole of it here. I have been told that it was prepared by Lincoln, but purged of its most glaring grammatical errors by James McNamar, who afterwards became Lincoln's rival in an important love affair.*
* In a letter dated May 5, 1866, McNamar says: "I corrected at his request some of the grammatical errors in his first address to the voters of Sangamon county, his principal hobby being the navigation of the Sangamon river."
The circular is dated March 9, 1832, and addressed to the "People of Sangamon County." In it he takes up all the leading questions of the day: railroads, river navigation, internal improvements, and usury. He dwells particularly on the matter of public education, alluding to it as the most important subject before the people. Realizing his own defects arising from a lack of school instruction he contends that every man and his children, however poor, should be permitted to obtain at least a moderate education, and thereby be enabled "to read the Scriptures and other works both of a moral and religious nature for themselves." The closing paragraph was so constructed as to appeal to the chivalrous sentiments of Clary's Grove. "I was born and have ever remained," he declares, "in the most humble walks of life. I have no wealthy or popular relatives or friends to recommend me. My case is thrown exclusively upon the independent voters of the county; and if elected they will have conferred a favor upon me for which I shall be unremitting in my labors to compensate. But if," he dryly concludes, "the good people in their wisdom shall see fit to keep me in the background, I have been too familiar with disappointments to be very much chagrined."
The election being near at hand only a few days remained for his canvass. One * who was with him at the time describing his appearance, says: "He wore a mixed jeans coat, clawhammer style, short in the sleeves and bobtail—in fact it was so short in the tail he could not sit on it; flax and tow-linen pantaloons, and a straw hat. I think he wore a vest, but do not remember how it looked. He wore pot-metal boots." His maiden effort on the stump was a speech on the occasion of a public sale at Pappsville, a village eleven miles west of Springfield. After the sale was over and speech-making had begun, a fight—a "general fight," as one of the bystanders relates—ensued, and Lincoln, noticing one of his friends about to succumb to the energetic attack of an infuriated ruffian, interposed to prevent it. He did so most effectually.
* A. Y. Ellis, letter, June 5, 1866, MS.
Hastily descending from the rude platform he edged his way through the crowd, and seizing the bully by the neck and seat of his trowsers, threw him by means of his strength and long arms, as one witness stoutly insists, "twelve feet away." Returning to the stand and throwing aside his hat he inaugurated his campaign with the following brief but juicy declaration:
"Fellow Citizens, I presume you all know who I am. I am humble Abraham Lincoln. I have been solicited by many friends to become a candidate for the Legislature. My politics are short and sweet, like the old woman's dance. I am in favor of a national bank. I am in favor of the internal improvement system and a high protective tariff. These are my sentiments and political principles. If elected I shall be thankful; if not it will be all the same."
I obtained this speech from A. Y. Ellis, who in 1865 wrote it out. Ellis was his friend and supporter, and took no little interest in his canvass. "I accompanied him," he relates, "on one of his electioneering trips to Island Grove, and he made a speech which pleased his party friends very well indeed, though some of the Jackson men tried to make sport of it. He told several anecdotes, and applied them, as I thought, very well. He also told the boys several stories which drew them after him. I remember them, but modesty and my veneration for his memory forbid me to relate them." His story-telling propensity, and the striking fitness of his yarns—many of them being of the bar-room order—in illustrating public questions, as we shall see further along in these chapters, was really one of the secrets of his popularity and strength. The election, as he had predicted, resulted in his defeat—the only defeat, as he himself afterward stated, that he ever suffered at the hands of the people. But there was little defeat in it after all. Out of the eight unsuccessful candidates he stood third from the head of the list, receiving 657 votes. Five others received less. The most gratifying feature of it all was the hearty support of his neighbors at New Salem. Of the entire 208 votes in the precinct he received every one save three.
It may not be amiss to explain the cause of this remarkable endorsement of Lincoln by the voters in New Salem. It arose chiefly from his advocacy of the improvement of the Sangamon river. He proposed the digging of a canal a few miles east of the point where the Sangamon enters the Illinois river, thereby giving the former two mouths. This, he explained to the farmers, would prevent the accumulation of back-water and consequent overflow of their rich alluvial bottom lands in the spring. It would also avert the sickness and evil results of stagnant pools, which formed in low places after the high waters receded. His scheme—that is the name by which it would be known to-day—commended itself to the judgment of his neighbors, and the flattering vote he received shows how they endorsed it.
The unsuccessful result of the election did not dampen his hopes nor sour his ambition. The extensive acquaintance, the practice in public speaking, the confidence gained with the people, together with what was augmented in himself, made a surplus of capital on which he was free to draw and of which he afterwards frequently availed himself. The election being over, however, he found himself without money, though with a goodly supply of experience, drifting again. His political experience had forever weaned him from the dull routine of common labor. Labor afforded him no time for study and no incentive to profitable reflection. What he seemed to want was some lighter work, employment in a store or tavern where he could meet the village celebrities, exchange views with strangers, discuss politics, horse-races, cock-fights, and narrate to listening loafers his striking and significant stories. In the communities where he had lived, the village store-keeper held undisturbed sway. He took the only newspapers, owned the only collection of books and half the property in the village; and in general was the social, and oftentimes the political head of the community. Naturally, therefore the prominence the store gave the merchant attracted Lincoln. But there seemed no favorable opening for him—clerks in New Salem were not in demand just then.
My cousins, Rowan and James Herndon, were at that time operating a store, and tiring of their investment and the confinement it necessitated, James sold his interest to an idle, shiftless fellow named William Berry. Soon after Rowan disposed of his to Lincoln. That the latter, who was without means and in search of work, could succeed to the ownership of even a half interest in a concern where but a few days before he would in all probability gladly have exchanged his services for his board, doubtless seems strange to the average young business man of to-day. I once asked Rowan Herndon what induced him to make such liberal terms in dealing with Lincoln, whom he had known for so short a time.
"I believed he was thoroughly honest," was the reply, "and that impression was so strong in me I accepted his note in payment of the whole. He had no money, but I would have advanced him still more had he asked for it."
Lincoln and Berry had been installed in business but a short time until one Reuben Radford, the proprietor of another New Salem grocery, who, happening to incur the displeasure of the Clary's Grove boys, decided suddenly one morning, in the commercial language of later days, to "retire from business." A visit by night of the Clary's Grove contingent always hastened any man's retirement from business. The windows were driven in, and possession taken of the stock without either ceremony or inventory. If, by break of day, the unfortunate proprietor found any portion of his establishment standing where he left it the night before, he might count himself lucky. In Radford's case, fearing "his bones might share the fate of his windows," he disposed of his stock and good-will to William Greene for a consideration of four hundred dollars. The latter employed Lincoln to make an inventory of the goods, and when completed, the new merchant, seeing in it something of a speculation, offered Greene an advance of two hundred and fifty dollars on his investment. The offer was accepted, and the stock and fixtures passed into the ownership and control of the now enterprising firm of Lincoln & Berry. They subsequently absorbed the remnant of a store belonging to one Rutledge, which last transaction cleared the field of all competitors and left them in possession of the only mercantile concern in New Salem.
To effect these sales not a cent of money was required—the buyer giving the seller his note and the latter assigning it to someone else in another trade. Berry gave his note to James Herndon, Lincoln his to Rowan Herndon, while Lincoln & Berry as a firm, executed their obligation to Greene, Radford, and Rutledge in succession. Surely Wall Street at no time in its history has furnished a brace of speculators who in so brief a period accomplished so much and with so little money. A few weeks only were sufficient to render apparent Lincoln's ill adaptation to the requirements of a successful business career. Once installed behind the counter he gave himself up to reading and study, depending for the practical management of the business on his partner. A more unfortunate selection than Berry could not have been found; for, while Lincoln at one end of the store was dispensing political information, Berry at the other was disposing of the firm's liquors, being the best customer for that article of merchandise himself. To put it more plainly, Lincoln's application to Shakespeare and Bums was only equalled by Berry's attention to spigot and barrel. That the latter in the end succeeded in squandering a good portion of their joint assets, besides wrecking his own health, is not to be wondered at. By the spring of 1833 they, like their predecessors, were ready to retire. Two brothers named Trent coming along, they sold to them on the liberal terms then prevalent the business and good-will; but before the latter's notes fell due, they in turn had failed and fled. The death of Berry following soon after, released him from the payment of any notes or debts, and thus Lincoln was left to meet the unhonored obligations of the ill-fated partnership, or avoid their payment by dividing the responsibility and pleading the failure of the business. That he assumed all the liability and set resolutely to work to pay everything, was strictly in keeping with his fine sense of honor and justice. He was a long time meeting these claims, even as late as 1848 sending to me from Washington portions of his salary as Congressman to be applied on the unpaid remnant of the Berry & Lincoln indebtedness—but in time he extinguished it all, even to the last penny.
Conscious of his many shortcomings as a merchant, and undaunted by the unfortunate complications from which he had just been released, Lincoln returned to his books. Rowan Herndon, with whom he had been living, having removed to the country, he became for the first time a sojourner at the tavern, as it was then called—a public-house kept by Rutledge, Onstatt, and Alley in succession. "It was a small log house," he explained to me in later years, "covered with clapboards, and contained four rooms." It was second only in importance to the store, for there he had the opportunity of meeting passing strangers—lawyers and others from the county seat, whom he frequently impressed with his knowledge as well as wit. He had, doubtless, long before determined to prepare himself for the law; in fact, had begun to read Blackstone while in the store, and now went at it with renewed zeal. He borrowed law-books of his former comrade in the Black Hawk war, John T. Stuart, who was practicing law in Springfield, frequently walking there to return one and borrow another. His determination to master any subject he undertook and his application to study were of the most intense order. On the road to and from Springfield he would read and recite from the book he carried open in his hand, and claimed to have mastered forty pages of Blackstone during the first day after his return from Stuart's office. At New Salem he frequently sat barefooted under the shade of a tree near the store, poring over a volume of Chitty or Blackstone; sometimes lying on his back, putting his feet up the tree, which provokes one of his biographers to denote the latter posture as one which might have been "unfavorable to mental application, in the case of a man with shorter extremities."
That Lincoln's attempt to make a lawyer of himself under such adverse and unpromising circumstances excited comment is not to be wondered at. Russell Godby, an old man who still survives, told me in 1865, that he had often employed Lincoln to do farm work for him, and was surprised to find him one day sitting barefoot on the summit of a woodpile and attentively reading a book. "This being an unusual thing for farm hands in that early day to do, I asked him," relates Godby, "what he was reading." 'I'm not reading,' he answered. 'I'm studying.' 'Studying what?' I enquired. 'Law, sir,' was the emphatic response. It was really too much for me, as I looked at him sitting there proud as Cicero. 'Great God Almighty!' I exclaimed, and passed on.
But Lincoln kept on at his studies. Wherever he was and whenever he could do so the book was brought into use. He carried it with him in his rambles through the woods and his walks to the river. When night came he read it by the aid of any friendly light he could find. Frequently he went down to the cooper's shop and kindled a fire out of the waste material lying about, and by the light it afforded read until far into the night.
One of his companions at this time relates that, "while clerking in the store or serving as postmaster he would apply himself as opportunity offered to his studies, if it was but five minutes time—would open his book which he always kept at hand, study it, reciting to himself; then entertain the company present or wait on a customer without apparent annoyance from the interruption. Have frequently seen him reading while walking along the streets. Occasionally he would become absorbed with his book; would stop and stand for a few moments, then walk on, or pass from one house to another or from one crowd or squad of men to another. He was apparently seeking amusement, and with his thoughtful face and ill-fitting clothes was the last man one would have singled out for a student. If the company he was in was unappreciative, or their conversation at all irksome, he would open his book and commune with it for a time, until a happy thought suggested itself and then the book would again return to its wonted resting-place under his arm. He never appeared to be a hard student, as he seemed to master his studies with little effort, until he commenced the study of the law. In that he became wholly engrossed, and began for the first time to avoid the society of men, in order that he might have more time for study. He was not what is usually termed a quick-minded man, although he would usually arrive at his conclusions very readily. He seemed invariably to reflect and deliberate, and never acted from impulse so far as to force a wrong conclusion on a subject of any moment." *
* R. B. Rutledge, letter, Nov. 30. 1866, MS.
It was not long until he was able to draw up deeds, contracts, mortgages, and other legal papers for his neighbors. He figured conspicuously as a pettifogger before the justice of the peace, but regarding it merely as a kind of preliminary practice, seldom made any charge for his services. Meanwhile he was reading not only law books but natural philosophy and other scientific subjects. He was a careful and patient reader of newspapers, the Sangamon Journal—published at Springfield—Louisville Journal, St. Louis Republican, and Cincinnati Gazette being usually within his reach. He paid a less degree of attention to historical works, although he read Rollin and Gibbon while in business with Berry. He had a more pronounced fondness for fictitious literature, and read with evident relish Mrs. Lee Hentz's novels, which were very popular books in that day, and which were kindly loaned him by his friend A. Y. Ellis. The latter was a prosperous and shrewd young merchant who had come up from Springfield and taken quite a fancy to Lincoln. The two slept together and Lincoln frequently assisted him in the store. He says that Lincoln was fond of short, spicy stories one and two columns long, and cites as specimens, "Cousin Sally Dillard," "Becky William's Courtship," "The Down-Easter and the Bull," and others, the very titles suggesting the character of the productions. He remembered everything he read, and could afterwards without apparent difficulty relate it. In fact, Mr. Lincoln's fame as a storyteller spread far and wide. Men quoted his sayings, repeated his jokes, and in remote places he was known as a story-teller before he was heard of either as lawyer or politician.
It has been denied as often as charged that Lincoln narrated vulgar stories; but the truth is he loved a story however extravagant or vulgar, if it had a good point. If it was merely a ribald recital and had no sting in the end, that is, if it exposed no weakness or pointed no moral, he had no use for it either in conversation or public speech; but if it had the necessary ingredients of mirth and moral no one could use it with more telling effect. As a mimic he was unequalled, and with his characteristic gestures, he built up a reputation for story-telling—although fully as many of his narratives were borrowed as original—which followed him through life. One who listened to his early stories in New Salem says: "His laugh was striking. Such awkward gestures belonged to no other man. They attracted universal attention, from the old sedate down to the schoolboy. Then in a few moments he was as calm and thoughtful as a judge on the bench, and as ready to give advice on the most important matters; fun and gravity grew on him alike."
Lincoln's lack of musical adaptation has deprived us of many a song. For a ballad or doggerel he sometimes had quite a liking. He could memorize or recite the lines but some one else had to do the singing. Listen to one in which he shows "How St. Patrick Came to be Born on the 17th of March." Who composed it or where Lincoln obtained it I have never been able to learn. Ellis says he often inflicted it on the crowds who collected in his store of winter evenings. Here it is:
"The first factional fight in old Ireland, they say, Was all on account of Saint Patrick's birthday, It was somewhere about midnight without any doubt, And certain it is, it made a great rout. On the eighth day of March, as some people say, St Patrick at midnight he first saw the day; While others assert 'twas the ninth he was born, Twas all a mistake—between midnight and morn. Some blamed the baby, some blamed the clock; Some blamed the doctor, some the crowing cock. With all these close questions sure no one could know, Whether the babe was too fast or the clock was too slow. Some fought for the eighth, for the ninth some would die; He who wouldn't see right would have a black eye. At length these two factions so positive grew, They each had a birthday, and Pat he had two. Till Father Mulcahay who showed them their sins, He said none could have two birthdays but as twins. 'Now Boys, don't be fighting for the eight or the nine Don't quarrel so always, now why not combine.' Combine eight with nine. It is the mark; Let that be the birthday. Amen! said the clerk. So all got blind drunk, which completed their bliss, And they've kept up the practice from that day to this." * * From MS., furnished by Ellis in August, 1866.
As a salesman, Lincoln was lamentably deficient. He was too prone to lead off into a discussion of politics or morality, leaving someone else to finish the trade which he had undertaken. One of his employers says: "He always disliked to wait on the ladies, preferring, he said, to wait on the men and boys. I also remember he used to sleep on the store counter when they had too much company at the tavern. He wore flax and tow linen pantaloons—I thought about five inches too short in the legs—and frequently had but one suspender, no vest or coat. He wore a calico shirt, such as he had in the Black Hawk war; coarse brogans, tan color; blue yarn socks and straw hat, old style, and without a band." His friend Ellis attributed his shyness in the presence of the ladies to the consciousness of his awkward appearance and the unpretentious condition of his wearing apparel. It was more than likely due to pure bashfulness. "On one occasion," continues Ellis, "while we boarded at the tavern, there came a family consisting of an old lady, her son, and three stylish daughters, from the State of Virginia, who stopped there for two or three weeks, and during their stay I do not remember of Mr. Lincoln's ever appearing at the same table with them."
As a society man, Lincoln was singularly deficient while he lived in New Salem, and even during the remainder of his life. He never indulged in gossip about the ladies, nor aided in the circulation of village scandal. For woman he had a high regard, and I can testify that during my long acquaintance with him his conversation was free from injurious comment in individual cases—freer from unpleasant allusions than that of most men. At one time Major Hill charged him with making defamatory remarks regarding his wife. Hill was insulting in his language to Lincoln who never lost his temper. When he saw a chance to edge a word in, Lincoln denied emphatically using the language or anything like that attributed to him. He entertained, he insisted, a high regard for Mrs. Hill, and the only thing he knew to her discredit was the fact that she was Major Hill's wife.
At this time in its brief history New Salem was what in the parlance of large cities would be called a fast place; and it was difficult for a young man of ordinary moral courage to resist the temptations that beset him on every hand. It remains a matter of surprise that Lincoln was able to retain his popularity with the hosts of young men of his own age, and still not join them in their drinking bouts and carousals. "I am certain," contends one of his companions, "that he never drank any intoxicating liquors—he did not even in those days smoke or chew tobacco." In sports requiring either muscle or skill he took no little interest. He indulged in all the games of the day, even to a horse-race or cock-fight. At one eventful chicken fight, where a fee of twenty-five cents for the entrance of each fowl was assessed, one Bap. McNabb brought a little red rooster, whose fighting qualities had been well advertised for days in advance by his owner. Much interest was naturally taken in the contest. As the outcome of these contests was generally a quarrel, in which each man, charging foul play, seized his victim, they chose Lincoln umpire, relying not only on his fairness but his ability to enforce his decisions. In relating what followed I cannot improve on the description furnished me in February, 1865, by one* who was present.
* A. Y. Ellis, MS.
"They formed a ring, and the time having arrived, Lincoln, with one hand on each hip and in a squatting position, cried, 'Ready.' Into the ring they toss their fowls, Bap's red rooster along with the rest. But no sooner had the little beauty discovered what was to be done than he dropped his tail and ran. The crowd cheered, while Bap. in disappointment picked him up and started away, losing his quarter and carrying home his dishonored fowl. Once arrived at the latter place he threw his pet down with a feeling of indignation and chagrin. The little fellow, out of sight of all rivals, mounted a wood pile and proudly flirting out his feathers, crowed with all his might. Bap. looked on in disgust. 'Yes, you little cuss,' he exclaimed, irreverently, 'you're great on dress parade, but not worth a d——n in a fight.'" It is said—how truthfully I do not know—that at some period during the late war Mr. Lincoln in conversation with a friend likened McClellan to Bap. McNabb's rooster. So much for New Salem sports.
While wooing that jealous-eyed mistress, the law, Lincoln was earning no money. As another has said, "he had a running board bill to pay, and nothing to pay it with." By dint of sundry jobs here and there, helping Ellis in his store to-day, splitting rails for James Short to-morrow, he managed to keep his head above the waves. His friends were firm—no young man ever had truer or better ones—but he was of too independent a turn to appeal to them or complain of his condition. He never at any time abandoned the idea of becoming a lawyer. That was always a spirit which beckoned him on in the darkest hour of his adversity. Someone, probably a Democrat who voted for him in the preceding fall, recommended him to John Calhoun, then surveyor of the county, as suitable material for an assistant. This office, in view of the prevailing speculation in lands and town lots, was the most important and possibly the most profitable in the county. Calhoun, the incumbent, was a Yankee and a typical gentleman. He was brave, intellectual, self-possessed, and cultivated. He had been educated for the law, but never practiced much after coming to Illinois—taught school in preference. As an instructor he was the popular one of his day and age. I attended the school he taught when I was a boy, in Springfield, and was in later years clerk of the city under his administration as Mayor. Lincoln, I know, respected and admired him. After Lincoln's removal to Springfield they frequently held joint debates on political questions. At one time I remember they discussed the tariff question in the court house, using up the better part of two evenings in the contest. Calhoun was polite, affable, and an honest debater, never dodging any question. This made him a formidable antagonist in argumentative controversy. I have heard Lincoln say that Calhoun gave him more trouble in his debates than Douglas ever did, because he was more captivating in his manner and a more learned man than Douglas.
But to resume. The recommendation of Lincoln's friends was sufficient to induce Calhoun to appoint him one of his deputies. At the time he received notice of his selection by Calhoun, Lincoln was out in the woods near New Salem splitting rails. A friend named Pollard Simmons, who still survives and has related the incident to me, walked out to the point where he was working with the cheering news. Lincoln, being a Whig and knowing Calhoun's pronounced Democratic tendencies, enquired if he had to sacrifice any principle in accepting the position. "If I can be perfectly free in my political action I will take the office," he remarked; "but if my sentiments or even expression of them is to be abridged in any way I would not have it or any other office." A young man hampered by poverty as Lincoln was at this time, who had the courage to deal with public office as he did, was certainly made of unalloyed material. No wonder in after years when he was defeated by Douglas he could inspire his friends by the admonition not to "give up after one nor one hundred defeats."
After taking service with Calhoun, Lincoln found he had but little if any practical knowledge of surveying—all that had to be learned. Calhoun furnished him with books, directing him to study them till he felt competent to begin work. He again invoked the assistance of Mentor Graham, the schoolmaster, who aided him in his efforts at calculating the results of surveys and measurements. Lincoln was not a mathematician by nature, and hence, with him, learning meant labor. Graham's daughter is authority for the statement that her father and Lincoln frequently sat up till midnight engrossed in calculations, and only ceased when her mother drove them out after a fresh supply of wood for the fire. Meanwhile Lincoln was keeping up his law studies. "He studied to see the subject-matter clearly," says Graham, "and to express it truly and strongly. I have known him to study for hours the best way of three to express an idea." He was so studious and absorbed in his application at one time, that his friends, according to a statement made by one* of them, "noticed that he was so emaciated we feared he might bring on mental derangement." It was not long, however, until he had mastered surveying as a study, and then he was sent out to work by his superior—Calhoun. It has never been denied that his surveys were exact and just, and he was so manifestly fair that he was often chosen to settle disputed questions of comers and measurements. It is worthy of note here that, with all his knowledge of lands and their value and the opportunities that lay open to him for profitable and safe investments, he never made use of the information thus obtained from official sources, nor made a single speculation on his own account. The high value he placed on public office was more fully emphasized when as President, in answer to a delegation of gentlemen who called to press the claims of one of his warm personal friends for an important office, he declined on the ground that "he did not regard it as just to the public to pay the debts of personal friendship with offices that belonged to the people."
* Henry McHenry, MS., Oct. 5, 1865.
As surveyor under Calhoun he was sent for at one time to decide or locate a disputed corner for some persons in the northern part of the county. Among others interested was his friend and admirer Henry McHenry. "After a good deal of disputing we agreed," says the latter, "to send for Lincoln and to abide by his decision. He came with compass, flag-staff, and chain. He stopped with me three or four days and surveyed the whole section. When in the neighborhood of the disputed corner by actual survey he called for his staff and driving it in the ground at a certain spot said, 'Gentlemen, here is the corner.' We dug down into the ground at the point indicated and, lo! there we found about six or eight inches of the original stake sharpened at the end, and beneath which was the usual piece of charcoal placed there by Rector the surveyor who laid the ground off for the government many years before." So fairly and well had the young surveyor done his duty that all parties went away completely satisfied. As late as 1865 the corner was preserved by a mark and pointed out to strangers as an evidence of the young surveyor's skill. Russell Godby, mentioned in the earlier pages of this chapter, presented to me a certificate of survey given to him by Lincoln. It was written January 14,1834, and is signed "J. Calhoun, S. S. C., by A. Lincoln." "The survey was made by Lincoln," says Godby, "and I gave him as pay for his work two buckskins, which Hannah Armstrong 'foxed' on his pants so that the briers would not wear them out."
Honors were now crowding thick and fast upon him. On May 7, 1833, he was commissioned postmaster at New Salem, the first office he ever held under the Federal Government. The salary was proportionate to the amount of business done. Whether Lincoln solicited the appointment himself, or whether it was given him without the asking, I do not know; but certain it is his "administration" gave general satisfaction. The mail arrived once a week, and we can imagine the extent of time and labor required to distribute it, when it is known that "he carried the office around in his hat." Mr. Lincoln used to tell me that when he had a call to go to the country to survey a piece of land, he placed inside his hat all the letters belonging to people in the neighborhood and distributed them along the way. He made head-quarters in Samuel Hill's store, and there the office may be said to have been located, as Hill himself had been postmaster before Lincoln. Between the revenue derived from the post-office and his income from land surveys Lincoln was, in the expressive language of the day, "getting along well enough." Suddenly, however, smooth sailing ceased and all his prospects of easy times ahead were again brought to naught. One Van Bergen brought suit against him and obtained judgment on one of the notes given in payment of the store debt—a relic of the unfortunate partnership with Berry. His personal effects were levied on and sold, his horse and surveying instruments going with the rest. But again a friend, one James Short, whose favor he had gained, interposed; bought in the property and restored it to the hope-less young surveyor. It will be seen now what kind of friends Lincoln was gaining. The bonds he was thus making were destined to stand the severest of tests. His case never became so desperate but a friend came out of the darkness to relieve him.
There was always something about Lincoln in his earlier days to encourage his friends. He was not only grateful for whatever aid was given him, but he always longed to help some one else. He had an unfailing disposition to succor the weak and the unfortunate, and was always, in his sympathy, struggling with the under dog in the fight. He was once overtaken when about fourteen miles from Springfield by one Chandler, whom he knew slightly, and who, having already driven twenty miles, was hastening to reach the land office before a certain other man who had gone by a different road. Chandler explained to Lincoln that he was poor and wanted to enter a small tract of land which adjoined his, that another man of considerable wealth had also determined to have it, and had mounted his horse and started for Springfield. "Meanwhile, my neighbors," continued Chandler, "collected and advanced me the necessary one hundred dollars, and now, if I can reach the land office first, I can secure the land." Lincoln noticed that Chandler's horse was too much fatigued to stand fourteen miles more of a forced march, and he therefore dismounted from his own and turned him over to Chandler, saying, "Here's my horse—he is fresh and full of grit; there's no time to be lost; mount him and put him through. When you reach Springfield put him up at Herndon's tavern and I'll call and get him." Thus encouraged Chandler moved on, leaving Lincoln to follow on the jaded animal. He reached Springfield over an hour in advance of his rival and thus secured the coveted tract of land. By nightfall Lincoln rode leisurely into town and was met by the now radiant Chandler, jubilant over his success. Between the two a friendship sprang up which all the political discords of twenty-five years never shattered nor strained.
About this time Lincoln began to extend somewhat his system—if he really ever had a system in anything—of reading.' He now began to read the writings of Paine, Volney, and Voltaire. A good deal of religious skepticism existed at New Salem, and there were frequent discussions at the store and tavern, in which Lincoln took part. What views he entertained on religious questions will be more fully detailed in another place.
No little of Lincoln's influence with the men of New Salem can be attributed to his extraordinary feats of strength. By an arrangement of ropes and straps, harnessed about his hips, he was enabled one day at the mill to astonish a crowd of village celebrities by lifting a box of stones weighing near a thousand pounds. There is no fiction either, as suggested by some of his biographers, in the story that he lifted a barrel of whisky from the ground and drank from the bung; but in performing this latter almost incredible feat he did not stand erect and elevate the barrel, but squatted down and lifted it to his knees, rolling it over until his mouth came opposite the bung. His strength, kindness of manner, love of fairness and justice, his original and unique sayings, his power of mimicry, his perseverance—-all made a combination rarely met with on the frontier. Nature had burnt him in her holy fire, and stamped him with the seal of her greatness.
In the summer of 1834 Lincoln determined to make another race for the legislature; but this time he ran distinctly as a Whig. He made, it is presumed, the usual number of speeches, but as the art of newspaper reporting had not reached the perfection it has since attained, we are not favored with even the substance of his efforts on the stump. I have Lincoln's word for it that it was more of a hand-shaking campaign than anything else. Rowan Herndon relates that he came to his house during harvest, when there were a large number of men at work in the field. He was introduced to them, but they did not hesitate to apprize him of their esteem for a man who could labor; and their admiration for a candidate for office was gauged somewhat by the amount of work he could do. Learning these facts, Lincoln took hold of a cradle, and handling it with ease and remarkable speed, soon distanced those who undertook to follow him. The men were satisfied, and it is presumed he lost no votes in that crowd. One Dr. Barrett, seeing Lincoln, enquired of the latter's friends: "Can't the party raise any better material than that?" but after hearing his speech the doctor's opinion was considerably altered, for he declared that Lincoln filled him with amazement; "that he knew more than all of the other candidates put together." The election took place in August. Lincoln's friend, John T. Stuart, was also a candidate on the legislative ticket. He encouraged Lincoln's canvas in every way, even at the risk of sacrificing his own chances. But both were elected. The four successful candidates were Dawson, who received 1390 votes,* Lincoln 1376, Carpenter 1170, and Stuart 1164.
* In all former biographies of Lincoln, including the Nicolay and Hay history in the "Century Magazine," Dawson's vote is fixed at 1370, and Lincoln is thereby made to lead the ticket; but in the second issue of the Sangamon Journal after the election—August 16, 1834—the count is corrected, and Dawson's vote is increased to 1390. Dr. A. W. French, of Springfield, is the possessor of an official return of the votes cast at the New Salem precinct, made out in the handwriting of Lincoln, which also gives Dawson's vote at 1390.
At last Lincoln had been elected to the legislature, and by a very flattering majority. In order, as he himself said, "to make a decent appearance in the legislature," he had to borrow money to buy suitable clothing and to maintain his new dignity. Coleman Smoot, one of his friends, advanced him "two hundred dollars, which he returned, relates the generous Smoot, according to promise." Here we leave our rising young statesman, to take up a different but very interesting period of his history.
Since the days when Indiana Lincoln sat on the river's bank with little Kate Roby, dangling his bare feet in the water, there has been no hint in these pages of tender relations with any one of the opposite sex. Now we approach in timely order the "grand passion" of his life—a romance of much reality, the memory of which threw a melancholy shade over the remainder of his days. For the first time our hero falls in love. The courtship with Anne Rutledge and her untimely death form the saddest page in Mr. Lincoln's history. I am aware that most of his biographers have taken issue with me on this phase of Mr. Lincoln's life. Arnold says: "The picture has been somewhat too highly colored, and the story made rather too tragic." Dr. Holland and others omit the subject altogether, while the most recent biography—the admirable history by my friends Nicolay and Hay.—devotes but five lines to it. I knew Miss Rutledge myself, as well as her father and other members of the family, and have been personally acquainted with every one of the score or more of witnesses whom I at one time or another interviewed on this delicate subject. From my own knowledge and the information thus obtained, I therefore repeat, that the memory of Anne Rutledge was the saddest chapter in Mr. Lincoln's life.*
* In a letter dated Dec. 4, 1866, one of Miss Rutledge's brothers writes: "When he first came to New Salem and up to the day of Anne's death Mr. Lincoln was all life and animation. He seemed to see the bright side of every picture."
James Rutledge, the father of this interesting girl, was one of the founders of New Salem, having come there from Kentucky in 1829. He was born in South Carolina and belonged to the noted Rutledge family of that State. I knew him as early as 1833, and have often shared the hospitality of his home. My father was a politician and an extensive stock dealer in that early day, and he and Mr. Rutledge were great friends. The latter was a man of no little force of character; those who knew him best loved him the most. Like other Southern people he was warm,—almost to impulsiveness,—social, and generous. His hospitality, an inherited quality that flashed with him before he was born, developed by contact with the brave and broadminded people whom he met in Illinois. Besides his business interests in the store and mill at New Salem, he kept the tavern where Lincoln came to board in 1833. His family, besides himself and wife, consisted of nine children, three of whom were born in Kentucky, the remaining six in Illinois. Anne, the subject of this chapter, was the third child. She was a beautiful girl, and by her winning ways attached people to her so firmly that she soon became the most popular young lady in the village. She was quick of apprehension, industrious, and an excellent housekeeper. She had a moderate education, but was not cultured except by contrast with those around her. One of her strong points was her womanly skill. She was dexterous in the use of the needle—an accomplishment of far more value in that day than all the acquirements of art in china painting and hammered brass are in this—and her needle-work was the wonder of the day. At every "quilting" Anne was a necessary adjunct, and her nimble fingers drove the needle more swiftly than anyone's else. Lincoln used to escort her to and from these quilting-bees, and on one occasion even went into the house—where men were considered out of place—and sat by her side as she worked on the quilt.
He whispered into her ear the old, old story. Her heart throbbed and her soul was thrilled with a joy as old as the world itself. Her fingers momentarily lost their skill. In her ecstasy she made such irregular and uneven stitches that the older and more sedate women noted it, and the owner of the quilt, until a few years ago still retaining it as a precious souvenir, pointed out the memorable stitches to such persons as visited her.
L. M. Greene, who remembered Anne well, says, "She was amiable and of exquisite beauty, and her intellect was quick, deep, and philosophic as well as brilliant. She had a heart as gentle and kind as an angel, and full of love and sympathy. Her sweet and angelic nature was noted by every one who met her. She was a woman worthy of Lincoln's love." This is a little overstated as to beauty—Greene writes as if he too had been in love with her—but is otherwise nearly correct.
"Miss Rutledge," says a lady* who knew her, "had auburn hair, blue eyes, fair complexion. She was pretty, slightly slender, but in everything a good hearted young woman. She was about five feet two inches high, and weighed in the neighborhood of a hundred and twenty pounds. She was beloved by all who knew her. She died as it were of grief. In speaking of her death and her grave Lincoln once said to me, 'My heart lies buried there.'"
* Mrs. Hardin Bale.
Before narrating the details of Lincoln's courtship with Miss Rutledge, it is proper to mention briefly a few facts that occurred before their attachment began.
About the same time that Lincoln drifted into New Salem there came in from the Eastern States John McNeil, a young man of enterprise and great activity, seeking his fortune in the West. He went to work at once, and within a short time had accumulated by commendable effort a comfortable amount of property. Within three years he owned a farm, and a half interest with Samuel Hill in the leading store. He had good capacity for business, and was a valuable addition to that already pretentious village—New Salem. It was while living at James Cameron's house that this plucky and industrious young business man first saw Anne Rutledge. At that time she was attending the school of Mentor Graham, a pedagogue of local renown whose name is frequently met with in these pages, and who flourished in and around New Salem from 1829 to 1860. McNeil fell deeply in love with the school-girl—she was then only seventeen—and paid her the usual unremitting attentions young lovers of that age had done before him and are still doing to-day. His partner in the store, Samuel Hill, a young man of equal force of character, who afterwards amassed a comfortable fortune, and also wielded no little influence as a local politician, laid siege to the heart of this same attractive maiden, but he yielded up the contest early. Anne rejected him, and he dropped from the race. McNeil had clear sailing from this time forward. He was acquiring property and money day by day. As one of the pioneers puts it, "Men were honest then, and paid their debts at least once a year. The merchant surrounded by a rich country suffered little from competition. As he placed his goods on the shelf he added an advance of from seventy-five to one hundred and fifty per cent over cost price, and thus managed to get along." After "managing" thus for several years, McNeil, having disposed of his interest in the store to Hill, determined to return to New York, his native State, for a visit. He had accumulated up to this time, as near as we can learn, ten or possibly twelve thousand dollars. Before leaving he made to Anne a singular revelation. He told her the name McNeil was an assumed one; that his real name was McNamar.
"I left behind me in New York," he said, "my parents and brothers and sisters. They are poor, and were in more or less need when I left them in 1829. I vowed that I would come West, make a fortune, and go back to help them. I am going to start now and intend, if I can, to bring them with me on my return to Illinois and place them on my farm." He expressed a sense of deep satisfaction in being able to clear up all mysteries which might have formed in the mind of her to whom he confided his love. He would keep nothing, he said, from her. They were engaged to be married, and she should know it all. The change of his name was occasioned by the fear that if the family in New York had known where he was they would have settled down on him, and before he could have accumulated any property would have sunk him beyond recovery. Now, however, he was in a condition to help them, and he felt overjoyed at the thought. As soon as the journey to New York could be made he would return. Once again in New Salem he and his fair one could consummate the great event to which they looked forward with undisguised joy and unbounded hope. Thus he explained to Anne the purpose of his journey—a story with some remarkable features, all of which she fully believed.
"She would have believed it all the same if it had been ten times as incredible. A wise man would have rejected it with scorn, but the girl's instinct was a better guide, and McNamar proved to be all that he said he was, although poor Anne never saw the proof which others got of it."*
* Lamon, p. 161.
At last McNamar, mounting an old horse that had participated in the Black Hawk war, began his journey. In passing through Ohio he became ill with a fever. For almost a month he was confined to his room, and a portion of the time was unconscious. As he approached a return to good health he grew nervous over the delay in his trip. He told no one around him his real name, destination, or business. He knew how his failure to write to New Salem would be construed, and the resulting irritation gave way to a feeling of desperation. In plainer language, he concluded it was "all up with him now." Meanwhile a different view of the matter was taken by Miss Rutledge. Her friends encouraged the idea of cruel desertion. The change of McNeil to McNamar had wrought in their minds a change of sentiment. Some contended that he had undoubtedly committed a crime in his earlier days, and for years had rested secure from apprehension under the shadow of an assumed name; while others with equal assurance whispered in the unfortunate girl's ear the old story of a rival in her affections. Anne's lady friends, strange to relate, did more to bring about a discordant feeling than all others. Women are peculiar creatures. They love to nettle and mortify one another; and when one of their own sex has fallen, how little sympathy they seem to have! But under all this fire, in the face of all these insidious criticisms, Anne remained firm. She had faith, and bided her time.
McNamar, after much vexatious delay, finally reached his birthplace in New York, finding his father in the decline of years and health. He provided for his immediate needs, and by his assiduous attentions undertook to atone for the years of his neglect; but all to no purpose. The old gentleman gradually faded from the world, and early one winter morning crossed the great river. McNamar was thus left to settle up the few unfinished details of his father's estate, and to provide for the pressing needs of the family. His detention necessitated a letter to Anne, explaining the nature and cause of the delay. Other letters followed; but each succeeding one growing less ardent in tone, and more formal in phraseology than its predecessor, Anne began to lose faith. Had his love gradually died away like the morning wind? was a question she often asked herself. She had stood firm under fire before, but now her heart grew sick with hope deferred. At last the correspondence ceased altogether.
At this point we are favored with the introduction of the ungainly Lincoln, as a suitor for the hand of Miss Rutledge. Lincoln had learned of McNamar's strange conduct, and conjecturing that all the silken ties that bound the two together had been sundered, ventured to step in himself. He had seen the young lady when a mere girl at Mentor Graham's school, and he, no doubt, then had formed a high opinion of her qualities.
But he was too bashful, as his friend Ellis declares, to tell her of it. No doubt, when he began to pay her attentions she was the most attractive young lady whom up to that time he had ever met. She was not only modest and winning in her ways, and full of good, womanly common-sense, but withal refined, in contrast with the uncultured people who surrounded both herself and Lincoln. "She had a secret, too, and a sorrow,—the unexplained and painful absence of McNamar,—which, no doubt, made her all the more interesting to him whose spirit was often even more melancholy than her own."
In after years, McNamar himself, describing her to me, said: "Miss Rutledge was a gentle, amiable maiden, without any of the airs of your city belles, but winsome and comely withal; a blonde in complexion, with golden hair, cherry-red lips, and a bonny blue eye. As to her literary attainments, she undoubtedly was as classic a scholar as Mr Lincoln. She had at the time she met him, I believe, attended a literary institution at Jacksonville, in company with her brother."
McNamar seems to have considered Lincoln's bashfulness as proof against the alluring charms of Miss Rutledge or anybody else, for he continues:
"Mr. Lincoln was not to my knowledge paying particular attention to any of the young ladies of my acquaintance when I left for my home in New York. There was no rivalry between us on that score; on the contrary, I had every reason to believe him my warm, personal friend. But by-and-by I was left so far behind in the race I did not deem my chances worthy of notice. From this time forward he made rapid strides to that imperishable fame which justly fills a world."
Lincoln began to court Miss Rutledge in dead earnest. Like David Copperfield, he soon realized that he was in danger of becoming deeply in love, and as he approached the brink of the pit he trembled lest he should indeed fall in. As he pleaded and pressed his cause the Rutledges and all New Salem encouraged his suit. McNamar's unexplained absence and apparent neglect furnished outsiders with all the arguments needed to encourage Lincoln and convince Anne. Although the attachment was growing and daily becoming an intense and mutual passion, the young lady remained firm and almost inflexible. She was passing through another fire. A long struggle with her feelings followed; but at length the inevitable moment came. She consented to have Lincoln, provided he gave her time to write to McNamar and obtain his release from her pledge. The slow-moving mails carried her tender letter to New York. Days and weeks—which to the ardent Lincoln must have seemed painfully long—passed, but the answer never came. In a half-hearted way she turned to Lincoln, and her looks told him that he had won. She accepted his proposal. Now that they were engaged he told her what she already knew, that he was poverty itself. She must grant him time to gather up funds to live on until he had completed his law studies. After this trifling delay "nothing on God's footstool," argued the emphatic lover, could keep them apart. To this the thoughtful Anne consented. To one of her brothers, she said: "As soon as his studies are completed we are to be married." But the ghost of another love would often rise unbidden before her. Within her bosom raged the conflict which finally undermined her health. Late in the summer she took to her bed. A fever was burning in her head. Day by day she sank, until all hope was banished. During the latter days of her sickness, her physician had forbidden visitors to enter her room, prescribing absolute quiet. But her brother relates that she kept enquiring for Lincoln so continuously, at times demanding to see him, that the family at last sent for him. On his arrival at her bedside the door was closed and he was left alone with her. What was said, what vows and revelations were made during this sad interview, were known only to him and the dying girl. A few days afterward she became unconscious and remained so until her death on the 25th day of August, 1835. She was buried in what is known as the Concord grave-yard, about seven miles north-west of the town of Petersburg.*
* "I have heard mother say that Anne would frequently sing for Lincoln's benefit. She had a clear, ringing voice. Early in her illness he called, and she sang a hymn for which he always expressed a great preference. It begins.. 'Vain man, thy fond pursuits forbear.' You will find it in one of the standard hymn-books. It was likewise the last thing she ever sung."—Letter, John M. Rutledge, MS., Nov. 25, 1866.
The most astonishing and sad sequel to this courtship was the disastrous effect of Miss Rutledge's death on Mr. Lincoln's mind. It operated strangely on one of his calm and stoical make-up. As he returned from the visit to the bedside of Miss Rutledge, he stopped at the house of a friend, who relates that his face showed signs of no little mental agony. "He was very much distressed," is the language of this friend, "and I was not surprised when it was rumored subsequently that his reason was in danger." One of Miss Rutledge's brothers* says: "The effect upon Mr. Lincoln's mind was terrible. He became plunged in despair, and many of his friends feared that reason would desert her throne. His extraordinary emotions were regarded as strong evidence of the existence of the tenderest relations between himself and the deceased." The truth is Mr. Lincoln was strangely wrought up over the sad ending of the affair. He had fits of great mental depression, and wandered up and down the river and into the woods woefully abstracted—at times in the deepest distress. If, when we read what the many credible persons who knew him at the time tell us, we do not conclude that he was deranged, we must admit that he walked on that sharp and narrow line which divides sanity from insanity. To one friend he complained that the thought "that the snows and rains fall upon her grave filled him with indescribable grief."**
* R. B. Rutledge, MS., letter, Oct. 21,1866. ** Letter, Wm. Greene, MS., May 29, 1865.
He was watched with especial vigilance during damp, stormy days, under the belief that dark and gloomy weather might produce such a depression of spirits as to induce him to take his own life. His condition finally became so alarming, his friends consulted together and sent him to the house of a kind friend, Bowlin Greene, who lived in a secluded spot hidden by the hills, a mile south of town. Here he remained for some weeks under the care and ever watchful eye of this noble friend, who gradually brought him back to reason, or at least a realization of his true condition. In the years that followed Mr. Lincoln never forgot the kindness of Greene through those weeks of suffering and peril. In 1842, when the latter died, and Lincoln was selected by the Masonic lodge to deliver the funeral oration, he broke down in the midst of his address. "His voice was choked with deep emotion; he stood a few moments while his lips quivered in the effort to form the words of fervent praise he sought to utter, and the tears ran down his yellow and shrivelled cheeks. Every heart was hushed at the spectacle. After repeated efforts he found it impossible to speak, and strode away, bitterly sobbing, to the widow's carriage and was driven from the scene."
It was shortly after this that Dr. Jason Duncan placed in Lincoln's hands a poem called "Immortality." The piece starts out with the line, "Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud." Lincoln's love for this poem has certainly made it immortal. He committed these lines to memory, and any reference to or mention of Miss Rutledge would suggest them, as if "to celebrate a grief which lay with continual heaviness on his heart." There is no question that from this time forward Mr. Lincoln's spells of melancholy became more intense than ever. In fact a tinge of this desperate feeling of sadness followed him to Springfield. He himself was somewhat superstitious about it, and in 1840-41 wrote to Dr. Drake, a celebrated physician in Cincinnati, describing his mental condition in a long letter. Dr. Drake responded, saying substantially, "I cannot prescribe in your case without a personal interview." Joshua F. Speed, to whom Lincoln showed the letter addressed to Dr. Drake, writing to me from Louisville, November 30, 1866, says: "I think he (Lincoln) must have informed Dr. Drake of his early love for Miss Rutledge, as there was a part of the letter which he would not read." It is shown by the declaration of Mr. Lincoln himself made to a fellow member* of the Legislature within two years after Anne Rutledge's death that "although he seemed to others to enjoy life rapturously, yet when alone he was so overcome by mental depression he never dared to carry a pocket knife."
* Robert L. Wilson, MS., letter, Feb. 10, 1866
It may not be amiss to suggest before I pass from mention of McNamar that, true to his promise, he drove into New Salem in the fall of 1835 with his mother and brothers and sisters. They had come through from New York in a wagon, with all their portable goods. Anne Rutledge had meanwhile died, and McNamar could only muse in silence over the fading visions of "what might have been." On his arrival he met Lincoln, who, with the memory of their mutual friend, now dead, constantly before him, "seemed desolate and sorely distressed." The little acre of ground in Concord cemetery contained the form of his first love, rudely torn from him, and the great world, throbbing with life but cold and heartless, lay spread before him.
Before taking up an account of Lincoln's entry into the Legislature, which, following strictly the order of time, properly belongs here, I beg to digress long enough to narrate what I have gathered relating to another courtship—an affair of the heart which culminated in a sequel as amusing as the one with Anne Rutledge was sad. I experienced much difficulty in obtaining the particulars of this courtship. After no little effort I finally located and corresponded with the lady participant herself, who in 1866 furnished me with Lincoln's letters and her own account of the affair, requesting the suppression of her name and residence. Since then, however, she has died, and her children have not only consented to a publication of the history, but have furnished me recently with more facts and an excellent portrait of their mother made shortly after her refusal of Lincoln's hand.
Mary S. Owens—a native of Green county, Kentucky, born September 29, 1808—first became acquainted with Lincoln while on a visit to a sister, the wife of Bennet Able, an early settler in the country about New Salem. Lincoln was a frequent visitor at the house of Able, and a warm friend of the family. During the visit of Miss Owens in 1833, though only remaining a month, she lingered long enough to make an impression on Lincoln; but returned to Kentucky and did not reappear in New Salem till 1836. Meanwhile Anne Rutledge had died, and Lincoln's eyes began to wander after the dark-haired visitor from Kentucky. Miss Owens differed from Miss Rutledge in early education and the advantages of wealth. She had received an excellent education, her father being one of the wealthiest and most influential men of his time and locality. A portion of her schooling was obtained in a Catholic convent, though in religious faith she was a Baptist. According to a description furnished me by herself she "had fair skin, deep blue eyes, and dark curling hair; height five feet, five inches; weight about a hundred and fifty pounds." She was good-looking in girlhood; by many esteemed handsome, but became fleshier as she grew older. At the time of her second visit she reached New Salem on the day of the Presidential election, passing the polls where the men had congregated, on the way to her sister's house. One man in the crowd who saw her then was impressed with her beauty. Years afterwards, in relating the incident, * he wrote me:
"She was tall, portly, had large blue eyes and the finest trimmings I ever saw. She was jovial, social, loved wit and humor, had a liberal English education, and was considered wealthy. None of the poets or romance writers have ever given us a picture of a heroine so beautiful as a good description of Miss Owens in 1836 would be."
* L. M. Greene.
A lady friend* says she was "handsome, truly handsome, matronly-looking, over ordinary size in height and weight."
A gentleman** who saw her a few years before her death describes her as "a nervous, muscular woman, very intellectual, with a forehead massive and angular, square, prominent, and broad."
* Mrs. Hardin Bale. ** Johnson G. Greene.
At the time of her advent into the society of New Salem she was polished in her manners, pleasing in her address, and attractive in many ways. She had a little dash of coquetry in her intercourse with that class of young men who arrogated to themselves claims of superiority, but she never yielded to this disposition to an extent that would willingly lend encouragement to an honest suitor sincerely desirous of securing her hand, when she felt she could not in the end yield to a proposal of marriage if he should make the offer. She was a good conversationalist and a splendid reader, very few persons being found to equal her in this accomplishment. She was light-hearted and cheery in her disposition, kind and considerate for those with whom she was thrown in contact.
One of Miss Owens' descendants is authority for the statement that Lincoln had boasted that "if Mary Owens ever returned to Illinois a second time he would marry her;" that a report of this came to her ears, whereupon she left her Kentucky home with a pre-determination to show him if she met him that she was not to be caught simply by the asking. On this second visit Lincoln paid her more marked attention than before, and his affections became more and more enlisted in her behalf. During the earlier part of their acquaintance, following the natural bent of her temperament she was pleasing and entertaining to him. Later on he discovered himself seriously interested in the blue-eyed Kentuckian, whom he had really underestimated in his preconceived opinions of her. In the meantime she too had become interested, having discovered the sterling qualities of the young man who was paying her such devoted attention; yet while she admired she did not love him. He was ungainly and angular in his physical make-up, and to her seemed deficient in the nicer and more delicate attentions which she felt to be due from the man whom she had pictured as an ideal husband. He had given her to understand that she had greatly charmed him; but he was not himself certain that he could make her the husband with whom he thought she would be most happy. Later on by word and letter he told her so. His honesty of purpose showed itself in all his efforts to win her hand. He told her of his poverty, and while advising her that life with him meant to her who had been reared in comfort and plenty, great privation and sacrifice, yet he wished to secure her as a wife. She, however, felt that she did not entertain for him the same feeling that he professed for her and that she ought to entertain before accepting him, and so declined his offer. Judging from his letters alone it has been supposed by some that she, remembering the rumor she had heard of his determination to marry her, and not being fully certain of the sincerity of his purposes, may have purposely left him in the earlier stages of his courtship somewhat in uncertainty. Later on, however, when by his manner and repeated announcement to her that his hand and heart were at her disposal, he demonstrated the honesty and sincerity of his intentions, she declined his offer kindly but with no uncertain meaning.
The first letter I received from Mrs. Vineyard—for she was married to Jesse Vineyard, March 27, 1841—was written at Weston, Mo., May 1, 1866. Among other things she says: "After quite a struggle with my feelings I have at last decided to send you the letters in my possession written by Mr. Lincoln, believing as I do that you are a gentleman of honor and will faithfully abide by all you have said. My associations with your lamented friend were in Menard county whilst visiting a sister who then resided near Petersburg. I have learned that my maiden name is now in your possession; and you have ere this, no doubt, been informed that I am a native Kentuckian."

The letters written by Lincoln not revealing enough details of the courtship, I prepared a list of questions for the lady to answer in order that the entire history of their relations might be clearly shown. I perhaps pressed her too closely in such a delicate matter, for she responded in a few days as follows:
"Weston, Mo., May 22, 1866.
"Mr. W. H. Herndon,
"My Dear Sir: Really, you catechise me in true lawyer style; but I feel you will have the goodness to excuse me if I decline answering all your questions in detail, being well assured that few women would have ceded as much as I have under all the circumstances.
"You say you have heard why our acquaintance terminated as it did. I too have heard the same bit of gossip; but I never used the remark which Madame Rumor says I did to Mr. Lincoln. I think I did on one occasion say to my sister, who was very anxious for us to be married, that I thought Mr. Lincoln was deficient in those little links which make up the chain of woman's happiness—at least it was so in my case. Not that I believed it proceeded from a lack of goodness of heart; but his training had been different from mine; hence there was not that congeniality which would otherwise have existed.
"From his own showing you perceive that his heart and hand were at my disposal; and I suppose that my feelings were not sufficiently enlisted to have the matter consummated. About the beginning of the year 1838 I left Illinois, at which time our acquaintance and correspondence ceased, without ever again being renewed.
"My father, who resided in Green county, Kentucky, was a gentleman of considerable means; and I am persuaded that few persons placed a higher estimate on education than he did.
"Respectfully yours,
"Mary S. Vineyard."
The reference to Lincoln's deficiency "in those little links which make up the chain of woman's happiness" is of no little significance. It proved that his training had indeed been different from hers. In a short time I again wrote Mrs. Vineyard to enquire as to the truth of a story current in New Salem, that one day as she and Mrs. Bowlin Greene were climbing up the hill to Abie's house they were joined by Lincoln; that Mrs. Greene was obliged to carry her child, a fat baby boy, to the summit; that Lincoln strolled carelessly along, offering no assistance to the woman who bent under the load. Thereupon Miss Owens, censuring him for his neglect, reminded him that in her estimation he would not make a good husband. In due time came her answer:
"Weston, Mo., July 22, 1866.
"Mr. W. H. Herndon:
"Dear Sir: I do not think you are pertinacious in asking the question relative to old Mrs. Bowlin Greene, because I wish to set you right on that question. Your information, no doubt, came through my cousin, Mr. Gaines Greene, who visited us last winter. Whilst here, he was laughing at me about Mr. Lincoln, and among other things spoke about the circumstance in connection with Mrs. Greene and child. My impression is now that I tacitly admitted it, for it was a season of trouble with me, and I gave but little heed to the matter. We never had any hard feelings towards each other that I know of. On no occasion did I say to Mr. Lincoln that I did not believe he would make a kind husband, because he did not tender his services to Mrs. Greene in helping of her carry her babe. As I said to you in a former letter, I thought him lacking in smaller attentions. One circumstance presents itself just now to my mind's eye. There was a company of us going to Uncle Billy Greene's. Mr. Lincoln was riding with me, and we had a very bad branch to cross. The other gentlemen were very officious in seeing that their partners got safely over. We were behind, he riding in, never looking back to see how I got along. When I rode up beside him, I remarked, 'You are a nice fellow! I suppose you did not care whether my neck was broken or not.' He laughingly replied (I suppose by way of compliment), that he knew I was plenty smart to take care of myself.
"In many things he was sensitive almost to a fault. He told me of an incident: that he was crossing a prairie one day and saw before him, 'a hog mired down,' to use his own language. He was rather 'fixed up,' and he resolved that he would pass on without looking at the shoat. After he had gone by, he said the feeling was irresistible; and he had to look back, and the poor thing seemed to say wistfully, 'There now, my last hope is gone;' that he deliberately got down and relieved it from its difficulty.
"In many things we were congenial spirits. In politics we saw eye to eye, though since then we differed as widely as the South is from the North. But methinks I hear you say, 'Save me from a political woman!' So say I.
"The last message I ever received from him was about a year after we parted in Illinois. Mrs. Able visited Kentucky, and he said to her in Springfield, 'Tell your sister that I think she was a great fool because she did not stay here and marry me.' Characteristic of the man!
"Respectfully yours,
"Mary S. Vineyard."
We have thus been favored with the lady's side of this case, and it is but fair that we should hear the testimony of her honest but ungainly suitor. Fortunately for us and for history we have his view of the case in a series of letters which have been preserved with zealous care by the lady's family.*
* The copies of these letters were carefully made by Mr. Weik from the originals, now in the possession of B. R. Vineyard, St. Joseph, Mo.
The first letter was written from Vandalia, December 13, 1836, where the Legislature to which he belonged was in session. After reciting the progress of legislation and the flattering prospect that then existed for the removal of the seat of government to Springfield, he gets down to personal matters by apprising her of his illness for a few days, coupled with the announcement that he is mortified by daily trips to the post-office in quest of her letter, which it seemed never would arrive. "You see," he complains, "I am mad about that old letter yet. I don't like to risk you again. I'll try you once more, anyhow." Further along in the course of the missive, he says: "You recollect, I mentioned at the outset of this letter, that I had been unwell. That is the fact, though I believe I am about well now; but that, with other things I cannot account for, have conspired, and have gotten my spirits so low that I feel that I would rather be in any place in the world than here. I really cannot endure the thought of staying here ten weeks. Write back as soon as you get this, and if possible, say something that will please me; for really, I have not been pleased since I left you."
"This letter is so dry and stupid," he mournfully concludes, "that I am ashamed to send it, but with my present feelings I cannot do any better."
After the adjournment of the Legislature he returned to Springfield, from which point it was a matter of easy driving to reach New Salem, where his lady-love was sojourning, and where he could pay his addresses in person. It should be borne in mind that he had by this time removed to Springfield, the county seat, and entered on the practice of the law. In the gloom resulting from lack of funds and the dim prospect for business, he found time to communicate with the friend whose case was constantly uppermost in his mind. Here is one characteristic letter:
"Springfield, May 7, 1837.
"Friend Mary:
"I have commenced two letters to send you before this, both of which displeased me before I got half done, and so I tore them up. The first I thought wasn't serious enough, and the second was on the other extreme. I shall send this, turn out as it may.
"This thing of living in Springfield is rather a dull business after all—at least it is so to me. I am quite as lonesome here as [I] ever was anywhere in my life. I have been spoken to by but one woman since I've been here, and should not have been by her if she could have avoided it. I've never been to church yet, and probably shall not be soon. I stay away because I am conscious I should not know how to behave myself. I am often thinking of what we said of your coming to live at Springfield. I am afraid you would not be satisfied. There is a great deal of flourishing about in carriages here, which it would be your doom to see without sharing in it. You would have to be poor without the means of hiding your poverty. Do you believe you could bear that patiently? Whatever woman may cast her lot with mine, should anyone ever do so, it is my intention to do all in my power to make her happy and contented, and there is nothing I can imagine that would make me more unhappy than to fail in the effort. I know I should be much happier with you than the way I am, provided I saw no signs of discontent in you.
"What you have said to me may have been in jest or I may have misunderstood it. If so, then let it be forgotten; if otherwise I much wish you would think seriously before you decide. For my part I have already decided. What I have said I will most positively abide by, provided you wish it. My opinion is you had better not do it. You have not been accustomed to hardship, and it may be more severe than you imagine. I know you are capable of thinking correctly on any subject; and if you deliberate maturely upon this before you decide, then I am willing to abide your decision.
"You must write me a good long letter after you get this. You have nothing else to do, and though it might not seem interesting to you after you have written it, it would be a good deal of company in this busy wilderness. Tell your sister I don't want to hear any more about selling out and moving. That gives me the hypo whenever I think of it.
"Yours, etc.
"Lincoln."
Very few if any men can be found who in fond pursuit of their love would present their case voluntarily in such an unfavorable light. In one breath he avows his affection for the lady whose image is constantly before him, and in the next furnishes her reasons why she ought not to marry him! During the warm, dry summer months he kept up the siege without apparent diminution of zeal. He was as assiduous as ever, and in August was anxious to force a decision. On the 16th he had a meeting with her which terminated much like a drawn battle—at least it seems to have afforded him but little encouragement, for on his return to Springfield he immediately indulged in an epistolary effusion stranger than any that preceded it.
"Friend Mary:
"You will no doubt think it rather strange that I should write you a letter on the same day on which we parted; and I can only account for it by supposing that seeing you lately makes me think of you more than usual, while at our late meeting we had but few expressions of thoughts. You must know that I cannot see you or think of you with entire indifference; and yet it may be that you are mistaken in regard to what my real feelings towards you are. If I knew you were not, I should not trouble you with this letter. Perhaps any other man would know enough without further information, but I consider it my peculiar right to plead ignorance and your bounden duty to allow the plea.
"I want in all cases to do right; and most particularly so in all cases with women. I want, at this particular time, more than anything else, to do right with you, and if I knew it would be doing right, as I rather suspect it would, to let you alone, I would do it. And for the purpose of making the matter as plain as possible, I now say, that you can now drop the subject, dismiss your thoughts (if you ever had any) from me forever, and leave this letter unanswered, without calling forth one accusing murmur from me. And I will even go farther, and say, that if it will add anything to your comfort or peace of mind to do so, it is my sincere wish that you should. Do not understand by this that I wish to cut your acquaintance. I mean no such thing. What I do wish is that our further acquaintance shall depend upon yourself. If such further acquaintance would contribute nothing to your happiness, I am sure it would not to mine. If you feel yourself in any degree bound to me, I am now willing to release you, provided you wish it; while, on the other hand, I am willing and even anxious to bind you faster if I can be convinced that it will in any considerable degree add to your happiness. This, indeed, is the whole question with me. Nothing would make me more miserable, nothing more happy, than to know you were so.
"In what I have now said, I think I cannot be misunderstood; and to make myself understood is the sole object of this letter.
"If it suits you best to not answer this—farewell—a long life and a merry one attend you. But if you conclude to write back, speak as plainly as I do. There can be neither harm nor danger in saying to me anything you think, just in the manner you think it.
"My respects to your sister.
"Your friend,
"Lincoln."
For an account of the final outcome of this affaire du cour the reader is now referred to the most ludicrous letter Mr. Lincoln ever wrote. It has been said, but with how much truth I do not know, that during his term as President the lady to whom it was written—Mrs. O. H. Browning, wife of a fellow-member of the Legislature—before giving a copy of it to a biographer, wrote to Lincoln asking his consent to the publication, but that he answered warning her against it because it was too full of truth. The only biographer who ever did insert it apologized for its appearance in his book, regarding it for many reasons as an extremely painful duty. "If it could be withheld," he laments, "and the act decently reconciled to the conscience of a biographer* professing to be honest and candid, it should never see the light in these pages. Its grotesque humor, its coarse exaggerations in describing the person of a lady whom the writer was willing to marry; its imputation of toothless and weatherbeaten old age to a woman really young and handsome; its utter lack of that delicacy of tone and sentiment which one naturally expects a gentleman to adopt when he thinks proper to discuss the merits of his late mistress—all these, and its defective orthography, it would certainly be more agreeable to suppress than to publish. But if we begin by omitting or mutilating a document which sheds so broad a light upon one part of his life and one phase of his character, why may we not do the like as fast and as often as the temptation arises? and where shall the process cease?"
* Lamon, p. 181.
I prefer not to take such a serious view of the letter or its publication. My idea is, that Mr. Lincoln got into one of his irresistible moods of humor and fun—a state of feeling into which he frequently worked himself to avert the overwhelming effects of his constitutional melancholy—and in the inspiration of the moment penned this letter, which many regard as an unfortunate composition. The class who take such a gloomy view of the matter should bear in mind that the letter was written by Mr. Lincoln in the fervor of early manhood, just as he was emerging from a most embarrassing situation, and addressed to a friend who, he supposed, would keep it sacredly sealed from the public eye. As a matter of fact Mr. Lincoln was not gifted with a ready perception of the propriety of things in all cases. Nothing with him was intuitive. To have profound judgment and just discrimination he required time to think; and if facts or events were forced before him in too rapid succession the machinery of his judgment failed to work. A knowledge of this fact will account for the letter, and also serve to rob the offence—if any was committed—of half its severity.
The letter was written in the same month Miss Owens made her final departure from Illinois.
"Springfield, April 1, 1838.
"Dear Madam:—
"Without apologizing for being egotistical, I shall make the history of so much of my life as has elapsed since I saw you the subject of this letter. And, by the way, I now discover that, in order to give a full and intelligible account of the things I have done and suffered since I saw you, I shall necessarily have to relate some that happened before.
"It was, then, in the autumn of 1836 that a married lady of my acquaintance and who was a great friend of mine, being about to pay a visit to her father and other relatives residing in Kentucky, proposed to me that on her return she would bring a sister of hers with her on condition that I would engage to become her brother-in-law with all convenient despatch. I, of course, accepted the proposal, for you know I could not have done otherwise, had I really been averse to it; but privately, between you and me I was most confoundedly well pleased with the project. I had seen the said sister some three years before, thought her intelligent and agreeable, and saw no good objection to plodding life through hand in hand with her. Time passed on, the lady took her journey, and in due time returned, sister in company sure enough. This astonished me a little; for it appeared to me that her coming so readily showed that she was a trifle too willing; but, on reflection, it occurred to me that she might have been prevailed on by her married sister to come, without anything concerning me ever having been mentioned to her; and so I concluded that, if no other objection presented itself, I would consent to waive this. All this occurred to me on hearing of her arrival in the neighborhood; for, be it remembered, I had not yet seen her, except about three years previous, as above mentioned. In a few days we had an interview; and, although I had seen her before, she did not look as my imagination had pictured her. I knew she was over-size, but she now appeared a fair match for Falstaff. I knew she was called an 'old maid,' and I felt no doubt of the truth of at least half of the appellation; but now, when I beheld her, I Could not for my life avoid thinking of my mother; and this, not from withered features, for her skin was too full of fat to permit of its contracting into wrinkles, but from her want of teeth, weather-beaten appearance in general, and from a kind of notion that ran in my head that nothing could have commenced at the size of infancy and reached her present bulk in less than thirty-five or forty years; and, in short, I was not at all pleased with her. But what could I do? I had told her sister I would take her for better or for worse; and I made a point of honor and conscience in all things to stick to my word, especially if others had been induced to act on it, which in this case I had no doubt they had; for I was now fairly convinced that no other man on earth would have her, and hence the conclusion that they were bent on holding me to my bargain. 'Well,' thought I, 'I have said it, and, be the consequences what they may, it shall not be my fault if I fail to do it.' At once I determined to consider her my wife; and, this done, all my powers of discovery were put to work in search of perfections in her which might be fairly set off against her defects. I tried to imagine her handsome, which, but for her unfortunate corpulency, was actually true. Exclusive of this, no woman that I have ever seen has a finer face. I also tried to convince myself that the mind was much more to be valued than the person; and in this she was not inferior, as I could discover, to any with whom I had been acquainted.
"Shortly after this, without coming to any positive understanding with her, I set out for Vandalia, when and where you first saw me. During my stay there I had letters from her which did not change my opinion of either her intellect or intention, but on the contrary confirmed it in both.
"All this while, although I was fixed, 'firm as the surge-repelling rock,' in my resolution, I found I was continually repenting the rashness which had led me to make it. Through life, I have been in no bondage, either real or imaginary, from the thraldom of which I so much desired to be free. After my return home, I saw nothing to change my opinions of her in any particular. She was the same, and so was I. I now spent my time in planning how I might get along through life after my contemplated change of circumstances should have taken place, and how I might procrastinate the evil day for a time, which I really dreaded as much, perhaps more, than an Irishman does the halter.
"After all my suffering upon this deeply interesting subject, here I am, wholly, unexpectedly, completely, out of the 'scrape;; and now I want to know if you can guess how I got out of it—out, clear, in every sense of the term; no violation of word, honor, or conscience. I don't believe you can guess, and so I might as well tell you at once. As the lawyer says, it was done in the manner following, to-wit: After I had delayed the matter as long as I thought I could in honor do (which, by the way, had brought me round into the last fall), I concluded I might as well bring it to a consummation without further delay; and so I mustered my resolution, and made the proposal to her direct; but, shocking to relate, she answered, No. At first I supposed she did it through an affectation of modesty, which I thought but ill became her under the peculiar circumstances of her case; but on my renewal of the charge, I found she repelled it with greater firmness than before. I tried it again and again, but with the same success, or rather with the same want of success.
"I finally was forced to give it up; at which I very unexpectedly found myself mortified almost beyond endurance. I was mortified, it seemed to me, in a hundred different ways. My vanity was deeply wounded by the reflection that I had been too stupid to discover her intentions, and at the same time never doubting that I understood them perfectly; and also that she, whom I had taught myself to believe nobody else would have, had actually rejected me with all my fancied greatness. And, to cap the whole, I then for the first time began to suspect that I was really a little in love with her. But let it all go. I'll try and outlive it. Others have been made fools of by the girls; but this can never with truth be said of me. I most emphatically, in this instance, made a fool of myself. I have now come to the conclusion never again to think of marrying, and for this reason: I can never be satisfied with any one who would be blockhead enough to have me.
"When you receive this, write me a long yarn about something to amuse me. Give my respects to Mr. Browning.
"Your sincere friend,
"A. Lincoln"
Mrs. O. H. Browning.
As before mentioned Miss Owens was afterwards married and became the mother of five children. Two of her sons served in the Confederate army. She died July 4, 1877. Speaking of Mr. Lincoln a a short time before her death she referred to him as "a man with a heart full of kindness and a head full of sense."
In December, 1834, Lincoln prepared himself for the Legislature to which he had been elected by such a complimentary majority. Through the generosity of his friend Smoot he purchased a new suit of clothes, and entering the stage at New Salem, rode through to Vandalia, the seat of government. He appreciated the dignity of his new position, and instead of walking to the capitol, as some of his biographers have contended, availed himself of the usual mode of travel. At this session of the Legislature he was anything but conspicuous. In reality he was very modest, but shrewd enough to impress the force of his character on those persons whose influence might some day be of advantage to him. He made but little stir, if we are to believe the record, during the whole of this first session. Made a member of the committee on Public Accounts and Expenditures, his name appears so seldom in the reports of the proceedings that we are prone to conclude that he must have contented himself with listening to the flashes of border oratory and absorbing his due proportion of parliamentary law. He was reserved in manner, but very observant; said little, but learned much; made the acquaintance of all the members and many influential persons on the outside. The lobby at that day contained the representative men of the state—men of acknowledged prominence and respectability, many of them able lawyers, drawn thither in advocacy of some pet bill. Schemes of vast internal improvements attracted a retinue of log-rollers, who in later days seem to have been an indispensable necessity in the movement of complicated legislative machinery. Men of capital and brains were there. He early realized the importance of knowing all these, trusting to the inspiration of some future hour to impress them with his skill as an organizer or his power as an orator. Among the members of the outside or "third body" was Stephen A. Douglas, whom Lincoln then saw for the first time. Douglas had come from Vermont only the year before, but was already undertaking to supplant John J. Hardin in the office of States Attorney for the district in which both lived. What impression he made on Lincoln, what opinions each formed of the other, or what the extent of their acquaintance then was, we do not know. It is said that Lincoln afterwards in mentioning their first meeting observed of the newly-arrived Vermonter that he was the "least man he had ever seen." The Legislature proper contained the youth and blood and fire of the frontier. Some of the men who participated in these early parliamentary battles were destined to carry the banners of great political parties, some to lead in war and some in the great council chamber of the nation. Some were to fill the Governor's office, others to wear the judicial ermine, and one was destined to be Chief Magistrate and die a martyr to the cause of human liberty.
The society of Vandalia and the people attracted thither by the Legislature made it, for that early day, a gay place indeed. Compared to Lincoln's former environments, it had no lack of refinement and polish. That he absorbed a good deal of this by contact with the men and women who surrounded him there can be no doubt. The "drift of sentiment and the sweep of civilization" at this time can best be measured by the character of the legislation. There were acts to incorporate banks, turnpikes, bridges, insurance companies, towns, railroads, and female academies. The vigor and enterprise of New England fusing with the illusory prestige of Kentucky and Virginia was fast forming a new civilization to spread over the prairies! At this session Lincoln remained quietly in the background, and contented himself with the introduction of a resolution in favor of securing to the State a part of the proceeds of sales of public lands within its limits. With this brief and modest record he returned to his constituents at New Salem. With zealous perseverance, he renewed his application to the law and to surveying, continuing his studies in both departments until he became, as he thought, reliable and proficient. By reason of a change in the office of Surveyor for the county he became a deputy under Thomas M. Neale, who had been elected to succeed John Calhoun. The speculation in lands made a brisk business for the new surveyor, who even added Calhoun, his predecessor, to the list of deputies. Lincoln had now become somewhat established in the good-will and respect of his constituents. His bashfulness and timidity was gradually giving way to a feeling of self-confidence, and he began to exult over his ability to stand alone. The brief taste of public office which he had just enjoyed, and the distinction it gave him only whetted his appetite for further honors. Accordingly, in 1836 we find him a candidate for the Legislature again. I well remember this campaign and the election which followed, for my father, Archer G. Herndon, was also a candidate, aspiring to a seat in the State Senate. The Legislature at the session previous had in its apportionment bill increased the delegation from Sangamon county to seven Representatives and two Senators. Party conventions had not yet been invented, and there being no nominating machinery to interfere, the field was open for any and all to run. Lincoln again resorted, in opening his canvass, to the medium of the political handbill. Although it had not operated with the most satisfactory results in his first campaign, yet he felt willing to risk it again. Candidates of that day evinced far more willingness to announce their position than political aspirants do now. Without waiting for a convention to construct a platform, or some great political leader to "sound the key-note of the campaign," they stepped to the forefront and blew the bugle themselves. This custom will account for the boldness of Lincoln's utterances and the unequivocal tone of his declarations. His card—a sort of political fulmination—was as follows:
"New Salem, June 13, 1836.
"To the Editor of The Journal:
"In your paper of last Saturday I see a communication over the signature of "Many Voters" in which the candidates who are announced in the Journal are called upon to 'show their hands.' Agreed. Here's mine: "I go for all sharing the privileges of the government who assist in bearing its burdens. Consequently, I go for admitting all whites to the right of suffrage who pay taxes or bear arms (by no means excluding females).
"If elected I shall consider the whole people of Sangamon my constituents, as well those that oppose as those that support me.
"While acting as their Representative, I shall be governed by their will on all subjects upon which I have the means of knowing what their will is; and upon all others I shall do what my own judgment teaches me will best advance their interests. Whether elected or not, I go for distributing the proceeds of the sales of public lands to the several States to enable our State, in common with others, to dig canals and construct railroads without borrowing money and paying the interest on it.
"If alive on the first Monday in November, I shall vote for Hugh L. White, for President.
"Very respectfully,
"A. Lincoln"
It is generally admitted that the bold and decided stand Lincoln took—though too audacious and emphatic for statesmen of a later day—suited the temper of the times. Leaving out of sight his expressed preference for White of Tennessee,—on whom all the anti-Jackson forces were disposed to concentrate, and which was but a mere question of men,—there is much food for thought in the second paragraph. His broad plan for universal suffrage certainly commends itself to the ladies, and we need no further evidence to satisfy our minds of his position on the subject of "Woman's Rights," had he lived. In fact, I cannot refrain from noting here what views he in after years held with reference to the great questions of moral and social reforms, under which he classed universal suffrage, temperance, and slavery. "All such questions," he observed one day, as we were discussing temperance in the office, "must first find lodgment with the most enlightened souls who stamp them with their approval. In God's own time they will be organized into law and thus woven into the fabric of our institutions."
The canvass which followed this public avowal of creed, was more exciting than any which had preceded it. There were joint discussions, and, at times, much feeling was exhibited. Each candidate had his friends freely distributed through the crowd, and it needed but a few angry interruptions or insinuating rejoinders from one speaker to another to bring on a conflict between their friends. Frequently the speakers led in the battle themselves, as in the case of Ninian W. Edwards—afterwards a brother-in-law of Lincoln—who, in debate, drew a pistol on his opponent Achilles Morris, a prominent Democrat. An interesting relic of this canvass recently came to light, in a letter which Mr. Lincoln wrote a week after he had announced his candidacy. It is addressed to Colonel Robert Allen, a Democratic politician of local prominence, who had been circulating some charges intended to affect Lincoln's chances of election. The affair brought to the surface what little satire there was in Lincoln's nature, and he administers—by way of innuendo—such a flaying as the gallant colonel doubtless never wanted to have repeated. The strangest part of it all is that the letter was recently found and given to the public by Allen's own son.* It is as follows:
* The MS. is now in possession of the Lincoln Monument Association of Springfield.
"New Salem, June 21, 1836.
"Dear Colonel:
"I am told that during my absence last week you passed through the place and stated publicly that you were in possession of a fact or facts, which if known to the public would entirely destroy the prospects of N. W. Edwards and myself at the ensuing election, but that through favor to us you would forbear to divulge them. No one has needed favors more than I, and generally few have been less unwilling to accept them, but in this case favor to me would be injustice to the public, and therefore I must beg your pardon for declining it. That I once had the confidence of the people of Sangamon county is sufficiently evident; and if I have done anything, either by design or misadventure, which if known would subject me to a forfeiture of that confidence, he that knows of that thing, and conceals it, is a traitor to his country's interest.
"I find myself wholly unable to form any conjecture of what fact or facts, real or supposed, you spoke; but my opinion of your veracity will not permit me for a moment to doubt that you at least believed what you said. I am flattered with the personal regard you manifested for me; but I do hope that on mature reflection you will view the public interest as a paramount consideration and therefore let the worst come.
"I assure you that the candid statement of facts on your part, however low it may sink me, shall never break the ties of personal friendship between us.
"I wish an answer to this, and you are at liberty to publish both if you choose.
"Very respectfully,
"A. Lincoln."
Col. Robert Allen.
Lincoln was sure the letter never would be published or answered, because Allen had no facts whatever upon which to base any such charges. He also knew that Allen, who was a hide-bound Democrat, was in politics the most unreliable man in Sangamon county. A vein of irony runs all through the letter, especially where in such a delicate way he pays tribute to the veracity of Allen, who, although a generous fellow in the ordinary sense of the term, was unlimited in exaggeration and a veritable bag of wind. The effort to smoke him out seems to have been of little effect, but enough appears in Lincoln's letter to show that he was thoroughly warmed up.
A joint debate in which all the candidates participated, took place on the Saturday preceding the election. "The speaking began in the forenoon," says one of the participants, "the candidates speaking alternately until everyone who could speak had had his turn, generally consuming the whole afternoon." Dr. Early, a Democratic candidate, in his speech took issue with Ninian W. Edwards, stigmatizing some of the latter's statements as untrue. This brought Edwards to his feet with a similar retort. His angry tone and menacing manner, as he mounted a table and with clenched fist hurled defiance at his challenger, foreboded a tumultuous scene. "The excitement that followed," relates another one of the candidates,* "was intense—so much so that fighting men thought a duel must settle the difficulty. Mr. Lincoln by the programme followed Early. Taking up the subject in dispute, he handled it so fairly and with such ability, all were astonished and pleased." The turbulent spirits were quieted and the difficulty was easily overcome.
Lincoln's friend Joshua F. Speed relates that during this campaign he made a speech in Springfield a few days before the election. "The crowd was large," says Speed, "and great numbers of his friends and admirers had come in from the country. I remember that his speech was a very able one, using with great power and originality all the arguments used to sustain the principles of the Whig party as against its great rival, the Democratic party of that day. The speech produced a profound impression—the crowd was with him."
George Forquer, an old citizen, a man of recognized prominence and ability as a lawyer, was present. Forquer had been a Whig—one of the champions of the party—but had then recently joined the Democratic party, and almost simultaneous with the change had been appointed Register of the Land Office, which office he then held. Just about that time Mr. Forquer had completed a neat frame house—the best house then in Springfield—and over it had erected a lightning rod, the only one in the place and the first one Mr. Lincoln had ever seen. He afterwards told me that seeing Forquer's lightning rod had led him to the study of the properties of electricity and the utility of the rod as a conductor. At the conclusion of Lincoln's speech the crowd was about dispersing, when Forquer rose and asked to be heard. He commenced by saying that the young man would have to be taken down, and was sorry the task devolved on him. He then proceeded to answer Lincoln's speech in a style which, while it was able and fair, in his whole manner asserted and claimed superiority. Lincoln stood a few steps away with arms folded, carefully watching the speaker and taking in everything he said. He was laboring under a good deal of suppressed excitement. Forquer's sting had roused the lion within him. At length Forquer concluded, and he mounted the stand to reply.
"I have heard him often since," continued Speed, "in the courts and before the people, but never saw him appear and acquit himself so well as upon that occasion. His reply to Forquer was characterized by great dignity and force. I shall never forget the conclusion of that speech: 'Mr. Forquer commenced his speech by announcing that the young man would have to be taken down. It is for you, fellow citizens, not for me to say whether I am up or down. The gentleman has seen fit to allude to my being a young man; but he forgets that I am older in years than I am in the tricks and trades of politicians. I desire to live, and I desire place and distinction; but I would rather die now than, like the gentleman, live to see the day that I would change my politics for an office worth three thousand dollars a year, and then feel compelled to erect a lightning rod to protect a guilty conscience from an offended God,'" The effect of this rejoinder was wonderful, and gave Forquer and his lightning rod a notoriety the extent of which no one envied him.
In the election which followed, Sangamon county in a political sense was entirely turned over. Hitherto the Democrats had always carried it, but now the Whigs gained control by an average majority of four hundred. This time Lincoln led his ticket. The nine elected were, Abraham Lincoln, Ninian W. Edwards, John Dawson, Andrew McCormick, Dan Stone, Wm. F. Elkin, Robert L. Wilson, Job Fletcher, and Archer G. Herndon. The last two were senators. On assembling at Vandalia they were at once, on account of their stature, dubbed the "Long Nine." In height they averaged over six feet, and in weight over two hundred pounds. "We were not only noted," says one* of them, "for our number and length, but for our combined influence. All the bad or objectional laws passed at that session of the Legislature and for many years afterwards were chargeable to the management and influence of the 'Long Nine.'" It is not my purpose to enter into a detailed account of legislation at this period or to rehearse the history of the political conditions. Many and ingenious were the manoeuvres, but it would fill page after page to narrate them. One thing which deserves mention in passing was "that Yankee contrivance," the convention system, which for the first time was brought into use. The Democrats, in obedience to the behests of Jackson, had adopted it, and, singularly enough, among the very first named for office under the operation of the new system was Stephen A. Douglas, who was elected to the Legislature from Morgan county. Its introduction was attributed to Ebenezer Peck, of Chicago, a Democrat who had once, it was said, served in the Canadian Parliament. This latter supposed connection with a monarchical institution was sufficient to bring down on his head the united hostility of the Whigs, a feeling in which even Lincoln joined. But after witnessing for a time the wonderful effects of its discipline in Democratic ranks, the Whigs too fell in, and resorted to the use of the improved machinery.
* 'DeWitt Clinton of Illinois.'"
The Legislature of which Mr. Lincoln thus became a member was one that will never be forgotten in Illinois. Its legislation in aid of the so-called internal improvement system was significantly reckless and unwise. The gigantic and stupendous operations of the scheme dazzled the eyes of nearly everybody, but in the end it rolled up a debt so enormous as to impede the otherwise marvelous progress of Illinois. The burdens imposed by this Legislature under the guise of improvements became so monumental in size it is little wonder that at intervals for years afterward the monster of repudiation often showed its hideous face above the waves of popular indignation. These attempts at a settlement of the debt brought about a condition of things which it is said led the Little Giant, in one of his efforts on the stump, to suggest that "Illinois ought to be honest if she never paid a cent." However much we may regret that Lincoln took part and aided in this reckless legislation, we must not forget that his party and all his constituents gave him their united endorsement. They gave evidence of their approval of his course by two subsequent elections to the same office. It has never surprised me in the least that Lincoln fell so harmoniously in with the great system of improvement. He never had what some people call "money sense." By reason of his peculiar nature and construction he was endowed with none of the elements of a political economist. He was enthusiastic and theoretical to a certain degree; could take hold of, and wrap himself up in, a great moral question; but in dealing with the financial and commercial interests of a community or government he was equally as inadequate as he was ineffectual in managing the economy of his own household. In this respect alone I always regarded Mr. Lincoln as a weak man.
One of his biographers, describing his legislative career at this time, says of him: "He was big with prospects: his real public service was just now about to begin. In the previous Legislature he had been silent, observant, studious. He had improved the opportunity so well that of all men in this new body, of equal age in the service, he was the smartest parliamentarian and cunningest 'log roller.' He was fully determined to identify himself conspicuously with the liberal legislation in contemplation, and dreamed of a fame very different from that which he actually obtained as an anti-slavery leader. It was about this time he told his friend Speed that he aimed at the great distinction of being called the 'DeWitt Clinton of Illinois.'"
The representatives in the Legislature from Sangamon county had been instructed by a mass convention of their constituents to vote "for a general system of internal improvements." Another convention of delegates from all the counties in the State met at Vandalia and made a similar recommendation to the members of the Legislature, specifying that it should be "commensurate with the wants of the people." Provision was made for a gridiron of railroads. The extreme points of the State, east and west, north and south, were to be brought together by thirteen hundred miles of iron rails. Every river and stream of the least importance was to be widened, deepened, and made navigable. A canal to connect the Illinois River and Lake Michigan was to be dug, and thus the great system was to be made "commensurate with the wants of the people." To effect all these great ends, a loan of twelve million dollars was authorized before the session closed. Work on all these gigantic enterprises was to begin at the earliest practicable moment; cities were to spring up everywhere; capital from abroad was to come pouring in; attracted by the glowing reports of marvelous progress and great internal wealth, people were to come swarming in by colonies, until in the end Illinois was to outstrip all the others, and herself become the Empire State of the Union.
Lincoln served on the Committee on Finance, and zealously labored for the success of the great measures proposed, believing they would ultimately enrich the State, and redound to the glory of all who aided in their passage. In advocating these extensive and far-reaching plans he was not alone. Stephen A. Douglas, John A. McClernand, James Shields, and others prominent in the subsequent history of the State, were equally as earnest in espousing the cause of improvement, and sharing with him the glory that attended it. Next in importance came the bill to remove the seat of government from Vandalia. Springfield, of course, wanted it. So also did Alton, Decatur, Peoria, Jacksonville, and Illiopolis. But the Long Nine, by their adroitness and influence, were too much for their contestants. They made a bold fight for Springfield, intrusting the management of the bill to Lincoln. The friends of other cities fought Springfield bitterly, but under Lincoln's leadership the Long Nine contested with them every inch of the way. The struggle was warm and protracted. "Its enemies," relates one of Lincoln's colleagues,* "laid it on the table twice. In those darkest hours when our bill to all appearances was beyond resuscitation, and all our opponents were jubilant over our defeat, and when friends could see no hope, Mr. Lincoln never for one moment despaired; but collecting his colleagues to his room for consultation, his practical common-sense, his thorough knowledge of human nature, then made him an overmatch for his compeers and for any man that I have ever known." The friends of the bill at last surmounted all obstacles, and only a day or two before the close of the session secured its passage by a joint vote of both houses.
* R. S. Wilson, MS.
Meanwhile the great agitation against human slavery, which like a rare plant had flourished amid the hills of New England in luxuriant growth, began to make its appearance in the West. Missionaries in the great cause of human liberty were settling everywhere. Taunts, jeers, ridicule, persecution, assassination even, were destined to prove ineffectual in the effort to suppress or exterminate these pioneers of Abolitionism. These brave but derided apostles carried with them the seed of a great reform. Perhaps, as was then said of them, they were somewhat in advance of their season, and perhaps too, some of the seed might be sown in sterile ground and never come to life, but they comforted themselves with the assurance that it would not all die. A little here and there was destined to grow to life and beauty.
It is not surprising, I think, that Lincoln should have viewed this New England importation with mingled suspicion and alarm. Abstractly, and from the standpoint of conscience, he abhorred slavery. But born in Kentucky, and surrounded as he was by slave-holding influences, absorbing their prejudices and following in their line of thought, it is not strange, I repeat, that he should fail to estimate properly the righteous indignation and unrestrained zeal of a Yankee Abolitionist. On the last day but one of the session, he solicited his colleagues to sign with him a mild and carefully worded protest against certain resolutions on the subject of domestic slavery, which had been passed by both houses of the Legislature. They all declined, however, save one, Dan Stone,* who with his associate will probably be known long after mention of all other members of the Long Nine has dropped from history.
* Following are the resolutions against the passage of which Lincoln and Stone made their protest: Resolved by the General Assembly of the State of Illinois: That we highly disapprove of the formation of Abolition societies and of the doctrines promulgated by them, That the right of property in slaves is sacred to the slave- holding States by the Federal Constitution, and that they cannot be deprived of that right without their consent, That the General Government cannot abolish slavery in the District of Columbia against the consent of the citizens of said District, without a manifest breach of good faith, That the Governor be requested to transmit to the States of Virginia, Alabama, Mississippi, New York, and Connecticut, a copy of the foregoing report and resolutions.
The language and sentiment are clearly Lincolnian, and over twenty years afterward, when it was charged that Lincoln was an Abolitionist, and this protest was cited as proof, it was only necessary to call for a careful reading of the paper for an unqualified and overwhelming refutation of the charge. The records of the Legislature for March 3, 1837, contain this entry:
"Resolutions upon the subject of domestic slavery having passed both branches of the General Assembly at its present session, the undersigned hereby protest against the passage of the same.
"They believe that the institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy, but that the promulgation of abolition doctrines tends rather to increase than abate its evils.
"They believe that the Congress of the United States has no power under the Constitution to interfere with the institution of slavery in the different States.
"They believe that the Congress of the United States has the power under the Constitution to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, but that the power ought not to be exercised unless at the request of the people of the District. The difference between these opinions and, those contained in the above resolutions is their reason for entering this protest.
"Dan Stone,
"A. Lincoln,
"Representatives from the county of Sangamon."
This document so adroitly drawn and worded, this protest pruned of any offensive allusions, and cautiously framed so as to suit the temper of the times, stripped of its verbal foliage reveals in naked grandeur the solemn truth that "the institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy." A quarter of a century later finds one of these protesters righting the injustice and correcting the bad policy of the inhuman and diabolical institution.
The return of the "Long Nine" to Springfield was the occasion of much enthusiasm and joy. The manifestations of public delight had never been equalled before, save when the steamer Talisman made its famous trip down the Sangamon in 1831. The returning legislators were welcomed with public dinners and the effervescent buncombe of local orators. Amid the congratulations of warm friends and the approval of their enthusiastic constituents, in which Lincoln received the lion's share of praise, they separated, each departing to his own home.
After his return from the Legislature, Lincoln determined to remove to Springfield, the county seat, and begin the practice of the law. Having been so instrumental in securing the removal of the State Capital from Vandalia, and having received such encouraging assurances from Major John T. Stuart and other leading citizens, he felt confident of a good start.*
* "Lincoln used to come to our office—Stuart's and mine—in Springfield from New Salem and borrow law-books. Sometimes he walked but generally rode. He was the most uncouth looking young man I ever saw. He seemed to have but little to say; seemed to feel timid, with a tinge of sadness visible in the countenance, but when he did talk all this disappeared for the time and he demonstrated that he was both strong and acute. He surprised us more and more at every visit."—Henry E. Dummer, Statement, Sept 16th, 1865.
He had little, if any, money, but hoped to find in Springfield, as he had in New Salem, good and influential friends, who, recognizing alike his honesty and his nobility of character, would aid him whenever a crisis came and their help was needed. In this hope he was by no means in error, for his subsequent history shows that he indeed united his friends to himself with hooks of steel. I had up to this time frequently seen Mr. Lincoln—had often, while visiting my cousins, James and Rowan Herndon, at New Salem, met him at their house—but became warmly attached to him soon after his removal to Springfield. There was something in his tall and angular frame, his ill-fitting garments, honest face, and lively humor that imprinted his individuality on my affection and regard. What impression I made on him I had no means of knowing till many years afterward. He was my senior by nine years, and I looked up to him, naturally enough, as my superior in everything—a thing I continued to do till the end of his days.

Now that the State capital was to be located at Springfield, that place began, by way of asserting its social superiority, to put on a good many airs. Wealth made its gaudy display, and thus sought to attain a pre-eminence from which learning and refinement are frequently cut off. Already, people had settled there who could trace their descent down a long line of distinguished ancestry. The established families were mainly from Kentucky. They re-echoed the sentiments and reflected the arrogance and elegance of a slave-holding aristocracy. "The Todds, Stuarts, and Edwardses were there, with priests, dogs, and servants;" there also were the Mathers, Lambs, Opdykes, Forquers, and Fords. Amid all "the flourishing about in carriages" and the pretentious elegance of that early day was Lincoln. Of origin, doubtful if not unknown; "poor, without the means of hiding his poverty," he represented yet another importation from Kentucky which is significantly comprehended by the term, "the poor whites." Springfield, containing between one and two thousand people, was near the northern line of settlement in Illinois. Still it was the center of a limited area of wealth and refinement. Its citizens were imbued with the spirit of push and enterprise. Lincoln therefore could not have been thrown into a better or more appreciative community.
In March, 1837, he was licensed to practice law. His name appears for the first time as attorney for the plaintiff in the case of Hawthorne vs. Woolridge. He entered the office and became the partner of his comrade in the Black Hawk war, John T. Stuart, who had gained rather an extensive practice, and who, by the loan of sundry textbooks several years before, had encouraged Lincoln to continue in the study of law. Stuart had emigrated from Kentucky in 1828, and on account of his nativity, if for no other reason, had great influence with the leading people in Springfield. He used to relate that on the next morning after his arrival in Springfield he was standing in front of the village store, leaning against a post in the sidewalk and wondering how to introduce himself to the community, when he was approached by a well-dressed old gentleman, who, interesting himself in the newcomer's welfare, enquired after his history and business. "I'm from Kentucky," answered Stuart, "and my profession is that of a lawyer, sir. What is the prospect here?" Throwing his head back and closing his left eye the old gentleman reflected a moment. "Young man, d———d slim chance for that kind of a combination here," was the response.
At the time of Lincoln's entry into the office, Stuart was just recovering from the effects of a congressional race in which he had been the loser. He was still deeply absorbed in politics, and was preparing for the next canvass, in which he was finally successful—defeating the wily and ambitious Stephen A. Douglas. In consequence of the political allurements, Stuart did not give to the law his undivided time or the full force of his energy and intellect. Thus more or less responsibility in the management of business and the conduct of cases soon devolved on Lincoln. The entries in the account books of the firm are all in the handwriting of Lincoln. Most of the declarations and pleas were written by him also. This sort of exercise was never congenial to him, and it was the only time, save a brief period under Judge Logan, that he served as junior partner and performed the labor required of one who serves in that rather subordinate capacity. He had not yet learned to love work. The office of the firm was in the upper story of a building opposite the north-west corner of the present Court-house Square. In the room underneath, the county court was held. The furniture was in keeping with the pretensions of the firm—a small lounge or bed, a chair containing a buffalo robe, in which the junior member was wont to sit and study, a hard wooden bench, a feeble attempt at a book-case, and a table which answered for a desk. Lincoln's first attempt at settlement in Springfield, which preceded a few days his partnership with Stuart, has been graphically described by his friend, Joshua F. Speed, who generously offered to share his quarters with the young legal aspirant. Speed, who was a prosperous young merchant, reports that Lincoln's personal effects consisted of a pair of saddle-bags containing two or three lawbooks and a few pieces of clothing. "He had ridden into town on a borrowed horse," relates Speed, "and engaged from the only cabinet-maker in the village a single bedstead. He came into my store, set his saddle-bags on the counter, and enquired what the furniture for a single bedstead would cost. I took slate and pencil, made a calculation, and found the sum for furniture complete would amount to seventeen dollars in all. Said he: 'It is probably cheap enough; but I want to say that, cheap as it is, I have not the money to pay. But if you will credit me until Christmas, and my experiment here as a lawyer is a success, I will pay you then. If I fail in that I will probably never pay you at all.' The tone of his voice was so melancholy that I felt for him. I looked up at him and I thought then, as I think now, that I never saw so gloomy and melancholy a face in my life. I said to him, 'So small a debt seems to affect you so deeply, I think I can suggest a plan by which you will be able to attain your end without incurring any debt. I have a very large room and a very large double bed in it, which you are perfectly welcome to share with me if you choose.' 'Where is your room?' he asked.
"'Upstairs,' said I, pointing to the stairs leading from the store to my room. Without saying a word he took his saddle-bags on his arm, went upstairs, set them down on the floor, came down again, and with a face beaming with pleasure and smiles, exclaimed, 'Well, Speed, I'm moved.'"
William Butler, who was prominent in the removal of the capital from Vandalia to Springfield, took no little interest in Lincoln, while a member of the Legislature. After his removal to Springfield, Lincoln boarded at Butler's house for several years. He became warmly attached to the family, and it is probable the matter of pay never entered Butler's mind. He was not only able but willing to befriend the young lawyer in this and many other ways.
Stephen T. Logan was judge of the Circuit court, and Stephen A. Douglas was prosecuting attorney. Among the attorneys we find many promising spirits. Edward D. Baker, John T. Stuart, Cyrus Walker, Samuel H. Treat, Jesse B. Thomas, George Forquer, Dan Stone, Ninian W. Edwards, John J. Hardin, Schuyler Strong, A. T. Bledsoe, and Josiah Lamborn—a galaxy of names, each destined to shed more or less lustre on the history of the State. While I am inclined to believe that Lincoln did not, after entering Stuart's office, do as much deep and assiduous studying as people generally credit him with, yet I am confident he absorbed not a little learning by contact with the great minds who thronged about the courts and State Capitol. The books of Stuart and Lincoln, during 1837, show a practice more extensive than lucrative, for while they received a number of fees, only two or there of them reached fifty dollars; and one of these has a credit of: "Coat to Stuart, $15.00," showing that they were compelled, now and then, even to "trade out" their earnings. The litigation was as limited in importance as in extent. There were no great corporations, as in this progressive day, retaining for counsel the brains of the bar in every county seat, but the greatest as well as the least had to join the general scramble for practice. The courts consumed as much time deciding who had committed an assault or a trespass on a neighbor's ground, as it spent in the solution of questions arising on contracts, or unravelling similar legal complications. Lawyers depended for success, not on their knowledge of the law or their familiarity with its under-lying principles, but placed their reliance rather on their frontier oratory and the influence of their personal bearing before the jury.
Lincoln made Speed's store headquarters. There politics, religion, and all other subjects were discussed. There also public sentiment was made. The store had a large fire-place in the rear, and around it the lights of the town collected every evening. As the sparks flew from the crackling logs, another and more brilliant fire flashed when these great minds came into collision. Here were wont to gather Lincoln, Douglas, Baker, Calhoun, Browning, Lamborn, Jesse B. Thomas and others. Only those who were present and listened to these embryonic statesmen and budding orators will ever be able to recall their brilliant thoughts and appreciate their youthful enthusiasm. In the fall and winter of 1837, while I was attending college at Jacksonville, the persecution and death of Elijah P. Lovejoy at Alton took place. This cruel and uncalled for murder had aroused the anti-slavery sentiment everywhere. It penetrated the college, and both faculty and students were loud and unrestrained in their denunciation of the crime. My father, who was thoroughly pro-slavery in his ideas, believing that the college was too strongly permeated with the virus of Abolitionism, forced me to withdraw from the institution and return home. But it was too late. My soul had absorbed too much of what my father believed was rank poison. The murder of Lovejoy filled me with more desperation than the slave scene in New Orleans did Lincoln; for while he believed in non-interference with slavery, so long as the Constitution permitted and authorized its existence, I, although acting nominally with the Whig party up to 1853, struck out for Abolitionism pure and simple.
On my return to Springfield from college, I hired to Joshua F. Speed as clerk in his store. My salary, seven hundred dollars per annum, was considered good pay then. Speed, Lincoln, Charles R. Hurst, and I slept in the room upstairs over the store. I had worked for Speed before going to college, and after hiring to him this time again, continued in his employ for several years. The young men who congregated about the store formed a society for the encouragement of debate and literary efforts. Sometimes we would meet in a lawyer's office and often in Speed's room. Besides the debates, poems and other original productions were read. Unfortunately we ruled out the ladies. I am free to admit I would not encourage a similar thing nowadays; but in that early day the young men had not the comforts of books and newspapers which are within the reach of every boy now. Some allowance therefore should be made for us. I have forgotten the name of the society—if it had any—and can only recall a few of its leading spirits. Lincoln, James Matheney, Noah Rickard, Evan Butler, Milton Hay, and Newton Francis were members. I joined also. Matheney was secretary.* We were favored with all sorts of literary productions. Lincoln one night entertained us with a few lines of rhyme intended to illustrate some weakness in woman—her frailty, perhaps. Unfortunately, the manuscript has not been preserved. Matheney was able, several years ago, to repeat a single stanza, but claimed that after the lapse of so many years it was all he could recall. Perhaps in the end it is best his memory was no more retentive. Reproduced here exactly as in the original, it might suggest more than one construction or offend against the canons of approved taste; in either event I shall omit it.
* Near Hoffman's Row, where the Courts were held in 1839-40, lived a shoemaker who frequently would get drunk and invariably whipped his wife. Lincoln, hearing of this, told the man if he ever repeated it he would thrash him soundly himself. Meanwhile he told Evan Butler, Noah Rickard, and myself of it, and we decided if the offense occurred again to join with Lincoln in suppressing it. In due course of time we heard of it. We dragged the offender up to the court-house, stripped him of his shirt, and tied him to a post or pump which stood over the well in the yard back of the building. Then we sent for his wife and arming her with a good limb bade her "light in." We sat on our haunches and watched the performance. The wife did her work lustily and well. When we thought the culprit had had enough Lincoln released him; we helped him on with his shirt and he crept sorrowfully homeward. Of course he threatened vengeance, but still we heard no further reports of wife-whipping from him.—James H. Matheney.
Besides this organization we had a society in Springfield, which contained and commanded all the culture and talent of the place. Unlike the other one its meetings were public, and reflected great credit on the community. We called it the "Young Men's Lyceum." Late in 1837, Lincoln delivered before the society a carefully prepared address on the "Perpetuation of Our Free Institutions."*
*Mr. Lincoln's speech was brought out by the burning of a negro in St. Louis a few weeks before by a mob. Lincoln took this incident as a sort of text for his remarks. James Matheney was appointed by the Lyceum to request of Lincoln a copy of his speech and see to its publication.
The inspiration and burthen of it was law and order. It has been printed in full so often, and is always to be found in the list of Lincoln's public speeches, that I presume I need not reproduce it here. It was highly sophomoric in character and abounded in striking and lofty metaphor. In point of rhetorical effort it excels anything he ever afterward attempted. Probably it was the thing people expect from a young man of twenty-eight. The address was published in the Sangamon Journal and created for the young orator a reputation which soon extended beyond the limits of the locality in which he lived. As illustrative of his style of oratory, I beg to introduce the concluding paragraph of the address. Having characterized the surviving soldiers of the Revolution as "living histories," he closes with this thrilling flourish: "But these histories are gone. They can be read no more forever. They were a fortress of strength; but what invading foeman never could do, the silent artillery of time has—the levelling of its walls. They are gone. They were a forest of giant oaks; but the all-resistless hurricane has swept over them, and left only here and there a lonely trunk, despoiled of its verdure, shorn of its foliage, unshading and unshaded, to murmur in a few more gentle breezes, and to combat with its mutilated limbs a few more rude storms, then to sink and be no more. They were pillars of the temple of liberty, and now that they have crumbled away, that temple must fall, unless we, their descendants, supply their places with other pillars hewn from the same solid quarry of sober reason. Passion has helped us, but can do so no more. It will in future be our enemy. Reason—cold, calculating, unimpassioned reason—must furnish all the materials for our future support and defense. Let these materials be moulded into general intelligence, sound morality, and in particular, a reverence for the Constitution and the laws. * * * Upon these let the proud fabric of freedom rest as the rock of its basis, and as truly as has been said of the only greater institution, 'The gates of hell shall not prevail against it.'"
In time Lincoln's style changed: he became more eloquent but with less gaudy ornamentation. He grew in oratorical power, dropping gradually the alliteration and rosy metaphor of youth, until he was able at last to deliver that grandest of all orations—the Gettysburg address.
One evening, while the usual throng of loungers surrounded the inviting fireplace in Speed's store, the conversation turned on political matters. The disputants waxed warm and acrimonious as the discussion proceeded. Business being over for the day, I strolled back and seating myself on a keg listened with eager interest to the battle going on among these would-be statesmen. Douglas, I recollect, was leading on the Democratic side. He had already learned the art of dodging in debate, but still he was subtle, fiery, and impetuous. He charged the Whigs with every blunder and political crime he could imagine. No vulnerable spot seemed to have escaped him. At last, with great vehemence, he sprang up and abruptly made a challenge to those who differed with him to discuss the whole matter publicly, remarking that, "This store is no place to talk politics," In answer to Douglas's challenge the contest was entered into. It took place in the Presbyterian Church. Douglas, Calhoun, Lamborn, and Thomas represented the Democrats; and Logan, Baker, Browning, and Lincoln, in the order named, presented the Whig side of the question. One evening was given to each man, and it therefore required over a week to complete the tournament. Lincoln occupied the last evening, and although the people by that time had necessarily grown a little tired of the monotony and well-worn repetition, yet Lincoln's manner of presenting his thoughts and answering his Democratic opponents excited renewed interest. So deep was the impression he created that he was asked to furnish his speech to the Sangamon Journal for publication, and it afterwards appeared in the columns of that organ.

Meanwhile Mr. Lincoln had attended one special session of the Legislature in July, 1837. The session was called to take some action with regard to the financial condition of the State. The Bank of the United States and the New York and Philadelphia Banks had suspended specie payments. This action had precipitated general ruin among business men and interests over the entire country. The called session of the Legislature was intended to save the Illinois banks from impending dissolution. Lincoln retained his position on the Committee on Finance, and had lost none of his enthusiasm over the glorious prospects of internal improvements. The Legislature, instead of abridging, only extended the already colossal proportions of the great system. In this they paid no heed to the governor, whose head seems to have been significantly clear on the folly of the enterprise.
In 1838 Mr. Lincoln was again elected to the Legislature. At this session, as the nominee of the Whig party, he received thirty-eight votes for Speaker. Wm. L. D. Ewing, his successful competitor, the Democratic candidate, received forty-three votes, and was elected. Besides retaining his place on the Finance Committee, Lincoln was assigned to the Committee on Counties. The enthusiasm and zeal of the friends of internal improvements began to flag now in view of the fact that the bonds issued were beginning to find their true level in point of value. Lincoln, together with others of kindred views, tried to bolster the "system" up; but soon the discouraging fact became apparent that no more money could be obtained, and the Legislature began to descant on what part of the debt was lawful and what unlawful. Repudiation seemed not far off. Mr. Lincoln despaired now of ever becoming the "DeWitt Clinton of Illinois." We find him admitting "his share of the responsibility in the present crisis," and finally concluding that he was "no financier" after all. No sooner had the Legislature adjourned than he decided—if he had not already so determined—to run for the same place again. He probably wanted it for a vindication. He was pursued now more fiercely than ever, and he was better able to endure the vilification of a political campaign than when he first offered himself to the voters in New Salem.
Among the Democratic orators who stumped the county at this time was one Taylor—commonly known as Col. Dick Taylor. He was a showy, bombastic man, with a weakness for fine clothes and other personal adornments. Frequently he was pitted against Lincoln, and indulged in many bitter flings at the lordly ways and aristocratic pretensions of the Whigs. He had a way of appealing to "his horny-handed neighbors," and resorted to many other artful tricks of a demagogue. When he was one day expatiating in his accustomed style, Lincoln, in a spirit of mischief and, as he expressed it, "to take the wind out of his sails," slipped up to the speaker's side, and catching his vest by the lower edge gave it a sharp pull. The latter instantly opened and revealed to his astonished hearers a ruffled shirt-front glittering with watch-chain, seals, and other golden jewels. The effect was startling. The speaker stood confused and dumbfounded, while the audience roared with laughter. When it came Lincoln's turn to answer he covered the gallant colonel over in this style: "While Colonel Taylor was making these charges against the Whigs over the country, riding in fine carriages, wearing ruffled shirts, kid gloves, massive gold watch-chains with large gold seals, and flourishing a heavy gold-headed cane, I was a poor boy, hired on a flat-boat at eight dollars a month, and had only one pair of breeches to my back, and they were buckskin. Now if you know the nature of buckskin when wet and dried by the sun, it will shrink; and my breeches kept shrinking until they left several inches of my legs bare between the tops of my socks and the lower part of my breeches; and whilst I was growing taller they were becoming shorter, and so much tighter that they left a blue streak around my legs that can be seen to this day. If you call this aristocracy I plead guilty to the charge."*
* From MS. of Ninian W. Edwards.
It was during this same canvass that Lincoln by his manly interference protected his friend E. D. Baker from the anger of an infuriated crowd. Baker was a brilliant and effective speaker, and quite as full too of courage as invective. He was addressing a crowd in the court room, which was immediately underneath Stuart and Lincoln's office. Just above the platform on which the speaker stood was a trap door in the floor, which opened into Lincoln's office. Lincoln at the time, as was often his habit, was lying on the floor looking down through the door at the speaker. I was in the body of the crowd. Baker was hot-headed and impulsive, but brave as a lion. Growing warm in his arraignment of the Democratic party, he charged that "wherever there was a land office there was a Democratic newspaper to defend its corruptions." This angered the brother of the editor of our town paper, who was present, and who cried out, "Pull him down," at the same time advancing from the crowd as if to perform the task himself. Baker, his face pale with excitement, squared himself for resistance. A shuffling of feet, a forward movement of the crowd, and great confusion followed. Just then a long pair of legs were seen dangling from the aperture above, and instantly the figure of Lincoln dropped on the platform. Motioning with his hands for silence and not succeeding, he seized a stone water-pitcher standing near by, threatening to break it over the head of the first man who laid hands on Baker. "Hold on, gentlemen," he shouted, "this is the land of free speech. Mr. Baker has a right to speak and ought to be heard. I am here to protect him, and no man shall take him from this stand if I can prevent it." His interference had the desired effect. Quiet was soon restored, and the valiant Baker was allowed to proceed. I was in the back part of the crowd that night, and an enthusiastic Baker man myself. I knew he was a brave man, and even if Lincoln had not interposed, I felt sure he wouldn't have been pulled from the platform without a bitter struggle.
This canvass—1840—was Mr. Lincoln's last campaign for the Legislature. Feeling that he had had enough honor out of the office he probably aspired for a place of more distinction. Jesse B. Thomas, one of the men who had represented the Democratic side in the great debate in the Presbyterian Church, in a speech at the court-house during this campaign, indulged in some fun at the expense of the "Long Nine," reflecting somewhat more on Lincoln than the rest. The latter was not present, but being apprised by his friends of what had been said, hastened to the meeting, and soon after Thomas closed, stepped upon the platform and responded. The substance of his speech on this occasion was not so memorable as the manner of its delivery. He felt the sting of Thomas's allusions, and for the first time, on the stump or in public, resorted to mimicry for effect. In this, as will be seen later along, he was without a rival. He imitated Thomas in gesture and voice, at times caricaturing his walk and the very motion of his body. Thomas, like everybody else, had some peculiarities of expression and gesture, and these Lincoln succeeded in rendering more prominent than ever. The crowd yelled and cheered as he continued. Encouraged by these demonstrations, the ludicrous features of the speaker's performance gave way to intense and scathing ridicule. Thomas, who was obliged to sit near by and endure the pain of this unique ordeal, was ordinarily sensitive; but the exhibition goaded him to desperation. He was so thoroughly wrought up with suppressed emotion that he actually gave way to tears. I was not a witness of this scene, but the next day it was the talk of the town, and for years afterwards it was called the "skinning" of Thomas. Speed was there, so were A. Y. Ellis, Ninian W. Edwards, and David Davis, who was just then coming into prominence. The whole thing was so unlike Lincoln, it was not soon forgotten either by his friends or enemies. I heard him afterwards say that the recollection of his conduct that evening filled him with the deepest chagrin. He felt that he had gone too far, and to rid his good-nature of a load, hunted up Thomas and made ample apology. The incident and its sequel proved that Lincoln could not only be vindictive but manly as well.
He was selected as an Elector on the Harrison ticket for President in 1840, and as such stumped over a good portion of the State. In debate he frequently met Douglas, who had already become the standard-bearer and exponent of Democratic principles. These joint meetings were spirited affairs sometimes; but at no time did he find the Little Giant averse to a conflict. "He was very sensitive," relates one of his colleagues on the stump, "where he thought he had failed to meet the expectations of his friends. I remember a case. He was pitted by the Whigs in 1840 to debate with Mr. Douglas, the Democratic champion. Lincoln did not come up to the requirements of the occasion. He was conscious of his failure, and I never saw any man so much distressed. He begged to be permitted to try it again, and was reluctantly indulged; and in the next effort he transcended our highest expectations.* I never heard and never expect to hear such a triumphant vindication as he then gave of Whig measures or policy. He never after, to my knowledge, fell below himself."
* Joseph Gillespie, MS. letter, June 5, '66.
The campaign ended in his election to the Legislature. He was again the caucus nominee of the Whigs for Speaker, receiving thirty-six votes; but his former antagonist, William L. D. Ewing, was elected by a majority of ten votes over him. The proceedings of, and laws enacted by, this Legislature are so much a matter of history and so generally known that it seems a needless task on my part to enter into details. It is proper to note, however, in passing, that Mr. Lincoln was neither prompt nor constant in his attendance during the session. He had been to a certain extent "upset" by another love affair, the particulars of which must be assigned to a future chapter.
The year 1840 finds Mr. Lincoln entering his thirty-second year and still unmarried. "I have come to the conclusion," he suggests in a facetious letter, two years before, "never again to think of marrying." But meanwhile he had seen more of the world. The State Capital had been removed to Springfield, and he soon observed the power and influence one can exert with high family and social surroundings to draw upon. The sober truth is that Lincoln was inordinately ambitious. He had already succeeded in obtaining no inconsiderable political recognition, and numbered among his party friends men of wealth and reputation; but he himself was poor, besides lacking the graces and ease of bearing obtained through mingling in polite society—in fact, to use the expressive language of Mary Owens, he was "deficient in those little links which make up the chain of woman's happiness." Conscious, therefore, of his humble rank in the social scale, how natural that he should seek by marriage in an influential family to establish strong connections and at the same time foster his political fortunes! This may seem an audacious thing to insinuate, but on no other basis can we reconcile the strange course of his courtship and the tempestuous chapters in his married life. It is a curious history, and the facts, long chained down, are gradually coming to the surface. When all is at last known, the world I believe will divide its censure between Lincoln and his wife.
Mary Todd, who afterwards became the wife of Mr. Lincoln, was born in Lexington, Kentucky, December 13, 1818. "My mother," related Mrs. Lincoln to me in 1865, "died when I was still young. I was educated by Madame Mantelli, a lady who lived opposite Mr. Clay's, and who was an accomplished French scholar. Our conversation at school was carried on entirely in French—in fact we were allowed to speak nothing else. I finished my education at Mrs. Ward's Academy, an institution to which many people from the North sent their daughters. In 1837 I visited Springfield, Illinois, remaining three months. I returned to Kentucky, remaining till 1839, when I again set out for Illinois, which State finally became my home."
The paternal grandfather of Mary Todd, General Levi Todd, was born in 1756, was educated in Virginia, and studied law in the office of General Lewis of that State. He emigrated to Kentucky, was a lieutenant in the campaigns conducted by General George Rogers Clark against the Indians, and commanded a battalion in the battle of Blue Licks, August 18, 1782, where his brother, John Todd, was killed. He succeeded Daniel Boone in command of the militia, ranking as major-general, and was one of the first settlers in Lexington, Ky. February 25, 1779, he married Miss Jane Briggs. The seventh child of this union, born February 25, 1791, was Robert S. Todd, the father of Mrs. Lincoln. On her maternal side Mrs. Lincoln was highly connected. Her great-grandfather, General Andrew Porter, was in the war of the Revolution. He succeeded Peter Muhlenberg as major-general of the Pennsylvania militia. Her great uncles, George B. Porter, who was governor of Michigan, James Madison Porter, secretary of the navy under President Tyler, and David R. Porter, governor of Pennsylvania, were men of ability and distinction. Her mother, Anne Eliza Parker, was a cousin of her father, Robert S. Todd. The latter had served in both houses of the Kentucky Legislature, and for over twenty years was president of the Bank of Kentucky at Lexington. He died July 16, 1849.
To a young lady in whose veins coursed the blood that had come down from this long and distinguished ancestral line, who could even go back in the genealogical chart to the sixth century, Lincoln, the child of Nancy Hanks, whose descent was dimmed by the shadow of tradition, was finally united in marriage.
When Mary Todd came to her sister's house in Springfield in 1839, she was in her twenty-first year. She was a young woman of strong, passionate nature and quick temper, and had "left her home in Kentucky to avoid living under the same roof with a stepmother."* She came to live with her oldest sister, Elizabeth, who was the wife of Lincoln's colleague in the Legislature, Ninian W. Edwards. She had two other sisters, Frances, married to Dr. William Wallace, and Anne, who afterwards became the wife of C. M. Smith, a prominent and wealthy merchant. They all resided in Springfield. She was of the average height, weighing when I first saw her about a hundred and thirty pounds. She was rather compactly built, had a well rounded face, rich dark-brown hair, and bluish-gray eyes. In her bearing she was proud, but handsome and vivacious. Her education had been in no wise defective; she was a good conversationalist, using with equal fluency the French and English languages. When she used a pen, its point was sure to be sharp, and she wrote with wit and ability. She not only had a quick intellect but an intuitive judgment of men and their motives. Ordinarily she was affable and even charming in her manners; but when offended or antagonized, her agreeable qualities instantly disappeared beneath a wave of stinging satire or sarcastic bitterness, and her entire better nature was submerged. In her figure and physical proportions, in education, bearing, temperament, history—in everything she was the exact reverse of Lincoln.
* Mrs. Edwards, statement, Aug. 3, 1887.
On her return to Springfield she immediately entered society, and soon became one of the belles, leading the young men of the town a merry dance. She was a very shrewd observer, and discreetly and without apparent effort kept back all the unattractive elements in her unfortunate organization. Her trenchant wit, affability, and candor pleased the young men not less than her culture and varied accomplishments impressed the older ones with whom she came in contact. The first time I met her was at a dance at the residence of Col. Robert Allen, a gentleman mentioned in the preceding chapter. I engaged her for a waltz, and as we glided through it I fancied I never before had danced with a young lady who moved with such grace and ease. A few moments later, as we were promenading through the hall, I thought to compliment her graceful dancing by telling her that while I was conscious of my own awkward movements, she seemed to glide through the waltz with the ease of a serpent. The strange comparison was as unfortunate as it was hideous. I saw it in an instant, but too late to recall it. She halted for a moment, drew back, and her eyes flashed as she retorted: "Mr. Herndon, comparison to a serpent is rather severe irony, especially to a newcomer."

Through the influence of Joshua F. Speed, who was a warm friend of the Edwardses, Lincoln was led to call on Miss Todd. He was charmed with her wit and beauty, no less than by her excellent social qualities and profound knowledge of the strong and weak points in individual character. One visit succeeded another. It was the old story. Lincoln had again fallen in love. "I have often happened in the room where they were sitting," relates Mrs. Edwards, describing this courtship, "and Mary invariably led the conversation. Mr. Lincoln would sit at her side and listen. He scarcely said a word, but gazed on her as if irresistibly drawn towards her by some superior and unseen power. He could not maintain himself in a continued conversation with a lady reared as Mary was. He was not educated and equipped mentally to make himself either interesting or attractive to the ladies. He was a good, honest, and sincere young man whose rugged, manly qualities I admired; but to me he somehow seemed ill-constituted by nature and education to please such a woman as my sister. Mary was quick, gay, and in the social world somewhat brilliant. She loved show and power, and was the most ambitious woman I ever knew. She used to contend when a girl, to her friends in Kentucky, that she was destined to marry a President. I have heard her say that myself, and after mingling in society in Springfield she repeated the seemingly absurd and idle boast. Although Mr. Lincoln seemed to be attached to Mary, and fascinated by her wit and sagacity, yet I soon began to doubt whether they could always be so congenial. In a short time I told Mary my impression that they were not suited, or, as some persons who believe matches are made in heaven would say, not intended for each other." But Mrs. Edwards' advice was seed, sown on rocky soil. The courtship ran on smoothly to the point of engagement, when a new and disturbing element loomed up ahead in their paths. It was no less than the dashing and handsome Stephen A. Douglas, who now appeared on the scene in the guise of a rival. As a society man Douglas was infinitely more accomplished, more attractive and influential than Lincoln, and that he should supplant the latter in the affections of the proud and aristocratic Miss Todd is not to be marveled at. He was unremitting in his attentions to the lady, promenaded the streets arm-in-arm with her—frequently passing Lincoln—and in every way made plain his intention to become the latter's rival. There are those who believe this warm reciprocation of young Douglas' affection was a mere flirtation on Mary Todd's part, intended to spur Lincoln up, to make him more demonstrative, and manifest his love more positively and with greater fervor. But a lady relative who lived with Lincoln and his wife for two years after their marriage is authority for the statement coming from Mrs. Lincoln herself that "she loved Douglas, and but for her promise to marry Lincoln would have accepted him." The unfortunate attitude she felt bound to maintain between these two young men ended in a spell of sickness. Douglas, still hopeful, was warm in the race, but the lady's physician,—her brother-in-law,—Dr. William Wallace, to whom she confided the real cause of her illness, saw Douglas and induced him to end his pursuit,* which he did with great reluctance.
* Mrs. Harriett Chapman, statement, Nov. 8, 1887.
If Miss Todd intended by her flirtation with Douglas to test Lincoln's devotion, she committed a grievous error. If she believed, because he was ordinarily so undemonstrative, that he was without will-power and incapable of being aroused, she certainly did not comprehend the man. Lincoln began now to feel the sting. Miss Todd's spur had certainly operated and with awakening effect. One evening Lincoln came into our store and called for his warm friend Speed. Together they walked back to the fireplace, where Lincoln, drawing from his pocket a letter, asked Speed to read it. "The letter," relates Speed, "was addressed to Mary Todd, and in it he made a plain statement of his feelings, telling her that he had thought the matter over calmly and with great deliberation, and now felt that he did not love her sufficiently to warrant her in marrying him. This letter he desired me to deliver. Upon my declining to do so he threatened to intrust it to some other person's hand. I reminded him that the moment he placed the letter in Miss Todd's hand, she would have the advantage over him. 'Words are forgotten,' I said, 'misunderstood, unnoticed in a private conversation, but once put your words in writing and they stand a living and eternal monument against you.' Thereupon I threw the unfortunate letter in the fire. 'Now,' I continued, 'if you have the courage of manhood, go see Mary yourself; tell her, if you do not love her, the facts, and that you will not marry her. Be careful not to say too much, and then leave at your earliest opportunity.' Thus admonished, he buttoned his coat, and with a rather determined look started out to perform the serious duty for which I had just given him explicit directions."
That night Speed did not go upstairs to bed with us, but under pretense of wanting to read, remained in the store below. He was waiting for Lincoln's return. Ten o'clock passed, and still the interview with Miss Todd had not ended. At length, shortly after eleven, he came stalking in. Speed was satisfied, from the length of Lincoln's stay, that his directions had not been followed.
"Well, old fellow, did you do as I told you and as you promised?" were Speed's first words.
"Yes, I did," responded Lincoln, thoughtfully, "and when I told Mary I did not love her, she burst into tears and almost springing from her chair and wringing her hands as if in agony, said something about the deceiver being himself deceived." Then he stopped.
"What else did you say?" inquired Speed, drawing the facts from him.
"To tell you the truth, Speed, it was too much for me. I found the tears trickling down my own cheeks. I caught her in my arms and kissed her," "And that's how you broke the engagement," sneered Speed. "You not only acted the fool, but your conduct was tantamount to a renewal of the engagement, and in decency you cannot back down now."
* Statement, Joshua F. Speed, Sep. 17, 1866, MS.
"Well," drawled Lincoln, "if I am in again, so be it. It's done, and I shall abide by it." Convinced now that Miss Todd regarded the engagement ratified,—instead of broken, as her tall suitor had at first intended,—Lincoln continued his visits, and things moved on smoothly as before. Douglas had dropped out of the race, and everything pointed to an early marriage. It was probably at this time that Mr. and Mrs. Edwards began to doubt the wisdom of the marriage, and now and then to intimate the same to the lady; but they went no farther in their opposition and placed no obstacle in their paths.
The time fixed for the marriage was the first day in January, 1841. Careful preparations for the happy occasion were made at the Edwards mansion. The house underwent the customary renovation; the furniture was properly arranged, the rooms neatly decorated, the supper prepared, and the guests invited. The latter assembled on the evening in question, and awaited in expectant pleasure the interesting ceremony of marriage. The bride, bedecked in veil and silken gown, and nervously toying with the flowers in her hair, sat in the adjoin-ing room. Nothing was lacking but the groom. For some strange reason he had been delayed. An hour passed, and the guests as well as the bride were becoming restless. But they were all doomed to disappointment. Another hour passed; messengers were sent out over town, and each returning with the same report, it became apparent that Lincoln, the principal in this little drama, had purposely failed to appear! The bride, in grief, disappeared to her room; the wedding supper was left untouched; the guests quietly and wonderingly withdrew; the lights in the Edwards mansion were blown out, and darkness settled over all for the night. What the feelings of a lady as sensitive, passionate, and proud as Miss Todd were we can only imagine—no one can ever describe them. By daybreak, after persistent search, Lincoln's friends found him. Restless, gloomy, miserable, desperate, he seemed an object of pity. His friends, Speed among the number, fearing a tragic termination, watched him closely in their rooms day and night. "Knives and razors, and every instrument that could be used for self-destruction were removed from his reach."* Mrs. Edwards did not hesitate to regard him as insane, and of course her sister Mary shared in that view. But the case was hardly so desperate. His condition began to improve after a few weeks, and a letter written to his partner Stuart, on the 23d of January; 1841, three weeks after the scene at Edwards' house, reveals more perfectly how he felt. He says: "I am now the most miserable man living. If what I feel were equally distributed to the whole human family, there would not be one cheerful face on earth. Whether I shall ever be better, I cannot tell; I awfully forebode I shall not. To remain as I am is impossible. I must die or be better, as it appears to me... I fear I shall be unable to attend to any business here, and a change of scene might help me. If I could be myself I would rather remain at home with Judge Logan. I can write no more."
* J. F. Speed, MS. letter, January 6, 1866,
During all this time the Legislature to which Lincoln belonged was in special session, but for a time he was unable to attend.* Towards the close of the session, however, he resumed his seat. He took little if any part in the proceedings, made no speeches, and contented himself with answers to the monotonous roll-call, and votes on a few of the principal measures. After the adjournment of the Legislature, his warm friend Speed, who had disposed of his interests in Springfield, induced Lincoln to accompany him to Kentucky. Speed's parents lived in a magnificent place a few miles from Louisville. Their farm was well stocked, and they, in the current phrase, "lived well." Thither he was taken, and there amid the quiet surroundings he found the "change of scene" which he told Stuart might help him. He was living under the cloud of melancholia, and sent to the Sangamon Journal a few lines under the gloomy title of "Suicide." They were published in the paper, and a few years since I hunted over the files, and coming across the number containing them, was astonished to find that some one had cut them out. I have always supposed it was done by Lincoln or by some one at his instigation.
* His illness and consequent incapacity for duty in the Legislature, continued for almost three weeks. On the 19th of January, 1841, John J. Hardin announced his illness in the House. Four days afterward he wrote the letter to Stuart from which I have quoted a few lines.
Speed's mother was much impressed with the tall and swarthy stranger her son had brought with him. She was a God-fearing mother, and besides aiding to lighten his spirits, gave him a Bible, advising him to read it and by adopting its precepts obtain a release from his troubles which no other agency, in her judgment, could bring him. "He was much depressed. At first he almost contemplated suicide. In the deepest of his depression he said one day he had done nothing to make any human being remember that he had lived; and that to connect his name with the events transpiring in his day and generation, and so impress himself upon them as to link his name with something that would redound to the interest of his fellow-men, was what he desired to live for."* The congenial associations at the Speed farm,** the freedom from unpleasant reminders, the company of his staunch friend, and above all the motherly care and delicate attentions of Mrs. Speed exerted a marked influence over Lincoln.
* Letter, J. F. Speed, February 9, 1866, MS. ** At the time of Lincoln's visit at the Speed mansion, James Speed, a brother of Joshua, and afterward Attorney- General in Lincoln's Cabinet, was practicing law in Louisville. Lincoln came into his office daily. "He read my books," related Mr. Speed in after years; "talked with me about his life, his reading, his studies, his aspirations." Mr. Speed discredits the thought that Lincoln was insane at the time, although he understood he was saddened and melancholy over an unfortunate love affair.
He improved gradually, day by day gaining strength and confidence in himself, until at last the great cloud lifted and passed away. In the fall he and Speed returned to Springfield. At this point, as affording us the most reliable account of Mr. Lincoln's condition and views, it is proper to insert a portion of his correspondence with Mr. Speed. For some time Mr. Speed was reluctant to give these letters to the world. After some argument, however, he at last shared my view that they were properly a matter of history, and sent them to me, accompanied by a letter, in which he says:
"I enclose you copies of all the letters of any interest from Mr. Lincoln to me. Some explanation may be needed that you may rightly understand their import. In the winter of 1840 and 1841, he was unhappy about his engagement to his wife—not being entirely satisfied that his heart was going with his hand. How much he suffered then on that account none knew so well as myself; he disclosed his whole heart to me.*
* Lincoln wrote a letter—a long one which he read to me—to Dr. Drake of Cincinnati, descriptive of his case. Its date would be in December, 1840, or early in January, 1841. I think that he must have informed Dr. Drake of his early love for Miss Rutledge, as there was a part of the letter which he would not read... I remember Dr. Drake's reply, which was, that he would not undertake to prescribe for him without a personal interview."—Joshua F. Speed, MS. letter, November 30, 1866.
"In the summer of 1841 I became engaged to my wife. He was here on a visit when I courted her; and, strange to say, something of the same feeling which I regarded as so foolish in him took possession of me and kept me very unhappy from the time of my engagement until I was married. This will explain the deep interest he manifested in his letters on my account.
"One thing is plainly discernible; if I had not been married and happy—far more happy than I ever expected to be—he would not have married."
The first of these letters is one which he gave Speed when the latter started on his journey from Illinois to Kentucky. It bears no date, but was handed him January 1, 1842, as Speed has testified, in another letter to me, that he left Springfield on that day. It is full of consolation and advice how best to conduct himself when the periods of gloom which he feels sure will follow come upon his friend. "I know," he says, "what the painful point with you is at all times when you are unhappy; it is an apprehension that you do not love her as you should. What nonsense! How came you to court her?... Did you court her for her wealth? Why, you say she had none. But you say you reasoned yourself into it. What do you mean by that? Was it not that you found yourself unable to reason yourself out of it? Did you not think, and partly form the purpose, of courting her the first time you ever saw her or heard of her? What had reason to do with it at that early stage? There was nothing at that time for reason to work upon. Whether she was moral, amiable, sensible, or even of good character, you did not nor could then know, except perhaps you might infer the last from the company you found her in.... Say candidly, were not those heavenly black eyes the whole basis of all your reasoning on the subject? After you and I had once been at the residence, did you not go and take me all the way to Lexington and back for no other purpose but to get to see her again on our return on that evening to take a trip for that express object?"
The next paragraph is significant as affording us an idea of how the writer perhaps viewed Miss Todd's flirtation with Douglas: "What earthly consideration," he asks, "would you take to find her scouting and despising you and giving herself up to another? But of this you need have no apprehension, and therefore you cannot bring it home to your feelings."
February 3, he writes again, acknowledging receipt of a letter dated January 25. The object of Speed's affection had been ill, and her condition had greatly intensified his gloomy spirits. Lincoln proffers his sympathy. "I hope and believe," he continues, "that your present anxiety about her health and her life must and will forever banish those horrid doubts which I know you sometimes felt as to the truth of your affection for her. If they can once and forever be removed (and I almost feel a presentiment that the Almighty has sent your present affliction expressly for that object), surely nothing can come in their stead to fill their immeasurable measure of misery... It really appears to me that you yourself ought to rejoice and not sorrow at this indubitable evidence of your undying affection for her. Why, Speed, if you did not love her, although you might not wish her death, you would most certainly be resigned to it. Perhaps this point is no longer a question with you, and my pertinacious dwelling upon it is a rude intrusion upon your feelings. If so you must pardon me. You know the hell I have suffered on that point, and how tender I am upon it. You know I do not mean wrong. I have been quite clear of hypo since you left, even better than I was along in the fall."
The next letter, February 13, was written on the eve of Speed's marriage. After assurances of his desire to befriend him in everything, he suggests: "But you will always hereafter be on ground that I have never occupied, and consequently, if advice were needed, I might advise wrong. I do fondly hope, however, that you will never again need any comfort from abroad... I incline to think it probable that your nerves will occasionally fail you for awhile; but once you get them firmly graded now, that trouble is over forever. If you went through the ceremony calmly or even with sufficient composure not to excite alarm in any present, you are safe beyond question, and in two or three months, to say the most, will be the happiest of men."
Meanwhile Lincoln had been duly informed of Speed's marriage, and on the 25th he responds:
"Yours of the 16th, announcing that Miss Fanny and you are 'no more twain, but one flesh,' reached me this morning. I have no way of telling how much happiness I wish you both, though I believe you both can conceive it. I feel somewhat jealous of both of you now. You will be so exclusively concerned for one another that I shall be forgotten entirely... I shall be very lonesome without you. How miserably things seem to be arranged in this world! If we have no friends we have no pleasure; and if we have them we are sure to lose them, and be doubly pained by the loss."
In another letter, written the same day, he says, "I have no doubt it is the peculiar misfortune of both you and me to dream dreams of Elysium far exceeding all that anything earthly can realize. Far short of your dreams as you may be, no woman could do more to realize them than that same blackeyed Fanny. If you could but contemplate her through my imagination, it would appear ridiculous to you that any one should for a moment think of being unhappy with her. My old father used to have a saying, that, 'If you make a bad bargain hug it all the tighter,' and it occurs to me that if the bargain just closed can possibly be called a bad one it is certainly the most pleasant one for applying that maxim to which my fancy can by any effort picture."
Speed having now safely married, Lincoln's mind began to turn on things nearer home. His relations with Mary Todd were still strained, but reminders of his period of gloom the year before began now to bring her again into view. In a letter to Speed, March 27, he says:
"It cannot be told how it thrills me with joy to hear you say you are 'far happier than you ever expected to be.' That much, I know, is enough. I know you too well to suppose your expectations were not at least sometimes extravagant, and if the reality exceeds them all, I say, 'Enough, dear Lord.' I am not going beyond the truth when I tell you that the short space it took me to read your last letter gave me more pleasure than the total sum of all I have enjoyed since that fatal first of January, 1841. Since then it seems to me I should have been entirely happy but for the never-absent idea that there is one still unhappy whom I have contributed to make so. That kills my soul. I cannot but reproach myself for even wishing to be happy while she is otherwise. She accompanied a large party on the railroad cars to Jacksonville last Monday, and on her return spoke, so that I heard of it, of having enjoyed the trip exceedingly. God be praised for that!"
The last paragraph of this letter contains a bit of sentiment by Lincoln in acknowledgment of a violet. In the margin of the letter which he gave me, Speed made this note in pencil: "The violet was sent by my wife, who dropped it in the letter as I was in the act of sealing it. How beautiful the acknowledgment!" This is the paragraph: "The sweet violet you enclosed came safely to hand, but it was so dry, and mashed so flat, that it crumbled to dust at the first attempt to handle it. The juice that mashed out of it stained a place in the letter, which I mean to preserve and cherish for the sake of her who procured it to be sent. My renewed good wishes to her."
Meanwhile the coldness that existed between Lincoln and his "Mary" was gradually passing away, and with it went all of Lincoln's resolution never to renew the engagement. In a letter, July 4, he says: "I must gain confidence in my own ability to keep my resolves when they are made. In that ability I once prided myself as the only chief gem of my character; that gem I lost, how and where you know too well. I have not regained it; and until I do I cannot trust myself in any matter of much importance. I believe now that had you understood my case at the time as well as I understood yours afterwards, by the aid you would have given me I should have sailed through clear; but that does not now afford me sufficient confidence to begin that or the like of that again.... I always was superstitious; I believe God made me one of the instruments of bringing Fanny and you together, which union I have no doubt he had foreordained. Whatever he designs he will do for me yet. 'Stand still and see the salvation of the Lord,' is my text just now. If, as you say, you have told Fanny all, I should have no objection to her seeing this letter, but for its reference to our friend here; let her seeing it depend upon whether she has ever known anything of my affairs; and if she has not, do not let her. I do not think I can come to Kentucky this season. I am so poor and make so little headway in the world that I drop back in a month of idleness as much as I gain in a year's sowing."
The last letter, and the one which closes this series, was written October 5, 1842. In it he simply announces his "duel with Shields," and then goes on to "narrate the particulars of the duelling business, which still rages in this city." This referred to a challenge from the belligerent Shields to William Butler, and another from General Whitesides to Dr. Merryman. In the latter, Lincoln acted as the "friend of Merryman," but in neither çase was there any encounter, and both ended in smoke. The concluding paragraph of this letter is the most singular in the entire correspondence. I give it entire without further comment:
"But I began this letter not for what I have been writing, but to say something on that subject which you know to be of such infinite solicitude to me. The immense sufferings you endured from the first days of September till the middle of February you never tried to conceal from me, and I well understood. You have now been the husband of a lovely woman nearly eight months. That you are happier now than the day you married her, I well know, for without, you could not be living. But I have your word for it, too, and the returning elasticity of spirits which is manifested in your letters. But I want to ask a close question: 'Are you in feeling as well as judgment glad you are married as you are?' From anybody but me this would be an impudent question, not to be tolerated, but I know you will pardon it in me. Please answer it quickly, as I am impatient to know." Lincoln again applied himself to the law. He re-entered the practice, after the long hiatus of rest, with renewed vigor. He permitted the memory of his engagement with Mary Todd to trouble him no longer. Their paths had diverged, the pain of the separation was over, and the whole thing was a history of the past. And so it might ever have remained but for the intervention of a very shrewd and sagacious lady—one who was capable of achieving success anywhere in the ranks of diplomacy. This lady was the wife of Simeon Francis, the editor of the Sangamon Journal. She was a warm friend of Mary Todd and a leader in society. Her husband was warmly attached to Lincoln. He ran the Whig organ, and entertained great admiration for Lincoln's brains and noble qualities. The esteem was mutual, and it is no stretch of the truth to say that for years Lincoln exercised undisputed control of the columns of the Journal himself. Whatever he wrote or had written, went into the editorial page without question. Mrs. Francis, sharing her husband's views of Lincoln's glorious possibilities, and desiring to do Mary Todd a kindly act, determined to bring about a reconciliation. She knew that Miss Todd had by letter a few days after "that fatal first of January, 1841," as Lincoln styled it, released him from the engagement, and that since then their relations had been strained, if not entirely broken off. As she viewed it, a marriage between a man as promising in the political world as Lincoln, and a woman as accomplished and brilliant in society as Mary Todd, would certainly add to the attractions of Springfield and reflect great credit on those who brought the union about. She was a great social entertainer, and one day arranged a gathering at her house for the express purpose of bringing these two people together. Both were invited and both attended; but neither suspected the other's presence. Having arranged things so ingeniously and with so much discretion, it was no difficult task for the hostess to bring the couple together by a warm introduction and the encouraging admonition, "Be friends again." Much to the surprise of both they found the web woven around them. They entered into the spirit of the reconciliation, and found Mrs. Francis' roof an inviting place for many succeeding meetings. A wall reared itself between them and the past, and they started again under the auspicious omens of another engagement. The tact of a woman and the diplomacy of society had accomplished what love had long since despaired of ever doing or seeing done.
The meetings in the parlor of Mrs. Francis' house were conducted with no little privacy. At first even Mrs. Edwards knew nothing of it, but presently it came to her ears. "I asked Mary," said this lady, "why she was so secretive about it. She said evasively that after all that had occurred, it was best to keep the courtship from all eyes and ears. Men and women and the whole world were uncertain and slippery, and if misfortune befell the engagement all knowledge of it would be hidden from the world." *
* Statement, January 10, 1866, MS.
It is unnecessary to prolong the account of this strange and checkered courtship. The intervention of the affair with Shields, which will be detailed in a subsequent chapter, in no way impeded, if it did not hasten the marriage. One morning in November, Lincoln, hastening to the room of his friend James H. Matheney before the latter had arisen from bed, informed him that he was to be married that night, and requested him to attend as best man.* That same morning Miss Todd called on her friend Julia M. Jayne, who afterward married Lyman Trumbull, and made a similar request. The Edwardses were notified, and made such meager preparations as were possible on so short notice. License was obtained during the day, the minister, Charles N. Dresser,** was sent for, and in the evening of November 4, 1842, "as pale and trembling as if being driven to slaughter," Abraham Lincoln was at last married to Mary Todd.*
* "Marriages in Springfield up to that time had been rather commonplace affairs. Lincoln's was perhaps the first one ever performed with all the requirements of the Episcopal ceremony. A goodly number of friends had gathered, and while witnessing the ceremony one of the most amusing incidents imaginable occurred. No description on paper can do it justice. Among those present was Thomas C. Brown, one of the judges of the Supreme Court. He was in truth an "old-timer," and had the virtue of saying just what he thought, without regard to place or surroundings. He had been on the bench for many years and was not less rough than quaint and curious. There was, of course, a perfect hush in the room as the ceremony progressed. Brown was standing just behind Lincoln. Old Parson Dresser, in canonical robes, with much and impressive solemnity recited the Episcopal service. He handed Lincoln the ring, who, placing it on the bride's finger, repeated the Church formula, 'With this ring I thee endow with all my goods and chattels, lands and tenements.' Brown, who had never witnessed such a proceeding, was struck with its utter absurdity. 'God Almighty! Lincoln,' he ejaculated, loud enough to be heard by all, 'the statute fixes all that!' This unlooked-for interruption almost upset the old parson; he had a keen sense of the ridiculous, and for the moment it seemed as if he would break down; but presently recovering his gravity, he hastily pronounced them husband and wife."—Letter, James H. Matheney, MS., Aug. 21,1888. ** "My father, Rev. Charles Dresser, was a graduate of Brown University, Providence, R. I., of the class of 1823."— Thomas W. Dresser, MS. letter, Sept. 17, 1888.

One great trial of his life was now over, and another still greater one was yet to come. To me it has always seemed plain that Mr. Lincoln married Mary Todd to save his honor, and in doing that he sacrificed his domestic peace. He had searched himself subjectively, introspectively, thoroughly: he knew he did not love her, but he had promised to marry her! The hideous thought came up like a nightmare. As the "fatal first of January, 1841," neared, the clouds around him blackened the heavens and his life almost went out with the storm. But soon the skies cleared. Friends interposed their aid to avert a calamity, and at last he stood face to face with the great conflict between honor and domestic peace. He chose the former, and with it years of self-torture, sacrificial pangs, and the loss forever of a happy home.*
* While dressing for the wedding in his room at Butler's house, the latter's little boy, Speed, seeing Lincoln so handsomely attired, in boyish innocence asked him where he was going? "To hell, I suppose," was Lincoln's reply.
With Miss Todd a different motive, but one equally as unfortunate, prompted her adherence to the union. To marry Lincoln meant not a life of luxury and ease, for Lincoln was not a man to accumulate wealth; but in him she saw position in society, prominence in the world, and the grandest social distinction. By that means her ambition would be satisfied. Until that fatal New Year's day in 1841 she may have loved him, but his action on that occasion forfeited her affection. He had crushed her proud, womanly spirit. She felt degraded in the eyes of the world. Love fled at the approach of revenge. Some writer—it is Junius, I believe—has said that, "Injuries may be forgiven and forgotten, but insults admit of no compensation: they degrade the mind in its own self-esteem and force it to recover its level by revenge." Whether Mrs. Lincoln really was moved by the spirit of revenge or not she acted along the lines of human conduct. She led her husband a wild and merry dance. If, in time, she became soured at the world it was not without provocation, and if in later years she unchained the bitterness of a disappointed and outraged nature, it followed as logically as an effect does the cause.
I have told this sad story as I know and have learned it. In rehearsing the varied scenes of the drama,* I have unearthed a few facts that seem half-buried, perhaps, but they were not destined to lay buried deep or long. The world will have the truth as long as the name of Lincoln is remembered by mankind.
* For many years I had reason to believe that Sarah Rickard, who was a sister of Mrs. William Butler, had been the recipient of some attentions at the hand of Mr. Lincoln. The lady, long since married, is now living in a Western State. I applied to her for information recently, and after some entreaty received this answer in her own handwriting: "As an old friend I will answer the question propounded to me, though I can scarcely see what good it can do history. Mr. Lincoln did make a proposal of marriage to me in the summer, or perhaps later, in the year of 1840. He brought to my attention the accounts in the Bible of the patriarch Abraham's marriage to Sarah, and used that historical union as an argument in his own behalf. My reason for declining his proposal was the wide difference in our ages. I was then only sixteen, and had given the subject of matrimony but very little, if any, thought. I entertained the highest regard for Mr. Lincoln. He seemed almost like an older brother, being, as it were, one of my sister's family."
There were two things Mr. Lincoln always seemed willing to forget. One was his unparliamentary escape with Joseph Gillespie from the Legislature by jumping through the church window, in 1839, and the other was the difficulty with James Shields, or, as he expressed it in a letter to Speed, the "duel with Shields." Other incidents in his career he frequently called up in conversation with friends, but in after years he seldom if ever referred to the affair with Shields. People in Illinois did gradually forget or, at least, cease mention of it, but in more remote quarters where Mr. Lincoln was less extensively known, the thing, much to his regret, kept rising to the surface. During a visit which I made to the Eastern States in 1858, I was often asked for an account of the so-called duel; so often, in fact, that on my return home I told Mr. Lincoln of it. "If all the good things I have ever done," he said regretfully, "are remembered as long and well as my scrape with Shields, it is plain I shall not soon be forgotten."
James Shields, a "gallant, hot-headed bachelor from Tyrone county, Ireland," and a man of inordinate vanity, had been elected Auditor of State. Encouraged somewhat by the prominence the office gave him, he at once assumed a conspicuous position in the society of Springfield. He was extremely sensitive by nature, but exposed himself to merciless ridicule by attempting to establish his supremacy as a beau among the ladies. Blind to his own defects, and very pronounced in support of every act of the Democratic party, he made himself the target for all the bitterness and ridicule of the day. It happened that the financial resources of the State, owing to the collapse of the great internal improvement system, were exceedingly limited, and people were growing restless under what they deemed excessive taxation. The State officers were all Democrats, and during the summer they issued an order declining to receive any more State Banknotes or bills in payment of taxes. This made the tax-payer's burdens greater than ever, as much of this paper remained outstanding in the hands of the people. The order met with opposition from every quarter—the Whigs of course losing no opportunity to make it as odious as possible. It was perfectly natural, therefore, that such an ardent Whig as Lincoln should join in the popular denunciation. Through the columns of the Springfield Journal, of which he had the undisputed use, he determined to encourage the opposition by the use of his pen. No object seemed to merit more ridicule and caricature than the conspicuous figure of the Auditor of State. At this time Lincoln was enjoying stolen conferences under the hospitable roof of Mrs. Francis with Mary Todd and her friend Julia M. Jayne. These two young ladies, to whom he confided his purpose, encouraged it and offered to lend their aid. Here he caught the idea of puncturing
Shields. The thing took shape in an article published in that Journal, purporting to have come from a poor widow, who with her pockets full of State Bank paper was still unable to obtain the coveted receipt for her taxes. It was written by Lincoln and was headed:
A Letter from the Lost Townships.
Lost Townships, August 27,1842.
Dear Mr. Printer,
I see you printed that long letter I sent you a spell ago. I'm quite encouraged by it, and can't keep from writing again. I think the printing of my letters will be a good thing all round—it will give me the benefit of being known by the world, and give the world the advantage of knowing what's going on in the Lost Townships, and give your paper respectability besides. So here comes another. Yesterday afternoon I hurried through cleaning up the dinner dishes and stepped over to neighbor S——— to see if his wife Peggy was as well as mout be expected, and hear what they called the baby. Well, when I got there and just turned round the corner of his log cabin, there he was, setting on the doorstep reading a newspaper. "How are you, Jeff?" says I. He sorter started when he heard me, for he hadn't seen me before. "Why," says he, "I'm mad as the devil, Aunt 'Becca!" "What about?" says I; "ain't its hair the right color? None of that nonsense, Jeff; there ain't an honester women in the Lost Townships than"—"Than who?" says he; "what the mischief are you about?" I began to see I was running the wrong trail, and so says I, "Oh! nothing: I guess I was mistaken a little, that's all. But what is it you're mad about?"
"Why," says he, "I've been tugging ever since harvest, getting out wheat and hauling it to the river to raise State Bank paper enough to pay my tax this year and a little school debt I owe; and now, just as I've got it, here I open this infernal Extra Register, expecting to find it full of 'Glorious Democratic Victories' and 'High Comb'd Cocks,' when, lo and behold! I find a set of fellows, calling themselves officers of the State, have forbidden the tax collectors and school commissioners to receive State paper at all; and so here it is dead on my hands. I don't now believe all the plunder I've got will fetch ready cash enough to pay my taxes and that school debt."
I was a good deal thunderstruck myself; for that was the first I had heard of the proclamation, and my old man was pretty much in the same fix with Jeff. We both stood a moment staring at one another without knowing what to say. At last says I, "Mr. S———, let me look at that paper." He handed it to me, when I read the proclamation over.
"There now," says he, "did you ever see such a piece of impudence and imposition as that?" I saw Jeff was in a good tune for saying some ill-natured things, and so I tho't I would just argue a little on the contrary side, and make him rant a spell if I could. "Why," says I, looking as dignified and thoughtful as I could, "it seems pretty tough, to be sure, to have to raise silver where there's none to be raised; but then, you see, 'there will be danger of loss' if it ain't done."
"Loss! damnation!" says he. "I defy Daniel Webster, I defy King Solomon, I defy the world—I defy—I defy—yes, I defy even you, Aunt 'Becca, to show how the people can lose anything by paying their taxes in State paper."
"Well," says I, "you see what the officers of State say about it, and they are a desarnin' set of men. But," says I, "I guess you're mistaken about what the proclamation says. It don't say the people will lose anything by the paper money being taken for taxes. It only says 'there will be danger of loss'; and though it is tolerable plain that the people can't lose by paying their taxes in something they can get easier than silver, instead of having to pay silver; and though it's just as plain that the State can't lose by taking State Bank paper, however low it may be, while she owes the bank more than the whole revenue, and can pay that paper over on her debt, dollar for dollar;—still there is danger of loss to the 'officers of State'; and you know, Jeff, we can't get along without officers of State."
"Damn officers of State!" says he; "that's what Whigs are always hurrahing for."
"Now, don't swear so, Jeff," says I; "you know I belong to the meetin', and swearin' hurts my feelings."
"Beg pardon, Aunt 'Becca," says he; "but I do say it's enough to make Dr. Goddard swear, to have tax to pay in silver, for nothing only that Ford may get his two thousand a year, and Shields his twenty-four hundred a year, and Carpenter his sixteen hundred a year, and all without 'danger of loss' by taking it in State paper. Yes, yes: it's plain enough now what these officers of State mean by 'danger of loss.' Wash, I s'pose, actually lost fifteen hundred dollars out of the three thousand that two of these 'officers of State' let him steal from the treasury, by being compelled to take it in State paper. Wonder if we don't have a proclamation before long, commanding us to make up this loss to Wash in silver."
And so he went on till his breath run out, and he had to stop. I couldn't think of anything to say just then, and so I begun to look over the paper again. "Ay! here's another proclamation, or something like it."
"Another?" says Jeff; "and whose egg is it, pray?"
I looked to the bottom of it, and read aloud, "Your obedient servant, James Shields, Auditor." "Aha!" says Jeff, "one of them same three fellows again. Well, read it, and let's hear what of it."
I read on till I came to where it says, "The object of this measure is to suspend the collection of the revenue for the current year."
"Now stop, now stop!" says he; "that's a lie a'ready, and I don't want to hear of it."
"Oh! may be not," says I.
"I say it—is—a—lie. Suspend the collection, indeed! Will the collectors, that have taken their oaths to make the collection, dare to suspend it? Is there anything in law requiring them to perjure themselves at the bidding of James Shields?
"Will the greedy gullet of the penitentiary be satisfied with swallowing him instead of all of them, if they should venture to obey him? And would he not discover some 'danger of loss,' and be off about the time it came to taking their places?
"And suppose the people attempt to suspend, by refusing to pay; what then? The collectors would just jerk up their horses and cows, and the like, and sell them to the highest bidder for silver in hand, without valuation or redemption. Why, Shields didn't believe that story himself: it was never meant for the truth. If it was true, why was it not writ till five days after the proclamation? Why didn't Carlin and Carpenter sign it as well as Shields? Answer me that, Aunt 'Becca. I say it's a lie, and not a well told one at that. It grins out like a copper dollar. Shields is a fool as well as a liar. With him truth is out of the question; and as for getting a good, bright, passable lie out of him, you might as well try to strike fire from a cake of tallow. I stick to it, it's all an infernal Whig lie!"
"A Whig lie! Highty tighty!"
"Yes, a Whig lie; and it's just like everything the cursed British Whigs do. First they'll do some divilment, and then they'll tell a lie to hide it. And they don't care how plain a lie it is: they think they can cram any sort of a one down the throats of the ignorant Locofocos, as they call the Democrats."
"Why, Jeff, you're crazy: you don't mean to say Shields is a Whig!"
"Yes, I do."
"Why, look here! the proclamation is in your own Democratic paper, as you call it."
"I know it; and what of that? They only printed it to let us Democrats see the deviltry the Whigs are at."
"Well, but Shields is the auditor of this Loco—I mean this Democratic State."
"So he is, and Tyler appointed him to office."
"Tyler appointed him?"
"Yes (if you must chaw it over), Tyler appointed him; or, if it wasn't him, it was old Granny Harrison, and that's all one. I tell you, Aunt 'Becca, there's no mistake about his being a Whig. Why, his very looks shows it; everything about him shows it: if I was deaf and blind, I could tell him by the smell. I seed him when I was down in Springfield last winter. They had a sort of a gatherin' there one night among the grandees, they called a fair. All the gals about town was there, and all the handsome widows and married women, finickin' about trying to look like gals, tied as tight in the middle, and puffed out at both ends, like bundles of fodder that hadn't been stacked yet, but wanted stackin' pretty bad. And then they had tables all around the house kivered over with [ ] caps and pincushions and ten thousand such little knic-knacks, tryin' to sell'em to the fellows that were bowin' and scrapin' and kungeerin' about'em. They wouldn't let no Democrats in, for fear they'd disgust the ladies, or scare the little gals, or dirty the floor. I looked in at the window, and there was this same fellow Shields floatin' about on the air, without heft or earthly substances, just like a lock of cat fur where cats had been fighting.
"He was paying his money to this one, and that one, and t'other one, and sufferin' great loss because it wasn't silver instead of State paper; and the sweet distress he seemed to be in,—his very features, in the ecstatic agony of his soul, spoke audibly and distinctly, 'Dear girls, it is distressing, but I cannot marry you all. Too well I know how much you suffer; but do, do remember, it is not my fault that I am so handsome and so interesting.'
"As this last was expressed by a most exquisite contortion of his face, he seized hold of one of their hands, and squeezed, and held on to it about a quarter of an hour. 'Oh, my good fellow!' says I to myself, 'if that was one of our Democratic gals in the Lost Townships, the way you'd get a brass pin let into you would be about up to the head.' He a Democrat! Fiddlesticks! I tell you, Aunt 'Becca, he's a Whig, and no mistake: nobody but a Whig could make such a conceity dunce of himself."
"Well," says I, "maybe he is; but, if he is, I'm mistaken the worst sort. Maybe so, maybe so; but, if I am, I'll suffer by it; I'll be a Democrat if it turns out that Shields is a Whig, considerin' you shall be a Whig if he turns out a Democrat."
"A bargain, by jingoes!" says he; "but how will we find out?"
"'Why," says I, "we'll just write and ax the printer."
"Agreed again!" says he; "and by thunder! if it does turn out that Shields is a Democrat, I never will"—
"Jefferson! Jefferson!"
"What do you want, Peggy?"
"Do get through your everlasting clatter some time, and bring me a gourd of water; the child's been crying for a drink this livelong hour."
"Let it die, then; it may as well die for water as to be taxed to death to fatten officers of State."
Jeff run off to get the water, though, just like he hadn't been saying anything spiteful for he's a raal good-hearted fellow, after all, once you get at the foundation of him.
I walked into the house, and, "Why, Peggy," says I, "I declare we like to forgot you altogether." "Oh, yes," says she, "when a body can't help themselves, everybody soon forgets'em; but, thank God! by day after to-morrow I shall be well enough to milk the cows, and pen the calves, and wring the contrary ones' tails for'em, and no thanks to nobody."
"Good evening, Peggy," says I, and so I sloped, for I seed she was mad at me for making Jeff neglect her so long.
And now, Mr. Printer, will you be sure to let us know in your next paper whether this Shields is a Whig or a Democrat? I don't care about it for my self, for I know well enough how it is already; but I want to convince Jeff. It may do some good to let him, and others like him, know who and what these officers of State are. It may help to send the present hypocritical set to where they belong, and to fill the places they now disgrace, with men who will do more work for less pay, and take a fewer airs while they are doing it. It ain't sensible to think that the same men who get us into trouble will change their course; and yet it's pretty plain if some change for the better is not made, it's not long that either Peggy or I or any of us will have a cow left to milk, or a calf's tail to wring.
Yours truly,
Rebecca ———.
Within a week another epistle from Aunt Rebecca appeared, in which, among other things, she offered the gallant Shields her hand. This one was written by Miss Todd and Miss Jayne. I insert it without further comment:
Lost Townships, September 8, 1842. Dear Mr. Printer:
I was a-standin' at the spring yesterday a-wash-in' out butter when I seed Jim Snooks a-ridin' up towards the house for very life, when, jist as I was a-wonderin' what on airth was the matter with him, he stops suddenly, and ses he, "Aunt 'Becca, here's somethin' for you and with that he hands out your letter. Well, you see, I steps out towards him, not thinkin' that I had both hands full of butter; and seein' I couldn't take the letter, you know, without greasin' it, I ses, "Jim, jist you open it, and read it for me." Well, Jim opens it and reads it; and would you believe it, Mr. Editor, I was so completely dumfounded and turned into stone that there I stood in the sun a-workin' the butter, and it a-running on the ground, while he read the letter, that I never thunk what I was about till the hull on't run melted on the ground and was lost. Now, sir, it's not for the butter, nor the price of the butter, but, the Lord have massy on us, I wouldn't have sich another fright for a whole firkin of it. Why, when I found out that it was the man what Jeff seed down to the fair that had demanded the author of my letters, threatnin' to take personal satisfaction of the writer, I was so skart that I tho't I should quill-wheel right where I was.
You say that Mr. S——— is offended at being compared to cats' fur, and is as mad as a March hare (that ain't fur), because I told about the squeezin'.
Now I want you to tell Mr. S——— that, rather than fight, I'll make any apology; and, if he wants personal satisfaction, let him only come here, and he may squeeze my hand as hard as I squeezed the butter, and, if that ain't personal satisfaction, I can only say that he is the fust man that was not satisfied with squeezin' my hand. If this should not answer, there is one thing more that I would rather do than get a lickin'. I have long expected to die a widow; but, as Mr. S——— is rather goodlooking than otherwise, I must say I don't care if we compromise the matter by—really, Mr. Printer, I can't help blushin'—but I—it must come out—I—but widowed modesty—well, if I must, I must—wouldn't he—may be sorter let the old grudge drap if I was to consent to be—be—h-i-s w-i-f-e? I know he's a fightin' man, and would rather fight than eat; but isn't marryin' better than fightin', though it does sometimes run in to it? And I don't think, upon the whole, that I'd be sich a bad match neither: I'm not over sixty, and am jist four feet three in my bare feet, and not much more around the girth; and for color, I wouldn't turn my back to nary a gal in the Lost Townships. But, after all, maybe I'm countin' my chickins before they are hatched, and dreamin' of matrimonial bliss when the only alternative reserved for me may be a lickin'. Jeff tells me the way these fire-eaters do is to give the challenged party choice of weapons, etc., which bein' the case, I'll tell you in confidence that I never fights with anything but broomsticks or hot water or a shovelful of coals or' some such thing; the former of which, being somewhat like a shillalah, may not be very objectional to him. I will give him choice, however, in one thing, and that is, whether, when we fight, I shall wear breeches or he petticoats, for, I presume that change is sufficient to place us on an equality.
Yours, etc.,
Rebecca ———.
P. S.—Jist say to your friend, if he concludes to marry rather than fight, I shall only inforce one condition, that is, if he should ever happen to gallant any young gals home of nights from our house, he must not squeeze their hands.
Not content with their epistolary efforts, the ladies invoked the muse. "Rebecca" deftly transformed herself into "Cathleen," and in jingling rhyme sang the praises of Shields, and congratulated him over the prospect of an early marriage to the widow. Following are the verses, rhyme, metre, and all:
Ye Jew's-harps awake! The Auditor's won. Rebecca the widow has gained Erin's son; The pride of the north from Emerald Isle Has been wooed and won by a woman's smile. The combat's relinquished, old loves all forgot: To the widow he's bound. Oh, bright be his lot! In the smiles of the conquest so lately achieved. Joyful be his bride, "widowed modesty" relieved, The footsteps of time tread lightly on flowers, May the cares of this world ne'er darken his hours! But the pleasures of life are fickle and coy As the smiles of a maiden sent off to destroy. Happy groom! in sadness far distant from thee The fair girls dream only of past times of glee Enjoyed in thy presence; whilst the soft blarnied stone Will be fondly remembered as relics of yore, And hands that in rapture you oft would have pressed, In prayer will be clasped that your lot may be blest. Cathleen.
The satire running through these various compositions, and the publicity their appearance in the Journal gave them, had a most wonderful effect on the vain and irascible Auditor of State. He could no longer endure the merriment and ridicule that met him from every side. A man of cooler head might have managed it differently, but in the case of a high-tempered man like Shields he felt that his integrity had been assailed and that nothing but an "affair of honor" would satisfy him. Through General John D. Whiteside he demanded of editor Francis the name of the author. The latter hunted up Lincoln, who directed him to give his name and say nothing about the ladies. The further proceedings in this grotesque drama were so graphically detailed by the friends of both parties in the columns of the Journal at that time, that I copy their letters as a better and more faithful narrative than can be obtained from any other source. The letter of Shields' second, General Whiteside, appearing first in the Journal, finds the same place in this chapter:
"To the Editor of the Sangamon Journal: Springfield, Oct. 3, 1842.
"SIR: To prevent misrepresentation of the recent affair between Messrs. Shields and Lincoln, I think it proper to give a brief narrative of the facts of the case, as they came within my knowledge; for the truth of which I hold myself responsible, and request you to give the same publication. An offensive article in relation to Mr. Shields appeared in the Sangamon Journal of the 2d of September last; and, on demanding the author, Mr. Lincoln was given up by the editor. Mr. Shields, previous to this demand, made arrangements to go to Quincy on public business; and before his return Mr. Lincoln had left for Tremont to attend the court, with the intention, as we learned, of remaining on the circuit several weeks. Mr. Shields, on his return, requested me to accompany him to Tremont; and, on arriving there, we found that Dr. Merryman and Mr. Butler had passed us in the night, and got there before us. We arrived in Tremont on the 17th ult., and Mr. Shields addressed a note to Mr. Lincoln immediately, informing him that he was given up as the author of some articles that appeared in the Sangamon Journal (one more over the signature having made its appearance at this time), and requesting him to retract the offensive allusions contained in said articles in relation to his private character. Mr. Shields handed this note to me to deliver to Mr. Lincoln, and directed me, at the same time, not to enter into any verbal communication, or be the bearer of any verbal explanation, as such were always liable to misapprehension. This note was delivered by me to Mr. Lincoln, stating, at the same time, that I would call at his convenience for an answer. Mr. Lincoln, in the evening of the same day, handed me a letter addressed to Mr. Shields. In this he gave or offered no explanation, but stated therein that he could not submit to answer further, on the ground that Mr. Shields's note contained an assumption of facts and also a menace. Mr. Shields then addressed him another note, in which he disavowed all intention to menace, and requested to know whether he (Mr. Lincoln) was the author of either of the articles which appeared in the Journal, headed 'Lost Townships,' and signed 'Rebecca'; and, if so, he repeated his request of a retraction of the offensive matter in relation to his private character; if not, his denial would be held sufficient. This letter was returned to Mr. Shields unanswered, with a verbal statement 'that there could be no further negotiation between them until the first note was withdrawn.' Mr. Shields thereupon sent a note designating me as a friend, to which Mr. Lincoln replied by designating Dr. Merryman. These three last notes passed on Monday morning, the 19th. Dr. Merryman handed me Mr. Lincoln's last note when by ourselves. I remarked to Dr. Merryman that the matter was now submitted to us, and that I would propose that he and myself should pledge our words of honor to each other to try to agree upon terms of amicable arrangement, and compel our principals to accept of them. To this he readily assented, and we shook hands upon the pledge. It was then mutually agreed that we should adjourn to Springfield, and there procrastinate the matter, for the purpose of effecting the secret arrangement between him and myself. All this I kept concealed from Mr. Shields. Our horse had got a little lame in going to Tremont, and Dr. Merryman invited me to take a seat in his buggy. I accepted the invitation the more readily, as I thought that leaving Mr. Shields in Tremont until his horse would be in better condition to travel would facilitate the private agreement between Dr. Merryman and myself. I travelled to Springfield part of the way with him, and part with Mr. Lincoln; but nothing passed between us on the journey in relation to the matter in hand. We arrived in Springfield on Monday night. About noon on Tuesday, to my astonishment, a proposition was made to meet in Missouri, within three miles of Alton, on the next Thursday! The weapons, cavalry broadswords of the largest size; the parties to stand on each side of a barrier, and to be confined to a limited space. As I had not been consulted at all on the subject, and considering the private understanding between Dr. Merryman and myself, and it being known that Mr. Shields was left at Tremont, such a proposition took me by surprise. However, being determined not to violate the laws of the State, I declined agreeing upon the terms until we should meet in Missouri. Immediately after, I called upon Dr. Merryman and withdrew the pledge of honor between him and myself in relation to a secret arrangement. I started after this to meet Mr. Shields, and met him about twenty miles from Springfield. It was late on Tuesday night when we both reached the city and learned that Dr. Merryman had left for Missouri, Mr. Lincoln having left before the proposition was made, as Dr. Merryman had himself informed me. The time and place made it necessary to start at once. We left Springfield at eleven o'clock on Tuesday night, travelled all night, and arrived in Hillsborough on Wednesday morning, where we took in General Ewing. From there we went to Alton, where we arrived on Thursday; and, as the proposition required three friends on each side, I was joined by General Ewing and Dr. Hope, as the friends of Mr. Shields. We then crossed to Missouri, where a proposition was made by General Hardin and Dr. English (who had arrived there in the mean time as mutual friends) to refer the matter to, I think, four friends for a settlement. This I believed Mr. Shields would refuse, and declined seeing him; but Dr. Hope, who conferred with him upon the subject, returned and stated that Mr. Shields declined settling the matter through any other than the friends he had selected to stand by him on that occasion. The friends of both the parties finally agreed to withdraw the papers (temporarily) to give the friends of Mr. Lincoln an opportunity to explain. Whereupon the friends of Mr. Lincoln, to wit, Messrs. Merryman, Bledsoe, and Butler, made a full and satisfactory explanation in relation to the article which appeared in the Sangamon Journal of the 2d, the only one written by him. This was all done without the knowledge or consent of Mr. Shields, and he refused to accede to it, until Dr. Hope, General Ewing, and myself declared the apology sufficient, and that we could not sustain him in going further. I think it necessary to state further, that no explanation or apology had been previously offered on the part of Mr. Lincoln to Mr. Shields, and that none was ever communicated by me to him, nor was any even offered to me, unless a paper read to me by Dr. Merryman after he had handed me the broadsword proposition on Tuesday. I heard so little of the reading of the paper, that I do not know fully what it purported to be; and I was the less inclined to inquire, as Mr. Lincoln was then gone to Missouri, and Mr. Shields not yet arrived from Tremont. In fact, I could not entertain any offer of the kind, unless upon my own responsibility; and that I was not disposed to do after what had already transpired.
"I make this statement, as I am about to be absent for some time, and I think it due to all concerned to give a true version of the matter before I leave.
"Your obedient servant,
"John D. Whiteside."
Springfield, October 8, 1842.
Editors of the Journal:
Gents:—By your paper of Friday, I discover that General Whiteside has published his version of the late affair between Messrs. Shields and Lincoln, I now bespeak a hearing of my version of the same affair, which shall be true and full as to all material facts.
On Friday evening, the 16th of September, I learned that Mr. Shields and General Whiteside had started in pursuit of Mr. Lincoln, who was at Tremont, attending court. I knew that Mr. Lincoln was wholly unpractised both as to the diplomacy and weapons commonly employed in similar affairs; and I felt it my duty, as a friend, to be with him, and, so far as in my power, to prevent any advantage being taken of him as to either his honor or his life. Accordingly, Mr. Butler and myself started, passed Shields and Whiteside in the night, and arrived at Tremont ahead of them on Saturday morning. I told Mr. Lincoln what was brewing, and asked him what course he proposed to himself. He stated that he was wholly opposed to duelling, and would do anything to avoid it that might not degrade him in the estimation of himself and friends; but, if such degradation or a fight were the only alternatives, he would fight.
In the afternoon Shields and Whiteside arrived, and very soon the former sent to Mr. Lincoln, by the latter, the following note or letter:—
Tremont, September 17, 1842.
A. Lincoln, Esq.:—
I regret that my absence on public business compelled me to postpone a matter of private consideration a little longer than I could have desired. It will only be necessary, however, to account for it by informing you that I have been to Quincy on business that would not admit of delay. I will now state briefly the reasons of my troubling you with this communication, the disagreeable nature of which I regret, as I had hoped to avoid any difficulty with any one in Springfield while residing there, by endeavoring to conduct myself in such a way amongst both my political friends and opponents, as to escape the necessity of any. Whilst thus abstaining from giving provocation, I have become the object of slander, vituperation, and personal abuse which, were I capable of submitting to, I would prove myself worthy of the whole of it.
In two or three of the last numbers of the Sangamon Journal, articles of the most personal nature, and calculated to degrade me, have made their appearance. On inquiring, I was informed by the editor of that paper, through the medium of my friend, General Whiteside, that you are the author of those articles. This information satisfies me that I have become, by some means or other, the object of secret hostility. I will not take the trouble of inquiring into the reason of all this, but I will take the liberty of requiring a full, positive, and absolute retraction of all offensive allusions used by you in these communications, in relation to my private character and standing as a man, as an apology for the insults conveyed in them.
This may prevent consequences which no one will regret more than myself.
Your ob't serv't,
Jas. Shields.
About sunset, General Whiteside called again, and secured from Mr. Lincoln the following answer to Mr. Shields's note:—
Tremont, September 17, 1842.
Jas. Shields, Esq.:—
Your note of to-day was handed me by General Whiteside. In that note you say you have been informed, through the medium of the editor of the Journal, that I am the author of certain articles in that paper which you deem personally abusive of you; and, without stopping to inquire whether I really am the author, or to point out what is offensive in them, you demand an unqualified retraction of all that is offensive, and then proceed to hint at consequences.
Now, sir, there is in this so much assumption of facts, and so much of menace as to consequences, that I cannot submit to answer that note any further than I have, and to add, that the consequences to which I suppose you allude would be matter of as great regret to me as it possibly could to you.
Respectfully,
A. Lincoln.

In about an hour, General Whiteside called again with another note from Mr. Shields; but after conferring with Mr. Butler for a long time, say two or three hours, returned without presenting the note to Mr. Lincoln. This was in consequence of an assurance from Mr. Butler that Mr. Lincoln could not receive any communication from Mr. Shields, unless it were a withdrawal of his first note, or a challenge. Mr. Butler further stated to General Whiteside, that, on the withdrawal of the first note, and a proper and gentlemanly request for an explanation, he had no doubt one would be given. General Whiteside admitted that that was the course Mr. Shields ought to pursue, but deplored that his furious and intractable temper prevented his having any influence with him to that end. General Whiteside then requested us to wait with him until Monday morning, that he might endeavor to bring Mr. Shields to reason.
On Monday morning he called and presented Mr. Lincoln the same note as Mr. Butler says he had brought on Saturday evening. It was as follows:—
Tremont, September 17, 1842.
A. Lincoln, Esq.:—
In your reply to my note of this date, you intimate that I assume facts and menace consequences, and that you cannot submit to answer it further. As now, sir, you desire it, I will be a little more particular. The editor of the Sangamon Journal gave me to understand that you are the author of an article which appeared, I think, in that paper of the 2d September inst., headed "The Lost Townships" and signed Rebecca or 'Becca. I would therefore take the liberty of asking whether you are the author of said article, or any other of the same signature which has appeared in any of the late numbers of that paper. If so, I repeat my request of an absolute retraction of all offensive allusions contained therein in relation to my private character and standing.
If you are not the author of any of the articles, your denial will be sufficient. I will say further, it is not my intention to menace, but to do myself justice.
Your ob't serv't,
Jas. Shields.
This Mr. Lincoln perused, and returned to General Whiteside, telling him verbally, that he did not think it consistent with his honor to negotiate for peace with Mr. Shields, unless Mr. Shields would withdraw his former offensive letter.
In a very short time General Whiteside called with a note from Mr. Shields, designating General Whiteside as his friend, to which Mr. Lincoln instantly replied designating me as his. On meeting General Whiteside, he proposed that we should pledge our honor to each other that we would endeavor to settle the matter amicably; to which I agreed, and stated to him the only conditions on which it could be settled; viz., the withdrawal of Mr. Shields's first note, which he appeared to think reasonable, and regretted that the note had been written, saying however, that he had endeavored to prevail on Mr. Shields to write a milder one, but had not succeeded. He added, too, that I must promise not to mention it, as he would not dare to let Mr. Shields know that he was negotiating peace; for, said he, "He would challenge me next, and as soon cut my throat as not." Not willing that he should suppose my principal less dangerous than his own, I promised not to mention our pacific intentions to Mr. Lincoln or any other person; and we started for Springfield forthwith.
We all, except Mr. Shields, arrived in Springfield late at night on Monday. We discovered that the affair had, somehow, got great publicity in Springfield, and that an arrest was probable. To prevent this, it was agreed by Mr. Lincoln and myself that he should leave early on Tuesday morning. Accordingly, he prepared the following instructions for my guide, on a suggestion from Mr. Butler that he had reason to believe that an attempt would be made by the opposite party to have the matter accommodated:
In case Whiteside shall signify a wish to adjust this affair without further difficulty, let him know that, if the present papers be withdrawn, and a note from Mr. Shields asking to know if I am the author of the articles of which he complains, and asking that I shall make him gentlemanly satisfaction if I am the author, and this without menace or dictation as to what that satisfaction shall be, a pledge is made that the following answer shall be given:
"I did write the 'Lost Township' letter which appeared in the Journal of the 2d inst., but had no participation in any form in any other article alluding to you. I wrote that wholly for political effect. I had no intention of injuring your personal or private character, or standing as a man or a gentleman; and I did not then think, and do not now think, that that article could produce, or has produced, that effect against you; and had I anticipated such an effect, I would have forborne to write it. And I will add, that your conduct towards me, so far as I knew, had always been gentlemanly, and that I had no personal pique against you, and no cause for any."
If this should be done, I leave it with you to manage what shall and what shall not be published.
If nothing like this is done, the preliminaries of the fight are to be:
1st. Weapons:—Cavalry broadswords of the largest size, precisely equal in all respects, and such as now used by the cavalry company at Jacksonville.
2d. Position:—A plank ten feet long, and from nine to twelve inches broad, to be firmly fixed on edge on the ground as the lines between us, which neither is to pass his foot over upon forfeit of his life. Next, a line drawn on the ground on either side of said plank and parallel with it, each at the distance of the whole length of the sword and three feet additional from the plank; and the passing of his own such line by either party during the fight shall be deemed a surrender of the contest.
3d. Time:—On Thursday evening at five o'clock, if you can get it so; but in no case to be at a greater distance of time than Friday evening at 5 o'clock.
4th. Place:—Within three miles of Alton, on the opposite side of the river, the particular spot to be agreed on by you.
Any preliminary details coming within the above rules, you are at liberty to make at your discretion; but you are in no case to swerve from these rules, or to pass beyond their limits.
In the course of the forenoon I met General Whiteside, and he again intimated a wish to adjust the matter amicably. I then read to him Mr. Lincoln's instructions to an adjustment, and the terms of the hostile meeting, if there must be one, both at the same time.
He replied that it was useless to talk of an adjustment, if it could only be effected by the withdrawal of Mr. Shields's paper, for such withdrawal Mr. Shields would never consent to; adding, that he would as soon think of asking Mr. Shields to "butt his brains out against a brick wall as to withdraw that paper." He proceeded: "I see but one course—that is a desperate remedy: 'tis to tell them, if they will not make the matter up, they must fight us." I replied, that, if he chose to fight Mr. Shields to compel him to do right, he might do so; but as for Mr. Lincoln, he was on the defensive, and, I believe, in the right, and I should do nothing to compel him to do wrong. Such withdrawal having been made indispensable by Mr. Lincoln, I cut the matter short as to an adjustment, and I proposed to General Whiteside to accept the terms of the fight, which he refused to do until Mr. Shields' arrival in town, but agreed, verbally, that Mr. Lincoln's friends should procure the broadswords, and take them to the ground. In the afternoon he came to me, saying that some persons were swearing out affidavits to have us arrested, and that he intended to meet Mr. Shields immediately, and proceed to the place designated, lamenting, however, that I would not delay the time, that he might procure the interference of Governor Ford and General Ewing to mollify Mr. Shields. I told him that an accommodation, except upon the terms I mentioned, was out of question; that to delay the meeting was to facilitate our arrest; and, as I was determined not to be arrested, I should leave the town in fifteen minutes. I then pressed his acceptance of the preliminaries, which he disclaimed upon the ground that it would interfere with his oath of office as Fund Commissioner. I then, with two other friends, went to Jacksonville, where we joined Mr. Lincoln about 11 o'clock on Tuesday night. Wednesday morning we procured the broadswords, and proceeded to Alton, where we arrived about 11 o'clock A. M., on Thursday. The other party were in town before us. We crossed the river, and they soon followed. Shortly after, General Hardin and Dr. English presented to General Whiteside and myself the following note:
Alton, September 22, 1842.
Messrs. Whiteside and Merryman: As the mutual personal friends of Messrs. Shields and Lincoln, but without authority from either, we earnestly desire to see a reconciliation of the misunderstanding which exists between them. Such difficulties should always be arranged amicably, if it is possible to do so with honor to both parties.
Believing, ourselves, that such an arrangement can possibly be effected, we respectfully but earnestly submit the following proposition for your consideration:
Let the whole difficulty be submitted to four or more gentlemen, to be selected by ourselves, who shall consider the affair, and report thereupon for your consideration. John J. Hardin,
R. W. English.
To this proposition General Whiteside agreed: I declined doing so without consulting Mr. Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln remarked that, as they had accepted the proposition, he would do so, but directed that his friends should make no terms except those first proposed. Whether the adjustment was finally made upon these very terms and no other, let the following documents attest:
Missouri, September 22, 1842.
Gentlemen:—All papers in relation to the matter in controversy between Mr. Shields and Mr. Lincoln having been withdrawn by the friends of the parties concerned, the friends of Mr. Shields ask the friends of Mr. Lincoln to explain all offensive matter in the articles which appeared in the Sangamon Journal of the 2d, 9 th, and 16th of September, under the signature of "Rebecca," and headed "Lost Townships."
It is due General Hardin and Mr. English to state that their interference was of the most courteous and gentlemanly character.
John D. Whiteside.
Wm. Lee D. Ewing.
T. M. Hope.
Missouri, September 22, 1842.
Gentlemen:—All papers in relation to the matter in controversy between Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Shields having been withdrawn by the friends of the parties concerned, we, the undersigned, friends of Mr. Lincoln, in accordance with your request that explanation of Mr. Lincoln's publication in relation to Mr. Shields in the Sangamon Journal of the 2d, 9th, and 16th of September be made, take pleasure in saying, that, although Mr. Lincoln was the writer of the article signed "Rebecca" in the Journal of the 2d, and that only, yet he had no intention of injuring the personal or private character or standing of Mr. Shields as a gentleman or a man, and that Mr. Lincoln did not think, nor does he now think, that said article could produce such an effect; and, had Mr. Lincoln anticipated such an effect, he would have forborne to write it. We will state further, that said article was written solely for political effect, and not to gratify any personal pique against Mr. Shields, for he had none and knew of no cause for any. It is due to General Hardin and Mr. English to say that their interference was of the most courteous and gentlemanly character.
E. H. Merryman.
A. T. Bledsoe.
Wm. Butler.
Let it be observed now, that Mr. Shields's friends, after agreeing to the arbitrament of four disinterested gentlemen, declined the contract, saying that Mr. Shields wished his own friends to act for him. They then proposed that we should explain without any withdrawal of papers. This was promptly and firmly refused, and General Whiteside himself pronounced the papers withdrawn. They then produced a note requesting us to "disavow" all offensive intentions in the publications, etc., etc. This we declined answering, and only responded to the above request for an explanation.
These are the material facts in relation to the matter, and I think present the case in a very different light from the garbled and curtailed statement of General Whiteside. Why he made that statement I know not, unless he wished to detract from the honor of Mr. Lincoln. This was ungenerous, more particularly as he on the ground requested us not to make in our explanation any quotations from the "Rebecca papers;" also, not to make public the terms of reconciliation, and to unite with them in defending the honorable character of the adjustment.
General Whiteside, in his publication, says: "The friends of both parties agreed to withdraw the papers (temporarily) to give the friends of Mr. Lincoln an opportunity to explain." This I deny. I say the papers were withdrawn to enable Mr. Shields's friends to ask an explanation; and I appeal to the documents for proof of my position.
By looking over these documents, it will be seen that Mr. Shields had not before asked for an explanation, but had all the time been dictatorially insisting on a retraction.
General Whiteside, in his communication, brings to light much of Mr. Shields's manifestations of bravery behind the scenes. I can do nothing of the kind for Mr. Lincoln. He took his stand when I first met him at Tremont, and maintained it calmly to the last, without difficulty or difference between himself and his friends.
I cannot close this article, lengthy as it is, without testifying to the honorable and gentlemanly conduct of General Ewing and Dr. Hope, nor indeed can I say that I saw anything objectionable in the course of General Whiteside up to the time of his communication. This is so replete with prevarication and misrepresentation, that I cannot accord to the General that candor which I once supposed him to possess. He complains that I did not procrastinate time according to agreement. He forgets that by his own act he cut me off from that chance in inducing me, by promise, not to communicate our secret contract to Mr. Lincoln. Moreover, I could see no consistency in wishing for an extension of time at that stage of the affair, when in the outset they were in so precipitate a hurry that they could not wait three days for Mr. Lincoln to return from Tremont, but must hasten there, apparently with the intention of bringing the matter to a speedy issue. He complains, too, that, after inviting him to take a seat in the buggy I never broached the subject to him on our route here. But was I, the defendant in the case, with a challenge hanging over me, to make advances, and beg a reconciliation?
Absurd! Moreover, the valorous General forgets that he beguiled the tedium of the journey by recounting to me his exploits in many a well-fought battle,—dangers by "flood and field," in which I don't believe he ever participated,—doubtless with a view to produce a salutary effect on my nerves, and impress me with a proper notion of his fire-eat-ing propensities..
One more main point of his argument and I have done. The General seems to be troubled with a convenient shortness of memory on some occasions. He does not remember that any explanations were offered at any time, unless it were a paper read when the "broadsword proposition" was tendered, when his mind was so confused by the anticipated clatter of broadswords, or something else, that he did "not know fully what it purported to be." The truth is, that, by unwisely refraining from mentioning it to his principal, he placed himself in a dilemma which he is now endeavoring to shuffle out of. By his inefficiency and want of knowledge of those laws which govern gentlemen in matters of this kind, he has done great injustice to his principal, a gentleman who, I believe, is ready at all times to vindicate his honor manfully, but who has been unfortunate in the selection of his friends, and this fault he is now trying to wipe out by doing an act of still greater injustice to Mr. Lincoln.
E. H. Merryman.
* The following letter from Lincoln to his friend Speed furnishes the final outcome of the "duelling business." "Springfield, October 5, 1842. "Dear Speed:- "You have heard of my duel with Shields, and I have now to inform you that the duelling business still rages in this city. Day before yesterday Shields challenged Butler, who accepted, proposed fighting next morning at sunrising in Bob Allen's meadow, one hundred yards distance, with rifles. To this Whiteside, Shields's second, said 'no' because of the law. Thus ended duel No. 2. Yesterday Whiteside chose to consider himself insulted by Dr. Merryman, so sent him a kind of quasi-challenge inviting him to meet him at the Planter's House in St. Louis, on the next Friday, to settle their difficulty. Merryman made me his friend, and sent Whiteside a note, inquiring to know if he meant his note as a challenge, and if so, that he would, according to the law in such case made and provided, prescribe the terms of the meeting. Whiteside returned for answer that if Merryman would meet him at the Planter's House as desired, he would challenge him. Merryman replied in a note, that he denied Whiteside's right to dictate time and place, but that he (Merryman) would waive the question of time, and meet him at Louisiana, Mo. Upon my presenting this note to Whiteside, and stating verbally its contents, he declined receiving it, saying he had business in St. Louis, and it was as near as Louisiana. Merryman then directed me to notify Whiteside that he should publish the correspondence between them, with such comments as he saw fit. This I did. Thus it stood at bed-time last night. This morning Whiteside, by his friend Shields, is praying for a new trial, on the ground that he was mistaken in Merryman's proposition to meet him at Louisiana, Mo., thinking it was the State of Louisiana. This Merryman hoots at, and is preparing his publication; while the town is in a ferment, and a street-fight somewhat anticipated. "Yours forever, "Lincoln."
Dr. Merryman's elaborate and graphic account of the meeting at the duelling ground and all the preliminary proceedings is as full and complete a history of this serio-comic affair as any historian could give. Mr. Lincoln, as mentioned in the outset of this chapter, in the law office and elsewhere, as a rule, refrained from discussing it. I only remember of hearing him say this, in reference to the duel: "I did not intend to hurt Shields unless I did so clearly in self-defense. If it had been necessary I could have split him from the crown of his head to the end of his backbone," and when one takes into into consideration the conditions of weapons and position required in his instructions to Dr. Merryman the boast does not seem impossible.
The marriage of Lincoln in no way diminished his love for politics; in fact, as we shall see later along, it served to stimulate his zeal in that direction. He embraced every opportunity that offered for a speech in public. Early in 1842 he entered into the Washingtonian movement organized to suppress the evils of intemperance. At the request of the society he delivered an admirable address, on Washington's birthday, in the Presbyterian Church, which, in keeping with former efforts, has been so often published that I need not quote it in full. I was then an ardent temperance reformer myself, and remember well how one paragraph of Lincoln's speech offended the church members who were present. Speaking of certain Christians who objected to the association of drunkards, even with the chance of reforming them, he said: "If they (the Christians) believe, as they profess, that Omnipotence condescended to take on himself the form of sinful man, and as such die an ignominious death, surely they will not refuse submission to the infinitely lesser condescension, for the temporal and perhaps eternal salvation of a large, erring, and unfortunate class of their fellow-creatures. Nor is the condescension very great. In my judgment such of us as have never fallen victims have been spared more from the absence of appetite than from any mental or moral superiority over those who have. Indeed, I believe, if we take habitual drunkards as a class, their heads and their hearts will bear an advantageous comparison with those of any other class." The avowal of these sentiments proved to be an unfortunate thing for Lincoln. The professing Christians regarded the suspicion suggested in the first sentence as a reflection on the sincerity of their belief, and the last one had no better effect in reconciling them to his views. I was at the door of the church as the people passed out, and heard them discussing the speech. Many of them were open in the expression of their displeasure. "It's a shame," I heard one man say, "that he should be permitted to abuse us so in the house of the Lord." The truth was the society was composed mainly of the roughs and drunkards of the town, who had evinced a desire to reform. Many of them were too fresh from the gutter to be taken at once into the society of such people as worshipped at the church where the speech was delivered. Neither was there that concert of effort so universal to-day between the churches and temperance societies to rescue the fallen. The whole thing, I repeat, was damaging to Lincoln, and gave rise to the opposition on the part of the churches which confronted him several years afterwards when he became a candidate against the noted Peter Cartwright for Congress. The charge, therefore, that in matters of religion he was a skeptic was not without its supporters, especially where his opponent was himself a preacher. But, nothing daunted, Lincoln kept on and labored zealously in the interest of the temperance movement. He spoke often again in Springfield, and also in other places over the country, displaying the same courage and adherence to principle that characterized his every undertaking.
Meanwhile, he had one eye open for politics as he moved along. He was growing more self-reliant in the practice of law every day, and felt amply able to take charge of and maintain himself in any case that happened to come into his hands. His propensity for the narration of an apt story was of immeasurable aid to him before a jury, and in cases where the law seemed to lean towards the other side won him many a case. In 1842, Martin Van Buren, who had just left the Presidential chair, made a journey through the West. He was accompanied by his former Secretary of the Navy, Mr. Paulding, and in June they reached the village of Rochester, distant from Springfield six miles. It was evening when they arrived, and on account of the muddy roads they decided to go no farther, but to rest there for the night. Word was sent into Springfield, and of course the leading Democrats of the capital hurried out to meet the distinguished visitor. Knowing the accommodations at Rochester were not intended for or suited to the entertainment of an ex-President, they took with them refreshments in quantity and variety, to make up for all deficiencies. Among others, they prevailed on Lincoln, although an ardent and pronounced Whig, to accompany them. They introduced him to the venerable statesman of Kinderhook as a representative lawyer, and a man whose wit was as ready as his store of anecdotes was exhaustless. How he succeeded in entertaining the visitor and the company, those who were present have often since testified. Van Buren himself entertained the crowd with reminiscences of politics in New York, going back to the days of Hamilton and Burr, and many of the crowd in turn interested him with graphic descriptions of early life on the western frontier. But they all yielded at last to the piquancy and force of Lincoln's queer stories. "Of these," relates one of the company,* "there was a constant supply, one following another in rapid succession, each more irresistible than its predecessor. The fun continued until after midnight, and until the distinguished traveller insisted that his sides were sore from laughing." The yarns which Lincoln gravely spun out, Van Buren assured the crowd, he never would forget.
* Jos. Gillespie, MS. letter, September 6, 1866.

After April 14, 1841, when Lincoln retired from the partnership with Stuart, who had gone to Congress, he had been associated with Stephen T. Logan, a man who had, as he deserved, the reputation of being the best nisi prius lawyer in the State. Judge Logan was a very orderly but somewhat technical lawyer. He had some fondness for politics, and made one race for Congress, but he lacked the elements of a successful politician. He was defeated, and returned to the law. He was assiduous in study and tireless in search of legal principles. He was industrious and very thrifty, delighted to make and save money, and died a rich man. Lincoln had none of Logan's qualities. He was anything but studious, and had no money sense. He was five years younger, and yet his mind and makeup so impressed Logan that he was invited into the partnership with him. Logan's example had a good effect on Lincoln, and it stimulated him to unusual endeavors. For the first time he realized the effectiveness of order and method in work, but his old habits eventually overcame him. He permitted his partner to do all the studying in the preparation of cases, while he himself trusted to his general knowledge of the law and the inspiration of the surroundings to overcome the judge or the jury. Logan was scrupulously exact, and used extraordinary care in the preparation of papers. His words were well chosen, and his style of composition was stately and formal. This extended even to his letters. This Lincoln lacked in every particular. I have before me a letter written by Lincoln at this time to the proprietors of a wholesale store in Louisville, for whom suit had been brought, in which, after notifying the latter of the sale of certain real estate in satisfaction of their judgment, he adds: "As to the real estate we cannot attend to it. We are not real estate agents, we are lawyers. We recommend that you give the charge of it to Mr. Isaac S. Britton, a trustworthy man, and one whom the Lord made on purpose for such business." He gravely signs the firm name, Logan and Lincoln, to this unlawyerlike letter and sends it on its way. Logan never would have written such a letter. He had too much gravity and austere dignity to permit any such looseness of expression in letters to his clients or to anyone else.
In 1843, Logan and Lincoln both had their eyes set on the race for Congress. Logan's claim to the honor lay in his age and the services he had rendered the Whig party, while Lincoln, overflowing with ambition, lay great stress on his legislative achievements, and demanded it because he had been defeated in the nominating conventions by both Hardin and Baker in the order named. That two such aspiring politicians, each striving to obtain the same prize, should not dwell harmoniously together in the same office is not strange. Indeed, we may reasonably credit the story that they considered themselves rivals, and that numerous acrimonious passages took place between them. I was not surprised, therefore, one morning, to see Mr. Lincoln come rushing up into my quarters and with more or less agitation tell me he had determined to sever the partnership with Logan. I confess I was surprised when he invited me to become his partner. I was young in the practice and was painfully aware of my want of ability and experience; but when he remarked in his earnest, honest way, "Billy, I can trust you, if you can trust me," I felt relieved, and accepted the generous proposal. It has always been a matter of pride with me that during our long partnership, continuing on until it was dissolved by the bullet of the assassin Booth, we never had any personal controversy or disagreement. I never stood in his way for political honors or office, and I believe we understood each other perfectly. In after years, when he became more prominent, and our practice grew to respectable proportions, other ambitious practitioners undertook to supplant me in the partnership. One of the latter, more zealous than wise, charged that I was in a certain way weakening the influence of the firm. I am flattered to know that Lincoln turned on this last named individual with the retort, "I know my own business, I reckon. I know Billy Herndon better than anybody, and even if what you say of him is true I intend to stick by him." Lincoln's effort to obtain the Congressional nomination in 1843 brought out several unique and amusing incidents. He and Edward D. Baker were the two aspirants from Sangamon county, but Baker's long residence, extensive acquaintance, and general popularity were obstacles Lincoln could not overcome; accordingly, at the last moment, Lincoln reluctantly withdrew from the field. In a letter to his friend Speed, dated March 24, 1843, describes the situation as follows: "We had a meeting of the Whigs of the county here on last Monday, to appoint delegates to a district convention; and Baker beat me, and got the delegation instructed to go for him. The meeting, in spite of my attempt to decline it, appointed me one of the delegates; so that in getting Baker the nomination I shall be fixed a good deal like a fellow who is made groomsman to a man that has cut him out, and is marrying his own dear gal." Only a few days before this he had written a friend anent the Congressional matter, "Now if you should hear any one say that Lincoln don't want to go to Congress, I wish you, as a personal friend of mine, would tell him you have reason to believe he is mistaken. The truth is I would like to go very much. Still, circumstances may happen which may prevent my being a candidate. If there are any who be my friends in such an enterprise, what I now want is that they shall not throw me away just yet."* To another friend in the adjoining county of Menard a few days after the meeting of the Whigs in Sangamon, he explains how Baker defeated him.
* Letter to R. S. Thomas, Virginia, Ill., Feb. 14, '43, MS.
The entire absence of any feeling of bitterness, or what the politicians call revenge, is the most striking feature of the letter. "It is truly gratifying," he says, "to me to learn that while the people of Sangamon have cast me off, my old friends of Menard, who have known me longest and best, stick to me. It would astonish if not amuse the older citizens to learn that I (a strange, friendless, uneducated, penniless boy, working on a flat-boat at ten dollars per month) have been put down here as the candidate of pride, wealth, and aristocratic family distinction. Yet so, chiefly, it was. There was, too, the strangest combination of church influence against me. Baker is a Campbellite, and therefore as I suppose, with few exceptions, got all that church. My wife has some relations in the Presbyterian churches and some with the Episcopalian churches, and therefore, wherever it would tell, I was set down as either the one or the other, while it was everywhere contended that no Christian ought to go for me, because I belonged to no church, was suspected of being a deist, and had talked about fighting a duel. With all these things Baker, of course, had nothing to do; nor do I complain of them. As to his own church going for him I think that was right enough; and as to the influences I have spoken of in the other, though they were very strong, it would be grossly untrue and unjust to charge that they acted upon them in a body, or were very near so. I only mean that those influences levied a tax of considerable per cent, and throughout the religious controversy." To a proposition offering to instruct the Menard delegation for him he replies: "You say you shall instruct your delegates for me unless I object. I certainly shall not object. That would be too pleasant a compliment for me to tread in the dust. And besides, if anything should happen (which, however, is not probable) by which Baker should be thrown out of the fight, I would be at liberty to accept the nomination if I could get it. I do, however, feel myself bound not to hinder him in any way from getting the nomination. I should despise myself were I to attempt it."
Baker's friends had used as an argument against Lincoln that he belonged to a proud and aristocratic family, referring doubtless to some of the distinguished relatives who were connected with him by marriage. The story reaching Lincoln's ears, he laughed heartily over it one day in a Springfield store and remarked:
"That sounds strange to me, for I do not remember of but one who ever came to see me, and while he was in town he was accused of stealing a jew's-harp."* In the convention which was held shortly after at the town of Pekin neither Baker nor Lincoln obtained the coveted honor; but John J. Hardin, of Morgan, destined to lose his life at the head of an Illinois regiment in the Mexican war, was nominated, and in the following August, elected by a good majority. Lincoln bore his defeat manfully. He was no doubt greatly disappointed, but by no means soured. He conceived the strange notion that the publicity given his so-called "aristocratic family distinction" would cost him the friendship of his humbler constituents—his Clary's Grove friends. He took his friend James Matheney out into the woods with him one day and, calling up the bitter features of the canvass, protested "vehemently and with great emphasis" that he was anything but aristocratic and proud. "Why, Jim," he said, "I am now and always shall be the same Abe Lincoln I was when you first saw me."
* Letter, A. Y. Ellis, July 16,'66, MS.
In the campaign of 1844 Lincoln filled the honorable post of Presidential Elector, and he extended the limits of his acquaintance by stumping the State. This was the year the gallant and magnetic Clay went down in defeat. Lincoln, in the latter end of the canvass, crossed over into Indiana and made several speeches. He spoke at Rockport and also at Gentryville, where he met the Grigsbys, the Gentrys, and other friends of his boyhood. The result of the election was a severe disappointment to Mr. Lincoln as well as to all other Whigs. No election since the foundation of the Government created more widespread regret than the defeat of Clay by Polk. Men were never before so enlisted in any man's cause, and when the great Whig chieftain went down his followers fled from the field in utter demoralization. Some doubted the success of popular government, while others, more hopeful still in the face of the general disaster, vowed they would never shave their faces or cut their hair till Henry Clay became President. As late as 18801 saw one man who had lived up to his insane resolution. One political society organized to aid Clay's election sent the defeated candidate an address, in which they assured him that, after the smoke of battle had cleared away, he would ever be remembered as one "whose name honored defeat and gave it a glory which victory could not have brought." In Lincoln's case his disappointment was no greater than that of any other Whig. Many persons have yielded to the impression that Mr. Lincoln visited Clay at his home in Lexington and felt a personal loss in his defeat, but such is not the case. He took no more gloomy view of the situation than the rest of his party. He had been a leading figure himself in other campaigns, and was fully inured to the chilling blasts of defeat. They may have driven him in, but only for a short time, for he soon evinced a willingness to test the temper of the winds again.

No sooner had Baker been elected to Congress in August, 1844, than Lincoln began to manifest a longing for the tempting prize to be contended for in 1846. Hardin and Baker both having been required to content themselves with a single term each, the struggle among Whig aspirants narrowed down to Logan and Lincoln.*
* The Whig candidates for Congress in the Springfield district "rotated" in the following order: Baker succeeded Hardin in 1844, Lincoln was elected in 1846, and Logan was nominated but defeated in 1848. Lincoln publicly declined to contest the nomination with Baker in 1844; Hardin did the same for Lincoln in 1846—although both seem to have acted reluctantly; and Lincoln refused to run against Logan in 1848. Many persons insist that an agreement among these four conspicuous Whig leaders to content themselves with one term each actually existed. There is, however, no proof of any bargain, although there seems to have been a tacit understanding of the kind—maintained probably to keep other and less tractable candidates out of the field.
The latter's claim seemed to find such favorable lodgment with the party workers, and his popularity seemed so apparent, that Logan soon realized his own want of strength and abandoned the field to his late law partner. The convention which nominated Lincoln met at Petersburg May 1, 1846. Hardin, who, in violation of what was then regarded as precedent, had been seeking the nomination, had courteously withdrawn. Logan, ambitious to secure the honor next time for himself, with apparent generosity presented Lincoln's name to the convention, and there being no other candidate he was chosen unanimously. The reader need not be told whom the Democrats placed in the field against him. It was Peter Cartwright, the famous Methodist divine and circuit rider. An energetic canvass of three months, followed, during which Lincoln kept his forces well in hand. He was active and alert, speaking everywhere, and abandoning his share of business in the law office entirely. He had a formidable competitor in Cartwright, who not only had an extensive following by reason of his church influence, but rallied many more supporters around his standard by his pronounced Jacksonian attitude. He had come into Illinois with the early immigrants from Kentucky and Tennessee, and had at one time or another preached to almost every Methodist congregation between Springfield and Cairo. He had extensive family connections all over the district, was almost twenty-five years older than Lincoln, and in every respect a dangerous antagonist. Another thing which operated much to Lincoln's disadvantage was the report circulated by Cartwright's friends with respect to Lincoln's religious views. He was charged with the grave offence of infidelity, and sentiments which he was reported to have expressed with reference to the inspiration of the Bible were given the campaign varnish and passed from hand to hand. His slighting allusion expressed in the address at the Presbyterian Church before the Washington Temperance Society, February 2d, four years before, to the insincerity of the Christian people was not forgotten. It, too, played its part; but all these opposing circumstances were of no avail. Cartwright was personally very popular, but it was plain the people of the Springfield district wanted no preacher to represent them in Congress. They believed in an absolute separation of Church and State. The election, therefore, of such a man as Cartwright would not, to their way of thinking, tend to promote such a result. I was enthusiastic and active in Lincoln's interest myself. The very thought of my associate's becoming a member of Congress was a great stimulus to my self-importance. Many other friends in and around Springfield were equally as vigilant, and, in the language of another, "long before the contest closed we snuffed approaching victory in the air." Our laborious efforts met with a suitable reward. Lincoln was elected by a majority of 1511 in the district, a larger vote than Clay's two years before, which was only 914. In Sangamon county his majority was 690, and exceeded that of any of his predecessors on the Whig ticket, commencing with Stuart in 1834 and continuing on down to the days of Yates in 1852.
Before Lincoln's departure for Washington to enter on his duties as a member of Congress, the Mexican war had begun. The volunteers had gone forward, and at the head of the regiments from Illinois some of the bravest men and the best legal talent in Springfield had marched. Hardin, Baker, Bissell, and even the dramatic Shields had enlisted. The issues of the war and the manner of its prosecution were in every man's mouth. Naturally, therefore, a Congressman-elect would be expected to publish his views and define his position early in the day. Although, in common with the Whig party, opposing the declaration of war, Lincoln, now that hostilities had commenced, urged a vigorous prosecution. He admonished us all to permit our Government to suffer no dishonor, and to stand by the flag till peace came and came honorably to us. He declared these sentiments in a speech at a public meeting in Springfield, May 29, 1847. In the following December he took his seat in Congress. He was the only Whig from Illinois. His colleagues in the Illinois delegation were John A. McClernand, O. B. Ficklin, William A. Richardson, Thomas J. Turner, Robert Smith, and John Wentworth. In the Senate Douglas had made his appearance for the first time. The Little Giant is always in sight! Robert C. Winthrop, of Massachusetts, was chosen Speaker. John Quincy Adams, Horace Mann, Caleb Smith, Alexander H. Stephens, Robert Toombs, Howell Cobb, and Andrew Johnson were important members of the House. With many of these the newly elected member from Illinois was destined to sustain another and far different relation.
On the 5th of December, the day before the House organized, Lincoln wrote me a letter about our fee in a law-suit, and reported the result of the Whig caucus the night before. On the 13th, he wrote again: "Dear William:—Your letter, advising me of the receipt of our fee in the bank case, is just received, and I don't expect to hear another as good a piece of news from Springfield while I am away." He then directed me from the proceeds of this fee to pay a debt at the bank, and out of the balance left to settle sundry dry-goods and grocery bills. The modest tone of the last paragraph is its most striking feature. "As you are all so anxious for me to distinguish myself," he said, "I have concluded to do so before long." January 8 he writes: "As to speech-making, by way of getting the hang of the House, I made a little speech two or three days ago on a post-office question of no general interest. I find speaking here and elsewhere about the same thing. I was about as badly scared, and no worse, as I am when I speak in court. I expect to make one within a week or two in which I hope to succeed well enough to wish you to see it." Meanwhile, in recognition of the assurances I had sent him from friends who desired to approve his course by a re-election, he says: "It is very pleasant to me to learn from you that there are some who desire that I should be re-elected. I most heartily thank them for the kind partiality, and I can say, as Mr. Clay said of the annexation of Texas, that, 'personally, I would not object' to a re-election, although I thought at the time, and still think, it would be quite as well for me to return to the law at the end of a single term. I made the declaration that I would not be a candidate again, more from a wish to deal fairly with others, to keep peace among our friends, and to keep the district from going to the enemy, than for any cause personal to myself, so that if it should happen that nobody else wishes to be elected I could not refuse the people the right of sending me again. But to enter myself as a competitor of others, or to authorize any one so to enter me, is what my word and honor forbid."
His announcement of a willingness to accept a re-election if tendered him by the people was altogether unnecessary, for within a few days after this letter was written his constituents began to manifest symptoms of grave disapproval of his course on the Mexican war question. His position on this subject was evidenced by certain resolutions offered by him in the House three weeks before. These latter were called the "Spot Resolutions," and they and the speech which followed on the 12th of January in support of them not only sealed Lincoln's doom as a Congressman, but in my opinion, lost the district to the Whigs in 1848, when Judge Logan had succeeded at last in obtaining the nomination.
Although differing with the President as to the justice or even propriety of a war with Mexico, Lincoln was not unwilling to vote, and with the majority of his party did vote, the supplies necessary to carry it on. He did this, however, with great reluctance, protesting all the while that "the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally begun by the President." The "Spot Resolutions," which served as a text for his speech on the 12th of January, and which caused such unwonted annoyance in the ranks of his constituents, were a series following a preamble loaded with quotations from the President's messages. These resolutions requested the President to inform the House: "First, Whether the spot on which the blood of our citizens was shed as in his messages declared was or was not within the territory of Spain, at least after the treaty of 1819, until the Mexican revolution. Second, Whether that spot is or is not within the territory which was wrested from Spain by the revolutionary government of Mexico. Third, Whether that spot is or is not within a settlement of people, which settlement has existed ever since long before the Texas revolution, and until its inhabitants fled before the approach of the United States army." There were eight of these interrogatories, but it is only necessary to reproduce the three which foreshadow the position Lincoln was then intending to assume. On the 12th of January, as before stated, he followed them up with a carefully prepared and well-arranged speech, in which he made a severe arraignment of President Polk and justified the pertinence and propriety of the inquiries he had a few days before addressed to him. The speech is too long for insertion here. It was constructed much after the manner of a legal argument. Reviewing the evidence furnished by the President in his various messages, he undertook to "smoke him out" with this: "Let the President answer the interrogatories I proposed, as before mentioned, or other similar ones. Let him answer fully, fairly, candidly. Let him answer with facts, not with arguments. Let him remember, he sits where Washington sat; and so remembering, let him answer as Washington would answer. As a nation should not, and the Almighty will not, be evaded, so let him attempt no evasion, no equivocation. And if, so answering, he can show the soil was ours where the first blood of the war was shed; that it was not within an inhabited country, or if within such; that the inhabitants had submitted themselves to the civil authority of Texas or of the United States; and that the same is true of the site of Fort Brown, then I am with him for his justification... But if he cannot or will not do this—if, on any pretence, or no pretence, he shall refuse or omit it—then I shall be fully convinced of what I more than suspect already—that he is deeply conscious of being in the wrong; that he feels the blood of this war, like the blood of Abel, is crying to Heaven against him; that he ordered General Taylor into the midst of a peaceful Mexican settlement purposely to bring on a war; that, originally having some strong motive—which I will not now stop to give my opinion concerning—to involve the countries in a war, and trusting to escape scrutiny by fixing the public gaze upon the exceeding brightness of military glory,—that attractive rainbow that rises in showers of blood, that serpent's eye that charms to destroy,—he plunged into it, and has swept on and on, till disappointed in his calculation of the ease with which Mexico might be subdued, he now finds himself he knows not where. He is a bewildered, confounded, and miserably perplexed man. God grant that he may be able to show that there is not something about his conscience more painful than all his mental perplexity." This speech, however clear may have been its reasoning, however rich in illustration, in restrained and burning earnestness, yet was unsuccessful in "smoking out" the President. He remained within the official seclusion his position gave him, and declined to answer. In fact it is doubtless true that Lincoln anticipated no response, but simply took that means of defining clearly his own position.
On the 19th inst., having occasion to write me with reference to a note with which one of our clients, one Louis Candler, had been "annoying" him, not the least of which annoyance," he complains, "is his cursed unreadable and ungodly handwriting," he adds a line, in which with noticeable modesty he informs me: "I have made a speech, a copy of which I send you by mail." He doubtless felt he was taking rather advanced and perhaps questionable ground. And so he was, for very soon after, murmurs of dissatisfaction began to run through the Whig ranks. I did not, as some of Lincoln's biographers would have their readers believe, inaugurate this feeling of dissatisfaction. On the contrary, as the law partner of the Congress-man, and as his ardent admirer, I discouraged the defection all I could. Still, when I listened to the comments of his friends everywhere after the delivery of his speech, I felt that he had made a mistake. I therefore wrote him to that effect, at the same time giving him my own views, which I knew were in full accord with the views of his Whig constituents. My argument in substance was: That the President of the United States is Commander-in-Chief of the Army and Navy; that as such commander it was his duty, in the absence of Congress, if the country was about to be invaded and armies were organized in Mexico for that purpose, to go—if necessary—into the very heart of Mexico and prevent the invasion. I argued further that it would be a crime in the Executive to let the country be invaded in the least degree. The action of the President was a necessity, and under a similar necessity years afterward Mr. Lincoln himself emancipated the slaves, although he had no special power under the Constitution to do so. In later days, in what is called the Hodges letter, concerning the freedom of the slaves, he used this language: "I felt that measures otherwise unconstitutional might become lawful by becoming indispensable." Briefly stated, that was the strain of my argument. My judgment was formed on the law of nations and of war. If the facts were as I believed them, and my premises correct, then I assumed that the President's acts became lawful by becoming indispensable.
February 1 he wrote me, "Dear William: You fear that you and I disagree about the war. I regret this, not because of any fear we shall remain disagreed after you have read this letter, but because if you misunderstand I fear other good friends may also."
Speaking of his vote in favor of the amendment to the supply bill proposed by George Ashmun, of Massachusetts, he continues:
"That vote affirms that the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President; and I will stake my life that if you had been in my place you would have voted just as I did. Would you have voted what you felt and knew to be a lie? I know you would not. Would you have gone out of the House,—skulked the vote? I expect not. If you had skulked one vote you would have had to skulk many more before the close of the session. Richardson's resolutions, introduced before I made any move or gave any vote upon the subject, make the direct question of the justice of the war; so that no man can be silent if he would. You are compelled to speak; and your only alternative is to tell the truth or tell a lie. I cannot doubt which you would do... I do not mean this letter for the public, but for you. Before it reaches you you will have seen and read my pamphlet speech and perhaps have been scared anew by it. After you get over your scare read it over again, sentence by sentence, and tell me honestly what you think of it. I condensed all I could for fear of being cut off by the hour rule; and when I got through I had spoken but forty-five minutes.
"Yours forever,
"A. Lincoln."
I digress from the Mexican war subject long enough to insert, because in the order of time it belongs here, a characteristic letter which he wrote me regarding a man who was destined at a later day to play a far different rôle in the national drama. Here it is:
"Washington, Feb. 2, 1848.
"Dear William:
"I just take up my pen to say that Mr. Stephens, of Georgia, a little, slim, pale-faced, consumptive man, with a voice like Logan's, has just concluded the very best speech of an hour's length I ever heard. My old, withered, dry eyes are full of tears yet. If he writes it out anything like he delivered it our people shall see a good many copies of it.
"Yours truly,
"A. Lincoln."
To Wm. H. Herndon, Esq.
February 15 he wrote me again in criticism of the President's invasion of foreign soil. He still believed the Executive had exceeded the limit of his authority. "The provision of the Constitution giving the war-making power to Congress," he insists, "was dictated, as I understand it, by the following reasons: kings had always been involving and impoverishing their people in wars, pretending generally, if not always, that the good of the people was the object. This, our convention understood to be the most oppressive of all kingly oppressions; and they resolved to so frame the Constitution that no one man should hold the power of bringing this oppression upon us. But your view destroys the whole matter, and places our President where kings have always stood."
In June the Whigs met in national convention at Philadelphia to nominate a candidate for President. Lincoln attended as a delegate. He advocated the nomination of Taylor because of his belief that he could be elected, and was correspondingly averse to Clay because of the latter's signal defeat in 1844. In a letter from Washington a few days after the convention he predicts the election of "Old Rough." He says: "In my opinion we shall have a most overwhelming glorious triumph. One unmistakable sign is that all the odds and ends are with us—Barn-burners, Native Americans, Tyler-men, disappointed office-seeking Locofocos, and the Lord knows what not.... Taylor's nomination takes the Locos on the blind side. It turns the war thunder against them. The war is now to them the gallows of Haman, which they built for us and on which they are doomed to be hanged themselves."
Meanwhile, in spite of the hopeful view Lincoln seemed to take of the prospect, things in his own district were in exceedingly bad repair. I could not refrain from apprising him of the extensive defections from the party ranks, and the injury his course was doing him. My object in thus writing to him was not to threaten him. Lincoln was not a man who could be successfully threatened; one had to approach him from a different direction. I warned him of public disappointment over his course, and I earnestly desired to prevent him from committing what I believed to be political suicide. June 22d he answered a letter I had written him on the 15th. He had just returned from a Whig caucus held in relation to the coming Presidential election. "The whole field of the nation was scanned; all is high hope and confidence," he said, exultingly. "Illinois is expected to better her condition in this race. Under these circumstances judge how heartrending it was to come to my room and find and read your discouraging letter of the 15th." But still he does not despair. "Now, as to the young men," he says, "you must not wait to be brought forward by the older men. For instance, do you suppose that I should ever have got into notice if I had waited to be hunted up and pushed forward by older men? You young men get together and form a Rough and Ready club, and have regular meetings and speeches. Take in everybody that you can get.... As you go along gather up all the shrewd, wild boys about town, whether just of age or a little under age. Let every one play the part he can play best—some speak, some sing, and all halloo. Your meetings will be of evenings; the older men and the women will go to hear you, so that it will not only contribute to the election of 'Old Zack,' but will be an interesting pastime and improving to the faculties of all engaged." He was evidently endeavoring through me to rouse up all the enthusiasm among the youth of Springfield possible under the circumstances. But I was disposed to take a dispirited view of the situation, and therefore was not easily warmed up. I felt at this time, somewhat in advance of its occurrence, the death throes of the Whig party. I did not conceal my suspicions, and one of the Springfield papers gave my sentiments liberal quotation in its columns. I felt gloomy over the prospect, and cut out these newspaper slips and sent them to Lincoln. Accompanying these I wrote him a letter equally melancholy in tone, in which among other things I reflected severely on the stubbornness and bad judgment of the old fossils in the party, who were constantly holding the young men back. This brought from him a letter, July 10, 1848, which is so clearly Lincolnian and so full of plain philosophy, that I copy it in full. Not the least singular of all is his allusion to himself as an old man, although he had scarcely passed his thirty-ninth year.
"Washington, July 10, 1848.
"Dear William:
"Your letter covering the newspaper slips was received last night. The subject of that letter is exceedingly painful to me, and I cannot but think there is some mistake in your impression of the motives of the old men. I suppose I am now one of the old men; and I declare on my veracity, which I think is good with you, that nothing could afford me more satisfaction than to learn that you and others of my young friends at home were doing battle in the contest and endearing themselves to the people and taking a stand far above any I have ever been able to reach in their admiration. I cannot conceive that other men feel differently. Of course I cannot demonstrate what I say; but I was young once, and I am sure I was never ungenerously thrust back. I hardly know what to say. The way for a young man to rise is to improve himself every way he can, never suspecting that anybody wishes to hinder him. Allow me to assure you that suspicion and jealousy never did help any man in any situation. There may sometimes be ungenerous attempts to keep a young man down; and they will succeed, too, if he allows his mind to be diverted from its true channel to brood over the attempted injury. Cast about and see if this feeling has not injured every person you have ever known to fall into it.
"Now, in what I have said I am sure you will suspect nothing but sincere friendship. I would save you from a fatal error. You have been a laborious, studious young man. You are far better informed on almost all subjects than I ever have been. You cannot fail in any laudable object unless you allow your mind to be improperly directed. I have some the advantage of you in the world's experience merely by being older; and it is this that induces me to advise.
"Your friend, as ever,
"A. Lincoln."

Before the close of the Congressional session he made two more speeches. One of these, which he hastened to send home in pamphlet form, and which he supposes "nobody will read," was devoted to the familiar subject of internal improvements, and deserves only passing mention. The other, delivered on the 27th of July, was in its way a masterpiece; and it is no stretch of the truth to say that while intended simply as a campaign document and devoid of any effort at classic oratory, it was, perhaps, one of the best speeches of the session. It is too extended for insertion here without abridgment; but one who reads it will lay it down convinced that Lincoln's ascendency for a quarter of a century among the political spirits in Illinois was by no means an accident; neither will the reader wonder that Douglas, with all his forensic ability, averted, as long as he could, a contest with a man whose plain, analytical reasoning was not less potent than his mingled drollery and caricature were effective. The speech in the main is an arraignment of General Cass, the Democratic candidate for President, who had already achieved great renown in the political world, principally on account of his career as a soldier in the war of 1812, and is a triumphant vindication of his Whig opponent, General Taylor, who seemed to have had a less extensive knowledge of civil than of military affairs, and was discreetly silent about both. Lincoln caricatured the military pretensions of the Democratic candidate in picturesque style. This latter section of the speech has heretofore been omitted by most of Mr. Lincoln's biographers because of its glaring inappropriateness as a Congressional effort. I have always failed to see wherein its comparison with scores of others delivered in the halls of Congress since that time could in any way detract from the fame of Mr. Lincoln, and I therefore reproduce it here:
"But the gentleman from Georgia [Mr. Iverson] further says, we have deserted all our principles, and taken shelter under General Taylor's military coattail; and he seems to think this is exceedingly degrading. Well, as his faith is, so be it unto him. But can he remember no other military coat-tail, under which a certain other party have been sheltering for near a quarter of a century? Has he no acquaintance with the ample military coat-tail of General Jackson? Does he not know that his own party have run the last five Presidential races under that coat-tail? and that they are now running the sixth under the same cover? Yes, sir, that coat-tail was used not only for General Jackson himself, but has been clung to with the grip of death by every Democratic candidate since. You have never ventured, and dare not now venture from under it. Your campaign papers have constantly been 'Old Hickory's,' with rude likenesses of the old general upon them; hickory poles and hickory brooms your never-ending emblems. Mr. Polk himself was 'Young Hickory,' 'Little Hickory,' or something so; and even now your campaign paper here is proclaiming that Cass and Butler are of the 'Hickory stripe.' No, sir, you dare not give it up. Like a horde of hungry ticks, you have stuck to the tail of the Hermitage lion to the end of his life; and you are still sticking to it, and drawing a loathsome sustenance from it, after he is dead. A fellow once advertised that he had made a discovery by which he could make a new man out of an old one and have enough of the stuff left to make a little yellow dog. Just such a discovery has General Jackson's popularity been to you. You not only twice made Presidents of him out of it, but you have enough of the stuff left to make Presidents of several comparatively small men since; and it is your chief reliance now to make still another.
"Mr. Speaker, old horses and military coat-tails, or tails of any sort, are not figures of speech such as I would be the first to introduce into discussion here; but as the gentleman from Georgia has thought fit to introduce them, he and you are welcome to all you have made or can make by them.
"If you have any more old horses, trot them out; any more tails, just cock them and come at us. I repeat, I would not introduce this mode of discussion here; but I wish gentlemen on the other side to understand that the use of degrading figures is a game at which they may find themselves unable to take all the winnings. [A voice 'No, we give it up.'] Aye! you give it up, and well you may; but for a very different reason from that which you would have us understand. The point—the power to hurt—of all figures consists in the truthfulness of their application; and, understanding this, you may well give it up. They are weapons which hit you, but miss us.
"But in my hurry I was very near closing on this subject of military tails before I was done with it. There is one entire article of the sort I have not discussed yet; I mean the military tail you Democrats are now engaged in dove-tailing on to the great Michigander. Yes, sir, all his biographers (and they are legion) have him in hand, tying him to a military tail, like so many mischievous boys tying a dog to a bladder of beans. True, the material is very limited, but they are at it might and main. He invaded Canada without resistance, and he outvaded it without pursuit. As he did both under orders, I suppose there was to him neither credit nor discredit; but they are made to constitute a large part of the tail. He was not at Hull's surrender, but he was close by; he was volunteer aid to General Harrison on the day of the battle of the Thames; and as you said in 1840 Harrison was picking whortleberries two miles off while the battle was fought, I suppose it is a just conclusion with you to say Cass was aiding Harrison to pick whortleberries. This is about all, except the mooted question of the broken sword. Some authors say he broke it: some say he threw it away; and some others, who ought to know, say nothing about it. Perhaps it would be a fair historical compromise to say if he did not break it, he did not do anything else with it.
"By the way, Mr. Speaker, did you know I am a military hero? Yes, sir, in the days of the Black Hawk war, I fought, bled, and came away. Speaking of General Cass's career, reminds me of my own. I was not at Stillman's defeat, but I was about as near it as Cass was to Hull's surrender; and, like him, I saw the place very soon afterward. It is quite certain I did not break my sword, for I had none to break, but I bent my musket pretty badly on one occasion. If Cass broke his sword, the idea is, he broke it in desperation; I bent the musket by accident. If General Cass went in advance of me picking whortleberries, I guess I surpassed him in charges upon the wild onions. If he saw any live fighting Indians, it was more than I did, but I had a good many bloody struggles with the mosquitos; and, although I never fainted from loss of blood, I can truly say I was often very hungry. Mr. Speaker, if ever I should conclude to doff whatever our Democratic friends may suppose there is of black-cockade Federalism about me, and, thereupon they shall take me up as their candidate for the Presidency, I protest that they shall not make fun of me as they have of General Cass by attempting to write me into a military hero."
After the adjournment of Congress on the 14th of August, Lincoln went through New York and some of the New England States making a number of speeches for Taylor, none of which, owing to the limited facilities attending newspaper reporting in that day, have been preserved. He returned to Illinois before the close of the canvass and continued his efforts on the stump till the election. At the second session of Congress, which began in December, he was less conspicuous than before. The few weeks spent with his constituents had perhaps taught him that in order to succeed as a Congressman it is not always the most politic thing to tell the truth because it is the truth, or do right because it is right. With the opening of Congress, by virtue of the election of Taylor, the Whigs obtained the ascendency in the control of governmental machinery. He attended to the duties of the Congressional office diligently and with becoming modesty. He answered the letters of his constituents, sent them their public documents, and looked after their pension claims. His only public act of any moment was a bill looking to the emancipation of the slaves in the District of Columbia. He interested Joshua R. Giddings and others of equally as pronounced anti-slavery views in the subject, but his bill eventually found a lodgment on "the table," where it was carefully but promptly laid by a vote of the House.
Meanwhile, being chargeable with the distribution of official patronage, he began to flounder about in explanation of his action in a sea of seemingly endless perplexities. His recommendation of the appointment of T. R. King to be Register or Receiver of the Land Office had produced no little discord among the other aspirants for the place. He wrote to a friend who endorsed and urged the appointment, "either to admit it is wrong, or come forward and sustain him." He then transmits to this same friend a scrap of paper—probably a few lines approving the selection of King—which is to be copied in the friend's own handwriting. "Get everybody," he insists, "(not three or four, but three or four hundred) to sign it, and then send to me. Also have six, eight, or ten of our best known Whig friends to write me additional letters, stating the truth in this matter as they understood it. Don't neglect or delay in the matter. I understand," he continues, "information of an indictment having been found against him three years ago for gaming or keeping a gaming house has been sent to the Department." He then closes with the comforting assurance: "I shall try to take care of it at the Department till your action can be had and forwarded on." And still people insist that Mr. Lincoln was such a guileless man and so free from the politician's sagacity!
In June I wrote him regarding the case of one Walter Davis, who was soured and disappointed because Lincoln had overlooked him in his recommendation for the Springfield post-office. "There must be some mistake," he responds on the 5th, "about Walter Davis saying I promised him the post-office. I did not so promise him. I did tell him that if the distribution of the offices should fall into my hands he should have something; and if I shall be convinced he has said any more than this I shall be disappointed. I said this much to him because, as I understand, he is of good character, is one of the young men, is of the mechanics, is always faithful and never troublesome, a Whig, and is poor, with the support of a widow-mother thrown almost exclusively on him by the death of his brother. If these are wrong reasons then I have been wrong; but I have certainly not been selfish in it, because in my greatest need of friends he was against me and for Baker."
Judge Logan's defeat in 1848 left Lincoln still in a measure in charge of the patronage in his district. After his term in Congress expired the "wriggle and struggle" for office continued; and he was often appealed to for his influence in obtaining, as he termed it, "a way to live without work." Occasionally, when hard pressed, he retorted with bitter sarcasm. I append a letter written in this vein to a gentleman still living in central Illinois, who, I suppose, would prefer that his name should be withheld:
"Springfield, Dec. 15, 1849.
"——— Esq.
"Dear Sir:
"On my return from Kentucky I found your letter of the 7th of November, and have delayed answering it till now for the reason I now briefly state. From the beginning of our acquaintance I had felt the greatest kindness for you and had supposed it was reciprocated on your part. Last summer, under circumstances which I mentioned to you, I was painfully constrained to withhold a recommendation which you desired, and shortly afterwards I learned, in such a way as to believe it, that you were indulging in open abuse of me. Of course my feelings were wounded. On receiving your last letter the question occurred whether you were attempting to use me at the same time you would injure me, or whether you might not have been misrepresented to me. If the former, I ought not to answer you; if the latter, I ought, and so I have remained in suspense. I now enclose you the letter, which you may use if you see fit.
"Yours, etc.
"A. Lincoln."
No doubt the man, when Lincoln declined at first to recommend him, did resort to more or less abuse. That would have been natural, especially with an unsuccessful and disappointed office-seeker. I am inclined to the opinion, and a careful reading of the letter will warrant it, that Lincoln believed him guilty. If the recommendation which Lincoln, after so much reluctance, gave was ever used to further the applicant's cause I do not know it.
With the close of Lincoln's congressional career he drops out of sight as a political factor, and for the next few years we take him up in another capacity. He did not solicit or contend for a renomination to Congress, and such was the unfortunate result of his position on public questions that it is doubtful if he could have succeeded had he done so.
Immediately following the adjournment of Congress in August, 1848, Mr. Lincoln set out for Massachusetts to take part in the presidential campaign. Being the only Whig in the delegation in Congress from Illinois, he was expected to do gallant work for his chief, General Taylor. As this chapter in his career seems to have escaped the notice of former biographers, the writers have thought best to insert here extracts from the various descriptions which they have been able to obtain of the tour and its incidents.
One of the most interesting accounts is from the pen of Hon. Edward L. Pierce, of Milton, Mass., whose memory is not less tenacious than is his style happy and entertaining. He says:
"It is not known at whose instance Mr. Lincoln made his visits to Massachusetts in 1848. The Whigs of the State were hard pressed at the time by a formidable secession growing out of General Taylor's nomination, and led by Henry Wilson, Charles Francis Adams, Charles Allen, Charles Sumner, Stephen C. Phillips, John G. Palfrey, E. Rockwood Hoar, Richard H. Dana, Jr., Anson Burlingame, John A. Andrew, and other leaders who had great weight with the people and were all effective public speakers. Generally the State had had a sufficient supply of orators of its own, but in that emergency some outside aid was sought. Gen. Leslie Coombs was invited from Kentucky, and Mr. Lincoln was induced to come also, on his way home from Washington at the end of the session.
"The Whig State Convention met at Worcester, September 13th. The Free-Soil secession was greater here than in any part of the State. It was led by Judge Charles Allen, who was elected to Congress from the district. There was a meeting of the Whigs at the City Hall on the evening before the convention. Ensign Kellogg presided and except his introductory remarks, Mr. Lincoln's speech, which lasted one and a half or two hours, was the only one. The Boston Advertiser's report was nearly a column in length. It said: 'Mr. Lincoln has a very tall and thin figure, with an intellectual face, showing a searching mind and a cool judgment. He spoke in a clear and cool and very eloquent manner, carrying the audience with him in his able arguments and brilliant illustrations, only interrupted by warm and frequent applause. He began by expressing a real feeling of modesty in addressing an audience "this side of the mountains," a part of the country where, in the opinion of the people of his section, everybody was supposed to be instructed and wise. But he had devoted his attention to the question of the coming presidential election, and was not unwilling to exchange with all whom he might meet the ideas to which he had arrived.' This passage gives some reason to suppose that, conscious of his powers, he was disposed to try them before audiences somewhat different from those to which he had been accustomed, and therefore he had come to New England. The first part of his speech was a reply, at some length, to the charge that General Taylor had no political principles; and he maintained that the General stood on the true Whig principle, that the will of the people should prevail against executive influence or the veto power of the President. He justified the Whigs for omitting to put a national platform before the people, and, according to a Free-Soil report, said that a political platform should be frowned down whenever and wherever presented. But the stress of his speech was against the Free-Soilers, whose position as to the exclusion of slavery from the territories, he claimed, to be that of the Whigs; while the former were subject to the further criticism that they had but one principle, reminding him of the Yankee peddler, who, in offering for sale a pair of pantaloons, described them as 'large enough for any man, and small enough for any boy,' He condemned the Free-Soilers as helping to elect Cass, who was less likely to promote freedom in the territories than Taylor and passed judgment on them as having less principle than any party. To their defence of their right and duty to act independently, 'leaving consequences to God,' he replied, that 'when divine or human law does not clearly point out what is our duty, it must be found out by an intelligent judgment, which takes in the results of action.' The Free-Soilers were much offended by a passage which does not appear in the Whig report. Referring to the anti-slavery men, he said they were better treated in Massachusetts than in the West, and, turning to William S. Lincoln, of Worcester, who had lived in Illinois, he remarked that in that State they had recently killed one of them. This allusion to Lovejoy's murder at Alton, was thought by the Free-Soilers to be heartless, and it was noted that Mr. Lincoln did not repeat it in other speeches. It was probably a casual remark, which came into his mind at the moment, and meant but little, if anything. Cheers were given at the end of the speech for the eloquent Whig member from Illinois. The Whig reports spoke of the speech as 'masterly and convincing' and 'one of the best ever made in Worcester;' while the Free-Soil report describes it as 'a pretty tedious affair,' The next morning he spoke at an open-air meeting, following Benjamin F. Thomas and Ex-Governor Levi Lincoln, but his speech was cut short by the arrival by train of the delegates from Boston, who, with the speakers, proceeded at once to the hall. The convention listened to a long address to the people, reported by a committee, and then to a brilliant speech from Rufus Choate, followed by others from Robert C. Winthrop, the Whig Speaker of the House of Representatives, Charles Hudson, M. C., and Benjamin F. Thomas. Mr. Lincoln listened to these, but was not himself called out.
Mr. Lincoln spoke at Washingtonian Hall, Bromfield street, Boston, on the 15th, his address lasting an hour and a half, and, according to the report, 'seldom equaled for sound reasoning, cogent argument and keen satire.' Three cheers were given for 'the Lone Star of Illinois,' on account of his being the only Whig member from the State. He spoke at Lowell the 16th, and at the Lower Mills, Dorchester, now a part of Boston, on Monday, the 18th. At this last place the meeting was held in Richmond Hall, and the chairman was N. F. Safford, living till 1891, who introduced him as one of the Lincolns of Hingham, and a descendant of Gen. Benjamin Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln, as he began, disclaimed descent from the Revolutionary officer, but said, playfully, that he had endeavored in Illinois to introduce the principles of the Lincolns of Massachusetts. A few of his audience are still living. They were struck with his height, as he arose in the low-studded hall. He spoke at Chelsea on the 19th, and a report states that his speech 'for aptness of illustration, solidity of argument, and genuine eloquence, was hard to beat.' Charles Sumner had defended the Free-Soil cause at the same place the evening before. Mr. Lincoln spoke at Dedham, in Temperance Hall, on the 20th, in the daytime. Two Whig nominating conventions met there the same day, at one of which Horace Mann was nominated for a second term in Congress. A report states that he 'spoke in an agreeable and entertaining way.' He left abruptly to take a train in order to meet another engagement, and was escorted to the station by the Dorchester band. The same evening he spoke at Cambridge. The report describes him as 'a capital specimen of a Sucker Whig, six feet at least in his stockings.' Of his speech, it was said that 'it was plain, direct and to the point, powerful and convincing, and telling with capital effect upon the immense audience. It was a model speech for the campaign.' His last speech was on the 22d, at Tremont Temple, with George Lunt presiding, in company with William H. Seward, whom he followed, ending at 10.30 P. M. The Whig newspaper, the Atlas, the next morning gave more than a column to Mr. Seward's speech, but stated that it had no room for the notes which had been taken of Mr. Lincoln's, describing it, however, as 'powerful and convincing, and cheered to the echo.' The Free-Soil paper (Henry Wilson's) refers to the meeting, mentioning Mr. Seward, but not Mr. Lincoln. The next day Mr. Lincoln left Boston for Illinois. The 'Atlas' on Monday contained this paragraph: 'In answer to the many applications which we daily receive from different parts of the State for this gentleman to speak, we have to say that he left Boston on Saturday morning on his way home to Illinois.'
It is evident from all the contemporaneous reports, that Mr. Lincoln made a marked impression on all his audiences. Their attention was drawn at once to his striking figure; they enjoyed his quaintness and humor; and they recognized his logical power and his novel way of putting things. Still, so far as his points are given in the public journals, he did not rise at any time above partisanship, and he gave no sign of the great future which awaited him as a political antagonist, a master of language, and a leader of men. But it should be noted, in connection with this estimate, that the Whig case, as put in that campaign, was chiefly one of personalities, and was limited to the qualities and career of Taylor as a soldier, and to ridicule of his opponent, General Cass. Mr. Lincoln, like the other Whig speakers, labored to prove that Taylor was a Whig.
Seward's speech at Tremont Temple, to which Lincoln listened, seems to have started a more serious vein of thought on slavery in the mind of the future President. That evening, when they were together as fellow-lodgers at a hotel, Lincoln said: "Governor Seward, I have been thinking about what you said in your speech. I reckon you are right. We have got to deal with this slavery question, and got to give much more attention to it hereafter than we have been doing." *
* Seward's Life, vol. ii, p. 80.
It is curious now to recall how little support, in the grave moments of his national career which came twelve years later, Mr. Lincoln received from the Whigs of Massachusetts, then conspicuous in public life, whom he met on his visit. Mr. Lunt, who presided at Faneuil Hall, was to the end of his life a pro-slavery conservative. Judge Thomas, in Congress, during the early part of the civil war, was obstructive to the President's policy. Mr. Winthrop voted against Lincoln in 1860 and 1864. Mr. Choate died in 1859, but, judged by his latest utterances, his marvelous eloquence would have been no patriotic inspiration if he had outlived the national struggle. On the other hand, the Free-Soilers of Massachusetts, whom Mr. Lincoln came here to discredit, became, to a man, his supporters; and on many of their leaders he relied as his support in the great conflict. Sumner was chairman of the Senate Committee on Foreign Affairs during the war; Wilson was chairman of the Committee on Military Affairs; Adams was Minister to England; and Andrew War-Governor of the State. These, as well as Palfrey, Burlingame and Dana, who, in 1848, almost every evening addressed audiences against both Taylor and Cass, while Mr. Lincoln was here, were earnest and steadfast in their devotion to the Government during the civil war; and the last three received important appointments from him. How the press treated Mr. Lincoln may be learned from the following editorial in the Lowell Journal and Courier, in its issue of September 18, 1848:
Whig Meeting.
The sterling Whigs of Lowell came together last Saturday evening, at the City Hall. The meeting was called to order by the Chairman of the Whig Central Committee, Hon. Linus Child. Homer Bartlett, Esq., was chosen chairman, and A. Gilman, secretary. After a few animating remarks from the Chairman, he introduced George Woodman, Esq., of Boston, who made a very pertinent and witty offhand speech, which was frequently interrupted by the spontaneous plaudits of the audience. At the close of his speech Mr. Woodman introduced the Hon. Abraham Lincoln, of Illinois. It would be doing injustice to his speech to endeavor to give a sketch of it. It was replete with good sense, sound reasoning, and irresistible argument, and spoken with that perfect command of manner and matter which so eminently distinguishes the Western orators. He disabused the public of the erroneous suppositions that Taylor was not a Whig; that Van Buren was anything more than a thorough Loco-foco on all subjects other than Free Territory, and hardly safe on that; and showed up, in a masterly manner, the inconsistency and folly of those Whigs, who, being drawn off from the true and oldest free-soil organization known among the parties of the Union, would now lend their influence and votes to help Mr. Van Buren into the presidential chair. His speech was interrupted by frequent cheers of the audience. At the close the secretary, by request, read the letter of General Taylor to Captain Alison, which had just been received, in which he says: "From the beginning till now, I have declared myself to be a Whig, on all proper occasions."
Ex-Governor Gardner, after a brief history of the Whig Convention at Worcester, Mass., contributes this pleasing reminiscence:
"Gov. Levi Lincoln, the oldest living Ex-Governor of Massachusetts, resided in Worcester. He was a man of culture and wealth; lived in one of the finest houses in that town, and was a fine specimen of a gentleman of the old school. It was his custom to give a dinner party when any distinguished assemblage took place in Worcester, and to invite its prominent participants. He invited to dine, on this occasion, a company of gentlemen, among them myself, who was a delegate from Boston. The dining-room and table arrangements were superb, the dinner exquisite, the wines abundant, rare, and of the first quality.
"I well remember the jokes between Governor Lincoln and Abraham Lincoln as to their presumed relationship. At last the latter said: 'I hope we both belong, as the Scotch say, to the same clan; but I know one thing, and that is, that we are both good Whigs.'
"That evening there was held in Mechanics' Hall (an immense building) a mass-meeting of delegates and others, and Lincoln was announced to speak. No one there had ever heard him on the stump, and in fact knew anything about him. When he was announced, his tall, angular, bent form, and his manifest awkwardness and low tone of voice, promised nothing interesting. But he soon warmed to his work. His style and manner of speaking were novelties in the East. He repeated anecdotes, told stories admirable in humor and in point, interspersed with bursts of true eloquence, which constantly brought down the house. His sarcasm of Cass, Van Buren and the Democratic party was inimitable, and whenever he attempted to stop, the shouts of 'Go on! go on!' were deafening. He probably spoke over an hour, but so great was the enthusiasm time could not be measured. It was doubtless one of the best efforts of his life. He spoke a day or two afterward in Faneuil Hall, with William H. Seward, but I did not hear him.
"In 1861 business called me to Washington, and I paid my respects to the President at the White House. He came forward smiling and with extended hand, saying: 'You and I are no strangers; we dined together at Governor Lincoln's in 1848.' When one remembers the increased burden on the President's mind at this trying time, the anxieties of the war, the army, the currency, and the rehabilitating the civil officers of the country, it seemed astonishing to me to hear him continue: 'Sit down. Yes, I had been chosen to Congress then from the wild West, and with hayseed in my hair I went to Massachusetts, the most cultured State in the Union, to take a few lessons in deportment. That was a grand dinner—a superb dinner; by far the finest I ever saw in my life. And the great men who were there, too! Why, I can tell you just how they were arranged at table. He began at one end, and mentioned the names in order, and, I verily believe, without the omission of a single one."
This chapter would be incomplete without the account of Mr. George H. Monroe, a young man living in Dedham, Mass., in 1848, who, forty years later, wrote out his recollections of Mr. Lincoln's visit to that town. Mr. Monroe has a vivid and retentive memory, and has since been identified with the public life and journalism of Massachusetts:—
"Massachusetts, on account of the great defection of Whigs to the Free-Soilers, and Daniel Webster's sudden and damaging attitude toward General Taylor's nomination to the presidency, began to be considered rather doubtful ground for the Whigs. The national committee sent Mr. Lincoln to the State, after Congress had adjourned, to make some speeches. Our people knew very little about him then. I lived in Dedham, the shire town of Norfolk county, and was secretary of a Whig club there. One of the county courts was in session, and it was determined to have a meeting in the daytime, before it adjourned. I was commissioned to go to Boston to engage the speaker. I went at once to see my friend, Colonel Schouler, of the Boston Atlas. He told me that a new man had just come into the State from Washington, who, he thought, would answer our purpose exactly, and said he would get him for me if possible. That man was Abraham Lincoln. When the day for the meeting came I went to the Tremont House and found Mr. Lincoln there. I remember well how tall, awkward and ungainly he was in appearance. I remember how reticent he was, too, but I attributed this to my own youth, for I was only just past twenty-one years of age. He was as sober a man in point of expression as ever I saw. There were others in the party later, but in the journey out in the cars he scarcely said a word to one of us. I did not see him smile on any part of the journey. He seemed uneasy and out of sympathy with his surroundings, as it were. I should say that the atmosphere of Boston was not congenial to him. We took him to one of the most elegant houses in the town of Dedham, and here he seemed still less, if possible, at home. The thing began to look rather blue for us. When we went over to the hall it was not much better. It was a small hall, and it was only about half full; for Mr. Lincoln had not spoken in Boston yet, and there was nothing in his name particularly to attract. But at last he arose to speak, and almost instantly there was a change. His indifferent manner vanished as soon as he opened his mouth. He went right to his work. He wore a black alpaca sack, and he turned up the sleeves of this, and then the cuffs of his shirt. Next he loosened his necktie, and soon after he took it off altogether. All the time he was gaining upon his audience. He soon had it as by a spell. I never saw men more delighted. His style was the most familiar and off-hand possible. His eye had lighted up and changed the whole expression of his countenance. He began to bubble out with humor. But the chief charm of the address lay in the homely way he made his points. There was no attempt at eloquence or finish of style. But, for plain pungency of humor, it would have been difficult to surpass his speech. In this making of points which come home to the general mind, I don't think Lincoln was ever surpassed by any American orator. I often thought of it afterward, when he was exhibiting this faculty in a more ambitious way on a broader field. The speech which I am trying to describe was not a long one. It abruptly ended in a half-hour's time. The bell that called to the steam cars sounded. Mr. Lincoln instantly stopped. 'I am engaged to speak at Cambridge to-night,' said he, 'and I must leave.' The whole audience seemed to rise in protest. 'Oh, no! go on! finish it!' was heard on every hand. One gentleman arose and pledged himself to take his horse and carry him across the country. But Mr. Lincoln was inexorable. 'I can't take any risks,' said he.
"'I have engaged to go to Cambridge, and I must be there. I came here as I agreed, and I am going there in the same way.' A more disappointed audience was never seen; but Mr. Lincoln had fairly wakened it up, and it stayed through the afternoon and into the evening to listen to other speakers. We tried to get him to come again, but it was impossible. I heard the speech finished afterward in Tremont Temple, Boston; and it is a notable fact that on the same evening, and from the same platform, William H. Seward also spoke, and made the only political speech he ever delivered in Boston. Who could have dreamed then that in Lincoln we were listening to the man who was to be the future president of the United States, and to leave a reputation second only to that of Washington! Mr. Lincoln moved his Boston audience in much the same way I have described, but Mr. Seward made the first speech, and was looked upon as the chief star, of course. Seward's speech was much more ambitious and comprehensive than that of Lincoln. The latter had not begun to treat broad principles in the 1848 campaign. Mr. Seward's argument was a triumph of intellect, after the most careful preparation. I don't think Mr. Lincoln had ever written his speech at all. He aimed at not much more than to be bright, effective and taking with his audience, and his success was perfect here."

After the wedding of Lincoln and Miss Todd at the Edwards mansion we hear but little of them as a married couple till the spring of 1843, when the husband writes to his friend Speed, who had been joined to his "black-eyed Fanny" a little over a year, with regard to his life as a married man. "Are you possessing houses and lands," he writes, "and oxen and asses and men-servants and maid-servants, and begetting sons and daughters? We are not keeping house, but boarding at the Globe Tavern, which is very well kept now by a widow lady of the name of Beck. Our room (the same Dr. Wallace occupied there) and boarding only costs us four dollars a week." Gaining a livelihood was slow and discouraging business with him, for we find him in another letter apologizing for his failure to visit Kentucky, "because," he says, "I am so poor and make so little headway in the world that I drop back in a month of idleness as much as I gain in a year's sowing." But by dint of untiring efforts and the recognition of influential friends he managed through rare frugality to move along. In his struggles, both in the law and for political advancement, his wife shared in his sacrifices. She was a plucky little woman, and in fact endowed with a more restless ambition than he. She was gifted with a rare insight into the motives that actuate mankind, and there is no doubt that much of Lincoln's success was in a measure attributable to her acuteness and the stimulus of her influence. His election to Congress within four years after their marriage afforded her extreme gratification. She loved power and prominence, and when occasionally she came down to our office, it seemed to me then that she was inordinately proud of her tall and ungainly husband. She saw in him bright prospects ahead, and his every move was watched by her with the closest interest. If to other persons he seemed homely, to her he was the embodiment of noble manhood, and each succeeding day impressed upon her the wisdom of her choice of Lincoln over Douglas—if in reality she ever seriously accepted the latter's attentions. "Mr. Lincoln may not be as handsome a figure," she said one day in the office during her husband's absence, when the conversation turned on Douglas, "but the people are perhaps not aware that his heart is as large as his arms are long."
Mrs. Lincoln accompanied her husband to Washington and remained during one session of Congress. While there they boarded at the same house with Joshua R. Giddings, and when in 1856 the valiant old Abolitionist came to take part in the canvass in Illinois, he early sought out Lincoln, with whom he had been so favorably impressed several years before. On his way home from Congress Lincoln came by way of Niagara Falls and down Lake Erie to Toledo or Detroit. It happened that, some time after, I went to New York and also returned by way of Niagara Falls. In the office, a few days after my return, I was endeavoring to entertain my partner with an account of my trip, and among other things described the Falls. In the attempt I indulged in a good deal of imagery. As I warmed up with the subject my descriptive powers expanded accordingly. The mad rush of water, the roar, the rapids, and the rainbow furnished me with an abundance of material for a stirring and impressive picture. The recollection of the gigantic and awe-inspiring scene stimulated my exuberant powers to the highest pitch. After well-nigh exhausting myself in the effort I turned to Lincoln for his opinion. "What," I inquired, "made the deepest impression on you when you stood in the presence of the great natural wonder?" I shall never forget his answer, because it in a very characteristic way illustrates how he looked at everything. "The thing that struck me most forcibly when I saw the Falls," he responded, "was, where in the world did all that water come from?" He had no eye for the magnificence and grandeur of the scene, for the rapids, the mist, the angry waters, and the roar of the whirlpool, but his mind, working in its accustomed channel, heedless of beauty or awe, followed irresistibly back to the first cause. It was in this light he viewed every question. However great the verbal foliage that concealed the nakedness of a good idea Lincoln stripped it all down till he could see clear the way between cause and effect. If there was any secret in his power this surely was it.
After seeing Niagara Falls he continued his journey homeward. At some point on the way, the vessel on which he had taken passage stranded on a sand bar. The captain ordered the hands to collect all the loose planks, empty barrels and boxes and force them under the sides of the boat. These empty casks were used to buoy it up. After forcing enough of them under the vessel she lifted gradually and at last swung clear of the opposing sand bar. Lincoln had watched this operation very intently. It no doubt carried him back to the days of his navigation on the turbulent Sangamon, when he and John Hanks had rendered similar service at New Salem dam to their employer, the volatile Offut. Continual thinking on the subject of lifting vessels over sand bars and other obstructions in the water suggested to him the idea of inventing an apparatus for that purpose. Using the principle involved in the operation he had just witnessed, his plan was to attach a kind of bellows on each side of the hull of the craft just below the water line, and, by an odd system of ropes and pulleys, whenever the keel grated on the sand these bellows were to be filled with air, and thus buoyed up, the vessel was expected to float clear of the shoal. On reaching home he at once set to work to demonstrate the feasibility of his plan. Walter Davis, a mechanic having a shop near our office, granted him the use of his tools, and likewise assisted him in making the model of a miniature vessel with the arrangement as above described. Lincoln manifested ardent interest in it. Occasionally he would bring the model in the office, and while whittling on it would descant on its merits and the revolution it was destined to work in steamboat navigation. Although I regarded the thing as impracticable I said nothing, probably out of respect for Lincoln's well-known reputation as a boatman. The model was sent or taken by him to Washington, where a patent was issued, but the invention was never applied to any vessel, so far as I ever learned, and the threatened revolution in steamboat architecture and navigation never came to pass. The model still reposes in undisturbed slumber on the shelves in the Patent Office, and is the only evidence now existing of Lincoln's success as an inventor.*
* Following is a copy of Lincoln's application for the patent on his "Improved Method of Lifting Vessels Over Shoals": "What I claim as my invention, and desire to secure by letters patent, is the combination of expansible buoyant chambers placed at the sides of a vessel with the main shaft or shafts by means of the sliding spars, which pass down through the buoyant chambers and are made fast to their bottoms and the series of ropes and pulleys or their equivalents in such a manner that by turning the main shaft or shafts in one direction the buoyant chambers will be forced downwards into the water, and at the same time expanded and filled with air for buoying up the vessel by the displacement of water, and by turning the shafts in an opposite direction the buoyant chambers will be contracted into a small space and secured against injury. "A. Lincoln."
Shortly before the close of his term in Congress he appears in a new rôle. Having failed of a re-election he became an applicant for the office of Commissioner of the General Land Office. He had been urged to this step by many of his Whig friends in Illinois, but he was so hedged about with other aspirants from his own State that he soon lost all heart in the contest. He was too scrupulous, and lacked too much the essentials of self-confidence and persistence, to be a successful suitor for office. In a letter to Joshua Speed, who had written him of a favorable reference to him by Mr. Crittenden, of Kentucky,* he says, February 20, 1849, "I am flattered to learn that Mr. Crittenden has any recollection of me which is not unfavorable; and for the manifestation of your kindness towards me I sincerely thank you."
* Lincoln had asked Speed to see Crittenden (then Governor of Kentucky) and secure from the latter a recommendation for Baker, who wanted a first-class foreign mission. Crittenden did not approve of Baker, but suggested that he would favor Lincoln, whom he regarded as a rising man. Speed suggested to Lincoln to apply for the place himself. "I have pledged myself to Baker," he answered, "and cannot under any circumstances consent to the use of my name so long as he is urged for the same place."
"Still, there is nothing about me to authorize me to think of a first-class office, and a second-class one would not compensate me for being sneered at by others who want it for themselves. I believe that, so far as the Whigs in Congress are concerned, I could have the General Land Office almost by common consent; but then Sweet and Dav. Morrison and Browning and Cyrus Edwards all want it, and what is worse, while I think I could easily take it myself I fear I shall have trouble to get it for any other man in Illinois. The reason is that McGaughey, an Indiana ex-member of Congress, is here after it, and being personally known he will be hard to beat by any one who is not." But, as the sequel proved, there was no need to fear the Hoosier statesman, for although he had the endorsement of General Scott and others of equal influence, yet he was left far behind in the race, and along with him Lincoln, Morrison, Browning, and Edwards. A dark horse in the person of Justin Butterfield, sprang into view, and with surprising facility captured the tempting prize. This latter and successful aspirant was a lawyer of rather extensive practice and reputation in Chicago. He was shrewd, adroit, and gifted with a knowledge of what politicians would call good management—a quality or characteristic in which Lincoln was strikingly deficient. He had endorsed the Mexican war, but, strangely enough, had lost none of his prestige with the Whigs on that account.*
* The following letter by Butterfield's daughter is not without interest: "Chicago, Oct. l2th, 1888. "Mr. Jesse W. Weik. "Dear Sir: "My father was born in Keene, N. H., in 1790, entered Williams College, 1807, and removed to Chicago in 1835. After the re-accession of the Whigs to power he was on the 21st of June in 1849 appointed Commissioner of the Land Office by President Taylor. A competitor for the position at that time was Abraham Lincoln, who was beaten, it was said, by 'the superior dispatch of Butterfield in reaching Washington by the Northern route,' but more correctly by the paramount influence of his friend Daniel Webster. "He held the position of Land Commissioner until disabled by paralysis in 1852. After lingering for three years in a disabled ana enfeebled condition, he died at his home in Chicago, October 23d, 1855, in his sixty-third year. "Very respectfully, "Elizabeth Sawyer."
The close of Congress and the inauguration of Taylor were the signal for Lincoln's departure from Washington. He left with the comforting assurance that as an office-seeker he was by no means a success. Besides his lack of persistence, he had an unconscious feeling of superiority and pride that admitted of no such flexibility of opinion as the professional suitor for office must have, in order to succeed. He remained but a few days at his home in Illinois, however, before he again set out for Washington. The administration of President Taylor feeling that some reward was due Lincoln for his heroic efforts on the stump and elsewhere in behalf of the Whig party and its measures, had offered him the office of either Governor or Secretary of Oregon, and with the view of considering this and other offers he returned to Washington. Lincoln used to relate of this last-named journey an amusing incident illustrating Kentucky hospitality. He set out from Ransdell's tavern in Springfield, early in the morning. The only other passenger in the stage for a good portion of the distance was a Kentuckian, on his way home from Missouri. The latter, painfully impressed no doubt with Lincoln's gravity and melancholy, undertook to relieve the general monotony of the ride by offering him a chew of tobacco. With a plain "No, sir, thank you; I never chew," Lincoln declined, and a long period of silence followed. Later in the day the stranger, pulling from his pocket a leather-covered case, offered Lincoln a cigar, which he also politely declined on the ground that he never smoked. Finally, as they neared the station where horses were to be changed, the Kentuckian, pouring out a cup of brandy from a flask which had lain concealed in his satchel, offered it to Lincoln with the remark, "Well, stranger, seeing you don't smoke or chew, perhaps you'll take a little of this French brandy. It's a prime article and a good appetizer besides." His tall and uncommunicative companion declined this last and best evidence of Kentucky hospitality on the same ground as the tobacco. When they separated that afternoon, the Kentuckian, transferring to another stage, bound for Louisville, shook Lincoln warmly by the hand. "See here, stranger," he said, good-humoredly, "you're a clever, but strange companion. I may never see you again, and I don't want to offend you, but I want to say this: my experience has taught me that a man who has no vices has d———d few virtues. Good-day." Lincoln enjoyed this reminiscence of the journey, and took great pleasure in relating it. During this same journey occurred an incident for which Thomas H. Nelson, of Terre Haute, Indiana, who was appointed Minister to Chili by Lincoln, when he was President, is authority. "In the spring of 1849," relates Nelson, "Judge Abram Hammond, who was afterwards Governor of Indiana, and I arranged to go from Terre Haute to Indianapolis in the stage coach. An entire day was usually consumed in the journey. By daybreak the stage had arrived from the West, and as we stepped in we discovered that the entire back seat was occupied by a long, lank individual, whose head seemed to protrude from one end of the coach and his feet from the other. He was the sole occupant, and was sleeping soundly. Hammond slapped him familiarly on the shoulder, and asked him if he had chartered the stage for the day. The stranger, now wide awake, responded, 'Certainly not,' and at once took the front seat, politely surrendering to us the place of honor and comfort. We took in our travelling companion at a glance. A queer, odd-looking fellow he was, dressed in a well-worn and ill-fitting suit of bombazine, without vest or cravat, and a twenty-five-cent palm hat on the back of his head. His very prominent features in repose seemed dull and expressionless. Regarding him as a good subject for merriment we perpetrated several jokes. He took them all with the utmost innocence and good-nature, and joined in the laugh, although at his own expense. At noon we stopped at a wayside hostelry for dinner. We invited him to eat with us, and he approached the table as if he considered it a great honor. He sat with about half his person on a small chair, and held his hat under his arm during the meal. Resuming our journey after dinner, conversation drifted into a discussion of the comet, a subject that was then agitating the scientific world, in which the stranger took the deepest interest. He made many startling suggestions and asked many questions. We amazed him with words of learned length and thundering sound. After an astounding display of wordy pyrotechnics the dazed and bewildered stranger asked: 'What is going to be the upshot of this comet business?' I replied that I was not certain, in fact I differed from most scientists and philosophers, and was inclined to the opinion that the world would follow the darned thing off! Late in the evening we reached Indianapolis, and hurried to Browning's hotel, losing sight of the stranger altogether. We retired to our room to brush and wash away the dust of the journey. In a few minutes I descended to the portico, and there descried our long, gloomy fellow-traveller in the center of an admiring group of lawyers, among whom were Judges McLean and Huntington, Edward Hannigan, Albert S. White, and Richard W. Thompson, who seemed to be amused and interested in a story he was telling. I enquired of Browning, the landlord, who he was. "Abraham Lincoln, of Illinois, a member of Congress," was the response. I was thunderstruck at the announcement. I hastened upstairs and told Hammond the startling news, and together we emerged from the hotel by a back door and went down an alley to another house, thus avoiding further contact with our now distinguished fellow-traveller. Curiously enough, years after this, Hammond had vacated the office of Governor of Indiana a few days before Lincoln arrived in Indianapolis, on his way to Washington to be inaugurated President. I had many opportunities after the stage ride to cultivate Mr. Lincoln's acquaintance, and was a zealous advocate of his nomination and election to the Presidency. Before leaving his home for Washington, Mr. Lincoln caused John P. Usher and myself to be invited to accompany him. We agreed to join him in Indianapolis. On reaching that city the Presidential party had already arrived, and upon inquiry we were informed that the President-elect was in the dining-room of the hotel, at supper. Passing through, we saw that every seat at the numerous tables was occupied, but failed to find Mr. Lincoln. As we were nearing the door to the office of the hotel, a long arm reached to my shoulder and a shrill voice exclaimed, 'Hello, Nelson! do you think, after all, the world is going to follow the darned thing off?' It was Mr. Lincoln."
The benefits and advantages of the territorial posts offered by President Taylor to Lincoln were freely discussed by the latter's friends. Some urged his acceptance on the usual ground that when Oregon was admitted as a State, he might be its first Senator. Lincoln himself had some inclination to accept. He told me himself that he felt by his course in Congress he had committed political suicide, and wanted to try a change of locality—hence the temptation to go to Oregon. But when he brought the proposition home to his fireside, his wife put her foot squarely down on it with a firm and emphatic No. That always ended it with Lincoln. The result of the whole thing proved a fortunate deliverance for him, the propriety of which became more apparent as the years rolled by.*
* About this time Grant Goodrich, a lawyer in Chicago, proposed to take Lincoln into partnership with him. Goodrich had an extensive and paying practice there, but Lincoln refused the offer, giving as a reason that he tended to consumption, and if he removed to a city like Chicago, he would have to sit down and study harder than ever. The close application required of him and the confinement in the office, he contended, would soon kill him. He preferred going around on the circuit, and even if he earned smaller fees he felt much happier.
While a member of Congress and otherwise immersed in politics Lincoln seemed to lose all interest in the law. Of course, what practice he himself controlled passed into other hands. I retained all the business I could, and worked steadily on until, when he returned, our practice was as extensive as that of any other firm at the bar. Lincoln realized that much of this was due to my efforts, and on his return he therefore suggested that he had no right to share in the business and profits which I had made. I responded that, as he had aided me and given me prominence when I was young and needed it, I could afford now to be grateful if not generous. I therefore recommended a continuation of the partnership, and we went on as before. I could notice a difference in Lincoln's movement as a lawyer from this time forward. He had begun to realize a certain lack of discipline—a want of mental training and method. Ten years had wrought some change in the law, and more in the lawyers, of Illinois. The conviction had settled in the minds of the people that the pyrotechnics of court room and stump oratory did not necessarily imply extensive or profound ability in the lawyer who resorted to it. The courts were becoming graver and more learned, and the lawyer was learning as a preliminary and indispensable condition to success that he must be a close reasoner, besides having at command a broad knowledge of the principles on which the statutory law is constructed. There was of course the same riding on circuit as before, but the courts had improved in tone and morals, and there was less laxity—at least it appeared so to Lincoln. Political defeat had wrought a marked effect on him. It went below the skin and made a changed man of him. He was not soured at his seeming political decline, but still he determined to eschew politics from that time forward and devote himself entirely to the law. And now he began to make up for time lost in politics by studying the law in earnest. No man had greater power of application than he. Once fixing his mind on any subject, nothing could interfere with or disturb him. Frequently I would go out on the circuit with him. We, usually, at the little country inns occupied the same bed. In most cases the beds were too short for him, and his feet would hang over the foot-board, thus exposing a limited expanse of shin bone. Placing a candle on a chair at the head of the bed, he would read and study for hours. I have known him to study in this position till two o'clock in the morning. Meanwhile, I and others who chanced to occupy the same room would be safely and soundly asleep. On the circuit in this way he studied Euclid until he could with ease demonstrate all the propositions in the six books. How he could maintain his mental equilibrium or concentrate his thoughts on an abstract mathematical proposition, while Davis, Logan, Swett, Edwards, and I so industriously and volubly filled the air with our interminable snoring was a problem none of us could ever solve. I was on the circuit with Lincoln probably one-fourth of the time. The remainder of my time was spent in Springfield looking after the business there, but I know that life on the circuit was a gay one. It was rich with incidents, and afforded the nomadic lawyers ample relaxation from all the irksome toil that fell to their lot. Lincoln loved it. I suppose it would be a fair estimate to state that he spent over half the year following Judges Treat and Davis around on the circuit. On Saturdays the court and attorneys, if within a reasonable distance, would usually start for their homes. Some went for a fresh supply of clothing, but the greater number went simply to spend a day of rest with their families. The only exception was Lincoln, who usually spent his Sundays with the loungers at the country tavern, and only went home at the end of the circuit or term of court. "At first," * relates one of his colleagues on the circuit, "we wondered at it, but soon learned to account for his strange disinclination to go home. Lincoln himself never had much to say about home, and we never felt free to comment on it. Most of us had pleasant, inviting homes, and as we struck out for them I'm sure each one of us down in our hearts had a mingled feeling of pity and sympathy for him."
* David Davis, MS.
If the day was long and he was oppressed, the feeling was soon relieved by the narration of a story. The tavern loungers enjoyed it, and his melancholy, taking to itself wings, seemed to fly away. In the role of a story-teller I am prone to regard Mr. Lincoln as without an equal. I have seen him surrounded by a crowd numbering as many as two and in some cases three hundred persons, all deeply interested in the outcome of a story which, when he had finished it, speedily found repetition in every grocery and lounging place within reach. His power of mimicry, as I have before noted, and his manner of recital, were in many respects unique, if not remarkable. His countenance and all his features seemed to take part in the performance. As he neared the pith or point of the joke or story every vestige of seriousness disappeared from his face. His little gray eyes sparkled; a smile seemed to gather up, curtain like, the corners of his mouth; his frame quivered with suppressed excitement; and when the point—or "nub" of the story, as he called it—came, no one's laugh was heartier than his. These backwoods allegories are out of date now, and any lawyer, ambitious to gain prominence, would hardly dare thus to entertain a crowd, except at the risk of his reputation; but with Lincoln it gave him, in some mysterious way, a singularly firm hold on the people.
Lincoln was particularly strong in Menard county, and while on the circuit there he met with William Engle and James Murray, two men who were noted also for their story-telling proclivities. I am not now asserting for the country and the period what would at a later day be considered a very high standard of taste. Art had not such patrons as to-day, but the people loved the beautiful as Nature furnished it, and the good as they found it, with as much devotion as the more refined classes now are joined to their idols. Newspapers were scarce, and the court-house, with its cluster of itinerant lawyers, disseminated much of the information that was afterwards broken up into smaller bits at the pioneer's fireside. A curious civilization indeed, but one through which every Western State distant from the great arterial river or seaboard lias had to pass.
When Lincoln, Murray, and Engle met, there was sure to be a crowd. All were more or less masters in their art. I have seen the little country tavern where these three were wont to meet after an adjournment of court, crowded almost to suffocation with an audience of men who had gathered to witness the contest among the members of the strange triumvirate. The physician of the town, all the lawyers, and not unfrequently a preacher could be found in the crowd that filled the doors and windows. The yarns they spun and the stories, they told would not bear repetition here, but many of them had morals which, while exposing the weaknesses of mankind, stung like a whip-lash. Some were no doubt a thousand years old, with just enough "verbal varnish" and alterations of names and dates to make them new and crisp. By virtue of the last-named application, Lincoln was enabled to draw from Balzac a "droll story," and locating it in "Egypt"* or in Indiana, pass it off for a purely original conception. Every recital was followed by its "storm of laughter and chorus of cheers." After this had all died down, some unfortunate creature, through whose thickened skull the point had just penetrated, would break out in a guffaw, starting another wave of laughter which, growing to the proportions of a billow, would come rolling in like a veritable breaker.
* The word Egypt, so frequently used in this book, refers to that portion of Illinois which lies south of the famous National Road.
I have known these story-telling jousts to continue long after midnight—in some cases till the very small hours of the morning. I have seen Judge Treat, who was the very impersonation of gravity itself, sit up till the last and laugh until, as he often expressed it, "he almost shook his ribs loose." The next day he would ascend the bench and listen to Lincoln in a murder trial, with all the seeming severity of an English judge in wig and gown. Amid such surroundings, a leading figure in such society, alternately reciting the latest effusion of the bar room or mimicking the clownish antics of the negro minstrel, he who was destined to be an immortal emancipator, was steadily and unconsciously nearing the great trial of his life. We shall see further on how this rude civilization crystallized both his logic and his wit for use in another day.
Reverting again to Mr. Lincoln as a lawyer, it is proper to add that he detested the mechanical work of the office. He wrote few papers—less perhaps than any other man at the bar. Such work was usually left to me for the first few years we were together. Afterwards we made good use of students who came to learn the law in our office. A Chicago lawyer,* in a letter to me about Mr. Lincoln, in 1866, says: "Lincoln once told me that he had taken you in as a partner, supposing you had system and would keep things in order, but that he found out you had no more system than he had, but that you were in reality a good lawyer, so that he was doubly disappointed." Lincoln knew no such thing as order or method in his law practice. He made no preparation in advance, but trusted to the hour for its inspiration and to Providence for his supplies. In the matter of letter-writing** he made no distinction between one of a business nature or any other kind.
* W. C. Whitney, MS. ** "I wish you would learn of Everett what he would take, over and above a discharge, for all trouble we have been at to take his business out of our hands and give it to somebody else. It is impossible to collect money on that or any other claim here, now, and although you know I am not a very petulant man, I declare that I am almost out of patience with Mr. Everett's endless importunities. It seems like he not only writes all the letters he can himself, but he gets everybody else in Louisville and vicinity to be constantly writing to us about his claim. I have always said that Mr. Everett is a very clever fellow, and I am very sorry he cannot be obliged; but it does seem to me he ought to know we are interested to collect his claim, and therefore would do it if we could. I am neither joking nor in a pet when I say we would thank him to transfer his business to some other, without any compensation for what we have done, provided he will see the court costs paid for which we are security."—MS. letter to Joshua F. Speed, March 27, 1842.
If a happy thought or expression struck him he was by no means reluctant to use it. As early as 1839 wrote to a gentleman about a matter of business, observing crustily that "a d———d hawk-billed Yankee is here besetting me at every turn I take, saying that Robert Kenzie never received the $80 to which he was entitled." In July, 1851, he wrote a facetious message to one of his clients, saying: "I have news from Ottawa that we win our case. As the Dutch justice said when he married folks, 'Now where ish my hundred tol-lars.'"*
* The following unpublished letter in possession of C. F. Gunther, Esq., Chicago, Ills., shows how he proposed to fill a vacancy in the office of Clerk of the United States Court It reads like the letter of a politician in the midst of a canvass for office: "Springfield, ILL., December 6,1854. "Hon. Justice McLean. "Sir: I understand it is in contemplation to displace the present Clerk and appoint a new one for the Circuit and District Courts of Illinois. I am very friendly to the present incumbent, and both for his own sake and that of his family, I wish him to be retained so long as it is possible for the Court to do so. "In the contingency of his removal, however, I have recommended William Butler as his successor, and I do not wish what I write now to be taken as any abatement of that recommendation. "William J. Black is also an applicant for the appointment, and I write this at the solicitation of his friends to say that he is every way worthy of the office, and that I doubt not the conferring it upon him will give great satisfaction. "Your ob't servant, "A. Lincoln."
He was proverbially careless as to habits. In a letter to a fellow-lawyer in another town, apologizing for failure to answer sooner, he explains: "First, I have been very busy in the United States Court; second, when I received the letter I put it in my old hat and buying a new one the next day the old one was set aside, and so the letter was lost sight of for a time." This hat of Lincoln's—a silk plug—was an extraordinary receptacle. It was his desk and his memorandum-book. In it he carried his bank-book and the bulk of his letters. Whenever in his reading or researches he wished to preserve an idea, he jotted it down on an envelope or stray piece of paper and placed it inside the lining. Afterwards when the memorandum was needed there was only one place to look for it.*
How Lincoln appeared and acted in the law office has been graphically and, I must confess, truthfully told by a gentleman now in New York, who was for several years a student in our office. I beg to quote a few lines from him: "My brother met Mr. Lincoln in Ottawa, Ill.,** one day, and said to him: 'I have a brother whom I would very much like to have enter your office as a student.' 'All right!' was his reply; 'send him down and we will take a look at him.' I was then studying law at Grand Rapids, Mich., and on hearing from my brother I immediately packed up and started for Springfield. I arrived there on Saturday night. On Sunday Mr. Lincoln was pointed out to me. I well remember this first sight of him. He was striding along, holding little Tad, then about six years old, by the hand, who could with the greatest difficulty keep up with his father."
* Lincoln had always on the top of our desk a bundle of papers into which he slipped anything he wished to keep and afterwards refer to. It was a receptacle of general information. Some years ago, on removing the furniture from the office, I took down the bundle and blew from the top the liberal coat of dust that had accumulated thereon. Immediately uuderneath the string was a slip bearing this endorsement, in his hand: "When you can't find it anywhere else, look in this." ** John H. Littlefield, Brooklyn Eagle, October 16, 1887.
"In the morning I applied at the office of Lincoln and Herndon for admission as a student. The office was on the second floor of a brick building on the public square, opposite the court-house. You went up one flight of stairs and then passed along a hallway to the rear office, which was a medium-sized room. There was one long table in the center of the room, and a shorter one running in the opposite direction, forming a T, and both were covered with green baize. There were two windows which looked into the back yard. In one corner was an old-fashioned secretary with pigeonholes and a drawer, and here Mr. Lincoln and his partner kept their law papers. There was also a book-case containing about 200 volumes of law as well as miscellaneous books. The morning I entered the office Mr. Lincoln and his partner, Mr. Herndon, were both present. Mr. Lincoln addressed his partner thus: 'Billy, this is the young man of whom I spoke to you. Whatever arrangement you make with him will be satisfactory to me.' Then, turning to me, he said, 'I hope you will not become so enthusiastic in your studies of Blackstone and Kent as did two young men whom we had here. Do you see that spot over there?' pointing to a large ink stain on the wall. 'Well, one of these young men got so enthusiastic in his pursuit of legal lore that he fired an inkstand at the other one's head, and that is the mark he made.' I immediately began to clean up about the office a little. Mr. Lincoln had been in Congress and had the usual amount of seeds to distribute to the farmers. These were sent out with Free Soil and Republican documents. In my efforts to clean up, I found that some of the seeds had sprouted in the dirt that had collected in the office. Judge Logan and Milton Hay occupied the front offices on the same floor with Lincoln and Herndon, and one day Mr. Hay came in and said with apparent astonishment: 'What's happened here?' 'Oh, nothing,' replied Lincoln, pointing to me, 'only this young man has been cleaning up a little.' One of Lincoln's striking characteristics was his simplicity, and nowhere was this trait more strikingly exhibited than in his willingness to receive instruction from anybody and everybody. One day he came into the office and addressing his partner, said: 'Billy, what's the meaning of antithesis?' Mr. Herndon gave him the definition of the word, and I said: 'Mr. Lincoln, if you will allow me, I will give you an example.' 'All right, John, go ahead,' said Mr. Lincoln in his hearty manner. 'Phillips says, in his essay on Napoleon, "A pretended patriot, he impoverished the country; a professed Catholic, he imprisoned the Pope,'" etc. Mr. Lincoln thanked me and seemed very much pleased. Returning from off the circuit once he said to Mr. Herndon: 'Billy, I heard a good story while I was up in the country. Judge D——— was complimenting the landlord on the excellence of his beef. "I am surprised," he said, "that you have such good beef. You must have to kill a whole critter when you want any." "Yes," said the landlord, "we never kill less than a whole critter." "Lincoln's favorite position when unravelling some knotty law point was to stretch both of his legs at full length upon a chair in front of him. In this position, with books on the table near by and in his lap, he worked up his case. No matter how deeply interested in his work, if any one came in he had something humorous and pleasant to say, and usually wound up by telling a joke or an anecdote. I have heard him relate the same story three times within as many hours to persons who came in at different periods, and every time he laughed as heartily and enjoyed it as if it were a new story. His humor was infectious. I had to laugh because I thought it funny that Mr. Lincoln enjoyed a story so repeatedly told.
"There was no order in the office at all. The firm of Lincoln and Herndon kept no books. They divided their fees without taking any receipts or making any entries on books. One day Mr. Lincoln received $5000 as a fee in a railroad case. He came in and said: 'Well, Billy,' addressing his partner, Mr. Herndon, 'here is our fee; sit down and let me divide.' He counted out $2,500 to his partner, and gave it to him with as much nonchalance as he would have given a few cents for a paper. Cupidity had no abiding place in his nature.
"I took a good deal of pains in getting up a speech which I wanted to deliver during a political campaign. I told Mr. Lincoln that I would like to read it to him. He sat down in one chair, put his feet into another one, and said: 'John, you can fire away with that speech; I guess I can stand it.' I unrolled the manuscript, and proceeded with some trepidation. 'That's a good point, John,' he would say, at certain places, and at others: 'That's good—very good indeed,' until I felt very much elated over my effort. I delivered the speech over fifty times during the campaign. Elmer E. Ellsworth, afterwards colonel of the famous Zouaves, who was killed in Alexandria, early in the war, was nominally a student in Lincoln's office. His head was so full of military matters, however, that he thought little of law. Of Ellsworth, Lincoln said: 'That young man has a real genius for war!'"
During the six years following his retirement from Congress, Lincoln, realizing in a marked degree his want of literary knowledge, extended somewhat his research in that direction. He was naturally indisposed to undertake anything that savored of exertion, but his brief public career had exposed the limited area of his literary attainments. Along with his Euclid therefore he carried a well-worn copy of Shakespeare, in which he read no little in his leisure moments. "In travelling on the circuit," relates one of his associates at the bar,* "he was in the habit of rising earlier than his brothers of the bar. On such occasions he was wont to sit by the fire, having uncovered the coals, and muse, and ponder, and soliloquize, inspired, no doubt, by that strange psychological influence which is so poetically described by Poe in 'The Raven.'
* Lawrence Weldon, letter, Feb. 10,1866, MS.
On one of these occasions, at the town of Lincoln, sitting in the position described, he quoted aloud and at length the poem called 'Immortality.' When he had finished he was questioned as to the authorship and where it could be found. He had forgotten the author, but said that to him it sounded as much like true poetry as anything he had ever heard. He was particularly pleased with the last two stanzas."
Beyond a limited acquaintance with Shakespeare, Byron, and Burns, Mr. Lincoln, comparatively speaking, had no knowledge of literature. He was familiar with the Bible, and now and then evinced a fancy for some poem or short sketch to which his attention was called by some one else, or which he happened to run across in his cursory reading of books or newspapers. He never in his life sat down and read a book through, and yet he could readily quote any number of passages from the few volumes whose pages he had hastily scanned. In addition to his well-known love for the poem "Immortality" or "Why should the Spirit of Mortal be Proud," he always had a great fondness for Oliver Wendell Holmes' "Last Leaf," the fourth stanza of which, beginning with the verse, "The mossy marbles rest," I have often heard him repeat. He once told me of a song a young lady had sung in his hearing at a time when he was laboring under some dejection of spirits. The lines struck his fancy, and although he did not know the singer—having heard her from the sidewalk as he passed her house—he sent her a request to write the lines out for him. Within a day or two he came into the office, carrying in his hand a delicately perfumed envelope which bore the address, "Mr. Lincoln—Present," in an unmistakable female hand. In it, written on gilt-edged paper, were the lines of the song. The plaintive strain of the piece and its melancholy sentiment struck a responsive chord in a heart already filled with gloom and sorrow. Though ill-adapted to dissipate one's depression, something about it charmed Lincoln, and he read and re-read it with increasing relish. I had forgotten the circumstance until recently, when, in going over some old papers and letters turned over to me by Mr. Lincoln, I ran across the manuscript, and the incident was brought vividly to my mind. The envelope, still retaining a faint reminder of the perfumed scent given it thirty years before, bore the laconic endorsement, "Poem—I like this," in the handwriting of Mr. Lincoln. Unfortunately no name accompanied the manuscript, and unless the lady on seeing this chooses to make herself known, we shall probably not learn who the singer was. The composition is headed, "The Enquiry." I leave it to my musical friends to render it into song. Following are the lines:
"Tell me, ye winged winds That round my pathway roar, Do ye not know some spot Where mortals weep no more? Some lone and pleasant vale Some valley in the West, Where, free from toil and pain, The weary soul may rest? The loud wind dwindled to a whisper low, And sighed for pity as it answered, No. "Tell me, thou mighty deep, Whose billows round me play, Knows't thou some favored spot, Some island far away, Where weary man may find The bliss for which he sighs; Where sorrow never lives And friendship never dies? The loud waves rolling in perpetual flow Stopped for awhile and sighed to answer, No. "And thou, serenest moon, That with such holy face Dost look upon the Earth Asleep in Night's embrace? Tell me, in all thy round Hast thou not seen some spot Where miserable man Might find a happier lot? Behind a cloud the moon withdrew in woe, And a voice sweet but sad responded, No. "Tell me, my secret soul, Oh, tell me, Hope and Faith, Is there no resting-place From sorrow, sin, and death? Is there no happy spot Where mortals may be blessed, Where grief may find a balm And weariness a rest? Faith, Hope, and Love, best boon to mortals given, Waved their bright wings and whispered, Yes, in Heaven."* * Persons familiar with literature will recognize this as a poem written by Charles Mackay, an English writer who represented a London newspaper in the United States during the Rebellion as its war correspondent. It was set to music as a chant, and as such was frequently rendered in public by the famous Hutchinson family of singers. I doubt if Mr. Lincoln ever knew who wrote it.
Judge S. H. Treat, recently deceased, thus describes Lincoln's first appearance in the Supreme Court of Illinois. "A case being called for hearing, Mr. Lincoln stated that he appeared for the appellant and was ready to proceed with the argument. He then said: 'This is the first case I have ever had in this court, and I have therefore examined it with great care. As the Court will perceive by looking at the abstract of the record, the only question in the case is one of authority. I have not been able to find any authority to sustain my side of the case, but I have found several cases directly in point on the other side. I will now give these authorities to the court, and then submit the case." A lawyer in Beardstown relates this: * "Lincoln came into my office one day with the remark: 'I see you've been suing some of my clients, and I've come down to see about it.' He had reference to a suit I had brought to enforce the specific performance of a contract. I explained the case to him, and showed my proofs. He seemed surprised that I should deal so frankly with him, and said he would be as frank with me; that my client was justly entitled to a decree, and he should so represent it to the court; and that it was against his principles to contest a clear matter of right. So my client got a deed for a farm which, had another lawyer been in Mr. Lincoln's place, would have been consumed by the costs of litigation for years, with the result probably the same in the end."
* J. Henry Shaw, letter, June 13, 1866, MS.
A young man once wrote to Lincoln, enquiring for the best mode of obtaining a thorough knowledge of the law, "The mode is very simple," he responded, "though laborious and tedious. It is only to get books and read and study them carefully. Begin with Blackstone's Commentaries, and after reading carefully through, say twice, take up Chitty's Pleadings, Greenleaf's Evidence, and Story's Equity in succession. Work, work, work, is the main thing."*
* Letter to J. M. Brockman, Sept. 25, 1859, MS.
Lincoln never believed in suing for a fee. If a client would not pay on request he never sought to enforce collection. I remember once a man who had been indicted for forgery or fraud employed us to defend him. The illness of the prosecuting attorney caused some delay in the case, and our client, becoming dissatisfied at our conduct of the case, hired some one else, who superseded us most effectually. The defendant declining to pay us the fee demanded, on the ground that we had not represented him at the trial of the cause, I brought suit against him in Lincoln's absence and obtained judgment for our fee. After Lincoln's return from the circuit the fellow hunted him up and by means of a carefully constructed tale prevailed on him to release the judgment without receiving a cent of pay. The man's unkind treatment of us deserved no such mark of generosity from Lincoln, and yet he could not resist the appeal of any one in poverty and want. He could never turn from a woman in tears. It was no surprise to me or any of his intimate friends that so many designing women with the conventional widows' weeds and easy-flowing tears overcame him in Washington. It was difficult for him to detect an impostor, and hence it is not to be marvelled at that he cautioned his secretaries: "Keep them away—I cannot stand it."
On many questions I used to grow somewhat enthusiastic, adopting sometimes a lofty metaphor by way of embellishment. Lincoln once warned me: "Billy, don't shoot too high—aim lower and the common people will understand you. They are the ones you want to reach—at least they are the ones you ought to reach. The educated and refined people will understand you any way. If you aim too high your ideas will go over the heads of the masses, and only hit those who need no hitting." While it is true that from his peculiar construction Lincoln dwelt entirely in the head and in the land of thought, and while he was physically a lazy man, yet he was intellectually energetic; he was not only energetic, but industrious; not only industrious, but tireless; not only tireless, but indefatigable. Therefore if in debate with him a man stood on a questionable foundation he might well watch whereon he stood. Lincoln could look a long distance ahead and calculate the triumph of right. With him justice and truth were paramount. If to him a thing seemed untrue he could not in his nature simulate truth. His retention by a man to defend a lawsuit did not prevent him from throwing it up in its most critical stage if he believed he was espousing an unjust cause. This extreme conscientiousness and disregard of the alleged sacredness of the professional cloak robbed him of much so-called success at the bar. He once wrote to one of our clients: "I do not think there is the least use of doing anything more with your lawsuit. I not only do not think you are sure to gain it, but I do think you are sure to lose it. Therefore the sooner it ends the better."*
* Letter to H. Keeling, Esq., March 3, 1858, MS.
Messrs. Stuart and Edwards once brought a suit against a client of ours which involved the title to considerable property. At that time we had only two or three terms of court, and the docket was somewhat crowded. The plaintiff's attorneys were pressing us for a trial, and we were equally as anxious to ward it off. What we wanted were time and a continuance to the next term. We dared not make an affidavit for continuance, founded on facts, because no such pertinent and material facts as the law contemplated existed. Our case for the time seemed hopeless. One morning, however, I accidentally overheard a remark from Stuart indicating his fear lest a certain fact should happen to come into our possession. I felt some relief, and at once drew up a fictitious plea, averring as best I could the substance of the doubts I knew existed in Stuart's mind. The plea was as skilfully drawn as I knew how, and was framed as if we had the evidence to sustain it. The whole thing was a sham, but so constructed as to work the desired continuance, because I knew that Stuart and Edwards believed the facts were as I pleaded them. This was done in the absence and without the knowledge of Lincoln. The plea could not be demurred to, and the opposing counsel dared not take the issue on it. It perplexed them sorely. At length, before further steps were taken, Lincoln came into court. He looked carefully over all the papers in the case, as was his custom, and seeing my ingenious subterfuge, asked, "Is this seventh plea a good one?" Proud of the exhibition of my skill, I answered that it was. "But," he inquired, incredulously, "is it founded on fact?" I was obliged to respond in the negative, at the same time following up my answer with an explanation of what I had overheard Stuart intimate, and of how these alleged facts could be called facts if a certain construction were put upon them. I insisted that our position was justifiable, and that our client must have time or be ruined. I could see at once it failed to strike Lincoln as just right. He scratched his head thoughtfully and asked, "Hadn't we better withdraw that plea? You know it's a sham, and a sham is very often but another name for a lie. Don't let it go on record. The cursed thing may come staring us in the face long after this suit has been forgotten." The plea was withdrawn. By some agency—not our own—the case was continued and our client's interests were saved.
I only relate this incident to illustrate Lincoln's far-seeing capacity; it serves to show how over-cautious he seemed to be with regard to how his record might look in the future. I venture the assertion that he was the only member of the bar in Springfield who would have taken such a conscientious view of the matter.
One phase of Lincoln's character, almost lost sight of in the commonly accepted belief in his humility and kindly feeling under all circumstances, was his righteous indignation when aroused. In such cases he was the most fearless man I ever knew. I remember a murder case in which we appeared for the defence, and during the trial of which the judge—a man of ability far inferior to Lincoln's—kept ruling against us. Finally, a very material question, in fact one around which the entire case seemed to revolve, came up, and again the Court ruled adversely. The prosecution was jubilant, and Lincoln, seeing defeat certain unless he recovered his ground, grew very despondent. The notion crept into his head that the Court's rulings, which were absurd and almost spiteful, were aimed at him, and this angered him beyond reason. He told me of his feelings at dinner, and said: "I have determined to crowd the Court to the wall and regain my position before night." From that time forward it was interesting to watch him. At the reassembling of court he arose to read a few authorities in support of his position. In his comments he kept within the bounds of propriety just far enough to avoid a reprimand for contempt of court.
He characterized the continued rulings against him as not only unjust but foolish; and, figuratively speaking, he pealed the Court from head to foot. I shall never forget the scene. Lincoln had the crowd, a portion of the bar, and the jury with him. He knew that fact, and it, together with the belief that injustice had been done him, nerved him to a feeling of desperation. He was wrought up to the point of madness. When a man of large heart and head is wrought up and mad, as the old adage runs, "he's mad all over." Lincoln had studied up the points involved, but knowing full well the calibre of the judge, relied mostly on the moral effect of his personal bearing and influence. He was alternately furious and eloquent, pursuing the Court with broad facts and pointed inquiries in marked and rapid succession. I remember he made use of this homely incident in illustration of some point: "In early days a party of men went out hunting for a wild boar. But the game came upon them unawares, and scampering away they all climbed the trees save one, who, seizing the animal by the ears, undertook to hold him, but despairing of success cried out to his companions in the trees, 'For God's sake, boys, come down and help me let go.'" The prosecution endeavored to break him down or even "head him off," but all to no purpose. His masterly arraignment of law and facts had so effectually badgered the judge that, strange as it may seem, he pretended to see the error in his former position, and finally reversed his decision in Lincoln's favor. The latter saw his triumph, and surveyed a situation of which he was the master. His client was acquitted, and he had swept the field.
In the case of Parker vs. Hoyt, tried in the United States Court in Chicago, Lincoln was one of the counsel for the defendant. The suit was on the merits of an infringement of a patent water wheel. The trial lasted several days and Lincoln manifested great interest in the case. In his earlier days he had run, or aided in running, a saw-mill, and explained in his argument the action of the water on the wheel in a manner so clear and intelligible that the jury were enabled to comprehend the points and line of defence without the least difficulty. It was evident he had carried the jury with him in a most masterly argument, the force of which could not be broken by the reply of the opposing counsel. After the jury retired he became very anxious and uneasy. The jury were in another building, the windows of which opened on the street, and had been out for some two hours. "In passing along the street, one of the jurors on whom we very much relied," relates Lincoln's associate in the case,* "he being a very intelligent man and firm in his convictions, held up to him one finger. Mr. Lincoln became very much excited, fearing it indicated that eleven of the jury were against him. He knew if this man was for him he would never yield his opinion. He added, if he was like a juryman he had in Tazewell county, the defendant was safe. He was there employed, he said, to prosecute a suit for divorce. His client was a pretty, refined, and interesting little woman, and in court. The defendant, her husband, was a gross, morose, querulous, fault-finding, and uncomfortable man, and entirely unfitted for the husband of such a woman; but although he was able to prove the use of very offensive and vulgar epithets applied by the husband to his wife, and all sorts of annoyances, yet there were no such acts of personal violence as were required by the statute to justify a divorce. Lincoln did the best he could, and appealed to the jury to have compassion on the woman, and not to bind her to such a man and such a life as awaited her if required to live longer with him. The jury took about the same view of it in their deliberations. They desired to find for his fair client, but could discover no evidence which would really justify a verdict for her. At last they drew up a verdict for the defendant, and all signed but one fellow, who on being approached with the verdict said, coolly: 'Gentlemen, I am going to lie down to sleep, and when you get ready to give a verdict for that little woman, then wake me and not until then; for before I will give a verdict against her I will lie here till I rot and the pismires carry me out through the key-hole.' 'Now,' observed Lincoln, 'if that juryman will stick like the man in Tazewell county we are safe.' Strange to relate, the jury did come in, and with a verdict for the defendant. Lincoln always regarded this as one of the gratifying triumphs of his professional life."
* Grant Goodrich, letter, Nov. 9, 1866, MS.
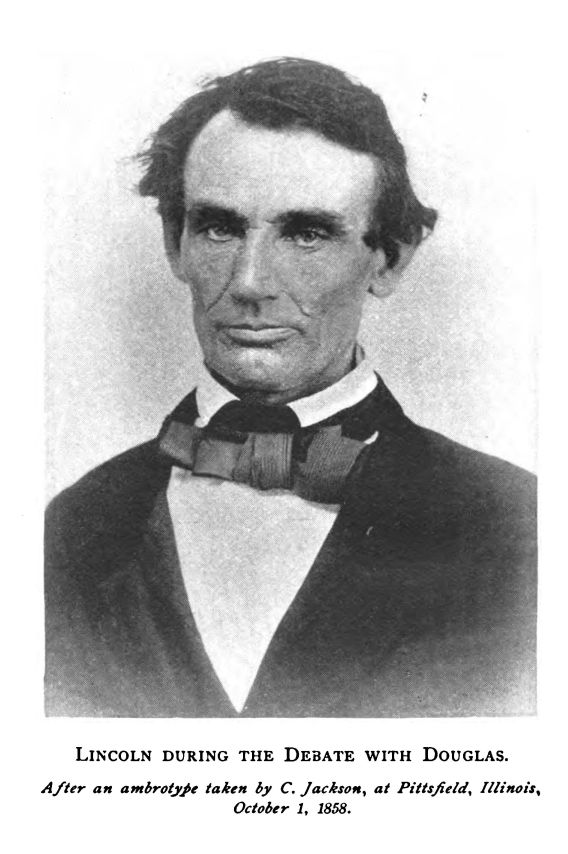

CONTENTS
THE TRUCE WITH DOUGLAS.—TESTIMONY OF IRWIN.
AN OFFICE DISCUSSION—LINCOLN'S IDEA OF WAR.
LINCOLN AND THE KNOW-NOTHINGS.
LINCOLN'S VIEWS ON THE RIGHTS OF SUFFRAGE.
THE BURIAL OF THE ASSASSIN BOOTH.
A TRIBUTE TO LINCOLN BY A COLLEAGUE AT THE BAR.
List of Illustrations
A LAW office is a dull, dry place so far as pleasurable or interesting incidents are concerned. If one is in search of stories of fraud, deceit, cruelty, broken promises, blasted homes, there is no better place to learn them than a law office. But to the majority of persons these painful recitals are anything but attractive, and it is well perhaps that it should be so. In the office, as in the court room, Lincoln, when discussing any point, was never arbitrary or insinuating. He was deferential, cool, patient, and respectful. When he reached the office, about nine o'clock in the morning, the first thing he did was to pick up a newspaper, spread himself out on an old sofa, one leg on a chair, and read aloud, much to my discomfort. Singularly enough Lincoln never read any other way but aloud. This habit used to annoy me almost beyond the point of endurance. I once asked him why he did so. This was his explanation: "When I read aloud two senses catch the idea: first, I see what I read; second, I hear it, and therefore I can remember it better." He never studied law books unless a case was on hand for consideration—never followed up the decisions of the supreme courts, as other lawyers did. It seemed as if he depended for his effectiveness in managing a lawsuit entirely on the stimulus and inspiration of the final hour. He paid but little attention to the fees and money matters of the firm—usually leaving all such to me. He never entered an item in the account book. If any one paid money to him which belonged to the firm, on arriving at the office he divided it with me. If I was not there, he would wrap up my share in a piece of paper and place it in my drawer—marking it with a pencil, "Case of Roe vs. Doe.—Herndon's half."
On many topics he was not a good conversationalist, because he felt that he was not learned enough. Neither was he a good listener. Putting it a little strongly, he was often not even polite. If present with others, or participating in a conversation, he was rather abrupt, and in his anxiety to say something apt or to illustrate the subject under discussion, would burst in with a story. In our office I have known him to consume the whole forenoon relating stories. If a man came to see him for the purpose of finding out something which he did not care to let him know and at the same time did not want to refuse him, he was very adroit. In such cases Lincoln would do most of the talking, swinging around what he suspected was the vital point, but never nearing it, interlarding his answers with a seemingly endless supply of stories and jokes. The interview being both interesting and pleasant, the man would depart in good humor, believing he had accomplished his mission. After he had walked away a few squares and had cooled off, the question would come up, "Well, what did I find out?" Blowing away the froth of Lincoln's humorous narratives he would find nothing substantial left.
"As he entered the trial," relates one of his colleagues at the bar,* "where most lawyers would object he would say he 'reckoned' it would be fair to let this in, or that; and sometimes, when his adversary could not quite prove what Lincoln knew to be the truth, he 'reckoned' it would be fair to admit the truth to be so-and-so. When he did object to the court, and when he heard his objections answered, he would often say, 'Well, I reckon I must be wrong.' Now, about the time he had practised this three-fourths through the case, if his adversary didn't understand him, he would wake up in a few minutes learning that he had feared the Greeks too late, and find himself beaten. He was wise as a serpent in the trial of a cause, but I have had too many scares from his blows to certify that he was harmless as a dove. When the whole thing was unravelled, the adversary would begin to see that what he was so blandly giving away was simply what he couldn't get and keep. By giving away six points and carrying the seventh he carried his case, and the whole case hanging on the seventh, he traded away everything which would give him the least aid in carrying that. Any man who took Lincoln for a simple-minded man would very soon wake up with his back in a ditch."
* Leonard Swett.
Lincoln's restless ambition found its gratification only in the field of politics. He used the law merely as a stepping-stone to what he considered a more attractive condition in the political world. In the allurements held out by the latter he seemed to be happy. Nothing in Lincoln's life has provoked more discussion than the question of his ability as a lawyer. I feel warranted in saying that he was at the same time a very great and a very insignificant lawyer. Judge David Davis, in his eulogy on Lincoln at Indianapolis, delivered at the meeting of the bar there in May, 1865, said this: "In all the elements that constituted a lawyer he had few equals. He was great at nisi prius and before an appellate tribunal. He seized the strong points of a cause and presented them with clearness and great compactness. His mind was logical and direct, and he did not indulge in extraneous discussion. Generalities and platitudes had no charm for him. An unfailing vein of humor never deserted him, and he was able to claim the attention of court and jury when the cause was most uninteresting by the appropriateness of his anecdotes. His power of comparison was large, and he rarely failed in a legal discussion to use that mode of reasoning. The framework of his mental and moral being was honesty, and a wrong case was poorly defended by him. The ability which some eminent lawyers possess of explaining away the bad points of a cause by ingenious sophistry was denied him. In order to bring into full activity his great powers it was necessary that he should be convinced of the right and justice of the matter which he advocated. When so convinced, whether the cause was great or small he was usually successful." *
* He never took advantage of a man's low character to prejudice the jury. Mr. Lincoln thought his duty to his client extended to what was honorable and high-minded, just and noble—nothing further. Hence the meanest man at the bar always paid great deference and respect to him.—David Davis, Sept. 10, 1866, MS.
This statement of Judge Davis in general is correct, but in some particulars is faulty. It was intended as a eulogy on Lincoln, and as such would not admit of as many limitations and modifications as if spoken under other circumstances. In 1866 Judge Davis said in a statement made to me in his home at Bloomington, which I still have, "Mr. Lincoln had no managing faculty nor organizing power; hence a child could conform to the simple and technical rules, the means and the modes of getting at justice, better than he. The law has its own rules, and a student could get at them or keep with them better than Lincoln. Sometimes he was forced to study these if he could not get the rubbish of a case removed. But all the way through his lack of method and organizing ability was clearly apparent." The idea that Mr. Lincoln was a great lawyer in the higher courts and a good nisi prius lawyer, and yet that a child or student could manage a case in court better than he, seems strangely inconsistent, but the facts of his life as a lawyer will reconcile this and other apparent contradictions.
I was not only associated with Mr. Lincoln in Springfield, but was frequently on the circuit with him, but of course not so much as Judge Davis, who held the court, and whom Lincoln followed around on the circuit for at least six months out of the year. I easily realized that Lincoln was strikingly deficient in the technical rules of the law. Although he was constantly reminding young legal aspirants to study and "work, work," yet I doubt if he ever read a single elementary law book through in his life. In fact, I may truthfully say, I never knew him to read through a law book of any kind. Practically, he knew nothing of the rules of evidence, of pleading, or practice, as laid down in the text-books, and seemed to care nothing about them. He had a keen sense of justice, and struggled for it, throwing aside forms, methods, and rules, until it appeared pure as a ray of light flashing through a fog-bank. He was not a general reader in any field of knowledge, but when he had occasion to learn or investigate any subject he was thorough and indefatigable in his search. He not only went to the root of a question, but dug up the root, and separated and analyzed every fibre of it. He was in every respect a case lawyer, never cramming himself on any question till he had a case in which the question was involved. He thought slowly and acted slowly; he must needs have time to analyze all the facts in a case and wind them into a connected story. I have seen him lose cases of the plainest justice, which the most inexperienced member of the bar would have gained without effort. Two things were essential to his success in managing a case. One was time; the other a feeling of confidence in the justice of the cause he represented. He used to say, "If I can free this case from technicalities and get it properly swung to the jury, I'll win it." But if either of these essentials were lacking, he was the weakest man at the bar. He was greatest in my opinion as a lawyer in the Supreme Court of Illinois. There the cases were never hurried. The attorneys generally prepared their cases in the form of briefs, and the movements of the court and counsel were so slow that no one need be caught by surprise. I was with Lincoln once and listened to an oral argument by him in which he rehearsed an extended history of the law. It was a carefully prepared and masterly discourse, but, as I thought, entirely useless. After he was through and we were walking home I asked him why he went so far back in the history of the law. I presumed the court knew enough history. "That's where you're mistaken," was his instant rejoinder. "I dared not trust the case on the presumption that the court knows everything—in fact I argued it on the presumption that the court didn't know anything," a statement which, when one reviews the decision of our appellate courts, is not so extravagant as one would at first suppose.
I used to grow restless at Lincoln's slow movements and speeches in court. "Speak with more vim," I would frequently say, "and arouse the jury—talk faster and keep them awake." In answer to such a suggestion he one day made use of this illustration: "Give me your little pen-knife, with its short blade, and hand me that old jack-knife, lying on the table." Opening the blade of the pen-knife he said: "You see, this blade at the point travels rapidly, but only through a small portion of space till it stops; while the long blade of the jack-knife moves no faster but through a much greater space than the small one. Just so with the long, labored movements of my mind. I may not emit ideas as rapidly as others, because I am compelled by nature to speak slowly, but when I do throw off a thought it seems to me, though it comes with some effort, it has force enough to cut its own way and travel a greater distance." This was said to me when we were alone in our office simply for illustration. It was not said boastingly.
As a specimen of Lincoln's method of reasoning I insert here the brief or notes of an argument used by him in a lawsuit as late as 1858. I copy from the original:
"Legislation and adjudication must follow and conform to the progress of society.
"The progress of society now begins to produce cases of the transfer for debts of the entire property of railroad corporations; and to enable transferees to use and enjoy the transferred property legislation and adjudication begin to be necessary.
"Shall this class of legislation just now beginning with us be general or special?
"Section Ten of our Constitution requires that it should be general, if possible, (Read the Section.)
"Special legislation always trenches upon the judicial department; and in so far violates Section Two of the Constitution. (Read it.)
"Just reasoning—policy—is in favor of general legislation—else the legislature will be loaded down with the investigation of smaller cases—a work which the courts ought to perform, and can perform much more perfectly. How can the Legislature rightly decide the facts between P. & B. and S. C. & Co.
"It is said that under a general law, whenever a R. R. Co. gets tired of its debts, it may transfer fraudulently to get rid of them. So they may—so may individuals; and which—the Legislature or the courts—is best suited to try the question of fraud in either case?
"It is said, if a purchaser have acquired legal rights, let him not be robbed of them, but if he needs legislation let him submit to just terms to obtain it.
"Let him, say we, have general law in advance (guarded in every possible way against fraud), so that, when he acquires a legal right, he will have no occasion to wait for additional legislation; and if he has practiced fraud let the courts so decide."
David Davis said this of Lincoln: "When in a lawsuit he believed his client was oppressed,—as in the Wright case,—he was hurtful in denunciation. When he attacked meanness, fraud, or vice, he was powerful, merciless in his castigation." The Wright case referred to was a suit brought by Lincoln and myself to compel a pension agent to refund a portion of a fee which he had withheld from the widow of a revolutionary soldier. The entire pension was $400, of which sum the agent had retained one-half. The pensioner, an old woman crippled and bent with age, came hobbling into the office and told her story. It stirred Lincoln up, and he walked over to the agent's office and made a demand for a return of the money, but without success. Then suit was brought. The day before the trial I hunted up for Lincoln, at his request, a history of the Revolutionary War, of which he read a good portion. He told me to remain during the trial until I had heard his address to the jury. "For," said he, "I am going to skin Wright, and get that money back." The only witness we introduced was the old lady, who through her tears told her story. In his speech to the jury, Lincoln recounted the causes leading to the outbreak of the Revolutionary struggle, and then drew a vivid picture of the hardships of Valley Forge, describing with minuteness the men, barefooted and with bleeding feet, creeping over the ice. As he reached that point in his speech wherein he narrated the hardened action of the defendant in fleecing the old woman of her pension his eyes flashed, and throwing aside his handkerchief, which he held in his right hand, he fairly launched into him. His speech for the next five or ten minutes justified the declaration of Davis, that he was "hurtful in denunciation and merciless in castigation." There was no rule of court to restrain him in his argument, and I never, either on the stump or on other occasions in court, saw him so wrought up. Before he closed, he drew an ideal picture of the plaintiff's husband, the deceased soldier, parting with his wife at the threshold of their home, and kissing their little babe in the cradle, as he started for the war. "Time rolls by," he said, in conclusion; "the heroes of '76 have passed away and are encamped on the other shore. The soldier has gone to rest, and now, crippled, blinded, and broken, his widow comes to you and to me, gentlemen of the jury, to right her wrongs. She was not always thus. She was once a beautiful young woman. Her step was as elastic, her face as fair, and her voice as sweet as any that rang in the mountains of old Virginia. But now she is poor and defenceless. Out here on the prairies of Illinois, many hundreds of miles away from the scenes of her childhood, she appeals to us, who enjoy the privileges achieved for us by the patriots of the Revolution, for our sympathetic aid and manly protection. All I ask is, shall we befriend her?" The speech made the desired impression on the jury. Half of them were in tears, while the defendant sat in the court room, drawn up and writhing under the fire of Lincoln's fierce invective. The jury returned a verdict in our favor for every cent we demanded. Lincoln was so much interested in the old lady that he became her surety for costs, paid her way home, and her hotel bill while she was in Springfield. When the judgment was paid we remitted the proceeds to her and made no charge for our services. Lincoln's notes for the argument were unique: "No contract.—Not professional services.—Unreasonable charge.—Money retained by Deft not given by Pl'ff.—Revolutionary War.—Describe Valley Forge privations.—Ice—Soldier's bleeding feet.—Pl'ffs husband.—Soldier leaving home for army.—Skin Def t.—Close." It must not be inferred from this that Lincoln was in the habit of slopping over. He never hunted up acts of injustice, but if they came to him he was easily enlisted. In 1855 he was attending court at the town of Clinton, Illinois. Fifteen ladies from a neighboring village in the county had been indicted for trespass. Their offence consisted in sweeping down on one Tanner, the keeper of a saloon in the village, and knocking in the heads of his barrels. Lincoln was not employed in the case, but sat watching the trial as it proceeded. In defending the ladies their attorney seemed to evince a little want of tact, and this prompted one of the former to invite Mr. Lincoln to add a few words to the jury, if he thought he could aid their cause. He was too gallant to refuse and, their attorney having consented, he made use of the following argument: "In this case I would change the order of indictment and have it read The State vs. Mr. Whiskey, instead of The State vs. The Ladies; and touching these there are three laws: The law of self-protection; the law of the land, or statute law; and the moral law, or law of God. First, the law of self-protection is a law of necessity, as evinced by our forefathers in casting the tea overboard and asserting their right to the pursuit of life, liberty, and happiness. In this case it is the only defense the ladies have, for Tanner neither feared God nor regarded man. Second, the law of the land, or statute law, and Tanner is recreant to both. Third, the moral law, or law of God, and this is probably a law for the violation of which the jury can fix no punishment." Lincoln gave some of his own observations on the ruinous effects of whiskey in society, and demanded its early suppression. After he had concluded, the Court, without awaiting the return of the jury, dismissed the ladies, saying: "Ladies, go home. I will require no bond of you, and if any fine is ever wanted of you, we will let you know."
After Lincoln's death a fellow-lawyer paid this tribute to him:* "He was wonderfully kind, careful, and just. He had an immense stock of common-sense, and he had faith enough in it to trust it in every emergency. Mr. Lincoln's love of justice and fair-play was his predominating trait. I have often listened to him when I thought he would certainly state his case out of court. It was not in his nature to assume or attempt to bolster up a false position.** He would abandon his case first.
* Joseph Gillespie, MS., Letter, Oct. 8, 1886. ** "Early in 1858 at Danville, Ill., I met Lincoln, Swett, and others who had returned from court in an adjoining county, and were discussing the various features of a murder trial in which Lincoln had made a vigorous fight for the prosecution and Swett had defended. The plea of the defense was insanity. On inquiring the name of the defendant I was surprised to learn that it was my old friend Isaac Wyant, formerly of Indiana. I told them that I had been Wyant's counsel frequently and had defended him from almost every charge in the calendar of crimes; and that he was a weak brother and could be led into almost everything. At once Lincoln began to manifest great interest in Wyant's history, and had to be told all about him. The next day on the way to the court house he told me he had been greatly troubled over what I related about Wyant; that his sleep had been disturbed by the fear that he had been too bitter and unrelenting in his prosecution of him. "I acted," he said, "on the theory that he was 'possuming insanity, and now I fear I have been too severe and that the poor fellow may be insane after all. If he cannot realize the wrong of his crime, then I was wrong in aiding to punish him.'"—Hon. Joseph E. McDonald, August, 1888. Statement to J. W. W.
He did so in the case of Buckmaster for the use of Dedham vs. Beems and Arthur, in our Supreme Court, in which I happened to be opposed to him. Another gentleman, less fastidious, took Mr. Lincoln's place and gained the case."
A widow who owned a piece of valuable land employed Lincoln and myself to examine the title to the property, with the view of ascertaining whether certain alleged tax liens were just or not. In tracing back the title we were not satisfied with the description of the ground in one of the deeds of conveyance. Lincoln, to settle the matter, took his surveying instruments and surveyed the ground himself. The result proved that Charles Matheney, a former grantor, had sold the land at so much per acre, but that in describing it he had made an error and conveyed more land than he received pay for. This land descended to our client, and Lincoln after a careful survey and calculation, decided that she ought to pay to Matheney's heirs the sum which he had shown was due them by reason of the erroneous conveyance. To this she entered strenuous objections, but when assured that unless she consented to this act of plain justice we would drop the case, she finally, though with great reluctance, consented. She paid the required amount, and this we divided up into smaller sums proportioned to the number of heirs. Lincoln himself distributed these to the heirs, obtaining a receipt from each one.*
* "Dear Herndon: "One morning, not long before Lincoln's nomination—a year perhaps—I was in your office and heard the following! Mr. Lincoln, seated at the baize-covered table in the center of the office, listened attentively to a man who talked earnestly and in a low tone. After being thus engaged for some time Lincoln at length broke in, and I shall never forget his reply. 'Yes,' he said, 'we can doubtless gain your case for you; we can set a whole neighborhood at loggerheads; we can distress a widowed mother and her six fatherless children and thereby get for you six hundred dollars to which you seem to have a legal claim, but which rightfully belongs, it appears to me, as much to the woman and her children as it does to you. You must remember that somethings legally right are not morally right. We shall not take your case, but will give you a little advice for which we will charge you nothing. You seem to be a sprightly, energetic man; we would advise you to try your hand at making six hundred dollars in some other way.' "Yours, "Lord." From undated MS., about 1866.
While Mr. Lincoln was no financier and had no propensity to acquire property,—no avarice of the get,—yet he had the capacity of retention, or the avarice of the keep. He never speculated in lands or anything else. In the days of land offices and "choice lots in a growing town" he had many opportunities to make safe ventures promising good returns, but he never availed himself of them. His brother lawyers were making good investments and lucky turns, some of them, Davis, for example, were rapidly becoming wealthy; but Lincoln cared nothing for speculation; in fact there was no ventursome spirit in him. His habits were very simple. He was not fastidious as to food or dress. His hat was brown, faded, and the nap usually worn or rubbed off. He wore a short cloak and sometimes a shawl. His coat and vest hung loosely on his gaunt frame, and his trousers were invariably too short. On the circuit he carried in one hand a faded green umbrella, with "A. Lincoln" in large white cotton or muslin letters sewed on the inside. The knob was gone from the handle, and when closed a piece of cord was usually tied around it in the middle to keep it from flying open. In the other hand he carried a literal carpet-bag, in which were stored the few papers to be used in court, and underclothing enough to last till his return to Springfield. He slept in a long, coarse, yellow flannel shirt, which reached half-way between his knees and ankles. It probably was not made to fit his bony figure as completely as Beau Brummers shirt, and hence we can somewhat appreciate the sensation of a young lawyer who, on seeing him thus arrayed for the first time, observed afterwards that, "He was the ungodliest figure I ever saw."
"He never complained of the food, bed, or lodgings. If every other fellow grumbled at the bill-of-fare which greeted us at many of the dingy taverns," says David Davis, "Lincoln said nothing." He was once presiding as judge in the absence of Davis, and the case before him was an action brought by a merchant against the father of a minor son for a suit of clothes sold to the son without parental authority. The real question was whether the clothes were necessary, and suited to the condition of the son's life. The father was a wealthy farmer; the bill for the clothing was twenty-eight dollars. I happened in court just as Lincoln was rendering his decision. He ruled against the plea of necessity. "I have rarely in my life," said he, "worn a suit of clothes costing twenty-eight dollars."
* H. C. Whitney, MS., letter, Nov. 13, 1865.
"Several of us lawyers," remarked one of his colleagues, "in the eastern end of the circuit annoyed Lincoln once while he was holding court for Davis by attempting to defend against a note to which there were many makers. We had no legal, but a good moral defense, but what we wanted most of all was to stave it off till the next term of court by one expedient or another. We bothered "the court" about it till late on Saturday, the day of adjournment. He adjourned for supper with nothing left but this case to dispose of. After supper he heard our twaddle for nearly an hour, and then made this odd entry: 'L. D. Chaddon vs. J. D. Beasley et al. April Term, 1856. Champaign County Court. Plea in abatement by B. Z. Green, a defendant not served, filed Saturday at 11 o'clock A. M., April 24, 1856, stricken from the files by order of court. Demurrer to declaration, if there ever was one, overruled. Defendants who are served now, at 8 o'clock, P. M., of the last day of the term, ask to plead to the merits, which is denied by the court on the ground that the offer comes too late, and therefore, as by nil dicet, judgment is rendered for Pl'ff. Clerk assess damages. A. Lincoln, Judge pro tem."' The lawyer who reads this singular entry will appreciate its oddity if no one else does. After making it one of the lawyers, on recovering his astonishment, ventured to enquire, "Well, Lincoln, how can we get this case up again?" Lincoln eyed him quizzically a moment, and then answered, "You have all been so 'mighty smart about this case you can find out how to take it up again yourselves."*
* "During my first attendance at court in Menard County," relates a lawyer who travelled the circuit with Lincoln, "some thirty young men had been indicted for playing cards, and Lincoln and I were employed in their defense. The prosecuting attorney, in framing the indictments, alternately charged the defendants with playing a certain game of cards called 'seven-up,' and in the next bill charged them with playing cards at a certain game called 'old sledge.' Four defendants were indicted in each bill. The prosecutor, being entirely unacquainted with games at cards, did not know the fact that both 'seven-up' and 'old sledge' were one and the same. Upon the trial on the bills describing the game as 'seven-up' our witnesses would swear that the game played was 'old sledge,' and vice versa on the bills alleging the latter. The result was an acquittal in every case under the instructions of the Court. The prosecutor never found out the dodge until the trials were over, and immense fun and rejoicing were indulged in at the result."
The same gentleman who furnishes this last incident, and who was afterward a trusted friend of Mr. Lincoln, Henry C. Whitney, has described most happily the delights of a life on the circuit. A bit of it, referring to Lincoln, I apprehend, cannot be deemed out of place here. "In October, 1854, Abraham Lincoln," he relates, "drove into our town (Urbana) to attend court. He had the appearance of a rough, intelligent farmer, and his rude, homemade buggy and raw-boned horse enforced this belief. I had met him for the first time in June of the same year. David Davis and Leonard Swett had just preceded him. The next morning he started North, on the Illinois Central Railroad, and as he went in an old omnibus he played on a boy's harp all the way to the depot. I used to attend the Danville court, and while there, usually roomed with Lincoln and Davis. We stopped at McCormick's hotel, an old-fashioned frame country tavern. Jurors, counsel, prisoners, everybody ate at a long table. The judge, Lincoln, and I had the ladies' parlor fitted up with two beds. Lincoln, Swett, McWilliams, of Bloomington, Voorhees, of Covington, Ind., O. L. Davis, Drake, Ward Lamon, Lawrence, Beckwith, and O. F. Harmon, of Danville, Whiteman, of Iroquois County, and Chandler, of Williamsport, Ind., constituted the bar. Lincoln, Davis, Swett, I, and others who came from the western part of the state would drive from Urbana. The distance was thirty-six miles. We sang and exchanged stories all the way. We had no hesitation in stopping at a farm-house and ordering them to kill and cook a chicken for dinner. By dark we reached Danville. Lamon would have whiskey in his office for the drinking ones, and those who indulged in petty gambling would get by themselves and play till late in the night. Lincoln, Davis, and a few local wits would spend the evening in Davis's room, talking politics, wisdom, and fun. Lincoln and Swett were the great lawyers, and Lincoln always wanted Swett in jury cases. We who stopped at the hotel would all breakfast together and frequently go out into the woods and hold court. We were of more consequence than a court and bar is now. The feelings were those of great fraternity in the bar, and if we desired to restrict our circle it was no trouble for Davis to freeze out any disagreeable persons. Lincoln was fond of going all by himself to any little show or concert. I have known him to slip away and spend the entire evening at a little magic lantern show intended for children. A travelling concert company, calling themselves the 'Newhall Family,' were sure of drawing Lincoln. One of their number, Mrs. Hillis, a good singer, he used to tell us was the only woman who ever seemed to exhibit any liking for him. I attended a negro-minstrel show in Chicago, where we heard Dixie sung. It was entirely new, and pleased him greatly. In court he was irrepressible and apparently inexhaustible in his fund of stories. Where in the world a man who had travelled so little and struggled amid the restrictions of such limited surroundings could gather up such apt and unique yarns we never could guess. Davis appreciated Lincoln's talent in this direction, and was always ready to stop business to hear one of his stories. Lincoln was very bashful when in the presence of ladies. I remember once we were invited to take tea at a friend's house, and while in the parlor I was called to the front gate to see a client. When I returned, Lincoln, who had undertaken to entertain the ladies, was twisting and squirming in his chair, and as bashful as a schoolboy. Everywhere, though we met a hard crowd at every court, and though things were free and easy, we were treated with great respect." Probably the most important lawsuit Lincoln and I conducted was one in which we defended the Illinois Central Railroad in an action brought by McLean County, Illinois, in August, 1853, to recover taxes alleged to be due the county from the road. The Legislature had granted the road immunity from taxation, and this was a case intended to test the constitutionality of the law. The road sent a retainer fee of $250. In the lower court the case was decided in favor of the railroad. An appeal to the Supreme Court followed, and there it was argued twice, and finally decided in our favor. This last decision was rendered some time in 1855. Mr. Lincoln soon went to Chicago and presented our bill for legal services. We only asked for $2000 more. The official to whom he was referred,—supposed to have been the superintendent George B. McClellan who afterwards became the eminent general,—looking at the bill expressed great surprise. "Why, sir," he exclaimed, "this is as much as Daniel Webster himself would have charged. We cannot allow such a claim." Stung by the rebuff, Lincoln withdrew the bill, and started for home. On the way he stopped at Bloomington. There he met Grant Goodrich, Archibald Williams, Norman B. Judd, O. H. Browning, and other attorneys, who, on learning of his modest charge for such valuable services rendered the railroad, induced him to increase the demand to $5000, and to bring suit for that sum. This was done at once. On the trial six lawyers certified that the bill was reasonable, and judgment for that sum went by default. The judgment was promptly paid.
Lincoln gave me my half, and much as we deprecated the avarice of great corporations, we both thanked the Lord for letting the Illinois Central Railroad fall into our hands.
In the summer of 1857 Lincoln was employed by Mr. Manny, of Rockford, Ill., to defend him in an action brought by McCormick,* who was one of the inventors of the reaping machine, for infringement of patent. Lincoln had been recommended to Manny by E. B. Washburne, then a member of Congress from northern Illinois. The case was to be tried before Judge McLean at Cincinnati, in the Circuit Court of the United States. The counsel for McCormick was Reverdy Johnson. Edwin M. Stanton and George Harding, of Philadelphia, were associated on the other side with Lincoln. The latter came to Cincinnati a few days before the argument took place, and stopped at the house of a friend. "The case was one of great importance pecuniarily," relates a lawyer** in Cincinnati, who was a member of the bar at the time, "and in the law questions involved. Reverdy Johnson represented the plaintiff. Mr. Lincoln had prepared himself with the greatest care; his ambition was up to speak in the case and to measure swords with the renowned lawyer from Baltimore. It was understood between his client and himself before his coming that Mr. Harding, of Philadelphia, was to be associated with him in the case, and was to make the 'mechanical argument.'
* The case, McCormick vs. Manny, is reported in 6 McLean's Rep., P. 539. ** W. M. Dickson.
After reaching Cincinnati, Mr. Lincoln was a little surprised and annoyed to learn that his client had also associated with him Mr. Edwin M. Stanton, of Pittsburg, and a lawyer of our own bar, the reason assigned being that the importance of the case required a man of the experience and power of Mr. Stanton to meet Mr. Johnson. The Cincinnati lawyer was appointed for his 'local influence.' These reasons did not remove the slight conveyed in the employment without consultation with him of this additional counsel. He keenly felt it, but acquiesced. The trial of the case came on; the counsel for defense met each morning for consultation. On one of these occasions one of the counsel moved that only two of them should speak in the case. This matter was also acquiesced in. It had always been understood that Mr. Harding was to speak to explain the mechanism of the reapers. So this motion excluded either Mr. Lincoln or Mr. Stanton,—which? By the custom of the bar, as between counsel of equal standing, and in the absence of any action of the client, the original counsel speaks. By this rule Mr. Lincoln had precedence. Mr. Stanton suggested to Mr. Lincoln to make the speech. Mr. Lincoln answered, 'No, you speak.' Mr. Stanton replied, 'I will,' and taking up his hat, said he would go and make preparation. Mr. Lincoln acquiesced in this, but was greatly grieved and mortified; he took but little more interest in the case, though remaining until the conclusion of the trial. He seemed to be greatly depressed, and gave evidence of that tendency to melancholy which so marked his character. His parting on leaving the city cannot be forgotten. Cordially' shaking the hand of his hostess he said: 'You have made my stay here most agreeable, and I am a thousand times obliged to you; but in reply to your request for me to come again, I must say to you I never expect to be in Cincinnati again. I have nothing against the city, but things have so happened here as to make it undesirable for me ever to return.' Lincoln felt that Stanton had not only been very discourteous to him, but had purposely ignored him in the case, and that he had received rather rude, if not unkind, treatment from all hands. Stanton, in his brusque and abrupt way, it is said, described him as a 'long, lank creature from Illinois, wearing a dirty linen duster for a coat, on the back of which the perspiration had splotched wide stains that resembled a map of the continent. Mr. Lincoln," adds Mr. Dickson, "remained in Cincinnati about a week, moving freely around, yet not twenty men knew him personally or knew he was here; not a hundred would have known who he was had his name been given to them. He came with the fond hope of making fame in a forensic contest with Reverdy Johnson. He was pushed aside, humiliated and mortified. He attached to the innocent city the displeasure that filled his bosom, and shook its dust from his feet." On his return to Springfield he was somewhat reticent regarding the trial, and, contrary to his custom, communicated to his associates at the bar but few of its incidents. He told me that he had been "roughly handled by that man Stanton"; that he overheard the latter from an adjoining room, while the door was slightly ajar, referring to Lincoln, inquire of another, "Where did that long-armed creature come from, and what can he expect to do in this case?" During the trial Lincoln formed a poor opinion of Judge McLean. He characterized him as an "old granny," with considerable vigor of mind, but no perception at all. "If you were to point your finger at him," he put it, "and a darning needle at the same time he never would know which was the sharpest."
As Lincoln grew into public favor and achieved such marked success in the profession, half the bar of Springfield began to be envious of his growing popularity. I believe there is less jealousy and bitter feeling among lawyers than professional men of any other class; but it should be borne in mind that in that early day a portion of the bar in every county seat, if not a majority of the lawyers everywhere, were politicians. Stuart frequently differed from Lincoln on political questions, and was full of envy. Likewise those who coincided with Lincoln in his political views were disturbed in the same way. Even Logan was not wholly free from the degrading passion. But in this respect Lincoln suffered no more than other great characters who preceded him in the world's history.
That which Lincoln's adversaries in a lawsuit feared most of all was his apparent disregard of custom or professional propriety in managing a case before a jury. He brushed aside all rules, and very often resorted to some strange and strategic performance which invariably broke his opponent down or exercised some peculiar influence over the jury. Hence the other side in a case were in constant fear of one of his dramatic strokes, or trembled lest he should "ring in" some ingeniously planned interruption not on the programme. In a case where Judge Logan—always earnest and grave—opposed him, Lincoln created no little merriment by his reference to Logan's style of dress. He carried the surprise in store for the latter, till he reached his turn before the jury. Addressing them, he said: "Gentlemen, you must be careful and not permit yourselves to be overcome by the eloquence of counsel for the defense. Judge Logan, I know, is an effective lawyer. I have met him too often to doubt that; but shrewd and careful though he be, still he is sometimes wrong. Since this trial has begun I have discovered that, with all his caution and fastidiousness, he hasn't knowledge enough to put his shirt on right." Logan turned red as crimson, but sure enough, Lincoln was correct, for the former had donned a new shirt, and by mistake had drawn it over his head with the pleated bosom behind. The general laugh which followed destroyed the effect of Logan's eloquence over the jury—the very point at which Lincoln aimed.
The trial of William Armstrong* for the murder of James P. Metzger, in May, 1858, at Beardstown, Illinois, in which Lincoln secured the acquittal of the defendant, was one of the gratifying triumphs in his career as a lawyer.
* This incident in Lincoln's career has been most happily utilized by Dr. Edward Eggleston in his story "The Graysons," recently published in the Century Magazine.
Lincoln's defense, wherein he floored the principal prosecuting witness, who had testified positively to seeing the fatal blow struck in the moonlight, by showing from an almanac that the moon had set, was not more convincing than his eloquent and irresistible appeal in his client's favor. The latter's mother, old Hannah Armstrong, the friend of his youth, had solicited him to defend her son. "He told the jury," relates the prosecuting attorney, "of his once being a poor, friendless boy; that Armstrong's parents took him into their house, fed and clothed him, and gave him a home. There were tears in his eyes as he spoke. The sight of his tall, quivering frame, and the particulars of the story he so pathetically told, moved the jury to tears also, and they forgot the guilt of the defendant in their admiration of his advocate. It was the most touching scene I ever witnessed."*
* J. Henry Shaw, letter, Aug. 22, 1866, MS.
Before passing it may be well to listen to the humble tribute of old Hannah Armstrong, the defendant's mother: "Lincoln had said to me, 'Hannah, your son will be cleared before sundown.' I left the court-room, and they came and told me that my son was cleared and a free man. I went up to the court-house. The jury shook hands with me; so did the judge and Lincoln; tears streamed down Lincoln's eyes.... After the trial I asked him what his fee would be; told him I was poor. 'Why, Hannah,' he said, 'I sha'n't charge you a cent, and anything else I can do for you, will do it willingly and without charge.' He afterwards wrote to me about a piece of land which certain men were trying to get from me, and said: 'Hannah, they can't get your land. Let them try it in the Circuit Court, and then you appeal it; bring it to the Supreme Court and I and Herndon will attend to it for nothing.'" *
The last suit of any importance in which Lincoln was personally engaged, was known as the Johnson sand-bar case. It involved the title to certain lands, the accretion on the shores of Lake Michigan, in or near Chicago. It was tried in the United States Circuit Court at Chicago in April and May, 1860. During the trial, the Court—Judge Drummond—and all the counsel on both sides dined at the residence of Isaac N. Arnold, afterwards a member of Congress. "Douglas and Lincoln," relates Mr. Arnold, "were at the time both candidates for the nomination for President. There were active and ardent political friends of each at the table, and when the sentiment was proposed, 'May Illinois furnish the next President,' it was drank with enthusiasm by the friends of both Lincoln and Douglas."**
* From statement, Nov. 24, 1865. ** Arnold's "Lincoln," p. 90.
I could fill this volume with reminiscences of Lincoln's career as a lawyer, but lest the reader should tire of what must savor in many cases of monotony it is best to move on. I have made this portion of the book rather full; but as Lincoln's individuality and peculiarities were more marked in the law office and court-room than anywhere else it will play its part in making up the picture of the man. Enough has been told to show how, in the face of adverse fortune and the lack of early training, and by force of his indomitable will and self-confidence, he gained such ascendency among the lawyers of Illinois. The reader is enabled thereby to understand the philosophy of his growth.
But now another field is preparing to claim him. There will soon be great need for his clear reason, masterly mind and heroic devotion to principle. The distant mutterings of an approaching contest are driving scattered factions into a union of sentiment and action. As the phalanxes of warriors are preparing for action, amid the rattle of forensic musketry, Lincoln, their courageous leader, equipped for battle, springs into view.
WHILE Lincoln in a certain sense was buried in the law from the time his career in Congress closed till, to use his own words, "the repeal of the Missouri Compromise aroused him again," yet he was a careful student of his times and kept abreast of the many and varied movements in politics. He was generally on the Whig electoral tickets, and made himself heard during each successive canvas,* but he seemed to have lost that zealous interest in politics which characterized his earlier days. He plodded on unaware of, and seemingly without ambition for, the great distinction that lay in store for him.
* In the campaign of 1852, when Pierce was the Democratic candidate for President, Douglas made speeches for him in almost every State in the Union. His "key-note" was sounded at Richmond, Va. Lincoln, whose reputation was limited by the boundaries of Illinois, was invited by the Scott Club of Springfield to answer it, but his soul and heart were not in the undertaking. He had not yet been awakened, and, considering it entire, the speech was a poor effort. Another has truthfully said of it, "If it was distinguished by one quality above another it was by its attempts at humor, and all those attempts were strained and affected, as well as very coarse. He displayed a jealous and petulant temper from the first to the last, wholly beneath the dignity of the occasion and the importance of the topic. Considered as a whole it may be said that none of his public performances was more unworthy of its really noble author than this one. The closing paragraph will serve as a fair sample of the entire speech: "Let us stand by our candidate [Gen. Scott] as faithfully as he has always stood by our country, and I much doubt if we do not perceive a slight abatement of Judge Douglas's confidence in Providence as well as the people. I suspect that confidence is not more firmly fixed with the Judge than it was with the old woman whose horse ran away with her in a buggy. She said she trusted in Providence till the 'britchen' broke, and then she didn't know what on 'airth' to do. The chance is the Judge will see the 'britchen' broke, and then he can at his leisure bewail the fate of Locofocoism as the victim of misplaced confidence."
John T. Stuart relates* that, as he and Lincoln were returning from the court in Tazewell county in 1850, and were nearing the little town of Dillon, they engaged in a discussion of the political situation.
* Statement, J. T. S., MS., July 21, 1865.
"As we were coming down the hill," are Stuart's words, "I said, 'Lincoln, the time is coming when we shall have to be all either Abolitionists or Democrats.' He thought a moment and then answered, ruefully and emphatically, 'When that time comes my mind is made up, for I believe the slavery question can never be successfully compromised.' I responded with equal emphasis, 'My mind is made up too.'" Thus it was with Lincoln. But he was too slow to suit the impetuous demand of the few pronounced Abolitionists whom he met in his daily walks. The sentiment of the majority in Springfield tended in the other direction, and, thus environed, Lincoln lay down like the sleeping lion. The future would yet arouse him. At that time I was an ardent Abolitionist in sentiment. I used to warn Lincoln against his apparent conservatism when the needs of the hour were so great; but his only answer would be, 'Billy, you're too rampant and spontaneous.' I was in correspondence with Sumner, Greeley, Phillips, and Garrison, and was thus thoroughly imbued with all the rancor drawn from such strong anti-slavery sources. I adhered to Lincoln, relying on the final outcome of his sense of justice and right. Every time a good speech on the great issue was made I sent for it. Hence you could find on my table the latest utterances of Giddings, Phillips, Sumner, Seward, and one whom I considered grander than all the others—Theodore Parker. Lincoln and I took such papers as the Chicago Tribune, New York Tribune, Anti-Slavery Standard, Emancipator, and National Era. On the other side of the question we took the Charleston Mercury and the Richmond Enquirer. I also bought a book called "Sociology," written by one Fitzhugh, which defended and justified slavery in every conceivable way. In addition I purchased all the leading histories of the slavery movement, and other works which treated on that subject. Lincoln himself never bought many books, but he and I both read those I have named. After reading them we would discuss the questions they touched upon and the ideas they suggested, from our different points of view. I was never conscious of having made much of an impression on Mr. Lincoln, nor do I believe I ever changed his views. I will go further and say, that, from the profound nature of his conclusions and the labored method by which he arrived at them, no man is entitled to the credit of having either changed or greatly modified them. I remember once, after having read one of Theodore Parker's sermons on slavery, saying to Mr. Lincoln substantially this: "I have always noticed that ill-gotten wealth does no man any good. This is as true of nations as individuals. I believe that all the ill-gotten gain wrenched by us from the negro through his enslavement will eventually be taken from us, and we will be set back where we began." Lincoln thought my prophecy rather direful. He doubted seriously if either of us would live to see the righting of so great a wrong; but years after, when writing his second Inaugural address, he endorsed the idea. Clothing it in the most beautiful language, he says: "Yet if God wills that it [ the war ] continue till all the wealth piled by the bondsman's two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn by the lash shall be paid by another drawn by the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said, 'The judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.'" The passage in May, 1854, of the Kansas-Nebraska bill swept out of sight the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise measures of 1850. This bill, designed and carried through by Douglas, was regarded by him as the masterpiece of all his varied achievements in legislation. It served to prove more clearly than anything he had ever before done his flexibility and want of political conscience. Although in years gone before he had invoked the vengeance of Heaven on the ruthless hand that should dare to disturb the sanctity of the compact of 1821, yet now he was the arrogant and audacious leader in the very work he had so heartily condemned. When we consider the bill and the unfortunate results which followed it in the border States we are irresistibly led to conclude that it was, all things considered, a great public wrong and a most lamentable piece of political jugglery. The stump speech which Thomas H. Benton charged that Douglas had "injected into the belly of the bill" contains all there was of Popular Sovereignty—"It being the true intent and meaning of this act not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States," an argument which, using Lincoln's words, "amounts to this: That if any one man chooses to enslave another no third man shall be allowed to object." The widespread feeling the passage of this law aroused everywhere over the Union is a matter of general history. It stirred up in New England the latent hostility to the aggression of slavery; it stimulated to extraordinary endeavors the derided Abolitionists, arming them with new weapons; it sounded the death-knell of the gallant old Whig party; it drove together strange, discordant elements in readiness to fight a common enemy; it brought to the forefront a leader in the person of Lincoln.
The revolt of Cook, Judd, and Palmer, all young and progressive, from the Democratic majority in the Legislature was the first sign of discontent in Illinois. The rude and partly hostile reception of Douglas, on his arrival in Chicago, did not in any degree tend to allay the feeling of disapproval so general in its manifestation. The warriors, young and old, removed their armor from the walls, and began preparations for the impending conflict. Lincoln had made a few speeches in aid of Scott during the campaign of 1852, but they were efforts entirely unworthy of the man. Now, however, a live issue was presented to him. No one realized this sooner than he. In the office discussions he grew bolder in his utterances. He insisted that the social and political difference between slavery and freedom was becoming more marked; that one must overcome the other; and that postponing the struggle between them would only make it the more deadly in the end. "The day of compromise," he still contended, "has passed. These two great ideas have been kept apart only by the most artful means. They are like two wild beasts in sight of each other, but chained and held apart. Some day these deadly antagonists will one or the other break their bonds, and then the question will be settled." In a conversation with a fellow-lawyer* he said of slavery: "It is the most glittering, ostentatious, and displaying property in the world, and now, if a young man goes courting, the only inquiry is how many negroes he or his lady-love owns. The love for slave property is swallowing up every other mercenary possession. Slavery is a great and crying injustice—an enormous national crime." At another time he made the observation that it was "singular that the courts would hold that a man never lost his right to his property that had been stolen from him, but that he instantly lost his right to himself if he was stolen." It is useless to add more evidence—for it could be piled mountain high—showing that at the very outset Mr. Lincoln was sound to the core on the injustice and crime of human slavery.
* Joseph Gillespie, MS. letter, June 9,'66.
After a brief rest at his home in Chicago Mr. Douglas betook himself to the country, and in October, during the week of the State Fair, we find him in Springfield. On Tuesday he made a speech in the State House which, in view of the hostile attitude of some of his own party friends, was a labored defense of his position. It was full of ingenious sophistry and skilful argument. An unprecedented concourse of people had gathered from all parts of the State, and Douglas, fresh from the halls of Congress, was the lion of the hour. On the following day Mr. Lincoln, as the champion of the opponents of Popular Sovereignty, was selected to represent those who disagreed with the new legislation, and to answer Douglas. His speech encouraged his friends no less than it startled his enemies. At this time I was zealously interested in the new movement, and not less so in Lincoln. I frequently wrote the editorials in the Springfield Journal the editor, Simeon Francis, giving to Lincoln and to me the utmost liberty in that direction. Occasionally Lincoln would write out matter for publication, but I believe I availed myself of the privilege oftener than he. The editorial in the issue containing the speeches of Lincoln and Douglas on this occasion was my own, and while in description it may seem rather strongly imbued with youthful enthusiasm, yet on reading it in maturer years I am still inclined to believe it reasonably faithful to the facts and the situation. "The anti-Nebraska speech of Mr. Lincoln," says the article, "was the profoundest in our opinion that he has made in his whole life. He felt upon his soul the truths burn which he uttered, and all present felt that he was true to his own soul. His feelings once or twice swelled within, and came near stifling utterance. He quivered with emotion. The whole house was as still as death. He attacked the Nebraska bill with unusual warmth and energy; and all felt that a man of strength was its enemy, and that he intended to blast it if he could by strong and manly efforts. He was most successful, and the house approved the glorious triumph of truth by loud and continued huzzas. Women waved their white handkerchiefs in token of woman's silent but heartfelt assent. Douglas felt the sting; the animal within him was roused because he frequently interrupted Mr. Lincoln. His friends felt that he was crushed by Lincoln's powerful argument, manly logic, and illustrations from nature around us. The Nebraska bill was shivered, and like a tree of the forest was torn and rent asunder by the hot bolts of truth. Mr. Lincoln exhibited Douglas in all the attitudes he could be placed, in a friendly debate. He exhibited the bill in all its aspects to show its humbuggery and falsehood, and, when thus torn to rags, cut into slips, held up to the gaze of the vast crowd, a kind of scorn and mockery was visible upon the face of the crowd and upon the lips of their most eloquent speaker. At the conclusion of this speech every man and child felt that it was unanswerable. He took the heart captive and broke like a sun over the understanding."
Anent the subject of editorial writing it may not be inappropriate to relate that Lincoln and I both kept on furnishing political matter of many varieties for the Springfield Journal until 1860. Many of the editorials that I wrote were intended directly or indirectly to promote the interest of Lincoln. I wrote one on the advisability of annexing Cuba to the United States, taking the rather advanced ground that slavery would be abolished in Cuba before it would in this country—a position which aroused no little controversy with other papers. One little incident occurs to me in this connection which may not be without interest to newspaper men. A newspaper had been started in Springfield called the Conservative, which, it was believed, was being run in the interest of the Democratic party. While pretending to support Fillmore it was kept alive by Buchanan men and other kindred spirits, who were somewhat pro-slavery in their views. The thing was damaging Lincoln and the friends of freedom more than an avowed Democratic paper could. The editor, an easy, good-natured fellow, simply placed in charge to execute the will of those who gave the paper its financial backing, was a good friend of mine, and by means of this friendship I was always well informed of matters in the Conservative editorial room. One day I read in the Richmond Enquirer an article endorsing slavery, and arguing that from principle the enslavement of either whites or blacks was justifiable and right. I showed it to Lincoln, who remarked that it was "rather rank doctrine for Northern Democrats to endorse. I should like to see," he said, with emphasis, "some of these Illinois newspapers champion that." I told him if he would only wait and keep his own counsel I would have a pro-slavery organ in Springfield publish that very article. He doubted it, but when I told him how it was to be done he laughed and said, "Go in." I cut the slip out and succeeded in getting it in the paper named. Of course it was a trick, but it acted admirably. Its appearance in the new organ, although without comment, almost ruined that valuable journal, and my good-natured friend the editor was nearly overcome by the denunciation of those who were responsible for the organ's existence. My connection, and Lincoln's too,—for he endorsed the trick,—with the publication of the condemned article was eventually discovered, and we were thereafter effectually prevented from getting another line in the paper. The anti-slavery people quoted the article as having been endorsed by a Democratic newspaper in Springfield, and Lincoln himself used it with telling effect. He joined in the popular denunciation, expressing great astonishment that such a sentiment could find lodgment in any paper in Illinois, although he knew full well how the whole thing had been carried through.
During the remainder of the State-Fair week, speeches were made by Lyman Trumbull, Sidney Breese, E. D. Taylor, and John Calhoun, none of which unfortunately have been preserved. Among those who mingled in the crowd and listened to them was Owen Lovejoy, a radical, fiery, brave, fanatical man, it may be, but one full of the virus of Abolitionism. I had been thoroughly inoculated with the latter myself, and so had many others, who helped to swell the throng. The Nebraska movement had kindled anew the old zeal, and inspired us with renewed confidence to begin the crusade. As many of us as could, assembled together to organize for the campaign before us. As soon therefore as Lincoln finished his speech in the hall of the House of Representatives, Lovejoy, moving forward from the crowd, announced a meeting in the same place that evening of all the friends of Freedom. That of course meant the Abolitionists with whom I had been in conference all the day. Their plan had been to induce Mr. Lincoln to speak for them at their meeting. Strong as I was in the faith, yet I doubted the propriety of Lincoln's taking any stand yet. As I viewed it, he was ambitious to climb to the United States Senate, and on grounds of policy it would not do for him to occupy at that time such advanced ground as we were taking. On the other hand, it was equally as dangerous to refuse a speech for the Abolitionists. I did not know how he felt on the subject, but on learning that Lovejoy intended to approach him with an invitation, I hunted up Lincoln and urged him to avoid meeting the enthusiastic champion of Abolitionism. "Go home at once," I said. "Take Bob with you and drive somewhere into the country and stay till this thing is over." Whether my admonition and reasoning moved him or not I do not know, but it only remains to state that under pretence of having business in Tazewell county he drove out of town in his buggy, and did not return till the apostles of Abolitionism had separated and gone to their homes.* I have always believed this little arrangement—it would dignify it too much to call it a plan—saved Lincoln. If he had endorsed the resolutions passed at the meeting, or spoken simply in favor of freedom that night, he would have been identified with all the rancor and extremes of Abolitionism. If, on the contrary, he had been invited to join them, and then had refused to take a position as advanced as theirs, he would have lost their support. In either event he was in great danger; and so he who was aspiring to succeed his old rival, James Shields, in the United States Senate was forced to avoid the issue by driving hastily in his one horse buggy to the court in Tazewell county. A singular coincidence suggests itself in the fact that, twelve years before, James Shields and a friend drove hastily in the same direction, and destined for the same point, to force Lincoln to take issue in another and entirely different matter.
* See Lincoln's Speech, Joint Debate, Ottawa, Ills., Aug. 20, 1858.
By request of party friends Lincoln was induced to follow after Douglas and, at the various places where the latter had appointments to speak, reply to him. On the 16th of October they met at Peoria, where Douglas enjoyed the advantages of an "open and close." Lincoln made an effective speech, which he wrote out and furnished to the Sangamon Journal for publication, and which can be found among his public utterances. His party friends in Springfield and elsewhere, who had urged him to push after Douglas till he cried, "enough," were surprised a few days after the Peoria debate to find him at home, with the information that by an agreement with the latter they were both to return home and speak no more during the campaign. Judge of his astonishment a few days later to find that his rival, instead of going direct to his home in Chicago, had stopped at Princeton and violated his express agreement by making a speech there! Lincoln was much displeased at this action of Douglas, which tended to convince him that the latter was really a man devoid of fixed political morals. I remember his explanation in our office made to me, William Butler, William Jayne, Ben. F. Irwin, and other friends, to account for his early withdrawal from the stump. After the Peoria debate Douglas approached him and flattered him by saying that he was giving him more trouble on the territorial and slavery questions than all the United States Senate, and he therefore proposed to him that both should abandon the field and return to their homes. Now Lincoln could never refuse a polite request—one in which no principle was involved. I have heard him say, "It's a fortunate thing I wasn't born a woman, for I cannot refuse anything, it seems." He therefore consented to the cessation of debate proposed by Douglas, and the next day both went to the town of Lacon, where they had been billed for speeches. Their agreement was kept from their friends, and both declined to speak—Douglas, on the ground of hoarseness, and Lincoln gallantly refusing to take advantage of "Judge Douglas's indisposition." Here they separated, Lincoln going directly home, and Douglas, as before related, stopping at Princeton and colliding in debate with Owen Lovejoy. Upon being charged afterwards with his breach of agreement Douglas responded that Lovejoy "bantered and badgered" him so persistently he could not gracefully resist the encounter. The whole thing thoroughly displeased Lincoln.*
* In a letter from Princeton, Ill., March 15, 1866, John H. Bryant, brother of the poet William Cullen Bryant, writes: "I have succeeded in finding an old file of our Princeton papers, from which I learn that Mr. Douglas spoke here on Wednesday, Oct. 18, 1854. This fixes the date. I recollect that he staid at Tiskilwa, six miles south of this, the night before, and a number of our Democrats went down the next morning and escorted him to this place. Douglas spoke first one half-hour and was answered by Lovejoy one half- hour, when Douglas talked till dark, giving no opportunity for reply. "Yours truly, "John H. Bryant."
During this campaign Lincoln was nominated and elected to the Legislature. This was done in the face of his unwillingness and over his protest. On the ticket with him was Judge Logan. Both were elected by a majority of about 600 votes. Lincoln, being ambitious to reach the United States Senate, and warmly encouraged in his aspirations by his wife, resigned his seat in the Legislature in order that he might the more easily be elected to succeed his old rival James Shields, who was then one of the senators from Illinois. His canvass for that exalted office was marked by his characteristic activity and vigilance. During the anxious moments that intervened between the general election and the assembling of the Legislature he slept, like Napoleon, with one eye open. While attending court at Clinton on the 11th of November, a few days after the election, he wrote to a party friend in the town of Paris: "I have a suspicion that a Whig has been elected to the Legislature from Edgar. If this is not so, why then, 'nix cum arous; but if it is so, then could you not make a mark with him for me for U. S. Senator? I really have some chance. Please write me at Springfield giving me the names, post-offices, and political positions of your Representative and Senator, whoever they may be. Let this be confidential.'"
That man who thinks Lincoln calmly sat down and gathered his robes about him, waiting for the people to call him, has a very erroneous knowledge of Lincoln. He was always calculating, and always planning ahead. His ambition was a little engine that knew no rest. The vicissitudes of a political campaign brought into play all his tact and management and developed to its fullest extent his latent industry. In common with other politicians he never overlooked a newspaper man who had it in his power to say a good or bad thing of him. The press of that day was not so powerful an institution as now, but ambitious politicians courted the favor of a newspaper man with as much zeal as the same class of men have done in later days. I remember a letter Lincoln once wrote to the editor of an obscure little country newspaper in southern Illinois in which he warms up to him in the following style.* "Friend Harding: I have been reading your paper for three or four years and have paid you nothing for it." He then encloses ten dollars and admonishes the editor with innocent complacency: "Put it into your pocket, saying nothing further about it." Very soon thereafter, he prepared an article on political matters and sent it to the rural journalist, requesting its publication in the editorial columns of his "valued paper," but the latter, having followed Lincoln's directions and stowed the ten dollars away in his pocket, and alive to the importance of his journal's influence, declined, "because," he said, "I long ago made it a rule to publish nothing as editorial matter not written by myself." Lincoln read the editor's answer to me. Although the laugh was on Lincoln he enjoyed the joke heartily. "That editor," he said, "has a rather lofty but proper conception of true journalism."
Meanwhile the Legislature had convened and the Senatorial question came on for solution. The history of this contest is generally understood, and the world has repeatedly been told how Lincoln was led to expect the place and would have won but for the apostasy of the five anti-Nebraska men of Democratic antecedents who clung to and finally forced the election of Lyman Trumbull. The student of history in after years will be taught to revere the name of Lincoln for his exceeding magnanimity in inducing his friends to abandon him at the critical period and save Trumbull, while he himself disappeared beneath the waves of defeat.*
* "After a number of ballots—Judd of Cook, Cook of La Salle, Palmer of Macoupin, and Allen and Baker of Madison voting for Trumbull—I asked Mr. Lincoln what he would advise us to do. He answered, 'Go for Trumbull by all means.' We understood the case to be that Shields was to be run by the Democrats at first and then to be dropped, and Joel A. Matteson put up; and it was calculated that certain of our men who had been elected on the 'Free Soil' issue would vote for him after they had acted with us long enough to satisfy their consciences and constituents. Our object was to force an election before they got through with their programme. We were savagely opposed to Matteson, and so was Mr. Lincoln, who said that if we did not drop in and unite upon Trumbull the five men above-named would go for Matteson and elect him, which would be an everlasting disgrace to the State. We reluctantly complied; went to Trumbull and elected him. I remember that Judge S. T. Logan gave up Lincoln with great reluctance. He begged hard to try him on one or two ballots more, but Mr. Lincoln urged us not to risk it longer. I never saw the latter more earnest and decided. He congratulated Trumbull warmly, although of course greatly disappointed and mortified at his own want of success."— Joseph Gillespie, letter, September 19, 1866, MS.
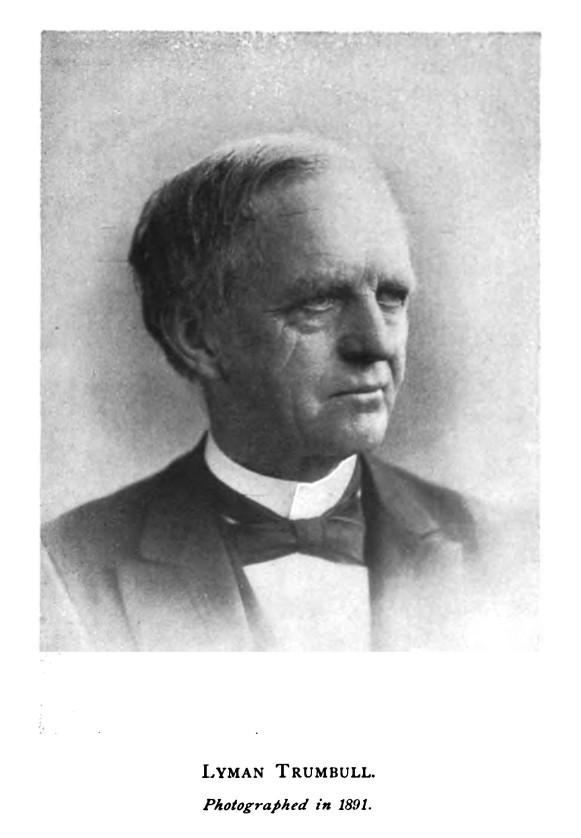

This frustration of Lincoln's ambition had a marked effect on his political views. It was plain to him now that the "irrepressible conflict" was not far ahead. With the strengthening of his faith in a just cause so long held in abeyance he became more defiant each day. But in the very nature of things he dared not be as bold and outspoken as I. With him every word and sentence had to be weighed and its effects calculated, before being uttered: but with me that operation had to be reversed if done at all. An incident that occurred about this time will show how his views were broadening. Some time after the election of Trumbull a young negro, the son of a colored woman in Springfield known as Polly, went from his home to St. Louis and there hired as a hand on a lower Mississippi boat,—for what special service, I do not recollect,—arriving in New Orleans without what were known as free papers. Though born free he was subjected to the tyranny of the "black code," all the more stringent because of the recent utterances of the Abolitionists in the North, and was kept in prison until his boat had left. Then, as no one was especially interested in him, he was forgotten. After a certain length of time established by law, he would inevitably have been sold into slavery to defray prison expenses had not Lincoln and I interposed our aid. The mother came to us with the story of the wrong done her son and induced us to interfere in her behalf. We went first to see the Governor of Illinois, who, after patient and thorough examination of the law, responded that he had no right or power to interfere. Recourse was then had to the Governor of Louisiana, who responded in like manner. We were sorely perplexed. A second interview with the Governor of Illinois resulting in nothing favorable Lincoln rose from his chair, hat in hand, and exclaimed with some emphasis: "By God, Governor, I'll make the ground in this country too hot for the foot of a slave, whether you have the legal power to secure the release of this boy or not." Having exhausted all legal means to recover the negro we dropped our relation as lawyers to the case. Lincoln drew up a subscription-list, which I circulated, collecting funds enough to purchase the young man's liberty. The money we sent to Col. A. P. Fields, a friend of ours in New Orleans, who applied it as directed, and it restored the prisoner to his overjoyed mother.
The political history of the country, commencing in 1854 and continuing till the outbreak of the Rebellion, furnishes the student a constant succession of stirring and sometimes bloody scenes. No sooner had Lincoln emerged from the Senatorial contest in February, 1855, and absorbed himself in the law, than the outrages on the borders of Missouri and Kansas began to arrest public attention. The stories of raids, election frauds, murders, and other crimes were moving eastward with marked rapidity. These outbursts of frontier lawlessness, led and sanctioned by the avowed pro-slavery element, were not only stirring up the Abolitionists to fever heat, but touching the hearts of humanity in general. In Illinois an association was formed to aid the cause of "Free-Soil" men in Kansas. In the meetings of these bands the Abolitionists of course took the most prominent part. At Springfield we were energetic, vigilant, almost revolutionary. We recommended the employment of any means, however desperate, to promote and defend the cause of freedom. At one of these meetings Lincoln was called on for a speech. He responded to the request, counselling moderation and less bitterness in dealing with the situation before us. We were belligerent in tone, and clearly out of patience with the Government. Lincoln opposed the notion of coercive measures with the possibility of resulting bloodshed, advising us to eschew resort to the bullet. "You can better succeed," he declared, "with the ballot. You can peaceably then redeem the Government and preserve the liberties of mankind through your votes and voice and moral influence.... Let there be peace. Revolutionize through the ballot box, and restore the Government once more to the affections and hearts of men by making it express, as it was intended to do, the highest spirit of justice and liberty. Your attempt, if there be such, to resist the laws of Kansas by force is criminal and wicked; and all your feeble attempts will be follies and end in bringing sorrow on your heads and ruin the cause you would freely die to preserve!" These judicious words of counsel, while they reduced somewhat our ardor and our desperation, only placed before us in their real colors the grave features of the situation. We raised a neat sum of money, Lincoln showing his sincerity by joining in the subscription, and forwarded it to our friends in Kansas.
The Whig party, having accomplished its mission in the political world, was now on the eve of a great break-up. Lincoln realized this and, though proverbially slow in his movements, prepared to find a firm footing when the great rush of waters should come and the maddening freshet sweep former landmarks out of sight. Of the strongest significance in this connection is a letter written by him at this juncture to an old friend in Kentucky, who called to his attention their differences of views on the wrong of slavery. Speaking of his observation of the treatment of the slaves, he says: "I confess I hate to see the poor creatures hunted down and caught and carried back to their unrequited toils; but I bite my lips and keep quiet. In 1841 you and I had rather a tedious low-water trip on a steamboat from Louisville to St. Louis. You may remember, as I well do, that from Louisville to the mouth of the Ohio, there were on board ten or a dozen slaves shackled together with irons. That sight was a continued torment to me; and I see something like it every time I touch the Ohio or any slave border. It is not fair for you to assume that I have no interest in a thing which has, and continually exercises, the power of making me miserable. You ought rather to appreciate how much the great body of the Northern people do crucify their feelings in order to maintain their loyalty to the Constitution and the Union. I do oppose the extension of slavery because my judgment and feeling so prompt me; and I am under no obligations to the contrary. If for this you and I must differ, differ we must."
Finding himself drifting about with the disorganized elements that floated together after the angry political waters had subsided, it became apparent to Lincoln that if he expected to figure as a leader he must take a stand himself. Mere hatred of slavery and opposition to the injustice of the Kansas-Nebraska legislation were not all that were required of him. He must be a Democrat, Know-Nothing, Abolitionist, or Republican, or forever float about in the great political sea without compass, rudder, or sail. At length he declared himself. Believing the times were ripe for more advanced movements, in the spring of 1856 I drew up a paper for the friends of freedom to sign, calling a county convention in Springfield to select delegates for the forthcoming Republican State convention in Bloomington. The paper was freely circulated and generously signed. Lincoln was absent at the time and, believing I knew what his "feeling and judgment" on the vital questions of the hour were, I took the liberty to sign his name to the call. The whole was then published in the Springfield Journal. No sooner had it appeared than John T. Stuart, who, with others, was endeavoring to retard Lincoln in his advanced movements, rushed into the office and excitedly asked if "Lincoln had signed that Abolition call in the Journal?" I answered in the negative, adding that I had signed his name myself. To the question, "Did Lincoln authorize you to sign it?" I returned an emphatic "No." "Then," exclaimed the startled and indignant Stuart, "you have ruined him." But I was by no means alarmed at what others deemed inconsiderate and hasty action. I thought I understood Lincoln thoroughly, but in order to vindicate myself if assailed I immediately sat down, after Stuart had rushed out of the office, and wrote Lincoln, who was then in Tazewell County attending court, a brief account of what I had done and how much stir it was creating in the ranks of his conservative friends. If he approved or disapproved my course I asked him to write or telegraph me at once. In a brief time came his answer: "All right; go ahead. Will meet you—radicals and all." Stuart subsided, and the conservative spirits who hovered around Springfield no longer held control of the political fortunes of Abraham Lincoln.
The Republican party came into existence in Illinois as a party at Bloomington, May 29, 1856. The State convention of all opponents of anti-Nebraska legislation, referred to in a foregoing paragraph, had been set for that day. Judd, Yates, Trumbull, Swett, and Davis were there; so also was Lovejoy, who, like Otis of colonial fame, was a flame of fire. The firm of Lincoln and Herndon was represented by both members in person. The gallant William H. Bissell, who had ridden at the head of the Second Illinois Regiment at the battle of Buena Vista in the Mexican war, was nominated as governor. The convention adopted a platform ringing with strong anti-Nebraska sentiments, and then and there gave the Republican party its official christening. The business of the convention being over, Mr. Lincoln, in response to repeated calls, came forward and delivered a speech of such earnestness and power that no one who heard it will ever forget the effect it produced. In referring to this speech some years ago I used the following rather graphic language: "I have heard or read all of Mr. Lincoln's great speeches, and I give it as my opinion that the Bloomington speech was the grand effort of his life. Heretofore he had simply argued the slavery question on grounds of policy,—the statesman's grounds,—never reaching the question of the radical and the eternal right. Now he was newly baptized and freshly born; he had the fervor of a new convert; the smothered flame broke out; enthusiasm unusual to him blazed up; his eyes were aglow with an inspiration; he felt justice; his heart was alive to the right; his sympathies, remarkably deep for him, burst forth, and he stood before the throne of the eternal Right. His speech was full of fire and energy and force; it was logic; it was pathos; it was enthusiasm; it was justice, equity, truth, and right set ablaze by the divine fires of a soul maddened by the wrong; it was hard, heavy, knotty, gnarly, backed with wrath. I attempted for about fifteen minutes as was usual with me then to take notes, but at the end of that time I threw pen and paper away and lived only in the inspiration of the hour. If Mr. Lincoln was six feet, four inches high usually, at Bloomington that day he was seven feet, and inspired at that. From that day to the day of his death he stood firm in the right. He felt his great cross, had his great idea, nursed it, kept it, taught it to others, in his fidelity bore witness of it to his death, and finally sealed it with his precious blood." The foregoing paragraph, used by me in a lecture in 1866, may to the average reader seem somewhat vivid in description, besides inclining to extravagance in imagery, yet although more than twenty years have passed since it was written I have never seen the need of altering a single sentence. I still adhere to the substantial truthfulness of the scene as described. Unfortunately Lincoln's speech was never written out nor printed, and we are obliged to depend for its reproduction upon personal recollection.
The Bloomington convention and the part Lincoln took in it met no such hearty response in Springfield as we hoped would follow. It fell flat, and in Lincoln's case drove from him many persons who had heretofore been his warm political friends. A few days after our return we announced a meeting at the court-house to ratify the action of the Bloomington convention. After the usual efforts to draw a crowd, however, only three persons had temerity enough to attend. They were Lincoln, the writer, and a courageous man named John Pain. Lincoln, in answer to the "deafening calls" for a speech, responded that the meeting was larger than he knew it would be, and that while he knew that he himself and his partner would attend he was not sure anyone else would, and yet another man had been found brave enough to come out. "While all seems dead," he exhorted, "the age itself is not. It liveth as sure as our Maker liveth. Under all this seeming want of life and motion, the world does move nevertheless. Be hopeful, and now let us adjourn and appeal to the people."
Not only in Springfield but everywhere else the founders of the Republican party—the apostles of freedom—went out to battle for the righteousness of their cause. Lincoln, having as usual been named as one of the Presidential electors, canvassed the State, making in all about fifty speeches. He was in demand everywhere. I have before me a package of letters addressed to him, inviting him to speak at almost every county seat in the State. Yates wanted him to go to one section of the State, Washburne to another, and Trumbull still another; while every cross-roads politician and legislative aspirant wanted him "down in our country, where we need your help." Joshua R. Giddings wrote him words of encouragement. "You may start," said the valiant old Abolitionist in a letter from Peoria,* "on the one great issue of restoring Kansas and Nebraska to freedom, or rather of restoring the Missouri Compromise, and in this State no power on earth can withstand you on that issue." The demand for Lincoln was not confined to his own State. Indiana sent for him, Wisconsin also, while Norman B. Judd and Ebenezer Peck, who were stumping Iowa, sent for him to come there.
* J. R. Giddings, MS. letter, Sept. 18, 1855.
A town committee invited him to come during "our Equestrian Fair on the 9th, 10th, and 11th," evidently anticipating a three days' siege. An enthusiastic officer in a neighboring town urges him: "Come to our place, because in you do our people place more confidence than in any other man. Men who do not read want the story told as you only can tell it. Others may make fine speeches, but it would not be 'Lincoln said so in his speech.'" A jubilant friend in Chicago writes: "Push on the column of freedom. Give the Buck Africans plenty to do in Egypt. The hour of our redemption draweth nigh. We are coming to Springfield with 20,000 majority!" A postmaster, acting under the courage of his convictions, implores him to visit his neighborhood. "The Democrats here," he insists, "are dyed in the wool. Thunder and lightning would not change their political complexion. I am postmaster here," he adds, confidentially, "for which reason I must ask you to keep this private, for if old Frank [President Pierce] were to hear of my support of Frémont I would get my walking papers sure enough." A settlement of Germans in southern Indiana asked to hear him; and the president of a college, in an invitation to address the students under his charge, characterizes him as "one providentially raised up for a time like this, and even should defeat come in the contest, it would be some consolation to remember we had Hector for a leader."
And thus it was everywhere. Lincoln's importance in the conduct of the campaign was apparent to all, and his canvass was characterized by his usual vigor and effectiveness. He was especially noted for his attempt to break down the strength of Fillmore, who was nominated as a third party candidate and was expected to divide the Republican vote. He tried to wean away Fillmore's adherents by an adroit and ingenious letter* sent to those suspected of the latter's support, and marked confidential, in which he strove to show that in clinging to their candidate they were really aiding the election of Buchanan. But the effort proved unavailing, for in spite of all his arguments and appeals a large number of the Fillmore men clung tenaciously to their leader, resulting in Buchanan's election. The vote in Illinois stood, Buchanan 105,344, Frémont 96,180, and Fillmore 37,451. At the same time Bissell was elected governor by a majority of 4729 over W. A. Richardson, Democrat. After the heat and burden of the day Lincoln returned home, bearing with him more and greater laurels than ever. The signs of the times indicated, and the result of the canvass demonstrated, that he and he alone was powerful enough to meet the redoubtable Little Giant in a greater conflict yet to follow.
* One of these letters which Lincoln wrote to counteract the Fillmore movement is still in my possession. As it is more or less characteristic I copy it entire: "Springfield, September 8,1856. "Harrison Maltby, Esq. "Dear Sir: "I understand you are a Fillmore man. Let me prove to you that every vote withheld from Frémont and given to Fillmore in this State actually lessens Fillmore's chance of being President. "Suppose Buchanan gets all the slave States and Pennsylvania and any other one State besides; then he is elected, no matter who gets all the rest. But suppose Fillmore gets the two slave States of Maryland and Kentucky, then Buchanan is not elected; Fillmore goes into the House of Representatives and may be made President by a compromise. But suppose again Fillmore's friends throw away a few thousand votes on him in Indiana and Illinois; it will inevitably give these States to Buchanan, which will more than compensate him for the loss of Maryland and Kentucky; it will elect him, and leave Fillmore no chance in the House of Representatives or out of it. "This is as plain as adding up the weight of three small hogs. As Mr. Fillmore has no possible chance to carry Illinois for himself it is plainly to his interest to let Frémont take it and thus keep it out of the hands of Buchanan. Be not deceived. Buchanan is the hard horse to beat in this race. Let him have Illinois, and nothing can beat him; and he will get Illinois if men persist in throwing away votes upon Mr. Fillmore. Does some one persuade you that Mr. Fillmore can carry Illinois? Nonsense! There are over seventy newspapers in Illinois opposing Buchanan, only three or four of which support Mr. Fillmore, all the rest going for Frémont. Are not these newspapers a fair index of the proportion of the votes? If not, tell me why. "Again, of these three or four Fillmore newspapers, two at least are supported in part by the Buchanan men, as I understand. Do not they know where the shoe pinches? They know the Fillmore movement helps them, and therefore they help it. "Do think these things over and then act according to your judgment. "Yours very truly, "A. LINCOLN." [Confidential.]
I SHALL be forced to omit much that happened during the interval between the election of Buchanan and the campaign of 1858, for the reason that it would not only swell this work to undue proportions, but be a mere repetition of what has been better told by other writers. It is proper to note in passing, however, that Mr. Lincoln's reputation as a political speaker was no longer bounded by the border lines of Illinois. It had passed beyond the Wabash, the Ohio, and the Mississippi rivers, and while his pronounced stand on the slavery question had increased the circle of his admirers in the North it provoked a proportionate amount of execration in the South. He could not help the feeling that he was now the leading Republican in his State, and he was therefore more or less jealous of his prerogative. Formidable in debate, plain in speech, without pretence of literary acquirements, he was none the less self-reliant. He already envied the ascendancy and domination Douglas exercised over his followers, and felt keenly the slight given him by others of his own faith whom he conceived were disposed to prevent his attaining the leadership of his party. I remember early in 1858 of his coming into the office one morning and speaking in very dejected terms of the treatment he was receiving at the hands of Horace Greeley. "I think Greeley," he complained, "is not doing me right. His conduct, I believe, savors a little of injustice. I am a true Republican and have been tried already in the hottest part of the anti-slavery fight, and yet I find him taking up Douglas, a veritable dodger,—once a tool of the South, now its enemy,—and pushing him to the front. He forgets that when he does that he pulls me down at the same time. I fear Greeley's attitude will damage me with Sumner, Seward, Wilson, Phillips, and other friends in the East." This was said with so much of mingled sadness and earnestness that I was deeply impressed. Lincoln was gloomy and restless the entire day. Greeley's letters were driving the enthusiasm out of him.*
* Greeley's letters were very pointed and sometimes savage. Here is one; "I have not proposed to instruct the Republicans of Illinois in their political duties, and I doubt very much that even so much as is implied in your letter can be fairly deduced from anything I have written. Now let me make one prediction. If you run a candidate [for Congress] against Harris and he is able to canvass he will beat you badly. He is more of a man at heart and morally than Douglas, and has gone into this fight with more earnestness and less calculation. Of the whole Douglas party he is the truest and best. I never spoke a dozen words with him in my life, having met him but once, but if I lived in his district I should vote for him. As I have never spoken of him in my paper, and suppose I never shall, I take the liberty to say this much to you. Now paddle your own dug- out! "Yours, "Horace Greeley."
He seemed unwilling to attend to any business, and finally, just before noon, left the office, going over to the United States Court room to play a game of chess with Judge Treat, and did not return again that day. I pondered a good deal over Lincoln's dejection, and that night, after weighing the matter well in mind, resolved to go to the eastern States myself and endeavor to sound some of the great men there. The next day, on apprising Lincoln of my determination, he questioned its propriety. Our relations, he insisted, were so intimate that a wrong construction might be put upon the movement. I listened carefully to him, but as I had never been beyond the Alleghanies I packed my valise and went, notwithstanding his objections. I had been in correspondence on my own account with Greeley, Seward, Sumner, Phillips, and others for several years, had kept them informed of the feelings of our people and the political campaigns in their various stages, but had never met any of them save Greeley. I enjoyed heartily the journey and the varied sights and scenes that attended it. Aside from my mission, the trip was a great success. The magnificent buildings, the display of wealth in the large cities and prosperous manufacturing towns, broadened the views of one whose vision had never extended beyond the limits of the Illinois prairies. In Washington I saw and dined with Trumbull, who went over the situation with me. Trumbull had written to Lincoln shortly before* that he thought it "useless to speculate upon the further course of Douglas or the effect it is to have in Illinois or other States. He himself does not know where he is going or where he will come out."
* Letter, December 25, 1857, MS.
At my interview with Trumbull, however, he directed me to assure Mr. Lincoln that Douglas did not mean to join the Republican party, however great the breach between himself and the administration might be. "We Republicans here," he said exultingly in another letter to Lincoln, "are in good spirits, and are standing back to let the fight go on between Douglas and his former associates. Lincoln will lose nothing by this if he can keep the attention of our Illinois people from being diverted from the great and vital question of the day to the minor and temporary issues which are now being discussed."*
* Letter, December 27,1857, MS.
In Washington I saw also Seward, Wilson, and others of equal prominence. Douglas was confined to his house by illness, but on receiving my card he directed me to be shown up to his room. We had a pleasant and interesting interview. Of course the conversation soon turned on Lincoln. In answer to an inquiry regarding the latter I remarked that Lincoln was pursuing the even tenor of his way. "He is not in anybody's way," I contended, "not even in yours, Judge Douglas." He was sitting up in a chair smoking a cigar. Between puffs he responded that neither was he in the way of Lincoln or any one else, and did not intend to invite conflict. He conceived that he had achieved what he had set out to do, and hence did not feel that his course need put him in opposition to Mr. Lincoln or his party. "Give Mr. Lincoln my regards," he said, rather warmly, "when you return, and tell him I have crossed the river and burned my boat." Leaving Washington, my next point was New York, where I met the editor of the Anti-Slavery Standard, Horace Greeley, Henry Ward Beecher, and others. I had a long talk with Greeley, who, I noticed, leaned towards Douglas. I found, however, he was not at all hostile to Lincoln.
I presented the latter's case in the best phase I knew how, but while I drew but little from him, I left feeling that he hadn't been entirely won over. He introduced me to Beecher, who, as everybody else did, inquired after Lincoln and through me sent him words of encouragement and praise.*
* Lincoln's greatest fear was that Douglas might be taken up by the Republicans. Senator Seward, when I met him in Washington, assured me there was no danger of it, insisting that the Republicans nor any one else could place any reliance on a man so slippery as Douglas.
From New York I went to Boston, and from the latter place I wrote Lincoln a letter which happily I found not long since in a bundle of Lincoln's letters, and which I insert here, believing it affords a better reflex of the situation at the time than anything I might see fit to say now. Here it is:
"Revere House,
"Boston, Mass., March 24, 1858.
"Friend Lincoln.
"I am in this city of notions, and am well—very well indeed. I wrote you a hasty letter from Washington some days ago, since which time I have been in Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, and now here. I saw Greeley, and so far as any of our conversation is interesting to you I will relate. And we talked, say twenty minutes. He evidently wants Douglas sustained and sent back to the Senate. He did not say so in so many words, yet his feelings are with Douglas. I know it from the spirit and drift of his conversation. He talked bitterly—somewhat so—against the papers in Illinois, and said they were fools. I asked him this question, 'Greeley, do you want to see a third party organized, or do you want Douglas to ride to power through the North, which he has so much abused and betrayed? and to which he replied, 'Let the future alone; it will all come right. Douglas is a brave man. Forget the past and sustain the righteous' Good God, righteous, eh!
"Since I have landed in Boston I have seen much that was entertaining and interesting. This morning I was introduced to Governor Banks. He and I had a conversation about Republicanism and especially about Douglas. He asked me this question, 'You will sustain Douglas in Illinois, wont you?' and to which I said 'No, never!' He affected to be much surprised, and so the matter dropped and turned on Republicanism, or in general—Lincoln. Greeley's and other sheets that laud Douglas, Harris, et al., want them sustained, and will try to do it. Several persons have asked me the same question which Banks asked, and evidently they get their cue, ideas, or what not from Greeley, Seward, et al. By-the-bye, Greeley remarked to me this, 'The Republican standard is too high; we want something practical.'
"This may not be interesting to you, but, however it may be, it is my duty to state what is going on, so that you may head it off—counteract it in some way. I hope it can be done. The Northern men are cold to me—somewhat repellent.
"Your friend,
"W. H. Herndon."
On my return home I had encouraging news to relate. I told Lincoln of the favorable mention I had heard of him by Phillips, Sumner, Seward, Garrison, Beecher, and Greeley. I brought with me additional sermons and lectures by Theodore Parker, who was warm in his commendation of Lincoln. One of these was a lecture on "The Effect of Slavery on the American People," which was delivered in the Music Hall in Boston, and which I gave to Lincoln, who read and returned it. He liked especially the following expression, which he marked with a pencil, and which he in substance afterwards used in his Gettysburg address: "Democracy is direct self-government, over all the people, for all the people, by all the people."
Meanwhile, passing by other events which have become interwoven in the history of the land, we reach April, 1858, at which time the Democratic State convention met and, besides nominating candidates for State offices, endorsed Mr. Douglas' services in the Senate, thereby virtually renominating him for that exalted office. In the very nature of things Lincoln was the man already chosen in the hearts of the Republicans of Illinois for the same office, and therefore with singular appropriateness they passed, with great unanimity, at their convention in Springfield on the 16th of June, the characteristic resolution: "That Hon. Abraham Lincoln is our first and only choice for United States Senator to fill the vacancy about to be created by the expiration of Mr. Douglas' term of office." There was of course no surprise in this for Mr. Lincoln. He had been all along led to expect it, and with that in view had been earnestly and quietly at work preparing a speech in acknowledgment of the honor about to be conferred on him. This speech he wrote on stray envelopes and scraps of paper, as ideas suggested themselves, putting them into that miscellaneous and convenient receptacle, his hat. As the convention drew near he copied the whole on connected sheets, carefully revising every line and sentence, and fastened them together, for reference during the delivery of the speech, and for publication. The former precaution, however, was unnecessary, for he had studied and read over what he had written so long and carefully that he was able to deliver it without the least hesitation or difficulty. A few days before the convention, when he was at work on the speech, I remember that Jesse K. Dubois,* who was Auditor of State, came into the office and, seeing Lincoln busily writing, inquired what he was doing or what he was writing.
* "After the convention Lincoln met me on the street and said, 'Dubois, I can tell you now what I was doing the other day when you came into my office. I was writing that speech, and I knew if I read the passage about the "house divided against itself" to you, you would ask me to change or modify it, and that I was determined not to do. I had willed it so, and was willing if necessary to perish with it."—Statement of Jesse K. Dubois, MS.
Lincoln answered gruffly, "It's something you may see or hear some time, but I'll not let you see it now." I myself knew what he was writing, but having asked neither my opinion nor that of anyone else, I did not venture to offer any suggestions. After he had finished the final draft of the speech, he locked the office door, drew the curtain across the glass panel in the door, and read it to me. At the end of each paragraph he would halt and wait for my comments. I remember what I said after hearing the first paragraph, wherein occurs the celebrated figure of the house divided against itself: "It is true, but is it wise or politic to say so?" He responded: "That expression is a truth of all human experience, 'a house divided against itself cannot stand,' and 'he that runs may read.' The proposition also is true, and has been for six thousand years. I want to use some universally known figure expressed in simple language as universally well-known, that may strike home to the minds of men in order to raise them up to the peril of the times. I do not believe I would be right in changing or omitting it. I would rather be defeated with this expression in the speech, and uphold and discuss it before the people, than be victorious without it." This was not the first time Lincoln had endorsed the dogma that our Government could not long endure part slave and part free. He had incorporated it in a speech at Bloomington in 1856, but in obedience to the emphatic protest of Judge T. Lyle Dickey and others, who conceived the idea that its "delivery would make Abolitionists of all the North and slavery propagandists of all the South, and thereby precipitate a struggle which might end in disunion," he consented to suspend its repetition, but only for that campaign.* Now, however, the situation had changed somewhat. There had been a shifting of scenes, so to speak. The Republican party had gained some in strength and more in moral effectiveness and force. Nothing could keep back in Lincoln any longer, sentiments of right and truth, and he prepared to give the fullest expression to both in all future contests.
* "After the meeting was over Mr. Lincoln and I returned to the Pike House, where we occupied the same room. Immediately on reaching the room I said to him, 'What in God's name could induce you to promulgate such an opinion?' He replied familiarly, 'Upon my soul, Dickey, I think it is true.' I reasoned to show it was not a correct opinion. He argued strenuously that the opinion was a sound one. At length I said, 'Suppose you are right, that our Government cannot last part free and part slave, what good is to be accomplished by inculcating that opinion (or truth, if you please) in the minds of the people?' After some minutes reflection he rose and approached me, extending his right hand to take mine, and said, 'From respect for your judgment, Dickey, I'll promise you I won't teach the doctrine again during this campaign.'"—Letter, T. Lyle Dickey, MS., December 8, 1866.

Before delivering his speech he invited a dozen or so of his friends over to the library of the State House, where he read and submitted it to them. After the reading he asked each man for his opinion. Some condemned and not one endorsed it. One man, more forcible than elegant, characterized it as a "d———d fool utterance", another said the doctrine was "ahead of its time" and still another contended that it would drive away a good many voters fresh from the Democratic ranks. Each man attacked it in his criticism. I was the last to respond. Although the doctrine announced was rather rank, yet it suited my views, and I said, "Lincoln, deliver that speech as read and it will make you President." At the time I hardly realized the force of my prophecy. Having patiently listened to these various criticisms from his friends—all of which with a single exception were adverse—he rose from his chair, and after alluding to the careful study and intense thought he had given the question, he answered all their objections substantially as follows: "Friends, this thing has been retarded long enough. The time has come when these sentiments should be uttered; and if it is decreed that I should go down because of this speech, then let me go down linked to the truth—let me die in the advocacy of what is just and right." The next day, the 17th, the speech was delivered just as we had heard it read. Up to this time Seward had held sway over the North by his "higher-law" sentiments, but the "house-divided-against-itself" speech by Lincoln in my opinion drove the nail into Seward's political coffin.*
* If any student of oratorical history, after reading Lincoln's speech on this occasion, will refer to Webster's reply to Hayne in the Senate, he will be struck with the similarity in figure and thought in the opening lines of both speeches. In fact, it may not be amiss to note that, in this instance, Webster's effort was carefully read by Lincoln and served in part as his model.
Lincoln had now created in reality a more profound impression than he or his friends anticipated. Many Republicans deprecated the advanced ground he had taken, the more so as the Democrats rejoiced that it afforded them an issue clear and well-defined. Numbers of his friends distant from Springfield, on reading his speech, wrote him censorious letters; and one well-informed co-worker* predicted his defeat, charging it to the first ten lines of the speech.
* Leonard Swett.
These complaints, coming apparently from every quarter, Lincoln bore with great patience. To one complainant who followed him into his office he said proudly, "If I had to draw a pen across my record, and erase my whole life from sight, and I had one poor gift or choice left as to what I should save from the wreck, I should choose that speech and leave it to the world unerased." Meanwhile Douglas had returned from Washington to his home in Chicago. Here he rested for a few days until his friends and co-workers had arranged the details of a public reception on the 9th of July, when he delivered from the balcony of the Tremont House a speech intended as an answer to the one made by Lincoln in Springfield. Lincoln was present at this reception, but took no part in it. The next day, however, he replied. Both speeches were delivered at the same place. Leaving Chicago, Douglas passed on down to Bloomington and Springfield, where he spoke on the 16th and 17th of July respectively. On the evening of the latter day Lincoln responded again in a most effective and convincing effort. The contest now took on a different phase. Lincoln's Republican friends urged him to draw Douglas into a joint debate, and he accordingly sent him a challenge on the 24th of July. It is not necessary, I suppose, to reproduce here the correspondence that passed between these great leaders. On the 30th Douglas finally accepted the proposition to "divide time, and address the same audiences," naming seven different places, one in each Congressional district, outside of Chicago and Springfield, for joint meetings.*
* Among the items of preparation on Lincoln's part hitherto withheld is the following letter, which explains itself:

"Springfield, June 28, 1858. "A. Campbell, Esq. "My Dear Sir:—In 1856 you gave me authority to draw on you for any sum not exceeding five hundred dollars. I see clearly that such a privilege would be more available now than it was then. I am aware that times are tighter now than they were then. Please write me at all events, and whether you can now do anything or not I shall continue grateful for the past. "Yours very truly, "A. Lincoln." * The following recent letter from Mr. Campbell is not without interest: La Salle, Ill., Dec. 12th, 1888. "Jesse W. Weik, Esq. "My Dear Sir:—I gave Mr. Lincoln some money in the office of Lincoln & Herndon in Springfield in 1856, but I do not remember the exact amount. It was, however, between two and three hundred dollars. I never had Mr. Lincoln's obligation for the payment of any money. I never kept any account of nor charged my memory with any money I gave him. It was given to defray his personal expenses and otherwise promote the interest of a cause which I sincerely believed to be for the public good, and without the thought or expectation of a dollar of it ever being returned. From what I knew and learned of his careful habits in money matters in the campaign of 1856 I am entirely confident that every dollar and dime I ever gave was carefully and faithfully applied to the uses and purposes for which it was given. "Sincerely yours, "A. Campbell."
The places and dates were, Ottawa, August 21; Freeport, August 27; Jonesboro, September 15; Charleston, September 18; Galesburg, October 7; Quincy, October 13; and Alton, October 15. "I agree to your suggestion," wrote Douglas, "that we shall alternately open and close the discussion. I will speak at Ottawa one hour, you can reply, occupying an hour and a half, and I will then follow for half an hour. At Freeport you shall open the discussion and speak one hour, I will follow for an hour and a half, and you can then reply for half an hour. We will alternate in like manner in each successive place." To this arrangement Lincoln on the 31st gave his consent, "although," he wrote, "by the terms as you propose you take four openings and closes to my three."
History furnishes few characters whose lives and careers were so nearly parallel as those of Lincoln and Douglas. They met for the first time at the Legislature in Vandalia in 1834, where Lincoln was a member of the House of Representatives and Douglas was in the lobby. The next year Douglas was also a member. In 1839 both were admitted to practice in the Supreme Court of Illinois on the same day.* In 1841 both courted the same young lady. In 1846 both represented Illinois in Congress at Washington, the one in the upper and the other in the lower House. In 1858 they were opposing candidates for United States Senator; and finally, to complete the remarkable counterpart, both were candidates for the Presidency in 1860. While it is true that their ambitions ran in parallel lines, yet they were exceedingly unlike in all other particulars.
* December 3d.
Douglas was short,—something over five feet high,—heavy set, with a large head, broad shoulders, deep chest, and striking features. He was polite and affable, but fearless. He had that unique trait, magnetism, fully developed in his nature, and that attracted a host of friends and readily made him a popular idol. He had had extensive experience in debate, and had been trained by contact for years with the great minds and orators in Congress. He was full of political history, well informed on general topics, eloquent almost to the point of brilliancy, self-confident to the point of arrogance, and a dangerous competitor in every respect. What he lacked in ingenuity he made up in strategy, and if in debate he could not tear down the structure of his opponent's argument by a direct and violent attack, he was by no means reluctant to resort to a strained restatement of the latter's position or to the extravagance of ridicule. Lincoln knew his man thoroughly and well.*
* An erroneous impression has grown up in recent years concerning Douglas's ability and standing as a lawyer. One of the latest biographies of Lincoln credits him with many of the artifices of the "shyster." This is not only unfair, but decidedly untrue. I always found Douglas at the bar to be a broad, fair, and liberal-minded man. Although not a thorough student of the law his large fund of good common- sense kept him in the front rank. He was equally generous and courteous, and he never stooped to gain a case. I know that Lincoln entertained the same view of him. It was only in politics that Douglas demonstrated any want of inflexibility and rectitude, and then only did Lincoln manifest a lack of faith in his morals.
He had often met Douglas on the stump; was familiar with his tactics, and though fully aware of his "want of fixed political morals," was not averse to measuring swords with the elastic and flexible "Little Giant."
Lincoln himself was constructed on an entirely different foundation. His base was plain common sense, direct statement, and the inflexibility of logic. In physical make-up he was cold—at least not magnetic—and made no effort to dazzle people by his bearing. He cared nothing for a following, and though he had often before struggled for a political prize, yet in his efforts he never had strained his well-known spirit of fairness or open love of the truth. He analyzed everything, laid every statement bare, and by dint of his broad reasoning powers and manliness of admission inspired his hearers with deep conviction of his earnestness and honesty. Douglas may have electrified the crowds with his eloquence or charmed them with his majestic bearing and dexterity in debate, but as each man, after the meetings were over and the applause had died away, went to his home, his head rang with Lincoln's logic and appeal to manhood.
A brief description of Mr. Lincoln's appearance on the stump and of his manner when speaking may not be without interest. When standing erect he was six feet four inches high. He was lean in flesh and ungainly in figure. Aside from the sad, pained look due to habitual melancholy, his face had no characteristic or fixed expression. He was thin through the chest, and hence slightly stoop-shouldered. When he arose to address courts, juries, or crowds of people, his body inclined forward to a slight degree. At first he was very awkward, and it seemed a real labor to adjust himself to his surroundings. He struggled for a time under a feeling of apparent diffidence and sensitiveness, and these only added to his awkwardness. I have often seen and sympathized with Mr. Lincoln during these moments. When he began speaking, his voice was shrill, piping, and unpleasant. His manner, his attitude, his dark, yellow face, wrinkled and dry, his oddity of pose, his diffident movements—everything seemed to be against him, but only for a short time. After having arisen, he generally placed his hands behind him, the back of his left hand in the palm of his right, the thumb and fingers of his right hand clasped around the left arm at the wrist. For a few moments he played the combination of awkwardness, sensitiveness, and diffidence. As he proceeded he became somewhat animated, and to keep in harmony with his growing warmth his hands relaxed their grasp and fell to his side. Presently he clasped them in front of him, interlocking his fingers, one thumb meanwhile chasing another. His speech now requiring more emphatic utterance, his fingers unlocked and his hands fell apart. His left arm was thrown behind, the back of his hand resting against his body, his right hand seeking his side. By this time he had gained sufficient composure, and his real speech began. He did not gesticulate as much with his hands as with his head. He used the latter frequently, throwing it with vim this way and that. This movement was a significant one when he sought to enforce his statement. It sometimes came with a quick jerk, as if throwing off electric sparks into combustible material. He never sawed the air nor rent space into tatters and rags as some orators do. He never acted for stage effect. He was cool, considerate, reflective—in time self-possessed and self-reliant. His style was clear, terse, and compact. In argument he was logical, demonstrative, and fair. He was careless of his dress, and his clothes, instead of fitting neatly as did the garments of Douglas on the latter's well-rounded form, hung loosely on his giant frame. As he moved along in his speech he became freer and less uneasy in his movements; to that extent he was graceful. He had a perfect naturalness, a strong individuality; and to that extent he was dignified. He despised glitter, show, set forms, and shams. He spoke with effectiveness and to move the judgment as well as the emotions of men. There was a world of meaning and emphasis in the long, bony finger of his right hand as he dotted the ideas on the minds of his hearers. Sometimes, to express joy or pleasure, he would raise both hands at an angle of about fifty degrees, the palms upward, as if desirous of embracing the spirit of that which he loved. If the sentiment was one of detestation—denunciation of slavery, for example—both arms, thrown upward and fists clenched, swept through the air, and he expressed an execration that was truly sublime. This was one of his most effective gestures, and signified most vividly a fixed determination to drag down the object of his hatred and trample it in the dust. He always stood squarely on his feet, toe even with toe; that is, he never put one foot before the other. He neither touched nor leaned on anything for support. He made but few changes in his positions and attitudes. He never ranted, never walked backward and forward on the platform. To ease his arms he frequently caught hold, with his left hand, of the lapel of his coat, keeping his thumb upright and leaving his right hand free to gesticulate. The designer of the monument recently erected in Chicago has happily caught him in just this attitude. As he proceeded with his speech the exercise of his vocal organs altered somewhat the tone of his voice. It lost in a measure its former acute and shrilling pitch, and mellowed into a more harmonious and pleasant sound. His form expanded, and, notwithstanding the sunken breast, he rose up a splendid and imposing figure. In his defence of the Declaration of Independence—his greatest inspiration—he was tremendous in the directness of his utterances; he rose to impassioned eloquence, unsurpassed by Patrick Henry, Mirabeau, or Vergniaud, as his soul was inspired with the thought of human right and Divine justice.* His little gray eyes flashed in a face aglow with the fire of his profound thoughts; and his uneasy movements and diffident manner sunk themselves beneath the wave of righteous indignation that came sweeping over him. Such was Lincoln the orator.
* Horace White, who was present and reported the speech for his paper, the Chicago Tribune. Letter, June 9, 1865, MS.
We can somewhat appreciate the feeling with which Douglas, aggressive and fearless though he was, welcomed a contest with such a man as Lincoln. Four years before, in a joint debate with him, he had asked for a cessation of forensic hostilities, conceding that his opponent of rail-splitting fame had given him "more trouble than all the United States Senate together." Now he was brought face to face with him again.*
* "Douglas and I, for the first time this canvass, crossed swords here yesterday. The fire flew some, and I am glad to know I am yet alive."—Lincoln to J. O. Cunningham, Ottawa, Ill., August 22, 1858, MS.
It is unnecessary and not in keeping with the purpose of this work to reproduce here the speeches made by either Lincoln or Douglas in their justly renowned debate. Briefly stated, Lincoln's position was announced in his opening speech at Springfield: "'A house divided against itself cannot stand.' I believe this Government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved, I do not expect the house to fall—but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all the one thing or the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction; or its advocates will push it forward till it becomes alike lawful in all the states, old as well as new, North as well as South." The position of Douglas on the question of slavery was one of indifference. He advocated with all his power the doctrine of "Popular Sovereignty," a proposition, as quaintly put by Lincoln, which meant that, "if one man chooses to enslave another, no third man has a right to object." At the last joint discussion in Alton, Lincoln, after reflecting on the patriotism of any man who was so indifferent to the wrong of slavery that he cared not whether it was voted up or down, closed his speech with this stirring summary: "That [slavery] is the real issue. That is the issue that will continue in this country when these poor tongues of Judge Douglas and myself shall be silent. It is the eternal struggle between these two principles—right and wrong—throughout the world. They are the two principles that have stood face to face from the beginning of time, and will ever continue to struggle. The one is the common right of humanity, and the other the divine right of kings. It is the same principle, in whatever shape it develops itself. It is the same spirit that says: 'You work and toil and earn bread, and I eat it.' No matter in what shape it comes, whether from the mouth of a king who seeks to bestride the people of his own nation and live by the fruit of their labor, or from one race of men as an apology for enslaving another race, it is the same tyrannical principle."
It is unnecessary, I presume, to insert here the seven questions which Douglas propounded to Lincoln at their first meeting at Ottawa, nor the historic four which Lincoln asked at Freeport. It only remains to say that in answering Lincoln at
Freeport, Douglas accomplished his own political downfall. He was swept entirely away from his former foundation, and even the glory of a subsequent election to the Senate never restored him to it.
During the canvass Mr. Lincoln, in addition to the seven meetings with Douglas, filled thirty-one appointments made by the State Central Committee, besides speaking at many other times and places not previously advertised. In his trips to and fro over the State, between meetings, he would stop at Springfield sometimes, to consult with his friends or to post himself up on questions that occurred during the canvass. He kept me busy hunting up old speeches and gathering facts and statistics at the State library. I made liberal clippings bearing in any way on the questions of the hour from every newspaper I happened to see, and kept him supplied with them; and on one or two occasions, in answer to letters and telegrams, I sent books forward to him. He had a little leather bound book, fastened in front with a clasp, in which he and I both kept inserting newspaper slips and newspaper comments until the canvass opened. In arranging for the joint meetings and managing the crowds Douglas enjoyed one great advantage. He had been United States Senator for several years, and had influential friends holding comfortable government offices all over the State. These men were on hand at every meeting, losing no opportunity to applaud lustily all the points Douglas made and to lionize him in every conceivable way. The ingeniously contrived display of their enthusiasm had a marked effect on certain crowds—a fact of which Lincoln frequently complained to his friends. One who accompanied him during the canvass* relates this: "Lincoln and I were at the Centralia agricultural fair the day after the debate at Jonesboro. Night came on and we were tired, having been on the fair grounds all day. We were to go north on the Illinois Central railroad. The train was due at midnight, and the depot was full of people. I managed to get a chair for Lincoln in the office of the superintendent of the railroad, but small politicians would intrude so that he could scarcely get a moment's sleep. The train came and was filled instantly. I got a seat near the door for Lincoln and myself. He was worn out, and had to meet Douglas the next day at Charleston. An empty car, called a saloon car, was hitched on to the rear of the train and locked up. I asked the conductor, who knew Lincoln and myself well,—we were both attorneys of the road,—if Lincoln could not ride in that car; that he was exhausted and needed rest; but the conductor refused. I afterwards got him in by a stratagem. At the same time George B. McClellan in person was taking Douglas around in a special car and special train; and that was the unjust treatment Lincoln got from the Illinois Central railroad. Every interest of that road and every employee was against Lincoln and for Douglas."
* Henry C. Whitney, MS., July 21, 1865.
The heat and dust and bonfires of the campaign at last came to an end. The election took place on the second of November, and while Lincoln received of the popular vote a majority of over four thousand, yet the returns from the legislative districts foreshadowed his defeat. In fact, when the Senatorial election took place in the Legislature, Douglas received fifty-four and Lincoln forty-six votes—one of the results of the lamentable apportionment law then in operation.*
* Horace Greeley was one of the most vigilant men during the debate. He wrote to Lincoln and me many letters which I still retain. In a letter to me during the campaign, October 6, he says with reference to Douglas: "In his present position I could not of course support him, but he need not have been in this position had the Republicans of Illinois been as wise and far-seeing as they are earnest and true.... but seeing things are as they are, I do not wish to be quoted as authority for making trouble and division among our friends." Soon after hearing of the result of November election he again writes: "I advise you privately that Mr. Douglas would be the strongest candidate that the Democratic party could present for President; but they will not present him. The old leaders wouldn't endorse it. As he is doomed to be slaughtered at Charleston it is good policy to fatten him meantime. He will cut up the better at killing time." An inquiry for his preference as to Presidential timber elicited this response, December 4th. "As to President, my present judgment is Edward Bates, with John M. Read for Vice; but I am willing to go anything that looks strong. I don't wish to load the team heavier than it will pull through. As to Douglas, he is like the man's boy who (he said) 'didn't weigh so much as he expected, and he always knew he wouldn't.' I never thought him very sound coin; but I didn't think it best to beat him on the back of his anti- Lecompton fight, and I am still of that opinion."
The letters of Lincoln at this period are the best evidence of his feelings now obtainable, and of how he accepted his defeat. To Henry Asbury, a friend who had written him a cheerful letter admonishing him not to give up the battle, he responded;
"Springfield, November 19, 1858.
"Mr. Henry Asbury,
"My Dear Sir:—Yours of the 13th was received some days ago. The fight must go on. The cause of civil liberty must not be surrendered at the end of one or even one hundred defeats. Douglas had the ingenuity to be supported in the late contest both as the best means to break down and to uphold the slave interest. No ingenuity can keep these antagonistic elements in harmony long. Another explosion will soon come.
"Yours truly,
"A. Lincoln."
To another friend* on the same day he writes:
* Dr. Henry.
"I am glad I made the late race. It gave me a hearing on the great and durable questions of the age which I could have had in no other way; and though I now sink out of view and shall be forgotten, I believe I have made some marks which will tell for the cause of liberty long after I am gone." Before passing to later events in Mr. Lincoln's life it is proper to include in this chapter, as a specimen of his oratory at this time, his eloquent reference to the Declaration of Independence found in a speech delivered at Beardstown, August 12, and not at Lewiston five days later, as many biographers have it. Aside from its concise reasoning, the sublime thought it suggests entitles it to rank beside that great masterpiece, his Gettysburg address. After alluding to the suppression by the Fathers of the Republic of the slave trade, he says: "These by their representatives in old Independence Hall said to the whole race of men: 'We hold these truths to be self-evident: that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.' This was their majestic interpretation of the economy of the universe. This was their lofty, and wise, and noble understanding of the justice of the Creator to his creatures—yes, gentlemen, to all his creatures, to the whole great family of man. In their enlightened belief, nothing stamped with the divine image and likeness was sent into the world to be trodden on and degraded and imbruted by its fellows. They grasped not only the whole race of man then living, but they reached forward and seized upon the farthest posterity. They erected a beacon to guide their children, and their children's children, and the countless myriads who should inhabit the earth in other ages. Wise statesmen as they were, they knew the tendency of prosperity to breed tyrants, and so they established these great self-evident truths, that when in the distant future some man, some faction, some interest, should set up the doctrine that none but rich men, none but white men, or none but Anglo-Saxon white men were entitled to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness, their posterity might look up again to the Declaration of Independence and take courage to renew the battle which their fathers began, so that truth and justice and mercy and all the humane and Christian virtues might not be extinguished from the land; so that no man would hereafter dare to limit and circumscribe the great principles on which the temple of liberty was being built.
"Now, my countrymen, if you have been taught doctrines conflicting with the great landmarks of the Declaration of Independence; if you have listened to suggestions which would take away from its grandeur and mutilate the fair symmetry of its proportions; if you have been inclined to believe that all men are not created equal in those inalienable rights enumerated by our chart of liberty: let me entreat you to come back. Return to the fountain whose waters spring close by the blood of the Revolution. Think nothing of me; take no thought for the political fate of any man whomsoever, but come back to the truths that are in the Declaration of Independence. You may do anything with me you choose, if you will but heed these sacred principles. You may not only defeat me for the Senate, but you may take me and put me to death. While pretending no indifference to earthly honors, I do claim to be actuated in this contest by something higher than an anxiety for office. I charge you to drop every paltry and insignificant thought for any man's success. It is nothing; I am nothing; Judge Douglas is nothing. But do not destroy that immortal emblem of humanity—the Declaration of American Independence."
One of the newspaper men* who heard this majestic oration wrote me as follows:
* Horace White, MS., May 17, 1865.
"The apostrophe to the Declaration of Independence to which you refer was written by myself from a vivid recollection of Mr. Lincoln's speech at Beardstown, August 12, 1858. On the day following the delivery of the speech, as Mr. Lincoln and I were proceeding by steamer from Beardstown to Havana, I said to him that I had been greatly impressed by his concluding remarks of the day previous, and that if he would write them out for me I felt confident their publication would be highly beneficial to our cause as well as honorable to his own fame. He replied that he had but a faint recollection of any portion of the speech; that, like all his campaign speeches, it was necessarily extemporaneous; and that its good or bad effect depended upon the inspiration of the moment. He added that I had probably overestimated the value of the remarks referred to. In reply to my question whether he had any objection to my writing them out from memory and putting them in the form of a verbatim report, he said, 'None at all.' I accordingly did so. I felt confident then and I feel equally assured now that I transcribed the peroration with absolute fidelity as to ideas and commendable fidelity as to language. I certainly aimed to reproduce his exact words, and my recollection of the passage as spoken was very clear. After I had finished writing I read it to Mr. Lincoln. When I had finished the reading he said, 'Well, those are my views, and if I said anything on the subject I must have said substantially that, but not nearly so well as that is said.' I remember this remark quite distinctly, and if the old steamer Editor is still in existence I could show the place where we were sitting. Having secured his assent to the publication I forwarded it to our paper, but inasmuch as my report of the Beardstown meeting had been already mailed I incorporated the remarks on the Declaration of Independence in my letter from Lewiston two or three days subsequently.... I do not remember ever having related these facts before, although they have often recurred to me as I have seen the peroration resuscitated again and again, and published (with good effect, I trust) in the newspapers of this country and England."
The importance of a more accurate and elaborate history of the debate between Lincoln and Douglas has induced Mr. Weik and me to secure, for publication in these pages, the account by Horace White, of this world-renowned forensic contest. Mr. White's means of knowledge, as fully set forth in the article, are exceptional, and his treatment of the subject is not less entertaining than truthful. It is certainly a great contribution to history and we insert it without further comment:
"It was my good fortune to accompany Mr. Lincoln during his political campaign against Senator Douglas in 1858, not only at the joint debates but also at most of the smaller meetings where his competitor was not present. We traveled together many thousands of miles. I was in the employ of the Chicago Tribune, then called the Press and Tribune. Senator Douglas had entered upon his campaign with two short-hand reporters, James B. Sheridan and Henry Binmore, whose duty it was to 'write it up' in the columns of the Chicago Times. The necessity of counteracting or matching that force became apparent very soon, and I was chosen to write up Mr. Lincoln's campaign.
"I was not a short-hand reporter. The verbatim reporting for the Chicago Tribune in the joint debates was done by Mr. Robert R. Hitt, late Assistant Secretary of State, and the present Representative in Congress from the 6th District of Illinois. Verbatim reporting was a new feature in journalism in Chicago, and Mr. Hitt was the pioneer thereof. The publication of Senator Douglas's opening speech in that campaign, delivered on the evening of July 9th, by the Tribune the next morning, was a feat hitherto unexampled in the West, and most mortifying to the Democratic newspaper, the Times, and to Sheridan and Binmore, who, after taking down the speech as carefully as Mr. Hitt had done, had gone to bed intending to write it out next day, as was then customary.
"All of the seven joint debates were reported by Mr. Hitt for the Tribune, the manuscript passing through my hands before going to the printers, but no changes were made by me except in a few cases where confusion on the platform; or the blowing of the wind, had caused some slight hiatus or evident mistake in catching the speaker's words. I could not resist the temptation to italicise a few passages in Mr. Lincoln's speeches, where his manner of delivery had been especially emphatic.
"The volume containing the debates, published in 1860 by Follett, Foster & Co., of Columbus, Ohio, presents Mr. Lincoln's speeches as they appeared in the Chicago Tribune, and Mr. Douglas's as they appeared in the Chicago Times. Of course, the speeches of both were published simultaneously in both papers. The Chicago Times' reports of Mr. Lincoln's speeches were not at all satisfactory to Mr. Lincoln's friends, and this led to a charge that they were purposely mutilated in order to give his competitor a more scholarly appearance before the public—a charge indignantly denied by Sheridan and Binmore. There was really no foundation for this charge. Of course, Sheridan and Binmore took more pains with Mr. Douglas's speeches than with those of his opponent. That was their business. It was what they were paid for, and what they were expected to do. The debates were all held in the open air, on rude platforms hastily put together, shaky, and overcrowded with people. The reporters' tables were liable to be jostled and their manuscript agitated by the wind. Some gaps were certain to occur in the reporters' notes and these, when occurring in Mr. Douglas's speeches, would certainly be straightened out by his own reporters, who would feel no such responsibility for the rough places in Mr. Lincoln's. Then it must be added that there were fewer involved sentences in Mr. Douglas's extempore speeches than in Mr. Lincoln's. Douglas was the more practiced and more polished speaker of the two, and it was easier for a reporter to follow him. All his sentences were round and perfect in his mind before he opened his lips. This was not always the case with Mr. Lincoln's.
"My acquaintance with Mr. Lincoln began four years before the campaign of which I am writing, in October, 1854. I was then in the employ of the Chicago Evening Journal. I had been sent to Springfield to report the political doings of State Fair week for that newspaper. Thus it came about that I occupied a front seat in the Representatives' Hall, in the old State House, when Mr. Lincoln delivered the speech already described in this volume. The impression made upon me by the orator was quite overpowering.
"I had not heard much political speaking up to that time. I have heard a great deal since. I have never heard anything since, either by Mr. Lincoln, or by anybody, that I would put on a higher plane of oratory. All the strings that play upon the human heart and understanding were touched with masterly skill and force, while beyond and above all skill was the overwhelming conviction pressed upon the audience that the speaker himself was charged with an irresistible and inspiring duty to his fellow men. This conscientious impulse drove his arguments through the heads of his hearers down into their bosoms, where they made everlasting lodgment. I had been nurtured in the Abolitionist faith, and was much more radical than Mr. Lincoln himself on any point where slavery was concerned, yet it seemed to me, when this speech was finished, as though I had had a very feeble conception of the wickedness of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill. I was filled, as never before, with the sense of my own duty and responsibility as a citizen toward the aggressions of the slave power.
"Having, 'since then, heard all the great public speakers of this country subsequent to the period of Clay and Webster, I award the palm to Mr. Lincoln as the one who, although not first in all respects, would bring more men, of doubtful or hostile leanings, around to his way of thinking by talking to them on a platform, than any other.
"Although I heard him many times afterward I shall longest remember him as I then saw the tall, angular form with the long, angular arms, at times bent nearly double with excitement, like a large flail animating two smaller ones, the mobile face wet with perspiration which he discharged in drops as he threw his head this way and that like a projectile—not a graceful figure, yet not an ungraceful one. After listening to him a few minutes, when he had got well warmed with his subject, nobody would mind whether he was graceful or not. All thought of grace or form would be lost in the exceeding attractiveness of what he was saying.
"Returning to the campaign of 1858—I was sent by my employers to Springfield to attend the Republican State Convention of that year. Again I sat at a short distance from Mr. Lincoln when he delivered the 'house-divided-against-itself' speech, on the 17th of June. This was delivered from manuscript, and was the only one I ever heard him deliver in that way. When it was concluded he put the manuscript in my hands and asked me to go to the State Journal office and read the proof of it. I think it had already been set in type. Before I had finished this task Mr. Lincoln himself came into the composing room of the State Journal and looked over the revised proofs. He said to me that he had taken a great deal of pains with this speech, and that he wanted it to go before the people just as he had prepared it. He added that some of his friends had scolded him a good deal about the opening paragraph and 'the house divided against itself,' and wanted him to change it or leave it out altogether, but that he believed he had studied this subject more deeply than they had, and that he was going to stick to that text whatever happened.
"On the 9th of July, Senator Douglas returned to Chicago from Washington City. He had stopped a few days at Cleveland, Ohio, to allow his friends to arrange a grand entrée for him. It was arranged that he should arrive about eight o'clock in the evening by the Michigan Central Railway, whose station was at the foot of Lake street, in which street the principal hotel, the Tremont House, was situated, and that he should be driven in a carriage drawn by six horses to the hotel, where he should make his first speech of the campaign. To carry out this arrangement it was necessary that he should leave the Michigan Southern Railway at Laporte and go to Michigan City, at which place the Chicago committee of reception took him in charge. It was noted by the Chicago Times that some malicious person at Michigan City had secretly spiked the only cannon in the town, so that the Douglas men were obliged to use an anvil on the occasion.
"When Mr. Douglas and his train arrived at the Lake street station, the crowd along the street to the hotel, four or five blocks distant, was dense, and, for the Chicago of that day, tremendous. It was with great difficulty that the six-horse team got through it at all. Banners, bands of music, cannon and fireworks added their various inspiration to the scene. About nine o'clock Mr. Douglas made his appearance on a balcony on the Lake street side of the hotel and made his speech. Mr. Lincoln sat in a chair just inside the house, very near the speaker, and was an attentive listener.
"Mr. Douglas's manner on this occasion was courtly and conciliatory. His argument was plausible but worthless—being, for the most part, a rehash of his 'popular sovereignty' dogma; nevertheless, he made a good impression. He could make more out of a bad case, I think, than any other man this country has ever produced, and I hope the country will never produce his like again in this particular. If his fate had been cast in the French Revolution, he would have out-demagogued the whole lot of them. I consider the use he made of this chip called popular sovereignty, riding upon it safely through some of the stormiest years in our history, and having nothing else to ride upon, a feat of dexterity akin to genius. But mere dexterity would not alone have borne him along his pathway in life. He had dauntless courage, unwearied energy, engaging manners, boundless ambition, unsurpassed powers of debate, and strong personal magnetism. Among the Democrats of the North his ascendency was unquestioned and his power almost absolute. He was exactly fitted to hew his way to the Presidency, and he would have done so infallibly if he had not made the mistake of coquetting with slavery. This was a mistake due to the absence of moral principle. If he had been as true to freedom as Lincoln was he would have distanced Lincoln in the race. It was, in fact, no easy task to prevent the Republicans from flocking after him in 1858, when he had, for once only, sided with them, in reference to the Lecompton Constitution. There are some reasons for believing that Douglas would have separated himself from the slave-holders entirely after the Lecompton fight, if he had thought that the Republicans would join in re-electing him to the Senate. Yet the position taken by the party in Illinois was perfectly sound. Douglas was too slippery to make a bargain with. He afterward redeemed himself in the eyes of his opponents by an immense service to the Union, which no other man could have rendered; but, up to this time, there was nothing for anti slavery men to do but to beat him if they could.
"I will add here that I had no personal acquaintance with Mr. Douglas, although my opportunities for meeting him were frequent. I regarded him as the most dangerous enemy of liberty, and, therefore, as my enemy. I did not want to know him. Accordingly, one day when Mr. Sheridan courteously offered to present me to his chief, I declined without giving any reason. Of course, this was a mistake; but, at the age of twenty-four, I took my politics very seriously. I thought that all the work of saving the country had to be done then and there. I have since learned to leave something to time and Providence.
"Mr. Lincoln's individual campaign began at Beardstown, Cass county, August 12th. Douglas had been there the previous day, and I had heard him. His speech had consisted mainly of tedious repetitions of 'popular sovereignty,' but he had taken occasion to notice Lincoln's conspiracy charge, and had called it 'an infamous lie.' He had also alluded to Senator Trumbull's charge that he (Douglas) had, two years earlier, been engaged in a plot to force a bogus constitution on the people of Kansas without giving them an opportunity to vote upon it. 'The miserable, craven-hearted wretch,' said Douglas, 'he would rather have both ears cut off than to use that language in my presence, where I could call him to account.' Before entering upon this subject, Douglas turned to his reporters and said 'Take this down.' They did so and it was published a few days later in the St. Louis Republican. This incident furnished the text of the Charleston joint debate on the 18th of September.
"Mr. Douglas's meeting at Beardstown was large and enthusiastic, but was composed of a lower social stratum than the Republican meeting of the following day. Mr. Lincoln came up the Illinois River from the town of Naples in the steamer Sam Gaty. Cass county and the surrounding region was by no means hopeful Republican ground. Yet Mr. Lincoln's friends mustered forty horsemen and two bands of music, beside a long procession on foot to meet him at the landing. Schuyler county sent a delegation of three hundred, and Morgan county was well represented. These were mostly Old Line Whigs who had followed Lincoln in earlier days. Mr. Lincoln's speech at Beardstown was one of the best he ever made in my hearing, and was not a repetition of any other. In fact, he never repeated himself except when some remark or question from the audience led him back upon a subject that he had already discussed. Many times did I marvel to see him get on a platform at some out-of-the-way place and begin an entirely new speech, equal, in all respects, to any of the joint debates, and continue for two hours in a high strain of argumentative power and eloquence, without saying anything that I had heard before. After the Edwardsville meeting I said to him that it was wonderful to me that he could find new things to say everywhere, while Douglas was parroting his popular sovereignty speech at every place. He replied that Douglas was not lacking in versatility, but that he had a theory that the popular sovereignty speech was the one to win on, and that the audiences whom he addressed would hear it only once and would never know whether he made the same speech elsewhere or not, and would never care. Most likely, if their attention were called to the subject, they would think that was the proper thing to do. As for himself, he said that he could not repeat to-day what he had said yesterday. The subject kept enlarging and widening in his mind as he went on, and it was much easier to make a new speech than to repeat an old one.
"It was at Beardstown that Mr. Lincoln uttered the glowing words that have come to be known as the apostrophe to the Declaration of Independence, the circumstances attending which are narrated in another part of this book. Probably the apostrophe, as printed, is a trifle more florid than as delivered, and, therefore, less forcible.
"The following passage, from the Beardstown speech, was taken down by me on the platform by long-hand notes and written out immediately afterward:
THE CONSPIRACY CHARGE.
"'I made a speech in June last in which I pointed out, briefly and consecutively, a series of public measures leading directly to the nationalization of slavery—the spreading of that institution over all the Territories and all the States, old as well as new, North as well as South. I enumerated the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, which, every candid man must acknowledge, conferred upon emigrants to Kansas and Nebraska the right to carry slaves there and hold them in bondage, whereas formerly they had no such right; I alluded to the events which followed that repeal, events in which Judge Douglas's name figures quite prominently; I referred to the Dred Scott decision and the extraordinary means taken to prepare the public mind for that decision; the efforts put forth by President Pierce to make the people believe that, in the election of James Buchanan, they had endorsed the doctrine that slavery may exist in the free Territories of the Union—the earnest exhortation put forth by President Buchanan to the people to stick to that decision whatever it might be—the close-fitting niche in the Nebraska bill, wherein the right of the people to govern themselves is made 'subject to the constitution of the United States'—the extraordinary haste made by Judge Douglas to give this decision an endorsement at the capitol of Illinois. I alluded to other concurring circumstances, which I need not repeat now, and I said that, though I could not open the bosoms of men and find out their secret motives, yet, when I found the framework of a barn, or a bridge, or any other structure, built by a number of carpenters—Stephen and Franklin and Roger and James—and so built that each tenon had its proper mortice, and the whole forming a symmetrical piece of workmanship, I should say that those carpenters all worked on an intelligible plan, and understood each other from the beginning. This embraced the main argument in my speech before the Republican State Convention in June. Judge Douglas received a copy of my speech some two weeks before his return to Illinois. He had ample time to examine and reply to it if he chose to do so. He did examine and he did reply to it, but he wholly overlooked the body of my argument, and said nothing about the 'conspiracy charge,' as he terms it. He made his speech up of complaints against our tendencies to negro equality and amalgamation. Well, seeing that Douglas had had the process served on him, that he had taken notice of the process, that he had come into court and pleaded to a part of the complaint, but had ignored the main issue, I took a default on him. I held that he had no plea to make to the general charge. So when I was called on to reply to him, twenty-four hours afterward, I renewed the charge as explicitly as I could. My speech was reported and published on the following morning, and, of course, Judge Douglas saw it. He went from Chicago to Bloomington and there made another and longer speech, and yet took no notice of the 'conspiracy charge.' He then went to Springfield and made another elaborate argument, but was not prevailed upon to know anything about the outstanding indictment. I made another speech at Springfield, this time taking it for granted that Judge Douglas was satisfied to take his chances in the campaign with the imputation of the conspiracy hanging over him. It was not until he went into a small town, Clinton, in De Witt county, where he delivered his fourth or fifth regular speech, that he found it convenient to notice this matter at all. At that place (I was standing in the crowd when he made his speech ), he bethought himself that he was charged with something, and his reply was that his 'self-respect alone prevented him from calling it a falsehood.' Well, my friends, perhaps he so far lost his self-respect in Beardstown as to actually call it a falsehood.
"'But now I have this reply to make: that while the Nebraska bill was pending, Judge Douglas helped to vote down a clause giving the people of the Territories the right to exclude slavery if they chose; that neither while the bill was pending, nor at any other time, would he give his opinion whether the people had the right to exclude slavery, though respectfully asked; that he made a report, which I hold in my hand, from the Committee on Territories, in which he said the rights of the people of the Territories, in this regard, are 'held in abeyance,' and cannot be immediately exercised; that the Dred Scott decision expressly denies any such right, but declares that neither Congress nor the Territorial Legislature can keep slavery out of Kansas and that Judge Douglas endorses that decision. All these charges are new; that is, I did not make them in my original speech. They are additional and cumulative testimony. I bring them forward now and dare Judge Douglas to deny one of them. Let him do so and I will prove them by such testimony as shall confound him forever. I say to you, that it would be more to the purpose for Judge Douglas to say that he did not repeal the Missouri Compromise; that he did not make slavery possible where it was impossible before; that he did not leave a niche in the Nebraska bill for the Dred Scott decision to rest in; that he did not vote down a clause giving the people the right to exclude slavery if they wanted to; that he did not refuse to give his individual opinion whether a Territorial Legislature could exclude slavery; that he did not make a report to the Senate, in which he said that the rights of the people, in this regard, were held in abeyance and could not be immediately exercised; that he did not make a hasty endorsement of the Dred Scott decision over at Springfield;* that he does not now endorse that decision; that that decision does not take away from the Territorial Legislature the right to exclude slavery; and that he did not, in the original Nebraska bill, so couple the words State and Territory together that what the Supreme Court has done in forcing open all the Territories to slavery it may yet do in forcing open all the States. I say it would be vastly more to the point for Judge Douglas to say that he did not do some of these things; that he did not forge some of these links of testimony, than to go vociferating about the country that possibly he may hint that somebody is a liar.'
* This refers to Douglas's speech of June 12, 1857.
"The next morning, August 13th, we boarded the steamer Editor and went to Havana, Mason county. Mr. Lincoln was in excellent spirits. Several of his old Whig friends were on board, and the journey was filled up with politics and story-telling. In the latter branch of human affairs, Mr. Lincoln was most highly gifted. From the beginning to the end of our travels the fund of anecdotes never failed, and, wherever we happened to be, all the people within ear-shot would begin to work their way up to this inimitable storyteller. His stories were always apropos of something going on, and oftenest related to things that had happened in his own neighborhood. He was constantly being reminded of one, and, when he told it, his facial expression was so irresistibly comic that the bystanders generally exploded in laughter before he reached what he called the 'nub' of it. Although the intervals between the meetings were filled up brimful with mirth in this way, Mr. Lincoln indulged very sparingly in humor in his speeches. I asked him one day why he did not oftener turn the laugh on Douglas. He replied that he was too much in earnest, and that it was doubtful whether turning the laugh on anybody really gained any votes.
"We arrived at Havana while Douglas was still speaking. The deputation that met Mr. Lincoln at the landing suggested that he should go up to the grove where the Democratic meeting was going on and hear what Douglas was saying. But he declined to do so, saying: 'The Judge was so put out by my listening to him at Bloomington and Clinton that I promised to leave him alone at his own meetings for the rest of the campaign. I understand that he is calling Trumbull and myself liars, and if he should see me in the crowd he might be so ashamed of himself as to omit the most telling part of his argument.' I strolled up to the Douglas meeting just before its conclusion, and there met a friend who had heard the whole. He was in a state of high indignation. He said that Douglas must certainly have been drinking before he came on the platform, because he had called Lincoln 'a liar, a coward, a wretch and a sneak.'
"When Mr. Lincoln replied, on the following day, he took notice of Douglas's hard words in this way:
"I am informed that my distinguished friend yesterday became a little excited, nervous (?) perhaps, and that he said something about fighting, as though looking to a personal encounter between himself and me. Did anybody in this audience hear him use such language? (Yes, Yes.) I am informed, further, that somebody in his audience, rather more excited or nervous than himself, took off his coat and offered to take the job off Judge Douglas's hands and fight Lincoln himself. Did anybody here witness that warlike proceeding? (Laughter and cries of 'yes.') Well, I merely desire to say that I shall fight neither Judge Douglas nor his second. I shall not do this for two reasons, which I will explain. In the first place a fight would prove nothing which is in issue in this election. It might establish that Judge Douglas is a more muscular man than myself, or it might show that I am a more muscular man than Judge Douglas. But this subject is not referred to in the Cincinnati platform, nor in either of the Springfield platforms. Neither result would prove him right or me wrong. And so of the gentleman who offered to do his fighting for him. If my fighting Judge Douglas would not prove any thing, it would certainly prove nothing for me to fight his bottle-holder. My second reason for not having a personal encounter with Judge Douglas is that I don't believe he wants it himself. He and I are about the best friends in the world, and when we get together he would no more think of fighting me than of fighting his wife. Therefore, when the Judge talked about fighting he was not giving vent to any ill-feeling of his own, but was merely trying to excite—well, let us say enthusiasm against me on the part of his audience. And, as I find he was tolerably successful in this, we will call it quits.'
"At Havana I saw Mrs. Douglas (née Cutts) standing with a group of ladies a short distance from the platform on which her husband was speaking, and I thought I had never seen a more queenly face and figure. I saw her frequently afterward in this campaign, but never personally met her till many years later, when she had become the wife of General Williams of the regular army, and the mother of children who promised to be as beautiful as herself. There is no doubt in my mind that this attractive presence was very helpful to Judge Douglas in the campaign. It is certain that the Republicans considered her a dangerous element.
"From Havana we went to Lewistown and thence to Peoria, still following on the heels of the Little Giant, but nothing of special interest happened at either place. As we came northward Mr. Lincoln's meetings grew in size, but at Lewistown the Douglas gathering was much the larger of the two and was the most considerable in point of numbers I had yet seen.
"The next stage brought us to Ottawa, the first joint debate, August 21st. Here the crowd was enormous. The weather had been very dry and the town was shrouded in dust raised by the moving populace. Crowds were pouring into town from sunrise till noon in all sorts of conveyances, teams, railroad trains, canal boats, cavalcades, and processions on foot, with banners and inscriptions, stirring up such clouds of dust that it was hard to make out what was underneath them. The town was covered with bunting, and bands of music were tooting around every corner, drowned now and then by the roar of cannon. Mr. Lincoln came by railroad and Mr. Douglas by carriage from La Salle. A train of seventeen passenger cars from Chicago attested the interest felt in that city in the first meeting of the champions. Two great processions escorted them to the platform in the public square. But the eagerness to hear the speaking was so great that the crowd had taken possession of the square and the platform, and had climbed on the wooden awning overhead, to such an extent that the speakers and the committees and reporters could not get to their places. Half an hour was consumed in a rough-and-tumble skirmish to make way for them, and, when finally this was accomplished, a section of the awning gave way with its load of men and boys, and came down on the heads of the Douglas committee of reception. But, fortunately, nobody was hurt.
"Here I was joined by Mr. Hitt and also by Mr. Chester P. Dewey of the New York Evening Post, who remained with us until the end of the campaign. Hither, also, came quite an army of young newspaper men, among whom was Henry Villard, in behalf of Forney's Philadelphia Press. I have preserved Mr. Dewey's sketch of the two orators as they appeared on the Ottawa platform, and I introduce it here as a graphic description by a new hand:
"'Two men presenting wider contrasts could hardly be found, as the representatives of the two great parties. Everybody knows Douglas, a short, thick-set, burly man, with large, round head, heavy hair, dark complexion, and fierce, bull-dog look. Strong in his own real power, and skilled by a thousand conflicts in all the strategy of a hand-to-hand or a general fight; of towering ambition, restless in his determined desire for notoriety, proud, defiant, arrogant, audacious, unscrupulous, 'Little Dug' ascended the platform and looked out impudently and carelessly on the immense throng which surged and struggled before him. A native of Vermont, reared on a soil where no slave stood, he came to Illinois a teacher, and from one post to another had risen to his present eminence. Forgetful of the ancestral hatred of slavery to which he was the heir, he had come to be a holder of slaves, and to owe much of his fame to continued subservience to Southern influence.
"'The other—Lincoln—is a native of Kentucky, of poor white parentage, and, from his cradle, has felt the blighting influence of the dark and cruel shadow which rendered labor dishonorable and kept the poor in poverty, while it advanced the rich in their possessions. Reared in poverty, and to the humblest aspirations, he left his native State, crossed the line into Illinois, and began his career of honorable toil. At first a laborer, splitting rails for a living—deficient in education, and applying himself even to the rudiments of knowledge—he, too, felt the expanding power of his American manhood, and began to achieve the greatness to which he has succeeded. With great difficulty, struggling through the tedious formularies of legal lore, he was admitted to the bar, and rapidly made his way to the front ranks of his profession. Honored by the people with office, he is still the same honest and reliable man. He volunteers in the Black Hawk war, and does the State good service in its sorest need. In every relation of life, socially and to the State, Mr. Lincoln has been always the pure and honest man. In physique he is the opposite to Douglas. Built on the Kentucky type, he is very tall, slender and angular, awkward even in gait and attitude. His face is sharp, large-featured and unprepossessing. His eyes are deep-set under heavy brows, his forehead is high and retreating, and his hair is dark and heavy. In repose, I must confess that 'Long Abe's' appearance is not comely. But stir him up and the fire of his genius plays on every feature. His eye glows and sparkles; every lineament, now so ill-formed, grows brilliant and expressive, and you have before you a man of rare power and of strong magnetic influence. He takes the people every time, and there is no getting away from his sturdy good sense, his unaffected sincerity and the unceasing play of his good humor, which accompanies his close logic and smoothes the way to conviction. Listening to him on Saturday, calmly and unprejudiced, I was convinced that he had no superior as a stump-speaker. He is clear, concise and logical, his language is eloquent and at perfect command. He is altogether a more fluent speaker than Douglas, and in all the arts of debate fully his equal. The Republicans of Illinois have chosen a champion worthy of their heartiest support, and fully equipped for the conflict with the great Squatter Sovereign.'
"One trifling error of fact will be noticed by the readers of these volumes in Mr. Dewey's sketch. It relates to Douglas, and it is proper to correct it here. Mr. Douglas was never a slave-holder. As a trustee or guardian, he held a plantation in Louisiana with the slaves thereon, which had belonged to Col. Robert Martin, of North Carolina, the maternal grandfather of his two sons by his first marriage. It is a fact that Douglas refused to accept this plantation and its belongings as a gift to himself from Colonel Martin in the life-time of the latter. It was characteristic of him that he declined to be an owner of slaves, not because he sympathized with the Abolitionists, but because, as he said once in a debate with Senator Wade, 'being a Northern man by birth, by education and residence, and intending always to remain such, it was impossible for me to know, understand, and provide for the happiness of those people.'
"At the conclusion of the Ottawa debate, a circumstance occurred which, Mr. Lincoln said to me afterwards, was extremely mortifying to him. Half a dozen Republicans, roused to a high pitch of enthusiasm for their leader, seized him as he came down from the platform, hoisted him upon their shoulders and marched off with him, singing the 'Star Spangled Banner,' or 'Hail Columbia,' until they reached the place where he was to spend the night. What use Douglas made of this incident, is known to the readers of the joint debates. He said a few days later, at Joliet, that Lincoln was so used up in the discussion that his knees trembled, and he had to be carried from the platform, and he caused this to be printed in the newspapers of his own party. Mr. Lincoln called him to account for this fable at Jonesboro.
"The Ottawa debate gave great satisfaction to our side. Mr. Lincoln, we thought, had the better of the argument, and we all came away encouraged. But the Douglas men were encouraged also. In his concluding half hour, Douglas spoke with great rapidity and animation, and yet with perfect distinctness, and his supporters cheered him wildly.
"The next joint debate was to take place at Freeport, six days later. In the interval, Mr. Lincoln addressed meetings at Henry, Marshall county; Augusta, Hancock county, and Macomb, McDonough county. During this interval he prepared the answers to the seven questions put to him by Douglas at Ottawa, and wrote the four questions which he propounded to Douglas at Freeport. The second of these, viz.: 'Can the people of a United States Territory, in any lawful way, against the wish of any citizen of the United States, exclude slavery from its limits prior to the formation of a State Constitution?' was made the subject of a conference between Mr. Lincoln and a number of his friends from Chicago, among whom were Norman B. Judd and Dr. C. H. Ray, the latter the chief editor of the Tribune. This conference took place at the town of Dixon. I was not present, but Doctor Ray told me that all who were there counseled Mr. Lincoln not to put that question to Douglas, because he would answer it in the affirmative and thus probably secure his re-election. It was their opinion that Lincoln should argue strongly from the Dred Scott decision, which Douglas endorsed, that the people of the Territories could not lawfully exclude slavery prior to the formation of a State Constitution, but that he should not force Douglas to say yes or no. They believed that the latter would let that subject alone as much as possible in order not to offend the South, unless he should be driven into a corner. Mr. Lincoln replied that to draw an affirmative answer from Douglas on this question was exactly what he wanted, and that his object was to make it impossible for Douglas to get the vote of the Southern States in the next Presidential election. He considered that fight much more important than the present one and he would be willing to lose this in order to win that.*
* Mr. Lincoln's words are given in Mr. Arnold's biography thus: "I am after larger game; the battle of 1860 is worth a hundred of this." Mr. Arnold's authority is not mentioned, but these are exactly the words that Doctor Ray repeated to me.
"The result justified Mr. Lincoln's prevision. Douglas did answer in the affirmative. If he had answered in the negative he would have lost the Senatorial election, and that would have ended his political career. He took the chance of being able to make satisfactory explanations to the slaveholders, but they would have nothing to do with him afterward.
"The crowd that assembled at Freeport on the 27th of August was even larger than that at Ottawa. Hundreds of people came from Chicago and many from the neighboring State of Wisconsin. Douglas came from Galena the night before the debate, and was greeted with a great torch-light procession. Lincoln came the following morning from Dixon, and was received at the railway station by a dense crowd, filling up all the adjacent streets, who shouted themselves hoarse when his tall form was seen emerging from the train. Here, again, the people had seized upon the platform, and all the approaches to it, an hour before the speaking began, and a hand-to-hand fight took place to secure possession.
"After the debate was finished, we Republicans did not feel very happy. We held the same opinion that Mr. Judd and Doctor Ray had—that Douglas's answer had probably saved him from defeat. We did not look forward, and we did not look South, and even if we had done so, we were too much enlisted in this campaign to swap it for another one which was two years distant. Mr. Lincoln's wisdom was soon vindicated by his antagonist, one of whose earliest acts, after he returned to Washington City, was to make a speech (February 23, 1859) defending himself against attacks upon the 'Freeport heresy,'as the Southerners called it. In that debate Jefferson Davis was particularly aggravating, and Douglas did not reply to him with his usual spirit.
"It would draw this chapter out to unreasonable length, if I were to give details of all the small meetings of this campaign. After the Freeport joint debate, we went to Carlinville, Macoupin county, where John M. Palmer divided the time with Mr. Lincoln. From this place we went to Clinton, De Witt county, via Springfield and Decatur. During this journey an incident occurred which gave unbounded mirth to Mr. Lincoln at my expense.
"We left Springfield about nine o'clock in the evening for Decatur, where we were to change cars and take the north-bound train on the Illinois Central Railway. I was very tired and I curled myself up as best I could on the seat to take a nap, asking Mr. Lincoln to wake me up at Decatur, which he promised to do. I went to sleep, and when I did awake I had the sensation of having been asleep a long time. It was daylight and I knew that we should have reached Decatur before midnight. Mr. Lincoln's seat was vacant. While I was pulling myself together, the conductor opened the door of the car and shouted, 'State Line.' This was the name of a shabby little town on the border of Indiana. There was nothing to do but to get out and wait for the next train going back to Decatur. About six o'clock in the evening I found my way to Clinton. The meeting was over, of course, and the Chicago Tribune had lost its expected report, and I was out of pocket for railroad fares. I wended my way to the house of Mr. C. H. Moore, where Mr. Liacoin was staying, and where I, too, had been an expected guest. When Mr. Lincoln saw me coming up the garden path, his lungs began to crow like a chanticleer, and I thought he would laugh, sans intermission, an hour by his dial. He paused long enough to say that he had fallen asleep, also, and did not wake up till the train was starting from Decatur. He had very nearly been carried past the station himself, and, in his haste to get out, had forgotten all about his promise to waken me. Then he began to laugh again. The affair was so irresistibly funny, in his view, that he told the incident several times in Washington City when I chanced to meet him, after he became President, to any company who might be present, and with such contagious drollery that all who heard it would shake with laughter.
"Our course took us next to Bloomington, McLean county; Monticello, Piatt county, and Paris, Edgar county. At the last-mentioned place (September 8th) we were joined by Owen Lovejoy, who had never been in that part of the State before. The fame of Lovejoy as an Abolitionist had preceded him, however, and the people gathered around him in a curious and hesitating way, as though he were a witch who might suddenly give them lock-jaw or bring murrain on their cattle, if he were much provoked. Lovejoy saw this and was greatly amused by it, and when he made a speech in the evening, Mr. Lincoln having made his in the day-time, he invited the timid ones to come up and feel of his horns and examine his cloven foot and his forked tail. Lovejoy was one of the most effective orators of his time. After putting his audience in good humor in this way, he made one of his impassioned speeches which never failed to gain votes where human hearts were responsive to the wrongs of slavery. Edgar county was in the Democratic list, but this year it gave a Republican majority on the legislative and congressional tickets, and I think Lovejoy's speech was largely accountable for the result.
"My notes of the Paris meeting embrace the following passage from Mr. Lincoln's speech:
WHAT IS POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY?
"'Let us inquire what Judge Douglas really invented when he introduced the Nebraska Bill? He called it Popular Sovereignty. What does that mean? It means the sovereignty of the people over their own affairs—in other words, the right of the people to govern themselves. Did Judge Douglas invent this? Not quite. The idea of Popular Sovereignty was floating about several ages before the author of the Nebraska Bill was born—indeed, before Columbus set foot on this continent. In the year 1776 it took form in the noble words which you are all familiar with: 'We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal,' etc. Was not this the origin of Popular Sovereignty as applied to the American people? Here we are told that governments are instituted among men deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed. If that is not Popular Sovereignty, then I have no conception of the meaning of words. If Judge Douglas did not invent this kind of Popular Sovereignty, let us pursue the inquiry and find out what kind he did invent. Was it the right of emigrants to Kansas and Nebraska to govern themselves, and a lot of 'niggers,' too, if they wanted them? Clearly this was no invention of his, because General Cass put forth the same doctrine in 1848 in his so-called Nicholson letter, six years before Douglas thought of such a thing. Then what was it that the 'Little Giant' invented? It never occurred to General Cass to call his discovery by the odd name of Popular Sovereignty. He had not the face to say that the right of the people to govern 'niggers' was the right of the people to govern themselves. His notions of the fitness of things were not moulded to the brazenness of calling the right to put a hundred 'niggers' through under the lash in Nebraska a 'sacred right of self-government.' And here, I submit to you, was Judge Douglas's discovery, and the whole of it. He discovered that the right to breed and flog negroes in Nebraska was Popular Sovereignty.'
"The next meetings in their order were Hillsboro, Montgomery county; Greenville, Bond county, and Edwardsville, Madison county. At Edwardsville (September 13th) I was greatly impressed with Mr. Lincoln's speech, so much so, that I took down the following passages, which, as I read them now, after the lapse of thirty-one years, bring back the whole scene with vividness before me—the quiet autumn day in the quaint old town; the serious people clustered around the platform; Joseph Gillespie officiating as chairman, and the tall, gaunt, earnest man, whose high destiny and tragic death were veiled from our eyes, appealing to his old Whig friends, and seeking to lift them up to his own level:
"'I have been requested,' he said, 'to give a concise statement of the difference, as I understand it, between the Democratic and the Republican parties on the leading issues of the campaign. This question has been put to me by a gentleman whom I do not know. I do not even know whether he is a friend of mine or a supporter of Judge Douglas in this contest, nor does that make any difference. His question is a proper one. Lest I should forget it, I will give you my answer before proceeding with the line of argument I have marked out for this discussion.
"'The difference between the Republican and the Democratic parties on the leading issues of this contest, as I understand it, is that the former consider slavery a moral, social and political wrong, while the latter do not consider it either a moral, a social or a political wrong; and the action of each, as respects the growth of the country and the expansion of our population, is squared to meet these views. I will not affirm that the Democratic party consider slavery morally, socially and politically right, though their tendency to that view has, in my opinion, been constant and unmistakable for the past five years. I prefer to take, as the accepted maxim of the party, the idea put forth by Judge Douglas, that he 'don't care whether slavery is voted down or voted up.' I am quite willing to believe that many Democrats would prefer that slavery should be always voted down, and I know that some prefer that it be always 'voted up;' but I have a right to insist that their action, especially if it be their constant action, shall determine their ideas and preferences on this subject. Every measure of the Democratic party of late years, bearing directly or indirectly on the slavery question, has corresponded with this notion of utter indifference, whether slavery or freedom shall outrun in the race of empire across to the Pacific—every measure, I say, up to the Dred Scott decision, where, it seems to me, the idea is boldly suggested that slavery is better than freedom. The Republican party, on the contrary, hold that this government was instituted to secure the blessings of freedom, and that slavery is an unqualified evil to the negro, to the white man, to the soil, and to the State. Regarding it as an evil, they will not molest it in the States where it exists, they will not overlook the constitutional guards which our fathers placed around it; they will do nothing that can give proper offense to those who hold slaves by legal sanction; but they will use every constitutional method to prevent the evil from becoming larger and involving more negroes, more white men, more soil, and more States in its deplorable consequences. They will, if possible, place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in course of ultimate peaceable extinction in God's own good time. And to this end they will, if possible, restore the government to the policy of the fathers—the policy of preserving the new Territories from the baneful influence of human bondage, as the northwestern Territories were sought to be preserved by the ordinance of 1787, and the Compromise Act of 1820. They will oppose, in all its length and breadth, the modern Democratic idea, that slavery is as good as freedom, and ought to have room for expansion all over the continent, if people can be found to carry it. All, or nearly all, of Judge Douglas's arguments are logical, if you admit that slavery is as good and as right as freedom, and not one of them is worth a rush if you deny it. This is the difference, as I understand it, between the Republican and Democratic parties....
"'My friends, I have endeavored to show you the logical consequences of the Dred Scott decision, which holds that the people of a Territory cannot prevent the establishment of slavery in their midst. I have stated what cannot be gainsaid, that the grounds upon which this decision is made are equally applicable to the free States as to the free Territories, and that the peculiar reasons put forth by Judge Douglas for endorsing this decision, commit him, in advance, to the next decision and to all other decisions coming from the same source. And when, by all these means, you have succeeded in dehumanizing the negro; when you have put him down and made it impossible for him to be but as the beasts of the field; when you have extinguished his soul in this world and placed him where the ray of hope is blown out as in the darkness of the damned, are you quite sure that the demon you have roused will not turn and rend you? What constitutes the bulwark of our own liberty and independence? It is not our frowning battlements, our bristling sea coasts, our army and our navy. These are not our reliance against tyranny. All of those may be turned against us without making us weaker for the struggle. Our reliance is in the love of liberty which God has planted in us. Our defense is in the spirit which prizes liberty as the heritage of all men, in all lands everywhere. Destroy this spirit and you have planted the seeds of despotism at your own doors. Familiarize yourselves with the chains of bondage and you prepare your own limbs to wear them. Accustomed to trample on the rights of others, you have lost the genius of your own independence and become the fit subjects of the first cunning tyrant who rises among you. And let me tell you, that all these things are prepared for you by the teachings of history, if the elections shall promise that the next Dred Scott decision and all future decisions will be quietly acquiesced in by the people.'
"From Edwardsville we went to the Jonesboro joint debate. The audience here was small, not more than 1,000 or 1,500, and nearly all Democrats. This was in the heart of Egypt. The country people came into the little town with ox teams mostly, and a very stunted breed of oxen, too. Their wagons were old-fashioned, and looked as though they were ready to fall in pieces. A train with three or four carloads of Douglas men came up, with Douglas himself, from Cairo. All who were present listened to the debate with very close attention, and there was scarcely any cheering on either side. Of course we did not expect any in that place. The reason why Douglas did not get much, was that Union county was a stronghold of the 'Danites,' or Buchanan Democrats. These were a pitiful minority everywhere except in the two counties of Union and Bureau. The reason for this peculiarity in the two counties named, must lie in the fact that Union county was the home of the United States Marshal for the Southern District, W. L. Dougherty; and Bureau, that of the Marshal for the Northern District, Charles N. Pine. Evidently both these men worked their offices for all they were worth, and the result would seem to show that Marshalships are peculiarly well fitted to the purpose of turning voters from their natural leanings. In Bureau county the 'Danites' polled more votes than the Douglas Democrats. In Union, they divided the party into two nearly equal parts. In no other county did they muster a corporal's guard; James W. Sheahan, the editor of the Times, told me, with great glee, after the election, that at one of the voting places in Chicago, where the two Democratic judges of election were Irish, a few 'Danite' votes were offered, but that the judges refused to receive them, saying gravely, 'We don't take that kind.' They thought it was illegal voting.
"The only thing noteworthy that I recall at Jonesboro was not political and not even terrestrial. It was the splendid appearance of Donati's comet in the sky, the evening before the debate. Mr. Lincoln greatly admired this strange visitor, and he and I sat for an hour or more in front of the hotel looking at it.
"From Jonesboro we went to Centralia, where a great State Fair was sprawling over the prairie, but there was no speaking there. It was not good form to have political bouts at State Fairs, and I believe that the managers had prohibited them. After one day at this place, where great crowds clustered around both Lincoln and Douglas whenever they appeared on the grounds, we went to Charleston, Coles county, September 18th, where the fourth joint debate took place.
"This was a very remarkable gathering, the like of which we had not seen elsewhere. It consisted of a great outpouring ( or rather inpouring ) of the rural population, in their own conveyances. There was only one line of railroad here, and only one special train on it. Yet, to my eye, the crowd seemed larger than at either Ottawa or Freeport, in fact the largest of the series, except the one at Galesburg, which came later. The campaign was now at its height, the previous debates having stirred the people into a real fever. 'It is astonishing,' said Mr. Dewey, in his letter from Charleston to the Evening Post, 'how deep an interest in politics this people take. Over long weary miles of hot, dusty prairie, the processions of eager partisans come on foot, on horseback, in wagons drawn by horses or mules; men, women and children, old and young; the half-sick just out of the last 'shake,' children in arms, infants at the maternal fount; pushing on in clouds of dust under a blazing sun, settling down at the town where the meeting is, with hardly a chance for sitting, and even less opportunity for eating, waiting in anxious groups for hours at the places of speaking; talking, discussing, litigious, vociferous, while the roar of artillery, the music of bands, the waving of banners, the huzzas of the crowds, as delegation after delegation appears; the cry of peddlers vending all sorts of wares, from an infallible cure for 'agur' to a monster water-melon in slices to suit purchasers—combine to render the occasion one scene of confusion and commotion. The hour of one arrives, and a perfect rush is made for the grounds; a column of dust rising to the heavens, and fairly deluging those who are hurrying on through it. Then the speakers come, with flags and banners and music, surrounded by cheering partisans. Their arrival at the grounds and immediate approach to the stand, is the signal for shouts that rend the heavens. They are introduced to the audience amid prolonged and enthusiastic cheers, they are interrupted by frequent applause and they sit down finally among the same uproarious demonstrations. The audience sit or stand patiently, throughout, and, as the last word is spoken, make a break for their homes, first hunting up lost members of their families, gathering their scattered wagon loads together, and, as the daylight fades away, entering again upon the broad prairies and slowly picking their way back to the place of beginning.'
"Both Lincoln and Douglas left the train at Mattoon, distant some ten miles from Charleston, to accept the escort of their respective partisans. Mattoon was then a comparatively new place, a station on the Illinois Central Railway peopled by Northern men. Nearly the whole population of this town turned out to escort Mr. Lincoln along the dusty highway to Charleston. In his procession was a chariot containing thirty-two young ladies, representing the thirty-two States of the Union, and carrying banners to designate the same. Following this, was one young lady on horseback holding aloft a banner inscribed, 'Kansas—I will be free.' As she was very good looking, we thought that she would not remain free always. The muses had been wide awake also, for, on the side of the chariot, was the stirring legend:
'Westward the star of empire takes its way; The girls link-on to Lincoln, as their mothers did to Clay.'
"The Douglas procession was likewise a formidable one. He, too, had his chariot of young ladies, and, in addition, a mounted escort. The two processions stretched an almost interminable distance along the road, and were marked by a moving cloud of dust.
"Before the Charleston debate, Mr. Lincoln had received (from Senator Trumbull, I suppose) certain official documents to prove that Douglas had attempted, in 1856, to bring Kansas into the Union without allowing the people to vote upon her constitution, and with these he put the Little Giant on the defensive, and pressed him so hard that we all considered that our side had won a substantial victory.
"The Democrats seemed to be uneasy and dissatisfied, both during the debate and afterward. Mr. Isaac N. Arnold, in his biography of Lincoln, page 148, relates an incident in the Charleston debate on the authority of 'a spectator' ( not named ), to this effect: that near the end of Mr. Lincoln's closing speech, Douglas became very much excited and walked rapidly up and down the platform behind Lincoln, holding a watch in his hand; that the instant the watch showed the half hour, he called out 'Sit down! Lincoln, sit down! Your time is up.'
"This must be a pure invention. My notes show nothing of the kind. I sat on the platform within ten feet of Douglas all the time that Lincoln was speaking. If any such dramatic incident had occurred, I should certainly have made a note of it, and even without notes I think I should have remembered it. Douglas was too old a campaigner to betray himself in this manner, whatever his feelings might have been.
"After the debate was ended and the country people had mostly dispersed, the demand for speeches was still far from being satisfied. Two meetings were started in the evening, with blazing bonfires in the street to mark the places. Richard J. Oglesby, the Republican nominee for Congress (afterward General, Governor and Senator ), addressed one of them. At the Douglas meeting, Richard T. Merrick and U. F. Linder were the speakers. Merrick was a young lawyer from Maryland, who had lately settled in Chicago, and a fluent and rather captivating orator. Linder was an Old Line Whig, of much natural ability, who had sided with the Democrats on the break-up of his own party. Later in the campaign Douglas wrote him a letter saying: 'For God's sake, Linder, come up here and help me.' This letter got into the newspapers, and, as a consequence, the receiver of it was immediately dubbed, 'For-God's-Sake Linder,' by which name he was popularly know all the rest of his days.
"There was nothing of special interest between the Charleston debate and that which took place at Galesburg, October 7th. Here we had the largest audience of the whole series and the worst day, the weather being very cold and raw, notwithstanding which, the people flocked from far and near. One feature of the Republican procession was a division of one hundred ladies and an equal number of gentlemen on horseback as a special escort to the carriage containing Mr. Lincoln. The whole country seemed to be swarming and the crowd stood three hours in the college grounds, in a cutting wind, listening to the debate. Mr. Lincoln's speech at Galesburg was, in my judgment, the best of the series.
"At Quincy, October 13th, we had a fine day and a very large crowd, although not so large as at Galesburg. The usual processions and paraphernalia were on hand. Old Whiggery was largely represented here, and, in front of the Lincoln procession, was a live raccoon on a pole, emblematic of a by-gone day and a by-gone party. When this touching reminder of the past drew near the hotel where we were staying, an old weather-beaten follower of Henry Clay, who was standing near me, was moved to tears. After mopping his face he made his way up to Mr. Lincoln, wrung his hand and burst into tears again. The wicked Democrats carried at the head of their procession a dead 'coon, suspended by its tail. This was more in accord with existing facts than the other specimen, but our prejudices ran in favor of live 'coons in that part of Illinois. Farther north we did not set much store by them. Here I saw Carl Schurz for the first time. He was hotly in the fray, and was an eager listener to the Quincy debate. Another rising star, Frank P. Blair, Jr., was battling for Lincoln in the southern part of the State.
"The next day both Lincoln and Douglas, and their retainers, went on board the steamer City of Louisiana, bound for Alton. Here the last of the joint debates took place, October 15th. The day was pleasant but the audience was the smallest of the series, except the one at Jonesboro. The debate passed off quietly and without any incident worthy of note.
"The campaign was now drawing to a close. Everybody who had borne an active part in it was pretty well fagged out, except Mr. Lincoln. He showed no signs of fatigue. Douglas's voice was worn down to extreme huskiness. He took great pains to save what was left of his throat, but to listen to him moved one's pity. Nevertheless, he went on doggedly, bravely, and with a jaunty air of confidence. Mr. Lincoln's voice was as clear and far-reaching as it was the day he spoke at Beardstown, two months before—a high-pitched tenor, almost a falsetto, that could be heard at a greater distance than Douglas's heavy basso. The battle continued till the election (November 2d), which took place in a cold, pelting rainstorm, one of the most uncomfortable in the whole year. But nobody minded the weather. The excitement was intense all day in all parts of the State. The Republican State ticket was elected by a small plurality, the vote being as follows:
FOR STATE TREASURER.
Miller (Republican),........... 125,430 Fondey (Douglas Democrat),..... 121,609 Dougherty (Buchanan Democrat),. 5,079
"The Legislature consisted of twenty-five Senators and seventy-five Representatives. Thirteen Senators held over from the preceding election. Of these, eight were Democrats and five Republicans. Of the twelve Senators elected this year, the Democrats elected six and the Republicans six. So the new Senate was composed of fourteen Democrats and eleven Republicans.
"Of the seventy-five members of the House of Representatives, the Democrats elected forty and the Republicans thirty-five.
"On joint ballot, therefore, the Democrats had fifty-four and the Republicans forty-six. And by this vote was Mr. Douglas re-elected Senator.
"Mr. Isaac N. Arnold, in his biography, says that Mr. Lincoln lost the election because a number of the holding-over Senators, representing districts that actually gave Republican majorities in this election, were Democrats. This is an error, and an inexcusable one for a person who is writing history. The apportionment of the State into Legislative districts had become, by the growth and movement of population, unduly favorable to the Democrats; that is, it required fewer votes on the average to elect a member in a Democratic district than in a Republican district. But ideal perfection is never attained in such matters. By the rules of the game Douglas had fairly won. The Republicans claimed that the Lincoln members of the Lower House of the Legislature received more votes, all told, than the Douglas members. These figures are not, at this writing, accessible to me, but my recollection is that, even on this basis, Douglas scored a small majority. There were five thousand Democratic votes to be accounted for, which had been cast for Dougherty for State Treasurer, and of these, the Douglas candidates for the Legislature would naturally get more than the Lincoln candidates.
"What is more to the purpose, is that the Republicans gained 29,241 votes, as against a Democratic gain of 21,332 (counting the Douglas and Buchanan vote together), over the presidential election of 1856. There were 37,444 votes for Fillmore in that year, and there was also an increase of the total vote of 13,129. These 50,573 votes, or their equivalents, were divided between Lincoln and Douglas in the ratio of 29 to 21.
"Mr. Lincoln, as he said at the Dixon Conference, had gone after 'larger game,' and he had bagged it to a greater extent than he, or anybody, then, imagined. But the immediate prize was taken by his great rival.
"I say great rival, with a full sense of the meaning of the words. I heard Mr. Douglas deliver his speech to the members of the Illinois Legislature, April 25, 1861, in the gathering tumult of arms. It was like a blast of thunder. I do not think that it is possible for a human being to produce a more prodigious effect with spoken words, than he produced on those who were within the sound of his voice. He was standing in the same place where I had first heard Mr. Lincoln. The veins of his neck and forehead were swollen with passion, and the perspiration ran down his face in streams. His voice had recovered its clearness from the strain of the previous year, and was frequently broken with emotion. The amazing force that he threw into the words: 'When hostile armies are marching under new and odious banners against the government of our country, the shortest way to peace is the most stupendous and unanimous preparation for war,' seemed to shake the whole building. That speech hushed the breath of treason in every corner of the State. Two months later he was in his grave. He was only forty-eight years old.
"The next time I saw Mr. Lincoln, after the election, I said to him that I hoped he was not so much disappointed as I had been. This, of course, 'reminded him of a little story.' I have forgotten the story, but it was about an over-grown boy who had met with some mishap, 'stumped' his toe, perhaps, and who said that 'it hurt too much to laugh, and he was too big to cry.'
"Mention has been made of the 'Danites' in the campaign. They were the Buchanan office-holders and their underlings, and, generally, a contemptible lot. The chief dispenser of patronage for Illinois was John Slidell, Senator from Louisiana. He took so much interest in his vocation that he came to Chicago as early as the month of July, to see how the postmasters were doing their work. He hated Douglas intensely, and slandered him vilely, telling stories about the cruel treatment and dreadful condition of the negroes on the Douglas plantation in Louisiana. These stories were told to Dr. Daniel Brainard, the surgeon of the U. S. Marine Hospital. Brainard was a Buchanan Democrat, like all the other federal officeholders, but was a very distinguished surgeon; in fact, at the head of his profession, and a man of wealth and social standing. He became convinced that Slidell's story about the Douglas negroes was true, and he communicated it to Doctor Ray, and urged him to publish it in the Tribune. Doctor Ray did so, without, however, giving any names. It made no little commotion. Presently, the New Orleans Picayune denied the truth of the statement, concerning the condition and treatment of the negroes, and called it 'an election canard.' Then the Chicago Times called for the authority, and the Tribune gave the names of Brainard and Slidell. The latter at once published a card in the Washington Union, denying that he had ever made the statements attributed to him by Brainard. The latter was immediately in distress. He first denied that he had made the statements imputed to him, but afterward admitted that he had had conversations with a Republican editor about the hardships of the Douglas negroes, but denied that he had given Slidell as authority. Nobody doubted that the authorship of the story was correctly stated in the first publication. It was much too circumstantial to have been invented, and Doctor Ray was not the man to publish lies knowingly.
"The 'Danites' held a State convention at Springfield, September 8th, or, rather, they had called one for that date, but the attendance was so small that they organized it as a convention of the Sixth Congressional District. John C. Breckinridge and Daniel S. Dickinson had been announced as speakers for the occasion, but neither of them appeared. Breckinridge took no notice of this meeting, or of his invitation to be present. A telegram was read from Dickinson, sending 'a thousand greetings,' and this, the Douglas men said, was liberal, being about ten to each delegate. Ex-Gov. John Reynolds was the principal speaker. Douglas was in Springfield the same day. He met his enemies by chance at the railway station, and glared defiance at them.
"Mention should be made of the services of Senator Trumbull in the campaign. Mr. Trumbull was a political debator, scarcely, if at all, inferior to either Lincoln or Douglas. He had given Douglas more trouble in the Senate, during the three years he had been there, than anybody else in that body. He had known Douglas from his youth, and he knew all the joints in his armor. He possessed a courage equal to any occasion, and he wielded a blade of tempered steel. He was not present at any of the joint debates, or at any of Mr. Lincoln's separate meetings, but addressed meetings wherever the State Central Committee sent him. Mr. Lincoln often spoke of him to me, and always in terms of admiration. That Mr. Lincoln was sorely disappointed at losing the Senatorship in 1855, when Trumbull was elected, is quite true, but he knew, as well as anybody, that in the then condition of parties, such a result could not be avoided. Judd, Palmer and Cook had been elected to the Legislature as Democrats. The Republican party was not yet born. The political elements were in the boiling stage. These men could not tell what kind of crystallization would take place. The only safe course for them, looking to their constituencies, was to vote for a Democrat who was opposed to the extension of slavery. Such a man they found in Lyman Trumbull, and they knew that no mistake would be made in choosing him. I say that Mr. Lincoln knew all this as fully as anybody could. I do not remember having any talk with him on that subject, for it was then somewhat stale. But I do remember the hearty good feeling that he cherished toward Trumbull and the three men here mentioned, who were chiefly instrumental in securing Trumbull's election.
"Douglas scented danger when Trumbull took the field, and, with his usual adroitness, sought to gain sympathy by making it appear that it was no fair game. At Havana, in the speech already alluded to, he made a rather moving remonstrance against this 'playing of two upon one,' as he called it. Mr. Lincoln, in his speech at the same place, thought it worth while to reply:
"'I understand,' he said, 'that Judge Douglas, yesterday, referred to the fact that both Judge Trumbull and myself are making speeches throughout the State to beat him for the Senate, and that he tried to create sympathy by the suggestion that this was playing two upon one against him. It is true that Judge Trumbull has made a speech in Chicago, and I believe he intends to co-operate with the Republican Central Committee in their arrangements for the campaign, to the extent of making other speeches in different parts of the State. Judge Trumbull is a Republican like myself, and he naturally feels a lively interest in the success of his party. Is there anything wrong about that? But I will show you how little Judge Douglas's appeal to your sympathies amounts to. At the next general election, two years from now, a Legislature will be elected, which will have to choose a successor to Judge Trumbull. Of course, there will be an effort to fill his place with a Democrat. This person, whoever he may be, is probably out making stump-speeches against me, just as Judge Douglas is. He may be one of the present Democratic members of the Lower House of Congress—but, whoever he is, I can tell you that he has got to make some stump-speeches now, or his party will not nominate him for the seat occupied by Judge Trumbull. Well, are not Judge Douglas and this man playing two upon one against me, just as much as Judge Trumbull and I are playing two upon one against Judge Douglas? And, if it happens that there are two Democratic aspirants for Judge Trumbull's place, are they not playing three upon one against me, just as we are playing two upon one against Judge Douglas?'
"Douglas had as many helpers as Lincoln had. His complaint implied that there was nobody on the Democratic side who was anywhere near being a match for Trumbull, and this was the fact.
"I think that this was the most important intellectual wrestle that has ever taken place in this country, and that it will bear comparison with any which history mentions. Its consequences we all know. It gave Mr. Lincoln such prominence in the public eye that his nomination to the Presidency became possible and almost inevitable. It put an apple of discord in the Democratic party which hopelessly divided it at Charleston, thus making Republican success in 1860 morally certain. This was one of Mr. Lincoln's designs, as has been already shown. Perhaps the Charleston schism would have taken place, even if Douglas had not been driven into a corner at Freeport, and compelled to proclaim the doctrine of 'unfriendly legislation,' but it is more likely that the break would have been postponed a few years longer.
"Everything stated in this chapter is taken from memoranda made at the time of occurrence. I need not say that I conceived an ardent attachment to Mr. Lincoln. Nobody could be much in his society without being strongly drawn to him.
"Horace White"
New York, February 27, 1890
BEFORE Mr. Lincoln surrenders himself completely to the public—for it is apparent he is fast approaching the great crisis of his career—it may not be entirely inappropriate to take a nearer and more personal view of him. A knowledge of his personal views and actions, a glimpse through the doorway of his home, and a more thorough acquaintance with his marked and strong points as they developed, will aid us greatly in forming our general estimate of the man. When Mr. Lincoln entered the domain of investigation he was a severe and persistent thinker, and had wonderful endurance; hence he was abstracted, and for that reason at times was somewhat unsocial, reticent, and uncommunicative. After his marriage it cannot be said that he liked the society of ladies; in fact, it was just what he did not like, though one of his biographers says otherwise. Lincoln had none of the tender ways that please a woman, and he could not, it seemed, by any positive act of his own make her happy. If his wife was happy, she was naturally happy, or made herself so in spite of countless drawbacks. He was, however, a good husband in his own peculiar way, and in his own way only.
If exhausted from severe and long-continued thought, he had to touch the earth again to renew his strength. When this weariness set in he would stop thought, and get down and play with a little dog or kitten to recover; and when the recovery came he would push it aside to play with its own tail. He treated men and women in much the same way. For fashionable society he had a marked dislike, although he appreciated its value in promoting the welfare of a man ambitious to succeed in politics. If he was invited out to dine or to mingle in some social gathering, and came in contact with the ladies, he treated them with becoming politeness; but the consciousness of his shortcomings as a society man rendered him unusually diffident, and at the very first opportunity he would have the men separated from their ladies and crowded close around him in one corner of the parlor, listening to one of his characteristic stories. That a lady * as proud and as ambitious to exercise the rights of supremacy in society as Mary Todd should repent of her marriage to the man I have just described surely need occasion no surprise in the mind of anyone. Both she and the man whose hand she accepted acted along the lines of human conduct, and both reaped the bitter harvest of conjugal infelicity.
* Mrs. Lincoln was decidedly pro-slavery in her views. One day she was invited to take a ride with a neighboring family, some of whose members still reside in Springfield. "If ever my husband dies," she ejaculated during the ride, "his spirit will never find me living outside the limits of a slave State."
In dealing with Mr. Lincoln's home life perhaps I am revealing an element of his character that has heretofore been kept from the world; but in doing so I feel sure I am treading on no person's toes, for all the actors in this domestic drama are dead, and the world seems ready to hear the facts. As his married life, in the opinion of all his friends, exerted a peculiar influence over Mr. Lincoln's political career there can be no impropriety, I apprehend, in throwing the light on it now. Mrs. Lincoln's disposition and nature have been dwelt upon in another chapter, and enough has been told to show that one of her greatest misfortunes was her inability to control her temper. Admit that, and everything can be explained. However cold and abstracted her husband may have appeared to others, however impressive, when aroused, may have seemed his indignation in public, he never gave vent to his feelings at home. He always meekly accepted as final the authority of his wife in all matters of domestic concern.*
* One day a man making some improvements in Lincoln's yard suggested to Mrs. Lincoln the propriety of cutting down one of the trees, to which she willingly assented. Before doing so, however, the man came down to our office and consulted Lincoln himself about it. "What did Mrs. Lincoln say?" enquired the latter. "She consented to have it taken away." "Then, in God's name," exclaimed Lincoln, "cut it down to the roots!"
This may explain somewhat the statement of Judge Davis that, "as a general rule, when all the lawyers of a Saturday evening would go home and see their families and friends, Lincoln would find some excuse and refuse to go. We said nothing, but it seemed to us all he was not domestically happy." He exercised no government of any kind over his household. His children did much as they pleased. Many of their antics he approved, and he restrained them in nothing. He never reproved them or gave them a fatherly frown. He was the most indulgent parent I have ever known. He was in the habit, when at home on Sunday, of bringing his two boys, Willie and Thomas—or "Tad"—down to the office to remain while his wife attended church. He seldom accompanied her there. The boys were absolutely unrestrained in their amusement. If they pulled down all the books from the shelves, bent the points of all the pens, overturned inkstands, scattered law-papers over the floor, or threw the pencils into the spittoon, it never disturbed the serenity of their father's good-nature. Frequently absorbed in thought, he never observed their mischievous but destructive pranks—as his unfortunate partner did, who thought much, but said nothing—and, even if brought to his attention, he virtually encouraged their repetition by declining to show any substantial evidence of parental disapproval. After church was over the boys and their father, climbing down the office stairs, ruefully turned their steps homeward. They mingled with the throngs of well-dressed people returning from church, the majority of whom might well have wondered if the trio they passed were going to a fireside where love and white-winged peace reigned supreme. A near relative of Mrs. Lincoln, in explanation of the unhappy condition of things in that lady's household, offered this suggestion: "Mrs. Lincoln came of the best stock, and was raised like a lady. Her husband was her opposite, in origin, in education, in breeding, in everything; and it is therefore quite natural that she should complain if he answered the door-bell himself instead of sending the servant to do so; neither is she to be condemned if, as you say, she raised 'merry war' because he persisted in using his own knife in the butter, instead of the silver-handled one intended for that purpose." * Such want of social polish on the part of her husband of course gave Mrs. Lincoln great offense, and therefore in commenting on it she cared neither for time nor place. Her frequent outbursts of temper precipitated many an embarrassment from which Lincoln with great difficulty' extricated himself.
* A lady relative who lived for two years with the Lincolns told me that Mr. Lincoln was in the habit of lying on the floor with the back of a chair for a pillow when he read. One evening, when in this position in the hall, a knock was heard at the front door and although in his shirt-sleeves he answered the call. Two ladies were at the door whom he invited into the parlor, notifying them in his open familiar way, that he would "trot the women folks out." Mrs. Lincoln from an adjoining room witnessed the ladies' entrance and overheard her husband's jocose expression. Her indignation was so instantaneous she made the situation exceedingly interesting for him, and he was glad to retreat from the mansion. He did not return till very late at night and then slipped quietly in at a rear door.

Mrs. Lincoln, on account of her peculiar nature, could not long retain a servant in her employ. The sea was never so placid but that a breeze would ruffle its waters. She loved show and attention, and if, when she glorified her family descent or indulged in one of her strange outbreaks, the servant could simulate absolute obsequiousness or had tact enough to encourage her social pretensions, Mrs. Lincoln was for the time her firmest friend. One servant, who adjusted herself to suit the lady's capricious ways, lived with the family for several years. She told me that at the time of the debate between Douglas and Lincoln she often heard the latter's wife boast that she would yet be mistress of the White House. The secret of her ability to endure the eccentricities of her mistress came out in the admission that Mr. Lincoln gave her an extra dollar each week on condition that she would brave whatever storms might arise, and suffer whatever might befall her, without complaint. It was a rather severe condition, but she lived rigidly up to her part of the contract. The money was paid secretly and without the knowledge of Mrs. Lincoln. Frequently, after tempestuous scenes between the mistress and her servant, Lincoln at the first opportunity would place his hand encouragingly on the latter's shoulder with the admonition, "Mary, keep up your courage." It may not be without interest to add that the servant afterwards married a man who enlisted in the army. In the spring of 1865 his wife managed to reach Washington to secure her husband's release from the service. After some effort she succeeded in obtaining an interview with the President. He was glad to see her, gave her a basket of fruit, and directed her to call the next day and obtain a pass through the lines and money to buy clothes for herself and children. That night he was assassinated.
The following letter to the editor of a newspaper in Springfield will serve as a specimen of the perplexities which frequently beset Mr. Lincoln when his wife came in contact with others. What in this instance she said to the paper carrier we do not know; we can only intelligently infer. I have no personal recollection of the incident, although I knew the man to whom it was addressed quite well. The letter only recently came to light. I insert it without further comment.
[Private.]
"Springfield, Ill., February 20, 1857.
"John E. Rosette, Esq.
"Dear Sir:—Your note about the little paragraph in the Republican was received yesterday, since which time I have been too unwell to notice it. I had not supposed you wrote or approved it. The whole originated in mistake. You know by the conversation with me that I thought the establishment of the paper unfortunate, but I always expected to throw no obstacle in its way, and to patronize it to the extent of taking and paying for one copy. When the paper was brought to my house, my wife said to me, 'Now are you going to take another worthless little paper?' I said to her evasively, 'I have not directed the paper to be left.' From this, in my absence, she sent the message to the carrier. This is the whole story.
"Yours truly,
"A. Lincoln."
A man once called at the house to learn why Mrs. Lincoln had so unceremoniously discharged his niece from her employ. Mrs. Lincoln met him at the door, and being somewhat wrought up, gave vent to her feelings, resorting to such violent gestures and emphatic language that the man was glad to beat a hasty retreat. He at once started out to find Lincoln, determined to exact from him proper satisfaction for his wife's action. Lincoln was entertaining a crowd in a store at the time. The man, still laboring under some agitation, called him to the door and made the demand. Lincoln listened for a moment to his story. "My friend," he interrupted, "I regret to hear this, but let me ask you in all candor, can't you endure for a few moments what I have had as my daily portion for the last fifteen years?" These words were spoken so mournfully and with such a look of distress that the man was completely disarmed. It was a case that appealed to his feelings. Grasping the unfortunate husband's hand, he expressed in no uncertain terms his sympathy, and even apologized for having approached him. He said no more about the infuriated wife, and Lincoln afterward had no better friend in Springfield.
Mr. Lincoln never had a confidant, and therefore never unbosomed himself to others. He never spoke of his trials to me or, so far as I knew, to any of his friends. It was a great burden to carry, but he bore it sadly enough and without a murmur. I could always realize when he was in distress, without being told. He was not exactly an early riser, that is, he never usually appeared at the office till about nine o'clock in the morning. I usually preceded him an hour. Sometimes, however, he would come down as early as seven o'clock—in fact, on one occasion I remember he came down before daylight. If, on arriving at the office, I found him in, I knew instantly that a breeze had sprung up over the domestic sea, and that the waters were troubled. He would either be lying on the lounge looking skyward, or doubled up in a chair with his feet resting on the sill of a back window. He would not look up on my entering, and only answered my "Good morning" with a grunt. I at once busied myself with pen and paper, or ran through the leaves of some book; but the evidence of his melancholy and distress was so plain, and his silence so significant, that I would grow restless myself, and finding some excuse to go to the courthouse or elsewhere, would leave the room.
The door of the office opening into a narrow hallway was half glass, with a curtain on it working on brass rings strung on wire. As I passed out on these occasions I would draw the curtain across the glass, and before I reached the bottom of the stairs I could hear the key turn in the lock, and Lincoln was alone in his gloom. An hour in the clerk's office at the court-house, an hour longer in a neighboring store having passed, I would return. By that time either a client had dropped in and Lincoln was propounding the law, or else the cloud of despondency had passed away, and he was busy in the recital of an Indiana story to whistle off the recollections of the morning's gloom. Noon having arrived I would depart homeward for my dinner. Returning within an hour, I would find him still in the office,—although his house stood but a few squares away,—lunching on a slice of cheese and a handful of crackers which, in my absence, he had brought up from a store below. Separating for the day at five or six o'clock in the evening, I would still leave him behind, either sitting on a box at the foot of the stairway, entertaining a few loungers, or killing time in the same way on the court-house steps. A light in the office after dark attested his presence there till late along in the night, when, after all the world had gone to sleep, the tall form of the man destined to be the nation's President could have been seen strolling along in the shadows of trees and buildings, and quietly slipping in through the door of a modest frame house, which it pleased the world, in a conventional way, to call his home.
Some persons may insist that this picture is too highly colored. If so, I can only answer, they do not know the facts. The majority of those who have a personal knowledge of them are persistent in their silence. If their lips could be opened and all could be known, my conclusions and statements, to say the least of them, would be found to be fair, reasonable, and true. A few words more as to Lincoln's domestic history, and I pass to a different phase of his life. One of his warmest and closest friends, who still survives, maintains the theory that, after all, Lincoln's political ascendancy and final elevation to the Presidency were due more to the influence of his wife than to any other person or cause. "The fact," insists this friend, "that Mary Todd, by her turbulent nature and unfortunate manner, prevented her husband from becoming a domestic man, operated largely in his favor; for he was thereby kept out in the world of business and politics. Instead of spending his evenings at home, reading the papers and warming his toes at his own fireside, he was constantly out with the common people, was mingling with the politicians, discussing public questions with the farmers who thronged the offices in the court-house and state house, and exchanging views with the loungers who surrounded the stove of winter evenings in the village store. The result of this continuous contact with the world was, that he was more thoroughly known than any other man in his community. His wife, therefore, was one of the unintentional means of his promotion. If, on the other hand, he had married some less ambitious but more domestic woman, some honest farmer's quiet daughter,—one who would have looked up to and worshipped him because he uplifted her,—the result might have been different. For, although it doubtless would have been her pride to see that he had clean clothes whenever he needed them; that his slippers were always in their place; that he was warmly clad and had plenty to eat; and, although the privilege of ministering to his every wish and whim might have been to her a pleasure rather than a duty; yet I fear he would have been buried in the pleasures of a loving home, and the country would never have had Abraham Lincoln for its President."
In her domestic troubles I have always sympathized with Mrs. Lincoln. The world does not know what she bore, or how ill-adapted she was to bear it. Her fearless, witty, and austere nature shrank instinctively from association with the calm, imperturbable, and simple ways of her thoughtful and absent-minded husband. Besides, who knows but she may have acted out in her conduct toward her husband the laws of human revenge? The picture of that eventful evening in 1841, when she stood at the Edwards mansion clad in her bridal robes, the feast prepared and the guests gathered, and when the bridegroom came not, may have been constantly before her, and prompted her to a course of action which kept in the background the better elements of her nature. In marrying Lincoln she did not look so far into the future as Mary Owens, who declined his proposal because "he was deficient in those little links which make up the chain of woman's happiness." *
* Mrs. Lincoln died at the residence of her sister Mrs. Ninian W. Edwards, in Springfield, July 16, 1882. Her physician during her last illness says this of her: "In the late years of her life certain mental peculiarities were developed which finally culminated in a slight apoplexy, producing paralysis, of which she died. Among the peculiarities alluded to, one of the most singular was the habit she had during the last year or so of her life of immuring herself in a perfectly dark room and, for light, using a small candle-light, even when the sun was shining bright out-of-doors. No urging would induce her to go out into the fresh air. Another peculiarity was the accumulation of large quantities of silks and dress goods in trunks and by the cart-load, which she never used and which accumulated until it was really feared that the floor of the store-room would give way. She was bright and sparkling in conversation, and her memory remained singularly good up to the very close of her life. Her face was animated and pleasing; and to me she was always an interesting woman; and while the whole world was finding fault with her temper and disposition, it was clear to me that the trouble was really a cerebral disease."—Dr. Thomas W. Dresser, letter, January 3, 1889, MS.
By reason of his practical turn of mind Mr. Lincoln never speculated any more in the scientific and philosophical than he did in the financial world. He never undertook to fathom the intricacies of psychology and metaphysics.* Investigation into first causes, abstruse mental phenomena, the science of being, he brushed aside as trash—mere scientific absurdities. He discovered through experience that his mind, like the minds of other men, had its limitations, and hence he economized his forces and his time by applying his powers in the field of the practical. Scientifically regarded he was a realist as opposed to an idealist, a sensationist as opposed to an intuitionist, a materialist as opposed to a spiritualist.
* "He was contemplative rather than speculative. He wanted something solid to rest upon, and hence his bias for mathematics and the physical sciences. He bestowed more attention on them than upon metaphysical speculations. I have heard him descant upon the problem whether a ball discharged from a gun in a horizontal position would be longer in reaching the ground than one dropped at the instant of discharge from the muzzle. He said it always appeared to him that they would both reach the ground at the same time, even before he had read the philosophical explanation."—Joseph Gillespie, letter, December 8, 1866, MS.
There was more or less superstition in his nature, and, although he may not have believed implicitly in the signs of his many dreams, he was constantly endeavoring to unravel them. His mind was readily impressed with some of the most absurd superstitions. His visit to the Voodoo fortune-teller in New Orleans in 1831; his faith in the virtues of the mad-stone, when he took his son Robert to Terre Haute, Indiana, to be cured of the bite of a rabid dog; and the strange double image of himself which he told his secretary, John Hay, he saw reflected in a mirror just after his election in 1860, strongly attest his inclination to superstition. He held most firmly to the doctrine of fatalism all his life. His wife, after his death, told me what I already knew, that "his only philosophy was, what is to be will be, and no prayers of ours can reverse the decree." He always contended that he was doomed to a sad fate, and he repeatedly said to me when we were alone in our office: "I am sure I shall meet with some terrible end." In proof of his strong leaning towards fatalism he once quoted the case of Brutus and Caesar, arguing that the former was forced by laws and conditions over which he had no control to kill the latter, and, vice versâ, that the latter was specially created to be disposed of by the former. This superstitious view of life ran through his being like the thin blue vein through the whitest marble, giving the eye rest from the weariness of continued unvarying color.*
* I have heard him frequently quote the couplet, "There's a divinity that shapes our ends, Rough-hew them how we will."
For many years I subscribed for and kept on our office table the Westminster and Edinburgh Review and a number of other English periodicals. Besides them I purchased the works of Spencer, Darwin, and the utterances of other English scientists, all of which I devoured with great relish. I endeavored, but had little success in inducing Lincoln to read them. Occasionally he would snatch one up and peruse it for a little while, but he soon threw it down with the suggestion that it was entirely too heavy for an ordinary mind to digest.*
* In 1856 I purchased in New York a life of Edmund Burke. I have forgotten now who the author was, but I remember I read it through in a short time. One morning Lincoln came into the office and, seeing the book in my hands, enquired what I was reading. I told him, at the same time observing that it was an excellent work and handing the book over to him. Taking it in his hand he threw himself down on the office sofa and hastily ran over its pages, reading a little here and there. At last he closed and threw it on the table with the exclamation, "No, I've read enough of it. It's like all the others. Biographies as generally written are not only misleading, but false. The author of this life of Burke makes a wonderful hero out of his subject. He magnifies his perfections—if he had any—and suppresses his imperfections. He is so faithful in his zeal and so lavish in praise of his every act that one is almost driven to believe that Burke never made a mistake or a failure in his life." He lapsed into a brown study, but presently broke out again, "Billy, I've wondered why book-publishers and merchants don't have blank biographies on their shelves, always ready for an emergency; so that, if a man happens to die, his heirs or his friends, if they wish to perpetuate his memory, can purchase one already written, but with blanks. These blanks they can at their pleasure fill up with rosy sentences full of high-sounding praise. In most instances they commemorate a lie, and cheat posterity out of the truth. History," he concluded, "is not history unless it is the truth." This emphatic avowal of sentiment from Mr. Lincoln not only fixes his estimate of ordinary biography, but is my vindication in advance if assailed for telling the truth.
A gentleman in Springfield gave him a book called, I believe, "Vestiges of Creation," which interested him so much that he read it through. The volume was published in Edinburgh, and undertook to demonstrate the doctrine of development or evolution. The treatise interested him greatly, and he was deeply impressed with the notion of the so-called "universal law"—evolution; he did not extend greatly his researches, but by continued thinking in a single channel seemed to grow into a warm advocate of the new doctrine. Beyond what I have stated he made no further investigation into the realm of philosophy. "There are no accidents," he said one day, "in my philosophy. Every effect must have its cause. The past is the cause of the present, and the present will be the cause of the future. All these are links in the endless chain stretching from the finite to the infinite." From what has been said it would follow logically that he did not believe, except in a very restricted sense, in the freedom of the will. We often argued the question, I taking the opposite view; he changed the expression, calling it the freedom of the mind, and insisted that man always acted from a motive. I once contended that man was free and could act without a motive. He smiled at my philosophy, and answered that it was "impossible, because the motive was born before the man."
The foregoing thoughts are prefatory to the much-mooted question of Mr. Lincoln's religious belief. For what I have heretofore said on this subject, both in public lectures and in letters which have frequently found their way into the newspapers, I have been freely and sometimes bitterly assailed, but I do not intend now to reopen the discussion or to answer the many persons who have risen up and asked to measure swords with me. I merely purpose to state the bare facts, expressing no opinion of my own, and allowing each and every one to put his or her construction on them.
Inasmuch as he was so often a candidate for public office Mr. Lincoln said as little about his religious opinions as possible, especially if he failed to coincide with the orthodox world. In illustration of his religious code I once heard him say that it was like that of an old man named Glenn, in Indiana, whom he heard speak at a church meeting, and who said: "When I do good I feel good, when I do bad I feel bad, and that's my religion." In 1834, while still living in New Salem and before he became a lawyer, he was surrounded by a class of people exceedingly liberal in matters of religion. Volney's "Ruins" and Paine's "Age of Reason" passed from hand to hand, and furnished food for the evening's discussion in the tavern and village store. Lincoln read both these books and thus assimilated them into his own being. He prepared an extended essay—called by many, a book—in which he made an argument against Christianity, striving to prove that the Bible was not inspired, and therefore not God's revelation, and that Jesus Christ was not the son of God. The manuscript containing these audacious and comprehensive propositions he intended to have published or given a wide circulation in some other way. He carried it to the store, where it was read and freely discussed. His friend and employer, Samuel Hill, was among the listeners, and, seriously questioning the propriety of a promising young man like Lincoln fathering such unpopular notions, he snatched the manuscript from his hands and thrust it into the stove. The book went up in flames, and Lincoln's political future was secure. But his infidelity and his sceptical views were not diminished. He soon removed to Springfield, where he attracted considerable notice by his rank doctrine. Much of what he then said may properly be credited to the impetuosity and exuberance of youth. One of his closest friends, whose name is withheld, narrating scenes and reviewing discussions that in 1838 took place in the office of the county clerk, says: "Sometimes Lincoln bordered on atheism. He went far that way, and shocked me. I was then a young man, and believed what my good mother told me.... He would come into the clerk's office where I and some young men were writing and staying, and would bring the Bible with him; would read a chapter and argue against it.... Lincoln was enthusiastic in his infidelity. As he grew older he grew more discreet; didn't talk much before strangers about his religion; but to friends, close and bosom ones, he was always open and avowed, fair and honest; to strangers, he held them off from policy." John T. Stuart, who was Lincoln's first partner, substantially endorses the above. "He was an avowed and open infidel," declares Stuart, "and sometimes bordered on atheism;.... went further against Christian beliefs and doctrines and principles than any man I ever heard; he shocked me. I don't remember the exact line of his argument; suppose it was against the inherent defects, so-called, of the Bible, and on grounds of reason. Lincoln always denied that Jesus was the Christ of God—denied that Jesus was the son of God as understood and maintained by the Christian Church." David Davis tells us this: "The idea that Lincoln talked to a stranger about his religion or religious views, or made such speeches and remarks about it as are published, is to me absurd. I knew the man so well; he was the most reticent, secretive man I ever saw or expect to see. He had no faith, in the Christian sense of the term—had faith in laws, principles, causes and effects." Another man * testifies as follows: "Mr. Lincoln told me that he was a kind of immortalist; that he never could bring himself to believe in eternal punishment; that man lived but a little while here; and that if eternal punishment were man's doom, he should spend that little life in vigilant and ceaseless preparation by never-ending prayer." Another intimate friend** furnishes this: "In my intercourse with Mr. Lincoln I learned that he believed in a Creator of all things, who had neither beginning nor end, possessing all power and wisdom, established a principle in obedience to which worlds move and are upheld, and animal and vegetable life come into existence. A reason he gave for his belief was that in view of the order and harmony of all nature which we behold, it would have been more miraculous to have come about by chance than to have been created and arranged by some great thinking power."
* William H. Hannah. ** I. W. Keys.
As to the Christian theory that Christ is God or equal to the Creator, he said that it had better be taken for granted; for by the test of reason we might become infidels on that subject, for evidence of Christ's divinity came to us in a somewhat doubtful shape; but that the system of Christianity was an ingenious one at least, and perhaps was calculated to do good." Jesse W. Fell, to whom Lincoln first confided the details of his biography, furnishes a more elaborate account of the latter's religious views than anyone else. In a statement made September 22, 1870, Fell says: "If there were any traits of character that stood out in bold relief in the person of Mr. Lincoln they were those of truth and candor. He was utterly incapable of insincerity or professing views on this or any other subject he did not entertain. Knowing such to be his true character, that insincerity, much more duplicity, were traits wholly foreign to his nature, many of his old friends were not a little surprised at finding in some of the biographies of this great man statements concerning his religious opinions so utterly at variance with his known sentiments. True, he may have changed or modified these sentiments* after his removal from among us, though this is hardly reconcilable with the history of the man, and his entire devotion to public matters during his four years' residence at the national capital.
* "Executive Mansion, Washington, May 27, 1865. "Friend Herndon: "Mr. Lincoln did not to my knowledge in any way change his religious ideas, opinions, or beliefs from the time he left Springfield to the day of his death. I do not know just what they were, never having heard him explain them in detail; but I am very sure he gave no outward indication of his mind having undergone any change in that regard while here. \ "Yours truly, "Jno. G. Nicolay."
It is possible, however, that this may be the proper solution of this conflict of opinions; or it may be that, with no intention on the part of any one to mislead the public mind, those who have represented him as believing in the popular theological views of the times may have misapprehended him, as experience shows to be quite common where no special effort has been made to attain critical accuracy on a subject of this nature. This is the more probable from the well-known fact, that Mr. Lincoln seldom communicated to any one his views on this subject; but be this as it may, I have no hesitation whatever in saying that whilst he held many opinions in common with the great mass of Christian believers, he did not believe in what are regarded as the orthodox or evangelical views of Christianity.
"On the innate depravity of man, the character and office of the great Head of the Church, the atonement, the infallibility of the written revelation, the performance of miracles, the nature and design of present and future rewards and punishments (as they are popularly called), and many other subjects he held opinions utterly at variance with what are usually taught in the Church. I should say that his expressed views on these and kindred topics were such as, in the estimation of most believers, would place him outside the Christian pale. Yet, to my mind, such was not the true position, since his principles and practices and the spirit of his whole life were of the very kind we universally agree to call Christian; and I think this conclusion is in no wise affected by the circumstance that he never attached himself to any religious society whatever.
"His religious views were eminently practical, and are summed up, as I think, in these two propositions: the Fatherhood of God, and the brotherhood of man. He fully believed in a superintending and overruling Providence that guides and controls the operations of the world, but maintained that law and order, and not their violation or suspension, are the appointed means by which this Providence is exercised.*
* "A convention of preachers held, I think, at Philadelphia, passed a resolution asking him to recommend to Congress an amendment to the Constitution directly recognizing the existence of God. The first draft of his message prepared after this resolution was sent him did contain a paragraph calling the attention of Congress to the subject. When I assisted him in reading the proof he struck it out, remarking that he had not made up his mind as to its propriety."—MS. letter, John D. Defrees, December 4, 1866.
"I will not attempt any specification of either his belief or disbelief on various religious topics, as derived from conversations with him at different times during a considerable period; but as conveying a general view of his religious or theological opinions, will state the following facts. Some eight or ten years prior to his death, in conversing with him upon this subject, the writer took occasion to refer, in terms of approbation, to the sermons and writings generally of Dr. W. E. Channing; and, finding he was considerably interested in the statement I made of the opinions held by that author, I proposed to present him (Lincoln) a copy of Channing's entire works, which I soon after did. Subsequently the contents of these volumes, together with the writings of Theodore Parker, furnished him, as he informed me, by his friend and law partner, William H. Herndon, became naturally the topics of conversation with us; and, though far from believing there was an entire harmony of views on his part with either of those authors, yet they were generally much admired and approved by him.
"No religious views with him seemed to find any favor except of the practical and rationalistic order; and if, from my recollections on this subject, I was called upon to designate an author whose views most nearly represented Mr. Lincoln's on this subject, I would say that author was Theodore Parker." The last witness to testify before this case is submitted to the reader is no less a person than Mrs. Lincoln herself. In a statement made at a time and under circumstances detailed in a subsequent chapter she said this: "Mr. Lincoln had no faith and no hope in the usual acceptation of those words. He never joined a Church; but still, as I believe, he was a religious man by nature. He first seemed to think about the subject when our boy Willie died, and then more than ever about the time he went to Gettysburg; but it was a kind of poetry in his nature, and he was never a technical Christian."
No man had a stronger or firmer faith in Providence—God—than Mr. Lincoln, but the continued use by him late in life of the word God must not be interpreted to mean that he believed in a personal God. In 1854 he asked me to erase the word God from a speech which I had written and read to him for criticism because my language indicated a personal God, whereas he insisted no such personality ever existed.
My own testimony, however, in regard to Mr. Lincoln's religious views may perhaps invite discussion. The world has always insisted on making an orthodox Christian of him, and to analyze his sayings or sound his beliefs is but to break the idol. It only remains to say that, whether orthodox or not, he believed in God and immortality; and even if he questioned the existence of future eternal punishment he hoped to find a rest from trouble and a heaven beyond the grave. If at any time in his life he was sceptical of the divine origin of the Bible he ought not for that reason to be condemned; for he accepted the practical precepts of that great book as binding alike upon his head and his conscience. The benevolence of his impulses, the seriousness of his convictions, and the nobility of his character are evidences unimpeachable that his soul was ever filled with the exalted purity and sublime faith of natural religion.
The result of the campaign of 1858 wrought more disaster to Lincoln's finances than to his political prospects. The loss of over six months from his business, and the expenses of the canvass, made a severe drain on his personal income. He was anxious to get back to the law once more and earn a little ready money. A letter written about this time to his friend Norman B. Judd, Chairman of the Republican State Committee, will serve to throw some light on the situation he found himself in. "I have been on expenses so long, without earning anything," he says, "that I am absolutely without money now for even household expenses. Still, if you can put in $250 for me towards discharging the debt of the committee, I will allow it when you and I settle the private matter between us. This, with what I have already paid, with an outstanding note of mine, will exceed my subscription of $500. This, too, is exclusive of my ordinary expenses during the campaign, all of which, being added to my loss of time and business, bears prettily heavily upon one no better off than I am. But as I had the post of honor, it is not for me to be over-nice." At the time this letter was written his property consisted of the house and lot on which he lived, a few law books and some household furniture. He owned a small tract of land in Iowa which yielded him nothing, and the annual income from his law practice did not exceed $3,000; yet the party's committee in Chicago were dunning their late standard-bearer, who, besides the chagrin of his defeat, his own expenses, and the sacrifice of his time, was asked to aid in meeting the general expenses of the campaign. At this day one is a little surprised that some of the generous and wealthy members of the party in Chicago or elsewhere did not come forward and volunteer their aid. But they did not, and whether Lincoln felt in his heart the injustice of this treatment or not, he went straight ahead in his own path and said nothing about it.
Political business being off his hands, he now conceived the idea of entering the lecture field. He began preparations in the usual way by noting down ideas on stray pieces of paper, which found a lodgment inside his hat, and finally brought forth in connected form a lecture on "Inventions." He recounted the wonderful improvements in machinery, the arts, and sciences. Now and then he indulged in a humorous paragraph, and witticisms were freely sprinkled throughout the lecture. During the winter he delivered it at several towns in the central part of the State, but it was so commonplace, and met with such indifferent success, that he soon dropped it altogether.* The effort met with the disapproval of his friends, and he himself was filled with disgust.
* "As we were going to Danville court I read to Lincoln a lecture by Bancroft on the wonderful progress of man, delivered in the preceding November. Sometime later he told us—Swett and me—that he had been thinking much on the subject and believed he would write a lecture on 'Man and His Progress.' Afterwards I read in a paper that he had come to either Bloomington or Clinton to lecture and no one turned out. The paper added, 'That doesn't look much like his being President.' I once joked him about it; he said good-naturedly, 'Don't; that plagues me.'"—Henry C. Whitney, letter, Aug. 27, 1867, MS. "Springfield, March 28, 1859. "W. M. Morris, Esq., "Dear Sir:—Your kind note inviting me to deliver a lecture at Galesburg is received. I regret to say I cannot do so now; I must stick to the courts awhile. I read a sort of lecture to three different audiences during the last month and this; but I did so under circumstances which made it a waste of no time whatever. "Yours very truly, "A. Lincoln."
If his address in 1852, over the death of Clay, proved that he was no eulogist, then this last effort demonstrated that he was no lecturer. Invitations to deliver the lecture—prompted no doubt by the advertisement given him in the contest with Douglas—came in very freely; but beyond the three attempts named, he declined them all. "Press of business in the courts" afforded him a convenient excuse, and he retired from the field.
During the fall of 1859 invitations to take part in the canvass came from over half-a-dozen States where elections were to be held, Douglas, fresh from the Senate, had gone to Ohio, and thither in September Lincoln, in response to the demands of party friends everywhere, followed.*
* "He returned to the city two years after with a fame as wide as the continent, with the laurels of the Douglas contest on his brow, and the Presidency in his grasp. He returned, greeted with the thunder of cannon, the strains of martial music, and the joyous plaudits of thousands of citizens thronging the streets. He addressed a vast concourse on Fifth Street Market; was entertained in princely style at the Burnet House, and there received with courtesy the foremost citizens come to greet this rising star. With high hope and happy heart he left Cincinnati after a three days' sojourn. But a perverse fortune attended him and Cincinnati in their intercourse. Nine months after Mr. Lincoln left us, after he had been nominated for the Presidency, when he was tranquilly waiting in his cottage home at Springfield the verdict of the people, his last visit to Cincinnati and the good things he had had at the Burnet House were rudely brought to his memory by a bill presented to him from its proprietors. Before leaving the hotel he had applied to the clerk for his bill; was told that it was paid, or words to that effect. This the committee had directed, but afterwards neglected its payment. The proprietors shrewdly surmised that a letter to the nominee for the Presidency would bring the money. The only significance in this incident is in the letter it brought from Mr. Lincoln, revealing his indignation at the seeming imputation against his honor, and his greater indignation at one item of the bill. 'As to wines, liquors, and cigars, we had none, absolutely none. These last may have been in Room 15 by order of committee, but I do not recollect them at all.'—W. M. Dickson, "Harper's Magazine," June, 1884.
He delivered telling and impressive speeches at Cincinnati and Columbus,* following Douglas at both places. He made such a favorable impression among his Ohio friends that, after a glorious Republican victory, the State committee asked the privilege of publishing his speeches, along with those of Douglas, to be used and distributed as a campaign document.
* Douglas had written a long and carefully prepared article on "Popular Sovereignty in the Territories," which appeared for the first time in the September (1859) number of "Harper's Magazine." It went back some distance into the history of the government, recounting the proceedings of the earliest Congresses, and sought to mark out more clearly than had heretofore been done "the dividing line between Federal and Local authority." In a speech at Columbus, O, Lincoln answered the "copy-right essay" categorically. After alluding to the difference of position between himself and Judge Douglas on the doctrine of Popular Sovereignty, he said: "Judge Douglas has had a good deal of trouble with Popular Sovereignty. His explanations, explanatory of explanations explained, are interminable. The most lengthy and, as I suppose, the most maturely considered of his long series of explanations is his great essay in "Harper's Magazine."
This request he especially appreciated, because after some effort he had failed to induce any publisher in Springfield to undertake the enterprise,* thus proving anew that "a prophet is not without honor, save in his own country." In December he visited Kansas, speaking at Atchison, Troy, Leavenworth, and other towns near the border. His speeches there served to extend his reputation still further westward. Though his arguments were repetitions of the doctrine laid down in the contest with Douglas, yet they were new to the majority of his Kansas** hearers and were enthusiastically approved. By the close of the year he was back again in the dingy law office in Springfield.
* A gentleman is still living, who at the time of the debate between Lincoln and Douglas, was a book publisher in Springfield. Lincoln had collected newspaper slips of all the speeches made during the debate, and proposed to him their publication in book form; but the man declined, fearing there would be no demand for such a book. Subsequently, when the speeches were gotten out in book form in Ohio, Mr. Lincoln procured a copy and gave it to his Springfield friend, writing on the fly-leaf, "Compliments of A. Lincoln." ** How Mr. Lincoln stood on the questions of the hour, after his defeat by Douglas, is clearly shown in a letter written on the 14th of May, 1859, to a friend in Kansas, who had forwarded him an invitation to attend a Republican convention there. "You will probably adopt resolutions," he writes, "in the nature of a platform. I think the only danger will be the temptation to lower the Republican standard in order to gather recruits. In my judgment such a step would be a serious mistake, and open a gap through which more would pass out than pass in. And this would be the same whether the letting down should be in deference to Douglasism or to the Southern opposition element; either would surrender the object of the Republican organization— the preventing of the spread and nationalization of slavery. This object surrendered, the organization would go to pieces. I do not mean by this that no Southern man must be placed upon our national ticket for 1860. There are many men in the slave states for any one of whom I could cheerfully vote, to be either President or Vice-president, provided he would enable me to do so with safety to the Republican cause, without lowering the Republican standard. This is the indispensable condition of a union with us; it is idle to talk of any other. Any other would be as fruitless to the South as distasteful to the North, the whole ending in common defeat. Let a union be attempted on the basis of ignoring the slavery question, and magnifying other questions which the people are just now caring about, and it will result in gaining no single electoral vote in the South, and losing every one in the North."—MS. letter to M. W. Delahay.
The opening of the year 1860 found Mr. Lincoln's name freely mentioned in connection with the Republican nomination for the Presidency. To be classed with Seward, Chase, McLean, and other celebrities was enough to stimulate any Illinois lawyer's pride; but in Mr. Lincoln's case, if it had any such effect, he was most artful in concealing it. Now and then some ardent friend, an editor, for example, would run his name up to the mast-head, but in all cases he discouraged the attempt. "In regard to the matter you spoke of," he answered one man who proposed his name, "I beg that you will not give it a further mention. Seriously, I do not think I am fit for the Presidency."*
* Letter, March 5, 1859, to Thomas J. Pickett.
The first effort in his behalf as a Presidential aspirant was the action taken by his friends at a meeting held in the State House early in 1860, in the rooms of O. M. Hatch, then Secretary of State. Besides Hatch there were present Norman B. Judd, chairman of the Republican State Committee, Ebenezer Peck, Jackson Grimshaw, and others of equal prominence in the party. "We all expressed a personal preference for Mr. Lincoln," relates one who was a participant in the meeting,* "as the Illinois candidate for the Presidency, and asked him if his name might be used at once in connection with the nomination and election. With his characteristic modesty he doubted whether he could get the nomination even if he wished it, and asked until the next morning to answer us whether his name might be announced. Late the next day he authorized us, if we thought proper to do so, to place him in the field." To the question from Mr. Grimshaw whether, if the nomination for President could not be obtained, he would accept the post of Vice-president, he answered that he would not; that his name having been used for the office of President, he would not permit it to be used for any other office, however honorable it might be. This meeting was preliminary to the Decatur convention, and was also the first concerted action in his behalf on the part of his friends.
* Jackson Grimshaw. Letter, Quincy, Ill., April 28, 1866, MS.
In the preceding October he came rushing into the office one morning, with the letter from New York City, inviting him to deliver a lecture there, and asked my advice and that of other friends as to the subject and character of his address. We all recommended a speech on the political situation. Remembering his poor success as a lecturer himself, he adopted our suggestions. He accepted the invitation of the New York committee, at the same time notifying them that his speech would deal entirely with political questions, and fixing a day late in February as the most convenient time. Meanwhile he spent the intervening time in careful preparation. He searched through the dusty volumes of congressional proceedings in the State library, and dug deeply into political history. He was painstaking and thorough in the study of his subject, but when at last he left for New York we had many misgivings—and he not a few himself—of his success in the great metropolis. What effect the unpretentious Western lawyer would have on the wealthy and fashionable society of the great city could only be conjectured. A description of the meeting at Cooper Institute, a list of the names of the prominent men and women present, or an account of Lincoln in the delivery of the address would be needless repetitions of well-known history.*
* On his return home Lincoln told me that for once in his life he was greatly abashed over his personal appearance. The new suit of clothes which he donned on his arrival in New York were ill-fitting garments, and showed the creases made while packed in the valise; and for a long time after he began his speech and before he became "warmed up" he imagined that the audience noticed the contrast between his Western clothes and the neat-fitting suits of Mr. Bryant and others who sat on the platform. The collar of his coat on the right side had an unpleasant way of flying up whenever he raised his arm to gesticulate. He imagined the audience noticed that also. After the meeting closed, the newspaper reporters called for slips of his speech. This amused him, because he had no idea what slips were, and besides, didn't suppose the newspapers cared to print his speech verbatim.
It only remains to say that his speech was devoid of all rhetorical imagery, with a marked sup-pression of the pyrotechnics of stump oratory. It was constructed with a view to accuracy of statement, simplicity of language, and unity of thought. In some respects like a lawyer's brief, it was logical, temperate in tone, powerful—irresistibly driving conviction home to men's reasons and their souls. No former effort in the line of speech-making had cost Lincoln so much time and thought as this one. It is said by one of his biographers, that those afterwards engaged in getting out the speech as a campaign document were three weeks in verifying the statements and finding the historical records referred to and consulted by him. This is probably a little over-stated as to time, but unquestionably the work of verification and reference, was in any event a very labored and extended one.* The day following the Cooper Institute meeting, the leading New York dailies published the speech in full, and made favorable editorial mention of it and of the speaker as well. It was plain now that Lincoln had captured the metropolis. From New York he travelled to New England to visit his son Robert, who was attending college.
* Mr. Lincoln obtained most of the facts of his Cooper Institute speech from Eliott's "Debates on the Federal Constitution." There were six volumes, which he gave to me when he went to Washington in 1861.
In answer to the many calls and invitations which showered on him, he spoke at various places in Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire. In all these places he not only left deep impressions of his ability, but he convinced New England of his intense earnestness in the great cause. The newspapers treated him with no little consideration. One paper* characterized his speech as one of "great fairness," delivered with "great apparent candor and wonderful interest. For the first half hour his opponents would agree with every word he uttered; and from that point he would lead them off little by little until it seemed as if he had got them all into his fold. He is far from prepossessing in personal appearance, and his Voice is disagreeable; and yet he wins your attention from the start.. He indulges in no flowers of rhetoric, no eloquent passages.... He displays more shrewdness, more knowledge of the masses of mankind than any public speaker we have heard since Long Jim Wilson left for California."
* Manchester Mirror.
Lincoln's return to Springfield after his dazzling success in the East was the signal for earnest congratulations on the part of his friends. Seward was the great man of the day, but Lincoln had demonstrated to the satisfaction of his friends that he was tall enough and strong enough to measure swords with the Auburn statesman. His triumph in New York and New England had shown that the idea of a house divided against itself induced as strong cooperation and hearty support in prevention of a great wrong in the East as the famous "irrepressible conflict" attracted warriors to Seward's standard in the Mississippi valley. It was apparent now to Lincoln that the Presidential nomination was within his reach. He began gradually to lose his interest in the law and to trim his political sails at the same time. His recent success had stimulated his self-confidence to unwonted proportions. He wrote to influential party workers everywhere. I know the idea prevails that Lincoln sat still in his chair in Springfield, and that one of those unlooked-for tides in human affairs came along and cast the nomination into his lap; but any man who has had experience in such things knows that great political prizes are not obtained in that way. The truth is, Lincoln was as vigilant as he was ambitious, and there is no denying the fact that he understood the situation perfectly from the start. In the management of his own interests he was obliged to rely almost entirely on his own resources. He had no money with which to maintain a political bureau, and he lacked any kind of personal organization whatever. Seward had all these things, and, behind them all, a brilliant record in the United States Senate with which to dazzle his followers. But with all his prestige and experience the latter was no more adroit and no more untiring in pursuit of his ambition than the man who had just delivered the Cooper Institute speech. A letter written by Lincoln about this time to a friend in Kansas serves to illustrate his methods, and measures the extent of his ambition.

The letter is dated March 10, and is now in my possession. For obvious reasons I withhold the friend's name: "As to your kind wishes for myself," writes Lincoln, "allow me to say I cannot enter the ring on the money basis—first, because in the main it is wrong; and secondly, I have not and cannot get the money. I say in the main the use of money is wrong; but for certain objects in a political contest the use of some is both right and indispensable. With me, as with yourself, this long struggle has been one of great pecuniary loss. I now distinctly say this: If you shall be appointed a delegate to Chicago I will furnish one hundred dollars to bear the expenses of the trip." There is enough in this letter to show that Lincoln was not only determined in his political ambition, but intensely practical as well. His eye was constantly fastened on Seward, who had already freely exercised the rights of leadership in the party. All other competitors he dropped out of the problem. In the middle of April he again writes his Kansas friend: "Reaching home last night I found yours of the 7th. You know I was recently in New England. Some of the acquaintances while there write me since the election that the close vote in Connecticut and the quasi-defeat in Rhode Island are a drawback upon the prospects of Governor Seward; and Trumbull writes Dubois to the same effect. Do not mention this as coming from me. Both these States are safe enough in the fall." But, while Seward may have lost ground near his home, he was acquiring strength in the West. He had invaded the very territory Lincoln was intending to retain by virtue of his course in the contest with Douglas. Lincoln's friend in Kansas, instead of securing that delegation for him, had suffered the Seward men to outgeneral him, and the prospects were by no means flattering. "I see by the dispatches," writes Lincoln, in a burst of surprise, "that, since you wrote, Kansas has appointed delegates and instructed for Seward. Don't stir them up to anger, but come along to the convention and I will do as I said about expenses." Whether the friend ever accepted Lincoln's generous offer I do not know,* but it may not be without interest to state that within ten days after the latter's inauguration he appointed him to a Federal office with comfortable salary attached, and even asked for his preferences as to other contemplated appointments in his own State.**
* This case illustrates quite forcibly Lincoln's weakness in dealing with individuals. This man I know had written Lincoln, promising to bring the Kansas delegation to Chicago for him if he would only pay his expenses. Lincoln was weak enough to make the promise, and yet such was his faith in the man that he appointed him to an important judicial position and gave him great prominence in other ways. What President or candidate for President would dare do such a thing now? ** The following is in my possession: "Executive Mansion, March 13,1861. "———, Esq. "My Dear Sir: "You will start for Kansas before I see you again; and when I saw you a moment this morning I forgot to ask you about some of the Kansas appointments, which I intended to do. If you care much about them you can write, as I think I shall not make the appointments just yet. "Yours in haste, "A. Lincoln."
In the rapid, stirring scenes that crowd upon each other from this time forward the individuality of Lincoln is easily lost sight of. He was so thoroughly interwoven in the issues before the people of Illinois that he had become a part of them. Among his colleagues at the bar he was no longer looked upon as the Circuit-Court lawyer of earlier days. To them it seemed as if the nation were about to lay its claim upon him. His tall form enlarged, until, to use a figurative expression, he could no longer pass through the door of our dingy office. Reference has already been made to the envy of his rivals at the bar, and the jealousy of his political contemporaries. Very few indeed were free from the degrading passion; but it made no difference in Lincoln's treatment of them. He was as generous and deferred to them as much as ever. The first public movement by the Illinois people in his interest was the action of the State convention, which met at Decatur on the 9th and 10th of May. It was at this convention that Lincoln's friend and cousin, John Hanks, brought in the two historic rails which both had made in the Sangamon bottom in 1830, and which served the double purpose of electrifying the Illinois people and kindling the fire of enthusiasm that was destined to sweep over the nation. In the words of an ardent Lincoln delegate, "These rails were to represent the issue in the coming contest between labor free and labor slave; between democracy and aristocracy. Little did I think," continues our jubilant and effusive friend, "of the mighty consequences of this little incident; little did I think that the tall, and angular, and bony rail-splitter who stood in girlish diffidence bowing with awkward grace would fill the chair once filled by Washington, and that his name would echo in chants of praise along the corridor of all coming time." A week later the hosts were gathered for the great convention in Chicago. David Davis had rented rooms in the Tremont House and opened up "Lincoln's headquarters." I was not a delegate, but belonged to the contingent which had Lincoln's interests in charge. Judge Logan was the Springfield delegate, and to him Lincoln had given a letter authorizing the withdrawal of his name whenever his friends deemed such action necessary or proper. Davis was the active man, and had the business management in charge. If any negotiations were made, he made them. The convention was held in a monster building called the Wigwam. No one who has ever attempted a description of it has overdrawn its enthusiasm and exciting scenes. Amid all the din and confusion, the curbstone contentions, the promiscuous wrangling of delegates, the deafening roar of the assembled hosts, the contest narrowed down to a neck-and-neck race between the brilliant statesman of Auburn and the less pretentious, but manly rail-splitter from the Sangamon bottoms. With the proceedings of the convention the world is already well familiar. On the first ballot Seward led, but was closely followed by Lincoln; on the second Lincoln gained amazingly; on the third the race was an even one until the dramatic change by Carter, of Ohio, when Lincoln, swinging loose, swept grandly to the front. The cannon planted on the roof of the Wigwam belched forth a boom across the Illinois prairies. The sound was taken up and reverberated from Maine to California. With the nomination of Hannibal Hamlin, of Maine, the convention adjourned. The delegates—victorious and vanquished alike— turned their steps homeward, and the great campaign of 1860 had begun. The day before the nomination the editor of the Springfield Journal arrived in Chicago with a copy of the Missouri Democrat, in which Lincoln had marked three passages referring to Seward's position on the slavery question. On the margin of the paper he had written in pencil, "I agree with Seward in his 'Irrepressible Conflict,' but I do not endorse his 'Higher Law' doctrine." Then he added in words underscored, "Make no contracts that will bind me." This paper was brought into the room where Davis, Judd, Logan, and I were gathered, and was read to us. But Lincoln was down in Springfield, some distance away from Chicago, and could therefore not appreciate the gravity of the situation; at least so Davis argued, and, viewing it in that light, the latter went ahead with his negotiations. What the consequences of these deals were will appear later on. The new's of his nomination found Lincoln at Springfield in the office of the Journal. Naturally enough he was nervous, restless, and laboring under more or loss suppressed excitement. He had been tossing ball—a pastime frequently indulged in by the lawyers of that day, and had played a few games of billiards to keep down, as another has expressed it "the unnatural excitement that threatened to possess him." When the telegram containing the result of the last ballot came in, although apparently calm and undisturbed, a close observer could have detected in the compressed lip and serious countenance evidences of deep and unusual emotion. As the balloting progressed he had gone to the office of the Journal, and was sitting in a large arm-chair there when the news of his nomination came. What a line of scenes, stretching from the barren glade in Kentucky to the jubilant and enthusiastic throng in the Wigwam at Chicago, must have broken in upon his vision as he hastened from the newspaper office to "tell a little woman down the street the news!" In the evening his friends and neighbors called to congratulate him. He thanked them feelingly and shook them each by the hand. A day later the committee from the convention, with George Ashmun, of Massachusetts, at its head, called, and delivered formal notice of his nomination. This meeting took place at his house. His response was couched in polite and dignified language, and many of the committee, who now met him for the first time, departed with an improved impression of the new standard-bearer. A few days later he wrote his official letter of acceptance, in which he warmly endorsed the resolutions of the convention. His actions and utterances so far had begun to dissipate the erroneous notion prevalent in some of the more remote Eastern States, that he was more of a backwoods boor than a gentleman; but with the arrival of the campaign in dead earnest, people paid less attention to the candidates and more to the great issues at stake. Briefly stated, the Republican platform was a declaration that "the new dogma, that the Constitution carries slavery into all the Territories, is a dangerous political heresy, revolutionary in tendency and subversive of the peace and harmony of the country; that the normal condition of all the Territories is that of freedom; that neither Congress, the territorial legislature, nor any individual can give legal existence to slavery in any territory; that the opening of the slave trade would be a crime against humanity." Resolutions favoring a homestead law, river and harbor improvements, and the Pacific railroad were also included in the platform. With these the Republicans, as a lawyer would say, went to the country. The campaign which followed was one with few parallels in American history. There was not only the customary exultation and enthusiasm over candidates, but there was patient listening and hard thinking among the masses. The slavery question, it was felt, must soon be decided. Threats of disunion were the texts of many a campaign speech in the South: in fact, as has since been shown, a deep laid conspiracy to overthrow the Union was then forming, and was only awaiting the election of a Republican President to show its hideous head. The Democratic party was struggling under the demoralizing effects of a split, in which even the Buchanan administration had taken sides. Douglas, the nominee of one wing, in his desperation had entered into the canvass himself, making speeches with all the power and eloquence at his command. The Republicans, cheered over the prospect, had joined hands with the Abolitionists, and both were marching to victory under the inspiration of Lincoln's sentiment, that "the further spread of slavery should be arrested, and it should be placed where the public mind shall rest in the belief of its ultimate extinction."
As the canvass advanced and waxed warm I tendered my services and made a number of speeches in the central part of the State. I remember, in the midst of a speech at Petersburg, and just as I was approaching an oratorical climax, a man out of breath came rushing up to me and thrust a message into my hand. I was somewhat frustrated and greatly alarmed, fearing it might contain news of some accident in my family; but great was my relief when I read it, which I did aloud. It was a message from Lincoln, telling me to be be of good cheer, that Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Indiana had gone Republican.*
* The handwriting of the note was a little tremulous, showing that Lincoln was excited and nervous when he wrote it. Following is a copy of the original MS.: "Springfield, Ill., October 10, 1860. "Dear William: I cannot give you details, but it is entirely certain that Pennsylvania and Indiana have gone Republican very largely. Pennsylvania 25,000, and Indiana 5000 to 10,000. Ohio of course is safe. "Yours as ever, "A. Lincoln."
These were then October States, and this was the first gun for the great cause. It created so much demonstration, such a burst of enthusiasm and confusion, that the crowd forgot they had any speaker; they ran yelling and hurrahing out of the hall, and I never succeeded in finishing the speech.
As soon as officially notified of his nomination* Mr. Lincoln moved his headquarters from our office to a room in the State House building, and there, with his secretary, John G. Nicolay, he spent the busy and exciting days of his campaign. Of course he attended to no law business, but still he loved to come to our office of evenings, and spend an hour with a few choice friends in a friendly privacy which was denied him at his public quarters. These were among the last meetings we had with Lincoln as our friend and fellow at the bar; and they are also the most delightful recollections any of us have retained of him.**
* Following is Lincoln's letter of acceptance: "Springfield, III., June 23, 1860. "Sir: I accept the nomination tendered me by the convention over which you presided, of which I am formally apprised in a letter of yourself and others, acting as a committee of the convention for that purpose. The declaration of principles which accompanies your letter meets my approval, and it shall be my care not to violate it or disregard it in any part. Imploring the assistance of Divine Providence, and with due regard to the views and feelings of all who were represented in the convention, to the rights of all the states and territories and people of the nation, to the inviolability of the Constitution, and the perpetual union, prosperity, and harmony of all, I am most happy to cooperate for the practical success of the principles declared by the convention. "Your obliged friend and fellow-citizen, "Abraham Lincoln." "Hon. George Ashmun." ** One of what Lincoln regarded as the remarkable features of his canvass for President was the attitude of some of his neighbors in Springfield. A poll of the voters had been made in a little book and given to him. On running over the names he found that the greater part of the clergy of the city—in fact all but three—were against him. This depressed him somewhat, and he called in Dr. Newton Bateman, who as Superintendent of Public Instruction occupied the room adjoining his own in the State House, and whom he 'habitually addressed as "Mr. Schoolmaster." He commented bitterly on the attitude of the preachers and many of their followers, who, pretending to be believers in the Bible and God-fearing Christians, yet by their votes demonstrated that they cared not whether slavery was voted up or down. "God cares and humanity cares," he reflected, "and if they do not they surely have not read their Bible aright."
At last the turmoil and excitement and fatigue of the campaign were over: the enthusiastic political workers threw aside their campaign uniforms, the boys blew out their torches, and the voter approached the polls with his ballot. On the morning of election day I stepped in to see Mr. Lincoln, and was surprised to learn that he did not intend to cast his vote. I knew of course that he did so because of a feeling that the candidate for a Presidential office ought not to vote for his own electors; but when I suggested the plan of cutting off the Presidential electors and voting for the State officers, he was struck with the idea, and at last consented. His appearance at the polls, accompanied by Ward Lamon, the lamented young Ellsworth, and myself, was the occasion of no little surprise because of the general impression which prevailed that he did not intend to vote. The crowd around the polls opened a gap as the distinguished voter approached, and some even removed their hats as he deposited his ticket and announced in a subdued voice his name, "Abraham Lincoln."
The election was held on the 6th of November. The result showed a popular vote of 1,857,610 for Lincoln; 1,291,574 for Douglas; 850,022 for Breckenridge; and 646,124 for Bell. In the electoral college Lincoln received 180 votes, Breckenridge 72, Bell 39, and Douglas 12.* Mr. Lincoln having now been elected, there remained, before taking up the reins of government, the details of his departure from Springfield, and the selection of a cabinet.
* Lincoln electors were chosen in seventeen of the free States, as follows: Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, Vermont, New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, California, Oregon; and in one State,—New Jersey,— owing to a fusion between Democrats, Lincoln secured four and Douglas three of the electors. Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North, and South Carolina, and Texas went for Breckenridge; Kentucky, Tennessee, and Virginia for Bell; while Douglas secured only one entire State—Missouri.
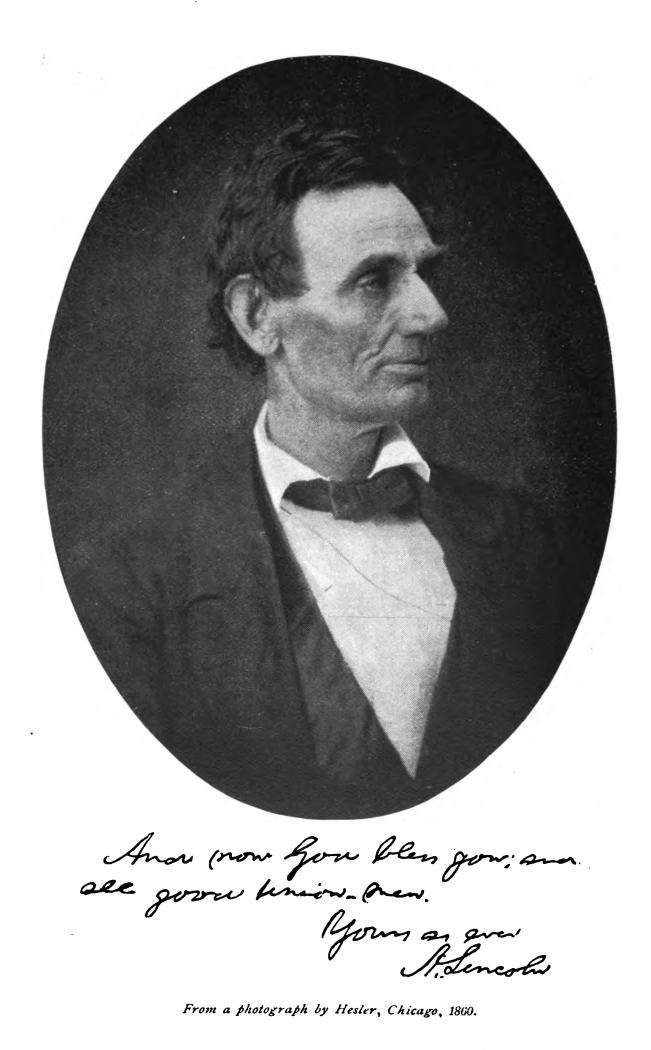

The election over, Mr. Lincoln scarcely had time enough to take a breath until another campaign and one equally trying, so far as a test of his constitution and nerves was concerned, as the one through which he had just passed, opened up before him. I refer to the siege of the cabinet-makers and office-seekers. It proved to be a severe and protracted strain and one from which there seemed to be no relief, as the President-elect of this renowned democratic Government is by custom and precedent expected to meet and listen to everybody who calls to see him. "Individuals, deputations, and delegations," says one of Mr. Lincoln's biographers, "from all quarters pressed in upon him in a manner that might have killed a man of less robust constitution. The hotels of Springfield were filled with gentlemen who came with light baggage and heavy schemes. The party had never been in office. A clean sweep of the 'ins' was expected, and all the 'outs' were patriotically anxious to take the vacant places. It was a party that had never fed; and it was voraciously hungry. Mr. Lincoln and Artemus Ward saw a great deal of fun in it; and in all human probability it was the fun alone that enabled Mr. Lincoln to bear it."
His own election of course disposed of any claims Illinois might have had to any further representation in the cabinet, but it afforded Mr. Lincoln no relief from the argumentative interviews and pressing claims of the endless list of ambitious statesmen in the thirty-two other states, who swarmed into Springfield from every point of the compass. He told each one of them a story, and even if he failed to put their names on his slate they went away without knowing that fact, and never forgot the visit.*
* A newspaper correspondent who had been sent down from Chicago to "write up" Mr. Lincoln soon after his nomination, was kind enough several years ago to furnish me with an account of his visit. As some of his reminiscences are more or less interesting, I take the liberty of inserting a portion of his letter. "A what-not in the corner of the room," he relates, "was laden with various kinds of shells. Taking one in my hand, I said, 'This, I suppose, is called a Trocus by the geologist or naturalist.' Mr. Lincoln paused a moment as if reflecting and then replied, 'I do not know, for I never studied either geology or natural history.' I then took to examining the few pictures that hung on the walls, and was paying more than ordinary attention to one that hung above, the sofa. He was immediately at my left and pointing to it said, 'That picture gives a very fair representation of my homely face.'... The time for my departure nearing, I made the usual apologies and started to go. 'You cannot get out of the town before a quarter past eleven,' remonstrated Mr. Lincoln, 'and you may as well stay a little longer.' Under pretence of some unfinished matters down town, however, I very reluctantly withdrew from the mansion. 'Well,' said Mr. Lincoln, as we passed into the hall, 'suppose you come over to the State House before you start for Chicago.' After a moment's deliberation I promised to do so. Mr. Lincoln, following without his hat, and continuing the conversation, shook hands across the gate, saying, 'Now, come over.' I wended my way to my hotel, and after a brief period was in his office at the State House. Resuming conversation, he said, 'If the man comes with the key before you go, I want to give you a book.' I certainly hoped the man would come with the key. Some conversation had taken place at the house on which his book treated,—but I had forgotten this,—and soon Mr. Lincoln absented himself for perhaps two minutes and returned with a copy of the debates between himself and Judge Douglas. He placed the book on his knee, as he sat back on two legs of his chair, and wrote on the fly-leaf, 'J. S. Bliss, from A. Lincoln.' Besides this he marked a complete paragraph near the middle of the book. While sitting in the position described little Willie, his son, came in and begged his father for twenty- five cents. 'My son,' said the father, 'what do you want with twenty-five cents?' 'I want it to buy candy with,' cried the boy. 'I cannot give you twenty-five cents, my son, but will give you five cents,' at the same time putting his thumb and finger into his vest pocket and taking therefrom five cents in silver, which he placed upon the desk before the boy. But this did not reach Willie's expectations; he scorned the pile, and turning away clambered down-stairs and through the spacious halls of the Capitol, leaving behind him his five cents and a distinct reverberation of sound. Mr. Lincoln turned to me and said, 'He will be back after that in a few minutes.' 'Why do you think so?' said I. 'Because, as soon as he finds I will give him no more he will come and get it.' After the matter had been nearly forgotten and conversation had turned in an entirely different channel, Willie came cautiously in behind my chair and that of his father, picked up the specie, and went away without saying a word."—J. S. Bliss, letter, Jan. 29, 1867, MS.
He had a way of pretending to assure his visitor that in the choice of his advisers he was "free to act as his judgment dictated," although David Davis, acting as his manager at the Chicago convention, had negotiated with the Indiana and Pennsylvania delegations, and assigned places in the cabinet to Simon Cameron and Caleb Smith, besides making other "arrangements" which Mr. Lincoln was expected to ratify. Of this he was undoubtedly aware, although in answer to a letter from Joshua R. Giddings, of Ohio, congratulating him on his nomination, he said,*
* Letter, May 21st, 1860, MS.
"It is indeed most grateful to my feelings that the responsible position assigned me comes without conditions." Out of regard to the dignity of the exalted station he was about to occupy, he was not as free in discussing the matter of his probable appointments with some of his personal friends as they had believed he would be. In one or two instances, I remember, the latter were offended at his seeming disregard of the claims of old friendship. My advice was not asked for on such grave subjects, nor had I any right or reason to believe it would be; hence I never felt slighted or offended. On some occasions in our office, when Mr. Lincoln had come across from the State House for a rest or a chat with me, he would relate now and then some circumstance—generally an amusing one—connected with the settlement of the cabinet problem, but it was said in such a way that one would not have felt free to interrogate him about his plans. Soon after his election I received from my friend Joseph Medill, of Chicago, a letter which argued strongly against the appointment of Simon Cameron to a place in the cabinet, and which the writer desired I should bring to Mr. Lincoln's attention. I awaited a favorable opportunity, and one evening when we were alone in our office I gave it to him. It was an eloquent protest against the appointment of a corrupt and debased man, and coming from the source it did—the writer being one of Lincoln's best newspaper supporters—made a deep impression on him. Lincoln read it over several times, but refrained from expressing any opinion. He did say however that he felt himself under no promise or obligation to appoint anyone; that if his friends made any agreements for him they did so over his expressed direction and without his knowledge. At another time he said that he wanted to give the South, by way of placation, a place in his cabinet; that a fair division of the country entitled the Southern States to a reasonable representation there, and if not interfered with he would make such a distribution as would satisfy all persons interested. He named three persons who would be acceptable to him. They were Botts, of Virginia; Stephens, of Georgia; and Maynard, of Tennessee. He apprehended no such grave danger to the Union as the mass of people supposed would result from Southern threats, and said he could not in his heart believe that the South designed the overthrow of the Government. This is the extent of my conversation about the cabinet. Thurlow Weed, the veteran in journalism and politics, came out from New York and spent several days with Lincoln. He was not only the representative of Senator Seward, but rendered the President-elect signal service in the formation of his cabinet. In his autobiography Mr. Weed relates numerous incidents of this visit. He was one day opposing the claims of Montgomery Blair, who aspired to a cabinet appointment, when Mr. Lincoln inquired of Weed whom he would recommend. "Henry Winter Davis," was the response. "David Davis, I see, has been posting you up on this question," retorted Lincoln. "He has Davis on the brain. I think Maryland must be a good State to move from." The President then told a story of a witness in court in a neighboring county, who on being asked his age replied, "Sixty." Being satisfied he was much older the question was repeated, and on receiving the same answer, the court admonished the witness, saying, "The court knows you to be much older than sixty." "Oh, I understand now," was the rejoinder; "you're thinking of those ten years I spent on the eastern shore of Maryland; that was so much time lost and don't count." Before Mr. Lincoln's departure from Springfield, people who knew him personally were frequently asked what sort of man he was. I received many letters, generally from the Eastern States, showing that much doubt still existed in the minds of the people whether he would prove equal to the great task that lay in store for him. Among others who wrote me on the subject was the Hon. Henry Wilson, late Vice-president of the United States, whom I had met during my visit to Washington in the spring of 1858. Two years after Mr. Lincoln's death, Mr. Wilson wrote me as follows: "I have just finished reading your letter dated December 21, 1860, in answer to a letter of mine asking you to give me your opinion of the President just elected. In this letter to me you say of Mr. Lincoln what more than four years of observation confirmed. After stating that you had been his law partner for over eighteen years and his most intimate and bosom friend all that time you say, 'I know him better than he does himself. I know this seems a little strong, but I risk the assertion. Lincoln is a man of heart—aye, as gentle as a woman's and as tender—but he has a will strong as iron. He therefore loves all mankind, hates slavery and every form of despotism. Put these together—love for the slave, and a determination, a will, that justice, strong and unyielding, shall be done when he has the right to act, and you can form your own conclusion. Lincoln will fail here, namely, if a question of political economy—if any question comes up which is doubtful, questionable, which no man can demonstrate, then his friends can rule him; but when on justice, right, liberty, the Government, the Constitution, and the Union, then you may all stand aside: he will rule then, and no man can move him—no set of men can do it. There is no fail here. This is Lincoln, and you mark my prediction. You and I must keep the people right; God will keep Lincoln right.' These words of yours made a deep impression upon my mind, and I came to love and trust him even before I saw him. After an acquaintance of more than four years I found that your idea of him was in all respects correct—that he was the loving, tender, firm, and just man you represented him to be; while upon some questions in which moral elements did not so clearly enter he was perhaps too easily influenced by others. Mr. Lincoln was a genuine democrat in feelings, sentiments, and actions. How patiently and considerately he listened amid the terrible pressure of public affairs to the people who thronged his ante-room! I remember calling upon him one day daring the war on pressing business. The ante- room was crowded with men and women seeking admission. He seemed oppressed, careworn, and weary, I said to him, 'Mr. President, you are too exhausted to see this throng waiting to see you; you will wear yourself out and ought not see these people today.' He replied, with one of those smiles in which sadness seemed to mingle, 'They don't want much; they get but little, and I must see them.' During the war his heart was oppressed and his life burdened with the conflict between the tenderness of his nature and what seemed to be the imperative demands of duty. In the darkest hours of the conflict desertions from the army were frequent, and army officers urgently pressed the execution of the sentences of the law; but it was with the greatest effort that he would bring himself to consent to the execution of the judgment of the military tribunals. I remember calling early one sabbath morning with a wounded Irish officer, who came to Washington to say that a soldier who had been sentenced to be shot in a day or two for desertion had fought gallantly by his side in battle. I told Mr. Lincoln we had come to ask him to pardon the poor soldier. After a few moments' reflection he said, 'My officers tell me the good of the service demands the enforcement of the law; but it makes my heart ache to have the poor fellows shot. I will pardon this soldier, and then you will all join in blaming me for it. You censure me for granting pardons, and yet you all ask me to do so.' I say again, no man had a more loving and tender nature than Mr. Lincoln."
Before departing for Washington Mr. Lincoln went to Chicago* for a few days' stay, and there by previous arrangement met his old friend, Joshua F. Speed. Both were accompanied by their wives, and while the latter were out shopping the two husbands repaired to Speed's room at the hotel. "For an hour or more," relates Speed, "we lived over again the scenes of other days. Finally Lincoln threw himself on the bed, and fixing his eyes on a spot in the ceiling asked me this question, 'Speed, what is your pecuniary condition? are you rich or poor?' I answered, addressing him by his new title, 'Mr. President, I think I can anticipate what you are going to say. I'll speak candidly to you on the subject. My pecuniary condition is satisfactory to me now; you would perhaps call it good. I do not think you have within your gift any office I could afford to take.' Mr. Lincoln then proposed to make Guthrie, of Kentucky, Secretary of War, but did not want to write to him—asked me to feel of him. I did as requested, but the Kentucky statesman declined on the ground of his advanced age, and consequent physical inability to fill the position. He gave substantial assurance of his loyal sentiments, however, and insisted that the Union should be preserved at all hazards."
* A lady called one day at the hotel where the Lincolns were stopping in Chicago to take Mrs. Lincoln out for a promenade or a drive. She was met in the parlor by Mr. Lincoln, who, after a hurried trip upstairs to ascertain the cause of the delay in his wife's appearance, returned with the report that "She will be down as soon as she has all her trotting harness on."
Late in January Mr. Lincoln informed me that he was ready to begin the preparation of his inaugural address. He had, aside from his law books and the few gilded volumes that ornamented the centre-table in his parlor at home, comparatively no library. He never seemed to care to own or collect books. On the other hand I had a very respectable collection, and was adding to it every day. To my library Lincoln very frequently had access. When, therefore, he began on his inaugural speech he told me what works he intended to consult. I looked for a long list, but when he went over it I was greatly surprised. He asked me to furnish him with Henry Clay's great speech delivered in 1850; Andrew Jackson's proclamation against Nullification; and a copy of the Constitution. He afterwards called for Webster's reply to Hayne, a speech which he read when he lived at New Salem, and which he always regarded as the grandest specimen of American oratory. With these few "volumes," and no further sources of reference, he locked himself up in a room upstairs over a store across the street from the State House, and there, cut off from all communication and intrusion, he prepared the address. Though composed amid the unromantic surroundings of a dingy, dusty, and neglected back room, the speech has become a memorable document. Posterity will assign to it a high rank among historical utterances; and it will ever bear comparison with the efforts of Washington, Jefferson, Adams, or any that preceded its delivery from the steps of the national Capitol.
After Mr. Lincoln's rise to national prominence, and especially since his death, I have often been asked if I did not write this or that paper for him; if I did not prepare or help prepare some of his speeches. I know that other and abler friends of Lincoln have been asked the same question.* To people who made such enquiries I always responded, "You don't understand Mr. Lincoln. No man ever asked less aid then he; his confidence in his own ability to meet the requirements of every hour was so marked that his friends never thought of tendering their aid, and therefore no one could share his responsibilities. I never wrote a line for him; he never asked me to. I was never conscious of having exerted any influence over him. He often called out my views on some philosophical question, simply because I was a fond student of philosophy, and conceding that I had given the subject more attention than he; he often asked as to the use of a word or the turn of a sentence, but if I volunteered to recommend or even suggest a change of language which involved a change of sentiment I found him the most inflexible man I have ever seen."
* "I know it was the general impression in Washington that I knew all about Lincoln's plans and ideas, but the truth is, I knew nothing. He never confided to me anything of his purposes."—David Davis, statement, September 20, 1866.
One more duty—an act of filial devotion—remained to be done before Abraham Lincoln could announce his readiness to depart for the city of Washington—a place from which it was unfortunately decreed he should never return. In the first week of February he slipped quietly away from Springfield and rode to Farmington in Coles County, where his aged step-mother was still living. Here, in the little country village, he met also the surviving members of the Hanks and Johnston families. He visited the grave of his father, old Thomas Lincoln, which had been unmarked and neglected for almost a decade, and left directions that a suitable stone should be placed there to mark the spot. Retracing his steps in the direction of Springfield he stopped over-night in the town of Charleston, where he made a brief address, recalling many of his boyhood exploits, in the public hall. In the audience were many persons who had known him first as the stalwart young ox-driver when his father's family drove into Illinois from southern Indiana. One man had brought with him a horse which the President-elect, in the earlier days of his law practice, had recovered for him in a replevin suit; another one was able to recite from personal recollection the thrilling details of the famous wrestling match between Lincoln the flat-boatman in 1830 and Daniel Needham; and all had some reminiscence of his early manhood to relate. The separation from his step-mother was particularly touching.*
* Lincoln's love for his second mother was a most filial and affectionate one. His letters show that he regarded the relation truly as that of mother and son. November 4, 1851, he writes her after the death of his father: "Dear Mother: "Chapman tells me he wants you to go and live with him. If I were you I would try it awhile. If you get tired of it (as I think you will not) you can return to your own home. Chapman feels very kindly to you; and I have no doubt he will make your situation very pleasant. "Sincerely your son, "A. Lincoln."
On the 9th of the same month he writes his step-brother John D. Johnston: "If the land can be sold so that I can get three hundred dollars to put to interest for mother I will not object if she does not. But before I will make a deed the money must be had, or secured beyond all doubt at ten per cent."
The parting, when the good old woman, with tears streaming down her cheeks, gave him a mother's benediction, expressing the fear that his life might be taken by his enemies, will never be forgotten by those who witnessed it. Deeply impressed by this farewell scene Mr. Lincoln reluctantly withdrew from the circle of warm friends who crowded around him, and, filled with gloomy forebodings of the future, returned to Springfield. The great questions of state having been pretty well settled in his own mind, and a few days yet remaining before his final departure, his neighbors and old friends called to take leave of him and pay their "best respects." Many of these callers were from New Salem, where he had made his start in life, and each one had some pleasant or amusing incident of earlier days to call up when they met. Hannah Armstrong, who had "foxed" his trowsers with buckskin in the days when he served as surveyor under John Calhoun, and whose son Lincoln had afterwards acquitted in the trial for murder at Beardstown, gave positive evidence of the interest she took in his continued rise in the world.
She bade him good-bye, but was filled with a presentiment that she would never see him alive again. "Hannah," he said, jovially, "if they do kill me I shall never die again." Isaac Cogsdale, another New Salem pioneer, came, and to him Lincoln again admitted his love for the unfortunate Anne Rutledge. Cogsdale afterwards told me of this interview. It occurred late in the afternoon. Mr. Nicolay, the secretary, had gone home, and the throng of visitors had ceased for the day. Lincoln asked about all the early families of New Salem, calling up the peculiarities of each as he went over the list. Of the Rutledges he said: "I have loved the name of Rutledge to this day. I have kept my mind on their movements ever since." Of Anne he spoke with some feeling: "I loved her dearly. She was a handsome girl, would have made a good, loving wife; she was natural, and quite intellectual, though not highly educated. I did honestly and truly love the girl, and think often of her now."
Early in February the last item of preparation for the journey to Washington had been made. Mr. Lincoln had disposed of his household goods and furniture to a neighbor, had rented his house; and as these constituted all the property he owned in Illinois there was no further occasion for concern on that score. In the afternoon of his last day in Springfield he came down to our office to examine some papers and confer with me about certain legal matters in which he still felt some interest. On several previous occasions he had told me he was coming over to the office "to have a long talk with me," as he expressed it. We ran over the books and arranged for the completion of all unsettled and unfinished matters. In some cases he had certain requests to make—certain lines of procedure he wished me to observe. After these things were all disposed of he crossed to the opposite side of the room and threw himself down on the old office sofa, which, after many years of service, had been moved against the wall for support. He lay for some moments, his face towards the ceiling, without either of us speaking. Presently he inquired, "Billy,"—he always called me by that name,—"how long have we been together?" "Over sixteen years," I answered. "We've never had a cross word during all that time, have we?" to which I returned a vehement, "No, indeed we have not." He then recalled some incidents of his early practice and took great pleasure in delineating the ludicrous features of many a lawsuit on the circuit. It was at this last interview in Springfield that he told me of the efforts that had been made by other lawyers to supplant me in the partnership with him. He insisted that such men were weak creatures, who, to use his own language, "hoped to secure a law practice by hanging to his coat-tail." I never saw him in a more cheerful mood. He gathered a bundle of books and papers he wished to take with him and started to go; but before leaving he made the strange request that the sign-board which swung on its rusty hinges at the foot of the stairway should remain. "Let it hang there undisturbed,"* he said, with a significant lowering of his voice. "Give our clients to understand that the election of a President makes no change in the firm of Lincoln and Herndon. If I live I'm coming back some time, and then we'll go right on practising law as if nothing had ever happened." He lingered for a moment as if to take a last look at the old quarters, and then passed through the door into the narrow hallway. I accompanied him downstairs. On the way he spoke of the unpleasant features surrounding the Presidential office. "I am sick of office-holding already," he complained, "and I shudder when I think of the tasks that are still ahead." He said the sorrow of parting from his old associations was deeper than most persons would imagine, but it was more marked in his case because of the feeling which had become irrepressible that he would never return alive. I argued against the thought, characterizing it as an illusory notion not in harmony or keeping with the popular ideal of a President. "But it is in keeping with my philosophy," was his quick retort. Our conversation was frequently broken in upon by the interruptions of passers-by, who, each in succession, seemed desirous of claiming his attention. At length he broke away from them all. Grasping my hand warmly and with a fervent "Good-bye," he disappeared down the street, and never came back to the office again. On the morning following this last interview, the 11th day of February, the Presidential party repaired to the railway station, where the train which was to convey them to Washington awaited the ceremony of departure.
* In answer to the many inquiries made of me, I will say here that during this last interview Mr. Lincoln, for the first time, brought up the subject of an office under his administration. He asked me if I desired an appointment at his hands, and, if so, what I wanted. I answered that I had no desire for a Federal office, that I was then holding the office of Bank Commissioner of Illinois under appointment of Governor Bissel, and that if he would request my retention in office by Yates, the incoming Governor, I should be satisfied. He made the necessary recommendation, and Governor Yates complied. I was present at the meeting between Yates and Lincoln, and I remember that the former, when Lincoln urged my claims for retention in office, asked Lincoln to appoint their mutual friend A. Y. Ellis postmaster at Springfield. I do not remember whether Lincoln promised to do so or not, but Ellis was never appointed.
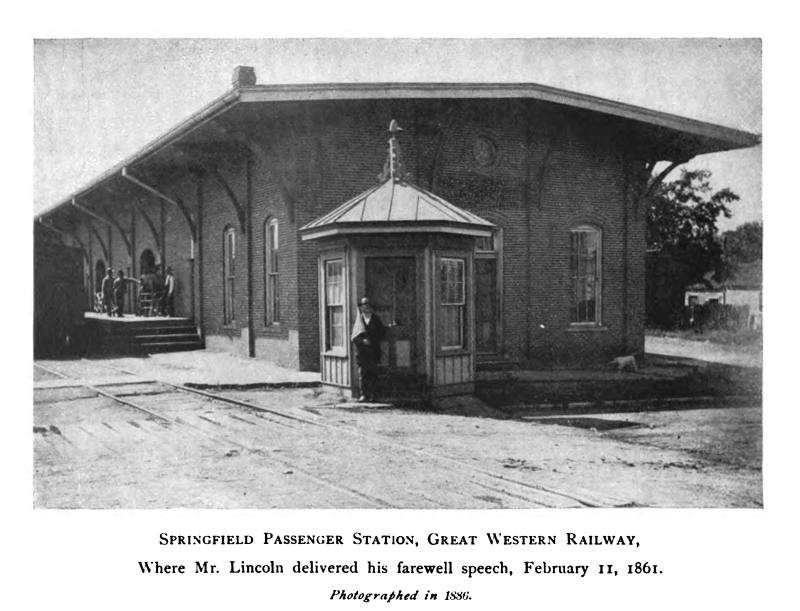

The intention was to stop at many of the principal cities along the route, and plenty of time had been allotted for the purpose. Mr. Lincoln had told me that a man named Wood had been recommended to him by Mr. Seward, and he had been placed in charge of the party as a sort of general manager. The party, besides the President, his wife, and three sons, Robert, William, and Thomas, consisted of his brother-in-law, Dr. W. S. Wallace, David Davis, Norman B. Judd, Elmer E. Ellsworth, Ward H. Lamon, and the President's two secretaries, John G. Nicolay and John Hay. Colonel E. V. Sumner and other army gentlemen were also in the car, and some friends of Mr. Lincoln—among them O. H. Browning, Governor Yates, and ex-Governor Moore—started with the party from Springfield, but dropped out at points along the way. The day was a stormy one, with dense clouds hanging heavily overhead. A goodly throng of Springfield people had gathered to see the distinguished party safely off. After the latter had entered the car the people closed about it until the President appeared on the rear platform. He stood for a moment as if to suppress evidences of his emotion, and removing his hat made the following brief but dignified and touching address: * "Friends: No one who has never been placed in a like position can understand my feelings at this hour, nor the oppressive sadness I feel at this parting. For more than a quarter of a century I have lived among you, and during all that time I have received nothing but kindness at your hands. Here I have lived from my youth until now I am an old man. Here the most sacred ties of earth were assumed. Here all my children were born; and here one of them lies buried. To you, dear friends, I owe all that I have, all that I am. All the strange, checkered past seems to crowd now upon my mind. To-day I leave you. I go to assume a task more difficult than that which devolved upon Washington. Unless the great God who assisted him shall be with and aid me, I must fail; but if the same omniscient mind and almighty arm that directed and protected him shall guide and support me I shall not fail—I shall succeed. Let us all pray that the God of our fathers may not forsake us now. To him I commend you all. Permit me to ask that with equal sincerity and faith you will invoke his wisdom and guidance for me. With these words I must leave you, for how long I know not. Friends, one and all, I must now bid you an affectionate farewell."
* I was not present when Mr. Lincoln delivered his farewell at the depot in Springfield, and never heard what he said. I have adopted the version of his speech as published in our papers. There has been some controversy over the exact language he used on that occasion, and Mr. Nicolay has recently published the speech from what he says is the original MS., partly in his own and partly in the handwriting of Mr. Lincoln. Substantially, however, it is like the speech as reproduced here from the Springfield paper.
At the conclusion of this neat and appropriate farewell the train rolled slowly out, and Mr. Lincoln, still standing in the doorway of the rear car, took his last view of Springfield. The journey had been as well advertised as it had been carefully planned, and therefore, at every town along the route, and at every stop, great crowds were gathered to catch a glimpse of the President-elect.*
* "Before Mr. Lincoln's election in 1860 I, then a child of eleven years, was presented with his lithograph. Admiring him with my whole heart, I thought still his appearance would be much improved should he cultivate his whiskers. Childish thoughts must have utterance. So I proposed the idea to him, expressing as well as I was able the esteem in which he was held among honest men. A few days after I received this kind and friendly letter?
"* Springfield, III., October 19, 1860. "'Miss Grace Bedell. "'My Dear Little Miss:—Your very agreeable letter of the 15th is received. I regret the necessity of saying I have no daughter. I have three sons—one seventeen, one nine, and one seven. They with their mother constitute my whole family. As to the whiskers, as I have never worn any, do you not think that people would call it a piece of silly affectation were I to begin wearing them now? "'I am your true friend and sincere well-wisher, "'A. Lincoln.' "It appears I was not forgotten, for after his election to the Presidency, while on his journey to Washington, the train stopped at Westfield, Chautauqua County, at which place I then resided. Mr. Lincoln said, 'I have a correspondent in this place, a little girl whose name is Grace Bedell, and I would like to see her.' I was conveyed to him; he stepped from the cars, extending his hand and saying, 'You see I have let these whiskers grow for you, Grace,' kissed me, shook me cordially by the hand, and was gone. I was frequently afterward assured of his remembrance.'" Grace G. Bedell, MS. letter, Dec. 14, 1866.
Mr. Lincoln usually gratified the wishes of the crowds, who called him out for a speech whether it was down on the regular programme of movements or not. In all cases his remarks were well-timed and sensibly uttered. At Indianapolis, where the Legislature was in session, he halted for a day and delivered a speech the burden of which was an answer to the Southern charges of coercion and invasion. From Indianapolis he moved on to Cincinnati and Columbus, at the last-named place meeting the Legislature of Ohio. The remainder of the journey convinced Mr. Lincoln of his strength in the affections of the people. Many, no doubt, were full of curiosity to see the now famous rail-splitter, but all were outspoken and earnest in their assurances of support. At Steubenville, Pittsburg, Cleveland, Buffalo, Albany, New York, and Philadelphia he made manly and patriotic speeches. These speeches, plain in language and simple in illustration, made every man who heard them a stronger friend than ever of the Government. He was skilful enough to warn the people of the danger ahead and to impress them with his ability to deal properly with the situation, without in any case outlining his intended policy or revealing the forces he held in reserve.* At Pittsburg he advised deliberation and begged the American people to keep their temper on both sides of the line. At Cleveland he insisted that "the crisis, as it is called, is an artificial crisis and has no foundation in fact;" and at Philadelphia he assured his listeners that under his administration there would be "no bloodshed unless it was forced upon the Government, and then it would be compelled to act in self-defence."
* The following are extracts from Mr. Lincoln's letters written during the campaign in answer to his position with reference to the anticipated uprisings in the Southern States. They are here published for the first time: [From a letter to L. Montgomery Bond, Esq., Oct. 15, 1860.] "I certainly am in no temper and have no purpose to embitter the feelings of the South, but whether I am inclined to such a course as would in fact embitter their feelings you can better judge by my published speeches than by anything I would say in a short letter if I were inclined now, as I am not, to define my position anew." [From a letter to Samuel Haycraft, dated, Springfield, Ill., June 4, 1860.] "Like yourself I belonged to the old Whig party from its origin to its close. I never belonged to the American party organization, nor ever to a party called a Union party; though I hope I neither am or ever have been less devoted to the Union than yourself or any other patriotic man." [Private and Confidential.] Springfield, Ill., Nov. 13, 1860. "Hon. Samuel Haycraft. "My Dear Sir:—Yours of the 9th is just received. I can only answer briefly. Rest fully assured that the good people of the South who will put themselves in the same temper and mood towards me which you do will find no cause to complain of me. "Yours very truly, "A. Lincoln."
This last utterance was made in front of Independence Hall, where, a few moments before, he had unfurled to the breeze a magnificent new flag, an impressive ceremony performed amid the cheers swelling from the vast sea of upturned faces before him. From Philadelphia his journey took him to Harrisburg, where he visited both branches of the Legislature then in session. For an account of the remainder of this now famous trip I beg to quote from the admirable narrative of Dr. Holland. Describing the welcome tendered him by the Legislature at Harrisburg, the latter says: "At the conclusion of the exercises of the day Mr. Lincoln, who was known to be very weary, was permitted to pass undisturbed to his apartments in the Jones House. It was popularly understood that he was to start for Washington the next morning, and the people of Harrisburg supposed they had only taken a temporary leave of him. He remained in his rooms until nearly six o'clock, when he passed into the street, entered a carriage unobserved in company with Colonel Lamon, and was driven to a special train on the Pennsylvania railroad in waiting for him. As a matter of precaution the telegraph wires were cut the moment he left Harrisburg, so that if his departure should be discovered intelligence of it could not be communicated at a distance. At half-past ten the train arrived at Philadelphia, and here Mr. Lincoln was met by a detective, who had a carriage in readiness in which the party were driven to the depot of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore railroad. At a quarter past eleven they arrived and very fortunately found the regular train, which should have left at eleven, delayed. The party took berths in the sleeping, car, and without change of cars passed directly through Baltimore to Washington, where Mr. Lincoln arrived at half-past six o'clock in the morning and found Mr. Washburne anxiously awaiting him. He was taken into a carriage and in a few minutes he was talking over his adventures with Senator Seward at Willard's Hotel." The remaining members of the Presidential party from whom Mr. Lincoln separated at Harrisburg left that place on the special train intended for him; and as news of his safe arrival in Washington had been already telegraphed over the country no attempt was made to interrupt their safe passage through Baltimore. As is now generally well known many threats had up to that time been made that Mr. Lincoln, on his way to Washington, should never pass through Baltimore alive. It was reported and believed that conspiracies had been formed to attack the train, blow it up with explosives or in some equally effective way dispose of the President-elect. Mr. Seward and others were so deeply impressed with the grave features of the reports afloat that Allan Pinkerton, the noted detective of Chicago, was employed to investigate the matter and ferret out the conspiracy, if any existed. This shrewd operator went to Baltimore, opened an office as a stock-broker, and through his assistants—the most adroit and serviceable of whom was a woman—was soon in possession of inside information. The change of plans and trains at Harrisburg was due to his management and advice. Some years before his death Mr. Pinkerton furnished me with a large volume of the written reports of his subordinates and an elaborate account by himself of the conspiracy and the means he employed to ferret it out. The narrative, thrilling enough in some particulars, is too extended for insertion here. It is enough for us to know that the tragedy was successfully averted and that Mr. Lincoln was safely landed in Washington.
In January preceding his departure from Springfield Mr. Lincoln, becoming somewhat annoyed, not to say alarmed, at the threats emanating from Baltimore and other portions of the country adjacent to Washington, that he should not reach the latter place alive, and that even if successful in reaching the Capitol his inauguration should in some way be prevented, determined to ascertain for himself what protection would be given him in case an effort should be made by an individual or a mob to do him violence. He sent a young military officer in the person of Thomas Mather, then Adjutant-General of Illinois, to Washington with a letter to General Scott, in which he recounted the threats he had heard and ventured to inquire as to the probability of any attempt at his life being made on the occasion of his inauguration. General Mather, on his arrival in Washington, found General Scott confined to his room by illness and unable to see visitors. On Mather calling a second time and sending in his letter he was invited up to the sick man's chamber. "Entering the room." related Mather in later years, "I found the old warrior, grizzly and wrinkled, propped up in the bed by an embankment of pillows behind his back. His hair and beard were considerably disordered, the flesh seemed to lay in rolls across his warty face and neck, and his breathing was not without great labor. In his hand he still held Lincoln's letter. He was weak from long-continued illness, and trembled very perceptibly. It was evident that the message from Lincoln had wrought up the old veteran's feelings. 'General Mather,' he said to me, in great agitation, 'present my compliments to Mr. Lincoln when you return to Springfield, and tell him I expect him to come on to Washington as soon as he is ready. Say to him that I'll look after those Maryland and Virginia rangers myself; I'll plant cannon at both ends of Pennsylvania avenue, and if any of them show their heads or raise a finger I'll blow them to hell.' On my return to Springfield," concludes Mather, "I hastened to assure Mr. Lincoln that, if Scott were alive on the day of the inauguration, there need be no alarm lest the performance be interrupted by any one. I felt certain the hero of Lundy's Lane would give the matter the care and attention it deserved."
Having at last reached his destination in safety, Mr. Lincoln spent the few days preceding his inauguration at Willard's Hotel, receiving an uninterrupted stream of visitors and friends. In the few unoccupied moments allotted him, he was carefully revising his inaugural address. On the morning of the 4th of March he rode from his hotel with Mr. Buchanan in an open barouche to the Capitol.
There, slightly pale and nervous, he was introduced to the assembled multitude by his old friend Edward D. Baker, and in a fervid and impressive manner delivered his address. At its conclusion the customary oath was administered by the venerable Chief Justice Taney, and he was now clothed with all the powers and privileges of Chief Magistrate of the nation. He accompanied Mr. Buchanan to the White House, and here the historic bachelor of Lancaster bade him farewell, bespeaking for him a peaceful, prosperous, and successful administration.
One who witnessed the impressive scene left the following graphic description of the inauguration and its principal incidents: "Near noon I found myself a member of the motley crowd gathered about the side entrance to Willard's Hotel. Soon an open barouche drove up, and the only occupant stepped out. A large, heavy, awkward-moving man, far advanced in years, short and thin gray hair, full face, plentifully seamed and wrinkled, head curiously inclined to the left shoulder, a low-crowned, broad-brimmed silk hat, an immense white cravat like a poultice, thrusting the old-fashioned standing collar up to the ears, dressed in black throughout, with swallow-tail coat not of the newest style. It was President Buchanan, calling to take his successor to the Capitol. In a few minutes he reappeared, with Mr. Lincoln on his arm; the two took seats side-by-side, and the carriage rolled away, followed by a rather disorderly and certainly not very imposing procession. I had ample time to walk to the Capitol, and no difficulty in securing a place where everything could be seen and heard to the best advantage. The attendance at the inauguration was, they told me, unusually small, many being kept away by anticipated disturbance, as it had been rumored—truly, too—that General Scott himself was fearful of an outbreak, and had made all possible military preparations to meet the emergency. A square platform had been built out from the steps to the eastern portico, with benches for distinguished spectators on three sides. Douglas, the only one I recognized, sat at the extreme end of the seat on the right of the narrow passage leading from the steps. There was no delay, and the gaunt form of the President-elect was soon visible, slowly making his way to the front. To me, at least, he was completely metamorphosed—partly by his own fault, and partly through the efforts of injudicious friends and ambitious tailors. He was raising (to gratify a very young lady, it is said) a crop of whiskers, of the blacking-brush variety, coarse, stiff, and ungraceful; and in so doing spoiled, or at least seriously impaired, a face which, though never handsome, had in its original state a peculiar power and pathos. On the present occasion the whiskers were reinforced by brand-new clothes from top to toe; black dress-coat, instead of the usual frock, black cloth or satin vest, black pantaloons, and a glossy hat evidently just out of the box. To cap the climax of novelty, he carried a huge ebony cane, with a gold head the size of an egg. In these, to him, strange habiliments, he looked so miserably uncomfortable that I could not help pitying him. Reaching the platform, his discomfort was visibly increased by not knowing what to do with hat and cane; and so he stood there, the target for ten thousand eyes, holding cane in one hand and hat in the other, the very picture of helpless embarrassment. After some hesitation he pushed the cane into a corner of the railing, but could not find a place for the hat except on the floor, where I could see he did not like to risk it. Douglas, who fully took in the situation, came to rescue of his old friend and rival, and held the precious hat until the owner needed it again; a service which, if predicted two years before, would probably have astonished him. The oath of office was administered by Chief Justice Taney, whose black robes, attenuated figure, and cadaverous countenance reminded me of a galvanized corpse. Then the President came forward, and read his inaugural address in a clear and distinct voice. It was attentively listened to by all, but the closest listener was Douglas, who leaned forward as if to catch every word, nodding his head emphatically at those passages which most pleased him. There was some applause, not very much nor very enthusiastic. I must not forget to mention the presence of a Mephistopheles in the person of Senator Wigfall, of Texas, who stood with folded arms leaning against the doorway of the Capitol, looking down upon the crowd and the ceremony with a contemptuous air, which sufficiently indicated his opinion of the whole performance. To him the Southern Confederacy was already an accomplished fact. He lived to see it the saddest of fictions."
Lincoln, the President, did not differ greatly from Lincoln the lawyer and politician. In the latter capacity only had his old friends in Illinois known him. For a long time after taking his seat they were curious to know what change, if any, his exalted station had made in him. He was no longer amid people who had seen him grow from the village lawyer to the highest rank in the land, and whose hands he could grasp in the confidence of a time-tried friendship; but now he was surrounded by wealth, power, fashion, influence, by adroit politicians and artful schemers of every sort. In the past his Illinois and particularly his Springfield friends* had shared the anxiety and responsibility of every step he had made; but now they were no longer to continue in the partnership. Many of them wanted no office, but all of them felt great interest as well as pride in his future. A few attempted to keep up a correspondence with him, but his answers were tardy and irregular.
* Lincoln, even after his elevation to the Presidency, always had an eye out for his friends, as the following letters will abundantly prove: "Executive Mansion, Washington, April 20, 1864. "Calvin Truesdale, Esq. "Postmaster, Rock Island, Ill.: "Thomas J. Pickett, late agent of the Quartermaster's Department for the Island of Rock Island, has been removed or suspended from that position on a charge of having sold timber and stone from the island for his private benefit. Mr. Pickett is an old acquaintance and friend of mine, and I will thank you, if you will, to set a day or days and place on and at which to take testimony on the point. Notify Mr. Pickett and one J. B. Danforth (who as I understand makes the charge) to be present with their witnesses. Take the testimony in writing offered by both sides, and report it in full to me. Please do this for me. "Yours truly, "A. Lincoln." The man Pickett was formerly the editor of a newspaper in northern Illinois, and had, to use an expression of later days, inaugurated in the columns of his paper Lincoln's boom for the Presidency. When he afterwards fell under suspicion, no one came to his rescue sooner than the President himself. The following letter needs no explanation: "Executive Mansion, Washington, August 27, 1862. "Hon. Wash. Talcott. "My Dear Sir:—I have determined to appoint you collector. I now have a very special request to make of you, which is, that you will make no war upon Mr. Washburne, who is also my friend, and of longer standing than yourself. I will even be obliged if you can do something for him if occasion presents. "Yours truly, "A. Lincoln." Mr. Talcott, to whom it was addressed, was furnished a letter of introduction by the President, as follows: "The Secretary of the Treasury and the Commissioner of Internal Revenue will please see Mr. Talcott, one of the best men there is, and, if any difference, one they would like better than they do me. "A. Lincoln." August 18, 1862.
Because he did not appoint a goodly portion of his early associates to comfortable offices, and did not interest himself in the welfare of everyone whom he had known in Illinois, or met while on the circuit, the erroneous impression grew that his elevation had turned his head. There was no foundation for such an unwarranted conclusion. Lincoln had not changed a particle. He was overrun with duties and weighted down with cares; his surroundings were different and his friends were new, but he himself was the same calm, just, and devoted friend as of yore. His letters were few and brief, but they showed no lack of gratitude or appreciation, as the following one to me will testify:
"Executive Mansion, February 3, 1862.
"Dear William:
"Yours of January 30th is just received. Do just as you say about the money matters. As you well know, I have not time enough to write a letter of respectable length. God bless you, says
"Your friend,
"A. Lincoln."*
* On February 19,1863, I received this despatch from Mr. Lincoln: "Would you accept a job of about a month's duration, at St Louis, $5 a day and mileage. Answer. "A. Lincoln."
His letters to others were of the same warm and generous tenor, but yet the foolish notion prevailed that he had learned to disregard the condition and claims of his Springfield friends. One of the latter who visited Washington returned somewhat displeased because Mr. Lincoln failed to inquire after the health and welfare of each one of his old neighbors. The report spread that he cared nothing for his home or the friends who had made him what he was. Those who entertained this opinion of the man forgot that he was not exactly the property of Springfield and Illinois, but the President of all the States in the Union.*
In this connection it may not be out of order to refer briefly to the settlement by Mr. Lincoln of the claims his leading Illinois friends had on him. As before observed his own election to the Presidency cancelled Illinois as a factor in the cabinet problem, but in no wise disposed of the friends whom the public expected and whom he himself intended should be provided for. Of these latter the oldest and most zealous and effective was David Davis.** It is not extravagance, taking their long association together in mind, to say that Davis had done more for Lincoln than any dozen other friends he had. Of course, after Lincoln was securely installed in office, the people, especially in Illinois, awaited his recognition of Davis. What was finally done is minutely told in a letter by Leonard Swett, which it is proper here to insert:
* The following letter from a disappointed Illinois friend will serve to illustrate the perplexities that beset Lincoln in disposing of the claims of personal friendship. It was written by a man of no inconsiderable reputation in Illinois, where he at one time filled a State office: "Lincoln is a singular man, and I must confess I never knew him. He has for twenty years past used me as a plaything to accomplish his own ends; but the moment he was elevated to his proud position he seems all at once to have entirely changed his whole nature and become altogether a new being. He knows no one, and the road to his favor is always open to his enemies, while the door is hermetically sealed to his old friends." ** "I had done Lincoln many, many favors, had electioneered for him, spent my money for him, worked and toiled for him."—David Davis, statement, September 20, 1866.
"Chicago, Ill., August 29,1887.
"William H. Herndon.
"My Dear Sir:—Your inquiry in reference to the circumstances of the appointment of David Davis as one of the Justices of the Supreme Court reached me last evening. In reply I beg leave to recall the fact, that in 1860 the politicians of Illinois were divided into three divisions, which were represented in the Decatur convention by the votes on the nomination for Governor. The largest vote was for Norman B. Judd, of Chicago, his strength in the main being the northern part of the State. I was next in order of strength, and Richard Yates the third, but the divisions were not materially unequal. The result was Yates was nominated, his strength being about Springfield and Jacksonville, extending to Quincy on the west, and mine was at Bloomington and vicinity and south and southeast.
"These divisions were kept up awhile after Mr. Lincoln's election, and were considered in the distribution of Federal patronage. A vacancy in the United States Senate occurred early in 1861 by the death of Stephen A. Douglas, and Governor Yates appointed Oliver H. Browning, of Quincy, to fill the vacancy. There was also a vacancy upon the Supreme Bench of the United States to be filled from this general vicinity by Mr. Lincoln in the early part of his administration, and Judge Davis, of Bloomington, and Mr. Browning, of Quincy, were aspirants for the position. Mr. Browning had the advantage that Lincoln was new in his seat, and Senators were august personages; and, being in the Senate and a most courteous and able gentleman, Mr. Browning succeeded in securing nearly all the senatorial strength, and Mr. Lincoln was nearly swept off his feet by the current of influence. Davis' supporters were the circuit lawyers mainly in the eastern and central part of the State. These lawyers were at home, and their presence was not a living force felt constantly by the President at Washington.
"I was then living at Bloomington, and met Judge Davis every day. As months elapsed we used to get word from Washington in reference to the condition of things; finally, one day the word came that Lincoln had said, 'I do not know what I may do when the time comes, but there has never been a day when if I had to act I should not have appointed Browning.' Judge Davis, General Orme, and myself held a consultation in my law-office at Bloomington. We decided that the remark was too Lincolnian to be mistaken and no man but he could have put the situation so quaintly. We decided also that the appointment was gone, and sat there glum over the situation. I finally broke the silence, saying in substance, 'The appointment is gone and I am going to pack my carpet-sack for Washington.' 'No, you are not,' said Davis. 'Yes, I am,' was my reply. 'Lincoln is being swept off his feet by the influence of these Senators, and I will have the luxury of one more talk with him before he acts.'
"I did go home, and two days thereafter, in the morning about seven o'clock—for I knew Mr. Lincoln's habits well—was at the White House and spent most of the forenoon with him. I tried to impress upon him that he had been brought into prominence by the Circuit Court lawyers of the old eighth Circuit, headed by Judge Davis. 'If,' I said. 'Judge Davis, with his tact and force, had not lived, and all other things had been as they were, I believe you would not now be sitting where you are.' He replied gravely, 'Yes, that is so.' 'Now it is a common law of mankind,' said I, 'that one raised into prominence is expected to recognize the force that lifts him, or, if from a pinch, the force that lets him out. The Czar Nicholas was once attacked by an assassin; a kindly hand warded off the blow and saved his life. The Czar hunted out the owner of that hand and strewed his pathway with flowers through life. The Emperor Napoleon III. has hunted out everybody who even tossed him a biscuit in his prison at Ham and has made him rich. Here is Judge Davis, whom you know to be in every respect qualified for this position, and you ought in justice to yourself and public expectation to give him this place.' We had an earnest pleasant forenoon, and I thought I had the best of the argument, and I think he thought so too.
"I left him and went to Willard's Hotel to think over the interview, and there a new thought struck me. I therefore wrote a letter to Mr. Lincoln and returned to the White House. Getting in, I read it to him and left it with him. It was, in substance, that he might think if he gave Davis this place the latter when he got to Washington would not give him any peace until he gave me a place equally as good; that I recognized the fact that he could not give this place to Davis, which would be charged to the Bloomington faction in our State politics, and then give me anything I would have and be just to the party there; that this appointment, if made, should kill 'two birds with one stone;' that I would accept it as one-half for me and one-half for the Judge; and that thereafter, if I or any of my friends ever troubled him, he could draw that letter as a plea in bar on that subject. As I read it Lincoln said, 'If you mean that among friends as it reads I will take it and make the appointment.' He at once did as he said.
"He then made a request of the Judge after his appointment in reference to a clerk in his circuit, and wrote him a notice of the appointment, which Davis received the same afternoon I returned to Bloomington.
"Judge Davis was about fifteen years my senior. I had come to his circuit at the age of twenty-four, and between him and Lincoln I had grown up leaning in hours of weakness on their own great arms for support. I was glad of the opportunity to put in the mite of my claims upon Lincoln and give it to Davis, and have been glad I did it every day since.
"An unknown number of people have almost every week since, speaking perhaps extravagantly, asked me in a quasi-confidential manner, 'How was it that you and Lincoln were so intimate and he never gave you anything?' I have generally said, 'It seems to me that is my question, and so long as I don't complain I do not see why you should.' I may be pardoned also for saying that I have not considered every man not holding an office out of place in life. I got my eyes open on this subject before I got an office, and as in Washington I saw the Congressman in decline I prayed that my latter end might not be like his.
"Yours truly,
"Leonard Swett."
Before his departure for Washington, Mr. Lincoln had on several occasions referred in my presence to the gravity of the national questions that stared him in the face; yet from what he said I caught no definite idea of what his intentions were. He told me he would rely upon me to keep him informed of the situation about home, what his friends were saying of him, and whether his course was meeting with their approval. He suggested that I should write him frequently, and that arrangements would be made with his private secretary, Mr. Nicolay, that my letters should pass through the latter's hands unopened. This plan was adhered to, and I have every reason now to believe that all my letters to Lincoln, although they contained no great secrets of state, passed unread into his hands. I was what the newspaper men would call a "frequent contributor." I wrote oftener than he answered, sometimes remitting him his share of old fees, sometimes dilating on national affairs, but generally confining myself to local politics and news in and around Springfield. I remember of writing him two copious letters, one on the necessity of keeping up the draft, the other admonishing him to hasten his Proclamation of Emancipation. In the latter I was especially fervid, assuring, him if he emancipated the slaves, he could "go down the other side of life filled with the consciousness of duty well done, and along a pathway blazing with eternal glory." How my rhetoric or sentiments struck him I never learned, for in the rush of executive business he never responded to either of the letters. Late in the summer of 1861, as elsewhere mentioned in these chapters, I made my first and only visit to Washington while he was President. My mission was intended to promote the prospects of a brother-in-law, Charles W. Chatterton, who desired to lay claim to an office in the Bureau of Indian Affairs. Mr. Lincoln accompanied me to the office of the Commissioner of Indian Affairs,—William P. Dole of Paris, Illinois,—told a good story, and made the request which secured the coveted office—an Indian agency—in an amazingly short time. This was one of the few favors I asked of Mr. Lincoln, and he granted it "speedily—without delay; freely—without purchase; and fully—without denial." I remained in Washington for several days after this, and, notwithstanding the pressure of business, he made me spend a good portion of the time at the White House. One thing he could scarcely cease from referring to was the persistence of the office-seekers. They slipped in, he said, through the half-opened doors of the Executive Mansion; they dogged his steps if he walked; they edged their way through the crowds and thrust their papers in his hands when he rode;* and, taking it all in all, they well-nigh worried him to death.
* He said that one day, as he was passing down Pennsylvania avenue, a man came running after him, hailed him, and thrust a bundle of papers in his hands. It angered him not a little, and he pitched the papers back, saying, "I'm not going to open shop here."
He said that, if the Government passed through the Rebellion without dismemberment, there was the strongest danger of its falling a prey to the rapacity of the office-seeking class. "This human struggle and scramble for office," were his words, "for a way to live without work, will finally test the strength of our institutions." A good part of the day during my stay I would spend with him in his office or waiting-room. I saw the endless line of callers, and met the scores of dignitaries one usually meets at the White House, even now; but nothing took place worthy of special mention here. One day Horace Maynard and Andrew Johnson, both senators from Tennessee, came in arm-in-arm. They declined to sit down, but at once set to work to discuss with the President his recent action in some case in which they were interested. Maynard seemed very earnest in what he said. "Beware, Mr. President," he said, "and do not go too fast. There is danger ahead," "I know that," responded Lincoln, good-naturedly, "but I shall go just so fast and only so fast as I think I'm right and the people are ready for the step." Hardly half-a-dozen words followed, when the pair wheeled around and walked away. The day following I left Washington for home. I separated from Mr. Lincoln at the White House. He followed me to the rear portico, where I entered the carriage to ride to the railroad depot. He grasped me warmly by the hand and bade me a fervent "Good-bye." It was the last time I ever saw him alive.
Mrs. Ninian Edwards, who, it will be remembered, was the sister of Mrs. Lincoln, some time before her death furnished me an account of her visit to Washington, some of the incidents of which are so characteristic that I cannot refrain from giving them room here. This lady, without endeavoring to suppress mention of her sister's many caprices and eccentricities while mistress of the White House, remarked that, having been often solicited by the Lincolns to visit them, she and her husband, in answer to the cordial invitation, at last made the journey to Washington, "One day while there," she relates, "in order to calm his mind, to turn his attention away from business and cheer him up, I took Mr. Lincoln down through the conservatory belonging to the Executive Mansion, and showed him the world of flowers represented there. He followed me patiently through. 'How beautiful these flowers are! how gorgeous these roses! Here are exotics,' I exclaimed, in admiration, 'gathered from the remotest corners of the earth, and grand beyond description.' A moody silence followed, broken finally by Mr. Lincoln with this observation: 'Yes, this whole thing looks like spring; but do you know I have never been in here before. I don't know why it is so, but I never cared for flowers; I seem to have no taste, natural or acquired, for such things.' I induced him one day," continued Mrs. Edwards, "to walk to the Park north of the White House. He hadn't been there, he said, for a year. On such occasions, when alone or in the company of a close friend, and released from the restraint of his official surroundings, he was wont to throw from his shoulders many a burden. He was a man I loved and respected. He was a good man, an honest and true one. Much of his seeming disregard, which has been tortured into ingratitude, was due to his peculiar construction. His habits, like himself, were odd and wholly irregular. He would move around in a vague, abstracted way, as if unconscious of his own or any one else's existence. He had no expressed fondness for anything, and ate mechanically. I have seen him sit down at the table absorbed in thought, and never, unless recalled to his senses, would he think of food. But, however peculiar and secretive he may have seemed, he was anything but cold. Beneath what the world saw lurked a nature as tender and poetic as any I ever knew. The death of his son Willie, which occurred in Washington, made a deep impression on him. It was the first death in his family, save an infant who died a few days after its birth in Springfield. On the evening we strolled through the Park he spoke of it with deep feeling, and he frequently afterward referred to it. When I announced my intention of leaving Washington he was much affected at the news of my departure. We were strolling through the White House grounds, when he begged me with tears in his eyes to remain longer. 'You have such strong control and such an influence over Mary,' he contended, 'that when troubles come you can console me.' The picture of the man's despair never faded from my vision. Long after my return to Springfield, on reverting to the sad separation, my heart ached because I was unable in my feeble way to lighten his burden."
In the summer of 1866 I wrote to Mrs. Lincoln, then in Chicago, asking for a brief account of her own and her husband's life or mode of living while at the White House. She responded as follows: *
* From MSS. in Author's possession.
"375 West Washington Street, Chicago, Ill., August 28, 1866.
"Hon. Wm. H. Herndon.
"My Dear Sir:—Owing to Robert's absence from Chicago your last letter to him was only shown me last evening. The recollection of my beloved husband's truly affectionate regard for you, and the knowledge of your great love and reverence for the best man that ever lived, would of itself cause you to be cherished with the sincerest regard by my sons and myself. In my overwhelming bereavement those who loved my idolized husband aside from disinterested motives are very precious to me and mine. My grief has been so uncontrollable that, in consequence, I have been obliged to bury myself in solitude, knowing that many whom I would see could not fully enter into the state of my feelings. I have been thinking for some time past I would like to see you and have a long conversation. I wish to know if you will be in Springfield next Wednesday week, September 4; if so, at ten o'clock in the morning you will find me at the St. Nicholas Hotel. Please mention this visit to Springfield to no one. It is a most sacred one, as you may suppose, to visit the tomb which contains my all in life—my husband. If it will not be convenient, or if business at the time specified should require your absence, should you visit Chicago any day this week I will be pleased to see you. I remain,
"Very truly,
"Mary Lincoln."
I met Mrs. Lincoln at the hotel in Springfield according to appointment. Our interview was somewhat extended in range, but none the less interesting. Her statement made at the time now lies before me. "My husband intended," she said, "when he was through with his Presidential term, to take me and our boys with him to Europe. After his return from Europe he intended to cross the Rocky Mountains and go to California, where the soldiers were to be digging out gold to pay the national debt. During his last days he and Senator Sumner became great friends, and were closely attached to each other. They were down the river after Richmond was taken—were full of joy and gladness at the thought of the war being over. Up to 1864 Mr. Lincoln wanted to live in Springfield, and if he died be buried there also; but after that and only a short time before his death he changed his mind slightly, but never really settled on any particular place. The last time I remember of his referring to the matter he said he thought it would be good for himself and me to spend a year or more travelling. As to his nature, he was the kindest man, most tender husband, and loving father in the world. He gave us all unbounded liberty, saying to me always when I asked for anything, 'You know what you want, go and get it,' and never asking if it were necessary. He was very indulgent to his children. He never neglected to praise them for any of their good acts. He often said, 'It is my pleasure that my children are free and happy, and unrestrained by parental tyranny. Love is the chain whereby to bind a child to its parents.'
"My husband placed great reliance on my knowledge of human nature, often telling me, when about to make some important appointment, that he had no knowledge of men and their motives. It was his intention to remove Seward as soon as peace with the South was declared. He greatly disliked Andrew Johnson. Once the latter, when we were in company, followed us around not a little. It displeased Mr. Lincoln so much he turned abruptly and asked, loud enough to be heard by others, 'Why is this man forever following me?' At another time, when we were down at City Point, Johnson, still following us, was drunk. Mr. Lincoln in desperation exclaimed, 'For God's sake don't ask Johnson to dine with us, Sumner, who was along, joined in the request. Mr. Lincoln was mild in his manners, but he was a terribly firm man when he set his foot down. None of us, no man or woman, could rule him after he had once fully made up his mind. I could always tell when in deciding anything he had reached the ultimatum. At first he was very cheerful, then he lapsed into thoughtfulness, bringing his lips together in a firm compression. When these symptoms developed I fashioned myself accordingly, and so did all others have to do sooner or later. When we first went to Washington many thought Mr. Lincoln was weak, but he rose grandly with the circumstances. I told him once of the assertion I had heard coming from the friends of Seward, that the latter was the power behind the throne; that he could rule him. He replied, 'I may not rule myself, but certainly Seward shall not. The only ruler I have is my conscience—following God in it—and these men will have to learn that yet.'
"Some of the newspaper attacks on him gave him great pain. I sometimes read them to him, but he would beg me to desist, saying, 'I have enough to bear now, but yet I care nothing for them. If I'm right I'll live, and if wrong I'll die anyhow; so let them fight at me unrestrained.' My playful response would be, 'The way to learn is to hear both sides.' I once assured him Chase and certain others who were scheming to supplant him ought to be restrained in their evil designs. 'Do good to them who hate you,' was his generous answer, 'and turn their ill-will into friendship.'
"I often told Mr. Lincoln that God would not let any harm come of him. We had passed through four long years—terrible and bloody years—unscathed, and I believed we would be released from all danger. He gradually grew into that belief himself, and the old gloomy notion of his unavoidable taking-off was becoming dimmer as time passed away. Cheerfulness merged into joyfulness. The skies cleared, the end of the war rose dimly into view when the great blow came and shut him out forever."
For a glimpse of Lincoln's habits while a resident of Washington and an executive officer, there is no better authority than John Hay, who served as one of his secretaries. In 1866, Mr. Hay, then a member of the United States Legation in Paris, wrote me an interesting account, which so faithfully delineates Lincoln in his public home that I cannot refrain from quoting it entire. Although the letter was written in answer to a list of questions I asked, and was prepared without any attempt at arrangement, still it is none the less interesting. "Lincoln went to bed ordinarily," it begins, "from ten to eleven o'clock, unless he happened to be kept up by important news, in which case he would frequently remain at the War Department till one or two. He rose early. When he lived in the country at the Soldiers' Home he would be up and dressed, eat his breakfast (which was extremely frugal, an egg, a piece of toast, coffee, etc.), and ride into Washington, all before eight o'clock. In the winter, at the White House, he was not quite so early. He did not sleep well, but spent a good while in bed. 'Tad' usually slept with him. He would lie around the office until he fell asleep, and Lincoln would shoulder him and take him off to bed. He pretended to begin business at ten o'clock in the morning, but in reality the ante-rooms and halls were full long before that hour—people anxious to get the first axe ground. He was extremely unmethodical; it was a four years' struggle on Nicolay's part and mine to get him to adopt some systematic rules. He would break through every regulation as fast as it was made. Anything that kept the people themselves away from him he disapproved, although they nearly annoyed the life out of him by unreasonable complaints and requests. He wrote very few letters, and did not read one in fifty that he received. At first we tried to bring them to his notice, but at last he gave the whole thing over to me, and signed, without reading them, the letters I wrote in his name. He wrote perhaps half-a-dozen a week himself—not more. Nicolay received members of Congress and other visitors who had business with the Executive office, communicated to the Senate and House the messages of the President, and exercised a general supervision over the business. I opened and read the letters, answered them, looked over the newspapers, supervised the clerks who kept the records, and in Nicolay's absence did his work also. When the President had any rather delicate matter to manage at a distance from Washington he rarely wrote, but sent Nicolay or me. The House remained full of people nearly all day. At noon the President took a little lunch—a biscuit, a glass of milk in winter, some fruit or grapes in summer. He dined between five and six, and we went off to our dinner also. Before dinner was over, members and Senators would come back and take up the whole evening. Sometimes, though rarely, he shut himself up and would see no one. Sometimes he would run away to a lecture, or concert, or theatre for the sake of a little rest. He was very abstemious—ate less than any man I know. He drank nothing but water, not from principle but because he did not like wine or spirits. Once, in rather dark days early in the war, a temperance committee came to him and said that the reason we did not win was because our army drank so much whiskey as to bring the curse of the Lord upon them. He said it was rather unfair on the part of the aforesaid curse, as the other side drank more and worse whiskey than ours did. He read very little. He scarcely ever looked into a newspaper unless I called his attention to an article on some special subject. He frequently said, 'I know more about it than any of them.' It is absurd to call him a modest man. No great man was ever modest. It was his intellectual arrogance and unconscious assumption of superiority that men like Chase and Sumner never could forgive. I believe that Lincoln is well understood by the people; but there is a patent-leather, kid-glove set who know no more of him than an owl does of a comet blazing into his blinking eyes.* Their estimates of him are in many causes disgraceful exhibitions of ignorance and prejudice. Their effeminate natures shrink instinctively from the contact of a great reality like Lincoln's character. I consider Lincoln's republicanism incarnate—with all its faults and all its virtues. As, in spite of some rudeness, republicanism is the sole hope of a sick world, so Lincoln, with all his foibles, is the greatest character since Christ."
* Bancroft's eulogy on Lincoln never pleased the latter's lifelong friends—those who knew him so thoroughly and well. February 16, 1866, David Davis, who had heard it, wrote me: "You will see Mr. Bancroft's oration before this reaches you. It is able, but Mr. Lincoln is in the background. His analysis of Mr. Lincoln's character is superficial. It did not please me. How did it satisfy you?" On the 22d he again wrote: "Mr. Bancroft totally misconceived Mr. Lincoln's character in applying 'unsteadiness' and confusion to it. Mr. Lincoln grew more steady and resolute, and his ideas were never confused. If there were any changes in him after he got here they were for the better. I thought him always master of his subject. He was a much more self-possessed man than I thought. He thought for himself, which is a rare quality nowadays. How could Bancroft know anything about Lincoln except as he judged of him as the public do? He never saw him, and is himself as cold as an icicle. I should never have selected an old Democratic politician, and that one from Massachusetts, to deliver an eulogy on Lincoln."
In 1863 Mr. Lincoln was informed one morning that among the visitors in the ante-room of the White House was a man who claimed to be his relative. He walked out and was surprised to find his boyhood friend and cousin, Dennis Hanks. The latter had come to see his distinguished relative on a rather strange mission. A number of persons living in Coles County, in Illinois, offended at the presence and conduct of a few soldiers who were at home from the war on furlough at the town of Charleston, had brought about a riot, in which encounter several of the latter had been killed. Several of the civilian participants who had acted as leaders in the strife had been arrested and sent to Fort McHenry or some other place of confinement equally as far from their homes. The leading lawyers and politicians of central Illinois were appealed to, but they and all others who had tried their hands had been signally unsuccessful in their efforts to secure the release of the prisoners. Meanwhile some one of a sentimental turn had conceived the idea of sending garrulous old Dennis Hanks to Washington, fondly believing that his relationship to the President might in this last extremity be of some avail. The novelty of the project secured its adoption by the prisoners' friends, and Dennis, arrayed in a suit of new clothes, set out for the national capital. I have heard him describe this visit very minutely. How his appearance in Washington and his mission struck Mr. Lincoln can only be imagined. The President, after listening to him and learning the purpose of his visit, retired to an adjoining room and returned with an extremely large roll of papers labelled, "The Charleston Riot Case," which he carefully untied and gravely directed his now diplomatic cousin to read. Subsequently, and as if to continue the joke, he sent him down to confer with the Secretary of War. He soon returned from the latter's office with the report that the head of the War Department could not be found; and it was well enough that he did not meet that abrupt and oftentimes demonstrative official. In the course of time, however, the latter happened in at the Executive Mansion, and there, in the presence of Dennis, the President sought to reopen the now noted Charleston case. Adopting Mr. Hanks' version, the Secretary, with his characteristic plainness of speech, referring to the prisoners, declared that "every d-d one of them should be hung." Even the humane and kindly enquiry of the President, "If these men should return home and become good citizens, who would be hurt?" failed to convince the distinguished Secretary that the public good could be promoted by so doing. The President not feeling willing to override the judgment of his War Secretary in this instance, further consideration of the case ceased, and his cousin returned to his home in Illinois with his mission unaccomplished.*
* The subsequent history of these riot cases I believe is that the prisoners were returned to Illinois to be tried in the State courts there; and that by successive changes of venue and continuances the cases were finally worn out.
Dennis retained a rather unfavorable impression of Mr. Stanton, whom he described as a "frisky little Yankee with a short coat-tail." "I asked Abe," he said to me once, "why he didn't kick him out. I told him he was too fresh altogether."
Lincoln's answer was, "If I did, Dennis, it would be difficult to find another man to fill his place." The President's cousin * sat in the office during the endless interviews that take place between the head of the nation and the latter's loyal subjects. He saw modesty and obscurity mingling with the arrogance of pride and distinction. One day an attractive and handsomely dressed woman called to procure the release from prison of a relative in whom she professed the deepest interest. She was a good talker, and her winning ways seemed to be making a deep impression on the President. After listening to her story he wrote a few lines on a card, enclosing it in an envelope and directing her to take it to the Secretary of War. Before sealing it he showed it to Dennis. It read: "This woman, dear Stanton, is a little smarter than she looks to be." She had, woman-like, evidently overstated her case. Before night another woman called, more humble in appearance, more plainly clad. It was the old story. Father and son both in the army, the former in prison. Could not the latter be discharged from the army and sent home to help his mother? A few strokes of the pen, a gentle nod of the head, and the little woman, her eyes filling with tears and expressing a grateful acknowledgment her tongue could not utter, passed out.
* During this visit Mr. Lincoln presented Dennis with a silver watch, which the latter still retains as a memento alike of the donor and his trip to Washington.
BEFORE passing to a brief and condensed view of the great panorama of the war it will interest the reader and no doubt aid him greatly in drawing the portrait of Lincoln to call up for the purpose two friends of his, whose testimony is not only vivid and minute, but for certain reasons unusually appropriate and essential. The two were devoted and trusted friends of Lincoln; and while neither held office under him, both were offered and both declined the same. That of itself ought not to be considered as affecting or strengthening their statements, and yet we sometimes think that friends who are strong enough to aid us, and yet, declining our aid, take care of themselves, are brave enough to tell us the truth. The two friends of Lincoln here referred to are Joshua F. Speed and Leonard Swett. In quoting them I adhere strictly to their written statements now in my possession. The former, under date of December 6, 1866, says: "Mr. Lincoln was so unlike all the men I had ever known before or seen or known since that there is no one to whom I can compare him. In all his habits of eating, sleeping, reading, conversation, and study he was, if I may so express it, regularly irregular; that is, he had no stated time for eating, no fixed time for going to bed, none for getting up. No course of reading was chalked out. He read law, history, philosophy, or poetry; Burns, Byron, Milton, or Shakespeare and the newspapers, retaining them all about as well as an ordinary man would any one of them who made only one at a time his study. I once remarked to him that his mind was a wonder to me; that impressions were easily made upon it and never effaced. 'No,' said he, 'you are mistaken; I am slow to learn, and slow to forget that which I have learned. My mind is like a piece of steel—very hard to scratch anything on it, and almost impossible after you get it there to rub it out.' I give this as his own illustration of the character of his mental faculties; it is as good as any I have seen from anyone.
"The beauty of his character was its entire simplicity. He had no affectation in anything. True to nature, true to himself, he was true to everybody and everything around him. When he was ignorant on any subject, no matter how simple it might make him appear, he was always willing to acknowledge it. His whole aim in life was to be true to himself, and being true to himself he could be false to no one.
"He had no vices, even as a young man. Intense thought with him was the rule and not, as with most of us, the exception. He often said that he could think better after breakfast, and better walking than sitting, lying, or standing. His world-wide reputation for telling anecdotes and telling them so well was in my judgment necessary to his very existence. Most men who have been great students, such as he was, in their hours of idleness have taken to the bottle, to cards or dice. He had no fondness for any of these. Hence he sought relaxation in anecdotes. So far as I now remember of his study for composition, it was to make short sentences and a compact style. Illustrative of this it might be well to state that he was a great admirer of the style of John C. Calhoun. I remember reading to him one of Mr. Calhoun's speeches in reply to Mr. Clay in the Senate, in which Mr. Clay had quoted precedent. Mr. Calhoun replied (I quote from memory) that 'to legislate upon precedent is but to make the error of yesterday the law of today.' Lincoln thought that was a great truth and grandly uttered.
"Unlike all other men, there was entire harmony between his public and private life. He must believe he was right, and that he had truth and justice with him, or he was a weak man; but no man could be stronger if he thought he was right.
"His familiar conversations were like his speeches and letters in this: that while no set speech of his (save the Gettysburg address) will be considered as entirely artistic and complete, yet, when the gems of American literature come to be selected, as many will be culled from Lincoln's speeches as from any American orator. So of his conversation, and so of his private correspondence; all abound in gems.
"My own connection or relation with Mr. Lincoln during the war has so often been commented on, and its extent so often enlarged upon, I feel impelled to state that during his whole administration he never requested me to do anything, except in my own State, and never much in that except to advise him as to what measures and policy would be most conducive to the growth of a healthy Union sentiment.
"My own opinion of the history of the Emancipation Proclamation is that Mr. Lincoln foresaw the necessity for it long before he issued it. He was anxious to avoid it, and came to it only when he saw that the measure would subtract from its labor, and add to our army quite a number of good fighting men. I have heard of the charge of duplicity against him by certain Western members of Congress. I never believed the charge, because he has told me from his own lips that the charge was false. I, who knew him so well, could never after that credit the report. At first I was opposed to the Proclamation, and so told him. I remember well our conversation on the subject. He seemed to treat it as certain that I would recognize the wisdom of the act when I should see the harvest of good which we would ere long glean from it. In that conversation he alluded to an incident in his life, long passed, when he was so much depressed that he almost contemplated suicide. At the time of his deep depression he said to me that he had 'done nothing to make any human being remember that he had lived,' and that to connect his name with the events transpiring in his day and generation, and so impress himself upon them as to link his name with something that would redound to the interest of his fellow man, was what he desired to live for. He reminded me of that conversation, and said with earnest emphasis, 'I believe that in this measure [meaning his Proclamation] my fondest hope will be realized.' Over twenty years had passed between the two conversations.
"The last interview but one I had with him was about ten days prior to his last inauguration. Congress was drawing to a close; it had been an important session; much attention had to be given to the important bills he was signing; a great war was upon him and the country; visitors were coming and going to the President with their varying complaints and grievances from morning till night with almost as much regularity as the ebb and flow of the tide; and he was worn down in health and spirits. On this occasion I was sent for, to come and see him. Instructions were given that when I came I should be admitted. When I entered his office it was quite full, and many more—among them not a few Senators and members of Congress—still waiting. As soon as I was fairly inside, the President remarked that he desired to see me as soon as he was through giving audiences, and that if I had nothing to do I could take the papers and amuse myself in that or any other way I saw fit till he was ready. In the room, when I entered, I observed sitting near the fireplace, dressed in humble attire, two ladies modestly waiting their turn. One after another of the visitors came and went, each bent on his own particular errand, some satisfied and others evidently displeased at the result of their mission. The hour had arrived to close the door against all further callers. No one was left in the room now except the President, the two ladies, and me. With a rather peevish and fretful air he turned to them and said, 'Well, ladies, what can I do for you?' They both commenced to speak at once. From what they said he soon learned that one was the wife and the other the mother of two men imprisoned for resisting the draft in western Pennsylvania. 'Stop,' said he, 'don't say any more. Give me your petition.' The old lady responded, 'Mr. Lincoln, we've got no petition; we couldn't write one and had no money to pay for writing one, and I thought best to come and see you.' 'Oh,' said he, 'I understand your cases.' He rang his bell and ordered one of the messengers to tell General Dana to bring him the names of all the men in prison for resisting the draft in western Pennsylvania. The General soon came with the list. He enquired if there was any difference in the charges or degrees of guilt. The General replied that he knew of none. 'Well, then,' said he, 'these fellows have suffered long enough, and I have thought so for some time, and now that my mind is on the subject I believe I will turn out the whole flock. So, draw up the order, General, and I will sign it.' It was done and the General left the room. Turning to the women he said, 'Now, ladies, you can go.' The younger of the two ran forward and was in the act of kneeling in thankfulness. 'Get up,' he said; 'don't kneel to me, but thank God and go.' The old lady now came forward with tears in her eyes to express her gratitude. 'Good-bye, Mr. Lincoln,' said she; 'I shall probably never see you again till we meet in heaven.' These were her exact words. She had the President's hand in hers, and he was deeply moved. He instantly took her right hand in both of his and, following her to the door, said, 'I am afraid with all my troubles I shall never get to the resting-place you speak of; but if I do I am sure I shall find you. That you wish me to get there is, I believe, the best wish you could make for me. Good-bye.'
"We were now alone. I said to him, 'Lincoln, with my knowledge of your nervous sensibility, it is a wonder that such scenes as this don't kill you.' He thought for a moment and then answered in a languid voice, 'Yes, you are to a certain degree right. I ought not to undergo what I so often do. I am very unwell now; my feet and hands of late seem to be always cold, and I ought perhaps to be in bed; but things of the sort you have just seen don't hurt me, for, to tell you the truth, that scene is the only thing to-day that has made me forget my condition or given me any pleasure. I have, in that order, made two people happy and alleviated the distress of many a poor soul whom I never expect to see. That old lady,' he continued, 'was no counterfeit. The mother spoke out in all the features of her face. It is more than one can often say that in doing right one has made two people happy in one day. Speed, die when I may, I want it said of me by those who know me best, that I always plucked a thistle and planted a flower when I thought a flower would grow.' What a fitting sentiment! What a glorious recollection!"
The recollections of Lincoln by Mr. Swett are in the form of a letter dated January 17, 1866. There is so much of what I know to be true in it, and it is so graphically told, that although there maybe some repetition of what has already been touched upon in the preceding chapters, still I believe that the portrait of Lincoln will be made all the more lifelike by inserting the letter without abridgment.
"Chicago, Ill., Jan. 17, 1866.
"Wm. H. Herndon, Esq.
"Springfield, Ill.
"Dear Sir: I received your letter to day, asking me to write you Friday. Fearing if I delay, you will not get it in time, I will give you such hasty thoughts as may occur to me to-night. I have mislaid your second lecture, so that I have not read it at all, and have not read your first one since about the time it was published. What I shall say, therefore, will be based upon my own ideas rather than a review of the lecture.
"Lincoln's whole life was a calculation of the law of forces and ultimate results. The whole world to him was a question of cause and effect. He believed the results to which certain causes tended; he did not believe that those results could be materially hastened or impeded. His whole political history, especially since the agitation of the slavery question, has been based upon this theory. He believed from the first, I think, that the agitation of slavery would produce its overthrow, and he acted upon the result as though it was present from the beginning. His tactics were to get himself in the right place and remain there still, until events would find him in that place. This course of action led him to say and do things which could not be understood when considered in reference to the immediate surroundings in which they were done or said. You will remember, in his campaign against Douglas in 1858, the first ten lines of the first speech he made defeated him. The sentiment of the 'house divided against itself' seemed wholly inappropriate. It was a speech made at the commencement of a campaign, and apparently made for the campaign. Viewing it in this light alone, nothing could have been more unfortunate or inappropriate. It was saying just the wrong thing; yet he saw it was an abstract truth, and standing by the speech would ultimately find him in the right place. I was inclined at the time to believe these words were hastily and inconsiderately uttered, but subsequent facts have convinced me they were deliberate and had been matured. Judge T. L. Dickey says, that at Bloomington, at the first Republican Convention in 1856, he uttered the same sentences in a speech delivered there, and that after the meeting was over, he (Dickey) called his attention to these remarks.
"Lincoln justified himself in making them by stating they were true; but finally, at Dickey's urgent request, he promised that for his sake, or upon his advice, he would not repeat them. In the summer of 1859, when he was dining with a party of his intimate friends at Bloomington, the subject of his Springfield speech was discussed. We all insisted it was a great mistake, but he justified himself, and finally said, 'Well, gentlemen, you may think that speech was a mistake, but I never have believed it was, and you will see the day when you will consider it was the wisest thing I ever said.'
"He never believed in political combinations, and consequently, whether an individual man or class of men supported or opposed him, never made any difference in his feelings, or his opinions of his own success. If he was elected, he seemed to believe that no person or class of persons could ever have defeated him, and if defeated, he believed nothing could ever have elected him. Hence, when he was a candidate, he never wanted anything done for him in the line of political combination or management. He seemed to want to let the whole subject alone, and for everybody else to do the same. I remember, after the Chicago Convention, when a great portion of the East were known to be dissatisfied at his nomination, when fierce conflicts were going on in New York and Pennsylvania, and when great exertions seemed requisite to harmonize and mould in concert the action of our friends, Lincoln always seemed to oppose all efforts made in the direction of uniting the party. I arranged with Mr. Thurlow Weed after the Chicago Convention to meet him at Springfield. I was present at the interview, but Lincoln said nothing. It was proposed that Judge Davis should go to New York and Pennsylvania to survey the field and see what was necessary to be done. Lincoln consented, but it was always my opinion that he consented reluctantly.
"He saw that the pressure of a campaign was the external force coercing the party into unity. If it failed to produce that result, he believed any individual effort would also fail. If the desired result followed, he considered it attributable to the great cause, and not aided by the lesser ones. He sat down in his chair in Springfield and made himself the Mecca to which all politicians made pilgrimages. He told them all a story, said nothing, and sent them away. All his efforts to procure a second nomination were in the same direction. I believe he earnestly desired that nomination. He was much more eager for it than he was for the first, and yet from the beginning he discouraged all efforts on the part of his friends to obtain it. From the middle of his first term all his adversaries were busily at work for themselves. Chase had three or four secret societies and an immense patronage extending all over the country. Frémont was constantly at work, yet Lincoln would never do anything either to hinder them or to help himself.
"He was considered too conservative, and his adversaries were trying to outstrip him in satisfying the radical element. I had a conversation with him upon this subject in October, 1863, and tried to induce him to recommend in his annual message a constitutional amendment abolishing slavery. I told him I was not very radical, but I believed the result of the war would be the extermination of slavery; that Congress would pass the amendment making the slave free, and that it was proper at that time to be done. I told him also, if he took that stand, it was an outside position, and no one could maintain himself upon any measure more radical, and if he failed to take the position, his rivals would. Turning to me suddenly he said, 'Is not the question of emancipation doing well enough now?' I replied it was. 'Well,'said he, 'I have never done an official act with a view to promote my own personal aggrandizement, and I don't like to begin now. I can see that emancipation is coming; whoever can wait for it will see it; whoever stands in its way will be run over by it.'
"His rivals were using money profusely; journals and influences were being subsidized against him. I accidentally learned that a Washington newspaper, through a purchase of the establishment, was to be turned against him, and consulted him about taking steps to prevent it. The only thing I could get him to say was that he would regret to see the paper turned against him. Whatever was done had to be done without his knowledge. Mr. Bennett of the Herald, with his paper, you know, is a power. The old gentleman wanted to be noticed by Lincoln, and he wanted to support him. A friend of his, who was certainly in his secrets, came to Washington and intimated if Lincoln would invite Bennett to come over and chat with him, his paper would be all right. Mr. Bennett wanted nothing, he simply wanted to be noticed. Lincoln in talking about it said, 'I understand it; Bennett has made a great deal of money, some say not very properly, now he wants me to make him respectable. I have never invited Mr. Bryant or Mr. Greeley here; I shall not, therefore, especially invite Mr. Bennett.' All Lincoln would say was, that he was receiving everybody, and he should receive Mr. Bennett if he came.
"Notwithstanding his entire inaction, he never for a moment doubted his second nomination. One time in his room discussing with him who his real friends were, he told me, if I would not show it, he would make a list of how the Senate stood. When he got through, I pointed out some five or six, and I told him I knew he was mistaken about them. Said he, 'You may think so, but you keep that until the convention and tell me then whether I was right.' He was right to a man. He kept a kind of account book of how things were progressing, for three or four months, and whenever I would get nervous and think things were going wrong, he would get out his estimates and show how everything on the great scale of action, such as the resolutions of legislatures, the instructions of delegates, and things of that character, were going exactly as he expected. These facts, with many others of a kindred nature, have convinced me that he managed his politics upon a plan entirely different from any other man the country has ever produced.
"He managed his campaigns by ignoring men and by ignoring all small causes, but by closely calculating the tendencies of events and the great forces which were producing logical results.
"In his conduct of the war he acted upon the theory that but one thing was necessary, and that was a united North. He had all shades of sentiments and opinions to deal with, and the consideration was always presented to his mind, how can I hold these discordant elements together?
"It was here that he located his own greatness as a President. One time, about the middle of the war, I left his house about eleven o'clock at night, at the Soldiers' Home. We had been discussing the discords in the country, and particularly the States of Missouri and Kentucky. As we separated at the door he said, 'I may not have made as great a President as some other men, but I believe I have kept these discordant elements together as well as anyone could.' Hence, in dealing with men he was a trimmer, and such a trimmer the world has never seen. Halifax, who was great in his day as a trimmer, would blush by the side of Lincoln; yet Lincoln never trimmed in principles, it was only in his conduct with men. He used the patronage of his office to feed the hunger of these various factions. Weed always declared that he kept a regular account-book of his appointments in New York, dividing his various favors so as to give each faction more than it could get from any other source, yet never enough to satisfy its appetite.
"They all had access to him, they all received favors from him, and they all complained of ill treatment; but while unsatisfied, they all had 'large expectations,' and saw in him the chance of obtaining more than from anyone else whom they could be sure of getting in his place. He used every force to the best possible advantage. He never wasted anything, and would always give more to his enemies than he would to his friends; and the reason was, because he never had anything to spare, and in the close calculation of attaching the factions to him, he counted upon the abstract affection of his friends as an element to be offset against some gift with which he must appease his enemies. Hence, there was always some truth in the charge of his friends that he failed to reciprocate their devotion with his favors. The reason was, that he had only just so much to give away—'He always had more horses than oats.'
"An adhesion of all forces was indispensable to his success and the success of the country; hence he husbanded his means with the greatest nicety of calculation. Adhesion was what he wanted; if he got it gratuitously he never wasted his substance paying for it.
"His love of the ludicrous was not the least peculiar of his characteristics. His love of fun made him overlook everything else but the point of the joke sought after. If he told a good story that was refined and had a sharp point, he did not like it any the better because it was refined. If it was outrageously vulgar, he never seemed to see that part of it, if it had the sharp ring of wit; nothing ever reached him but the wit. Almost any man that will tell a very vulgar story, has, in a degree, a vulgar mind; but it was not so with him; with all his purity of character and exalted morality and sensibility, which no man can doubt, when hunting for wit he had no ability to discriminate between the vulgar and the refined substances from which he extracted it. It was the wit he was after, the pure jewel, and he would pick it up out of the mud or dirt just as readily as he would from a parlor table.
"He had great kindness of heart. His mind was full of tender sensibilities, and he was extremely humane, yet while these attributes were fully developed in his character, and, unless intercepted by his judgment, controlled him, they never did control him contrary to his judgment. He would strain a point to be kind, but he never strained it to breaking. Most men of much kindly feeling are controlled by this sentiment against their judgment, or rather that sentiment beclouds their judgment. It was never so with him; he would be just as kind and generous as his judgment would let him be—no more. If he ever deviated from this rule, it was to save life. He would sometimes, I think, do things he knew to be impolitic and wrong to save some poor fellow's neck. I remember one day being in his room when he was sitting at his table with a large pile of papers before him, and after a pleasant talk he turned quite abruptly and said, 'Get out of the way, Swett; to-morrow is butcher-day, and I must go through these papers and see if I cannot find some excuse to let these poor fellows off.' The pile of papers he had were the records of courts martial of men who on the following day were to be shot. He was not examining the records to see whether the evidence sustained the findings; he was purposely in search of occasions to evade the law, in favor of life.
"Some of Lincoln's friends have insisted that he lacked the strong attributes of personal affection which he ought to have exhibited; but I think this is a mistake. Lincoln had too much justice to run a great government for a few favors; and the complaints against him in this regard, when properly digested, seem to amount to this and no more, that he would not abuse the privileges of his situation.
"He was certainly a very poor hater. He never judged men by his like or dislike for them. If any given act was to be performed, he could understand that his enemy could do it just as well as anyone. If a man had maligned him or been guilty of personal ill-treatment, and was the fittest man for the place, he would give him that place just as soon as he would give it to a friend.
"I do not think he ever removed a man because he was his enemy or because he disliked him.
"The great secret of his power as an orator, in my judgment, lay in the clearness and perspicuity of his statements. When Mr. Lincoln had stated a case it was always more than half argued and the point more than half won. It is said that some one of the crowned heads of Europe proposed to marry when he had a wife living. A gentleman, hearing of this proposition, replied, how could he? 'Oh,' replied his friend, 'he could marry and then he could get Mr. Gladstone to make an explanation about it.' This was said to illustrate the convincing power of Mr. Gladstone's statement.
"Mr. Lincoln had this power greater than any man I have ever known. The first impression he generally conveyed was, that he had stated the case of his adversary better and more forcibly than his opponent could state it himself. He then answered that statement of facts fairly and fully, never passing by or skipping over a bad point.
"When this was done he presented his own case. There was a feeling, when he argued a case, in the mind of any man who listened to it, that nothing had been passed over; yet if he could not answer the objections he argued, in his own mind, and himself arrive at the conclusion to which he was leading others, he had very little power of argumentation. The force of his logic was in conveying to the minds of others the same clear and thorough analysis he had in his own, and if his own mind failed to be satisfied, he had little power to satisfy anybody else. He never made a sophistical argument in his life, and never could make one. I think he was of less real aid in trying a thoroughly bad case than any man I was ever associated with. If he could not grasp the whole case and believe in it, he was never inclined to touch it.
"From the commencement of his life to its close, I have sometimes doubted whether he ever asked anybody's advice about anything. He would listen to everybody; he would hear everybody; but he rarely, if ever, asked for opinions. I never knew him in trying a case to ask the advice of any lawyer he was associated with.
"As a politician and as President, he arrived at all his conclusions from his own reflections, and when his opinion was once formed, he never doubted but what it was right.
"One great public mistake of his character, as generally received and acquiesced in, is that he is considered by the people of this country as a frank, guileless, and unsophisticated man. There never was a greater mistake. Beneath a smooth surface of candor and apparent declaration of all his thoughts and feelings, he exercised the most exalted tact and the wisest discrimination. He handled and moved men remotely as we do pieces upon a chess-board. He retained through life all the friends he ever had, and he made the wrath of his enemies to praise him. This was not by cunning or intrigue, in the low acceptation of the term, but by far-seeing reason and discernment. He always told enough only of his plans and purposes to induce the belief that he had communicated all, yet he reserved enough to have communicated nothing. He told all that was unimportant with a gushing frankness, yet no man ever kept his real purposes closer, or penetrated the future further with his deep designs.
"You ask me whether he changed his religious opinions towards the close of his life. I think not. As he became involved in matters of the greatest importance, full of great responsibility and great doubt, a feeling of religious reverence, a belief in God and his justice and overruling power increased with him. He was always full of natural religion; he believed in God as much as the most approved Church member, yet he judged of Him by the same system of generalization as he judged everything else. He had very little faith in ceremonials or forms. In fact he cared nothing for the form of anything. But his heart was full of natural and cultivated religion. He believed in the great laws of truth, and the rigid discharge of duty, his accountability to God, the ultimate triumph of the right and the overthrow of wrong. If his religion were to be judged by the lines and rules of Church creeds he would fall far short of the standard; but if by the higher rule of purity of conduct, of honesty of motive, of unyielding fidelity to the right, and acknowledging God as the supreme ruler, then he filled all the requirements of true devotion, and his whole life was a life of love to God, and love of his neighbor as of himself.
"Yours truly,
"Leonard Swett."
The outlines of Mr. Lincoln's Presidential career are alone sufficient to fill a volume, and his history after he had been sworn into office by Chief Justice Taney is so much a history of the entire country, and has been so admirably and thoroughly told by others, that I apprehend I can omit many of the details and still not impair the portrait I have been endeavoring to draw in the mind of the reader. The rapid shifting of scenes in the drama of secession, the disclosure of rebellious plots and conspiracies, the threats of Southern orators and newspapers, all culminating in the attack on Fort Sumter, brought the newly installed President face to face with the stern and grave realities of a civil war.*
* "Lincoln then told me of his last interview with Douglas. 'One day Douglas came rushing in,' he related, 'and said he had just got a telegraph despatch from some friends in Illinois urging him to come out and help set things right in Egypt, and that he would go, or stay in Washington, just where I thought he could do the most good. I told him to do as he chose, but that he could probably do best in Illinois. Upon that he shook hands with me and hurried away to catch the next train. I never saw him again.'"—Henry C. Whitney, MS. letter, November 13, 1866.
Mr. Lincoln's military knowledge had been acquired in the famous campaign against the Indian Chief Black Hawk on the frontier in 1832, the thrilling details of which he had already given the country in a Congressional stump-speech; and to this store of experience he had made little if any addition. It was therefore generally conceded that in grappling with the realities of the problem which now confronted both himself and the country he would be wholly dependent on those who had made the profession of arms a life-work. Those who held such hastily conceived notions of Mr. Lincoln were evidently misled by his well-known and freely advertised Democratic manners. Anybody had a right, it was supposed, to advise him of his duty; and he was so conscious of his shortcomings as a military President that the army officers and Cabinet would run the Government and conduct the war. That was the popular idea. Little did the press, or people, or politicians then know that the country lawyer who occupied the executive chair was the most self-reliant man who ever sat in it, and that when the crisis came his rivals in the Cabinet, and the people everywhere, would learn that he and he alone would be master of the situation.
It is doubtless true that for a long time after his entry into office he did not assert himself; that is, not realizing the gigantic scale upon which the war was destined to be fought, he may have permitted the idea to go forth that being unused to the command of armies he would place himself entirely in the hands of those who were.*
* I was in Washington in the Indian service for a few days before August, 1861, and I merely said to Lincoln one day, 'Everything is drifting into the war, and I guess you will have to put me in the army.' He looked up from his work and said, good-humoredly, 'I'm making generals now. In a few days I will be making quartermasters, and then I'll fix you.'"—-H. C. Whitney, MS. letter, June 13, 1866.
The Secretary of State, whose ten years in the Senate had acquainted him with our relations to foreign powers, may have been lulled into the innocent belief that the Executive would have no fixed or definite views on international questions. So also of the other Cabinet officers; but alas for their fancied security! It was the old story of the sleeping lion. Old politicians, eying him with some distrust and want of confidence, prepared themselves to control his administration, not only as a matter of right, but believing that he would be compelled to rely upon them for support. A brief experience taught them he was not the man they bargained for.

Next in importance to the attack on Fort Sumter, from a military standpoint, was the battle of Bull Run. How the President viewed it is best illustrated by an incident furnished by an old friend * who was an associate of his in the Legislature of Illinois, and who was in Washington when the engagement took place.
* Robert L. Wilson, MS., Feb. 10, 1866.
"The night after the battle," he relates, "accompanied by two Wisconsin Congressmen, I called at the White House to get the news from Manassas, as it was then called, having failed in obtaining any information at Seward's office and elsewhere. Stragglers were coming with all sorts of wild rumors, but nothing more definite than that there had been a great engagement; and the bearer of each report had barely escaped with his life. Messengers bearing despatches to the President and Secretary of War were constantly arriving, but outsiders could gather nothing worthy of belief. Having learned that Mr. Lincoln was at the War Department we started thither, but found the building surrounded by a great crowd, all as much in the dark as we. Removing a short distance away we sat down to rest. Presently Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Nicolay, his private secretary, came along, headed for the White House. It was proposed by my companions that as I was acquainted with the President I should join him and ask for the news. I did so, but he said that he had already told more than under the rules of the War Department he had any right to, and that, although he could see no harm in it, the Secretary of War had forbidden his imparting information to persons not in the military service. 'These war fellows,' he said, complainingly, 'are very strict with me, and I regret that I am prevented from telling you anything; but I must obey them, I suppose, until I get the hang of things.' 'But, Mr. President,' I insisted, 'if you cannot tell me the news, you can at least indicate its nature, that is, whether good or bad.' The suggestion struck him favorably. Grasping my arm he leaned over, and placing his face near my ear, said, in a shrill but subdued voice, 'It's d———d bad.' It was the first time I had ever heard him use profane language, if indeed it was profane in that connection; but later, when the painful details of the fight came in, I realized that, taking into consideration the time and the circumstances, no other term would have contained a truer qualification of the word 'bad.'"
"About one week after the battle of Bull Run," relates another old friend—Whitney—from Illinois, "I made a call on Mr. Lincoln, having no business except to give him some presents which the nuns at the Osage Mission school in Kansas had sent to him through me. A Cabinet meeting had just adjourned, and I was directed to go at once to his room. He was keeping at bay a throng of callers, but, noticing me enter, arose and greeted me with his old-time cordiality. After the room had been partially cleared of visitors Secretary Seward came in and called up a case which related to the territory of New Mexico. 'Oh, I see,' said Lincoln; 'they have neither Governor nor Government. Well, you see Jim Lane; the secretary is his man, and he must hunt him up,' Seward then left, under the impression, as I then thought, that Lincoln wanted to get rid of him and diplomacy at the same time. Several other persons were announced, but Lincoln notified them all that he was busy and could not see them. He was playful and sportive as a child, told me all sorts of anecdotes, dealing largely in stories about Charles James Fox, and enquired after several odd characters whom we both knew in Illinois. While thus engaged General James was announced. This officer had sent in word that he would leave town that evening, and must confer with the President before going. 'Well, as he is one of the fellows who make cannons,' observed Lincoln, 'I suppose I must see him. Tell him when I get through with Whitney I'll see him.' No more cards came up, and James left about five o'clock, declaring that the President was closeted with 'an old Hoosier from Illinois, and was telling dirty yarns while the country was quietly going to hell.' But, however indignant General James may have felt, and whatever the people may have thought, still the President was full of the war. He got down his maps of the seat of war," continues Whitney, "and gave me a full history of the preliminary discussions and steps leading to the battle of Bull Run. He was opposed to the battle, and explained to General Scott by those very maps how the enemy could by the aid of the railroad reinforce their army at Manassas Gap until they had brought every man there, keeping us meanwhile successfully at bay. 'I showed to General Scott our paucity of railroad advantages at that point,' said Lincoln, 'and their plenitude, but Scott was obdurate and would not listen to the possibility of defeat. Now you see I was right, and Scott knows it, I reckon. My plan was, and still is, to make a strong feint against Richmond and distract their forces before attacking Manassas. That problem General McClellan is now trying to work out.' Mr. Lincoln then told me of the plan he had recommended to McClellan, which was to send gunboats up one of the rivers—not the James—in the direction of Richmond, and divert the enemy there while the main attack was made at Manassas. I took occasion to say that McClellan was ambitious to be his successor. 'I am perfectly willing,' he answered, 'if he will only put an end to this war.'"*
* This interview with Lincoln was written out during the war, and contains many of his peculiarities of expression.
The interview of Mr. Whitney with the President on this occasion is especially noteworthy because the latter unfolded to him his idea of the general plan formed in his mind to suppress the rebellion movement and defeat the Southern army. "The President," continues Mr. Whitney, "now explained to me his theory of the Rebellion by the aid of the maps before him. Running his long forefinger down the map he stopped at Virginia. 'We must drive them away from here (Manassas Gap),' he said, 'and clear them out of this part of the State so that they cannot threaten us here (Washington) and get into Maryland. We must keep up a good and thorough blockade of their ports. We must march an army into east Tennessee and liberate the Union sentiment there. Finally we must rely on the people growing tired and saying to their leaders: 'We have had enough of this thing, we will bear it no longer.'"
Such was Mr. Lincoln's plan for heading off the Rebellion in the summer of 1861. How it enlarged as the war progressed, from a call for seventy-five thousand volunteers to one for five hundred thousand men and five hundred millions of dollars, is a matter now of well-known history. The war once inaugurated, it was plain the North had three things to do. These were: the opening of the Mississippi River; the blockade of the Southern ports; and the capture of Richmond. To accomplish these great and vital ends the deadly machinery of war was set in motion. The long-expected upheaval had come, and as the torrent of fire broke forth the people in the agony of despair looking aloft cried out, "Is our leader equal to the task?" That he was the man for the hour is now the calm, unbiassed judgment of all mankind.
The splendid victories early in 1862 in the southwest, which gave the Union cause great advance toward the entire redemption of Kentucky, Tennessee, and Missouri from the presence of rebel armies and the prevalence of rebel influence, were counterbalanced by the dilatory movements and inactive policy of McClellan, who had been appointed in November of the preceding year to succeed the venerable Scott. The forbearance of Lincoln in dealing with McClellan was only in keeping with his well-known spirit of kindness; but, when the time came and circumstances warranted it, the soldier-statesman found that the President not only comprehended the scope of the war, but was determined to be commander-in-chief of the army and navy himself. When it pleased him to place McClellan again at the head of affairs, over the protest of such a wilful and indomitable spirit as Stanton, he displayed elements of rare leadership and evidence of uncommon capacity. His confidence in the ability and power of Grant, when the press and many of the people had turned against the hero of Vicksburg, was but another proof of his sagacity and sound judgment.
As the bloody drama of war moves along we come now to the crowning act in Mr. Lincoln's career—that sublime stroke with which his name will be forever and indissolubly united—the emancipation of the slaves. In the minds of many people there had been a crying need for the liberation of the slaves. Laborious efforts had been made to hasten the issuance by the President of the Emancipation Proclamation, but he was determined not to be forced into premature and inoperative measures. Wendell Phillips abused and held him up to public ridicule from the stump in New England. Horace Greeley turned the batteries of the New York Tribune against him; and, in a word, he encountered all the rancor and hostility of his old friends the Abolitionists. General Frémont having in the fall of 1861 undertaken by virtue of his authority as a military commander to emancipate the slaves in his department, the President annulled the order, which he characterized as unauthorized and premature. This precipitated an avalanche of fanatical opposition. Individuals and delegations, many claiming to have been sent by the Lord, visited him day after day, and urged immediate emancipation. In August, 1862, Horace Greeley repeated the "prayer of twenty millions of people" protesting against any further delay. Such was the pressure from the outside. All his life Mr. Lincoln had been a believer in the doctrine of gradual emancipation. He advocated it while in Congress in 1848; yet even now, as a military necessity, he could not believe the time was ripe for the general liberation of the slaves. All the coercion from without, and all the blandishments from within, his political household failed to move him. An heroic figure, indifferent alike to praise and blame, he stood at the helm and waited. In the shadow of his lofty form the smaller men could keep up their petty conflicts. Towering thus, he overlooked them all, and fearlessly abided his time. At last the great moment came. He called his Cabinet together and read the decree. The deed was done, unalterably, unhesitatingly, irrevocably, and triumphantly. The people, at first profoundly impressed, stood aloof, but, seeing the builder beside the great structure he had so long been rearing, their confidence was abundantly renewed. It was a glorious work, "sincerely believed to be an act of justice warranted by the constitution upon military necessity," and upon it its author "invoked the considerate judgment of mankind and the gracious favor of Almighty God." I believe Mr. Lincoln wished to go down in history as the liberator of the black man. He realized to its fullest extent the responsibility and magnitude of the act, and declared it was "the central act of his administration and the great event of the nineteenth century." Always a friend of the negro, he had from boyhood waged a bitter unrelenting warfare against his enslavement. He had advocated his cause in the courts, on the stump, in the Legislature of his State and that of the nation, and, as if to crown it with a sacrifice, he sealed his devotion to the great cause of freedom with his blood. As the years roll slowly by, and the participants in the late war drop gradually out of the ranks of men, let us pray that we may never forget their deeds of patriotic valor; but even if the details of that bloody struggle grow dim, as they will with the lapse of time, let us hope that so long as a friend of free man and free labor lives the dust of forgetfulness may never settle on the historic form of Abraham Lincoln.
As the war progressed, there was of course much criticism of Mr. Lincoln's policy, and some of his political rivals lost no opportunity to encourage opposition to his methods. He bore everything meekly and with sublime patience, but as the discontent appeared to spread he felt called upon to indicate his course. On more than one occasion he pointed out the blessings of the Emancipation Proclamation or throttled the clamorer for immediate peace. In the following letter to James C. Conkling* of Springfield, Ill., in reply to an invitation to attend a mass meeting of "Unconditional Union" men to be held at his old home, he not only disposed of the advocates of compromise, but he evinced the most admirable skill in dealing with the questions of the day.
* "Springfield, III., January 11, 1889. "Jesse W. Weik, Esq. "Dear Sir: "I enclose you a copy of the letter dated August 26, 1863, by Mr. Lincoln to me. It has been carefully compared with the original and is a correct copy, except that the words commencing 'I know as fully as one can know' to the words 'You say you will fight to free negroes' were not included in the original, but were telegraphed the next day with instructions to insert. The following short note in Mr. Lincoln's own handwriting accompanied the letter: [Private.] "'War Department, "'Washington City, D. C., August 27, 1862. "'My Dear Conkling: "'I cannot leave here now. Herewith is a letter instead. You are one of the best public readers. I have but one suggestion—read it very slowly. And now God bless you, and all good Union men. "'Yours as ever, "'A. Lincoln."
"Mr. Bancroft, the historian, in commenting on this letter, considers it addressed to me as one who was criticising Mr. Lincoln's policy. On the contrary, I was directed by a meeting of 'Unconditional Union' men to invite Mr. Lincoln to attend a mass meeting composed of such men, and he simply took occasion to address his opponents through the medium of the letter.
"Executive Mansion, Washington, August 26, 1863.
"Hon. James C. Conkling.
"My Dear Sir:
"Your letter inviting me to attend a mass meeting of Unconditional Union men, to be held at the Capitol of Illinois, on the 3d day of September, has been received.
"It would be very agreeable to me to thus meet my old friends at my own home; but I cannot, just now, be absent from here so long as a visit there would require.
"The meeting is to be of all those who maintain unconditional devotion to the Union; and I am sure my old political friends will thank me for tendering, as I do, the nation's gratitude to those other noble men, whom no partisan malice, or partisan's hope, can make false to the nation's life.
"There are those who are dissatisfied with me. To such I would say: You desire peace; and you blame me that we do not have it. But how can we attain it? There are but three conceivable ways.
"First, to suppress the rebellion by force of arms. This I am trying to do. Are you for it? If you are, so far we are agreed. If you are not for it, a second way is, to give up the Union. I am against this. Are you for it? If you are, you should say so plainly. If you are not for force, nor yet for dissolution, there only remains some imaginable compromise. I do not believe any compromise, embracing the maintenance of the Union, is now possible. All I learn leads to a directly opposite belief. The strength of the rebellion is its military—its army. That army dominates all the country and all the people within its range. Any offer of terms made by any man or men within that range in opposition to that army is simply nothing for the present, because such man or men have no power whatever to enforce their side of a compromise, if one were made with them. To illustrate: suppose refugees from the South, and peace men of the North, get together in convention and frame and proclaim a compromise embracing a restoration of the Union; in what way can that compromise be used to keep Lee's army out of Pennsylvania? Meade's army can keep Lee's army out of Pennsylvania, and I think can ultimately drive it out of existence.
"But no paper compromise, to which the controllers of Lee's army are not agreed, can at all affect that army. In an effort at such compromise we should waste time, which the enemy would improve to our disadvantage; and that would be all. A compromise, to be effective, must be made either with those who control the rebel army, or with the people first liberated from the domination of that army by the success of our own army. Now allow me to assure you that no word or intimation from that rebel army or from any of the men controlling it, in relation to any peace compromise, has ever come to my knowledge or belief.
"All changes and insinuations to the contrary are deceptive and groundless. And I promise you that, if any such proposition shall hereafter come, it shall not be rejected and kept a secret from you. I freely acknowledge myself the servant of the people, according to the bond of service—the United States Constitution, and that, as such, I am responsible to them.
"But to be plain, you are dissatisfied with me about the negro. Quite likely there is a difference of opinion between you and myself upon that subject.
"I certainly wish that all men could be free, while I suppose you do not. Yet I have neither adopted nor proposed any measure which is not consistent with even your view, provided you are for the Union. I suggested compensated emancipation; to which you replied you wished not to be taxed to buy negroes. But I had not asked you to be taxed to buy negroes, except in such way as to save you from greater taxation to save the Union exclusively by other means.
"You dislike the Emancipation Proclamation, and, perhaps, would have it retracted. You say it is unconstitutional—I think differently. I think the constitution invests its Commander-in-chief with the law of war in time of war. The most that can be said, if so much, is that slaves are property. Is there—has there ever been—any question that by the law of war, property, both of enemies and friends, may be taken when needed?
"And is it not needed wherever taking it helps us or hurts the enemy? Armies the world over destroy enemies' property when they cannot use it; and even destroy their own to keep it from the enemy. Civilized belligerents do all in their power to help themselves or hurt the enemy, except a few things regarded as barbarous or cruel.
"Among the exceptions are the massacre of vanquished foes and non-combatants, male and female.
"But the proclamation, as law, either is valid or is not valid.
"If it is not valid, it needs no retraction. If it is valid, it cannot be retracted any more than the dead can be brought to life. Some of you profess to think its retraction would operate favorably for the Union.
"Why better after the retraction than before the issue?
"There was more than a year and a half of trial to suppress the rebellion before the proclamation issued, the last one hundred days of which passed under an explicit notice that it was coming, unless averted by those in revolt returning to their allegiance.
"The war has certainly progressed as favorably for us since the issue of the proclamation as before.
"I know as fully as one can know the opinion of others that some of the commanders of our armies in the field who have given us our most important successes believe the emancipation policy and the use of the colored troops constituted the heaviest blow yet dealt to the Rebellion, and that at least one of these important successes could not have been achieved when it was but for the aid of black soldiers. Among the commanders holding these views are some who have never had any affinity with what is called abolitionism or with Republican party policies, but who held them purely as military opinions. I submit these opinions as being entitled to some weight against the objections often urged that emancipation and arming the blacks are unwise as military measures, and were not adopted as such in good faith.
"You say you will not fight to free negroes. Some of them seem willing to fight for you; but no matter.
"Fight you, then, exclusively to save the Union. I issued the proclamation on purpose to aid you in saving the Union. Whenever you shall have conquered all resistance to the Union, if I shall urge you to continue fighting, it will be an apt time then for you to declare you will not fight to free negroes.
"I thought that in your struggle for the Union, to whatever extent the negroes should cease helping the enemy, to that extent it weakened the enemy in his resistance to you. Do you think differently? I thought that whatever negroes can be got to do as soldiers leaves just so much less for white soldiers to do, in saving the Union. Does it appear otherwise to you?
"But negroes, like other people, act upon motives. Why should they do anything for us, if we will do nothing for them? If they stake their lives for us, they must be prompted by the strongest motive—even the promise of freedom. And the promise being made, must be kept.
"The signs look better. The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea. Thanks to the great North-west for it. Nor yet wholly to them. Three hundred miles up they met New England, Empire, Keystone, and Jersey, hewing their way right and left. The Sunny South too, in more colors than one, also lent a hand.
"On the spot, their part of the history was jotted down in black and white. The job was a great national one; and let none be barred who bore an honorable part in it. And while those who have cleared the great river may well be proud, even that is not all. It is hard to say that anything has been more bravely and well done than at Antietam, Murfreesboro, Gettysburg, and on many fields of lesser note. Nor must Uncle Sam's web-feet be forgotten. At all the watery margins they have been present. Not only on the deep sea, the broad bay, and the rapid river, but also up the narrow, muddy bayou, and wherever the ground was a little damp, they have been, and made their tracks, thanks to all. For the great republic—for the principle it lives by and keeps alive—for man's vast future—thanks to all.
"Peace does not appear so distant as it did. I hope it will come soon and come to stay, and so come as to be worth the keeping in all future time. It will then have been proved that, among free men, there can be no successful appeal from the ballot to the bullet; and that they who take such appeal are sure to lose their case and pay the cost. And then there will be some black men who can remember that, with silent tongue, and clenched teeth, and steady eye, and well-poised bayonet, they have helped mankind on to this great consummation; while I fear there will be some white ones, unable to forget that, with malignant heart and deceitful speech, they have strove to hinder it.
"Still, let us not be over-sanguine of a speedy final triumph. Let us be quite sober. Let us diligently apply the means, never doubting that a just God, in his own good time, will give us the rightful result.
"Yours very truly,
"A. Lincoln."
The summer and fall of 1864 were marked by Lincoln's second Presidential campaign, he, and Andrew Johnson, of Tennessee, for Vice-President, having been nominated at Baltimore on the 8th of June. Frémont, who had been placed in the field by a convention of malcontents at Cleveland, Ohio, had withdrawn in September, and the contest was left to Lincoln and General George B. McClellan, the nominee of the Democratic convention at Chicago. The canvass was a heated and bitter one. Dissatisfied elements appeared everywhere. The Judge Advocate-General of the army (Holt) created a sensation by the publication of a report giving conclusive proof of the existence of an organized secret association at the North, controlled by prominent men in the Democratic party, whose objects were the overthrow by revolution of the administration in the interest of the rebellion.*
* "Mr. Lincoln was advised, and I also so advised him, that the various military trials in the Northern and Border States, where the courts were free and untrammelled, were unconstitutional and wrong; that they would not and ought not to be sustained by the Supreme Court; that such proceedings were dangerous to liberty. He said he was opposed to hanging; that he did not like to kill his fellow- man; that if the world had no butchers but himself it would go bloodless. When Joseph E. McDonald went to Lincoln about these military trials and asked him not to execute the men who had been convicted by the military commission in Indiana he answered that he would not hang them, but added, 'I'll keep them in prison awhile to keep them from killing the Government.' I am fully satisfied therefore that Lincoln was opposed to these military commissions, especially in the Northern States, where everything was open and free."—David Davis, statement, September 10, 1866, to W. H. H. "I was counsel for Bowles, Milligan, et al.** who had been convicted of conspiracy by military tribunal in Indiana. Early in 1865 I went to Washington to confer with the President, whom I had known, and with whom in earlier days I had practised law on the circuit in Illinois. My clients had been sentenced, and unless the President interfered were to have been executed. Mr. Hendricks, who was then in the Senate, and who seemed to have little faith in the probability of executive clemency, accompanied me to the White House. It was early in the evening, and so many callers and visitors had preceded us we anticipated a very brief interview. Much to our surprise we found Mr. Lincoln in a singularly cheerful and reminiscent mood. He kept us with him till almost eleven o'clock. He went over the history of my clients' crime as shown by the papers in the case, and suggested certain errors and imperfections in the record. The papers, he explained, would have to be returned for correction, and that would consume no little time. 'You may go home, Mr. McDonald,' he said, with a pleased expression, 'and Ill send for you when the papers get back; but I apprehend and hope there will be such a jubilee over yonder,' he added, pointing to the hills of Virginia just across the river, 'we shall none of us want any more killing done.' The papers started on their long and circuitous journey, and sure enough, before they reached Washington again Mr. Lincoln's prediction of the return of peace had proved true."—Hon. Joseph E. McDonald, statement, August 28,1888, to J. W. W.
Threats were rife of a revolution at the North, especially in New York City, if Mr. Lincoln were elected. Mr. Lincoln went steadily on in his own peculiar way. In a preceding chapter Mr. Swett has told us how indifferent he appeared to be regarding any efforts to be made in his behalf. He did his duty as President, and rested secure in the belief that he would be re-elected whatever might be done for or against him. The importance of retaining Indiana in the column of Republican States was not to be overlooked. How the President viewed it, and how he proposed to secure the vote of the State, is shown in the following letter written to General Sherman:
"Executive Mansion,
"Washington, September 19, 1864.
"Major General Sherman:
"The State election of Indiana occurs on the 11th of October, and the loss of it to the friends of the Government would go far towards losing the whole Union cause. The bad effect upon the November election, and especially the giving the State government to those who will oppose the war in every possible way, are too much to risk if it can be avoided. The draft proceeds, notwithstanding its strong tendency to lose us the State. Indiana is the only important State voting in October whose soldiers cannot vote in the field. Anything you can safely do to let her soldiers or any part of them go home and vote at the State election will be greatly in point. They need not remain for the Presidential election, but may return to you at once. This is in no sense an order, but is merely intended to impress you with the importance to the army itself of your doing all you safely can, yourself being the judge of what you can safely do.
"Yours truly,
"A. Lincoln." *
* Unpublished MS.
The election resulted in an overwhelming victory for Lincoln. He received a majority of over four hundred thousand in the popular vote—a larger majority than had ever been received by any other President up to that time. He carried not only Indiana, but all the New England States, New York, Pennsylvania, all the Western States, West Virginia, Tennessee, Louisiana, Arkansas, and the newly admitted State of Nevada. McClellan carried but three states: New Jersey, Delaware, and Kentucky. The result, as Grant so aptly expressed it in his telegram of congratulation, was "a victory worth more to the country than a battle won." A second time Lincoln stood in front of the great Capitol to take the oath of office administered by his former rival, Salmon P. Chase, whom he himself had appointed to succeed the deceased Roger B. Taney. The problem of the war was now fast working its own solution. The cruel stain of slavery had been effaced from the national escutcheon, and the rosy morn of peace began to dawn behind the breaking clouds of the great storm.*
* Bearing on the mission of the celebrated Peace Commission the following bit of inside history is not without interest: "I had given notice that at one o'clock on the 31st of January I would call a vote on the proposed constitutional amendment abolishing slavery in the United States. The opposition caught up a report that morning that Peace Commissioners were on the way to the city or were in the city. Had this been true I think the proposed amendment would have failed, as a number who voted for it could easily have been prevailed upon to vote against it on the ground that the passage of such a proposition would be offensive to the commissioners. Accordingly I wrote the President this note: "'House of Representatives, "'January 31, 1865. "'Dear Sir: "'The report is in circulation in the House that Peace Commissioners are on their way or in the city, and is being used against us. If it is true, I fear we shall lose the bill. Please authorize me to contradict it, if it is not true. "'Respectfully, "'J. M. Ashley.' To the President. Almost immediately came the reply, written on the back of my note: "'So far as I know there are no peace Commissioners in the city or likely to be in it. "'A. Lincoln.' January 31, 1865. "Mr. Lincoln knew that the commissioners were then on their way to Fortress Monroe, where he expected to meet them, and afterwards did meet them. You see how he answered my note for my purposes, and yet how truly. You know how he afterwards met the so-called commission, whom he determined at the time he wrote this note should not come to the city. One or two gentlemen were present when he wrote the note, to whom he read it before sending it to me."—J. M. Ashley, M. C., letter, November 23, 1866, MS.
Lincoln, firm but kind, in his inaugural address bade his misguided brethren of the South come back. With a fraternal affection characteristic of the man, and strictly in keeping with his former utterances, he asked for the return of peace. "With malice towards none, with charity for all," he implored his fellow-countrymen, "with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation's wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphans, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and a lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations." With the coming of spring the great armies, awakening from their long winter's sleep, began preparations for the closing campaign. Sherman had already made that grandest march of modern times, from the mountains of Tennessee through Georgia to the sea, while Grant, with stolid indifference to public criticism and newspaper abuse, was creeping steadily on through swamp and ravine to Richmond. Thomas had defeated Hood in Tennessee, sending the latter back with his army demoralized, cut in pieces, and ruined. The young and daring Sheridan had driven Early out of the Shenandoah Valley after a series of brilliant engagements. The "Kearsarge" had sunk the "Alabama" in foreign waters. Farragut had captured Mobile, and the Union forces held undisputed possession of the West and the Mississippi Valley from the lakes to the gulf. Meanwhile Sherman, undaunted by the perils of a further march through the enemy's country, returning from the sea, was aiming for Richmond, where Grant, with bull-dog tenacity, held Lee firmly in his grasp. Erelong, the latter, with his shattered army reduced to half its original numbers, evacuated Richmond, with Grant in close pursuit. A few days later the boys in blue overtook those in gray at Appomattox Court-house, and there, under the warm rays of an April sun, the life was at last squeezed out of the once proud but now prostrate Confederacy. "The sun of peace had fairly risen. The incubus of war that had pressed upon the nation's heart for four long, weary years was lifted; and the nation sprang to its feet with all possible demonstrations of joyous exultation."
Mr. Lincoln himself had gone to the scene of hostilities in Virginia. He watched the various military manoeuvres and operations, which involved momentous consequences to the country; he witnessed some of the bloody engagements participated in by the army of the Potomac. Within a day after its surrender he followed the victorious Union army into the city of Richmond. In this unfortunate city—once the proud capital of Virginia—now smoking and in ruins, he beheld the real horrors of grim war. Here too he realized in a bountiful measure the earnest gratitude of the colored people, who everywhere crowded around him and with cries of intense exultation greeted him as their deliverer. He now returned to Washington, not like Napoleon fleeing sorrowfully from Waterloo bearing the tidings of his own defeat, but with joy proclaiming the era of Union victory and peace among men. "The war was over. The great rebellion which for four long years had been assailing the nation's life was quelled. Richmond, the rebel capital, was taken; Lee's army had surrendered; and the flag of the Union was floating in reassured supremacy over the whole of the National domain. Friday, the 14th of April, the anniversary of the surrender of Fort Sumter in 1861 by Major Anderson to the rebel forces, had been designated by the Government as the day on which the same officer should again raise the American flag upon the fort in the presence of an assembled multitude, and with ceremonies befitting so auspicious an occasion. The whole land rejoiced at the return of peace and the prospect of renewed prosperity to the country. President Lincoln shared this common joy, but with a deep intensity of feeling which no other man in the whole land could ever know. He saw the full fruition of the great work which had rested so heavily on his hands and heart for four years past. He saw the great task—as momentous as had ever fallen to the lot of man—which he had approached with such unfeigned diffidence, nearly at an end. The agonies of war had passed away; he had won the imperishable renown which is the reward of those who save their country; and he could devote himself now to the welcome task of healing the wounds which war had made, and consolidating by a wise and magnanimous policy the severed sections of our common Union. His heart was full of the generous sentiments which these circumstances were so well calculated to inspire. He was cheerful and hopeful of the success of his broad plans for the treatment of the conquered people of the South. With all the warmth of his loving nature, after the four years of storm through which he had been compelled to pass, he viewed the peaceful sky on which the opening of his second term had dawned. His mind was free from forebodings and filled only with thoughts of kindness and of future peace." But alas for the vanity of human confidence! The demon of assassination lurked near. In the midst of the general rejoicing at the return of peace Mr. Lincoln was stricken down by the assassin, John Wilkes Booth, in Ford's Theatre at Washington. The story of his death, though oft repeated, is the saddest and most impressive page in American history. I cannot well forbear reproducing its painful and tragic details here.*
* For the details of the assassination and the capture and subsequent history of the conspirators, I am indebted to Mrs. Gertrude Garrison, of New York, who has given the subject no little study and investigation. J. W. W.

"Mr. Lincoln for years had a presentiment that he would reach a high place and then be stricken down in some tragic way. He took no precautions to keep out of the way of danger. So many threats had been made against him that his friends were alarmed, and frequently urged him not to go out unattended. To all their entreaties he had the same answer: 'If they kill me the next man will be just as bad for them. In a country like this, where our habits are simple, and must be, assassination is always possible, and will come if they are determined upon it.'
"Whatever premonition of his tragic fate he may have had, there is nothing to prove that he felt the nearness of the awful hour. Doomed men rise and go about their daily duties as unoppressed, often, as those whose paths know no shadow. On that never-to-be-forgotten 14th of April President Lincoln passed the day in the usual manner. In the morning his son, Captain Robert Lincoln, breakfasted with him. The young man had just returned from the capitulation of Lee, and he described in detail all the circumstances of that momentous episode of the close of the war, to which the President listened with the closest interest. After breakfast the President spent an hour with Speaker Colfax, talking about his future policy, about to be submitted to his Cabinet. At eleven o'clock he met the Cabinet. General Grant was present. He spent the afternoon with Governor Oglesby, Senator Yates, and other friends from Illinois. He was invited by the manager of Ford's theatre, in Washington, to attend in the evening a performance of the play, 'Our American Cousin,' with Laura Keene as the leading lady. This play, now so well known to all play-goers, in which the late Southern afterward made fortune and fame, was then comparatively unheralded. Lincoln was fond of the drama. Brought up in a provincial way, in the days when theatres were unknown outside of the larger cities, the beautiful art of the actor was fresh and delightful to him.
"He loved Shakespeare, and never lost an opportunity of seeing his characters rendered by the masters of dramatic art. But on that evening, it is said, he was not eager to go. The play was new, consequently not alluring to him; but he yielded to the wishes of Mrs. Lincoln and went. They took with them Miss Harris and Major Rathbone, daughter and stepson of Senator Harris, of New York.
"The theatre was crowded. At 9: 20 the President and his party entered. The audience rose and cheered enthusiastically as they passed to the 'state box' reserved for them. Little did anyone present dream that within the hour enthusiasm would give place to shrieks of horror. It was ten o'clock when Booth came upon the scene to enact the last and greatest tragedy of the war. He had planned carefully, but not correctly. A good horse awaited him at the rear of the theatre, on which he intended to ride into friendly shelter among the hills of Maryland. He made his way to the President's box—a double one in the second tier, at the left of the stage. The separating partition had been removed, and both boxes thrown into one.
"Booth entered the theatre nonchalantly, glanced at the stage with apparent interest, then slowly worked his way around into the outer passage leading toward the box occupied by the President. At the end of an inner passage leading to the box door, one of the President's "messengers" was stationed to prevent unwelcome intrusions. Booth presented a card to him, stating that Mr. Lincoln had sent for him, and was permitted to pass. After gaining an entrance and closing the hall door, he took a piece of board prepared for the occasion, and placed one end of it in an indentation in the wall, about four feet from the floor, and the other against the molding of the door panel a few inches higher, making it impossible for any one to enter from without. The box had two doors. He bored a gimlet hole in the panel of one, reaming it out with his knife, so as to leave it a little larger than a buckshot on the inside, while on the other side it was big enough to give his eye a wide range. Both doors had spring locks. To secure against their being locked he had loosened the screws with which the bolts were fastened.
"So deliberately had he planned that the very seats in the box had been arranged to suit his purpose by an accomplice, one Spangler, an attaché of the theatre. The President sat in the left-hand corner of the box, nearest the audience, in an easy arm-chair. Next him, on the right, sat Mrs. Lincoln. A little distance to the right of both, Miss Harris was seated, with Major Rathbone at her left, and a little in the rear of Mrs. Lincoln, who, intent on the play, was leaning forward, with one hand resting on her husband's knee. The President was leaning upon one hand, and with the other was toying with a portion of the drapery. His face was partially turned to the audience, and wore a pleasant smile.
"The assassin swiftly entered the box through the door at the right, and the next instant fired. The ball entered just behind the President's left ear, and, though not producing instantaneous death, completely obliterated all consciousness.
"Major Rathbone heard the report, and an instant later saw the murderer, about six feet from the President, and grappled with him, but his grasp was shaken off. Booth dropped his pistol and drew a long, thin, deadly-looking knife, with which he wounded the major. Then, touching his left hand to the railing of the box, he vaulted over to the stage, eight or nine feet below. In that descent an unlooked-for and curious thing happened, which foiled all the plans of the assassin and was the means of bringing him to bay at last. Lincoln's box was draped with the American flag, and Booth, in jumping, caught his spur in its folds, tearing it down and spraining his ankle. He crouched as he fell, falling upon one knee, but soon straightened himself and stalked theatrically across the stage, brandishing his knife and shouting the State motto of Virginia, 'Sic semper tyrannis!' afterward adding, 'The South is avenged!' He made his exit on the opposite side of the stage, passing Miss Keene as he went out. A man named Stewart, a tall lawyer of Washington, was the only person with presence of mind enough to spring upon the stage and follow him, and he was too late.
"It had all been done so quickly and dramatically that many in the audience were dazed, and could not understand that anything not a part of the play had happened. When, at last, the awful truth was known to them there ensued a scene, the like of which was never known in a theatre before. Women shrieked, sobbed, and fainted. Men cursed and raved, or were dumb with horror and amazement. Miss Keene stepped to the front and begged the frightened and dismayed audience to be calm. Then she entered the President's box with water and stimulants. Medical aid was summoned and came with flying feet, but came too late. The murderer's bullet had done its wicked work well. The President hardly stirred in his chair, and never spoke or showed any signs of consciousness again.

"They carried him immediately to the house of Mr. Petersen, opposite the theatre, and there, at 7:22 the next morning, the 15th of April, he died.
"The night of Lincoln's assassination was a memorable one in Washington. Secretary Seward was attacked and wounded while lying in bed with a broken arm.
"The murder of the President put the authorities on their guard against a wide-reaching conspiracy, and threw the public into a state of terror. The awful event was felt even by those who knew not of it. Horsemen clattered through the silent streets of Washington, spreading the sad tidings, and the telegraph wires carried the terrible story everywhere. The nation awakened from its dream of peace on the 15th of April, 1865, to learn that its protector, leader, friend, and restorer had been laid low by a stage-mad 'avenger.' W. O. Stoddard, in his 'Life of Lincoln,' says: 'It was as if there had been a death in every house throughout the land. By both North and South alike the awful news was received with a shudder and a momentary spasm of unbelief. Then followed one of the most remarkable spectacles in the history of the human race, for there is nothing else at all like it on record. Bells had tolled before at the death of a loved ruler, but never did all bells toll so mournfully as they did that day. Business ceased. Men came together in public meetings as if by a common impulse, and party lines and sectional hatreds seemed to be obliterated.
"The assassination took place on Friday evening, and on the following Sunday funeral services were held in all the churches in the land, and every church was draped in mourning."
The death of Mr. Lincoln was an indescribable shock to his fellow countrymen. The exultation of victory over the final and successful triumph of Union arms was suddenly changed to the lamentations of grief. In every household throughout the length and breadth of the land there was a dull and bitter agony as the telegraph bore tidings of the awful deed. The public heart, filled with joy over the news from Appomattox, now sank low with a sacred terror as the sad tidings from the Capitol came in. In the great cities of the land all business instantly ceased. Flags drooped half-mast from every winged messenger of the sea, from every church spire, and from every public building. Thousands upon thousands, drawn by a common feeling, crowded around every place of public resort and listened eagerly to whatever any public speaker chose to say. Men met in the streets and pressed each other's hands in silence, and burst into tears. The whole nation, which the previous day had been jubilant and hopeful, was precipitated into the depths of a profound and tender woe. It was a memorable spectacle to the world—a whole nation plunged into heartfelt grief and the deepest sorrow.
The body of the dead President, having been embalmed, was removed from the house in which the death occurred to the White House, and there appropriate funeral services were held. After the transfer of the remains to the Capitol, where the body was exposed to view in the Rotunda for a day, preparations were made for the journey to the home of the deceased in Illinois. On the following day (April 21) the funeral train left Washington amid the silent grief of the thousands who had gathered to witness its departure. At all the great cities along the route stops were made, and an opportunity was given the people to look on the face of the illustrious dead. The passage of this funeral train westward through country, village, and city, winding across the territory of vast States, along a track of more than fifteen hundred miles, was a pageant without a parallel in the history of the continent or the world. At every halt in the sombre march vast crowds, such as never before had collected together, filed past the catafalque for a glimpse of the dead chieftain's face. Farmers left their farms, workmen left their shops, societies and soldiers marched in solid columns, and the great cities poured forth their population in countless masses. From Washington the funeral train moved to Baltimore, thence to Harrisburg, Philadelphia, New York, Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Columbus, Indianapolis, Chicago, and at last to Springfield.
As the funeral cortège passed through New York it was reverently gazed upon by a mass of humanity impossible to enumerate. No ovation could be so eloquent as the spectacle of the vast population, hushed and bareheaded under the bright spring sky, gazing upon his coffin. Lincoln's own words over the dead at Gettysburg came to many as the stately car went by: "The world will little note nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here."
It was remembered, too, that on the 22d of February, 1861, as he raised the American flag over Independence Hall, in Philadelphia, he spoke of the sentiment in the Declaration of Independence which gave liberty not only to this country, but, "I hope," he said, "to the world for all future time. But if this country cannot be saved without giving up that principle, I was about to say I would rather be assassinated upon this spot than surrender it." When he died the veil that hid his greatness was torn aside, and the country then knew what it had possessed and lost in him. A New York paper, of April 29, 1865, said: "No one who personally knew him but will now feel that the deep, furrowed sadness of his face seemed to forecast his fate. The genial gentleness of his manner, his homely simplicity, the cheerful humor that never failed, are now seen to have been but the tender light that played around the rugged heights of his strong and noble nature. It is small consolation that he died at the moment of the war when he could best be spared, for no nation is ever ready for the loss of such a friend. But it is something to remember that he lived to see the slow day breaking. Like Moses, he had marched with us through the wilderness. From the height of patriotic vision he beheld the golden fields of the future waving in peace and plenty. He beheld, and blessed God, but was not to enter in."
In a discourse delivered on Lincoln on the 23d of that month, Henry Ward Beecher said:
"And now the martyr is moving in triumphal march, mightier than when alive. The nation rises up at every stage of his coming. Cities and states are his pall-bearers, and the cannon speaks the hours with solemn progression. Dead, dead, dead, he yet speaketh. Is Washington dead? Is Hampden dead? Is any man that was ever fit to live dead? Disenthralled of flesh, risen to the unobstructed sphere where passion never comes, he begins his illimitable work. His life is now grafted upon the infinite, and will be fruitful as no earthly life can be. Pass on, thou that hast overcome. Ye people, behold the martyr whose blood, as so many articulate words, pleads for fidelity, for law, for liberty."
The funeral train reached Springfield on the 3d of May. The casket was borne to the State House and placed in Representative Hall—the very chamber in which in 1854 the deceased had pronounced that fearful invective against the sin of human slavery. The doors were thrown open, the coffin lid was removed, and we who had known the illustrious dead in other days, and before the nation lay its claim upon him, moved sadly through and looked for the last time on the silent, upturned face of our departed friend. All day long and through the night a stream of people filed reverently by the catafalque. Some of them were his colleagues at the bar; some his old friends from New Salem; some crippled soldiers fresh from the battle-fields of the war; and some were little children who, scarce realizing the impressiveness of the scene, were destined to live and tell their children yet to be born the sad story of Lincoln's death.
At ten o'clock in the morning of the second day, as a choir of two-hundred-and-fifty voices sang "Peace, Troubled Soul," the lid of the casket was shut down forever. The remains were borne outside and placed in a hearse, which moved at the head of a procession in charge of General Joseph Hooker to Oak Ridge cemetery. There Bishop Matthew Simpson delivered an eloquent and impressive funeral oration, and Rev. Dr. Gurley, of Washington, offered up the closing prayer. While the choir chanted "Unveil Thy Bosom, Faithful Tomb," the vault door opened and received to its final rest all that was mortal of Abraham Lincoln.
"It was soon known that the murder of Lincoln was one result of a conspiracy which had for its victims Secretary Seward and probably Vice-President Johnson, Secretary Stanton, General Grant, and perhaps others. Booth had left a card for Mr. Johnson the day before, possibly with the intention of killing him. Mr. Seward received wounds, from which he soon recovered. Grant, who was to have accompanied Lincoln to the theatre on the night of the assassination, and did not, escaped unassailed. The general conspiracy was poorly planned and lamely executed. It involved about twenty-five persons. Mrs. Surratt, David C. Harold, Lewis Payne, Edward Spangler, Michael O'Loughlin, J. W. Atzerodt, Samuel Arnold, and Dr. Samuel Mudd, who set Booth's leg, which was dislocated by the fall from the stage-box, were among the number captured and tried.
"After the assassination Booth escaped unmolested from the theatre, mounted his horse, and rode away, accompanied by Harold, into Maryland. Cavalrymen scoured the country, and eleven days after the shooting discovered them in a barn on Garrett's farm, near Port Royal on the Rappahannock. The soldiers surrounded the barn and demanded a surrender. After the second demand Harold surrendered, under a shower of curses from Booth, but Booth refused, declaring that he would never be taken alive. The captain of the squad then fired the barn. A correspondent thus describes the scene:
"'The blaze lit up the recesses of the great barn till every wasp's nest and cobweb in the roof were luminous, flinging streaks of red and violet across the tumbled farm gear in the corner. They tinged the beams, the upright columns, the barricades, where clover and timothy piled high held toward the hot incendiary their separate straws for the funeral pile. They bathed the murderer's retreat in a beautiful illumination, and, while in bold outlines his figure stood revealed, they rose like an impenetrable wall to guard from sight the hated enemy who lit them. Behind the blaze, with his eye to a crack, Colonel Conger saw Wilkes Booth standing upright upon a crutch. At the gleam of fire Booth dropped his crutch and carbine, and on both hands crept up to the spot to espy the incendiary and shoot him dead. His eyes were lustrous with fever, and swelled and rolled in terrible beauty, while his teeth were fixed, and he wore the expression of one in the calmness before frenzy. In vain he peered, with vengeance in his look; the blaze that made him visible concealed his enemy. A second he turned glaring at the fire, as if to leap upon it and extinguish it, but it had made such headway that he dismissed the thought. As calmly as upon the battle-field a veteran stands amidst the hail of ball and shell and plunging iron, Booth turned and pushed for the door, carbine in poise, and the last resolve of death, which we name despair, set on his high, bloodless forehead.
"'Just then Sergeant Boston Corbett fired through a crevice and shot Booth in the neck. He was carried out of the barn and laid upon the grass, and there died about four hours afterward. Before his misguided soul passed into the silence of death he whispered something which Lieutenant Baker bent down to hear. "Tell mother I die for my country," he said, faintly. Reviving a moment later he re peated the words, and added, "I thought I did for the best."
"His days of hiding and fleeing from his pursuers had left him pale, haggard, dirty, and unkempt. He had cut off his mustache and cropped his hair close to his head, and he and Harold both wore the Confederate gray uniform.'
"Booth's body was taken to Washington, and a post mortem examination of it held on board the monitor "Montauk," and on the night of the 27th of April it was given in charge of two men in a rowboat, who, it is claimed, disposed of it in secrecy—how, none but themselves know. Numerous stories have been told of the final resting-place of that hated dead man. Whoever knows the truth of it tells it not.
"Sergeant Corbett, who shot Booth, fired without orders. The last instructions given by Colonel Baker to Colonel Conger and Lieutenant Baker were: 'Don't shoot Booth, but take him alive.' Corbett was something of a fanatic, and for a breach of discipline had once been court-martialled and sentenced to be shot. The order, however, was not executed, but he had been drummed out of the regiment. He belonged to Company L of the Sixteenth New York Cavalry. He was English by birth, but was brought up in this country, and learned the trade of hat finisher. While living in Boston he Joined the Methodist Episcopal Church. Never having been baptized, he was at a loss to know what name to adopt, but after making it a subject of prayer he took the name of Boston, in honor of the place of his conversion. He was ever undisciplined and erratic. He is said to be living in Kansas, and draws a pension from the Government.
"Five of the conspirators were tried, and four, Payne, Harold, Atzerodt and Mrs. Surratt, were hanged. Dr. Mudd was sent to the Dry Tortugas for a period of years, and there did such good work among the yellow-fever sufferers during an epidemic that he was pardoned and returned to this country. He died only about two years ago at his home in Maryland, near Washington. John Surratt fled to Italy, and there entered the Papal guards. He was discovered by Archbishop Hughes, and by the courtesy of the Italian government, though the extradition laws did not cover his case, was delivered over to the United States for trial. At his first trial the jury hung; at the second, in which Edwards Pierrepont was the Government counsel, Surratt got off on the plea of limitations. He undertook to lecture, and began at Rockville, Md. The Evening Star, of Washington, reported the lecture, which was widely copied, and was of such a feeble character that it killed him as a lecturer. He went to Baltimore, where, it is said, he still lives. Spangler, the scene-shifter, who was an accomplice of Booth, was sent to the Dry Tortugas, served out his term and died about ten years ago. McLoughlin, who was arrested because of his acquaintance with the conspirators, was sent to the Dry Tortugas and there died.
"Ford's Theatre was never played in after that memorable night. Ten or twelve days after the assassination Ford attempted to open it, but Stanton prevented it, and the Government bought the theatre for $100,000, and converted it into a medical museum. Ford was a Southern sympathizer. He ran two theatres until four years ago, one in Washington and one in Baltimore. Alison Naylor, the livery man who let Booth have his horse, still lives in Washington. Major Rathbone, who was in the box with Lincoln when he was shot, died within the last four years. Stewart, the man who jumped on the stage to follow Booth, and announced to the audience that he had escaped through the alley, died lately. Strange, but very few persons can now be found who were at the theatre that night. Laura Keene died a few years ago.
Booth the assassin was the third son of the eminent English tragedian Junius Brutus Booth, and the brother of the equally renowned Edwin Booth. He was only twenty-six years old when he figured as the chief actor in this horrible drama. He began his dramatic career as John Wilkes, and as a stock actor gained a fair reputation, but had not achieved any special success. He had played chiefly in the South and West, and but a few times in New York. Some time before the assassination of Lincoln he had abandoned his profession on account of a bronchial affection. Those who knew him and saw him on that fatal Friday say that he was restless, like one who, consciously or unconsciously, was overshadowed by some awful fate.
He knew that the President and his party intended to be present at Ford's theatre in the evening, and he asked an acquaintance if he should attend the performance, remarking that if he did he would see some unusually fine acting. He was a handsome man. His eyes were large and dark, his hair dark and inclined to curl, his features finely moulded, his form tall, and his address pleasing.
Frederick Stone, counsel for Harold after Booth's death, is authority for the statement that the occasion for Lincoln's assassination was the sentiment expressed by the President in a speech delivered from the steps of the White House on the night of April 11, when he said: "If universal amnesty is granted to the insurgents I cannot see how I can avoid exacting in return universal suffrage, or at least suffrage on the basis of intelligence and military service." Booth was standing before Mr. Lincoln on the outskirts of the crowd. "That means nigger citizenship," he said to Harold by his side. "Now, by God! I'll put him through." But whatever may have been the incentive, Booth seemed to crave the reprehensible fame that attaches to a bold and dramatically wicked deed. He may, it is true, have been mentally unhinged, but, whether sane or senseless, he made for himself an infamous and endless notoriety when he murdered the patient, forbearing man who had directed our ship of state through the most tempestuous waters it ever encountered.
In the death of Lincoln the South, prostrate and bleeding, lost a friend; and his unholy taking-off at the very hour of the assured supremacy of the Union cause ran the iron into the heart of the North. His sun went down suddenly, and whelmed the country in a darkness which was felt by every heart; but far up the clouds sprang apart, and soon the golden light, flooding the heavens with radiance, illuminated every uncovered brow with the hope of a fair to-morrow. His name will ever be the watchword of liberty. His work is finished, and sealed forever with the veneration given to the blood of martyrs. Yesterday a man reviled and abused, a target for the shafts of malice and hatred: to-day an apostle. Yesterday a power: to-day a prestige, sacred, irresistible. The life and the tragic death of Mr. Lincoln mark an epoch in history from which dates the unqualified annunciation by the American people of the greatest truth in the bible of republicanism—the very keystone of that arch of human rights which is destined to overshadow and remodel every government upon the earth. The glorious brightness of that upper world, as it welcomed his faint and bleeding spirit, broke through upon the earth at his exit—it was the dawn of a day growing brighter as the grand army of freedom follows in the march of time.
Lincoln's place in history will be fixed—aside from his personal characteristics—by the events and results of the war. As a great political leader who quelled a rebellion of eight millions of people, liberated four millions of slaves, and demonstrated to the world the ability of the people to maintain a government of themselves, by themselves, for themselves, he will assuredly occupy no insignificant place.
To accomplish the great work of preserving the Union cost the land a great price. Generations of Americans yet unborn, and humanity everywhere, for years to come will mourn the horrors and sacrifices of the first civil war in the United States; but above the blood of its victims, above the bones of its dead, above the ashes of desolate hearths, will arise the colossal figure of Abraham Lincoln as the most acceptable sacrifice offered by the nineteenth century in expiation of the great crime of the seventeenth. Above all the anguish and tears of that immense hecatomb will appear the shade of Lincoln as the symbol of hope and of pardon.
This is the true lesson of Lincoln's life: real and enduring greatness, that will survive the corrosion and abrasion of time, of change, and of progress, must rest upon character. In certain brilliant and what is understood to be most desirable endowments how many Americans have surpassed him. Yet how he looms above them all! Not eloquence, nor logic, nor grasp of thought; not statesmanship, nor power of command, nor courage; not any nor all of these have made him what he is, but these, in the degree in which he possessed them, conjoined to those qualities comprised in the term character, have given him his fame—have made him for all time to come the great American, the grand, central figure in American—perhaps the world's—history.
The substance of this chapter I delivered in the form of a lecture to a Springfield audience in 1866. W. H. H.
SOON after the death of Mr. Lincoln Dr. J. G. Holland came out to Illinois from his home in Massachusetts to gather up materials for a life of the dead President. The gentleman spent several days with me, and I gave him all the assistance that lay in my power. I was much pleased with him, and awaited with not a little interest the appearance of his book. I felt sure that even after my long and intimate acquaintance with Mr. Lincoln I never fully knew and understood him, and I therefore wondered what sort of a description Dr. Holland, after interviewing Lincoln's old-time friends, would make of his individual characteristics. When the book appeared he said this: "The writer has conversed with multitudes of men who claimed to know Mr. Lincoln intimately: yet there are not two of the whole number who agree in their estimate of him. The fact was that he rarely showed more than one aspect of himself to one man. He opened himself to men in different directions. To illustrate the effect of the peculiarity of Mr. Lincoln's intercourse with men it may be said that men who knew him through all his professional and political life offered opinions as diametrically opposite to these, viz.: that he was a very ambitious man, and that he was without a particle of ambition; that he was one of the saddest men that ever lived, and that he was one of the jolliest men that ever lived; that he was very religious, but that he was not a Christian; that he was a Christian, but did not know it; that he was so far from being a religious man or a Christian that 'the less said upon that subject the better;' that he was the most cunning man in America, and that he had not a particle of cunning in him; that he had the strongest personal attachments, and that he had no personal attachments at all—only a general good feeling towards everybody; that he was a man of indomitable will, and that he was a man almost without a will; that he was a tyrant, and that he was the softest-hearted, most brotherly man that ever lived; that he was remarkable for his pure-mindedness, and that he was the foulest in his jests and stories of any man in the country; that he was a witty man, and that he was only a retailer of the wit of others; that his apparent candor and fairness were only apparent, and that they were as real as his head and his hands; that he was a boor, and that he was in all respects a gentleman; that he was a leader of the people, and that he was always led by the people; that he was cool and impassive, and that he was susceptible of the strongest passions. It is only by tracing these separate streams of impression back to their fountain that we are able to arrive at anything like a competent comprehension of the man, or to learn why he came to be held in such various estimation. Men caught only separate aspects of his character—only the fragments that were called into exhibition by their own qualities."
Dr. Holland had only found what Lincoln's friends had always experienced in their relations with him—that he was a man of many moods and many sides. He never revealed himself entirely to any one man, and therefore he will always to a certain extent remain enveloped in doubt. Even those who were with him through long years of hard study and under constantly varying circumstances can hardly say they knew him through and through. I always believed I could read him as thoroughly as any man, and yet he was so different in many respects from any other one I ever met before or since his time that I cannot say I comprehended him. In this chapter I give my recollection of his individual characteristics as they occur to me, and allow the world to form its own opinion. If my recollection of the man destroys any other person's ideal, I cannot help it. By a faithful and lifelike description of Lincoln the man, and a study of his peculiar and personal traits, perhaps some of the apparent contradictions met with by Dr. Holland will have melted from sight.
Mr. Lincoln was six feet four inches high, and when he left the city of his home for Washington was fifty-one years old, having good health and no gray hairs, or but few, on his head. He was thin, wiry, sinewy, raw-boned; thin through the breast to the back, and narrow across the shoulders; standing he leaned forward—was what may be called stoop-shouldered, inclining to the consumptive by build. His usual weight was one hundred and eighty pounds. His organization—rather his structure and functions—worked slowly.
His blood had to run a long distance from his heart to the extremities of his frame, and his nerve force had to travel through dry ground a long distance before his muscles were obedient to his will. His structure was loose and leathery; his body was shrunk and shrivelled; he had dark skin, dark hair, and looked woe-struck. The whole man, body and mind, worked slowly, as if it needed oiling. Physically he was a very powerful man, lifting with ease four hundred, and in one case six hundred, pounds. His mind was like his body, and worked slowly but strongly. Hence there was very little bodily or mental wear and tear in him. This peculiarity in his construction gave him great advantage over other men in public life. No man in America—scarcely a man in the world—could have stood what Lincoln did in Washington and survived through more than one term of the Presidency.
When he walked he moved cautiously but firmly; his long arms and giant hands swung down by his side. He walked with even tread, the inner sides of his feet being parallel. He put the whole foot flat down on the ground at once, not landing on the heel; he likewise lifted his foot all at once, not rising from the toe, and hence he had no spring to his walk. His walk was undulatory—catching and pocketing tire, weariness, and pain, all up and down his person, and thus preventing them from locating. The first impression of a stranger, or a man who did not observe closely, was that his walk implied shrewdness and cunning—that he was a tricky man; but, in reality, it was the walk of caution and firmness. In sitting down on a common chair he was no taller than ordinary men. His legs and arms were abnormally, unnaturally long, and in undue proportion to the remainder of his body. It was only when he stood up that he loomed above other men.
Mr. Lincoln's head was long, and tall from the base of the brain and from the eyebrows. His head ran backwards, his forehead rising as it ran back at a low angle, like Clay's, and unlike Webster's, which was almost perpendicular. The size of his hat measured at the hatter's block was seven and one-eighth, his head being, from ear to ear, six and one-half inches, and from the front to the back of the brain eight inches. Thus measured it was not below the medium size. His forehead was narrow but high; his hair was dark, almost black, and lay floating where his fingers or the winds left it, piled up at random. His cheek-bones were high, sharp, and prominent; his jaws were long and up-curved; his nose was large, long, blunt, and a little awry towards the right eye; his chin was sharp and upcurved; his eyebrows cropped out like a huge rock on the brow of a hill; his long, sallow face was wrinkled and dry, with a hair here and there on the surface; his cheeks were leathery; his ears were large, and ran out almost at right angles from his head, caused partly by heavy hats and partly by nature; his lower lip was thick, hanging, and undercurved, while his chin reached for the lip upcurved; his neck was neat and trim, his head being well balanced on it; there was the lone mole on the right cheek, and Adam's apple on his throat.
Thus stood, walked, acted, and looked Abraham Lincoln. He was not a pretty man by any means, nor was he an ugly one; he was a homely man, careless of his looks, plain-looking and plain-acting. He had no pomp, display, or dignity, so-called. He appeared simple in his carriage and bearing. He was a sad-looking man; his melancholy dripped from him as he walked. His apparent gloom impressed his friends,* and created sympathy for him—one means of his great success.
* Lincoln's melancholy never failed to impress any man who ever saw or knew him. The perpetual look of sadness was his most prominent feature. The cause of this peculiar condition was a matter of frequent discussion among his friends. John T. Stuart said it was due to his abnormal digestion. His liver failed to work properly—did not secrete bile—and his bowels were equally as inactive. "I used to advise him to take blue-mass pills," related Stuart, "and he did take them before he went to Washington, and for five months while he was President, but when I came on to Congress he told me he had ceased, using them because they made him cross." The reader can hardly realize the extent of this peculiar tendency to gloom. One of Lincoln's colleagues in the Legislature of Illinois is authority for the statement coming from Lincoln himself that this "mental depression became so intense at times he never dared carry a pocket knife." Two things greatly intensified his characteristic sadness: one was the endless succession of troubles in his domestic life, which he had to bear in silence; and the other was unquestionably the knowledge of his own obscure and lowly origin. The recollection of these things burned a deep impress on his sensitive soul. As to the cause of this morbid condition my idea has always been that it was occult, and could not be explained by any course of observation and reasoning. It was ingrained, and, being ingrained, could not be reduced to rule, or the cause arrayed. It was necessarily hereditary, but whether it came down from a long line of ancestors and far back, or was simply the reproduction of the saddened life of Nancy Hanks, cannot well be determined. At any rate it was part of his nature, and could no more be shaken off than he could part with his brains.
He was gloomy, abstracted, and joyous—rather humorous—by turns; but I do not think he knew what real joy was for many years.
Mr. Lincoln sometimes walked our streets cheerily, he was not always gloomy, and then it was that on meeting a friend he greeted him with plain "Howd'y?" clasping his hand in both of his own, and gave him a hearty soul-welcome. On a winter's morning he might be seen stalking towards the market-house, basket on arm, his old gray shawl wrapped around his neck, his little boy Willie or Tad running along at his heels asking a thousand boyish questions, which his father, in deep abstraction, neither heeded nor heard.*
* "I lived next door to the Lincolns for many years, knew the family well. Mr. Lincoln used to come to our house, his feet encased in a pair of loose slippers, and with an old, faded pair of trousers fastened with one suspender. He frequently came to our house for milk. Our rooms were low, and he said one day,'Jim, you'll have to lift your loft a little higher; I can't straighten out under it very well.' To my wife, who was short of stature, he used to say that little people had some advantages: they required less 'wood and wool to make them comfortable.' In his yard Lincoln had but little shrubbery. He once planted some rose bushes, to which he called my attention, but soon neglected them altogether. He never planted any vines or fruit trees, seemed to have no fondness for such things. At one time, yielding to my suggestion, he undertook to keep a garden in the rear part of his yard, but one season's experience sufficed to cure him of all desire for another. He kept his own horse, fed and curried it when at home; he also fed and milked his own cow, and sawed his own wood. Mr. Lincoln and his wife agreed moderately well. Frequently Mrs. Lincoln's temper would get the better of her. If she became furious, as she often did, her husband tried to pay no attention to her. He would sometimes laugh at her, but generally he would pick up one of the children and walk off. I have heard her say that if Mr. Lincoln had remained at home more she could have loved him better. One day while Mr. Lincoln was absent— he had gone to Chicago to try a suit in the United States Court—his wife and I formed a conspiracy to take off the roof and raise his house. It was originally a frame structure one story and a half high. When Lincoln returned he met a gentleman on the sidewalk and, looking at his own house and manifesting great surprise, inquired: 'Stranger, can you tell me where Lincoln lives?' The gentleman gave him the necessary information, and Lincoln gravely entered his own premises."—Statement, James Gourly, February 9, 1866.
If a friend met or passed him, and he awoke from his reverie, something would remind him of a story he had heard in Indiana, and tell it he would, and there was no alternative but to listen.
Thus, I repeat, stood and walked and talked this singular man. He was odd, but when that gray eye and that face and those features were lit up by the inward soul in fires of emotion, then it was that all those apparently ugly features sprang into organs of beauty or disappeared in the sea of inspiration that often flooded his face. Sometimes it appeared as if Lincoln's soul was fresh from its Creator.
I have asked the friends and foes of Mr. Lincoln alike what they thought of his perceptions. One gentleman of unquestioned ability and free from all partiality or prejudice said, "Mr. Lincoln's perceptions were slow, a little perverted, if not somewhat distorted and diseased." If the meaning of this is that Mr. Lincoln saw things from a peculiar angle of his being, and from this was susceptible to nature's impulses, and that he so expressed himself, then I have no objection to what is said.
Otherwise I dissent. Mr. Lincoln's perceptions were slow, cold, clear, and exact. Everything came to him in its precise shape and color. To some men the world of matter and of man comes ornamented with beauty, life, and action; and hence more or less false and inexact. No lurking illusion or other error, false in itself and clad for the moment in robes of splendor, ever passed undetected or unchallenged over the threshold of his mind—that point which divides vision from the realm and home of thought. Names to him were nothing, and titles naught—assumption always standing back abashed at his cold, intellectual glare. Neither his perceptions nor intellectual vision were perverted, distorted, or diseased. He saw all things through a perfect mental lens. There was no diffraction or refraction there. He was not impulsive, fanciful, or imaginative; but cold, calm, and precise. He threw his whole mental light around the object, and, after a time, substance and quality stood apart, form and color took their appropriate places, and all was clear and exact in his mind. His fault, if any, was that he saw things less than they really were; less beautiful and more frigid. He crushed the unreal, the inexact, the hollow, and the sham. He saw things in rigidity rather than in vital action. He saw what no man could dispute, but he failed to see what might have been seen.
To some minds the world is all life, a soul beneath the material; but to Mr. Lincoln no life was individual that did not manifest itself to him. His mind was his standard. His mental action was deliberate, and he was pitiless and persistent in pursuit of the truth. No error went undetected, no falsehood unexposed, if he once was aroused in search of the truth. The true peculiarity of Mr. Lincoln has not been seen by his various biographers; or, if seen, they have failed wofully to give it that importance which it deserves. Newton beheld the law of the universe in the fall of an apple from a tree to the ground; Owen saw the animal in its claw; Spencer saw evolution in the growth of a seed; and Shakespeare saw human nature in the laugh of a man. Nature was suggestive to all these men. Mr. Lincoln no less saw philosophy in a story and an object lesson in a joke. His was a new and original position, one which was always suggesting something to him. The world and man, principles and facts, all were full of suggestions to his susceptible soul. They continually put him in mind of something. His ideas were odd and original for the reason that he was a peculiar and original creation himself.
His power in the association of ideas was as great as his memory was tenacious and strong. His language indicated oddity and originality of vision as well as expression. Words and language are but the counterparts of the idea—the other half of the idea; they are but the stinging, hot, leaden bullets that drop from the mould; in a rifle, with powder stuffed behind them and fire applied, they are an embodied force resistlessly pursuing their object. In the search for words Mr. Lincoln was often at a loss. He was often perplexed to give proper expression to his ideas; first, because he was not master of the English language; and secondly, because there were, in the vast store of words, so few that contained the exact coloring, power, and shape of his ideas. This will account for the frequent resort by him to the use of stories, maxims, and jokes in which to clothe his ideas, that they might be comprehended. So true was this peculiar mental vision of his that, though mankind has been gathering, arranging, and classifying facts for thousands of years, Lincoln's peculiar standpoint could give him no advantage over other men's labor. Hence he tore down to their deepest foundations all arrangements of facts, and constructed new ones to govern himself. He was compelled from his peculiar mental organization to do this. His labor was great and continuous.
The truth about Mr. Lincoln is that he read less and thought more than any man in his sphere in America. No man can put his finger on any great book written in the last or present century that he read thoroughly. When young he read the Bible, and when of age he read Shakespeare; but, though he often quoted from both, he never read either one through. He is acknowledged now to have been a great man, but the question is what made him great. I repeat, that he read less and thought more than any man of his standing in America, if not in the world. He possessed originality and power of thought in an eminent degree. Besides his well established reputation for caution, he was concentrated in his thoughts and had great continuity of reflection. In everything he was patient and enduring. These are some of the grounds of his wonderful success.
Not only were nature, man, and principle suggestive to Mr. Lincoln, not only had he accurate and exact perceptions, but he was causative; his mind, apparently with an automatic movement, ran back behind facts, principles, and all things to their origin and first cause—to that point where forces act at once as effect and cause. He would stop in the street and analyze a machine. He would whittle a thing to a point, and then count the numberless inclined planes and their pitch making the point. Mastering and defining this, he would then cut that point back and get a broad transverse section of his pine-stick, and peel and define that. Clocks, omnibuses, language, paddle-wheels, and idioms never escaped his observation and analysis. Before he could form an idea of anything, before he would express his opinion on a subject, he must know its origin and history in substance and quality, in magnitude and gravity. He must know it inside and outside, upside and downside. He searched and comprehended his own mind and nature thoroughly, as I have often heard him say. He must analyze a sensation, an idea, and run back in its history to its origin, and purpose. He was remorseless in his analysis of facts and principles. When all these exhaustive processes had been gone through with he could form an idea and express it; but no sooner. He had no faith, and no respect for "say so's," come though they might from tradition or authority. Thus everything had to run through the crucible, and be tested by the fires of his analytic mind; and when at last he did speak, his utterances rang out with the clear and keen ring of gold upon the counters of the understanding. He reasoned logically through analogy and comparison. All opponents dreaded his originality of idea, his condensation, definition, and force of expression; and woe be to the man who hugged to his bosom a secret error if Lincoln got on the chase of it. I repeat, woe to him! Time could hide the error in no nook or corner of space in which he would not detect and expose it.
Though gifted with accurate and acute perception, though a profound thinker as well as analyzer, still Lincoln's judgment on many and minor matters was oftentimes childish. By the word judgment I do not mean what mental philosophers would call the exercise of reason, will—understanding; but I use the term in its popular sense. I refer to that capacity or power which decides on the fitness, the harmony, or, if you will, the beauty and appropriateness of things. I have always thought, and sometimes said, Lincoln lacked this quality in his mental structure. He was on the alert if a principle was involved or a man's rights at stake in a transaction; but he never could see the harm in wearing a sack-coat instead of a swallowtail to an evening party, nor could he realize the offense of telling a vulgar yarn if a preacher happened to be present.*
* Sometime in 1857 a lady reader or elocutionist came to Springfield and gave a public reading in a hall immediately north of the State House. As lady lecturers were then rare birds, a very large crowd greeted her. Among other things she recited "Nothing to Wear," a piece in which is described the perplexities that beset "Miss Flora McFlimsey" in her efforts to appear fashionable. In the midst of one stanza, in which no effort is made to say anything particularly amusing, and during the reading of which the audience manifested the most respectful silence and attention, some one in the rear seats burst out into a loud, coarse laugh—a sudden and explosive guffaw. It startled the speaker and audience, and kindled a storm of unsuppressed laughter and applause. Everyone looked back to ascertain the cause of the demonstration, and was greatly surprised to find that it was Mr. Lincoln. He blushed and squirmed with the awkward diffidence of a schoolboy. What prompted him to laugh no one was able to explain. He was doubtless wrapped up in a brown study, and, recalling some amusing episode, indulged in laughter without realizing his surroundings. The experience mortified him greatly.
As already expressed, Mr. Lincoln had no faith. In order to believe, he must see and feel, and thrust his hand into the place. He must taste, smell, and handle before he had faith or even belief. Such a mind manifestly must have its time. His forte and power lay in digging out for himself and securing for his mind its own food, to be assimilated unto itself. Thus, in time he would form opinions and conclusions that no human power could overthrow. They were as irresistible as the rush of a flood; as convincing as logic embodied in mathematics. And yet the question arises: "Had Mr. Lincoln great, good common-sense?" A variety of opinions suggest themselves in answer to this. If the true test is that a man shall judge the rush and whirl of human actions and transactions as wisely and accurately as though indefinite time and proper conditions were at his disposal, then I am compelled to follow the logic of things and admit that he had no great stock of common-sense; but if, on the other hand, the time and conditions were ripe, his common-sense was in every case equal to the emergency. He knew himself, and never trusted his dollar or his fame in casual opinions—never acted hastily or prematurely on great matters.
Mr. Lincoln believed that the great leading law of human nature is motive. He reasoned all ideas of a disinterested action out of my mind. I used to hold that an action could be pure, disinterested, and wholly free from selfishness; but he divested me of that delusion. His idea was that all human actions were caused by motives, and that at the bottom of these motives was self. He defied me to act without motive and unselfishly; and when I did the act and told him of it, he analyzed and sifted it to the last grain. After he had concluded, I could not avoid the admission that he had demonstrated the absolute selfishness of the entire act. Although a profound analyzer of the laws of human nature he could form no just construction of the motives of the particular individual. He knew but little of the play of the features as seen in the "human face divine." He could not distinguish between the paleness of anger and the crimson tint of modesty. In determining what each play of the features indicated he was pitiably weak.
The great predominating elements of Mr. Lincoln's peculiar character were: first, his great capacity and power of reason; second, his conscience and his excellent understanding; third, an exalted idea of the sense of right and equity; fourth, his intense veneration of the true and the good. His conscience, his heart and all the faculties and qualities of his mind bowed submissively to the despotism of his reason. He lived and acted from the standard of reason—that throne of logic, home of principle—the realm of Deity in man. It is from this point Mr. Lincoln must be viewed. Not only was he cautious, patient, and enduring; not only had he concentration and great continuity of thought; but he had profound analytical power. His vision was clear, and he was emphatically the master of statement. His pursuit of the truth, as before mentioned, was indefatigable. He reasoned from well-chosen principles with such clearness, force, and directness that the tallest intellects in the land bowed to him. He was the strongest man I ever saw, looking at him from the elevated standpoint of reason and logic. He came down from that height with irresistible and crashing force. His Cooper Institute and other printed speeches will prove this; but his speeches before the courts—especially the Supreme Court of Illinois—if they had been preserved, would demonstrate it still more plainly. Here he demanded time to think and prepare. The office of reason is to determine the truth. Truth is the power of reason, and Lincoln loved truth for its own sake. It was to him reason's food.
Conscience, the second great quality of Mr. Lincoln's character, is that faculty which induces in us love of the just. Its real office is justice; right and equity are its correlatives. As a court, it is in session continuously; it decides all acts at all times. Mr. Lincoln had a deep, broad, living conscience. His reason, however, was the real judge; it told him what was true or false, and therefore good or bad, right or wrong, just or unjust, and his conscience echoed back the decision. His conscience ruled his heart; he was always just before he was generous. It cannot be said of any mortal that he was always absolutely just. Neither was Lincoln always just; but his general life was. It follows that if Mr. Lincoln had great reason and great conscience he must have been an honest man; and so he was. He was rightfully entitled to the appellation "Honest Abe." Honesty was his polar star.
Mr. Lincoln also had a good understanding; that is, the faculty that comprehends the exact state of things and determines their relations, near or remote. The understanding does not necessarily enquire for the reason of things. While Lincoln was odd and original, while he lived out of himself and by himself, and while he could absorb but little from others, yet a reading of his speeches, messages, and letters satisfies us that he had good understanding. But the strongest point in his make-up was the knowledge he had of himself; he comprehended and understood his own capacity—what he did and why he did it—better perhaps than any man of his day. He had a wider and deeper comprehension of his environments, of the political conditions especially, than men who were more learned or had had the benefits of a more thorough training.
He was a very sensitive man,—modest to the point of diffidence,—and often hid himself in the masses to prevent the discovery of his identity. He was not indifferent, however, to approbation and public opinion. He had no disgusting egotism and no pompous pride, no aristocracy, no haughtiness, no vanity. Merging together the qualities of his nature he was a meek, quiet, unobtrusive gentleman.
As many contradictory opinions prevail in reference to Mr. Lincoln's heart and humanity as on the question of his judgment. As many persons perhaps contend that he was cold and obdurate as that he was warm and affectionate. The first thing the world met in contact with him was his head and conscience; after that he exposed the tender side of his nature—his heart, subject at all times to his exalted sense of right and equity, namely his conscience. In proportion as he held his conscience subject to his head, he held his heart subject to his head and conscience. His humanity had to defer to his sense of justice and, the eternal right. His heart was the lowest of these organs, if we may call them such—the weakest of the three. Some men have reversed this order and characterized his heart as his ruling organ. This estimate of Mr. Lincoln endows him with love regardless of truth, justice, and right. The question still is, was Lincoln cold and heartless, or warm and affectionate? Can a man be all heart, all head, and all conscience? Some of these are masters over the others, some will be dominant, ruling with imperial sway, and thus giving character to the man. What, in the first place, do we mean by a warm-hearted man? Is it one who goes out of himself and reaches for others spontaneously, seeking to correct some abuse to mankind because of a deep love for humanity, apart from equity and truth, and who does what he does for love's sake? If so, Mr. Lincoln was a cold man. If a man, woman, or child approached him, and the prayer of such an one was granted, that itself was not evidence of his love. The African was enslaved and deprived of his rights; a principle was violated in doing so. Rights imply obligations as well as duties. Mr. Lincoln was President; he was in a position that made it his duty, through his sense of right, his love of principle, the constitutional obligations imposed upon him by the oath of office, to strike the blow against slavery. But did he do it for love? He has himself answered the question "I would not free the slaves if I could preserve the Union without it." When he freed the slaves there was no heart in the act. This argument can be used against his too enthusiastic friends.
In general terms his life was cold—at least characterized by what many persons would deem great indifference. He had, however, a strong latent capacity to love: but the object must first come in the guise of a principle, next it must be right and true—then it was lovely in his sight. He loved humanity when it was oppressed—an abstract love—as against the concrete love centered in an individual. He rarely used terms of endearment, and yet he was proverbially tender and gentle. He gave the key-note to his own character when he said: "With malice towards none, with charity for all." In proportion to his want of deep, intense love he had 110 hate and bore no malice. His charity for an imperfect man was as broad as his devotion to principle was enduring.
"But was not Mr. Lincoln a man of great humanity?" asks a friend at my elbow; to which I reply, "Has not that question been answered already?" Let us suppose it has not. We must understand each other. What is meant by his humanity? Is it meant that he had much of human nature in him? If so, I grant that he was a man of humanity. If, in the event of the above definition being unsatisfactory or untrue, it is meant that he was tender and kind, then I again agree. But if the inference is that he would sacrifice truth or right in the slightest degree for the love of a friend, then he was neither tender nor kind; nor did he have any humanity. The law of human nature is such that it cannot be all head, all conscience, and all heart in one person at the same time. Our Maker so constituted things that, where God through reason blazed the way, we might boldly walk therein. The glory of Mr. Lincoln's power lay in the just and magnificent equipoise of head, conscience, and heart; and here his fame must rest or not at all.
Not only were Mr. Lincoln's perceptions good; not only was nature suggestive to him; not only was he original and strong; not only had he great reason, good understanding; not only did he love the true and the good—the eternal right; not only was he tender and sympathetic and kind;—but, in due proportion and in legitimate subordination, he had a glorious combination of them all. Through his perceptions—the suggestiveness of nature, his originality and strength; through his magnificent reason, his understanding, his conscience, his tenderness, quick sympathy, his heart; he approximated as nearly as human nature and the imperfections of man would permit to an embodiment of the great moral principle, "Do unto others as ye would they should do unto you."
Of Mr. Lincoln's will-power there are two opinions also: one that he lacked any will; the other that he was all will. Both these contradictory views have their vehement and honest champions. For the great underlying principles of mind in man he had great respect. He loved the true first, the right second, and the good last. His mind struggled for truth, and his soul reached out for substances. He cared not for forms, ways, methods—the non-substantial things of this world. He could not, by reason of his structure and mental organization, care anything about them. He did not have an intense care for any particular or individual man—the dollar, property, rank, orders, manners, or similar things; neither did he have any avarice or other like vice in his nature. He detested somewhat all technical rules in law, philosophy, and other sciences—mere forms everywhere—because they were, as a general thing, founded on arbitrary thoughts and ideas, and not on reason, truth, and the right. These things seemed to him lacking in substance, and he disregarded them because they cramped the originality of his genius. What suited a little narrow, critical mind did not suit Mr. Lincoln any more than a child's clothes would fit his father's body. Generally he took no interest in town affairs or local elections; he attended no meetings that pertained to local interests. He did not care—because by reason of his nature he could not—who succeeded to the presidency of this or that society or railroad company; who made the most money; who was going to Philadelphia, and what were the costs of such a trip; who was going to be married; who among his friends got this office or that—who was elected street commissioner Or health inspector. No principle of truth, right, or justice being involved in any of these things he could not be moved by them.*
* A bitter, malignant fool who always had opposed Lincoln and his friends, and had lost no opportunity to abuse them, induced Lincoln to go to the Governor of Illinois and recommend him for an important office in the State Militia. There being no principle at stake Lincoln could not refuse the request. When his friends heard of it they were furious in their denunciation of his action. It mortified him greatly to learn that he had displeased them. "And yet," he said, a few days later, dwelling on the matter to me in the office, "I couldn't well refuse the little the fellow asked of me."
He could not understand why men struggled so desperately for the little glory or lesser salary the small offices afforded. He made this remark to me one day in Washington: "If ever this free people—this Government—is utterly demoralized, it will come from this human struggle for office—a way to live without work." It puzzled him a good deal, he said, to get at the root of this dreaded disease, which spread like contagion during the nation's death struggle.
Because he could not feel a deep interest in the things referred to, nor manifest the same interest in those who were engaged in the popular scramble, he was called indifferent—nay, ungrateful—to his friends. This estimate of the man was a very unjust as well as unfair one. Mr. Lincoln loved his friends with commendable loyalty: in many cases he clung to them tenaciously, like iron to iron welded; and yet, because he could not be actively aroused, nor enter into the spirit of their anxiety for office, he was called ungrateful. But he was not so. He may have seemed passive and lacking in interest; he may not have measured his friendly duties by the applicant's hot desire; but yet he was never ungrateful. Neither was he a selfish man. He would never have performed an act, even to promote himself to the Presidency, if by that act any human being was wronged. If it is said that he preferred Abraham Lincoln to anyone else in the pursuit of his ambition, and that because of this he was a selfish man, then I can see no impropriety in the charge. Under the same conditions we should all be equally guilty.

Remembering that Mr. Lincoln's mind moved logically, slowly, and cautiously, the question of his will and its power is easily solved. Although he cared but little for simple facts, rules, and methods, he did care for the truth and right of principle. In debate he courteously granted all the forms and non-essential things to his opponent. Sometimes he yielded nine points out of ten. The nine he brushed aside as husks or rubbish; but the tenth, being a question of substance, he clung to with all his might. On the underlying principles of truth and justice his will was as firm as steel and as tenacious as iron. It was as solid, real, and vital as an idea on which the world turns. He scorned to support or adopt an untrue position, in proportion as his conscience prevented him from doing an unjust thing. Ask him to sacrifice in the slightest degree his convictions of truth*—as he was asked to do when he made his "house-divided-against-itself speech"—and his soul would have exclaimed with indignant scorn, "The world perish first!"
Such was Lincoln's will. Because on one line of questions—the non-essential—he was pliable, and on the other he was as immovable as the rocks, have arisen the contradictory notions prevalent regarding him.
* "Mr. Lincoln seems to me too true and honest a man to have his eulogy written, and I have no taste for writing eulogies. I am sure that, if he were alive, he would feel that the exact truth regarding himself was far more worthy of himself and of his biographer than any flattering picture. I loved the man as he was, with his rugged features, his coarse, rebellious hair, his sad, dreamy eyes; and I love to see him, and I hope to describe him, as he was, and not otherwise."—Robert Dale Owen, January 22, 1867, MS.
It only remains to say that he was inflexible and unbending in human transactions when it was necessary to be so, and not otherwise. At one moment he was pliable and expansive as gentle air; at the next as tenacious and unyielding as gravity itself.
Thus I have traced Mr. Lincoln through his perceptions, his suggestiveness, his judgment, and his four predominant qualities: powers of reason, understanding, conscience, and heart. In the grand review of his peculiar characteristics, nothing creates such an impressive effect as his love of the truth. It looms up over everything else. His life is proof of the assertion that he never yielded in his fundamental conception of truth to any man for any end.
All the follies and wrong Mr. Lincoln ever fell into or committed sprang out of these weak points: the want of intuitive judgment; the lack of quick, sagacious knowledge of the play and meaning of men's features as written on the face; the want of the sense of propriety of things; his tenderness and mercy; and lastly, his unsuspecting nature. He was deeply and sincerely honest himself, and assumed that others were so. He never suspected men; and hence in dealing with them he was easily imposed upon.
All the wise and good things Mr. Lincoln ever did sprang out of his great reason, his conscience, his understanding, his heart, his love of the truth, the right, and the good. I am speaking now of his particular and individual faculties and qualities, not of their combination or the result of any combinations. Run out these qualities and faculties abstractly, and see what they produce. For instance, a tender heart, a strong reason, a broad under standing, an exalted conscience, a love of the true and the good must, proportioned reasonably and applied practically, produce a man of great power and great humanity.
As illustrative of a combination in Mr. Lincoln's organization, it may be said that his eloquence lay in the strength of his logical faculty, his supreme power of reasoning, his great understanding, and his love of principle; in his clear and accurate vision; in his cool and masterly statement of principles around which the issues gather; and in the statement of those issues and the grouping of the facts that are to carry conviction to the minds of men of every grade of intelligence. He was so clear that he could not be misunderstood or long misrepresented. He stood square and bolt upright to his convictions, and anyone who listened to him would be convinced that he formed his thoughts and utterances by them. His mind was not exactly a wide, broad, generalizing, and comprehensive mind, nor yet a versatile, quick, and subtle one, bounding here and there as emergencies demanded; but it was deep, enduring, strong, like a majestic machine running in deep iron grooves with heavy flanges on its wheels.
Mr. Lincoln himself was a very sensitive man, and hence, in dealing with others, he avoided wounding their hearts or puncturing their sensibility. He was unusually considerate of the feelings of other men, regardless of their rank, condition, or station. At first sight he struck one with his plainness, simplicity of manner, sincerity, candor, and truthfulness. He had no double interests and no overwhelming dignity with which to chill the air around his visitor. He was always easy of approach and thoroughly democratic. He seemed to throw a charm around every man who ever met him. To be in his presence was a pleasure, and no man ever left his company with injured feelings unless most richly deserved.
The universal testimony, "He is an honest man," gave him a firm hold on the masses, and they trusted him with a blind religious faith. His sad, melancholy face excited their sympathy, and when the dark days came it was their heart-strings that entwined and sustained him. Sympathy, we are told, is one of the strongest and noblest incentives to human action. With the sympathy and love of the people to sustain him, Lincoln had unlimited power over them; he threw an invisible and weightless harness over them, and drove them through disaster and desperation to final victory. The trust and worship by the people of Lincoln were the result of his simple character. He held himself not aloof from the masses. He became one of them. They feared together, they struggled together, they hoped together; thus melted and moulded into one, they became one in thought, one in will, one in action. If Lincoln cautiously awaited the full development of the last fact in the great drama before he acted, when longer waiting would be a crime, he knew that the people were determinedly at his back. Thus, when a blow was struck, it came with the unerring aim and power of a bolt from heaven. A natural king—not ruling men, but leading them along the drifts and trends of their own tendencies, always keeping in mind the consent of the governed, he developed what the future historian will call the sublimest order of conservative statesmanship.

Whatever of life, vigor, force, and power of eloquence his peculiar qualities gave him; whatever there was in a fair, manly, honest, and impartial administration of justice under law to all men at all times; whatever there was in a strong will in the right governed by tenderness and mercy; whatever there was in toil and sublime patience; whatever there was in these things or a wise combination of them, Lincoln is justly entitled to in making up the impartial verdict of history. These limit and define him as a statesman, as an orator, as an executive of the nation, and as a man. They developed in all the walks of his life; they were his law; they were his nature, they were Abraham Lincoln.
This long, bony, sad man floated down the Sangamon river in a frail canoe in the spring of 1831. Like a piece of driftwood he lodged at last, without a history, strange, penniless, and alone. In sight of the capital of Illinois, in the fatigue of daily toil he struggled for the necessaries of life. Thirty years later this same peculiar man left the Sangamon river, backed by friends, by power, by the patriotic prayers of millions of people, to be the ruler of the greatest nation in the world.
As the leader of a brave people in their desperate struggle for national existence, Abraham Lincoln will always be an interesting historical character.
His strong, honest, sagacious, and noble life will always possess a peculiar charm. Had it not been for his conservative statesmanship, his supreme confidence in the wisdom of the people, his extreme care in groping his way among facts and before ideas, this nation might have been two governments to-day. The low and feeble circulation of his blood; his healthful irritability, which responded so slowly to the effects of stimuli; the strength of his herculean frame; his peculiar organism, conserving its force; his sublime patience; his wonderful endurance; his great hand and heart, saved this country from division, when division meant its irreparable ruin.
The central figure of our national history, the sublime type of our civilization, posterity, with the record of his career and actions before it, will decree that, whether Providence so ordained it or not, Abraham Lincoln was the man for the hour.
The following letters by Mr. Lincoln to his relatives were at one time placed in my hands. As they have never before been published entire I have thought proper to append them here. They are only interesting as showing Mr. Lincoln's affection for his father and step-mother, and as specimens of the good, sound sense with which he approached every undertaking. The list opens with a letter to his father written from Washington while a member of Congress:
"Washington, Dec. 24, 1848.
"My Dear Father:
"Your letter of the 7th was received night before last. I very cheerfully send you the twenty dollars, which sum you say is necessary to save your land from sale. It is singular that you should have forgotten a judgment against you—and it is more singular that the plaintiff should have let you forget it so long, particularly as I suppose you have always had property enough to satisfy a judgment of that amount. Before you pay it, it would be well to be sure you have not paid, or at least that you cannot prove you have paid it.
"Give my love to Mother and all the Connections.
"Affectionately, your son,
"A. Lincoln."
His step-brother, John D. Johnston, for whom Mr. Lincoln always exhibited the affection of a real brother, was the recipient of many letters. Some of them were commonplace, but between the lines of each much good, homely philosophy may be read. Johnston, whom I knew, was exactly what his distinguished step-brother charged—an idler. In every emergency he seemed to fall back on Lincoln for assistance. The aid generally came, but with it always some plain but sensible suggestion. The series opens as follows:
"Springfield, Feb. 23,1850.
"Dear Brother:
"Your letter about a mail contract was received yesterday. I have made out a bid for you at $120, guaranteed it myself, got our P. M. here to certify it, and send it on. Your former letter, concerning some man's claim for a pension, was also received. I had the claim examined by those who are practised in such matters, and they decide he cannot get a pension.
"As you make no mention of it, I suppose you had not learned that we lost our little boy. He was sick fifteen days, and died in the morning of the first day of this month. It was not our first, but our second child. We miss him very much.
"Your Brother, in haste,
"A. Lincoln."
"To John D. Johnston."
Following is another, which, however, bears no date:
"Dear Johnston:
"Your request for eighty dollars I do not think it best to comply with now. At the various times when I have helped you a little you have said to me, 'We can get along very well now,' but in a very short time I find you in the same difficulty again. Now this can only happen by some defect in your conduct. What that defect is, I think I know. You are not lazy, and still you are an idler. I doubt whether, since I saw you, you have done a good whole day's work in any one day. You do not very much dislike to work, and still you do not work much, merely because it does not seem to you that you could get much for it. This habit of uselessly wasting time is the whole difficulty; and it is vastly important to you, and still more so to your children, that you should break the habit. It is more important to them because they have longer to live, and can keep out of an idle habit, before they are in it, easier than they can get out after they are in.
"You are in need of some ready money, and what I propose is that you shall go to work 'tooth and nail' for somebody who will give you money for it. Let father and your boys take charge of things at home, prepare for a crop, and make the crop, and you go to work for the best money wages, or in discharge of any debt you owe, that you can get,—and to secure you a fair reward for your labor, I now promise you that for every dollar you will, between this and the first of next May, get for your own labor, either in money or as your own indebtedness, I will then give you one other dollar. By this, if you hire yourself at ten dollars a month, from me you will get ten more, making twenty dollars a month for your work. In this I do not mean you shall go off to St. Louis, or the lead mines, or the gold mines in California, but I mean for you to go at it for the best wages you can get close to home in Coles County. Now if you will do this, you will be soon out of debt, and, what is better, you will have a habit that will keep you from getting in debt again. But if I should now clear you out, next year you would be just as deep in as ever. You say you would give your place in heaven for $70 or $80. Then you value your place in heaven very cheap, for I am sure you can, with the offer I make, get the seventy or eighty dollars for four or five months' work.
"You say, if I will furnish you the money, you will deed me the land, and if you don't pay the money back you will deliver possession. Nonsense! If you can't now live with the land, how will you then live without it? You have always been kind to me, and I do not mean to be unkind to you. On the contrary, if you will but follow my advice, you will find it worth more than eight times eighty dollars to you.
"Affectionately,
"Your brother,
"A. Lincoln."
The following, written when the limit of Thomas Lincoln's life seemed rapidly approaching, shows in what esteem his son held the relation that existed between them:
"Springfield, Jan y 12, 1851.
"Dear Brother:
"On the day before yesterday I received a letter from Harriett, written at Greenup. She says she has just returned from your house; and that Father is very low, and will hardly recover. She also says that you have written me two letters; and that although you do not expect me to come now, you wonder that I do not write. I received both your letters, and although I have not answered them, it is not because I have forgotten them, or [not] been interested about them, but because it appeared to me I could write nothing which could do any good. You already know I desire that neither Father or Mother shall be in want of any comfort either in health or sickness while they live; and I feel sure you have not failed to use my name, if necessary, to procure a doctor, or anything else for Father in his present sickness. My business is such that I could hardly leave home now, if it were not, as it is, that my own wife is sick a-bed (it is a case of baby-sickness, and I suppose is not dangerous). I sincerely hope Father may yet recover his health; but at all events tell him to remember to call upon and confide in our great, and good, and merciful Maker, who will not turn away from him in any extremity. He notes the fall of a sparrow, and numbers the hairs of our heads; and He will not forget the dying man who puts his trust in Him. Say to him that if we could meet now it is doubtful whether it would not be more painful than pleasant; but that if it be his lot to go now he will soon have a joyous meeting with many loved ones gone before, and where the rest of us, through the help of God, hope ere long to join them.
"Write me again when you receive this.
"Affectionately,
"A. Lincoln."
Lincoln's mentor-like interest in his step-mother and his shiftless and almost unfortunate step-brother was in no wise diminished by the death of his father. He writes:
"Springfield, Aug. 31,1851.
"Dear Brother:
"Inclosed is the deed for the land. We are all well, and have nothing in the way of news. We have had no cholera here for about two weeks.
"Give my love to all, and especially to Mother.
"Yours as ever,
"A. Lincoln."
No more practical or kindly-earnest advice could have been given than this:
"Shelbyville, Nov. 4, 1851.
"Dear Brother:
"When I came into Charleston day before yesterday I learned that you are anxious to sell the land where you live, and move to Missouri. I have been thinking of this ever since, and cannot but think such a notion is utterly foolish. What can you do in Missouri better than here? Is the land richer? Can you there, any more than here, raise corn and wheat and oats without work? Will anybody there, any more than here, do your work for you? If you intend to go to work, there is no better place than right where you are; if you do not intend to go to work you cannot get along anywhere. Squirming and crawling about from place to place can do no good. You have raised no crop this year, and what you really want is to sell the land, get the money and spend it. Part with the land you have, and, my life upon it, you will never after own a spot big enough to bury you in. Half you will get for the land you spend in moving to Missouri, and the other half you will eat and drink and wear out, and no foot of land will be bought. Now I feel it is my duty to have no hand in such a piece of foolery. I feel that it is so even on your own account, and particularly on Mother's account. The eastern forty acres I intend to keep for Mother while she lives; if you will not cultivate it, it will rent for enough to support her; at least it will rent for something. Her dower in the other two forties she can let you have, and no thanks to me.
"Now do not misunderstand this letter. I do not write it in any unkindness. I write it in order, if possible, to get you to face the truth, which truth is, you are destitute because you have idled away all your time. Your thousand pretences for not getting along better are all nonsense; they deceive nobody but yourself. Go to work is the only cure for your case.
"A word for Mother: Chapman tells me he wants you to go and live with him. If I were you I would try it awhile. If you get tired of it (as I think you will not) you can return to your own home. Chapman feels very kindly to you; and I have no doubt he will make your situation very pleasant.
"Sincerely your son,
"A. Lincoln."
The list closes with this one written by Lincoln while on the circuit:
"Shelbyville, Nov. 9, 1851.
"Dear Brother:
''When I wrote you before, I had not received your letter. I still think as I did; but if the land can be sold so that I get three hundred dollars to put to interest for Mother, I will not object if she does not. But before I will make a deed, the money must be had, or secured beyond all doubt at ten per cent.
"As to Abraham, I do not want him on my own account; but I understand he wants to live with me so that he can go to school and get a fair start in the world, which I very much wish him to have. When I reach home, if I can make it convenient to take, I will take him, provided there is no mistake between us as to the object and terms of my taking him.
"In haste, as ever,
"A. Lincoln."
"In the spring term of the Tazewell County Court in 1847, which at that time was held in the village of Tremont, I was detained as a witness an entire week. Lincoln was employed in several suits, and among them was one of Case vs. Snow Bros. The Snow Bros., as appeared in evidence (who were both minors), had purchased from an old Mr. Case what was then called a "prairie team," consisting of two or three yoke of oxen and prairie plow, giving therefor their joint note for some two hundred dollars; but when pay-day came refused to pay, pleading the minor act. The note was placed in Lincoln's hands for collection. The suit was called and a jury impanelled. The Snow Bros, did not deny the note, but pleaded through their counsel that they were minors, and that Mr. Case knew they were at the time of the contract and conveyance. All this was admitted by Mr. Lincoln, with his peculiar phrase, 'Yes, gentlemen, I reckon that's so.' The minor act was read and its validity admitted in the same manner. The counsel of the defendants were permitted without question to state all these things to the jury, and to show by the statute that these minors could not be held responsible for their contract. By this time you may well suppose that I began to be uneasy. 'What!' thought I, 'this good old man, who confided in these boys, to be wronged in this way, and even his counsel, Mr. Lincoln, to submit in silence!' I looked at the court, Judge Treat, but could read nothing in his calm and dignified demeanor. Just then, Mr. Lincoln slowly got up, and in his strange, half-erect attitude and clear, quiet accent began: 'Gentlemen of the Jury, are you willing to allow these boys to begin life with this shame and disgrace attached to their character? If you are, I am not. The best judge of human character that ever wrote has left these immortal words for all of us to ponder:
"Good name in man or woman, dear my lord, Is the immediate jewel of their souls: Who steals my purse steals trash;'tis something, nothing; 'Twas mine,'tis his, and has been slave to thousands; But he that filches from me my good name Robs me of that which not enriches him And makes me poor indeed."'
"Then rising to his full height, and looking upon the defendants with the compassion of a brother, his long right arm extended toward the opposing counsel, he continued: 'Gentlemen of the jury, these poor innocent boys would never have attempted this low villany had it not been for the advice of these lawyers.' Then for a few minutes he showed how even the noble science of law may be prostituted. With a scathing rebuke to those who thus belittle their profession, he concluded: 'And now, gentlemen, you have it in your power to set these boys right before the world.' He plead for the young men only; I think he did not mention his client's name. The jury, without leaving their seats, decided that the defendants must pay the debt; and the latter, after hearing Lincoln, were as willing to pay it as the jury were determined they should. I think the entire argument lasted not above five minutes."—George W. Minier, statement, Apr. 10, 1882.
Among Lincoln's colleagues at the Springfield bar, after his re-entry into politics in 1854, and until his elevation to the Presidency, were, John T. Stuart, Stephen T. Logan, John A. McClernand, Benjamin S. Edwards, David Logan, E. B. Herndon, W. I. Ferguson, James H. Matheney, C. C. Brown, N. M. Broadwell, Charles W. Keyes, John E. Rosette, C. S. Zane, J. C. Conkling, Shelby M. Cullom, and G. W. Shutt. There were others, notably John M. Palmer and Richard J. Oglesby, who came in occasionally from other counties and tried suits with and against us, but they never became members of our bar, strictly speaking, till after the war had closed.—W. H. H.
"The conversation took place in the office of Lincoln & Herndon, in the presence of P. L. Harrison, William H. Herndon, Pascal Enos, and myself. It originated in this way: After the debate at Springfield on the 4th and 5th of October, 1854, William Jayne, John Cassiday, Pascal Enos, the writer, and others whose names I do not now remember, filled out and signed a written request to Lincoln to follow Douglas until he 'ran him into his hole' or made him halloo 'Enough,' and that day Lincoln was giving in his report. He said that the next morning after the Peoria debate Douglas came to him and flattered him that he knew more on the question of Territorial organization in this government than all the Senate of the United States, and called his mind to the trouble the latter had given him. He added that Lincoln had already given him more trouble than all the opposition in the Senate, and then proposed to Lincoln that if he (Lincoln) would go home and not follow him, he (Douglas) would go to no more of his appointments, would make no more speeches, and would go home and remain silent during the rest of the campaign. Lincoln did not make another speech till after the election."—B. F, Irwin's statement, Feb. 8, 1866, unpublished MS.
See ante pp. 368-369.
Following is a copy of the call to select delegates to the Bloomington Convention held May 29, 1856, when the Republican party in Illinois came into existence. It will be remembered that I signed Lincoln's name under instructions from him by telegraph. The original document I gave several years ago to a friend in Boston, Mass.:
"We, the undersigned, citizens of Sangamon County, who are opposed to the repeal of the Missouri Compromise, and the present administration, and who are in favor of restoring to the general government the policy of Washington and Jefferson, would suggest the propriety of a County Convention, to be held in the city of Springfield on Saturday, the 24th day of May, at 2 o'clock, p. M., to appoint delegates to the Bloomington Convention.
"A. Lincoln,
"W. H. Herndon and others."
The decided stand Lincoln took in this instance, and his speech in the Convention, undoubtedly paved the way for his leadership in the Republican party.—W. H. H.
One morning in 1859, Lincoln and I, impressed with the probability of war between the two sections of the country, were discussing the subject in the office. "The position taken by the advocates of State Sovereignty," remarked Lincoln, "always reminds me of the fellow who contended that the proper place for the big kettle was inside of the little one." To me, war seemed inevitable, but when I came to view the matter squarely, I feared a difficulty the North would have in controlling the various classes of people and shades of sentiment, so as to make them an effective force in case of war: I feared the lack of some great head and heart to lead us onward. Lincoln had great confidence in the masses, believing that, when they were brought face to face with the reality of the conflict, all differences would disappear, and that they would be merged into one. To illustrate his idea he made use of this figure: "Go to the river bank with a coarse sieve and fill it with gravel. After a vigorous shaking you will observe that the small pebbles and sand have sunk from view and fallen to the ground. The next larger in size, unable to slip between the wires, will still be found within the sieve. By thorough and repeated shakings you will find that, of the pebbles still left in the sieve, the largest ones will have risen to the top. Now," he continued, "if, as you say, war is inevitable and will shake the country from centre to circumference, you will find that the little men will fall out of view in the shaking. The masses will rest on some solid foundation, and the big men will have climbed to the top. Of these latter, one greater than all the rest will leap forth armed and equipped—the people's leader in the conflict." Little did I realize the strength of the masses when united and fighting for a common purpose; and much less did I dream that the great leader soon to be tried was at that very moment touching my elbow!—W. H. H.
Among other things used against Lincoln in the campaign of 1860 was the charge that he had been a member of a Know-Nothing lodge. When the charge was laid at his door he wrote the following letter to one of his confidential political friends. I copy from the original MS.:
[Confidential.]
"Springfield, Ills., July 21, 1860.
"Hon. A. Jonas.
"My Dear Sir:
"Yours of the 20th is received. I suppose as good, or even better, men than I may have been in American or Know-Nothing lodges; but, in point of fact, I never was in one, at Quincy or elsewhere. I was never in Quincy but one day and two nights while Know-Nothing lodges were in existence, and you were with me that day and both those nights. I had never been there before in my life; and never afterwards, till the joint debate with Douglas in 1858. It was in 1854, when I spoke in some hall there, and after the speaking you, with others, took me to an oyster saloon, passed an hour there, and you walked with me to, and parted with me at, the Quincy House quite late at night. I left by stage for Naples before daylight in the morning, having come in by the same route after dark the evening previous to the speaking, when I found you waiting at the Quincy House to meet me. A few days after I was there, Richardson, as I understood, started the same story about my having been in a Know-Nothing lodge. When I heard of the charge, as I did soon after, I taxed my recollection for some incident which could have suggested it; and I remembered that, on parting with you the last night, I went to the office of the Hotel to take my stage passage for the morning, was told that no stage office for that line was kept there, and that I must see the driver before retiring, to insure his calling for me in the morning; and a servant was sent with me to find the driver, who, after taking me a square or two, stopped me, and stepped perhaps a dozen steps farther, and in my hearing called to some one, who answered him, apparently from the upper part of a building, and promised to call with the stage for me at the Quincy House. I returned and went to bed, and before day the stage called and took me. This is all.
"That I never was in a Know-Nothing lodge in Quincy I should expect could be easily proved by respectable men who were always in the lodges, and never saw me there. An affidavit of one or two such would put the matter at rest.
"And now, a word of caution. Our adversaries think they can gain a point if they could force me to openly deny the charge, by which some degree of offence would be given to the Americans. For this reason it must not publicly appear that I am paying any attention to the charge,
"Yours truly,
"A. Lincoln."
At one time, while holding the office of attorney for the city of Springfield, I had a case in the Supreme Court, which involved the validity or constitutionality of a law regulating the matter of voting. Although a city case, it really abridged the right of suffrage. Being Lincoln's partner I wanted him to assist me in arguing the questions involved. He declined to do so, saying: "I am opposed to the limitation or lessening of the right of suffrage; if anything, I am in favor of its extension or enlargement. I want to lift men up—to broaden rather than contract their privileges."—W. H. H.
"Upon reaching Washington with the body of Booth—having come up the Potomac—it was at once removed from the tug-boat to a gun-boat that lay at the dock at the Navy Yard, where it remained about thirty-six hours. It was there examined by the Surgeon-General and staff and other officers, and identified by half a score of persons who had known him well. Toward evening of the second day Gen. L. C. Baker, then chief of the 'Detective Bureau of the War Department,' received orders from Secretary of War Stanton to dispose of the body. Stanton said, 'Put it where it will not be disturbed until Gabriel blows his last trumpet.' I was ordered to assist him. The body was placed in a row-boat, and, taking with us one trusty man to manage the boat, we quietly floated down the river. Crowds of people all along the shore were watching us. For a blind we took with us a heavy ball and chain, and it was soon going from lip to lip that we were about to sink the body in the Potomac. Darkness soon came on, completely concealing our movements, and under its cover we pulled slowly back to the old Penitentiary, which during the war was used as an arsenal. The body was then lifted from the boat and carried through a door opening on the river front. Under the stone floor of what had been a prison cell a shallow grave was dug, and the body, with the United States blanket for a 'winding-sheet,' was there interred. There also it remained till Booth's accomplices were hanged. It was then taken up and buried with his companions in crime. I have since learned that the remains were again disinterred and given to his friends, and that they now rest in the family burial-place in Baltimore, Md."—From MS. of L. B. Baker, late Lieut. and A. Q. M. 1st D. C. Cav.
"The weird and melancholy association of eloquence and poetry had a strong fascination for Mr. Lincoln's mind. Tasteful composition, either of prose or poetry, which faithfully contrasted the realities of eternity with the unstable and fickle fortunes of time, made a strong impression on his mind. In the indulgence of this melancholy taste it is related of him that the poem, 'Immortality,' he knew by rote and appreciated very highly. He had a strange liking for the verses, and they bear a just resemblance to his fortune. Mr. Lincoln, at the time of his assassination, was encircled by a halo of immortal glory such as had never before graced the brow of mortal man. He had driven treason from its capital city, had slept in the palace of its once proud and defiant, but now vanquished leader, and had saved his country and its accrued glories of three-quarters of a century from destruction. He rode, not with the haughty and imperious brow of an ancient conqueror, but with the placid complacency of a pure patriot, through the streets of the political Babylon of modern times. He had ridden over battlefields immortal in history, when, in power at least, he was the leader. Having assured the misguided citizens of the South that he meant them no harm beyond a determination to maintain the government, he returned buoyant with hope to the Executive Mansion where for four long years he had been held, as it were, a prisoner.
"Weary with the stories of state, he goes to seek the relaxation of amusement at the theatre; sees the gay crowd as he passes in; is cheered and graciously smiled upon by fair women and brave men; beholds the gorgeous paraphernalia of the stage, the brilliantly lighted scene, the arched ceiling, with its grotesque and inimitable figuring to heighten the effect and make the occasion one of unalloyed pleasure. The hearts of the people beat in unison with his over a redeemed and ransomed land. A pause in the play—a faint pistol shot is heard. No one knows its significance save the hellish few who are in the plot. A wild shriek, such as murder wrings from the heart of woman, follows: the proud form of Mr. Lincoln has sunk in death. The scene is changed to a wild confusion such as no poet can describe, no painter delineate. Well might the murdered have said and oft repeated:
"Tis the wink of an eye,'tis the draught of a breath, From the blossom of health to the paleness of death, From the gilded saloon to the bier and the shroud,— Oh, why should the spirit of mortal be proud?"
[From a speech by Hon. Lawrence Weldon, at a bar-meeting held in the United States Court at Springfield, Ills., in June, 1865.]
An interesting recollection of Lincoln comes from the pen of Colonel LeGrand B. Cannon, of New York. One cannot fail to be impressed with the strength of the side-light thrown by these reminiscences on a life as peculiar, in some respects, as it was grand and unique in others:
"It was my great good fortune," relates Colonel Cannon, "to know something of Mr. Lincoln distinct from his official life. Intensely in earnest I entered the service at the opening of the Rebellion as a staff officer in the regular army and was assigned to the Department of Virginia, with headquarters at Fort Monroe. Major-General Wool was in command of the Department, and I was honored by him as his chief of-staff, and enjoyed his entire confidence. It was the only gate open for communication with the rebel government, and General Wool was the agent for such intercourse.
"In the early stages of the war there was a want of harmony between the army and navy about us which seriously embarrassed military operations, resulting in the President and Secretaries Chase and Stanton coming to Fort Monroe to adjust matters. Domestic comforts were limited at headquarters, and the President occupied my room. I was (in accordance with military etiquette) assigned to him as 'Aide-in-Waiting' and Secretary. Although I had frequently met the President as 'Bearer of Dispatches,' I was not a little prejudiced, and a good deal irritated, at the levity which he was charged with indulging in. In grave matters, jesting and frolicking seemed to me shocking, with such vital matters at stake, and I confess to thinking of Nero.
"But all this changed when I came to know him; and I very soon discerned that he had a sad nature; but that, although a terrible burden, his sadness did not originate in his great official responsibilities. I had heard that his home was not pleasant, but did not know that there was more beyond it.
"The day after Mr. Lincoln came to us he said to me: 'I suppose you have neither a Bible nor a copy of Shakespeare here?' I replied that I had a Bible, and the General had Shakespeare, and that the latter never missed a night without reading it. 'Won't he lend it to me?' inquired the President. I answered, 'Yes,' and, of course, obtained it for him.
"The day following he read by himself in one of my offices, two hours or more, entirely alone, I being engaged in a connecting room on duty. He finally interrupted me, inviting me to rest while he would read to me. He read from Macbeth, Lear, and finally. King John. In reading the passage where Constance bewails to the King the loss of her child, I noticed that his voice trembled and he was deeply moved. Laying the book on the table he said:
"'Did you ever dream of a lost friend and feel that you were having a sweet communion with that friend, and yet a consciousness that it was not a reality?'
"'Yes,' I replied, 'I think almost any one may have had such an experience.'
"'So do I,' he mused; 'I dream of my dead boy, Willie, again and again.'
"I shall never forget the sigh nor the look of sorrow that accompanied this expression. He was utterly overcome; his great frame shook, and, bowing down on the table, he wept as only such a man in the breaking down of a great sorrow could weep. It is needless to say that I wept in sympathy, and quietly left the room that he might recover without restraint.
"Lincoln never again referred to his boy, but he made me feel that he had given me a sacred confidence, and he ever after treated me with a tenderness and regard that won my love.
"Again, some days later, I had been absent on a reconnoissance, and returned late in the afternoon. I was in my room dressing for dinner (which was a very formal affair, as, besides the Administration, we had, almost daily, distinguished foreigners to dine) when the President came in. Seeing me in full uniform he said:
"'Why, Colonel, you're fixing up mighty fine. Suppose you lend me your comb and brush, and I'll put on a few touches, too.'
"I handed the desired articles to him and he toyed with the comb awhile and then laid it down, exclaiming:
"'This thing will never get through my hair. Now, if you have such a thing as they comb a horse's tail with, I believe I can use it.' After a merry laugh, he continued: 'By the way, I can tell you a good story about my hair. When I was nominated, at Chicago, an enterprising fellow thought that a great many people would like to see how Abe Lincoln looked, and, as I had not long before sat for a photograph, this fellow having seen it, rushed over and bought the negative. He at once got out no end of wood-cuts, and, so active was their circulation, they were selling in all parts of the country. Soon after they reached Springfield I heard a boy crying them for sale on the streets. 'Here's your likeness of Abe Lincoln!' he shouted.
"'Buy one; price only two shillings! Will look a good deal better when he gets his hair combed!'"


"Abe" Lincoln's
Anecdotes and Stories
A COLLECTION OF THE BEST
STORIES TOLD BY LINCOLN
WHICH MADE HIM
FAMOUS AS
AMERICA'S BEST STORY TELLER
Compiled by
R. D. WORDSWORTH
THE MUTUAL BOOK COMPANY
Publishers
BOSTON,
MASS.
Compiled, 1908,
for
The
Mutual Book Company
It was once said of Shakespeare that the great mind that conceived the tragedies of "Hamlet," "Macbeth," etc., would have lost its reason if it had not found vent in the sparkling humor of such comedies as "The Merry Wives of Windsor" and "The Comedy of Errors."
The great strain on the mind of Abraham Lincoln produced by four years of civil war might likewise have overcome his reason had it not found vent in the yarns and stories he constantly told. No more fun-loving or humor-loving man than Abraham Lincoln ever lived. He enjoyed a joke even when it was on himself, and probably, while he got his greatest enjoyment from telling stories, he had a keen appreciation of the humor in those that were told him.
For a while during the Civil War, General Fremont was without a command. One day in discussing Fremont's case with George W. Julian, President Lincoln said he did not know where to place him, and that it reminded him of the old man who advised his son to take a wife, to which the young man responded: "All right; whose wife shall I take?"
On one occasion when Mr. Lincoln was going to attend a political convention one of his rivals, a liveryman, provided him with a slow horse, hoping that he would not reach his destination in time. Mr. Lincoln got there, however, and when he returned with the horse he said: "You keep this horse for funerals, don't you?" "Oh, no," replied the liveryman. "Well, I'm glad of that, for if you did you'd never get a corpse to the grave in time for the resurrection."
In an interview between President Lincoln and Petroleum V. Nasby, the name came up of a recently deceased politician of Illinois whose merit was blemished by great vanity. His funeral was very largely attended.
"If General —— had known how big a funeral he would have had," said Mr. Lincoln, "he would have died years ago."
"General Blank asks for more men," said Secretary of War Stanton to the President one day, showing the latter a telegram from the commander named, appealing for re-enforcements.
"I guess he's killed off enough men, hasn't he?" queried the President. "I don't mean Confederates—our own men. What's the use in sending volunteers down to him if they're only used to fill graves?"
"His dispatch seems to imply that, in his opinion, you have not the confidence in him he thinks he deserves," the War Secretary went on to say, as he looked over the telegram again.
"Oh," was the President's reply, "he needn't lose any of his sleep on that account. Just telegraph him[Pg 5] to that effect; also, that I don't propose to send him any more men."
Secretary of War Stanton told the President the following story, which greatly amused the latter, as he was especially fond of a joke at the expense of some high military or civil dignitary.
Stanton had little or no sense of humor.
When Secretary Stanton was making a trip up the Broad River in North Carolina, in a tugboat, a Federal picket yelled out, "What have you got on board of that tug?"
The severe and dignified answer was, "The Secretary of War and Major-General Foster."
Instantly the picket roared back, "We've got major-generals enough up here. Why don't you bring us up some hardtack?"
When Mr. Lincoln delivered his first inaugural he was introduced by his friend, United States Senator E. D. Baker, of Oregon. He carried a cane and a little roll—the manuscript of his inaugural address. There was a moment's pause after the introduction, as he vainly looked for a spot where he might place his high silk hat.
Stephen A. Douglas, the political antagonist of his whole public life, the man who had pressed him hardest in the campaign of 1860, was seated just behind him. Douglas stepped forward quickly, and took the hat which Mr. Lincoln held helplessly in his hand.
"If I can't be President," Douglas whispered smilingly to Mrs. Brown, a cousin of Mrs. Lincoln and a member of the President's party, "I at least can hold his hat."
A man called upon the President and solicited a pass for Richmond.
"Well," said the President, "I would be very happy to oblige, if my passes were respected; but the fact is, sir, I have, within the past two years, given passes to two hundred and fifty thousand men to go to Richmond, and not one has got there yet."
The applicant quietly and respectfully withdrew on his tiptoes.
Lincoln made his first appearance in society when he was first sent to Springfield, Ill., as a member of the State Legislature. It was not an imposing figure which he cut in a ballroom, but still he was occasionally to be found there. Miss Mary Todd, who afterward became his wife, was the magnet which drew the tall, awkward young man from his den. One evening Lincoln approached Miss Todd, and said, in his peculiar idiom:
"Miss Todd, I should like to dance with you the worst way."
The young woman accepted the inevitable, and hobbled around the room with him. When she returned to her seat, one of her companions asked mischievously:
"Well, Mary, did he dance with you the worst way?"
"Yes," she answered, "the very worst."
Lincoln loved anything that savored of wit or humor among the soldiers. He used to relate two stories to show, he said, that neither death nor danger could quench the grim humor of the American soldier:
"A soldier of the Army of the Potomac was being carried to the rear of battle with both legs shot off, who,[Pg 7] seeing a pie-woman, called out, 'Say, old lady, are them pies sewed or pegged?'
"And there was another one of the soldiers at the battle of Chancellorsville, whose regiment, waiting to be called into the fight, was taking coffee. The hero of the story put to his lips a crockery mug which he had carried with care through several campaigns. A stray bullet, just missing the drinker's head, dashed the mug into fragments and left only the handle on his finger. Turning his head in that direction, he scowled, 'Johnny, you can't do that again!'"
During one of the periods when things were at a standstill, the Washington authorities, being unable to force General McClellan to assume an aggressive attitude, President Lincoln went to the general's headquarters to have a talk with him, but for some reason he was unable to get an audience.
Mr. Lincoln returned to the White House much disturbed at his failure to see the commander of the Union forces, and immediately sent for two general officers, to have a consultation. On their arrival, he told them he must have some one to talk to about the situation, and as he had failed to see General McClellan, he wished their views as to the possibility or probability of commencing active operations with the Army of the Potomac.
"Something's got to be done," said the President, emphatically, "and done right away, or the bottom will fall out of the whole thing. Now, if McClellan doesn't want to use the army for a while, I'd like to borrow it from him and see if I can't do something or other with it.
"If McClellan can't fish, he ought at least to be cutting bait at a time like this."
Mrs. Lincoln knew her husband was not "pretty," but she liked to have him presentable when he appeared before the public. Stephen Fiske, in "When Lincoln Was First Inaugurated," tells of Mrs. Lincoln's anxiety to have the President-elect "smoothed down" a little when receiving a delegation that was to greet them upon reaching New York City.
"The train stopped," writes Mr. Fiske, "and through the windows immense crowds could be seen; the cheering drowning the blowing off of steam of the locomotive. Then Mrs. Lincoln opened her handbag and said:
"'Abraham, I must fix you up a bit for these city folks.'
"Mr. Lincoln gently lifted her upon the seat before him; she parted, combed and brushed his hair and arranged his black necktie.
"'Do I look nice now, mother?' he affectionately asked.
"'Well, you'll do, Abraham,' replied Mrs. Lincoln critically. So he kissed her and lifted her down from the seat, and turned to meet Mayor Wood, courtly and suave, and to have his hand shaken by the other New York officials."
"Several of us lawyers," remarked one of his colleagues, "in the eastern end of the circuit, annoyed Lincoln once while he was holding court for Davis by attempting to defend against a note to which there were many makers. We had no legal, but a good moral defense, but what we wanted most of all was to stave it off till the next term of court by one expedient or another.
"We bothered 'the court' about it till late on[Pg 9] Saturday, the day of adjournment. He adjourned for supper with nothing left but this case to dispose of. After supper he heard our twaddle for nearly an hour, and then made this odd entry:
"'L. D. Chaddon vs. J. D. Beasley et al., April Term, 1856. Champaign County Court. Plea in abatement by B. Z. Green, a defendant not served, filed Saturday at 11 o'clock a.m., April 24, 1856, stricken from the files by order of court. Demurrer to declaration, if there ever was one, overruled. Defendants who are served now, at 8 o'clock p.m., of the last day of the term, ask to plead to the merits, which is denied by the court on the ground that the offer comes too late, and therefore, as by nil dicet, judgment is rendered for Pl'ff. Clerk assess damages. A. Lincoln, Judge pro tem.'
"The lawyer who reads this singular entry will appreciate its oddity if no one else does. After making it, one of the lawyers, on recovering from his astonishment, ventured to inquire: 'Well, Lincoln, how can we get this case up again?'
"Lincoln eyed him quizzically for a moment, and then answered, 'You have all been so mighty smart about this case, you can find out how to take it up again yourselves.'"
"Old Pap," as the soldiers called General George H. Thomas, was aggravatingly slow at a time when the President wanted him to "get a move on"; in fact, the gallant "Rock of Chickamauga" was evidently entered in a snail-race.
"Some of my generals are so slow," regretfully remarked Lincoln one day, "that molasses in the coldest days of winter is a race horse compared to them.
"They're brave enough, but somehow or other they get fastened in a fence corner, and can't figure their way out."
Ward Lamon, Marshal of the District of Columbia during Lincoln's time in Washington, was a powerful man; his strength was phenomenal, and a blow from his fist was like unto that coming from the business end of a sledge.
Lamon tells this story, the hero of which is not mentioned by name, but in all probability his identity can be guessed:
"On one occasion, when the fears of the loyal element of the city (Washington) were excited to fever-heat, a free fight near the old National Theatre occurred about eleven o'clock one night. An officer, in passing the place, observed what was going on, and seeing the great number of persons engaged, he felt it to be his duty to command the peace.
"The imperative tone of his voice stopped the fighting for a moment, but the leader, a great bully, roughly pushed back the officer and told him to go away or he would whip him. The officer again advanced and said, 'I arrest you,' attempting to place his hand on the man's shoulder, when the bully struck a fearful blow at the officer's face.
"This was parried, and instantly followed by a blow from the fist of the officer, striking the fellow under the chin and knocking him senseless. Blood issued from his mouth, nose and ears. It was believed that the man's neck was broken. A surgeon was called, who pronounced the case a critical one, and the wounded man was hurried away on a litter to the hospital.
"There the physicians said there was concussion of the brain, and that the man would die. All the medical skill the officer could procure was employed in the hope of saving the life of the man. His conscience smote him for having, as he believed, taken the life of a fellow-creature, and he was inconsolable.
"Being on terms of intimacy with the President,[Pg 11] about two o'clock that night the officer went to the White House, woke up Mr. Lincoln, and requested him to come into his office, where he told him his story. Mr. Lincoln listened with great interest until the narrative was completed, and then asked a few questions, after which he remarked:
"'I am sorry you had to kill the man, but these are times of war, and a great many men deserve killing. This one, according to your story, is one of them; so give yourself no uneasiness about the matter. I will stand by you.'
"'That is not why I came to you. I knew I did my duty, and had no fears of your disapproval of what I did,' replied the officer; and then he added: 'Why I came to you was, I felt great grief over the unfortunate affair, and I wanted to talk to you about it.'
"Mr. Lincoln then said, with a smile, placing his hand on the officer's shoulder: 'You go home now and get some sleep; but let me give you this piece of advice—hereafter, when you have occasion to strike a man, don't hit him with your fist; strike him with a club, a crowbar, or with something that won't kill him.'"
An old acquaintance of the President visited him in Washington. Lincoln desired to give him a place. Thus encouraged, the visitor, who was an honest man, but wholly inexperienced in public affairs or business, asked for a high office, Superintendent of the Mint.
The President was aghast, and said: "Good gracious! Why didn't he ask to be the Secretary of the Treasury, and have done with it?"
Afterward, he said: "Well, now, I never thought Mr. —— had anything more than average ability, when we were young men together. But, then, I suppose he thought the same thing about me, and—here I am!"
When Mr. Lincoln was a candidate for the Legislature, it was the practice at that date in Illinois for two rival candidates to travel over the district together. The custom led to much good-natured raillery between them; and in such contests Lincoln was rarely, if ever, worsted. He could even turn the generosity of a rival to account by his whimsical treatment.
On one occasion, says Mr. Weir, a former resident of Sangamon county, he had driven out from Springfield in company with a political opponent to engage in joint debate. The carriage, it seems, belonged to his opponent. In addressing the gathering of farmers that met them, Lincoln was lavish in praise of the generosity of his friend.
"I am too poor to own a carriage," he said, "but my friend has generously invited me to ride with him. I want you to vote for me if you will; but if not, then vote for my opponent, for he is a fine man."
His extravagant and persistent praise of his opponent appealed to the sense of humor in his rural audience, to whom his inability to own a carriage was by no means a disqualification.
President Lincoln, having arranged to go to New York, was late for his train, much to the disgust of those who were to accompany him, and all were compelled to wait several hours until the next train steamed out of the station. President Lincoln was much amused at the dissatisfaction displayed, and then ventured the remark that the situation reminded him of "a little story." Said he:
"Out in Illinois, a convict who had murdered his cellmate was sentenced to be hanged. On the day set for the execution, crowds lined the roads leading to the[Pg 13] spot where the scaffold had been erected, and there was much jostling and excitement. The condemned man took matters coolly, and as one batch of perspiring, anxious men rushed past the cart in which he was riding, he called out, 'Don't be in a hurry, boys. You've got plenty of time. There won't be any fun until I get there.'
"That's the condition of things now," concluded the President; "there won't be any fun at New York until I get there."
From the day of his nomination by the Chicago convention, gifts poured in upon Lincoln. Many of these came in the form of wearing apparel. Mr. George Lincoln, of Brooklyn, who brought to Springfield, in January, 1861, a handsome silk hat to the President-elect, the gift of a New York hatter, told some friends that in receiving the hat Lincoln laughed heartily over the gifts of clothing, and remarked to Mrs. Lincoln: "Well, wife, if nothing else comes out of this scrape, we are going to have some new clothes, are we not?"
When President Lincoln heard of the Confederate raid at Fairfax, in which a brigadier-general and a number of valuable horses were captured, he gravely observed:
"Well, I am sorry for the horses."
"Sorry for the horses, Mr. President!" exclaimed the Secretary of War, raising his spectacles and throwing himself back in his chair in astonishment.
"Yes," replied Mr. Lincoln, "I can make a brigadier-general in five minutes, but it is not easy to replace a hundred and ten horses."
"Every man has his own peculiar and particular way of getting at and doing things," said President Lincoln one day, "and he is often criticised because that way is not the one adopted by others. The great idea is to accomplish what you set out to do. When a man is successful in whatever he attempts, he has many imitators, and the methods used are not so closely scrutinized, although no man who is of good intent will resort to mean, underhanded, scurvy tricks.
"That reminds me of a fellow out in Illinois, who had better luck in getting prairie chickens than any one in the neighborhood. He had a rusty old gun no other man dared to handle; he never seemed to exert himself, being listless and indifferent when out after game, but he always brought home all the chickens he could carry, while some of the others, with their finely trained dogs and latest improved fowling-pieces, came home alone.
"'How is it, Jake?' inquired one sportsman, who, although a good shot, and knew something about hunting, was often unfortunate, 'that you never come home without a lot of birds?'
"Jake grinned, half closed his eyes, and replied: 'Oh, I don't know that there's anything queer about it. I jes' go ahead an' git 'em.'
"'Yes, I know you do; but how do you do it?'
"'You'll tell.'
"'Honest, Jake, I won't say a word. Hope to drop dead this minute.'
"'Never say nothing, if I tell you?'
"'Cross my heart three times.'
"This reassured Jake, who put his mouth close to the ear of his eager questioner, and said, in a whisper:
"'All you got to do is jes' to hide in a fence corner an' make a noise like a turnip. That'll bring the chickens every time.'"
The President had decided to select a new War Minister, and the leading Republican Senators thought the occasion was opportune to change the whole seven Cabinet ministers. They, therefore, earnestly advised him to make a clean sweep, and select seven new men, and so restore the waning confidence of the country.
The President listened with patient courtesy, and when the Senators had concluded, he said, with a characteristic gleam of humor in his eye:
"Gentlemen, your request for a change of the whole Cabinet because I have made one change reminds me of a story I once heard in Illinois, of a farmer who was much troubled by skunks. His wife insisted on his trying to get rid of them.
"He loaded his shotgun one moonlight night and awaited developments. After some time the wife heard the shotgun go off, and in a few minutes the farmer entered the house.
"'What luck have you?' asked she.
"'I hid myself behind the wood-pile,' said the old man, 'with the shotgun pointed towards the hen roost, and before long there appeared not one skunk, but seven. I took aim, blazed away, killed one, and he raised such a fearful smell that I concluded it was best to let the other six go.'"
The Senators laughed and retired.
Lincoln admitted that he was not particularly energetic when it came to real hard work.
"My father," said he one day, "taught me how to work, but not to love it. I never did like to work, and I don't deny it. I'd rather read, tell stories, crack jokes, talk, laugh—anything but work."
Judge Kelly, of Pennsylvania, who was one of the committee to advise Lincoln of his nomination, and who was himself a great many feet high, had been eyeing Lincoln's lofty form with a mixture of admiration and possibly jealousy.
This had not escaped Lincoln, and as he shook hands with the judge he inquired, "What is your height?"
"Six feet three. What is yours, Mr. Lincoln?"
"Six feet four."
"Then," said the judge, "Pennsylvania bows to Illinois. My dear man, for years my heart has been aching for a President that I could look up to, and I've at last found him."
Old Dennis Hanks was sent to Washington at one time by persons interested in securing the release from jail of several men accused of being copperheads. It was thought Old Dennis might have some influence with the President.
The latter heard Dennis' story and then said: "I will send for Mr. Stanton. It is his business."
Secretary Stanton came into the room, stormed up and down, and said the men ought to be punished more than they were. Mr. Lincoln sat quietly in his chair and waited for the tempest to subside, and then quietly said to Stanton he would like to have the papers next day.
When he had gone, Dennis said:
"'Abe,' if I was as big and as ugly as you are, I would take him over my knee and spank him."
The President replied: "No, Stanton is an able and valuable man for this Nation, and I am glad to bear his anger for the service he can give the Nation."
"Abe's" school teacher, Crawford, endeavored to teach his pupils some of the manners of the "polite society" of Indiana—1823 or so. This was a part of his system:
One of the pupils would retire, and then come in as a stranger, and another pupil would have to introduce him to all the members of the school in what was considered "good manners."
As "Abe" wore a linsey-woolsey shirt, buckskin breeches which were too short and very tight, and low shoes, and was tall and awkward, he no doubt created considerable merriment when his turn came. He was growing at a fearful rate; he was fifteen years of age, and two years later attained his full height of six feet four inches.
The first corps of the army commanded by General Reynolds was once reviewed by the President on a beautiful plain at the north of Potomac Creek, about eight miles from Hooker's headquarters. The party rode thither in an ambulance over a rough corduroy road, and as they passed over some of the more difficult portions of the jolting way the ambulance driver, who sat well in front, occasionally let fly a volley of suppressed oaths at his wild team of six mules.
Finally, Mr. Lincoln, leaning forward, touched the man on the shoulder and said:
"Excuse me, my friend, are you an Episcopalian?"
The man, greatly startled, looked around and replied:
"No, Mr. President; I am a Methodist."
"Well," said Lincoln, "I thought you must be an Episcopalian, because you swear just like Governor Seward, who is a church warden."
When Lincoln was a young lawyer in Illinois, he and a certain judge once got to bantering one another about trading horses; and it was agreed that the next morning at nine o'clock they should make a trade, the horses to be unseen up to that hour, and no backing out, under a forfeiture of $25. At the hour appointed, the Judge came up, leading the sorriest-looking specimen of a horse ever seen in those parts. In a few minutes Mr. Lincoln was seen approaching with a wooden saw-horse upon his shoulders.
Great were the shouts and laughter of the crowd, and both were greatly increased when Lincoln, on surveying the Judge's animal, set down his saw-horse and exclaimed:
"Well, Judge, this is the first time I ever got the worst of it in a horse trade."
Immediately after Mr. Lincoln's nomination for President at the Chicago convention, a Committee, of which Governor Morgan, of New York, was chairman, visited him in Springfield, Ill., where he was officially informed of his nomination.
After this ceremony had passed, Mr. Lincoln remarked to the company that as a fit ending to an interview so important and interesting as that which had just taken place, he supposed good manners would require that he should treat the committee with something to drink; and opening the door that led into the rear, he called out, "Mary! Mary!" A girl responded to the call, to whom Mr. Lincoln spoke a few words in an undertone, and, closing the door, returned again and talked with his guests. In a few minutes the maid entered, bearing a large waiter, containing several glass tumblers, and a large pitcher, and placed them upon the[Pg 19] center-table. Mr. Lincoln arose, and gravely addressing the company, said: "Gentlemen, we must pledge our mutual health in the most healthy beverage that God has given to man—it is the only beverage I have ever used or allowed my family to use, and I cannot conscientiously depart from it on the present occasion. It is pure Adam's ale from the spring." And, taking the tumbler, he touched it to his lips, and pledged them his highest respects in a cup of cold water. Of course, all his guests admired his consistency, and joined in his example.
These lines were found written in young Lincoln's own hand at the bottom of a page whereon he had been ciphering. Lincoln always wrote a clear, regular "fist." In this instance he evidently did not appreciate the sacredness of the name of the Deity, when he used a little "g."
Lincoln once said he did not remember the time when he could not write.
Mr. Roland Diller, who was one of Mr. Lincoln's neighbors in Springfield, tells the following:
"I was called to the door one day by the cries of children in the street, and there was Mr. Lincoln, striding by with two of his boys, both of whom were wailing aloud. 'Why, Mr. Lincoln, what's the matter with the boys?' I asked.
"'Just what's the matter with the whole world,' Lincoln replied. 'I've got three walnuts, and each wants two.'"
At one time the President had the appointment of a large additional number of brigadier and major-generals. Among the immense number of applications, Mr. Lincoln came upon one wherein the claims of a certain worthy (not in the service at all) "for a generalship" were glowingly set forth. But the applicant didn't specify whether he wanted to be brigadier or major-general.
The President observed this difficulty, and solved it by a lucid indorsement. The clerk, on receiving the paper again, found written across its back, "Major-General, I reckon. A. Lincoln."
Lincoln had been in the telegraph office at Springfield during the casting of the first and second ballots in the Republican National Convention at Chicago, and then left and went over to the office of the State Journal, where he was sitting conversing with friends while the third ballot was being taken.
In a few moments came across the wires the announcement of the result. The superintendent of the telegraph company wrote on a scrap of paper: "Mr. Lincoln, you are nominated on the third ballot," and a boy ran with the message to Lincoln.
He looked at it in silence, amid the shouts of those around him; then rising and putting it in his pocket, he said quietly: "There's a little woman down at our house would like to hear this; I'll go down and tell her."
About two years before Lincoln was nominated for the Presidency he went to Bloomington, Illinois, to try a case of some importance. His opponent—who afterward reached a high place in his profession—was[Pg 21] a young man of ability, sensible but sensitive, and one to whom the loss of a case was a great blow. He therefore studied hard and made much preparation.
This particular case was submitted to the jury late at night, and, although anticipating a favorable verdict, the young attorney spent a sleepless night in anxiety. Early next morning he learned, to his great chagrin, that he had lost the case.
Lincoln met him at the court-house some time after the jury had come in, and asked him what had become of his case.
With lugubrious countenance and in a melancholy tone the young man replied, "It's gone to hell."
"Oh, well," replied Lincoln, "then you will see it again."
President Lincoln and Postmaster-General Blair were talking of the war. "Blair," said the President, "did you ever know that fright has sometimes proven a cure for boils?" "No, Mr. President, how is that?" "I'll tell you. Not long ago when a colonel, with his cavalry, was at the front, and the Rebs were making things rather lively for us, the colonel was ordered out to a reconnoissance. He was troubled at the time with a big boil where it made horseback riding decidedly uncomfortable. He finally dismounted and ordered the troops forward without him. Soon he was startled by the rapid reports of pistols and the helter-skelter approach of his troops in full retreat before a yelling rebel force. He forgot everything but the yells, sprang into his saddle, and made capital time over the fences and ditches till safe within the lines. The pain from his boil was gone, and the boil too, and the colonel swore that there was no cure for boils so sure as fright from rebel yells."
Lincoln was constantly bothered by members of delegations of "goody-goodies," who knew all about running the War, but had no inside information as to what was going on. Yet they poured out their advice in streams, until the President was heartily sick of the whole business, and wished the War would find some way to kill off these nuisances.
"How many men have the Confederates now in the field?" asked one of these bores one day.
"About one million two hundred thousand," replied the President.
"Oh, my! Not so many as that, surely, Mr. Lincoln."
"They have fully twelve hundred thousand, no doubt of it. You see, all of our generals when they get whipped say the enemy outnumbers them from three or five to one, and I must believe them. We have four hundred thousand men in the field, and three times four make twelve,—don't you see it? It is as plain to be seen as the nose on a man's face; and at the rate things are now going, with the great amount of speculation and the small crop of fighting, it will take a long time to overcome twelve hundred thousand rebels in arms.
"If they can get subsistence they have everything else, except a just cause. Yet it is said that 'thrice is he armed that hath his quarrel just.' I am willing, however, to risk our advantage of thrice in justice against their thrice in numbers."
Mr. Lovejoy, heading a committee of Western men, discussed an important scheme with the President, and the gentlemen were then directed to explain it to Secretary of War Stanton.
Upon presenting themselves to the Secretary, and showing the President's order, the Secretary said: "Did Lincoln give you an order of that kind?"
"He did, sir."
"Then he is a d—d fool," said the angry Secretary.
"Do you mean to say that the President is a d—d fool?" asked Lovejoy in amazement.
"Yes, sir, if he gave you such an order as that."
The bewildered Illinoisan betook himself at once to the President and related the result of the conference.
"Did Stanton say I was a d—d fool?" asked Lincoln at the close of the recital.
"He did, sir, and repeated it."
After a moment's pause, and looking up, the President said: "If Stanton said I was a d—d fool, then I must be one, for he is nearly always right, and generally says what he means. I will slip over and see him."
McClellan was a thorn in Lincoln's side—"always up in the air," as the President put it—and yet he hesitated to remove him. "The Young Napoleon" was a good organizer, but no fighter. Lincoln sent him everything necessary in the way of men, ammunition, artillery and equipments, but he was forever unready.
Instead of making a forward movement at the time expected, he would notify the President that he must have more men. These were given him as rapidly as possible, and then would come a demand for more horses, more this and that, usually winding up with a demand for still "more men."
Lincoln bore it all in patience for a long time, but one day, when he had received another request for more men, he made a vigorous protest.
"If I gave McClellan all the men he asks for," said the President, "they couldn't find room to lie down. They'd have to sleep standing up."
When General W. T. Sherman, November 12th, 1864, severed all communication with the North and started for Savannah with his magnificent army of sixty thousand men, there was much anxiety for a month as to his whereabouts. President Lincoln, in response to an inquiry, said: "I know what hole Sherman went in at, but I don't know what hole he'll come out at."
Colonel McClure had been in consultation with the President one day, about two weeks after Sherman's disappearance, and in this connection related this incident:
"I was leaving the room, and just as I reached the door the President turned around, and, with a merry twinkling of the eye, inquired, 'McClure, wouldn't you like to hear something from Sherman?'
"The inquiry electrified me at the instant, as it seemed to imply that Lincoln had some information on the subject. I immediately answered, 'Yes, most of all, I should like to hear from Sherman.'
"To this President Lincoln answered, with a hearty laugh: 'Well, I'll be hanged if I wouldn't myself.'"
General "Joe" Hooker, the fourth commander of the noble but unfortunate Army of the Potomac, was appointed to that position by President Lincoln in January, 1863. General Scott, for some reason, disliked Hooker and would not appoint him. Hooker, after some months of discouraging waiting, decided to return to California, and called to pay his respects to President Lincoln. He was introduced as Captain Hooker, and to the surprise of the President began the following speech:
"Mr. President, my friend makes a mistake. I am not Captain Hooker, but was once Lieutenant-Colonel Hooker of the regular army. I was lately a farmer in California, but since the Rebellion broke out I have been trying to get into service, but I find I am not wanted.
"I am about to return home; but before going, I was anxious to pay my respects to you, and express my wishes for your personal welfare and success in quelling this Rebellion. And I want to say to you a word more.
"I was at Bull Run the other day, Mr. President, and it is no vanity in me to say, I am a darned sight better general than you had on the field."
This was said, not in the tone of a braggart, but of a man who knew what he was talking about. Hooker did not return to California, but in a few weeks Captain Hooker received from the President a commission as Brigadier-General Hooker.
One day an old lady from the country called on President Lincoln, her tanned face peering up to his through a pair of spectacles. Her errand was to present Mr. Lincoln a pair of stockings of her own make a yard long. Kind tears came to his eyes as she spoke to him, and then, holding the stockings one in each hand, dangling wide apart for general inspection, he assured her that he should take them with him to Washington, where (and here his eyes twinkled) he was sure he should not be able to find any like them.
Quite a number of well-known men were in the room with the President when the old lady made her presentation. Among them was George S. Boutwell, who afterwards became Secretary of the Treasury.
The amusement of the company was not at all diminished by Mr. Boutwell's remark, that the lady had evidently made a very correct estimate of Mr. Lincoln's latitude and longitude.
President Lincoln appointed as consul to a South American country a young man from Ohio who was a dandy. A wag met the new appointee on his way to the White House to thank the President. He was dressed in the most extravagant style. The wag horrified him by telling him that the country to which he was assigned was noted chiefly for the bugs that abounded there and made life unbearable.
"They'll bore a hole clean through you before a week has passed," was the comforting assurance of the wag as they parted at the White House steps. The new consul approached Lincoln with disappointment clearly written all over his face. Instead of joyously thanking the President, he told him the wag's story of the bugs. "I am informed, Mr. President," he said, "that the place is full of vermin and that they could eat me up in a week's time." "Well, young man," replied Lincoln, "if that's true, all I've got to say is that if such a thing happened they would leave a mighty good suit of clothes behind."
Lincoln never failed to take part in all political campaigns in Illinois, as his reputation as a speaker caused his services to be in great demand. As was natural, he was often the target at which many of the "Smart Alecks" of that period shot their feeble bolts, but Lincoln was so ready with his answers that few of them cared to engage him a second time.
In one campaign Lincoln was frequently annoyed by a young man who entertained the idea that he was a born orator. He had a loud voice, was full of language, and so conceited that he could not understand why the people did not recognize and appreciate his abilities.
This callow politician delighted in interrupting public speakers, and at last Lincoln determined to squelch him. One night while addressing a large meeting at Springfield, the fellow became so offensive that "Abe" dropped the threads of his speech and turned his attention to the tormentor.
"I don't object," said Lincoln, "to being interrupted with sensible questions, but I must say that my boisterous friend does not always make inquiries which properly come under that head. He says he is afflicted with headaches, at which I don't wonder, as it is a well-known fact that nature abhors a vacuum, and takes her own way of demonstrating it.
"This noisy friend reminds me of a certain steamboat that used to run on the Illinois River. It was an energetic boat, was always busy. When they built it, however, they made one serious mistake, this error being in the relative sizes of the boiler and the whistle. The latter was usually busy too, and people were aware that it was in existence.
"This particular boiler to which I have reference was a six-foot one, and did all that was required of it in the way of pushing the boat along; but as the builders of the vessel had made the whistle a six-foot one, the consequence was that every time the whistle blew the boat had to stop."
Three or four days after the battle of Bull Run, some gentlemen who had been on the field called upon the President.
He inquired very minutely regarding all the circumstances of the affair, and, after listening with the utmost attention, said, with a touch of humor:
"So it is your notion that we whipped the rebels and then ran away from them!"
When a surveyor, Mr. Lincoln first platted the town of Petersburg, Ill. Some twenty or thirty years afterward the property-owners along one of the outlying streets had trouble in fixing their boundaries. They consulted the official plat and got no relief. A committee was sent to Springfield to consult the distinguished surveyor, but he failed to recall anything that would give them aid, and could only refer them to the record. The dispute therefore went into the courts. While the trial was pending, an old Irishman named McGuire, who had worked for some farmer during the summer, returned to town for the winter. The case being mentioned in his presence, he promptly said: "I can tell you all about it. I helped carry the chain when Abe Lincoln laid out this town. Over there where they are quarreling about the lines, when he was locating the street, he straightened up from his instrument and said: 'If I run that street right through, it will cut three or four feet off the end of ——'s house. It's all he's got in the world and he could never get another. I reckon it won't hurt anything out here if I skew the line a little and miss him.'"
The line was "skewed," and hence the trouble, and more testimony furnished as to Lincoln's abounding kindness of heart, that would not willingly harm any human being.
"It seems to me," remarked the President one day while reading over some of the appealing telegrams sent to the War Department by General McClellan, "that McClellan has been wandering around and has sort of got lost. He's been hollering for help ever since he went South—wants somebody to come to his deliverance and get him out of the place he's got into.
"He reminds me of the story of a man out in Illinois who, in company with a number of friends, visited the State penitentiary. They wandered all through the institution and saw everything, but just about the time to depart this particular man became separated from his friends and couldn't find his way out.
"He roamed up and down one corridor after another, becoming more desperate all the time, when, at last, he came across a convict who was looking out from between the bars of his cell-door. Here was salvation at last. Hurrying up to the prisoner he hastily asked:
"'Say! How do you get out of this place?'"
Ward Lamon told this story of President Lincoln, whom he found one day in a particularly gloomy frame of mind. Lamon said:
"The President remarked, as I came in, 'I fear I have made Senator Wade, of Ohio, my enemy for life.'
"'How?' I asked.
"'Well,' continued the President, 'Wade was here just now urging me to dismiss Grant, and, in response to something he said, I remarked, "Senator, that reminds me of a story."'
"'What did Wade say,' I inquired of the President.
"'He said, in a petulant way,' the President responded, '"It is with you, sir, all story, story! You are the father of every military blunder that has been made during the war. You are on your road to hell, sir, with this government, by your obstinacy, and you are not a mile off this minute."'
"'What did you say then?'
"'I good-naturedly said to him,' the President replied, '"Senator, that is just about from here to the Capitol, is it not?" He was very angry, grabbed up his hat and cane, and went away.'"
Speed, who was a prosperous young merchant of Springfield, reports that Lincoln's personal effects consisted of a pair of saddle-bags, containing two or three lawbooks, and a few pieces of clothing. Riding on a borrowed horse, he thus made his appearance in Springfield. When he discovered that a single bedstead would cost seventeen dollars he said, "It is probably cheap enough, but I have not enough money to pay for it." When Speed offered to trust him, he said: "If I fail here as a lawyer, I will probably never pay you at all." Then Speed offered to share a large double bed with him.
"Where is your room?" Lincoln asked.
"Upstairs," said Speed, pointing from the store leading to his room. Without saying a word, he took his saddle-bags on his arm, went upstairs, set them down on the floor, came down again, and with a face beaming with pleasure and smiles, exclaimed: "Well, Speed, I'm moved."
"By the way," remarked President Lincoln one day to Colonel Cannon, a close personal friend, "I can tell you a good story about my hair. When I was nominated at Chicago, an enterprising fellow thought that a great many people would like to see how 'Abe' Lincoln looked, and, as I had not long before sat for a photograph, the fellow, having seen it, rushed over and bought the negative.
"He at once got no end of wood-cuts, and so active was their circulation that they were soon selling in all parts of the country.
"Soon after they reached Springfield, I heard a boy crying them for sale on the streets. 'Here's your likeness of "Abe" Lincoln!' he shouted. 'Buy one; price only two shillings! Will look a great deal better when he gets his hair combed!'"
Where men bred in courts, accustomed to the world, or versed in diplomacy, would use some subterfuge, or would make a polite speech, or give a shrug of the shoulders, as the means of getting out of an embarrassing position, Lincoln raised a laugh by some bold west-country anecdote, and moved off in the cloud of merriment produced by the joke. When Attorney-General Bates was remonstrating apparently against the appointment of some indifferent lawyer to a place of judicial importance, the President interposed with: "Come now, Bates, he's not half as bad as you think. Besides that, I must tell you, he did me a good turn long ago. When I took to the law I was going to court one morning, with some ten or twelve miles of bad road before me, and I had no horse.
"The Judge overtook me in his carriage.
"'Hallo, Lincoln! are you not going to the court-house? Come in and I will give you a seat!'
"Well, I got in, and the Judge went on reading his papers. Presently the carriage struck a stump on one side of the road, then it hopped off to the other. I looked out, and I saw the driver was jerking from side to side in his seat, so I says:
"'Judge, I think your coachman has been taking a little too much this morning.'
"'Well, I declare, Lincoln,' said he, 'I should not much wonder if you were right, for he has nearly upset me half a dozen times since starting.'
"So, putting his head out of the window, he shouted, 'Why, you infernal scoundrel, you are drunk!'
"Upon which, pulling up his horses, and turning around with great gravity, the coachman said:
"'Begorra! that's the first rightful decision that you have given for the last twelvemonth.'"
While the company were laughing, the President beat a quiet retreat from the neighborhood.
On one occasion, in going to meet an appointment in the southern part of the Sucker State—that section of Illinois called Egypt—Lincoln, with other friends, was traveling in the "caboose" of a freight train, when the freight was switched off the main track to allow a special train to pass.
Lincoln's more aristocratic rival (Stephen A. Douglas) was being conveyed to the same town in this special. The passing train was decorated with banners and flags, and carried a band of music, which was playing "Hail to the Chief."
As the train whistled past, Lincoln broke out in a fit of laughter, and said: "Boys, the gentleman in that car evidently smelt no royalty in our carriage."
It was the President's overweening desire to accommodate all persons who came to him soliciting favors, but the opportunity was never offered until an untimely and unthinking disease, which possessed many of the characteristics of one of the most dreaded maladies, confined him to his bed at the White House.
The rumor spread that the President was afflicted with this disease, while the truth was that it was merely a very mild attack of varioloid. The office-seekers didn't know the facts, and for once the Executive Mansion was clear of them.
One day, a man from the West, who didn't read the papers, but wanted the postoffice in his town, called at the White House. The President, being then practically a well man, saw him. The caller was engaged in a voluble endeavor to put his capabilities in the most favorable light, when the President interrupted him with the remark that he would be compelled to make the interview short, as his doctor was due.
"Why, Mr. President, are you sick?" queried the visitor.
"Oh, nothing much," replied Mr. Lincoln, "but the physician says he fears the worst."
"What worst, may I ask?"
"Smallpox," was the answer; "but you needn't be scared. I'm only in the first stages now."
The visitor grabbed his hat, sprang from his chair, and without a word bolted for the door.
"Don't be in a hurry," said the President placidly; "sit down and talk awhile."
"Thank you, sir; I'll call again," shouted the Westerner, as he disappeared through the opening in the wall.
"Now, that's the way with people," the President said, when relating the story afterward. "When I can't give them what they want, they're dissatisfied, and say harsh things about me; but when I've something to give to everybody they scamper off."
When Lincoln's attention was called to the fact that, at one time in his boyhood, he had spelled the name of the Deity with a small "g," he replied:
"That reminds me of a little story. It came about that a lot of Confederate mail was captured by the Union forces, and, while it was not exactly the proper thing to do, some of our soldiers opened several letters written by the Southerners at the front to their people at home.
"In one of these missives the writer, in a postscript, jotted down this assertion:
"'We'll lick the Yanks termorrer, if goddlemity (God Almighty) spares our lives.'
"That fellow was in earnest, too, as the letter was written the day before the second battle of Manassas."
To a curiosity-seeker who desired a permit to pass the lines to visit the field of Bull Run, after the first battle, Lincoln made the following reply: "A man in Cortlandt county raised a porker of such unusual size that strangers went out of their way to see it.
"One of them the other day met the old gentleman and inquired about the animal.
"'Wall, yes,' the old fellow said, 'I've got such a critter, mi'ty big un; but I guess I'll have to charge you about a shillin' for lookin' at him.'
"The stranger looked at the old man for a minute or so, pulled out the desired coin, handed it to him, and started to go off. 'Hold on,' said the other, 'don't you want to see the hog?'
"'No,' said the stranger; 'I have seen as big a hog as I want to see!'
"And you will find that fact the case with yourself, if you should happen to see a few live rebels there as well as dead ones."
One of the last, if not the very last story told by President Lincoln, was to one of his Cabinet who came to see him, to ask if it would be proper to permit "Jake" Thompson to slip through Maine in disguise and embark for Portland.
The President, as usual, was disposed to be merciful, and to permit the arch-rebel to pass unmolested, but Secretary Stanton urged that he should be arrested as a traitor.
"By permitting him to escape the penalties of treason," persisted the War Secretary, "you sanction it." "Well," replied Mr. Lincoln, "let me tell you a story. There was an Irish soldier here last summer, who wanted something to drink stronger than water,[Pg 35] and stopped at a drug-shop, where he espied a soda-fountain. 'Mr. Doctor,' said he, 'give me, plase, a glass of soda-wather, an' if yez can put in a few drops of whiskey unbeknown to any one, I'll be obleeged.' Now," continued Mr. Lincoln, "if 'Jake' Thompson is permitted to go through Maine unbeknown to any one, what's the harm? So don't have him arrested."
A cashiered officer, seeking to be restored through the power of the executive, became insolent, because the President, who believed the man guilty, would not accede to his repeated requests, at last said, "Well, Mr. President, I see you are fully determined not to do me justice!"
This was too aggravating even for Mr. Lincoln; rising, he suddenly seized the disgraced officer by the coat collar, and marched him forcibly to the door, saying as he ejected him into the passage:
"Sir, I give you fair warning never to show your face in this room again. I can bear censure, but not insult. I never wish to see your face again."
A gentleman, visiting a hospital at Washington, heard an occupant of one of the beds laughing and talking about the President, who had been there a short time before and gladdened the wounded with some of his stories. The soldier seemed in such good spirits that the gentleman inquired:
"You must be very slightly wounded?"
"Yes," replied the brave fellow, "very slightly—I have only lost one leg, and I'd be glad enough to lose the other, if I could hear some more of 'Old Abe's' stories."
A Commissioner to the Hawaiian Islands was to be appointed, and eight applicants had filed their papers, when a delegation from the South appeared at the White House on behalf of a ninth. Not only was their man fit—so the delegation urged—but was also in bad health, and a residence in that balmy climate would be of great benefit to him.
The President was rather impatient that day, and before the members of the delegation had fairly started in, suddenly closed the interview with this remark:
"Gentlemen, I am sorry to say that there are eight other applicants for that place, and they are all 'sicker'n' your man."
John Morrissey, the noted prize fighter, was the "Boss" of Tammany Hall during the Civil War period. It pleased his fancy to go to Congress, and his obedient constituents sent him there. Morrissey was such an absolute despot that the New York City democracy could not make a move without his consent, and many of the Tammanyites were so afraid of him that they would not even enter into business ventures without consulting the autocrat.
President Lincoln had been seriously annoyed by some of his generals, who were afraid to make the slightest move before asking advice from Washington. One commander, in particular, was so cautious that he telegraphed the War Department upon the slightest pretext, the result being that his troops were lying in camp doing nothing, when they should have been in the field.
"This general reminds me," the President said one day, while talking to Secretary Stanton, at the War Department, "of a story I once heard about a Tammany[Pg 37] man. He happened to meet a friend, also a member of Tammany, on the street, and in the course of the talk the friend, who was beaming with smiles and good nature, told the other Tammanyite that he was going to be married.
"This first Tammany man looked more serious than men usually do upon hearing of the impending happiness of a friend. In fact, his face seemed to take on a look of anxiety and worry.
"'Ain't you glad to know that I'm to get married?' demanded the second Tammanyite, somewhat in a huff.
"'Of course I am,' was the reply; 'but,' putting his mouth close to the ear of the other, 'have ye asked Morrissey yet?'
"Now this general of whom we are speaking, wouldn't dare order out the guard without asking Morrissey," concluded the President.
Lincoln was, naturally enough, much surprised one day, when a man of rather forbidding countenance drew a revolver and thrust the weapon into his face. In such circumstances "Abe" at once concluded that any attempt at debate or argument was a waste of time and words.
"What seems to be the matter?" inquired Lincoln with all the calmness and self-possession he could muster.
"Well," replied the stranger, who did not appear at all excited, "some years ago I swore an oath that if I ever came across an uglier man than myself I'd shoot him on the spot."
A feeling of relief evidently took possession of Lincoln at this rejoinder, as the expression upon his countenance lost all suggestion of anxiety.
"Shoot me," he said to the stranger; "for if I am an uglier man than you I don't want to live."
General Fisk, attending a reception at the White House, saw waiting in the anteroom a poor old man from Tennessee, and learned that he had been waiting three or four days to get an audience, on which probably depended the life of his son, under sentence of death for some military offense.
General Fisk wrote his case in outline on a card and sent it in, with a special request that the President would see the man. In a moment the order came; and past impatient senators, governors and generals, the old man went.
He showed his papers to Mr. Lincoln, who said he would look into the case and give him the result next day.
The old man, in an agony of apprehension, looked up into the President's sympathetic face and actually cried out:
"Tomorrow may be too late! My son is under sentence of death. It ought to be decided now!"
His streaming tears told how much he was moved.
"Come," said Mr. Lincoln, "wait a bit and I'll tell you a story;" and then he told the old man General Fisk's story about the swearing driver, as follows:
"The general had begun his military life as a colonel, and when he raised his regiment in Missouri he proposed to his men that he should do all the swearing of the regiment. They assented; and for months no instance was known of the violation of the promise.
"The colonel had a teamster named John Todd, who, as roads were not always the best, had some difficulty in commanding his temper and his tongue.
"John happened to be driving a mule team through a series of mudholes a little worse than usual, when, unable to restrain himself any longer, he burst forth into a volley of energetic oaths.
"The colonel took notice of the offense and brought John to account.
"'John,' said he, 'didn't you promise to let me do all the swearing of the regiment?'
"'Yes, I did, colonel,' he replied, 'but the fact was, the swearing had to be done then or not at all, and you weren't there to do it.'"
As he told the story the old man forgot his boy, and both the President and his listener had a hearty laugh together at its conclusion.
Then he wrote a few words which the old man read, and in which he found new occasion for tears; but the tears were tears of joy, for the words saved the life of his son.
Judge Breese, of the Supreme bench, one of the most distinguished of American jurists, and a man of great personal dignity, was about to open court at Springfield, when Lincoln called out in his hearty way: "Hold on, Breese! Don't open court yet! Here's Bob Blackwell just going to tell a story!" The Judge passed on without replying, evidently regarding it as beneath the dignity of the Supreme Court to delay proceedings for the sake of a story.
Mr. Lincoln once said in a speech: "Fellow citizens, my friend, Mr. Douglas, made the startling announcement today that the Whigs are all dead.
"If that be so, fellow-citizens, you will now experience the novelty of hearing a speech from a dead man; and I suppose you might properly say, in the language of the old hymn:
"'Hark! from the tombs a doleful sound.'"
The President was heard to declare one day that the story given below was one of the funniest he ever heard.
One of General Fremont's batteries of eight Parrott guns, supported by a squadron of horse commanded by Major Richards, was in sharp conflict with a battery of the enemy near at hand. Shells and shot were flying thick and fast, when the commander of the battery, a German, one of Fremont's staff, rode suddenly up to the cavalry, exclaiming, in loud and excited terms, "Pring up de shackasses! Pring up de shackasses! For Cot's sake, hurry up the shackasses, im-me-di-ate-ly!"
The necessity of this order, though not quite apparent, will be more obvious when it is remembered that "shackasses" are mules, carry mountain howitzers, which are fired from the back of that much-abused but valuable animal; and the immediate occasion for the "shackasses" was that two regiments of rebel infantry were at that moment discovered ascending a hill immediately behind our batteries.
The "shackasses," with the howitzers loaded with grape and canister, were soon on the ground.
The mules squared themselves, as they well knew how, for the shock.
A terrific volley was poured into the advancing column, which immediately broke and retreated.
Two hundred and seventy-eight dead bodies were found in the ravine next day, piled closely together as they fell, the effects of that volley from the backs of the "shackasses."
Governor Blank went to the War Department one day in a towering rage:
"I suppose you found it necessary to make large[Pg 41] concessions to him, as he returned from you perfectly satisfied," suggested a friend.
"Oh, no," the President replied, "I did not concede anything. You have heard how that Illinois farmer got rid of a big log that was too big to haul out, too knotty to split, and too wet and soggy to burn.
"'Well, now,' said he, in response to the inquiries of his neighbors one Sunday, as to how he got rid of it, 'well, now, boys, if you won't divulge the secret, I'll tell you how I got rid of it—I ploughed around it.'
"Now," remarked Lincoln, in conclusion, "don't tell anybody, but that's the way I got rid of Governor Blank. I ploughed all round him, but it took me three mortal hours to do it, and I was afraid every minute he'd see what I was at."
During a public "reception," a farmer from one of the border counties of Virginia told the President that the Union soldiers, in passing his farm, had helped themselves not only to hay, but to his horse, and he hoped the President would urge the proper officer to consider his claim immediately.
Mr. Lincoln said that this reminded him of an old acquaintance of his, "Jack" Chase, a lumberman on the Illinois, a steady, sober man, and the best raftsman on the river. It was quite a trick to take the logs over the rapids; but he was skilful with a raft and always kept her straight in her channel. Finally a steamer was put on, and "Jack" was made captain of her. He always used to take the wheel, going through the rapids. One day when the boat was plunging and wallowing along the boiling current, and "Jack's" utmost vigilance was being exercised to keep her in the narrow channel, a boy pulled his coat-tail and hailed him with:
"Say, Mister Captain! I wish you would just stop your boat a minute—I've lost my apple overboard!"
"General Grant is a copious worker and fighter," President Lincoln wrote to General Burnside in July, 1863, "but a meagre writer or telegrapher."
Grant never wrote a report until the battle was over.
President Lincoln wrote a letter to Grant on July 13th, 1863, which indicated the strength of the hold the successful fighter had upon the man in the White House.
It ran as follows:
"I do not remember that you and I ever met personally.
"I write this now as a grateful acknowledgment for the almost inestimable service you have done the country.
"I write to say a word further.
"When you first reached the vicinity of Vicksburg, I thought you should do what you finally did—march the troops across the neck, run the batteries with the transports, and thus go below; and I never had any faith, except a general hope, that you knew better than I, that the Yazoo Pass expedition, and the like, could succeed.
"When you got below and took Port Gibson, Grand Gulf and vicinity, I thought you should go down the river and join General Banks; and when you turned northward, east of Big Black, I feared it was a mistake.
"I now wish to make the personal acknowledgment that you were right and I was wrong."
When Hood's army had been scattered into fragments, President Lincoln, elated by the defeat of what had so long been a menacing force on the borders of Tennessee, was reminded by its collapse of the fate of a savage dog belonging to one of his neighbors in the[Pg 43] frontier settlements in which he lived in his youth. "The dog," he said, "was the terror of the neighborhood, and its owner, a churlish and quarrelsome fellow, took pleasure in the brute's forcible attitude.
"Finally, all other means having failed to subdue the creature, a man loaded a lump of meat with a charge of powder, to which was attached a slow fuse; this was dropped where the dreaded dog would find it, and the animal gulped down the tempting bait.
"There was a dull rumbling, a muffled explosion, and fragments of the dog were seen flying in every direction. The grieved owner, picking up the shattered remains of his cruel favorite, said: 'He was a good dog, but as a dog, his days of usefulness are over.' Hood's army was a good army," said Lincoln by way of comment, "and we were all afraid of it, but as an army, its usefulness is gone."
One of the droll stories brought into play by the President as an ally in support of his contention, proved most effective. Politics was rife among the generals of the Union Army, and there was more "wire-pulling" to prevent the advancement of fellow commanders than the laying of plans to defeat the Confederates in battle.
However, when it so happened that the name of a particularly unpopular general was sent to the Senate for confirmation, the protest against his promotion was almost unanimous. The nomination didn't seem to please anyone. Generals who were enemies before conferred together for the purpose of bringing every possible influence to bear upon the Senate and securing the rejection of the hated leader's name. The President was surprised. He had never known such unanimity before.
"You remind me," said the President to a delegation of officers which called upon him one day to present a fresh protest to him regarding the nomination, "of a visit a certain Governor paid to the Penitentiary of his State. It had been announced that the Governor would hear the story of every inmate of the institution, and was prepared to rectify, either by commutation or pardon, any wrongs that had been done to any prisoner.
"One by one the convicts appeared before His Excellency, and each one maintained that he was an innocent man, who had been sent to prison because the police didn't like him, or his friends and relatives wanted his property, or he was too popular, etc., etc. The last prisoner to appear was an individual who was not at all prepossessing. His face was against him; his eyes were shifty; he didn't have the appearance of an honest man, and he didn't act like one.
"'Well,' asked the Governor, impatiently, 'I suppose you're innocent like the rest of these fellows?'
"'No, Governor,' was the unexpected answer; 'I was guilty of the crime they charged against me, and I got just what I deserved.'
"When he had recovered from his astonishment, the Governor, looking the fellow squarely in the face, remarked with emphasis: 'I'll have to pardon you, because I don't want to leave so bad a man as you are in the company of such innocent sufferers as I have discovered your fellow-convicts to be. You might corrupt them and teach them wicked tricks. As soon as I get back to the capital, I'll have the papers made out.'
"You gentlemen," continued the President, "ought to be glad that so bad a man, as you represent this officer to be, is to get his promotion, for then you won't be forced to associate with him and suffer the contamination of his presence and influence. I will do all I can to have the Senate confirm him."
And he was confirmed.
Two young men called on the President from Springfield, Illinois. Lincoln shook hands with them, and asked about the crops, the weather, etc.
Finally one of the young men said, "Mother is not well, and she sent me up to inquire of you how the suit about the Wells property is getting on."
Lincoln, in the same even tone with which he had asked the question, said: "Give my best wishes and respects to your mother, and tell her I have so many outside matters to attend to now that I have put that case, and others, in the hand of a lawyer friend of mine, and if you will call on him (giving name and address) he will give you all the information you want."
After they had gone, a friend who was present, said: "Mr. Lincoln, you did not seem to know the young men?"
He laughed and replied: "No, I had never seen them before, and I had to beat around the bush until I found who they were. It was up-hill work, but I topped it at last."
President Lincoln had not been in the White House very long before Mrs. Lincoln became seized with the idea that a fine new barouche was about the proper thing for "the first lady in the land." The President did not care particularly about it one way or the other, and told his wife to order whatever she wanted.
Lincoln forgot all about the new vehicle, and was overcome with astonishment one afternoon when, having acceded to Mrs. Lincoln's desire to go driving, he found a beautiful barouche standing in front of the door of the White House.
His wife watched him with an amused smile, but the only remark he made was, "Well, Mary, that's about the slickest 'glass hack' in town, isn't it?"
When the enemies of General Grant were bothering the President with emphatic and repeated demands that the "Silent Man" be removed from command, Mr. Lincoln remained firm. He would not consent to lose the services of so valuable a soldier. "Grant fights," said he in response to the charges made that Grant was a butcher, a drunkard, an incompetent and a general who did not know his business.
"That reminds me of a story," President Lincoln said one day to a delegation of the "Grant-is-no-good" style.
"Out in my State of Illinois there was a man nominated for sheriff of the county. He was a good man for the office, brave, determined and honest, but not much of an orator. In fact, he couldn't talk at all; he couldn't make a speech to save his life.
"His friends knew he was a man who would preserve the peace of the county and perform the duties devolving upon him all right, but the people of the county didn't know it. They wanted him to come out boldly on the platform at political meetings and state his convictions and principles; they had been used to speeches from candidates, and were somewhat suspicious of a man who was afraid to open his mouth.
"At last the candidate consented to make a speech, and his friends were delighted. The candidate was on hand, and, when he was called upon, advanced to the front and faced the crowd. There was a glitter in his eye that wasn't pleasing, and the way he walked out to the front of the stand showed that he knew just what he wanted to say.
"'Feller Citizens,' was his beginning, the words spoken quietly, 'I'm not a speakin' man; I ain't no orator, an' I never stood up before a lot of people in my life before; I'm not goin' to make no speech, 'xcept to say that I can lick any man in the crowd!'"
A gentleman was relating to the President how a friend of his had been driven away from New Orleans as a Unionist, and how, on his expulsion, when he asked to see the writ by which he was expelled, the deputation which called on him told him the Government would do nothing illegal, and so they had issued no illegal writs, and simply meant to make him go of his own free will.
"Well," said Mr. Lincoln, "that reminds me of a hotel-keeper down at St. Louis, who boasted that he never had a death in his hotel, for whenever a guest was dying in his house, he carried him out to die in the gutter."
"I was speaking one time to Mr. Lincoln," said Governor Saunders, of Nebraska, "of a little Nebraskan settlement on the Weeping Water, a stream in our State."
"'Weeping Water!' said he.
"Then with a twinkle in his eye, he continued:
"'I suppose the Indians out there call it Minneboohoo, don't they? They ought to, if Laughing Water is Minnehaha in their language.'"
An officer of low volunteer rank persisted in telling and re-telling his troubles to the President on a summer afternoon when Lincoln was tired and careworn.
After listening patiently, he finally turned upon the broad Potomac in the distance, said in a peremptory tone that ended the interview:
"Now, my man, go away, go away. I cannot meddle in your case. I could as easily bail out the Potomac River with a teaspoon as attend to all the details of the army."
Lincoln made a political speech at Pappsville, Illinois, when a candidate for the Legislature the first time. A free-for-all fight began soon after the opening of the meeting, and Lincoln, noticing one of his friends about to succumb to the energetic attack of an infuriated ruffian, edged his way through the crowd, and, seizing the bully by the neck and the seat of his trousers, threw him, by means of his strength and long arms, as one witness stoutly insists, "twelve feet away." Returning to the stand, and throwing aside his hat, he inaugurated his campaign with the following brief but pertinent declaration:
"Fellow-citizens, I presume you all know who I am. I am humble Abraham Lincoln. I have been solicited by many friends to become a candidate for the Legislature. My politics are short and sweet, like the old woman's dance. I am in favor of the national bank; I am in favor of the internal improvement system and a high protective tariff. These are my sentiments; if elected, I shall be thankful; if not, it will be all the same."
It so happened that an official of the War Department had escaped serious punishment for a rather flagrant offense, by showing where grosser irregularities existed in the management of a certain Bureau of the Department. So valuable was the information furnished that the culprit who "gave the snap away" was not even discharged.
"That reminds me," the President said, when the case was laid before him, "of a story about Daniel Webster, when the latter was a boy.
"When quite young, at school, Daniel was one day guilty of a gross violation of the rules. He was detected[Pg 49] in the act, and called up by the teacher for punishment.
"This was to be the old-fashioned 'feruling' of the hand. His hands happened to be very dirty.
"Knowing this, on the way to the teacher's desk, he spit upon the palm of his right hand, wiping it off upon the side of his pantaloons.
"'Give me your hand, sir,' said the teacher, very sternly.
"Out went the right hand, partly cleansed. The teacher looked at it a moment, and said:
"'Daniel, if you will find another hand in this school-room as filthy as that, I will let you off this time!'
"Instantly from behind his back came the left hand.
"'Here it is, sir,' was the ready reply.
"'That will do,' said the teacher, 'for this time; you can take your seat, sir.'"
When a grocery clerk at New Salem, the annual election came around. A Mr. Graham was clerk, but his assistant was absent, and it was necessary to find a man to fill his place. Lincoln, a "tall young man," had already concentrated on himself the attention of the people of the town, and Graham easily discovered him. Asking him if he could write, "Abe" modestly replied, "I can make a few rabbit-tracks." His rabbit-tracks proving to be legible and even graceful, he was employed.
The voters soon discovered that the new assistant clerk was honest and fair, and performed his duties satisfactorily, and when, the work done, he began to "entertain them with stories," they found that their town had made a valuable personal and social acquisition.
Peter Cartwright, the famous and eccentric old Methodist preacher, who used to ride a church circuit, as Mr. Lincoln and others did the court circuit, did not like Lincoln very well, probably because Mr. Lincoln was not a member of his flock and once defeated the preacher for Congress. This was Cartwright's description of Lincoln: "This Lincoln is a man six feet four inches tall, but so angular that if you should drop a plummet from the center of his head it would cut him three times before it touched his feet."
A prominent volunteer officer who, early in the War, was on duty in Washington and often carried reports to Secretary Stanton at the War Department, told a characteristic story on President Lincoln. Said he:
"I was with several other young officers, also carrying reports to the War Department, and one morning we were late. In this instance we were in a desperate hurry to deliver the papers, in order to be able to catch the train returning to camp.
"On the winding, dark staircase of the old War Department, which many will remember, it was our misfortune, while taking about three stairs at a time, to run a certain head like a catapult into the body of the President, striking him in the region of the right lower vest pocket.
"The usual surprised and relaxed grunt of a man thus assailed came promptly.
"We quickly sent an apology in the direction of the dimly seen form, feeling that the ungracious shock was expensive, even to the humblest clerk in the department.
"A second glance revealed to us the President as the victim of the collision. Then followed a special[Pg 51] tender of 'ten thousand pardons,' and the President's reply:
"'One's enough; I wish the whole army would charge like that.'"
"You can't do anything with them Southern fellows," the old man at the table was saying.
"If they get whipped, they'll retreat to them Southern swamps and bayous along with the fishes and crocodiles. You haven't got the fish-nets made that'll catch 'em."
"Look here, old gentleman," remarked President Lincoln, who was sitting alongside, "we've got just the nets for traitors, in the bayous or anywhere."
"Hey? What nets?"
"Bayou-nets!" and "Uncle Abraham" pointed his joke with his fork, spearing a fishball savagely.
In one of his many stories of Lincoln, his law partner, W. H. Herndon, told this as illustrating Lincoln's shrewdness as a lawyer:
"I was with Lincoln once and listened to an oral argument by him in which he rehearsed an extended history of the law. It was a carefully prepared and masterly discourse, but, as I thought, entirely useless. After he was through and we were walking home, I asked him why he went so far back in the history of the law. I presumed the court knew enough history.
"'That's where you're mistaken,' was his instant rejoinder. 'I dared not trust the case on the presumption that the court knows everything—in fact I argued it on the presumption that the court didn't know anything,' a statement, which, when one reviews the decision of our appellate courts, is not so extravagant as one would at first suppose."
No matter who was with the President, or how intently absorbed, his little son "Tad" was always welcome. He almost always accompanied his father.
Once, on the way to Fortress Monroe, he became very troublesome. The President was much engaged in conversation with the party who accompanied him, and he at length said:
"'Tad,' if you will be a good boy, and not disturb me any more until we get to Fortress Monroe, I will give you a dollar."
The hope of reward was effectual for a while in securing silence, but, boylike, "Tad" soon forgot his promise, and was as noisy as ever. Upon reaching their destination, however, he said, very promptly: "Father, I want my dollar." Mr. Lincoln looked at him half-reproachfully for an instant, and then, taking from his pocketbook a dollar note, he said: "Well, my son, at any rate, I will keep my part of the bargain."
Mr. Lincoln, one day, was talking with the Rev. Dr. Sunderland about the Emancipation Proclamation and the future of the negro. Suddenly a ripple of amusement broke the solemn tone of his voice. "As for the negroes, Doctor, and what is going to become of them: I told Ben Wade the other day, that it made me think of a story I read in one of my first books, 'Ã?sop's Fables.' It was an old edition, and had curious rough wood cuts, one of which showed three white men scrubbing a negro in a potash kettle filled with cold water. The text explained that the men thought that by scrubbing the negro they might make him white. Just about the time they thought they were succeeding, he took cold and died. Now, I am afraid that by the time we get through this war the negro will catch cold and die."
George M. Pullman, the great sleeping car builder, once told a joke in which Lincoln was the prominent figure. In fact, there wouldn't have been any joke had it not been for "Long Abe." At the time of the occurrence, which was the foundation for the joke—and Pullman admitted that the latter was on him—Pullman was the conductor of his only sleeping-car. The latter was an experiment, and Pullman was doing everything possible to get the railroads to take hold of it.
"One night," said Pullman in telling the story, "as we were about going out of Chicago—this was long before Lincoln was what you might call a renowned man—a long, lean, ugly man, with a wart on his cheek, came into the depot. He paid me fifty cents, and half a berth was assigned him. Then he took off his coat and vest and hung them up, and they fitted the peg about as well as they fitted him. Then he kicked off his boots, which were of surprising length, turned into the berth, and, undoubtedly having an easy conscience, was sleeping like a healthy baby before the car left the depot.
"Pretty soon along came another passenger and paid his fifty cents. In two minutes he was back at me, angry as a wet hen.
"'There's a man in that berth of mine,' said he hotly, 'and he's about ten feet high. How am I going to sleep there, I'd like to know? Go and look at him.'
"In I went—mad, too. The tall, lank man's knees were under his chin, his arms were stretched across the bed and his feet were stored comfortably—for him. I shook him until he awoke, and then told him if he wanted the whole berth he would have to pay $1.
"'My dear sir,' said the tall man, 'a contract is a contract. I have paid you fifty cents for half this berth, and, as you see, I'm occupying it. There's the[Pg 54] other half,' pointing to a strip about six inches wide. 'Sell that and don't disturb me again.'
"And so saying, the man with a wart on his face went to sleep again. He was Abraham Lincoln, and he never grew any shorter afterward. We became great friends, and often laughed over the incident."
The President did not consider that every soldier who ran away in battle, or did not stand firmly to receive a bayonet charge, was a coward. He was of opinion that self-preservation was the first law of Nature, but he didn't want this statute construed too liberally by the troops.
At the same time he took occasion to illustrate a point he wished to make by a story in connection with a darky who was a member of the Ninth Illinois Infantry Regiment. This regiment was one of those engaged at the capture of Fort Donelson. It behaved gallantly, and lost as heavily as any.
"Upon the hurricane-deck of one of our gunboats," said the President in telling the story, "I saw an elderly darky, with a very philosophical and retrospective cast of countenance, squatted upon his bundle, toasting his shins against the chimney, and apparently plunged into a state of profound meditation.
"As the negro rather interested me, I made some inquiries, and found that he had really been with the Ninth Illinois Infantry at Donelson, and began to ask him some questions about the capture of the place.
"'Were you in the fight?'
"'Had a little taste of it, sa.'
"'Stood your ground, did you?'
"'No, sa, I runs.'
"'Run at the first fire, did you?'
"'Yes, sa, and would hab run soona, had I knowd it war comin'.'
"'Why, that wasn't very creditable to your courage.'
"'Dat isn't in my line, sa—cookin's my profeshun.'
"'Well, but have you no regard for your reputation?'
"'Reputation's nuffin to me by de side ob life.'
"'Do you consider your life worth more than other people's?'
"'It's worth more to me, sa.'
"'Then you must value it very highly?'
"'Yes, sa, I does, more dan all dis wuld, more dan a million ob dollars, sa, for what would dat be wuth to a man wid de bref out ob him? Self-preserbation am de fust law wid me.'
"'But why should you act upon a different rule from other men?'
"'Different men set different values on their lives; mine is not in de market.'
"'But if you lost it you would have the satisfaction of knowing that you died for your country.'
"'Dat no satisfaction when feelin's gone.'
"'Then patriotism and honor are nothing to you?'
"'Nufin whatever, sa—I regard them as among the vanities.'
"'If our soldiers were like you, traitors might have broken up the government without resistance.'
"'Yes, sa, dar would hab been no help for it. I wouldn't put my life in de scale 'g'inst any gobernment dat eber existed, for no gobernment could replace de loss to me.'
"'Do you think any of your company would have missed you if you had been killed?'
"'Maybe not, sa; a dead white man ain't much to dese sojers, let alone a dead nigga—but I'd a missed myse'f, and dat was de p'int wid me.'
"I only tell this story," concluded the President, "in order to illustrate the result of the tactics of some of the Union generals who would be sadly 'missed' by themselves, if by no one else, if they ever got out of the Army."
Mr. Lincoln prepared his first inaugural address in a room over a store in Springfield. His only reference works were Henry Clay's great compromise speech of 1850, Andrew Jackson's Proclamation against Nullification, Webster's great reply to Hayne, and a copy of the Constitution.
When Mr. Lincoln started for Washington, to be inaugurated, the inaugural address was placed in a special satchel and guarded with special care. At Harrisburg the satchel was given in charge of Robert T. Lincoln, who accompanied his father. Before the train started from Harrisburg the precious satchel was missing. Robert thought he had given it to a waiter at the hotel, but a long search failed to reveal the missing satchel with its precious document. Lincoln was annoyed, angry, and finally in despair. He felt certain that the address was lost beyond recovery, and, as it lacked only ten days until the inauguration, he had no time to prepare another. He had not even preserved the notes from which the original copy had been written.
Mr. Lincoln went to Ward Lamon, his former law partner, then one of his body-guards, and informed him of the loss in the following words:
"Lamon, I guess I have lost my certificate of moral character, written by myself. Bob has lost my gripsack containing my inaugural address."
Of course the misfortune reminded him of a story.
"I feel," said Mr. Lincoln, "a good deal as the old member of the Methodist Church did when he lost his wife at the camp meeting, and went up to an old elder of the church and asked him if he could tell him whereabouts in h—l his wife was. In fact, I am in a worse fix than my Methodist friend, for if it were only a wife that were missing, mine would be sure to bob up somewhere."
The clerk at the hotel told Mr. Lincoln that he would probably find his missing satchel in the baggage-room. Arriving there, Mr. Lincoln saw a satchel which he thought was his, and it was passed out to him. His key fitted the lock, but alas! when it was opened the satchel contained only a soiled shirt, some paper collars, a pack of cards and a bottle of whisky. A few minutes later the satchel containing the inaugural address was found among the pile of baggage.
The recovery of the address also reminded Mr. Lincoln of a story, which is thus narrated by Ward Lamon in his "Recollections of Abraham Lincoln":
The loss of the address and the search for it was the subject of a great deal of amusement. Mr. Lincoln said many funny things in connection with the incident. One of them was that he knew a fellow once who had saved up fifteen hundred dollars, and had placed it in a private banking establishment. The bank soon failed, and he afterward received ten per cent of his investment. He then took his one hundred and fifty dollars and deposited it in a savings bank, where he was sure it would be safe. In a short time this bank also failed, and he received at the final settlement ten per cent on the amount deposited. When the fifteen dollars was paid over to him, he held it in his hand and looked at it thoughtfully; then he said, "Now, darn you, I have got you reduced to a portable shape, so I'll put you in my pocket." Suiting the action to the word, Mr. Lincoln took his address from the bag and carefully placed it in the inside pocket of his vest, but held on to the satchel with as much interest as if it still contained his "certificate of moral character."
Many requests and petitions made to Mr. Lincoln when he was President were ludicrous and trifling, but he always entered into them with that humor-loving[Pg 58] spirit that was such a relief from the grave duties of his great office.
Once a party of Southerners called on him in behalf of one Betsy Ann Dougherty. The spokesman, who was an ex-governor, said:
"Mr. President, Betsy Ann Dougherty is a good woman. She lived in my county and did my washing for a long time. Her husband went off and joined the rebel army, and I wish you would give her a protection paper." The solemnity of this appeal struck Mr. Lincoln as uncommonly ridiculous.
The two men looked at each other—the Governor desperately in earnest, and the President masking his humor behind the gravest exterior. At last Mr. Lincoln asked, with inimitable gravity, "Was Betsy Ann a good washerwoman?" "Oh, yes, sir, she was, indeed."
"Was your Betsy Ann an obliging woman?" "Yes, she was certainly very kind," responded the Governor, soberly.
"Could she do other things than wash?" continued Mr. Lincoln with the same portentous gravity.
"Oh, yes; she was very kind—very."
"Where is Betsy Ann?"
"She is now in New York, and wants to come back to Missouri, but she is afraid of banishment."
"Is anybody meddling with her?"
"No; but she is afraid to come back unless you will give her a protection paper."
Thereupon Mr. Lincoln wrote on a visiting card the following:
"Let Betsy Ann Dougherty alone as long as she behaves herself.
"A. LINCOLN."
He handed this card to her advocate, saying, "Give this to Betsy Ann."
"But, Mr. President, couldn't you write a few words to the officers that would insure her protection?"
"No," said Mr. Lincoln, "officers have no time now to read letters. Tell Betsy Ann to put a string in this card and hang it around her neck. When the officers see this, they will keep their hands off your Betsy Ann."
Lincoln was a strong believer in the virtue of dealing honestly with the people.
"If you once forfeit the confidence of your fellow-citizens," he said to a caller at the White House, "you can never regain their respect and esteem.
"It is true that you may fool all the people some of the time; you can even fool some of the people all the time; but you can't fool all of the people all the time."
At one time a certain Major Hill charged Lincoln with making defamatory remarks regarding Mrs. Hill.
Hill was insulting in his language to Lincoln, who never lost his temper.
When he saw his chance to edge a word in, Lincoln denied emphatically using the language or anything like that attributed to him.
He entertained, he insisted, a high regard for Mrs. Hill, and the only thing he knew to her discredit was the fact that she was Major Hill's wife.
A lawyer, who was a stranger to Mr. Lincoln, once expressed to General Linder the opinion that Mr. Lincoln's practice of telling stories to the jury was a waste of time.
"Don't lay that flattering unction to your soul," Linder answered; "Lincoln is like Tansey's horse, he 'breaks to win.'"
It is true that Lincoln did not drink, never swore, was a stranger to smoking and lived a moral life generally, but he did like horse-racing and chicken fighting. New Salem, Illinois, where Lincoln was "clerking," was known the neighborhood around as a "fast" town, and the average young man made no very desperate resistance when tempted to join in the drinking and gambling bouts.
"Bap." McNabb was famous for his ability in both the raising and the purchase of roosters of prime fighting quality, and when his birds fought the attendance was large. It was because of the "flunking" of one of "Bap.'s" roosters that Lincoln was enabled to make a point when criticising McClellan's unreadiness and lack of energy.
One night there was a fight on the schedule, one of "Bap." McNabb's birds being a contestant. "Bap." brought a little red rooster, whose fighting qualities had been well advertised for days in advance, and much interest was manifested in the outcome. As the result of these contests was generally a quarrel, in which each man, charging foul play, seized his victim, they chose Lincoln umpire, relying not only on his fairness but his ability to enforce his decisions. Judge Herndon, in his "Abraham Lincoln," says of this notable event:
"I cannot improve on the description furnished me in February, 1865, by one who was present.
"They formed a ring, and the time having arrived, Lincoln, with one hand on each hip and in a squatting position, cried, 'Ready.' Into the ring they toss their fowls, 'Bap.'s' red rooster along with the rest. But no sooner had the little beauty discovered what was to be done than he dropped his tail and ran.
"The crowd cheered, while 'Bap.' in disappointment, picked him up and started away, losing his quarter (entrance fee) and carrying home his dishonored[Pg 61] fowl. Once arrived at the latter place he threw his pet down with a feeling of indignation and chagrin.
"The little fellow, out of sight of all rivals, mounted a woodpile and proudly flirting out his feathers, crowed with all his might. 'Bap.' looked on in disgust.
"'Yes, you little cuss,' he exclaimed, irreverently, 'you're great on dress parade, but not worth a darn in a fight.'"
It is said, according to Judge Herndon, that Lincoln considered McClellan as "great on dress parade," but not so much in a fight.
Lincoln made his first speech when he was a mere boy, going barefoot, his trousers held up by one suspender, and his shock of hair sticking through a hole in the crown of his cheap straw hat.
"Abe," in company with Dennis Hanks, attended a political meeting, which was addressed by a typical stump speaker—one of those loud-voiced fellows who shouted at the top of his voice, and waved his arms wildly.
At the conclusion of the speech, which did not meet the views either of "Abe" or Dennis, the latter declared that "Abe" could make a better speech than that. Whereupon he got a dry-goods box and called on "Abe" to reply to the campaign orator.
Lincoln threw his old straw hat on the ground, and, mounting the dry-goods box, delivered a speech which held the attention of the crowd and won him considerable applause. Even the campaign orator admitted that it was a fine speech and answered every point in his own "oration."
Dennis Hanks, who thought "Abe" was about the greatest man that ever lived, was delighted, and he often told how young "Abe" got the better of the trained campaign speaker.
An applicant for a sutlership in the army relates this story: "In the winter of 1864, after serving three years in the Union Army, and being honorably discharged, I made application for the post sutlership at Point Lookout. My father being interested, we made application to Mr. Stanton, the Secretary of War. We obtained an audience, and were ushered into the presence of the most pompous man I ever met. As I entered he waved his hand for me to stop at a given distance from him, and then he put these questions, viz.:
"'Did you serve three years in the army?'
"'I did sir.'
"'Were you honorably discharged?'
"'I was, sir.'
"'Let me see your discharge.'
"I gave it to him. He looked it over, then said: 'Were you ever wounded?' I told him yes, at the battle of Williamsburg, May 5, 1861.
"He then said: 'I think we can give this position to a soldier who has lost an arm or leg, he being more deserving;' and he then said I looked hearty and healthy enough to serve three years more. He would not give me a chance to argue my case.
"The audience was at an end. He waved his hand to me. I was then dismissed from the august presence of the Honorable Secretary of War.
"My father was waiting for me in the hallway, who saw by my countenance that I was not successful. I said to my father:
"'Let us go over to Mr. Lincoln; he may give us more satisfaction.'
"He said it would do me no good, but we went over. Mr. Lincoln's reception room was full of ladies and gentlemen when we entered.
"My turn soon came. Lincoln turned to my father and said:
"'Now, gentlemen, be pleased to be as quick as possible with your business, as it is growing late.'
"My father then stepped up to Lincoln and introduced me to him. Lincoln then said:
"'Take a seat, gentlemen, and state your business as quickly as possible.'
"There was but one chair by Lincoln, so he motioned my father to sit, while I stood. My father stated the business to him as stated above. He then said:
"'Have you seen Mr. Stanton?'
"We told him yes, that he had refused. He (Mr. Lincoln) then said:
"'Gentlemen, this is Mr. Stanton's business; I cannot interfere with him; he attends to all these matters and I am sorry I cannot help you.'
"He saw that we were disappointed, and did his best to revive our spirits. He succeeded well with my father, who was a Lincoln man, and who was a staunch Republican.
"Mr. Lincoln then said:
"'Now, gentlemen, I will tell you what it is; I have thousands of applications like this every day, but we cannot satisfy all for this reason, that these positions are like office seekers—there are too many pigs for the teats.'
"The ladies who were listening to the conversation placed their handkerchiefs to their faces and turned away. But the joke of 'Old Abe' put us all in a good humor. We then left the presence of the greatest and most just man who ever lived to fill the Presidential chair."
Some gentlemen were once finding fault with the President because certain generals were not given commands.
"The fact is," replied President Lincoln, "I have got more pegs than I have holes to put them in."
Lincoln was a very quiet man, and went about his business in a quiet way, making the least noise possible. He heartily disliked those boisterous people who were constantly deluging him with advice, and shouting at the tops of their voices whenever they appeared at the White House. "These noisy people create a great clamor," said he one day, in conversation with some personal friends, "and remind me, by the way, of a good story I heard out in Illinois while I was practicing, or trying to practice, some law there. I will say, though, that I practiced more law than I ever got paid for.
"A fellow who lived just out of town, on the bank of a large marsh, conceived a big idea in the money-making line. He took it to a prominent merchant, and began to develop his plans and specifications. 'There are at least ten million frogs in that marsh near me, an' I'll just arrest a couple of carloads of them and hand them over to you. You can send them to the big cities and make lots of money for both of us. Frogs' legs are great delicacies in the big towns, an' not very plentiful. It won't take me more'n two or three days to pick 'em. They make so much noise my family can't sleep, and by this deal, I'll get rid of a nuisance and gather in some cash.'
"The merchant agreed to the proposition, promised the fellow he would pay him well for the two carloads. Two days passed, then three, and finally two weeks were gone before the fellow showed up again, carrying a small basket. He looked weary and 'done up,' and he wasn't talkative a bit. He threw the basket on the counter with the remark, 'There's your frogs.'
"'You haven't two carloads in that basket, have you?' inquired the merchant.
"'No,' was the reply, 'and there ain't two carloads in this blasted world.'
"'I thought you said there were at least ten millions[Pg 65] of 'em in that marsh near you, according to the noise they made,' observed the merchant. 'Your people couldn't sleep because of 'em.'
"'Well,' said the fellow, 'accordin' to the noise they made, there was, I thought, a hundred million of 'em, but when I had waded and swum that there marsh day and night for two blessed weeks, I couldn't harvest but six. There's two or three left yet, an' the marsh is as noisy as it uster be. We haven't catched up on any of our lost sleep yet. Now, you can have these here six, an' I won't charge you a cent fer 'em.'
"You can see by this little yarn," remarked the President, "that these boisterous people make too much noise in proportion to their numbers."
Some of Mr. Lincoln's intimate friends once called his attention to a certain member of his Cabinet who was quietly working to secure a nomination for the Presidency, although knowing that Mr. Lincoln was to be a candidate for re-election. His friends insisted that the Cabinet officer ought to be made to give up his Presidential aspirations or be removed from office. The situation reminded Mr. Lincoln of a story: "My brother and I," he said, "were once plowing corn, I driving the horse and he holding the plow. The horse was lazy, but on one occasion he rushed across the field so that I, with my long legs, could scarcely keep pace with him. On reaching the end of the furrow, I found an enormous chin-fly fastened upon him, and knocked him off. My brother asked me what I did that for. I told him I didn't want the old horse bitten in that way. 'Why,' said my brother, 'that's all that made him go.' Now," said Mr. Lincoln, "if Mr. —— has a Presidential chin-fly biting him, I'm not going to knock him off, if it will only make his department go."
Lincoln "got even" with the Illinois Central Railroad Company, in 1855, in a most substantial way, at the same time secured sweet revenge for an insult, unwarranted in every way, put upon him by one of the officials of that corporation.
Lincoln and Herndon defended the Illinois Central Railroad in an action brought by McLean County, Illinois, in August, 1853, to recover taxes alleged to be due the county from the road. The Legislature had granted the road immunity from taxation, and this was a case intended to test the constitutionality of the law. The road sent a retainer fee of $250.
In the lower court the case was decided in favor of the railroad. An appeal to the Supreme Court followed, was argued twice, and finally decided in favor of the road. This last decision was rendered some time in 1855. Lincoln then went to Chicago, and presented the bill for legal services. Lincoln and Herndon only asked for $2,000 more.
The official to whom he was referred, after looking at the bill, expressed great surprise.
"Why, sir," he exclaimed, "this is as much as Daniel Webster himself would have charged. We cannot allow such a claim."
"Why not?" asked Lincoln.
"We could have hired first-class lawyers at that figure," was the response.
"We won the case, didn't we?" queried Lincoln.
"Certainly," replied the official.
"Daniel Webster, then," retorted Lincoln in no amiable tone, "couldn't have done more," and "Abe" walked out of the official's office.
Lincoln withdrew the bill, and started for home. On the way he stopped at Bloomington, where he met Grant Goodrich, Archibald Williams, Norman B. Judd, O. H. Browning, and other attorneys, who, on learning[Pg 67] of his modest charge for the valuable services rendered the railroad, induced him to increase the demand to $5,000, and to bring suit for that sum.
This was done at once. On the trial six lawyers certified that the bill was reasonable, and judgment for that sum went by default; the judgment was promptly paid, and, of course, his partner, Herndon, got "your half, Billy" without delay.
On the occasion of a serenade, the President was called for by the crowd assembled. He appeared at a window with his wife (who was somewhat below the medium height), and made the following "brief remarks":
"Here I am, and here is Mrs. Lincoln. That's the long and the short of it."
Mr. T. W. S. Kidd, of Springfield, says that he once heard a lawyer opposed to Lincoln trying to convince a jury that precedent was superior to law, and that custom made things legal in all cases. When Lincoln arose to answer him he told the jury he would argue his case in the same way.
"Old 'Squire Bagly, from Menard, came into my office and said, 'Lincoln, I want your advice as a lawyer. Has a man what's been elected justice of the peace a right to issue a marriage license?' I told him he had not; when the old 'squire threw himself back in his chair very indignantly, and said, 'Lincoln, I thought you was a lawyer. Now Bob Thomas and me had a bet on this thing, and we agreed to let you decide; but if this is your opinion I don't want it, for I know a thunderin' sight better, for I have been 'squire now for eight years and have done it all the time.'"
One of Mr. Lincoln's warm friends was Dr. Robert Boal, of Lacon, Illinois. Telling of a visit he paid to the White House soon after Mr. Lincoln's inauguration, he said: "I found him the same Lincoln as a struggling lawyer and politician that I did in Washington as President of the United States, yet there was a dignity and self-possession about him in his high official authority. I paid him a second call in the evening. He had thrown off his reserve somewhat, and would walk up and down the room with his hands to his sides and laugh at the joke he was telling, or at one that was told to him. I remember one story he told to me on this occasion.
"Tom Corwin, of Ohio, had been down to Alexandria, Va., that day and had come back and told Lincoln a story which pleased him so much that he broke out in a hearty laugh and said: 'I must tell you Tom Corwin's latest. Tom met an old man at Alexandria who knew George Washington, and he told Tom that George Washington often swore. Now, Corwin's father had always held the father of our country up as a faultless person and told his son to follow in his footsteps.
"'"Well," said Corwin, "when I heard that George Washington was addicted to the vices and infirmities of man, I felt so relieved that I just shouted for joy."'"
Being in Washington one day, the Rev. Robert Collyer thought he'd take a look around. In passing through the grounds surrounding the White House, he cast a glance toward the Presidential residence, and was astonished to see three pairs of feet resting on the ledge of an open window in one of the apartments of the second story. The divine paused for a moment, calmly surveyed the unique spectacle, and then resumed his walk toward the War Department. Seeing a laborer[Pg 69] at work not far from the Executive Mansion, Mr. Collyer asked him what it all meant. To whom, did the feet belong, and particularly, the mammoth ones? "You old fool," answered the workman, "that's the Cabinet, which is a-settin', an' them thar big feet belongs to 'Old Abe.'"
By the Act of Emancipation President Lincoln built for himself forever the first place in the affections of the African race in this country. The love and reverence manifested for him by many of these people has, on some occasions, almost reached adoration. One day, Colonel McKaye, of New York, who had been one of a committee to investigate the condition of the freedmen, upon his return from Hilton Head and Beaufort called upon the President, and in the course of the interview said that up to the time of the arrival among them in the South of the Union forces they had no knowledge of any other power. Their masters fled upon the approach of our soldiers, and this gave the slaves the conception of a power greater than their masters exercised. This power they called "Massa Linkum."
Colonel McKaye said their place of worship was a large building they called "the praise house," and the leader of the "meeting," a venerable black man, was known as "the praise man."
On a certain day, when there was quite a large gathering of the people, considerable confusion was created by different persons attempting to tell who and what "Massa Linkum" was. In the midst of the excitement the white-headed leader commanded silence. "Brederen," said he, "you don't know nosen' what you'se talkin' 'bout. Now, you just listen to me. Massa Linkum, he ebery whar. He know ebery ting."
Then, solemnly looking up, he added: "He walk de earf like de Lord!"
A soldier tells the following story of an attempt upon the life of Mr. Lincoln:
"One night I was doing sentinel duty at the entrance to the Soldiers' Home. This was about the middle of August, 1864. About eleven o'clock I heard a rifle shot, in the direction of the city, and shortly afterwards I heard approaching hoof-beats. In two or three minutes a horse came dashing up. I recognized the belated President. The President was bare-headed. The President simply thought his horse had taken fright at the discharge of the firearms.
"On going back to the place where the shot had been heard, we found the President's hat. It was a plain silk hat, and upon examination we discovered a bullet hole through the crown.
"The next day, upon receiving the hat, the President remarked that it was made by some foolish marksman, and was not intended for him; but added that he wished nothing said about the matter.
"The President said, philosophically: 'I long ago made up my mind that if anybody wants to kill me, he will do it. Besides, in this case, it seems to me, the man who would succeed me would be just as objectionable to my enemies—if I have any.'
"One dark night, as he was going out with a friend, he took along a heavy cane, remarking, good-naturedly:
"'Mother (Mrs. Lincoln) has got a notion into her head that I shall be assassinated, and to please her I take a cane when I go over to the War Department at night—when I don't forget it.'"
A Union general, operating with his command in West Virginia, allowed himself and his men to be trapped, and it was feared his force would be captured by the[Pg 71] Confederates. The President heard the report read by the operator, as it came over the wire, and remarked:
"Once there was a man out West who was 'heading' a barrel, as they used to call it. He worked like a good fellow in driving down the hoops, but just about the time he thought he had the job done, the head would fall in. Then he had to do the work all over again.
"All at once a bright idea entered his brain, and he wondered how it was he hadn't figured it out before. His boy, a bright, smart lad, was standing by, very much interested in the business, and, lifting the young one up, he put him inside the barrel, telling him to hold the head in its proper place, while he pounded down the hoops on the sides. This worked like a charm, and he soon had the 'heading' done.
"Then he realized that his boy was inside the barrel, and how to get him out he couldn't for his life figure out. General Blank is now inside the barrel, 'headed in,' and the job now is to get him out."
An Eastern newspaper writer told how Lincoln, after his first nomination, received callers, the majority of them at his law office:
"While talking to two or three gentlemen and standing up, a very hard looking customer rolled in and tumbled into the only vacant chair and the one lately occupied by Mr. Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln's keen eye took in the fact, but gave no evidence of the notice.
"Turning around at last he spoke to the odd specimen, holding out his hand at such a distance that our friend had to vacate the chair if he accepted the proffered shake. Mr. Lincoln quietly resumed his chair.
"It was a small matter, yet one giving proof more positively than a larger event of that peculiar way the man has of mingling with a mixed crowd."
Preston King once introduced A. J. Bleeker to the President, and the latter, being an applicant for office, was about to hand Mr. Lincoln his vouchers, when he was asked to read them. Bleeker had not read very far when the President disconcerted him by the exclamation, "Stop a minute! You remind me exactly of the man who killed the dog; in fact, you are just like him."
"In what respect?" asked Bleeker, not feeling he had received a compliment.
"Well," replied the President, "this man had made up his mind to kill his dog, an ugly brute, and proceeded to knock out his brains with a club. He continued striking the dog after the latter was dead until a friend protested, exclaiming, 'You needn't strike him any more; the dog is dead; you killed him at the first blow.'
"'Oh, yes,' said he, 'I know that; but I believe in punishment after death.' So, I see, do you."
Bleeker acknowledged it was possible to overdo a good thing, and then came back at the President with an anecdote of a good priest who converted an Indian from heathenism to Christianity; the only difficulty he had with him was to get him to pray for his enemies. "This Indian had been taught to overcome and destroy all his friends he didn't like," said Bleeker, "but the priest told him that while that might be the Indian method, it was not the doctrine of Christianity of the Bible. 'Saint Paul distinctly says,' the priest told him, 'If thine enemy hunger, feed him; if he thirst, give him drink.'
"The Indian shook his head at this, but when the priest added, 'For in so doing thou shalt heap coals of fire on his head,' Poor Lo was overcome with emotion, fell on his knees, and with outstretched hands and uplifted eyes invoked all sorts of blessings on the heads[Pg 73] of all his enemies, supplicating for pleasant hunting-grounds, a large supply of squaws, lots of pappooses and all other Indian comforts.
"Finally the good priest interrupted him (as you did me, Mr. President), exclaiming, 'Stop, my son! You have discharged your Christian duty, and have done more than enough.'
"'Oh, no, father,' replied the Indian; 'let me pray. I want to burn him down to the stump!'"
Personal encounters were of frequent occurrence in Gentryville in early days, and the prestige of having thrashed an opponent gave the victor marked social distinction. Green B. Taylor, with whom "Abe" worked the greater part of one winter on a farm, furnished an account of the noted fight between John Johnston, "Abe's" step-brother, and William Grigsby, in which stirring drama "Abe" himself played an important role before the curtain was rung down.
Taylor's father was the second for Johnston, and William Whitten officiated in a similar capacity for Grigsby. "They had a terrible fight," related Taylor, "and it soon became apparent that Grigsby was too much for Lincoln's man, Johnston. After they had fought a long time without interference, it having been agreed not to break the ring, 'Abe' burst through, caught Grigsby, threw him off and some feet away. There Grigsby stood, proud as Lucifer, and, swinging a bottle of liquor over his head, swore he was 'the big buck of the lick.'
"'If any one doubts it,' he shouted, 'he has only to come on and whet his horns.'"
A general engagement followed this challenge, but at the end of hostilities the field was cleared and the wounded retired amid the exultant shouts of their victors.
Mr. Alcott, of Elgin, Ill., tells of seeing Mr. Lincoln coming away from church unusually early one Sunday morning. "The sermon could not have been more than half way through," says Mr. Alcott. "'Tad' was hung across his left arm like a pair of saddle bags, and Mr. Lincoln was striding along with long, deliberate steps toward his home. On one of the street corners he encountered a group of his fellow-townsmen. Mr. Lincoln anticipated the question which was about to be put by the group, and, taking his figure of speech from practices with which they were only too familiar, said: 'Gentlemen, I entered this colt, but he kicked around so I had to withdraw him.'"
When the United States found that a war with Black Hawk could not be dodged, Governor Reynolds, of Illinois, issued a call for volunteers, and among the companies that immediately responded was one from Menard County, Illinois. Many of these volunteers were from New Salem and Clary's Grove, and Lincoln, being out of business, was the first to enlist.
The company being full, the men held a meeting at Richland for the election of officers. Lincoln had won many hearts, and they told him that he must be their captain. It was an office to which he did not aspire, and for which he felt he had no special fitness; but he finally consented to be a candidate.
There was but one other candidate, a Mr. Kirkpatrick, who was one of the most influential men of the region. Previously, Kirkpatrick had been an employer of Lincoln, and was so overbearing in his treatment of the young man that the latter left him.
The simple mode of electing a captain adopted by the company was by placing the candidates apart, and[Pg 75] telling the men to go and stand with the one they preferred. Lincoln and his competitor took their positions, and then the word was given. At least three out of every four went to Lincoln at once.
When it was seen by those who had arranged themselves with the other candidate that Lincoln was the choice of the majority of the company, they left their places, one by one, and came over to the successful side, until Lincoln's opponent in the friendly strife was left standing almost alone.
"I felt badly to see him cut so," says a witness of the scene.
Here was an opportunity for revenge. The humble laborer was his employer's captain, but the opportunity was never improved. Mr. Lincoln frequently confessed that no subsequent success of his life had given him half the satisfaction that this election did.
The lawyers on the circuit traveled by Lincoln got together one night and tried him on the charge of accepting fees which tended to lower the established rates. It was the understood rule that a lawyer should accept all the client could be induced to pay. The tribunal was known as "The Ogmathorial Court."
Ward Lamon, his law partner at the time, tells about it:
"Lincoln was found guilty and fined for his awful crime against the pockets of his brethren of the bar. The fine he paid with great good humor, and then kept the crowd of lawyers in uproarious laughter until after midnight.
"He persisted in his revolt, however, declaring that with his consent his firm should never during its life, or after its dissolution, deserve the reputation enjoyed by those shining lights of the profession, 'Catch 'em and Cheat 'em.'"
Lincoln had assisted in the prosecution of a man who had robbed his neighbor's hen roosts. Jogging home along the highway with the foreman of the jury that had convicted the hen stealer, he was complimented by Lincoln on the zeal and ability of the prosecution, and remarked: "Why, when the country was young, and I was stronger than I am now, I didn't mind packing off a sheep now and again, but stealing hens!" The good man's scorn could not find words to express his opinion of a man who would steal hens.
President Lincoln often avoided interviews with delegations representing various States, especially when he knew the objects of their errands, and was aware he could not grant their requests. This was the case with several commissioners from Kentucky, who were put off from day to day.
They were about to give up in despair, and were leaving the White House lobby, their speech being interspersed with vehement and uncomplimentary terms concerning "Old Abe," when "Tad" happened along. He caught at these words, and asked one of them if they wanted to see "Old Abe," laughing at the same time.
"Yes," he replied.
"Wait a minute," said "Tad," and rushed into his father's office. Said he, "Papa, may I introduce some friends to you?"
His father, always indulgent and ready to make him happy, kindly said, "Yes, my son, I will see your friends."
"Tad" went to the Kentuckians again, and asked a very dignified looking gentleman of the party his name. He was told his name. He then said, "Come, gentlemen," and they followed him.
Leading them up to the President, "Tad," with much dignity, said, "Papa, let me introduce to you Judge ——, of Kentucky;" and quickly added, "Now, Judge, you introduce the other gentlemen."
The introductions were gone through with, and they turned out to be the gentlemen Mr. Lincoln had been avoiding for a week. Mr. Lincoln reached for the boy, took him in his lap, kissed him, and told him it was all right, and that he had introduced his friend like a little gentleman as he was. Tad was eleven years old at this time.
The President was pleased with Tad's diplomacy, and often laughed at the incident as he told others of it. One day while caressing the boy, he asked him why he called those gentlemen "his friends." "Well," said Tad, "I had seen them so often, and they looked so good and sorry, and said they were from Kentucky, that I thought they must be our friends." "That is right, my son," said Mr. Lincoln; "I would have the whole human race your friends and mine, if it were possible."
There was a rough gallantry among the young people; and Lincoln's old comrades and friends in Indiana have left many tales of how he "went to see the girls;" of how he brought in the biggest back-log and made the brightest fire; of how the young people, sitting around it, watching the way the sparks flew, told their fortunes.
He helped pare apples, shell corn and crack nuts. He took the girls to meeting and to spelling school, though he was not often allowed to take part in the spelling-match, for the one who "chose first" always chose "Abe" Lincoln, and that was equivalent to winning, as the others knew that "he would stand up the longest."
Governor Hoyt of Wisconsin tells a story of Mr. Lincoln's great admiration for physical strength. Mr. Lincoln, in 1859, made a speech at the Wisconsin State Agricultural Fair. After the speech, in company with the Governor, he strolled about the grounds, looking at the exhibits. They came to a place where a professional "strong man" was tossing cannon balls in the air and catching them on his arms and juggling with them as though they were as light as baseballs. Mr. Lincoln had never before seen such an exhibition, and he was greatly surprised and interested.
When the performance was over, Governor Hoyt, seeing Mr. Lincoln's interest, asked him to go up and be introduced to the athlete. He did so, and, as he stood looking down musingly on the man, who was very short, and evidently wondering that one so much smaller than he could be so much stronger, he suddenly broke out with one of his quaint speeches. "Why," he said, "why, I could lick salt off the top of your hat."
When Mr. Lincoln was quite a small boy he met with an accident that almost cost him his life. He was saved by Austin Gollaher, a young playmate. Mr. Gollaher lived to be more than ninety years of age, and to the day of his death related with great pride his boyhood association with Lincoln.
"Yes," Mr. Gollaher once said, "the story that I once saved Abraham Lincoln's life is true. He and I had been going to school together for a year or more, and had become greatly attached to each other. Then school disbanded on account of there being so few scholars, and we did not see each other much for a long while.
"One Sunday my mother visited the Lincolns, and I was taken along. 'Abe' and I played around[Pg 79] all day. Finally, we concluded to cross the creek to hunt for some partridges young Lincoln had seen the day before. The creek was swollen by a recent rain, and, in crossing on the narrow footlog, 'Abe' fell in. Neither of us could swim. I got a long pole and held it out to 'Abe,' who grabbed it. Then I pulled him ashore.
"He was almost dead, and I was badly scared. I rolled and pounded him in good earnest. Then I got him by the arms and shook him, the water meanwhile pouring out of his mouth. By this means I succeeded in bringing him to, and he was soon all right.
"Then a new difficulty confronted us. If our mothers discovered our wet clothes they would whip us. This we dreaded from experience, and determined to avoid. It was June, the sun was very warm, and we soon dried our clothing by spreading it on the rocks about us. We promised never to tell the story, and I never did until after Lincoln's tragic end."
Mr. Lincoln had advised Lieutenant-General Winfield Scott, commanding the United States Army, of the threats of violence on inauguration day, 1861. General Scott was sick in bed at Washington when Adjutant-General Thomas Mather, of Illinois, called upon him in President-elect Lincoln's behalf, and the veteran commander was much wrought up. Said he to General Mather:
"Present my compliments to Mr. Lincoln when you return to Springfield, and tell him I expect him to come on to Washington as soon as he is ready; say to him that I will look after those Maryland and Virginia rangers myself. I will plant cannon at both ends of Pennsylvania Avenue, and if any of them show their heads or raise a finger, I'll blow them to h——."
United States Senator Benjamin Wade, of Ohio, Henry Winter Davis, of Maryland, and Wendell Phillips were strongly opposed to President Lincoln's re-election, and Wade and Davis issued a manifesto. Phillips made several warm speeches against Lincoln and his policy.
When asked if he had read the manifesto or any of Phillips' speeches, the President replied:
"I have not seen them, nor do I care to see them. I have seen enough to satisfy me that I am a failure, not only in the opinion of the people in rebellion, but of many distinguished politicians of my own party. But time will show whether I am right or they are right, and I am content to abide its decision.
"I have enough to look after without giving much of my time to the consideration of the subject of who shall be my successor in office. The position is not an easy one, and the occupant, whoever he may be, for the next four years, will have little leisure to pluck a thorn or plant a rose in his own pathway."
It was urged that this opposition must be embarrassing to his Administration, as well as damaging to the party. He replied: "Yes, that is true; but our friends, Wade, Davis, Phillips, and others are hard to please. I am not capable of doing so. I cannot please them without wantonly violating not only my oath, but the most vital principles upon which our government was founded.
"As to those who, like Wade and the rest, see fit to depreciate my policy and cavil at my official acts, I shall not complain of them. I accord them the utmost freedom of speech and liberty of the press, but shall not change the policy I have adopted in the full belief that I am right.
"I feel on this subject as an old Illinois farmer once expressed himself while eating cheese. He was interrupted[Pg 81] in the midst of his repast by the entrance of his son, who exclaimed, 'Hold on, dad! there's skippers in that cheese you're eating!'
"'Never mind, Tom,' said he, as he kept on munching his cheese, 'if they can stand it I can.'"
A lady reader or elocutionist came to Springfield in 1857. A large crowd greeted her. Among other things she recited "Nothing to Wear," a piece in which is described the perplexities that beset "Miss Flora McFlimsey" in her efforts to appear fashionable.
In the midst of one stanza in which no effort is made to say anything particularly amusing, and during the reading of which the audience manifested the most respectful silence and attention, some one in the rear seats burst out with a loud, coarse laugh, a sudden and explosive guffaw.
It startled the speaker and audience, and kindled a storm of unsuppressed laughter and applause. Everybody looked back to ascertain the cause of the demonstration, and were greatly surprised to find that it was Mr. Lincoln.
He blushed and squirmed with the awkward diffidence of a schoolboy. What caused him to laugh, no one was able to explain. He was doubtless wrapped up in a brown study, and recalling some amusing episode indulged in laughter without realizing his surroundings. The experience mortified him greatly.
(Dispatch to General Grant, August 17th, 1864.)
"I have seen your dispatch expressing your unwillingness to break your hold where you are. Neither am I willing.
"Hold on with a bulldog grip."
As the time drew near at which Mr. Lincoln said he would issue the Emancipation Proclamation, some clergymen, who feared the President might change his mind, called on him to urge him to keep his promise.
"We were ushered into the Cabinet room," says Dr. Sunderland. "It was very dim, but one gas jet burning. As we entered, Mr. Lincoln was standing at the farther end of the long table, which filled the center of the room. As I stood by the door, I am so very short that I was obliged to look up to see the President. Mr. Robbins introduced me, and I began at once by saying: 'I have come, Mr. President, to anticipate the new year with my respects, and if I may, to say to you a word about the serious condition of this country.'
"'Go ahead, Doctor,' replied the President; 'every little helps.' But I was too much in earnest to laugh at his sally at my smallness."
Judge T. Lyle Dickey of Illinois related that when the excitement over the Kansas-Nebraska bill first broke out, he was with Lincoln and several friends attending court. One evening several persons, including himself and Lincoln, were discussing the slavery question. Judge Dickey contended that slavery was an institution which the Constitution recognized, and which could not be disturbed. Lincoln argued that ultimately slavery must become extinct. "After a while," said Judge Dickey, "we went upstairs to bed. There were two beds in our room, and I remember that Lincoln sat up in his night shirt on the edge of the bed arguing the point with me. At last we went to sleep. Early in the morning I woke up and there was Lincoln half sitting up in bed. 'Dickey', said he, 'I tell you this nation cannot exist half slave and half free.' 'Oh, Lincoln,' said I, 'go to sleep.'"
Lincoln at one time thought seriously of learning the blacksmith's trade. He was without means, and felt the immediate necessity of undertaking some business that would give him bread. While entertaining this project an event occurred which, in his undetermined state of mind, seemed to open a way to success in another quarter.
Reuben Radford, keeper of a small store in the village of New Salem, had incurred the displeasure of the "Clary Grove Boys," who exercised their "regulating" prerogatives by irregularly breaking his windows. William G. Greene, a friend of young Lincoln, riding by Radford's store soon afterward, was hailed by him and told that he intended to sell out. Mr. Greene went into the store, and offered him at random $400 for his stock, which offer was immediately accepted.
Lincoln "happened in" the next day, and being familiar with the value of the goods, Mr. Greene proposed to him to take an inventory of the stock, and see what sort of a bargain he had made. This he did, and it was found that the goods were worth $600.
Lincoln then made an offer of $125 for his bargain, with the proposition that he and a man named Berry, as his partner, take over Greene's notes given to Radford. Mr. Greene agreed to the arrangement, but Radford declined it, except on condition that Greene would be their security. Greene at last assented.
Lincoln was not afraid of the "Clary Grove Boys"; on the contrary, they had been his most ardent friends since the time he thrashed "Jack" Armstrong, champion bully of "The Grove"—but their custom was not heavy.
The business soon became a wreck; Greene had to not only assist in closing it up, but pay Radford's notes as well. Lincoln afterwards spoke of these notes which he finally made good to Greene, as "the National Debt."
One of President Lincoln's friends, visiting at the White House, was finding considerable fault with the constant agitation in Congress of the slavery question. He remarked that, after the adoption of the Emancipation policy, he had hoped for something new.
"There was a man down in Maine," said the President, in reply, "who kept a grocery store, and a lot of fellows used to loaf around for their toddy. He only gave 'em New England rum, and they drank pretty considerable of it. But after a while they began to get tired of that, and kept asking for something new—something new—all the time. Well, one night, when the whole crowd were around, the grocer brought out his glasses, and says he, 'I've got something New for you to drink, boys, now.'
"'Honor bright?' says they.
"'Honor bright,' says he, and with that he sets out a jug. 'Thar,' says he, 'that's something New; it's New England rum!' says he.
"Now," remarked the President, in conclusion, "I guess we're a good deal like that crowd, and Congress is a good deal like that store-keeper!"
When Governor Custer of Pennsylvania described the terrible butchery at the battle of Fredericksburg, Mr. Lincoln was almost broken-hearted.
The Governor regretted that his description had so sadly affected the President. He remarked: "I would give all I possess to know how to rescue you from this terrible war." Then Mr. Lincoln's wonderful recuperative powers asserted themselves and this marvelous man was himself.
Lincoln's whole aspect suddenly changed, and he relieved his mind by telling a story.
"This reminds me, Governor," he said, "of an old farmer out in Illinois that I used to know.
"He took it into his head to go into hog-raising. He sent out to Europe and imported the finest breed of hogs he could buy.
"The prize hog was put in a pen, and the farmer's two mischievous boys, James and John, were told to be sure not to let it out. But James, the worst of the two, let the brute out the next day. The hog went straight for the boys, and drove John up a tree; then the hog went for the seat of James' trousers, and the only way the boy could save himself was by holding on to the hog's tail.
"The hog would not give up his hunt, nor the boy his hold! After they had made a good many circles around the tree, the boy's courage began to give out, and he shouted to his brother, 'I say, John, come down quick, and help me let go this hog!'
"Now, Governor, that is exactly my case. I wish some one would come and help me to let the hog go."
Once, when Lincoln was pleading a case, the opposing lawyer had all the advantage of the law; the weather was warm, and his opponent, as was admissible in frontier courts, pulled off his coat and vest as he grew warm in the argument.
At that time, shirts with buttons behind were unusual. Lincoln took in the situation at once. Knowing the prejudices of the primitive people against pretension of all sorts, or any affectation of superior social rank, arising, he said: "Gentlemen of the jury, having justice on my side, I don't think you will be at all influenced by the gentleman's pretended knowledge of the law, when you see he does not even know which side of his shirt should be in front." There was a general laugh, and Lincoln's case was won.
During the War Congress appropriated $10,000 to be expended by the President in defending United States Marshals in cases of arrests and seizures where the legality of their actions was tested in the courts. Previously the Marshals sought the assistance of the Attorney-General in defending them, but when they found that the President had a fund for that purpose they sought to control the money.
In speaking of these Marshals one day, Mr. Lincoln said:
"They are like a man in Illinois, whose cabin was burned down, and, according to the kindly custom of early days in the West, his neighbors all contributed something to start him again. In his case they had been so liberal that he soon found himself better off than before the fire, and he got proud. One day a neighbor brought him a bag of oats, but the fellow refused it with scorn.
"'No,' said he, 'I'm not taking oats now. I take nothing but money.'"
A certain rich man in Springfield, Illinois, sued a poor attorney for $2.50, and Lincoln was asked to prosecute the case. Lincoln urged the creditor to let the matter drop, adding, "You can make nothing out of him, and it will cost you a good deal more than the debt to bring suit." The creditor was still determined to have his way, and threatened to seek some other attorney. Lincoln then said, "Well, if you are determined that suit should be brought, I will bring it; but my charge will be $10."
The money was paid him, and peremptory orders were given that the suit be brought that day. After the client's departure, Lincoln went out of the office, returning in about an hour with an amused look on his[Pg 87] face. Asked what pleased him, he replied, "I brought suit against ——, and then hunted him up, told him what I had done, handed him half of the $10, and we went over to the squire's office. He confessed judgment and paid the bill."
Lincoln added that he didn't see any other way to make things satisfactory for his client as well as the other.
Mr. Lincoln being found fault with for making another "call," said that if the country required it, he would continue to do so until the matter stood as described by a Western provost marshal, who says:
"I listened a short time since to a butternut-clad individual, who succeeded in making good his escape, expatiate most eloquently on the rigidness with which the conscription was enforced south of the Tennessee River. His response to a question propounded by a citizen ran somewhat in this wise:
"'Do they conscript close over the river?'
"'Stranger, I should think they did! They take every man who hasn't been dead more than two days!'
"If this is correct, the Confederacy has at least a ghost of a chance left."
And of another, a Methodist minister in Kansas, living on a small salary, who was greatly troubled to get his quarterly instalment. He at last told the non-paying trustees that he must have his money, as he was suffering for the necessaries of life.
"Money!" replied the trustees; "you preach for money? We thought you preached for the good of souls!"
"Souls!" responded the reverend; "I can't eat souls; and if I could it would take a thousand such as yours to make a meal!"
"That soul is the point, sir," said the President.
Among the men whom Captain Lincoln met in the Black Hawk campaign were Lieutenant-Colonel Zachary Taylor, Lieutenant Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederacy, and Lieutenant Robert Anderson, all of the United States Army.
Judge Arnold, in his "Life of Abraham Lincoln," relates that Lincoln and Anderson did not meet again until some time in 1861. After Anderson had evacuated Fort Sumter, on visiting Washington, he called at the White House to pay his respects to the President. Lincoln expressed his thanks to Anderson for his conduct at Fort Sumter, and then said:
"Major, do you remember of ever meeting me before?"
"No, Mr. President, I have no recollection of ever having had that pleasure."
"My memory is better than yours," said Lincoln; "you mustered me into the service of the United States in 1832, at Dixon's Ferry, in the Black Hawk War."
When Abe Lincoln used to be drifting around the country, practicing law in Fulton and Menard counties, Illinois, an old fellow met him going to Lewiston, riding a horse which, while it was a serviceable enough animal, was not of the kind to be truthfully called a fine saddler. It was a weatherbeaten nag, patient and plodding, and it toiled along with Abe—and Abe's books, tucked away in saddle-bags, lay heavy on the horse's flank.
"Hello, Uncle Tommy," said Abe.
"Hello, Abe," responded Uncle Tommy. "I'm powerful glad to see ye, Abe, fer I'm gwyne to have sumthin' fer ye at Lewiston co't, I reckon."
"How's that, Uncle Tommy?" said Abe.
"Well, Jim Adams, his land runs 'long o' mine, he's[Pg 89] pesterin' me a heap, an' I got to get the law on Jim, I reckon."
"Uncle Tommy, you haven't had any fights with Jim, have you?"
"No."
"He's a fair to middling neighbor, isn't he?"
"Only tollable, Abe."
"He's been a neighbor of yours for a long time, hasn't he?"
"Nigh on to fifteen year."
"Part of the time you get along all right, don't you?"
"I reckon we do, Abe."
"Well, now, Uncle Tommy, you see this horse of mine? He isn't as good a horse as I could straddle, and I sometimes get out of patience with him, but I know his faults. He does fairly well as horses go, and it might take me a long time to get used to some other horse's faults. For all horses have faults. You and Uncle Jimmy must put up with each other, as I and my horse do with one another."
"I reckon, Abe," said Uncle Tommy, as he bit off about four ounces of Missouri plug, "I reckon you're about right."
And Abe Lincoln, with a smile on his gaunt face, rode on toward Lewiston.
In February, 1860, not long before his nomination for the Presidency, Lincoln made several speeches in Eastern cities. To an Illinois acquaintance, whom he met at the Astor House, in New York, he said:
"I have the cottage at Springfield, and about three thousand dollars in money. If they make me Vice-President with Seward, as some say they will, I hope I shall be able to increase it to twenty thousand, and that is as much as any man ought to want."
President Lincoln was compelled to acknowledge that he made at least one mistake in "sizing up" men. One day a very dignified man called at the White House, and Lincoln's heart fell when his visitor approached. The latter was portly, his face was full of apparent anxiety, and Lincoln was willing to wager a year's salary that he represented some Society for the Easy and Speedy Repression of Rebellions.
The caller talked fluently, but at no time did he give advice or suggest a way to put down the Confederacy. He was full of humor, told a clever story or two, and was entirely self-possessed.
At length the President inquired, "You are a clergyman, are you not, sir?"
"Not by a jug full," returned the stranger heartily.
Grasping him by the hand Lincoln shook it until the visitor squirmed. "You must lunch with us. I am glad to see you. I was afraid you were a preacher."
"I went to the Chicago Convention," the caller said, "as a friend of Mr. Seward. I have watched you narrowly ever since your inauguration, and I called merely to pay my respects. What I want to say is this: I think you are doing everything for the good of the country that is in the power of man to do. You are on the right track. As one of your constituents I now say to you, do in future as you d—— please, and I will support you!"
This was spoken with tremendous effect.
"Why," said Mr. Lincoln, in great astonishment, "I took you to be a preacher. I thought you had come here to tell me how to take Richmond," and he again grasped the hand of his strange visitor.
Accurate and penetrating as Mr. Lincoln's judgment was concerning men, for once he had been wholly mistaken. The scene was comical in the extreme. The two men stood gazing at each other. A smile[Pg 91] broke from the lips of the solemn wag and rippled over the wide expanse of his homely face like sunlight overspreading a continent, and Mr. Lincoln was convulsed with laughter.
He stayed to lunch.
Lincoln never told a better story than this:
A country meeting-house, that was used once a month, was quite a distance from any other house.
The preacher, an old-line Baptist, was dressed in coarse linen pantaloons, and shirt of the same material. The pants, manufactured after the old fashion, with baggy legs, and a flap in the front, were made to attach to his frame without the aid of suspenders.
A single button held his shirt in position, and that was at the collar. He rose up in the pulpit, and with a loud voice announced his text thus: "I am the Christ whom I shall represent today."
About this time a little blue lizard ran up his roomy pantaloons. The old preacher, not wishing to interrupt the steady flow of his sermon, slapped away on his leg, expecting to arrest the intruder, but his efforts were unavailing, and the little fellow kept on ascending higher and higher.
Continuing the sermon, the preacher loosened the central button which graced the waistband of his pantaloons, and with a kick off came that easy-fitting garment.
But, meanwhile, Mr. Lizard had passed the equatorial line of the waistband, and was calmly exploring that part of the preacher's anatomy which lay underneath the back of his shirt.
Things were now growing interesting, but the sermon was still grinding on. The next movement on the preacher's part was for the collar button, and with one sweep of his arm off came the tow linen shirt.
The congregation sat for an instant as if dazed; at length one old lady in the rear part of the room rose up, and, glancing at the excited object in the pulpit, shouted at the top of her voice: "If you represent Christ, then I'm done with the Bible."
In the far-away days when "Abe" went to school in Indiana, they had exercises, exhibitions and speaking-meetings in the schoolhouse or the church, and "Abe" was the "star." His father was a Democrat, and at that time "Abe" agreed with his parent. He would frequently make political and other speeches to the boys and explain tangled questions.
Booneville was the county seat of Warrick county, situated about fifteen miles from Gentryville. Thither "Abe" walked to be present at the sittings of the court, and listened attentively to the trials and the speeches of the lawyers.
One of the trials was that of a murderer. He was defended by Mr. John Breckenridge, and at the conclusion of his speech "Abe" was so enthusiastic that he ventured to compliment him. Breckenridge looked at the shabby boy, thanked him and passed on his way.
Many years afterwards, in 1862, Breckenridge called on the President, and he was told, "It was the best speech that I, up to that time, had ever heard. If I could, as I then thought, make as good a speech as that, my soul would be satisfied."
During the Lincoln-Douglas debates of 1858, the latter accused Lincoln of having, when in Congress, voted against the appropriation for supplies to be sent the United States soldiers in Mexico. In reply, Lincoln said: "This is a perversion of the facts. I was opposed to the policy of the administration in declaring war[Pg 93] against Mexico; but when war was declared I never failed to vote for the support of any proposition looking to the comfort of our poor fellows who were maintaining the dignity of our flag in a war that I thought unnecessary and unjust."
He gradually became more and more excited; his voice thrilled and his whole frame shook. Sitting on the stand was O. B. Ficklin, who had served in Congress with Lincoln in 1847. Lincoln reached back, took Ficklin by the coat-collar, back of his neck, and in no gentle manner lifted him from his seat as if he had been a kitten, and roared: "Fellow-citizens, here is Ficklin, who was at that time in Congress with me, and he knows it is a lie."
He shook Ficklin until his teeth chattered. Fearing he would shake Ficklin's head off, Ward Lamon grasped Lincoln's hand and broke his grip.
After the speaking was over, Ficklin, who had warm personal friendship with him, said: "Lincoln, you nearly shook all the Democracy out of me today."
Lincoln never indulged in profanity, but confessed that when Lee was beaten at Malvern Hill, after seven days of fighting, and Richmond, but twelve miles away, was at McClellan's mercy, he felt very much like swearing when he learned that the Union general had retired to Harrison's Landing.
Lee was so confident his opponent would not go to Richmond that he took his army into Maryland—a move he would not have made had an energetic fighting man been in McClellan's place.
It is true McClellan followed and defeated Lee in the bloodiest battle of the War—Antietam—afterwards following him into Virginia; but Lincoln could not bring himself to forgive the general's inaction before Richmond.
The following is told by Thomas H. Nelson, of Terre Haute, Indiana, who was appointed minister to Chili by Lincoln:
Judge Abram Hammond, afterwards Governor of Indiana, and myself, had arranged to go from Terre Haute to Indianapolis in a stage-coach.
As we stepped in we discovered that the entire back seat was occupied by a long, lank individual, whose head seemed to protrude from one end of the coach and his feet from the other. He was the sole occupant and was sleeping soundly. Hammond slapped him familiarly on the shoulder, and asked him if he had chartered the coach that day.
"Certainty not," and he at once took the front seat, politely giving us the place of honor and comfort. An odd-looking fellow he was, with a twenty-five cent hat, without vest or cravat. Regarding him as a good subject for merriment, we perpetrated several jokes.
He took them all with utmost innocence and good nature, and joined in the laugh, although at his own expense.
After an astounding display of wordy pyrotechnics, the dazed and bewildered stranger asked: "What will be the upshot of this comet business?"
Late in the evening we reached Indianapolis, and hurried to Browning's hotel, losing sight of the stranger altogether.
We retired to our room to brush our clothes. In a few minutes I descended to the portico, and there descried our long, gloomy fellow traveler in the center of an admiring group of lawyers, among whom were Judges McLean and Huntington, Albert S. White and Richard W. Thompson, who seemed to be amused and interested in a story he was telling. I inquired of Browning, the landlord, who he was. "Abraham Lincoln, of Illinois, a member of Congress," was his response.
I was thunderstruck at the announcement. I hastened upstairs and told Hammond the startling news, and together we emerged from the hotel by a back door, and went down an alley to another house, thus avoiding further contact with our distinguished fellow traveler.
Years afterward, when the President-elect was on his way to Washington, I was in the same hotel looking over the distinguished party, when a long arm reached to my shoulder and a shrill voice exclaimed, "Hello, Nelson! do you think, after all, the whole world is going to follow the darned thing off?" The words were my own in answer to his question in the stage-coach. The speaker was Abraham Lincoln.
A slight variation of the traditional sentry story is related by C. C. Buel. It was a cold, blusterous winter night. Says Mr. Buel:
"Mr. Lincoln emerged from the front door, his lank figure bent over as he drew tightly about his shoulders the shawl which he employed for such protection; for he was on his way to the War Department, at the west corner of the grounds, where in times of battle he was wont to get the midnight dispatches from the field. As the blast struck him he thought of the numbness of the pacing sentry, and, turning to him, said: 'Young man, you've got a cold job tonight; step inside, and stand guard there.'
"'My orders keep me out here,' the soldier replied.
"'Yes,' said the President, in his argumentative tone; 'but your duty can be performed just as well inside as out here, and you'll oblige me by going in.'
"'I have been stationed outside,' the soldier answered, and resumed his beat.
"'Hold on there!' said Mr. Lincoln, as he turned back again; 'it occurs to me that I am Commander-in-Chief of the army, and I order you to go inside.'"
"Abe's" nephew—or one of them—related a story in connection with Lincoln's first love (Anne Rutledge), and his subsequent marriage to Miss Mary Todd. This nephew was a plain, every-day farmer, and thought everything of his uncle, whose greatness he quite thoroughly appreciated, although he did not pose to any extreme as the relative of a President of the United States.
Said he one day, in telling his story:
"Us child'en, w'en we heerd Uncle 'Abe' wuz a-goin' to be married, axed Gran'ma ef Uncle 'Abe' never hed a gal afore, an' she says, sez she, 'Well, "Abe" wuz never a han' nohow to run 'round visitin' much, or go with the gals, neither, but he did fall in love with a Anne Rutledge, who lived out near Springfield, an' after she died he'd come home an' ev'ry time he'd talk 'bout her, he cried dreadful. He never could talk of her nohow 'thout he'd jes' cry an' cry, like a young feller.'
"Onct he tol' Gran'ma they wuz goin; ter be hitched, they havin' promised each other, an' thet is all we ever heered 'bout it. But, so it wuz, that arter Uncle 'Abe' hed got over his mournin', he wuz married ter a woman w'ich hed lived down in Kentuck.
"Uncle 'Abe' hisself tol' us he wuz married the nex' time he come up ter our place, an' w'en we ast him why he didn't bring his wife up to see us, he said: 'She's very busy and can't come.'
"But we knowed better'n that. He wuz too proud to bring her up, 'cause nothin' would suit her, nohow. She wuzn't raised the way we wuz, an' wuz different from us, and we heerd, tu, she wuz as proud as cud be.
"No, an' he never brought none uv the child'en, neither.
"But then, Uncle 'Abe,' he wuzn't to blame. We never thought he wuz stuck up."
Transcriber's Notes
Minor punctuation errors have been
silently corrected.
Page 92: Changed
"Lincon" to "Lincoln."
(Orig: Lincon
said: "This is a perversion of the facts.)
Page 93: Changed "yoice" to "voice."
(Orig: his voice thrilled and his whole frame
shook)


IN the following pages I have endeavored to give the life of Abraham Lincoln, from his birth to his inauguration as President of the United States. The reader will judge the character of the performance by the work itself: for that reason I shall spare him the perusal of much prefatory explanation.
At the time of Mr. Lincoln's death, I determined to write his history, as I had in my possession much valuable material for such a purpose. I did not then imagine that any person could have better or more extensive materials than I possessed. I soon learned, however, that Mr. William H. Herndon of Springfield, Ill., was similarly engaged. There could be no rivalry between us; for the supreme object of both was to make the real history and character of Mr. Lincoln as well known to the public as they were to us. He deplored, as I did, the many publications pretending to be biographies which came teeming from the press, so long as the public interest about Mr. Lincoln excited the hope of gain. Out of the mass of works which appeared, of one only—Dr. Holland's—is it possible to speak with any degree of respect.
Early in 1869, Mr. Herndon placed at my disposal his remarkable collection of materials,—the richest, rarest, and fullest collection it was possible to conceive. Along with them came an offer of hearty co-operation, of which I have availed myself so extensively, that no art of mine would serve to conceal it. Added to my own collections, these acquisitions have enabled me to do what could not have been done before,—prepare an authentic biography of Mr. Lincoln.
Mr. Herndon had been the partner in business and the intimate personal associate of Mr. Lincoln for something like a quarter of a century; and Mr. Lincoln had lived familiarly with several members of his family long before their individual acquaintance began. New Salem, Springfield, the old judicial circuit, the habits and friends of Mr. Lincoln, were as well known to Mr. Herndon as to himself. With these advantages, and from the numberless facts and hints which had dropped from Mr. Lincoln during the confidential intercourse of an ordinary lifetime, Mr. Herndon was able to institute a thorough system of inquiry for every noteworthy circumstance and every incident of value in Mr. Lincoln's career.
The fruits of Mr. Herndon's labors are garnered in three enormous volumes of original manuscripts and a mass of unarranged letters and papers. They comprise the recollections of Mr. Lincoln's nearest friends; of the surviving members of his family and his family-connections; of the men still living who knew him and his parents in Kentucky; of his schoolfellows, neighbors, and acquaintances in Indiana; of the better part of the whole population of New Salem; of his associates and relatives at Springfield; and of lawyers, judges, politicians, and statesmen everywhere, who had any thing of interest or moment to relate. They were collected at vast expense of time, labor, and money, involving the employment of many agents, long journeys, tedious examinations, and voluminous correspondence. Upon the value of these materials it would be impossible to place an estimate. That I have used them conscientiously and justly is the only merit to which I lay claim.
As a general thing, my text will be found to support itself; but whether the particular authority be mentioned or not, it is proper to remark, that each statement of fact is fully sustained by indisputable evidence remaining in my possession. My original plan was to verify every important statement by one or more appropriate citations; but it was early abandoned, not because it involved unwelcome labor, but because it encumbered my pages with a great array of obscure names, which the reader would probably pass unnoticed.
I dismiss this volume into the world, with no claim for it of literary excellence, but with the hope that it will prove what it purports to be,—a faithful record of the life of Abraham Lincoln down to the 4th of March, 1861.
Ward H. Lamon.
Washington City, May, 1872.
CONTENTS
ILLUSTRATIONS
Mrs. Sarah Lincoln, Mother of the President
CHAPTER I.
Birth.—His father and mother.—History of Thomas Lincoln and his family
a necessary part of Abraham Lincoln's biography.—Thomas Lincoln's
ancestors.—Members of the family remaining in Virginia.—Birth of
Thomas Lincoln.—Removal to Kentucky.—Life in the Wilderness.—Lincolns
settle in Mercer County.—Thomas Lincoln's father shot by
Indians.—Widow and family remove to Washington County.—Thomas
poor.—Wanders into Breckinridge County.—Goes to Hardin County.—Works
at the carpenter's trade.—Cannot read or write.—Personal
appearance.—Called "Linckhom," or "Linckhera."—Thomas Lincoln as
a carpenter.—Marries Nancy Hanks.—Previously courted Sally
Bush.—Character of Sally Bush.—The person and character of Nancy
Hanks.—Thomas and Nancy Lincoln go to live in a shed.—Birth of a
daughter.—They remove to Nolin Creek.—Birth of Abraham.—Removal to
Knob Creek.—Little Abe initiated into wild sports.—His sadness.—Goes
to school.—Thomas Lincoln concludes to move.—Did not fly from the
taint of slavery.—Abraham Lincoln always reticent about the history and
character of his family.—Record in his Bible... 1
CHAPTER II.
Thomas Lincoln builds a boat.—Floats down to the Ohio.—Boat
capsizes.—Lands in Perry County, Indiana.—Selects a location.—Walks
back to Knob Creek for wife and children.—Makes his way through
the wilderness.—Settles between the two Pigeon Creeks.—Gentry
ville.—Selects a site.—Lincoln builds a half-faced camp.—Clears
ground and raises a small crop.—Dennis Hanks.—Lincoln builds a
cabin.—State of the country.—Indiana admitted to the Union.—Rise
of Gentryville.—Character of the people.—Lincoln's patent for his
land.—His farm, cabin, furniture.—The milk-sickness.—Death of Nancy
Hanks Lincoln.—Funeral discourse by David Elkin.—Grave.—Tom Lincoln
marries Sally Bush.—Her goods and chattels.—Her surprise at the
poverty of the Lincoln cabin.—Clothes and comforts Abe and his
sister.—Abe leads a new life.—Is sent to school.—Abe's appearance and
dress.—Learning "manners"—Abe's essays.—Tenderness for animals.—The
last of school.—Abe excelled the masters.—Studied privately.—Did not
like to work.—Wrote on wooden shovel and boards.—How Abe studied.—The
books he read.—The "Revised Statute of Indiana."—Did not read the
Bible.—No religious opinions.—How he behaved at home.—Touching
recital by Mrs. Lincoln.—Abe's memory.—Mimicks the preachers.—Makes
"stump-speeches" in the field.—Cruelly maltreated by his father.—Works
out cheerfully.—Universal favorite.—The kind of people he lived
amongst.—Mrs. Crawford's reminiscences.—Society about Gentryville.
—His step-mother.—His sister.—The Johnstons and Hankses.—Abe a
ferryman and farm-servant.—His work and habits.—Works for Josiah
Crawford.—Mrs. Crawford's account of him.—Crawford's books.—Becomes
a wit and a poet.—Abe the tallest and strongest man in the
settlement.—Hunting in the Pigeon Creek region.—His activity.—Love of
talking and reading.—Fond of rustic sports.—Furnishes the
literature.—Would not be slighted.—His satires.—Songs and
chronicles.—Gentryville as "a centre of business."—Abe and other
boys loiter about the village.—Very temperate.—"Clerks" for Col.
Jones.—Abe saves a drunken man's life.—Fond of music.—Marriage of his
sister Nancy.—Extracts from his copy-book.—His Chronicles.—Fight with
the Grigs-bys.—Abe "the big buck of the lick."—"Speaking meetings"
at Gentryville.—Dennis Hanks's account of the way he and Abe became so
learned.—Abe attends a court.—Abe expects to be President.—Going
to mill.—Kicked in the head by a horse.—Mr. Wood.—Piece on
temperance.—On national politics.—Abe tired of home.—Works for
Mr. Gentry.—Knowledge of astronomy and geography.—Goes to New
Orleans.—Counterfeit money.—Fight with negroes.—Scar on his face.
—An apocryphal story...........19
CHAPTER III.
Abe's return from New Orleans.—Sawing planks for a new house.—The
milk-sickness.—Removal to Illinois.—Settles near Decatur.—Abe leaves
home.—Subsequent removals and death of Thomas Lincoln.—Abe's relations
to the family.—Works with John Hanks after leaving home.—Splitting
rails.—Makes a speech on the improvement of the Sangamon River.—Second
voyage to New Orleans.—Loading and departure of the boat.—"Sticks" on
New Salem dam.—Abe's contrivance to get her off.—Model in the Patent
Office.—Arrival at New Orleans.—Negroes chained.—Abe touched by the
sight.—Returns on a steamboat.—Wrestles with Daniel Needham.........73
CHAPTER IV.
The site of New Salem.—The village as it existed.—The
first store.—Number of inhabitants.—Their
houses.—Springfield.—Petersburg.—Mr. Lincoln appears a second time
at New Salem.—Clerks at an election.—Pilots a boat to
Beardstown.—Country store.—Abe as "first clerk."—"Clary's Grove
Boys."—Character of Jack Armstrong.—He and Abe become intimate
friends.—Abe's popularity.—Love of peace.—Habits of study.—Waylaying
strangers for information.—Pilots the steamer "Talisman" up and down
the Sangamon.......85
CHAPTER V.
Offutt's business gone to ruin.—The Black Hawk War.—Black Hawk crosses
the Mississippi.—Deceived by his allies.—The governor's call for
troops.—Abe enlists—Elected captain.—A speech.—Organization of the
army.—Captain Lincoln under arrest.—The march.—Captain Lincoln's
company declines to form.—Lincoln under arrest.—Stillman's
defeat.—Wasting rations.—Hunger.—Mutiny.—March to Dixon.—Attempt
to capture Black Hawk's pirogues.—Lincoln saves the life of
an Indian.—Mutiny.—Lincoln's novel method of quelling
it.—Wrestling.—His magnanimity.—Care of his men.—Dispute with a
regular officer.—Reach Dixon.—Move to Fox River.—A stampede.—Captain
Lincoln's efficiency as an officer.—Amusements of the camp.—Captain
Lincoln re-enlists as a private.—Independent spy company.—Progress of
the war.—Capture of Black Hawk.—Release.—Death.—Grave.—George
W. Harrison's recollections.—Duties of the spy company.—Company
disbanded.—Lincoln's horse stolen.—They start home on foot.—Buy
a canoe.—Feast on a raft.—Sell the boat.—Walk again.—Arrive at
Petersburg.—A sham battle........98
CHAPTER VI.
The volunteers from Sangamon return shortly before the State
election.—Abe a candidate for the Legislature.—Mode of bringing
forward candidates.—Parties and party names.—State and national
politics.—Mr. Lincoln's position.—Old way of conducting
elections.—Mr. Lincoln's first stump-speech.—"A general fight."—Mr.
Lincoln's part in it.—His dress and appearance.—Speech at Island
Grove.—His stories.—A third speech.—Agrees with the Whigs in the
policy of internal improvements.—His own hobby.—Prepares an address to
the people.—Mr. Lincoln defeated.—Received every vote but three cast
in his own precinct....121
CHAPTER VII.
Results of the canvass.—An opening in business.—The firm of Lincoln
& Berry.—How they sold liquor.—What Mr. Douglas said.—The store a
failure.—Berry's bad habits.—The credit system.—Lincoln's debts.—He
goes to board at the tavern.—Studies law.—Walks to Springfield for
books.—Progress in the law.—Does business for his neighbors.—Other
studies.—Reminiscences of J. Y. Ellis.—Shy of ladies.—His
apparel.—Fishing, and spouting Shakspeare and Burns.—Mr. Lincoln
annoyed by company.—Retires to the country.—Bowlin Greene.—Mr.
Lincoln's attempt to speak a funeral discourse.—John Calhoun.—Lincoln
studies surveying.—Gets employment.—Lincoln appointed postmaster.—How
he performed the duties.—Sale of Mr. Lincoln's personal property under
execution.—Bought by James Short.—Lincoln's visits.—Old Hannah.—Ah.
Trent.—Mr. Lincoln as a peacemaker.—His great strength.—The
judicial quality.—Acting second in fights.—A candidate for the
Legislature.—Elected.—Borrows two hundred dollars from Coleman
Smoot.—How they got acquainted.—Mr. Lincoln writes a little book on
infidelity.—It is burnt by Samuel Hill........135
CHAPTER VIII.
James Rutledge.—His family.—Ann Rutledge.—John McNeil.—Is engaged
to Ann.—His strange story.—The loveliness of Ann's person
and character.—Mr. Lincoln courts her.—They are engaged to be
married.—Await the return of McNeil.—Ann dies of a broken
heart.—Mr. Lincoln goes crazy.—Cared for by Bowlin Greene.—The poem
"Immortality."—Mr. Lincoln's melancholy broodings.—Interviews with
Isaac Cogdale after his election to the Presidency.—Mr. Herndon's
interview with McNamar.—Ann's grave.—The Concord cemetery...159
CHAPTER IX.
Bennett Able and family.—Mary Owens.—Mr. Lincoln falls in love with
her.—What she thought of him.—A misunderstanding.—Letters from Miss
Owens.—Mr. Lincoln's letters to her.—Humorous account of the affair in
a letter from Mr. Lincoln to another lady......172
CHAPTER X.
Mr. Lincoln takes his seat in the Legislature.—Schemes of internal
improvement.—Mr. Lincoln a silent member.—Meets Stephen A.
Douglas.—Log-rolling.—Mr. Lincoln a candidate for re-election.—The
canvass.—"The Long Nine."—Speech at Mechanicsburg.—Fight.—Reply to
Dr. Early.—Reply to George Forquer.—Trick on Dick Taylor.—Attempts
to create a third party.—Mr. Lincoln elected.—Federal and State
politics.—The Bank of the United States.—Suspension of specie
payments.—Mr. Lincoln wishes to be the De Witt Clinton of
Illinois.—The internal-improvement system.—Capital located
at Springfield.—Mr. Lincoln's conception of the duty of a
representative.—His part in passing the "system."—Begins
his antislavery record.—Public sentiment against the
Abolitionists.—History of antislavery in Illinois.—The
Covenanters.—Struggle to amend the Constitution.—The "black
code."—Death of Elijah P. Lovejoy.—Protest against proslavery
resolutions.—No sympathy with extremists.—Suspension of
specie payments.—Mr. Lincoln re-elected in 1838.—Candidate for
Speaker.—Finances.—Utter failure of the internal-improvement
"system."—Mr. Lincoln re-elected in 1840.—He introduces a bill.—His
speech.—Financial expedients.—Bitterness of feeling.—Democrats seek
to hold a quorum.—Mr. Lincoln jumps out of a window.—Speech by Mr.
Lincoln.—The alien question.—The Democrats undertake to "reform" the
judiciary.—Mr. Douglas a leader.—Protest of Mr. Lincoln and
other Whigs.—Reminiscences of a colleague.—Dinner to "The Long
Nine."—"Abraham Lincoln one of nature's noblemen."..........184
CHAPTER XI.
Capital removed to Springfield.—Mr. Lincoln settles there to practise
law.—First case.—Members of the bar.—Mr. Lincoln's partnership with
John T. Stuart.—Population and condition of Springfield.—Lawyers
and politicians.—Mr. Lincoln's intense ambition.—Lecture before the
Springfield Lyceum.—His style.—Political discussions run
high.—Joshua F. Speed his most intimate friend.—Scene in Speed's
store.—Debate.—Douglas, Calhoun, Lamborn, and Thomas, against Lincoln,
Logan, Baker, and Browning.—Presidential elector in 1840.—Stumping
for Harrison.—Scene between Lincoln and Douglas in the Court-House.—A
failure.—Redeems himself.—Meets Miss Mary Todd.—She takes Mr. Lincoln
captive.—She refuses Douglas.—Engaged.—Miss Matilda Edwards.—Mr.
Lincoln undergoes a change of heart.—Mr. Lincoln reveals to Mary the
state of his mind.—She releases him.—A reconciliation.—Every thing
prepared for the wedding.—Mr. Lincoln fails to appear.—Insane.—Speed
takes him to Kentucky.—Lines on "Suicide."—His gloom.—Return
to Springfield.—Secret meetings with Miss Todd.—Sudden
marriage.—Correspondence with Mr. Speed on delicate subjects.—Relics
of a great man and a great agony.—Miss Todd attacks James Shields in
certain witty and sarcastic letters.—Mr. Lincoln's name "given up"
as the author.—Challenged by Shields.—A meeting and an
explanation.—Correspondence.—Candidate for Congressional
nomination.—Letters to Speed and Morris.—Defeat.. 223
CHAPTER XII.
Mr. Lincoln a candidate for elector in 1844.—Debates with
Calhoun.—Speaks in Illinois and Indiana.—At Gentryville.—Lincoln,
Baker, Logan, Hardin, aspirants for Congress.—Supposed
bargain.—Canvass for Whig nomination in 1846.—Mr. Lincoln
nominated.—Opposed by Peter Cartwright.—Mr. Lincoln called a
deist.—Elected.—Takes his seat.—Distinguished members.—Opposed
to the Mexican War.—The "Spot Resolutions."—Speech of Mr.
Lincoln.—Murmurs of disapprobation.—Mr. Lincoln for "Old Rough" in
1848.—Defections at home.—Mr. Lincoln's campaign.—Speech.—Passage
not generally published.—Letter to his father.—Second session.—The
"Gott Resolution."—Mr. Lincoln's substitute..............274
CHAPTER XIII.
Mr. Lincoln in his character of country lawyer.—Public feeling at
the time of his death.—Judge Davis's address at a bar-meeting.—Judge
Drummond's address.—Mr. Lincoln's partnership with John T.
Stuart.—With Stephen. T. Logan.—With William H. Herndon.—Mr.
Lincoln "a case-lawyer."—Slow.—Conscientious.—Henry McHenry's
case.—Circumstantial evidence.—A startling case.—Mr. Lincoln's
account of it.—His first case in the Supreme Court.—Could not defend a
bad case.—Ignorance of technicalities.—The Eighth Circuit.—Happy
on the circuit.—Style of travelling.—His relations.—Young Johnson
indicted.—Mr. Lincoln's kindness.—Jack Armstrong's son tried
for murder.—Mr. Lincoln defends him.—Alleged use of a false
almanac.—Prisoner discharged.—Old Hannah's account of it.—Mr.
Lincoln's suit against Illinois Central Railway Company.—McCormick
Reaping Machine case.—Treatment by Edwin M. Stanton........311
CHAPTER XIV.
Mr. Lincoln not a candidate for re-election.—Judge Logan's defeat.—Mr.
Lincoln an applicant for Commissioner of the Land Office.—Offered the
Governorship of Oregon.—Views concerning the Missouri Compromise
and Compromise of 1850.—Declines to be a candidate for Congress in
1850.—Death of Thomas Lincoln.—Correspondence between Mr. Lincoln
and John Johnston.—Eulogy on Henry Clay.—In favor of voluntary
emancipation and colonization.—Answer to Mr. Douglas's Richmond
speech.—Passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill.—Mr. Lincoln's views
concerning slavery.—Opposed to conferring political privileges
upon negroes.—Aroused by the repeal of the Missouri
Compromise.—Anti-Nebraska party.—Mr. Lincoln the leader.—Mr. Douglas
speaks at Chicago.—At Springfield.—Mr. Lincoln replies.—A
great speech.—Mr. Douglas rejoins.—The Abolitionists.—Mr.
Herndon.—Determined to make Mr. Lincoln an Abolitionist.—They refuse
to enter the Know-Nothing lodges.—The Abolitionists desire to force
Mr. Lincoln to take a stand.—He runs away from Springfield.—He
is requested to "follow up" Mr. Douglas.—Speech at
Peoria.—Extract.—Slavery and popular sovereignty.—Mr. Lincoln and
Mr. Douglas agree not to speak any more.—The election.—Mr. Lincoln
announced for the Legislature by Wm. Jayne.—Mrs. Lincoln withdraws his
name.—Jayne restores it.—He is elected.—A candidate for United-States
Senator.—Resigns his seat.—Is censured.—Anti-Nebraska majority in
the Legislature.—The balloting.—Danger of Governor Matteson's
election.—Mr. Lincoln advises his friends to vote for Judge
Trumbull.—Trumbull elected.—Charges of conspiracy and corrupt
bargain.—Mr. Lincoln's denial.—Mr. Douglas imputes to Mr. Lincoln
extreme Abolitionist views.—Mr. Lincoln's answer.............333
CHAPTER XV.
The struggle in Kansas.—The South begins the struggle.—The North meets
it.—The Missourians and other proslavery forces.—Andrew H. Reeder
appointed governor.—Election frauds.—Mr. Lincoln's views on
Kansas.—Gov. Shannon arrives in the Territory.—The Free State men
repudiate the Legislature.—Mr. Lincoln's "little speech" to the
Abolitionists of Illinois.—Mr. Lincoln's party relations.—Mr. Lincoln
agrees to meet the Abolitionists.—Convention at Bloomington.—Mr.
Lincoln considered a convert.—His great speech.—Conservative
resolutions.—Ludicrous failure of a ratification meeting at
Springfield.—Mr. Lincoln's remarks.—Plot to break up the Know-Nothing
party.—"National" Republican Convention.—Mr. Lincoln receives
a hundred and ten votes for Vice-President.—National Democratic
Convention.—Mr. Lincoln a candidate for elector.—His
canvass.—Confidential letter.—Imperfect fellowship with the
Abolitionists.—Mr. Douglas's speech on Kansas in June, 1857.—Mr.
Lincoln's reply.—Mr. Douglas committed to support of the Lecompton
Constitution.—The Dred Scott Decision discussed.—Mr. Lincoln
against negro equality.—Affairs in Kansas.—Election of a new
Legislature.—Submission of the Lecompton Constitution to
the people.—Method of voting on it.—Constitution finally
rejected.—Conflict in Congress.—Mr. Douglas's defection.—Extract from
a speech by Mr. Lincoln........366
CHAPTER XVI.
Mr. Douglas opposes the Administration.—His course in
Congress.—Squatter sovereignty in full operation.—Mr. Lincoln's
definition of popular sovereignty and squatter sovereignty.—Mr.
Douglas's private conferences with Republicans.—"Judge Trumbull's
opinion.—Mr. Douglas nominated for senator by a Democratic
Convention.—Mr. Lincoln's idea of what Douglas might accomplish at
Charleston.—Mr. Lincoln writing a celebrated speech.—He is nominated
for senator.—A startling doctrine.—A council of friends.—Same
doctrine advanced at Bloomington.—The "house-divided" speech.—Mr.
Lincoln promises to explain.—What Mr. Lincoln thought of Mr.
Douglas.—What Mr. Douglas thought of Mr. Lincoln.—Popular canvass for
senator.—Mr. Lincoln determines to "kill Douglas" as a
Presidential aspirant.—Adroit plan to draw him out on squatter
sovereignty.—Absurdities of Mr. Douglas.—The election.—Success of Mr.
Douglas.—Reputation acquired by Mr. Lincoln..................389
CHAPTER XVII.
Mr. Lincoln writes and delivers a lecture.—The Presidency.—Mr.
Lincoln's "running qualities."—He thinks himself unfit.—Nominated by
"Illinois Gazette."—Letter to Dr. Canisius.—Letter to Dr. Wallace
on the protective tariff policy.—Mr. Lincoln in Ohio and Kansas.—A
private meeting of his friends.—Permitted to use his name for
the Presidency.—An invitation to speak in New York.—Choosing a
subject.—Arrives in New York.—His embarrassments.—Speech in Cooper
Institute.—Comments of the press.—He is charged with mercenary
conduct.—Letter concerning the charge.—Visits New England.—Style
and character of his speeches.—An amusing encounter with a clerical
politician...421
CHAPTER XVIII.
Meeting of the Republican State Convention.—Mr. Lincoln present.—John
Hanks and the rails.—Mr. Lincoln's speech.—Meeting of the Republican
National Convention at Chicago.—The platform.—Combinations to secure
Mr. Lincoln's nomination.—The balloting.—Mr. Lincoln nominated.—Mr.
Lincoln at Springfield waiting the results of the Convention.—How
he received the news.—Enthusiasm at Springfield.—Official
notification.—The "Constitutional Union" party.—The Democratic
Conventions at Charleston and Baltimore.—The election.—The
principle upon which Mr. Lincoln proposed to make appointments.—Mr.
Stephens.—Mr. Gilmore.—Mr. Guthrie.—Mr. Seward.—Mr. Chase.—Mr.
Bates.—The cases of Smith and Cameron.—Mr. Lincoln's visit
to Chicago.—Mr. Lincoln's visit to his relatives in Coles
County.—Apprehensions about assassination.—A visit from Hannah
Armstrong... 444
CHAPTER XIX.
Difficulties and peculiarities of Mr. Lincoln's position.—A general
review of his character.—His personal appearance and habits.—His house
and other property.—His domestic relations.—His morbid melancholy
and superstition.—Illustrated by his literary tastes.—His humor.—His
temperate habits and abstinence from sensual pleasures.—His
ambition.—Use of politics for personal advancement.—Love of power
and place.—Of justice.—Not a demagogue or a trimmer.—His religious
views.—Attempt of the Rev. Mr. Smith to convert him.—Mr. Bateman's
story as related by Dr. Holland.—Effect of his belief upon his mind and
character...........466
CHAPTER XX.
Departure of the Presidential party from Springfield.—Affecting address
by Mr. Lincoln to his friends and neighbors.—His opinions concerning
the approaching civil war.—Discovery of a supposed plot to murder
him at Baltimore.—Governor Hicks's proposal to "kill Lincoln and his
men."—The plan formed to defeat the conspiracy.—The midnight ride
from Harrisburg to Washington.—Arrival in Washington.—Before the
Inauguration.—Inauguration Day.—Inaugural Address.—Mr. Lincoln's
Oath.—Mr. Lincoln President of the United States.—Mr. Buchanan bids
him farewell............505
ABRAHAM LINCOLN was born on the twelfth day of February, 1809. His father's name was Thomas Lincoln, and his mother's maiden name was Nancy Hanks. At the time of his birth, they are supposed to have been married about three years. Although there appears to have been but little sympathy or affection between Thomas and Abraham Lincoln, they were nevertheless connected by ties and associations which make the previous history of Thomas Lincoln and his family a necessary part of any reasonably full biography of the great man who immortalized the name by wearing it.
Thomas Lincoln's ancestors were among the early settlers of Rockingham County in Virginia; but exactly whence they came, or the precise time of their settlement there, it is impossible to tell. They were manifestly of English descent; but whether emigrants directly from England to Virginia, or an offshoot of the historic Lincoln family in Massachusetts, or of the highly-respectable Lincoln family in Pennsylvania, are questions left entirely to conjecture. We have absolutely no evidence by which to determine them, Thomas Lincoln himself stoutly denied that his progenitors were either Quakers or Puritans; but he furnished nothing except his own word to sustain his denial: on the contrary, some of the family (distant relatives of Thomas Lincoln) who remain in Virginia believe themselves to have sprung from the New-England stock. They found their opinion solely on the fact that the Christian names given to the sons of the two families were the same, though only in a few cases, and at different times. But this might have arisen merely from that common religious sentiment which induces parents of a devotional turn to confer scriptural names on their children, or it might have been purely accidental. Abrahams, Isaacs, and Jacobs abound in many other families who claim no kindred on that account. In England, during the ascendency of the Puritans, in times of fanatical religious excitement, the children were almost universally baptized by the names of the patriarchs and Old-Testament heroes, or by names of their own pious invention, signifying what the infant was expected to do and to suffer in the cause of the Lord. The progenitors of all the American Lincolns were Englishmen, and they may have been Puritans. There is, therefore, nothing unreasonable in the supposition that they began the practice of conferring such names before the emigration of any of them; and the names, becoming matters of family pride and family tradition, have continued to be given ever since. But, if the fact that Christian names of a particular class prevailed among the Lincolns of Massachusetts and the Lincolns of Virginia at the same time is no proof of consanguinity, the identity of the surname is entitled to even less consideration. It is barely possible that they may have had a common ancestor; but, if they had, he must have lived and died so obscurely, and so long ago, that no trace of him can be discovered. It would be as difficult to prove a blood relationship between all the American Lincolns, as it would be to prove a general cousinship among all the Smiths or all the Joneses.1
1 At the end of this volume will be found a very interesting account of the family, given by Mr. Lincoln himself. The original is in his own handwriting, and is here reproduced in fac-simile.
A patronymic so common as Lincoln, derived from a large geographical division of the old country, would almost certainly be taken by many who had no claim to it by reason of descent from its original possessors.
Dr. Holland, who, of all Mr. Lincoln's biographers, has entered most extensively into the genealogy of the family, says that the father of Thomas was named Abraham; but he gives no authority for his statement, and it is as likely to be wrong as to be right. The Hankses—John and Dennis—who passed a great part of their lives in the company of Thomas Lincoln, tell us that the name of his father was Mordecai; and so also does Col. Chapman, who married Thomas Lincoln's step-daughter. The rest of those who ought to know are unable to assign him any name at all. Dr. Holland says further, that this Abraham (or Mordecai) had four brothers,—Jacob, John, Isaac, and Thomas; that Isaac went to Tennessee, where his descendants are now; that Thomas went to Kentucky after his brother Abraham; but that Jacob and John "are supposed to have" remained in Virginia.1 This is doubtless true, at least so far as it relates to Jacob and John; for there are at this day numerous Lincolns residing in Rockingham County,—the place from which the Kentucky Lincolns emigrated. One of their ancestors, Jacob,—who seems to be the brother referred to,—was a lieutenant in the army of the Revolution, and present at the siege of Yorktown. His military services were made the ground of a claim against the government, and Abraham Lincoln, whilst a representative in Congress from Illinois, was applied to by the family to assist them in prosecuting it. A correspondence of some length ensued, by which the presumed relationship of the parties was fully acknowledged on both sides. But, unfortunately, no copy of it is now in existence. The one preserved by the Virginians was lost or destroyed during the late war. The family, with perfect unanimity, espoused the cause of the Confederate States, and suffered many losses in consequence, of which these interesting papers may have been one.
1 The Life of Abraham Lincoln, by J. G. Holland, p. 20.
Abraham (or Mordecai) the father of Thomas Lincoln, was the owner of a large and fertile tract of land on the waters of Linnville's Creek, about eight miles north of Harrisonburg, the court-house town of Rockingham County. It is difficult to ascertain the precise extent of this plantation, or the history of the title to it, inasmuch as all the records of the county were burnt by Gen. Hunter in 1864. It is clear, however, that it had been inherited by Lincoln, the emigrant to Kentucky, and that four, if not all, of his children were born upon it. At the time Gen. Sheridan received the order "to make the Valley of the Shenandoah a barren waste," this land was well improved and in a state of high cultivation; but under the operation of that order it was ravaged and desolated like the region around it.
Lincoln, the emigrant, had three sons and two daughters. Thomas was the third son and the fourth child. He was born in 1778; and in 1780, or a little later, his father removed with his entire family to Kentucky.
Kentucky was then the paradise of the borderer's dreams. Fabulous tales of its sylvan charms and pastoral beauties had for years been floating about, not only along the frontiers of Pennsylvania, Virginia, and North Carolina, but farther back in the older settlements. For a while it had been known as the "Cane Country," and then as the "Country of Kentucky." Many expeditions were undertaken to explore it; two or three adventurers, and occasionally only one at a time, passing down the Ohio in canoes. But they all stopped short of the Kentucky River. The Indians were terrible; and it was known that they would surrender any other spot of earth in preference to Kentucky. The canes that were supposed to indicate the promised land—those canes of wondrous dimensions, that shot up, as thick as they could stand, from a soil of inestimable fertility—were forever receding before those who sought them. One party after another returned to report, that, after incredible dangers and hardships, they had met with no better fortune than that which had attended the efforts of their predecessors, and that they had utterly failed to find the "canes." At last they were actually found by Simon Kenton, who stealthily planted a little patch of corn, to see how the stalk that bore the yellow grain would grow beside its "brother" of the wilderness. He was one day leaning against the stem of a great tree, watching his little assemblage of sprouts, and wondering at the strange fruitfulness of the earth which fed them, when he heard a footstep behind him. It was the great Daniel Boone's. They united their fortunes for the present, but subsequently each of them became the chief of a considerable settlement. Kenton's trail had been down the Ohio, Boone's from North Carolina; and from both those directions soon came hunters, warriors, and settlers to join them. But the Indians had no thought of relinquishing their fairest hunting-grounds without a long and desperate struggle. The rich carpet of natural grasses which fed innumerable herds of buffalo, elk, and deer, all the year round; the grandeur of its primeval forests, its pure fountains, and abundant streams,—made it even more desirable to them than to the whites. They had long contended for the possession of it; and no tribe, or confederacy of tribes, had ever been able to hold it to the exclusion of the rest. Here, from time immemorial, the northern and southern, the eastern and western Indians had met each other in mortal strife, mutually shedding the blood which ought to have been husbanded for the more deadly conflict with a common foe. The character of this savage warfare had earned for Kentucky the appellation of "the dark and bloody ground;" and, now that the whites had fairly begun their encroachments upon it, the Indians were resolved that the phrase should lose none of its old significance. White settlers might therefore count upon fighting for their lives as well as their lands.
Boone did not make his final settlement till 1775. The Lincolns came about 1780. This was but a year or two after Clark's expedition into Illinois; and it was long, long before St. Clair's defeat and Wayne's victory. Nearly the whole of the north-west territory was then occupied by hostile Indians. Kentucky volunteers had yet before them many a day of hot and bloody work on the Ohio, the Muskingum, and the Miami, to say nothing of the continual surprises to which they were subjected at home. Every man's life was in his hand. From cabin to cabin, from settlement to settlement, his trail was dogged by the eager savage. If he went to plough, he was liable to be shot down between the handles; if he attempted to procure subsistence by hunting, he was hunted himself. Unless he abandoned his "clearing" and his stock to almost certain devastation, and shut up himself and his family in a narrow "fort," for months at a time, he might expect every hour that their roof would be given "to the flames, and their flesh to the eagles."
To make matters worse, "the western country," and particularly Kentucky, had become the rendezvous of Tories, runaway conscripts, deserters, debtors, and criminals. Gen. Butler, who went there as a Commissioner from Congress, to treat with certain Indian tribes, kept a private journal, in which he entered a very graphic, but a very appalling description of the state of affairs in Kentucky. At the principal "points," as they were called, were collected hungry speculators, gamblers, and mere desperadoes,—these distinctions being the only divisions and degrees in society. Among other things, the journal contains a statement about land-jobbing and the traffic in town lots, at Louisville, beside which the account of the same business in "Martin Chuzzlewit" is absolutely tame. That city, now one of the most superb in the Union, was then a small collection of cabins and hovels, inhabited by a class of people of whom specimens might have been found a few months ago at Cheyenne or Promontory Point. Notwithstanding the high commissions borne by Gen. Butler and Gen. Parsons, the motley inhabitants of Louisville flatly refused even to notice them. They would probably have sold them a "corner lot" in a swamp, or a "splendid business site" in a mud-hole; but for mere civilities there was no time. The whole population were so deeply engaged in drinking, card-playing, and selling town lots to each other, that they persistently refused to pay any attention to three men who were drowning in the river near by, although their dismal cries for help were distinctly heard throughout the "city."
On the journey out, the Lincolns are said to have endured many hardships and encountered all the usual dangers, including several skirmishes with the Indians. They settled in Mercer County, but at what particular spot is uncertain. Their house was a rough log-cabin, their farm a little clearing in the midst of a vast forest. One morning, not long after their settlement, the father took Thomas, his youngest son, and went to build a fence, a short distance from the house; while the other brothers, Mordecai and Josiah, were sent to another field, not far away. They were all intent about their work, when a shot from a party of Indians in ambush broke the "listening stillness" cf the woods. The father fell dead; Josiah ran to a stockade two or three miles off; Mordecai, the eldest boy, made his way to the house, and, looking out from the loophole in the loft, saw an Indian in the act of raising his little brother from the ground. He took deliberate aim at a silver ornament on the breast of the Indian, and brought him down. Thomas sprang toward the cabin, and was admitted by his mother, while Mordecai renewed his fire at several other Indians that rose from the covert of the fence or thicket. It was not long until Josiah returned from the stockade with a party of settlers; but the Indians had fled, and none were found but the dead one, and another who was wounded and had crept into the top of a fallen tree.
When this tragedy was enacted, Mordecai, the hero of it, was a well-grown boy. He seems to have hated Indians ever after with a hatred which was singular for its intensity, even in those times. Many years afterwards, his neighbors believed that he was in the habit of following peaceable Indians, as they passed through the settlements, in order to get surreptitious shots at them; and it was no secret that he had killed more than one in that way.
Immediately after the death of her husband, the widow abandoned the scene of her misfortunes, and removed to Washington County, near the town of Springfield, where she lived until the youngest of her children had grown up. Mor-decai and Josiah remained there until late in life, and were always numbered among the best people in the neighborhood. Mordecai was the eldest son of his father; and under the law of primogeniture, which was still a part of the Virginia code, he inherited some estate in lands. One of the daughters wedded a Mr. Krume, and the other a Mr. Brumfield.
Thomas seems to have been the only member of the family whose character was not entirely respectable. He was idle, thriftless, poor, a hunter, and a rover. One year he wandered away off to his uncle, on the Holston, near the confines of Tennessee. Another year he wandered into Breckinridge County, where his easy good-nature was overcome by a huge bully, and he performed the only remarkable achievement of his life, by whipping him. In 1806, we find him in Hardin County, trying to learn the carpenter's trade. Until then, he could neither read nor write; and it was only after his marriage that his ambition led him to seek accomplishments of this sort.
Thomas Lincoln was not tall and thin, like Abraham, but comparatively short and stout, standing about five feet ten inches in his shoes. His hair was dark and coarse, his complexion brown, his face round and full, his eyes gray, and his nose large and prominent. He weighed, at different times, from one hundred and seventy to one hundred and ninety-six. He was built so "tight and compact," that Dennis Hanks declares he never could find the points of separation between his ribs, though he felt for them often. He was a little stoop-shouldered, and walked with a slow, halting step. But he was sinewy and brave, and, his habitually peaceable disposition once fairly overborne, was a tremendous man in a rough-and-tumble fight. He thrashed the monstrous bully of Breckinridge County in three minutes, and came off without a scratch.
His vagrant career had supplied him with an inexhaustible fund of anecdotes, which he told cleverly and well. He loved to sit about at "stores," or under shade-trees, and "spin yarns,"—a propensity which atoned for many sins, and made him extremely popular. In politics, he was a Democrat,—a Jackson Democrat. In religion he was nothing at times, and a member of various denominations by turns,—a Free-Will Baptist in Kentucky, a Presbyterian in Indiana, and a Disciple—vulgarly called Campbellite—in Illinois. In this latter communion he seems to have died.
It ought, perhaps, to be mentioned, that both in Virginia and Kentucky his name was commonly pronounced "Linck-horn," and in Indiana, "Linckhern." The usage was so general, that Tom Lincoln came very near losing his real name altogether. As he never wrote it at all until after his marriage, and wrote it then only mechanically, it was never spelled one way or the other, unless by a storekeeper here and there, who had a small account against him. Whether it was properly "Lincoln," "Linckhorn," or "Linckhern," was not definitely settled until after Abraham began to write, when, as one of the neighbors has it, "he remodelled the spelling and corrected the pronunciation."
By the middle of 1806, Lincoln had acquired a very limited knowledge of the carpenter's trade, and set up on his own account; but his achievements in this line were no better than those of his previous life. He was employed occasionally to do rough work, that requires neither science nor skill; but nobody alleges that he ever built a house, or pretended to do more than a few little odd jobs connected with such an undertaking. He soon got tired of the business, as he did of every thing else that required application and labor. He was no boss, not even an average journeyman, nor a steady hand. When he worked at the trade at all, he liked to make common benches, cupboards, and bureaus; and some specimens of his work of this kind are still extant in Kentucky and Indiana, and bear their own testimony to the quality of their workmanship.
Some time in the year 1806 he married Nancy Hanks. It was in the shop of her uncle, Joseph Hanks, at Elizabethtown, in Hardin County, that he had essayed to learn the trade. We have no record of the courtship, but any one can readily imagine the numberless occasions that would bring together the niece and the apprentice. It is true that Nancy did not live with her uncle; but the Hankses were all very clannish, and she was doubtless a welcome and frequent guest at his house. It is admitted by all the old residents of the place that they were honestly married, but precisely when or how no one can tell. Diligent and thorough searches by the most competent persons have failed to discover any trace of the fact in the public records of Hardin and the adjoining counties. The license and the minister's return in the case of Lincoln and Sarah Johnston, his second wife, were easily found in the place where the law required them to be; but of Nancy Hanks's marriage there exists no evidence but that of mutual acknowledgment and cohabitation. At the time of their union, Thomas was twenty-eight years of age, and Nancy about twenty-three.
Lincoln had previously courted a girl named Sally Bush, who lived in the neighborhood of Elizabethtown; but his suit was unsuccessful, and she became the wife of Johnston, the jailer. Her reason for rejecting Lincoln comes down to us in no words of her own; but it is clear enough that it was his want of character, and the "bad luck," as the Hankses have it, which always attended him. Sally Bush was a modest and pious girl, in all things pure and decent. She was very neat in her personal appearance, and, because she was particular in the selection of her gowns and company, had long been accounted a "proud body," who held her head above common folks. Even her own relatives seem to have participated in this mean accusation; and the decency of her dress and behavior appear to have made her an object of common envy and backbiting. But she had a will as well as principles of her own, and she lived to make them both serviceable to the neglected and destitute son of Nancy Hanks. Thomas Lincoln took another wife, but he always loved Sally Bush as much as he was capable of loving anybody; and years afterwards, when her husband and his wife were both dead, he returned suddenly from the wilds of Indiana, and, representing himself as a thriving and prosperous farmer, induced her to marry him. It will be seen hereafter what value was to be attached to his representations of his own prosperity.
Nancy Hanks, who accepted the honor which Sally Bush refused, was a slender, symmetrical woman, of medium stature, a brunette, with dark hair, regular features, and soft, sparkling hazel eyes. Tenderly bred she might have been beautiful; but hard labor and hard usage bent her handsome form, and imparted an unnatural coarseness to her features long before the period of her death. Toward the close, her life and her face were equally sad; and the latter habitually wore the wo-ful expression which afterwards distinguished the countenance of her son in repose.
By her family, her understanding was considered something wonderful. John Hanks spoke reverently of her "high and intellectual forehead," which he considered but the proper seat of faculties like hers. Compared with the mental poverty of her husband and relatives, her accomplishments were certainly very great; for it is related by them with pride and delight that she could actually read and write. The possession of these arts placed her far above her associates, and after a little while even Tom began to meditate upon the importance of acquiring them. He set to work accordingly, in real earnest, having a competent mistress so near at hand; and with much effort she taught him what letters composed his name, and how to put them together in a stiff and clumsy fashion. Henceforth he signed no more by making his mark; but it is nowhere stated that he ever learned to write any thing else, or to read either written or printed letters.
Nancy Hanks was the daughter of Lucy Hanks. Her mother was one of four sisters,—Lucy, Betsy, Polly, and Nancy. Betsy married Thomas Sparrow; Polly married Jesse Friend, and Nancy, Levi Hall. Lucy became the wife of Henry Sparrow, and the mother of eight children. Nancy the younger was early sent to live with her uncle and aunt, Thomas and Betsy Sparrow. Nancy, another of the four sisters, was the mother of that Dennis F. Hanks whose name will be frequently met with in the course of this history. He also was brought up, or was permitted to come up, in the family of Thomas Sparrow, where Nancy found a shelter.
Little Nancy became so completely identified with Thomas and Betsy Sparrow that many supposed her to have been their child. They reared her to womanhood, followed her to Indiana, dwelt under the same roof, died of the same disease, at nearly the same time, and were buried close beside her. They were the only parents she ever knew; and she must have called them by names appropriate to that relationship, for several persons who saw them die, and carried them to their graves, believe to this day that they were, in fact, her father and mother. Dennis Hanks persists even now in the assertion that her name was Sparrow; but Dennis was pitiably weak on the cross-examination: and we shall have to accept the testimony of Mr. Lincoln himself, and some dozens of other persons, to the contrary.
All that can be learned of that generation of Hankses to which Nancy's mother belonged has now been recorded as fully as is compatible with circumstances. They claim that their ancestors came from England to Virginia, whence they migrated to Kentucky with the Lincolns, and settled near them in Mercer County. The same, precisely, is affirmed of the Sparrows. Branches of both families maintained a more or less intimate connection with the fortunes of Thomas Lincoln, and the early life of Abraham was closely interwoven with theirs.
Lincoln took Nancy to live in a shed on one of the alleys of Elizabethtown. It was a very sorry building, and nearly bare of furniture. It stands yet, or did stand in 1866, to witness for itself the wretched poverty of its early inmates. It is about fourteen feet square, has been three times removed, twice used as a slaughter-house, and once as a stable. Here a daughter was born on the tenth day of February, 1807, who was called Nancy during the life of her mother, and after her death Sarah.
But Lincoln soon wearied of Elizabethtown and carpenter-work. He thought he could do better as a farmer; and, shortly after the birth of Nancy (or Sarah), removed to a piece of land on the south fork of Nolin Creek, three miles from Hodgensville, within the present county of La Rue, and about thirteen miles from Elizabethtown. What estate he had, or attempted to get, in this land, is not clear from the papers at hand. It is said he bought it, but was unable to pay for it. It was very poor, and the landscape of which it formed a part was extremely desolate. It was then nearly destitute of timber, though it is now partially covered in spots by a young and stunted growth of post-oak and hickory. On every side the eye rested only upon weeds and low bushes, and a kind of grass which the present owner of the farm describes as "barren grass." It was, on the whole, as bad a piece of ground as there was in the neighborhood, and would hardly have sold for a dollar an acre. The general appearance of the surrounding country was not much better. A few small but pleasant streams—Nolin Creek and its tributaries—wandered through the valleys. The land was generally what is called "rolling;" that is, dead levels interspersed by little hillocks. Nearly all of it was arable; but, except the margins of the watercourses, not much of it was sufficiently fertile to repay the labor of tillage. It had no grand, un violated forests to allure the hunter, and no great bodies of deep and rich soils to tempt the husbandman. Here it was only by incessant labor and thrifty habits that an ordinary living could be wrung from the earth.
The family took up their residence in a miserable cabin, which stood on a little knoll in the midst of a barren glade.
A few stones tumbled down, and lying about loose, still indicate the site of the mean and narrow tenement which sheltered the infancy of one of the greatest political chieftains of modern times. Near by, a "romantic spring" gushed from beneath a rock, and sent forth a slender but silvery stream, meandering through those dull and unsightly plains. As it furnished almost the only pleasing feature in the melancholy desert through which it flowed, the place was called after it, "Rock Spring Farm." In addition to this single natural beauty, Lincoln began to think, in a little while, that a couple of trees would look well, and might even be useful, if judiciously planted in the vicinity of his bare house-yard. This enterprise he actually put into execution; and three decayed pear-trees, situated on the "edge" of what was lately a rye-field, constitute the only memorials of him or his family to be seen about the premises. They were his sole permanent improvement.
In that solitary cabin, on this desolate spot, the illustrious Abraham Lincoln was born on the twelfth day of February, 1809.
The Lincolns remained on Nolin Creek until Abraham was four years old. They then removed to a place much more picturesque, and of far greater fertility. It was situated about six miles from Hodgensville, on Knob Creek, a very clear stream, which took its rise in the gorges of Muldrews Hill, and fell into the Rolling Fork two miles above the present town of New Haven. The Rolling Fork emptied into Salt River, and Salt River into the Ohio, twenty-four miles below Louisville. This farm was well timbered, and more hilly than the one on Nolin Creek. It contained some rich valleys, which promised such excellent yields, that Lincoln bestirred himself most vigorously, and actually got into cultivation the whole of six acres, lying advantageously up and down the branch. This, however, was not all the work he did, for he still continued to pother occasionally at his trade; but, no matter what he turned his hand to, his gains were equally insignificant. He was satisfied with indifferent shelter, and a diet of "corn-bread and milk" was all he asked. John Hanks naively observes, that "happiness was the end of life with him." The land he now lived upon (two hundred and thirty-eight acres) he had pretended to buy from a Mr. Slater. The deed mentions a consideration of one hundred and eighteen pounds. The purchase must have been a mere speculation, with all the payments deferred, for the title remained in Lincoln but a single year. The deed was made to him Sept. 2, 1813; and Oct. 27, 1814, he conveyed two hundred acres to Charles Milton for one hundred pounds, leaving thirty-eight acres of the tract unsold. No public record discloses what he did with the remainder. If he retained any interest in it for-the time, it was probably permitted to be sold for taxes. The last of his voluntary transactions, in regard to this land, took place two years before his removal to Indiana; after which, he seems to have continued in possession as the tenant of Milton.
In the mean time, Dennis Hanks endeavored to initiate young Abraham, now approaching his eighth year, in the mysteries of fishing, and led him on numerous tramps up and down the picturesque branch,—the branch whose waters were so pure that a white pebble could be seen in a depth of ten feet. On Nolin he had hunted ground-hogs with an older boy, who has since become the Rev. John Duncan, and betrayed a precocious zest in the sport. On Knob Creek, he dabbled in the water, or roved the hills and climbed the trees, with a little companion named Gallaher. On one occasion, when attempting to "coon" across the stream, by swinging over on a sycamore-tree, Abraham lost his hold, and, tumbling into deep water, was saved only by the utmost exertions of the other boy. But, with all this play, the child was often serious and sad. With the earliest dawn of reason, he began to suffer and endure; and it was that peculiar moral training which developed both his heart and his intellect with such singular and astonishing rapidity. It is not likely that Tom Lincoln cared a straw about his education. He had none himself, and is said to have admired "muscle" more than mind. Nevertheless, as Abraham's sister was going to school for a few days at a time, he was sent along, as Dennis Hanks remarks, more to bear her company than with any expectation or desire that he would learn much himself. One of the masters, Zachariah Riney, taught near the Lincoln cabin. The other, Caleb Hazel, kept his school nearly four miles away, on the "Friend" farm; and the hapless children were compelled to trudge that long and weary distance with spelling-book and "dinner,"—the latter a lunch of corn-bread, Tom Lincoln's favorite dish. Hazel could teach reading and writing, after a fashion, and a little arithmetic. But his great qualification for his office lay in the strength of his arm, and his power and readiness to "whip the big boys."
But, as time wore on, the infelicities of Lincoln's life in this neighborhood became insupportable. He was gaining neither riches nor credit; and, being a wanderer by natural inclination, began to long for a change. His decision, however, was hastened by certain troubles which culminated in a desperate combat between him and one Abraham Enlow. They fought like savages; but Lincoln obtained a signal and permanent advantage by biting off the nose of his antagonist, so that he went bereft all the days of his life, and published his audacity and its punishment wherever he showed his face. But the affray, and the fame of it, made Lincoln more anxious than ever to escape from Kentucky. He resolved, therefore, to leave these scenes forever, and seek a roof-tree beyond the Ohio.
It has pleased some of Mr. Lincoln's biographers to represent this removal of his father as a flight from the taint of slavery. Nothing could be further from the truth. There were not at the time more than fifty slaves in all Hardin County, which then composed a vast area of territory. It was practically a free community. Lincoln's more fortunate relatives in other parts of the State were slaveholders; and there is not the slightest evidence that he ever disclosed any conscientious scruples concerning the "institution."
The lives of his father and mother, and the history and character of the family before their settlement in Indiana, were topics upon which Mr. Lincoln never spoke but with great reluctance and significant reserve.
In his family Bible he kept a register of births, marriages, and deaths, every entry being carefully made in his own handwriting. It contains the date of his sister's birth and his own; of the marriage and death of his sister; of the death of his mother; and of the birth and death of Thomas Lincoln. The rest of the record is almost wholly devoted to the Johnstons and their numerous descendants and connections. It has not a word about the Hankses or the Sparrows. It shows the marriage of Sally Bush, first with Daniel Johnston, and then with Thomas Lincoln; but it is entirely silent as to the marriage of his own mother. It does not even give the date of her birth, but barely recognizes her existence and demise, to make the vacancy which was speedily filled by Sarah Johnston.1
1 The leaf of the Bible which contains these entries is in the possession of Col. Chapman.
An artist was painting his portrait, and asked him for a sketch of his early life. He gave him this brief memorandum: "I was born Feb. 12,1809, in the then Hardin County, Kentucky, at a point within the now county of La Rue, a mile or a mile and a half from where Hodgens Mill now is. My parents being dead, and my own memory not serving, I know of no means of identifying the precise locality. It was on Nolin Creek."
To the compiler of the "Dictionary of Congress" he gave the following: "Born Feb. 12, 1809, in Hardin County, Kentucky. Education defective. Profession, a lawyer. Have been a captain of volunteers in the Black-Hawk War. Postmaster at a very small office. Four times a member of the Illinois Legislature, and was a member of the Lower House of Congress."
To a campaign biographer who applied for particulars of his early history, he replied that they could be of no interest; that they were but
"The short and simple annals of the poor."
"The chief difficulty I had to encounter," writes this latter gentleman, "was to induce him to communicate the homely facts and incidents of his early life. He seemed to be painfully impressed with the extreme poverty of his early surroundings, the utter absence of all romantic and heroic elements; and I know he thought poorly of the idea of attempting a biographical sketch for campaign purposes.... Mr. Lincoln communicated some facts to me about his ancestry, which he did not wish published, and which I have never spoken of or alluded to before. I do not think, however, that Dennis Hanks, if he knows any thing about these matters, would be very likely to say any thing about them."
THOMAS LINCOLN was something of a waterman. In the frequent changes of occupation, which had hitherto made his life so barren of good results, he could not resist the temptation to the career of a flat-boatman. He had accordingly made one, or perhaps two trips to New Orleans, in the company and employment of Isaac Bush, who was probably a near relative of Sally Bush. It was therefore very natural, that when, in the fall of 1816, he finally determined to emigrate, he should attempt to transport his goods by water. He built himself a boat, which seems to have been none of the best, and launched it on the Rolling Fork, at the mouth of Knob Creek, a half-mile from his cabin. Some of his personal property, including carpenter's tools, he put on board, and the rest he traded for four hundred gallons of whiskey. With this crazy boat and this singular cargo, he put out into the stream alone, and floating with the current down the Rolling Fork, and then down Salt River, reached the Ohio without any mishap. Here his craft proved somewhat rickety when contending with the difficulties of the larger stream, or perhaps there was a lack of force in the management of her, or perhaps the single navigator had consoled himself during the lonely voyage by too frequent applications to a portion of his cargo: at all events, the boat capsized, and the lading went to the bottom. He fished up a few of the tools "and most of the whiskey," and, righting the little boat, again floated down to a landing at Thompson's Ferry, two and a half miles west of Troy, in Perry County, Indiana. Here he sold his treacherous boat, and, leaving his remaining property in the care of a settler named Posey, trudged off on foot to select "a location" in the wilderness. He did not go far, but found a place that he thought would suit him only sixteen miles distant from the river. He then turned about, and walked all the way back to Knob Creek, in Kentucky, where he took a fresh start with his wife and her children. Of the latter there were only two,—Nancy (or Sarah), nine years of age, and Abraham, seven. Mrs. Lincoln had given birth to another son some years before, but he had died when only three days old. After leaving Kentucky, she had no more children.
This time Lincoln loaded what little he had left upon two horses, and "packed through to Posey's." Besides clothing and bedding, they carried such cooking utensils as would be needed by the way, and would be indispensable when they reached their destination. The stock was not large. It consisted of "one oven and lid, one skillet and lid, and some tin-ware." They camped out during the nights, and of course cooked their own food. Lincoln's skill as a hunter must now have stood him in good stead.
Where he got the horses used upon this occasion, it is impossible to say; but they were likely borrowed from his brother-in-law, Krume, of Breckinridge County, who owned such stock, and subsequently moved Sarah Johnston's goods to Indiana, after her marriage with Lincoln.
When they got to Posey's, Lincoln hired a wagon, and, loading on it the whiskey and other things he had stored there, went on toward the place which has since become famous as the "Lincoln Farm." He was now making his way through an almost untrodden wilderness. There was no road, and for a part of the distance not even a foot-trail. He was slightly assisted by a path of a few miles in length, which had been "blazed out" by an earlier settler named Hoskins. But he was obliged to suffer long delays, and cut out a passage for the wagon with his axe. At length, after many detentions and difficulties he reached the point where he intended to make his future home. It was situated between the forks of Big Pigeon and Little Pigeon Creeks, a mile and a half east of Gentryville, a village which grew up afterwards, and now numbers about three hundred inhabitants. The whole country was covered with a dense forest of oaks, beeches, walnuts, sugar-maples, and nearly all the varieties of trees that flourish in North America. The woods were usually open, and devoid of underbrush; the trees were of the largest growth, and beneath the deep shades they afforded was spread out a rich greensward. The natural grazing was very good, and hogs found abundant sustenance in the prodigious quantity of mast. There was occasionally a little glade or prairie set down in the midst of this vast expanse of forest. One of these, not far from the Lincoln place, was a famous resort for the deer, and the hunters knew it well for its numerous "licks." Upon this prairie the militia "musters" were had at a later day, and from it the south fork of the Pigeon came finally to be known as the "Prairie Fork."
Lincoln laid off his curtilage on a gentle hillock having a slope on every side. The spot was very beautiful, and the soil was excellent. The selection was wise in every respect but one. There was no water near, except what was collected in holes in the ground after a rain; but it was very foul, and had to be strained before using. At a later period we find Abraham and his step-sister carrying water from a spring situated a mile away. Dennis Hanks asserts that Tom Lincoln "riddled his land like a honeycomb," in search of good water, and was at last sorely tempted to employ a Yankee, who came around with a divining-rod, and declared that for the small consideration of five dollars in cash, he would make his rod point to a cool, flowing spring beneath the surface.
Here Lincoln built "a half-faced camp,"—a cabin enclosed on three sides and open on the fourth. It was built, not of logs, but of poles, and was therefore denominated a "camp," to distinguish it from a "cabin." It was about fourteen feet square, and had no floor. It was no larger than the first house he lived in at Elizabethtown, and on the whole not as good a shelter. But Lincoln was now under the influence of a transient access of ambition, and the camp was merely preliminary to something better. He lived in it, however, for a whole year, before he attained to the dignity of a residence in a cabin. "In the mean time he cleaned some land, and raised a small crop of corn and vegetables."
In the fall of 1817, Thomas and Betsy Sparrow came out from Kentucky, and took up their abode in the old camp which the Lincolns had just deserted for the cabin. Betsy was the aunt who had raised Nancy Hanks. She had done the same in part for our friend Dennis Hanks, who was the offspring of another sister, and she now brought him with her. Dennis thus became the constant companion of young Abraham; and all the other members of that family, as originally settled in Indiana, being dead, Dennis remains a most important witness as to this period of Mr. Lincoln's life.
Lincoln's second house was a "rough, rough log" one: the timbers were not hewed; and until after the arrival of Sally Bush, in 1819, it had neither floor, door, nor window. It stood about forty yards from what Dennis Hanks calls that "darned little half-faced camp," which was now the dwelling of the Sparrows. It was "right in the bush,"—in the heart of a virgin wilderness. There were only seven or eight older settlers in the neighborhood of the two Pigeon Creeks. Lincoln had had some previous acquaintance with one of them,—a Mr. Thomas Carter; and it is highly probable that nothing but this trivial circumstance induced him to settle here.1
1 The principal authorities for this part of our narrative are necessarily Dennis and John Hanks; but their statements have been carefully collated with those of other persons, both in Kentucky and Indiana.
The nearest town was Troy, situated on the Ohio, about half a mile from the mouth of Anderson Creek. Gentryville had as yet no existence. Travelling was on horseback or on foot, and the only resort of commerce was to the pack-horse or the canoe. But a prodigious immigration was now sweeping into this inviting country. Harrison's victories over the Indians had opened it up to the peaceful settler; and Indiana was admitted into the Union in 1816, with a population of sixty-five thousand. The county in which Thomas Lincoln settled was Perry, with the county-seat at Troy; but he soon found himself in the new county of Spencer, with the court-house at Rockport, twenty miles south of him, and the thriving village of Gentryville within a mile and a half of his door.
A post-office was established at Gentryville in 1824 or 1825. Dennis Hanks helped to hew the logs used to build the first storeroom. The following letter from Mr. David Turnham, now of Dale, Spencer County, presents some interesting and perfectly authentic information regarding the village and the settlements around it in those early times:—
"Yours of the 5th inst. is at hand. As you wish me to answer several questions, I will give you a few items of the early settlement of Indiana.
"When my father came here in the spring of 1819, he settled in Spencer County, within one mile of Thomas Lincoln, then a widower. The chance for schooling was poor; but, such as it was, Abraham and myself attended the same schools.
"We first had to go seven miles to mill; and then it was a hand-mill that would grind from ten to fifteen bushels of corn in a day. There was but little wheat grown at that time; and, when we did have wheat, we had to grind it on the mill described, and use it without bolting, as there were no bolts in the country. In the course of two or three years, a man by the name of Huffman built a mill on Anderson River, about twelve miles distant. Abe and I had to do the milling on horseback, frequently going twice to get one grist. Then they began building horse-mills of a little better quality than the hand-mills.
"The country was very rough, especially in the low lands, so thick with bush that a man could scarcely get through on foot. These places were called Roughs. The country abounded in game, such as bears, deer, turkeys, and the smaller game.
"About the time Huffman built his mill, there was a road laid out from Corydon to Evansville, running by Mr. Lincoln's farm, and through what is now Gentryville. Corydon was then the State capital.
"About the year 1823, there was another road laid out from Rockport to Bloomington, crossing the aforesaid at right angles, where Gentryville now stands. James Gentry entered the land; and in about a year Gideon Romine brought goods there, and shortly after succeeded in getting a post-office, by the name of Gentryville Post-office. Then followed the laying out of lots, and the selling of them, and a few were improved. But for some cause the lots all fell back to the original owner. The lots were sold in 1824 or 1825. Romine kept goods there a short time, and sold out to Gentry, but the place kept on increasing slowly. William Jones came in with a store, that made it improve a little faster, but Gentry bought him out. Jones bought a tract of land one-half mile from Gentryville, moved to it, went into business there, and drew nearly all the custom. Gentry saw that it was ruining his town: he compromised with Jones, and got him back to Gentryville; and about the year 1847 or 1848 there was another survey of lots, which remains.
"This is as good a history of the rise of Gentryville as I can give, after consulting several of the old settlers.
"At that time there were a great many deer-licks; and Abe and myself would go to those licks sometimes, and watch of nights to kill deer, though Abe was not so fond of a gun as I was. There were ten or twelve of these licks in a small prairie on the creek, lying between Mr. Lincoln's and Mr. Wood's (the man you call Moore). This gave it the name of Prairie Fork of Pigeon Creek.
"The people in the first settling of this country were very sociable, kind, and accommodating; but there was more drunkenness and stealing on a small scale, more immorality, less religion, less well-placed confidence."
The steps taken by Lincoln to complete his title to the land upon which he settled are thus recited by the Commissioner of the General Land Office:—
"In reply to the letter of Mr. W. H. Herndon, who is writing the biography of the late President, dated June 19, 1865, herewith returned, I have the honor to state, pursuant to the Secretary's reference, that on the 15th of October, 1817, Mr. Thomas Lincoln, then of Perry County, Indiana, entered under the old credit system,—
"1. The South-West Quarter of Section 82, in Township 4, South of Range 5 West, lying in Spencer County, Indiana.
"2. Afterwards the said Thomas Lincoln relinquished to the United States the East half of said South-West Quarter; and the amount paid thereon was passed to his credit to complete payment of the West half of said South-West Quarter of Section 32, in Township 4, South of Range 5 West; and accordingly a patent was issued to said Thomas Lincoln for the latter tract. The patent was dated June 6, 1827, and was signed by John Quincy Adams, then President of the United States, and countersigned by George Graham, then Commissioner of the General Land Office." 1
1 The patent was issued to Thomas Lincoln alias Linckhern the other half he never paid, and finally lost the whole of the land.
It will be observed, that, although Lincoln squatted upon the land in the fall of 1816, he did not enter it until October of the next year; and that the patent was not issued to him until June, 1827, but a little more than a year before he left it altogether. Beginning by entering a full quarter section, he was afterwards content with eighty acres, and took eleven years to make the necessary payments upon that. It is very probable that the money which finally secured the patent was furnished by Gentry or Aaron Grigsby, and the title passed out of Lincoln in the course of the transaction. Dennis Hanks says, "He settled on a piece of government land,—eighty acres. This land he afterwards bought under the Two-Dollar Act; was to pay for it in instalments; one-half he paid."
For two years Lincoln continued to live along in the old way. He did not like to farm, and he never got much of his land under cultivation. His principal crop was corn; and this, with the game which a rifleman so expert would easily take from the woods around him, supplied his table. It does not appear that he employed any of his mechanical skill in completing and furnishing his own cabin. It has already been stated that the latter had no window, door, or floor. But the furniture—if it may be called furniture—was even worse than the house. Three-legged stools served for chairs. A bedstead was made of poles stuck in the cracks of the logs in one corner of the cabin, while the other end rested in the crotch of a forked stick sunk in the earthen floor. On these were laid some boards, and on the boards a "shake-down" of leaves covered with skins and old petticoats. The table was a hewed puncheon, supported by four legs. They had a few pewter and tin dishes to eat from, but the most minute inventory of their effects makes no mention of knives or forks. Their cooking utensils were a Dutch oven and a skillet. Abraham slept in the loft, to which he ascended by means of pins driven into holes in the wall.
In the summer of 1818, the Pigeon-Creek settlements were visited by a fearful disease, called, in common parlance, "the milk-sickness." It swept off the cattle which gave the milk, as well as the human beings who drank it. It seems to have prevailed in the neighborhood from 1818 to 1829; for it is given as one of the reasons for Thomas Lincoln's removal to Illinois at the latter date. But in the year first mentioned its ravages were especially awful. Its most immediate effects were severe retchings and vomitings; and, while the deaths from it were not necessarily sudden, the proportion of those who finally died was uncommonly large.1 Among the number who were attacked by it, and lingered on for some time in the midst of great sufferings, were Thomas and Betsy Sparrow and Mrs. Nancy Lincoln.
1 The peculiar disease which carried off so many of Abraham's family, and induced the removal of the remainder to Illinois, deserves more than a passing allusion. The following, regarding its nature and treatment, is from the pen of an eminent physician of Danville, Illinois:— Ward H. Lamon, Esq. Dear Sir,—Your favor of the 17th inst. has been received. You request me to present you with my theory in relation to the origin of the disease called "milk-sickness," and also a "general statement of the best treatment of the disease," and the proportion of fatal cases. I have quite a number of cases of the so-called disease in Danville, Ill., and its vicinity; but perhaps you are not aware, that, between the great majority of the medical faculty in this region of country and myself, there is quite a discrepancy of opinion. They believe in the existence of the disease in Vermilion County; while, on the contrary, I am firmly of opinion, that, instead of genuine milk- sickness, it is only a modified form of malarial fever with which we here have to contend. Though sceptical of its existence in this part of the country, we have too much evidence from different intelligent sources to doubt, for a moment, that, in many parts of the West and South-west, there is a distinct malady, witnessed more than fifty years ago, and different from every other heretofore recognized in any system of Nosology. In the opinion of medical men, as well as in that of the people in general, where milk-sickness prevails, cattle, sheep, and horses contract the disease by feeding on wild pasture-lands; and, when those pastures have been enclosed and cultivated, the cause entirely disappears. This has also been the observation of the farmers and physicians of Vermilion County, Illinois. From this it might be inferred that the disease had a vegetable origin. But it appears that it prevails as early in the season as March and April in some localities; and I am informed that, in an early day, say thirty-five or forty years ago, it showed itself in the winter-time in this county. This seems to argue that it may be produced by water holding some mineral substance in solution. Even in this case, however, some vegetable producing the disease may have been gathered and preserved with the hay on which the cattle were fed at the time; for in that early day the farmers were in the habit of cutting wild grass for their stock. On the whole, I am inclined to attribute the cause to a vegetable origin. The symptoms of what is called milk-sickness in this county— and they are similar to those described by authors who have written on the disease in other sections of the Western country—are a whitish coat on the tongue, burning sensation of the stomach severe vomiting, obstinate constipation of the bowels, coolness of the extremities, great restlessness and jactitation, pulse rather small, somewhat more frequent than natural, and slightly corded. In the course of the disease, the coat on the tongue becomes brownish and dark, the countenance dejected, and the prostration of the patient is great. A fatal termination may take place in sixty hours, or life may be prolonged for a period of fourteen days. These are the symptoms of the acute form of the disease. Sometimes it runs into the chronic form, or it may assume that form from the commencement; and, after months or years, the patient may finally die, or recover only a partial degree of health. The treatment which I have found most successful is pills composed of calomel and opium, given at intervals of two, three, or four hours, so as to bring the patient pretty strongly under the influence of opium by the time the second or third dose had been administered; some effervescing mixture, pro re nata; injections; castor oil, when the stomach will retain it; blisters to the stomach; brandy or good whiskey freely administered throughout the disease; and quinine after the bowels have been moved. Under the above treatment, modified according to the circumstances, I would not expect to lose more than one case in eight or ten, as the disease manifests itself in this county.... As ever, Theo. Lemon.
It was now found expedient to remove the Sparrows from the wretched "half-faced camp," through which the cold autumn winds could sweep almost unobstructed, to the cabin of the Lincolns, which in truth was then very little better. Many in the neighborhood had already died, and Thomas Lincoln had made all their coffins out of "green lumber cut with a whip-saw." In the mean time the Sparrows and Nancy were growing alarmingly worse. There was no physician in the county,—not even a pretender to the science of medicine; and the nearest regular practitioner was located at Yellow Banks, Ky., over thirty miles distant. It is not probable that they ever secured his services. They would have been too costly, and none of the persons who witnessed and describe these scenes speak of his having been there. At length, in the first days of October, the Sparrows died; and Thomas Lincoln sawed up his green lumber, and made rough boxes to enclose the mortal remains of his wife's two best and oldest friends. A day or two after, on the 5th of October, 1818, Nancy Hanks Lincoln rested from her troubles. Thomas Lincoln took to his green wood again, and made a box for Nancy. There were about twenty persons at her funeral. They took her to the summit of a deeply-wooded knoll, about half a mile south-east of the cabin, and laid her beside the Sparrows. If there were any burial ceremonies, they were of the briefest. But it happened that a few months later an itinerant preacher, named David Elkin, whom the Lincolns had known in Kentucky, wandered into the settlement; and he either volunteered or was employed to preach a sermon, which should commemorate the many virtues and pass in silence the few frailties of the poor woman who slept in the forest. Many years later the bodies of Levi Hall and his wife, Nancy Hanks, were deposited in the same earth with that of Mrs. Lincoln. The graves of two or three children belonging to a neighbor's family are also near theirs. They are all crumbled in, sunken, and covered with wild vines in deep and tangled mats. The great trees were originally cut away to make a small cleared space for this primitive graveyard; but the young dogwoods have sprung up unopposed in great luxuriance, and in many instances the names of pilgrims to the burial-place of the great Abraham Lincoln's mother are carved in their bark. With this exception, the spot is wholly unmarked. Her grave never had a stone, nor even a board, at its head or its foot; and the neighbors still dispute as to which one of those unsightly hollows contains the ashes of Nancy Lincoln.
Thirteen months after the burial of Nancy Hanks, and nine or ten months after the solemnities conducted by Elkin, Thomas Lincoln appeared at Elizabethtown, Ky., in search of another wife. Sally Bush had married Johnston, the jailer, in the spring of the same year in which Lincoln had married Nancy Hanks. She had then rejected him for a better match, but was now a widow. In 1814 many persons in and about Elizabethtown had died of a disease which the people called the "cold plague," and among them the jailer. Both parties being free again, Lincoln came back, very unexpectedly to Mrs. Johnston, and opened his suit in an exceedingly abrupt manner. "Well, Miss Johnston," said he, "I have no wife, and you have no husband. I came a purpose to marry you: I knowed you from a gal, and you knowed me from a boy. I have no time to lose; and, if you are willin', let it be done straight off." To this she replied, "Tommy, I know you well, and have no objection to marrying you; but I cannot do it straight off, as I owe some debts that must first be paid." "The next morning," says Hon. Samuel Haycraft, the clerk of the courts and the gentleman who reports this quaint courtship, "I issued his license, and they were married straight off on that day, and left, and I never saw her or Tom Lincoln since." From the death of her husband to that day, she had been living, "an honest, poor widow," "in a round log-cabin," which stood in an "alley" just below Mr. Haycraft's house. Dennis Hanks says that it was only "on the earnest solicitation of her friends" that Mrs. Johnston consented to marry Lincoln. They all liked Lincoln, and it was with a member of her family that he had made several voyages to New Orleans. Mr. Helm, who at that time was doing business in his uncle's store at Elizabethtown, remarks that "life among the Hankses, the Lincolns, and the Enlows was a long ways below life among the Bushes." Sally was the best and the proudest of the Bushes; but, nevertheless, she appears to have maintained some intercourse with the Lincolns as long as they remained in Kentucky. She had a particular kindness for little Abe, and had him with her on several occasions at Helm's store, where, strange to say, he sat on a nail-keg, and ate a lump of sugar, "just like any other boy."
Mrs. Johnston has been denominated a "poor widow;" but she possessed goods, which, in the eyes of Tom Lincoln, were of almost unparalleled magnificence. Among other things, she had a bureau that cost forty dollars; and he informed her, on their arrival in Indiana, that, in his deliberate opinion, it was little less than sinful to be the owner of such a thing. He demanded that she should turn it into cash, which she positively refused to do. She had quite a lot of other articles, however, which he thought well enough in their way, and some of which were sadly needed in his miserable cabin in the wilds of Indiana. Dennis Hanks speaks with great rapture of the "large supply of household goods" which she brought out with her. There was "one fine bureau, one table, one set of chairs, one large clothes-chest, cooking utensils, knives, forks, bedding, and other articles." It was a glorious day for little Abe and Sarah and Dennis when this wondrous collection of rich furniture arrived in the Pigeon Creek settlement. But all this wealth required extraordinary means of transportation; and Lincoln had recourse to his brother-in-law, Ralph Krume, who lived just over the line, in Breckinridge County. Krume came with a four-horse team, and moved Mrs. Johnston, now Mrs. Lincoln, with her family and effects, to the home of her new husband in Indiana. When she got there, Mrs. Lincoln was much "surprised" at the contrast between the glowing representations which her husband had made to her before leaving Kentucky and the real poverty and meanness of the place. She had evidently been given to understand that the bridegroom had reformed his old Kentucky ways, and was now an industrious and prosperous farmer. She was scarcely able to restrain the expression of her astonishment and discontent; but, though sadly overreached in a bad bargain, her lofty pride and her high sense of Christian duty saved her from hopeless and useless repinings.
On the contrary, she set about mending what was amiss with all her strength and energy. Her own goods furnished the cabin with tolerable decency. She made Lincoln put down a floor, and hang windows and doors. It was in the depth of winter; and the children, as they nestled in the warm beds she provided them, enjoying the strange luxury of security from the cold winds of December, must have thanked her from the bottoms of their newly-comforted hearts. She had brought a son and two daughters of her own,—John, Sarah, and Matilda; but Abe and his sister Nancy (whose name was speedily changed to Sarah), the ragged and hapless little strangers to her blood, were given an equal place in her affections. They were half naked, and she clad them from the stores of clothing she had laid up for her own. They were dirty, and she washed them; they had been ill-used, and she treated them with motherly tenderness. In her own modest language, she "made them look a little more human." "In fact," says Dennis Hanks, "in a few weeks all had changed; and where every thing was wanting, now all was snug and comfortable. She was a woman of great energy of remarkable good sense, very industrious and saving, and also very neat and tidy in her person and manners, and knew exactly how to manage children. She took an especial liking to young Abe. Her love for him was warmly returned, and continued to the day of his death. But few children loved their parents as he loved his step-mother. She soon dressed him up in entire new clothes, and from that time on he appeared to lead a new life. He was encouraged by her to study, and any wish on his part was gratified when it could be done. The two sets of children got along finely together, as if they had all been the children of the same parents. Mrs. Lincoln soon discovered that young Abe was a boy of uncommon natural talents, and that, if rightly trained, a bright future was before him, and she did all in her power to develop those talents." When, in after years, Mr. Lincoln spoke of his "saintly mother," and of his "angel of a mother," he referred to this noble woman,1 who first made him feel "like a human being,"—whose goodness first touched his childish heart, and taught him that blows and taunts and degradation were not to be his only portion in the world.2
1 The author has many times heard him make the application. While he seldom, if ever, spoke of his own mother, he loved to dwell on the beautiful character of Sally Bush. 2 The following description of her personal appearance is from the pen of her granddaughter, the daughter of Dennis Hanks:— "When I landed in Indiana," says Mrs. Lincoln, "Abe was about nine years old, and the country was wild and desolate. It is certain enough that her presence took away much that was desolate in his lot. She clothed him decently, and had him sent to school as soon as there was a school to send him to. But, notwithstanding her determination to do the best for him, his advantages in this respect were very limited. He had already had a few days', or perhaps a few weeks' experience, under the discipline of Riney and Hazel, in Kentucky; and, as he was naturally quick in the acquisition of any sort of knowledge, it is likely that by this time he could read and write a little. He was now to have the benefit of a few months more of public instruction; but the poverty of the family, and the necessity for his being made to work at home in the shop and on the farm, or abroad as a hired boy, made his attendance at school, for any great length of time, a thing impossible. Accordingly, all his school-days added together would not make a single year in the aggregate. "His wife, my grandmother, is a very tall woman; straight as an Indian, fair complexion, and was, when I first remember her, very handsome, sprightly, talkative, and proud; wore her hair curled till gray; is kind-hearted and very charitable, and also very industrious."—Mrs. H. A, Chapman.
Abraham began his irregular attendance at the nearest school very soon after he fell under the care of the second Mrs. Lincoln. It was probably in the winter of 1819, she having come out in the December of that year. It has been seen that she was as much impressed by his mental precocity as by the good qualities of his heart.
Hazel Dorsey was his first master.1 He presided in a small house near the Little Pigeon Creek meeting-house, a mile and a half from the Lincoln cabin. It was built of unhewn logs, and had "holes for windows," in which "greased paper" served for glass. The roof was just high enough for a man to stand erect. Here he was taught reading, writing, and ciphering. They spelled in classes, and "trapped" up and down. These juvenile contests were very exciting to the participants; and it is said by the survivors, that Abe was even then the equal, if not the superior, of any scholar in his class.
1 The account of the schools is taken from the Grigsbys, Turnham, and others, who attended them along with Abe, as well as from the members of his own family.
The next teacher was Andrew Crawford. Mrs. Gentry says he began pedagogue in the neighborhood in the winter of 1822-3, whilst most of his other scholars are unable to fix an exact date. He "kept" in the same little schoolhouse which had been the scene of Dorsey's labors, and the windows were still adorned with the greased leaves of old copybooks that had come down from Dorsey's time. Abe was now in his fifteenth year, and began to exhibit symptoms of gallantry toward the weaker sex, as we shall presently discover. He was growing at a tremendous rate, and two years later attained his full height of six feet four inches. He was long, wiry, and strong; while his big feet and hands, and the length of his legs and arms, were out of all proportion to his small trunk and head. His complexion was very swarthy, and Mrs. Gentry says that his skin was shrivelled and yellow even then. He wore low shoes, buckskin breeches, linsey-woolsey shirt, and a cap made of the skin of an opossum or a coon. The breeches clung close to his thighs and legs, but failed by a large space to meet the tops of his shoes. Twelve inches remained uncovered, and exposed that much of "shinbone, sharp, blue, and narrow."1 "He would always come to school thus, good-humoredly and laughing," says his old friend, Nat Grigsby. "He was always in good health, never was sick, had an excellent constitution, and took care of it."
1 "They had no woollen clothing in the family until about the year 1824."—Dennis Hanks.
Crawford taught "manners." This was a feature of backwoods education to which Dorsey had not aspired, and Crawford had doubtless introduced it as a refinement which would put to shame the humbler efforts of his predecessor. One of the scholars was required to retire, and re-enter as a polite gentleman is supposed to enter a drawing-room. He was received at the door by another scholar, and conducted from bench to bench, until he had been introduced to all the "young ladies and gentlemen" in the room. Abe went through the ordeal countless times. If he took a serious view of the business, it must have put him to exquisite torture; for he was conscious that he was not a perfect type of manly beauty, with his long legs and blue shins, his small head, his great ears, and shrivelled skin. If, however, it struck him as at all funny, it must have filled him with unspeakable mirth, and given rise to many antic tricks and sly jokes, as he was gravely led about, shamefaced and gawky, under the very eye of the precise Crawford, to be introduced to the boys and girls of his most ancient acquaintance.
But, though Crawford inculcated manners, he by no means neglected spelling. Abe was a good speller, and liked to use his knowledge, not only to secure honors for himself, but to help his less fortunate schoolmates out of their troubles, and he was exceedingly ingenious in the selection of expedients for conveying prohibited hints. One day Crawford gave out the difficult word defied. A large class was on the floor, but they all provokingly failed to spell it. D-e-f-i-d-e, said one; d-e-f-y-d-e, said another; d-e-f-y-d,—d-e-f-y-e-d, cried another and another. But it was all wrong: it was shameful, that, among all these big boys and girls, nobody could spell "defied;" Crawford's wrath gathered in clouds over his terrible brow. He made the helpless culprits shake with fear. He declared he would keep the whole class in all day and all night, if "defied" was not spelled. There was among them a Miss Roby, a girl fifteen years of age, whom we must suppose to have been pretty, for Abe was evidently half in love with her. "I saw Lincoln at the window," says she: "he had his finger in his eye, and a smile on his face; I instantly took the hint, that I must change the letter y into an i. Hence I spelled the word,—the class let out. I felt grateful to Lincoln for this simple thing."
Nat Grigsby tells us, with unnecessary particularity, that "essays and poetry were not taught in this school." "Abe took it (them) up on his own account." He first wrote short sentences against "cruelty to animals," and at last came forward with a regular "composition" on the subject. He was very much annoyed and pained by the conduct of the boys, who were in the habit of catching terrapins, and putting coals of fire on their backs. "He would chide us," says Nat, "tell us it was wrong, and would write against it."
The third and last school to which Abe went was taught by a Mr. Swaney, in 1826. To get there, he had to travel four and a half miles; and this going back and forth so great a distance occupied entirely too much of his time. His attendance was therefore only at odd times, and was speedily broken off altogether. The schoolhouse was much like the other one near the Pigeon Creek meeting-house, except that it had two chimneys instead of one. The course of instruction was precisely the same as under Dorsey and Crawford, save that Swaney, like Dorsey, omitted the great department of "manners." "Here," says John Hoskins, the son of the settler who had "blazed out" the trail for Tom Lincoln, "we would choose up, and spell as in old times every Friday night." Hoskins himself tore down "the old schoolhouse" long since, and built a stable with the logs. He is now half sorry for his haste, and reverently presented Mr. Herndon a piece of the wood as a precious memento of his old friend Abe. An oak-tree, blackened and killed by the smoke that issued from the two chimneys, spreads its naked arms over the spot where the schoolhouse stood. Among its roots is a fine, large spring, over whose limpid waters Abe often bent to drink, and laughed at the reflection of his own homely face.
Abe never went to school again in Indiana or elsewhere. Mr. Turnham tells us, that he had excelled all his masters, and it was "no use" for him to attempt to learn any thing from them. But he continued his studies at home, or wherever he was hired out to work, with a perseverance which showed that he could scarcely live without some species of mental excitement. He was by no means fond of the hard manual labor to which his own necessities and those of his family compelled him. Many of his acquaintances state this fact with strong emphasis,—among them Dennis Hanks and Mrs. Lincoln. His neighbor, John Romine, declares that Abe was "awful lazy. He worked for me; was always reading and thinking; used to get mad at him. He worked for me in 1829, pulling fodder. I say Abe was awful lazy: he would laugh and talk and crack jokes and tell stories all the time; didn't love work, but did dearly love his pay. He worked for me frequently, a few days only at a time.... Lincoln said to me one day, that his father taught him to work, but never learned him to love it."
1 Whenever Mrs. Sarah Lincoln speaks, we follow her implicitly. Regarding Abe's habits and conduct at home, her statement is a very full one. It is, however, confirmed and supplemented by all the other members of the family who were alive in 1866.
Abe loved to lie under a shade-tree, or up in the loft of the cabin, and read, cipher, and scribble. At night he sat by the chimney "jamb," and ciphered, by the light of the fire, on the wooden fire-shovel. When the shovel was fairly covered, he would shave it off with Tom Lincoln's drawing-knife, and begin again. In the daytime he used boards for the same purpose, out of doors, and went through the shaving process everlastingly. His step-mother1 repeats often, that "he read every book he could lay his hand on." She says, "Abe read diligently.... He read every book he could lay his hands on; and, when he came across a passage that struck him, he would write it down on boards if he had no paper, and keep it there until he did get paper. Then he would re-write it, look at it, repeat it. He had a copy-book, a kind of scrapbook, in which he put down all things, and thus preserved them."
John Hanks came out from Kentucky when Abe was fourteen years of age, and lived four years with the Lincolns. We cannot describe some of Abe's habits better than John has described them for us: "When Lincoln—Abe and I—returned to the house from work, he would go to the cupboard, snatch a piece of corn-bread, take down a book, sit down on a chair, cock his legs up high as his head, and read. He and I worked barefooted, grubbed it, ploughed, mowed, and cradled together; ploughed corn, gathered it, and shucked corn. Abraham read constantly when he had an opportunity."
Among the books upon which Abe "laid his hands" were "Ã?sop's Fables," "Robinson Crusoe," Bunyan's "Pilgrim's Progress," a "History of the United States," and Weems's "Life of Washington." All these he read many times, and transferred extracts from them to the boards and the scrapbook. He had procured the scrap-book because most of his literature was borrowed, and he thought it profitable to take copious notes from the books before he returned them. David Turnham had bought a volume of "The Revised Statutes of Indiana;" but, as he was "acting constable" at the time, he could not lend it to Abe. But Abe was not to be baffled in his purpose of going through and through every book in the neighborhood; and so, says Mr. Turnham, "he used to come to my house and sit and read it." 1 Dennis Hanks would fain have us believe that he himself was the purchaser of this book, and that he had stood as a sort of first preceptor to Abe in the science of law. "I had like to forgot," writes Dennis, with his usual modesty, "How did Abe get his knowledge of law? This is the fact about it. I bought the 'Statute of Indiana,' and from that he learned the principles of law, and also myself. Every man should become acquainted of the principles of law." The Bible, according to Mrs. Lincoln, was not one of his studies: "he sought more congenial books." At that time he neither talked nor read upon religious subjects. If he had any opinions about them, he kept them to himself.
1 He also read at Turnham's house Scott's Lessons and Sindbad the Sailor.
Abraham borrowed Weems's "Life of Washington" from his neighbor, old Josiah Crawford,—not Andrew Crawford, the school-teacher, as some of his biographers have it. The "Life" was read with great avidity in the intervals of work, and, when not in use, was carefully deposited on a shelf, made of a clapboard laid on two pins. But just behind the shelf there was a great crack between the logs of the wall; and one night, while Abe was dreaming in the loft, a storm came up, and the rain, blown through the opening, soaked his precious book from cover to cover. Crawford was a sour and churlish fellow at best, and flatly refused to take the damaged book back again. He said, that, if Abe had no money to pay for it, he could work it out. Of course, there was no alternative; and Abe was obliged to discharge the debt by "pulling fodder" three days, at twenty-five cents a day. Crawford afterwards paid dearly for his churlishness.
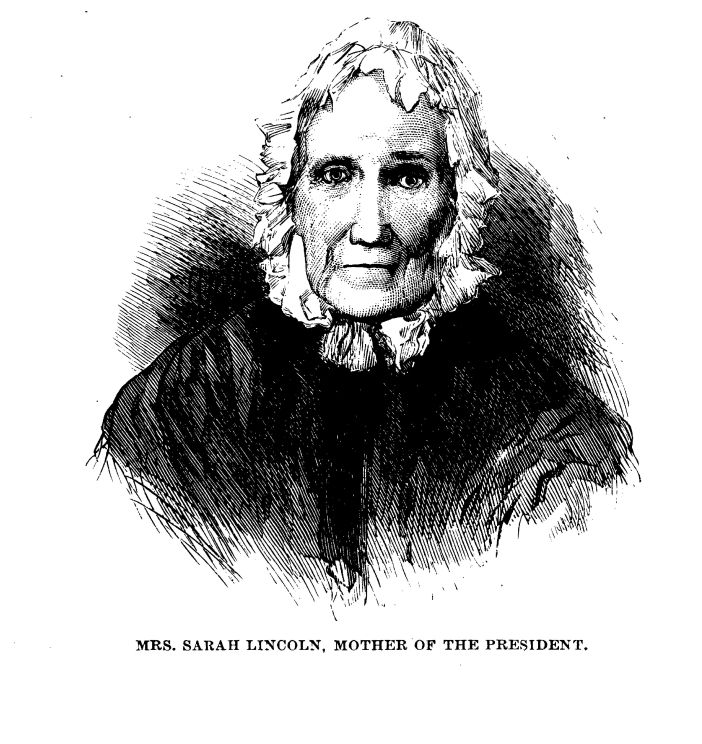

At home, with his step-mother and the children, he was the most agreeable fellow in the world. "He was always ready to do every thing for everybody." When he was not doing some special act of kindness, he told stories or "cracked jokes." "He was as full of his yarns in Indiana as ever he was in Illinois." Dennis Hanks was a clever hand at the same business, and so was old Tom Lincoln. Among them they must have made things very lively, during the long winter evenings, for John Johnston and the good old lady and the girls.
Mrs. Lincoln was never able to speak of Abe's conduct to her without tears. In her interview with Mr. Herndon, when the sands of her life had nearly run out, she spoke with deep emotion of her own son, but said she thought that Abe was kinder, better, truer, than the other. Even the mother's instinct was lost as she looked back over those long years of poverty and privation in the Indiana cabin, when Abe's grateful love softened the rigors of her lot, and his great heart and giant frame were always at her command. "Abe was a poor boy," said she; "and I can say what scarcely one woman—a mother—can say in a thousand. Abe never gave me a cross word or look, and never refused, in fact or appearance, to do any thing I requested him. I never gave him a cross word in all my life.... His mind and mine—what little I had—seemed to run together.... He was here after he was elected President." (At this point the aged speaker turned away to weep, and then, wiping her eyes with her apron, went on with the story). "He was dutiful to me always. I think he loved me truly. I had a son, John, who was raised with Abe. Both were good boys; but I must say, both now being dead, that Abe was the best boy I ever saw, or expect to see. I wish I had died when my husband died. I did not want Abe to run for President; did not want him elected; was afraid somehow,—felt in my heart; and when he came down to see me, after he was elected President, I still felt that something told me that something would befall Abe, and that I should see him no more."
Is there any thing in the language we speak more touching than that simple plaint of the woman whom we must regard as Abraham Lincoln's mother? The apprehension in her "heart" was well grounded. She "saw him no more." When Mr. Herndon rose to depart, her eyes again filled with tears; and, wringing his hands as if loath to part with one who talked so much of her beloved Abe, she said, "Good-by, my good son's friend. Farewell."
Abe had a very retentive memory. He frequently amused his young companions by repeating to them long passages from the books he had been reading. On Monday mornings he would mount a stump, and deliver, with a wonderful approach to exactness, the sermon he had heard the day before. His taste for public speaking appeared to be natural and irresistible. His step-sister, Matilda Johnston, says he was an indefatigable "preacher." "When father and mother would go to church, Abe would take down the Bible, read a verse, give out a hymn, and we would sing. Abe was about fifteen years of age. He preached, and we would do the crying. Sometimes he would join in the chorus of tears. One day my brother, John Johnston, caught a land terrapin, brought it to the place where Abe was preaching, threw it against the tree, and crushed the shell. It suffered much,—quivered all over. Abe then preached against cruelty to animals, contending that an ant's life was as sweet to it as ours to us."
But this practice of "preaching" and political speaking, into which Abe had fallen, at length became a great nuisance to old, Tom. It distracted everybody, and sadly interfered with the work. If Abe had confined his discourses to Sunday preaching, while the old folks were away, it would not have been so objectionable. But he knew his power, liked to please everybody, and would be sure to set up as an orator wherever he found the greatest number of people together. When it was announced that Abe had taken the "stump" in the harvest-field, there was an end of work. The hands flocked around him, and listened to his curious speeches with infinite delight. "The sight of such a thing amused all," says Mrs. Lincoln; though she admits that her husband was compelled to break it up with the strong hand; and poor Abe was many times dragged from the platform, and hustled off to his work in no gentle manner.1
1 We are told by Col. Chapman that Abe's father habitually treated him with great barbarity. Dennis Hanks insists that he loved him sincerely, but admits that he now and then knocked him from the fence for merely answering traveller's questions about the roads.
Abe worked occasionally with Tom Lincoln in the shop; but he did it reluctantly, and never intended to learn even so much of the trade as Lincoln was able to teach him. The rough work turned out at that shop was far beneath his ambition, and he had made up his mind to lead a life as wholly unlike his father's as he could possibly make it. He therefore refused to be a carpenter. But he could not afford to be idle; and, as soon as he was able to earn wages, he was hired out among the neighbors. He worked for many of them a few months at a time, and seemed perfectly willing to transfer his services wherever they were wanted, so that his father had no excuse for persecuting him with entreaties about learning to make tables and cupboards.
Abe was now becoming a man, and was, in fact, already taller than any man in the neighborhood. He was a universal favorite, and his wit and humor made him heartily welcome at every cabin between the two Pigeon Creeks. Any family was glad when "Abe Linkern" was hired to work with them; for he did his work well, and made them all merry while he was about it. The women were especially pleased, for Abe was not above doing any kind of "chores" for them. He was always ready to make a fire, carry water, or nurse a baby. But what manner of people were these amongst whom he passed the most critical part of his life? We must know them if we desire to know him.
There lived in the neighborhood of Gentryville a Mrs. Elizabeth Crawford, wife to the now celebrated Josiah with the sour temper and the blue nose. Abe was very fond of her, and inclined to "let himself out" in her company. She fortunately possessed a rare memory, and Mr. Herndon's rich collection of manuscripts was made richer still by her contributions. We have from her a great mass of valuable, and sometimes extremely amusing, information. Among it is the following graphic, although rude, account of the Pigeon Creek people in general:—
"You wish me to tell you how the people used to go to meeting,—how far they went. At that time we thought it nothing to go eight or ten miles. The old ladies did not stop for the want of a shawl, or cloak, or riding-dress, or two horses, in the winter-time; but they would put on their husbands' old overcoats, and wrap up their little ones, and take one or two of them up on their beasts, and their husbands would walk, and they would go to church, and stay in the neighborhood until the next day, and then go home. The old men would start out of their fields from their work, or out of the woods from hunting, with their guns on their shoulders, and go to church. Some of them dressed in deer-skin pants and moccasins, hunting-shirts with a rope or leather strap around them. They would come in laughing, shake hands all around, sit down and talk about their game they had killed, or some other work they had done, and smoke their pipes together with the old ladies. If in warm weather, they would kindle up a little fire out in the meeting-house yard, to light their pipes. If in winter-time, they would hold church in some of the neighbors' houses. At such times they were always treated with the utmost of kindness: a bottle of whiskey, a pitcher of water, sugar and glass, were set out, or a basket of apples, or turnips, or some pies and cakes. Apples were scarce them times. Sometimes potatoes were used as a treat. (I must tell you that the first treat I ever received in old Mr. Linkern's house, that was our President's father's house, was a plate of potatoes, washed and pared very nicely, and handed round. It was something new to me, for I never had seen a raw potato eaten before. I looked to see how they made use of them. They took off a potato, and ate them like apples.) Thus they spent the time till time for preaching to commence, then they would all take their seats: the preacher would take his stand, draw his coat, open his shirt-collar, commence service by singing and prayer; take his text and preach till the sweat would roll off in great drops. Shaking hands and singing then ended the service. The people seemed to enjoy religion more in them days than they do now. They were glad to see each other, and enjoyed themselves better than they do now."
Society about Gentryville was little different from that of any other backwoods settlement of the same day. The houses were scattered far apart; but the inhabitants would travel long distances to a log-rolling, a house-raising, a wedding, or any thing else that might be turned into a fast and furious frolic. On such occasions the young women carried their shoes in their hands, and only put them on when about to join the company. The ladies drank whiskey-toddy, while the men took it straight; and both sexes danced the live-long night, barefooted, on puncheon floors.
The fair sex wore "cornfield bonnets, scoop-shaped, flaring in front, and long though narrow behind." Shoes were the mode when entering the ball-room; but it was not at all fashionable to scuff them out by walking or dancing in them. "Four yards of linsey-woolsey, a yard in width, made a dress for any woman." The waist was short, and terminated just under the arms, whilst the skirt was long and narrow. "Crimps and puckering frills" it had none. The coats of the men were home-made; the materials, jeans or linsey-woolsey. The waists were short, like the frocks of the women, and the long "claw-hammer" tail was split up to the waist. This, however, was company dress, and the hunting-shirt did duty for every day. The breeches were of buck-skin or jeans; the cap was of coon-skin; and the shoes of leather tanned at home. If no member of the family could make shoes, the leather was taken to some one who could, and the customer paid the maker a fair price in some other sort of labor.
The state of agriculture was what it always is where there is no market, either to sell or buy; where the implements are few and primitive, and where there are no regular mechanics. The Pigeon Creek farmer "tickled" two acres of ground in a day with his old shovel-plough, and got but half a crop. He cut one acre with his sickle, while the modern machine lays down in neat rows ten. With his flail and horse tramping, he threshed out fifteen bushels of wheat; while the machine of to-day, with a few more hands, would turn out three hundred and fifty. He "fanned" and "cleaned with a sheet." When he wanted flour, he took his team and went to a "horse-mill," where he spent a whole day in converting fifteen bushels of grain.1
1 "Size of the fields from ten, twelve, sixteen, twenty. Raised corn mostly; some wheat,—enough for a cake on Sunday morning. Hogs and venison hams were legal tender, and coon-skins also. We raised sheep and cattle, but they did not fetch much. Cows and calves were only worth six dollars; corn, ten cents; wheat, twenty-five cents at that time."— Dennis Hanks.
The minds of these people were filled with superstitions, which most persons imagine to be, at least, as antiquated as witch-burning. They firmly believed in witches and all kind of witch-doings. They sent for wizards to cure sick cattle. They shot the image of the witch with a silver ball, to break the spell she was supposed to have laid on a human being. If a dog ran directly across a man's path whilst he was hunting, it was terrible "luck," unless he instantly hooked his two little fingers together, and pulled with all his might, until the dog was out of sight. There were wizards who took charmed twigs in their hands, and made them point to springs of water and all kinds of treasure beneath the earth's surface. There were "faith doctors," who cured diseases by performing mysterious ceremonies and muttering cabalistic words. If a bird alighted in a window, one of the family would speedily die. If a horse breathed on a child, the child would have the whooping-cough. Every thing must be done at certain "times and seasons," else it would be attended with "bad luck." They must cut trees for rails in the early part of the day, and in "the light of the moon." They must make fence in "the light of the moon;" otherwise, the fence would sink. Potatoes and other roots were to be planted in the "dark of the moon," but trees, and plants which bore their fruits above ground, must be "put out in the light of the moon." The moon exerted a fearful influence, either kindly or malignant, as the good old rules were observed or not. It was even required to make soap "in the light of the moon," and, moreover, it must be stirred only one way, and by one person. Nothing of importance was to be begun on Friday. All enterprises inaugurated on that day went fatally amiss. A horse-colt could be begotten only "in the dark of the moon," and animals treated otherwise than "according to the signs in the almanac" were nearly sure to die.
Such were the people among whom Abe grew to manhood. With their sons and daughters he went to school. Upon their farms he earned his daily bread by daily toil. From their conversation he formed his earliest opinions of men and things, the world over. Many of their peculiarities became his; and many of their thoughts and feelings concerning a multitude of subjects were assimilated with his own, and helped to create that unique character, which, in the eyes of a great host of the American people, was only less curious and amusing than it was noble and august.
His most intimate companions were of course, for a long time, the members of his own family. The reader already knows something of Thomas Lincoln, and that pre-eminently good woman, Sally Bush. The latter, we know, washed, clothed, loved, and encouraged Abe in well-doing, from the moment he fell in her way. How much he owed to her goodness and affection, he was himself never able to estimate. That it was a great debt, fondly acknowledged and cheerfully repaid as far as in him lay, there can be no doubt. His own sister, the child of Nancy Hanks, was warmly attached to him. Her face somewhat resembled his. In repose it had the gravity which they both, perhaps, inherited from their mother; but it was capable of being lighted almost into beauty by one of Abe's ridiculous stories or rapturous sallies of humor. She was a modest, plain, industrious girl, and is kindly remembered by all who knew her. She was married to Aaron Grigsby at eighteen, and a year after died in child-bed. Like Abe, she occasionally worked out at the houses of the neighbors, and at one time was employed in Mrs. Crawford's kitchen, while her brother was a laborer on the same farm. She lies buried, not with her mother, but in the yard of the old Pigeon Creek meeting-house. It is especially pleasing to read the encomiums lavished upon her memory by the Grigsbys; for between the Grigsbys on one side, and Abe and his step-brother on the other, there once subsisted a fierce feud.

As we have already learned from Dennis Hanks, the two families—the Johnstons and the Lincolns—"got along finely together." The affectionate relations between Abe and his two step-sisters were the subject of common remark throughout the neighborhood. One of them married Dennis Hanks, and the other Levi Hall, or, as he is better known, Squire Hall,—a cousin of Abe. Both these women (the latter now Mrs. Moore) furnished Mr. Herndon very valuable memoirs of Abe's life whilst he dwelt under the same roof with them; and they have given an account of him which shows that the ties between them were of the strongest and tenderest kind. But what is most remarkable in their statements is, that they never opened their lips without telling how worthy of everybody's love their mother was, and how Abe revered her as much as they did. They were interesting girls, and became exemplary women.
John D. Johnston, the only son of Mrs. Lincoln, was not the best boy, and did not grow to be the best man, in all the Pigeon Creek region. He had no positive vice, except idleness, and no special virtue but good temper. He was not a fortunate man; never made money; was always needy, and always clamoring for the aid of his friends. Mr. Lincoln, all through John's life, had much trouble to keep him on his legs, and succeeded indifferently in all his attempts. In a subsequent chapter a letter will be given from him, which indirectly portrays his step-brother's character much better than it can be done here. But, as youths, the intimacy between them was very close; and in another place it will appear that Abe undertook his second voyage to New Orleans only on condition that John would go along.
But the most constant of his companions was his jolly cousin, Dennis Hanks. Of all the contributors to Mr. Herndon's store of information, good, bad, and indifferent, concerning this period of Mr. Lincoln's life, Dennis is the most amusing, insinuating, and prolific. He would have it distinctly understood that the well of his memory is the only proper source whence any thing like truth may be drawn.1 He has covered countless sheets of paper devoted to indiscriminate laudations of Abe and all his kindred. But in all this he does not neglect to say a word for himself.
1 The following random selections from his writings leave us no room to doubt Dennis's opinion of his own value:— "William, let in, don't keep any thing back, for I am in for the whole hog sure; for I know nobody can do any for you much, for all they know is from me at last. Every thing you see is from my notes,—this you can tell yourself. "I have in my possession a little book, the private life of A. Lincoln, comprising a full life of his early years, and a succinct record of his career as statesman and President, by O. J. Victor, author of Lives of Garibaldi, Winfield Scott, John Paul Jones, &c., New York, Beadle and Company, publishers, No. 118 Williams Street. Now, sir, I find a great many things pertaining to Abe Lincoln's life that is not true. If you would like to have the book, I will mail it to you. I will say this much to you: if you don't have my name very frequently in your book, it won't go at all; for I have been East for two months, have seen a great many persons in that time, stating to them that there would be a book, 'The Life of A. Lincoln,' published, giving a full account of the family, from England to this country. Now, William, if there be any thing you want to know, let me know: I will give you all the information I can. "I have seen a letter that you wrote to my daughter, Harriet Chapman, of inquiry about some things. I thought you were informed all about them. I don't know what she has stated to you about your questions; but you had better consult me about them. "Billy, it seems to me, from the letters that you write to me asking questions, that you ask the same questions over several times. How is this? Do you forget, or are you like the lawyer, trying to make me cross my path, or not? Now, I will. Look below for the answer."
At one place, "his cousin, Dennis Hanks," is said to have taught Abe to read and write. At another, he is represented as the benevolent purchaser of the volumes from which Abe (and Dennis too) derived a wonderfully clear and accurate conception of the science of law. In all studies their minds advanced pari passu. Whenever any differences are noted (and they are few and slight), Dennis is a step ahead, benignantly extending a helping hand to the lagging pupil behind. But Dennis's heart is big and kind: he defames no one; he is merely a harmless romancer. In the gallery of family portraits painted by Dennis, every face looks down upon us with the serenity of innocence and virtue. There is no spot on the fame of any one of them. No family could have a more vigorous or chivalrous defender than he, or one who repelled with greater scorn any rumor to their discredit. That Enlow story! Dennis almost scorned to confute it; but, when he did get at it, he settled it by a magnificent exercise of inventive genius. He knew "this Abe Enlow" well, he said, and he had been dead precisely fifty-five years. But, whenever the truth can be told without damage to the character of a Lincoln or a Hanks, Dennis will tell it candidly enough, provided there is no temptation to magnify himself. His testimony, however, has been sparingly used throughout these pages; and no statement has been taken from him unless it was more or less directly corroborated by some one else. The better part of his evidence Mr. Herndon took the precaution of reading carefully to John Hanks, who pronounced it substantially true; and that circumstance gives it undeniable value.
When Thomas and Betsy Sparrow died in the fall of 1818, Dennis was taken from the "little half-faced camp," and became one of the Lincoln family. Until Thomas Lincoln's second marriage, Dennis, Abe, and Sarah were all three poor, ragged, and miserable together. After that, Dennis got along better, as well as the rest. He was a lively, volatile, sympathetic fellow, and Abe liked him well from the beginning. They fished, hunted, and worked in company; loafed at the grocery, where Dennis got drunk, and Abe told stories; talked politics with Col. Jones; "swapped jokes" with Baldwin the blacksmith; and faithfully attended the sittings of the nearest justice of the peace, where both had opportunities to correct and annotate the law they thought they had learned from the "Statute of Indiana." Dennis was kind, genial, lazy, brimming over with humor, and full of amusing anecdotes. He revelled in song, from the vulgarest ballad to the loftiest hymn of devotion; from "The turbaned Turk, that scorns the world," to the holiest lines of Doctor Watts. These qualities marked him wherever he went; and in excessive good-nature, and in the ease with which he passed from the extreme of rigor to the extreme of laxity, he was distinguished above the others of his name.
There was one Hanks, however, who was not like Dennis, or any other Hanks we know any thing about: this was "old John," as he is familiarly called in Illinois,—a sober, honest, truthful man, with none of the wit and none of the questionable accomplishments of Dennis. He was the son of Joseph, the carpenter with whom Tom Lincoln learned the trade. He went to Indiana to live with the Lincolns when Abe was fourteen years of age, and remained there four years. He then returned to Kentucky, and subsequently went to Illinois, where he was speedily joined by the old friends he had left in Indiana. When Abe separated from the family, and went in search of individual fortune, it was in company with "old John." Together they split the rails that did so much to make Abe President; and "old John" set the ball in motion by carrying a part of them into the Decatur Convention on his own broad shoulders. John had no education whatever, except that of the muscles and the heart. He could neither read nor write; but his character was pure and respectable, and Lincoln esteemed him as a man, and loved him as a friend and relative.
About six years after the death of the first Mrs. Lincoln, Levi Hall and his wife and family came to Indiana, and settled near the Lincolns. Mrs. Hall was Nancy Hanks, the mother of our friend Dennis, and the aunt of Nancy Hanks, the mother of Abraham Lincoln. She had numerous children by her husband. One of them, Levi, as already mentioned, married one of Abe's step-sisters, while Dennis, his half-brother, married the other one. The father and mother of the Halls speedily died of the milk-sickness, but Levi was for many years a constant companion of Abe and Dennis.
In 1825 Abraham was employed by James Taylor, who lived at the mouth of Anderson's Creek. He was paid six dollars a month, and remained for nine months. His principal business was the management of a ferry-boat which Mr. Taylor had plying across the Ohio, as well as Anderson's Creek. But, in addition to this, he was required to do all sorts of farm-work, and even to perform some menial services about the house. He was hostler, ploughman, ferryman, out of doors, and man-of-all-work within doors. He ground corn with a hand-mill, or "grated" it when too young to be ground; rose early, built fires, put on the water in the kitchen, "fixed around generally," and had things prepared for cooking before the mistress of the house was stirring. He slept up stairs with young Green Taylor, who says that he usually read "till near midnight," notwithstanding the necessity for being out of his bed before day. Green was somewhat disposed to ill-use the poor hired boy, and once struck him with an ear of hard corn, and cut a deep gash over his eye. He makes no comment upon this generous act, except that "Abe got mad," but did not thrash him.
Abe was a hand much in demand in "hog-killing time." He butchered not only for Mr. Taylor, but for John Woods, John Duthan, Stephen McDaniels, and others. At this he earned thirty-one cents a day, as it was considered "rough work."
For a long time there was only one person in the neighborhood for whom Abe felt a decided dislike; and that was Josiah Crawford, who had made him "pull fodder," to pay for the Weems's "Washington." On that score he was "hurt" and "mad," and often declared "he would have revenge." But being a poor boy,—a circumstance of which Crawford had already taken shameful advantage to extort three days' labor,—he was glad to get work any place, and frequently "hired to his old adversary." Abe's first business in his employ was daubing his cabin, which was built of logs, unhewed, and with the bark on. In the loft of this house, thus finished by his own hands, he slept for many weeks at a time. He spent his evenings as he did at home,—writing on wooden shovels or boards with "a coal, or keel, from the branch." This family was rich in the possession of several books, which Abe read through time and again, according to his usual custom. One of them was the "Kentucky Preceptor," from which Mrs. Crawford insists that he "learned his school orations, speeches, and pieces to write." She tells us also that "Abe was a sensitive lad, never coming where he was not wanted;" that he always lifted his hat, and bowed, when he made his appearance; and that "he was tender and kind," like his sister, who was at the same time her maid-of-all-work. His pay was twenty-five cents a day; "and, when he missed time, he would not charge for it." This latter remark of good Mrs. Crawford reveals the fact that her husband was in the habit of docking Abe on his miserable wages whenever he happened to lose a few minutes from steady work.
The time came, however, when Abe got his "revenge" for all this petty brutality. Crawford was as ugly as he was surly. His nose was a monstrosity,—long and crooked, with a huge, misshapen "stub" at the end, surmounted by a host of pimples, and the whole as "blue" as the usual state of Mr. Crawford's spirits. Upon this member Abe levelled his attack in rhyme, song, and "chronicle;" and, though he could not reduce the nose, he gave it a fame as wide as to the Wabash and the Ohio. It is not improbable that he learned the art of making the doggerel rhymes in which he celebrated Crawford's nose from the study of Crawford's own "Kentucky Preceptor." At all events, his sallies upon this single topic achieved him great reputation as a "poet" and a wit, and caused Crawford intolerable anguish.
It is likely that Abe was reconciled to his situation in this family by the presence of his sister, and the opportunity it gave him of being in the company of Mrs. Crawford, for whom he had a genuine attachment; for she was nothing that her husband was, and every thing that he was not. According to her account, he split rails, ploughed, threshed, and did whatever else he was ordered to do; but she distinctly affirms that "Abe was no hand to pitch into his work like killing snakes." He went about it "calmly," and generally took the opportunity to throw "Crawford" down two or three times "before they went to the field." It is fair to presume, that, when Abe managed to inveigle his disagreeable employer into a tussle, he hoisted him high and threw him hard, for he felt that he had no reason to be careful of his bones. After meals Abe "hung about," lingered long to gossip and joke with the women; and these pleasant, stolen conferences were generally broken up with the exclamation, "Well, this won't buy the child a coat!" and the long-legged hired boy would stride away to join his master.
In the mean time Abe had become, not only the longest, but the strongest, man in the settlement. Some of his feats almost surpass belief, and those who beheld them with their own eyes stood literally amazed. Richardson, a neighbor, declares that he could carry a load to which the strength of "three ordinary men" would scarcely be equal. He saw him quietly pick up and walk away with "a chicken-house, made of poles pinned together, and covered, that weighed at least six hundred, if not much more." At another time the Richardsons were building a corn-crib: Abe was there; and, seeing three or four men preparing "sticks" upon which to carry some huge posts, he relieved them of all further trouble by shouldering the posts, single-handed, and walking away with them to the place where they were wanted. "He could strike with a mall," says old Mr. Wood, "a heavier blow than any man.... He could sink an axe deeper into wood than any man I ever saw."
For hunting purposes, the Pigeon Creek region was one of the most inviting on earth. The uplands were all covered with an original growth of majestic forest trees,1 whilst on the hillsides, and wherever an opening in the woods permitted the access of sunlight, there were beds of fragrant and beautiful wild-flowers, presenting, in contrast with the dense green around them, the most brilliant and agreeable effects. Here the game had vast and secluded ranges, which, until very recently, had heard the report of no white man's gun. In Abe's time, the squirrels, rabbits, partridges, and other varieties of smaller game, were so abundant as to be a nuisance. They devastated grain-fields and gardens; and while they were seldom shot for the table, the settlers frequently devised the most cunning means of destroying them in great quantities, in order to save the growing crops. Wild turkeys and deer were the principal reliance for food; but besides these were the bears, the wild-cats, and the panthers.1 The scream of the latter, the most ferocious and bloodthirsty of the cat kind, hastened Abe's homeward steps on many a dark night, as he came late from Dave Turnham's, "Uncle" Wood's, or the Gentryville grocery. That terrific cry appeals not only to the natural fear of the monster's teeth and claws, but, heard in the solitude of night and the forest, it awakens a feeling of superstitious horror, that chills the heart of the bravest.
"Now about the timber: it was black walnut and black oak, hickory and jack oak, elm and white oak, undergrowth, logwood in abundance, grape-vines and shoe-make bushes, and milk-sick plenty. All my relations died of that disease on Little Pigeon Creek, Spencer County."—Dennis Hanks.
Everybody about Abe made hunting a part of his business.2 Tom Lincoln and Dennis Hanks doubtless regaled him continually with wonderful stories of their luck and prowess; but he was no hunter himself, and did not care to learn. It is true, that, when a mere child, he made a fortunate shot at a flock of wild turkeys, through a crack in the wall of the "half-faced cabin;"3 and that, when grown up, he went for coons occasionally with Richardson, or watched deer-licks with Turnham; but a true and hearty sportsman he never was. As practised on this wild border, it was a solitary, unsociable way of spending time, which did not suit his nature; and, besides, it required more exertion than he was willing to make without due compensation. It could not be said that Abe was indolent; for he was alert, brisk, active, about every thing that he made up his mind to do. His step was very quick; and, when he had a sufficient object in view, he strode out on his long, muscular legs, swinging his bony arms as he moved along, with an energy that put miles behind him before a lazy fellow like Dennis Hanks or John Johnston could make up his mind to start. But, when he felt that he had time to spare, he preferred to give it to reading or to "talk;" and, of the two, he would take the latter, provided he could find a person who had something new or racy to say. He liked excessively to hear his own voice, when it was promoting fun and good fellowship; but he was also a most rare and attentive listener. Hunting was entirely too "still" an occupation for him.
1 "No Indians there when I first went to Indiana: I say, no, none. I say this: bear, deer, turkey, and coon, wild-cats, and other things, and frogs."—Dennis Hanks. 2 "You say, What were some of the customs? I suppose you mean take us all together. One thing I can tell you about: we had to work very hard cleaning ground for to keep body and soul together; and every spare time we had we picked up our rifle, and brought in a fine deer or turkey; and in the winter-time we went a coon-hunting, for coon-skins were at that time considered legal tender, and deer-skins' and hams. I tell you, Billy, I enjoyed myself better then than I ever have since."—Dennis Hanks. 3 "No doubt about the A. Lincoln's killing the turkey. He done it with his father's rifle, made by William Lutes, of Bullitt County, Kentucky. I have killed a hundred deer with her myself; turkeys too numerous to mention."—Dennis Hanks.
All manner of rustic sports were in vogue among the Pigeon Creek boys. Abe was especially formidable as a wrestler; and, from about 1828 onward, there was no man, far or near, that would give him a match. "Cat," "throwing the mall," "hopping and half-hammon" (whatsoever that may mean), and "four-corner bull-pen" were likewise athletic games in high honor.1
1 "You ask, What sort of plays? What we called them at that time were 'bull-pen,' 'corner and cat,' 'hopping and half- hammon;' playing at night 'old Sister Feby.' This I know, for I took a hand myself; and, wrestling, we could throw down anybody."—Dennis Hanks.
All sorts of frolics and all kinds of popular gatherings, whether for work or amusement, possessed irresistible attractions for Abe. He loved to see and be seen, to make sport and to enjoy it. It was a most important part of his education that he got at the corn-shuckings, the log-rollings, the shooting-matches, and the gay and jolly weddings of those early border times. He was the only man or boy within a wide compass who had learning enough to furnish the literature for such occasions; and those who failed to employ his talents to grace or commemorate the festivities they set on foot were sure to be stung by some coarse but humorous lampoon from his pen. In the social way, he would not suffer himself to be slighted with impunity; and, if there were any who did not enjoy his wit, they might content themselves with being the subjects of it. Unless he received some very pointed intimation that his presence was not wanted, he was among the first and earliest at all the neighborhood routs; and when his tall, singular figure was seen towering amongst the hunting-shirts, it was considered due notice that the fun was about to commence. "Abe Linkhern," as he was generally called, made things lively wherever he went: and, if Crawford's blue nose happened to have been carried to the assembly, it quickly subsided, on his arrival, into some obscure corner; for the implacable "Linkhern" was apt to make it the subject of a jest that would set the company in a roar. But when a party was made up, and Abe left out, as sometimes happened through the influence of Crawford, he sulked, fumed, "got mad," nursed his anger into rage, and then broke out in songs or "chronicles," which were frequently very bitter, sometimes passably humorous, and invariably vulgar.
At an early age he began to attend the "preachings" roundabout, but principally at the Pigeon Creek church, with a view to catching whatever might be ludicrous in the preacher's air or matter, and making it the subject of mimicry as soon as he could collect an audience of idle boys and men to hear him. A pious stranger, passing that way on a Sunday morning, was invited to preach for the Pigeon Creek congregation; but he banged the boards of the old pulpit, and bellowed and groaned so wonderfully, that Abe could hardly contain his mirth. This memorable sermon was a great favorite with him; and he frequently reproduced it with nasal tones, rolling eyes, and all manner of droll aggravations, to the great delight of Nat Grigsby and the wild fellows whom Nat was able to assemble. None that heard him, not even Nat himself (who was any thing but dull), was ever able to show wherein Abe's absurd version really departed from the original.
The importance of Gentryville, as a "centre of business," soon began to possess the imaginations of the dwellers between the two Pigeon Creeks. Why might it not be a great place of trade? Mr. Gentry was a most generous patron; it was advantageously situated where two roads crossed; it already had a blacksmith's shop, a grocery, and a store. Jones, it is true, had once moved away in a sulk, but Mr. Gentry's fine diplomacy had quickly brought him back, with all his goods and talents unreservedly devoted to the "improvement of the town;" and now, since there was literally nothing left to cloud the prospects of the "point," brisk times were expected in the near future.
Dennis Hanks, John Johnston, Abe, and the other boys in the neighborhood, loitered much about the store, the grocery, and the blacksmith's shop, at Gentryville. Dennis ingenuously remarks, "Sometimes we spent a little time at grog, pushing weights, wrestling, telling stories." The time that Abe "spent at grog" was, in truth, a "little time." He never liked ardent spirits at any period of his life; but "he did take his dram as others did."1 He was a natural politician, intensely ambitious, and anxious to be popular. For this reason, and this alone, he drank with his friends, although very temperately. If he could have avoided it without giving offence, he would gladly have done so. But he coveted the applause of his pot companions, and, because he could not get it otherwise, made a faint pretence of enjoying his liquor as they did. The "people" drank, and Abe was always for doing whatever the "people" did. All his life he held that whatsoever was popular—the habit or the sentiment of the masses—could not be essentially wrong. But, although a whiskey-jug was kept in every ordinarily respectable household, Abe never tasted it at home. His step-mother thought he carried his temperance to extremes.
1 The fact is proved by his most intimate acquaintances, both at Gentryville and New Salem.
Jones, the great Jones, without whom it was generally agreed that Gentryville must have gone into eclipse, but with whom, and through whom, it was somehow to become a sort of metropolitan cross-roads,—Jones was Abe's friend and mentor from the moment of their acquaintance. Abe is even said to have "clerked for him;" that is, he packed and unpacked boxes, ranged goods on the shelves, drew the liquids in the cellar, or exhibited the stone and earthen ware to purchasers; but in his service he was never promoted to keeping accounts, or even to selling the finer goods across the counter.1 But Mr. Jones was very fond of his "clerk,"—enjoyed his company, appreciated his humor, and predicted something great for him. As he did not doubt that Abe would one day be a man of considerable influence, he took pains to give him correct views of the nature of American institutions. An ardent Jackson man himself, he imparted to Abe the true faith, as delivered by that great democratic apostle; and the traces of this teaching were never wholly effaced from Mr. Lincoln's mind. Whilst he remained at Gentryville, his politics accorded with Mr. Jones's; and, even after he had turned Whig in Illinois, John Hanks tells us that he wanted to whip a man for traducing Jackson. He was an eager reader of newspapers whenever he could get them, and Mr. Jones carefully put into his hands the kind he thought a raw youth should have. But Abe's appetite was not to be satisfied by what Mr. Jones supplied; and he frequently borrowed others from "Uncle Wood," who lived about a mile from the Lincoln cabin, and for whom he sometimes worked.
1 "Lincoln drove a team, cut up pork, and sold goods for Jones. Jones told me that Lincoln read all his books, and I remember History of United States as one. Jones often said to me, that Lincoln would make a great man one of these days,—had said so long before, and to other people,—said so as far back as 1828-9.'"—Dougherty.
What manner of man kept the Gentryville grocery, we are not informed. Abe was often at his place, however, and would stay so long at nights, "telling stories" and "cracking jokes," that Dennis Hanks, who was ambitious in the same line, and probably jealous of Abe's overshadowing success, "got mad at him," and "cussed him." When Dennis found himself thrown in the shade, he immediately became virtuous, and wished to retire early.
John Baldwin, the blacksmith, was one of Abe's special friends from his boyhood onward. Baldwin was a story-teller and a joker of rare accomplishments; and Abe, when a very little fellow, would slip off to his shop and sit and listen to him by the hour. As he grew up, the practice continued as of old, except that Abe soon began to exchange anecdotes with his clever friend at the anvil. Dennis Hanks says Baldwin was his "particular friend," and that "Abe spent a great deal of his leisure time with him." Statesmen, plenipotentiaries, famous commanders, have many times made the White House at Washington ring with their laughter over the quaint tales of John Baldwin, the blacksmith, delivered second-hand by his inimitable friend Lincoln.
Abe and Dave Turnham had one day been threshing wheat,—probably for Turnham's father,—and concluded to spend the evening at Gentryville. They lingered there until late in the night, when, wending their way along the road toward Lincoln's cabin, they espied something resembling a man lying dead or insensible by the side of a mud-puddle. They rolled the sleeper over, and found in him an old and quite respectable acquaintance, hopelessly drunk. All efforts failed to rouse him to any exertion on his own behalf. Abe's companions were disposed to let him lie in the bed he had made for himself; but, as the night was cold and dreary, he must have frozen to death had this inhuman proposition been equally agreeable to everybody present. To Abe it seemed utterly monstrous; and, seeing he was to have no help, he bent his mighty frame, and, taking the big man in his long arms, carried him a great distance to Dennis Hanks's cabin. There he built a fire, warmed, rubbed, and nursed him through the entire night,—his companions of the road having left him alone in his merciful task. The man often told John Hanks, that it was mighty "clever in Abe to tote him to a warm fire that cold night," and was very sure that Abe's strength and benevolence had saved his life.
Abe was fond of music, but was himself wholly unable to produce three harmonious notes together. He made various vain attempts to sing a few lines of "Poor old Ned," but they were all equally ludicrous and ineffectual. "Religious songs did not appear to suit him at all," says Dennis Hanks; but of profane ballads and amorous ditties he knew the words of a vast number. When Dennis got happy at the grocery, or passed the bounds of propriety at a frolic, he was in the habit of raising a charming carol in praise of the joys which enter into the Mussulman's estate on earth,—of which he has vouchsafed us only three lines,—
"The turbaned Turk that scorns the world, And struts about with his whiskers curled, For no other man but himself to see."
It was a prime favorite of Abe's; and Dennis sang it with such appropriate zest and feeling, that Abe never forgot a single word of it while he lived.
Another was,—
"Hail Columbia, happy land! If you ain't drunk, I'll be damned,"—
a song which Dennis thinks should be warbled only in the "fields;" and tells us that they knew and enjoyed "all such [songs] as this." Dave Turnham was also a musical genius, and had a "piece" beginning,—
"There was a Romish lady Brought up in popery,"
which Abe thought one of the best he ever heard, and insisted upon Dave's singing it for the delectation of old Tom Lincoln, who relished it quite as much as Abe did.1
1 "I recollect some more:— 'Come, thou Fount of every blessing, Tune my heart to sing thy praise.' 'When I can read my title clear To mansions in the skies!' 'How tedious and tasteless the hours.' 'Oh! to grace how great a debtor!' Other little songs I won't say any thing about: they would not look well in print; but I could give them."—Dennis Hanks.
Mrs. Crawford says, that Abe did not attempt to sing much about the house: he was probably afraid to indulge in such offensive gayeties in the very habitation of the morose Crawford. According to Dennis Hanks, his melody was not of the sort that hath power to charm the savage; and he was naturally timid about trying it upon Crawford. But, when he was freed from those chilling restraints, he put forth his best endeavors to render "one [song] that was called 'William Riley,' and one that was called 'John Anderson's Lamentations,' and one that was made about Gen. Jackson and John Adams, at the time they were nominated for the presidency."
The Jackson song indicated clearly enough Abe's steadiness in the political views inculcated by Jones. Mrs. Crawford could recollect but a single stanza of it:—
"Let auld acquaintance be forgot, And never brought to mind, And Jackson be our President, And Adams left behind."
In the text of "John Anderson's Lamentations,"—a most distressful lyric to begin with,—Abe was popularly supposed to have interpolated some lines of his own, which conclusively attested his genius for poetic composition. At all events, he sang it as follows:—
"O sinners! poor sinners, take warning by me: The fruits of transgression behold now, and see; My soul is tormented, my body confined, My friends and dear children left weeping behind. "Much intoxication my ruin has been, And my dear companion hath barbarously slain: In yonder cold graveyard the body doth lie; Whilst I am condemned, and shortly must die. "Remember John Anderson's death, and reform Before death overtakes you, and vengeance comes on. My grief's overwhelming; in God I must trust: I am justly condemned; my sentence is just. "I am waiting the summons in eternity to be hurled; Whilst my poor little orphans are cast on the world. I hope my kind neighbors their guardeens will be, And Heaven, kind Heaven, protect them and me."
In 1826 Abe's sister Nancy (or Sarah) was married to Aaron Grigsby; and the festivities of the occasion were made memorable by a song entitled, "Adam and Eve's Wedding Song," which many believed Abe had himself composed. The conceits embodied in the doggerel were old before Abe was born; but there is some intrinsic as well as extraneous evidence to show that the doggerel itself was his. It was sung by the whole Lincoln family, before Nancy's marriage and since, but by nobody else in the neighborhood.
ADAM AND EVE'S WEDDING SONG. When Adam was created, he dwelt in Eden's shade, As Moses has recorded, and soon an Eve was made. Ten thousand times ten thousand Of creatures swarmed around Before a bride was formed, And yet no mate was found. The Lord then was not willing The man should be alone, But caused a sleep upon him, And took from him a bone, And closed the flesh in that place of; And then he took the same, And of it made a woman, And brought her to the man. Then Adam he rejoiced To see his loving bride, A part of his own body, The product of his side. This woman was not taken From Adam's feet, we see; So he must not abuse her, The meaning seems to be. This woman was not taken From Adam's head, we know; To show she must not rule him, 'Tis evidently so. This woman she was taken From under Adam's arm; So she must be protected From injuries and harm.
"It was considered at that time," says Mr. Richardson, "that Abe was the best penman in the neighborhood. One day, while he was on a visit at my mother's, I asked him to write some copies for me. He very willingly consented. He wrote several of them, but one of them I have never forgotten, although a boy at the time. It was this:—
'Good boys who to their books apply Will all be great men by and by.'"
Here are two original lines from Abe's own copy-book, probably the first he ever had, and which must not be confounded with the famous scrap-book in which his step-mother, lost in admiration of its contents, declares he "entered all things:"—
"Abraham Lincoln, his hand and pen: He will be good, but God knows when."
Again,—
"Abraham Lincoln is my name, And with my pen I write the same: I will be a good boy, but God knows when."
The same book contains the following, written at a later day, and with nothing to indicate that any part of it was borrowed:—
"Time! what an empty vapor'tis! And days how swift they are! Swift as an Indian arrow, Fly on like a shooting-star. The present moment just is here, Then slides away in haste, That we can never say they're ours, But only say they are past."
Abe wrote many "satires" and "chronicles," which are only remembered in fragments by a few old persons in the neighborhood. Even if we had them in full, they were most of them too indecent for publication. Such, at least, was the character of "a piece" which is said to have been "exceedingly humorous and witty," touching a church trial, wherein Brother Harper and Sister Gordon were the parties seeking judgment. It was very coarse, but it served admirably to raise a laugh in the grocery at the expense of the church.
His chronicles were many, and on a great variety of subjects. They were written, as his early admirers love to tell us, "in the scriptural style;" but those we have betray a very limited acquaintance with the model. In these "chapters" was celebrated every event of importance that took place in the neighborhood: weddings, fights, Crawford's nose, Sister Gordon's innocence, Brother Harper's wit, were all served up, fresh and gross, for the amusement of the groundlings.
Charles and Reuben Grigsby were married about the same time, and, being brothers, returned to their father's house with their brides upon the same day. The infare, the feast, the dance, the ostentatious retirement of the brides and grooms, were conducted in the old-fashioned way of all new countries in the United States, but a way which was bad enough to shock Squire Western himself. On this occasion Abe was not invited, and was very "mad" in consequence. This indignation found vent in a highly-spiced piece of descriptive writing, entitled "The Chronicles of Reuben," which are still in existence.
But even "The Chronicles," venomous and highly successful as they were, were totally insufficient to sate Abe's desire for vengeance on the Grigsbys. They were important people about Gentryville, and the social slight they had given him stung him bitterly. He therefore began on "Billy" in rhyme, after disposing of Charles and Reuben "in scriptural style." Mrs. Crawford attempted to repeat these verses to Mr. Herndon; but the good old lady had not proceeded far, when she blushed very red, and, saying that they were hardly decent, proposed to tell them to her daughter, who would tell them to her husband, who would write them down and send them to Mr. Herndon. They are probably much curtailed by Mrs. Crawford's modesty, but still it is impossible to transcribe them. We give what we can to show how the first steps of Abe's fame as a great writer were won. It must be admitted that the literary taste of the community in which these rhymes were popular could not have been very high.
"I will tell you about Joel and Mary: it is neither a joke or a story, for Reuben and Charles has married two girls, but Billy has married a boy." "The girls he had tried on every side, But none could he get to agree: All was in vain; he went home again, And, since that, he is married to Natty. "So Billy and Natty agreed very well, And mamma's well pleased at the match: The egg it is laid, but Natty's afraid The shell is so soft it never will hatch; But Betsey she said, 'You cursed bald head, My suitor you never can be; Besides'"——
Abe dropped "The Chronicles" at a point on the road where he was sure one of the Grigsbys would find them. The stratagem succeeded, and that delicate "satire" produced the desired effect. The Grigsbys were infuriated,—wild with a rage which would be satisfied only when Abe's face should be pounded into a jelly, and a couple of his ribs cracked by some member of the injured family. Honor, according to the Pigeon Creek code, demanded that somebody should be "licked" in expiation of an outrage so grievous,—if not Abe, then some friend of Abe's, whom he would depute to stand the brunt in his stead. "Billy," the eldest of the brothers, was selected to challenge him. Abe accepted generally; that is, agreed that there should be a fight about the matter in question. It was accordingly so ordered: the ground was selected a mile and a half from Gentryville, a ring was marked out, and the bullies for twenty miles around attended. The friends of both parties were present in force, and excitement ran high. When the time arrived for the champions to step into the ring, Abe displayed his chivalry in a manner that must have struck the bystanders with admiration. He announced, that whereas Billy was confessedly his inferior in size, shape, and talents, unable to hit with pen or fist with any thing like his power, therefore he would forego the advantage which the challenge gave him, and "turn over" his stepbrother, John Johnston, to do battle in his behalf. If this near relative should be sacrificed, he would abide the issue: he was merely anxious to see a fair and honorable fight. This proposition was considered highly meritorious, and the battle commenced on those general terms. John started out with fine pluck and spirit; but in a little while Billy got in some clever hits, and Abe began to exhibit symptoms of great uneasiness. Another pass or two, and John flagged quite decidedly, and it became evident that Abe was anxiously casting about for some pretext to break the ring. At length, when John was fairly down, and Billy on top, and all the spectators cheering, swearing, and pressing up to the very edge of the ring, Abe cried out that "Bill Boland showed foul play," and, bursting out of the crowd, seized Grigsby by the heels, and flung him off. Having righted John, and cleared the battle-ground of all opponents, "he swung a whiskey-bottle over his head, and swore that he was the big buck of the lick." It seems that nobody of the Grigsby faction, not one in that large assembly of bullies, cared to encounter the sweep of Abe's tremendously long and muscular arms; and so he remained master of the "lick." He was not content, however, with a naked triumph, but vaunted himself in the most offensive manner. He singled out the victorious but cheated Billy, and, making sundry hostile demonstrations, declared that he could whip him then and there. Billy meekly said "he did not doubt that," but that, if Abe would make things even between them by fighting with pistols, he would not be slow to grant him a meeting. But Abe replied that he was not going "to fool away his life on a single shot;" and so Billy was fain to put up with the poor satisfaction he had already received.
At Gentryville "they had exhibitions or speaking meetings." Some of the questions they spoke on were, The Bee and the Ant, Water and Fire: another was, Which had the most right to complain, the Negro or the Indian? Another, "Which was the strongest, Wind or Water?"1 The views which Abe then entertained on the Indian and the negro question would be intensely interesting now. But just fancy him discoursing on wind and water! What treasures of natural science, what sallies of humor, he must have wasted upon that audience of bumpkins! A little farther on, we shall see that Abe made pretensions to an acquaintance with the laws of nature which was considered marvellous in that day and generation.
1 "Lincoln did write what is called 'The Book of Chronicles,'—a satire on the Grigs-bys and Josiah Crawford,—not the schoolmaster, but the man who loaned Lincoln 'The Life of Washington.' The satire was good, sharp, cutting: it hurt us then, but it is all over now. There is no family in the land who, after this, loved Lincoln so well, and who now look upon him as so great a man. We all voted for him,—all that could,—children and grandchildren, first, last, and always."—Nat Grigsby.
Dennis Hanks insists that Abe and he became learned men and expert disputants, not by a course of judicious reading, but by attending "speech-makings, gatherings," &c.
"How did Lincoln and yourself learn so much in Indiana under such disadvantages?" said Mr. Herndon to Dennis, on one of his two oral examinations. The question was artfully put; for it touched the jaunty Dennis on the side of his vanity, and elicited a characteristic reply. "We learned," said he, "by sight, scent, and hearing. We heard all that was said, and talked over and over the questions heard; wore them slick, greasy, and threadbare. Went to political and other speeches and gatherings, as you do now: we would hear all sides and opinions, talk them over, discuss them, agreeing or disagreeing. Abe, as I said before, was originally a Democrat after the order of Jackson, so was his father, so we all were.... He preached, made speeches, read for us, explained to us, &c.... Abe was a cheerful boy, a witty boy, was humorous always; sometimes would get sad, not very often.... Lincoln would frequently make political and other speeches to the boys: he was calm, logical, and clear always. He attended trials, went to court always, read the Revised Statute of Indiana, dated 1824, heard law speeches, and listened to law trials, &c. Lincoln was lazy, a very lazy man. He was always reading, scribbling, writing, ciphering, writing poetry, and the like.... In Gentryville, about one mile west of Thomas Lincoln's farm, Lincoln would go and tell his jokes and stories, &c., and was so odd, original, and humorous and witty, that all the people in town would gather around him. He would keep them there till midnight. I would get tired, want to go home, cuss Abe most heartily. Abe was a good talker, a good reader, and was a kind of newsboy."
Boonville was the court-house town of Warrick County, and was situated about fifteen miles from Gentryville. Thither Abe walked whenever he had time to be present at the sittings of the court, where he could learn something of public business, amuse himself profitably, and withal pick up items of news and gossip, which made him an interesting personage when he returned home. During one of these visits he watched, with profound attention, the progress of a murder trial, in which a Mr. John Breckenridge was counsel for the defence. At the conclusion of the latter's speech, Abe, who had listened, literally entranced, accosted the man of eloquence, and ventured to compliment him on the success of his effort. "Breckenridge looked at the shabby boy" in amazement, and passed on his way. But many years afterwards, in 1862, when Abe was President, and Breckenridge a resident of Texas, probably needing executive clemency, they met a second time; when Abe said, "It was the best speech that I up to that time had ever heard. If I could, as I then thought, make as good a speech as that, my soul would be satisfied."
It is a curious fact, that through all Abe's childhood and boyhood, when he seemed to have as little prospect of the Presidency as any boy that ever was born, he was in the habit of saying, and perhaps sincerely believing, that that great prize would one day be his. When Mrs. Crawford reproved him for "fooling," and bedevilling the girls in her kitchen, and asked him "what he supposed would ever become of him," he answered that "he was going to be President of the United States."1
1 He frequently made use of similar expressions to several others.
Abe usually did the milling for the family, and had the neighbor boy, Dave Turnham, for his companion. At first they had to go a long distance, at least twelve or thirteen miles, to Hoffman's, on Anderson's Creek; but after a while a Mr. Gordon (the husband of Sister Gordon, about whom the "witty piece" was written) built a horse-mill within a few miles of the Lincolns. Here Abe had come one day with a grist, and Dave probably with him. He had duly hitched his "old mare," and started her with great impatience; when, just as he was sounding another "cluck," to stir up her imperturbable and lazy spirit, she let out with her heels, and laid Abe sprawling and insensible on the ground. He was taken up in that condition, and did not recover for many minutes; but the first use made of returning sense was to finish the interrupted "cluck." He and Mr. Herndon had many learned discussions in their quiet little office, at Springfield, respecting this remarkable phenomenon, involving so nice a question in "psychology."
Mr. William Wood, already referred to as "Uncle Wood," was a genuine friend and even a patron of Abe's. He lived only about a mile and a half from the Lincolns, and frequently had both old Tom and Abe to work for him,—the one as a rough carpenter, and the other as a common laborer. He says that Abe was in the habit of carrying "his pieces" to him for criticism and encouragement. Mr. Wood took at least two newspapers,—one of them devoted to politics, and one of them to temperance. Abe borrowed them both, and, reading them faithfully over and over again, was inspired with an ardent desire to write something on the subjects of which they treated. He accordingly composed an article on temperance, which Mr. Wood thought "excelled, for sound sense, any thing that the paper contained." It was forwarded, through the agency of a Baptist preacher, to an editor in Ohio, by whom it was published, to the infinite gratification of Mr. Wood and his protégé. Abe then tried his hand on "national politics," saying that "the American Government was the best form of government for an intelligent people; that it ought to be kept sound, and preserved forever; that general education should be fostered and carried all over the country; that the Constitution should be saved, the Union perpetuated, and the laws revered, respected, and enforced." This article was consigned, like the other, to Mr. Wood, to be ushered by him before the public. A lawyer named Pritchard chanced to pass that way, and, being favored with a perusal of Abe's "piece," pithily and enthusiastically declared, "The world can't beat it." "He begged for it," and it was published in some obscure paper; this new success causing the author a most extraordinary access of pride and happiness.
But in 1828 Abe had become very tired of his home. He was now nineteen years of age, and becoming daily more restive under the restraints of servitude which bound him. He was anxious to try the world for himself, and make his way according to his own notions. "Abe came to my house one day," says Mr. Wood, "and stood round about, timid and shy. I knew he wanted something, and said to him, 'Abe, what's your case?' He replied, 'Uncle, I want you to go to the river, and give me some recommendation to some boat.' I remarked, 'Abe, your age is against you: you are not twenty yet.' 'I know that, but I want a start,' said Abe. I concluded not to go for the boy's good." Poor Abe! old Tom still had a claim upon him, which even Uncle Wood would not help him to evade. He must wait a few weary months more before he would be of age, and could say he was his own man, and go his own way. Old Tom was a hard taskmaster to him, and, no doubt, consumed the greater part, if not all, of his wages.
In the beginning of March, 1828, Abe went to work for old Mr. Gentry, the proprietor of Gentryville. Early in the next month, the old gentleman furnished his son Allen with a boat, and a cargo of bacon and other produce, with which he was to go on a trading expedition to New Orleans, unless the stock was sooner exhausted. Abe, having been found faithful and efficient, was employed to accompany the young man as a "bow-hand," to work the "front oars." He was paid eight dollars per month, and ate and slept on board. Returning, Gentry paid his passage on the deck of a steamboat.
While this boat was loading at Gentry's Landing, near Rockport, on the Ohio, Abe saw a great deal of the pretty Miss Roby, whom he had saved from the wrath of Crawford the schoolmaster, when she failed to spell "defied." She says, "Abe was then a long, thin, leggy, gawky boy, dried up and shrivelled." This young lady subsequently became the wife of Allen Gentry, Abe's companion in the projected voyage. She probably felt a deep interest in the enterprise in hand, for the very boat itself seems to have had attractions for her. "One evening," says she, "Abe and I were sitting on the banks of the Ohio, or rather on the boat spoken of: I said to Abe that the sun was going down. He said to me, 'That's not so: it don't really go down; it seems so. The earth turns from west to east, and the revolution of the earth carries us under as it were: we do the sinking as you call it. The sun, as to us, is comparatively still; the sun's sinking is only an appearance.' I replied, 'Abe, what a fool you are!' I know now that I was the fool, not Lincoln. I am now thoroughly satisfied that Abe knew the general laws of astronomy and the movements of the heavenly bodies. He was better read then than the world knows, or is likely to know exactly. No man could talk to me that night as he did, unless he had known something of geography as well as astronomy. He often and often commented or talked to me about what he had read,—seemed to read it out of the book as he went along,—did so to others. He was the learned boy among us unlearned folks. He took great pains to explain; could do it so simply. He was diffident then too." 1
The trip of Gentry and Lincoln was a very profitable one, and Mr. Gentry, senior, was highly gratified by the result. Abe displayed his genius for mercantile affairs by handsomely putting off on the innocent folks along the river some counterfeit money which a shrewd fellow had imposed upon Allen. Allen thought his father would be angry with him for suffering himself to be cheated; but Abe consoled him with the reflection that the "old man" wouldn't care how much bad money they took in the course of business if they only brought the proper amount of good money home.2
1 "When he appeared in company, the boys would gather and cluster around him to hear him talk.... Mr. Lincoln was figurative in his speeches, talks, and conversations. He argued much from analogy, and explained things hard for us to understand by stories, maxims, tales, and figures. He would almost always point his lesson or idea by some story that was plain and near us, that we might instantly see the force and bearing of what he said."—Nat Grigsby. 2 "Gentry (Allen) was a great personal friend of Mr. Lincoln. He was a Democrat, but voted for Lincoln, sacrificing his party politics to his friendship. He says that on that trip they sold some of their produce at a certain landing, and by accident or fraud the bill was paid in counterfeit money. Gentry was grieving about it; but Lincoln said, 'Never mind, Allen: it will accidentally slip out of our fingers before we get to New Orleans, and then old Jim can't quarrel at us.' Sure enough, it all went off like hot cakes. I was told this in Indiana by many people about Rockport."—Herndon. It must be remembered that counterfeit money was the principal currency along the river at this period.
At Madame Bushane's plantation, six miles below Baton Rouge, they had an adventure, which reads strangely enough in the life of the great emancipator. The boat was tied up to the shore, in the dead hours of the night, and Abe and Allen were fast asleep in the "cabin," in the stern, when they were startled by footsteps on board. They knew instantly that it was a gang of negroes come to rob, and perhaps to murder them. Allen, thinking to frighten the intruders, cried out, "Bring the guns, Lincoln; shoot them!" Abe came without a gun, but he fell among the negroes with a huge bludgeon, and belabored them most cruelly. Not content with beating them off the boat, he and Gentry followed them far back into the country, and then, running back to their craft, hastily cut loose and made rapid time down the river, fearing lest they should return in greater numbers to take revenge. The victory was complete; but, in winning it, Abe received a scar which he carried with him to his grave.
"When he was eighteen years old, he conceived the project of building a little boat, and taking the produce of the Lincoln farm down the river to market. He had learned the use of tools, and possessed considerable mechanical talent, as will appear in some other acts of his life. Of the voyage and its results, we have no knowledge; but an incident occurred before starting which he related in later life to his Secretary of State, Mr. Seward, that made a very marked and pleasant impression upon his memory. As he stood at the landing, a steamer approached, coming down the river. At the same time two passengers came to the river's bank who wished to be taken out to the packet with their luggage. Looking among the boats at the landing, they singled out Abraham's, and asked him to scull them to the steamer. This he did; and, after seeing them and their trunks on board, he had the pleasure of receiving upon the bottom of his boat, before he shoved off, a silver half-dollar from each of his passengers. 'I could scarcely believe my eyes,' said Mr. Lincoln, in telling the story. 'You may think it was a very little thing,' continued he, 'but it was a most important incident in my life. I could scarcely believe that I, a poor boy, had earned a dollar in less than a day. The world seemed wider and fairer to me. I was a more hopeful and confident being from that time.'"1 If Mr. Lincoln ever made the statement for which Mr. Seward is given as authority, he drew upon his imagination for the facts. He may have sculled passengers to a steamer when he was ferryman for Taylor, but he never made a trip like the one described; never built a boat until he went to Illinois; nor did he ever sell produce on his father's account, for the good reason that his father had none to sell.
1 Holland's Life of Lincoln, p. 33.
ABE and Gentry returned from New Orleans some time in June, 1828, having been gone not quite three months. How much longer he remained in the service of Gentry, or whether he remained at all, we are unable to say; but he soon took up his old habits, and began to work around among his neighbors, or for his father, precisely as he had done before he got his partial glimpse of the great world down the river.
In the fall of 1829, Mr. Wood saw him cutting down a large tree in the woods, and whip-sawing it into planks. Abe said the lumber was for a new house his father was about to build; but Tom Lincoln changed his mind before the house was half done, and Abe sold his plank to Josiah Crawford, "the book man," who worked them into the south-east room of his house, where relic-seekers have since cut pieces from them to make canes.
In truth, the continued prevalence of that dreadful disease, the milk-sickness, with which Nancy Hanks and the Sparrows and the Halls had all died, was more than a sufficient reason for a new removal, now in contemplation by Thomas Lincoln. Every member of his family, from the first settlement in Indiana, except perhaps Abe and himself, had suffered with it. The cattle, which, it is true, were of little pecuniary value, and raised with great ease and little cost, were swept away by it in great numbers throughout the whole neighborhood. It was an awful scourge, and common prudence suggested flight. It is wonderful that it took a constitutional mover thirteen years to make up his mind to escape from it.1
1 "What made Thomas Lincoln leave? The reason is this: we were perplexed by a disease called milk-sick. I myself being the oldest, I was determined to leave, and hunt a country where the milk-sick was not. I married his eldest daughter. I sold out, and they concluded to go with me. Billy, I was tolerably popular at that time, for I had some money. My wife's mother could not think of parting with her, and we ripped up stakes, and started to Illinois, and landed at Decatur. This is the reason for leaving Indiana. I am to blame for it, if any. As for getting more land, this was not the case, for we could have entered ten thousand acres of the best land. When we left, it was on account of the milk. Billy, I had four good milch cows, too, with it in one week, and eleven young calves. This was enough to run me. Besides, liked to have lossed my own life with it. This reason was enough (ain't it?) for leaving."—Dennis Hanks.
In the spring of 1830, before the winter had fairly broken up, he and Abe, and Dennis Hanks and Levi Hall, with their respective families, thirteen in all, took the road for Illinois. Dennis and Levi, as already stated, were married to the daughters of Mrs. Lincoln. Hall had one son, and Dennis a considerable family of sons and daughters. Sarah (or Nancy) Lincoln, who had married Aaron Grigsby, was now dead.
John Hanks had gone to the new country from Kentucky in the fall of 1828, and settled near Decatur, whence he wrote Thomas Lincoln all about it, and advised him to come there. Dennis, whether because of the persuasions of John, or some observations made in a flying trip on his own account, was very full of the move, and would hear to no delay. Lincoln sold his farm to Gentry, senior, if, indeed, he had not done so before, and his corn and hogs to Dave Turnham. The corn brought only ten cents a bushel, and, according to the pricelist furnished by Dennis Hanks, the stock must have gone at figures equally mean.
Lincoln took with him to Illinois "some stock-cattle, one horse, one bureau, one table, one clothes-chest, one set of chairs, cooking utensils, clothing," &c. The goods of the three families—Hanks, Hall, and Lincoln—were loaded on a wagon belonging to Lincoln. This wagon was "ironed," a noticeable fact in those primitive days, and "was positively the first one that he (Lincoln) ever owned." It was drawn by four yoke of oxen,—two of them Lincoln's, and two of them Hanks's.
We have no particulars of the journey, except that Abe held the "gad," and drove the team; that the mud was very deep, that the spring freshets were abroad, and that in crossing the swollen and tumultuous Kaskaskia, the wagon and oxen were nearly swept away. On the first day of March, 1830, after fifteen days' tedious and heavy travel, they arrived at John Hanks's house, four miles north-west of Decatur. Lincoln settled (if any thing he did may be called settling) at a point ten miles west of Decatur. Here John Hanks had cut some logs in 1829, which he now gave to Lincoln to build a house with. With the aid of John, Dennis, Abe, and Hall, a house was erected on a small bluff, on the north bank of the north fork of the Sangamon. Abe and John took the four yoke of oxen and "broke up" fifteen acres of land, and then split rails enough to fence it in.
Abe was now over twenty-one. There was no "Uncle Wood to tell him that his age was against him:" he had done something more than his duty by his father; and, as that worthy was now again placed in a situation where he might do well if he chose, Abe came to the conclusion that it was time for him to begin life on his own account. It must have cost him some pain to leave his good step-mother; but, beyond that, all the old ties were probably broken without a single regret. From the moment he was a free man, foot-loose, able to go where, and to do what, he pleased, his success in those things which lay nearest his heart—that is, public and social preferment—was astonishing to himself, as well as to others.
It is with great pleasure that we dismiss Tom Lincoln, with his family and fortunes, from further consideration in these pages. After Abraham left him, he moved at least three times in search of a "healthy" location, and finally got himself fixed near Goose Nest Prairie, in Coles County, where he died of a disease of the kidneys, in 1851, at the ripe old age of seventy-three. The little farm (forty acres) upon which his days were ended, he had, with his usual improvidence, mortgaged to the School Commissioners for two hundred dollars,—its full value. Induced by love for his step-mother, Abraham had paid the debt, and taken a deed for the land, "with a reservation of a life-estate therein, to them, or the survivor of them." At the same time (1841), he gave a helping hand to John Johnston, binding himself to convey the land to him, or his heirs, after the death of "Thomas Lincoln and his wife," upon payment of the two hundred dollars, which was really advanced to save John's mother from utter penury. No matter how much the land might appreciate in value, John was to have it upon these terms, and no interest was to be paid by him, "except after the death of the survivor, as aforesaid." This, to be sure, was a great bargain for John, but he made haste to assign his bond to another person for "fifty dollars paid in hand."
As soon as Abraham got a little up in the world, he began to send his step-mother money, and continued to do so until his own death; but it is said to have "done her no good," for it only served to tempt certain persons about her, and with whom she shared it, to continue in a life of idleness. At the close of the Black Hawk War, Mr. Lincoln went to see them for a few days, and afterwards, when a lawyer, making the circuits with the courts, he visited them whenever the necessities of his practice brought him to their neighborhood. He did his best to serve Mrs. Lincoln and her son John, but took little notice of his father, although he wrote him an exhortation to believe in God when he thought he was on his death-bed.
But in regard to the relations between the family and Abe, after the latter began to achieve fame and power, nobody can tell the truth more clearly, or tell it in a more interesting and suggestive style, than our friend Dennis, with whom we are now about to part forever. It will be seen, that, when information reached the "Goose Nest Prairie" that Abe was actually chosen President of the United States, a general itching for public employment broke out among the Hankses, and that an equally general disappointment was the result. Doubtless all of them had expectations somewhat like Sancho Panza's, when he went to take the government of his island, and John Hanks, at least, would not have been disappointed but for the little disability which Dennis mentions in the following extract:—
"Did Abraham Lincoln treat John D. Johnston well?" "I will say this much about it. I think Abe done more for John than he deserved. John thought that Abe did not do enough for the old people. They became enemies a while on this ground. I don't want to tell all the things that I know: it would not look well in history. I say this: Abe treated John well."
"What kind of a man was Johnston?"—"I say this much: A kinder-hearted man never was in Coles County, Illinois, nor an honester man. I don't say this because he was my brother-in-law: I say it, knowing it. John did not love to work any the best. I flogged him for not working."
"Did Thomas Lincoln treat Abe cruelly?"—"He loved him. I never could tell whether Abe loved his father very well or not. I don't think he did, for Abe was one of those forward boys. I have seen his father knock him down off the fence when a stranger would, ask the way to a neighbor's house. Abe always would have the first word. The old man loved his children."
"Did any of the Johnston family ask for office?"—"No! Thomas Johnston went to Abe: he got this permit to take daguerrotypes in the army; this is all, for they are all dead except John's boys. They did not ask for any."
"Did you or John Hanks ask Lincoln for any office?"—"I say this: that John Hanks, of Decatur, did solicit him for an Indian Agency; and John told me that Abe as good as told him he should have one. But John could not read or write. I think this was the reason that Abe did not give John the place.
"As for myself, I did not ask Abe right out for an office, only this: I would like to have the post-office in Charleston; this was my wife that asked him. He told her that much was understood,—as much as to say that I would get it. I did not care much about it."
"Do you think Lincoln cared much for his relations?"—"I will say this much: when he was with us, he seemed to think a great deal of us; but I thought sometimes it was hypocritical, but I am not sure."
Abe left the Lincoln family late in March, or early in April. He did not go far away, but took jobs wherever he could get them, showing that he had separated himself from the family, not merely to rove, but to labor, and be an independent man. He made no engagement of a permanent character during this summer: his work was all done "by the job." If he ever split rails for Kirkpatrick, over whom he was subsequently elected captain of a volunteer company about to enter the Black Hawk War, it must have been at this time; but the story of his work for Kirkpatrick, like that of his making "a crap of corn" for Mr. Brown, is probably apocryphal.1 All this while he clung close to John Hanks, and either worked where he did, or not far away. In the winter following, he was employed by a Major Warrick to make rails, and walked daily three miles to his work, and three miles back again.
1 See Holland's Life of Lincoln, p. 40.
"After Abe got to Decatur," says John Hanks, "or rather to Macon (my country), a man by the name of Posey came into our neighborhood, and made a speech: it was a bad one, and I said Abe could beat it. I turned down a box, or keg, and Abe made his speech. The other man was a candidate. Abe wasn't. Abe beat him to death, his subject being the navigation of the Sangamon River. The man, after the speech was through, took Abe aside, and asked him where he had learned so much, and how he did so well. Abe replied, stating his manner and method of reading, and what he had read. The man encouraged Lincoln to persevere."
In February, 1831, a Mr. Denton Offutt wanted to engage John Hanks to take a flatboat to New Orleans. John was not well disposed to the business; but Offutt came to the house, and would take no denial; made much of John's fame as a river-man, and at length persuaded him to present the matter to Abe and John Johnston. He did so. The three friends discussed the question with great earnestness: it was no slight affair to them, for they were all young and poor. At length they agreed to Offutt's proposition, and that agreement was the turning-point in Abe's career. They were each to receive fifty cents a day, and the round sum of sixty dollars divided amongst them for making the trip. These were wages such as Abe had never received before, and might have tempted him to a much more difficult enterprise. When he went with Gentry, the pay was only eight dollars a month, and no such company and assistance as he was to have now. But Offutt was lavish with his money, and generous bargains like this ruined him a little while after.
In March, Hanks, Johnston, and Lincoln went down the Sangamon in a canoe to Jamestown (then Judy's Ferry), five miles east of Springfield. Thence they walked to Springfield, and found Mr. Offutt comforting himself at "Elliott's tavern in Old Town." He had contracted to have a boat ready at the mouth of Spring Creek, but, not looking after it himself, was, of course, "disappointed." There was only one way out of the trouble: the three hands must build a boat. They went to the mouth of Spring Creek, five miles north of Springfield, and there consumed two weeks cutting the timber from "Congress land." In the mean time, Abe walked back to Judy's Ferry, by way of Springfield, and brought down the canoe which they had left at the former place. The timber was hewed and scored, and then "rafted down to Saugamon-town." At the mouth of Spring Creek they had been compelled to walk a full mile for their meals; but at Sangamon-town they built a shanty, and boarded themselves. "Abe was elected cook," and performed the duties of the office much to the satisfaction of the party. The lumber was sawed at Kirkpatrick's mill, a mile and a half from the shanty. Laboring under many disadvantages like this, they managed to complete and launch the boat in about four weeks from the time of beginning.
Offutt was with the party at this point. He "was a Whig, and so was Abe; but he (Abe) could not hear Jackson wrongfully abused, especially where a lie and malice did the abuse." Out of this difference arose some disputes, which served to enliven the camp, as well as to arouse Abe's ire, and keep him in practice in the way of debate.
In those days Abe, as usual, is described as being "funny, jokey, full of yarns, stories, and rigs;" as being "long, tall, and green," "frequently quoting poetry," and "reciting proselike orations." They had their own amusements. Abe extracted a good deal of fun out of the cooking; took his "dram" when asked to, and played "seven up" at night, at which he made "a good game."
A juggler gave an exhibition at Sangamontown, in the upper room of Jacob Carman's house. Abe went to it, dressed in a suit of rough blue jeans. He had on shoes, but the trousers did not reach them by about twelve inches; and the naked shin, which had excited John Romine's laughter years ago in Indiana, was still exposed. Between the roundabout and the waist of the trousers, there was another wide space uncovered; and, considering these defects, Mr. Lincoln's attire was thought to be somewhat inelegant, even in those times. His hat, however, was a great improvement on coon-skins and opossum. It was woollen, broad-brimmed, and low-crowned. In this hat the "showman cooked eggs." Whilst Abe was handing it up to him, after the man had long solicited a similar favor from the rest of the audience, he remarked, "Mister, the reason I didn't give you my hat before was out of respect to your eggs, not care for my hat."
Loaded with barrel-pork, hogs, and corn, the boat set out from Sangamontown as soon as finished. Mr. Offutt was on board to act as his own merchant, intending to pick up additions to his cargo along the banks of the two Illinois rivers down which he was about to pass. On the 19th of April they arrived at New Salem, a little village destined to be the scene of the seven eventful years of Mr. Lincoln's life, which immediately followed the conclusion of the present trip. Just below New Salem the boat "stuck," for one night and the better part of a day on Rutledge's mill-dam,—one end of it hanging over the dam, and the other sunk deep in the water behind. Here was a case for Abe's ingenuity, and he exercised it with effect. Quantities of water were being taken in at the stern, the lading was sliding backwards, and every thing indicated that the rude craft was in momentary danger of breaking in two, or sinking outright. But Abe suggested some unheard-of expedient for keeping it in place while the cargo was shifted to a borrowed boat, and then, boring a hole in that part of the bottom extending over the dam, he "rigged up" an equally strange piece of machinery for tilting and holding it while the water ran out. All New Salem was assembled on shore, watching the progress of this singular experiment,—and with one voice affirm that Abe saved the boat; although nobody is able to tell us precisely how.1 The adventure turned Abe's thoughts to the class of difficulties, one of which he had just surmounted; and the result of his reflections was "an improved method for lifting vessels over shoals."2 Offutt declared that when he got back from New Orleans, he would build a steamboat for the navigation of the Sangamon, and make Abe the captain; he would build it with runners for ice, and rollers for shoals and dams, for with "Abe in command, by thunder, she'd have to go."
1 Many persons at New Salem describe in full Abe's conduct on this occasion. 2 "Occupying an ordinary and commonplace position in one of the show-cases in the targe hall of the Patent Office, is one little model which, in ages to come, will be prized as at once one of the most curious and one of the most sacred relics in that vast museum of unique and priceless things. This is a plain and simple model of a steamboat, roughly fashioned in wood, by the hand of Abraham Lincoln. It bears date in 1849, when the inventor was known simply as a successful lawyer and rising politician of Central Illinois. Neither his practice nor his politics took up so much of his time as to prevent him from giving much attention to contrivances which he hoped might be of benefit to the world, and of profit to himself. "The design of this invention is suggestive of one phase of Abraham Lincoln's early life, when he went up and down the Mississippi as a flat-boatman, and became familiar with some of the dangers and inconveniences attending the navigation of the Western rivers. It is an attempt to make it an easy matter to transport vessels over shoals and snags, and sawyers. The main idea is that of an apparatus resembling a noiseless bellows, placed on each side of the hull of the craft, just below the water-line, and worked by an odd but not complicated system of ropes, valves, and pulleys. When the keel of the vessel grates against the sand or obstruction, these bellows are to be filled with air; and, thus buoyed up, the ship is expected to float lightly and gayly over the shoal, which would otherwise have proved a serious interruption to her voyage. "The model, which is about eighteen or twenty inches long, and has the air of having been whittled with a knife out of a shingle and a cigar-box, is built without any elaboration or ornament, or any extra apparatus beyond that necessary to show the operation of buoying the steamer over the obstructions. Herein it differs from very many of the models which share with it the shelter of the immense halls of the Patent Office, and which are fashioned with wonderful nicety and exquisite finish, as if much of the labor and thought and affection of a lifetime had been devoted to their construction. This is a model of a different kind; carved as one might imagine a retired rail-splitter would whittle, strongly, but not smoothly, and evidently made with a view solely to convey, by the simplest possible means, to the minds of the patent authorities, an idea of the purpose and plan of the simple invention. The label on the steamer's deck informs us that the patent was obtained; but we do not learn that the navigation of the Western rivers was revolutionized by this quaint conception. The modest little model has reposed here sixteen years; and, since it found its resting-place here on the shelf, the shrewd inventor has found it his task to guide the Ship of State over shoals more perilous, and obstructions more obstinate, than any prophet dreamed of when Abraham Lincoln wrote his bold autograph on the prow of this miniature steamer."— Correspondent Boston Advertiser.
Over the dam, and in the deep pool beyond, they reloaded, and floated down to Blue Bank, a mile above the mouth of Salt Creek, where Offutt bought some more hogs. But the hogs were wild, and refused to be driven. Abe again came to the rescue; and, by his advice, their eyes were sewed up with a needle and thread, so that, if the animals fought any more, they should do it in the dark. Abe held their heads, and John Hanks their tails, while Offutt did the surgery. They were then thrown into a cart, whence Abe took them, one by one, in his great arms, and deposited them on board.
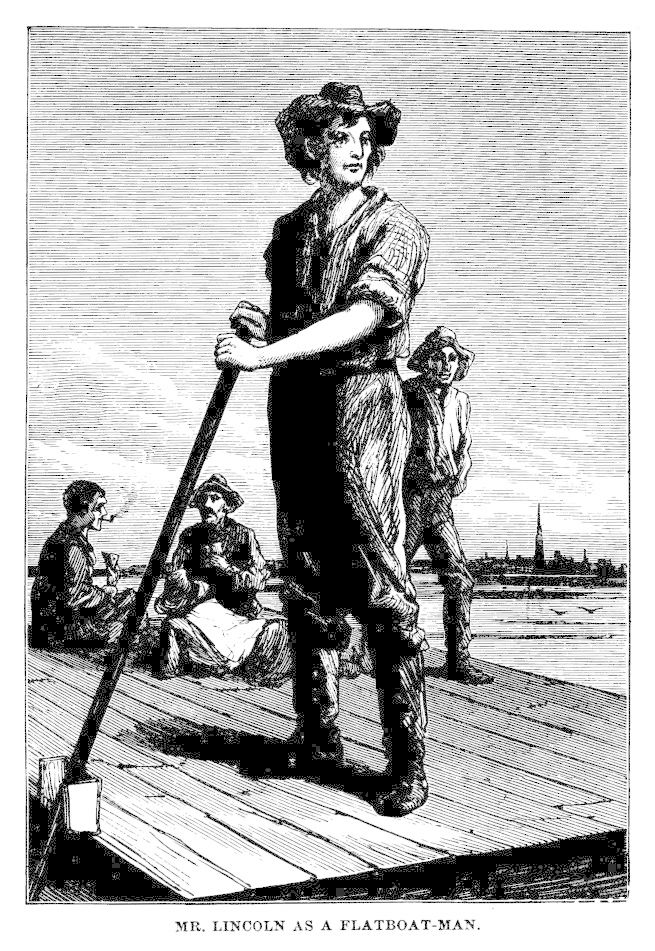

From this point they sped very rapidly down the Sangamon and the Illinois. Having constructed curious-looking sails of plank, "and sometimes cloth," they were a "sight to see," as they "rushed through Beardstown," where "the people came out and laughed at them." They swept by Alton and Cairo, and other considerable places, without tying up, but stopped at Memphis, Vicksburg, and Natchez.
In due time they arrived at New Orleans. "There it was," says John Hanks, "we saw negroes chained, maltreated, whipped, and scourged. Lincoln saw it; his heart bled, said nothing much, was silent from feeling, was sad, looked bad, felt bad, was thoughtful and abstracted. I can say, knowing it, that it was on this trip that he formed his opinions of slavery. It run its iron in him then and there,—May, 1831. I have heard him say so often and often."
Some time in June the party took passage on a steamboat going up the river, and remained together until they reached St. Louis, where Offutt left them, and Abe, Hanks, and Johnston started on foot for the interior of Illinois. At Edwardsville, twenty-five miles out, Hanks took the road to Springfield, and Abe and Johnston took that to Coles County, where Tom Lincoln had moved since Abraham's departure from home.
Abe never worked again in company with his friend and relative, good old John Hanks. Here their paths separated: Abe's began to ascend the heights, while John's continued along the common level. They were in the Black Hawk War during the same campaign, but not in the same division. But they corresponded, and, from 1833, met at least once a year, until Abe was elected President. Then Abe, delighting to honor those of his relatives who were worthy of it, invited John to go with him to see his step-mother. John also went to the inauguration at Washington, and tells, with pardonable pride, how he "was in his [Abe's] rooms several times." He then retired to his old home in Macon County, until the assassination and the great funeral, when he came to Springfield to look in the blackened face of his old friend, and witness the last ceremonies of his splendid burial.
Scarcely had Abe reached Coles County, and begun to think what next to turn his hand to, when he received a visit from a famous wrestler, one Daniel Needham, who regarded him as a growing rival, and had a fancy to try him a fall or two. He considered himself "the best man" in the country, and the report of Abe's achievements filled his big breast with envious pains. His greeting was friendly and hearty, but his challenge was rough and peremptory. Abe valued his popularity among "the boys" too highly to decline it, and met him by public appointment in the "greenwood," at Wabash Point, where he threw him twice with so much ease that Needham's pride was more hurt than his body. "Lincoln," said he, "you have thrown me twice, but you can't whip me."—"Needham," replied Abe, "are you satisfied that I can throw you? If you are not, and must be convinced through a threshing, I will do that, too, for your sake." Needham had hoped that the youngster would shrink from the extremity of a fight with the acknowledged "bully of the patch;" but finding him willing, and at the same time magnanimously inclined to whip him solely for his own good, he concluded that a bloody nose and a black eye would be the reverse of soothing to his feelings, and therefore surrendered the field with such grace as he could command.
ON the west bank of the Sangamon River, twenty miles north-west of Springfield, a traveller on his way to Havana will ascend a bluff one hundred feet higher than the low-water mark of the stream. On the summit he Will find a solitary log-hut. The back-bone of the ridge is about two hundred and fifty feet broad where it overlooks the river; but it widens gradually as it extends westerly toward the remains of an old forest, until it terminates in a broad expanse of meadow. On either side of this hill, and skirting its feet north and south, run streams of water in very deep channels, and tumble into the Sangamon almost within hearing. The hill, or more properly the bluff, rises from the river in an almost perpendicular ascent. "There is an old mill at the foot of the bluff, driven by water-power. The river washes the base of the bluff for about four hundred yards, the hill breaking off almost abruptly at the north. The river along this line runs about due north: it strikes the bluff coming around a sudden bend from the south-east, the river being checked and turned by the rocky hill. The mill-dam running across the Sangamon River just at the mill checks the rapidity of the water. It was here, and on this dam, that Mr. Lincoln's flatboat 'stuck on the 19th of April, 1831.' The dam is about eight feet high, and two hundred and twenty feet long, and, as the old Sangamon rolls her turbid waters over the dam, plunging them into the whirl and eddy beneath, the roar and hiss of waters, like the low, continuous, distant thunder, can be distinctly heard through the whole village, day and night, week-day and Sunday, spring and fall, or other high-water time. The river, at the base of the bluff, is about two hundred and fifty feet wide, the mill using up thirty feet, leaving the dam only about two hundred and twenty feet long."
In every direction but the West, the country is broken into hills or bluffs, like the one we are attempting to describe, which are washed by the river, and the several streams that empty into it in the immediate vicinity. Looking across the river from bluff to bluff, the distance is about a thousand yards; while here and there, on both banks, are patches of rich alluvial bottom-lands, eight or nine hundred yards in width, enclosed on one side by the hills, and on the other by the river. The uplands of the eastern bank are covered with original forests of immemorial age; and, viewed from "Salem Hill," the eye ranges over a vast expanse of green foliage, the monotony of which is relieved by the alternating swells and depressions of the landscape.
On the ridge of that hill, where the solitary cabin now stands, there was a few years ago a pleasant village. How it vanished like a mist of the morning, to what distant places its inhabitants dispersed, and what became of the dwellings they left behind, shall be questions for the local antiquarian. We have no concern with any part of the history, except that part which began in the summer of 1831 and ended in 1837,—the period during which it had the honor of sheltering a man whose enduring fame contrasts strangely with the evanescence of the village itself.
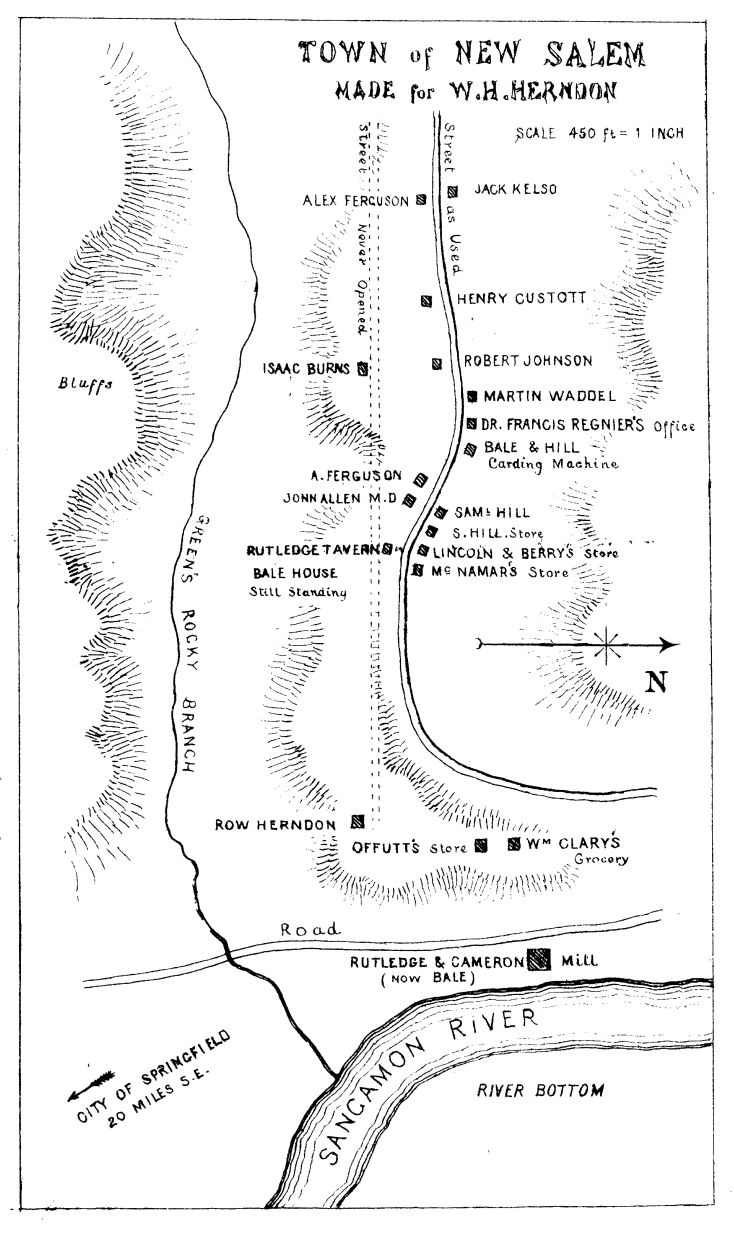
In 1829 James Rutledge and John Cameron built the mill on the Sangamon, and laid off the town on the hill. The place was then called Cameron's Mill; but in process of time, as cabins, stores, and groceries were added, it was dignified by the name of New Salem. "I claim," says one of the gentlemen who established the first store, "to be the explorer and discoverer of New Salem as a business point. Mr. Hill (now dead) and myself purchased some goods at Cincinnati, and shipped them to St. Louis, whence I set out on a voyage of discovery on the prairies of Illinois.... I, however, soon came across a noted character who lives in this vicinity, by the name of Thomas Wadkins, who set forth the beauties and other advantages of Cameron's Mill, as it was then called. I accordingly came home with him, visited the locality, contracted for the erection of a magnificent storehouse for the sum of fifteen dollars; and, after passing a night in the prairie, reached St. Louis in safety. Others soon followed."
In 1836 New Salem contained about twenty houses, inhabited by nearly a hundred people; but in 1831 there could not have been more than two-thirds or three-fourths that number. Many of the houses cost not more than ten dollars, and none of them more than one hundred dollars.
When the news flew through the country that the mill-dam was broken, the people assembled from far and near, and made a grand frolic of mending it. In like manner, when a new settler arrived, and the word passed around that he wanted to put up a house, everybody came in to the "raising;" and, after behaving like the best of good Samaritans to the new neighbor, they drank whiskey, ran foot-races, wrestled, fought, and went home.
"I first knew this hill, or bluff," says Mr. Herndon, in his remarkable lecture on Ann Rutledge, "as early as 1829. I have seen it in spring-time and winter, in summer-time and fall. I have seen it in daylight and night-time; have seen it when the sward was green, living, and vital; and I have seen it wrapped in snow, frost, and sleet. I have closely studied it for more than five long years....
"As I sat on the verge of the town, in presence of its ruins, I called to mind the street running east and west through the village, the river eastward; Green's Rocky Branch, with its hills, southward; Clary's Grove, westerly about three miles; Petersburg northward, and Springfield south-east; and now I cannot exclude from my memory or imagination the forms, faces, voices, and features of those I once knew so well. In my imagination the village perched on the hill is astir with the hum of busy men, and the sharp, quick buzz of women; and from the country come men and women on foot or on horseback, to see and be seen, to hear and to be heard, to barter and exchange what they have with the merchant and the laborer. There are Jack Armstrong and William Green, Kelso and Jason Duncan, Alley and Carman, Hill and McNamar, Herndon and Rutledge, Warburton and Sincho, Bale and Ellis, Abraham and Ann. Oh, what a history!"
In those days, which in the progressive West would be called ancient days, New Salem was in Sangamon County, with Springfield as the county-seat. Springfield itself was still a mere village, having a population of one thousand, or perhaps eleven hundred. The capital of the State was yet at Vandalia, and waited for the parliamentary tact of Abraham Lincoln and the "long nine" to bring it to Springfield. The same influence, which, after long struggles, succeeded in removing the capital, caused the new County of Menard to be erected out of Sangamon in 1839, of which Petersburg was made the county-seat, and within which is included the barren site of New Salem.
In July or August, 1831, Mr. Lincoln made his second appearance at New Salem. He was again in company with Denton Offutt, who had collected some goods at Beardstown, and now proposed to bring them to this place. Mr. Lincoln undoubtedly came there in the service of Offutt, but whilst the goods were being transported from Beardstown he seemed to be idling about without any special object in view. Many persons who saw him then for the first time speak of him as "doing nothing." He has given some encouragement to this idea himself by the manner in which he habitually spoke of his advent there,—describing himself as coming down the river after the winter of the deep snow, like a piece of "floating driftwood" borne along by the freshet, and accidentally lodged at New Salem.
On the day of the election, in the month of August, as Minter Graham, the school-teacher, tells us, Abe was seen loitering about the polling-place. It must have been but a few days after his arrival in the town, for nobody knew that he could write. They were "short of a clerk" at the polls; and, after casting about in vain for some one competent to fill the office, it occurred to one of the judges that perhaps the tall stranger possessed the needful qualifications. He thereupon accosted him, and asked if he could write. He replied, "Yes, a little."—"Will you act as clerk of the election today?" said the judge. "I will try," returned Abe, "and do the best I can, if you so request." He did try accordingly, and, in the language of the schoolmaster, "performed the duties with great facility, much fairness and honesty and impartiality. This was the first public official act of his life. I clerked with him," says Mr. Graham, swelling with his theme, "on the same day and at the same polls. The election-books are now in the city of Springfield, Ill., where they can be seen and inspected any day."
Whilst Abe was "doing nothing," or, in other words, waiting for Offutt's goods, one Dr. Nelson, a resident of New Salem, built a flatboat, and, placing his family and effects upon it, started for Texas. But as the Sangamon was a turbulent and treacherous stream at best, and its banks were now full to overflowing, Nelson needed a pilot, at least as far as Beardstown.
His choice fell upon Abe, who took him to the mouth of the doubtful river in safety, although Abe often declared that he occasionally ran out into the prairie at least three miles from the channel. Arriving at Beardstown, Nelson pushed on down the Illinois, and Abe walked back to New Salem.
The second storekeeper at New Salem was a Mr. George Warburton; but, "the country not having improved his morals in the estimation of his friends," George thought it advisable to transfer his storeroom and the remnant of his stock to Offutt. In the mean time, Offutt's long-expected goods were received from Beardstown. Abe unpacked them, ranged them on the shelves, rolled the barrels and kegs into their places, and, being provided with a brand-new book, pen, and ink, found himself duly installed as "first clerk" of the principal mercantile house in New Salem. A country store is an indescribable collection of miscellanies,—groceries, drygoods, hardware, earthenware, and stoneware, cups and saucers, plates and dishes, coffee and tea, sugar and molasses, boots and shoes, whiskey and lead, butter and eggs, tobacco and gunpowder, with an endless list of things unimaginable except by a housewife or a "merchant." Such was the store to the charge of which Abe was now promoted,—promoted from the rank of a common laborer to be a sort of brevet clerk.
But Offutt's ideas of commerce were very comprehensive; and, as "his business was already considerably scattered about the country," he thought he would scatter a little more. He therefore rented the mill at the foot of the hill, from Cameron and Rutledge, and set Abe to overlooking that as well as the store. This increase of business, however, required another clerk, and in a few days Abe was given a companion in the person of W. G. Green. They slept together on the same cot in the store; and as Mr. Green observes, by way of indicating the great intimacy that subsisted between them, "when one turned over, the other had to do so likewise." To complete his domestic arrangements, Abe followed the example of Mr. Offutt, and took boarding at John Cameron's, one of the owners of the mill.
Mr. Offutt is variously, though not differently, described as a "wild, harum-scarum, reckless fellow;" a "gusty, windy, brain-rattling man;" a "noisy, unsteady, fussy, rattlebrained man, wild and improvident." If anybody can imagine the character indicated by these terms, he can imagine Mr. Offutt,—Abe's employer, friend, and patron. Since the trip on the flatboat, his admiration for Abe had grown to be boundless. He now declared that "Abe knew more than any man in the United States;" that "he would some day be President of the United States," and that he could, at that present moment, outrun, whip, or throw down any man in Sangamon County. These loud boasts were not wasted on the desert air: they were bad seed sown in a rank soil, and speedily raised up a crop of sharp thorns for both Abe and Offutt. At New Salem, honors such as Offutt accorded to Abe were to be won before they were worn.
Bill Clary made light of Offutt's opinion respecting Abe's prowess; and one day, when the dispute between them had been running high in the store, it ended by a bet of ten dollars on the part of Clary that Jack Armstrong was "a better man." Now, "Jack was a powerful twister," "square built, and strong as an ox." He had, besides, a great backing; for he was the chief of the "Clary's Grove boys," and the Clary's Grove boys were the terror of the countryside. Although there never was under the sun a more generous parcel of ruffians than those over whom Jack held sway, a stranger's introduction was likely to be the most unpleasant part of his acquaintance with them. In fact, one of the objects of their association was to "initiate or naturalize new-comers," as they termed the amiable proceedings which they took by way of welcoming any one ambitious of admittance to the society of New Salem. They first bantered the gentleman to run a foot-race, jump, pitch the mall, or wrestle; and, if none of these propositions seemed agreeable to him, they would request to know what he would do in case another gentleman should pull his nose, or squirt tobacco-juice in his face. If he did not seem entirely decided in his views as to what should properly be done in such a contingency, perhaps he would be nailed in a hogshead, and rolled down New-Salem hill; perhaps his ideas would be brightened by a brief ducking in the Sangamon; or perhaps he would be scoffed, kicked, and cuffed by a great number of persons in concert, until he reached the confines of the village, and then turned adrift as being unfit company for the people of that settlement. If, however, the stranger consented to engage in a tussle with one of his persecutors, it was usually arranged that there should be "foul play," with nameless impositions and insults, which would inevitably change the affair into a fight; and then, if the subject of all these practices proved indeed to be a man of mettle, he would be promptly received into "good society," and in all probability would never have better friends on earth than the roystering fellows who had contrived his torments.
Thus far Abe had managed to escape "initiation" at the hands of Jack and his associates. They were disposed to like him, and to take him on faith, or at least to require no further evidence of his manhood than that which rumor had already brought them. Offutt, with his busy tongue, had spread wide the report of his wondrous doings on the river; and, better still, all New Salem, including many of the "Clary's Grove boys," had witnessed his extraordinary feats of strength and ingenuity at Rutledge's mill-dam. It was clear that no particular person was "spoiling" for a collision with him; and an exception to the rule might have been made in his favor, but for the offensive zeal and confidence of his employer.
The example of Offutt and Clary was followed by all the "boys;" and money, knives, whiskey, and all manner of things, were staked on the result of the wrestle. The little community was excited throughout, and Jack's partisans were present in great numbers; while Offutt and Bill Green were about the only persons upon whom Abe could rely if the contest should take the usual turn, and end in a fight. For these, and many other reasons, he longed to be safely and honorably out of the scrape; but Offutt's folly had made it impossible for him to evade the conflict without incurring the imputation, and suffering the penalties, of cowardice. He said, "I never tussle and scuffle, and I will not: I don't like this wooling and pulling." But these scruples only served to aggravate his case; and he was at last forced to take hold of Jack, which he did with a will and power that amazed the fellows who had at last baited him to the point of indignation. They took "side holds," and stood struggling, each with tremendous but equal strength, for several minutes, without any perceptible advantage to either. New trips or unexpected twists were of no avail between two such experienced wrestlers as these. Presently Abe profited by his height and the length of his arms to lift Jack clear off the ground, and, swinging him about, thought to land him on his back; but this feat was as futile as the rest, and left Jack standing as square and as firm as ever. "Now, Jack," said Abe, "let's quit: you can't throw me, and I can't throw you." But Jack's partisans, regarding this overture as a signal of the enemy's distress, and being covetous of jack-knives, whiskey, and "smooth quarters," cheered him on to greater exertions. Rendered desperate by these expectations of his friends, and now enraged at meeting more than his match, Jack resolved on "a foul," and, breaking holds, he essayed the unfair and disreputable expedient of "legging." But at this Abe's prudence deserted him, and righteous wrath rose to the ascendent. The astonished spectators saw him take their great bully by the throat, and, holding him out at arm's-length, shake him like a child. Then a score or two of the boys cried "Fight!" Bill Clary claimed the stakes, and Offutt, in the fright and confusion, was about to yield them; but "Lincoln said they had not won the money, and they should not have it; and, although he was opposed to fighting, if nothing else would do them, he would fight Armstrong, Clary, or any of the set." Just at this juncture James Rutledge, the original proprietor of New Salem, and a man of some authority, "rushed into the crowd," and exerted himself to maintain the peace. He succeeded; but for a few moments a general fight was impending, and Abe was seen with his back against Offutt's store "undismayed" and "resolute," although surrounded by enemies.1
1 Of the fight and what followed, we have the particulars from many persons who were witnesses.
Jack Armstrong was no bad fellow, after all. A sort of Western John Browdie, stout and rough, but great-hearted, honest, and true: his big hand, his cabin, his table, and his purse were all at the disposal of a friend in need. He possessed a rude sense of justice, and felt an incredible respect for a man who would stand single-handed, stanch, and defiant, in the midst of persecutors and foes. He had never disliked Abe, and had, in fact, looked for very clever things from him, even before his title to respectability had been made so incontestably clear; but his exhibition of pluck and muscle on this occasion excited Jack to a degree of admiration far beyond his power to conceal it. Abe's hand was hardly removed from his throat, when he was ready to grasp it in friendship, and swear brotherhood and peace between them. He declared him, on the spot, "the best fellow that ever broke into their settlement;" and henceforth the empire was divided, and Jack and Abe reigned like two friendly Cæsars over the roughs and bullies of New Salem. If there were ever any dissensions between them, it was because Jack, in the abundance of his animal spirits, was sometimes inclined to be an oppressor, whilst Abe was ever merciful and kind; because Jack would occasionally incite the "boys" to handle a stranger, a witless braggart, or a poor drunkard with a harshness that shocked the just and humane temper of his friend, who was always found on the side of the weak and the unfortunate. On the whole, however, the harmony that subsisted between them was wonderful. Wherever Lincoln worked, Jack "did his loafing;" and, when Lincoln was out of work, he spent days and weeks together at Jack's cabin, where Jack's jolly wife, "old Hannah," stuffed him with bread and honey, laughed at his ugliness, and loved him for his goodness.
Abe rapidly grew in favor with the people in and around New Salem, until nearly everybody thought quite as much of him as Mr. Offutt did. He was decidedly the most popular man that ever lived there. He could do more to quell a riot, compromise a feud; and keep peace among the neighbors generally, than any one else; and these were of the class of duties which it appears to have been the most agreeable for him to perform. One day a strange man came into the settlement, and was straightway beset by the same fellows who had meditated a drubbing for Abe himself. Jack Armstrong, of course, "had a difficulty with him;" "called him a liar, coward," and various other names not proper for print; but the man, finding himself taken at a disadvantage, "backed up to a woodpile," got a stick, and "struck Jack a blow that brought him to the ground." Being "as strong as two men, Jack wanted to whip the man badly," but Abe interfered, and, managing to have himself made "arbitrator," compromised the difficulty by a practical application of the golden rule. "Well, Jack," said he, "what did you say to the man?" Whereupon Jack repeated his words. "Well, Jack," replied Abe, "if you were a stranger in a strange place, as this man is, and you were called a d—d liar, &c., what would you do?"—"Whip him, by God!"—"Then this man has done no more to you than you would have done to him."—"Well, Abe," said the honest bruiser, "it's all right," and, taking his opponent by the hand, forgave him heartily, and "treated." Jack always treated his victim when he thought he had been too hard upon him.
Abe's duties in Offutt's store were not of a character to monopolize the whole of his time,1 and he soon began to think that here was a fine opportunity to remedy some of the defects in his education.
1 "During the time he was working for Offutt, and hands being scarce, Lincoln turned In and cut down trees, and split enough rails for Offutt to make a pen sufficiently large to contain a thousand hogs. The pen was built under New Salem hill, close to the mill.... I know where those rails are now; are sound to-day."—Minter Graham
He could read, write, and cipher as well as most men; but as his popularity was growing daily, and his ambition keeping pace, he feared that he might shortly be called to act in some public capacity which would require him to speak his own language with some regard to the rules of the grammar,—of which, according to his own confession, he knew nothing at all. He carried his troubles to the schoolmaster, saying, "I have a notion to study English grammar."—"If you expect to go before the public in any capacity," replied Mr. Graham, "I think it the best thing you can do."—"If I had a grammar," replied Abe, "I would commence now." There was no grammar to be had about New Salem; but the schoolmaster, having kept the run of that species of property, gladdened Abe's heart by telling him that he knew where there was one. Abe rose from the breakfast at which he was sitting, and learning that the book was at Vaner's, only six miles distant, set off after it as hard as he could tramp. It seemed to Mr. Graham a very little while until he returned and announced, with great pleasure, that he had it. "He then turned his immediate and most undivided attention" to the study of it. Sometimes, when business was not particularly brisk, he would lie under a shade-tree in front of the store, and pore over the book; at other times a customer would find him stretched on the counter intently engaged in the same way. But the store was a bad place for study; and he was often seen quietly slipping out of the village, as if he wished to avoid observation, when, if successful in getting off alone, he would spend hours in the woods, "mastering a book," or in a state of profound abstraction. He kept up his old habit of sitting up late at night; but, as lights were as necessary to his purpose as they were expensive, the village cooper permitted him to sit in his shop, where he burnt the shavings, and kept a blazing fire to read by, when every one else was in bed. The Greens lent him books; the schoolmaster gave him instructions in the store, on the road, or in the meadows: every visitor to New Salem who made the least pretension to scholarship was waylaid by Abe, and required to explain something which he could not understand. The result of it all was, that the village and the surrounding country wondered at his growth in knowledge, and he soon became as famous for the goodness of his understanding as for the muscular power of his body, and the unfailing humor of his talk.
Early in the spring of 1832, some enterprising gentlemen at Springfield determined to try whether the Sangamon was a navigable stream or not. It was a momentous question to the dwellers along the banks; and, when the steamboat "Talisman" was chartered to make the experiment, the popular excitement was intense, and her passage up and down was witnessed by great concourses of people on either bank. It was thought that Abe's experience on this particular river would render his assistance very valuable; and, in company with some others, he was sent down to Beardstown, to meet the "Talisman," and pilot her up. With Abe at the helm, she ran with comparative ease and safety as far as the New-Salem dam, a part of which they were compelled to tear away in order to let the steamer through. Thence she went on as high as Bogue's mill; but, having reached that point, the rapidly-falling water admonished her captain and pilots, that, unless they wished her to be left there for the season, they must promptly turn her prow down stream. For some time, on the return trip, she made not more than three or four miles a day, "on account of the high wind from the prairie." "I was sent for, being an old boatman," says J. R. Herndon, "and I met her some twelve or thirteen miles above New Salem.... We got to Salem the second day after I went on board. When we struck the dam, she hung. We then backed off, and threw the anchor over the dam, and tore away a part of the dam, and, raising steam, ran her over the first trial. As soon as she was over, the company that chartered her was done with her. I think the captain gave Mr. Lincoln forty dollars to run her down to Beardstown. I am sure I got forty dollars to continue on her until we landed at Beardstown. We that went down with her walked back to New Salem."
IN the spring of 1832, Mr. Offutt's business had gone to ruin: the store was sold out, the mill was handed over to its owners, Mr. Offutt himself departed for parts unknown, and his "head clerk" was again out of work. Just about that time a governor's proclamation arrived, calling for volunteers to meet the famous chief Black Hawk and his warriors, who were preparing for a grand, and, in all likelihood, a bloody foray, into their old hunting-grounds in the Rock-river country.
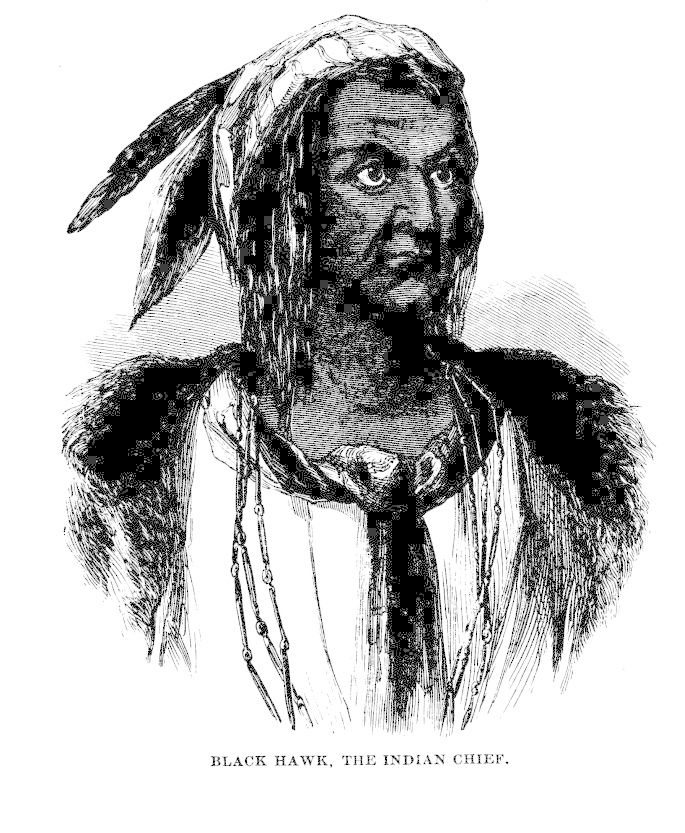

Black Hawk was a large Indian, of powerful frame and commanding presence. He was a soldier and a statesman. The history of his diplomacy with the tribes he sought to confederate shows that he expected to realize on a smaller scale the splendid plans of Pontiac and Tecumseh. In his own tongue he was eloquent, and dreamed dreams which, amongst the Indians, passed for prophecy. The prophet is an indispensable personage in any comprehensive scheme of Indian politics, and no chief has ever effected a combination of formidable strength without his aid. In the person of Black Hawk, the chief and the prophet were one. His power in both capacities was bent toward a single end,—the great purpose of his life,—the recovery of his birthplace and the ancient home of his people from the possession of the stranger.
Black Hawk was born on the Rock River in Wisconsin, in the year 1767. His grandfather lived near Montreal, whence his father Pyesa had emigrated, but not until he had become thoroughly British in his views and feelings. All his life long he made annual journeys to the councils of the tribes at Malden, where the gifts and persuasions of British agents confirmed him in his inclination to the British interests. When Pyesa was gathered to his fathers, his son took his place as the chief of the Sacs, hated the Americans, loved the friendly English, and went yearly to Malden, precisely as he thought Pyesa would have had him do. But Black Hawk's mind was infinitely superior to Pyesa's: his sentiments were loftier, his heart more susceptible; he had the gift of the seer, the power of the orator, with the high courage and the profound policy of a born warrior and a natural ruler. He "had brooded over the early history of his tribe; and to his views, as he looked down the vista of years, the former times seemed so much better than the present, that the vision wrought upon his susceptible imagination, which pictured it to be the Indian golden age. He had some remembrance of a treaty made by Gen. Harrison in 1804, to which his people had given their assent; and his feelings were with difficulty controlled, when he was required to leave the Rock-river Valley, in compliance with a treaty made with Gen. Scott. That valley, however, he peacefully abandoned with his tribe, on being notified, and went to the west of the Mississippi; but he had spent his youth in that locality, and the more he thought of it, the more determined he was to return thither. He readily enlisted the sympathies of the Indians, who are ever prone to ponder on their real or imaginary wrongs; and it may be readily conjectured that what Indian counsel could not accomplish, Indian prophecy would."1 He had moved when summoned to move, because he was then unprepared to fight; but he utterly denied that the chiefs who seemed to have ceded the lands long years before had any right to cede them, or that the tribe had ever willingly given up the country to the stranger and the aggressor. It was a fraud upon the simple Indians: the old treaty was a great lie, and the signatures it purported to have, made with marks and primitive devices, were not attached in good faith, and were not the names of honest Sacs. No: he would go over the river, he would have his own; the voice of the Great Spirit was in the air wherever he went; it was in his lodge through all the night-time, and it said "Go;" and Black Hawk must needs rise up and tell the people what the voice said.
1 Schoolcraft's History of the Indian Tribes.
It was by such arguments as these that Black Hawk easily persuaded the Sacs. But hostilities by the Sacs alone would be a hopeless adventure. He must find allies. He looked first to their kindred, the Foxes, who had precisely the same cause of war with the Sacs, and after them to the Winnebagoes, Sioux, Kickapoos, and many others. That Black Hawk was a wise and valiant leader, all the Indians conceded; and his proposals were heard by some of the tribes with eagerness, and by all of them with respect. At one time his confederacy embraced nine tribes,—the most formidable in the North-west, if we exclude the Sioux and the Chippewas, who were themselves inclined to accede. Early in 1831, the first chief of the Chippewas exhibited a miniature tomahawk, red with vermilion, which, having been accepted from Black Hawk, signified an alliance between them; and away up at Leech. Lake, an obscure but numerous band showed some whites a few British medals painted in imitation of blood, which meant that they were to follow the war-paths of Black Hawk.
In 1831 Black Hawk had crossed the river in small force, but had retired before the advance of Gen. Gaines, commanding the United States post at Rock Island. He then promised to remain on the other side, and to keep quiet for the future. But early in the spring of 1832 he re-appeared with greater numbers, pushed straight into the Rock-river Valley, and said he had "come to plant corn." He was now sixty-seven years of age: he thought his great plots were all ripe, and his allies fast and true. They would fight a few bloody battles, and then he would sit down in his old age and see the corn grow where he had seen it in his youth. But the old chief reckoned too much upon Indian fidelity: he committed the fatal error of trusting to their patriotism instead of their interests. Gen. Atkinson, now in command at Rock Island, set the troops in motion: the governor issued his call for volunteers; and, as the Indians by this time had committed some frightful barbarities, the blood of the settlers was boiling, and the regiments were almost instantly filled with the best possible material. So soon as these facts became known, the allies of Black Hawk, both the secret and the open, fell away from him, and left him, with the Sacs and the Foxes, to meet his fate.
In the mean time Lincoln had enlisted in a company from Sangamon. He had not been out in the campaign of the previous year, but told his friend Row Herndon, that, if he had not been down the river with Offutt, he would certainly have been with the boys in the field. But, notwithstanding his want of military experience, his popularity was so great, that he had been elected captain of a militia company on the occasion of a muster at Clary's Grove the fall before. He was absent at the time, but thankfully accepted and served. Very much to his surprise, his friends put him up for the captaincy of this company about to enter active service. They did not organize at home, however, but marched first to Beardstown, and then to Rushville in Schuyler County, where the election took place. Bill Kirkpatrick was a candidate against Lincoln, but made a very sorry showing. It has been said that Lincoln once worked for Kirkpatrick as a common laborer, and suffered some indignities at his hands; but the story as a whole is supported by no credible testimony. It is certain, however, that the planks for the boat built by Abe and his friends at the mouth of Spring Creek were sawed at the mill of a Mr. Kirkpatrick. It was then, likely enough, that Abe fell in the way of this man, and learned to dislike him. At all events, when he had distanced Kirkpatrick, and was chosen his captain by the suffrages of men who had been intimate with Kirkpatrick long before they had ever heard of Abe, he spoke of him spitefully, and referred in no gentle terms to some old dispute. "Damn him," said he to Green, "I've beat him: he used me badly in our settlement for my toil."
Capt. Lincoln now made a very modest speech to his comrades, reciting the exceeding gratification their partiality afforded him, how undeserved he thought it, and how wholly unexpected it was. In conclusion, "he promised very plainly that he would do the best he could to prove himself worthy of that confidence."
The troops rendezvoused at Beardstown and Rushville were formed into four regiments and a spy battalion. Capt. Lincoln's company was attached to the regiment of Col. Samuel Thompson. The whole force was placed under the command of Gen. Whiteside, who was accompanied throughout the campaign by the governor in person.
On the 27th of April, the army marched toward the mouth of Rock River, by way of Oquaka on the Mississippi. The route was one of difficulty and danger, a great part of it lying through a country largely occupied by the enemy. The men were raw, and restive under discipline. In the beginning they had no more respect for the "rules and regulations" than for Solomon's Proverbs, or the Westminster Confession. Capt. Lincoln's company is said to have been a particularly "hard set of men," who recognized no power but his. They were fighting men, and but for his personal authority would have kept the camp in a perpetual uproar.
At the crossing of Henderson River,—a stream about fifty yards wide, and eight or ten feet deep, with very precipitous banks,—they were compelled to make a bridge or causeway with timbers cut by the troops, and a filling-in of bushes, earth, or any other available material. This was the work of a day and night. Upon its completion, the horses and oxen were taken from the wagons, and the latter taken over by hand. But, when the horses came to cross, many of them were killed in sliding down the steep banks. "While in camp here," says a private in Capt. Lincoln's company, "a general order was issued prohibiting the discharge of fire-arms within fifty steps of the camp. Capt. Lincoln disobeyed the order by firing his pistol within ten steps of the camp, and for this violation of orders was put under arrest for that day, and his sword taken from him; but the next day his sword was restored, and nothing more was done in the matter."
From Henderson River the troops marched to Yellow Banks, on the Mississippi. "While at this place," Mr. Ben F. Irwin says, "a considerable body of Indians of the Cherokee tribe came across the river from the Iowa side, with the white flag hoisted. These were the first Indians we saw. They were very friendly, and gave us a general war-dance. We, in return, gave them a Sucker ho-down. All enjoyed the sport, and it is safe to say no man enjoyed it more than Capt. Lincoln."
From Yellow Banks, a rapid and exhaustive march of a few days brought the volunteers to the mouth of Rock River, where "it was agreed between Gen. Whiteside and Gen. Atkinson of the regulars, that the volunteers should march up Rock River, about fifty miles, to the Prophet's Town, and there encamp, to feed and rest their horses, and await the arrival of the regular troops, in keel-boats, with provisions. Judge William Thomas, who again acted as quartermaster to the volunteers, made an estimate of the amount of provisions required until the boats could arrive, which was supplied; and then Gen. Whiteside took up his line of march." 1 But Capt. Lincoln's company did not march on the present occasion with the alacrity which distinguished their comrades of other corps. The orderly sergeant attempted to "form company," but the company declined to be formed; the men, oblivious of wars and rumors of wars, mocked at the word of command, and remained between their blankets in a state of serene repose. For an explanation of these signs of passive mutiny, we must resort again to the manuscript of the private who gave the story of Capt. Lincoln's first arrest. "About the—of April, we reached the mouth of Rock River. About three or four nights afterwards, a man named Rial P. Green, commonly called 'Pot Green,' belonging to a Green-county company, came to oar company, and waked up the men, and proposed to them, that, if they would furnish him with a tomahawk and four buckets, he would get into the officers' liquors, and supply the men with wines and brandies. The desired articles were furnished him; and, with the assistance of one of our company, he procured the liquors. All this was entirely unknown to Capt. Lincoln. In the morning. Capt. Lincoln ordered his orderly to form company for parade; but when the orderly called the men to 'parade,' they called 'parade,' too, but couldn't fall into line. The most of the men were unmistakably drunk. The rest of the forces marched off, and left Capt. Lincoln's company behind. The company didn't make a start until about ten o'clock, and then, after marching about two miles, the drunken ones lay down and slept their drunk off. They overtook the forces that night. Capt. Lincoln was again put under arrest, and was obliged to carry a wooden sword for two days, and this although Capt. Lincoln was entirely blameless in the matter."
1 Ford's History of Illinois, chap. iv.
When Gen. Whiteside reached Prophetstown, where he was to rest until the arrival of the regulars and the supplies, he disregarded the plan of operations concerted between him and Atkinson, and, burning the village to the ground, pushed on towards Dixon's Ferry, forty miles farther up the river. Nearing that place, he left his baggage-wagons behind: the men threw away their allotments of provisions, or left them with the wagons; and in that condition a forced march was made to Dixon. There Whiteside found two battalions of mounted men under Majors Stillman and Bailey, who clamored to be thrown forward, where they might get up an independent but glorious "brush" with the enemy on comparatively private account. The general had it not in his heart to deny these adventurous spirits, and they were promptly advanced to feel and disclose the Indian force supposed to be near at hand. Stillman accordingly moved up the bank of "Old Man's Creek" (since called "Stillman's Run"), to a point about twenty miles from Dixon, where, just before nightfall, he went into camp, or was about to do so, when several Indians were seen hovering along some raised ground nearly a mile distant. Straightway Stillman's gallant fellows remounted, one by one, or two and two, and, without officers or orders, galloped away in pursuit. The Indians first shook a red flag, and then dashed off at the top of their speed. Three of them were overtaken and killed: but the rest performed with perfect skill the errand upon which they were sent; they led Stillman's command into an ambuscade, where lay Black Hawk himself with seven hundred of his warriors. The pursuers recoiled, and rode for their lives: Black Hawk bore down upon Stillman's camp; the fugitives, streaming back with fearful cries respecting the numbers and ferocity of the enemy, spread consternation through the entire force. Stillman gave a hasty order to fall back; and the men fell back much faster and farther than he intended, for they never faced about, or so much as stopped, until they reached Whiteside's camp at Dixon. The first of them reached Dixon about twelve o'clock; and others came straggling in all night long and part of the next day, each party announcing themselves as the sole survivors of that stricken field, escaped solely by the exercise of miraculous valor.1
1 "It is said that a big, tall Kentuckian, with a very loud voice, who was a colonel of the militia, but a private with Stillman, upon his arrival in camp, gave to Gen. Whiteside and the wondering multitude the following glowing and bombastic account of the battle. 'Sirs,' said he, 'our detachment was encamped amongst some scattering timber on the north side of Old Man's Creek, with the prairie from the north gently sloping down to our encampment. It was just after twilight, in the gloaming of the evening, when we discovered Black Hawk's army coming down upon us in solid column: they displayed in the form of a crescent upon the brow of the prairie, and such accuracy and precision of military movements were never witnessed by man; they were equal to the best troops of Wellington in Spain. I have said that the Indians came down in solid column, and displayed in the form of a crescent; and, what was most wonderful, there were large squares of cavalry resting upon the points of the curve, which squares were supported again by other columns fifteen deep, extending back through the woods, and over a swamp three-quarters of a mile, which again rested upon the main body of Black Hawk's army bivouacked upon the banks of the Kishwakee. It was a terrible and a glorious sight to see the tawny warriors as they rode along our flanks attempting to outflank us with the glittering moonbeams glistening from their polished blades and burnished spears. It was a sight well calculated to strike consternation into the stoutest and boldest heart; and accordingly our men soon began to break in small squads for tall timber. In a very little time the rout became general. The Indians were on our flanks, and threatened the destruction of the entire detachment. About this time Major Stillman, Col. Stephenson, Major Perkins, Capt. Adams, Mr. Hackelton, and myself, with some others, threw ourselves into the rear to rally the fugitives and protect the retreat. But in A short time all my companions fell, bravely fighting hand to hand with the savage enemy, and I alone was left upon the field of battle. About this time I discovered not far to the left, a corps of horsemen which seemed to be in tolerable order. I immediately deployed to the left, when, leaning down and placing my body in a recumbent posture upon the mane of my horse, so as to bring the heads of the horsemen between my eye and the horizon, I discovered by the light of the moon that they were gentlemen who did not wear hats, by which token I knew they were no friends of mine. I therefore made a retrograde movement, and recovered my former position, where I remained some time, meditating what further I could do in the service of my country, when a random ball came whistling by my ear, and plainly whispered to me, "Stranger, you have no further business here." Upon hearing this, I followed the example of my companions in arms, and broke for tall timber, and the way I run was not a little, and quit.' "This colonel was a lawyer just returning from the circuit, with a slight wardrobe and 'Chitty's Pleadings' packed in his saddle-bags, all of which were captured by the Indians. He afterwards related, with much vexation, that Black Hawk had decked himself out in his finery, appearing in the woods amongst his savage companions dressed in one of the colonel's ruffled shirts drawn over his deer-skin leggings, with a volume of 'Chitty's Pleadings' under each arm."— Ford's History of Illinois.
The affair is known to history as "Stillman's Defeat." "Old John Hanks" was in it, and speaks of it with shame and indignation, attributing the disaster to "drunken men, cowardice, and folly," though in this case we should be slow to adopt his opinion. Of folly, there was, no doubt, enough, both on the part of Whiteside and Stillman; but of drunkenness no public account makes any mention, and individual cowardice is never to be imputed to American troops. These men were as brave as any that ever wore a uniform, and some of them performed good service afterwards; but when they went into this action, they were "raw militia,"—a mere mob; and no mob can stand against discipline, even though it be but the discipline of the savage.
The next day Whiteside moved with all possible celerity to the field of Stillman's disaster, and, finding no enemy, was forced to content himself with the melancholy duty of burying the mutilated and unsightly remains of the dead. All of them were scalped; some had their heads cut off, others had their throats cut, and others still were mangled and dishonored in ways too shocking to be told.
The army was now suffering for want of provisions. The folly of the commander in casting off his baggage-train for the forced march on Dixon, the extravagance and improvidence of the men with their scanty rations, had exhausted the resources of the quartermasters, and, "except in the messes of the most careful and experienced," the camp was nearly destitute of food. "The majority had been living on parched corn and coffee for two or three days;" but, on the morning of the last march from Dixon, Quartermaster Thomas had succeeded in getting a little fresh beef from the only white inhabitant of that country, and this the men were glad to eat without bread. "I can truly say I was often hungry," said Capt. Lincoln, reviewing the events of this campaign. He was, doubtless, as destitute and wretched as the rest, but he was patient, quiet, and resolute. Hunger brought with it a discontented and mutinous spirit. The men complained bitterly of all they had been made to endure, and clamored loudly for a general discharge. But Capt. Lincoln kept the "even tenor of his way;" and, when his regiment was disbanded, immediately enlisted as a private soldier in another company.
From the battle-field Whiteside returned to his old camp at Dixon, but determined, before doing so, to make one more attempt to retrieve his ill-fortune. Black Hawk's pirogues were supposed to be lying a few miles distant, in a bend of the Rock River; and the capture of these would serve as some relief to the dreary series of errors and miscarriages which had hitherto marked the campaign. But Black Hawk had just been teaching him strategy in the most effective mode, and the present movement was undertaken with an excess of caution almost as ludicrous as Stillman's bravado. "To provide as well as might be against danger, one man was started at a time in the direction of the point. When he would get a certain distance, keeping in sight, a second would start, and so on, until a string of men extending five miles from the main army was made, each to look out for Indians, and give the sign to right, left, or front, by hanging a hat on a bayonet,—erect for the front, and right or left, as the case might be. To raise men to go ahead was with difficulty done, and some tried hard to drop back; but we got through safe, and found the place deserted, leaving plenty of Indian signs,—a dead dog and several scalps taken in Stillman's defeat, as we supposed them to have been taken." After this, the last of Gen. Whiteside's futile attempts, he returned to the battle-field, and thence to Dixon, where he was joined by Atkinson with the regulars and the long-coveted and much-needed supplies.
One day, during these many marches and countermarches, an old Indian found his way into the camp, weary, hungry, and helpless. He professed to be a friend of the whites; and, although it was an exceedingly perilous experiment for one of his color, he ventured to throw himself upon the mercy of the soldiers. But the men first murmured, and then broke out into fierce cries for his blood. "We have come out to fight the Indians," said they, "and by God we intend to do it!" The poor Indian, now, in the extremity of his distress and peril, did what he ought to have done before: he threw down before his assailants a soiled and crumpled paper, which he implored them to read before his life was taken. It was a letter of character and safe-conduct from Gen. Cass, pronouncing him a faithful man, who had done good service in the cause for which this army was enlisted. But it was too late: the men refused to read it, or thought it a forgery, and were rushing with fury upon the defenceless old savage, when Capt. Lincoln bounded between them and their appointed victim. "Men," said he, and his voice for a moment stilled the agitation around him, "this must not be done: he must not be shot and killed by us."—"But," said some of them, "the Indian is a damned spy." Lincoln knew that his own life was now in only less danger than that of the poor creature that crouched behind him. During the whole of this scene Capt. Lincoln seemed to "rise to an unusual height" of stature. The towering form, the passion and resolution in his face, the physical power and terrible will exhibited in every motion of his body, every gesture of his arm, produced an effect upon the furious mob as unexpected perhaps to him as to any one else. They paused, listened, fell back, and then sullenly obeyed what seemed to be the voice of reason, as well as authority. But there were still some murmurs of disappointed rage, and half-suppressed exclamations, which looked towards vengeance of some kind. At length one of the men, a little bolder than the rest, but evidently feeling that he spoke for the whole, cried out, "This is cowardly on your part, Lincoln!" Whereupon the tall captain's figure stretched a few inches higher again. He looked down upon these varlets who would have murdered a defenceless old Indian, and now quailed before his single hand, with lofty contempt. The oldest of his acquaintances, even Bill Green, who saw him grapple Jack Armstrong and defy the bullies at his back, never saw him so much "aroused" before. "If any man thinks I am a coward, let him test it," said he. "Lincoln," responded a new voice, "you are larger and heavier than we are."—"This you can guard against: choose your weapons," returned the rigid captain. Whatever may be said of Mr. Lincoln's choice of means for the preservation of military discipline, it was certainly very effectual in this case. There was no more disaffection in his camp, and the word "coward" was never coupled with his name again. Mr. Lincoln understood his men better than those who would be disposed to criticise his conduct. He has often declared himself, that his life and character were both at stake, and would probably have been lost, had he not at that supremely critical moment forgotten the officer and asserted the man. To have ordered the offenders under arrest would have created a formidable mutiny; to have tried and punished them would have been impossible. They could scarcely be called soldiers: they were merely armed citizens, with a nominal military organization. They were but recently enlisted, and their term of service was just about to expire. Had he preferred charges against them, and offered to submit their differences to a court of any sort, it would have been regarded as an act of personal pusillanimity, and his efficiency would have been gone forever.
Lincoln was believed to be the strongest man in his regiment, and no doubt was. He was certainly the best wrestler in it, and after they left Beardstown nobody ever disputed the fact. He is said to have "done the wrestling for the company;" and one man insists that he always had a handkerchief tied around his person, in readiness for the sport. For a while it was firmly believed that no man in the army could throw him down. His company confidently pitted him "against the field," and were willing to bet all they had on the result. At length, one Mr. Thompson came forward and accepted the challenge. He was, in fact, the most famous wrestler in the Western country. It is not certain that the report of his achievements had ever reached the ears of Mr. Lincoln or his friends; but at any rate they eagerly made a match with him as a champion not unworthy of their own. Thompson's power and skill, however, were as well known to certain persons in the army as Mr. Lincoln's were to others. Each side was absolutely certain of the victory, and bet according to their faith. Lincoln's company and their sympathizers put up all their portable property, and some perhaps not their own, including "knives, blankets, tomahawks," and all the most necessary articles of a soldier's outfit.
When the men first met, Lincoln was convinced that he could throw Thompson; but, after tussling with him a brief space in presence of the anxious assemblage, he turned to his friends and said, "This is the most powerful man I ever had hold of. He will throw me, and you will lose your all, unless I act on the defensive." He managed, nevertheless, "to hold him off for some time;" but at last Thompson got the "crotch hoist" on him, and, although Lincoln attempted with all his wonderful strength to break the hold by "sliding" away, a few moments decided his fate: he was fairly thrown. As it required two out of three falls to decide the bets, Thompson and he immediately came together again, and with very nearly the same result. Lincoln fell under, but the other man fell too. There was just enough of uncertainty about it to furnish a pretext for a hot dispute and a general fight. Accordingly, Lincoln's men instantly began the proper preliminaries to a fracas. "We were taken by surprise," says Mr. Green, "and, being unwilling to give up our property and lose our bets, got up an excuse as to the result. We declared the fall a kind of dog-fall; did so apparently angrily." The fight was coming on apace, and bade fair to be a big and bloody one, when Lincoln rose up and said, "Boys, the man actually threw me once fair, broadly so; and the second time, this very fall, he threw me fairly, though not so apparently so." He would countenance no disturbance, and his unexpected and somewhat astonishing magnanimity ended all attempts to raise one.
Mr. Lincoln's good friend, Mr. Green, the principal, though not the sole authority for the present account of his adventure in behalf of the Indian and his wrestle with Thompson, mentions one important incident which is found in no other manuscript, and which gives us a glimpse of Mr. Lincoln in a scene of another sort. "One other word in reference to Mr. Lincoln's care for the health, welfare, and justice to his men. Some officers of the United States had claimed that the regular army had a preference in the rations and pay. Mr. Lincoln was ordered to do some act which he deemed unauthorized. He, however, obeyed, but went to the officer and said to him, 'Sir, you forget that we are not under the rules and regulations of the War Department at Washington; are only volunteers under the orders and regulations of Illinois. Keep in your own sphere, and there will be no difficulty; but resistance will hereafter be made to your unjust orders: and, further, my men must be equal in all particulars, in rations, arms, camps, &c., to the regular army. The man saw that Mr. Lincoln was right, and determined to have justice done. Always after this we were treated equally well, and just as the regular army was, in every particular. This brave, just, and humane act in behalf of the volunteers at once attached officers and rank to him, as with hooks of steel."
When the army reached Dixon, the almost universal discontent of the men had grown so manifest and so ominous, that it could no longer be safely disregarded. They longed "for the flesh-pots of Egypt," and fiercely demanded their discharge. Although their time had not expired, it was determined to march them by way of Paw-Paw Grove to Ottawa, and there concede what the governor feared he had no power to withhold.
"While on our march from Dixon to Fox River," says Mr. Irwin, "one night while in camp, which was formed in a square enclosing about forty acres, our horses, outside grazing, got scared about nine o'clock; and a grand stampede took place. They ran right through our lines in spite of us, and ran over many of us. No man knows what noise a thousand horses make running, unless he had been there: it beats a young earthquake, especially among scared men, and certain they were scared then. We expected the Indians to be on us that night. Fire was thrown, drums beat, fifes played, which added additional fright to the horses. We saw no real enemy that night, but a line of battle was formed. There were no eyes for sleep that night: we stood to our posts in line; and what frightened the horses is yet unknown."
"During this short Indian campaign," continues the same gentleman, "we had some hard times,—often hungry; but we had a great deal of sport, especially of nights,—-foot-racing, some horse-racing, jumping, telling anecdotes, in which Lincoln beat all, keeping up a constant laughter and good-humor all the time; among the soldiers some card-playing, and wrestling, in which Lincoln took a prominent part. I think it safe to say he was never thrown in a wrestle. [Mr. Irwin, it seems, still regards the Thompson affair as "a dog-fall."] While in the army, he kept a handkerchief tied around him near all the time for wrestling purposes, and loved the sport as well as any one could. He was seldom ever beat jumping. During the campaign, Lincoln himself was always ready for an emergency. He endured hardships like a good soldier: he never complained, nor did he fear danger. When fighting was expected, or danger apprehended, Lincoln was the first to say, 'Let's go.' He had the confidence of every man of his company, and they strictly obeyed his orders at a word. His company was all young men, and full of sport.
"One night in Warren County, a white hog—a young sow—came into our lines, which showed more good sense, to my mind, than any hog I ever saw. This hog swam creeks and rivers, and went with us clear through to, I think, the mouth of Fox River; and there the boys killed it, or it would doubtless have come home with us. If it got behind in daylight as we were marching, which it did sometimes, it would follow on the track, and come to us at night. It was naturally the cleverest, friendly-disposed hog any man ever saw, and its untimely death was by many of us greatly deplored, for we all liked the hog for its friendly disposition and good manners; for it never molested any thing, and kept in its proper place."
On the 28th of May the volunteers were discharged. The governor had already called for two thousand more men to take their places; but, in the mean time, he made the most strenuous efforts to organize a small force out of the recently discharged, to protect the frontiers until the new levies were ready for service. He succeeded in raising one regiment and a spy company. Many officers of distinction, among them Gen. Whiteside himself, enlisted as private soldiers, and served in that capacity to the end of the war. Capt. Lincoln became Private Lincoln of the "Independent Spy Company," Capt. Early commanding; and, although he was never in an engagement, he saw some hard service in scouting and trailing, as well as in carrying messages and reports.
About the middle of June the new troops were ready for the field, and soon after moved up to Rock River. Meanwhile the Indians had overrun the country. "They had scattered their war-parties all over the North from Chicago to Galena, and from the Illinois River into the Territory of Wisconsin; they occupied every grove, waylaid every road, hung around every settlement, and attacked every party of white men that attempted to penetrate the country." There had been some desultory fighting at various points. Capt. Snyder, in whose company Gen. Whiteside was a private, had met the Indians at Burr Oak. Grove, and had a sharp engagement; Mr. St. Vrain, an Indian agent, with a small party of assistants, had been treacherously murdered near Fort Armstrong; several men had been killed at the lead mines, and the Wisconsin volunteers under Dodge had signally punished the Indians that killed them; Galena had been threatened and Fort Apple, twelve miles from Galena, had sustained a bloody siege of fifteen hours; Capt. Stephenson of Galena had performed an act which "equalled any thing in modern warfare in daring and desperate courage," by driving a party of Indians larger than his own detachment into a dense thicket, and there charging them repeatedly until he was compelled to retire, wounded himself, and leaving three of his men dead on the ground.
Thenceforward the tide was fairly turned against Black Hawk. Twenty-four hundred men, under experienced officers, were now in the field against him; and, although he succeeded in eluding his pursuers for a brief time, every retreat was equivalent to a reverse in battle, and all his manoeuvres were retreats. In the latter part of July he was finally overtaken by the volunteers under Henry, along the bluffs of the Wisconsin River, and defeated in a decisive battle. His ruin was complete: he abandoned all hope of conquest, and pressed in disorderly and disastrous retreat toward the Mississippi, in vain expectation of placing that barrier between him and his enemy.
On the fourth day, after crossing the Wisconsin, Gen. Atkinson's advance reached the high grounds near the Mississippi. Henry and his brigade, having won the previous victory, were placed at the rear in the order of march, with the ungenerous purpose of preventing them from winning another. But Black Hawk here resorted to a stratagem which very nearly saved the remnant of his people, and in the end completely foiled the intentions of Atkinson regarding Henry and his men. The old chief, with the high heart which even such a succession of reverses could not subdue, took twenty warriors and deliberately posted himself, determined to hold the army in check or lead it away on a false trail, while his main body was being transferred to the other bank of the river. He accordingly made his attack in a place where he was favored by trees, logs, and tall grass, which prevented the discovery of his numbers. Finding his advance engaged, Atkinson formed a line of battle, and ordered a charge; but Black Hawk conducted his retreat with such consummate skill that Atkinson believed he was just at the heels of the whole Indian army, and under this impression continued the pursuit far up the river.
When Henry came up to the spot where the fight had taken place, he readily detected the trick by various evidences about the ground. Finding the main trail in the immediate vicinity, he boldly fell upon it without orders, and followed it until he came up with the Indians in a swamp on the margin of the river, where he easily surprised and scattered them. Atkinson, hearing the firing in the swamp, turned back, and arrived just in time to assist in the completion of the massacre. A few of the Indians had already crossed the river: a few had taken refuge on a little willow island in the middle of the stream. The island was charged,—the men wading to it in water up to their arm-pits,—the Indians were dislodged and killed on the spot, or shot in the water while attempting to swim to the western shore. Fifty prisoners only were taken, and the greater part of these were squaws and children. This was the battle of the Bad Axe,—a terrific slaughter, considering the numbers engaged, and the final ruin of Black Hawk's fortunes.
Black Hawk and his twenty warriors, among whom was his own son, made the best of their way to the Dalles on the Wisconsin, where they seem to have awaited passively whatever fate their enemies should contrive for them. There were some Sioux and Winnebagoes in Atkinson's camp,—men who secretly pretended to sympathize with Black Hawk, and, while acting as guides to the army, had really led it astray on many painful and perilous marches. It is certain that Black Hawk had counted on the assistance of those tribes; but after the fight on the Wisconsin, even those who had consented to act as his emissaries about the person of the hostile commander not only deserted him, but volunteered to hunt him down. They now offered to find him, take him, and bring him in, provided that base and cowardly service should be suitably acknowledged. They were duly employed. Black Hawk became their prisoner, and was presented by them to the Indian agent with two or three shameless and disgusting speeches from his captors. He and his son were carried to Washington City, and then through the principal cities of the country, after which President Jackson released him from captivity, and sent him back to his own people. He lived to be eighty years old, honored and beloved by his tribe, and after his death was buried on an eminence overlooking the Mississippi, with such rites as are accorded only to the most distinguished of native captains,—sitting upright in war dress and paint, covered by a conspicuous mound of earth.
We have given a rapid and perhaps an unsatisfactory sketch of the comparatively great events which brought the Black Hawk War to a close. So much at least was necessary, that the reader might understand the several situations in which Mr. Lincoln found himself during the short term of his second enlistment. We fortunately possess a narrative of his individual experience, covering the whole of that period, from the pen of George W. Harrison, his friend, companion, and messmate. It is given in full; for there is no part of it that would not be injured by the touch of another hand. It is an extremely interesting story, founded upon accurate personal knowledge, and told in a perspicuous and graphic style, admirably suited to the subject.
"The new company thus formed was called the 'Independent Spy Company;' not being under the control of any regiment or brigade, but receiving orders directly from the commander-in-chief, and always, when with the army, camping within the lines, and having many other privileges, such as never having camp-duties to perform, drawing rations as much and as often as we pleased, &c, Dr. Early (deceased) of Springfield was elected captain. Five members constituted a tent, or 'messed' together. Qur mess consisted of Mr. Lincoln, Johnston (a half-brother of his), Fanchier, Wyatt, and myself. The 'Independent Spy Company' was used chiefly to carry messages, to send an express, to spy the enemy, and to ascertain facts. I suppose the nearest we were to doing battle was at Gratiot's Grove, near Galena. The spy company of Posey's brigade was many miles in advance of the brigade, when it stopped in the grove at noon for refreshments. Some of the men had turned loose their horses, and others still had theirs in hand, when five or six Sac and Fox Indians came near them. Many of the white men broke after them, some on horseback, some on foot, in great disorder and confusion, thinking to have much sport with their prisoners immediately. The Indians thus decoyed them about two miles from the little cabins in the grove, keeping just out of danger, when suddenly up sprang from the tall prairie grass two hundred and fifty painted warriors, with long spears in hand, and tomahawks and butcher-knives in their belts of deer-skin and buffalo, and raised such a yell that our friends supposed them to be more numerous than Black Hawk's whole clan, and, instantly filled with consternation, commenced to retreat. But the savages soon began to spear them, making it necessary to halt in the flight, and give them a fire, at which time they killed two Indians, one of them being a young chief gayly apparelled. Again, in the utmost horror, such as savage yells alone can produce, they fled for the little fort in the grove. Having arrived, they found the balance of their company, terrified by the screams of the whites and the yells of the savages, closely shut up in the double cabin, into which they quickly plunged, and found the much-needed respite. The Indians then prowled around the grove, shooting nearly all the company's horses, and stealing the balance of them. There, from cracks between the logs of the cabin, three Indians were shot and killed in the act of reaching for the reins of bridles on horses. They endeavored to conceal their bodies by trees in an old field which surrounded the fort; but, reaching with sticks for bridles, they exposed their heads and necks, and all of them were shot with two balls each through the neck. These three, and the two killed where our men wheeled and fired, make five Indians known to be killed; and on their retreat from the prairie to the grove, five white men were cut into small pieces. The field of this action is the greatest battle-ground we saw. The dead still lay unburied until after we arrived at sunrise the next day. The forted men, fifty strong, had not ventured to go out until they saw us, when they rejoiced greatly that friends and not dreaded enemies had come. They looked like men just out of cholera,—having passed through the cramping stage. The only part we could then act was to seek the lost men, and with hatchets and hands to bury them. We buried the white men, and trailed the dead young chief where he had been drawn on the grass a half-mile, and concealed in the thicket. Those who trailed this once noble warrior, and found him, were Lincoln, I think, Wyatt, and myself. By order of Gen. Atkinson, our company started on this expedition one evening, travelled all night, and reached Gratiot's at sunrise. A few hours after, Gen. Posey came up to the fort with his brigade of nearly a thousand men, when he positively refused to pursue the Indians,—being strongly solicited by Capt. Early, Lincoln, and others,—squads of Indians still showing themselves in a menacing manner one and a half miles distant.
"Our company was disbanded at Whitewater, Wis., a short time before the massacre at Bad Axe by Gen. Henry; and most of our men started for home on the following morning; but it so happened that the night previous to starting on this long trip, Lincoln's horse and mine were stolen, probably by soldiers of our own army, and we were thus compelled to start outside the cavalcade; but I laughed at our fate, and he joked at it, and we all started off merrily. But the generous men of our company walked and rode by turns with us; and we fared about equal with the rest. But for this generosity, our legs would have had to do the better work; for in that day, this then dreary route furnished no horses to buy or to steal; and, whether on horse or afoot, we always had company, for many of the horses' backs were too sore for riding.
"Thus we came to Peoria: here we bought a canoe, in which we two paddled our way to Pekin. The other members of our company, separating in various directions, stimulated by the proximity of home, could never have consented to travel at our usual tardy mode. At Pekin, Lincoln made an oar with which to row our little boat, while I went through the town in order to buy provisions for the trip. One of us pulled away at the one oar, while the other sat astern to steer, or prevent circling. The river being very low was without current, so that we had to pull hard to make half the speed of legs on land,—in fact, we let her float all night, and on the next morning always found the objects still visible that were beside us the previous evening. The water was remarkably clear, for this river of plants, and the fish appeared to be sporting with us as we moved over or near them.
"On the next day after we left Pekin, we overhauled a raft of saw-logs, with two men afloat on it to urge it on with poles and to guide it in the channel. We immediately pulled up to them and went on the raft, where we were made welcome by various demonstrations, especially by that of an invitation to a feast on fish, corn-bread, eggs, butter, and coffee, just prepared for our benefit. Of these good things we ate almost immoderately, for it was the only warm meal we had made for several days. While preparing it, and after dinner, Lincoln entertained them, and they entertained us for a couple of hours very amusingly.
"This slow mode of travel was, at the time, a new mode, and the novelty made it for a short time agreeable. We descended the Illinois to Havana, where we sold our boat, and again set out the old way, over the sand-ridges for Petersburg. As we drew near home, the impulse became stronger, and urged us on amazingly. The long strides of Lincoln, often slipping back in the loose sand six inches every step, were just right for me; and he was greatly diverted when he noticed me behind him stepping along in his tracks to keep from slipping.
"About three days after leaving the army at Whitewater, we saw a battle in full operation about two miles in advance of us. Lincoln was riding a young horse, the property of L. D. Matheny. I was riding a sprightly animal belonging to John T. Stuart. At the time we came in sight of the scene, our two voluntary footmen were about three-fourths of a mile in advance of us, and we about half a mile behind most of our company, and three or four on foot still behind us, leading some sore-backed horses. But the owners of our horses came running back, and, meeting us all in full speed, rightfully ordered us to dismount. We obeyed: they mounted, and all pressed on toward the conflict,—they on horseback, we on foot. In a few moments of hard walking and terribly close observation, Lincoln said to me, 'George, this can't be a very dangerous battle.' Reply: 'Much shooting, nothing falls.' It was at once decided to be a sham for the purpose of training cavalry, instead of Indians having attacked a few white soldiers, and a few of our own men, on their way home, for the purpose of killing them."
THE volunteers from Sangamon returned to their homes shortly before the State election, at which, among other officers, assembly-men were to be chosen. Lincoln's popularity had been greatly enhanced by his service in the war, and some of his friends urged him with warm solicitations to become a candidate at the coming election. He prudently resisted, and declined to consent, alleging in excuse his limited acquaintance in the county at large, until Mr. James Rutledge, the founder of New Salem, added the weight of his advice to the nearly unanimous desire of the neighborhood. It is quite likely that his recent military career was thought to furnish high promise of usefulness in civil affairs; but Mr. Rutledge was sure that he saw another proof of his great abilities in a speech which Abe was induced to make, just about this time, before the New-Salem Literary Society. The following is an account of this speech by R. B. Rutledge, the son of James:—
"About the year 1832 or 1833, Mr. Lincoln made his first effort at public speaking. A debating club, of which James Rutledge was president, was organized, and held regular meetings. As he arose to speak, his tall form towered above the little assembly. Both hands were thrust down deep in the pockets of his pantaloons. A perceptible smile at once lit up the faces of the audience, for all anticipated the relation of some humorous story. But he opened up the discussion in splendid style, to the infinite astonishment of his friends. As he warmed with his subject, his hands would forsake his pockets and would enforce his ideas by awkward gestures, but would very soon seek their easy resting-places. He pursued the question with reason and argument so pithy and forcible that all were amazed. The president at his fireside, after the meeting, remarked to his wife, that there was more in Abe's head than wit and fun; that he was already a fine speaker; that all he lacked was culture to enable him to reach the high destiny which he knew was in store for him. From that time Mr. Rutledge took a deeper interest in him.
"Soon after Mr. Rutledge urged him to announce himself as a candidate for the Legislature. This he at first declined to do, averring that it was impossible to be elected. It was suggested that a canvass of the county would bring him prominently before the people, and in time would do him good. He reluctantly yielded to the solicitations of his friends, and made a partial canvass."
In those days political animosities were fierce enough; but, owing to the absence of nominating conventions, party lines were not, as yet, very distinctly drawn in Illinois. Candidates announced themselves; but, usually, it was done after full consultation with influential friends, or persons of considerable power in the neighborhood of the candidate's residence. We have already seen the process by which Mr. Lincoln was induced to come forward. There were often secret combinations among a number of candidates, securing a mutual support; but in the present case there is no trace of such an understanding.
This (1832) was the year of Gen. Jackson's election. The Democrats stigmatized their opponents as "Federalists," while the latter were steadily struggling to shuffle off the odious name. For the present they called themselves Democratic Republicans; and it was not until 1833 or 1834, that they formally took to themselves the designation of Whig. The Democrats were known better as Jackson men than as Democrats, and were inexpressibly proud of either name. Four or five years afterward their enemies invented for their benefit the meaningless and hideous word "Locofoco."
Since 1826 every general election in the State had resulted in a Democratic victory. The young men were mostly Democrats; and the most promising talents in the State were devoted to the cause, which seemed destined to achieve success wherever there was a contest. In a new country largely peopled by adventurers from older States, there were necessarily found great numbers who would attach themselves to the winning side merely because it was the winning side.
It is unnecessary to restate here the prevailing questions in national politics,—Jackson's stupendous struggle with the bank, "hard money," "no monopoly," internal improvements, the tariff, and nullification, or the personal and political relations of the chieftains,—Jackson, Clay, and Calhoun. Mr. Lincoln will shortly disclose in one of his speeches from the stump which of those questions were of special interest to the people of Illinois, and consequently which of them principally occupied his own attention.
The Democrats were divided into "whole-hog men" and "nominal Jackson men;" the former being thoroughly devoted to the fortunes and principles of their leader, while the latter were willing to trim a little for the sake of popular support. It is probable that Mr. Lincoln might be fairly classed as a "nominal Jackson man," although the precise character of some of the views he then held, or is supposed to have held, on national questions, is involved in considerable doubt. He had not wholly forgotten Jones, or Jones's teachings. He still remembered his high disputes with Offutt in the shanty at Spring Creek, when he effectually defended Jackson against the "abuse" of his employer. He was not Whig, but "Whiggish," as Dennis Hanks expresses it. It is not likely that a man who deferred so habitually to the popular sentiment around him would have selected the occasion of his settlement in a new place to go over bodily to a hopeless political minority. At all events, we have at least three undisputed facts, which make it plain that he then occupied an intermediate position between the extremes of all parties. First, he received the votes of all parties at New Salem; second, he was the next year appointed postmaster by Gen. Jackson; and, third, the Democrats ran him for the legislature two years afterwards; and he was elected by a larger majority than any other candidate.
"Our old way of conducting elections," says Gov. Ford, "required each aspirant to announce himself as a candidate. The most prudent, however, always consulted a little caucus of select, influential friends. The candidates then travelled around the county, or State, in proper person, making speeches, conversing with the people, soliciting votes, whispering slanders against their opponents, and defending themselves against the attacks of their adversaries; but it was not always best to defend against such attacks. A candidate in a fair way to be elected should never deny any charge made against him; for, if he does, his adversaries will prove all that they have said, and much more. As a candidate did not offer himself as the champion of any party, he usually agreed with all opinions, and promised every thing demanded by the people, and most usually promised, either directly or indirectly, his support to all the other candidates at the same election. One of the arts was to raise a quarrel with unpopular men who were odious to the people, and then try to be elected upon the unpopularity of others, as well as upon his own popularity. These modes of electioneering were not true of all the candidates, nor perhaps of half of them, very many of them being gentlemen of first-class integrity."
That portion of the people whose influence lay in their fighting qualities, and who were prone to carry a huge knife in the belt of the hunting-shirt, were sometimes called the "butcher-knife boys," and sometimes "the half-horse and half-alligator men." This class, according to Gov. Ford, "made a kind of balance-of-power party." Their favorite was sure of success; and nearly all political contests were decided by "butcher-knife influence." "In all elections and in all enactments of the Legislature, great pains were taken by all candidates, and all men in office, to make their course and measures acceptable" to these knights of steel and muscle.
At a later date they enjoyed a succession of titles, such as "barefoot boys," "the flat-footed boys," and "the big-pawed boys."
In those times, Gov. Ford avers that he has seen all the rum-shops and groceries of the principal places of a county chartered by candidates, and kept open for the gratuitous accommodation of the free and independent electors for several weeks before the vote. Every Saturday afternoon the people flocked to the county-seat, to see the candidates, to hear speeches, to discuss prospects, to get drunk and fight.
"Toward evening they would mount their ponies, go reeling from side to side, galloping through town, and throwing up their caps and hats, screeching like so many infernal spirits broke loose from their nether prison; and thus they separated for their homes." These observations occur in Ford's account of the campaign of 1830, which resulted in the choice of Gov. Reynolds,—two years before Mr. Lincoln first became a candidate,—and lead us to suppose that the body of electors before whom that gentleman presented himself were none too cultivated or refined.
Mr. Lincoln's first appearance on the stump, in the course of the canvass, was at Pappsville, about eleven miles west of Springfield, upon the occasion of a public sale by the firm of Poog & Knap. The sale over, speech-making was about to begin, when Mr. Lincoln observed strong symptoms of inattention in his audience, who had taken that particular moment to engage in what Mr. James A. Herndon pronounces "a general fight." Lincoln saw that one of his friends was suffering more than he liked in the mêlée; and, stepping into the crowd, he shouldered them sternly away from his man, until he met a fellow who refused to fall back: him he seized by the nape of the neck and the seat of his breeches, and tossed him "ten or twelve feet easily." After this episode,—as characteristic of him as of the times,—he mounted the platform, and delivered, with awkward modesty, the following speech:—
"Gentlemen and Fellow-Citizens, I presume you all know who I am. I am humble Abraham Lincoln. I have been solicited by many friends to become a candidate for the Legislature. My politics are short and sweet, like the old woman's dance. I am in favor of a national bank. I am in favor of the internal-improvement system and a high protective tariff. These are my sentiments and political principles. If elected, I shall be thankful; if not, it will be all the same."
In these few sentences Mr. Lincoln adopted the leading principles of the Whig party,—Clay's "American System" in full. In his view, as we shall see by another paper from him when again a candidate in 1834, the internal-improvement system required the distribution of the proceeds of the sales of the public lands amongst the States. He says nothing of South Carolina, of nullification, of disunion; and on these subjects it is quite probable his views were like Mr. Webster's, and his sympathies with Jackson. The opinions announced in this speech, on all the subjects touched by the speaker, were as emphatically Whig as they could be made in words; yet as far as they related to internal improvements, and indirectly favored the increase of bank issues, they were such as most of the "nominal Jackson men" in Illinois professed to hold, and such as they united with the Whigs to enforce, then and afterwards, in the State Legislature. The "whole-hog men" would have none of them, and therein lay the distinction. Although the Democratic party continued to have a numerical majority for many years in the Legislature, the nominal men and the Whigs coalesced to control legislation in accordance with Whig doctrines. Even with such a record made and making by them, the "nominal men" persisted in calling themselves Democrats, while Jackson was vetoing the Maysville Road Bill, grappling with the National Bank, and exposing the oppressive character of the Tariff Act then in force, which imposed the highest scale of duties since the first enactment for "protection" in 1816. It was their practice to run men like themselves for the State offices where the chances of a plain-spoken Whig were hopeless; and, by means of the "nominal" character of the candidate, secure enough Democratic votes, united with the Whigs, to elect him. In the very next canvass Mr. Lincoln himself was taken up by such a combination and triumphantly elected. Such things were made feasible by the prevalent mode of making nominations without the salutary intervention of regular party conventions and committees. We repeat that Mr. Lincoln's position was midway between the extremes in local politics.
His friend, Mr. A. Y. Ellis, who was with him during a part of this campaign, says, "He wore a mixed jeans coat, claw-hammer style, short in the sleeves, and bobtail,—in fact, it was so short in the tail he could not sit on it,—flax and tow linen pantaloons, and a straw hat. I think he wore a vest, but do not remember how it looked. He then wore pot-metal boots.
"I accompanied him on one of his electioneering trips to Island Grove; and he made a speech which pleased his party friends very well indeed, though some of the Jackson men tried to make sport of it. He told several anecdotes in his speech, and applied them, as I thought, very well. He also told the boys several stories which drew them after him. I remember them; but modesty and my veneration for his memory forbid me to relate them."
Mr. J. R. Herndon, his friend and landlord, heard him make several speeches about this time, and gives us the following extract from one, which seems to have made a special impression upon the minds of his auditors: "Fellow-citizens, I have been told that some of my opponents have said that it was a disgrace to the county of Sangamon to have such a looking man as I am stuck up for the Legislature. Now, I thought this was a free country: that is the reason I address you today. Had I have known to the contrary, I should not have consented to run; but I will say one thing, let the shoe pinch where it may: when I have been a candidate before you some five or six times, and have been beaten every time, I will consider it a disgrace, and will be sure never to try it again; but I am bound to beat that man if I am beat myself."
These were not the only speeches he made in furtherance of his present claims, but they are all of which we have any intelligible account. There was one subject upon which he felt himself peculiarly competent to speak,—the practical application of the "internal-improvement system" to the river which flowed by the doors of the constituency he addressed. He firmly believed in the right of the Legislature of the State or the Congress of the United States to appropriate the public money to local improvements for the sole advantage of limited districts; and that he believed it good policy to exercise the right, his subsequent conduct in the Legislature, and an elaborate speech in Congress, are sufficient proof. In this doctrine he had the almost unanimous support of the people of Illinois. Almost every man in the State was a speculator in town lots or lands. Even the farmers had taken up or held the very lands they tilled with a view to a speculation in the near future. Long after the Democratic party in the South and East, leaving Mr. Calhoun in a state of isolation, had begun to inculcate different views of constitutional power and duty, it was a dangerous thing for a politician in Illinois to intimate his agreement with them. Mr. Lincoln knew well that the policy of local improvement at the general expense was at that moment decidedly the most popular platform he could mount; but he felt that this was not enough for his individual purposes, since it was no invention of his, and belonged to nearly everybody else as much as to him. He therefore prudently ingrafted upon it a hobby of his own: "The Improvement of the Sangamon River,"—a plan to straighten it by means of cuts, to clear out its obstructions, and make it a commercial highway at the cost of the State. That the idea was nearly, if not quite impracticable, the trip of "The Talisman" under Mr. Lincoln's piloting, and the fact that the river remained unimproved during all the years of the "internal-improvement" mania, would seem to be pretty clear evidence. But the theme was agreeable to the popular ear, and had been dear to Lincoln from the moment he laid his eyes on the Sangamon. It was the great topic of his speech against Posey and Ewing in Macon County, when, under the auspices of John Hanks, he "beat" those professional politicians so completely that they applauded him themselves. His experience in navigating the river was not calculated to make him forget it, and it had occupied his thoughts more or less from that day forward. Now that it might be turned to good use, where he was personally interested, he set about preparing a written address on it, and on some other questions of local interest, upon which he bestowed infinite pains. The "grammatical errors" in the first draft were corrected by Mr. McNamar, the pioneer of New Salem as a business point, and the gentleman who was destined to be Mr. Lincoln's rival in the most important love-affair of his life. He may have consulted the schoolmaster also; but, if he had done so, it is hardly to be surmised that the schoolmaster would have left so important a fact out of his written reminiscences. It is more probable that Mr. Lincoln confined his applications for assistance on this most important matter to the quarter where he could get light on politics as well as grammar. However that may have been, the following is the finished paper:—
To the People of Sangamon County.
Fellow-Citizens,—Having become a candidate for the honorable office of one of your Representatives in the next General Assembly of this State, in accordance with an established custom and the principles of true republicanism, it becomes my duty to make known to you, the people, whom I propose to represent, my sentiments with regard to local affairs.
Time and experience have verified to a demonstration the public utility of internal improvements. That the poorest and most thinly-populated countries would be greatly benefited by the opening of good roads, and in the clearing of navigable streams within their limits, is what no person will deny. Yet it is folly to undertake works of this or any other kind, without first knowing that we are able to finish them,—as half-finished work generally proves to be labor lost. There cannot justly be any objection to having railroads and canals, any more than to other good things, provided they cost nothing. The only objection is to paying for them; and the objection arises from the want of ability to pay.
With respect to the County of Sangamon, some more easy means of communication than it now possesses, for the purpose of facilitating the task of exporting the surplus products of its fertile soil, and importing necessary articles from abroad, are indispensably necessary. A meeting has been held of the citizens of Jacksonville and the adjacent country, for the purpose of deliberating and inquiring into the expediency of constructing a railroad from some eligible point on the Illinois River, through the town of Jacksonville, in Morgan County, to the town of Springfield, in Sangamon County. This is, indeed, a very desirable object. No other improvement that reason will justify us in hoping for can equal in utility the railroad. It is a never-failing source of communication between places of business remotely situated from each other. Upon the railroad the regular progress of commercial intercourse is not interrupted by either high or low water, or freezing weather, which are the principal difficulties that render our future hopes of water communication precarious and uncertain.
Yet however desirable an object the construction of a railroad through our country may be; however high our imaginations may be heated at thoughts of it,—there is always a heart-appalling shock accompanying the account of its cost, which forces us to shrink from our pleasing anticipations. The probable cost of this contemplated railroad is estimated at $290,000; the bare statement of which, in my opinion, is sufficient to justify the belief that the improvement of the Sangamon River is an object much better suited to our infant resources.
Respecting this view, I think I may say, without the fear of being contradicted, that its navigation may be rendered completely practicable as high as the mouth of the South Fork, or probably higher, to vessels of from twenty-five to thirty tons' burden, for at least one-half of all common years, and to vessels of much greater burden a part of the time. From my peculiar circumstances, it is probable, that for the last twelve months I have given as particular attention to the stage of the water in this river as any other person in the country. In the month of March, 1831, in company with others, I commenced the building of a flatboat on the Sangamon, and finished and took her out in the course of the spring. Since that time I have been concerned in the mill at New Salem. These circumstances are sufficient evidence that I have not been very inattentive to the stages of the water. The time at which we crossed the mill-dam being in the last days of April, the water was lower than it had been since the breaking of winter in February, or than it was for several weeks after. The principal difficulties we encountered in descending the river were from the drifted timber, which obstructions all know are not difficult to be removed. Knowing almost precisely the height of water at that time, I believe I am safe in saying that it has as often been higher as lower since.
From this view of the subject, it appears that my calculations with regard to the navigation of the Sangamon cannot but be founded in reason; but, whatever may be its natural advantages, certain it is, that it never can be practically useful to any great extent, without being greatly improved by art. The drifted timber, as I have before mentioned, is the most formidable barrier to this object. Of all parts of this river, none will require so much labor in proportion to make it navigable, as the last thirty or thirty-five miles; and going with the meanderings of the channel, when we are this distance above its mouth we are only between twelve and eighteen miles above Beardstown, in something near a straight direction; and this route is upon such low ground as to retain water in many places during the season, and in all parts such as to draw two-thirds or three-fourths of the river-water at all high stages.
This route is on prairie land the whole distance; so that it appears to me, by removing the turf a sufficient width, and damming up the old channel, the whole river in a short time would wash its way through, thereby curtailing the distance, and increasing the velocity of the current, very considerably: while there would be no timber on the banks to obstruct its navigation in future; and, being nearly straight, the timber which might float in at the head would be apt to go clear through. There are also many places above this where the river, in its zigzag course, forms such complete peninsulas, as to be easier to cut at the necks than to remove the obstructions from the bends, which, if done, would also lessen the distance.
What the cost of this work would be, I am unable to say. It is probable, however, that it would not be greater than is common to streams of the same length. Finally, I believe the improvement of the Sangamon River to be vastly important and highly desirable to the people of the county; and, if elected, any measure in the Legislature having this for its object, which may appear judicious, will meet my approbation and shall receive my support.
It appears that the practice of drawing money at exorbitant rates of interest has already been opened as a field for discussion; so I suppose I may enter upon it without claiming the honor, or risking the danger, which may await its first explorer. It seems as though we are never to have an end to this baneful and corroding system, acting almost as prejudicial to the general interests of the community as a direct tax of several thousand dollars annually laid on each county, for the benefit of a few individuals only, unless there be a law made fixing the limits of usury. A law for this purpose, I am of opinion, may be made, without materially injuring any class of people. In cases of extreme necessity, there could always be means found to cheat the law; while in all other cases it would have its intended effect. I would favor the passage of a law on this subject which might not be very easily evaded. Let it be such that the labor and difficulty of evading it could only be justified in cases of greatest necessity.1
1 Until the year 1833 there had been no legal limit to the rate of interest to be fixed by contract. But usury had been carried to such an unprecedented degree of extortion and oppression as to cause the Legislature to enact severe usury laws, by which all interest above twelve per cent was condemned. It had been no uncommon thing before this to charge one hundred and one hundred and fifty per cent, and sometimes two and three hundred per cent. But the common rate of interest, by contract, had been about fifty per cent.—Ford's History, page 233.
Upon the subject of education, not presuming to dictate any plan or system respecting it, I can only say that I view it as the most important subject which we as a people can be engaged in. That every man may receive at least a moderate education, and thereby be enabled to read the histories of his own and other countries, by which he may duly appreciate the value of our free institutions, appears to be an object of vital importance, even on this account alone, to say nothing of the advantages and satisfaction to be derived from all being able to read the Scriptures and other works, both of a religious and moral nature, for themselves.
For my part, I desire to see the time when education—and, by its means, morality, sobriety, enterprise, and industry—shall become much more general than at present, and should be gratified to have it in my power to contribute something to the advancement of any measure which might have a tendency to accelerate the happy period.
With regard to existing laws, some alterations are thought to be necessary. Many respectable men have suggested that our estray laws—the law respecting the issuing of executions, the road-law, and some others—are deficient in their present form, and require alterations. But, considering the great probability that the framers of those laws were wiser than myself, I should prefer not meddling with them, unless they were first attacked by others; in which case I should feel it both a privilege and a duty to take that stand, which, in my view, might tend most to the advancement of justice.
But, fellow-citizens, I shall conclude. Considering the great degree of modesty which should always attend youth, it is probable I have already been more presuming than becomes me. However, upon the subjects of which I have treated, I have spoken as I have thought. I may be wrong in regard to any or all of them; but, holding it a sound maxim, that it is better only sometimes to be right than at all times wrong, so soon as I discover my opinions to be erroneous, I shall be ready to renounce them.
Every man is said to have his peculiar ambition. Whether it be true or not, I can say, for one, that I have no other so great as that of being truly esteemed of my fellow-men, by rendering myself worthy of their esteem. How far I shall succeed in gratifying this ambition is yet to be developed. I am young, and unknown to many of you. I was born, and have ever remained, in the most humble walks of life. I have no wealthy or popular relations or friends to recommend. My case is thrown exclusively upon the independent voters of the county; and, if elected, they will have conferred a favor upon me, for which I shall be unremitting in my labors to compensate. But, if the good people in their wisdom shall see fit to keep me in the background, I have been too familiar with disappointments to be very much chagrined.
Your Friend and Fellow-Citizen,
A. LINCOLN.
New Salem, March 9, 1832.
Mr. Lincoln was defeated at the election, having four hundred and seventy votes less than the candidate who had the highest number. But his disappointment was softened by the action of his immediate neighbors, who gave him an almost unanimous support. With three solitary exceptions, he received the whole vote of his precinct,—two hundred and seventy-seven,—being one more than the whole number cast for both the candidates for Congress.
THE results of the canvass for the Legislature were precisely such as had been predicted, both by Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Rutledge: he had been defeated, as he expected himself; and it had done "him much good," in the politician's sense, as promised by Mr. Rutledge. He was now somewhat acquainted with the people outside of the New Salem district, and generally marked as a young man of good parts and popular manners. The vote given him at home demonstrated his local strength, and made his favor a thing of value to the politicians of all parties.
Soon after his return from the army, he had taken quarters at the house of J. R. Herndon, who loved him then, and always, with as much sincerity as one man can love another. Mr. Herndon's family likewise "became much attached to him." He "nearly always had one" of Herndon's children "around with him." Mr. Herndon says of him further, that he was "at home wherever he went;" making himself wonderfully agreeable to the people he lived with, or whom he happened to be visiting. Among other things, "he was very kind to the widow and orphan, and chopped their wood."
Lincoln, as we have seen already, was not enamored of the life of a common laborer,—mere hewing and drawing. He preferred to clerk, to go to war, to enter politics,—any thing but that dreary round of daily toil and poor pay. But he was now, as he would say, "in a fix:" clerks were not wanted every day in New Salem and he began to cast about for some independent business of his own, by which he could earn enough to pay board and buy books. In every community where he had lived, "the merchant" had been the principal man. He felt that, in view of his apprenticeship under those great masters, Jones and Offutt, he was fully competent to "run a store," and was impatient to find an opening in that line.
Unfortunately for him, the circumstances of the business men of New Salem were just then peculiarly favorable to his views. At least three of them were as anxious to sell out as Lincoln was to buy.
Lincoln, as already stated, was at this time living with "Row" Herndon. Row and his brother "Jim" had taken "a store down to New Salem early in that year." But Jim "didn't like the place," and sold out his interests to an idle, convivial fellow, named Berry. Six weeks later Row Herndon grew tired of his new partner, and sold his interest to Lincoln. The store was a mixed one,—dry goods and groceries.
About the same time Mr. Radford, who kept one of the New Salem groceries, fell into disfavor with the "Clary's Grove Boys," who generously determined that he should keep a grocery no longer. They accordingly selected a convenient night for breaking in his windows, and, in their own elegant phrase, "gutting his establishment." Convinced that these neighborly fellows were inclined to honor him with further attentions, and that his bones might share the fate of his windows, Radford determined to sell out with the earliest dawn of the coming day. The next day he was standing disconsolate in the midst of his wreck, when Bill Green rode up. Green thought he saw a speculation in Radford's distress, and offered him four hundred dollars for the whole concern. Radford eagerly closed with him; and in a few minutes Green owned the grocery, and Radford was ready for the road to a more congenial settlement. It is said that Green employed Lincoln to make an inventory of the stock. At all events, Lincoln was satisfied that Green's bargain was a very good one, and proposed that he and Berry should take it off his hands at a premium of two hundred and fifty dollars. Radford had Green's note for four hundred dollars; but he now surrendered, it and took Lincoln & Berry's for the same amount, indorsed by Green; while Lincoln & Berry gave Green a note for two hundred and fifty dollars, the latter's profit in the trade.
Mr. Rutledge "also owned a small grocery in the village;" and this was speedily absorbed by the enterprising firm of Lincoln & Berry, who now had the field to themselves, being sole proprietors "of the only store of the kind in New Salem."
Whether Mr. Lincoln sold liquor by the dram over the counter of this shop remains, and will forever remain, an undetermined question. Many of his friends aver that he did, and as many more aver that he did not. When Douglas, with that courtesy for which he distinguished himself in the debates with Lincoln, revived the story, Lincoln replied, that, even if it were true, there was but little difference between them; for, while he figured on one side of the counter, Douglas figured on the other. It is certain liquors were a part of the stock of all the purchases of Lincoln & Berry. Of course they sold them by the quantity, and probably by the drink. Some of it they gave away, for no man could keep store without setting out the customary dram to the patrons of the place.1
1 Here is the evidence of James Davis, a Democrat, "aged sixty," who is willing to "give the Devil his due:"— "Came to Clary's Grove in 1829; knew Lincoln well; knew Jim and Row Herndon: they sold out to Berry,—one of them did; afterwards the other sold out to Lincoln. The store was a mixed one,—dry goods, a few groceries, such as sugar, salt, &c., and whiskey solely kept for their customers, or to sell by the gallon, quart, or pint,—not otherwise. The Herndons probably had the Blankenship goods. Radford had a grocery-store,—salt, pepper, and suchlike things, with whiskey. It is said Green bought this out, and instantly sold to Berry & Lincoln. Lincoln & Berry broke. Berry subsequently kept a doggery, a whiskey saloon, as I do now, or did. Am a Democrat; never agreed in politics with Abe. He was an honest man. Give the Devil his due; he never sold whiskey by the dram in New Salem! I was in town every week for years; knew, I think, all about it. I always drank my dram, and drank at Berry's often; ought to know. Lincoln got involved, I think, in the first operation. Salem Hill was a barren."
The difficulty of gathering authentic evidence on this subject is well illustrated in the following extract from Mr. George Spears of Petersburg:—
"I took my horse this morning, and went over to New Salem, among the P——s and A——s, and made all the inquiries I could, but could learn nothing. The old ladies would begin to count up what had happened in New Salem when such a one of their children was born, and such a one had a bastard; but it all amounted to nothing. I could arrive at no dates, only when those children were born. Old Mrs. Potter affirms that Lincoln did sell liquors in a grocery. I can't tell whether he did or not."
All that winter (1832-3) Lincoln struggled along with a bad partner, and a business which began wrong, and grew worse every day. Berry had no qualities which atoned for his evil habits.. He preferred to consume the liquors on hand rather than to sell them, and exerted himself so successfully, that in a few months he had ruined the credit of the firm, squandered its assets, and destroyed his own health. The "store" was a dead failure; and the partners were weighed down with a parcel of debts, against which Lincoln could scarcely have borne up, even with a better man to help him. At last they sold out to two brothers named Trent. The Trents continued the business for a few months, when they broke up and ran away. Then Berry, encouraged by the example of the Trents, "cleared out" also, and, dying soon after, left poor Lincoln the melancholy task of settling up the affairs of their ill-starred partnership.
In all the preceding transactions, the absence of any cash consideration is the one thing very striking. It is a fair illustration of the speculative spirit pervading the whole people. Green bought from Radford on credit; Lincoln & Berry bought from Green on credit; they bought from the Herndons on credit; they bought from Rutledge on credit; and they sold to the Trents on credit. Those that did not die or run away had a sad time enough in managing the debts resulting from their connection with this unlucky grocery. Radford assigned Lincoln & Berry's note to a Mr. Van Bergen, who got judgment on it, and swept away all Lincoln's little personal property, including his surveying instruments,—his very means of livelihood, as we shall see at another place. The Herndons owed E. C. Blankenship for the goods they sold, and assigned Lincoln & Berry's note in payment. Mr. Lincoln struggled to pay, by slow degrees, this harassing debt to Blankenship, through many long and weary years. It was not until his return from Congress, in 1849, that he got the last dollar of it discharged. He paid Green his note of two hundred and fifty dollars, in small instalments, beginning in 1839, and ending in 1840. The history of his debt to Rutledge is not so well known. It was probably insignificant as compared with the others; and Mr. Rutledge proved a generous creditor, as he had always been a kind and considerate friend.
Certain that he had no abilities for trade, Mr. Lincoln took the best resolution he could have formed under the circumstances. He sat down to his books just where he was, believing that knowledge would be power, and power profit. He had no reason to shun his creditors, for these were the men of all others who most applauded the honesty of his conduct at the period of his greatest pecuniary misfortune. He talked to them constantly of the "old debt," "the national debt," as he sometimes called it,—promised to pay when he could, and they devoutly relied upon every word he said.
Row Herndon moved to the country, and Lincoln was compelled to change his boarding-place. He now began to live at a tavern for the first time in his life. It was kept by various persons during his stay,—first, it seems, by Mr. Rutledge, then by Henry Onstatt, and last by Nelson Alley. It was a small log-house, covered with clapboards, and contained four rooms.
Lincoln began to read law while he lived with Herndon. Some of his acquaintances insist that he began even earlier than this, and assert, by way of proof, that he was known to borrow a well-worn copy of Blackstone from A. T. Bogue, a pork-dealer at Beardstown. At all events, he now went to work in earnest, and studied law as faithfully as if he had never dreamed of any other business in life. As a matter of course, his slender purse was unequal to the purchase of the needful books: but this circumstance gave him little trouble; for, although he was short of funds, he was long in the legs, and had nothing to do but to walk off to Springfield, where his friend, John T. Stuart, cheerfully supplied his wants. Mr. Stuart's partner, H. C. Dummer, says, "He was an uncouth-looking lad, did not say much, but what he did say he said straight and sharp."
"He used to read law," says Henry McHenry, "in 1832 or 1833, barefooted, seated in the shade of a tree, and would grind around with the shade, just opposite Berry's grocery-store, a few feet south of the door." He occasionally varied the attitude by lying flat on his back, and "putting his feet up the tree"—a situation which might have been unfavorable to mental application in the case of a man with shorter extremities.
"The first time I ever saw Abe with a law-book in his hand," says Squire Godbey, "he was sitting astride of Jake Bales's woodpile in New Salem. Says I, 'Abe, what are you studying?'—'Law,' says Abe. 'Great God Almighty!' responded I." It was too much for Godbey: he could not suppress the blasphemy at seeing such a figure acquiring science in such an odd situation.
Minter Graham asserts that Abe did a little "of what we call sitting up to the fine gals of Illinois;" but, according to other authorities, he always had his book with him "when in company," and would read and talk alternately. He carried it along in his walks to the woods and the river; read it in daylight under the shade-tree by the grocery, and at night by any friendly light he could find,—most frequently the one he kindled himself in the shop of his old benefactor, the cooper.
Abe's progress in the law was as surprising as the intensity of his application to study. He never lost a moment that might be improved. It is even said that he read and recited to himself on the road and by the wayside as he came down from Springfield with the books he had borrowed from Stuart. The first time he went up he had "mastered" forty pages of Blackstone before he got back. It was not long until, with his restless desire to be doing something practical, he began to turn his acquisitions to account in forwarding the business of his neighbors. He wrote deeds, contracts, notes, and other legal papers, for them, "using a small dictionary and an old form-book;" "petifogged" incessantly before the justice of the peace, and probably assisted that functionary in the administration of justice as much as he benefited his own clients. This species of country "student's" practice was entered upon very early, and kept up until long after he was quite a distinguished man in the Legislature. But in all this he was only trying himself: as he was not admitted to the bar until 1837, he did not regard it as legitimate practice, and never charged a penny for his services. Although this fact is mentioned by a great number of persons, and the generosity of his conduct much enlarged upon, it is seriously to be regretted that no one has furnished us with a circumstantial account of any of his numerous cases before the magistrate.
But Mr. Lincoln did not confine himself entirely to the law. He was not yet quite through with Kirkham nor the schoolmaster. The "valuable copy" of the grammar "he delighted to peruse" is still in the possession of R. B. Rutledge, with the thumb-marks of the President all over it. "He also studied natural philosophy, chemistry, astronomy, &c. He had no regular teacher, but perhaps received more assistance from Minter Graham than from any other person."
He read with avidity all the newspapers that came to New Salem,—chiefly "The Sangamon Journal," "The Missouri Republican," and "The Louisville Journal." 1 The latter was his favorite: its wit and anecdotes were after his own heart; and he was a regular subscriber for it through several years when he could ill afford a luxury so costly.
1 According to Mr. McNamar, Lincoln took "The Sangamon Journal" and "The Louisville Journal" from 1832 to 1837; and Hill and Bale took "The Missouri Republican" and "The Cincinnati Gazette." "The Missouri Republican" was first issued as a daily in September, 1836. Its size was then twenty-five by thirty-six inches.
Mr. Lincoln was never a profound historical student: if he happened to need historical facts for the purposes of a political or legal discussion, he read them on the spur of the occasion. For this reason his opinions of current affairs all through his life were based more upon individual observation and reflection than upon scientific deductions from the experience of the world. Yet at this time, when he probably felt more keenly than ever after the want of a little learning to embellish the letters and speeches he was ambitious to compose, he is said to have read Rollin's "Ancient History," Gibbon's "Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire," and similar works, with great diligence and care. The books were borrowed from William Green, Bowlin Greene, and other parties in and about New Salem.
But he greatly preferred literature of another sort, such as Mrs. Lee Hentz's novels; some of which he found among the effects of Mr. Ellis, at the time his companion and occasional bedfellow. "He was very fond," Mr. Ellis declares, "of short stories, one and two columns long,—like 'Cousin Sally Dillard,' 'Becky Wilson's Courtship,' The Down-easter and the Bull,' 'How a bashful man became a married man, with five little bashful boys, and how he and his red-headed wife became Millerites, and before they were to ascend agreed to make a clean breast of it to each other;' and how, when the old lady was through, the Down-easter earnestly wished that Gabriel might blow his horn without delay." One New Salemite insists that Mr. Lincoln told this latter story "with embezzlements" (embellishments), and therefore he is firmly convinced that Mr. Lincoln "had a hand" in originating it. The catalogue of literature in which he particularly delighted at New Salem is completed by the statement of Mr. Rutledge, that he took great pleasure in "Jack Downing's Letters."
Mr. Lincoln still relished a popular song with a broad "point" or a palpable moral in it as much as he had ever enjoyed the vocal efforts of Dennis Hanks and his rollicking compeers of the Gentryville grocery. He even continued his own unhappy attempts, although with as little success as before, and quite as much to the amusement of his friends. To the choice collection of miscellaneous ballads acquired in Indiana, he now added several new favorites, like "Old Sukey Blue Skin," and some selections from the "Missouri Harmony," with variations by himself. He was also singularly fond of an Irish song, "which tells how St. Patrick came to be born on the 17th day of March."
"You ask me," says Mr. Ellis, "if I remember the first time I saw Mr. Lincoln. Yes, I do.... I was out collecting back tax for Gen. James D. Henry. I went from the tavern down to Jacob Bales's old mill, and then I first saw Mr. Lincoln. He was sitting on a saw-log talking to Jack and Rial Armstrong and a man by the name of Hohammer. I shook hands with the Armstrongs and Hohammer, and was conversing with them a few minutes, when we were joined by my old friend and former townsman, George Warburton, pretty tight as usual; and he soon asked me to tell him the old story about Ben Johnson and Mrs. Dale's blue dye, &c., which I did. And then Jack Armstrong said, 'Lincoln, tell Ellis the story about Gov. J. Sichner, his city-bred son, and his nigger Bob;' which he did, with several others, by Jack's calling for them. I found out then that Lincoln was a cousin to Charley Hanks of Island Grove. I told him I knew three of the boys,—Joe, Charley, and John,—and his uncle, old Billy Hanks, who lived up on the North Fork of the Sangamon River, afterwards near Decatur."1
1 "I myself knew old Billy Hanks, his mother's brother, and he was a very sensible old man. He was father to Mrs. Dillon, on Spring Creek; and Charley, Billy, jr., and John were his sons: they were all low-flung,—could neither read nor write. Some of them used to live in Island Grove, Sangamon County.... I remember the time that Lincoln and E. D. Baker ran in convention, to decide who should run for Congress in old Sangamon; that some of Baker's friends accused Mr. Lincoln of belonging to a proud and an aristocratic family,—meaning the Edwardses and Todds, I suppose; and, when it came to Mr. Lincoln's ears, he laughed heartily, and remarked, 'Well, that sounds strange to me: I do not remember of but one that ever came to see me, and while he was in town he was accused of stealing a jew's- harp.' Josh Speed remembers his saying this. I think you ought to remember it. Beverly Powell and myself lived with Bell and Speed, and I think he said so in their store. After that a Miss Hanks came to spend the winter with Mrs. Lincoln."—A. Y. Ellis.
This interview took place shortly after the Black Hawk War; but it was not until the next year (1833), the period at which we have now arrived, that Lincoln and Ellis became "intimate." At that time Ellis went there to keep a store, and boarded "at the same log-tavern" where Lincoln was. Lincoln, being "engaged in no particular business," merely endeavoring to make a lawyer, a surveyor, and a politician of himself, gave a great deal of his time to Ellis and Ellis's business. "He also used to assist me in the store," says this new friend, "on busy days, but he always disliked to wait on the ladies: he preferred trading with the men and boys, as he used to say. I also remember that he used to sleep in the store, on the counter, when they had too much company at the tavern.
"I well remember how he was dressed: he wore flax and tow linen pantaloons,—I thought about five inches too short in the legs,—and frequently he had but one suspender, no vest or coat. He wore a calico shirt, such as he had in the Black Hawk War; coarse brogans, tan color; blue yarn socks, and straw hat, old style, and without a band.
"Mr. Lincoln was in those days a very shy man of ladies. On one occasion, while we boarded at this tavern, there came a family, containing an old lady and her son and three stylish daughters, from the State of Virginia, and stopped there for two or three weeks; and, during their stay, I do not remember of Mr. Lincoln ever eating at the same table when they did. I then thought it was on account of his awkward appearance and his wearing apparel."
There lived at New Salem at this time, and for some years afterward, a festive gentleman named Kelso, a school-teacher, a merchant, or a vagabond, according to the run of his somewhat variable "luck." When other people got drunk at New Salem, it was the usual custom to tussle and fight, and tramp each other's toes, and pull each other's noses; but, when Kelso got drunk, he astonished the rustic community with copious quotations from Robert Burns and William Shakspeare,—authors little known to fame among the literary men of New Salem. Besides Shakspeare and Burns, Mr. Kelso was likewise very fond of fishing, and could catch his game "when no other man could get a bite." Mr. Lincoln hated fishing with all his heart. But it is the testimony of the country-side, from Petersburg to Island Grove, that Kelso "drew Lincoln after him by his talk;" that they became exceedingly intimate; that they loitered away whole days together, along the banks of the quiet streams; that Lincoln learned to love inordinately our "divine William" and "Scotia's Bard," whom his friend mouthed in his cups, or expounded more soberly in the intervals of fixing bait and dropping line. Finally he and Kelso boarded at the same place; and with another "merchant," named Sincho, of tastes congenial and wits as keen as Kelso's, they were "always found together, battling and arguing." Bill Green ventures the opinion, that Lincoln's incessant reading of Shakspeare and Burns had much to do in giving to his mind the "sceptical" tendency so fully developed by the labors of his pen in 1834-5, and in social conversations during many years of his residence at Springfield.
Like Offutt, Kelso disappeared suddenly from New Salem, and apparently from the recollection of men. Each with a peculiar talent of his own, kind-hearted, eccentric creatures, no man's enemy and everybody's prey, they strolled out into the great world, and left this little village to perish behind them. Of Kelso a few faint traces have been found in Missouri; but if he ever had a lodging more permanent than the wayside tavern, a haystack, or a hedge, no man was able to tell where it was. Of Offutt not a word was ever heard: the most searching and cunning inquiries have failed to discover any spot where he lingered for a single hour; and but for the humble boy, to whom he was once a gentle master, no human being that knew him then would bestow a thought upon his name. In short, to use the expressive language of Mr. Lincoln himself, he literally "petered out."
Mr. Lincoln was often annoyed by "company." His quarters at the tavern afforded him little privacy, and the shade of the tree in front of the grocery was scarcely a sufficiently secluded situation for the purposes of an ardent student. There were too many people to wonder and laugh at a man studying law with "his feet up a tree;" too many to worry him for the stories and jokes which it was supposed he could furnish on demand. For these reasons it became necessary that he should "retire to the country occasionally to rest and study." Sometimes he went to James Short's on the Sand Ridge; sometimes to Minter Graham's; sometimes to Bowlin Greenes; sometimes to Jack Armstrong's, and as often, perhaps, to Able's or Row Herndon's. All of these men served him faithfully and signally at one time and another, and to all of them he was sincerely attached. When Bowlin Greene died, in 1842, Mr. Lincoln, then in the enjoyment of great local reputation, undertook to deliver a funeral oration over the remains of his beloved friend; but, when he rose to speak, his voice was choked with deep emotion: he stood a few moments, while his lips quivered in the effort to form the words of fervent praise he sought to utter, and the tears ran down his yellow and shrivelled cheeks. Some of those who came to hear him, and saw his tall form thus sway in silence over the body of Bowlin Greene, say he looked so helpless, so utterly bereft and pitiable, that every heart in the audience was hushed at the spectacle. After repeated efforts, he found it impossible to speak, and strode away, openly and bitterly sobbing, to the widow's carriage, in which he was driven from the scene. Mr. Herndon's papers disclose less than we should like to know concerning this excellent man: they give us only this burial scene, with the fact that Bowlin Greene had loaned Mr. Lincoln books from their earliest acquaintance, and on one occasion had taken him to his home, and cared for him with the solicitude of a devoted friend through several weeks of great suffering and peril. The circumstances of the attempted eulogy are mentioned here to show the relations which subsisted between Mr. Lincoln and some of the benefactors we have enumerated.
But all this time Mr. Lincoln had a living to make, a running board-bill to pay, and nothing to pay it with. He was, it is true, in the hands of excellent friends, so far as the greater part of his indebtedness was concerned; but he was industrious by nature, and wanted to be working, and paying as he went. He would not have forfeited the good opinion of those confiding neighbors for a lifetime of ease and luxury. It was therefore a most happy thing for him, and he felt it to be so, when he attracted the attention of John Calhoun, the surveyor of Sangamon County.
Calhoun was the type of a perfect gentleman,—brave, courteous, able, and cultivated. He was a Democrat then, and a Democrat when he died. All the world knows how he was president of the Lecompton Convention; how he administered the trust in accordance with his well-known convictions; and how, after a life of devotion to Douglas, he was adroitly betrayed by that facile politician, and left to die in the midst of obloquy and disaster. At the time we speak of, he was one of the most popular men in the State of Illinois, and was one of the foremost chieftains of the political party which invariably carried the county and the district in which Mr. Lincoln lived. He knew Lincoln, and admired him. He was well assured that Lincoln knew nothing of surveying; but he was equally certain that he could soon acquire it. The speculative fever was at its height; he was overrun with business: the country was alive with strangers seeking land; and every citizen was buying and selling with a view to a great fortune in the "flush times" coming. He wanted a deputy with common sense and common honesty: he chose Lincoln, because nobody else possessed these qualities in a more eminent degree. He hunted him up; gave him a book; told him to study it, and said, that, as soon as he was ready, he should have as much work as he could do.
Lincoln took the book, and "retired to the country;" that is, he went out to Minter Graham's for about six weeks, in which time, by the aid of that good master, he became an expert surveyor, and was duly appointed Calhoun's deputy. Of course he made some money, merely his pay for work; but it is a remarkable fact, that, with his vast knowledge of the lands in Sangamon and adjacent counties, he never made a single speculation on his own account. It was not long until he acquired a considerable private business. The accuracy of his surveys were seldom, if ever, questioned. Disputes regarding "corners" and "lines" were frequently submitted to his arbitration; and the decision was invariably accepted as final. It often happened that his business kept him away from New Salem, and his other studies, for weeks at a time; but all this while he was gathering friends against the day of election.
In after years—from 1844 onward—it was his good or bad fortune frequently to meet Calhoun on the stump; but he never forgot his benefaction to him, and always regarded him as the ablest and best man with whom he ever had crossed steel. To the day of Calhoun's death they were warmly attached to each other. In the times when it was most fashionable and profitable to denounce Calhoun and the Le-compton Constitution, when even Douglas turned to revile his old friend and coadjutor, Mr. Lincoln was never known to breathe a word of censure on his personal character.
On the 7th of May, 1833, Mr. Lincoln was appointed postmaster at New Salem. His political opinions were not extreme; and the Jackson administration could find no man who was at the same time more orthodox and equally competent to perform the duties of the office. He was not able to rent a room, for the business is said to have been carried on in his hat; but, from the evidence before us, we imagine that he kept the office in Mr. Hill's store, Mr. Hill's partner, McNamar, having been absent since 1832. He held the place until late in 1836, when New Salem partially disappeared, and the office was removed to Petersburg. For a little while before his own appointment, he is said to have acted as "deputy-postmaster" under Mr. Hill.
The mail arrived duly once a week; and the labors of distributing and delivering it were by no means great. But Mr. Lincoln was determined that the dignity of the place should not suffer while he was the incumbent. He therefore made up for the lack of real business by deciphering the letters of the uneducated portion of the community, and by reading the newspapers aloud to the assembled inhabitants in front of Hill's store.
But his easy good-nature was sometimes imposed upon by inconsiderate acquaintances; and Mr. Hill relates one of the devices by which he sought to stop the abuse. "One Elmore Johnson, an ignorant but ostentatious, proud man, used to go to Lincoln's post-office every day,—sometimes three or four times a day, if in town,—and inquire, 'Any thing for me?' This bored Lincoln, yet it amused him. Lincoln fixed a plan,—wrote a letter to Johnson as coming from a negress in Kentucky, saying many good things about opossum, dances, corn-shuckings, &c.; 'John's! come and see me; and old master won't kick you out of the kitchen any more!' Elmore took it out; opened it; couldn't read a word; pretended to read it; went away; got some friends to read it: they read it correctly; he thought the reader was fooling him, and went to others with the same result. At last he said he would get Lincoln to read it, and presented it to Lincoln. It was almost too much for Lincoln, but he read it. The man never asked afterwards, 'Any thing here for me?"
It was in the latter part of 1834 that Mr. Lincoln's personal property was sold under the hammer, and by due process of law, to meet the judgment obtained by Van Bergen on the note assigned to him by Radford. Every thing he had was taken; but it was the surveyor's instruments which it hurt him most to part with, for by their use he was making a tolerable living, and building up a respectable business. This time, however, rescue came from an unexpected quarter.
When Mr. Lincoln first came to New Salem, he employed a woman to make him a pair of pantaloons, which, probably from the scarcity of material, were cut entirely too short, as his garments usually were. Soon afterwards the woman's brother came to town, and she pointed Abe out to him as he walked along the street. The brother's name was James Short. "Without the necessity of a formal introduction," says Short, "we fell in together, and struck up a conversation, the purport of which I have now forgotten. He made a favorable impression upon me by his conversation on first acquaintance through his intelligence and sprightliness, which impression was deepened from time to time, as I became better acquainted with him." This was a lucky "impression" for Abe. Short was a fast friend, and in the day of trouble a sure and able one. At the time the judgment was obtained, Short lived on the Sand Ridge, four miles from New Salem; and Lincoln was in the habit of walking out there almost daily. Short was then unconscious of the main reason of Mr. Lincoln's remarkable devotion to him: there was a lady in the house whom Lincoln secretly but earnestly loved, and of whom there is much to be said at another place. If the host had known every thing, however, poor Abe would have been equally welcome; for he made himself a strangely agreeable guest here, as he did everywhere else. In busy times he pulled off his roundabout, and helped Short in the field with more energy than any hired man would have displayed. "He was," said Short, "the best hand at husking corn on the stalk I ever saw. I used to consider myself very good; but he would gather two loads to my one."
These visits increased Short's disposition to serve him; and it touched him sorely when he heard Lincoln moaning about the catastrophe that hung over him in the form of Van Bergen's judgment. "An execution was issued," says he, "and levied on Lincoln's horse, saddle, bridle, compass, chain, and other surveyor's instruments. He was then very much discouraged, and said he would let the whole thing go by the board. He was at my house very much,—half the time. I did all I could to put him in better spirits. I went on the delivery-bond with him; and when the sale came off, which Mr. Lincoln did not attend, I bid in the above property at a hundred and twenty dollars, and immediately gave it up again to him. Mr. Lincoln afterwards repaid me when he had moved to Springfield. Greene also turned in on this judgment his horse, saddle, and bridle at a hundred and twenty-five dollars; and Lincoln afterwards repaid him."
But, after all, Mr. Lincoln had no friend more intimate than Jack Armstrong, and none that valued him more highly. Until he finally left New Salem for Springfield, he "rusticated" occasionally at Jack's hospitable cabin, situated "four miles in the country," as the polished metropolitans of New Salem would say. Jack's wife, Hannah, before alluded to, liked Abe, and enjoyed his visits not less than Jack did. "Abe would come out to our house," she says, "drink milk, eat mush, corn-bread, and butter, bring the children candy, and rock the cradle while I got him something to eat.... I foxed his pants; made his shirts... He has gone with us to father's; he would tell stories, joke people, girls and boys, at parties. He would nurse babies,—do any thing to accommodate anybody.... I had no books about my house; loaned him none. We didn't think about books and papers. We worked; had to live. Lincoln has staid at our house two or three weeks at a time."
If Jack had "to work to live," as his wife has it, he was likewise constrained to fight and wrestle and tumble about with his unhappy fellow-citizens, in order to enjoy the life he earned by labor. He frequently came "to town," where his sportive inclinations ran riot, except as they were checked and regulated by the amicable interposition of Abe,—the prince of his affections, and the only man who was competent to restrain him.
"The children at school had made a wide sliding walk," from the top of Salem Hill to the river-bank, down which they rode on sleds and boards,—a distance of two hundred and fifty or three hundred yards. Now, it was one of the suggestions of Jack's passion for innocent diversion to nail up in hogsheads such of the population as incurred his displeasure, and send them adrift along this frightful descent. Sol. Spears and one Scanlon were treated to an adventure of this kind; but the hogshead in which the two were caged "leaped over an embankment, and came near killing Scanlon." After that the sport was considered less amusing, and was very much discouraged by that portion of the community who feared, that, in the absence of more convenient victims, "the boys" might light on them. Under these circumstances, Jack, for once in his life, thought it best to abandon coercion, and negotiate for subjects. He selected an elderly person of bibulous proclivities, and tempted him with a great temptation. "Old man Jordan agreed to be rolled down the hill for a gallon of whiskey;" but Lincoln, fully impressed with the brutality of the pastime, and the danger to the old sot, "stopped it." Whether he did it by persuasion or force, we know not, but probably by a judicious employment of both.
"I remember once," says Mr. Ellis, "of seeing Mr. Lincoln out of temper, and laughing at the same time. It was at New Salem. The boys were having a jollification after an election. They had a large fire made of shavings and hemp-stalks; and some of the boys made a bet with a fellow that I shall call 'Ike,' that he couldn't run his little bob-tail pony through the fire. Ike took them up, and trotted his pony back about one hundred yards, to give him a good start, as he said. The boys all formed a line on either side, to make way for Ike and his pony. Presently here he come, full tilt, with his hat off; and, just as he reached the blazing fire, Ike raised in his saddle for the jump straight ahead; but pony was not of the same opinion, so he flew the track, and pitched poor Ike into the devouring element. Mr. Lincoln saw it, and ran to his assistance, saying, 'You have carried this thing far enough.' I could see he was mad, though he could not help laughing himself. The poor fellow was considerably scorched about the head and face. Jack Armstrong took him to the doctor, who shaved his head to fix him up, and put salve on the burn. I think Mr. Lincoln was a little mad at Armstrong, and Jack himself was very sorry for it. Jack gave Ike next morning a dram, his breakfast, and a seal-skin cap, and sent him home."
"One cold winter day, Lincoln saw a poor fellow named "Ab Trent" hard at work chopping up "a house," which Mr. Hill had employed him to convert into firewood. Ab was barefooted, and shivered pitifully while he worked. Lincoln watched him a few moments, and asked him what he was to get for the job. Ab answered, 'One dollar;' and, pointing to his naked and suffering feet, said that he wished to buy a pair of shoes. Lincoln seized the axe, and, ordering the boy to comfort himself at the nearest fire, chopped up 'the house' so fast that Ab and the owner were both amazed when they saw it done." According to Mr. Rutledge, "Ab remembered this act with the liveliest gratitude. Once he, being a cast-iron Democrat, determined to vote against his party and for Mr. Lincoln; but the friends, as he afterwards said with tears in his eyes, made him drunk, and he had voted against Abe. Thus he did not even have an opportunity to return the noble conduct of Mr. Lincoln by this small measure of thanks."
We have given some instances of Mr. Lincoln's unfailing disposition to succor the weak and the unfortunate. He never seems to have hesitated on account of actual or fancied danger to himself, but boldly espoused the side of the oppressed against the oppressor, whoever and whatever the latter might be. In a fisticuff or a rough-and-tumble fight, he was one of the most formidable men of the region in which he lived. It took a big bully, and a persevering one, to force him into a collision; but, being in, his enemy found good reason to beware of him. He was cool, calculating, but swift in action, and terribly strong. Nevertheless, he never promoted a quarrel, and would be at infinite trouble any time to compose one. An unnecessary broil gave him pain; and whenever there was the slightest hope of successful mediation, whether by soft speech or by the strong hand, he was instant and fearless for peace. His good-nature, his humor, his fertility in expedients, and his alliance, offensive and defensive, with Jack Armstrong, made him almost irresistible in his benevolent efforts to keep the ordinary ruffian of New Salem within decent bounds. If he was talking to Squire Godbey or Row Herndon (each of them give incidents of the kind), and he heard the sounds or saw the signs which betoken a row in the street, he would jump up, saying, "Let's go and stop it." He would push through the "ring" which was generally formed around the combatants, and, after separating the latter, would demand a truce and "a talk;" and so soon as he got them to talking, the victory was his. If it happened to be rough Jack himself who was at the bottom of the disturbance, he usually became very much ashamed of his conduct, and offered to "treat," or do any thing else that would atone for his brutality.
Lincoln has often been seen in the old mill on the river-bank to lift a box of stones weighing from a thousand to twelve hundred pounds. Of course it was not done by a straight lift of the hands: he "was harnessed to the box with ropes and straps." It was even said he could easily raise a barrel of whiskey to his mouth when standing upright, and take a drink out of the bung-hole; but of course one cannot believe it. Frequent exhibitions of such strength doubtless had much to do with his unbounded influence over the rougher class of men.
He possessed the judicial quality of mind in a degree so eminent, and it was so universally recognized, that he never could attend a horse-race without being importuned to act as a judge, or witness a bet without assuming the responsibility of a stakeholder. "In the spring or summer of 1832," says Henry McHenry, "I had a horse-race with George Warbur-ton. I got Lincoln, who was at the race, to be a judge of the race, much against his will and after hard persuasion. Lincoln decided correctly; and the other judge said, 'Lincoln is the fairest man I ever bad to deal with: if Lincoln is in this county when I die, I want him to be my administrator, for he is the only man I ever met with that was wholly and unselfishly honest.'" His ineffable purity in determining the result of a scrub-race had actually set his colleague to thinking of his latter end.
But Lincoln endured another annoyance much worse than this. He was so generally esteemed, and so highly admired, that, when any of his neighbors had a fight in prospect, one of the parties was sure to insist upon his acting as his second. Lincoln was opposed to fights, but there were some fights that had to be fought; and these were "set," a day fixed, and the neighborhood notified. In these cases there was no room for the offices of a mediator; and when the affair was pre-ordained, "and must come off," Mr. Lincoln had no excuse for denying the request of a friend.
"Two neighbors, Harry Clark and Ben Wilcox," says Mr. Rutledge, "had had a lawsuit. The defeated declared, that, although he was beaten in the suit, he could whip his opponent. This was a formal challenge, and was at once carried to the ears of the victor (Wilcox), and as promptly accepted. The time, place, and seconds were chosen with due regularity; Mr. Lincoln being Clark's, and John Brewer, Wilcox's second. The parties met, stripped themselves all but their breeches, went in, and Mr. Lincoln's principal was beautifully whipped. These combats were conducted with as much ceremony and punctiliousness as ever graced the duelling-ground. After the conflict, the seconds conducted their respective principals to the river, washed off the blood, and assisted them to dress. During this performance, the second of the party opposed to Mr. Lincoln remarked, 'Well, Abe, my man has whipped yours, and I can whip you.' Now, this challenge came from a man who was very small in size. Mr. Lincoln agreed to fight, provided he would chalk out his size on Mr. Lincoln's person, and every blow struck outside of that mark should be counted foul. After this sally, there was the best possible humor, and all parties were as orderly as if they had been engaged in the most harmless amusement."
In 1834 Lincoln was again a candidate for the Legislature, and this time was elected by a larger majority than any other man on the ticket. By this time the party with which he acted in the future was "discriminated as Whig;" and he did not hesitate to call himself a Whig, although he sought and received the votes of a great many Democrats. Just before the time had arrived for candidates to announce themselves, he went to John T. Stuart, and told him "the Democrats wanted to run him." He made the same statement to Ninian W. Edwards. Edwards and Stuart were both his personal and political friends, and they both advised him to let the Democrats have their way. Major Stuart's advice was certainly disinterested; for, in pursuance of it, two of the Whig candidates, Lincoln and Dawson, made a bargain with the Democrats which very nearly proved fatal to Stuart himself. He was at that time the favorite candidate of the Whigs for the Legislature; but the conduct of Lincoln and Dawson so demoralized the party, that his vote was seriously diminished. Up to this time Sangamon had been stanchly Democratic; but even in this election of 1834 we perceive slight evidences of that party's decay, and so early as 1836 the county became thoroughly Whig.
We shall give no details of this campaign, since we should only be repeating what is written of the campaign of 1832. But we cannot withhold one extract from the reminiscences of Mr. Row Herndon:—
"He (Lincoln) came to my house, near Island Grove, during harvest. There were some thirty men in the field. He got his dinner, and went out in the field where the men were at work. I gave him an introduction, and the boys said that they could not vote for a man unless he could make a hand. 'Well, boys,' said he, 'if that is all, I am sure of your votes.' He took hold of the cradle, and led the way all the round with perfect ease. The boys were satisfied, and I don't think he lost a vote in the crowd.
"The next day was speaking at Berlin. He went from my house with Dr. Barnett, the man that had asked me who this man Lincoln was. I told him that he was a candidate for the Legislature. He laughed and said, 'Can't the party raise no better material than that?' I said, 'Go to-morrow, and hear all before you pronounce judgment.' When he came back, I said, 'Doctor, what say you now?' 'Why, sir,' said he, 'he is a perfect take-in: he knows more than all of them put together.'"
Lincoln got 1,376 votes, Dawson 1,370, Carpenter 1,170, Stuart 1,164. Lincoln was at last duly elected a Representative by a very flattering majority, and began to look about for the pecuniary means necessary to maintain his new dignity. In this extremity he had recourse to an old friend named Coleman Smoot.
One day in 1832, while he was clerking for Offutt, a stranger came into the store, and soon disclosed the fact that his name was Smoot. Abe was behind the counter at the moment; but, hearing the name, he sprang over and introduced himself. Abe had often heard of Smoot, and Smoot had often heard of Abe. They had been as anxious to meet as ever two celebrities were; but hitherto they had never been able to manage it. "Smoot," said Lincoln, after a steady survey of his person, "I am very much disappointed in you: I expected to see an old Probst of a fellow." (Probst, it appears, was the most hideous specimen of humanity in all that country.) "Yes," replied Smoot; "and I am equally disappointed, for I expected to see a good-looking man when I saw you." A few neat compliments like the foregoing laid the foundation of a lasting intimacy between the two men, and in his present distress Lincoln knew no one who would be more likely than Smoot to respond favorably to an application for money.
"After he was elected to the Legislature," says Mr. Smoot, "he came to my house one day in company with Hugh Armstrong. Says he, 'Smoot, did you vote for me?' I told him I did. 'Well,' says he, 'you must loan me money to buy suitable clothing, for I want to make a decent appearance in the Legislature.' I then loaned him two hundred dollars, which he returned to me according to promise."
The interval between the election and his departure for the seat of government was employed by Mr. Lincoln partly in reading, partly in writing.
The community in which he lived was pre-eminently a community of free-thinkers in matters of religion; and it was then no secret, nor has it been a secret since, that Mr. Lincoln agreed with the majority of his associates in denying to the Bible the authority of divine revelation. It was his honest belief,—a belief which it was no reproach to hold at New Salem, Anno Domini 1834, and one which he never thought of concealing. It was no distinction, either good or bad, no honor, and no shame. But he had made himself thoroughly familiar with the writings of Paine and Volney,—"The Ruins" by one and "The Age of Reason" by the other. His mind was full of the subject, and he felt an itching to write. He did write, and the result was a "little book." It was probably merely an extended essay; but it is ambitiously spoken of as "a book" by himself and by the persons who were made acquainted with its contents. In this work he intended to demonstrate,—
"First, that the Bible was not God's revelation; and,
"Secondly, that Jesus was not the Son of God."
These were his leading propositions, and surely they were comprehensive enough; but the reader will be better able to guess at the arguments by which they were sustained, when he has examined some of the evidence recorded in Chapter XIX.
No leaf of this little volume has survived. Mr. Lincoln carried it in manuscript to the store of Mr. Samuel Hill, where it was read and discussed. Hill was himself an unbeliever, but his son considered this book "infamous." It is more than probable that Hill, being a warm personal friend of Lincoln, feared that the publication of the essay would some day interfere with the political advancement of his favorite. At all events, he snatched it out of his hand, and thrust it into the fire, from which not a shred escaped. The sequel will show that even Mr. Hill's provident forethought was not altogether equal to the prevention of the injury he dreaded.
THE reader is already familiar with the name of James Rutledge, the founder of New Salem, and the owner in part of the famous mill on the Sangamon. He was born in South Carolina, and was of the illustrious Rutledge family of that State. From South Carolina he emigrated to Kentucky, and thence to Illinois. In 1828 he settled at New Salem, built the mill and laid out the village in conjunction with Mr. Cameron, a retired minister of the Cumberland Presbyterians. Mr. Rutledge's character seems to have been pure and high; for wherever his name occurs in the voluminous records before us,—in the long talks and the numerous epistles of his neighbors,—it is almost invariably coupled with some expression of genuine esteem and respect.
At one time, and along with his other business,—which appears to have been quite extensive and various,—Mr. Rutledge kept the tavern, the small house with four rooms on the main street of New Salem, just opposite Lincoln's grocery. There Mr. Lincoln came to board late in 1832, or early in 1833. The family consisted of the father, mother, and nine children,—three of them born in Kentucky and six in Illinois; three grown up, and the rest quite young. Ann, the principal subject of this chapter, was the third child. She was born on the 7th of January, 1813, and was about nineteen years of age when Mr. Lincoln came to live in the house.
When Ann was a little maiden just turned of seventeen, and still attending the school of that redoubtable pedagogue Min-ter Graham, there came to New Salem a young gentleman of singular enterprise, tact, and capacity for business. He is identical with the man whom we have already quoted as "the pioneer of New Salem as a business point," and who built the first storehouse there at the extravagant cost of fifteen dollars. He took boarding with Mr. Rutledge's friend and partner, James Cameron, and gave out his name as John McNeil. He came to New Salem with no other capital than good sense and an active and plucky spirit; but somehow fortune smiled indiscriminately on all his endeavors, and very soon—as early as the latter part of 1832—he found himself a well-to-do and prosperous man, owning a snug farm seven miles north of New Salem, and a half-interest in the largest store of the place. This latter property his partner, Samuel Hill, bought from him at a good round sum; for McNeil now announced his intention of being absent for a brief period, and his purpose was such that he might need all his available capital.
In the mean time the partners, Hill and McNeil, had both fallen in love with Ann Rutledge, and both courted her with devoted assiduity. But the contest had long since been decided in favor of McNeil, and Ann loved him with all her susceptible and sensitive heart. When the time drew near for McNeil to depart, he confided to Ann a strange story,—and, in the eyes of a person less fond, a very startling story. His name was not John McNeil at all, but John McNamar. His family was a highly respectable one in the State of New York; but a few years before his father had failed in business, and there was great distress at home. He (John) then conceived the romantic plan of running away, and, at some undefined place in the far West, making a sudden fortune with which to retrieve the family disaster. He fled accordingly, changed his name to avoid the pursuit of his father, found his way to New Salem, and—she knew the rest. He was now able to perform that great act of filial piety which he set out to accomplish, would return at once to the relief of his parents, and, in all human probability, bring them back with him to his new home in Illinois. At all events, she might look for his return as speedily as the journey could be made with ordinary diligence; and thenceforward there should be no more partings between him and his fair Ann. She believed this tale, because she loved the man that told it; and she would have believed it all the same if it had been ten times as incredible. A wise man would have rejected it with scorn, but the girl's instinct was a better guide; and McNamar proved to be all that he said he was, although poor Ann never saw the proof which others got of it.
McNamar rode away "on old Charley," an antiquated steed that had seen hard usage in the Black Hawk War. Charley was slow, stumbled dreadfully, and caused his rider much annoyance and some hard swearing. On this provoking animal McNamar jogged through the long journey from New Salem to New York, and arrived there after many delays, only to find that his broken and dispirited father was fast sinking into the grave. After all his efforts, he was too late: the father could never enjoy the prosperity which the long-absent and long-silent son had brought him. McNamar wrote to Ann that there was sickness in the family, and he could not return at the time appointed. Then there were other and still other postponements; "circumstances over which he had no control" prevented his departure from time to time, until years had rolled away, and Ann's heart had grown sick with hope deferred. She never quite gave him up, but continued to expect him until death terminated her melancholy watch. His inexplicable delay, however, the infrequency of his letters, and their unsatisfactory character,—these and something else had broken her attachment, and toward the last she waited for him only to ask a release from her engagement, and to say that she preferred another and a more urgent suitor. But without his knowledge and formal renunciation of his claim upon her, she did not like to marry; and, in obedience to this refinement of honor, she postponed her union with the more pressing lover until Aug. 25, 1835, when, as many persons believe, she died of a broken heart.
Lincoln's friend Short was in some way related to the Rutledges, and for a while Lincoln visited Ann two or three times a week at his house. According to him, "Miss Rutledge was a good-looking, smart, lively girl, a good housekeeper, with a moderate education, and without any of the so-called accomplishments." L. M. Greene, who knew her well, talks about her as "a beautiful and very amiable young woman;" and "Nult" Greene is even more enthusiastic. "This young lady," in the language of the latter gentleman, "was a woman of exquisite beauty; but her intellect was quick, sharp, deep, and philosophic, as well as brilliant. She had as gentle and kind a heart as an angel, full of love, kindliness, and sympathy. She was beloved by everybody, and everybody respected and loved her, so sweet and angelic was she. Her character was more than good: it was positively noted throughout the county. She was a woman worthy of Lincoln's love." McNamar, her unfortunate lover, says, "Miss Ann was a gentle, amiable maiden, without any of the airs of your city belles, but winsome and comely withal; a blonde in complexion, with golden hair, cherry-red lips, and a bonny blue eye." Even the women of the neighborhood united with the men to praise the name of this beautiful but unhappy girl. Mrs. Hardin Bale "knew her well. She had auburn hair, blue eyes, fair complexion; was a slim, pretty, kind, tender, good-hearted woman; in height about five feet three inches, and weighed about a hundred and twenty pounds. She was beloved by all who knew her. McNamar, Hill, and Lincoln all courted her near the same time. She died as it were of grief. Miss Rutledge was beautiful." Such was Ann Rutledge, the girl in whose grave Mr. Lincoln said, "My heart lies buried." When Mr. Lincoln first saw Ann, she was probably the most refined woman with whom he had then ever spoken,—a modest, delicate creature, fascinating by reason of the mere contrast with the rude people by whom they were both surrounded. She had a secret, too, and a sorrow,—the unexplained and painful absence of McNamar,—which no doubt made her all the more interesting to him whose spirit was often even more melancholy than her own. It would be hard to trace the growth of such an attachment at a time and place so distant; but that it actually grew, and became an intense and mutual passion, the evidence before us is painfully abundant.
Mr. Lincoln was always welcome at the little tavern, at Short's on the Sand Ridge, or at the farm, half a mile from Short's, where the Rutledges finally abode. Ann's father was his devoted friend, and the mother he called affectionately "Aunt Polly." It is probable that the family looked upon McNamar's delay with more suspicion than Ann did herself. At all events, all her adult relatives encouraged the suit which Lincoln early began to press; and as time, absence, and apparent neglect, gradually told against McNamar, she listened to him with augmenting interest, until, in 1835, we find them formally and solemnly betrothed. Ann now waited only for the return of McNamar to marry Lincoln. David Rutledge urged her to marry immediately, without regard to any thing but her own happiness; but she said she could not consent to it until McNamar came back and released her from her pledge. At length, however, as McNamar's re-appearance became more and more hopeless, she took a different view of it, and then thought she would become Abe's wife as soon as he found the means of a decent livelihood. "Ann told me once," says James M. in a letter to R. B. Rutledge, in coming from camp-meeting on Rock Creek, "that engagements made too far ahead sometimes failed; that one had failed (meaning her engagement with McNamar), and gave me to understand, that, as soon as certain studies were completed, she and Lincoln would be married."
In the summer of 1835 Ann showed unmistakable symptoms of failing health, attributable, as most of the neighborhood believed, to the distressing attitude she felt bound to maintain between her two lovers. On the 25th of August, in that year, she died of what the doctors chose to call "brain-fever." In a letter to Mr. Herndon, her brother says, "You suggest that the probable cause of Ann's sickness was her conflicts, emotions, &c. As to this I cannot say. I, however, have my own private convictions. The character of her sickness was brain-fever." A few days before her death Lincoln was summoned to her bedside. What happened in that solemn conference was known only to him and the dying girl. But when he left her, and stopped at the house of John Jones, on his way home, Jones saw signs of the most terrible distress in his face and his conduct. When Ann actually died, and was buried, his grief became frantic: he lost all self-control, even the consciousness of identity, and every friend he had in New Salem pronounced him insane, mad, crazy. "He was watched with especial vigilance," as William Green tells us, "during storms, fogs, damp, gloomy weather, for fear of an accident." "At such times he raved piteously, declaring, among other wild expressions of his woe, 'I can never be reconciled to have the snow, rains, and storms to beat upon her grave!'"
About three-quarters of a mile below New Salem, at the foot of the main bluff, and in a hollow between two lateral bluffs, stood the house of Bowlin Greene, built of logs and weather-boarded. Thither the friends of Lincoln, who apprehended a total abdication of reason, determined to transport him, partly for the benefit of a mere change of scene, and partly to keep him within constant reach of his near and noble friend, Bowlin Greene. During this period of his darkened and wavering intellect, when "accidents" were momentarily expected, it was discovered that Bowlin Greene possessed a power to persuade and guide him proportioned to the affection that had subsisted between them in former and better times. Bowlin Greene came for him, but Lincoln was cunning and obstinate: it required the most artful practices of a general conspiracy of all his friends to "disarm his suspicions," and induce him to go and stay with his most anxious and devoted friend. But at last they succeeded; and Lincoln remained down under the bluff for two or three weeks, the object of undisguised solicitude and of the strictest surveillance. At the end of that time his mind seemed to be restored, and it was thought safe to let him go back to his old haunts,—to the study of law, to the writing of legal papers for his neighbors, to pettifogging before the justice of the peace, and perhaps to a little surveying. But Mr. Lincoln was never precisely the same man again. At the time of his release he was thin, haggard, and careworn,—like one risen from the verge of the grave. He had always been subject to fits of great mental depression, but after this they were more frequent and alarming. It was then that he began to repeat, with a feeling which seemed to inspire every listener with awe, and to carry him to the fresh grave of Ann at every one of his solemn periods, the lines entitled, "Immortality; or, Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud?" None heard him but knew that he selected these curiously empty, yet wonderfully sad, impressive lines, to celebrate a grief which lay with continual heaviness on his heart, but to which he could not with becoming delicacy directly allude. He muttered them as he rambled through the woods, or walked by the roaring Sangamon. He was heard to murmur them to himself as he slipped into the village at nightfall, after a long walk of six miles, and an evening visit to the Concord graveyard; and he would suddenly break out with them in little social assemblies after noticeable periods of silent gloom. They came unbidden to his lips, while the air of affliction in face and gesture, the moving tones and touching modulations of his voice, made it evident that every syllable of the recitation was meant to commemorate the mournful fate of Ann. The poem is now his: the name of the obscure author is forgotten, and his work is imperishably associated with the memory of a great man, and interwoven with the history of his greatest Sorrow. Mr. Lincoln's adoption of it has saved it from merited oblivion, and translated it from the "poet's corner" of the country newspaper to a place in the story of his own life,—a story that will continue to be written, or written about, as long as our language exists.
Many years afterwards, when Mr. Lincoln, the best lawyer of his section, with one exception, travelled the circuit with the court and a crowd of his jolly brethren, he always rose early, be fore any one else was stirring, and, raking together a few glowing coals on the hearth, he would sit looking into them, musing and talking with himself, for hours together. One morning, in the year of his nomination, his companions found him in this attitude, when "Mr. Lincoln repeated aloud, and at length, the poem 'Immortality,'" indicating his preference for the two last stanzas, but insisting that the entire composition "sounded to him as much like true poetry as any thing that he had ever heard."
In Carpenter's "Anecdotes and Reminiscences of President Lincoln," occurs the following passage:—?
"The evening of March 22, 1864, was a most interesting one to me. I was with the President alone in his office for several hours. Busy with pen and papers when I went in, he presently threw them aside, and commenced talking to me of Shakspeare, of whom he was very fond. Little 'Tad,' his son, coming in, he sent him to the library for a copy of the plays, and then read to me several of his favorite passages. Relapsing into a sadder strain, he laid the book aside, and, leaning back in his chair, said,—
"'There is a poem which has been a great favorite with me for years, which was first shown to me when a young man by a friend, and which I afterwards saw and cut from a newspaper, and learned by heart. I would,' he continued, 'give a great deal to know who wrote it; but I have never been able to ascertain.'
"Then, half closing his eyes, he repeated the verses to me:—
"'Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud? Like a swift-fleeting meteor, a fast-flying cloud, A flash of the lightning, a break of the wave, He passeth from life to his rest in the grave. The leaves of the oak and the willow shall fade, Be scattered around, and together be laid; And the young and the old, and the low and the high, Shall moulder to dust, and together shall lie. The infant a mother attended and loved; The mother that infant's affection who proved; The husband that mother and infant who blest,— Each, all, are away to their dwellings of rest. [The maid on whose cheek, on whose brow, in whose eye, Shone beauty and pleasure, her triumphs are by; And the memory of those who loved her and praised, Are alike from the minds of the living erased.] The hand of the king that the sceptre hath borne, The brow of the priest that the mitre hath worn, The eye of the sage, and the heart of the brave, Are hidden and lost in the depths of the grave. The peasant whose lot was to sow and to reap, The herdsman who climbed with his goats up the steep, The beggar who wandered in search of his bread, Have faded away like the grass that we tread. [The saint who enjoyed the communion of Heaven, The sinner who dared to remain unforgiven, The wise and the foolish, the guilty and just, Have quietly mingled their bones in the dust.] So the multitude goes, like the flower or the weed, That withers away to let others succeed; So the multitude comes, even those we behold, To repeat every tale that has often been told. For we are the same our fathers have been; We see the same sights our fathers have seen; We drink the same stream, we view the same sun, And run the same course our fathers have run. The thoughts we are thinking our fathers would think; From the death we are shrinking our fathers would shrink; To the life we are clinging they also would cling; But it speeds from us all like a bird on the wing. They loved, but the story we cannot unfold; They scorned, but the heart of the haughty is cold; They grieved, but no wail from their slumber will come; They joyed, but the tongue of their gladness is dumb. They died, ay, they died: we things that are now, That walk on the turf that lies over their brow, And make in their dwellings a transient abode, Meet the things that they met on their pilgrimage road. Yea, hope and despondency, pleasure and pain, Are mingled together in sunshine and rain; And the smile and the tear, the song and the dirge, Still follow each other like surge upon surge. 'Tis the wink of an eye,'tis the draught of a breath, From the blossom of health to the paleness of death, From the gilded saloon to the bier and the shroud,— Oh! why should the spirit of mortal be proud?'"
It was only a year or two after the death of Ann Rutledge that Mr. Lincoln told Robert L. Wilson, a distinguished colleague in the Legislature, parts of whose letter will be printed in another place, that, although "he appeared to enjoy life rapturously," it was a mistake; that, "when alone, he was so overcome by mental depression, that he never dared to carry a pocket-knife." And during all Mr. Wilson's extended acquaintance with him he never did own a knife, notwithstanding he was inordinately fond of whittling.
Mr. Herndon says, "He never addressed another woman, in my opinion, 'Yours affectionately,' and generally and characteristically abstained from the use of the word 'love.' That word cannot be found more than a half-dozen times, if that often, in all his letters and speeches since that time. I have seen some of his letters to other ladies, but he never says 'love.' He never ended his letters with 'Yours affectionately,' but signed his name, 'Your friend, A. Lincoln.'" After Mr. Lincoln's election to the Presidency, he one day met an old friend, Isaac Cogdale, who had known him intimately in the better days of the Rutledges at New Salem. "Ike," said he, "call at my office at the State House about an hour by sundown. The company will then all be gone." Cogdale went according to request; "and sure enough," as he expressed it, "the company dropped off one by one, including Lincoln's clerk."
"'I want to inquire about old times and old acquaintances,' began Mr. Lincoln. 'When we lived in Salem, there were the Greenes, Potters, Armstrongs, and Rutledges. These folks have got scattered all over the world,—some are dead. Where are the Rutledges, Greenes, &c.?'
"After we had spoken over old times," continues Cogdale,—"persons, circumstances,—in which he showed a wonderful memory, I then dared to ask him this question:—
"'May I now, in turn, ask you one question, Lincoln?'
"'Assuredly. I will answer your question, if a fair one, with all my heart.'
"'Well, Abe, is it true that you fell in love and courted Ann Rutledge?'
"'It is true,—true: indeed I did. I have loved the name of Rutledge to this day. I have kept my mind on their movements ever since, and love them dearly.'
"'Abe, is it true,'" still urged Cogdale, "that you ran a little wild about the matter?'
"'I did really. I ran off the track. It was my first. I loved the woman dearly. She was a handsome girl; would have made a good, loving wife; was natural and quite intellectual, though not highly educated. I did honestly and truly love the girl, and think often, often, of her now.'"
A few weeks after the burial of Ann, McNamar returned to New Salem. He saw Lincoln at the post-office, and was struck with the deplorable change in his appearance. A short time afterwards Lincoln wrote him a deed, which he still has, and prizes highly, in memory of his great friend and rival. His father was at last dead; but he brought back with him his mother and her family. In December of the same year his mother died, and was buried in the same graveyard with Ann. During his absence, Col. Rutledge had occupied his farm, and there Ann died; but "the Rutledge farm" proper adjoined this one to the south. "Some of Mr. Lincoln's corners, as a surveyor, are still visible on lines traced by him on both farms."
On Sunday, the fourteenth day of October, 1866, William H. Herndon knocked at the door of John McNamar, at his residence, but a few feet distant from the spot where Ann Rutledge breathed her last. After some preliminaries not necessary to be related, Mr. Herndon says, "I asked him the question:—
"'Did you know Miss Rutledge? If so, where did she die?'
"He sat by his open window, looking westerly; and, pulling me closer to himself, looked through the window and said, 'There, by that,'—choking up with emotion, pointing his long forefinger, nervous and trembling, to the spot,—'there, by that currant-bush, she died. The old house in which she and her father died is gone.'
"After further conversation, leaving the sadness to momentarily pass away, I asked this additional question:—
"'Where was she buried?'
"'In Concord burying-ground, one mile south-east of this place.'"
Mr. Herndon sought the grave. "S. C. Berry," says he, "James Short (the gentleman who purchased in Mr. Lincoln's compass and chain in 1834, under an execution against Lincoln, or Lincoln & Berry, and gratuitously gave them back to Mr. Lincoln), James Miles, and myself were together.
"I asked Mr. Berry if he knew where Miss Rutledge was buried,—the place and exact surroundings. He replied, 'I do. The grave of Miss Rutledge lies just north of her brother's, David Rutledge, a young lawyer of great promise, who died in 1842, in his twenty-seventh year.'
"The cemetery contains but an acre of ground, in a beautiful and secluded situation. A thin skirt of timber lies on the east, commencing at the fence of the cemetery. The ribbon of timber, some fifty yards wide, hides the sun's early rise. At nine o'clock the sun pours all his rays into the cemetery. An extensive prairie lies west, the forest north, a field on the east, and timber and prairie on the south. In this lonely ground lie the Berrys, the Rutledges, the Clarys, the Armstrongs, and the Joneses, old and respected citizens,—pioneers of an early day. I write, or rather did write, the original draught of this description in the immediate presence of the ashes of Miss Ann Rutledge, the beautiful and tender dead. The village of the dead is a sad, solemn place. Its very presence imposes truth on the mind of the living writer. Ann Rutledge lies buried north of lier brother, and rests sweetly on his left arm, angels to guard her. The cemetery is fast filling with the hazel and the dead."
A lecture delivered by William H. Herndon at Springfield, in 1866, contained the main outline, without the minuter details, of the story here related. It was spoken, printed, and circulated without contradiction from any quarter. It was sent to the Rutledges, McNeeleys, Greenes, Short, and many other of the old residents of New Salem and Petersburg, with particular requests that they should correct any error they might find in it. It was pronounced by them all truthful and accurate; but their replies, together with a mass of additional evidence, have been carefully collated with the lecture, and the result is the present chapter. The story of Ann Rutledge, Lincoln, and McNamar, as told here, is as well proved as the fact of Mr. Lincoln's election to the Presidency.
FOLLOWING strictly the chronological order hitherto observed in the course of this narrative, we should be compelled to break off the story of Mr. Lincoln's love-affairs at New Salem, and enter upon his public career in the Legislature and before the people. But, while by that means we should preserve continuity in one respect, we should lose it in another; and the reader would perhaps prefer to take in at one view all of Mr. Lincoln's courtships, save only that one which resulted in marriage.
Three-quarters of a mile, or nearly so, north of Bowlin Greene's, and on the summit of a hill, stood the house of Bennett Able, a small frame building eighteen by twenty feet. Able and his wife were warm friends of Mr. Lincoln; and many of his rambles through the surrounding country, reading and talking to himself, terminated at their door, where he always found the latch-string on the outside, and a hearty welcome within. In October, 1833, Mr. Lincoln met there Miss Mary Owens, a sister of Mrs. Able, and, as we shall presently learn from his own words, admired her, although not extravagantly. She remained but four weeks, and then went back to her home in Kentucky.
Miss Owens's mother being dead, her father married again; and Miss Owens, for good reasons of her own, thought she would rather live with her sister than with her stepmother. Accordingly, in the fall of 1836, she re-appeared at Able's, passing through New Salem on the day of the presidential election, where the men standing about the polls stared and wondered at her "beauty." Twenty eight or nine years of age, "she was," in the language of Mr. L. M. Greene, "tall and portly; weighed about one hundred and twenty pounds, and had large blue eyes, with the finest trimmings I ever saw. She was jovial, social, loved wit and humor, had a liberal English education, and was considered wealthy. Bill," continues our excellent friend, "I am getting old; have seen too much trouble to give a lifelike picture of this woman. I won't try it. None of the poets or romance-writers has ever given to us a picture of a heroine so beautiful as a good description of Miss Owens in 1836 would be."
Mrs. Hardin Bale, a cousin to Miss Owens, says "she was blue-eyed, dark-haired, handsome,—not pretty,—was rather large and tall, handsome, truly handsome, matronly looking, over ordinary size in height and weight.... Miss Owens was handsome, that is to say, noble-looking, matronly seeming."
Respecting her age and looks, Miss. Owens herself makes the following note, Aug. 6, 1866:—-
"Born in the year eight; fair skin, deep-blue eyes, with dark curling hair; height five feet five inches, weighing about one hundred and fifty pounds."
Johnson G. Greene is Miss Owens's cousin; and, whilst on a visit to her in 1866, he contrived to get her version of the Lincoln courtship at great length. It does not vary in any material part from the account currently received in the neighborhood, and given by various persons, whose oral or written testimony is preserved in Mr. Herndon's collection of manuscripts. Greene (J. G.) described her in terms about the same as those used by Mrs. Bale, adding that "she was a nervous and muscular woman," very "intellectual,"—"the most intellectual woman he ever saw,"—"with a forehead massive and angular, square, prominent, and broad."
After Miss Owens's return to New Salem, in the fall of 1813, Mr. Lincoln was unremitting in his attentions; and wherever she went he was at her side. She had many relatives in the neighborhood,—the Bales, the Greenes, the Grahams: and, if she went to spend an afternoon or an evening with any of these, Abe was very likely to be on hand to conduct her home. He asked her to marry him; but she prudently evaded a positive answer until she could make up her mind about questionable points of his character. She did not think him coarse or cruel; but she did think him thoughtless, careless, not altogether as polite as he might be,—in short, "deficient," as she expresses it, "in those little links which make up the great chain of woman's happiness." His heart was good, his principles were high, his honor sensitive; but still, in the eyes of this refined, young lady, he did not seem to be quite the gentleman. "He was lacking in the smaller attentions;" and, in fact, the whole affair is explained when she tells us that "his education was different from" hers.
One day Miss Owens and Mrs. Bowlin Greene were making their way slowly and tediously up the hill to Able's house, when they were joined by Lincoln. Mrs. Bowlin Greene was carrying "a great big fat child, heavy, and crossly disposed." Although the woman bent pitiably under her burden, Lincoln offered her no assistance, but, dropping behind with Miss Owens, beguiled the way according to his wishes. When they reached the summit, "Miss Owens said to Lincoln laughingly, 'You would not make a good husband. Abe.' They sat on the fence; and one word brought on another, till a split or breach ensued."
Immediately after this misunderstanding, Lincoln went off toward Havana on a surveying expedition, and was absent about three weeks. On the first day of his return, one of Able's boys was sent up "to town" for the mail. Lincoln saw him at the post-office, and "asked if Miss Owens was at Mr. Able's." The boy said "Yes."—"Tell her," said Lin-join, "that I'll be down to see her in a few minutes." Now, Miss Owens had determined to spend that evening at Minter Graham's; and when the boy gave in the report, "she thought a moment, and said to herself, 'If I can draw Lincoln up there to Graham's, it will be all right.'" This scheme was to operate as a test of Abe's love; but it shared the fate of some of "the best-laid schemes of mice and men," and went "all agley."
Lincoln, according to promise, went down to Able's, and asked if Miss Owens was in. Mrs. Able replied that she had gone to Graham's, about one and a half miles from Able's due south-west. Lincoln said, "Didn't she know I was coming?" Mrs. Able answered, "No;" but one of the children said, "Yes, ma, she did, for I heard Sam tell her so." Lincoln sat a while, and then went about his business. "The fat was now in the fire. Lincoln thought, as he was extremely poor, and Miss Owens very rich, it was a fling on him on that account. Abe was mistaken in his guesses, for wealth cut no figure in Miss Owens's eyes. Miss Owens regretted her course. Abe would not bend; and Miss Owens wouldn't. She said, if she had it to do over again she would play the cards differently.... She had two sons in the Southern army. She said that if either of them had got into difficulty, she would willingly have gone to old Abe for relief."
In Miss Owens's letter of July 22, 1866, it will be observed! that she tacitly admitted to Mr. Gaines Greene "the circumstances in connection with Mrs. Greene and child." Although she here denies the precise words alleged to have been used by her in the little quarrel at the top of the hill, she does not deny the impression his conduct left upon her mind, but presents additional evidence of it by the relation of another incident of similar character, from which her inferences were the same.
Fortunately we are not compelled, to rely upon tradition, however authentic, for the facts concerning this interesting episode in Mr. Lincoln's life. Miss Owens is still alive to tell her own tale, and we have besides his letters to the lady herself. Mr. Lincoln wrote his account of it as early as 1838. As in duty bound, we shall permit the lady to speak first. At her particular request, her present name and residence are suppressed.
———, May 1, 1866.
Mr. W. H. Herndon.
Dear Sir,—After quite a struggle with my feelings, I have at last decided to send you the letters in my possession written by Mr. Lincoln, believing, as I do, that you are a gentleman of honor, and will faithfully abide by all you have said.
My associations with your lamented friend were in Menard County, whilst visiting a sister, who then resided near Petersburg. I have learned that my maiden name is now in your possession; and you have ere this, no doubt, been informed that I am a native Kentuckian.
As regards Miss Rutledge, I cannot tell you any thing, she having died previous to my acquaintance with Mr. Lincoln; and I do not now recollect of ever hearing him mention her name. Please return the letters at your earliest convenience.
Very respectfully yours,
Mary S.———.
———, May 22,1866.
Mr. W. H. Herndon.
My dear Sir,—Really you catechise me in true lawyer style; but I feel you will have the goodness to excuse me if I decline answering all your questions in detail, being well assured that few women would have ceded as much as I have under all the circumstances.
You say you have heard why our acquaintance terminated as it did. I, too, have heard the same bit of gossip; but I never used the remark which Madam Rumor says I did to Mr. Lincoln. I think I did on one occasion say to my sister, who was very anxious for us to be married, that I thought Mr. Lincoln was deficient in those little links which make up the chain of woman's happiness,—at least, it was so in my case. Not that I believed it proceeded from a lack of goodness of heart: but his training had been different from mine; hence there was not that congeniality which would otherwise have existed.
From his own showing, you perceive that his heart and hand were at my disposal; and I suppose that my feelings were not sufficiently enlisted to have the matter consummated. About the beginning of the year 1833 I left Illinois, at which time our acquaintance and correspondence ceased without ever again being renewed.
My father, who resided in Green County, Kentucky, was a gentleman of considerable means; and I am persuaded that few persons placed a higher estimate on education than he did.
Respectfully yours,
Mart S.———.
———, July 22, 1866.
Mr. W. H. Herndon.
Dear Sir,—I do not think that you are pertinacious in asking the question relative to old Mrs. Bowlin Greene, because I wish to set you right on that question. Your information, no doubt, came through my cousin, Mr. Gaines Greene, who visited us last winter. Whilst here, he was laughing at me about Mr. Lincoln, and among other things spoke about the circumstance in connection with Mrs. Greene and child. My impression is now that I tacitly admitted it, for it was a season of trouble with me, and I gave but little heed to the matter. We never had any hard feelings toward each other that I know of. On no occasion did I say to Mr. Lincoln that I did not believe he would make a kind husband, because he did not tender his services to Mrs. Greene in helping of her carry her babe. As I said to you in a former letter, I thought him lacking in smaller attentions. One circumstance presents itself just now to my mind's eye. There was a company of us going to Uncle Billy Greene's. Mr. Lincoln was riding with me; and we had a very bad branch to cross. The other gentlemen were very officious in seeing that their partners got over safely. We were behind, he riding in, never looking back to see how I got along. When I rode up beside him, I remarked, "You are a nice fellow! I suppose you did not care whether my neck was broken or not." He laughingly replied (I suppose by way of compliment) that he knew I was plenty smart to take care of myself.
In many things he was sensitive, almost to a fault. He told me of an incident: that he was crossing a prairie one day, and saw before him "a hog mired down," to use his own language. He was rather "fixed up;" and he resolved that he would pass on without looking towards the shoat. After he had gone by, he said the feeling was irresistible; and he had to look back, and the poor thing seemed to say wistfully, "There, now, my last hope is gone;" that he deliberately got down, and relieved it from its difficulty.
In many things we were congenial spirits. In politics we saw eye to eye, though since then we differed as widely as the South is from the North. But methinks I hear you say, "Save me from a political woman!" So say I.
The last message I ever received from him was about a year after we parted in Illinois. Mrs. Able visited Kentucky; and he said to her in Springfield, "Tell your sister that I think she was a great fool, because she did not stay here, and marry me." Characteristic of the man.
Respectfully yours,
Mary S.———.
Vandalia, Dec. 13, 1836.
Mary,—I have been sick ever since my arrival, or I should have written sooner. It is but little difference, however, as I have very little even yet to write. And more, the longer I can avoid the mortification of looking in the post-office for your letter, and not finding it, the better. You see I am mad about that old letter yet. I don't like very well to risk you again. I'll try you once more, anyhow.
The new State House is not yet finished, and consequently the Legislature is doing little or nothing. The Governor delivered an inflammatory political message, and it is expected there will be some sparring between the parties about it as soon as the two Houses get to business. Taylor delivered up his petitions for the new county to one of our members this morning. I am told he despairs of its success, on account of all the members from Morgan County opposing it. There are names enough on the petition, I think, to justify the members from our county in going for it; but if the members from Morgan oppose it, which they say they will, the chance will be bad.
Our chance to take the seat of government to Springfield is better than I expected. An internal-improvement convention was held here since we met, which recommended a loan of several million of dollars, on the faith of the State, to construct railroads. Some of the Legislature are for it, and some against it: which has the majority I cannot tell. There is great strife and struggling for the office of the United States Senator here at this time. It is probable we shall ease their pains in a few days. The opposition men have no candidate of their own; and consequently they will smile as complacently at the angry snarl of the contending Van-Buren candidates and their respective friends, as the Christian does at Satan's rage. You recollect that I mentioned at the outset of this letter that I had been unwell. That is the fact, though I believe I am about well now; but that, with other things I cannot account for, have conspired, and have gotten my spirits so low that I feel that I would rather be any place in the world than here. I really cannot endure the thought of staying here ten weeks. Write back as soon as you get this, and, if possible, say something that will please me; for really I have not been pleased since I left you. This letter is so dry and stupid that I am ashamed to send it, but with my present feelings I cannot do any better.
Give my best respects to Mr. and Mrs. Able and family.
Your friend,
Lincoln.
Springfield, May 7, 1837.
Miss Mary S. Owens.
Friend Mary,—I have commenced two letters to send you before this, both of which displeased me before I got half done, and so I tore them up. The first I thought was not serious enough, and the second was on the other extreme. I shall send this, turn out as it may.
This thing of living in Springfield is rather a dull business, after all; at least, it is so to me. I am quite as lonesome here as I ever was anywhere in my life. I have been spoken to by but one woman since I've been here, and should not have been by her, if she could have avoided it. I've never been to church yet, nor probably shall not be soon. I stay away because I am conscious I should not know how to behave myself.
I am often thinking about what we said of your coming to live at Springfield. I am afraid you would not be satisfied. There is a great deal of flourishing about in carriages here, which it would be your doom to see without sharing it. You would have to be poor, without the means of hiding your poverty. Do you believe you could bear that patiently? Whatever woman may cast her lot with mine, should any ever do so, it is my intention to do all in my power to make her happy and contented; and there is nothing I can imagine that would make me more unhappy than to fail in the effort. I know I should be much happier with you than the way I am, provided I saw no signs of discontent in you. What you have said to me may have been in the way of jest, or I may have misunderstood it. If so, then let it be forgotten; if otherwise, I much wish you would think seriously before you decide. For my part, I have already decided. What I have said I will most positively abide by, provided you wish it. My opinion is, that you had better not do it. You have not been accustomed to hardship, and it may be more severe than you now imagine. I know you are capable of thinking correctly on any subject; and, if you deliberate maturely upon this before you decide, then I am willing to abide your decision.
You must write me a good long letter after you get this. You have nothing else to do; and, though it might not seem interesting to you after you have written it, it would be a good deal of company to me in this "busy wilderness." Tell your sister, I don't want to hear any more about selling out and moving, That gives me the hypo whenever I think of it.
Yours, &c.,
Lincoln.
Springfield, Aug. 16, 1837.
Friend Mary,—You will no doubt think it rather strange that I should write you a letter on the same day on which we parted; and I can only account for it by supposing that seeing you lately makes me think of you more than usual; while at our late meeting we had but few expressions of thoughts. You must know that I cannot see you, or think of you, with entire indifference; and yet it may be that you are mistaken in regard to what my real feelings toward you are. If I knew you were not, I should not trouble you with this letter. Perhaps any other man would know enough without further information; but I consider it my peculiar right to plead ignorance, and your bounden duty to allow the plea. I want in all cases to do right; and most particularly so in all cases with women. I want, at this particular time, more than any thing else, to do right with you: and if I knew it would be doing right, as I rather suspect it would, to let you alone, I would do it. And, for the purpose of making the matter as plain as possible, I now say that you can now drop the subject, dismiss your thoughts (if you ever had any) from me forever, and leave this letter unanswered, without calling forth one accusing murmur from me. And I will even go further, and say, that, if it will add any thing to your comfort or peace of mind to do so, it is my sincere wish that you should. Do not understand by this that I wish to cut your acquaintance. I mean no such thing. What I do wish is, that our further acquaintance shall depend upon yourself. If such further acquaintance would constitute nothing to your happiness, I am sure it would not to mine. If you feel yourself in any degree bound to me, I am now willing to release you, provided you wish it; while, on the other hand, I am willing, and even anxious, to bind you faster, if I can be convinced that it will, in any considerable degree, add to your happiness. This, indeed, is the whole question with me. Nothing would make me more miserable than to believe you miserable,—nothing more happy than to know you were so.
In what I have now said, I think I cannot be misunderstood; and to make myself understood is the only object of this letter.
If it suits you best to not answer this, farewell. A long life and a merry one attend you. But, if you conclude to write back, speak as plainly as I do. There can be neither harm nor danger in saying to me any thing you think, just in the manner you think it.
My respects to your sister. Your friend,
Lincoln.
After his second meeting with Mary, Mr. Lincoln had little time to prosecute his addresses in person; for early in December he was called away to his seat in the Legislature; but, if his tongue was silent in the cause, his pen was busy.
During the session of the Legislature of 1886-7, Mr. Lincoln made the acquaintance of Mrs. O. H. Browning, whose husband was also a member. The acquaintance ripened into friendship, and that winter and the next Mr. Lincoln spent a great deal of time in social intercourse with the Brownings. Mrs. Browning knew nothing as yet of the affair with Miss Owens; but as the latter progressed, and Lincoln became more and more involved, she noticed the ebb of his spirits, and often rallied him as the victim of some secret but consuming passion. With this for his excuse, Lincoln wrote her, after the adjournment of the Legislature, a full and connected account of the manner in which he had latterly been making "a fool of" himself. For many reasons the publication of this letter is an extremely painful duty. If it could be withheld, and the act decently reconciled to the conscience of a biographer professing to be honest and candid, it should never see the light in these pages. Its grotesque humor, its coarse exaggerations in describing the person of a lady whom the writer was willing to marry, its imputation of toothless and weatherbeaten old age to a woman really young and handsome, its utter lack of that delicacy of tone and sentiment which one naturally expects a gentleman to adopt when he thinks proper to discuss the merits of his late mistress,—all these, and its defective orthography, it would certainly be more agreeable to suppress than to publish. But, if we begin by omitting or mutilating a document which sheds so broad a light upon one part of his life and one phase of his character, why may we not do the like as fast and as often as the temptations arise? and where shall the process cease? A biography worth writing at all is worth writing fully and honestly; and the writer who suppresses or mangles the truth is no better than he who bears false witness in any other capacity. In April, 1838, Miss Owens finally departed from Illinois; and in that same month Mr. Lincoln wrote Mrs. Browning:—
Springfield, April 1, 1838.
Dear Madam,—Without appologising for being egotistical, I shall make the history of so much of my life as has elapsed since I saw you the subject of this letter. And, by the way, I now discover, that, in order to give a full and inteligible account of the things I have done and suffered since I saw you, I shall necessarily have to relate some that happened before.
It was, then, in the autumn of 1836, that a married lady of my acquaintance, and who was a great friend of mine, being about to pay a visit to her father & other relatives residing in Kentucky, proposed to me that on her return she would bring a sister of hers with her on condition that I would engage to become her brother-in-law with all convenient despatch. I, of course, accepted the proposal, for you know I could not have done otherwise, had I really been averse to it; but privately, between you and me, I was most confoundedly well pleased with the project. I had seen the said sister some three years before, thought her inteligent and agreeable, and saw no good objection to plodding life through hand in hand with her. Time passed on, the lady took her journey, and in due time returned, sister in company, sure enough. This astonished me a little; for it appeared to me that her coming so readily showed that she was a trifle too willing; but, on reflection, it occurred to me that she might have been prevailed on by her married sister to come, without any thing concerning me ever having been mentioned to her; and so I concluded, that, if no other objection presented itself, I would consent to wave this. All this occurred to me on hearing of her arrival in the neighborhood; for, be it remembered, I had not yet seen her, except about three years previous, as above mentioned. In a few days we had an interview; and, although I had seen her before, she did not look as my imagination had pictured her. I knew she was oversize, but she now appeared a fair match for Falstaff. I knew she was called an "old maid," and I felt no doubt of the truth of at least half of the appelation; but now, when I beheld her, I could not for my life avoid thinking of my mother; and this, not from withered features, for her skin was too full of fat 'to permit of its contracting into wrinkles, but from her want of teeth, weather-beaten appearance in general, and from a kind of notion that ran in my head that nothing could have commenced at the size of infancy and reached her present bulk in less than thirty-five or forty years; and, in short, I was not at all pleased with her. But what could I do? I had told her sister that I would take her for better or for worse; and I made a point of honor and conscience in all things to stick to my word, especially if others had been induced to act on it, which in this case I had no doubt they had; for I was now fairly convinced that no other man on earth would have her, and hence the conclusion that they were bent on holding me to my bargain. "Well," thought I, "I have said it, and, be the consequences what they may, it shall not be my fault if I fail to do it." At once I determined to consider her my wife; and, this done, all my powers of discovery were put to work in search of perfections in her which might be fairly sett off against her defects. I tried to imagine her handsome, which, but for her unfortunate corpulency, was actually true. Exclusive of this, no woman that I have ever seen has a finer face. I also tried to convince myself that the mind was much more to be valued than the person; and in this she was not inferior, as I could discover, to any with whom I had been acquainted.
Shortly after this, without attempting to come to any positive understanding with her, I sat out for Vandalia, when and where you first saw me. During my stay there I had letters from her which did not change my opinion of either her intelect or intention, but, on the contrary, confirmed it in both.
All this while, although I was fixed, "firm as the surge-repelling rock," in my resolution, I found I was continually repenting the rashness which had led me to make it. Through life, I have been in no bondage, either real or imaginary, from the thraldom of which I so much desired to be free. After my return home, I saw nothing to change my opinions of her in any particular. She was the same, and so was I. I now spent my time in planing how I might get along through life after my contemplated change of circumstances should have taken place, and how I might procrastinate the evil day for a time, which I really dreaded as much, perhaps more, than an Irishman does the halter.
After all my suffering upon this deeply-interesting subject, here I am, wholly, unexpectedly, completely, out of the "scrape;" and I now want to know if you can guess how I got out of it,—out, clear, in every sense of the term; no violation of word, honor, or conscience. I don't believe you can guess, and so I might as well tell you at once. As the lawyer says, it was done in the manner following, to wit: After I had delayed the matter as long as I thought I could in honor do (which, by the way, had brought me round into the last fall), I concluded I might as well bring it to a consumation without further delay; and so I mustered my resolution, and made the proposal to her direct: but, shocking to relate, she answered, No, At first I supposed she did it through an affectation of modesty, which I thought but ill became her under the peculiar circumstances of her case; but, on my renewal of the charge, I found she repeled it with greater firmness than before. I tried it again and again, but with the same success, or rather with the same want of success.
I finally was forced to give it up; at which I verry unexpectedly found myself mortified almost beyond endurance. I was mortified, it seemed to me, in a hundred different ways. My vanity was deeply wounded by the reflection that I had so long been too stupid to discover her intentions, and at the same time never doubting that I understood them perfectly; and also that she, whom I had taught myself to believe nobody else would have, had actually rejected me with all my fancied greatness. And, to cap the whole, I then, for the first time, began to suspect that I was really a little in love with her. But let it all go. I'll try and outlive it. Others have been made fools of by the girls; but this can never with truth be said of me. I most emphatically, in this instance, made a fool of myself. I have now come to the conclusion never again to think of marrying, and for this reason: I can never be satisfied with any one who would be blockhead enough to have me.
When you receive this, write me a long yarn about something to amuse me. Give my respects to Mr. Browning.
Your sincere friend,
A. Lincoln,
Mrs. O. H. Browning.
THE majority of Mr. Lincoln's biographers—and they are many and credulous—tell us that he walked from New Salem to Vandalia, a distance of one hundred miles, to take his seat, for the first time, in the Legislature of the State. But that is an innocent mistake; for he was resolved to appear with as much of the dignity of the senator as his circumstances would permit. It was for this very purpose that he had borrowed the two hundred dollars from Coleman Smoot; and, when the choice between riding and walking presented itself, he sensibly enough got into the stage, with his new clothes on, and rode to the scene of his labors.
When he arrived there, he found a singular state of affairs. Duncan had been chosen Governor at the recent August election by "the whole-hog Jackson men;" but he was absent in Congress during the whole of the campaign; and, now that he came to the duties of his office, it was discovered that he had been all the while an anti-Jackson man, and was quite willing to aid the Whigs in furtherance of some of their worst schemes. These schemes were then just beginning to be hatched in great numbers; but in due time they were enacted into laws, and prepared Illinois with the proper weights of public debt and "rag" currency, to sink her deeper than her neighbors into the miseries of financial ruin in 1837. The speculating fever was just reaching Illinois; the land and town-lot business had barely taken shape at Chicago; and State banks and multitudinous internal improvements were yet to be invented. But this Legislature was a very wise one in its own conceit, and was not slow to launch out with the first of a series of magnificent experiments. It contented itself, however, with chartering a State bank, with a capital of one million five hundred thousand dollars; rechartering, with a capital of three hundred thousand dollars, the Shawneetown Bank, which had broken twelve years before; and providing for a loan of five hundred thousand dollars, on the credit of the State, wherewith to make a beginning on the Illinois and Michigan Canal. The bill for the latter project was drawn and introduced by Senator James M. Strode, the gentleman who described with such moving eloquence the horrors of Stillman's defeat. These measures Gov. Ford considers "the beginning of all the bad legislation which followed in a few years, and which, as is well known, resulted in general ruin." Mr. Lincoln favored them all, and faithfully followed out the policy of which they were the inauguration at subsequent sessions of the same body. For the present, nevertheless, he was a silent member, although he was assigned a prominent place on the Committee on Public Accounts and Expenditures. The bank-charters were drawn by a Democrat who hoped to find his account in the issue; all the bills were passed by a Legislature "nominally" Democratic; but the Board of Canal Commissioners was composed exclusively of Whigs, and the Whigs straightway assumed control of the banks.
It was at a special session of this Legislature that Lincoln first saw Stephen A. Douglas, and, viewing his active little person with immense amusement, pronounced him "the least man he ever saw." Douglas had come into the State (from Vermont) only the previous year, but, having studied law for several months, considered himself eminently qualified to be State's attorney for the district in which he lived, and was now come to Vandalia for that purpose. The place was already filled by a man of considerable distinction; but the incumbent remaining at home, possibly in blissful ignorance of his neighbor's design, was easily supplanted by the supple Vermonter.
It is the misfortune of legislatures in general, as it was in those days the peculiar misfortune of the Legislature of Illinois, to be beset by a multitude of gentlemen engaged in the exclusive business of "log-rolling." Chief among the "rollers" were some of the most "distinguished" members, each assisted by an influential delegation from the district, bank, or "institution" to be benefited by the legislation proposed. An expert "log-roller," an especially wily and persuasive person, who could depict the merits of his scheme with roseate but delusive eloquence, was said to carry "a gourd of possum fat," and the unhappy victim of his art was said to be "greased and swallowed."
It is not to be supposed that anybody ever succeeded in anointing a single square inch of Mr. Lincoln's person with the "fat" that deluded; but historians aver that "the Long Nine," of whom he was the longest and cleverest, possessed "gourds" of extraordinary dimensions, and distributed "grease" of marvellous virtues. But of that at another place.
In 1836 Mr. Lincoln was again a candidate for the Legislature; his colleagues on the Whig ticket in Sangamon being, for Representatives, John Dawson, William F. Elkin, N. W. Edwards, Andrew McCormick, Dan Stone, and R. L. Wilson; and for Senators, A. G. Herndon and Job Fletcher. They were all elected but one, and he was beaten by John Calhoun.
Mr. Lincoln opened the campaign by the following manifesto:—
New Salem, June 13, 1836.
To the Editor of "The Journal."
In your paper of last Saturday, I see a communication over the signature of "Many Voters," in which the candidates who are announced in the "Journal" are called upon to "show their hands." Agreed. Here's mine.
I go for all sharing the privileges of the government who assist in bearing its burdens. Consequently, I go for admitting all whites to the right of suffrage who pay taxes or bear arms (by no means excluding females).
If elected, I shall consider the whole people of Sangamon my constituents, as well those that oppose as those that support me.
While acting as their Representative, I shall be governed by their will on all subjects upon which I have the means of knowing what their will is; and upon all others I shall do what my own judgment teaches me will best advance their interests. Whether elected or not, I go for distributing the proceeds of the sales of the public lands to the several States, to enable our State, in common with others, to dig canals and construct railroads without borrowing money and paying the interest on it.
If alive on the first Monday in November, I shall vote for Hugh L. White for President.
Very respectfully,
A. Lincoln.
The elections were held on the first Monday in August, and the campaign began about six weeks or two months before. Popular meetings were advertised in "The Sangamon Journal" and "The State Register,"—organs of the respective parties. Not unfrequently the meetings were joint, —composed of both parties,—when, as Lincoln would say, the candidates "put in their best licks," while the audience "rose to the height of the great argument" with cheers, taunts, cat-calls, fights, and other exercises appropriate to the free and untrammelled enjoyment of the freeman's boon.
The candidates travelled from one grove to another on horseback; and, when the "Long Nine" (all over six feet in height) took the road, it must have been a goodly sight to see.
"I heard Lincoln make a speech," says James Gourly, "in Mechanicsburg, Sangamon County, in 1836. John Neal had a fight at the time: the roughs got on him, and Lincoln jumped in and saw fair play. We staid for dinner at Green's, close to Mechanicsburg,—drank whiskey sweetened with honey. There the questions discussed were internal improvements, Whig principles." (Gourly was a great friend of Lincoln's, for Gourly had had a foot-race "with H. B. Truett, now of California," and Lincoln had been his "judge;" and it was a remarkable circumstance, that nearly everybody for whom Lincoln "judged" came out ahead.)
"I heard Mr. Lincoln during the same canvass," continues Gourly. "It was at the Court House, where the State House now stands. The Whigs and Democrats had a general quarrel then and there. N. W. Edwards drew a pistol on Achilles Morris." But Gourly's account of this last scene is unsatisfactory, although the witness is willing; and we turn to Lincoln's colleague, Mr. Wilson, for a better one. "The Saturday evening preceding the election the candidates were addressing the people in the Court House at Springfield. Dr. Early, one of the candidates on the Democratic side, made some charge that N. W. Edwards, one of the candidates on the Whig side, deemed untrue. Edwards climbed on a table, so as to be seen by Early, and by every one in the house, and at the top of his voice told Early that the charge was false. The excitement that followed was intense,—so much so, that fighting men thought that a duel must settle the difficulty. Mr. Lincoln, by the programme, followed Early. He took up the subject in dispute, and handled it fairly, and with such ability that every one was astonished and pleased. So that difficulty ended there. Then, for the first time, developed by the excitement of the occasion, he spoke in that tenor intonation of voice that ultimately settled down into that clear, shrill monotone style of speaking that enabled his audience, however large, to hear distinctly the lowest sound of his voice."
It was during this campaign, possibly at the same meeting, that Mr. Speed heard him reply to George Forquer. Forquer had been a leading Whig, one of their foremost men in the Legislature of 1834, but had then recently changed sides, and thereupon was appointed Register of the Land Office at Springfield. Mr. Forquer was an astonishing man: he not only astonished the people by "changing his coat in politics," but by building the best frame-house in Springfield, and erecting over it the only lightning-rod the entire region could boast of. At this meeting he listened attentively to Mr. Lincoln's first speech, and was much annoyed by the transcendent power with which the awkward young man defended the principles he had himself so lately abandoned. "The speech" produced a profound impression, "especially upon a large number of Lincoln's friends and admirers, who had come in from the country" expressly to hear and applaud him.
"At the conclusion of Lincoln's speech" (we quote from Mr. Speed), "the crowd was dispersing, when Forquer rose and asked to be heard. He commenced by saying that the young man would have to be taken down, and was sorry that the task devolved upon him. He then proceeded to answer Lincoln's speech in a style, which, while it was able and fair, yet, in his whole manner, asserted and claimed superiority. Lincoln stood near him, and watched him during the whole of his speech. When Forquer concluded, he took the stand again. I have often heard him since, in court and before the people, but never saw him appear so well as upon that occasion. He replied to Mr. Forquer with great dignity and force; but I shall never forget the conclusion of that speech. Turning to Mr. Forquer, he said, that he had commenced his speech by announcing that 'this young man would have to be taken down.' Turning then to the crowd, he said, 'It is for you, not for me, to say whether I am up or down. The gentleman has alluded to my being a young man: I am older in years than I am in the tricks and trades of politicians. I desire to live, and I desire place and distinction as a politician; but I would rather die now, than, like the gentleman, live to see the day that I would have to erect a lightning-rod to protect a guilty conscience from an offended God.'"
He afterwards told Speed that the sight of that same rod "had led him to the study of the properties of electricity and the utility of the rod as a conductor."
Among the Democratic orators stumping the county at this time was Dick Taylor, a pompous gentleman, who went abroad in superb attire, ruffled shirts, rich vest, and immense watch-chains, with shining and splendid pendants. But Dick was a severe Democrat in theory, made much of "the hard-handed yeomanry," and flung many biting sarcasms upon the aristocratic pretensions of the Whigs,—the "rag barons" and the manufacturing "lords." He was one day in the midst of a particularly aggravating declamation of this sort, "when Abe began to feel devilish, and thought he would take the wind out of Dick's sails by a little sport." He therefore "edged" slyly up to the speaker, and suddenly catching his vest by the lower corner, and giving it a sharp pull upward, it opened wide, and out fell upon the platform, in full view of the astonished audience, a mass of ruffled shirt, gold watch, chains, seals, and glittering jewels. Jim Matheny was there, and nearly broke his heart with mirth. "The crowd couldn't stand it, but shouted uproariously." It must have been then that Abe delivered the following speech, although Ninian W. Edwards places it in 1840:—
"While he [Col. Taylor] was making these charges against the Whigs over the country, riding in fine carriages, wearing ruffled shirts, kid gloves, massive gold watch-chains, with large gold seals, and flourishing a heavy gold-headed cane, he [Lincoln] was a poor boy, hired on a flatboat at eight dollars a month, and had only one pair of breeches to his back, and they were buckskin,—'and,' said Lincoln, 'if you know the nature of buckskin, when wet and dried by the sun, they will shrink,—and mine kept shrinking, until they left several inches of my legs bare between the tops of my socks and the lower part of my breeches; and, whilst I was growing taller, they were becoming shorter, and so much tighter, that they left a blue streak around my legs that can be seen to this day. If you call this aristocracy, I plead guilty to the charge.'" Hitherto Sangamon County had been uniformly Democratic; but at this election the Whigs carried it by an average majority of about four hundred, Mr. Lincoln receiving a larger vote than any other candidate. The result was in part due to a transitory and abortive attempt of the anti-Jackson and anti-Van-Buren men to build up a third party, with Judge White of Tennessee as its leader. This party was not supposed to be wedded to the "specie circular," was thought to be open to conviction on the bank question, clamored loudly about the business interests and general distress of the country, and was actually in favor of the distribution of the proceeds of the sales of the public lands. In the nomenclature of Illinois, its members might have been called "nominal Jackson men;" that is to say, men who continued to act with the Democratic party, while disavowing its cardinal principles,—traders, trimmers, cautious schismatics who argued the cause of Democracy from a brief furnished by the enemy. The diversion in favor of White was just to the hand of the Whigs, and they aided it in every practicable way. Always for an expedient when an expedient would answer, a compromise when a compromise would do, the "hand" Mr. Lincoln "showed" at the opening of the campaign contained the "White" card among the highest of its trumps. "If alive on the first Monday in November, I shall vote for Hugh L. White for President." A number of local Democratic politicians assisting him to play it, it won the game in 1836, and Sangamon County went over to the Whigs.
At this election Mr. Douglas was made a Representative from Morgan County, along with Col. Hardin, from whom he had the year before taken the State's attorneyship. The event is notable principally because Mr. Douglas was nominated by a convention, and not by the old system of self-announcement, which, under the influence of Eastern immigrants, like himself, full of party zeal, and attached to the customs of the places whence they came, was gradually but surely falling into disfavor. Mr. Douglas served only one session, and then became Register of the Land Office at Springfield. The next year he was nominated for Congress in the Peoria District, under the convention system, and in the same year Col. Stephenson was nominated for Governor in the same way. The Whigs were soon compelled to adopt the device which they saw marshalling the Democrats in a state of complete discipline; whilst they themselves were disorganized by a host of volunteer candidates and the operations of innumerable cliques and factions. At first "it was considered a Yankee contrivance," intended to abridge the liberties of the people; but the Whig "people" were as fond of victory, offices, and power as their enemies were, and in due time they took very kindly to this effectual means of gaining them. A speech of Ebenezer Peck of Chicago, "before a great meeting of the lobby, during the special session of 1835-6 at Vandalia," being a production of special ingenuity and power, is supposed to have contributed largely to the introduction of the convention system into the middle and southern parts of the State. Mr. Peck was then a fervent Democrat, whom the Whigs delighted to malign as a Canadian monarchist; but in after times he was the fast and able friend of their great leader, Abraham Lincoln.
One of the first and worst effects of the stricter organization of parties in Illinois, as well as in other States, was the strong diversion of public attention from State to Federal affairs. Individual candidates were no longer required to "show their hands:" they accepted "platforms" when they accepted nominations; and without a nomination it was mere quixotism to stand at all. District, State, and national conventions, acting and re-acting upon one another, produced a concert of sentiment and conduct which overlaid local issues, and repressed independent proceedings. This improved party machinery supplied the readiest and most effective means of distributing the rapidly-increasing patronage of the Federal Executive; and those who did not wish to be cut off from its enjoyment could do no less than re-affirm with becoming fervor, in their local assemblages, the latest deliverance of the faith by the central authority. The promoters of heresies and schisms, the blind leaders who misled a county or a State convention, and seduced it into the declaration of principles of its own, had their seats contested in the next general council of the party, were solemnly sat upon, condemned, "delivered over to Satan to be buffeted," and cast out of the household of faith, to wander in the wilderness and to live upon husks. It was like a feeble African bishop imputing heresy to the Christian world, with Rome at its head. A man like Mr. Lincoln, who earnestly "desired place and distinction as a politician," labored without hope while his party affinities remained the subject of a reasonable doubt. He must be "a whole-hog man" or nothing, a Whig or a Democrat. Mr. Lincoln chose his company with commendable decision, and wasted no tender regrets upon his "nominal" Democratic friends. For White against Harrison, in November, 1836, he led the Whigs into action when the Legislature met in December; and when the hard-cider campaign of 1840 commenced, with its endless meetings and processions, its coon-skins and log-cabins, its intrigue, trickery, and fun, his musical voice rose loudest above the din for "Old Tippecanoe;" and no man did better service, or enjoyed those memorable scenes more, than he who was to be the beneficiary of a similar revival in 1860.
When this legislature met in the winter of 1836-7, the bank and internal-improvement infatuation had taken full possession of a majority of the people, as well as of the politicians. To be sure, "Old Hickory" had given a temporary check to the wild speculations in Western land by the specie circular, about the close of his administration, whereby gold and silver were made "land-office money;" and the Government declined to exchange any more of the public domain for the depreciated paper of rotten and explosive banks. Millions of notes loaned by the banks on insufficient security or no security at all were by this timely measure turned back into the banks, or converted to the uses of a more legitimate and less dangerous business. But, even if the specie circular had not been repealed, it would probably have proved impotent against the evils it was designed to prevent, after the passage of the Act distributing among the States the surplus (or supposed surplus) revenues of the Federal Government.
The last dollar of the old debt was paid in 1833. There were from time to time large unexpended and unappropriated balances in the treasury. What should be done with them? There was no sub-treasury as yet, and questions concerning the mere safe-keeping of these moneys excited the most tremendous political contests. The United States Bank had always had the use of the cash in the treasury in the form of deposits; but the bank abused its trust,—used its enormous power over the currency and exchanges of the country to achieve political results in its own interest, and, by its manifold sins and iniquities, compelled Gen. Jackson to remove the deposits. Ultimately the bank took shelter in Pennsylvania, where it began a new fraudulent life under a surreptitious clause tacked to the end of a road law on its passage through the General Assembly. In due time the "beast," as Col. Benton loved to call it, died in its chosen lair a shameful and ignominious death, cheating the public with a show of solvency to the end, and leaving a fine array of bill-holders and depositors to mourn one of the most remarkable delusions of modern times.
Withdrawn, or rather withheld (for they were never withdrawn), from the Bank of the United States, the revenues of the Federal Government were deposited as fast as they accrued in specie-paying State banks. They were paid in the notes of the thousand banks, good, bad, and indifferent, whose promises to pay constituted the paper currency of the day. It was this money which the Whigs, aided by Democratic recusants, proposed to give away to the States. They passed an Act requiring it to be deposited with the States,—ostensibly as a safe and convenient method of keeping it; but nobody believed that it would ever be called for, or paid if it was. It was simply an extraordinary largess; and pending the very embarrassment caused by itself, when the government had not a dollar wherewith to pay even a pension, and the temporary expedient was an issue of treasury notes against the better judgment of the party in power, the possibility of withdrawing these deposits was never taken into the account. The Act went into effect on the 1st of January, 1837, and was one of the immediate causes of the suspension and disasters of that year. "The condition of our deposit banks was desperate,—wholly inadequate to the slightest pressure on their vaults in the ordinary course of business, much less that of meeting the daily government drafts and the approaching deposit of near forty millions with the States." Nevertheless, the deposits began at the rate of ten millions to the quarter. The deposit banks "blew up;" and all the others, including that of the United States, closed their doors to customers and bill-holders, which gave them more time to hold public meetings, imputing the distress of the country to the hard-money policy of Jackson and Van Buren, and agitating for the re-charter of Mr. Biddle's profligate concern as the only remedy human ingenuity could devise.
It was in the month previous to the first deposit with the States,—about the time when Gov. Ford says, "lands and town-lots were the only articles of export" from Illinois; when the counters of Western land-offices were piled high with illusory bank-notes in exchange for public lands, and when it was believed that the West was now at last about to bound forward in a career of unexampled prosperity, under the forcing process of public improvements by the States, with the aid and countenance of the Federal Government,—that Mr. Lincoln went up to attend the first session of the new Legislature at Vandalia. He was big with projects: his real public service was just now about to begin. In the previous Legislature he had been silent, observant, studious. He had improved the opportunity so well, that of all men in this new body, of equal age in the service, he was the smartest parliamentarian and the cunningest "log-roller." He was fully determined to identify himself conspicuously with the "liberal" legislation in contemplation, and dreamed of a fame very different from that which he actually obtained as an antislavery leader. It was about this time that he told his friend, Mr. Speed, that he aimed at the great distinction of being called "the De Witt Clinton of Illinois."
Meetings with a view to this sort of legislation had been held in all, or nearly all, the counties in the State during the preceding summer and fall. Hard-money, strict-construction, no-monopoly, anti-progressive Democrats were in a sad minority. In truth, there was little division of parties about these matters which were deemed so essential to the prosperity of a new State. There was Mr. Lincoln, and there was Mr. Douglas, in perfect unison as to the grand object to be accomplished, but mortally jealous as to which should take the lead in accomplishing it. A few days before the Legislature assembled, "a mass convention" of the people of Sangamon County "instructed" their members "to vote for a general system of internal improvements." The House of Representatives organized in the morning; and in the evening its hall was surrendered to a convention of delegates from all parts of the State, which "devised and recommended to the Legislature a system of internal improvements, the chief feature of which was, that it should be commensurate with the wants of the people." This result was arrived at after two days of debate, with "Col. Thomas Mather, of the State Bank, as president."
Mr. Lincoln served on the Committee on Finance, and was a most laborious member, instant in season and out of season, for the great measures of the Whig party. It was to his individual exertion that the Whigs were indebted in no small degree for the complete success of their favorite schemes at this session. A railroad from Galena to the mouth of the Ohio was provided for; another from Alton to Shawneetown; another from Alton to Mount Carmel; another from Alton to the eastern boundary of the State towards Terre Haute; another from Quincy by way of Springfield to the Wabash; another from Bloomington to Pekin; another from Peoria to Warsaw,—in all about thirteen hundred miles. But in this comprehensive "system," "commensurate with the wants of the people," the rivers were not to be overlooked; and accordingly the Kaskaskia, the Illinois, the Great Wabash, the Little Wabash, and the Rock rivers were to be duly improved. To set these little matters in motion, a loan of eight millions of dollars was authorized; and, to complete the canal from Chicago to Peru, another loan of four millions of dollars was voted at the same session,—two hundred thousand dollars being given as a gratuity to those counties which seemed to have no special interest in any of the foregoing projects. Work on all these roads was to commence, not only at the same time, but at both ends of each road, and at all the river-crossings. There were as yet no surveys of any route, no estimates, no reports of engineers, or even unprofessional viewers. "Progress" was not to wait on trifles; capitalists were supposed to be lying in wait to catch these precious bonds; the money would be raised in a twinkling, and being applied with all the skill of "a hundred De Witt Clintons,"—a class of gentlemen at that time extremely numerous and obtrusive,—the loan would build the railroads, the railroads would build cities, cities would create farms, foreign capital would rush to so inviting a field, the lands would be taken up with marvellous celerity, and the "land-tax" going into a sinking fund, that, with some tolls and certain sly speculations to be made by the State, would pay principal and interest of the debt without ever a cent of taxation upon the people. In short, everybody was to be enriched, while the munificence of the State in selling its credit and spending the proceeds would make its empty coffers overflow with ready money. It was a dark stroke of statesmanship, a mysterious device in finance, which, whether from being misunderstood, or from being mismanaged, bore from the beginning fruits the very reverse of those it had promised.
A Board of Canal Commissioners was already in existence; but now were established, as necessary parts of the new "system," a Board of Fund Commissioners and a Board of Commissioners of Public Works.
The capital stock of the Shawneetown Bank was increased to one million seven hundred thousand dollars, and that of the State Bank to three million one hundred thousand dollars. The State took the new stock, and proposed to pay for it "with the surplus revenues of the United States, and the residue by a sale of State bonds." The banks were likewise made fiscal agencies, to place the loans, and generally to manage the railroad and canal funds. The career of these banks is an extremely interesting chapter in the history of Illinois,—little less so than the rise and collapse of the great internal-improvement system. But, as it has already a place in a chronicle of wider scope and greater merit than this, it is enough to say that in due time they went the way of their kind,—the State lost by them, and they lost by the State, in morals as well as in money.
The means used in the Legislature to pass the "system" deserve some notice for the instruction of posterity. "First, a large portion of the people were interested in the success of the canal, which was threatened, if other sections of the State were denied the improvements demanded by them; and thus the friends of the canal were forced to log-roll for that work by supporting others which were to be ruinous to the country. Roads and improvements were proposed everywhere, to enlist every section of the State. Three or four efforts were made to pass a smaller system; and, when defeated, the bill would be amended by the addition of other roads, until a majority was obtained for it. Those counties which could not be thus accommodated were to share in the fund of two hundred thousand dollars. Three roads were appointed to terminate at Alton, before the Alton interest would agree to the system. The seat of government was to be removed to Springfield. Sangamon County, in which Springfield is situated, was then represented by two Senators and seven Representatives, called the 'Long Nine,' all Whigs but one. Amongst them were some dexterous jugglers and managers in politics, whose whole object was to obtain the seat of government for Springfield. This delegation, from the beginning of the session, threw itself as a unit in support of, or in opposition to, every local measure of interest, but never without a bargain for votes in return on the seat-of-government question. Most of the other counties were small, having but one Representative and many of them with but one for a whole representative district; and this gave Sangamon County a decided preponderance in the log-rolling system of those days. It is worthy of examination whether any just and equal legislation can ever be sustained where some of the counties are great and powerful, and others feeble. But by such means 'The Long-Nine' rolled along like a snowball, gathering accessions of strength at every turn, until they swelled up a considerable party for Springfield, which party they managed to take almost as a unit in favor of the internal-improvement system, in return for which the active supporters of that system were to vote for Springfield to be the seat of government. Thus it was made to cost the State about six millions of dollars to remove the seat of government from Vandalia to Springfield, half of which sum would have purchased all the real estate in that town at three prices; and thus by log-rolling on the canal measure; by multiplying railroads; by terminating three railroads at Alton, that Alton might become a great city in opposition to St. Louis; by distributing money to some of the counties to be wasted by the county commissioners; and by giving the seat of government to Springfield,—was the whole State bought up, and bribed to approve the most senseless and disastrous policy which ever crippled the energies of a growing country." 1
1 Ford's History of Illinois.
Enumerating the gentlemen who voted for this combination of evils,—among them Stephen A. Douglas, John A. McClernand, James Shields, and Abraham Lincoln,—and reciting the high places of honor and trust to which most of them have since attained, Gov. Ford pronounces "all of them spared monuments of popular wrath, evincing how safe it is to a politician, but how disastrous it may be to the country, to keep along with the present fervor of the people."
"It was a maxim with many politicians just to keep along even with the humor of the people, right or wrong;" and this maxim Mr. Lincoln held then, as ever since, in very high estimation. But the "humor" of his constituents was not only intensely favorable to the new scheme of internal improvements: it was most decidedly their "humor" to have the capital at Springfield, and to make a great man of the legislator who should take it there. Mr. Lincoln was doubtless thoroughly convinced that the popular view of all these matters was the right one; but, even if he had been unhappily afflicted with individual scruples of his own, he would have deemed it but simple duty to obey the almost unanimous voice of his constituency. He thought he never could serve them better than by giving them just what they wanted; and that to collect the will of his people, and register it by his own vote, was the first and leading obligation of a representative. It happened that on this occasion the popular feeling fell in very pleasantly with his young dream of rivalling the fame of Clinton; and here, also, was a fine opportunity of repeating, in a higher strain and on a loftier stage, the ingenious arguments, which, in the very outset of his career, had proved so hard for "Posey and Ewing," when he overthrew those worthies in the great debate respecting the improvement of the Sangamon River.
"The Internal-Improvement Bill," says Mr. Wilson (one of the "Long Nine"), "and a bill to permanently locate the seat of government of the State, were the great measures of the session of 1836-7. Vandalia was then the seat of government, and had been for a number of years. A new state house had just been built. Alton, Decatur, Peoria, Jacksonville, Illiapolis, and Springfield were the points seeking the location, if removed from Vandalia. The delegation from Sangamon were a unit, acting in concert in favor of the permanent location at Springfield. The bill was introduced at an early day in the session, to locate, by a joint vote of both Houses of the Legislature. The friends of the other points united to defeat the bill, as each point thought the postponement of the location to some future period would give strength to their location. The contest on this bill was long and severe. Its enemies laid it on the table twice,—once on the table to the fourth day of July, and once indefinitely postponed it. To take a bill from the table is always attended with difficulty; but when laid on the table to a day beyond the session, or when indefinitely postponed, it requires a vote of reconsideration, which always is an intense struggle. In these dark hours, when our bill to all appearances was beyond resuscitation, and all our opponents were jubilant over our defeat, and when friends could see no hope, Mr. Lincoln never for one moment despaired; but, collecting his colleagues to his room for consultation, his practical common sense, his thorough knowledge of human nature, then made him an overmatch for his compeers, and for any man that I have ever known."
"We surmounted all obstacles, passed the bill, and, by a joint vote of both Houses, located the seat of government of the State of Illinois at Springfield, just before the adjournment of the Legislature, which took place on the fourth day of March, 1837. The delegation acting during the whole session upon all questions as a unit, gave them strength and influence, that enabled them to carry through their measures and give efficient aid to their friends. The delegation was not only remarkable for their numbers, but for their length, most of them measuring six feet and over. It was said at the time that that delegation measured fifty-four feet high. Hence they were known as 'The Long Nine.' So that during that session, and for a number of years afterwards, all the bad laws passed at that session of the Legislature were chargeable to the management and influence of 'The Long Nine.'
"He (Mr. Lincoln) was on the stump and in the halls of the Legislature a ready debater, manifesting extraordinary ability in his peculiar manner of presenting his subject. He did not follow the beaten track of other speakers and thinkers, but appeared to comprehend the whole situation of the subject, and take hold of its principles. He had a remarkable faculty for concentration, enabling him to present his subject in such a manner, as nothing but conclusions were presented."
It was at this session of the Legislature, March 3, 1837, that Mr. Lincoln began that antislavery record upon which his fame through all time must chiefly rest. It was a very mild beginning; but even that required uncommon courage and candor in the day and generation in which it was done.
The whole country was excited concerning the doctrines and the practices of the Abolitionists. These agitators were as yet but few in numbers: but in New England they comprised some of the best citizens, and the leaders were persons of high character, of culture and social influence; while, in the Middle States, they were, for the most part, confined to the Society of Friends, or Quakers. All were earnest, active, and uncompromising in the propagation of their opinions; and, believing slavery to be the "sum of all villanies," with the utmost pertinacity they claimed the unrestricted right to disseminate their convictions in any manner they saw fit, regardless of all consequences. They paid not the slightest heed to the wishes or the opinions of their opponents. They denounced all compromises with an unsparing tongue, and would allow no law of man to stand, in their eyes, above the law of God.
George Thompson, identified with emancipation in the British West Indies, had come and gone. For more than a year he addressed public meetings in New England, the Central States, and Ohio, and contributed not a little to the growing excitement by his fierce denunciations of the slave-holding class, in language with which his long agitation in England had made him familiar. He was denounced, insulted, and mobbed; and even in Boston he was once posted as an "infamous foreign scoundrel," and an offer was made of a hundred dollars to "snake him out" of a public meeting. In fact, Boston was not at all behind other cities and towns in its condemnation of the Abolitionists. A great meeting in Faneuil Hall, called by eighteen hundred leading citizens,—Whigs and Democrats,—condemned their proceedings in language as strong and significant as Richard Fletcher, Peleg Sprague, and Harrison Gray Otis could write it. But Garrison still continued to publish "The Liberator," filling it with all the uncompromising aggressiveness of his sect, and distributing it throughout the Southern States. It excited great alarm in the slaveholding communities where its secret circulation, in the minds of the slaveholders, tended to incite the slaves to insurrections, assassinations, and running away; but in the place where it was published it was looked upon with general contempt and disgust. When the Mayor of Baltimore wrote to the Mayor of Boston to have it suppressed, the latter (the eloquent Otis) replied, "that his officers had ferreted out the paper and its editor, whose office was an obscure hole; his only visible auxiliary a negro boy; his supporters a few insignificant persons of all colors."
At the close of the year 1835, President Jackson had called the attention of Congress to the doings of these people in language corresponding to the natural wrath with which he viewed the character of their proceedings. "I must also," said he, "invite your attention to the painful excitements in the South by attempts to circulate through the mails inflammatory appeals addressed to the passions of slaves, in prints and various sorts of publications calculated to stimulate them to insurrection, and to produce all the horrors of civil war. It is fortunate for the country that the good sense, the generous feeling, and deep-rooted attachment of the people of the non-slaveholding States to the Union and their fellow-citizens of the same blood in the South have given so strong and impressive a tone to the sentiments entertained against the proceedings of the misguided persons who have engaged in these unconstitutional and wicked attempts, and especially against the emissaries from foreign parts, who have dared to interfere in this matter, as to authorize the hope that these attempts will no longer be persisted in.... I would therefore call the special attention of Congress to the subject, and respectfully suggest the propriety of passing such a law as will prohibit, under severe penalties, the circulation in the Southern States, through the mail, of incendiary publications, intended to instigate the slaves to insurrection."
Mr. Clay said the sole purpose of the Abolitionists was to array one portion of the Union against the other. "With that in view, in all their leading prints and publications, the alleged horrors of slavery are depicted in the most glowing and exaggerated colors, to excite the imaginations and stimulate the rage of the people of the Free States against the people of the slaveholding States.... Why are the Slave States wantonly and cruelly assailed? Why does the abolition press teem with publications tending to excite hatred and animosity on the part of the Free States against the Slave States?... Why is Congress petitioned? Is their purpose to appeal to our understanding, and actuate our humanity? And do they expect to accomplish that purpose by holding us up to the scorn and contempt and detestation of the people of the Free States and the whole civilized world?... Union on the one side will beget union on the other.... One section will stand in menacing, hostile array against another; the collision of opinion will be quickly followed by the clash of arms."
Mr. Everett, then (1836) Governor of Massachusetts, informed the Legislature, for the admonition of these unsparing agitators against the peace of the South, that "every thing that tends to disturb the relations created by this compact [the Constitution] is at war with its spirit; and whatever, by direct and necessary operation, is calculated to excite an insurrection among the slaves, has been held by highly respectable legal authority an offence against the peace of this Commonwealth, which may be prosecuted as a misdemeanor at common law." It was proposed in the Legislature to pass an act defining the offence with more certainty, and attaching to it a severer penalty. The Abolitionists asked to be heard before the committee; and Rev. S. J. May, Ellis Gray Loring, Prof. Charles Follen, Samuel E. Sewell, and others of equal ability and character, spoke in their behalf. They objected to the passage of such an act in the strongest terms, and derided the value of a Union which could not protect its citizens in one of their most cherished rights. During the hearing, several bitter altercations took place between them and the chairman.
In New York, Gov. Marcy called upon the Legislature "to do what may be done consistently with the great principles of civil liberty, to put an end to the evils which the Abolitionists are bringing upon us and the whole country." The "character" and the "interests" of the State were equally at stake, and both would be sacrificed unless these furious and cruel fanatics were effectually suppressed.
In May, 1836, the Federal House of Representatives resolved, by overwhelming votes, that Congress had no right to interfere with slavery in the States, or in the District of Columbia, and that henceforth all abolition petitions should be laid on the table without being printed or referred. And, one day later than the date of Mr. Lincoln's protest, Mr. Van Buren declared in his inaugural, that no bill abolishing slavery in the District of Columbia, or meddling with it in the States where it existed, should ever receive his signature. "There was no other form," says Benton, "at that time, in which slavery agitation could manifest itself, or place it could find a point to operate; the ordinance of 1787 and the compromise of 1820 having closed up the Territories against it. Danger to slave property in the States, either by direct action, or indirectly through the District of Columbia, were the only points of expressed apprehension."
Abolition agitations fared little better in the twenty-fifth Congress than in the twenty-fourth. At the extra session in September of 1837, Mr. Slade of Vermont introduced two petitions for the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia; but, after a furious debate and a stormy scene, they were disposed of by the adoption of the following:—
"Resolved, That all petitions, memorials, and papers, touching the abolition of slavery, or the buying, selling, or transferring of slaves, in any State, District, or Territory, of the United States, be laid on the table, without being debated, printed, read, or referred; and that no further action whatever shall be had thereon."
In Illinois, at the time we speak of (March, 1837), an Abolitionist was rarely seen, and scarcely ever heard of. In many parts of the State such a person would have been treated as a criminal. It is true, there were a few Covenanters, with whom hatred of slavery in any form and wherever found was an essential part of their religion. Up to 1824 they had steadily refused to vote, or in any other way to acknowledge the State government, regarding it as "an heathen and unbaptized institution," because the Constitution failed to recognize "Jesus Christ as the head of the government, and the Holy Scriptures as the only rule of faith and practice." It was only when it was proposed to introduce slavery into Illinois by an alteration of that "heathen" Constitution, that the Covenanters consented to take part in public affairs. The movement which drew them out proved to be a long and unusually bitter campaign, lasting full eighteen months, and ending in the fall of 1824, with a popular majority of several thousand against calling a convention for the purpose of making Illinois a Slave State. Many of the antislavery leaders in this contest—conspicuous among whom was Gov. Coles—were gentlemen from Slave States, who had emancipated their slaves before removal, and were opposed to slavery, not upon religious or moral grounds, but because they believed it would be a material injury to the new country. Practically no other view of the question was discussed; and a person who should have undertaken to discuss it from the "man and brother" stand-point of more modern times would have been set down as a lunatic. A clear majority of the people were against the introduction of slavery into their own State; but that majority were fully agreed with their brethren of the minority, that those who went about to interfere with slavery in the most distant manner in the places where it already existed were deserving of the severest punishment, as the common enemies of society. It was in those days a mortal offence to call a man an Abolitionist, for Abolitionist was synonymous with thief. Between a band of men who stole horses and a band of men who stole negroes, the popular mind made small distinctions in the degrees of guilt. They were regarded as robbers, disturbers of the peace, the instigators of arson, murder, poisoning, rape; and, in addition to all this, traitors to the government under which they lived, and enemies to the Union which gave us as a people liberty and strength. In testimony of these sentiments, Illinois enacted a "black code" of most preposterous and cruel severity,—a code that would have been a disgrace to a Slave State, and was simply an infamy in a free one. It borrowed the provisions of the most revolting laws known among men, for exiling, selling, beating, bedevilling, and torturing negroes, whether bond or free. Under this law Gov. Coles, the leader of the antislavery party, who had emancipated his slaves, and settled them around him in his new home, but had neglected to file a bond with the condition that his freedmen should behave well and never become a charge upon the public, was fined two hundred dollars in each case; and, so late as 1852, the writer of these pages very narrowly escaped the same penalty for the same offence.
In 1835-36 Rev. Elijah P. Lovejoy had been publishing a moderately antislavery paper at St. Louis. But the people of that city did not look with favor upon his enterprise; and, after meeting with considerable opposition, in the summer of 1836 he moved his types and press across the river to Alton, Ill. Here he found an opposition more violent than that from which he had fled. His press was thrown into the river the night after its arrival; and he was informed that no abolition paper would be allowed in the town. The better class of citizens, however, deprecated the outrage, and pledged themselves to reimburse Mr. Lovejoy, in case he would agree not to make his paper an abolition journal. Mr. Lovejoy assured them it was not his purpose to establish such a paper in Alton, but one of a religious character: at the same time he would not give up his right as an American citizen to publish whatever he pleased on any subject, holding himself answerable to the laws of his country in so doing. With this general understanding, he was permitted to go forward. He continued about a year, discussing in his paper the slavery question occasionally; not, however, in a violent manner, but with a tone of moderation. This policy, however, was not satisfactory: it was regarded as a violation of his pledge; and the contents of his office were again destroyed. Mr. Lovejoy issued an appeal for aid to re-establish his paper, which met with a prompt and generous response. He proposed to bring up another press, and announced that armed men would protect it: meantime, a committee presented him with some resolutions adopted at a large meeting of the citizens of Alton, reminding him that he had previously given a pledge that in his paper he would refrain from advocating abolitionism) and also censuring him for not having kept his promise, and desiring to know if he intended to continue the publication of such doctrines in the future. His response consisted of a denial of the right of any portion of the people of Acton to prescribe what questions he should or should not discuss in his paper. Great excitement followed: another press was brought up on the 21st of September, which shortly after followed the fate of its predecessors. Another arrived Nov. 7, 1837, and was conveyed to a stone warehouse by the riverside, where Mr. Lovejoy and a few friends (some of them not Abolitionists) resolved to defend it to the last. That night they were attacked. First there was a brief parley, then a volley of stones, then an attempt to carry the building by assault. At this juncture a shot was fired out of a second-story window, which killed a young man in the crowd. It was said to have been fired by Lovejoy; and, as the corpse was borne away, the wrath of the populace knew no bounds. It was proposed to get powder from the magazine, and blow the warehouse up. Others thought the torch would be a better agent; and, finally, a man ran up a ladder to fire the roof. Lovejoy came out of the door, and, firing one shot, retreated within, where he rallied the garrison for a sortie. In the mean time many shots were fired both by the assailants and the assailed. The house was once actually set on fire by one person from the mob, and saved by another. But the courage of Mr. Lovejoy's friends was gradually sinking, and they responded but faintly to his strong appeals for action. As a last resource, he rushed to the door with a single companion, gun in hand, and was shot dead on the threshold. The other man was wounded in the leg, the warehouse was in flames, the mob grew more ferocious over the blood that had been shed, and riddled the doors and windows with volleys from all sorts of fire-arms. The Abolitionists had fought a good fight; but seeing now nothing but death before them, in that dismal, bloody, and burning house, they escaped down the river-bank, by twos and threes, as best they could, and their press was tumbled after them, into the river. And thus ended the first attempt to establish an abolition paper in Illinois. The result was certainly any thing but encouraging, and indicated pretty clearly what must have been the general state of public feeling throughout the State in regard to slavery agitation.
In fact, no State was more alive to the necessity of repressing the Abolitionists than Illinois; and accordingly it was proposed in the Legislature to take some action similar to that which had been already taken, or was actually pending, in the legislatures of sister Commonwealths, from Massachusetts through the list. A number of resolutions were reported, and passed with no serious opposition. The record does not disclose the precise form in which they passed; but that is of little consequence now. That they were extreme enough may be gathered from the considerate language of the protest, and from the fact that such a protest was considered necessary at all. The protest was undoubtedly the product of Mr. Lincoln's pen, for his adroit directness is seen in every word of it. He could get but one man—his colleague, Dan Stone—to sign with him.
March 3,1837.
The following protest was presented to the House, which was read, and ordered to be spread on the journals, to wit:—
Resolutions upon the subject of domestic slavery having passed both branches of the General Assembly at its present session, the undersigned hereby protest against the passage of the same.
They believe that the institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy; but that the promulgation of abolition doctrines tends rather to increase than abate its evils.
They believe that the Congress of the United States has no power, under the Constitution, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the different States.
They believe that the Congress of the United States has the power, under the Constitution, to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, but that the power ought not to be exercised, unless at the request of the people of the District.
The difference between these opinions and those contained in the said resolutions is their reason for entering this protest.
(Signed) Dan Stone,
A. Lincoln, Representatives from the County of Sanqamon.
Mr. Lincoln says nothing here about slavery in the Territories. The Missouri Compromise being in full force, and regarded as sacred by all parties, it was one of its chief effects that both sections were deprived of any pretext for the agitation of that question, from which every statesman, Federalist or Republican, Whig or Democratic, apprehended certain disaster to the Union. Neither would Mr. Lincoln suffer himself to be classed with the few despised Quakers, Covenanters, and Puritans, who were so frequently disturbing the peace of the country by abolition-memorials to Congress and other public bodies. Slavery, says the protest, is wrong in principle, besides being bad in economy; but "the promulgation of abolition doctrines" is still worse. In the States which choose to have it, it enjoys a constitutional immunity beyond the reach of any "higher law;" and Congress must not touch it, otherwise than to shield and protect it. Even in the District of Columbia, Mr. Lincoln and Dan Stone would leave it entirely to the will of the people. In fact, the whole paper, plain and simple as it is, seems to have been drawn with no object but to avoid the imputation of extreme views on either side. And from that day to the day of his inauguration, Mr. Lincoln never saw the time when he would have altered a word of it. He never sided with the Lovejoys. In his eyes their work tended "rather to increase than to abate" the evils of slavery, and was therefore unjust, as well as futile. Years afterwards he was the steady though quiet opponent of Owen Lovejoy, and declared that Lovejoy's nomination for Congress over Leonard Swett "almost turned him blind." When, in 1860, the Democrats called Mr. Lincoln an Abolitionist, and cited the protest of 1837 to support the charge, friends pointed to the exact language of the document as his complete and overwhelming refutation.
On the 10th of May, the New York banks suspended specie payments, and two days afterwards the Bank of the United States and the Philadelphia banks did likewise. From these the stoppage and the general ruin, among business men and speculators alike, spread throughout the country. Nevertheless, the Fund Commissioners of Illinois succeeded in placing a loan during the summer, and before the end of the year work had begun on many railroads. "Money was as plenty as dirt. Industry, in place of being stimulated, actually languished. We exported nothing, and every thing was paid for by the borrowed money expended among us." And this money was bank-paper, such as a pensioner upon the Government of the United States scorned to take in payment of his gratuity, after the deposit banks had suspended or broken, with thirty-two millions of Government money in their possession.
The banks which had received such generous legislation from the Legislature that devised the internal-improvement system were not disposed to see that batch of remarkable enterprises languish for want of their support. One of them took at par and sold nine hundred thousand dollars of bonds; while the other took one million seven hundred and sixty-five thousand dollars, which it used as capital, and expanded its business accordingly. But the banks were themselves in greater danger than the internal-improvement system. If the State Bank refused specie payments for sixty days, its charter was forfeited under the Act of Assembly. But they were the main-stay of all the current speculations, public and private; and having besides large sums of public money in their hands, the governor was induced to call a special session of the Legislature in July, 1837, to save them from impending dissolution. This was done by an act authorizing or condoning the suspension of specie payments. The governor had not directly recommended this, but he had most earnestly recommended the repeal or modification of the internal-improvement system; and that the Legislature positively refused. This wise body might be eaten by its own dogs, but it was determined not to eat them; and in this direction there was no prospect of relief for two years more. According to Gov. Ford, the cool, reflecting men of the State anxiously hoped that their rulers might be able to borrow no more money, but in this they were immediately and bitterly disappointed. The United States Bank took some of their bonds. Some were sold at par in this country, and others at nine per cent discount in Europe.
In 1838, a governor (Carlin) was elected who was thought by many to be secretly hostile to the "system;" and a new Legislature was chosen, from which it was thought something might be hoped. Mr. Lincoln was again elected, with a reputation so much enhanced by his activity and address in the last Legislature, that this time he was the candidate of his party for speaker. The nomination, however, was a barren honor, and known to be such when given. Col. Ewing was chosen by a plurality of one,—two Whigs and two Democrats scattering their votes. Mr. Lincoln kept his old place on the Finance Committee. At the first session the governor held his peace regarding the "system;" and, far from repealing it, the Legislature added a new feature to it, and voted another $800,000.
But the Fund Commissioners were in deep water and muddy water: they had reached the end of their string. The credit of the State was gone, and already were heard murmurs of repudiation. Bond County had in the beginning pronounced the system a swindle upon the people; and Bond County began to have admirers. Some of the bonds had been lent to New York State banks to start upon; and the banks had presently failed. Some had been sold on credit. Some were scattered about in various places on special deposit. Others had been sent to London for sale, where the firm that was selling them broke with the proceeds of a part of them in their hands. No expedients sufficed any longer. There was no more money to be got, and nothing left to do, but to "wind up the system," and begin the work of common sense by providing for the interest on the sums already expended. A special session of the Legislature in 1838-9 did the "winding up," and thenceforth, for some years, there was no other question so important in Illinois State politics as how to pay the interest on the vast debt outstanding for this account. Many gentlemen discovered that De Witt Clintons were rare, and in certain contingencies very precious. Among these must have been Mr. Lincoln. But being again, elected to the Legislature in 1840, again the acknowledged leader and candidate of his party for speaker, he ventured in December of that year to offer an expedient for paying the interest on the debt; but it was only an expedient, and a very poor one, to avoid the obvious but unpopular resort of direct taxation.
"Mr. Lincoln moved to strike out the bill and amendment, and insert the following:—
"An Act providing for the payment of interest on the State debt.
"Section 1.—Be it enacted by the people of the State of Illinois represented in the General Assembly, that the governor be authorized and required to issue, from time to time, such an amount of State bonds, to be called the 'Illinois Interest Bonds,' as may be absolutely necessary for the payment of the interest upon the lawful debt of the State, contracted before the passage of this Act.
"Section 2.—Said bonds shall bear interest at the rate of——per cent per annum, payable half-yearly at——, and be reimbursable in years from their respective issuings.
"Section 3.—That the State's portion of the tax hereafter arising from all lands which were not taxable in the year one thousand eight hundred and forty is hereby set apart as an exclusive fund for the payment of interest on the said 'Illinois Interest Bonds;' and the faith of the State is hereby pledged that said fund shall be applied to that object, and no other, except at any time there should be a surplus; in which case such surplus shall became a part of the general funds of the treasury.
"Section 4.—That hereafter the sum of thirty cents for each hundred dollars' worth of all taxable property shall be paid into the State treasury; and no more than forty cents for each hundred dollars' worth of such taxable property shall be levied and collected for county purposes."
It was a loose document. The governor was to determine the "amount" of bonds "necessary," and the sums for which they should be issued. Interest was to be paid only upon the "lawful" debt; and the governor was left to determine what part of it was lawful, and what unlawful. The last section lays a specific tax; but the proceeds are in no way connected with the "interest bonds."
"Mr. Lincoln said he submitted this proposition with great diffidence. He had felt his share of the responsibility devolving upon us in the present crisis; and, after revolving in his mind every scheme which seemed to afford the least prospect of relief, he submitted this as the result of his own deliberations.
"The details of the bill might be imperfect; but he relied upon the correctness of its general features.
"By the plan proposed in the original bill of hypothecating our bonds, he was satisfied we could not get along more than two or three months before some other step would be necessary: another session would have to be called, and new provisions made.
"It might be objected that these bonds would not be salable, and the money could not be raised in time. He was no financier; but he believed these bonds thus secured would be equal to the best in market. A perfect security was provided for the interest; and it was this characteristic that inspired confidence, and made bonds salable. If there was any distrust, it could not be because our means of fulfilling promises were distrusted. He believed it would have the effect to raise our other bonds in market.
"There was another objection to this plan, which applied to the original bill; and that was as to the impropriety of borrowing money to pay interest on borrowed money,—that we are hereby paying compound interest. To this he would reply, that, if it were a fact that our population and wealth were increasing in a ratio greater than the increased interest hereby incurred, then this was not a good objection. If our increasing means would justify us in deferring to a future time the resort to taxation, then we had better pay compound interest than resort to taxation now. He was satisfied, that, by a direct tax now, money enough could not be collected to pay the accruing interest. The bill proposed to provide in this way for interest not otherwise provided for. It was not intended to apply to those bonds for the interest on which a security had already been provided.
"He hoped the House would seriously consider the proposition. He had no pride in its success as a measure of his own, but submitted it to the wisdom of the House, with the hope, that, if there was any thing objectionable in it, it would be pointed out and amended."
Mr. Lincoln's measure did not pass. There was a large party in favor, not only of passing the interest on the State debt, which fell due in the coming January and July, but of repudiating the whole debt outright. Others thought the State ought to pay, not the full face of its bonds, but only the amount received for them; while others still contended that, whereas, many of the bonds had been irregularly, illegally, and even fraudulently disposed of, there ought to be a particular discrimination made against these, and these only. "At last Mr. Cavarly, a member from Green, introduced a bill of two sections, authorizing the Fund Commissioners to hypothecate internal-improvement bonds to the amount of three hundred thousand dollars, and which contained the remarkable provision, that the proceeds were to be applied by that officer to the payment of all interest legally due on the public debt; thus shifting from the General Assembly, and devolving on the Fund Commissioner, the duty of deciding on the legality of the debt. Thus, by this happy expedient, conflicting opinions were reconciled without direct action on the matter in controversy, and thus the two Houses were enabled to agree upon a measure to provide temporarily for the interest on the public debt. The Legislature further provided, at this session, for the issue of interest bonds, to be sold in the market at what they would bring; and an additional tax of ten cents on the hundred dollars' worth of property was imposed and pledged, to pay the interest on these bonds. By these contrivances, the interest for January and July, 1841, was paid. The Fund Commissioner hypothecated internal-improvement bonds for the money first due; and his successor in office, finding no sale for Illinois stocks, so much had the credit of the State fallen, was compelled to hypothecate eight hundred and four thousand dollars of interest bonds for the July interest. On this hypothecation he was to have received three hundred and twenty-one thousand six hundred dollars, but was never paid more than two hundred and sixty-one thousand five hundred dollars. These bonds have never been redeemed from the holders, though eighty of them were afterwards repurchased, and three hundred and fifteen thousand dollars of them were received from the Shawneetown Bank for State stock in that institution."1
1 Ford's History of Illinois.
This session (the session of 1840-1) had been called two weeks earlier than usual, to provide for the January interest on the debt. But the banks had important business of their own in view, and proceeded to improve the occasion. In 1837, and every year since then, the banks had succeeded in getting acts of the Legislature which condoned their suspension of specie payments. But, by the terms of the last act, their charters were forfeited unless they resumed before the adjournment of the next session. The Democrats, however, maintained that the present special session was a session in the sense of the law, and that, before its adjournment, the banks must hand out "the hard," or die. On the other hand, the Whigs held this session, and the regular session which began on the first Monday in December, to be one and the same, and proposed to give the banks another winter's lease upon life and rags. But the banks were a power in the land, and knew how to make themselves felt. They were the depositories of the State revenues. The auditor's warrants were drawn upon them, and the members of the Legislature paid in their money. The warrants were at a discount of fifty per cent; and, if the banks refused to cash them, the members would be compelled to go home more impecunious than they came. The banks, moreover, knew how to make "opportune loans to Democrats;" and, with all these aids, they organized a brilliant and eventually a successful campaign. In the eyes of the Whigs they were "the institutions of the country," and the Democrats were guilty of incivism in attacking them. But the Democrats retorted with a string of overwhelming slang about rag barons, rags, printed lies, bank vassals, ragocracy, and the "British-bought, bank, blue-light, Federal, Whig party." It was a fierce and bitter contest; and, witnessing it, one might have supposed that the very existence of the State, with the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness, depended upon the result. The Democrats were bent upon carrying an adjournment sine die; which, according to their theory, killed the banks. To defeat this, the Whigs resorted to every expedient of parliamentary tactics, and at length hit upon one entirely unknown to any of the standard manuals: they tried to absent themselves in sufficient numbers to leave no quorum behind. "If the Whigs absented themselves," says Mr. Gillespie, a Whig member, "there would not be a quorum left, even with the two who should be deputed to call the ayes and noes. The Whigs immediately held a meeting, and resolved that they would all stay out, except Lincoln and me, who were to call the ayes and noes. We appeared in the afternoon: motion to adjourn sine die was made, and we called the ayes and noes. The Democrats discovered the game, and the sergeant-at-arms was sent out to gather up the absentees. There was great excitement in the House, which was then held in a church at Springfield. We soon discovered that several Whigs had been caught and brought in, and that the plan had been spoiled; and we—Lincoln and I—determined to leave the hall, and, going to the door, found it locked, and then raised a window and jumped out, but not until the Democrats had succeeded in adjourning. Mr. Grid-ley of McLean accompanied us in our exit.... I think Mr. Lincoln always regretted that he entered into that arrangement, as he deprecated every thing that savored of the revolutionary."
In the course of the debate on the Apportionment Bill, Mr. Lincoln had occasion to address the House in defence of "The Long Nine," who were especially obnoxious to the Democrats. The speech concluded with the following characteristic passage:—
"The gentleman had accused old women of being partial to the number nine; but this, he presumed, was without foundation. A few years since, it would be recollected by the House, that the delegation from this county were dubbed by way of eminence 'The Long Nine,' and, by way of further distinction, he had been called 'The Longest of the Nine.' Now," said Mr. Lincoln, "I desire to say to my friend from Monroe (Mr. Bissell), that if any woman, old or young, ever thought there was any peculiar charm in this distinguished specimen of number nine, I have as yet been so unfortunate as not to have discovered it." (Loud applause.)
But this Legislature was full of excitements. Besides the questions about the public debt and the bank-charters, the Democrats proposed to legislate the Circuit judges out of office, and reconstruct the Supreme Court to suit themselves. They did this because the Supreme judges had already decided one question of some political interest against them, and were now about to decide another in the same way. The latter was a question of great importance; and, in order to avoid the consequences of such a decision, the Democrats were eager for the extremest measures.
The Constitution provided that all free white male inhabitants should vote upon six months' residence. This, the Democrats held, included aliens; while the Whigs held the reverse. On this grave judicial question, parties were divided precisely upon the line of their respective interests. The aliens numbered about ten thousand, and nine-tenths of them voted steadily with the Democracy. Whilst a great outcry concerning it was being made from both sides, and fierce disputes raged in the newspapers and on the stump, two Whigs at Galena got up an amicable case, to try it in a quiet way before a Whig judge, who held the Circuit Courts in their neighborhood. The judge decided for his friends, like a man that he was. The Democrats found it out, and raised a popular tumult about it that would have put Demetrius the silversmith to shame. They carried the case to the Supreme Court, where it was argued before the Whig majority, in December, 1889, by able and distinguished counsellors,—Judge Douglas being one of them; but the only result was a continuance to the next June. In the mean time Judge Smith, the only Democrat on the bench, was seeking favor with his party friends by betraying to Douglas the secrets of the consultation-room.
With his aid, the Democrats found a defect in the record, which sent the case over to December, 1840, and adroitly secured the alien vote for the great elections of that memorable year. The Legislature elected then was overwhelmingly Democratic; and, having good reason to believe that the aliens had small favor to expect from this court, they determined forthwith to make a new one that would be more reasonable. There were now nine Circuit judges in the State, and four Supreme judges, under the Act of 1835. The offices of the Circuit judges the Democrats concluded to abolish, and to create instead nine Supreme judges, who should perform circuit duties. This they called "reforming the judiciary;" and "thirsting for vengeance," as Gov. Ford says, they went about the work with all the zeal, but with very little of the disinterested devotion, which reformers are generally supposed to have. Douglas, counsel for one of the litigants, made a furious speech "in the lobby," demanding the destruction of the court that was to try his cause; and for sundry grave sins which he imputed to the judges he gave Smith—his friend Smith—as authority. It was useless to oppose it: this "reform" was a foregone conclusion. It was called the "Douglas Bill;" and Mr. Douglas was appointed to one of the new offices created by it. But Mr. Lincoln, E. D. Baker, and other Whig members, entered upon the journal the following protest:—
"For the reasons thus presented, and for others no less apparent, the undersigned cannot assent to the passage of the bill, or permit it to become a law without this evidence of their disapprobation; and they now protest against the re-organization of the judiciary: Because,
"1st. It violates the great principles of free government by subjecting the judiciary to the Legislature.
"2d. It is a fatal blow at the independence of the judges and the constitutional term of their offices.
"3d. It is a measure not asked for, or wished for, by the people.
"4th. It will greatly increase the expense of our courts, or else greatly diminish their utility.
"5th. It will give our courts a political and partisan character, thereby impairing public confidence in their decisions.
"6th. It will impair our standing with other States and the world.
"7th. It is a party measure for party purposes, from which no practical good to the people can possibly arise, but which may be the source of immeasurable evils.
"The undersigned are well aware that this protest will be altogether unavailing with the majority of this body. The blow has already fallen; and we are compelled to stand by, the mournful spectators of the ruin it will cause."
Mr. Lincoln was elected in 1840, to serve, of course, until the next election in August, 1842; but for reasons of a private nature, to be explained hereafter, he did not appear during the session of 1841-2.
In concluding this chapter, taking leave of New Salem, Vandalia, and the Legislature, we cannot forbear another quotation from Mr. Wilson, Lincoln's colleague from Sangamon, to whom we are already so largely in debt:—
"In 1838 many of the Long Nines were candidates for re-election to the Legislature. A question of the division of the county was one of the local issues. Mr. Lincoln and myself, among others, residing in the portion of the county sought to be organized into a new county, and opposing the division, it became necessary that I should make a special canvass through the north-west part of the county, then known as Sand Ridge. I made the canvass; Mr. Lincoln accompanied me; and, being personally well acquainted with every one, we called at nearly every house. At that time it was the universal custom to keep some whiskey in the house, for private use and to treat friends. The subject was always mentioned as a matter of etiquette, but with the remark to Mr. Lincoln, 'You never drink, but maybe your friend would like to take a little.' I never saw Mr. Lincoln drink. He often told me he never drank; had no desire for drink, nor the companionship of drinking men. Candidates never treated anybody in those times unless they wanted to do so.
"Mr. Lincoln remained in New Salem until the spring of 1837, when he went to Springfield, and went into the law-office of John T. Stuart as a partner in the practice of law, and boarded with William Butler.
"During his stay in New Salem he had no property other than what was necessary to do his business, until after he stopped in Springfield. He was not avaricious to accumulate property, neither was he a spendthrift. He was almost always during those times hard up. He never owned land.
"The first trip he made around the circuit after he commenced the practice of law, I had a horse, saddle, and bridle, and he had none. I let him have mine. I think he must have been careless, as the saddle skinned the horse's back.
"While he lived in New Salem he visited me often. He would stay a day or two at a time: we generally spent the time at the stores in Athens. He was very fond of company: telling or hearing stories told was a source of great amusement to him. He was not in the habit of reading much,—never read novels. Whittling pine boards and shingles, talking and laughing, constituted the entertainment of the days and evenings.
"In a conversation with him about that time, he told me, that, although he appeared to enjoy life rapturously, still he was the victim of terrible melancholy. He sought company, and indulged in fun and hilarity without restraint, or stint as to time; but when by himself, he told me that he was so overcome by mental depression that he never dared carry a knife in his pocket; and as long as I was intimately acquainted with him, previous to his commencement of the practice of the law, he never carried a pocket-knife. Still he was not misanthropic: he was kind and tender-hearted in his treatment to others.
"In the summer of 1837 the citizens of Athens and vicinity gave the delegation then called the 'Long Nine' a public dinner, at which Mr. Lincoln and all the others were present. He was called out by the toast, 'Abraham Lincoln, one of Nature's noblemen.' I have often thought, that, if any man was entitled to that compliment, it was he."
UNDER the Act of Assembly, due in great part to Mr. Lincoln's exertions, the removal of the archives and other public property of the State from Vandalia to Springfield began on the fourth day of July, 1839, and was speedily completed. At the time of the passage of the Act, in the winter of 1836-7, Mr. Lincoln determined to follow the capital, and establish his own residence at Springfield. The resolution was natural and necessary; for he had been studying law in all his intervals of leisure, and wanted a wider field than the justice's court at New Salem to begin the practice. Henceforth Mr. Lincoln might serve in the Legislature, attend to his private business, and live snugly at home. In addition to the State courts, the Circuit and District Courts of the United States sat here. The eminent John McLean of Ohio was the justice of the Supreme Court who sat in this circuit, with Judge Pope of the District Court, from 1839 to 1849, and after that with Judge Drummond. The first terms of these courts, and the first session of the Legislature at Springfield, were held in December, 1839. The Senate sat in one church, and the House in another.
Mr. Lincoln got his license as an attorney early in 1837, "and commenced practice regularly as a lawyer in the town of Springfield in March" of that year. His first case was that of Hawthorne vs. Wooldridge, dismissed at the cost of the plaintiff, for whom Mr. Lincoln's name was entered. There were then on the list of attorneys at the Springfield bar many names of subsequent renown. Judge Stephen T. Logan was on the bench of the Circuit Court under the Act of 1835. Stephen A. Douglas had made his appearance as the public prosecutor at the March term of 1836; and at the same term E. D. Baker had been admitted to practice. Among the rest were John T. Stuart, Cyrus Walker, S. H. Treat, Jesse B. Thomas, George Forquer, Dan Stone, Ninian W. Edwards, John J. Hardin, Schuyler Strong, A. T. Bledsoe, and Josiah Lamborn.
By this time Mr. Lincoln enjoyed considerable local fame as a politician, but none, of course, as a lawyer. He therefore needed a partner, and got one in the person of John T. Stuart, an able and distinguished Whig, who had relieved his poverty years before by the timely loan of books with which to study law, and who had from the first promoted his political fortunes with zeal as disinterested as it was effective. The connection promised well for Mr. Lincoln, and no doubt did well during the short period of its existence. The courtroom was in Hoffman's Row; and the office of Stuart & Lincoln was in the second story above the court-room. It was a "little room," and generally a "dirty one." It contained "a small dirty bed,"—on which Lincoln lounged and slept,—a buffalo-robe, a chair, and a bench. Here the junior partner, when disengaged from the cares of politics and the Legislature, was to be found pretty much all the time, "reading, abstracted and gloomy." Springfield was a small village, containing between one and two thousand inhabitants. There were no pavements: the street-crossings were made of "chunks," stones, and sticks. Lincoln boarded with Hon. William Butler, a gentleman who possessed in an eminent degree that mysterious power which guides the deliberations of party conventions and legislative bodies to a foregone conclusion. Lincoln was very poor, worth nothing, and in debt,—circumstances which are not often alleged in behalf of the modern legislator; but "Bill Butler" was his friend, and took him in with little reference to board-bills and the settlement of accounts. According to Dr. Jayne, he "fed and clothed him for years;" and this signal service, rendered at a very critical time, Mr. Lincoln forgot wholly when he was in Congress, and Butler wanted to be Register of the Land Office, as well as when he was President of the United States, and opportunities of repayment were multitudinous. It is doubtless all true; but the inference of personal ingratitude on the part of Mr. Lincoln will not bear examination. It will be shown at another place that Mr. Lincoln regarded all public offices within his gift as a sacred trust, to be administered solely for the people, and as in no sense a fund upon which he could draw for the payment of private accounts. He never preferred his friends to his enemies, but rather the reverse, as if fearful that he might by bare possibility be influenced by some unworthy motive. He was singularly cautious to avoid the imputation of fidelity to his friends at the expense of his opponents.
In Coke's and Blackstone's time the law was supposed to be "a jealous mistress;" but in Lincoln's time, and at Springfield, she was any thing but exacting. Politicians courted her only to make her favor the stepping-stone to success in other employments. Various members of that bar have left great reputations to posterity, but none of them were earned solely by the legitimate practice of the law. Douglas is remembered as a statesman, Baker as a political orator, Hardin as a soldier, and some now living, like Logan and Stuart, although eminent in the law, will be no less known to the history of the times as politicians than as lawyers. Among those who went to the law for a living, and to the people for fame and power, was Mr. Lincoln. He was still a member of the Legislature when he settled at Springfield, and would probably have continued to run for a seat in that body as often as his time expired, but for the unfortunate results of the "internal-improvement system," the hopeless condition of the State finances, and a certain gloominess of mind, which arose from private misfortunes that befell him about the time of his retirement. We do not say positively that these were the reasons why Mr. Lincoln made no effort to be re-elected to the Legislature of 1840; but a careful study of all the circumstances will lead any reasonable man to believe that they were. He was intensely ambitious, longed ardently for place and distinction, and never gave up a prospect which seemed to him good when he was in a condition to pursue it with honor to himself and fairness to others. Moreover State politics were then rapidly ceasing to be the high-road to fame and fortune. Although the State of Illinois was insolvent, unable to pay the interest on her public debt, and many were talking about repudiating the principal, the great campaign of 1840 went off upon national issues, and little or nothing was said about questions of State policy. Mr. Lincoln felt and obeyed this tendency of the public mind, and from 1837 onward his speeches—those that were printed and those that were not—were devoted chiefly, if not exclusively, to Federal affairs.
In January, 1837, he delivered a lecture before the Springfield Lyceum on the subject of the "Perpetuation of our Free Institutions." As a mere declamation, it is unsurpassed in the annals of the West. Although delivered in mid-winter, it is instinct with the peculiar eloquence of the most fervid Fourth of July.
"In the great journal of things," began the orator, "happening under the sun, we, the American People, find our account running under date of the nineteenth century of the Christian era. We find ourselves in the peaceful possession of the fairest portion of the earth, as regards extent of territory, fertility of soil, and salubrity of climate. We find ourselves under the government of a system of political institutions conducing more essentially to the ends of civil and religious liberty than any of which the history of former times tells us. We, when mounting the stage of existence, found ourselves the legal inheritors of these fundamental blessings. We toiled not in the acquisition or establishment of them: they are a legacy bequeathed us by a once hardy, brave, and patriotic, but now lamented and departed race of ancestors. Theirs was the task (and nobly they performed it) to possess themselves, and, through themselves, us, of this goodly land, and to uprear upon its hills and valleys a political edifice of liberty and equal rights: 'tis ours only to transmit these—the former unprofaned by the foot of an invader, the latter undecayed by the lapse of time and untorn by usurpation—to the latest generation that fate shall permit the world to know. This task, gratitude to our fathers, justice to ourselves, duty to posterity,—all imperatively require us faithfully to perform.
"How, then, shall we perform it? At what point shall we expect the approach of danger? Shall we expect some transatlantic military giant to step the ocean and crush us at a blow? Never! All the armies of Europe, Asia, and Africa combined, with all the treasure of the earth (our own excepted) in their military chest, with a Bonaparte for a commander, could not, by force, take a drink from the Ohio, or make a track on the Blue Ridge, in a trial of a thousand years!
"At what point, then, is the approach of danger to be expected? I answer, if it ever reach us, it must spring up amongst us. It cannot come from abroad. If destruction be our lot, we must ourselves be its author and finisher. As a nation of freemen, we must live through all time, or die by suicide.
"I hope I am not over-wary; but, if I am not, there is even now something of ill-omen amongst us. I mean the increasing disregard for law which pervades the country, the growing disposition to substitute the wild and furious passions in lieu of the sober judgment of courts, and the worse than savage mobs for the executive ministers of justice. This disposition is awfully fearful in any community, and that it now exists in ours, though grating to our feelings to admit it, it would be a violation of truth and an insult to our intelligence to deny. Accounts of outrages committed by mobs form the every-day news of the times. They have pervaded the country from New England to Louisiana; they are neither peculiar to the eternal snows of the former, nor the burning sun of the latter. They are not the creature of climate; neither are they confined to the slaveholding or non-slaveholding States. Alike they spring up among the pleasure-hunting masters of Southern slaves and the order-loving citizens of the land of steady habits. Whatever, then, their cause may be, it is common to the whole country."
The orator then adverts to the doings of recent mobs in various parts of the country, and insists, that, if the spirit that produced them continues to increase, the laws and the government itself must fall before it: bad citizens will be encouraged, and good ones, having no protection against the lawless, will be glad to receive an individual master who will be able to give them the peace and order they desire. That will be the time when the usurper will put down his heel on the neck of the people, and batter down the "fair fabric" of free institutions. "Many great and good men," he says, "sufficiently qualified for any task they should undertake, may ever be found, whose ambition would aspire to nothing beyond a seat in Congress, a gubernatorial or a presidential chair; but such belong not to the family of the lion or the tribe of the eagle.1 What! Think you these places would satisfy an Alexander, a Cæsar, or a Napoleon? Never! Towering genius disdains a beaten path. It seeks regions hitherto unexplored. It sees no distinction in adding story to story upon the monuments of fame erected to the memory of others. It denies that it is glory enough to serve under any chief. It scorns to tread in the footsteps of any predecessor, however illustrious. It thirsts and burns for distinction; and, if possible, it will have it, whether at the expense of emancipating slaves or enslaving freemen.... Another reason which once was, but which, to the same extent, is now no more, has done much in maintaining our institutions thus far. I mean the powerful influence which the interesting scenes of the Revolution had upon the passions of the people as distinguished from their judgment." This influence, the lecturer maintains, was kept alive by the presence of the surviving soldiers of the Revolution, who were in some sort "living histories," and concludes with this striking peroration:—
"But those histories are gone. They can be read no more forever. They were a fortress of strength; but what invading foeman could never do, the silent artillery of time has done,—the levelling of its walls. They are gone. They were a forest of giant oaks; but the all-resistless hurricane has swept over them, and left only here and there a lonely trunk, despoiled of its verdure, shorn of its foliage, unshading and unshaded, to murmur in a few more gentle breezes, and to combat with its mutilated limbs a few more rude storms, then to sink and be no more. They were the pillars of the temple of liberty; and now that they have crumbled away, that temple must fall, unless we, the descendants, supply their places with other pillars hewn from the same solid quarry of sober reason. Passion has helped us, but can do so no more. It will in future be our enemy. Reason—cold, calculating, unimpassioned reason—must furnish all the materials for our future support and defence. Let those materials be moulded into general intelligence, sound morality, and, in particular, a reverence for the Constitution and the laws; and that we improved to the last, that we revered his name to the last, that during his long sleep we permitted no hostile foot to pass or desecrate his resting-place, shall be that which to learn the last trump shall awaken our Washington. Upon these let the proud fabric of freedom rest as the rock of its basis, and as truly as has been said of the only greater institution, 'The gates of hell shall not prevail against it."'
1 The italics are the orator's.
These extracts from a lecture carefully composed by Mr. Lincoln at the mature age of twenty-eight, and after considerable experience in the public service, are worthy of attentive perusal. To those familiar with his sober and pure style at a later age, these sophomoric passages will seem incredible. But they were thought "able and eloquent" by the "Young Men's Lyceum" of Springfield: he was "solicited to furnish a copy for publication," and they were duly printed in "The Sangamon Journal." In the mere matter of rhetoric, they compare favorably with some of his other productions of nearly the same date. This was what he would have called his "growing time;" and it is intensely interesting to witness the processes of such mental growth as his. In time, gradually, but still rapidly, his style changes completely: the constrained and unnatural attempts at striking and lofty metaphor disappear, and the qualities which produced the Gettysburg address—that model of unadorned eloquence—begin to be felt. He finds the people understand him better when he comes down from his stilts, and talks to them from their own level.
Political discussions at Springfield were apt to run into heated and sometimes unseemly personal controversies. When Douglas and Stuart were candidates for Congress in 1838, they fought like tigers in Herndon's grocery, over a floor that was drenched with slops, and gave up the struggle only when both were exhausted. Then, as a further entertainment to the populace, Mr. Stuart ordered out a "barrel of whiskey and wine."
On the election-day in 1840, it was reported to Mr. Lincoln that one Radford, a contractor on the railroad, had brought up his men, and taken full possession of one of the polling-places. Lincoln started off to the precinct on a slow trot. Radford knew him well, and a little stern advice reversed proceedings without any fighting. Among other remarks, Lincoln said, "Radford, you'll spoil and blow if you live much longer." He wanted to hit Radford, but could get no chance to do so, and contented himself with confiding his intentions to Speed. "I intended just to knock him down, and leave him kicking."
The same year, Col. Baker was making a speech to a promiscuous audience in the court-room,—"a rented room in Hoffman's Row." It will be remembered that Lincoln's office was just above, and he was listening to Baker through a large hole or trap-door in the ceiling. Baker warmed with his theme, and, growing violent and personally offensive, declared at length, "that wherever there was a land-office, there was a Democratic newspaper to defend its corruptions." "This," says John B. Webber, "was a personal attack on my brother, George Webber. I was in the Court House, and in my anger cried, 'Pull him down!'" A scene of great confusion ensued, threatening to end in a general riot, in which Baker was likely to suffer. But just at the critical moment Lincoln's legs were seen coming through the hole; and directly his tall figure was standing between Baker and the audience, gesticulating for silence. "Gentlemen," said he, "let us not disgrace the age and country in which we live. This is a land where freedom of speech is guaranteed. Mr Baker has a right to speak, and ought to be permitted to do so. I am here to protect him, and no man shall take him from this stand if I can prevent it." Webber only recollects that "some one made some soothing, kind remarks," and that he was properly "held until the excitement ceased," and the affair "soon ended in quiet and peace."
In 1838, or 1840, Jesse B. Thomas made an intemperate attack upon the "Long Nine," and especially upon Mr. Lincoln, as the longest and worst of them. Lincoln was not present at the meeting; but being sent for, and informed of what had passed, he ascended the platform, and made a reply which nobody seems to remember, but which everybody describes as a "terrible skinning" of his victim. Ellis says, that, at the close of a furious personal denunciation, he wound up by "mimicking" Thomas, until Thomas actually cried with vexation and anger. Edwards, Speed, Ellis, Davis, and many others, refer to this scene, and, being asked whether Mr. Lincoln could not be vindictive upon occasion, generally respond, "Remember the Thomas skinning."
The most intimate friend Mr. Lincoln ever had, at this or any other time, was probably Joshua F. Speed. In 1836 he settled himself in Springfield, and did a thriving business as a merchant. Ellis was one of his clerks, and so also was William H. Herndon, Mr. Lincoln's future partner. This store was for years Lincoln's familiar haunt. There he came to while away the tedious evenings with Speed and the congenial company that naturally assembled around these choice spirits. He even slept in the store room as often as he slept at home, and here made to Speed the most confidential communications he ever made to mortal man. If he had on earth "a bosom crony," it was Speed, and that deep and abiding attachment subsisted unimpaired to the day of Mr. Lincoln's death. In truth, there were good reasons why he should think of Speed with affection and gratitude, for through life no man rendered him more important services.
One night in December, 1839, Lincoln, Douglas, Baker, and some other gentlemen of note, were seated at Speed's hospitable fire in the store. They got to talking politics, got warm, hot, angry. Douglas sprang up and said, "Gentlemen, this is no place to talk politics: we will discuss the questions publicly with you," and much more in a high tone of banter and defiance. A few days afterwards the Whigs had a meeting, at which Mr. Lincoln reported a resolution challenging the Democrats to a joint debate. The challenge was accepted; and Douglas, Calhoun, Lamborn, and Jesse B. Thomas were deputed by the Democrats to meet Logan, Baker, Browning, and Lincoln on the part of the Whigs. The intellectual encounter between these noted champions is still described by those who witnessed it as "the great debate." It took place in the Second Presbyterian Church, in the hearing of as many people as could get into the building, and was adjourned from night to night. When Mr. Lincoln's turn came, the audience was very thin; but, for all that, his speech was by many persons considered the best one of the series. To this day, there are some who believe he had assistance in the preparation of it. Even Mr. Herndon accused Speed of having "had a hand in it," and got a flat denial for his answer. At all events, the speech was a popular success, and was written out, and published in "The Sangamon Journal," of March 6, 1840. The exordium was a sort of complaint that must have had a very depressing effect upon both the speaker and his hearers:—
"Fellow-Citizens,—It is peculiarly embarrassing to me to attempt a continuance of the discussion, on this evening, which has been conducted in this hall on several preceding ones. It is so, because on each of these evenings there was a much fuller attendance than now, without any reason for its being so, except the greater interest the community feel in the speakers who addressed them then, than they do in him who is to do so now. I am, indeed, apprehensive that the few who have attended have done so more to spare me of mortification, than in the hope of being interested in any thing I may be able to say. This circumstance casts a damp upon my spirits which I am sure I shall be unable to overcome during the evening.
"The subject heretofore and now to be discussed is the Sub-Treasury scheme of the present administration, as a means of collecting, safe-keeping, transferring, and disbursing the revenues of the nation, as contrasted with a National Bank for the same purposes. Mr. Douglas has said that we (the Whigs) have not dared to meet them (the Locos) in argument on this question. I protest against this assertion. I say we have again and again, during this discussion, urged facts and arguments against the Sub-Treasury which they have neither dared to deny nor attempted to answer. But lest some may be led to believe that we really wish to avoid the question, I now propose, in my humble way, to urge these arguments again; at the same time begging the audience to mark well the positions I shall take, and the proofs I shall offer to sustain them, and that they will not again allow Mr. Douglas or his friends to escape the force of them by a round and groundless assertion that we dare not meet them in argument.
"Of the Sub-Treasury, then, as contrasted with a National Bank, for the before-enumerated purposes, I lay down the following propositions, to wit:—
"1st. It will injuriously affect the community by its operation on the circulating medium.
"2d. It will be a more expensive fiscal agent.
"3d. It will be a less secure depository for the public money."
Mr. Lincoln's objections to the Sub-Treasury were those commonly urged by its enemies, and have been somewhat conclusively refuted by the operation of that admirable institution from the hour of its adoption to the present. "The extravagant expenditures" of Mr. Van Buren's administration, however, was a standard topic of the Whigs in those days, and, sliding gracefully off from the Sub-Treasury, Mr. Lincoln dilated extensively upon this more attractive subject. This part of his speech was entirely in reply to Mr. Douglas. But, when he came to answer Mr. Lamborn's remarks, he "got in a hard hit" that must have brought down the house.
"Mr. Lamborn insists that the difference between the Van Buren party and the Whigs is, that, although the former sometimes err in practice, they are always correct in principle, whereas the latter are wrong in principle; and, the better to impress this proposition, he uses a figurative expression in these words: 'The Democrats are vulnerable in the heel, but they are sound in the heart and head.' The first branch of the figure,—that is, that the Democrats are vulnerable in the heel,—I admit is not merely figuratively but literally true. Who that looks but for a moment at their Swartwouts, their Prices, their Harringtons, and their hundreds of others, scampering away with the public money to Texas, to Europe, and to every spot of the earth where a villain may hope to find refuge from justice, can at all doubt that they are most distressingly affected in their heels with a species of 'running itch.' It seems that this malady of their heels operates on the sound-headed and honest-hearted creatures very much like the cork-leg in the comic song did on its owner, which, when he had once got started on it, the more he tried to stop it, the more it would run away. At the hazard of wearing this point threadbare, I will relate an anecdote which seems to be too strikingly in point to be omitted. A witty Irish soldier who was always boasting of his bravery when no danger was near, but who invariably retreated without orders at the first charge of the engagement, being asked by his captain why he did so, replied, 'Captain, I have as brave a heart as Julius Cæsar ever had, but somehow or other, whenever danger approaches, my cowardly legs will run away with it.' So with Mr. Lamborn's party. They take the public money into their hands for the most laudable purpose that wise heads and honest hearts can dictate; but, before they can possibly get it out again, their rascally vulnerable heels will run away with them."
But, as in the lecture before the Lyceum, Mr. Lincoln reserved his most impressive passage, his boldest imagery, and his most striking metaphor, for a grand and vehement peroration.
"Mr. Lamborn refers to the late elections in the States, and, from their results, confidently predicts every State in the Union will vote for Mr. Van Buren at the next presidential election. Address that argument to cowards and knaves: with the free and the brave it will affect nothing. It may be true: if it must, let it. Many free countries have lost their liberty, and ours may lose hers; but, if she shall, be it my proudest plume, not that I was the last to desert, but that I never deserted her. I know that the great volcano at Washington, aroused and directed by the evil spirit that reigns there, is belching forth the lava of political corruption in a current broad and deep, which is sweeping with frightful velocity over the whole length and breadth of the land, bidding fair to leave unscathed no green spot or living thing; while on its bosom are riding, like demons on the wave of hell, the imps of that evil spirit, and fiendishly taunting all those who dare to resist its destroying course with the hopelessness of their efforts; and, knowing this, I cannot deny that all may be swept away. Broken by it, I, too, may be; bow to it, I never will. The probability that we may fall in the struggle ought not to deter us from the support of a cause we believe to be just. It shall not deter me. If ever I feel the soul within me elevate and expand to those dimensions, not wholly unworthy of its almighty Architect, it is when I contemplate the cause of my country, deserted by all the world beside, and I standing up boldly, alone, hurling defiance at her victorious oppressors. Here, without contemplating consequences, before Heaven and in face of the world, I swear eternal fealty to the just cause, as I deem it, of the land of my life, my liberty, and my love. And who that thinks with me will not fearlessly adopt that oath that I take? Let none falter who thinks he is right, and we may succeed. But if, after all, we shall fail, be it so: we still shall have the proud consolation of saying to our consciences, and to the departed shade of our country's freedom, that the cause approved of our judgment and adored of our hearts, in disaster, in chains, in torture, in death, we never faltered in defending."
Considering that the times were extremely peaceful, and that the speaker saw no bloodshed except what flowed from the noses of belligerents in the groceries about Springfield, the speech seems to have been unnecessarily defiant.
In 1840 Mr. Lincoln was a candidate for presidential elector on the Harrison ticket, and stumped a large part of the State. He and Douglas followed Judge Treat's court all around the circuit, "and spoke in the afternoons." The Harrison club at Springfield became thoroughly familiar with his voice. But these one-sided affairs were not altogether suited to his temper: through his life he preferred a joint discussion, and the abler the man pitted against him, the better he liked it. He knew he shone in retort, and sought every opportunity to practise it. From 1838 to 1858, he seems to have followed up Douglas as a regular business during times of great political excitement, and only on one or two occasions did he find the "Little Giant" averse to a conflict. Here, in 1840, they came in collision, as they did in 1839, and as they continued to do through twenty or more years, until Lincoln became President of the United States, and Douglas's disappointments were buried with his body. Once during this Harrison campaign they had a fierce discussion before a meeting assembled in the market-house. In the course of his speech, Lincoln imputed to Van Buren the great sin of having voted in the New York State Convention for negro suffrage with a property qualification. Douglas denied the fact; and Lincoln attempted to prove his statement by reading a certain passage from Holland's "Life of Van Buren," containing a letter from Van Buren to one Mr. Fithian. Whereupon "Douglas got mad," snatched up the book, and, tossing it into the crowd, remarked sententiously, although not conclusively, "Damn such a book!"
"He was very sensitive," says Mr. Gillespie, "where he thought he had failed to come up to the expectations of his friends. I remember a case. He was pitted by the Whigs, in 1840, to debate with Mr. Douglas, the Democratic champion. Lincoln did not come up to the requirements of the occasion. He was conscious of his failure; and I never saw any man so much distressed. He begged to be permitted to try it again, and was reluctantly indulged; and in the next effort he transcended our highest expectations. I never heard, and never expect to hear, such a triumphant vindication as he then gave of Whig measures or policy. He never after, to my knowledge, fell below himself."
It must by this time be clear to the reader that Mr. Lincoln was never agitated by any passion more intense than his wonderful thirst for distinction. There is good evidence that it furnished the feverish dreams of his boyhood; and no man that knew him well can doubt that it governed all his conduct, from the hour when he astonished himself by his oratorical success against Posey and Ewing, in the back settlements of Macon County, to the day when the assassin marked him as the first hero of the restored Union, re-elected to his great office, surrounded by every circumstance that could minister to his pride, or exalt his sensibilities,—a ruler whose power was only less wide than his renown. He never rested in the race he had determined to run; he was ever ready to be honored; he struggled incessantly for place. There is no instance where an important office seemed to be within his reach, and he did not try to get it. Whatsoever he did in politics, at the bar, in private life, had more or less reference to this great object of his life. It is not meant to be said that he was capable of any shameful act, any personal dishonor, any surrender or concealment of political convictions. In these respects, he was far better than most men. It was not in his nature to run away from the fight, or to desert to the enemy; but he was quite willing to accept his full share of the fruits of victory.
Born in the humblest circumstances, uneducated, poor, acquainted with flatboats and groceries, but a stranger to the drawing-room, it was natural that he should seek in a matrimonial alliance those social advantages which he felt were necessary to his political advancement. This was, in fact, his own view of the matter; but it was strengthened and enforced by the counsels of those whom he regarded as friends.

In 1839 Miss Mary, daughter of Hon. Robert S. Todd of Lexington, Ky., came to live with her sister, Mrs. Ninian W. Edwards, at Springfield. Like Miss Owens, Miss Todd had a stepmother, with whom she failed to "agree," and for that reason the Edwardses offered her a home with them. She was young,—just twenty-one,—her family was of the best, and her connections in Illinois among the most refined and distinguished people. Her mother having died when she was a little girl, she had been educated under the care of a French lady, "opposite Mr. Clay's." She was gifted with rare talents, had a keen sense of the ridiculous, a ready insight into the weaknesses of individual character, and a most fiery and ungovernable temper. Her tongue and her pen were equally sharp. High-bred, proud, brilliant, witty, and with a will that bent every one else to her purpose, she took Mr. Lincoln captive the very moment she considered it expedient to do so.
Mr. Lincoln was a rising politician, fresh from the people, and possessed of great power among them: Miss Todd was of aristocratic and distinguished family, able to lead through the awful portals of "good society" whomsoever they chose to countenance. It was thought that a union between them could not fail of numerous benefits to both parties. Mr. Edwards thought so; Mrs. Edwards thought so; and it was not long before Mary Todd herself thought so. She was very ambitious, and even before she left Kentucky announced her belief that she was "destined to be the wife of some future President." For a little while she was courted by Douglas as well as by Lincoln; but she is said to have refused the "Little Giant," "on account of his bad morals." Being asked which of them she intended to have, she answered, "The one that has the best chance of being President." She decided in favor of Lincoln, and, in the opinion of some of her husband's friends, aided to no small extent in the fulfilment of the prophecy which the bestowal of her hand implied. A friend of Miss Todd was the wife of an elderly but wealthy gentleman; and being asked by one of the Edwards coterie why she had married "such an old, dried-up husband, such a withered-up old buck," she answered that "He had lots of horses and gold." But Mary Todd spoke up in great surprise, and said, "Is that true? I would rather marry a good man, a man of mind, with hope and bright prospects ahead for position, fame, and power, than to marry all the horses, gold, and bones in the world."
Mrs. Edwards, Miss Todd's sister, tells us that Mr. Lincoln "was charmed with Mary's wit and fascinated with her quick sagacity, her will, her nature and culture." "I have happened in the room," she says, "where they were sitting often and often, and Mary led the conversation. Lincoln would listen, and gaze on her as if drawn by some superior power,—irresistibly so: he listened, but never scarcely said a word.... Lincoln could not hold a lengthy conversation with a lady,—was not sufficiently educated and intelligent in the female line to do so."
Mr. Lincoln and Mary were engaged, and their marriage was only a question of time. But Mr. Lincoln's love-affairs were destined never to run smoothly, and now one Miss Matilda Edwards made her "sweet appearance," and brought havoc in her train. She was the sister of Ninian W. Edwards, and came to spend a year with her brother. She was very fair, and soon was the reigning belle. No sooner did Lincoln know her than he felt his heart change. The other affair, according to the Edwardses, according to Stuart, according to Herndon, according to Lincoln and everybody else, was a "policy match;" but this was love. For a while he evidently tried hard to go on as before, but his feelings were too strong to be concealed. Mr. Edwards endeavored to reconcile matters by getting his sister to marry Speed; but the rebellious beauty refused Speed incontinently (as she did Douglas too), and married Mr. Schuyler Strong. Poor Lincoln never whispered a word of his passion to her: his high sense of honor prevented that, and perhaps she would not have listened to him if it had been otherwise.
At length, after long reflection, in great agony of spirit, Mr. Lincoln concluded that duty required him to make a candid statement of his feelings to the lady who was entitled to his hand. He wrote her a letter, and told her gently but plainly that he did not love her. He asked Speed to deliver it; but Speed advised him to burn it. "Speed," said Mr. Lincoln, "I always knew you were an obstinate man. If you won't deliver it, I'll get some one else to do it." But Speed now had the letter in his hand; and, emboldened by the warm friendship that existed between them, replied, "I shall not deliver it, nor give it to you to be delivered. Words are forgotten, misunderstood, passed by, not noticed in a private conversation; but once put your words in writing, and they stand as a living and eternal monument against you. If you think you have will and manhood enough to go and see her, and speak to her what you say in that letter, you may do that." Lincoln went to see her forthwith, and reported to Speed. He said, that, when he made his somewhat startling communication, she rose and said, "'The deceiver shall be deceived: woe is me!' alluding to a young man she had fooled." Mary told him she knew the reason of his change of heart, and released him from his engagement. Some parting endearments took place between them, and then, as the natural result of those endearments, a reconciliation.
We quote again from Mrs. Edwards:—
"Lincoln and Mary were engaged; every thing was ready and prepared for the marriage, even to the supper. Mr. Lincoln failed to meet his engagement. Cause, insanity!
"In his lunacy he declared he hated Mary and loved Miss Edwards. This is true, yet it was not his real feelings. A crazy man hates those he loves when at himself. Often, often, is this the case. The world had it that Mr. Lincoln backed out, and this placed Mary in a peculiar situation; and to set herself right, and free Mr. Lincoln's mind, she wrote a letter to Mr. Lincoln, stating that she would release him from his engagement.... The whole of the year was a crazy spell. Miss Edwards was at our house, say a year. I asked Miss Edwards if Mr. Lincoln ever mentioned the subject of his love to her. Miss Edwards said, 'On my word, he never mentioned such a subject to me: he never even stooped to pay me a compliment.'"
In the language of Mr. Edwards, "Lincoln went as crazy as a loon," and was taken to Kentucky by Speed, who kept him "until he recovered." He "did not attend the Legislature in 1841-2 for this reason."
Mr. Herndon devoutly believes that Mr. Lincoln's insanity grew out of a most extraordinary complication of feelings,—aversion to the marriage proposed, a counter-attachment to Miss Edwards, and a new access of unspeakable tenderness for the memory of Ann Rutledge,—the old love struggling with a new one, and each sending to his heart a sacrificial pang as he thought of his solemn engagement to marry a third person. In this opinion Mr. Speed appears to concur, as shown by his letter below. At all events, Mr. Lincoln's derangement was nearly, if not quite, complete. "We had to remove razors from his room," says Speed, "take away all knives, and other dangerous things. It was terrible." And now Speed determined to do for him what Bowlin Greene had done on a similar occasion at New Salem. Having sold out his store on the 1st of January, 1841, he took Mr. Lincoln with him to his home in Kentucky, and kept him there during most of the summer and fall, or until he seemed sufficiently restored to be given his liberty again at Springfield, when he was brought back to his old quarters. During this period, "he was at times very melancholy," and, by his own admission, "almost contemplated self-destruction." It was about this time that he wrote some gloomy lines under the head of "Suicide," which were published in "The Sangamon Journal." Mr. Herndon remembered something about them; but, when he went to look for them in the office-file of the "Journal," he found them neatly cut out,—"supposed to have been done," says he, "by Lincoln." Speed's mother was much pained by the "deep depression" of her guest, and gave him a Bible, advising him to read it, to adopt its precepts, and pray for its promises. He acknowledged this attempted service, after he became President, by sending her a photograph of himself, with this inscription: "To my very good friend, Mrs. Lucy G. Speed, from whose pious hands I received an Oxford Bible twenty years ago." But Mrs. Speed's medicine, the best ever offered for a mind diseased, was of no avail in this case. Among other things, he told Speed, referring probably to his inclination to commit suicide, "that he had done nothing to make any human being remember that he had lived, and that to connect his name with the events transpiring in his day and generation, and so impress himself upon them as to link his name with something that would redound to the interest of his fellow-man, was what he desired to live for." Of this conversation he pointedly reminded Speed at the time, or just before the time, he issued the Emancipation Proclamation.
What took place after his return to Springfield cannot be better told than in the words of the friends of both parties. "Mr. Edwards and myself," says Mrs. Edwards, "after the first crash of things, told Mary and Lincoln that they had better not ever marry; that their natures, minds, education, raising, &c., were so different, that they could not live happy as man and wife; had better never think of the subject again. All at once we heard that Mr. Lincoln and Mary had secret meetings at Mr. S. Francis's, editor of 'The Springfield Journal.' Mary said the reason this was so, the cause why it was, was that the world, woman and man, were uncertain and slippery, and that it was best to keep the secret courtship from all eyes and ears. Mrs. Lincoln told Mr. Lincoln, that, though she had released him in the letter spoken of, yet she would hold the question an open one,—that is, that she had not changed her mind, but felt as always.... The marriage of Mr. Lincoln and Mary was quick and sudden,—one or two hours' notice." How poor Mr. Lincoln felt about it, may be gathered from the reminiscences of his friend, J. H. Matheny, who says, "that Lincoln and himself, in 1842, were very friendly; that Lincoln came to him one evening and said, 'Jim, I shall have to marry that girl.'" He was married that evening, but Matheny says, "he looked as if he was going to the slaughter," and that Lincoln "had often told him, directly and individually, that he was driven into the marriage; that it was concocted and planned by the Edwards family; that Miss Todd—afterwards Mrs. Lincoln—was crazy for a week or so, not knowing what to do; and that he loved Miss Edwards, and went to see her, and not Mrs. Lincoln."
The license to marry was issued on the 4th of November, 1842, and on the same day the marriage was celebrated by Charles Dresser, "M.G." With this date carefully borne in mind, the following letters are of surpassing interest. They are relics, not only of a great man, but of a great agony.
The first is from Mr. Speed to Mr. Herndon, and explains the circumstances under which the correspondence took place. Although it is in part a repetition of what the reader already knows, it is of such peculiar value, that we give it in full:—
W. H. Herndon, Esq.
Dear Sir,—I enclose you copies of all the letters of any interest from Mr. Lincoln to me.
Some explanation may be needed, that you may rightly understand their import.
In the winter of 1840 and 1841 he was unhappy about his engagement to his wife,—not being entirely satisfied that his heart was going with his hand. How much he suffered then on that account, none know so well as myself: he disclosed his whole heart to me.
In the summer of 1841 I became engaged to my wife. He was here on a visit when I courted her; and, strange to say, something of the same feeling which I regarded as so foolish in him took possession of me, and kept me very unhappy from the time of my engagement until I was married.
This will explain the deep interest he manifested in his letters on my account.
Louisville, Nov. 30, 1866.
If you use the letters (and some of them are perfect gems) do it care fully, so as not to wound the feelings of Mrs. Lincoln.
One thing is plainly discernible: if I had not been married and happy,—far more happy than I ever expected to be,—he would not have married.
I have erased a name which I do not wish published. If I have failed to do it anywhere, strike it out when you come to it. That is the word———.
I thank you for your last lecture. It is all new to me, but so true to my appreciation of Lincoln's character, that, independent of my knowledge of you, I would almost swear to it.
Lincoln wrote a letter (a long one, which he read to me) to Dr. Drake, of Cincinnati, descriptive of his case. Its date would be in December, 1840, or early in January, 1841. I think that he must have informed Dr. D. of his early love for Miss Rutledge, as there was a part of the letter which he would not read.
It would be worth much to you, if you could procure the original.
Charles D. Drake, of St. Louis, may have his father's papers. The date which I give you will aid in the search.
I remember Dr. Drake's reply, which was, that he would not undertake to prescribe for him without a personal interview. I would advise you to make some effort to get the letter.
Your friend, &c.,
J. F. Speed.
The first of the papers from Mr. Lincoln's pen is a letter of advice and consolation to his friend, for whom he apprehends the terrible things through which, by the help of that friend, he has himself just passed.
My dear Speed,—Feeling, as you know I do, the deepest solicitude for the success of the enterprise you are engaged in, I adopt this as the last method I can invent to aid you, in case (which God forbid) you shall need any aid. I do not place what I am going to say on paper, because I can say it better in that way than I could by word of mouth; but, were I to say it orally before we part, most likely you would forget it at the very time when it might do you some good. As I think it reasonable that you will feel very badly sometime between this and the final consummation of your purpose, it is intended that you shall read this just at such a time. Why I say it is reasonable that you will feel very badly yet, is because of three special causes added to the general one which I shall mention.
The general cause is, that you are naturally of a nervous temperament, and this I say from what I have seen of you personally, and what you have told me concerning your mother at various times, and concerning your brother William at the time his wife died. The first special cause is your exposure to bad weather on your journey, which my experience clearly proves to be very severe on defective nerves. The second is the absence of all business and conversation of friends, which might divert your mind, give it occasional rest from the intensity of thought which will sometimes wear the sweetest idea threadbare, and turn it to the bitterness of death.
The third is the rapid and near approach of that crisis on which all your thoughts and feelings concentrate.
If from all these causes you shall escape, and go through triumphantly, without another "twinge of the soul," I shall be most happily but most egregiously deceived. If, on the contrary, you shall, as I expect you will at some time, be agonized and distressed, let me, who have some reason to speak with judgment on such a subject, beseech you to ascribe it to the causes I have mentioned, and not to some false and ruinous suggestion of the Devil.
"But," you will say, "do not your causes apply to every one engaged in a like undertaking?" By no means. The particular causes, to a greater or less extent, perhaps, do apply in all cases; but the general one,—nervous debility, which is the key and conductor of all the particular ones, and without which they would be utterly harmless, though it does pertain to you,—does not pertain to one in a thousand. It is out of this that the painful difference between you and the mass of the world springs.
I know what the painful point with you is at all times when you are unhappy: it is an apprehension that you do not love her as you should. What nonsense! How came you to court her? Was it because you thought she deserved it, and that you had given her reason to expect it? If it was for that, why did not the same reason make you court Ann Todd, and at least twenty others of whom you can think, and to whom it would apply with greater force than to her? Did you court her for her wealth? Why, you know she had none. But you say you reasoned yourself into it. What do you mean by that? Was it not that you found yourself unable to reason yourself out of it? Did you not think, and partly form the purpose, of courting her the first time you ever saw her or heard of her? What had reason to do with it at that early stage? There was nothing at that time for reason to work upon. Whether she was moral, amiable, sensible, or even of good character, you did not, nor could then know, except, perhaps, you might infer the last from the company you found her in.
All you then did or could know of her was her personal appearance and deportment; and these, if they impress at all, impress the heart, and not the head.
Say candidly, were not those heavenly black eyes the whole basis of all your early reasoning on the subject? After you and I had once been at the residence, did you not go and take me all the way to Lexington and back, for no other purpose but to get to see her again, on our return on that evening to take a trip for that express object?
What earthly consideration would you take to find her scouting and despising you, and giving herself up to another? But of this you have no apprehension; and therefore you cannot bring it home to your feelings.
I shall be so anxious about you, that I shall want you to write by every mail. Your friend,
Lincoln.
Springfield, Ill., Feb. 3, 1842.
Dear Speed,—Your letter of the 25th January came to hand to-day. You well know that I do not feel my own sorrows much more keenly than I do yours, when I know of them; and yet I assure you I was not much hurt by what you wrote me of your excessively bad feeling at the time you wrote. Not that I am less capable of sympathizing with you now than ever, not that I am less your friend than ever, but because I hope and believe that your present anxiety and distress about her health and her life must and will forever banish those horrid doubts which I know you sometimes felt as to the truth of your affection for her. If they can once and forever be removed (and I almost feel a presentiment that the Almighty has sent your present affliction expressly for that object), surely, nothing can come in their stead to fill their immeasurable measure of misery. The death-scenes of those we love are surely painful enough; but these we are prepared for and expect to see: they happen to all, and all know they must happen. Painful as they are, they are not an unlooked-for sorrow. Should she, as you fear, be destined to an early grave, it is indeed a great consolation to know that she is so well prepared to meet it.. Her religion, which you once disliked so much, I will venture you now prize most highly.
But I hope your melancholy bodings as to her early death are not well founded. I even hope that ere this reaches you, she will have returned with improved and still-improving health, and that you will have met her, and forgotten the sorrows of the past in the enjoyment of the present. I would say more if I could, but it seems that I have said enough. It really appears to me that you yourself ought to rejoice, and not sorrow, at this indubitable evidence of your undying affection for her.
Why, Speed, if you did not love her, although you might not wish her death, you would most certainly be resigned to it. Perhaps this point is no longer a question with you, and my pertinacious dwelling upon it is a rude intrusion upon your feelings. If so, you must pardon me. You know the hell I have suffered on that point, and how tender I am upon it. You know I do not mean wrong. I have been quite clear of hypo since you left, even better than I was along in the fall. I have seen———but once. She seemed very cheerful, and so I said nothing to her about what we spoke of.
Old Uncle Billy Herndon is dead, and it is said this evening that Uncle Ben Ferguson will not live. This, I believe, is all the news, and enough at that, unless it were better.
Write me immediately on the receipt of this.
Your friend as ever,
Lincoln.
Springfield, Ill., Feb. 13, 1842.
Dear Speed,—Yours of the 1st inst. came to hand three or four days ago. When this shall reach you, you will have been Fanny's husband several days. You know my desire to befriend you is everlasting; that I will never cease while I know how to do any thing.
But you will always hereafter be on ground that I have never occupied, and consequently, if advice were needed, I might advise wrong. I do fondly hope, however, that you will never again need any comfort from abroad. But, should I be mistaken in this, should excessive pleasure still be accompanied with a painful counterpart at times, still let me urge you, as I have ever done, to remember, in the depth and even agony of despondency, that very shortly you are to feel well again. I am now fully convinced that you love her as ardently as you are capable of loving. Your ever being happy in her presence, and your intense anxiety about her health, if there were nothing else, would place this beyond all dispute in my mind. I incline to think it probable that your nerves will fail you occasionally for a while; but once you get them firmly graded now, that trouble is over forever.
I think if I were you, in case my mind were not exactly right, I would avoid being idle. I would immediately engage in some business, or go to making preparations for it, which would be the same thing.
If you went through the ceremony calmly, or even with sufficient composure not to excite alarm in any present, you are safe beyond question, and in two or three months, to say the most, will be the happiest of men.
I would desire you to give my particular respects to Fanny; but perhaps you will not wish her to know you have received this, lest she should desire to see it. Make her write me an answer to my last letter to her; at any rate, 1 would set great value upon a note or letter from her.
Write me whenever you have leisure.
Yours forever,
A. Lincoln.
P. S.—I have been quite a man since you left.
Springfield, Feb. 25, 1842.
Dear Speed,—Yours of the 16th inst., announcing that Miss Fanny and you are "no more twain, but one flesh," reached me this morning. I have no way of telling how much happiness I wish you both, though I believe you both can conceive it. I feel somewhat jealous of both of you now: you will be so exclusively concerned for one another, that I shall be forgotten entirely. My acquaintance with Miss Fanny (I call her this, lest you should think I am speaking of your mother) was too short for me to reasonably hope to long be remembered by her; and still I am sure I shall not forget her soon. Try if you cannot remind her of that debt she owes me,—and be sure you do not interfere to prevent her paying it.
I regret to learn that you have resolved to not return to Illinois. I shall be very lonesome without you. How miserable things seem to be arranged in this world! If we have no friends, we have no pleasure; and, if we have them, we are sure to lose them, and be doubly pained by the loss. I did hope she and you would make your home here; but I own I have no right to insist. You owe obligations to her ten thousand times more sacred than you can owe to others, and in that light let them be respected and observed. It is natural that she should desire to remain with her relatives and friends. As to friends, however, she could not need them anywhere: she would have them in abundance here.
Give my kind remembrance to Mr. Williamson and his family, particularly Miss Elizabeth; also to your mother, brother, and sisters. Ask little Eliza Davis if she will ride to town with me if I come there again.
And, finally, give Fanny a double reciprocation of all the love she sent me. Write me often, and believe me
Yours forever,
Lincoln.
P. S.—Poor Easthouse is gone at last. He died a while before day this morning. They say he was very loath to die.
Springfield, Feb. 25, 1842.
Dear Speed,—I received yours of the 12th, written the day you went down to William's place, some days since, but delayed answering it till I should receive the promised one of the 16th, which came last night. I opened the letter with intense anxiety and trepidation; so much, that, although it turned out better than I expected, I have hardly yet, at the distance of ten hours, become calm.
I tell you, Speed, our forebodings (for which you and I are peculiar) are all the worst sort of nonsense. I fancied, from the time I received your letter of Saturday, that the one of Wednesday was never to come, and yet it did come, and, what is more, it is perfectly clear, both from its tone and handwriting, that you were much happier, or, if you think the term preferable, less miserable, when you wrote it, than when you wrote the last one before. You had so obviously improved at the very time I so much fancied you would have grown worse. You say that something indescribably horrible and alarming still haunts you. You will not say that three months from now, I will venture. When your nerves once get steady now, the whole trouble will be over forever. Nor should you become impatient at their being even very slow in becoming steady. Again you say, you much fear that that Elysium of which you have dreamed so much is never to be realized. Weil, if it shall not, I dare swear it will not be the fault of her who is now your wife. I now have no doubt, that it is the peculiar misfortune of both you and me to dream dreams of Elysium far exceeding all that any thing earthly can realize. Far short of your dreams as you may be, no woman could do more to realize them than that same black-eyed Fanny. If you could but contemplate her through my imagination, it would appear ridiculous to you that any one should for a moment think of being unhappy with her. My old father used to have a saying, that, "If you make a bad bargain, hug it all the tighter;" and it occurs to me, that, if the bargain you have just closed can possibly be called a bad one, it is certainly the most pleasant one for applying that maxim to which my fancy can by any effort picture.
I write another letter, enclosing this, which you can show her, if she desires it. I do this because she would think strangely, perhaps, should you tell her that you received no letters from me, or, telling her you do, refuse to let her see them. I close this, entertaining the confident hope that every successive letter I shall have from you (which I here pray may not be few, nor far between) may show you possessing a more steady hand and cheerful heart than the last preceding it.
As ever, your friend,
Lincoln.
Springfield, March 27, 1842.
Dear Speed,—Yours of the 10th inst. was received three or four days since. You know I am sincere when I tell you the pleasure its contents gave me was and is inexpressible. As to your farm matter, I have no sympathy with you. I have no farm, nor ever expect to have, and consequently have not studied the subject enough to be much interested with it. I can only say that I am glad you are satisfied and pleased with it.
But on that other subject, to me of the most intense interest whether in joy or sorrow, I never had the power to withhold my sympathy from you. It cannot be told how it now thrills me with joy to hear you say you are "far happier than you ever expected to be." That much I know is enough. I know you too well to suppose your expectations were not, at least, sometimes extravagant, and, if the reality exceeds them all, I say, Enough, dear Lord. I am not going beyond the truth when I tell you, that the short space it took me to read your last letter gave me more pleasure than the total sum of all I have enjoyed since that fatal 1st of January, 1841. Since then it seems to me I should have been entirely happy, but for the never-absent idea that there is one still unhappy whom I have contributed to make so. That still kills my soul. I cannot but reproach myself for even wishing to be happy while she is otherwise. She accompanied a large party on the railroad cars to Jacksonville last Monday, and on her return spoke, so that I heard of it, of having enjoyed the trip exceedingly. God be praised for that.
You know with what sleepless vigilance I have watched you ever since the commencement of your affair; and, although I am almost confident it is useless, I cannot forbear once more to say, that I think it is even yet possible for your spirits to flag down and leave you miserable. If they should, don't fail to remember that they cannot long remain so. One thing I can tell you which I know you will be glad to hear, and that is that I have seen———and scrutinized her feelings as well as I could, and am fully convinced she is far happier now than she has been for the last fifteen months past.
You will see by the last "Sangamon Journal" that I have made a temperance speech on the 22d of February, which I claim that Fanny and you shall read as an act of charity to me; for I cannot learn that anybody else has read it, or is likely to. Fortunately, it is not very long, and I shall deem it a sufficient compliance with my request if one of you listens while the other reads it.
As to your Lockridge matter, it is only necessary to say that there has been no court since you left, and that the next commences to-morrow morning, during which I suppose we cannot fail to get a judgment.
I wish you would learn of Everett what he would take, over and above a discharge, for all trouble we have been at, to take his business out of our hands and give it to somebody else. It is impossible to collect money on that or any other claim here now, and, although you know I am not a very petulant man, I declare I am almost out of patience with Mr. Everett's endless importunity. It seems like he not only writes all the letters he can himself, but gets everybody else in Louisville and vicinity to be constantly writing to us about his claim. I have always said that Mr. Everett is a very clever fellow, and I am very sorry he cannot be obliged; but it does seem to me he ought to know we are interested to collect his claim, and therefore would do it if we could.
I am neither joking nor in a pet when I say we would thank him to transfer his business to some other, without any compensation for what we have done, provided he will see the court cost paid, for which we are security.
The sweet violet you enclosed came safely to hand, but it was so dry, and mashed so flat, that it crumbled to dust at the first attempt to handle it. The juice that mashed out of it stained a place in the letter, which I mean to preserve and cherish for the sake of her who procured it to be sent. My renewed good wishes to her in particular, and generally to all such of your relations who know me.
As ever,
Lincoln.
Springfield, Ill., July 4, 1842.
Dear Speed,—Yours of the 16th June was received only a day or two since. It was not mailed at Louisville till the 25th. You speak of the great time that has elapsed since I wrote you. Let me explain that. Your letter reached here a day or two after I had started on the circuit. I was gone five or six weeks, so that I got the letters only a few weeks before Butler started to your country. I thought it scarcely worth while to write you the news which he could and would tell you more in detail. On his return, he told me you would write me soon, and so I waited for your letter. As to my having been displeased with your advice, surely you know better than that. I know you do, and therefore will not labor to convince you. True, that subject is painful to me; but it is not your silence, or the silence of all the world, that can make me forget it. I acknowledge the correctness of your advice too; but, before I resolve to do the one thing or the other, I must gain my confidence in my own ability to keep my resolves when they are made. In that ability you know I once prided myself, as the only or chief gem of my character: that gem I lost, how and where you know too well. I have not yet regained it; and, until I do, I cannot trust myself in any matter of much importance. I believe now, that, had you understood my case at the time as well as I understood yours afterwards, by the aid you would have given me I should have sailed through clear; but that does not now afford me sufficient confidence to begin that or the like of that again.
You make a kind acknowledgment of your obligations to me for your present happiness. I am much pleased with that acknowledgment. But a thousand times more am I pleased, to know that you enjoy a degree of happiness worthy of an acknowledgment. The truth is, I am not sure that there was any went with me in the part I took in your difficulty: I was drawn to it as by fate. If I would, I could not have done less than I did. I always was superstitious: I believe God made me one of the instruments of bringing your Fanny and you together, which union I have no doubt he had fore-ordained. Whatever he designs, he will do for me yet. "Stand still, and see the salvation of the Lord" is my text just now. If, as you say, you have told Fanny all, I should have no objection to her seeing this letter, but for its reference to our friend here: let her seeing it depend upon whether she has ever known any thing of my affairs; and, if she has not, do not let her.
I do not think I can come to Kentucky this season. I am so poor, and make so little headway in the world, that I drop back in a month of idleness as much as I gain in a year's sowing. I should like to visit you again. I should like to see that "sis" of yours that was absent when I was there, though I suppose she would run away again, if she were to hear I was coming.
My respects and esteem to all your friends there, and, by your permission, my love to your Fanny. Ever yours, Lincoln.
Springfield, Oct. 5, 1842.
Dear Speed,—You have heard of my duel with Shields, and I have now to inform you that the duelling business still rages in this city. Day before yesterday Shields challenged Butler, who accepted, and proposed fighting next morning at sunrising in Bob Allen's meadow, one hundred yards' distance, with rifles. To this Whitesides, Shields's second, said "no," because of the law. Thus ended duel No. 2. Yesterday Whiteside chose to consider himself insulted by Dr. Merryman, so sent him a kind of quasi-challenge, inviting him to meet him at the Planter's House in St. Louis, on the next Friday, to settle their difficulty. Merryman made me his friend, and sent W. a note, inquiring to know if he meant his note as a challenge, and, if so, that he would, according to the law in such case made and provided, prescribe the terms of the meeting. W. returned for answer, that, if M. would meet him at the Planter's House as desired, he would challenge him. M. replied in a note, that he denied W.'s right to dictate time and place, but that he (M.) would waive the question of time, and meet him at Louisiana, Mo. Upon my presenting this note to W., and stating verbally its contents, he declined receiving it, saying he had business in St. Louis, and it was as near as Louisiana. Merryman then directed me to notify Whiteside that he should publish the correspondence between them, with such comments as he thought fit. This I did. Thus it stood at bedtime last night. This morning Whiteside, by his friend Shields, is praying for a new trial, on the ground that he was mistaken in Merryman's proposition to meet him at Louisiana, Mo., thinking it was the State of Louisiana. This Merryman hoots at, and is preparing his publication; while the town is in a ferment, and a street-fight somewhat anticipated.
But I began this letter, not for what I have been writing, but to say something on that subject which you know to be of such infinite solicitude to me. The immense sufferings you endured from the first days of September till the middle of February you never tried to conceal from me, and I well understood. You have now been the husband of a lovely woman nearly eight months. That you are happier now than the day you married her, I well know; for without you could not be living. But I have your word for it, too, and the returning elasticity of spirits which is manifested in your letters. But I want to ask a close question, "Are you now in feeling, as well as judgment, glad you are married as you are?" From anybody but me this would be an impudent question, not to be tolerated; but I know you will pardon it in me. Please answer it quickly, as I am impatient to know.
I have sent my love to your Fanny so often, I fear she is getting tired of it. However, I venture to tender it again,
Yours forever,
Lincoln.
In the last of these letters, Mr. Lincoln refers to his "duel with Shields." That was another of the disagreeable consequences which flowed from his fatal entanglement with Mary. Not content with managing a timid, although half-frantic and refractory, lover, her restless spirit led her into new fields of adventure. Her pen was too keen to be idle in the political controversies of the time. As a satirical writer, she had no rival of either sex at Springfield, and few, we venture to say, anywhere else. But that is a dangerous talent: the temptations to use it unfairly are numerous and strong; it inflicts so much pain, and almost necessarily so much injustice, upon those against whom it is directed, that its possessor rarely, if ever, escapes from a controversy without suffering from the desperation it provokes. Mary Todd was not disposed to let her genius rust for want of use; and, finding no other victim handy, she turned her attention to James Shields, "Auditor." She had a friend, one Miss Jayne, afterwards Mrs. Trumbull, who helped to keep her literary secrets, and assisted as much as she could in worrying the choleric Irishman. Mr. Francis, the editor, knew very well that Shields was "a fighting-man;" but the "pieces" sent him by the wicked ladies were so uncommonly rich in point and humor, that he yielded to a natural inclination, and printed them, one and all. Below we give a few specimens:—
LETTER FROM THE LOST TOWNSHIPS.
Lost Townships, Aug. 27, 1842.
Dear Mr. Printer,—I see you printed that long letter I sent you a spell ago: I'm quite encouraged by it, and can't keep from writing again. I think the printing of my letters will be a good thing all round,—it will give me the benefit of being known by the world, and give the world the advantage of knowing what's going on in the Lost Townships, and give your paper respectability besides. So here comes another. Yesterday afternoon I hurried through cleaning up the dinner-dishes, and stepped over to Neighbor S——, to see if his wife Peggy was as well as mought be expected, and hear what they called the baby. Well, when I got there, and just turned round the corner of his log-cabin, there he was setting on the doorstep reading a newspaper.
"How are you, Jeff?" says I. He sorter started when he heard me, for he hadn't seen me before.
"Why," says he, "I'm mad as the devil, Aunt'Becca!"
"What about?" says I: "ain't its hair the right color? None of that nonsense, Jeff: there ain't an honester woman in the Lost Townships than"—
"Than who?" says he: "what the mischief are you about?"
I began to see I was running the wrong trail, and so says I, "Oh! nothing: I guess I was mistaken a little, that's all. But what is it you're mad about?" "Why," says he, "I've been tugging ever since harvest getting out wheat and hauling it to the river, to raise State-Bank paper enough to pay my tax this year, and a little school-debt I owe; and now, just as I've got it, here I open this infernal 'Extra Register,' expecting to find it full of 'Glorious Democratic Victories' and 'High-Comb'd Cocks,' when, lo and behold! I find a set of fellows calling themselves officers of State have forbidden the tax-collectors and school-commissioners to receive State paper at all; and so here it is, dead on my hands. I don't now believe all the plunder I've got will fetch ready cash enough to pay my taxes and that school-debt."
I was a good deal thunderstruck myself; for that was the first I had heard of the proclamation, and my old man was pretty much in the same fix with Jeff. We both stood a moment staring at one another, without knowing what to say. At last says I, "Mr. S———, let me look at that paper." He handed it to me, when I read the proclamation over.
"There, now," says he, "did you ever see such a piece of impudence and imposition as that?" I saw Jeff was in a good tune for saying some ill-natured things, and so I tho't I would just argue a little on the contrary side, and make him rant a spell if I could.
"Why," says I, looking as dignified and thoughtful as I could, "it seems pretty tough, to be sure, to have to raise silver where there's none to be raised; but then, you see, 'there will be danger of loss' if it ain't done."
"Loss, damnation 1" says he. "I defy Daniel Webster, I defy King Solomon, I defy the world,—I defy—I defy—yes, I defy even you, Aunt'Becca, to show how the people can lose any thing by paying their taxes in State paper."
"Well," says I, "you see what the officers of State say about it, and they are a desarnin' set of men. But," says I, "I guess you're mistaken about what the proclamation says. It don't say the people will lose any thing by the paper money being taken for taxes. It only says 'there will be danger of loss;' and though it is tolerable plain that the people can't lose by paying their taxes in something they can get easier than silver, instead of having to pay silver; and though it is just as plain that the State can't lose by taking State-Bank paper, however low it may be, while she owes the bank more than the whole revenue, and can pay that paper over on her debt, dollar for dollar,—still there is danger of loss to the 'officers of State;' and you know, Jeff, we can't get along without officers of State."
"Damn officers of State!" says he: "that's what you Whigs are always hurrahing for."
"Now, don't swear so, Jeff," says I: "you know I belong to the meetin', and swearin' hurts my feelins'."
"Beg pardon, Aunt'Becca," says he; "but I do say it's enough to make Dr. Goddard swear, to have tax to pay in silver, for nothing only that Ford may get his two thousand a year, and Shields his twenty-four hundred a year, and Carpenter his sixteen hundred a year, and all without 'danger of loss' by taking it in State paper. Yes, yes: it's plain enough now what these officers of State mean by 'danger of loss.' Wash, I s'pose, actually lost fifteen hundred dollars out of the three thousand that two of these 'officers of State' let him steal from the treasury, by being compelled to take it in State paper. Wonder if we don't have a proclamation before long commanding us to make up this loss to Wash in silver."
And so he went on till his breath run out, and he had to stop. I couldn't think of any thing to say just then; and so I begun to look over the paper again. "Ay! here's another proclamation, or something like it."
"Another!" says Jeff; "and whose egg is it, pray?"
I looked to the bottom of it, and read aloud, "Your obedient servant, Jas. Shields, Auditor."
"Aha!" says Jeff, "one of them same three fellows again. Well, read it, and let's hear what of it."
I read on till I came to where it says, "The object of this measure is to suspend the collection of the revenue for the current year."
"Now stop, now stop!" says he: "that's a lie a'ready, and I don't want to hear of it."
"Oh! maybe not," says I.
"I say it—is—a—lie. Suspend the collection, indeed! Will the collectors, that have taken their oaths to make the collection, dare to suspend it? Is there any thing in the law requiring them to perjure themselves at the bidding of James Shields? Will the greedy gullet of the penitentiary be satisfied with swallowing him instead of all them, if they should venture to obey him? And would he not discover some 'danger of loss,' and be off, about the time it came to taking their places?
"And suppose the people attempt to suspend, by refusing to pay, what then? The collectors would just jerk up their horses and cows, and the like, and sell them to the highest bidder for silver in hand, without valuation or redemption. Why, Shields didn't believe that story himself: it was never meant for the truth. If it was true, why was it not writ till five days after the proclamation? Why didn't Carlin and Carpenter sign it as well as Shields? Answer me that, Aunt'Becca. I say it's a lie, and not a well-told one at that. It grins out like a copper dollar. Shields is a fool as well as a liar. With him truth is out of the question; and, as for getting a good bright passable lie out of him, you might as well try to strike fire from a cake of tallow. I stick to it, it's all an infernal Whig lie!"
"A Whig lie! Highty tighty!"
"Yes, a Whig lie; and it's just like every thing the cursed British Whigs do. First they'll do some divilment, and then they'll tell a lie to hide it. And they don't care how plain a lie it is: they think they can cram any sort of a one down the throats of the ignorant Locofocos, as they call the Democrats."
"Why, Jeff, you're crazy: you don't mean to say Shields is a Whig!"
"Yes, I do."
"Why, look here! the proclamation is in your own Democratic paper, as you call it."
"I know it; and what of that? They only printed it to let us Democrats see the deviltry the Whigs are at."
"Well, but Shields is the auditor of this Loco—I mean this Democratic State."
"So he is, and Tyler appointed him to office."
"Tyler appointed him?"
"Yes (if you must chaw it over), Tyler appointed him; or, if it wasn't him, it was old Granny Harrison, and that's all one. I tell you, Aunt'Becca, there's no mistake about his being a Whig. Why, his very looks shows it,—every thing about him shows it: if I was deaf and blind, I could tell him by the smell. I seed him when I was down in Springfield last winter. They had a sort of a gatherin' there one night among the grandees, they called a fair. All the gals about town was there; and all the handsome widows and married women, finickin' about, trying to look like gals, tied as tight in the middle, and puffed out at both ends, like bundles of fodder that hadn't been stacked yet, but wanted stackin' pretty bad. And then they had tables all round the house kivered over with [ ] caps, and pincushions, and ten thousand such little knick-knacks, tryin' to sell'em to the fellows that were bowin' and scrapin' and kungeerin' about'em. They wouldn't let no Democrats in, for fear they'd disgust the ladies, or scare the little gals, or dirty the floor. I looked in at the window, and there was this same fellow Shields floatin' about on the air, without heft or earthly substance, just like a lock of cat-fur where cats had been fightin'.
"He was paying his money to this one, and that one, and t'other one, and sufferin' great loss because it wasn't silver instead of State paper; and the sweet distress he seemed to be in,—his very features, in the ecstatic agony of his soul, spoke audibly and distinctly, 'Dear girls, it is distressing, but I cannot marry you all. Too well I know how much you suffer; but do, do remember, it is not my fault that I am so handsome and so interesting.'
"As this last was expressed by a most exquisite contortion of his face, he seized hold of one of their hands, and squeezed, and held on to it about a quarter of an hour. 'O my good fellow!' says I to myself, 'if that was one of our Democratic gals in the Lost Townships, the way you'd get a brass pin let into you, would be about up to the head.' He a Democrat! Fiddlesticks! I tell you, Aunt'Becca, he's a Whig, and no mistake: nobody but a Whig could make such a conceity dunce of himself."
"Well," says I, "maybe he is; but, if he is, I'm mistaken the worst sort. Maybe so, maybe so; but, if I am, I'll suffer by it; I'll be a Democrat if it turns out that Shields is a Whig; considerin' you shall be a Whig if he turns out a Democrat."
"A bargain, by jingoes!" says he; "but how will we find out?"
"Why," says I, "we'll just write, and ax the printer."
"Agreed again!" says he; "and, by thunder! if it does turn out that Shields is a Democrat, I never will"—
"Jefferson,—Jefferson"—
"What do you want, Peggy?"
"Do get through your everlasting clatter sometime, and bring me a gourd of water: the child's been crying for a drink this live-long hour."
"Let it die, then: it may as well die for water as to be taxed to death to fatten officers of State."
Jeff run off to get the water, though, just like he hadn't been sayin' any thing spiteful; for he's a raal good-hearted fellow, after all, once you get at the foundation of him.
I walked into the house, and "Why, Peggy," says I, "I declare, we like to forgot you altogether."
"Oh, yes!" says she, "when a body can't help themselves, everybody soon forgets'em; but, thank God! by day after to-morrow I shall be well enough to milk the cows, and pen the calves, and wring the contrary ones' tails for'em, and no thanks to nobody."
"Good-evening, Peggy," says I; and so I sloped, for I seed she was mad at me for making Jeff neglect her so long.
And now, Mr. Printer, will you be sure to let us know in your next paper whether this Shields is a Whig or a Democrat? I don't care about it for myself, for I know well enough how it is already; but I want to convince Jeff. It may do some good to let him, and others like him, know who and what those officers of State are. It may help to send the present hypocritical set to where they belong, and to fill the places they now disgrace with men who will do more work for less pay, and take a fewer airs while they are doing it. It ain't sensible to think that the same men who get us into trouble will change their course; and yet it's pretty plain, if some change for the better is not made, it's not long that either Peggy or I, or any of us, will have a cow left to milk, or a calf's tail to wring.
Yours, truly,
Rebecca———.
Lost Townships, Sept. 8,1842. Dear Mr. Printer,—I was a-standin' at the spring yesterday a-washin' out butter, when I seed Jim Snooks a-ridin' up towards the house for very life like, when, jist as I was a wonderin' what on airth was the matter with him, he stops suddenly, and ses he, "Aunt'Becca, here's somethin' for you;" and with that he hands out your letter. Well, you see I steps out towards him, not thinkin' that I had both hands full of butter; and seein' I couldn't take the letter, you know, without greasin' it, I ses, "Jim, jist you open it, and read it for me." Well, Jim opens it, and reads it; and would you believe it, Mr. Editor? I was so completely dumfounded, and turned into stone, that there I stood in the sun, a-workin' the butter, and it a-runnin' on the ground, while he read the letter, that I never thunk what I was about till the hull on't run melted on the ground, and was lost. Now, sir, it's not for the butter, nor the price of the butter, but, the Lord have massy on us, I wouldn't have sich another fright for a whole firkin of it. Why, when I found out that it was the man what Jeff seed down to the fair that had demanded the author of my letters, threatnin' to take personal satisfaction of the writer, I was so skart that I tho't I should quill-wheel right where I was.
You say that Mr. S. is offended at being compared to cat's fur, and is as mad as a March hare (that ain't far), because I told about the squeezin'. Now, I want you to tell Mr. S, that, rather than fight, I'll make any apology; and, if he wants personal satisfaction, let him only come here, and he may squeeze my hand as hard as I squeeze the butter, and, if that ain't personal satisfaction, I can only say that he is the fust man that was not satisfied with squeezin' my hand. If this should not answer, there is one thing more that I would do rather than get a lickin'. I have all along expected to die a widow; but, as Mr. S. is rather good-looking than otherwise, I must say I don't care if we compromise the matter by—really, Mr. Printer, I can't help blushin'—but I—it must come out—I—but widowed modesty—well, if I must, I must—wouldn't he—maybe sorter, let the old grudge drap if I was to consent to be—be—h-i-s w-i-f-e? I know he's a fightin' man, and would rather fight than eat; but isn't marryin' better than fightin', though it does sometimes run into it? And I don't think, upon the whole, that I'd be sich a bad match neither: I'm not over sixty, and am just four feet three in my bare feet, and not much more round the girth; and for color, I wouldn't turn my back to nary gal in the Lost Townships. But, after all, maybe I'm countin' my chickins before they' re hatched, and dreamin' of matrimonial bliss when the only alternative reserved for me may be a lickin'. Jeff tells me the way these fire-eaters do is to give the challenged party choice of weapons, &c., which bein' the case, I'll tell you in confidence that I never fights with any thing but broomsticks, or hot water, or a shovelful of coals, or some such thing; the former of which being somewhat like a shillalah, may not be very objectionable to him. I will give him choice, however, in one thing, and that is, whether, when we fight, I shall wear breeches or he petticoats; for I presume that change is sufficient to place us on an equality.
Yours, &c.
Rebecca———.
P. S.—Jist say to your friend, if he concludes to marry rather than fight, I shall only inforce one condition: that is, if he should ever happen to gallant any young gals home of nights from our house, he must not squeeze their hands.
It is by no means a subject of wonder that these publications threw Mr. James Shields into a state of wrath. A thin-skinned, sensitive, high-minded, and high-tempered man, tender of his honor, and an Irishman besides, it would have been strange indeed, if he had not felt like snuffing blood. But his rage only afforded new delights to his tormentors; and when it reached its height, "Aunt'Becca" transformed herself to "Cathleen," and broke out in rhymes like the following, which Miss Jayne's brother "Bill" kindly consented to "drop" for the amiable ladies.
[For The Journal.] Ye Jew's-harps awake! The A———s won: Rebecca the widow has gained Erin's son; The pride of the North from Emerald Isle Has been wooed and won by a woman's smile. The combat's relinquished, old loves all forgot: To the widow he's bound. Oh, bright be his lot! In the smiles of the conquest so lately achieved, Joyful be his bride, "widowed modesty" relieved. The footsteps of time tread lightly on flowers, May the cares of this world ne'er darken his hours! But the pleasures of life are fickle and coy As the smiles of a maiden sent off to destroy. Happy groom! in sadness, far distant from thee, The Fair girls dream only of past times of glee Enjoyed in thy presence; whilst the soft blarnied store Will be fondly remembered as relics of yore, And hands that in rapture you oft would have prest In prayer will be clasped that your lot may be blest. Cathleen.
It was too bad. Mr. Shields could stand it no longer. He sent Gen. Whiteside to Mr. Francis, to demand the name of the person who wrote the letters from the "Lost Townships;" and Mr. Francis told him it was A. Lincoln. This information led to a challenge, a sudden scampering off of parties and friends to Missouri, a meeting, an explanation, and a peaceful return.
Abraham Lincoln in the field of honor, sword in hand, manoeuvred by a second learned in the duello, would be an attractive spectacle under any circumstances. But with a celebrated man for an antagonist, and a lady's humor the occasion, the scene is one of transcendent interest; and the documents which describe it are well entitled to a place in his history. The letter of Mr. Shields's second, being first in date, is first in order.
Springfield, Oct. 3, 1842. To the Editor op "The Sangamon Journal."
Sir,—To prevent misrepresentation of the recent affair between Messrs. Shields and Lincoln, I think it proper to give a brief narrative of the facts of the case, as they came within my knowledge; for the truth of which I hold myself responsible, and request you to give the same publication. An offensive article in relation to Mr. Shields appeared in "The Sangamon Journal" of the 2d September last; and, on demanding the author, Mr. Lincoln was given up by the editor. Mr. Shields, previous to this demand, made arrangements to go to Quincy on public business; and before his return Mr. Lincoln had left for Tremont, to attend the court, with the intention, as we learned, of remaining on the circuit several weeks. Mr. Shields, on his return, requested me to accompany him to Tremont; and, on arriving there, we found that Dr. Merryman and Mr. Butler had passed us in the night, and got there before us. We arrived in Tremont on the 17th ult.; and Mr. Shields addressed a note to Mr. Lincoln immediately, informing him that he was given up as the author of some articles that appeared in "The Sangamon Journal" (one more over the signature having made its appearance at this time), and requesting him to retract the offensive allusions contained in said articles in relation to his private character. Mr. Shields handed this note to me to deliver to Mr. Lincoln, and directed me, at the same time, not to enter into any verbal communication, or be the bearer of any verbal explanation, as such were always liable to misapprehension. This note was delivered by me to Mr. Lincoln, stating, at the same time, that I would call at his convenience for an answer. Mr. Lincoln, in the evening of the same day, handed me a letter addressed to Mr. Shields. In this he gave or offered no explanation, but stated therein that he could not submit to answer further, on the ground that Shields's note contained an assumption of facts and also a menace. Mr. Shields then addressed him another note, in which he disavowed all intention to menace, and requested to know whether he (Mr. Lincoln) was the author of either of the articles which appeared in "The Journal," headed "Lost Townships," and signed "Rebecca;" and, if so, he repeated his request of a retraction of the offensive matter in relation to his private character; if not, his denial would be held sufficient. This letter was returned to Mr. Shields unanswered, with a verbal statement "that there could be no further negotiation between them until the first note was withdrawn." Mr. Shields thereupon sent a note designating me as his friend, to which Mr. Lincoln replied by designating Dr. Merryman. These three last notes passed on Monday morning, the 19th. Dr. Merryman handed me Mr. Lincoln's last note when by ourselves. I remarked to Dr. Merryman that the matter was now submitted to us, and that I would propose that he and myself should pledge our words of honor to each other to try to agree upon terms of amicable arrangement, and compel our principals to accept of them. To this he readily assented, and we shook hands upon the pledge. It was then mutually agreed that we should adjourn to Springfield, and there procrastinate the matter, for the purpose of effecting the secret arrangement between him and myself. All this I kept concealed from Mr. Shields. Our horse had got a little lame in going to Tremont, and Dr. Merryman invited me to take a seat in his buggy. I accepted the invitation the more readily, as I thought, that leaving Mr. Shields in Tremont until his horse would be in better condition to travel would facilitate the private agreement between Dr. Merryman and myself. I travelled to Springfield part of the way with him, and part with Mr. Lincoln; but nothing passed between us on the journey in relation to the matter in hand. We arrived in Springfield on Monday night. About noon on Tuesday, to my astonishment, a proposition was made to meet in Missouri, within three miles of Alton, on the next Thursday! The weapons, cavalry broadswords of the largest size; the parties to stand on each side of a barrier, and to be confined to a limited space. As I had not been consulted at all on the subject, and considering the private understanding between Dr. Merryman and myself, and it being known that Mr. Shields was left at Tremont, such a proposition took me by surprise. However, being determined not to violate the laws of the State, I declined agreeing upon the terms until we should meet in Missouri. Immediately after, I called upon Dr. Merryman, and withdrew the pledge of honor between him and myself in relation to a secret arrangement. I started after this to meet Mr. Shields, and met him about twenty miles from Springfield. It was late on Tuesday night when we both reached the city, and learned that Dr. Merryman had left for Missouri, Mr. Lincoln having left before the proposition was made, as Dr. Merryman had himself informed me. The time and place made it necessary to start at once. We left Springfield at eleven o'clock on Tuesday night, travelled all night, and arrived in Hillsborough on Wednesday morning, where we took in Gen. Ewing. From there we went to Alton, where we arrived on Thursday; and, as the proposition required three friends on each side, I was joined by Gen. Ewing and Dr. Hope, as the friends of Mr. Shields.
We then crossed to Missouri, where a proposition was made by Gen. Hardin and Dr. English (who had arrived there in the mean time as mutual friends) to refer the matter to, I think, four friends for a settlement. This I believed Mr. Shields would refuse, and declined seeing him; but Dr. Hope, who conferred with him upon the subject, returned, and stated that Mr. Shields declined settling the matter through any other than the friends he had selected to stand by him on that occasion. The friends of both the parties finally agreed to withdraw the papers (temporarily) to give the friends of Mr. Lincoln an opportunity to explain. Whereupon the friends of Mr. Lincoln, to wit, Messrs. Merryman, Bledsoe, and Butler, made a full and satisfactory explanation in relation to the article which appeared in "The Sangamon Journal" of the 2d, the only one written by him. This was all done without the knowledge or consent of Mr. Shields; and he refused to accede to it until Dr. Hope, Gen. Ewing, and myself declared the apology sufficient, and that we could not sustain him in going further. I think it necessary to state further, that no explanation or apology had been previously offered on the part of Mr. Lincoln to Mr. Shields, and that none was ever communicated by me to him, nor was any ever offered to me, unless a paper read to me by Dr. Merryman after he had handed me the broadsword proposition on Tuesday. I heard so little of the reading of the paper, that I do not know fully what it purported to be; and I was the less inclined to inquire, as Mr. Lincoln was then gone to Missouri, and Mr. Shields not yet arrived from Tremont. In fact, I could not entertain any offer of the kind, unless upon my own responsibility; and that I was not disposed to do after what had already transpired.
I make this statement, as I am about to be absent for some time, and I think it due to all concerned to give a true version of the matter before I leave.
Your obedient servant,
John D. Whiteside.
To which Mr. Merryman replied:—
Springfield, Oct. 8, 1842.
Editors of "The Journal."
Gents,—By your paper of Friday, I discover that Gen. Whiteside has published his version of the late affair between Messrs. Shields and Lincoln. I now bespeak a hearing of my version of the same affair, which shall be true and full as to all material facts.
On Friday evening, the 16th of September, I learned that Mr. Shields and Gen. Whiteside had started in pursuit of Mr. Lincoln, who was at Tremont, attending court. I knew that Mr. Lincoln was wholly unpractised both as to the diplomacy and weapons commonly employed in similar affairs; and I felt it my duty, as a friend, to be with him, and, so far as in my power, to prevent any advantage being taken of him as to either his honor or his life. Accordingly, Mr. Butler and myself started, passed Shields and Whiteside in the night, and arrived at Tremont ahead of them on Saturday morning. I told Mr. Lincoln what was brewing, and asked him what course he proposed to himself. He stated that he was wholly opposed to duelling, and would do any thing to avoid it that might not degrade him in the estimation of himself and friends; but, if such degradation or a fight were the only alternative, he would fight.
In the afternoon Shields and Whiteside arrived, and very soon the former sent to Mr. Lincoln by the latter the following note or letter:—
Tremont, Sept. 17,1842.
A. Lincoln, Esq.—I regret that my absence on public business compelled me to postpone a matter of private consideration a little longer than I could have desired. It will only be necessary, however, to account for it by informing you that I have been to Quincy on business that would not admit of delay. I will now state briefly the reasons of my troubling you with this communication, the disagreeable nature of which I regret, as I had hoped to avoid any difficulty with any one in Springfield while residing there, by endeavoring to conduct myself in such a way amongst both my political friends and opponents, as to escape the necessity of any. Whilst thus abstaining from giving provocation, I have become the object of slander, vituperation, and personal abuse, which, were I capable of submitting to, I would prove myself worthy of the whole of it.
In two or three of the last number's of "The Sangamon Journal," articles of the most personal nature, and calculated to degrade me, have made their appearance. On inquiring, I was informed by the editor of that paper, through the medium of my friend, Gen. Whiteside, that you are the author of those articles. This information satisfies me that I have become, by some means or other, the object of your secret hostility. I will not take the trouble of inquiring into the reason of all this; but I will take the liberty of requiring a full, positive, and absolute retraction of all offensive allusions used by you in these communications, in relation to my private character and standing as a man, as an apology for the insults conveyed in them.
This may prevent consequences which no one will regret more than myself.
Your ob't serv't,
[Copy.] Jas. Shields.
About sunset Gen. Whiteside called again, and received from Mr. Lincoln the following answer to Mr. Shields's note:—
Tremont, Sept. 17, 1812
Jas. Shields, Esq.—Your note of to-day was handed me by Gen. Whiteside. In that note, you say you have been informed, through the medium of the editor of "The Journal," that I am the author of certain articles in that paper which you deem personally abusive of you; and, without stopping to inquire whether I really am the author, or to point out what is offensive in them, you demand an unqualified retraction of all that is offensive, and then proceed to hint at consequences.
Now, sir, there is in this so much assumption of facts, and so much of menace as to consequences, that I cannot submit to answer that note any further than I have, and to add, that the consequence to which I suppose you allude would be matter of as great regret to me as it possibly could to you. Respectfully,
A. Lincoln.
In about an hour Gen. Whiteside called again with another note from Mr. Shields; but after conferring with Mr. Butler for a long time, say two or three hours, returned without presenting the note to Mr. Lincoln. This was in consequence of an assurance from Mr. Butler that Mr. Lincoln could not receive any communication from Mr. Shields, unless it were a withdrawal of his first note, or a challenge. Mr. Butler further stated to Gen. Whiteside, that, on the withdrawal of the first note, and a proper and gentlemanly request for an explanation, he had no doubt one would be given. Gen. Whiteside admitted that that was the course Mr. Shields ought to pursue, but deplored that his furious and intractable temper prevented his having any influence with him to that end. Gen. W. then requested us to wait with him until Monday morning, that he might endeavor to bring Mr. Shields to reason.
On Monday morning he called and presented Mr. Lincoln the same note as, Mr. Butler says, he had brought on Saturday evening. It was as follows:—
Tremont, Sept. 17, 1842.
A. Lincoln, Esq.—In your reply to my note of this date, you intimate that I assume facts and menace consequences, and that you cannot submit to answer it further. As now, sir, you desire it, I will be a little more particular. The editor of "The Sangamon Journal" gave me to understand that you are the author of an article which appeared, I think, in that paper of the 2d September inst., headed "The Lost Townships," and signed Rebecca or 'Becca. I would therefore take the liberty of asking whether you are the author of said article, or any other over the same signature which has appeared in any of the late numbers of that paper. If so, I repeat my request of an absolute retraction of all offensive allusion contained therein in relation to my private character and standing. If you are not the author of any of the articles, your denial will be sufficient. I will say further, it is not my intention to menace, but to do myself justice.
Your ob't serv't,
[Copy.] Jas. Shields.
This Mr. Lincoln perused, and returned to Gen. Whiteside, telling him verbally, that he did not think it consistent with his honor to negotiate for peace with Mr. Shields, unless Mr. Shields would withdraw his former offensive letter.
In a very short time Gen. Whiteside called with a note from Mr. Shields, designating Gen. Whiteside as his friend, to which Mr. Lincoln instantly replied, designating me as his. On meeting Gen. Whiteside, he proposed that we should pledge our honor to each other that we would endeavor to settle the matter amicably; to which I agreed, and stated to him the only conditions on which it could be so settled; viz., the withdrawal of Mr. Shields's first note; which he appeared to think reasonable, and regretted that the note had been written,—saying, however, that he had endeavored to prevail on Mr. Shields to write a milder one, but had not succeeded. He added, too, that I must promise not to mention it, as he would not dare to let Mr. Shields know that he was negotiating peace; for, said he, "He would challenge me next, and as soon cut my throat as not." Not willing that he should suppose my principal less dangerous than his own, I promised not to mention our pacific intentions to Mr. Lincoln or any other person; and we started for Springfield forthwith.
We all, except Mr. Shields, arrived in Springfield late at night on Monday. We discovered that the affair had, somehow, got great publicity in Springfield, and that an arrest was probable. To prevent this, it was agreed by Mr. Lincoln and myself that he should leave early on Tuesday morning. Accordingly, he prepared the following instructions for my guide, on a suggestion from Mr. Butler that he had reason to believe that an attempt would be made by the opposite party to have the matter accommodated:—
In case Whiteside shall signify a wish to adjust this affair without further difficulty, let him know, that, if the present papers be withdrawn, and a note from Mr. Shields asking to know if I am the author of the articles of which he complains, and asking that I shall make him gentlemanly satisfaction if I am the author, and this without menace or dictation as to what that satisfaction shall be, a pledge is made that the following answer shall be given:—
"I did write the 'Lost Township' letter which appeared in the 'Journal' of the 2d inst., but had no participation in any form in any other article alluding to you. I wrote that wholly for political effect. I had no intention of injuring your personal or private character, or standing as a man or a gentleman; and I did not then think, and do not now think, that that article could produce, or has produced, that effect against you; and, had I anticipated such an effect, would have forborne to write it. And I will add, that your conduct towards me, so far as I knew, had always been gentlemanly, and that I had no personal pique against you, and no cause for any."
If this should be done, I leave it with you to manage what shall and what shall not be published.
If nothing like this is done, the preliminaries of the fight are to be:—
1st, Weapons.—Cavalry broadswords of the largest size, precisely equal in all respects, and such as now used by the cavalry company at Jacksonville.
2d, Position.—A plank ten feet long, and from nine to twelve inches broad, to be firmly fixed on edge on the ground as the line between us, which neither is to pass his foot over upon forfeit of his life. Next, a line drawn on the ground on either side of said plank and parallel with it, each at the distance of the whole length of the sword and three feet additional from the plank; and the passing of his own such line by either party during the fight shall be deemed a surrender of the contest.
3d, Time.—On Thursday evening at 5 o'clock, if you can get it so; but in no case to be at a greater distance of time than Friday evening at 5 o'clock.
4th, Place.—Within three miles of Alton, on the opposite side of the river, the particular spot to be agreed on by you.
Any preliminary details coming within the above rules, you are at liberty to make at your discretion; but you are in no case to swerve from these rules, or to pass beyond their limits.
In the course of the forenoon I met Gen. Whiteside, and he again intimated a wish to adjust the matter amicably. I then read to him Mr. Lincoln's instructions to an adjustment, and the terms of the hostile meeting, if there must be one, both at the same time.
He replied that it was useless to talk of an adjustment, if it could only be effected by the withdrawal of Mr. Shields's paper, for such withdrawal Mr. Shields would never consent to; adding, that he would as soon think of asking Mr. Shields to "butt his brains out against a brick wall as to withdraw that paper." He proceeded: "I see but one course,—that is a desperate remedy:'tis to tell them, if they will not make the matter up, they must fight us." I replied, that, if he chose to fight Mr. Shields to compel him to do right, he might do so; but as for Mr. Lincoln, he was on the defensive, and, I believed, in the right, and I should do nothing to compel him to do wrong. Such withdrawal having been made indispensable by Mr. Lincoln, I cut this matter short as to an adjustment, an I proposed to Gan. Whiteside to accept the terms of the fight, which he refused to do until Mr. Shields's arrival in town, but agreed, verbally, that Mr. Lincoln's friends should procure the broadswords, and take them to the ground. In the afternoon he came to me, saying that some persons were swearing out affidavits to have us arrested, and that he intended to meet Mr. Shields immediately, and proceed to the place designated; lamenting, however, that I would not delay the time, that he might procure the interference of Gov. Ford and Gen. Ewing to mollify Mr. Shields. I told him that an accommodation, except upon the terms I mentioned, was out of the question; that to delay the meeting was to facilitate our arrest; and, as I was determined not to be arrested, I should leave town in fifteen minutes. I then pressed his acceptance of the preliminaries, which he disclaimed upon the ground that it would interfere with his oath of office as Fund Commissioner. I then, with two other friends, went to Jacksonville, where we joined Mr. Lincoln about 11 o'clock on Tuesday night. Wednesday morning we procured the broadswords, and proceeded to Alton, where we arrived about 11, A.M., on Thursday. The other party were in town before us. We crossed the river, and they soon followed. Shortly after, Gen. Hardin and Dr. English presented to Gen. Whiteside and myself the following note:—
Alton, Sept. 22, 1842.
Messrs. Whiteside and Merryman.—As the mutual personal friends of Messrs. Shields and Lincoln, but without authority from either, we earnestly desire to see a reconciliation of the misunderstanding which exists between them. Such difficulties should always be arranged amicably, if it is possible to do so with honor to both parties.
Believing ourselves, that such an arrangement can possibly be effected, we respectfully, but earnestly, submit the following proposition for your consideration:—
Let the whole difficulty be submitted to four or more gentlemen, to be selected by yourselves, who shall consider the affair, and report thereupon for your consideration.
John J. Hardin.
E. W. English.
To this proposition Gen. Whiteside agreed: I declined doing so without consulting Mr. Lincoln. Mr. Lincoln remarked, that, as they had accepted the proposition, he would do so, but directed that his friends should make no terms except those first proposed. Whether the adjustment was finally made upon these very terms, and no other, let the following documents attest:—
Missouri, Sept. 22, 1842.
Gentlemen,—All papers in relation to the matter in controversy between Mr. Shields and Mr. Lincoln having been withdrawn by the friends of the parties concerned, the friends of Mr. Shields ask the friends of Mr. Lincoln to explain all offensive matter in the articles which appeared in "The Sangamon Journal" of the 2d, 9th, and 16th of September, under the signature of "Rebecca," and headed "Lost Townships."
It is due to Gen. Hardin and Mr. English to state that their interference was of the most courteous and gentlemanly character.
John D. Whiteside.
Wm. Lee D. Ewino.
T. M. Hope.
Missouri, Sept. 22, 1842.
Gentlemen,—All papers in relation to the matter in controversy between Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Shields having been withdrawn by the friends of the parties concerned, we, the undersigned, friends of Mr. Lincoln, in accordance with your request that explanation of Mr. Lincoln's publication in relation to Mr. Shields in "The Sangamon Journal" of the 2d, 9th, and 16th of September be made, take pleasure in saying, that, although Mr. Lincoln was the writer of the article signed "Rebecca" in the "Journal" of the 2d, and that only, yet he had no intention of injuring the personal or private character or standing of Mr. Shields as a gentleman or a man, and that Mr. Lincoln did not think, nor does he now think, that said article could produce such an effect; and, had Mr. Lincoln anticipated such an effect, he would have forborne to write it. We will further state, that said article was written solely for political effect, and not to gratify any personal pique against Mr. Shields, for he had none, and knew of no cause for any It is due to Gen. Hanlin and Mr. English to say that their interference was of the most courteous and gentlemanly character.
E. H. Merryman.
A. T. Bledsoe.
Wm. Butler.
Let it be observed now, that Mr. Shields's friends, after agreeing to the arbitrament of four disinterested gentlemen, declined the contract, saying that Mr. Shields wished his own friends to act for him. They then proposed that we should explain without any withdrawal of papers. This was promptly and firmly refused, and Gen. Whiteside himself pronounced the papers withdrawn. They then produced a note requesting us to "disavow" all offensive intentions in the publications, &c., &c. This we declined answering, and only responded to the above request for an explanation.
These are the material facts in relation to the matter, and I think present the case in a very different light from the garbled and curtailed statement of Gen. Whiteside. Why he made that statement I know not, unless he wished to detract from the honor of Mr. Lincoln. This was ungenerous, more particularly as he on the ground requested us not to make in our explanation any quotations from the "Rebecca papers;" also not to make public the terms of reconciliation, and to unite with them in defending the honorable character of the adjustment.
Gen. W., in his publication, says, "The friends of both parties agreed to withdraw the papers (temporarily) to give the friends of Mr. Lincoln an opportunity to explain." This I deny. I say the papers were withdrawn to enable Mr. Shields's friends to ask an explanation; and I appeal to the documents for proof of my position.
By looking over these documents, it will be seen that Mr. Shields had not before asked for an explanation, but had all the time been dictatorily insisting on a retraction.
Gen. Whiteside, in his communication, brings to light much of Mr. Shields's manifestations of bravery behind the scenes. I can do nothing of the kind for Mr. Lincoln. He took his stand when I first met him at Tremont, and maintained it calmly to the last, without difficulty or difference between himself and his friends.
I cannot close this article, lengthy as it is, without testifying to the honorable and gentlemanly conduct of Gen. Ewing and Dr. Hope, nor indeed can I say that I saw any thing objectionable in the course of Gen. Whiteside up to the time of his communication. This is so replete with prevarication and misrepresentation, that I cannot accord to the General that candor which I once supposed him to possess. He complains that I did not procrastinate time according to agreement. He forgets that by his own act he cut me off from that chance in inducing me, by promise, not to communicate our secret contract to Mr. Lincoln. Moreover, I could see no consistency in wishing for an extension of time at that stage of the affair, when in the outset they were in so precipitate a hurry, that they could not wait three days for Mr. Lincoln to return from Tremont, but must hasten there, apparently with the intention of bringing the matter to a speedy issue. He complains, too, that, after inviting him to take a seat in my buggy, I never broached the subject to him on our route here. But was I, the defendant in the case, with a challenge hanging over me, to make advances, and beg a reconciliation? Absurd! Moreover, the valorous general forgets that he beguiled the tedium of the journey by recounting to me his exploits in many a well-fought battle,—dangers by "flood and field" in which I don't believe he ever participated,—doubtless with a view to produce a salutary effect on my nerves, and impress me with a proper notion of his fire-eating propensities.
One more main point of his argument, and I have done. The General seems to be troubled with a convenient shortness of memory on some occasions. He does not remember that any explanations were offered at any time, unless it were a paper read when the "broadsword proposition" was tendered, when his mind was so confused by the anticipated clatter of broadswords, or something else, that he did "not know fully what it purported to be." The truth is, that by unwisely refraining from mentioning it to his principal, he placed himself in a dilemma which he is now endeavoring to shuffle out of. By his inefficiency, and want of knowledge of those laws which govern gentlemen in matters of this kind, he has done great injustice to his principal, a gentleman who I believe is ready at all times to vindicate his honor manfully, but who has been unfortunate in the selection of his friend; and this fault he is now trying to wipe out by doing an act of still greater injustice to Mr. Lincoln.
E. H. Merryman.
And so Mr. Lincoln acknowledged himself to have been the author of one of the "Lost Township Letters." Whether he was or not, was known only perhaps to Miss Todd and himself. At the time of their date, he was having secret meetings with her at Mr. Francis's house, and endeavoring to nerve himself to the duty of marrying her, with what success the letters to Speed are abundant evidence. It is probable that Mary composed them fresh from these stolen conferences; that some of Mr. Lincoln's original conceptions and peculiarities of style unwittingly crept into them, and that here and there he altered and amended the manuscript before it went to the printer. Such a connection with a lady's productions made it obligatory upon him to defend them. But why avow one, and disavow the rest? It is more than likely that he was determined to take just enough responsibility to fight upon, provided Shields should prove incorrigible, and not enough to prevent a peaceful issue, if the injured gentleman should be inclined to accept an apology.
After his marriage, Mr. Lincoln took up his residence at the "Globe Tavern," where he had a room and boarding for man and wife for the moderate sum of four dollars per week. But, notwithstanding cheap living, he was still as poor as ever, and gave "poverty" as one of his reasons for not paying a friendly visit which seemed to be expected of him.
At the bar and in political affairs he continued to work with as much energy as before, although his political prospects seem just now to have suffered an unexpected eclipse. In 1843, Lincoln, Hardin, and Baker were candidates for the Whig congressional nomination; but between Hardin and Baker there was "bitter hostility," and between Baker and Lincoln "suspicion and dislike." The contest was long and fierce; but, before it was over, Lincoln reluctantly withdrew in favor of Baker. He had had a hard time of it, and had been compelled to meet accusations of a very strange character. Among other things, he was charged with being an aristocrat; with having deserted his old friends, the people, by marrying a proud woman on account of her blood and family. This hurt him keenly, and he took great pains to disprove it; but this was not all. He was called an infidel by some, a Presbyterian here, an Episcopalian there; so that by turns he incurred the hostility of all the most powerful religious societies in the district.
On the 24th of March, he wrote to Mr. Speed as follows:—
Springfield, March 24, 1843.
Dear Speed,—... We had a meeting of the Whigs of the county here on last Monday to appoint delegates to a district convention; and Baker beat me, and got the delegation instructed to go for him. The meeting, in spite of my attempt to decline it, appointed me one of the delegates; so that, in getting Baker the nomination, I shall be fixed a good deal like a fellow who is made a groomsman to a man that has cut him out, and is marrying his own dear "gal." About the prospects of your having a namesake at our town, can't say exactly yet.
A. Lincoln.
He was now a Baker delegate, pledged to get him the nomination if he could; and yet he was far from giving up the contest in his own behalf. Only two days after the letter to Speed, he wrote to Mr. Morris:—
Springfield, Ill., March 26, 1843.
Friend Morris,—Your letter of the 23d was received on yesterday morning, and for which (instead of an excuse, which you thought proper to ask) I tender you my sincere thanks. It is truly gratifying to me to learn, that, while the people of Sangamon have cast me off, my old friends of Menard, who have known me longest and best, stick to me. It would astonish, if not amuse, the older citizens (a stranger, friendless, uneducated, penniless boy, working on a flat-boat at ten dollars per month) to learn that I have been put down here as the candidate of pride, wealth, and aristocratic family distinction. Yet so, chiefly, it was. There was, too, the strangest combination of church-influence against me. Baker is a Campbellite; and therefore, as I suppose, with few exceptions, got all that church.
My wife has some relations in the Presbyterian churches, and some with the Episcopal churches; and therefore, wherever it would tell, I was set down as either the one or the other, while it was everywhere contended that no Christian ought to go for me, because I belonged to no church, was suspected of being a deist, and had talked about fighting a duel. With all these things, Baker, of course, had nothing to do. Nor do I complain of them. As to his own church going for him, I think that was right enough: and as to the influences I have spoken of in the other, though they were very strong, it would be grossly untrue and unjust to charge that they acted upon them in a body, or were very near so. I only mean that those influences levied a tax of a considerable per cent upon my strength throughout the religious controversy. But enough of this.
You say, that, in choosing a candidate for Congress, you have an equal right with Sangamon; and in this you are undoubtedly earnest. In agreeing to withdraw if the Whigs of Sangamon should go against me, I did not mean that they alone were worth consulting, but that if she, with her heavy delegation, should be against me, it would be impossible for me to succeed; and therefore I had as well decline. And in relation to Menard having rights, permit me fully to recognize them, and to express the opinion, that, if she and Mason act circumspectly, they will in the convention be able so far to enforce their rights as to decide absolutely which one of the candidates shall be successful. Let me show the reason of this. Hardin, or some other Morgan candidate, will get Putnam, Marshall, Woodford, Tazewell, and Logan,—make sixteen. Then you and Mason, having three, can give the victory to either side.
You say you shall instruct your delegates for me, unless I object. I certainly shall not object. That would be too pleasant a compliment for me to tread in the dust. And besides, if any thing should happen (which, however, is not probable) by which Baker should be thrown out of the fight, I would be at liberty to accept the nomination if I could get it. I do, however, feel myself bound not to hinder him in any way from getting the nomination. I should despise myself were I to attempt it. I think, then, it would be proper for your meeting to appoint three delegates, and to instruct them to go for some one as a first choice, some one else as a second, and perhaps some one as a third; and, if in those instructions I were named as the first choice, it would gratify me very much.
If you wish to hold the balance of power, it is important for you to attend to and secure the vote of Mason also. You should be sure to have men appointed delegates that you know you can safely confide in. If yourself and James Short were appointed for your county, all would be safe; but whether Jim's woman affair a year ago might not be in the way of his appointment is a question. I don't know whether you know it, but I know him to be as honorable a man as there is in the world. You have my permission, and even request, to show this letter to Short; but to no one else, unless it be a very particular friend, who you know will not speak of it.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
P. S.—Will you write me again?

To Martin M. Morris, Petersburg, 111.
And finally to Speed on the same subject:—
Springfield, May 18, 1843.
Dear Speed,—Yours of the 9th inst. is duly received, which I do not meet as a "bore," but as a most welcome visitor. I will answer the business part of it first.
In relation to our Congress matter here, you were right in supposing I would support the nominee. Neither Baker nor I, however, is the man, but Hardin, so far as I can judge from present appearances. We shall have no split or trouble about the matter,—all will be harmony. In relation to the "coming events" about which Butler wrote you, I had not heard one word before I got your letter; but I have so much confidence in the judgment of a Butler on such a subject, that I incline to think there may be some reality in it. What day does Butler appoint? By the way, how do "events" of the same sort come on in your family? Are you possessing houses and lands, and oxen and asses, and men-servants and maid-servants, and begetting sons and daughters? We are not keeping house, but boarding at the Globe Tavern, which is very well kept now by a widow lady of the name of Beck. Our room (the same Dr. Wallace occupied there) and boarding only costs us four dollars a week. Ann Todd was married something more than a year since to a fellow by the name of Campbell, and who, Mary says, is pretty much of a "dunce," though he has a little money and property. They live in Boonville, Mo., and have not been heard from lately enough for me to say any thing about her health. I reckon it will scarcely be in our power to visit Kentucky this year. Besides poverty and the necessity of attending to business, those "coming events," I suspect, would be somewhat in the way. I most heartily wish you and your Fanny would not fail to come. Just let us know the time, and we will have a room provided for you at our house, and all be merry together for a while. Be sure to give my respects to your mother and family: assure her, that, if I ever come near her, I will not fail to call and see her. Mary joins in sending love to your Fanny and you.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
After the "race," still smarting from the mortification of defeat, and the disappointment of a cherished hope, he took his old friend Jim Matheny away off to a solitary place in the woods, "and then and there," "with great emphasis," protested that he had not grown proud, and was not an aristocrat. "Jim," said he, in conclusion, "I am now, and always shall be, the same Abe Lincoln that I always was."
IN 1844 Mr. Lincoln was again a candidate for elector on the Whig ticket. Mr. Clay, as he has said himself, was his "beau-ideal of a statesman," and he labored earnestly and as effectually as any one else for his election. For the most part, he still had his old antagonists to meet in the Springfield region, chief among whom this year was John Calhoun. With him and others he had joint debates, running through several nights, which excited much popular feeling. One of his old friends and neighbors, who attended all these discussions, speaks in very enthusiastic terms of Mr. Calhoun, and, after enumerating his many noble gifts of head and heart, concludes that "Calhoun came nearer of whipping Lincoln in debate than Douglas did."
Mr. Lincoln made many speeches in Illinois, and finally, towards the close of the campaign, he went over into Indiana, and there continued "on the stump" until the end. Among other places he spoke at Rockport on the Ohio,—where he had first embarked for New Orleans with Gentry,—at Gentryville, and at a place in the country about two miles from the cabin where his father had lived. While he was in the midst of his speech at Gentryville, his old friend, Nat Grigsby, entered the room. Lincoln recognized him on the instant, and, stopping short in his remarks, cried out, "There's Nat!" Without the slightest regard for the proprieties of the occasion, he suspended his address totally, and, striding from the platform, began scrambling through the audience and over the benches, toward the modest Nat, who stood near the door. When he reached him, Lincoln shook his hand "cordially;" and, after felicitating himself sufficiently upon the happy meeting, he returned to the platform, and finished his speech. When that was over, Lincoln could not make up his mind to part with Nat, but insisted that they must sleep together. Accordingly, they wended their way to Col. Jones's, where that fine old Jackson Democrat received his distinguished "clerk" with all the honors he could show him. Nat says, that in the night a cat "began mewing, scratching, and making a fuss generally." Lincoln got up, took the cat in his hands, and stroking its back "gently and kindly," made it sparkle for Nat's amusement. He then "gently" put it out of the door, and, returning to bed, "commenced telling stories and talking over old times."
It is hardly necessary to say, that the result of the canvass was a severe disappointment to Mr. Lincoln. No defeat but his own could have given him more pain; and thereafter he seems to have attended quietly to his own private business until the Congressional canvass of 1846.
It was thought for many years by some persons well informed, that between Lincoln, Logan, Baker, and Hardin,—four very conspicuous Whig leaders,—there was a secret personal understanding that they four should "rotate" in Congress until each had had a term. Baker succeeded Hardin in 1844; Lincoln was elected in 1846, and Logan was nominated, but defeated, in 1848. Lincoln publicly declined to contest the nomination with Baker in 1844; Hardin did the same for Lincoln in 1846 (although both seem to have acted reluctantly), and Lincoln refused to run against Logan in 1848. Col. Matheny and others insist, with great show of reason, that the agreement actually existed; and, if such was the case, it was practically carried out, although Lincoln was a candidate against Baker, and Hardin against Lincoln, as long as either of them thought there was the smallest prospect of success. They might have done this, however, merely to keep other and less tractable candidates out of the field. That Lincoln would cheerfully have made such a bargain to insure himself a seat in Congress, there can be no doubt; but the supposition that he did do it can scarcely be reconciled with the feeling displayed by him in the conflict with Baker, or the persistency of Hardin, to a very late hour, in the contest of 1846.
At all events, Mr. Lincoln and Gen. Hardin were the two, and the only two, candidates for the Whig nomination in 1846. The contest was much like the one with Baker, and Lincoln was assailed in much the same fashion. He was called a deist and an infidel, both before and after his nomination, and encountered in a less degree the same opposition from the members of certain religious bodies that had met him before. But with Hardin he maintained personal relations the most friendly. The latter proposed to alter the mode of making the nomination; and, in the letter conveying this desire to Mr. Lincoln, he also offered to stipulate that each candidate should remain within the limits of his own county. To this Mr. Lincoln replied, "As to your proposed stipulation that all the candidates shall remain in their own counties, and restrain their friends to the same, it seems to me, that, on reflection, you will see the fact of your having been in Congress has, in various ways, so spread your name in the district as to give you a decided advantage in such a stipulation. I appreciate your desire to keep down excitement, and I promise you to 'keep cool' under the circumstances."
On the 26th of February, 1846, "The Journal" contained Gen. Hardin's card declining to be "longer considered a candidate," and in its editorial comments occurred the following: "We have had, and now have, no doubt that he (Hardin) has been, and now is, a great favorite with the Whigs of the district. He states, in substance, that there was never any understanding on his part that his name was not to be presented in the canvasses of 1844 and 1846. This, we believe, is strictly true. Still, the doings of the Pekin Convention did seem to point that way; and the general's voluntary declination as to the canvass of 1844 was by many construed into an acquiescence on his part. These things had led many of his most devoted friends to not expect him to be a candidate at this time. Add to this the relation that Mr. Lincoln bears, and has borne, to the party, and it is not strange that many of those who are as strongly devoted to Gen. Hardin as they are to Mr. Lincoln should prefer the latter at this time. We do not entertain a doubt, that, if we could reverse the positions of the two men, that a very large portion of those who now have supported Mr. Lincoln most warmly would have supported Gen. Hardin quite as warmly." This article was admirably calculated to soothe Gen. Hardin, and to win over his friends. It was wise and timely. The editor was Mr. Lincoln's intimate friend. It is marked by Mr. Lincoln's style, and has at least one expression which was peculiar to him.
In its issue of May 7, "The Journal" announced the nomination as having been made at Petersburg, on the Friday previous, and said further, "This nomination was, of course, anticipated, there being no other candidate in the field. Mr. Lincoln, we all know, is a good Whig, a good man, an able speaker, and richly deserves, as he enjoys, the confidence of the Whigs of this district and of the State."
Peter Cartwright, the celebrated pioneer Methodist preacher, noted for his piety and combativeness, was Mr. Lincoln's competitor before the people. We know already the nature of the principal charges against Mr. Lincoln's personal character; and these, with the usual criticism upon Whig policy, formed the staple topics of the campaign on the Democratic side. But Peter himself did not escape with that impunity which might have been expected in the case of a minister of the gospel. Rough tongues circulated exaggerated stories of his wicked pugnacity and his worldly-mindedness, whilst the pretended servant of the Prince of peace. Many Democrats looked with intense disgust upon his present candidacy, and believed, that, by mingling in politics, he was degrading his office and polluting the Church. One of these Democrats told Mr. Lincoln what he thought, and said, that, although it was a hard thing to vote against his party, he would do it if it should be necessary to defeat Cartwright. Mr. Lincoln told him, that on the day of the election he would give him a candid opinion as to whether the vote was needed or not Accordingly, on that day, he called upon the gentleman, and said, "I have got the preacher,... and don't want your vote."
Clay's majority in this district in 1844 had been but nine hundred and fourteen; whereas it now gave Mr. Lincoln a majority of fifteen hundred and eleven, in a year which had no Presidential excitements to bring out electors. In 1848 Gen. Taylor's majority was smaller by ten, and the same year the Whig candidate for Congress was defeated by a hundred and six.
In the following letter to Mr. Speed, he intimates that the first sensations of pleasure attending his new distinction were not of long duration; at least, that there were moments in which, if he did not forget his greatness, it afforded him little joy.
Springfield, Oct. 22, 1846.
Dear Speed,—
You no doubt assign the suspension of our correspondence to the true philosophic cause; though it must be confessed by both of us, that this is rather a cold reason for allowing a friendship such as ours to die out by degrees. I propose now, that, upon receipt of this, you shall be considered in my debt, and under obligations to pay soon, and that neither shall remain long in arrears hereafter. Are you agreed?
Being elected to Congress, though I am very grateful to our friends for having done it, has not pleased me as much as I expected.
We have another boy, born the 10th of March. He is very much such a child as Bob was at his age, rather of a longer order. Bob is "short and low," and expect always will be. He talks very plainly,—almost as plainly as anybody. He is quite smart enough. I sometimes fear he is one of the little rare-ripe sort, that are smarter at about five than ever after. He has a great deal of that sort of mischief that is the offspring of much animal spirits. Since I began this letter, a messenger came to tell me Bob was lost; but by the time I reached the house his mother had found him, and had him whipped; and by now, very likely, he is run away again. Mary has read your letter, and wishes to be remembered to Mrs. S. and you, in which I most sincerely join her. As ever yours.
A. Lincoln.
At the meeting of the Thirtieth Congress Mr. Lincoln took his seat, and went about the business of his office with a strong determination to do something memorable. He was the only Whig member from Illinois, and would be carefully watched. His colleagues were several of them old acquaintances of the Vandalia times. They were John McClernand, O. B. Ficklin, William A. Richardson, Thomas J. Turner, Robert Smith, and John Wentworth (Long John). And at this session that alert, tireless, ambitious little man, Stephen A. Douglas, took his seat in the Senate.
The roll of this House shone with an array of great and brilliant names. Robert C. Winthrop was the Speaker. On the Whig side were John Quincy Adams, Horace Mann, Hunt of New York, Collamer of Vermont, Ingersoll of Pennsylvania, Botts and Goggin of Virginia, Morehead of Kentucky, Caleb B. Smith of Indiana, Stephens and Toombs of Georgia, Gentry of Tennessee, and Vinton and Schenck of Ohio. On the Democratic side were Wilmot of Pennsylvania, McLane of Maryland, McDowell of Virginia, Rhett of South Carolina, Cobb of Georgia, Boyd of Kentucky, Brown and Thompson of Mississippi, and Andrew Johnson and George W. Jones of Tennessee. In the Senate were Webster, Calhoun, Benton, Berrien, Clayton, Bell, Hunter, and William R. King.
The House organized on the 6th; and the day previous to that. Mr. Lincoln wrote to his friend and partner, William H. Herndon:—
Washington, Dec. 5, 1847.
Dear William,—You may remember that about a year ago a man by the name of Wilson (James Wilson, I think) paid us twenty dollars as an advance fee to attend to a case in the Supreme Court for him, against a Mr. Campbell, the record of which case was in the hands of Mr. Dixon of St. Louis, who never furnished it to us. When I was at Bloomington last fall, I met a friend of Wilson, who mentioned the subject to me, and induced me to write to Wilson, telling him that I would leave the ten dollars with you which had been left with me to pay for making abstracts in the case, so that the case may go on this winter; but I came away, and forgot to do it. What I want now is to send you the money to be used accordingly, if any one comes on to start the case, or to be retained by you if no one does.
There is nothing of consequence new here. Congress is to organize to-morrow. Last night we held a Whig caucus for the House, and nominated Winthrop of Massachusetts for Speaker, Sargent of Pennsylvania for Sergeant-at-arms, Homer of New Jersey Doorkeeper, and McCormick of District of Columbia Postmaster. The Whig majority in the House is so small, that, together with some little dissatisfaction, leaves it doubtful whether we will elect them all.
This paper is too thick to fold, which is the reason I send only a halfsheet.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
Again on the 13th, to the same gentleman:—
Washington, Dec. 13, 1847.
Dear William,—Your letter advising me of the receipt of our fee in the bank-case is just received, and I don't expect to hear another as good a piece of news from Springfield while I am away. I am under no obligations to the bank; and I therefore wish you to buy bank certificates, and pay my debt there, so as to pay it with the least money possible. I would as soon you should buy them of Mr. Ridgely, or any other person at the bank, as of any one else, provided you can get them as cheaply. I suppose, after the bank-debt shall be paid, there will be some money left, out of which I would like to have you pay Lavely and Stout twenty dollars, and Priest and somebody (oil-makers) ten dollars, for materials got for house-painting. If there shall still be any left, keep it till you see or hear from me.
I shall begin sending documents so soon as I can get them. I wrote you yesterday about a "Congressional Globe." As you are all so anxious for me to distinguish myself, I have concluded to do so before long.
Yours truly,
A. Lincoln.
Mr. Lincoln was a member of the Committee on Post-offices and Post-roads, and in that capacity had occasion to study the claim of a mail-contractor who had appealed to Congress against a decision of the Department. Mr. Lincoln made a speech on the case, in which, being his first, he evidently felt some pride, and reported progress to his friends at home:—
Washington, Jan. 8, 1848.
Dear William,—Your letter of Dec. 27 was received a day or two ago. I am much obliged to you for the trouble you have taken, and promise to take, in my little business there. As to speech-making, by way of getting the hang of the House, I made a little speech two or three days ago, on a post-office question of no general interest. I find speaking here and elsewhere about the same thing. I was about as badly scared, and no worse, as I am when I speak in court. I expect to make one within a week or two, in which I hope to succeed well enough to wish you to see it.
It is very pleasant to me to learn from you that there are some who desire that I should be re-elected. I most heartily thank them for the kind partiality; and I can say, as Mr. Clay said of the annexation of Texas, that "personally I would not object" to a re-election, although I thought at the time, and still think, it would be quite as well for me to return to the law at the end of a single term. I made the declaration, that I would not be a candidate again, more from a wish to deal fairly with others, to keep peace among our friends, and to keep the district from going to the enemy, than for any cause personal to myself; so that, if it should so happen that nobody else wishes to be elected, I could not refuse the people the right of sending me again. But to enter myself as a competitor of others, or to authorize any one so to enter me, is what my word and honor forbid.
I get some letters intimating a probability of so much difficulty amongst our friends as to lose us the district; but I remember such letters were written to Baker when my own case was under consideration, and I trust there is no more ground for such apprehension now than there was then.
Remember I am always glad to receive a letter from you.
Most truly your friend,
A. Lincoln.
Thoroughly hostile to Polk, and hotly opposed to the war, Mr. Lincoln took an active, although not a leading part in the discussions relating to the commencement and conduct of the latter. He was politician enough, however, to go with the majority of his party in voting supplies to the troops, and thanks to the generals, whilst censuring the President by solemnly declaring that the "war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally begun by the President of the United States." But his position, and the position of the Whigs, will be made sufficiently apparent by the productions of his own pen.
On the 22d of December, 1847, Mr. Lincoln introduced a preamble and resolutions, which attained great celebrity in Illinois under the title of "Spot Resolutions," and in all probability lost the party a great many votes in the Springfield district. They were as follows:—
Whereas, The President of the United States, in his Message of May 11, 1846, has declared that "the Mexican Government not only refused to receive him [the envoy of the United States], or listen to his propositions, but, after a long-continued series of menaces, has at last invaded our territory, and shed the blood of our fellow-citizens on our own soil;"
And again, in his Message of Dec. 8, 1846, that "we had ample cause of war against Mexico long before the breaking out of hostilities; but even then we forbore to take redress into our own hands until Mexico herself became the aggressor, by invading our soil in hostile array, and shedding the blood of our citizens;"
And yet again, in his Message of Dec. 7, 1847, that "the Mexican Government refused even to hear the terms of adjustment which he [our minister of peace] was authorized to propose, and finally, under wholly unjustifiable pretexts, involved the two countries in war, by invading the territory of the State of Texas, striking the first blow, and shedding the blood of our citizens on our own soil;" and,
Whereas, This House is desirous to obtain a full knowledge of all the facts which go to establish whether the particular spot on which the blood of our citizens was so shed was or was not at that time "our own soil;" therefore,
Resolved by the House of Representatives, That the President of the United States be respectfully requested to inform this House,—
1st. Whether the spot on which the blood of our citizens was shed, as in his Messages declared, was or was not within the territory of Spain, at least after the treaty of 1819, until the Mexican revolution.
2d. Whether that spot is or is not within the territory which was wrested from Spain by the revolutionary government of Mexico.
3d. Whether that spot is or is not within a settlement of people, which settlement has existed ever since long before the Texas revolution, and until its inhabitants fled before the approach of the United States army.
4th. Whether that settlement is or is not isolated from any and all other settlements by the Gulf and the Rio Grande on the south and west, and by wide, uninhabited regions on the north and east.
5th. Whether the people of that settlement, or a majority of them, or any of them, have ever submitted themselves to the government or laws of Texas or of the United States, by consent or by compulsion, either by accepting office, or voting at elections, or paying tax, or serving on juries, or having process served upon them, or in any other way.
6th. Whether the people of that settlement did or did not flee from the approach of the United States army, leaving unprotected their homes and their growing crops, before the blood was shed, as in the Messages stated; and whether the first blood, so shed, was or was not shed within the enclosure of one of the people who had thus fled from it.
7th. Whether our citizens, whose blood was shed, as in his Messages declared, were or were not at that time armed officers and soldiers, sent into that settlement by the military order of the President, through the Secretary of War.
8th. Whether the military force of the United States was or was not so sent into that settlement after Gen. Taylor had more than once intimated to the War Department, that, in his opinion, no such movement was necessary to the defence or protection of Texas.
Mr. Lincoln improved the first favorable opportunity (Jan. 12, 1818), to address the House in the spirit of the "Spot Resolutions."
In Committee of the Whole House, Jan. 12, 1848.
Mr. Lincoln addressed the Committee as follows:—
Mr. Chairman,—Some, if not at all, of the gentlemen on the other side of the House, who have addressed the Committee within the last two days, have spoken rather complainingly, if I have rightly understood them, of the vote given a week or ten days ago, declaring that the war with Mexico was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President. I admit that such a vote should not be given in mere party wantonness, and that the one given is justly censurable, if it have no other or better foundation. I am one of those who joined in that vote, and did so under my best impression of the truth of the case. How I got this impression, and how it may possibly be removed, I will now try to show. When the war began, it was my opinion that all those who, because of knowing too little, or because of knowing too much, could not conscientiously approve the conduct of the President (in the beginning of it), should, nevertheless, as good citizens and patriots, remain silent on that point, at least till the war should be ended. Some leading Democrats, including ex-President Van Buren, have taken this same view, as I understand them; and I adhered to it, and acted upon it, until since I took my seat here; and I think I should still adhere to it, were it not that the President and his friends will not allow it to be so. Besides the continual effort of the President to argue every silent vote given for supplies into an indorsement of the justice and wisdom of his conduct; besides that singularly candid paragraph in his late Message, in which he tells us that Congress, with great unanimity (only two in the Senate and fourteen in the House dissenting), had declared that "by the act of the Republic of Mexico a state of war exists between that government and the United States;" when the same journals that informed him of this also informed him, that, when that declaration stood disconnected from the question of supplies, sixty-seven in the House, and not fourteen merely, voted against it; besides this open attempt to prove by telling the truth what he could not prove by telling the whole truth, demanding of all who will not submit to be misrepresented, in justice to themselves, to speak out; besides all this, one of my colleagues [Mr. Richardson], at a very early day in the session, brought in a set of resolutions expressly indorsing the original justice of the war on the part of the President. Upon these resolutions, when they shall be put on their passage, I shall be compelled to vote; so that I cannot be silent if I would. Seeing this, I went about preparing myself to give the vote understandingly when it should come. I carefully examined the President's Messages, to ascertain what he himself had said and proved upon the point. The result of this examination was to make the impression, that, taking for true all the President states as facts, he falls far short of proving his justification; and that the President would have gone further with his proof, if it had not been for the small matter that the truth would not permit him. Under the impression thus made, I gave the vote before mentioned. I propose now to give concisely the process of the examination I made, and how I reached the conclusion I did.
The President, in his first Message of May, 1846, declares that the soil was ours on which hostilities were commenced by Mexico; and he repeats that declaration, almost in the same language, in each successive annual Message,—thus showing that he esteems that point a highly essential one. In the importance of that point I entirely agree with the President. To my judgment, it is the very point upon which he should be justified or condemned. In his Message of December, 1846, it seems to have occurred to him, as is certainly true, that title, ownership to soil, or any thing else, is not a simple fact, but is a conclusion following one or more simple facts; and that it was incumbent upon him to present the facts from which he concluded the soil was ours on which the first blood of the war was shed.
Accordingly, a little below the middle of page twelve, in the Message last referred to, he enters upon that task; forming an issue and introducing testimony, extending the whole to a little below the middle of page fourteen. Now, I propose to try to show that the whole of this, issue and evidence, is, from beginning to end, the sheerest deception. The issue, as he presents it, is in these words: "But there are those who, conceding all this to be true, assume the ground that the true western boundary of Texas is the Nueces, instead of the Rio Grande; and that, therefore, in marching our army to the east bank of the latter river, we passed the Texan line, and invaded the Territory of Mexico." Now, this issue is made up of two affirmatives, and no negative. The main deception of it is, that it assumes as true, that one river or the other is necessarily the boundary, and cheats the superficial thinker entirely out of the idea that possibly the boundary is somewhere between the two, and not actually at either. A further deception is, that it will let in evidence which a true issue would exclude. A true issue made by the President would be about as follows: "I say the soil was ours on which the first blood was shed; there are those who say it was not."
I now proceed to examine the President's evidence, as applicable to such an issue. When that evidence is analyzed, it is all included in the following propositions:—
1. That the Rio Grande was the western boundary of Louisiana, as we purchased it of France in 1803.
2. That the Republic of Texas always claimed the Rio Grande as her western boundary.
3. That, by various acts, she had claimed it on paper.
4. That Santa Anna, in his treaty with Texas, recognized the Rio Grande as her boundary.
5. That Texas before, and the United States after annexation, had exercised jurisdiction beyond the Nueces, between the two rivers.
6. That our Congress understood the boundary of Texas to extend beyond the Nueces.
Now for each of these in its turn:—
His first item is, that the Rio Grande was the western boundary of Louisiana, as we purchased it of France in 1803; and, seeming to expect this to be disputed, he argues over the amount of nearly a page to prove it true; at the end of which, he lets us know, that, by the treaty of 1819, we sold to Spain the whole country, from the Rio Grande eastward to the Sabine. Now, admitting for the present, that the Rio Grande was the boundary of Louisiana, what, under Heaven, had that to do with the present boundary between us and Mexico? How, Mr. Chairman, the line that once divided your land from mine can still be the boundary between us after I have sold my land to you, is, to me, beyond all comprehension. And how any man, with an honest purpose only of proving the truth, could ever have thought of introducing such a fact to prove such an issue, is equally incomprehensible. The outrage upon common right, of seizing as our own what we have once sold, merely because it was ours before we sold it, is only equalled by the outrage on common sense of any attempt to justify it.
The President's next piece of evidence is, that "The Republic of Texas always claimed this river (Rio Grande) as her western boundary." That is not true, in fact. Texas has claimed it, but she has not always claimed it. There is, at least, one distinguished exception. Her State Constitution—the public's most solemn and well-considered act, that which may, without impropriety, be called her last will and testament, revoking all others—makes no such claim. But suppose she had always claimed it. Has not Mexico always claimed the contrary? So that there is but claim against claim, leaving nothing proved until we get back of the claims, and find which has the better foundation.
Though not in the order in which the President presents his evidence, I now consider that class of his statements which are, in substance, nothing more than that Texas has, by various acts of her Convention and Congress, claimed the Rio Grande as her boundary—on paper. I mean here what he says about the fixing of the Rio Grande as her boundary in her old constitution (not her State Constitution), about forming congressional districts, counties, &c. Now, all this is but naked claim; and what I have already said about claims is strictly applicable to this. If I should claim your land by word of mouth, that certainly would not make it mine; and if I were to claim it by a deed which I had made myself, and with which you had nothing to do, the claim would be quite the same in substance, or rather in utter nothingness.
I next consider the President's statement that Santa Anna, in his treaty with Texas, recognized the Rio Grande as the western boundary of Texas. Besides the position so often taken that Santa Anna, while a prisoner of war, a captive, could not bind Mexico by a treaty, which I deem conclusive,—besides this, I wish to say something in relation to this treaty, so called by the President, with Santa Anna. If any man would like to be amused by a sight at that little thing, which the President calls by that big name, he can have it by turning to "Niles's Register," vol. 1. p. 336. And if any one should suppose that "Niles's Register" is a curious repository of so mighty a document as a solemn treaty between nations, I can only say that I learned, to a tolerable degree of certainty, by inquiry at the State Department, that the President himself never saw it anywhere else. By the way, I believe I should not err if I were to declare, that, during the first ten years of the existence of that document, it was never by anybody called a treaty; that it was never so called till the President, in his extremity, attempted, by so calling it, to wring something from it in justification of himself in connection with the Mexican war. It has none of the distinguishing features of a treaty. It does not call itself a treaty. Santa Anna does not therein assume to bind Mexico: he assumes only to act as president, commander-in-chief of the Mexican army and navy; stipulates that the then present hostilities should cease, and that he would not himself take up arms, nor influence the Mexican people to take up arms, against Texas during the existence of the war of independence. He did not recognize the independence of Texas; he did not assume to put an end to the war, but clearly indicated his expectation of its continuance; he did not say one word about boundary, and most probably never thought of it. It is stipulated therein that the Mexican forces should evacuate the Territory of Texas, passing to the other side of the Rio Grande; and in another article it is stipulated, that, to prevent collisions between the armies, the Texan army should not approach nearer than within five leagues,—of what is not said; but clearly, from the object stated, it is of the Rio Grande. Now, if this is a treaty recognizing the Rio Grande as the boundary of Texas, it contains the singular feature of stipulating that Texas shall not go within five leagues of her own boundary.
Next comes the evidence of Texas before annexation, and the United States afterwards, exercising jurisdiction beyond the Nueces, and between the two rivers. This actual exercise of jurisdiction is the very class or quality of evidence we want. It is excellent so far as it goes; but does it go far enough? He tells us it went beyond the Nueces; but he does not tell us it went to the Rio Grande. He tells us jurisdiction was exercised between the two rivers; but he does not tell us it was exercised over all the territory between them. Some simple-minded people think it possible to cross one river and go beyond it, without going all the way to the next; that jurisdiction may be exercised between two rivers without covering all the country between them. I know a man, not very unlike myself, who exercises jurisdiction over a piece of land between the Wabash and the Mississippi; and yet so far is this from being all there is between those rivers, that it is just a hundred and fifty-two feet long by fifty wide, and no part of it much within a hundred miles of either. He has a neighbor between him and the Mississippi,—that is, just across the street, in that direction,—whom, I am sure, he could neither persuade nor force to give up his habitation; but which, nevertheless, he could certainly annex, if it were to be done by merely standing on his own side of the street and claiming it, or even sitting down and writing a deed for it.
But next, the President tells us, the Congress of the United States understood the State of Texas they admitted into the Union to extend beyond the Nueces. Well, I suppose they did,—I certainly so understand it,—but how far beyond? That Congress did not understand it to extend clear to the Rio Grande, is quite certain by the fact of their joint resolutions for admission, expressly leaving all questions of boundary to future adjustment. And it may be added, that Texas herself is proved to have had the same understanding of it that our Congress had, by the fact of the exact conformity of her new Constitution to those resolutions.
I am now through the whole of the President's evidence; and it is a singular fact, that, if any one should declare the President sent the army into the midst of a settlement of Mexican people, who had never submitted, by consent or by force, to the authority of Texas or of the United States, and that there, and thereby, the first blood of the war was shed, there is not one word in all the President has said which would either admit or deny the declaration. In this strange omission chiefly consists the deception of the President's evidence,—an omission which, it does seem to me, could scarcely have occurred but by design. My way of living leads me to be about the courts of justice; and there I have sometimes seen a good lawyer, struggling for his client's neck in a desperate case, employing every artifice to work round, befog, and cover up with many words, some position pressed upon him by the prosecution, which he dared not admit, and yet could not deny. Party bias may help to make it appear so; but, with all the allowance I can make for such bias, it still does appear to me that just such, and from just such necessity, are the President's struggles in this case.
Some time after my colleague (Mr. Richardson) introduced the resolutions I have mentioned, I introduced a preamble, resolution, and interrogatories, intended to draw the President out, if possible, on this hitherto untrodden ground. To show their relevancy, I propose to state my understanding of the true rule for ascertaining the boundary between Texas and Mexico. It is, that, wherever Texas was exercising jurisdiction was hers; and wherever Mexico was exercising jurisdiction was hers; and that whatever separated the actual exercise of jurisdiction of the one from that of the other was the true boundary between them. If, as is probably true, Texas was exercising jurisdiction along the western bank of the Nueces, and Mexico was exercising it along the eastern bank of the Rio Grande, then neither river was the boundary, but the uninhabited country between the two was. The extent of our territory in that region depended, not on any treaty-fixed boundary (for no treaty had attempted it), but on revolution. Any people anywhere, being inclined and having the power, have the right to rise up and shake off the existing government, and form a new one that suits them better. This is a most valuable, a most sacred right,—a right which, we hope and believe, is to liberate the world. Nor is this right confined to cases in which the whole people of an existing government may choose to exercise it. Any portion of such people that can may revolutionize, and make their own of so much of the territory as they inhabit. More than this, a majority of any portion of such people may revolutionize, putting down a minority, intermingled with or near about them, who may oppose their movements. Such minority was precisely the case of the Tories of our own Revolution. It is a quality of revolutions not to go by old lines or old laws, but to break up both, and make new ones. As to the country now in question, we bought it of France in 1803, and sold it to Spain in 1819, according to the President's statement. After this, all Mexico, including Texas, revolutionized against Spain; and, still later, Texas revolutionized against Mexico. In my view, just so far as she carried her revolution, by obtaining the actual, willing or unwilling, submission of the people, so far the country was hers, and no farther.
Now, sir, for the purpose of obtaining the very best evidence as to whether Texas had actually carried her revolution to the place where the hostilities of the present war commenced, let the President answer the interrogatories I proposed, as before mentioned, or some other similar ones. Let him answer fully, fairly, and candidly. Let him answer with facts, and not with arguments. Let him remember he sits where Washington sat; and, so remembering, let him answer as Washington would answer. As a nation should not, and the Almighty will not, be evaded, so let him attempt no evasion, no equivocation. And if, so answering, he can show that the soil was ours where the first blood of the war was shed; that it was not within an inhabited country, or, if within such, that the inhabitants had submitted themselves to the civil authority of Texas, or of the United States, and that the same is true of the site of Fort Brown, then I am with him for his justification. In that case, I shall be most happy to reverse the vote I gave the other day. I have a selfish motive for desiring that the President may do this: I expect to give some votes, in connection with the war, which, without his so doing, will be of doubtful propriety, in my own judgment, but which will be free from the doubt if he does so. But if he cannot or will not do this,—if, on any pretence, or no pretence, he shall refuse or omit it,—then I shall be fully convinced of what I more than suspect already,—that he is deeply conscious of being in the wrong; that he feels the blood of this war, like the blood of Abel, is crying to Heaven against him; that he ordered Gen. Taylor into the midst of a peaceful Mexican settlement, purposely to bring on a war; that, originally having some strong motive—what I will not stop now to give my opinion concerning—to involve the two countries in a war, and trusting to escape scrutiny by fixing the public gaze upon the exceeding brightness of military glory,—that attractive rainbow that rises in showers of blood, that serpent's eye that charms to destroy,—he plunged into it, and has swept on and on, till, disappointed in his calculation of the ease with which Mexico might be subdued, he now finds himself he knows not where. How like the half-insane mumbling of a fever-dream is the whole war part of the late Message! At one time telling us that Mexico has nothing whatever that we can get but territory; at another, showing us how we can support the war by levying contributions on Mexico. At one time urging the national honor, the security of the future, the prevention of foreign interference, and even the good of Mexico herself, as among the objects of the war; at another, telling us that, "to reject indemnity by refusing to accept a cession of territory, would be to abandon all our just demands, and to wage the war, bearing all its expenses, without a purpose or definite object." So, then, the national honor, security of the future, and every thing but territorial indemnity, may be considered the no purposes and indefinite objects of the war! But having it now settled that territorial indemnity is the only object, we are urged to seize, by legislation here, all that he was content to take a few months ago, and the whole province of Lower California to boot, and to still carry on the war,—to take all we are fighting for, and still fight on. Again, the President is resolved, under all circumstances, to have full territorial indemnity for the expenses of the war; but he forgets to tell us how we are to get the excess after those expenses shall have surpassed the value of the whole of the Mexican territory. So, again, he insists that the separate national existence of Mexico shall be maintained; but he does not tell us how this can be done after we shall have taken all her territory. Lest the questions I here suggest be considered speculative merely, let me be indulged a moment in trying to show they are not.
The war has gone on some twenty months; for the expenses of which, together with an inconsiderable old score, the President now claims about one-half of the Mexican territory, and that by far the better half, so far as concerns our ability to make any thing out of it. It is comparatively uninhabited; so that we could establish land-offices in it, and raise some money in that way. But the other half is already inhabited, as I understand it, tolerably densely for the nature of the country; and all its lands, or all that are valuable, already appropriated as private property. How, then, are we to make any thing out of these lands with this encumbrance on them, or how remove the encumbrance? I suppose no one will say we should kill the people, or drive them out, or make slaves of them, or even confiscate their property? How, then, can we make much out of this part of the territory? If the prosecution of the war has, in expenses, already equalled the better half of the country, how long its future prosecution will be in equalling the less valuable half is not a speculative but a practical question, pressing closely upon us; and yet it is a question which the President seems never to have thought of.
As to the mode of terminating the war and securing peace, the President is equally wandering and indefinite. First, it is to be done by a more vigorous prosecution of the war in the vital parts of the enemy's country; and, after apparently talking himself tired on this point, the President drops down into a half-despairing tone, and tells us, that "with a people distracted and divided by contending factions, and a government subject to constant changes, by successive revolutions, the continued success of our arms may fail to obtain a satisfactory peace." Then he suggests the propriety of wheedling the Mexican people to desert the counsels of their own leaders, and, trusting in our protection, to set up a government from which we can secure a satisfactory peace, telling us that, "this may become the only mode of obtaining such a peace." But soon he falls into doubt of this, too, and then drops back on to the already half-abandoned ground of "more vigorous prosecution." All this shows that the President is in no wise satisfied with his own positions. First, he takes up one, and, in attempting to argue us into it, he argues himself out of it; then seizes another, and goes through the same process; and then, confused at being able to think of nothing new, he snatches up the old one again, which he has some time before cast off. His mind, tasked beyond its power, is running hither and thither, like some tortured creature on a burning surface, finding no position on which it can settle down and be at ease.
Again, it is a singular omission in this Message, that it nowhere intimates when the President expects the war to terminate. At its beginning, Gen. Scott was, by this same President, driven into disfavor, if not disgrace, for intimating that peace could not be conquered in less than three or four months. But now at the end of about twenty months, during which time our arms have given us the most splendid successes,—every department, and every part, land and water, officers and privates, regulars and volunteers, doing all that men could do, and hundreds of things which it had ever before been thought that men could not do,—after all this, this same President gives us a long Message without showing us that, as to the end, he has himself even an imaginary conception. As I have before said, he knows not where he is. He is a bewildered, confounded, and miserably perplexed man. God grant he may be able to show that there is not something about his conscience more painful than all his mental perplexity.
This speech he hastened to send home as soon as it was printed; for, while throughout he trod on unquestionable Whig ground, he had excellent reasons to fear the result. The following is the first letter to Mr. Herndon after the delivery of the speech, and notifying him of the fact:—
Washington, Jan. 19, 1848.
Dear William,—Enclosed you find a letter of Louis W. Candler. What is wanted is, that you shall ascertain whether the claim upon the note described has received any dividend in the Probate Court of Christian County, where the estate of Mr. Overton Williams has been administered on. If nothing is paid on it, withdraw the note and send it to me, so that Candler can see the indorser of it. At all events, write me all about it, till I can somehow get it off hands. I have already been bored more than enough about it; not the least of which annoyance is his cursed, unreadable, and ungodly handwriting.
I have made a speech, a copy of which I will send you by next mail.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
About the last of January, or the first of February, he began to hear the first murmurs of alarm and dissatisfaction from his district. He was now on the defensive, and compelled to write long and tedious letters to pacify some of the Whigs. Of this character are two extremely interesting epistles to Mr. Herndon:—
Washington, Feb. 1, 1848.
Dear William,—Your letter of the 19th ult. was received last night, and for which I am much obliged. The only thing in it that I wish to talk to you about at once is, that, because of my vote for Ashmun's amendment, you fear that you and I disagree about the war. I regret this, not because of any fear we shall remain disagreed after you have read this letter, but because if you misunderstand, I fear other good friends may also. That vote affirms, that the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President; and I will stake my life, that, if you had been in my place, you would have voted just as I did. Would you have voted what you felt and knew to be a lie? I know you would not. Would you have gone out of the House,—skulked the vote? I expect not. If you had skulked one vote, you would have had to skulk many more before the end of the session. Richardson's resolutions, introduced before I made any move, or gave any vote upon the subject, make the direct question of the justice of the war; so that no man can be silent if he would. You are compelled to speak; and your only alternative is to tell the truth or tell a lie. I cannot doubt which you would do.
This vote has nothing to do in determining my votes on the questions of supplies. I have always intended, and still intend, to vote supplies; perhaps not in the precise form recommended by the President, but in a better form for all purposes, except Locofoco party purposes. It is in this particular you seem mistaken. The Locos are untiring in their efforts to make the impression that all who vote supplies, or take part in the war, do, of necessity, approve the President's conduct in the beginning of it; but the Whigs have, from the beginning, made and kept the distinction between the two. In the very first act nearly all the Whigs voted against the preamble declaring that war existed by the act of Mexico; and yet nearly all of them voted for the supplies. As to the Whig men who have participated in the war, so far as they have spoken to my hearing, they do not hesitate to denounce as unjust the President's conduct in the beginning of the war. They do not suppose that such denunciation is directed by undying hatred to them, as "The Register" would have it believed. There are two such Whigs on this floor (Col. Haskell and Major James). The former fought as a colonel by the side of Col. Baker, at Cerro Gordo, and stands side by side with me in the vote that you seem dissatisfied with. The latter, the history of whose capture with Cassius Clay you well know, had not arrived here when that vote was given; but, as I understand, he stands ready to give just such a vote whenever an occasion shall present. Baker, too, who is now here, says the truth is undoubtedly that way; and, whenever he shall speak out, he will say so. Col. Donaphin, too, the favorite Whig of Missouri, and who overrun all Northern Mexico, on his return home, in a public speech at St. Louis, condemned the administration in relation to the war, if I remember. G. T. M. Davis, who has been through almost the whole war, declares in favor of Mr. Clay; from which I infer that he adopts the sentiments of Mr. Clay, generally at least. On the other hand, I have heard of but one Whig who has been to the war attempting to justify the President's conduct. That one was Capt. Bishop; editor of "The Charleston Courier," and a very clever fellow. I do not mean this letter for the public, but for you. Before it reaches you, you will have seen and read my pamphlet speech, and, perhaps, scared anew by it. After you get over your scare, read it over again, sentence by sentence, and tell me honestly what you think of it. I condensed all I could for fear of being cut off by the hour rule; and, when I got through, I had spoken but forty-five minutes. Yours forever,
A. Lincoln.
Washington, Feb. 15, 1848.
Dear William,—Your letter of the 29th January was received last night. Being exclusively a constitutional argument, I wish to submit some reflections upon it in the same spirit of kindness that I know actuates you. Let me first state what I understand to be your position. It is, that, if it shall become necessary to repel invasion, the President may, without violation of the Constitution, cross the line, and invade the territory of another country; and that whether such necessity exists in any given case, the President is the sole judge.
Before going farther, consider well whether this is, or is not, your position. If it is, it is a position that neither the President himself, nor any friend of his, so far as I know, has ever taken. Their only positions are, first, that the soil was ours where the hostilities commenced; and second, that, whether it was rightfully ours or not, Congress had annexed it, and the President, for that reason, was bound to defend it, both of which are as clearly proved to be false in fact as you can prove that your house is mine. That soil was not ours; and Congress did not annex, or attempt to annex it. But to return to your position. Allow the President to invade a neighboring nation whenever he shall deem it necessary to repel an invasion, and you allow him to do so whenever he may choose to say he deems it necessary for such purpose, and you allow him to make war at pleasure. Study to see if you can fix any limit to his power in this respect, after having given him so much as you propose. If to-day he should choose to say he thinks it necessary to invade Canada, to prevent the British from invading us, how could you stop him? You may say to him, "I see no probability of the British invading us;" but he will say to you, "Be silent: I see it, if you don't."
The provision of the Constitution giving the war-making power to Congress was dictated, as I understand it, by the following reasons: kings had always been involving and impoverishing their people in wars, pretending generally, if not always, that the good of the people was the object. This our convention understood to be the most oppressive of all kingly oppressions; and they resolved to so frame the Constitution that no one man should hold the power of bringing this oppression upon us. But your view destroys the whole matter, and places our President where kings have always stood.
Write soon again.
Yours truly,
A. Lincoln.
But the Whig National Convention to nominate a candidate for the Presidency was to meet at Philadelphia on the 1st of June, and Mr. Lincoln was to be a member. He was not a Clay man: he wanted a candidate that could be elected; and he was for "Old Rough," as the only available material at hand. But let him explain himself:—
Washington, April 30, 1848.
Dear Williams,—I have not seen in the papers any evidence of a movement to send a delegate from your circuit to the June Convention. I wish to say that I think it all important that a delegate should be sent. Mr. Clay's chance for an election is just no chance at all. He might get New York; and that would have elected in 1844, but it will not now, because he must now, at the least, lose Tennessee, which he had then, and in addition the fifteen new votes of Florida, Texas, Iowa, and Wisconsin. I know our good friend Browning is a great admirer of Mr. Clay, and I therefore fear he is favoring his nomination. If he is, ask him to discard feeling, and try if he can possibly, as a matter of judgment, count the votes necessary to elect him.
In my judgment we can elect nobody but Gen. Taylor; and we cannot elect him without a nomination. Therefore don't fail to send a delegate.
Your friend as ever,
A. Lincoln.
To Archibald Williams, Esq.
Washington, June 12, 1848.
Dear Williams,—On my return from Philadelphia, where I had been attending the nomination of "Old Rough," I found your letter in a mass of others which had accumulated in my absence. By many, and often, it had been said they would not abide the nomination of Taylor; but, since the deed has been done, they are fast falling in, and in my opinion we shall have a most overwhelming, glorious triumph. One unmistakable sign is, that all the odds and ends are with us,—Barnburners, Native Americans, Tyler men, disappointed, office-seeking Locofocos, and the Lord knows what. This is important, if in nothing else, in showing which way the wind blows. Some of the sanguine men here set down all the States as certain for Taylor but Illinois, and it is doubtful. Cannot something be done even in Illinois? Taylor's nomination takes the Locos on the blind side. It turns the war thunder against them. The war is now to them the gallows of Haman, which they built for us, and on which they are doomed to be hanged themselves.
Excuse this short letter. I have so many to write that I cannot devote much time to any one.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
But his young partner in the law gave him a great deal of annoyance. Mr. Herndon seems to have been troubled by patriotic scruples. He could not understand how the war had been begun unconstitutionally and unnecessarily by President Polk, nor how the Whigs could vote supplies to carry on the war without indorsing the war itself. Besides all this, he sent news of startling defections; and the weary Representative took up his pen again and again to explain, defend, and advise:—
Washington, June 22,1848.
Dear William,—Last night I was attending a sort of caucus of the Whig members, held in relation to the coming Presidential election. The whole field of the nation was scanned; and all is high hope and confidence. Illinois is expected to better her condition in this race. Under these circumstances, judge how heart-rending it was to come to my room and find and read your discouraging letter of the 15th. We have made no gains, but have lost "H. R. Robinson, Turner, Campbell, and four or five more." Tell Arney to reconsider, if he would be saved. Baker and I used to do something, but I think you attach more importance to our absence than is just. There is another cause: in 1840, for instance, we had two Senators and five Representatives in Sangamon; now, we have part of one Senator and two Representatives. With quite one-third more people than we had then, we have only half the sort of offices which are sought by men of the speaking sort of talent. This, I think, is the chief cause. Now, as to the young men. You must not wait to be brought forward by the older men. For instance, do you suppose that I should ever have got into notice if I had waited to be hunted up and pushed forward by older men. You young men get together and form a Rough and Ready Club, and have regular meetings and speeches. Take in everybody that you can get. Harrison, Grimsley, Z. A. Enos, Lee Kimball, and C. W. Matheny will do to begin the thing; but, as you go along, gather up all the shrewd, wild boys about town, whether just of age or a little under age,—Chris. Logan, Reddick Ridgely, Lewis Zwizler, and hundreds such. Let every one play the part he can play best,—some speak, some sing, and all hollow (holler ED). Your meetings will be of evenings; the older men, and the women, will go to hear you; so that it will not only contribute to the election of "Old Zack," but will be an interesting pastime, and improving to the intellectual faculties of all engaged. Don't fail to do this.
You ask me to send you all the speeches made about "Old Zack," the war, &c., &c. Now, this makes me a little impatient. I have regularly sent you "The Congressional Globe" and "Appendix," and you cannot have examined them, or you would have discovered that they contain every speech made by every man in both Houses of Congress, on every subject, during the session. Can I send any more? Can I send speeches that nobody has made? Thinking it would be most natural that the newspapers would feel interested to give at least some of the speeches to their readers, I, at the beginning of the session, made arrangements to have one copy of "The Globe" and "Appendix" regularly sent to each Whig paper of the district. And yet, with the exception of my own little speech, which was published in two only of the then five, now four, Whig papers, I do not remember having seen a single speech, or even extract from one, in any single one of those papers. With equal and full means on both sides, I will venture that "The State Register" has thrown before its readers more of Locofoco speeches in a month than all the Whig papers of the district have done of Whig speeches during the session.
If you wish a full understanding of the war, I repeat what I believe I said to you in a letter once before, that the whole, or nearly so, is to be found in the speech of Dixon of Connecticut. This I sent you in pamphlet, as well, as in "The Globe." Examine and study every sentence of that speech thoroughly, and you will understand the whole subject.
You ask how Congress came to declare that war had existed by the act of Mexico. Is it possible you don't understand that yet? You have at least twenty speeches in your possession that fully explain it. I will, however, try it once more. The news reached Washington of the commencement of hostilities on the Rio Grande, and of the great peril of Gen. Taylor's army. Everybody, Whigs and Democrats, was for sending them aid, in men and money. It was necessary to pass a bill for this. The Locos had a majority in both Houses, and they brought in a bill with a preamble, saying, Whereas, War exists by the act of Mexico, therefore we send Gen. Taylor money. The Whigs moved to strike out the preamble, so that they could vote to send the men and money, without saying any thing about how the war commenced; but, being in the minority, they were voted down, and the preamble was retained. Then, on the passage of the bill, the question came upon them, "Shall we vote for preamble and bill both together, or against both together?" They did not want to vote against sending help to Gen. Taylor, and therefore they voted for both together. Is there any difficulty in understanding this? Even my little speech shows how this was; and, if you will go to the library, you may get "The Journal" of 1845-46, in which you can find the whole for yourself.
We have nothing published yet with special reference to the Taylor race; but we soon will have, and then I will send them to everybody. I made an internal-improvement speech day before yesterday, which I shall send home as soon as I can get it written out and printed,—and which I suppose nobody will read.
Your friend as ever,
A. Lincoln.
Washington, July 10, 1848.
Dear William,—Your letter covering the newspaper slips was received last night. The subject of that letter is exceedingly painful to me; and I cannot but think there is some mistake in your impression of the motives of the old men. I suppose I am now one of the old men; and I declare, on my veracity, which I think is good with you, that nothing could afford me more satisfaction than to learn that you and others of my young friends at home were doing battle in the contest, and endearing themselves to the people, and taking a stand far above any I have ever been able to reach in their admiration. I cannot conceive that other old men feel differently. Of course, I cannot demonstrate what I say; but I was young once, and I am sure I was never ungenerously thrust back. I hardly know what to say. The way for a young man to rise is to improve himself every way he can, never suspecting that anybody wishes to hinder him. Allow me to assure you that suspicion and jealousy never did help any man in any situation. There may sometimes be ungenerous attempts to keep a young man down; and they will succeed, too, if he allows his mind to be diverted from its true channel, to brood over the attempted injury. Cast about, and see if this feeling has not injured every person you have ever known to fall into it.
Now, in what I have said, I am sure you will suspect nothing but sincere friendship. I would save you from a fatal error. You have been a laborious, studious young man. You are far better informed on almost all subjects than I have ever been. You cannot fail in any laudable object, unless you allow your mind to be improperly directed. I have some the advantage of you in the world's experience, merely by being older; and it is this that induces me to advise.
You still seem to be a little mistaken about "The Congressional Globe" and "Appendix." They contain all of the speeches that are published in any way. My speech and Dayton's speech, which you say you got in pamphlet form, are both, word for word, in the "Appendix." I repeat again, all are there.
Your friend, as ever,
A. Lincoln.
The "internal-improvement" speech to which Mr. Lincoln alludes in one of these letters was delivered on the 20th of June, and contained nothing remarkable or especially characteristic. It was in the main merely the usual Whig argument in favor of the constitutionality of Mr. Clay's "American System."
But, after the nominations at Baltimore and Philadelphia, everybody in either House of Congress who could compose any thing at all "on his legs," or in the closet, felt it incumbent upon him to contribute at least one electioneering speech to the political literature of the day. At last, on the 27th of July, Mr. Lincoln found an opportunity to make his. Few like it have ever been heard in either of those venerable chambers. It is a common remark of those who know nothing of the subject, that Mr. Lincoln was devoid of imagination; but the reader of this speech will entertain a different opinion. It opens to us a mind fertile in images sufficiently rare and striking, but of somewhat questionable taste. It must have been heard in amazement by those gentlemen of the House who had never known a Hanks, or seen a New Salem.
SPEECH ON THE PRESIDENCY AND GENERAL POLITICS. DELIVERED IN THE HOUSE, JULY 27, 1848.
Mr. Speaker,—Our Democratic friends seem to be in great distress because they think our candidate for the Presidency don't suit us. Most of them cannot find out that Gen. Taylor has any principles at all; some, however, have discovered that he has one, but that that one is entirely wrong. This one principle is his position on the veto power. The gentleman from Tennessee (Mr. Stanton), who has just taken his seat, indeed, has said there is very little, if any, difference on this question between Gen. Taylor and all the Presidents; and he seems to think it sufficient detraction from Gen. Taylor's position on it, that it has nothing new in it. But all others whom I have heard speak assail it furiously. A new member from Kentucky (Mr. Clarke) of very considerable ability, was in particular concern about it. He thought it altogether novel and unprecedented for a President, or a Presidential candidate, to think of approving bills whose constitutionality may not be entirely clear to his own mind. He thinks the ark of our safety is gone, unless Presidents shall always veto such bills as, in their judgment, may be of doubtful constitutionality. However clear Congress may be of their authority to pass any particular act, the gentleman from Kentucky thinks the President must veto it if he has doubts about it. Now, I have neither time nor inclination to argue with the gentleman on the veto power as an original question; but I wish to show that Gen. Taylor, and not he, agrees with the earliest statesmen on this question. When the bill chartering the first Bank of the United States passed Congress, its constitutionality was questioned; Mr. Madison, then in the House of Representatives, as well as others, had opposed it on that ground. Gen. Washington, as President, was called on to approve or reject it. He sought and obtained, on the constitutional question, the separate written opinions of Jefferson, Hamilton, and Edmund Randolph; they then being respectively Secretary of State, Secretary of the Treasury, and Attorney-General. Hamilton's opinion was for the power; while Randolph's and Jefferson's were both against it. Mr. Jefferson, in his letter dated Feb. 15, 1791, after giving his opinion decidedly against the constitutionality of that bill, closed with the paragraph which I now read:—
"It must be admitted, however, that, unless the President's mind, on a view of every thing which is urged for and against this bill, is tolerably clear that it is unauthorized by the Constitution; if the pro and the con hang so even as to balance his judgment, a just respect for the wisdom of the Legislature would naturally decide the balance in favor of their opinion; it is chiefly for cases where they are clearly misled by error, ambition, or interest, that the Constitution has placed a check in the negative of the President."
Gen. Taylor's opinion, as expressed in his Allison letter, is as I now read:—
"The power given by the veto is a high conservative power, but, in my opinion, should never be exercised, except in cases of clear violation of the Constitution, or manifest haste and want of consideration by Congress."
It is here seen, that, in Mr. Jefferson's opinion, if, on the constitutionality of any given bill, the President doubts, he is not to veto it, as the gentleman from Kentucky would have him to do, but is to defer to Congress, and approve it. And if we compare the opinions of Jefferson and Taylor, as expressed in these paragraphs, we shall find them more exactly alike than we can often find any two expressions having any literal difference. None but interested fault-finders can discover any substantial variation.
But gentlemen on the other side are unanimously agreed that Gen. Taylor has no other principle. They are in utter darkness as to his opinions on any of the questions of policy which occupy the public attention. But is there any doubt as to what he will do on the prominent question, if elected? Not the least. It is not possible to know what he will or would do in every imaginable case, because many questions have passed away, and others doubtless will arise, which none of us have yet thought of; but on the prominent questions of currency, tariff, internal improvements, and Wilmot Proviso, Gen. Taylor's course is at least as well defined as is Gen. Cass's. Why, in their eagerness to get at Gen. Taylor, several Democratic members here have desired to know whether, in case of his election, a bankrupt-law is to be established. Can they tell us Gen. Cass's opinion on this question? (Some member answered, He is against it.") Ay, how do you know he is? There is nothing about it in the platform, nor elsewhere, that I have seen. If the gentleman knows any thing which I do not, he can show it. But to return: Gen. Taylor, in his Allison letter, says,—
"Upon the subject of the tariff, the currency, the improvement of our great highways, rivers, lakes, and harbors, the will of the people, as expressed through their Representatives in Congress, ought to be respected and carried out by the Executive."
Now, this is the whole matter: in substance, it is this: The people say to Gen. Taylor, "If you are elected, shall we have a national bank?" He answers, "Your will, gentlemen, not mine"—"What about the tariff?"—"Say yourselves."—"Shall our rivers and harbors be improved?"—"Just as you please."—"If you desire a bank, an alteration of the tariff, internal improvements, any or all, I will not hinder you: if you do not desire them, I will not attempt to force them on you. Send up your members of Congress from the various districts, with opinions according to your own, and if they are for these measures, or any of them, I shall have nothing to oppose: if they are not for them, I shall not, by any appliances whatever, attempt to dragoon them into their adoption." Now, can there be any difficulty in understanding this? To you, Democrats, it may not seem like principle; but surely you cannot fail to perceive the position plain enough. The distinction between it and the position of your candidate is broad and obvious, and I admit you have a clear right to show it is wrong, if you can; but you have no right to pretend you cannot see it at all. We see it, and to us it appears like principle, and the best sort of principle at that,—the principle of allowing the people to do as they please with their own business. My friend from Indiana (Mr. C. B. Smith) has aptly asked, "Are you willing to trust the people?" Some of you answered substantially, "We are willing to trust the people; but the President is as much the representative of the people as Congress." In a certain sense, and to a certain extent, he is the representative of the people. He is elected by them as well as Congress is. But can he, in the nature of things, know the wants of the people as well as three hundred other men coming from all the various localities of the nation? If so, where is the propriety of having a Congress? That the Constitution gives the President a negative on legislation, all know; but that this negative should be so combined with platforms and other appliances as to enable him, and, in fact, almost compel him, to take the whole of legislation into his own hands, is what we object to, is what Gen. Taylor objects to, and is what constitutes the broad distinction between you and us. To thus transfer legislation is clearly to take it from those who understand with minuteness the interests of the people, and give it to one who does not and cannot so well understand it. I understand your idea,—that if a Presidential candidate avow his opinion upon a given question, or rather upon all questions, and the people, with full knowledge of this, elect him, they thereby distinctly approve all those opinions. This, though plausible, is a most pernicious deception. By means of it, measures are adopted or rejected contrary to the wishes of the whole of one party, and often nearly half of the other. The process is this: Three, four, or half a dozen questions are prominent at a given time; the party selects its candidate, and he takes his position on each of these questions. On all but one his positions have already been indorsed at former elections, and his party fully committed to them; but that one is new, and a large portion of them are against it. But what are they to do? The whole are strung together, and they must take all or reject all. They cannot take what they like, and leave the rest. What they are already committed to being the majority, they shut their eyes and gulp the whole. Next election, still another is introduced in the same way. If we run our eyes along the line of the past, we shall see that almost, if not quite, all the articles of the present Democratic creed have been at first forced upon the party in this very way. And just now, and just so, opposition to internal improvements is to be established if Gen. Cass shall be elected. Almost half the Democrats here are for improvements, but they will vote for Cass; and, if he succeeds, their votes will have aided in closing the doors against improvements. Now, this is a process which we think is wrong. We prefer a candidate, who, like Gen. Taylor, will allow the people to have their own way, regardless of his private opinion; and I should think the internal-improvement Democrats, at least, ought to prefer such a candidate. He would force nothing on them which they don't want; and he would allow them to have improvements which their own candidate, if elected, will not.
Mr. Speaker, I have said Gen. Taylor's position is as well defined as is that of Gen. Cass. In saying this, I admit I do not certainly know what he would do on the Wilmot Proviso. I am a Northern man, or, rather, a Western Free State man, with a constituency I believe to be, and with personal feelings I know to be, against the extension of slavery. As such, and with what information I have, I hope and believe Gen. Taylor, if elected, would not veto the proviso; but I do not know it. Yet, if I knew he would, I still would vote for him. I should do so, because, in my judgment, his election alone can defeat Gen. Cass; and because, should slavery thereby go into the territory we now have, just so much will certainly happen by the election of Cass, and, in addition, a course of policy leading to new wars, new acquisitions of territory, and still farther extensions of slavery. One of the two is to be President; which is preferable?
But there is as much doubt of Cass on improvements as there is of Taylor on the proviso. I have no doubt myself of Gen. Cass on this question, but I know the Democrats differ among themselves as to his position. My internal-improvement colleague (Mr. Wentworth) stated on this floor the other day, that he was satisfied Cass was for improvements, because he had voted for all the bills that he (Mr. W.) had. So far, so good. But Mr. Polk vetoed some of these very bills; the Baltimore Convention passed a set of resolutions, among other things, approving these vetoes; and Cass declares, in his letter accepting the nomination, that he has carefully read these resolutions, and that he adheres to them as firmly as he approves them cordially. In other words, Gen. Cass voted for the bills, and thinks the President did right to veto them; and his friends here are amiable enough to consider him as being on one side or the other, just as one or the other may correspond with their own respective inclinations. My colleague admits that the platform declares against the constitutionality of a general system of improvement, and that Gen. Cass indorses the platform; but he still thinks Gen. Cass is in favor of some sort of improvements. Well, what are they? As he is against general objects, those he is for must be particular and local. Now, this is taking the subject precisely by the wrong end.
Particularity—expending the money of the whole people for an object which will benefit only a portion of them—is the greatest real objection to improvements, and has been so held by Gen. Jackson, Mr. Polk, and all others, I believe, till now. But now, behold, the objects most general, nearest free from this objection, are to be rejected, while those most liable to it are to be embraced. To return: I cannot help believing that Gen. Cass, when he wrote his letter of acceptance, well understood he was to be claimed by the advocates of both sides of this question, and that he then closed the door against all further expressions of opinion, purposely to retain the benefits of that double position. His subsequent equivocation at Cleveland, to my mind, proves such to have been the case.
One word more, and I shall have done with this branch of the subject. You Democrats and your candidate, in the main, are in favor of laying down in advance a platform,—a set of party positions, as a unit; and then of enforcing the people, by every sort of appliance, to ratify them, however unpalatable some of them may be. We and our candidate are in favor of making Presidential elections and the legislation of the country distinct matters; so that the people can elect whom they please, and afterward legislate just as they please, without any hinderance, save only so much as may guard against infractions of the Constitution, undue haste, and want of consideration. The difference between us is clear as noonday. That we are right, we cannot doubt. We hold the true republican position. In leaving the people's business in their hands, we cannot be wrong. We are willing, and even anxious, to go to the people on this issue.
But I suppose I cannot reasonably hope to convince you that we have any principles. The most I can expect is, to assure you that we think we have, and are quite contented with them. The other day, one of the gentlemen from Georgia (Mr. Iverson), an eloquent man, and a man of learning, so far as I can judge, not being learned myself, came down upon us astonishingly. He spoke in what "The Baltimore American" calls the "scathing and withering style." At the end of his second severe flash I was struck blind, and found myself feeling with my fingers for an assurance of my continued physical existence. A little of the bone was left, and I gradually revived. He eulogized Mr. Clay in high and beautiful terms, and then declared that we had deserted all our principles, and had turned Henry Clay out, like an old horse, to root. This is terribly severe. It cannot be answered by argument; at least, I cannot so answer it. I merely wish to ask the gentleman if the Whigs are the only party he can think of, who sometimes turn old horses out to root? Is not a certain Martin Van Buren an old horse which your own party have turned out to root? and is he not rooting a little to your discomfort about now? But, in not nominating Mr. Clay, we deserted our principles, you say. Ah! in what? Tell us, ye men of principles, what principle we violated? We say you did violate principle in discarding Van Buren, and we can tell you how. You violated the primary, the cardinal, the one great living principle of all Democratic representative government,—the principle that the representative is bound to carry out the known will of his constituents. A large majority of the Baltimore Convention of 1844 were, by their constituents, instructed to procure Van Buren's nomination if they could. In violation, in utter, glaring contempt of this, you rejected him,—rejected him, as the gentleman from New York (Mr. Birdsall), the other day expressly admitted, for availability,—that same "general availability" which you charge upon us, and daily chew over here, as something exceedingly odious and unprincipled. But the gentleman from Georgia (Mr. Iverson) gave us a second speech yesterday, all well considered and put down in writing, in which Van Buren was scathed and withered a "few" for his present position and movements. I cannot remember the gentleman's precise language, but I do remember he put Van Buren down, down, till he got him where he was finally to "stink" and "rot."
Mr. Speaker, it is no business or inclination of mine to defend Martin Van Buren. In the war of extermination now waging between him and his old admirers, I say, Devil take the hindmost—and the foremost. But there is no mistaking the origin of the breach; and, if the curse of "stinking" and "rotting" is to fall on the first and greatest violators of principle in the matter, I disinterestedly suggest, that the gentleman from Georgia and his present co-workers are bound to take it upon themselves.
While I have Gen. Cass in hand, I wish to say a word about his political principles. As a specimen, I take the record of his progress on the Wilmot Proviso. In "The Washington Union" of March 2, 1847, there is a report of the speech of Gen. Cass, made the day before in the Senate, on the Wilmot Proviso, during the delivery of which, Mr. Miller of New Jersey is reported to have interrupted him as follows, to wit:—
"Mr. Miller expressed his great surprise at the change in the sentiments of the Senator from Michigan, who had been regarded as the great champion of freedom in the North-west, of which he was a distinguished ornament. Last year the Senator from Michigan was understood to be decidedly in favor of the Wilmot Proviso; and, as no reason had been stated for the change, he (Mr. Miller) could not refrain from the expression of his extreme surprise."
To this, Gen. Cass is reported to have replied as follows, to wit:—
"Mr. Cass said, that the course of the Senator from New Jersey was most extraordinary. Last year he (Mr. Cass) should have voted for the proposition had it come up. But circumstances had altogether changed. The honorable Senator then read several passages from the remarks as given above which he had committed to writing, in order to refute such a charge as that of the Senator from New Jersey."
In the "remarks above committed to writing," is one numbered 4, as follows, to wit:—
"4th. Legislation would now be wholly imperative, because no territory hereafter to be acquired can be governed without an act of Congress providing for its government. And such an act, on its passage, would open the whole subject, and leave the Congress called on to pass it free to exercise its own discretion, entirely uncontrolled by any declaration found in the statute-book."
In "Niles's Register," vol. lxxiii., p. 293, there is a letter of Gen. Cas? to A. O. P. Nicholson of Nashville, Tenn., dated Dec. 24, 1847, from which the following are correct extracts:—
"The Wilmot Proviso has been before the country some time. It has been repeatedly discussed in Congress, and by the public press. I am strongly impressed with the opinion that a great change has been going on in the public mind upon this subject,—in my own as well as others; and that doubts are resolving themselves into convictions, that the principle it involves should be kept out of the national Legislature, and left to the people of the Confederacy in their respective local governments.
"Briefly, then, I am opposed to the exercise of any jurisdiction by Congress over this matter; and I am in favor of leaving the people of any territory which may be hereafter acquired, the right to regulate it themselves, under the general principles of the Constitution. Because,
"1. I do not see in the Constitution any grant of the requisite power to Congress; and I am not disposed to extend a doubtful precedent beyond its necessity,—the establishment of territorial governments when needed,—leaving to the inhabitants all the rights compatible with the relations they bear to the Confederation."
These extracts show, that, in 1846, Gen. Cass was for the Proviso at once; that, in March, 1847, he was still for it, but not just then; and that in December, 1847, he was against it altogether. This is a true index to the whole man. When the question was raised in 1846, he was in a blustering hurry to take ground for it. He sought to be in advance, and to avoid the uninteresting position of a mere follower; but soon he began to see glimpses of the great Democratic ox-gad waving in his face, and to hear indistinctly a voice saying, "Back!" "Back, sir!" "Back a little!" He shakes his head, and bats his eyes, and blunders back to his position of March, 1847; but still the gad waves, and the voice grows more distinct, and sharper still,—"Back, sir!" "Back, I say!" "Further back!" and back he goes to the position of December, 1847; at which the gad is still, and the voice soothingly says, "So!" "Stand still at that."
Have no fears, gentlemen, of your candidate: he exactly suits you, and we congratulate you upon it. However much you may be distressed about our candidate, you have all cause to be contented and happy with your own. If elected, he may not maintain all, or even any, of his positions previously taken; but he will be sure to do whatever the party exigency, for the time being, may require; and that is precisely what you want. He and Van Buren are the same "manner of men;" and, like Van Buren, he will never desert you till you first desert him.
[After referring at some length to extra "charges" of Gen. Cass upon the Treasury, Mr. Lincoln continued:—-]
But I have introduced Gen. Cass's accounts here chiefly to show the wonderful physical capacities of the man. They show that he not only did the labor of several men at the same time, but that he often did it, at several places many hundred miles apart, at the same time. And at eating, too, his capacities are shown to be quite as wonderful. From October, 1821, to May, 1822, he ate ten rations a day in Michigan, ten rations a day here in Washington, and nearly five dollars' worth a day besides, partly on the road between the two places. And then there is an important discovery in his example,—the art of being paid for what one eats, instead of having to pay for it. Hereafter, if any nice young man shall owe a bill which he cannot pay in any other way, he can just board it out. Mr. Speaker, we have all heard of the animal standing in doubt between two stacks of hay, and starving to death: the like of that would never happen to Gen. Cass. Place the stacks a thousand miles apart, he would stand stock-still, midway between them, and eat them both at once; and the green grass along the line would be apt to suffer some, too, at the same time. By all means make him President, gentlemen. He will feed you bounteously—if—if—there is any left after he shall have helped himself.
But as Gen. Taylor is, par excellence, the hero of the Mexican War, and as you Democrats say we Whigs have always opposed the war, you think it must be very awkward and embarrassing for us to go for Gen. Taylor. The declaration that we have always opposed the war is true or false accordingly as one may understand the term "opposing the war." If to say "the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President," by opposing the war, then the Whigs have very generally opposed it. Whenever they have spoken at all, they have said this; and they have said it on what has appeared good reason to them: the marching an army into the midst of a peaceful Mexican settlement, frightening the inhabitants away, leaving their growing crops and other property to destruction, to you may appear a perfectly amiable, peaceful, unprovoking procedure; but it does not appear so to us. So to call such an act, to us appears no other than a naked, impudent absurdity, and we speak of it accordingly. But if when the war had begun, and had become the cause of the country, the giving of our money and our blood, in common with yours, was support of the war, then it is not true that we have always opposed the war. With few individual exceptions, you have constantly had our votes here for all the necessary supplies. And, more than this, you have had the services, the blood, and the lives of our political brethren in every trial, and on every field. The beardless boy and the mature man, the humble and the distinguished,—you have had them. Through suffering and death, by disease and in battle, they have endured and fought and fallen with you. Clay and Webster each gave a son, never to be returned. From the State of my own residence, besides other worthy but less known Whig names, we sent Marshall, Morrison, Baker, and Hardin: they all fought, and one fell, and in the fall of that one we lost our best Whig man. Nor were the Whigs few in number, or laggard in the day of danger. In that fearful, bloody, breathless struggle at Buena Vista, where each man's hard task was to beat back five foes or die himself, of the five high officers who perished, four were Whigs.
In speaking of this, I mean no odious comparison between the lion-hearted Whigs and Democrats who fought there. On other occasions, and among the lower officers and privates on that occasion, I doubt not the proportion was different. I wish to do justice to all. I think of all those brave men as Americans, in whose proud fame, as an American, I, too, have a share. Many of them, Whigs and Democrats, are my constituents and personal friends; and I thank them,—more than thank them,—one and all, for the high, imperishable honor they have conferred on our common State.
But the distinction between the cause of the President in beginning the war, and the cause of the country after it was begun, is a distinction which you cannot perceive. To you, the President and the country seem to be all one. You are interested to see no distinction between them; and I venture to suggest that possibly your interest blinds you a little. We see the distinction, as we think, clearly enough; and our friends, who have fought in the war, have no difficulty in seeing it also. What those who have fallen would say, were they alive and here, of course we can never know; but with those who have returned there is no difficulty. Col. Haskell and Major Gaines, members here, both fought in the war; and one of them underwent extraordinary perils and hardships; still they, like all other Whigs here, vote on the record that the war was unnecessarily and unconstitutionally commenced by the President. And even Gen. Taylor himself, the noblest Roman of them all, has declared that, as a citizen, and particularly as a soldier, it is sufficient for him to know that his country is at war with a foreign nation, to do all in his power to bring it to a speedy and honorable termination, by the most vigorous and energetic operations, without inquiring about its justice, or any thing else connected with it.
Mr. Speaker, let our Democratic friends be comforted with the assurance that we are content with our position, content with our company, and content with our candidate; and that although they, in their generous sympathy, think we ought to be miserable, we really are not, and that they may dismiss the great anxiety they have on our account.1
1 The following passage has generally been omitted from this speech, as published in the "Lives of Lincoln." The reason for the omission is quite obvious.
"But the gentleman from Georgia further says, we have deserted all our principles, and taken shelter under Gen. Taylor's military coat-tail; and he seems to think this is exceedingly degrading. Well, as his faith is, so be it unto him. But can he remember no other military coat-tail, under which a certain other party have been sheltering for near a quarter of a century? Has he no acquaintance with the ample military coat-tail of Gen. Jackson? Does he not know that his own party have run the last five Presidential races under that coat-tail? and that they are now running the sixth under the same cover? Yes, sir, that coat-tail was used, not only for Gen, Jackson himself, but has been clung to with the grip of death by every Democratic candidate since. You have never ventured, and dare not now venture, from under it. Your campaign papers have constantly been 'Old Hickories,' with rude likenesses of the old general upon them; hickory poles and hickory brooms your never-ending emblems. Mr. Polk himself was 'Young Hickory.' 'Little Hickory,' or something so; and even now your campaign paper here is proclaiming that Cass and Butler are of the 'Hickory stripe.' No, sir, you dare not give it up. Like a horde of hungry ticks, you have stuck to the tail of the Hermitage lion to the end of his life; and you are still sticking to it, and drawing a loathsome sustenance from it, after he is dead. A fellow once advertised that he had made a discovery by which he could make a new man out of an old one, and have enough of the stuff left to make a little yellow dog. Just such a discovery has Gen. Jackson's popularity been to you. You not only twice made President of him out of it, but you have enough of the stuff left to make Presidents of several comparatively small men since; and it is your chief reliance now to make still another.
"Mr. Speaker, old horses and military coat-tails, or tails of any sort, are not figures of speech such as I would be the first to introduce into discussions here; but, as the gentleman from Georgia has thought fit to introduce them, he and you are welcome to all you have made, or can make, by them. If you have any more old horses, trot them out; any more tails, just cock them, and come at us.
"I repeat, I would not introduce this mode of discussion here; but I wish gentlemen on the other side to understand, that the use of degrading figures is a game at which they may find themselves unable to take all the winnings. ["We give it up."] Ay, you give it up, and well you may; but for a very different reason from that which you would have us understand. The point—the power to hurt—of all figures, consists in the truthfulness of their application; and, understanding this, you may well give it up. They are weapons which hit you, but miss us.
"But, in my hurry, I was very near closing on this subject of military tails before I was done with it. There is one entire article of the sort I have not discussed yet; I mean the military tail you Democrats are now engaged in dovetailing on to the great Michigander. Yes, sir, all his biographers (and they are legion) have him in hand, tying him to a military tail, like so many mischievous boys tying a dog to a bladder of beans. True, the material is very limited, but they are at it might and main. He invaded Canada without resistance, and he outvaded it without pursuit. As he did both under orders, I suppose there was, to him, neither credit nor discredit; but they are made to constitute a large part of the tail. He was not at Hull's surrender, but he was close by; he was volunteer aid to Gen. Harrison on the day of the battle of the Thames; and, as you said in 1840 Harrison was picking whortleberries two miles off while the battle was fought, I suppose it is a just conclusion, with you, to say Cass was aiding Harrison to pick whortleberries. This is about all, except the mooted question of the broken sword. Some authors say he broke it; some say he threw it away; and some others, who ought to know, say nothing about it. Perhaps it would be a fair historical compromise to say, if he did not break it, he did not do any thing else with it.
"By the way, Mr. Speaker, did you know I am a military hero? Yes sir: in the days of the Black-Hawk War, I fought, bled, and came away. Speaking of Gen. Cass's career reminds me of my own. I was not at Stillman's defeat, but I was about as near it as Cass was to Hull's surrender; and, like him, I saw the place very soon afterwards. It is quite certain I did not break my sword, for I had none to break; but I bent my musket pretty badly on one occasion. If Cass broke his sword, the idea is, he broke it in desperation: I bent the musket by accident. If Gen. Cass went in advance of me picking whortleberries,
I guess I surpassed him in charges upon the wild onions. If he saw any live fighting Indians, it was more than I did, but I had a good many bloody struggles with the mosquitoes; and, although I never fainted from loss of blood, I can truly say I was often very hungry, "Mr. Speaker, if ever I should conclude to doff whatever our Democratic friends may suppose there is of black-cockade Federalism about me, and, thereupon, they shall take me up as their candidate for the Presidency, I protest that they shall not make fun of me, as they have of Gen. Cass, by attempting to write me into a military hero."
Congress adjourned on the 14th of August; but Mr. Lincoln went up to New England, and made various campaign speeches before he returned home. They were not preserved, and were probably of little importance.
Soon after his return to Washington, to take his seat at the second session of the Thirtieth Congress, he received a letter from his father, which astonished and perhaps amused him. His reply intimates grave doubts concerning the veracity of his correspondent.
Washington, Dec. 24, 1848. My dear Father,—Your letter of the 7th was received night before last. I very cheerfully send you the twenty dollars, which sum you say is necessary to save your land from sale. It is singular that you should have forgotten a judgment against you; and it is more singular that the plaintiff should have let you forget it so long; particularly as I suppose you always had property enough to satisfy a judgment of that amount. Before you pay it, it would be well to be sure you have not paid, or at least that you cannot prove you have paid it.
Give my love to mother and all the connections.
Affectionately your son,
A. Lincoln.
The second session was a quiet one. Mr. Lincoln did nothing to attract public attention in any marked degree. He attended diligently and unobtrusively to the ordinary duties of his office, and voted generally with the Whig majority. One Mr. Gott, however, of New York, offered a resolution looking to the abolition of the slave-trade in the District of Columbia, and Mr. Lincoln was one of only three or four Northern Whigs who voted to lay the resolution on the table. At another time, however, Mr. Lincoln proposed a substitute for the Gott resolution, providing for gradual and compensated emancipation, with the consent of the people of the District, to be ascertained at a general election. This measure he evidently abandoned, and it died a natural death among the rubbish of "unfinished business." His record on the Wilmot Proviso has been thoroughly exposed, both by himself and Mr. Douglas, and in the Presidential campaign by his friends and foes. He said himself, that he had voted for it "about forty-two times." It is not likely that he had counted the votes when he made this statement, but spoke according to the best of his "knowledge and belief."
The following letters are printed, not because they illustrate the author's character more than a thousand others would, but because they exhibit one of the many perplexities of Congressional life.
Springfield, April 25, 1849.
Dear Thompson,—A tirade is still kept up against me here for recommending T. R. King. This morning it is openly avowed that my supposed influence at Washington shall be broken down generally, and King's prospects defeated in particular. Now, what I have done in this matter, I have done at the request of you and some other friends in Tazewell; and I therefore ask you to either admit it is wrong, or come forward and sustain me. If the truth will permit, I propose that you sustain me in the following manner: copy the enclosed scrap in your own handwriting, and get everybody (not three or four, but three or four hundred) to sign it, and then send it to me. Also, have six, eight, or ten of our best known Whig friends there to write me individual letters, stating the truth in this matter as they understand it. Don't neglect or delay in the matter. I understand information of an indictment having been found against him about three years ago for gaming, or keeping a gaming-house, has been sent to the Department. I shall try to take care of it at the Department till your action can be had and forwarded on.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
Washington, June 5, 1849.
Dear William,—Your two letters were received last night. I have a great many letters to write, and so cannot write very long ones. There must be some mistake about Walter Davis saying I promised him the Post-office. I did not so promise him. I did tell him, that, if the distribution of the offices should fall into my hands, he should have something; and, if I shall be convinced he has said any more than this, I shall be disappointed.
I said this much to him, because, as I understand, he is of good character, is one of the young men, is of the mechanics, and always faithful, and never troublesome, a Whig and is poor, with the support of a widow-mother thrown almost exclusively on him by the death of his brother. If these are wrong reasons, then I have been wrong; but I have certainly not been selfish in it, because, in my greatest need of friends, he was against me and for Baker.
Yours as ever,
A. Lincoln.
P. S.—Let the above be confidential.
LIKE most other public men in America, Mr. Lincoln made his bread by the practice of his profession, and the better part of his fame by the achievements of the politician. He was a lawyer of some note, and, compared with the crowds who annually take upon themselves the responsible office of advocate and attorney, he might very justly have been called a good one; for he regarded his office as a trust, and selected and tried his cases, not with a view to personal gain, but to the administration of justice between suitors. And here, midway in his political career, it is well enough to pause, and take a leisurely survey of him in his other character of country lawyer, from the time he entered the bar at Springfield until he was translated from it to the Presidential chair. It is unnecessary to remind the reader (for by this time it must be obvious enough) that the aim of the writer is merely to present facts and contemporaneous opinions, with as little comment as possible.
In the courts and at the bar-meetings immediately succeeding his death, his professional brethren poured out in volumes their testimony to his worth and abilities as a lawyer. But, in estimating the value of this testimony, it is fair to consider the state of the public mind at the time it was given,—the recent triumph of the Federal arms under his direction; the late overwhelming indorsement of his administration; the unparalleled devotion of the people to his person as exhibited at the polls; the fresh and bitter memories of the hideous tragedy that took him off; the furious and deadly passions it inspired in the one party, and the awe, indignation, and terror it inspired in the other. It was no time for nice and critical examinations, either of his mental or his moral character; and it might have been attended with personal danger to attempt them. For days and nights together it was considered treason to be seen in public with a smile on the face. Men who spoke evil of the fallen chief, or even ventured a doubt concerning the ineffable purity and saintliness of his life, were pursued by mobs, were beaten to death with paving-stones, or strung up by the neck to lampposts. If there was any rivalry, it was as to who should be foremost and fiercest among his avengers, who should canonize him in the most solemn words, who should compare him to the most sacred character in all history, sacred and profane. He was prophet, priest, and king; he was Washington; he was Moses; and there were not wanting even those who likened him to the God and Redeemer of all the earth. These latter thought they discovered in his lowly origin, his kindly nature, his benevolent precepts, and the homely anecdotes in which he taught the people, strong points of resemblance between him and the divine Son of Mary. Even at this day, men are not wanting in prominent positions in life, who knew Mr. Lincoln well, and who do not hesitate to make such a comparison.

For many years, Judge David Davis was the near friend and the intimate associate of Mr. Lincoln. He presided in the court where Lincoln was oftenest heard: year in and year out they travelled together from town to town, from county to county, riding frequently in the same conveyance, and lodging in the same room. Although a judge on the bench, Mr. Davis watched the political course of his friend with affectionate solicitude, and more than once interposed most effectually to advance his fortunes. When Mr. Lincoln ascended to the Presidency, it was well understood that no man enjoyed more confidential relations with him than Judge Davis. At the first opportunity, he commissioned Judge Davis an Associate Justice of that august tribunal, the Supreme Court of the United States; and, upon his death, Judge Davis administered upon his estate at the request of his family. Add to this the fact, that, among American jurists, Judge Davis's fame is, if not peerless, at least not excelled by that of any man whose reputation rests upon his labors as they appear in the books of Reports, and we may very fairly consider him a competent judge of the professional character of Mr. Lincoln. At Indianapolis, Judge Davis spoke of him as follows:—
"I enjoyed for over twenty years the personal friendship of Mr. Lincoln. We were admitted to the bar about the same time, and travelled for many years what is known in Illinois as the Eighth Judicial Circuit. In 1848, when I first went on the bench, the circuit embraced fourteen counties, and Mr. Lincoln went with the court to every county. Railroads were not then in use, and our mode of travel was either on horseback or in buggies.
"This simple life he loved, preferring it to the practice of the law in a city, where, although the remuneration would be greater, the opportunity would be less for mixing with the great body of the people, who loved him, and whom he loved. Mr. Lincoln was transferred from the bar of that circuit to the office of President of the United States, having been without official position since he left Congress in 1849. In all the elements that constitute the great lawyer, he had few equals. He was great both at nisi prius and before an appellate tribunal. He seized the strong points of a cause, and presented them with clearness and great compactness. His mind was logical and direct, and he did not indulge in extraneous discussion. Generalities and platitudes had no charms for him. An unfailing vein of humor never deserted him; and he was always able to chain the attention of court and jury, when the cause was the most uninteresting, by the appropriateness of his anecdotes.
"His power of comparison was large, and he rarely failed in a legal discussion to use that mode of reasoning. The framework of his mental and moral being was honesty, and a wrong cause was poorly defended by him. The ability which some eminent lawyers possess, of explaining away the bad points of a cause by ingenious sophistry, was denied him. In order to bring into full activity his great powers, it was necessary that he should be convinced of the right and justice of the matter which he advocated. When so convinced, whether the cause was great or small, he was usually successful. He read law-books but little, except when the cause in hand made it necessary; yet he was usually self-reliant, depending on his own resources, and rarely consulting his brother lawyers, either on the management of his case or on the legal questions involved.
"Mr. Lincoln was the fairest and most accommodating of practitioners, granting all favors which he could do consistently with his duty to his client, and rarely availing himself of an unwary oversight of his adversary.
"He hated wrong and oppression everywhere; and many a man whose fraudulent conduct was undergoing review in a court of justice has writhed under his terrific indignation and rebukes. He was the most simple and unostentatious of men in his habits, having few wants, and those easily supplied.
"To his honor be it said, that he never took from a client, even when the cause was gained, more than he thought the service was worth and the client could reasonably afford to pay. The people where he practised law were not rich, and his charges were always small.
"When he was elected President, I question whether there was a lawyer in the circuit, who had been at the bar as long a time, whose means were not larger. It did not seem to be one of the purposes of his life to accumulate a fortune. In fact, outside of his profession, he had no knowledge of the way to make money, and he never even attempted it.
"Mr. Lincoln was loved by his brethren of the bar; and no body of men will grieve more at his death, or pay more sincere tributes to his memory. His presence on the circuit was watched for with interest, and never failed to produce joy and hilarity. When casually absent, the spirits of both bar and people were depressed. He was not fond of controversy, and would compromise a lawsuit whenever practicable."
More or other evidence than this may, perhaps, be superfluous. Such an eulogium, from such a source, is more than sufficient to determine the place Mr. Lincoln is entitled to occupy in the history, or, more properly speaking, the traditions, of the Western bar. If Sir Matthew Hale had spoken thus of any lawyer of his day, he would have insured to the subject of his praise a place in the estimation of men only less conspicuous and honorable than that of the great judge himself. At the risk, however, of unnecessary accumulation, we venture to record an extract from Judge Drummond's address at Chicago:—
"With a probity of character known to all, with an intuitive insight into the human heart, with a clearness of statement which was in itself an argument, with uncommon power and felicity of illustration,—often, it is true, of a plain and homely kind,—and with that sincerity and earnestness of manner which carried conviction, he was, perhaps, one of the most successful jury lawyers we ever had in the State. He always tried a case fairly and honestly. He never intentionally misrepresented the evidence of a witness, nor the argument of an opponent. He met both squarely, and, if he could not explain the one or answer the other, substantially admitted it. He never misstated the law, according to his own intelligent view of it. Such was the transparent candor and integrity of his nature, that he could not well, or strongly, argue a side or a cause that he thought wrong. Of course, he felt it his duty to say what could be said, and to leave the decision to others; but there could be seen in such cases the inward struggles of his own mind. In trying a case, he might occasionally dwell too long upon, or give too much importance to, an inconsiderable point; but this was the exception, and generally he went straight to the citadel of the cause or question, and struck home there, knowing, if that were won, the outworks would necessarily fall. He could hardly be called very learned in his profession, and yet he rarely tried a cause without fully understanding the law applicable to it; and I have no hesitation in saying he was one of the ablest lawyers I have ever known. If he was forcible before a jury, he was equally so with the court. He detected, with unerring sagacity, the weak points of an opponent's argument, and pressed his own views with overwhelming strength. His efforts were quite unequal; and it might happen that he would not, on some occasions, strike one as at all remarkable. But let him be thoroughly roused,—let him feel that he was right, and that some principle was involved in his cause,—and he would come out with an earnestness of conviction, a power of argument, and a wealth of illustration, that I have never seen surpassed."
Mr. Lincoln's partnership with John T. Stuart began on the 27th of April, 1837, and continued until the 14th of April, 1841, when it was dissolved, in consequence of Stuart's election to Congress. In that same year (1841), Mr. Lincoln united in practice with Stephen T. Logan, late presiding judge of the district, and they remained together until 1845.
Soon afterwards he formed a copartnership with William H. Herndon, his friend, familiar, and, we may almost say, biographer,—a connection which terminated only when the senior partner took an affectionate leave of the old circuit, the old office, home, friends, and all familiar things, to return no more until he came a blackened corpse. "He once told me of you," says Mr. Whitney in one of his letters to Mr. Herndon, "that he had taken you in as partner, supposing that you had a system, and would keep things in order, but that he found that you had no more system than he had, but that you were a fine lawyer; so that he was doubly disappointed." 1
1 The following letter exhibits the character of his early practice, and gives us a glimpse into his social and political life;— Springfield, Dec. 23,1839. Dear—,—Dr. Henry will write you all the political news. I write this about some little matters of business. You recollect you told me you had drawn the Chicago Masack money, and sent it to the claimants. A d——d hawk-billed Yankee is here besetting me at every turn I take, saying that Robert Kenzie never received the eighty dollars to which he was entitled. Can you tell any thing about the matter? Again, old Mr. Wright, who lives up South Fork somewhere, is teasing me continually about some deeds, which he says he left with you, but which I can find nothing of. Can you tell where they are? The Legislature is in session, and has suffered the bank to forfeit its charter without benefit of clergy. There seems but little disposition to resuscitate it. Whenever a letter comes from you to Mrs.———, I carry it to her, and then I see Betty: she is a tolerable nice fellow now. Maybe I will write again when I get more time. Your friend as ever, A. Lincoln. P. S.—The Democratic giant is here, but he is not now worth talking about. A. L.
As already stated by Judge Davis, Mr. Lincoln was not "a great reader of law-books;" but what he knew he knew well, and within those limits was self-reliant and even intrepid. He was what is sometimes called "a case-lawyer,"—a man who reasoned almost entirely to the court and jury from analagous causes previously decided and reported in the books, and not from the elementary principles of the law, or the great underlying reasons for its existence. In consultation he was cautious, conscientious, and painstaking, and was seldom prepared to advise, except after careful and tedious examination of the authorities. He did not consider himself bound to take every case that was brought to him, nor to press all the points in favor of a client who in the main was right and entitled to recover. He is known to have been many times on the verge of quarrelling with old and valued friends, because he could not see the justice of their claims, and, therefore, could not be induced to act as their counsel. Henry McHenry, one of his New-Salem associates, brought him a case involving the title to a piece of land. McHenry had placed a family in a cabin which Mr. Lincoln believed to be situated on the other side of the adversary's line. He told McHenry that he must move the family out. "McHenry said he should not do it. 'Well,' said Mr. Lincoln, 'if you do not, I shall not attend to the suit.' McHenry said he did not care a d—n whether he did or not; that he (Lincoln) was not all the lawyer there was in town. Lincoln studied a while, and asked about the location of the cabin,... and then said, 'McHenry, you are right: I will attend to the suit,' and did attend to it, and gained it; and that was all the harsh words that passed."
"A citizen of Springfield," says Mr. Herndon, "who visited our office on business about a year before Mr. Lincoln's nomination, relates the following:—
"'Mr. Lincoln was seated at his table, listening very attentively to a man who was talking earnestly in a low tone. After the would-be client had stated the facts of his case, Mr. Lincoln replied, "Yes, there is no reasonable doubt but that I can gain your case for you. I can set a whole neighborhood at loggerheads; I can distress a widowed mother and her six fatherless children, and thereby get for you six hundred dollars, which rightfully belongs, it appears to me, as much to the woman and her children as it does to you. You must remember that some things that are legally right are not morally right. I shall not take your case, but will give you a little advice, for which I will charge you nothing. You seem to be a sprightly, energetic man. I would advise you to try your hand at making six hundred dollars in some other way."'"
In the summer of 1841, Mr. Lincoln was engaged in a curious case. The circumstances impressed him very deeply with the insufficiency and danger of "circumstantial evidence;" so much so, that he not only wrote the following account of it to Speed, but another more extended one, which was printed in a newspaper published at Quincy, 111. His mind was full of it: he could think of nothing else. It is apparent that in his letter to Speed he made no pause to choose his words: there is nothing constrained, and nothing studied or deliberate about it; but its simplicity, perspicuity, and artless grace make it a model of English composition. What Goldsmith once said of Locke may better be said of this letter: "He never says more nor less than he ought, and never makes use of a word that he could have changed for a better."
Springfield, June 19,1841.
Dear Speed,—We have had the highest state of excitement here for a week past that our community has ever witnessed; and although the public feeling is somewhat allayed, the curious affair which aroused it is very far from being over yet, cleared of mystery. It would take a quire of paper to give you any thing like a full account of it, and I therefore only propose a brief outline. The chief personages in the drama are Archibald Fisher, supposed to be murdered, and Archibald Trailor, Henry Trailor, and William Trailor, supposed to have murdered him. The three Trailors are brothers: the first, Arch., as you know, lives in town; the second, Henry, in Clary's Grove; and the third, William, in Warren County; and Fisher, the supposed murdered, being without a family, had made his home with William. On Saturday evening, being the 29th of May, Fisher and William came to Henry's in a one-horse dearborn, and there staid over Sunday; and on Monday all three came to Springfield (Henry on horseback), and joined Archibald at Myers's, the Dutch carpenter. That evening at supper Fisher was missing, and so next morning some ineffectual search was made for him; and on Tuesday, at 1 o'clock, p.m., William and Henry started home without him. In a day or two Henry and one or two of his Clary-Grove neighbors came back for him again, and advertised his disappearance in the papers. The knowledge of the matter thus far had not been general, and here it dropped entirely, till about the 10th inst., when Keys received a letter from the postmaster in Warren County, that William had arrived at home, and was telling a very mysterious and improbable story about the disappearance of Fisher, which induced the community there to suppose he had been disposed of unfairly. Keys made this letter public, which immediately set the whole town and adjoining county agog. And so it has continued until yesterday. The mass of the people commenced a systematic search for the dead body, while Wickersbam was despatched to arrest Henry Trailor at the Grove, and Jim Maxcy to Warren to arrest William. On Monday last, Henry was brought in, and showed an evident inclination to insinuate that he knew Fisher to be dead, and that Arch, and William had killed him. He said he guessed the body could be found in Spring Creek, between the Beardstown Road and Hickox's mill. Away the people swept like a herd of buffalo, and cut down Hickox's mill-dam nolens volens, to draw the water out of the pond, and then went up and down, and down and up the creek, fishing and raking, and raking and ducking, and diving for two days, and, after all, no dead body found. In the mean time a sort of a scuffling-ground had been found in the brush in the angle, or point, where the road leading into the woods past the brewery, and the one leading in past the brick grove meet. From the scuffle-ground was the sign of something about the size of a man having been dragged to the edge of the thicket, where joined the track of some small wheeled carriage drawn by one horse, as shown by the road-tracks. The carriage-track led off toward Spring Creek. Near this drag-trail Dr. Merryman found two hairs, which, after a long scientific examination, he pronounced to be triangular human hair, which term, he says, includes within it the whiskers, the hair growing under the arms, and on other parts of the body; and he judged that these two were of the whiskers, because the ends were cut, showing that they had flourished in the neighborhood of the razor's operations. On Thursday last Jim Maxcy brought in William Trailor from Warren. On the same day Arch, was arrested, and put in jail. Yesterday (Friday) William was put upon his examining trial before May and Lavely. Archibald and Henry were both present. Lamborn prosecuted, and Logan, Baker, and your humble servant defended. A great many witnesses were introduced and examined, but I shall only mention those whose testimony seemed most important. The first of these was Capt. Ransdell. He swore, that, when William and Henry left Springfield for home on Tuesday before mentioned, they did not take the direct route,—which, you know, leads by the butcher-shop,—but that they followed the street north until they got opposite, or nearly opposite, May's new house, after which he could not see them from where he stood; and it was afterwards proved, that, in about an hour after they started, they came into the street by the butcher's shop from towards the brick-yard. Dr. Merryman and others swore to what is stated about the scuffle-ground, drag-trail, whiskers, and carriage-tracks. Henry was then introduced by the prosecution. He swore, that, when they started for home, they went out north, as Ransdell stated, and turned down west by the brick-yard into the woods, and there met Archibald; that they proceeded a small distance farther, when he was placed as a sentinel to watch for and announce the approach of any one that might happen that way; that William and Arch, took the dearborn out of the road a small distance to the edge of the thicket, where they stopped, and he saw them lift the body of a man into it; that they then moved off with the carriage in the direction of Hickox's mill, and he loitered about for something like an hour, when William returned with the carriage, but without Arch., and said they had put him in a safe place; that they went somehow, he did not know exactly how, into the road close to the brewery, and proceeded on to Clary's Grove. He also stated that some time during the day William told him that he and Arch, had killed Fisher the evening before; that the way they did it was by him (William) knocking him down with a club, and Arch, then choking him to death. An old man from Warren, called Dr. Gilmore, was then introduced on the part of the defence. He swore that he had known Fisher for several years; that Fisher had resided at his house a long time at each of two different spells,—once while he built a barn for him, and once while he was doctored for some chronic disease; that two or three years ago Fisher had a serious hurt in his head by the bursting of a gun, since which he had been subject to continued bad health and occasional aberration of mind. He also stated that on last Tuesday, being the same day that Maxcy arrested William Trailor, he (the doctor) was from home in the early part of the day, and on his return, about 11 o'clock, found Fisher at his house in bed, and apparently very unwell; that he asked him how he had come from Springfield; that Fisher said he had come by Peoria, and also told of several other places he had been at, more in the direction of Peoria, which showed that he at the time of speaking did not know where he had been wandering about in a state of derangement. He further stated, that in about two hours he received a note from one of Trail-or's friends, advising him of his arrest, and requesting him to go on to Springfield as a witness, to testify as to the state of Fisher's health in former times; that he immediately set off, calling up two of his neighbors as company, and, riding all evening and all night, overtook Maxcy and William at Lewiston in Fulton. County; That Maxcy refusing to discharge Trailor upon his statement, his two neighbors returned, and he came on to Springfield. Some question being made as to whether the doctor's story was not a fabrication, several acquaintances of his (among whom was the same postmaster who wrote to Keys, as before mentioned) were introduced as sort of compurgators, who swore that they knew the doctor to be of good character for truth and veracity, and generally of good character in every way. Here the testimony ended, and the Trailors were discharged, Arch, and William expressing, both in word and manner, their entire confidence that Fisher would be found alive at the doctor's by Galloway, Mallory, and Myers, who a day before had been despatched for that purpose; while Henry still protested that no power on earth could ever show Fisher alive. Thus stands this curious affair. When the doctor's story was first made public, it was amusing to scan and contemplate the countenances, and hear the remarks, of those who had been actively engaged in the search for the dead body: some looked quizzical, some melancholy, and some furiously angry. Porter, who had been very active, swore he always knew the man was not dead, and that he had not stirred an inch to hunt for him: Langford, who had taken the lead in cutting down Hickox's mill-dam, and wanted to hang Hickox for objecting, looked most awfully woebegone; he seemed the "wictim of hunrequited affection," as represented in the comic almanacs we used to laugh over. And Hart, the little drayman that hauled Molly home once, said it was too damned bad to have so much trouble, and no hanging, after all.
I commenced this letter on yesterday, since which I received yours of the 13th. I stick to my promise to come to Louisville. Nothing new here, except what I have written. I have not seen———since my last trip; and I am going out there as soon as I mail this letter.
Yours forever,
Lincoln.
On the 3d of December, 1839, Mr. Lincoln was admitted to practice in the Circuit Court of the United States; and on the same day the names of Stephen A. Douglas, S. H. Treat, Schuyler Strong, and two other gentlemen, were placed on the same roll. The "Little Giant" is always in sight!
The first speech he delivered in the Supreme Court of the State was one the like of which will never be heard again, and must have led the judges to doubt the sanity of the new attorney. We give it in the form in which it seems to be authenticated by Judge Treat:—
"A case being called for hearing in the Court, Mr. Lincoln stated that he appeared for the appellant, and was ready to proceed with the argument. He then said, 'This is the first case I have ever had in this court, and I have therefore examined it with great care. As the Court will perceive, by looking at the abstract of, the record, the only question in the case is one of authority. I have not been able to find any authority sustaining my side of the case, but I have found several cases directly in point on the other side. I will now give these cases, and then submit the case.'"
The testimony of all the lawyers, his contemporaries and rivals, is in the same direction. "But Mr. Lincoln's love of justice and fair play," says Mr. Gillespie, "was his predominating trait. I have often listened to him when I thought he would certainly state his case out of Court. It was not in his nature to assume, or to attempt to bolster up, a false position. He would abandon his case first. He did so in the case of Buckmaster for the use of Denham vs. Beenes and Arthur, in our Supreme Court, in which I happened to be opposed to him. Another gentleman, less fastidious, took Mr. Lincoln's place, and gained the case."
In the Patterson trial—a case of murder which attained some celebrity—in Champaign County, Ficklin and Lamon prosecuted, and Lincoln and Swett defended. After hearing the testimony, Mr. Lincoln felt himself morally paralyzed, and said, "Swett, the man is guilty: you defend him; I can't." They got a fee of five hundred or a thousand dollars; of which Mr. Lincoln declined to take a cent, on the ground that it justly belonged to Swett, whose ardor, courage, and eloquence had saved the guilty man from justice.
It was probably his deep sense of natural justice, his irresistible propensity to get at the equities of the matter in hand, that made him so utterly impatient of all arbitrary or technical rules. Of these he knew very little,—less than an average student of six months: "Hence," says Judge Davis, "a child could make use of the simple and technical rules, the means and mode of getting at justice, better than Lincoln could." "In this respect," says Mr. Herndon, "I really think he was very deficient."
Sangamon County was originally in the First Judicial Circuit; but under the Constitution of 1848, and sundry changes in the Judiciary Acts, it became the Eighth Circuit. It was in 1848 that Judge Davis came on the bench for the first time. The circuit was a very large one, containing fourteen counties, and comprising the central portion of the State. Lincoln travelled all over it—first with Judge Treat and then with Judge Davis—twice every year, and was thus absent from Springfield and home nearly, if not quite, six months out of every twelve. "In my opinion," says Judge Davis, "Lincoln was as happy as he could be, on this circuit, and happy in no other place. This was his place of enjoyment. As a general rule, of a Saturday evening, when all the lawyers would go home [the judge means those who were close enough to get there and back by the time their cases were called] and see their families and friends, Lincoln would refuse to go." "It was on this circuit," we are told by an authority equally high, "that he shone as a nisi prius lawyer; it was on this circuit Lincoln thought, spoke, and acted; it was on this circuit that the people met, greeted, and cheered on the man; it was on this circuit that he cracked his jokes, told his stories, made his money, and was happy as nowhere in the world beside." When, in 1857, Sangamon County was cut off from the Eighth Circuit by the act creating the Eighteenth, "Mr. Lincoln would still continue with Judge Davis, first finishing his business in Sangamon."
On his return from one of these long journeys, he found that Mrs. Lincoln had taken advantage of his absence, and, with the connivance and assistance of his neighbor, Gourly, had placed a second story and a new roof on his house. Approaching it for the first time after this rather startling alteration, and pretending not to recognize it, he called to a man on the street, "Stranger, can you tell me where Lincoln lives? He used to live here."
When Mr. Lincoln first began to "ride the circuit," he was too poor to own horseflesh or vehicle, and was compelled to borrow from his friends. But in due time he became the proprietor of a horse, which he fed and groomed himself, and to which he was very much attached. On this animal he would set out from home, to be gone for weeks together, with no baggage but a pair of saddle-bags, containing a change of linen, and an old cotton umbrella, to shelter him from sun or rain. When he got a little more of this world's goods, he set up a one-horse buggy,—a very sorry and shabby-looking affair, which he generally used when the weather promised to be bad. But the lawyers were always glad to see him, and the landlords hailed his coming with pleasure. Yet he was one of those peculiar, gentle, uncomplaining men, whom those servants of the public who keep "hotels" would generally put off with the most indifferent accommodations. It was a very significant remark of a lawyer thoroughly acquainted with his habits and disposition, that "Lincoln was never seated next the landlord at a crowded table, and never got a chicken liver or the best cut from the roast." If rooms were scarce, and one, two, three, or four gentlemen were required to lodge together, in order to accommodate some surly man who "stood upon his rights," Lincoln was sure to be one of the unfortunates. Yet he loved the life, and never went home without reluctance.
From Mr. S. O. Parks of Lincoln, himself a most reputable lawyer, we have two or three anecdotes, which we give in his own language:—
"I have often said, that, for a man who was for the quarter of a century both a lawyer and a politician, he was the most honest man I ever knew. He was not only morally honest, but intellectually so. He could not reason falsely: if he attempted it, he failed. In politics he never would try to mislead. At the bar, when he thought he was wrong, he was the weakest lawyer I ever saw. You know this better than I do. But I will give you an example or two which occurred in this county, and which you may not remember.
"A man was indicted for larceny: Lincoln, Young, and myself defended him. Lincoln was satisfied by the evidence that he was guilty, and ought to be convicted. He called Young and myself aside, and said, 'If you can say any thing for the man, do it. I can't: if I attempt, the jury will see that I think he is guilty, and convict him, of course.' The case was submitted by us to the jury without a word. The jury failed to agree; and before the next term the man died. Lincoln's honesty undoubtedly saved him from the penitentiary.
"In a closely-contested civil suit, Lincoln had proved an account for his client, who was, though he did not know it at the time, a very slippery fellow. The opposing attorney then proved a receipt clearly covering the entire cause of action. By the time he was through, Lincoln was missing. The court sent for him to the hotel. 'Tell the judge,' said he, 'that I can't come: my hands are dirty; and I came over to clean them!'
"In the case of Harris and Jones vs. Buckles, Harris wanted Lincoln to assist you and myself. His answer was characteristic: 'Tell Harris it's no use to waste money on me in that case: he'll get beat.'"
Mr. Lincoln was prone to adventures in which pigs were the other party. The reader has already enjoyed one from the pen of Miss Owen; and here is another, from an incorrigible humorist, a lawyer, named J. H. Wickizer:—
"In 1855 Mr. Lincoln and myself were travelling by buggy from Woodford County Court to Bloomington, 111.; and, in passing through a little grove, we suddenly heard the terrific squealing of a little pig near by us. Quick as thought Mr. Lincoln leaped out of the buggy, seized a club, pounced upon the old sow, and beat her lustily: she was in the act of eating one of her young ones. Thus he saved the pig, and then remarked, 'By jing! the unnatural old brute shall not devour her own progeny!' This, I think, was his first proclamation of freedom."
But Mr. Wickizer gives us another story, which most happily illustrates the readiness of Mr. Lincoln's wit:—
"In 1858, in the court at Bloomington, Mr. Lincoln was engaged in a case of no great importance; but the attorney on the other side, Mr. S———, a young lawyer of fine abilities (now a judge of the Supreme Court of the State), was always very sensitive about being beaten, and in this case manifested unusual zeal and interest. The case lasted until late at night, when it was finally submitted to the jury. Mr. S———spent a sleepless night in anxiety, and early next morning learned, to his great chagrin, that he had lost the case. Mr. Lincoln met him at the Court House, and asked him what had become of his case. With lugubrious countenance and melancholy tone, Mr. S-said, 'It's gone to hell.'—'Oh, well!' replied Lincoln, 'then you'll see it again!'"
Although the humble condition and disreputable character of some of his relations and connections were the subject of constant annoyance and most painful reflections, he never tried to shake them off, and never abandoned them when they needed his assistance. A son of his foster-brother, John Johnston, was arrested in———County for stealing a watch.
Mr. Lincoln went to the same town to address a mass meeting while the poor boy was in jail. He waited until the dusk of the evening, and then, in company with Mr. H. C. Whitney, visited the prison. "Lincoln knew he was guilty," says Mr. Whitney, "and was very deeply affected,—more than I ever saw him. At the next term of the court, upon the State's Attorney's consent, Lincoln and I went to the prosecution witnesses, and got them to come into open court, and state that they did not care to presecute." The boy was released; and that evening, as the lawyers were leaving the town in their buggies, Mr. Lincoln was observed to get down from his, and walk back a short distance to a poor, distressed-looking young man who stood by the roadside. It was young Johnston. Mr. Lincoln engaged for a few moments apparently in earnest and nervous conversation with him, then giving him some money, and returning to his buggy, drove on.
A thousand tales could be told of Mr. Lincoln's amusing tricks and eccentricities on these quiet rides from county to county, in company with judges and lawyers, and of his quaint sayings and curious doings at the courts in these Western villages. But, much against our will, we are compelled to make selections, and present a few only, which rest upon the most undoubted authority.
It is well known that he used to carry with him, on what Mr. Stuart calls "the tramp around the circuit," ordinary school-books,—from Euclid down to an English grammar,—and study them as he rode along, or at intervals of leisure in the towns where he stopped. He supplemented these with a copy of Shakspeare, got much of it by rote, and recited long passages from it to any chance companion by the way.
He was intensely fond of cutting wood with an axe; and he was often seen to jump from his buggy, seize an axe out of the hands of a roadside chopper, take his place on the log in the most approved fashion, and, with his tremendous long strokes, cut it in two before the man could recover from his surprise.
It was this free life that charmed him, and reconciled him to existence. Here he forgot the past, with all its cruelties and mortifications: here were no domestic afflictions to vex his weary spirit and to try his magnanimous heart.
"After he had returned from Congress," says Judge Davis, "and had lost his practice, Goodrich of Chicago proposed to him to open a law-office in Chicago, and go into partnership with him. Goodrich had an extensive practice there. Lincoln refused to accept, and gave as a reason, that he tended to consumption; that, if he went to Chicago, he would have to sit down and study hard, and it would kill him; that he would rather go around the circuit—the Eighth Judicial Circuit—than to sit down and die in Chicago."
In the summer of 1857, at a camp-meeting in Mason County, one Metzgar was most brutally murdered. The affray took place about half a mile from the place of worship, near some wagons loaded with liquors and provisions. Two men, James H. Norris and William D. Armstrong, were indicted for the crime. Norris was tried in Mason County, convicted of manslaughter, and sentenced to the penitentiary for the term of eight years. But Armstrong, the popular feeling being very high against him in Mason, "took a change of venue to Cass County," and was there tried (at Beardstown) in the spring of 1858. Hitherto Armstrong had had the services of two able counsellors, but now their efforts were supplemented by those of a most determined and zealous volunteer.
Armstrong was the son of Jack and Hannah Armstrong of New Salem, the child whom Mr. Lincoln had rocked in the cradle while Mrs. Armstrong attended to other household duties. His life was now in imminent peril: he seemed clearly guilty; and, if he was to be saved, it must be by the interposition of some power which could deface that fatal record in the Norris trial, refute the senses of witnesses, and make a jury forget themselves and their oaths. Old Hannah had one friend whom she devoutly believed could accomplish this. She wrote to Mr. Lincoln, and he replied that he would defend the boy. (She says she has lost his letter.) Afterwards she visited him at Springfield, and prepared him for the event as well as she could, with an understanding weakened by a long strain of severe and almost hopeless reflection.
When the trial came on, Mr. Lincoln appeared for the defence. His colleague, Mr. Walker, had possessed him of the record in the Norris case; and, upon close and anxious examination, he was satisfied that the witnesses could, by a well-sustained and judicious cross-examination, be made to contradict each other in some important particulars. Mr. Walker "handled" the victims of this friendly design, while Mr. Lincoln sat by and suggested questions. Nevertheless, to the unskilled mind, the testimony seemed to be absolutely conclusive against the prisoner, and every word of it fell like a new sentence of death. Norris had beaten the murdered man with a club from behind, while Armstrong had pounded him in the face with a slung-shot deliberately prepared for the occasion; and, according to the medical men, either would have been fatal without the other. But the witness whose testimony bore hardest upon Armstrong swore that the crime was committed about eleven o'clock at night, and that he saw the blows struck by the light of a moon nearly full, and standing in the heavens about where the sun would stand at ten o'clock in the morning. It is easy to pervert and even to destroy evidence like this; and here Mr. Lincoln saw an opportunity which nobody had dreamed of on the Norris trial. He handed to an officer of the court an almanac, and told him to give it back to him when he should call for it in presence of the jury. It was an almanac of the year previous to the murder.
"Mr. Lincoln," says Mr. Walker, "made the closing argument for the defence. At first he spoke slowly, and carefully reviewed the whole testimony,—picked it all to pieces, and showed that the man had not received his wounds at the place or time named by the witnesses, but afterwards, and at the hands of some one else" "The evidence bore heavily upon his client," says Mr. Shaw, one of the counsel for the prosecution. "There were many witnesses, and each one seemed to add one more cord that seemed to bind him down, until Mr. Lincoln was something in the situation of Gulliver after his first sleep in Lilliput. But, when he came to talk to the jury (that was always his forte), he resembled Gulliver again. He skilfully untied here and there a knot, and loosened here and there a peg, until, fairly getting warmed up, he raised himself in his full power, and shook the arguments of his opponents from him as if they were cobwebs." In due time he called for the almanac, and easily proved by it, that, at the time the main witness declared the moon was shining in great splendor, there was, in fact, no moon at all, but black darkness over the whole scene. In the "roar of laughter" and undisguised astonishment succeeding this apparent demonstration, court, jury, and counsel forgot to examine that seemingly conclusive almanac, and let it pass without a question concerning its genuineness.1
In conclusion, Mr. Lincoln drew a touching picture of Jack Armstrong (whose gentle spirit alas! had gone to that place of coronation for the meek), and Hannah,—this sweet-faced old lady with the silver locks,—welcoming to their humble cabin a strange and penniless boy, to whom Jack, with that Christian benevolence which distinguished him through life, became as a father, and the guileless Hannah even more than a mother. The boy, he said, stood before them pleading for the life of his benefactors' son,—the staff of the widow's declining years.
1 Mr. E. J. Loomis, assistant in charge of the "Nautical Almanac" office, Washington, D.C., under date of Aug. 1,1871, says,— "Referring to the 'Nautical Almanac' for 1857, I find, that, between the hours of ten and eleven o'clock on the night of the 29th of August, 1857, the moon was within one hour of setting. "The computed time of its setting on that night is 11 h. 57 m.,—three minutes before midnight. "The moon was only two days past its first quarter, and could hardly be mistaken for 'nearly full.'" "In the case of the People vs. Armstrong, I was assisting prosecuting counsel. The prevailing belief at that time, and I may also say at the present, in Cass County, was as follows:— "Mr. Lincoln, previous to the trial, handed an almanac of the year previous to the murder to an officer of the court, stating that he might call for one during the trial, and, if he did, to send him that one. An important witness for the People had fixed the time of the murder to be in the night, near a camp-meeting; 'that the moon was about in the same place that the sun would be at ten o'clock in the morning, and was nearly full,'therefore he could see plainly, &c. At the proper time, Mr. Lincoln called to the officer for an almanac; and the one prepared for the occasion was shown by Mr. 'Lincoln, he reading from it at the time referred to by the witness 'The moon had already set;' that in the roar of laughter the jury and opposing counsel forgot to look at the date. Mr. Carter, a lawyer of this city (Beardstown), who was present at, but not engaged in, the Armstrong case, says he is satisfied that the almanac was of the year previous, and thinks he examined it at the time. This was the general impression in the court-room. I have called on the sheriff who officiated at that time (James A. Dick), who says that he saw a 'Goudy's Almanac' lying upon Mr. Lincoln's table during the trial, and that Mr. Lincoln took it out of his own pocket. Mr. Dick does not know the date of it. I have seen several of the petit jurymen who sat upon the case, who only recollect that the almanac floored the witness. But one of the jurymen, the foreman, Mr. Milton Logan, says that it was the one for the year of the murder, and no trick about it; that he is willing to make an affidavit that he examined it as to date, and that it was an almanac of the year of the murder. My own opinion is, that when an almanac was called for by Mr. Lincoln, two were brought, one of the year of the murder, and one of the year previous; that Mr. Lincoln was entirely innocent of any deception in the matter. I the more think this, from the fact that Armstrong was not cleared by any want of testimony against him, but by the irresistible appeal of Mr. Lincoln in his favor."—Henry Shaw.
"The last fifteen minutes of his speech," his colleague declares, "was as eloquent as I ever heard; and such the power and earnestness with which he spoke to that jury, that all sat as if entranced, and, when he was through, found relief in a gush of tears." "He took the jury by storm," says one of the prosecutors. "There were tears in Mr. Lincoln's eyes while he spoke, but they were genuine. His sympathies were fully enlisted in favor of the young man, and his terrible sincerity could not help but arouse the same passion in the jury. I have said a hundred times that it was Lincoln's speech that saved that criminal from the gallows." In the language of Hannah, who sat by enchanted, "he told the stories about our first acquaintance,—what I did for him, and how I did it;" and she thinks it "was truly eloquent."
"As to the trial," continues Hannah, "Lincoln said to me, 'Hannah, your son will be cleared before sundown.' He and the other lawyers addressed the jury, and closed the case. I went down at Thompson's pasture: Stator came to me, and told me soon that my son was cleared and a free man. I went up to the Court House: the jury shook hands with me, so did the Court, so did Lincoln. We were all affected, and tears, streamed down Lincoln's eyes. He then remarked to me, 'Hannah, what did I tell you? I pray to God that William may be a good boy hereafter; that this lesson may prove in the end a good lesson to him and to all.'... After the trial was over, Lincoln came down to where I was in Beardstown. I asked him what he charged me; told him I was poor. He said, 'Why, Hannah, I sha'n't charge you a cent,—never. Any thing I can do for you I will do for you willing and freely without charges.' He wrote to me about some land which some men were trying to get from me, and said, 'Hannah, they can't get your land. Let them try it in the Circuit Court, and then you appeal it; bring it to Supreme Court, and I and Herndon will attend to it for nothing.'"
This boy William enlisted in the Union army. But in 1863 Hannah concluded she "wanted" him. She does not say that William was laboring under any disability, or that he had any legal right to his discharge. She merely "wanted" him, and wrote Mr. Lincoln to that effect. He replied promptly by telegraph:—
September, 1863.
Mrs. Hannah Armstrong,—I have just ordered the discharge of your boy William, as you say, now at Louisville, Ky.
A. Lincoln.
For many years Mr. Lincoln was the attorney of the Illinois Central Railway Company; and, having rendered in some recent causes most important and laborious services, he presented a bill in 1857 for five thousand dollars. He pressed for his money, and was referred to some under-official who was charged with that class of business. Mr. Lincoln would probably have modified his bill, which seemed exorbitant as charges went among country lawyers, but the company treated him with such rude insolence, that he contented himself with a formal demand, and then immediately instituted suit on the claim. The case was tried at Bloomington before Judge Davis; and, upon affidavits of N. B. Judd, O. H.
Browning, S. T. Logan, and Archy Williams, respecting the value of the services, was decided in favor of the plaintiff, and judgment given for five thousand dollars. This was much more money than Mr. Lincoln had ever had at one time.
In the summer of 1859 Mr. Lincoln went to Cincinnati to argue the celebrated McCormick reaping-machine case. Mr. Edwin M. Stanton, whom he never saw before, was one of his colleagues, and the leading counsel in the case; and although the other gentlemen engaged received him with proper respect, Mr. Stanton treated him with such marked and habitual discourtesy, that he was compelled to withdraw from the case. When he reached home he said that he had "never been so brutally treated as by that man Stanton;" and the facts justified the statement.
WE have seen already, from one of his letters to Mr. Herndon, that Mr. Lincoln was personally quite willing to be a candidate for Congress the second time. But his "honor" forbade: he had given pledges, and made private arrangements with other gentlemen, to prevent "the district from going to the enemy." Judge Logan was nominated in his place; and, although personally one of the most popular men in Illinois, he was sadly beaten, in consequence of the record which the Whig party had made "against the war." It was well as it was; for, if Mr. Lincoln had been the candidate, he would have been still more disastrously defeated, since it was mainly the votes he had given in Congress which Judge Logan found it so difficult to explain and impossible to defend.

Mr. Lincoln was an applicant, and a very urgent one, for the office of Commissioner of the General Land-Office in the new Whig administration. He moved his friends to urge him in the newspapers, and wrote to some of his late associates in Congress (among them Mr. Schenck of Ohio), soliciting their support. But it was all of no avail; Mr. Justin Butterfield (also an Illinoisian) beat him in the race to Washington, and got the appointment. It is said by one of Mr. Lincoln's numerous biographers, that he often laughed over his failure to secure this great office, pretending to think it beneath his merits; but we can find no evidence of the fact alleged, and have no reason to believe it.
Mr. Fillmore subsequently offered him the governorship of Oregon. The news reached him whilst away at court at Tremont or Bloomington. Mr. Stuart and others "coaxed him to take it;" the former insisting that Oregon would soon become a State, and he one of its senators. Mr. Lincoln saw it all, and said he would accept "if his wife would consent." But his wife "refused to do so;" and time has shown that she was right, as she usually was when it came to a question of practical politics.
From the time of his retirement from Congress to 1854, when the repeal of the Missouri Compromise and the Kansas-Nebraska Bill broke the hollow truce of 1856, which Mr. Clay and his compeers fondly regarded as a peace, Mr. Lincoln's life was one of comparative political inactivity. He did not believe that the sectional agitations could be permanently stilled by the devices which then seemed effectual to the foremost statesmen of either party and of both sections. But he was not disposed to be forward in the renewal of them. He probably hoped against conviction that time would allay the animosities which endangered at once the Union and the principles of free government, which had thus far preserved a precarious existence among the North American States.
Coming home to Springfield from the Tremont court in 1850 in company with Mr. Stuart, he said, "The time will come when we must all be Democrats or Abolitionists. When that time comes, my mind is made up. The 'slavery question' can't be compromised."—"So is my mind made up," replied his equally firm companion; and at that moment neither doubted on which side he would find the other when the great struggle took place.
The Whig party everywhere, in Congress and in their conventions, local and national, accepted the compromise of 1850 under the leadership of Mr. Clay and Mr. Webster. Mr. Lincoln did the same; for, from the hour that party lines were distinctly and closely drawn in his State, he was an unswerving party man. But although he said nothing against those measures, and much in favor of them, it is clear that he accepted the result with reluctance. He spoke out his disapproval of the Fugitive Slave Law as it was passed, believing and declaring wherever he went, that a negro man apprehended as a slave should have the privilege of a trial by jury, instead of the summary processes provided by the law.
"Mr. Lincoln and I were going to Petersburg in 1850, I think," says Mr. Herndon. "The political world was dead: the compromises of 1850 seemed to settle the negro's fate. Things were stagnant; and all hope for progress in the line of freedom seemed to be crushed out. Lincoln was speculating with me about the deadness of things, and the despair which arose out of it, and deeply regretting that his human strength and power were limited by his nature to rouse and stir up the world. He said gloomily, despairingly, sadly, 'How hard, oh! how hard it is to die and leave one's country no better than if one had never lived for it! The world is dead to hope, deaf to its own death-struggle, made known by a universal cry, What is to be done? Is any thing to be done? Who can do any thing? and how is it to be done? Did you ever think of these things?'"
In 1850 Mr. Lincoln again declined to be a candidate for Congress; and a newspaper called "The Tazewell Mirror" persisting in naming him for the place, he published a letter, refusing most emphatically to be considered a candidate. The concluding sentence alleged that there were many men among the Whigs of the district who would be as likely as he to bring "the district right side up."
Until the death of his excellent step-mother, Sarah Bush Lincoln, Mr. Lincoln never considered himself free for a moment from the obligation to look after and care for her family. She had made herself his mother; and he regarded her and her children as near relatives,—much nearer than any of the Hankses.
The limit of Thomas Lincoln's life was rapidly approaching. Mrs. Chapman, his step-daughter, wrote Mr. Lincoln to that effect; and so did John Johnston. He began to fear that the straitened circumstances of the household might make them think twice before they sent for a doctor, or procured other comforts for the poor old man, which he needed, perhaps, more than drugs. He was too busy to visit the dying man, but sent him a kind message, and directed the family to get whatever was wanted upon his credit.
Springfield, Jan. 12,1851.
Dear Brother,—On the day before yesterday I received a letter from Harriet, written at Greenup. She says she has just returned from your house, and that father is very low, and will hardly recover. She also says that you have written me two letters, and that, although you do not expect me to come now, you wonder that I do not write. I received both your letters; and, although I have not answered them, it is not because I have forgotten them, or not been interested about them, but because it appeared to me I could write nothing which could do any good. You already know I desire that neither father nor mother shall be in want of any comfort, either in health or sickness, while they live; and I feel sure you have not failed to use my name, if necessary, to procure a doctor or any thing else for father in his present sickness. My business is such that I could hardly leave home now, if it were not, as it is, that my own wife is sick a-bed. (It is a case of baby sickness, and, I suppose, is not dangerous.) I sincerely hope father may yet recover his health; but, at all events, tell him to remember to call upon and confide in our great and good and merciful Maker, who will not turn away from him in any extremity. He notes the fall of a sparrow, and numbers the hairs of our heads; and he will not forget the dying man who puts his trust in him. Say to him, that, if we could meet now, it is doubtful whether it would not be more painful than pleasant; but that, if it be his lot to go now, he will soon have a joyous meeting with loved ones gone before, and where the rest of us, through the help of God, hope ere long to join them.
Write me again when you receive this.
Affectionately,
A. Lincoln.
Before and after the death of Thomas Lincoln, John Johnston and Mr. Lincoln had a somewhat spirited correspondence regarding John's present necessities and future plans. John was idle, thriftless, penniless, and as much disposed to rove as poor old Tom had been in his earliest and worst days. This lack of character and enterprise on John's part added seriously to Mr. Lincoln's anxieties concerning his step-mother, and greatly embarrassed his attempts to provide for her. At length he wrote John the following energetic exhortation, coupled with a most magnanimous pecuniary offer. It is the letter promised in a previous chapter, and makes John an intimate acquaintance of the reader:—
Dear Johnston,—Your request for eighty dollars, I do not think it best to comply with now. At the various times when I have helped you a little, you have said to me, "We can get along very well now;" but in a very short time I find you in the same difficulty again. Now, this can only happen by some defect in your conduct. What that defect is, I think I know. You are not lazy, and still you are an idler. I doubt whether, since I saw you, you have done a good whole day's work in any one day. You do not very much dislike to work, and still you do not work much, merely because it does not seem to you that you could get much for it. This habit of uselessly wasting time is the whole difficulty; and it is vastly important to you, and still more so to your children, that you should break the habit. It is more important to them, because they have longer to live, and can keep out of an idle habit before they are in it easier than they can get out after they are in.
You are now in need of some money; and what I propose is, that you shall go to work, "tooth and nail," for somebody who will give you money for it. Let father and your boys take charge of things at home, prepare for a crop, and make the crop, and you go to work for the best money-wages, or in discharge of any debt you owe, that you can get; and, to secure you a fair reward for your labor, I now promise you, that, for every dollar you will, between this and the first of next May, get for your own labor, either in money or as your own indebtedness, I will then give you one other dollar. By this, if you hire yourself at ten dollars a month, from me you will get ten more, making twenty dollars a month for your work. In this I do not mean you shall go off to St. Louis, or the lead-mines, or the gold-mines in California; but I mean for you to go at it for the best wages you can get close to home, in Cole's County. Now, if you will do this, you will be soon out of debt, and, what is better, you will have a habit that will keep you from getting in debt again. But, if I should now clear you out of debt, next year you would be just as deep in as ever. You say you would almost give your place in heaven for $70 or $80. Then you value your place in heaven very cheap; for I am sure you can, with the offer I make, get the seventy or eighty dollars for four or five months' work. You say, if I will furnish you the money, you will deed me the land, and, if you don't pay the money back, you will deliver possession. Nonsense! If you can't now live with the land, how will you then live without it? You have always been kind to me, and I do not mean to be unkind to you. On the contrary, if you will but follow my advice, you will find it worth more than eighty times eighty dollars to you.
Affectionately your brother,
A. Lincoln
Again he wrote:—
Shelbyville, Nov. 4, 1851.
Dear Brother,—When I came into Charleston day before yesterday, I learned that you are anxious to sell the land where you live, and move to Missouri. I have been thinking of this ever since, and cannot but think such a notion is utterly foolish. What can you do in Missouri better than here? Is the land any richer? Can you there, any more than here, raise corn and wheat and oats without work? Will anybody there, any more than here, do your work for you? If you intend to go to work, there is no better place than right where you are: if you do not intend to go to work, you cannot get along anywhere. Squirming and crawling about from place to place can do no good. You have raised no crop this year; and what you really want is to sell the land, get the money, and spend it. Part with the land you have, and, my life upon it, you will never after own a spot big enough to bury you in. Half you will get for the land you will spend in moving to Missouri, and the other half you will eat and drink and wear out, and no foot of land will be bought. Now, I feel it is my duty to have no hand in such a piece of foolery. I feel that it is so even on your own account, and particularly on mother's account. The eastern forty acres I intend to keep for mother while she lives: if you will not cultivate it, it will rent for enough to support her; at least, it will rent for something. Her dower in the other two forties she can let you have, and no thanks to me. Now, do not misunderstand this letter: I do not write it in any unkindness. I write it in order, if possible, to get you to face the truth, which truth is, you are destitute because you have idled away all your time. Your thousand pretences for not getting along better are all nonsense: they deceive nobody but yourself. Go to work is the only cure for your case.
A word to mother. Chapman tells me he wants you to go and live with him. If I were you, I would try it a while. If you get tired of it (as I think you will not), you can return to your own home. Chapman feels very kindly to you; and I have no doubt he will make your situation very pleasant.
Sincerely your son,
A. Lincoln.
And again:—
Shelbyville, Nov. 9,1851.
Dear Brother,—When I wrote you before, I had not received your letter. I still think as I did; but if the land can be sold so that I get three hundred dollars to put to interest for mother, I will not object, if she does not. But, before I will make a deed, the money must be had, or secured beyond all doubt, at ten per cent.
As to Abram, I do not want him, on my own account; but I understand he wants to live with me, so that he can go to school, and get a fair start in the world, which I very much wish him to have. When I reach home, if I can make it convenient to take, I will take him, provided there is no mistake between us as to the object and terms of my taking him.
In haste as ever,
A. Lincoln.
On the 1st of July, 1852, Mr. Lincoln was chosen by a public meeting of his fellow-citizens at Springfield to deliver in their hearing a eulogy upon the life and character of Henry Clay; and on the 16th of the same month he complied with their request. Such addresses are usually called orations; but this one scarcely deserved the name. He made no effort to be eloquent, and in no part of it was he more than ordinarily animated. It is true that he bestowed great praise upon Mr. Clay; but it was bestowed in cold phrases and a tame style, wholly unlike the bulk of his previous compositions. In truth, Mr. Lincoln was never so devoted a follower of Mr. Clay as some of his biographers have represented him. He was for another man in 1836, most probably for another in 1840, and very ardently for another in 1848. Dr. Holland credits him with a visit to Mr. Clay at Ashland, and an interview which effectually cooled his ardor in behalf of the brilliant statesman. But, in fact, Mr. Lincoln never troubled himself to make such a pilgrimage to see or hear any man,—much less Mr. Clay. None of his friends—Judge Davis, Mr. Herndon, Mr. Speed, or any one else, so far as we are able to ascertain—ever heard of the visit. If it had been made at any time after 1838, it could scarcely have been concealed from Mr. Speed; and we are compelled to place it along with the multitude of groundless stories which have found currency with Mr. Lincoln's biographers.
If the address upon Clay is of any historical value at all, it is because it discloses Mr. Lincoln's unreserved agreement with Mr. Clay in his opinions concerning slavery and the proper method of extinguishing it. They both favored gradual emancipation by the voluntary action of the people of the Slave States, and the transportation of the whole negro population to Africa as rapidly as they should be freed from service to their masters: it was a favorite scheme with Mr. Lincoln then, as it was long after he became President of the United States. "Compensated" and "voluntary emancipation," on the one hand, and "colonization" of the freedmen on the other, were essential parts of every "plan" which sprung out of his own individual mind. On this occasion, after quoting Mr. Clay, he said, "This suggestion of the possible ultimate redemption of the African race and African continent was made twenty-five years ago. Every succeeding year has added strength to the hope of its realization. May it indeed be realized! Pharaoh's country was cursed with plagues, and his hosts were drowned in the Red Sea, for striving to retain a captive people who had already served them more than four hundred years. May like disasters never befall us! If, as the friends of colonization hope, the present and coming generations of our countrymen shall by any means succeed in freeing our land from the dangerous presence of slavery, and at the same time restoring a captive people to their long-lost fatherland, with bright prospects for the future, and this, too, so gradually that neither races nor individuals shall have suffered by the change, it will indeed be a glorious consummation. And if to such a consummation the efforts of Mr. Clay shall have contributed, it will be what he most ardently wished; and none of his labors will have been more valuable to his country and his kind."
During the campaign of 1852, Judge Douglas took the stump for Pierce "in twenty-eight States out of the thirty-one." His first speech was at Richmond, Va. It was published extensively throughout the Union, and especially in Illinois. Mr. Lincoln felt an ardent desire to answer it, and, according to his own account, got the "permission" of the "Scott Club" of Springfield to make the speech under its auspices. It was a very poor effort. If it was distinguished by one quality above another, it was by its attempts at humor; and all those attempts were strained and affected, as well as very coarse. He displayed a jealous and petulant temper from the first sentence to the last, wholly beneath the dignity of the occasion and the importance of the topic. Considered as a whole, it may be said that none of his public performances was more unworthy of its really noble author than this one. The reader has doubtless observed in the course of this narrative, as he will in the future, that Mr. Douglas's great success in obtaining place and distinction was a standing offence to Mr. Lincoln's self-love and individual ambition. He was intensely jealous of him, and longed to pull him down, or outstrip him in the race for popular favor, which they united in considering "the chief end of man." Some of the first sentences of this speech before the "Scott Club" betray this feeling in a most unmistakable and painful manner. "This speech [that of Mr. Douglas at Richmond] has been published with high commendations in at least one of the Democratic papers in this State, and I suppose it has been and will be in most of the others. When I first saw it and read it, I was reminded of old times, when Judge Douglas was not so much greater man than all the rest of us, as he is now,—of the Harrison campaign twelve years ago, when I used to hear and try to answer many of his speeches; and believing that the Richmond speech, though marked with the same species of 'shirks and quirks' as the old ones, was not marked with any greater ability, I was seized with a strange inclination to attempt an answer to it; and this inclination it was that prompted me to seek the privilege of addressing you on this occasion."
In the progress of his remarks, Mr. Lincoln emphatically indorsed Mr. Douglas's great speech at Chicago in 1850, in defence of the compromise measures, which Mr. Lincoln pronounced the work of no party, but which, "for praise or blame," belonged to Whigs and Democrats alike. The rest of the address was devoted to a humorous critique upon Mr. Douglas's language in the Richmond speech, to ridicule of the campaign biographies of Pierce, to a description of Gens. Shields and Pierce wallowing in the ditch in the midst of a battle, and to a most remarkable account of a militia muster which might have been seen at Springfield a few years previous. Mr. Douglas had expressed great confidence in the sober judgment of the people, and at the same time had, rather inconsistently as well as indecently, declared that Providence had saved us from one military administration by the timely removal of Gen. Taylor. To this Mr. Lincoln alluded in his closing paragraph, which is given as a fair sample of the whole:—
"Let us stand by our candidate as faithfully as he has always stood by our country, and I much doubt if we do not perceive a slight abatement in Judge Douglas's confidence in Providence, as well as in the people. I suspect that confidence is not more firmly fixed with the judge than it was with the old woman whose horse ran away with her in a buggy. She said she 'trusted in Providence till the britchin' broke, and then she didn't know what on airth to do.' The chance is, the judge will see the 'britchin' broke;' and then he can at his leisure bewail the fate of Locofocoism as the victim of misplaced confidence."
On the 4th of January, 1854, Mr. Douglas, Chairman of the Committee on Territories, of the Senate of the United States, reported a bill to establish a territorial government in Nebraska. This bill contained nothing in relation to the Missouri Compromise, which still remained upon the statute-book, although the principle on which it was based had been violated in the Compromise legislation of 1850. A Whig Senator from Kentucky gave notice, that, when the Committee's bill came before the Senate, he would move an amendment repealing the Missouri Compromise. With this admonition in mind, the Committee instructed Mr. Douglas to report a substitute, which he did on the 23d of the same month. The substitute made two Territories out of Nebraska, and called one of them Kansas. It annulled the Missouri Compromise, forbade its application to Kansas, Nebraska, or any other territory, and, as amended and finally passed, fixed the following rules:... "It being the true intent and meaning of this act not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State, nor to exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States." Mr. Douglas had long since denounced his imprecations upon "the ruthless hand" that should disturb that ancient compact of peace between the sections; and now he put forth his own ingenious hand to do the deed, and to take the curse, in both of which he was eminently successful. Not that the Missouri Act may not have been repugnant to the Constitution, for no court had ever passed upon it; but it was enacted for a holy purpose, was venerable in age, was consecrated in the hearts of the people by the unsurpassed eloquence of the patriots of a previous generation, and having the authority of law, of reason, and of covenant, it had till then preserved the Union, as its authors designed it should; and, being in truth a sacred thing, it was not a proper subject for the "ruthless" interference of mere politicians, like those who now devoted it to destruction. If, upon a regularly heard and decided issue, the Supreme Court should declare it unconstitutional, the recision of the compact could be attributed to no party,—neither to slavery nor to antislavery,—and the peace of the country might still subsist. But its repeal by the party that did it—a coalition of Southern Whigs and Democrats with Northern Democrats—was evidence of a design to carry slavery into the region north of 36° 30'; or the legislation was without a purpose at all. It was the first aggression of the South; but be it remembered in common justice, that she was tempted to it by the treacherous proffers of a restless but powerful Northern leader, who asked no recompense but her electoral votes. In due time he opened her eyes to the nature of the fraud; and, if he carried through the Kansas-Nebraska Act to catch the votes of the South in 1856, it cost him no inconvenience to give it a false and startling construction to catch the votes of the North in 1860. In the repeal of the Compromise, the Northern Democrats submitted with reluctance to the dictation of Douglas and the South. It was the great error of the party,—the one disastrous error of all its history. The party succeeded in 1856 only by the nomination of Mr. Buchanan, who was out of the country when the Kansas-Nebraska Act was passed, and who was known to have opposed it. But the questions which grew out of it, the false and disingenuous construction of the act by its author, the slavery agitations in Kansas and throughout the country, disrupted the party at Charleston, and made possible Mr. Lincoln's election by a minority of the votes cast. And to the Whig party, whose Senators and Representatives from the South voted for the Douglas Bill in a body, the renewal of the slavery agitation, invited and insured by their action, was the signal of actual dissolution.
Up to this date, Mr. Lincoln's views of slavery, and how they were formed, are as well known to the reader as they can be made known from the materials left behind for a history of them. It is clear that his feelings on the subject were inspired by individual cases of apparent hardship which had come under his observation. John Hanks, on the last trip to New Orleans, was struck by Lincoln's peculiarly active sympathy for the servile race, and insists, that, upon sight of their wrongs, "the iron entered his heart." In a letter to Mr. Speed, which will shortly be presented, Mr. Lincoln confesses to a similar experience in 1841, and speaks with great bitterness of the pain which the actual presence of chained and manacled slaves had given him. Indeed, Mr. Lincoln was not an ardent sympathizer with sufferings of any sort, which he did not witness with the eye of flesh. His compassion might be stirred deeply by an object present, but never by an object absent and unseen. In the former case he would most likely extend relief, with little inquiry into the merits of the case, because, as he expressed it himself, it "took a pain out of his own heart;" and he devoutly believed that every such act of charity or mercy sprung from motives purely selfish. None of his public acts, either before or after he became President, exhibits any special tenderness for the African race, or any extraordinary commiseration of their lot. On the contrary, he invariably, in words and deeds, postponed the interests of the blacks to the interests of the whites, and expressly subordinated the one to the other. When he was compelled, by what he deemed an overruling necessity, founded on both military and political considerations, to declare the freedom of the public enemy's slaves, he did so with avowed reluctance, and took pains to have it understood that his resolution was in no wise affected by sentiment. He never at any time favored the admission of negroes into the body of electors, in his own State or in the States of the South. He claimed that those who were incidentally liberated by the Federal arms were poor-spirited, lazy, and slothful; that they could be made soldiers only by force, and willing laborers not at all; that they seemed to have no interest in the cause of their own race, but were as docile in the service of the Rebellion as the mules that ploughed the fields or drew the baggage-trains; and, as a people, were useful only to those who were at the same time their masters and the foes of those who sought their good. With such views honestly formed, it is no wonder that he longed to see them transported to Hayti, Central America, Africa, or anywhere, so that they might in no event, and in no way, participate in the government of his country. Accordingly, he was, from the beginning, as earnest a colonizationist as Mr. Clay, and, even during his Presidency, zealously and persistently devised schemes for the deportation of the negroes, which the latter deemed cruel and atrocious in the extreme. He believed, with his rival, that this was purely a "white man's government;" but he would have been perfectly willing to share its blessings with the black man, had he not been very certain that the blessings would disappear when divided with such a partner. He was no Abolitionist in the popular sense; did not want to break over the safeguards of the Constitution to interfere with slavery where it had a lawful existence; but, wherever his power rightfully extended, he was anxious that the negro should be protected, just as women and children and unnaturalized men are protected, in life, limb, property, reputation, and every thing that nature or law makes sacred. But this was all: he had no notion of extending to the negro the privilege of governing him and other white men, by making him an elector. That was a political trust, an office to be exercised only by the superior race.
It was therefore as a white man, and in the interests of white men, that he threw himself into the struggle to keep the blacks out of the Territories. He did not want them there either as slaves or freemen; but he wanted them less as slaves than as freemen. He perceived clearly enough the motives of the South in repealing the Missouri Compromise. It did, in fact, arouse him "like a fire-bell in the night." He felt that a great conflict impended; and, although he had as yet no idea that it was an "irrepressible conflict between opposing and enduring forces," which must end in making all free or all slave, he thought it was serious enough to demand his entire mind and heart; and he freely gave them both.
Mr. Gillespie gives the substance of a conversation with him, which, judging from the context, must have taken place about this time. Prefacing with the remark that the slavery question was the only one "on which he (Mr. Lincoln) would become excited," he says,—
"I recollect meeting with him once at Shelbyville, when he remarked that something must be done, or slavery would overrun the whole country. He said there were about six hundred thousand non-slaveholding whites in Kentucky to about thirty-three thousand slaveholders; that, in the convention then recently held, it was expected that the delegates would represent these classes about in proportion to their respective numbers; but, when the convention assembled, there was not a single representative of the non-slaveholding class: every one was in the interest of the slaveholders; 'and,' said he, 'the thing is spreading like wildfire over the country. In a few years we will be ready to accept the institution in Illinois, and the whole country will adopt it.' I asked him to what he attributed the change that was going on in public opinion. He said he had put that question to a Kentuckian shortly before, who answered by saying, 'You might have any amount of land, money in your pocket, or bank-stock, and, while travelling around, nobody would be any wiser; but, if you had a darkey trudging at your heels, everybody would see him, and know that you owned a slave.' 'It is the most glittering, ostentatious, and displaying property in the world; and now,' says he, 'if a young man goes courting, the only inquiry is, how many negroes he or she owns. The love for slave property was swallowing up every other mercenary possession. Its ownership betokened, not only the possession of wealth, but indicated the gentleman of leisure, who was above and scorned labor.' These things Mr. Lincoln regarded as highly seductive to the thoughtless and giddy-headed young men who looked upon work as vulgar and ungentlemanly. Mr. Lincoln was really excited, and said, with great earnestness, that this spirit ought to be met, and, if possible, checked; that slavery was a great and crying injustice, an enormous national crime, and that we could not expect to escape punishment for it. I asked him how he would proceed in his efforts to check the spread of slavery. He confessed he did not see his way clearly. I think he made up his mind from that time that he would oppose slavery actively. I know that Mr. Lincoln always contended that no man had any right other than mere brute force gave him to a slave. He used to say that it was singular that the courts would hold that a man never lost his right to his property that had been stolen from him, but that he instantly lost his right to himself if he was stolen. Mr. Lincoln always contended that the cheapest way of getting rid of slavery was for the nation to buy the slaves, and set them free."
If the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill awakened Lincoln from his dream of security regarding the slavery question, which he hoped had been put to rest by the compromises of 1820 and 1850, it did the same with all likeminded people in the North. From that moment the Abolitionists, on the one hand, discerned a hope, not only of restricting slavery, but of ultimate emancipation; and the Southern Disunionists, on the other, who had lately met with numerous and signal defeats in their own section, perceived the means of inflaming the popular heart to the point of disunion. A series of agitations immediately began,—incessant, acrimonious, and in Kansas murderous and bloody,—which destroyed the Whig party at once, and continued until they severed the Democratic party at Charleston. All other issues were as chaff to this,—slavery or no slavery in the Territories,—while the discussion ranged far back of this practical question, and involved the much broader one, whether slavery possessed inherent rights under the Constitution. The Whigs South having voted for the repeal of the compromise, and the Whigs North against it, that party was practically no more. Some of its members went into the Know-Nothing lodges; some enlisted under the Abolition flag, and others drifted about and together until they formed themselves into a new organization, which they called Republican. It was a disbanded army; and, released from the authority of discipline and party tradition, a great part of the members engaged for a while in political operations of a very disreputable character. But the better class, having kept themselves unspotted from the pollution of Know-Nothingism, gradually but speedily formed the Republican party, which in due time drew into its mighty ranks nearly all the elements of opposition to the Democracy. Such a Whig was Mr. Lincoln, who lost no time in taking his ground. In Illinois the new party was not (in 1854) either Abolitionist, Republican, Know-Nothing, Whig, or Democratic, for it was composed of odds and ends of all; but simply the Anti-Nebraska party, of which Mr. Lincoln soon became the acknowledged leader.
Returning from Washington, Mr. Douglas attempted to speak at Chicago; but he was not heard, and, being hissed and hooted by the populace of the city, betook himself to more complaisant audiences in the country. Early in October, the State Fair being in progress there, he spoke at Springfield. His speech was ingenious, and, on the whole, able: but he was on the defensive; and the consciousness of the fact, both on his own part and that of the audience, made him seem weaker than he really was. By common consent the Anti-Nebraska men put up Mr. Lincoln to reply; and he did reply with such power as he had never exhibited before. He was not the Lincoln who had spoken that tame address over Clay in 1852, or he who had deformed his speech before the "Scott Club" with petty jealousies and gross vulgarisms, but a new and greater Lincoln, the like of whom no one in that vast multitude had ever heard before. He felt that he was addressing the people on a living and vital question, not merely for the sake of speaking, but to produce conviction, and achieve a great practical result. How he succeeded in his object may be gathered from the following extracts from a leading editorial in "The Springfield Journal," written by Mr. Herndon:—
"This Anti-Nebraska speech of Mr. Lincoln was the profoundest, in our opinion, that he has made in his whole life. He felt upon his soul the truths burn which he uttered, and all present felt that he was true to his own soul. His feelings once or twice swelled within, and came near stifling utterance.... He quivered with emotion. The whole house was as still as death.
"He attacked the Nebraska Bill with unusual warmth and energy; and all felt that a man of strength was its enemy, and that he intended to blast it if he could by strong and manly efforts. He was most successful, and the house approved the glorious triumph of truth by loud and continued huzzas. Women waved their white handkerchiefs in token of woman's silent but heartfelt assent. Douglas felt the sting: the animal within was roused, because he frequently interrupted Mr. Lincoln. His friends felt that he was crushed by Lincoln's powerful argument, manly logic, and illustrations from nature around us. The Nebraska Bill was shivered, and, like a tree of the forest, was torn and rent asunder by hot bolts of truth.... Mr. Lincoln exhibited Douglas in all the attitudes he could be placed in a friendly debate. He exhibited the bill in all its aspects to show its humbuggery and falsehood; and, when thus torn to rags, cut into slips, held up to the gaze of the vast crowd, a kind of scorn and mockery was visible upon the face of the crowd and upon the lips of the most eloquent speaker.... At the conclusion of this speech, every man, woman, and child felt that it was unanswerable.... He took the heart captive, and broke like a sun over the understanding."
Mr. Douglas rose to reply. He was excited, angry, imperious in his tone and manner, and his voice loud and shrill. Shaking his forefinger at the Democratic malcontents with furious energy, and declaiming rather than debating, he occupied to little purpose the brief interval remaining until the adjournment for supper. Then, promising to resume his address in the evening, he went his way; and that audience "saw him no more." Evening came, but not the orator. Many fine speeches were made during the continuance of that fair upon the one absorbing topic,—speeches by the ablest men in Illinois,—Judge Trumbull, Judge Breese, Col. Taylor (Democratic recusants), and Stephen A. Douglas and John Calhoun (then Surveyor-General of Nebraska). But it is no shame to any one of these, that their really impressive speeches were but slightly appreciated, nor long remembered, beside Mr. Lincoln's splendid and enduring performance,—enduring in the memory of his auditors, although preserved upon no written or printed page.
Among those whom the State Fair brought to Springfield for political purposes, were some who were neither Whigs, Democrats, Know-Nothings, nor yet mere Anti-Nebraska men: there were the restless leaders of the then insignificant Abolition faction. Chief among them was Owen Lovejoy; and second to him, if second to any, was William H. Herndon. But the position of this latter gentleman was one of singular embarrassment. According to himself, he was an Abolitionist "sometime before he was born," and hitherto he had made his "calling and election sure" by every word and act of a life devoted to political philanthropy and disinterested political labors. While the two great national parties divided the suffrages of the people, North and South, every thing in his eyes was "dead." He detested the bargains by which those parties were in the habit of composing sectional troubles, and sacrificing the "principle of freedom." When the Whig party "paid its breath to time," he looked upon its last agonies as but another instance of divine retribution. He had no patience with time-servers, and regarded with indignant contempt the "policy" which would postpone the natural rights of an enslaved race to the success of parties and politicians. He stood by at the sacrifice of the Whig party in Illinois with the spirit of Paul when he "held the clothes of them that stoned Stephen." He believed it was for the best, and hoped to see a new party rise in its place, great in the fervor of its faith, and animated by the spirit of Wilberforce, Garrison, and the Lovejoys. He was a fierce zealot, and gloried proudly in his title of "fanatic;" for it was his conviction that fanatics were at all times the salt of the earth, with power to save it from the blight that follows the wickedness of men. He believed in a God, but it was the God of nature,—the God of Socrates and Plato, as well as the God of Jacob. He believed in a Bible, but it was the open scroll of the universe; and in a religion clear and well defined, but it was a religion that scorned what he deemed the narrow slavery of verbal inspiration. Hot-blooded, impulsive, brave morally and physically, careless of consequences when moved by a sense of individual duty, he was the very man to receive into his inmost heart the precepts of Mr. Seward's "higher law." If he had pledged faith to slavery, no peril of life or body could have induced him to violate it. But he held himself no party to the compromises of the Constitution, nor to any law which recognized the justice of human bondage; and he was therefore free to act as his God and nature prompted.
Now, Mr. Herndon had determined to make an Abolitionist out of Mr. Lincoln when the proper time should arrive; and that time would be only when Mr. Lincoln could change front and "come out" without detriment to his personal aspirations. For, although Mr. Herndon was a zealot in the cause, he loved his partner too dearly to wish him to espouse it while it was unpopular and politically dangerous to belong to it. "I cared nothing for the ruin of myself," said he; "but I did not wish to see Mr. Lincoln sacrificed." He looked forward to a better day, and, in the mean time, was quite willing that Mr. Lincoln should be no more than a nominal Whig, or a strong Anti-Nebraska man; being quite sure, that, when the auspicious moment arrived, he would be able to present him to his brethren as a convert over whom there would surely be great joy. Still, there was a bare chance that he might lose him. Mr. Lincoln was beset by warm friends and by old coadjutors, and besought to pause in his antislavery course while there was yet time. Among these there was none more earnest or persuasive than John T. Stuart, who was but the type of a class. Tempted on the one side to be a Know-Nothing, and on the other side to be an Abolitionist, Mr. Lincoln said, as if in some doubt of his real position, "I think I am still a Whig." But Mr. Herndon was more than a match for the full array against him. An earnest man, instant in season and out of season, he spoke with the eloquence of apparent truth and of real personal love. Moreover, Mr. Lincoln's preconceptions inclined him to the way in which Mr. Herndon desired him to walk; and it is not surprising that in time he was, not only almost, but altogether, persuaded by a friend and partner, whose opportunities to reach and convince his wavering mind were, daily and countless. "From 1854 to 1860," says Mr. Herndon, "I kept putting in Lincoln's hands the speeches and sermons of Theodore Parker, the speeches of Phillips and Beecher. I took 'The Anti-slavery Standard' for years before 1856, 'The Chicago Tribune,' and 'The New York Tribune;' kept them in my office, kept them purposely on my table, and would read to Lincoln good, sharp, and solid things well put. Lincoln was a natural antislavery man, as I think, and yet he needed watching,—needed hope, faith, energy; and I think I warmed him. Lincoln and I were just the opposite one of another. He was cautious and practical; I was spontaneous, ideal, and speculative. He arrived at truths by reflection; I, by intuition; he, by reason; I, by my soul. He calculated; I went to toil asking no questions, never doubting. Lincoln had great faith in my intuitions, and I had great faith in his reason."
Of course such a man as we have described Mr. Herndon to be could have nothing but loathing and disgust for the secret oaths, the midnight lurking, and the proscriptive spirit of Know-Nothingism. "A number of gentlemen from Chicago," says he, "among them the editor of 'The Star of the West,' an Abolitionist paper published in Chicago, waited on me in my office, and asked my advice as to the policy of going into Know-Nothing Lodges, and ruling them for freedom. I opposed it as being wrong in principle, as well as a fraud on the lodges, and wished to fight it out in open daylight. Lincoln was opposed to Know-Nothingism, but did not say much in 1854 or 1855 (did afterwards). I told Lincoln what was said, and argued the question with him often, insisting that, as we were advocating freedom for the slave in tendency under the Kansas-Nebraska Bill, it was radically wrong to enslave the religious ideas and faith of men. The gentlemen who waited on me as before stated asked me if I thought that Mr. Lincoln could be trusted for freedom. I said to them, 'Can you trust yourselves? If you can, you can trust Lincoln forever.'"

With this explanation of the political views of Mr. Herndon, and his personal relations to Mr. Lincoln, the reader will more easily understand what follows.
"This State Fair," continues Mr. Herndon, "called thousands to the city. We Abolitionists all assembled here, taking advantage of the fair to organize and disseminate our ideas. As soon as Lincoln had finished his speech, Lovejoy, who had been in the hall, rushed up to the stand, and notified the crowd that there would be a meeting there in the evening: subject, Freedom. I had been with the Abolitionists that day, and knew their intentions: namely, to force Lincoln with our organization, and to take broader and deeper and more radical views and ideas than in his speech, which was simply Historic Kansas.... He (Lincoln) had not then announced himself for freedom, only discussed the inexpediency of repealing the Missouri Compromise Line. The Abolitionists that day determined to make Lincoln take a stand. I determined he should not at that time, because the time had not yet come when Lincoln should show his hand. When Lovejoy announced the Abolition gathering in the evening, I rushed to Lincoln, and said, 'Lincoln, go home; take Bob and the buggy, and leave the county: go quickly, go right off, and never mind the order of your going.' Lincoln took a hint, got his horse and buggy, and did leave quickly, not noting the order of his going. He staid away till all conventions and fairs were over."
But the speech against the repeal of the Compromise signally impressed all parties opposed to Mr. Douglas's late legislation,—Whigs, Abolitionists, and Democratic Free-soilers,—who agreed with perfect unanimity, that Mr. Lincoln should be pitted against Mr. Douglas wherever circumstances admitted of their meeting. As one of the evidences of this sentiment, Mr. William Butler drew up a paper addressed to Mr. Lincoln, requesting and "urging him to follow Douglas up until the election." It was signed by Mr. Butler, William Jayne, P. P. Eads, John Cassady, B. F. Irwin, and many others. Accordingly, Lincoln "followed" Douglas to Peoria, where the latter had an appointment, and again replied to him, in much the same spirit, and with the same arguments, as before. The speech was really a great one, almost perfectly adapted to produce conviction upon a doubting mind. It ought to be carefully read by every one who desires to know Mr. Lincoln's power as a debater, after his intellect was matured and ripened by years of hard experience. On the general subject of slavery and negroes in the Union, he spoke as follows:—
"Before proceeding, let me say, I think I have no prejudice against the Southern people: they are just what we would be in their situation. If slavery did not now exist among them, they would not introduce it: if it did now exist amongst us, we should not instantly give it up. This I believe of the masses North and South. Doubtless there are individuals on both sides who would not hold slaves under any circumstances, and others would gladly introduce slavery anew if it were out of existence. We know that some Southern men do free their slaves, go North, and become tip-top Abolitionists; while some Northern men go South, and become cruel slave-masters.
"When Southern people tell us they are no more responsible for the origin of slavery than we, I acknowledge the fact. When it is said that the institution exists, and that it is very difficult to get rid of it in any satisfactory way, I can understand and appreciate the saying. I surely will not blame them for not doing what I should not know how to do myself. If all earthly power were given me, I should not know what to do as to the existing institution. My first impulse would be to free all the existing slaves, and send them to Liberia,—to their own native land; but a moment's reflection would convince me that whatever of high hope (as I think there is) there may be in this, in the long run, its sudden execution is impossible. If they were all landed there in a day, they would all perish in the next ten days; and there are not surplus shipping and surplus money enough in the world to carry them there in many times ten days. What then? Free them all, and keep them among us as underlings? Is it quite certain that this betters their condition? I think I would not hold one in slavery at any rate, yet the point is not clear enough to me to denounce people upon. What next? Free them, and make them politically and socially our equals? My own feelings will not admit of this; and, if mine would, we all know that those of the great mass of white people would not. Whether this feeling accords with justice and sound judgment is not the sole question, if, indeed, it is any part of it. A universal feeling, whether well or ill founded, cannot be safely disregarded. We cannot, then, make them equals. It does seem to me that systems of gradual emancipation might be adopted; but for their tardiness in this I will not undertake to judge our brethren of the South. When they remind us of their constitutional rights, I acknowledge them, not grudgingly, but fully and fairly; and I would give them any legislation for the reclaiming of their fugitives which should not in its stringency be more likely to carry a free man into slavery than our ordinary criminal laws are to hang an innocent one.
"But all this, to my judgment, furnishes no more excuse for permitting slavery to go into our own free territory than it would for reviving the African slave-trade by law. The law which forbids the bringing of slaves from Africa, and that which has so long forbidden the taking them to Nebraska, can hardly be distinguished on any moral principle; and the repeal of the former could find quite as plausible excuses as that of the latter.
"But Nebraska is urged as a great Union-saving measure. Well, I, too, go for saving the Union. Much as I hate slavery, I would consent to the extension of it, rather than see the Union dissolved, just as I would consent to any great evil to avoid a greater one. But, when I go to Union-saving, I must believe, at least, that the means I employ have adaptation to the end. To my mind, Nebraska has no such adaptation. 'It hath no relish of salvation in it.' It is an aggravation, rather, of the only one thing which ever endangers the Union. When it came upon us, all was peace and quiet. The nation was looking to the forming of new bonds of Union, and a long course of peace and prosperity seemed to lie before us. In the whole range of possibility, there scarcely appears to me to have been any thing out of which the slavery agitation could have been revived, except the project of repealing the Missouri Compromise. Every inch of territory we owned already had a definite settlement of the slavery question, and by which all parties were pledged to abide. Indeed, there was no uninhabited country on the continent which we could acquire, if we except some extreme Northern regions, which are wholly out of the question. In this state of the case, the Genius of Discord himself could scarcely have invented a way of getting us by the ears, but by turning back and destroying the peace measures of the past.
"The structure, too, of the Nebraska Bill is very peculiar. The people are to decide the question of slavery for themselves; but when they are to decide, or how they are to decide, or whether, when the question is once decided, it is to remain so, or is to be subject to an indefinite succession of new trials, the law does not say. Is it to be decided by the first dozen settlers who arrive there, or is it to await the arrival of a hundred? Is it to be decided by a vote of the people, or a vote of the Legislature, or, indeed, on a vote of any sort? To these questions the law gives no answer. There is a mystery about this; for, when a member proposed to give the Legislature express authority to exclude slavery, it was hooted down by the friends of the bill. This fact is worth remembering. Some Yankees in the East are sending emigrants to Nebraska to exclude slavery from it; and, so far as I can judge, they expect the question to be decided by voting in some way or other. But the Missourians are awake too. They are within a stone's-throw of the contested ground. They hold meetings and pass resolutions, in which not the slightest allusion to voting is made. They resolve that slavery already exists in the Territory; that more shall go there; and that they, remaining in Missouri, will protect it, and that Abolitionists shall be hung or driven away. Through all this, bowie-knives and six-shooters are seen plainly enough, but never a glimpse of the ballot-box. And really, what is the result of this? Each party within having numerous and determined backers without, is it not probable that the contest will come to blows and bloodshed? Could there be a more apt invention to bring about a collision and violence on the slavery question than this Nebraska project is? I do not charge or believe that such was intended by Congress; but if they had literally formed a ring, and placed champions within it to fight out the controversy, the fight could be no more likely to come off than it is. And, if this fight should begin, is it likely to take a very peaceful, Union-saving turn? Will not the first drop of blood so shed be the real knell of the Union?"
No one in Mr. Lincoln's audience appreciated the force of this speech more justly than did Mr. Douglas himself. He invited the dangerous orator to a conference, and frankly proposed a truce. What took place between them was explicitly set forth by Mr. Lincoln to a little knot of his friends, in the office of Lincoln & Herndon, about two days after the election. We quote the statement of B. F. Irwin, explicitly indorsed by P. L. Harrison and Isaac Cogdale, all of whom are already indifferently well known to the reader. "W. H. Herndon, myself, P. L. Harrison, and Isaac Cogdale were present. What Lincoln said was about this: that the day after the Peoria debate in 1854, Douglas came to him (Lincoln), and flattered him that he (Lincoln) understood the Territorial question from the organization of the government better than all the opposition in the Senate of the United States; and he did not see that he could make any thing by debating it with him; and then reminded him (Lincoln) of the trouble they had given him, and remarked that Lincoln had given him more trouble than all the opposition in the Senate combined; and followed up with the proposition, that he would go home, and speak no more during the campaign, if Lincoln would do the same: to which proposition Lincoln acceded." This, according to Mr. Irwin's view of the thing, was running Douglas "into his hole," and making "him holler, Enough."
Handbills and other advertisements announced that Judge Douglas would address the people of Lacon the day following the Peoria encounter; and the Lacon Anti-Nebraska people sent a committee to Peoria to secure Mr. Lincoln for a speech in reply. He readily agreed to go, and on the way said not a word of the late agreement to the gentleman who had him in charge. Judge Douglas observed the same discreet silence among his friends. Whether they had both agreed to go to Lacon before this agreement was made, or had mutually contrived this clever mode of deception, cannot now be determined. But, when they arrived at Lacon, Mr. Douglas said he was too hoarse to speak, although, "a large portion of the people of the county assembled to hear him." Mr. Lincoln, with unheard-of magnanimity, "informed his friends that he would not like to take advantage of the judge's indisposition, and would not address the people." His friends could not see the affair in the same light, and "pressed him for a speech;" but he persistently and unaccountably "refused."
Of course, Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Douglas met no more during the campaign. Mr. Douglas did speak at least once more (at Princeton), but Mr. Lincoln scrupulously observed the terms of the agreement. He came home, wrote out his Peoria speech, and published it in seven consecutive issues of "The Illinois Daily Journal;" but he never spoke nor thought of speaking again. When his friends insisted upon having a reason for this most unexpected conduct, he gave the answer already quoted from Mr. Irwin.
The election took place on the 7th of November. During his absence, Mr. Lincoln had been announced as a candidate for the House of Representatives of the Illinois Legislature. William Jayne took the responsibility of making him a candidate. Mrs. Lincoln, however, "saw Francis, the editor, and had Lincoln's name taken out." When Mr. Lincoln returned, Jayne (Mrs. Lincoln's old friend "Bill") went to see him. "I went to see him," says Jayne, "in order to get his consent to run. This was at his house. He was then the saddest man I ever saw,—the gloomiest. He walked up and down the floor, almost crying; and to all my persuasions to let his name stand in the paper, he said, 'No, I can't. You don't know all. I say you don't begin to know one-half, and that's enough.' I did, however, go and have his name re-instated; and there it stood. He and Logan were elected by about six hundred majority." Mr. Jayne had caused originally both Judge Logan and Mr. Lincoln to be announced, and they were both elected. But, after all, Mrs. Lincoln was right, and Jayne and Lincoln were both wrong. Mr. Lincoln was a well-known candidate for the United States Senate, in the place of Mr. Shields, the incumbent, who had voted for the Kansas-Nebraska Bill; and, when the Legislature met and showed a majority of Anti-Nebraska men, he thought it a necessary preliminary of his candidacy that he should resign his seat in the House. He did so, and Mr. Jayne makes the following acknowledgment: "Mr. Lincoln resigned his seat, finding out that the Republicans, the Anti-Nebraska men, had carried the Legislature. A. M. Broadwell ran as a Whig Anti-Nebraska man, and was badly beaten. The people of Sangamon County was down on Lincoln,—hated him." None can doubt that even the shame of taking a woman's advice might have been preferable to this!
But Mr. Lincoln "had set his heart on going to the United States Senate." Counting in the Free-soil Democrats, who had revolted against Mr. Douglas's leadership, and been largely supported the Whigs in the late elections, there was now on joint ballot a clear Anti-Nebraska majority of two. A Senator was to be chosen to succeed Mr. Shields; and Mr. Lincoln had a right to expect the place. He had fairly earned the distinction, and nobody in the old Whig party was disposed to withhold it. But a few Abolitionists doubted his fidelity to their extreme views; and five Anti-Nebraska Senators and Representatives, who had been elected as Democrats, preferred to vote for a Senator with antecedents like their own. The latter selected Judge Trumbull as their candidate, and clung to him manfully through the whole struggle. They were five only in number; but in the situation of affairs then existing they were the sovereign five. They were men of conceded integrity, of good abilities in debate, and extraordinary political sagacity. Their names ought to be known to posterity, for their unfriendliness at this juncture saved Mr. Lincoln to the Republicans of Illinois, to be brought forward at the critical moment as a fresh and original candidate for the Presidency. They were Judd of Cook County, Palmer of Macoupin, Cook of La Salle, Baker and Allen of Madison. They called themselves Democrats, and, with the modesty peculiar to bolters, claimed to be the only "Simon-pure." "They could not act with the Democrats from principle, and would not act with the Whigs from policy;" but, holding off from the caucuses of both parties, they demanded that all Anti-Nebraska should come to them, or sacrifice the most important fruits of their late victory at the polls. But these were not the only enemies Mr. Lincoln could count in the body of his party. The Abolitionists suspected him, and were slow to come to his support. Judge Davis went to Springfield, and thinks he "got some" of this class "to go for" him; but it is probable they were "got" in another way. Mr. Lovejoy was a member, and required, as the condition of his support and that of his followers, that Mr. Lincoln should pledge himself to favor the exclusion of slavery from all the Territories of the United States. This was a long step in advance of any that Mr. Lincoln had previously taken. He was, as a matter of course, opposed to the introduction of slavery into the Territories north of the line of 36° 30'; but he had, up to this time, regarded all south of that as being honestly open to slavery. The villany of obliterating that line, and the necessity of its immediate restoration,—in short, the perfect sanctity of the Missouri settlement,—had formed the burden of all his speeches in-the preceding canvass. But these opinions by no means suited the Abolitionists, and they required him to change them forthwith. He thought it would be wise to do so, considering the peculiar circumstances of his case; but, before committing himself finally, he sought an understanding with Judge Logan. He told the judge what he was disposed to do, and said he would act upon the inclination, if the judge would not regard it as "treading upon his toes." The judge said he was opposed to the doctrine proposed; but, for the sake of the cause in hand, he would cheerfully risk his "toes." And so the Abolitionists were accommodated: Mr. Lincoln quietly made the pledge, and they voted for him.
On the eighth day of February, 1855, the two Houses met in convention to choose a Senator. On the first ballot, Mr. Shields had forty-one votes, and three Democratic votes were scattered. Mr. Lincoln had forty-five, Mr. Trumbull five, and Mr. Koerner two. On the seventh ballot, the Democrats left Shields, and, with two exceptions, voted for Gov. Matte-son. In addition to the party strength, Matteson received also the votes of two of the anti-Nebraska Democrats. That stout little knot, it was apparent, was now breaking up. For many reasons the Whigs detested Matteson most heartily, and dreaded nothing so much as his success. But of that there now appeared to be great danger; for, unless the Whigs abandoned Lincoln and went for Trumbull, the five Anti-Nebraska men would unite on Matteson, and elect him. Mr. Gillespie went to Lincoln for advice. "He said unhesitatingly, 'You ought to drop me, and go for Trumbull: that is the only way you can defeat Matteson.' Judge Logan came up about that time, and insisted on running Lincoln still; but the latter said, 'If you do, you will lose both Trumbull and myself; and I think the cause, in this case, is to be preferred to men.' We adopted his suggestion, and turned upon Trumbull, and elected him, although it grieved us to the heart to give up Mr. Lincoln. This, I think, shows that Mr. Lincoln was capable of sinking himself for the cause in which he was engaged." It was with great bitterness of spirit that the Whigs accepted this hard alternative. Many of them accused the little squad of Anti-Nebraska Democrats of "ungenerous and selfish" motives. One of them, "Mr. Waters of McDonough, was especially indignant, and utterly refused to vote for Mr. Trumbull at all. On the last ballot he threw away his ballot on Mr. Williams."
"Mr. Lincoln was very much disappointed," says Mr. Parks, a member of the Legislature, and one of Mr. Lincoln's special friends; "for I think, that, at that time, it was the height of his ambition to get into the United States Senate. He manifested, however, no bitterness towards Mr. Judd, or the other Anti-Nebraska Democrats, by whom politically he was beaten, but evidently thought that their motives were right. He told me several times afterwards, that the election of Trumbull was the best thing that could have happened."
In the great campaign of 1858, Mr. Douglas on various occasions insisted, that, in 1854, Mr. Lincoln and Judge Trumbull, being until then political enemies, had formed a secret agreement to abolitionize, the one the Whig, and the other the Democratic party; and, in order that neither might go unrewarded for a service so timely and patriotic, Mr. Trumbull had agreed on the one hand that Mr. Lincoln should have Shields's seat in the United States Senate (in 1855); and Mr. Lincoln had agreed, on the other, that Judge Trumbull should have Douglas's seat (in 1859). But Mr. Douglas alleged, that, when the first election (in 1854) came on, Judge Trumbull treated his fellow-conspirator with shameful duplicity, and cheated himself into the Senate just four years in advance of his appointed time; that, Mr. Lincoln's friends being greatly incensed thereat, Col. James H. Matheny, Mr. Lincoln's "friend and manager for twenty years," exposed the plot and the treachery; that, in order to silence and conciliate the injured party, Mr. Lincoln was promised the senatorial nomination in 1858, and thus a second time became a candidate in pursuance of a bargain more than half corrupt. But it is enough to say here, that Mr. Lincoln explicitly and emphatically denied the accusation as often as it was made, and bestowed upon the character of Judge Trumbull encomiums as lofty and as warm as he ever bestowed upon any contemporary. With the exception of Col. Matheny, we find none of Mr. Lincoln's peculiar friends complaining of Judge Trumbull; but as many of them as have spoken in the records before us (and they are numerous and prominent) speak of the purity, devotion, and excellence of Judge Trumbull in the most unreserved and unaffected manner. In fact and in truth, he did literally nothing to advance his own interest: he solicited no vote, and got none which did not come to him by reason of the political necessities of the time. His election consolidated the Anti-Nebraska party in the State, and, in the language of Mr. Parks, his "first encounter with Mr. Douglas in the Senate filled the people of Illinois with admiration for his abilities; and the ill feeling caused by his election gradually passed away."
But Mr. Douglas had a graver charge to make against Mr. Lincoln than that of a simple conspiracy with Trumbull to dispose of a great office. He seems to have known nothing of Mr. Lincoln's secret understanding with Lovejoy and his associates; but he found, that, on the day previous to the election for Senator, Lovejoy had introduced a series of extreme antislavery resolutions; and with these he attempted to connect Mr. Lincoln, by showing, that, with two exceptions, every member who voted for the resolutions on the 7th of February voted also for Mr. Lincoln on the 8th. The first of the resolutions favored the restoration of the prohibition of slavery north of 36° 30', and also a similar prohibition as to "all territory which now belongs to the United States, or which may hereafter come under their jurisdiction." The second resolution declared against the admission of any Slave State, no matter out of what Territory, or in what manner formed; and the third demanded, first, the unconditional repeal of the Fugitive-Slave Law, or, failing that, the right of habeas corpus and trial by jury for the person claimed as a slave. The first resolution was carried by a strict party vote; while the second and third were defeated. But Mr. Douglas asserted that Mr. Lincoln was committed in favor of all three, because the members that supported them subsequently supported him. Of all this Mr. Lincoln took no further notice than to say that Judge Douglas might find the Republican platform in the resolutions of the State Convention of that party, held at Bloomington in 1856. In fact, he maintained a singular reticence about the whole affair, probably dreading to go into it too deeply, lest his rival should unearth the private pledge to Lovejoy, of which Judge Logan has given us the history. When Judge Douglas produced a set of resolutions which he said had been passed by the Abolitionists at their Convention at Springfield, during the State Fair (the meeting alluded to by Mr. Herndon), and asserted that Mr. Lincoln was one of the committee that reported them, the latter replied with great spirit, and said what he could say with perfect truth,—that he was not near Springfield when that body met, and that his name had been used without his consent.
MR. LINCOLN predicted a bloody conflict in Kansas as the immediate effect of the repeal of the Missouri restriction. He had not long to wait for the fulfilment of his prophecy: it began, in fact, before he spoke; and if blood had not actually flowed on the plains of Kansas, occurrences were taking place on the Missouri border which could not avoid that result. The South invited the struggle by repealing a time-honored compromise, in such a manner as to convince the North that she no longer felt herself bound by any Congressional restrictions upon the institution of slavery; and that she intended, as far as her power would permit, to push its existence into all the Territories of the Union. The Northern States accepted the challenge promptly. The people of the Free States knew how to colonize and settle new Territories. The march of their westward settlements had for years assumed a steady tread as the population of these States augmented, and the facility for emigrating increased. When, therefore, the South threw down the barriers which had for thirty years consecrated all the Territories north of 36° 30' to free labor, and announced her intention of competing therein for the establishment of her "peculiar institution," the North responded by using the legitimate means at her command to throw into the exposed regions settlers who would organize the Territories in the interest of free labor. The "irrepressible conflict" was therefore opened in the Territories, with the people of the two sections of the country arrayed against each other as participants in, as well as spectators of, the contest. As participants, each section aided its representatives. The struggle opened in Kansas, and in favor of the South. During the passage of the bill organizing the Territory, preparations had been extensively made along the Missouri border, by "Blue Lodges" and "Social Bands," for the purpose of getting control of its Territorial government. The whole eastern border of the Territory was open to these marauders; and they were not slow to embrace the opportunity of meeting their enemies with so man y advantages in their favor. Public meetings were held in many of the frontier counties of Missouri, in which the people were not only advised to go over and take early possession of the Territory, but to hold themselves in readiness to remove all emigrants who should go there under the auspices of the Northern Aid Societies. It was with these "Border Ruffians," and some volunteers from Alabama and South Carolina, with a few vagabond "colonels" and "generals" from the Slave States generally, that the South began the struggle. Of course, the North did not look with complacency upon such a state of things. If the repeal of the Missouri Compromise startled the people of the Free States from their sense of security, the manner of applying "popular sovereignty," as indicated at its first introduction, was sufficient to arouse public sentiment to an unwonted degree. Kansas became at once a subject of universal interest. Societies were formed for throwing into her borders, with the utmost expedition, settlers who could be relied upon to mould her government in the interest of freedom. At the same time there was set in train all the political machinery that could be used to agitate the question, until the cry of "Bleeding Kansas" was heard throughout the land.
It is not necessary in this connection to set down, in order, the raids, assassinations, burnings, robberies, and election frauds which followed. Enough if their origin and character be understood. For this present purpose, a brief summary only will be given of what occurred during the long struggle to make Kansas a Slave State; for upon the practical issues which arose during the contest followed the discussions between Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Douglas, upon the merits of which the former was carried into the Presidential office.
The first Territorial governor appointed under the provisions of the Kansas-Nebraska Act was Andrew H. Reeder of Pennsylvania. He was appointed by President Pierce. He reached Kansas in the autumn of 1854, and proceeded to establish a Territorial Government. The first election was for a delegate to Congress. By the aid of the people of Missouri, it resulted in favor of the Democrats. The governor then ordered an election for a first Territorial Legislature, to be held on the 31st of March, 1855. To this election the Missourians came in greater force than before; and succeeded in electing proslavery men to both Houses of the Legislature, with a single exception in each house. The governor, a proslavery man, set aside the returns in six districts, as being fraudulent; whereupon new elections were held, which, with one exception, resulted in favor of the Free-State men. These parties, however, were refused their seats in the Legislature; while the persons chosen at the previous election were accepted.
The Legislature thus organized proceeded to enact the most hostile measures against the Free-State men. Many of these acts were promptly vetoed by the governor. The Legislature then petitioned the President for his removal. Their wishes were complied with; and Wilson G. Shannon of Ohio was appointed in his stead. In the mean time, the Free-State men entirely repudiated the Legislature, and refused to be bound by its enactments.
Such was the situation in Kansas when Mr. Lincoln addressed to Mr. Speed the following letter:—
Springfield, Aug. 24, 1855.
Dear Speed,—You know what a poor correspondent I am. Ever since I received your very agreeable letter of the 22d of May, I have been intending to write you an answer to it. You suggest that in political action now you and I would differ. I suppose we would; not quite as much, however, as you may think. You know I dislike slavery; and you fully admit the abstract wrong of it. So far there is no cause of difference. But you say, that, sooner than yield your legal right to the slave,—especially at the bidding of those who are not themselves interested,—you would see the Union dissolved. I am not aware that any one is bidding you yield that right: very certainly I am not. I leave that matter entirely to yourself. I also acknowledge your rights and my obligations under the Constitution in regard to your slaves. I confess I hate to see the poor creatures hunted down, and caught and carried back to their stripes and unrequited toils; but I bite my lip, and keep quiet. In 1841 you and I had together a tedious low-water trip on a steamboat from Louisville to St. Louis. You may remember, as I well do, that, from Louisville to the mouth of the Ohio, there were on board ten or a dozen slaves shackled together with irons. That sight was a continued torment to me; and I see something like it every time I touch the Ohio, or any other slave border. It is not fair for you to assume that I have no interest in a thing which has, and continually exercises, the power of making me miserable. You ought rather to appreciate how much the great body of the Northern people do crucify their feelings, in order to maintain their loyalty to the Constitution and the Union. I do oppose the extension of slavery because my judgment and feeling so prompt me; and I am under no obligations to the contrary. If for this you and I must differ, differ we must. You say, if you were President, you would send an army, and hang the leaders of the Missouri outrages upon the Kansas elections; still, if Kansas fairly votes herself a Slave State, she must be admitted, or the Union must be dissolved. But how if she votes herself a Slave State unfairly,—that is, by the very means for which you say you would hang men? Must she still be admitted, or the Union dissolved? That will be the phase of the question when it first becomes a practical one. In your assumption that there may be a fair decision of the slavery question in Kansas, I plainly see you and I would differ about the Nebraska law. I look upon that enactment, not as a law, but a violence from the beginning. It was conceived in violence, is maintained in violence, and is being executed in violence. I say it was conceived in violence, because the destruction of the Missouri Compromise, under the circumstances, was nothing less than violence. It was passed in violence, because it could not have passed at all but for the votes of many members in violence of the known will of their constituents. It is maintained in violence, because the elections since clearly demand its repeal; and the demand is openly disregarded.
You say men ought to be hung for the way they are executing that law; and I say the way it is being executed is quite as good as any of its antecedents. It is being executed in the precise way which was intended from the first; else why does no Nebraska man express astonishment or condemnation? Poor Reeder is the only public man who has been silly enough to believe that any thing like fairness was ever intended; and he has been bravely undeceived.
That Kansas will form a slave constitution, and with it will ask to be admitted into the Union, I take to be already a settled question, and so settled by the very means you so pointedly condemn. By every principle of law ever held by any court, North or South, every negro taken to Kansas is free; yet, in utter disregard of this,—in the spirit of violence merely,—that beautiful Legislature gravely passes a law to hang any man who shall venture to inform a negro of his legal rights. This is the substance and real object of the law. If, like Haman, they should hang upon the gallows of their own building, I shall not be among the mourners for their fate. In my humble sphere, I shall advocate the restoration of the Missouri Compromise so long as Kansas remains a Territory; and when, by all these foul means, it seeks to come into the Union as a Slave State, I shall oppose it. I am very loath, in any case, to withhold my assent to the enjoyment of property acquired or located in good faith; but I do not admit that good faith in taking a negro to Kansas to be held in slavery is a probability with any man. Any man who has sense enough to be the controller of his own property has too much sense to misunderstand the outrageous character of the whole Nebraska business. But I digress. In my opposition to the admission of Kansas, I shall have some company; but we may be beaten. If we are, I shall not, on that account, attempt to dissolve the Union. I think it probable, however, we shall be beaten. Standing as a unit among yourselves, you can, directly and indirectly, bribe enough of our men to carry the day, as you could on the open proposition to establish a monarchy. Get hold of some man in the North whose position and ability is such that he can make the support of your measure, whatever it may be, a Democratic party necessity, and the thing is done. Apropos of this, let me tell you an anecdote. Douglas introduced the Nebraska Bill in January. In February afterwards, there was a called session of the Illinois Legislature. Of the one hundred members composing the two branches of that body, about seventy were Democrats. These latter held a caucus, in which the Nebraska Bill was talked of, if not formally discussed. It was thereby discovered that just three, and no more, were in favor of the measure. In a day or two Douglas's orders came on to have resolutions passed approving the bill; and they were passed by large majorities!!! The truth of this is vouched for by a bolting Democratic member. The masses, too, Democratic as well as Whig, were even nearer unanimous against it; but, as soon as the party necessity of supporting it became apparent, the way the Democracy began to see the wisdom and justice of it was perfectly astonishing.
You say, that, if Kansas fairly votes herself a Free State, as a Christian you will rather rejoice at it. All decent slaveholders talk that way; and I do not doubt their candor. But they never vote that way. Although in a private letter, or conversation, you will express your preference that Kansas shall be free, you would vote for no man for Congress who would say the same thing publicly. No such man could be elected from any district in a Slave State. You think Stringfellow & Co. ought to be hung; and yet, at the next Presidential election, you will vote for the exact type and representative of Stringfellow. The slave-breeders and slave-traders are a small, odious, and detested class among you; and yet in politics they dictate the course of all of you, and are as completely your masters as you are the master of your own negroes. You inquire where I now stand. That is a disputed point. I think I am a Whig; but others say there are no Whigs, and that I am an Abolitionist. When I was at Washington, I voted for the Wilmot Proviso as good as forty times; and I never heard of any one attempting to un whig me for that. I now do no more than oppose the extension of slavery. I am not a Know-Nothing: that is certain. How could I be? How can any one who abhors the oppression of negroes be in favor of degrading classes of white people? Our progress in degeneracy appears to me to be pretty rapid. As a nation, we began by declaring that"all men are created equal." We now practically read it "all men are created equal, except negroes." When the Know-Nothings get control, it will read "all men are created equal, except negroes and foreigners and Catholics." When it comes to this, I should prefer emigrating to some country where they make no pretence of loving liberty,—to Russia, for instance, where despotism can be taken pure, and without the base, alloy of hypocrisy.
Mary will probably pass a day or two in Louisville in October. My kindest regards to Mrs. Speed. On the leading subject of this letter, I have more of her sympathy than I have of yours; and yet let me say I am
Your friend forever,
A. Lincoln.
Gov. Shannon arrived in the Territory Sept. 1,1855. On his way thither, he declared himself in favor of making Kansas a Slave State. He found affairs in a turbulent condition, which his policy by no means tended to mitigate or assuage. The Free-State party held a mass-meeting at Big Springs in the early part of September, at which they distinctly and earnestly repudiated the legislative government, which claimed to have been elected in March, as well as all laws passed by it; and they decided not to participate in an election for a delegate to Congress, which the Legislature had appointed to be held on the 1st of October following. They also held a Delegate Convention at Topeka, on the 19th of September, and appointed an Executive Committee for the Territory; and also an election for a Delegate to Congress, to be held on the second Tuesday in October. These two rival elections for a congressional delegate took place on different days; at the former of which, Whitfield, representing the proslavery party, was elected; while at the other, Gov. Reeder, representing the Free-State party, was chosen. On the 28d of October, the Free-State party held a constitutional Convention at Topeka, and formed a State constitution in their interest, under the provisions of which they subsequently acted, and also asked for admission into the Union.
While we are upon this phase of the Kansas question, it may not be amiss to postpone the relation of some intermediate events, in order to give the reader the benefit of an expression of Mr. Lincoln's views, which thus far has found place in no printed record.
Sometime in 1856 an association of Abolitionists was formed in Illinois to go to Kansas and aid the Free-State men in opposing the Government. The object of those engaged in this work was, in their opinion, a very laudable one,—no other than the defence of freedom, which they thought foully menaced in that far-off region. Among these gentlemen, and one of the most courageous and disinterested, was William H. Herndon. He says,—
"Mr. Lincoln was informed of our intents by some means. Probably the idea of resistance was more known than I now remember. He took the first opportunity he could to dissuade us from our partially-formed purpose. We spoke of liberty, justice, and God's higher law, and invoked the spirit of these as our holiest inspiration. In 1856 he addressed us on this very subject, substantially in these words:—
"'Friends, I agree with you in Providence; but I believe in the providence of the most men, the largest purse, and the longest cannon. You are in the minority,—in a sad minority; and you can't hope to succeed, reasoning from all human experience. You would rebel against the Government, and redden your hands in the blood of your countrymen. If you are in the minority, as you are, you can't succeed. I say again and again, against the Government, with a great majority of its best citizens backing it, and when they have the most men, the longest purse, and the biggest cannon, you can't succeed.
"'If you have the majority, as some of you say you have, you can succeed with the ballot, throwing away the bullet. You can peaceably, then, redeem the Government, and preserve the liberties of mankind, through your votes and voice and moral influence. Let there be peace. In a democracy, where the majority rule by the ballot through the forms of law, these physical rebellions and bloody resistances are radically wrong, unconstitutional, and are treason. Better bear the ills you have than fly to those you know not of. Our own Declaration of Independence says, that governments long established, for trivial causes should not be resisted. Revolutionize through the ballot-box, and restore the Government once more to the affections and hearts of men, by making it express, as it was intended to do, the highest spirit of justice and liberty. Your attempt, if there be such, to resist the laws of Kansas by force, is criminal and wicked; and all your feeble attempts will be follies, and end in bringing sorrow on your heads, and ruin the cause you would freely die to preserve!'
"This little speech," continues Mr. Herndon, "is not in print. It is a part of a much longer one, likewise not in print. This speech squelched the ideas of physical resistance, and directed our energies through other more effective channels, which his wisdom and coolness pointed out to us. This little speech, so timely and well made, saved many of us from great follies, if not our necks from the halter. The man who uttered it is no more; but this little speech, I hope, shall not soon be forgotten. Mr. Lincoln himself, after this speech, subscribed money to the people of Kansas under conditions, which I will relate in other ways. He was not alone in his gifts: I signed the same paper, I think, for the same amount, most cheerfully; and would do it again, only doubling the sum, adding no conditions, only the good people's wise discretion."
Early in 1856 it became painfully apparent to Mr. Lincoln that he must take a decisive stand upon the questions of the day, and become a Know-Nothing, a Democrat, a Republican, or an Abolitionist. Mere "Anti-Nebraska" would answer no longer: the members of that ephemeral coalition were seeking more permanent organizations. If interrogated concerning his position, he would probably have answered still, "I think I am a Whig." With the Abolition or Liberty party, he had thus far shown not a particle of sympathy. In 1840, 1844, 1848, and 1852, the Abolitionists, Liberty-men, or Free-Soilers, ran candidates of their own for the Presidency, and made no little noise and stir in the politics of the country; but they were as yet too insignificant in number to claim the adhesion of a practical man like Mr. Lincoln. In fact, his partner, one of the most earnest of them all, had not up to this time desired his fellowship. But now Mr. Herndon thought the hour had arrived when his hero should declare himself in unmistakable terms. He found, however, one little difficulty in the way: he was not precisely certain of his hero. Mr. Lincoln might go that way, and he might go the other way: his mind was not altogether made up; and there was no telling on which side the decision would fall. "He was button-holed by three ideas, and by men belonging to each class: first, he was urged to remain a Whig; secondly, he was urged to become a Know-Nothing, Say-Nothing, Do-Nothing; and, thirdly, he was urged to be baptized in Abolitionism: and in my imagination I can see Lincoln strung out three ways. At last two cords were snapped, he flying to Freedom."
And this is the way the cords were snapped: Mr. Herndon drew up a paper to be signed by men of his class in politics, calling a county convention to elect delegates to the State convention at Bloomington. "Mr. Lincoln was then backward," says Mr. Herndon, "dodge-y,—so" and so. I was determined to make him take a stand, if he would not do it willingly, which he might have done, as he was naturally inclined Abolitionward. Lincoln was absent when the call was signed, and circulated here. I signed Mr. Lincoln's name without authority; had it published in "The Journal." John T. Stuart was keeping his eye on Lincoln, with the view of keeping him on his side,—the totally-dead conservative side. Mr. Stuart saw the published call, and grew mad; rushed into my office, seemed mad, horrified, and said to me, 'Sir, did Mr. Lincoln sign that Abolition call which is published this morning?' I answered, 4 Mr. Lincoln did not sign that call.'—'Did Lincoln authorize you to sign it?' said Mr. Stuart. 'No: he never authorized me to sign it.'—'Then do you know that you have ruined Mr. Lincoln?'—'I did not know that I had ruined Mr. Lincoln; did not intend to do so; thought he was a made man by it; that the time had come when conservatism was a crime and a blunder.'—'You, then, take the responsibility of your acts; do you?'—'I do, most emphatically.'
"However, I instantly sat down and wrote to Mr. Lincoln, who was then in Pekin or Tremont,—possibly at court. He received my letter, and instantly replied, either by letter or telegraph,—most likely by letter,—that he adopted in toto what I had done, and promised to meet the radicals—Lovejoy, and suchlike men—among us."
At Bloomington Lincoln was the great figure. Beside him all the rest—even the oldest in the faith and the strongest in the work—were small. Yet he was universally regarded as a recent convert, although the most important one that could be made in the State of Illinois. "We met at Bloomington; and it was there," says Mr. Herndon in one of his lectures, "that Mr. Lincoln was baptized, and joined our church. He made a speech to us. I have heard or read all Mr. Lincoln's great speeches; and I give it as my opinion, on my best judgment, that the Bloomington speech was the grand effort of his life. Heretofore, and up to this moment, he had simply argued the slavery question on grounds of policy,—on what are called the statesman's grounds,—never reaching the question of the radical and the eternal right. Now he was newly baptized and freshly born: he had the fervor of a new convert; the smothered flame broke out; enthusiasm unusual to him blazed up; his eyes were aglow with an inspiration; he felt justice; his heart was alive to the right; his sympathies, remarkably deep for him, burst forth, and he stood before the throne of the eternal Right, in presence of his God, and then and there unburdened his penitential and fired soul. This speech was fresh, new, genuine, odd, original; filled with fervor not unmixed with a divine enthusiasm; his head breathing out through his tender heart its truths, its sense of right, and its feeling of the good and for the good. This speech was full of fire and energy and force: it was logic; it was pathos; it was enthusiasm; it was justice, equity, truth, right, and the good, set ablaze by the divine fires of a soul maddened by the wrong; it was hard, heavy, knotty, gnarly, edged, and heated. I attempted for about fifteen minutes, as was usual with me then, to take notes; but at the end of that time I threw pen and paper to the dogs, and lived only in the inspiration of the hour. If Mr. Lincoln was six feet four inches high usually, at Bloomington he was seven feet, and inspired at that. From that day to the day of his death, he stood firm on the right. He felt his great cross, had his great idea, nursed it, kept it, taught it to others, and in his fidelity bore witness of it to his death, and finally sealed it with his precious blood."

If any thing in the foregoing description by Mr. Herndon seems extravagant to the reader, something must be pardoned to the spirit of a patient friend and an impatient teacher, who saw in this scene the first fruits of his careful husbandry, and the end of his long vigil. He appears to have participated even then in the belief which Mr. Lincoln himself avowed,—that the latter was designed by the Dispenser of all things to occupy a great place in the world's history; and he felt that that day's doings had fixed his political character forever. The Bloomington Convention was called "Republican," and the Republican party of Illinois was there formed: but the most noted Abolitionists were in it, the spirit of the Lovejoys was present; and Mr. Herndon had a right to say, that, if Mr. Lincoln was not an Abolitionist, he was tending "Abolition-ward" so surely that no doubt could be entertained of his ultimate destination. But, after all, the resolutions of the convention were very "moderate." They merely denounced the administration for its course regarding Kansas, stigmatized the repeal of the Missouri Compromise as an act of bad faith, and opposed "the extension of slavery into Territories heretofore free." It was surely not because Mr. Lincoln was present, and aiding at the passage of such resolutions, that Mr. Herndon and others thereafter regarded him as a "newborn" Abolitionist. It must have been the general warmth of his speech against the South,—his manifest detestation of slaveholders and slaveholding, as exhibited in his words,—which led them to believe that his feelings at least, if not his opinions, were similar to theirs. But the reader will see, nevertheless, as we get along in our history, that the Bloomington resolutions were the actual standard of Mr. Lincoln's views; that he continued to express his determination to maintain the rights of the Slave States under the Constitution, and to make conspicuously plain his abhorrence of negro suffrage and negro equality. He certainly disliked the Southern politicians very much; but even that sentiment, growing daily more fierce and ominous in the masses of the new party, was in his case counterbalanced by his prejudices or his caution, and he never saw the day when he would willingly have clothed the negroes with political privileges.
Notwithstanding the conservative character of the resolutions, the proceedings of the Bloomington Convention were alarming to a portion of the community, and seem to have found little favor with the people of Springfield. About five days after its adjournment, Herndon and Lincoln bethought them of holding a ratification meeting. Mr. Herndon got out huge posters, announcing the event, and employed a band of musicians to parade the streets and "drum up a crowd." As the hour of meeting drew near, he "lit up the Court House with many blazes," rung the bells, and blew a horn. At seven o'clock the meeting should have been called to order, but it turned out to be extremely slim. There was nobody present, with all those brilliant lights, but A. Lincoln, W. H. Herndon, and John Pain. "When Lincoln came into the courtroom," says the bill-poster and horn-blower of this great demonstration, "he came with a sadness and a sense of the ludicrous on his face. He walked to the stand, mounted it in a kind of mockery,—mirth and sadness all combined,—and said, 'Gentlemen, this meeting is larger than I knew it would be. I knew that Herndon and myself would come, but I did not know that any one else would be here; and yet another has come,—you, John Pain. These are sad times, and seem out of joint. All seems dead, dead, dead: but the age is not yet dead; it liveth as sure as our Maker liveth. Under all this seeming want of life and motion, the world does move nevertheless. Be hopeful. And now let us adjourn, and appeal to the people.'
"This speech is in substance just as he delivered it, and substantially in the same sad but determined spirit; and so we did adjourn, did go out, and did witness the fact that 'the world was not dead.'"
The Bloomington Convention sent delegates to the general Republican Convention, which was to be held at Philadelphia in June. That body was to nominate candidates for the Presidency and Vice-Presidency, and high hopes were entertained of their success. But much remained to be done before such a revolution in sentiment could be expected. The American or Know-Nothing party—corrupt, hideous, and delusive, but still powerful—had adopted the old Whig platform on the several slavery questions, and planted itself decisively against the agitations of the Anti-Nebraska men and the Republicans. A "National Council" had taken this position for it the year previous, in terms beside which the resolutions of the Whigs and Democrats in 1852 were mild and inexpressive. Something, therefore, must be done to get this great organization out of the way, or to put its machinery under "Republican" control. We have seen a party of gentlemen from Chicago proposing to go into the lodges, and "rule them for freedom." Mr. Herndon and Mr. Lincoln rejected the plot with lofty indignation; but a section of the Free-Soil politicians were by no means so fastidious. They were for the most part bad, insincere, trading men, with whom the profession of principles of any kind was merely a convenient disguise, and who could be attached to no party, except from motives of self-interest. As yet, they were not quite certain whether it were possible to raise more hatred in the Northern mind against foreigners and Catholics than against slaveholders; and they prudently determined to be in a situation to try either. Accordingly, they went into the lodges, took the oaths, swore to stand by the platform of the "National Council" of 1855, and were perfectly ready to do that, or to betray the organization to the Republicans, as the prospect seemed good or bad. Believing the latter scheme to be the best, upon deliberation, they carried it out as far as in them lay, and then told the old, grim, honest, antislavery men, with whom they again sought association, that they had joined the Know-Nothings, and sworn irrevocable oaths to proscribe foreigners and Catholics, solely that they might rule the order "for freedom;" and, the Republicans standing in much need of aid just then, the excuse was considered very good. But it was too shameless a business for Lincoln and Herndon; and they most righteously despised it.
In February, 1856, the Republicans held what Mr. Greeley styles their "first National. Convention," at Pittsburg; but they made no nominations there. At the same time, a Know-Nothing American "National Council" was sitting at Philadelphia (to be followed by a nominating convention); and the Republicans at Pittsburg had not adjourned before they got news by telegraph, that the patriots who had entered the lodges on false pretences were achieving a great success: the American party was disintegrating, and a great section of it falling away to the Republicans. A most wonderful political feat had been performed, and the way was now apparently clear for a union of the all-formidable anti-Democratic elements in the Presidential canvass.
On the 17th of June the National Republican Convention met at Philadelphia, and nominated John C. Fremont for President, and William L. Dayton for Vice-President. Mr. Williams, Chairman of the Illinois Delegation, presented to the convention the name of Abraham Lincoln for the latter office; and it was received with great enthusiasm by some of the Western delegates. He received, however, but 110 votes, against 259 for Mr. Dayton, and 180 scattered; and Mr. Dayton was immediately thereafter unanimously declared the nominee.
While this convention was sitting, Mr. Lincoln was attending court at Urbana, in Champaign County. When the news reached that place that Mr. Dayton had been nominated, and "Lincoln had received 110 votes," some of the lawyers insisted that the latter must have been "our [their] Lincoln;" but he said, "No, it could not be: it must have been the great Lincoln from Massachusetts." He utterly refused to believe in the reality of this unexpected distinction until he saw the proceedings in full. He was just then in one of his melancholy moods, his spirits depressed, and his heart suffering the miseries of a morbid mind.
With an indorsement of the "self-evident truths" and "inalienable rights" of the Declaration of Independence, the Republican Convention adopted the following as the practical and essential features of its platform:—
"Resolved,... That we deny the authority of Congress, of a territorial Legislature, of any individual, or association of individuals, to give legal existence to slavery in any Territory of the United States while the present Constitution shall be maintained.
"Resolved, That the Constitution confers upon Congress sovereign power over the Territories of the United States for their government; and that, in the exercise of this power, it is both the right and the duty of Congress to prohibit in the Territories those twin relics of barbarism,—polygamy and slavery."
The National Democratic Convention had already placed in nomination Buchanan and Breckenridge. Their platform denounced as sectional the principles and purposes of their opponents; re-affirmed "the principles contained in the organic laws establishing the Territories of Kansas and Nebraska, as embodying the only sound and safe solution of the slavery question," and declared further,—
"That by the uniform application of Democratic principles to the organization of Territories and the admission of new States, with or without slavery as they may elect, the equal rights of all the States will be preserved intact, the original compacts of the Constitution maintained inviolate, and the perpetuity and expansion of the Union insured to its utmost capacity of embracing, in peace and harmony, every future American State that may be constituted or annexed with a republican form of government."
Mr. Lincoln was again a candidate for the office of Presidential elector, and made a thorough and energetic canvass. Some of his speeches were very striking; and probably no man in the country discussed the main questions in that campaign—Kansas, and slavery in the Territories—in a manner more original and persuasive. From first to last, he scouted the intimation that the election of Fremont would justify a dissolution of the Union, or that it could possibly become even the occasion of a dissolution. In his eyes, the apprehensions of disunion were a "humbug;" the threat of it mere bluster, and the fear of it silly timidity.
In the heat of the canvass, Mr. Lincoln wrote the following perfectly characteristic letter,—marked "Confidential:"—
Springfield, Sept. 8, 1856.
Harrison Maltby, Esq.
Dear Sir,—I understand you are a Fillmore man. Let me prove to you that every vote withheld from Fremont and given to Fillmore in this State actually lessens Fillmore's chance of being President.
Suppose Buchanan gets all the Slave States and Pennsylvania, and any other one State besides; then he is elected, no matter who gets all the rest.
But suppose Fillmore gets the two Slave States of Maryland and Kentucky; then Buchanan is not elected: Fillmore goes into the House of Representatives, and may be made President by a compromise.
But suppose, again, Fillmore's friends throw away a few thousand votes on him in Indiana and Illinois: it will inevitably give these States to Buchanan, which will more than compensate him for the loss of Maryland and Kentucky; will elect him, and leave Fillmore no chance in the H. R., or out of it.
This is as plain as adding up the weights of three small hogs. As Mr. Fillmore has no possible chance to carry Illinois for himself, it is plainly to his interest to let Fremont take it, and thus keep it out of the hands of Buchanan. Be not deceived. Buchanan is the hard horse to beat in this race. Let him have Illinois, and nothing can beat him; and he will get Illinois if men persist in throwing away votes upon Mr. Fillmore. Does some one persuade you that Mr. Fillmore can carry Illinois? Nonsense! There are over seventy newspapers in Illinois opposing Buchanan, only three or four of which support Mr. Fillmore, all the rest going for Fremont. Are not these newspapers a fair index of the proportion of the votes? If not, tell me why.
Again, of these three or four Fillmore newspapers, two, at least, are supported in part by the Buchanan men, as I understand. Do not they know where the shoe pinches? They know the Fillmore movement helps them, and therefore they help it.
Do think these things over, and then act according to your judgment.
Yours very truly,
A. Lincoln.
(Confidential.)
This letter was discovered by the Buchanan men, printed in their newspapers, and pronounced, as its author anticipated, "a mean trick." It was a dangerous document to them, and was calculated to undermine the very citadel of their strength.
Mr. Lincoln was still in imperfect fellowship—if, indeed, in any fellowship at all—with the extreme Abolitionists. He had met with Lovejoy and his followers at Bloomington, and was apparently co-operating with them for the same party purposes; but the intensity of his opposition to their radical views is intimated very strongly in this letter to Mr. Whitney:—
SprinGfield, July 9, 1856.
Dear Whitney,—I now expect to go to Chicago on the 15th, and I probably shall remain there or thereabout for about two weeks.
It turned me blind when I first heard Swett was beaten and Lovejoy nominated; but, after much anxious reflection, I really believe it is best to let it stand. This, of course, I wish to be confidential.
Lamon did get your deeds. I went with him to the office, got them, and put them in his hands myself.
Yours very truly,
A. Lincoln.
In June, 1857, Judge Douglas made a speech at Springfield, in which he attempted to vindicate the wisdom and fairness of the law under which the people of Kansas were about to choose delegates to a convention to be held at Lecompton to frame a State constitution. He declared with emphasis, that, if the Free-State party refused to vote at this election, they alone would be blamable for the proslavery constitution which might be formed. The Free-State men professed to have a vast majority,—"three-fourths," "four-fifths," "nine-tenths," of the voters of Kansas. If these wilfully staid away from the polls, and allowed the minority to choose the delegates and make the constitution, Mr. Douglas thought they ought to abide the result, and not oppose the constitution adopted. Mr. Douglas's speech indicated clearly that he himself would countenance no opposition to the forthcoming Lecompton Convention, and that he would hold the Republican politicians responsible if the result failed to be satisfactory to them.
Judge Douglas seldom spoke in that region without provoking a reply from his constant and vigilant antagonist. Mr. Lincoln heard this speech with a critical ear, and then, waiting only for a printed report of it, prepared a reply to be delivered a few weeks later. The speeches were neither of them of much consequence, except for the fact that Judge Douglas seemed to have plainly committed himself in advance to the support of the Lecompton Constitution. Mr. Lincoln took that much for granted; and, arguing from sundry indications that the election would be fraudulently conducted, he insisted that Mr. Douglas himself, as the author of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill, and the inventor of "popular sovereignty," had made this "outrage" possible. He did not believe there were any "Free-State Democrats" in Kansas to make it a Free State without the aid of the Republicans, whom he held to be a vast majority of the population. The latter, he contended, were not all registered; and, because all were not registered, he thought none ought to vote. But Mr. Lincoln advised no bloodshed, no civil war, no roadside assassinations. Even if an incomplete registry might justify a majority of the people in an obstinate refusal to participate in the regulation of their own affairs, it certainly would not justify them in taking up arms to oppose all government in the Territory; and Mr. Lincoln did not say so. We have seen already how, in the "little speech" reported by Mr. Herndon, he deprecated "all physical rebellions" in this country, and applied his views to this case.
Mr. Lincoln also discussed the Dred-Scott Decision at some length; and, while doing so, disclosed his firm belief, that, in some respects, such as "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness," the negroes were made by the Declaration of Independence the equals of white men. But it did not follow from this that he was in favor of political or social equality with them. "There is," said he, "a natural disgust in the minds of nearly all the white people to the idea of an indiscriminate amalgamation of the white and black races; and Judge Douglas evidently is basing his chief hope upon the chances of his being able to appropriate the benefit of this disgust to himself. If he can, by much drumming and repeating, fasten the odium of that idea upon his adversaries, he thinks he can struggle through the storm. He therefore clings to his hope, as a drowning man to the last plank. He makes an occasion for lugging it in from the opposition to the Dred-Scott Decision. He finds the Republicans insisting that the Declaration of Independence includes all men,—black as well as white; and forthwith he boldly denies that it includes negroes at all, and proceeds to argue gravely, that all who contend it does, do so only because they want to vote, eat, sleep, and marry with negroes. Now, I protest against the counterfeit logic which concludes, that, because I do not want a black woman for a slave, I must necessarily want her for a wife. I need not have her for either. I can just leave her alone. In some respects, she certainly is not my equal; but in her natural right to eat the bread she earns with her own hands, without asking leave of any one else, she is my equal, and the equal of all others."
These speeches were delivered, the one early and the other late, in the month of June: they present strongly, yet guardedly, the important issues which were to engage Mr. Lincoln and Mr. Douglas in the famous campaign of 1858, and leave us no choice but to look into Kansas, and observe what had taken place and what was happening there.
Violence still (June, 1857) prevailed throughout the Territory. The administration of President Pierce committed itself at the first in support of the proslavery party. It acknowledged the Legislature as the only legal government in the Territory, and gave it military assistance to enforce its enactments. Gov. Shannon, having by his course only served to increase the hostility between the parties, was recalled, and John W. Geary of Pennsylvania was appointed his successor. Gov. Geary, while adopting the policy of the administration, so far as recognizing the Legislative party as the only legally organized government, was yet disposed to see, that, so far as the two parties could be got to act together, each should be fairly protected. This policy, however, soon brought him into collision with some of the proslavery leaders in the Territory; and, not being sustained by Mr. Buchanan's administration, which had in the mean time succeeded the administration of President Pierce, he resigned his office. Hon. Robert J. Walker of Mississippi was appointed his successor, with Hon. F. P. Stanton of Tennessee as secretary. Both were strong Democrats; and both were earnest advocates of the policy of the administration, as expressed in the recent presidential canvass, and in Mr. Buchanan's inaugural Message,—the absolute freedom of the people of the Territories to form such governments as they saw fit, subject to the provisions of the Constitution. Gov. Walker and his secretary earnestly set themselves to work to carry out this policy. The governor, in various addresses to the people of the Territory, assured all parties that he would protect them in the free expression of their wishes in the election for a new Territorial legislature; and he besought the Free-State men to give up their separate Territorial organization, under which they had already applied for admission into the Union, and by virtue of which they claimed still to have an equitable legal existence. The governor was so earnest in his policy, and so fair-minded in his purposes, that he soon drew upon himself the opposition of the proslavery party of the Territory, now in a small minority, as well as the enmity of that party in the States. He assured the people they should have a fair election for the new Legislature to be chosen in October (1857), and which would come into power in January following. The people took him at his word; and he kept it. Enormous frauds were discovered in two districts, which were promptly set aside. The triumph of the Free-State party was complete: they elected a legislature in their interest by a handsome majority. And now began another phase of the struggle. The policy of the Governor and the Secretary was repudiated at Washington: the former resigned, and the latter was removed. Meanwhile, a convention held under the auspices of the old Legislature had formed a new constitution, known as the Lecompton Constitution, which the old Legislature proposed to submit to the people for ratification on the 21st of December. The manner of submitting it was singular, to say the least. The people were required to vote either for the constitution with slavery, or the constitution without slavery. As without slavery the constitution was in some of its provisions as objectionable as if it upheld slavery, the Free-State men refused to participate in its ratification. The vote on its submission, therefore, stood 4,206 for the constitution with slavery, and 567 without slavery; and it was this constitution, thus submitted and thus adopted, that Mr. Buchanan submitted to Congress on the 2d of February, 1858, as the free expression of the wishes of the people of Kansas; and its support was at once made an administration measure. Meantime the new Legislature elected by the people of the Territory in October submitted this same Lecompton Constitution to the people again, and in this manner: votes to be given for the constitution with slavery and without slavery, and also against the constitution entirely. The latter manner prevailed; the vote against the constitution in any form being over ten thousand. Thus the proslavery party in the Territory was overthrown. Under the auspices of the new Free-State Legislature, a constitutional convention was held at Wyandotte, in March, 1859. A Free-State constitution was adopted, under which Kansas was subsequently admitted into the Union.
Before leaving this Kansas question, there is one phase of the closing part of the struggle which it is worth while to note, particularly as it has a direct bearing upon the fortunes of Judge Douglas, and indirectly to the success of Mr. Lincoln. Douglas always insisted that his plan of "popular sovereignty" would give to the people of the Territories the utmost freedom in the formation of their local governments. When Mr. Buchanan attempted to uphold the Lecompton Constitution as being the free choice of the people of Kansas, Judge Douglas at once took issue with the administration on this question, and the Democratic party was split in twain. Up to the time of the vote of the people of the Territory on the constitution, Douglas had been an unswerving supporter of the administration policy in Kansas. His speech at Springfield, in the June previous, could not be misunderstood. He held all the proceedings which led to the Lecompton issue to be in strict accordance, not only with the letter, but the spirit, of the Kansas-Nebraska Act, and with the faith of the Democratic party as expounded by himself. But a few weeks later it became manifest that his opinions had undergone a change. Ominous rumors of a breach with the administration began to circulate among his friends. It was alleged at length that Mr. Douglas's delicate sense of justice had been shocked by the unfairness of certain elections in Kansas: it was even intimated that he, too, considered the Lecompton affair an "outrage" upon the sovereign people of Kansas, and that he would speedily join the Republicans—the special objects of his indignation in the June speech—in denouncing and defeating it. The Kansas-Nebraska Bill had borne its appropriate fruits,—the fruits all along predicted by Mr. Lincoln,—and Mr. Douglas commended them to anybody's eating but his own. His desertion was sudden and astonishing; but there was method in it, and a reason for it. The next year Illinois was to choose a senator to fill the vacancy created by the expiration of his own term; and the choice lay between the author of the Kansas-Nebraska Bill and its most conspicuous opponent in that State. The newspapers were not yet done publishing Mr. Lincoln's speech, in which occurred the following paragraph:—
"Three years and a half ago Judge Douglas brought forward his famous Nebraska Bill. The country was at once in a blaze. He scorned all opposition, and carried it through Congress. Since then he has seen himself superseded in a Presidential nomination by one indorsing the general doctrine of his measure, but at the same time standing clear of the odium of its untimely agitation and its gross' breach of national faith; and he has seen the successful rival constitutionally elected, not by the strength of friends, but by the division of his adversaries, being in a popular minority of nearly four hundred thousand votes. He has seen his chief aids in his own State, Shields and Richardson, politically speaking, successively tried, convicted, and executed for an offence not their own, but his. And now he sees his own case standing next on the docket for trial."
ALTHOUGH primarily responsible for all that had taken place in Kansas, Mr. Douglas appeared to be suddenly animated by a new and burning zeal in behalf of the Free-State party in the Territory. It struck him very forcibly, just when he needed most to be struck by a new idea, that the Lecompton Constitution was not "the act and deed of the people of Kansas."
Accordingly, Mr. Douglas took his stand against Lecompton at the first note of the long conflict in Congress. We shall make no analysis of the debates, nor set out the votes of senators and representatives which marked the intervals of that fierce struggle between sections, parties, and factions which followed. It is enough to say here, that Mr. Douglas was found speaking and voting with the Republicans upon every phase of the question. He had but one or two followers in the Senate, and a mere handful in the House; yet these were faithful to his lead until a final conference committee and the English Bill afforded an opportunity for some of them to escape. For himself he scorned all compromises, voted against the English Bill, and returned to Illinois to ask the votes of the people upon a winter's record wholly and consistently anti-Democratic. The fact is mentioned, not to obscure the fame of the statesman, nor to impugn the honesty of the politician, but because it had an important influence upon the canvass of the ensuing summer.
During the winter Mr. Douglas held frequent consultations with the leaders of the Republican party. Their meetings were secret, and for that reason the more significant. By this means, harmony of action was secured for the present, and something provided for the future. Mr. Douglas covertly announced himself as a convert to the Republicans, declared his uncompromising enmity to "the slave power," and said that, however he might be distrusted then, he would be seen "fighting their battles in 1860;" but for the time he thought it wise to conceal his ultimate intentions. He could manage the Democracy more effectually by remaining with them until better opportunities should occur. "He insisted that he would never be driven from the party, but would remain in it until he exposed the administration and the Disunionists; and, when he went out, he would go of his own accord. He was in the habit of remarking, that it was policy for him to remain in the party, in order to hold certain of the rank-and-file; so that, if he went over from the Democracy to any other party, he would be able to take the crowd along with him; and, when he got them all over, he would cut down the bridges, and sink the boats." When asked if he knew precisely where his present course was taking him, he answered repeatedly, "I do; and I have checked all my baggage, and taken a through ticket."
He was a proselyte not to be despised: his weight might be sufficient to turn the scale in the Presidential election. The Republicans were naturally pleased with his protestations of friendship, and more than pleased with his proffers of active service; but he was not content with this alone. He contrived to convince many of his late opponents that the Kansas-Nebraska Bill itself was actually conceived in the interests of antislavery, and that the device was the most cunning of political tricks, intended to give back to "freedom" all the vast expanse of territory which the Missouri line had dedicated forever to slavery. "Mr. Douglas's plan for destroying the Missouri line," said one Republican, "and thereby opening the way for the march of freedom beyond the limits forever prohibited by that line, and the opening up of Free States in territory which it was conceded belonged to the Slave States, and its march westward, embracing the whole line of the Pacific from the British possessions to Mexico, struck me as the most magnificent scheme ever conceived by the human mind. This character of conversation, so frequently employed by Mr. Douglas with those with whom he talked, made the deepest impression upon their minds, enlisted them in his behalf, and changed, in almost every instance, their opinion of the man." In support of this view, Mr. Douglas could point to Kansas, where the battle under his bill was being fought out. The Free-State men had, perhaps from the very beginning, been in a majority, and could take possession of the Territory or the new State, as the case might be, whenever they could secure a fair vote. The laboring classes of, the North were the natural settlers of the western Territories. If these failed in numbers, the enormous and increasing European immigration was at their back; and, if both together failed, the churches, aid societies, and antislavery organizations were at hand to raise, arm, and equip great bodies of emigrants, as they would regular forces for a public purpose. The South had no such facilities: its social, political, and material conditions made a sudden exodus of its voting population to new countries a thing impossible. It might send here a man with a few negroes, and there another. It might insist vehemently upon its supposed rights in the common Territories, and be ready to fight for them; but it could never cover the surface of those Territories with cosey farmsteads, or crowd them with intelligent and muscular white men; and yet these last would inevitably give political character to the rising communities. Such clearly were to be the results of "popular sovereignty," as Mr. Douglas had up to that time maintained it under the Nebraska Bill.
It signified the right of the people of a Territory "to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way" when, and not before, they came to frame a State constitution. The Missouri line, on the contrary, had been a sort of convention, which, by common consent, gave all north of it to freedom, and all south of it to slavery. But popular sovereignty disregarded all previous compacts, all ordinances, and all laws. With this doctrine in practice, the North were sure to be victors in every serious contest. But when Mr. Douglas changed ground again, and popular sovereignty became squatter sovereignty, he had reason to boast himself the most efficient, although the wiliest and coolest, antislavery agitator on the continent. The new doctrine implied the right of a handful of settlers to determine the slavery question in their first Legislature. It made no difference whether they did this by direct or "unfriendly legislation:" the result was the same.
"Popular sovereignty! popular sovereignty!" said Mr. Lincoln. "Let us for a moment inquire into this vast matter of popular sovereignty. What is popular sovereignty? We recollect, that, in an early period in the history of this struggle, there was another name for the same thing,—squatter sovereignty. It was not exactly popular sovereignty,—squatter sovereignty. What do these terms mean? What do those terms mean when used now? And vast credit is taken by our friend, the Judge, in regard to his support of it, when he declares the last years of his life have been, and all the future years of his life shall be, devoted to this matter of popular sovereignty. What is it? Why, it is the sovereignty of the people! What was squatter sovereignty? I suppose, if it had any significance at all, it was the right of the people to govern themselves, to be sovereign in their own affairs while they were squatted down in a country not their own, while they had squatted on a territory that did not belong to them; in the sense that a State belongs to the people who inhabit it, when it belongs to the nation. Such right to govern themselves was called 'squatter sovereignty.'"
Again, and on another occasion, but still before Mr. Douglas had substituted "squatter" for "popular" sovereignty,—a feat which was not performed until September, 1859,—Mr. Lincoln said,—
"I suppose almost every one knows, that in this controversy, whatever has been said has had reference to negro slavery. We have not been in a controversy about the right of the people to govern themselves in the ordinary matters of domestic concern in the States and Territories. Mr. Buchanan, in one of his late messages (I think when he sent up the Lecompton Constitution), urged that the main point to which the public attention had been directed was not in regard to the great variety of small domestic matters, but it was directed to negro slavery; and he asserts, that, if the people had had a fair chance to vote on that question, there was no reasonable ground of objection in regard to minor questions. Now, while I think that the people had not had given them, or offered them, a fair chance upon that slavery question, still, if there had been a fair submission to a vote upon that main question, the President's proposition would have been true to the uttermost. Hence, when hereafter I speak of popular sovereignty, I wish to be understood as applying what I say to the question of slavery only, not to other minor domestic matters of a Territory or a State.
"Does Judge Douglas, when he says that several of the past years of his life have been devoted to the question of popular sovereignty, and that all the remainder of his life shall be devoted to it,—does he mean to say, that he has been devoting his life to securing to the people of the Territories the right to exclude slavery from the Territories? If he means so to say, he means to deceive; because he and every one knows that the decision of the Supreme Court, which he approves, and makes an especial ground of attack upon me for disapproving, forbids the people of a Territory to exclude slavery. This covers the whole ground, from the settlement of a Territory till it reaches the degree of maturity entitling it to form a State constitution. So far as all that ground is concerned, the judge is not sustaining popular sovereignty, but absolutely opposing it. He sustains the decision which declares that the popular will of the Territories has no constitutional power to exclude slavery during their territorial existence. This being so, the period of time from the first settlement of a territory till it reaches the point of forming a State constitution is not the thing that the Judge has fought for, or is fighting for; but, on the contrary, he has fought for, and is fighting for, the thing that annihilates and crushes out that same popular sovereignty."
It is probable, that, in the numerous private conferences held by Mr. Douglas with Republican leaders in the winter of 1857-8, he managed to convince them that it was, after all, not popular sovereignty, but squatter sovereignty, that he meant to advance as his final and inevitable deduction from "the great principles" of the Nebraska Bill. This he knew, and they were sure, would give antislavery an unbroken round of solid victories in all the Territories. The South feared it much more than they did the Republican theory: it was, in the language of their first orator, "a shortcut to all the ends of Sewardism."
But Mr. Douglas's great difficulty was to produce any belief in his sincerity. At home, in Illinois, the Republicans distrusted him almost to a man; and at Washington, among his peers in the Senate and the House, it seemed necessary for him to repeat his plans and promises very often, and to mingle with them bitter and passionate declamations against the South. At last, however, he succeeded,—partially, at least. Senator Wilson believed him devoutly; Mr. Burlingame said his record was "laid up in light;" Mr. Colfax, Mr. Blair, and Mr. Covode were convinced; and gentlemen of the press began industriously to prepare the way for his entrance into the Republican party. Mr. Greeley was thoroughly possessed by the new idea, and went about propagating and enforcing it with all his might. Among all the grave counsellors employed in furthering Mr. Douglas's defection, it is singular that only one man of note steadily resisted his admission to a place of leadership in the Republican ranks: Judge Trumbull could not be persuaded; he had no faith in the man who proposed to desert, and had some admonitions to deliver, based upon the history of recent events. He was willing enough to take him "on probation," but wholly opposed to giving him any power. Covode was employed to mollify Judge Trumbull; but he met with no success, and went away without so much as delivering the message with which Mr. Douglas had charged him. The message was a simple proposition of alliance with the home Republicans, to the effect, that, if they agreed to return him to the Senate in 1858, he would fight their Presidential battle in 1860. Judge Trumbull did not even hear it, but he was well assured that Mr. Douglas was "an applicant for admission into the Republican party." "It was reported to me at that time," said he, "that such was the fact; and such appeared to be the universal understanding, among the Republicans at Washington. I will state another fact,—I almost quarrelled with some of my best Republican friends in 'regard to this matter. I was willing to receive Judge Douglas into the Republican party on probation; but I was not, as these Republican friends were, willing to receive him, and place him at the head of our ranks."
Toward the latter part of April, 1858, a Democratic State Convention met in Illinois, and, besides nominating a ticket for State officers, indorsed Mr. Douglas. This placed him in the field for re-election as an Anti-Lecompton Democrat; but it by no means shook the faith of his recently acquired Republican friends: they thought it very natural, under the circumstances, that his ways should be a little devious, and his policy somewhat dark. He had always said he could do more for them by seeming to remain within the Democratic party; and they looked upon this latest proceeding—his practical nomination by a Democratic convention—as the foundation for an act of stupendous treason between that time and the Presidential election. They continued to press the Republicans of Illinois to make no nomination against him,—to vote for him, to trust him, to follow him, as a sincere and manifestly a powerful antislavery leader. These representations had the effect of seducing away, for a brief time, Mr. Wash-burne and a few others among the lesser politicians of the State; but, when they found the party at large irrevocably opposed to the scheme, they reluctantly acquiesced in what they could not prevent,—Mr. Lincoln's nomination. But the plot made a profound impression on Mr. Lincoln's mind: it proved the existence of personal qualities in Mr. Douglas, which, to a simpler man, were unimaginable and inexplicable. A gentleman once inquired of Mr. Lincoln what he thought of Douglas's chances at Charleston. "Well," he replied, "were it not for certain matters that I know transpired, which I regarded at one time among the impossibilities, I would say he stood no possible chance. I refer to the fact, that, in the Illinois contest with myself, he had the sympathy and support of Greeley, of Burlingame, and of Wilson of Massachusetts, and other leading Republicans; that, at the same time, he received the support of Wise, and the influence of Breckinridge, and other Southern men; that he took direct issue with the administration, and secured, against all its power, one hundred and twenty-five thousand out of one hundred and thirty thousand Democratic votes cast in the State. A man that can bring such influence to bear with his own exertions may play the devil at Charleston."
From about the 7th to the 16th of June, 1858, Mr. Lincoln was busily engaged writing a speech: he wrote it in scraps,—a sentence now, and another again. It was originally scattered over numberless little pieces of paper, and was only reduced to consecutive sheets and connected form as the hour for its delivery drew near. It was to be spoken on or about the 16th, when the Republican State Convention would assemble at Springfield, and, as Mr. Lincoln anticipated, would nominate him for senator in Congress.
About the 13th of June, Mr. Dubois, the State auditor, entered the office of Lincoln & Herndon, and found Mr. Lincoln deeply intent upon the speech. "Hello, Lincoln! what are you writing?" said the auditor. "Come, tell me."—"I sha'n't tell you," said Lincoln. "It is none of your business, Mr. Auditor. Come, sit down, and let's be jolly."
On the 16th, the convention, numbering, with delegates and alternates, about a thousand men, met, and passed unanimously the following resolution:—
"That Hon. Abraham Lincoln is our first and only choice for United States senator to fill the vacancy about to be created by the expiration of Mr. Douglas's term of office."
That evening Mr. Lincoln came early to his office, along with Mr. Herndon. Having carefully locked the door, and put the key in his own pocket, he pulled from his bosom the manuscript of his speech, and proceeded to read it slowly and distinctly. When he had finished the first paragraph, he came to a dead pause, and turned to his astounded auditor with the inquiry, "How do you like that? What do you think of it?"—"I think," returned Mr. Herndon, "it is true; but is it entirely politic to read or speak it as it is written?"
—"That makes no difference," Mr. Lincoln said. "That expression is a truth of all human experience,—'a house divided against itself cannot stand;' and 'he that runs may read.' The proposition is indisputably true, and has been true for more than six thousand years; and—I will deliver it as written. I want to use some universally known figure, expressed in simple language as universally known, that may strike home to the minds of men, in order to rouse them to the peril of the times. I would rather be defeated with this expression in the speech, and it held up and discussed before the people, than to be victorious without it."
It may be questioned whether Mr. Lincoln had a clear right to indulge in such a venture, as a representative party man in a close contest. He had other interests than his own in charge: he was bound to respect the opinions, and, if possible, secure the success, of the party which had made him its leader. He knew that the strange doctrine, so strikingly enunciated, would alienate many well-affected voters. Was it his duty to cast these away, or to keep them? He was not asked to sacrifice any principle of the party, or any opinion of his own previously expressed, but merely to forego the trial of an experiment, to withhold the announcement of a startling theory, and to leave the creed of the party as it came from the hands of its makers, without this individual supplement, of which they had never dreamed. It is evident that he had not always been insensible to the force of this reasoning. At the Bloomington Convention he had uttered the same ideas in almost the same words; and their novelty, their tendency, their recognition of a state of incipient civil war in a country for the most part profoundly peaceful,—these, and the bloody work which might come of their acceptance by a great party, had filled the minds of some of his hearers with the most painful apprehensions. The theory was equally shocking to them, whether as partisans or as patriots. Among them was Hon. T. Lyle Dickey, who sought Mr. Lincoln, and begged him to suppress them in future. He vindicated his speech as he has just vindicated it in the interview with Mr. Herndon; but, after much persuasion, he promised at length not to repeat it.
It was now Mr. Herndon's turn to be surprised: the pupil had outstripped the teacher. He was intensely anxious for Mr. Lincoln's election: he feared the effect of this speech; and yet it was so exactly in accordance with his own faith, that he could not advise him to suppress it. It might be heresy to many others, but it was orthodoxy to him; and he was in the habit of telling the whole truth, without regard to consequences. If it cost a single defeat now, he was sure that its potency would one day be felt, and the wisdom of its present utterance acknowledged. He therefore urged Mr. Lincoln to speak it as he had written it, and to treat with the scorn of a prophet those who, having ears, would not hear, and, having eyes, would not see. The advice was not unacceptable, but Mr. Lincoln thought he owed it to other friends to counsel with them also.
About a dozen gentlemen were called to meet in the Library Room in the State House. "After seating them at the round table," says John Armstrong, one of the number, "he read that clause or section of his speech which reads, 'a house divided against itself cannot stand,' &c. He read it slowly and cautiously, so as to let each man fully understand it. After he had finished the reading, he asked the opinions of his friends as to the wisdom or policy of it. Every man among them condemned the speech in substance and spirit, and especially that section quoted above. They unanimously declared that the whole speech was too far in advance of the times; and they all condemned that section or part of his speech already quoted, as unwise and impolitic, if not false. William H. Herndon sat still while they were giving their respective opinions of its unwisdom and impolicy: then he sprang to his feet and said, 'Lincoln, deliver it just as it reads. If it is in advance of the times, let us—you and I, if no one else—lift the people to the level of this speech now, higher hereafter. The speech is true, wise, and politic, and will succeed now or in the future. Nay, it will aid you, if it will not make you President of the United States.'
"Mr. Lincoln sat still a short moment, rose from his chair, walked backwards and forwards in the hall, stopped and said, 'Friends, I have thought about this matter a great deal, have weighed the question well from all corners, and am thoroughly convinced the time has come when it should be uttered; and if it must be that I must go down because of this speech, then let me go down linked to truth,—die in the advocacy of what is right and just. This nation cannot live on injustice,—"a house divided against itself cannot stand," I say again and again.' This was spoken with some degree of emotion,—the effects of his love of truth, and sorrow from the disagreement of his friends with himself."
On the evening of the 17th this celebrated speech—known since as "The House-divided-against-itself Speech"—was delivered to an immense audience in the hall of the House of Representatives. Mr. Lincoln never penned words which had a more prodigious influence upon the public mind, or which more directly and powerfully affected his own career. It was as follows:—
Gentlemen of the Convention,—If we could first know where we are, and whither we are tending, we could then better judge what to do, and how to do it. We are now far on into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of that policy, that agitation had not only not ceased, but has constantly augmented. In my opinion, it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. "A house divided against itself cannot stand." I believe this Government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved,—I do not expect the house to fall; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the farther spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the States,—old as well as new, North as well as South.
Have we no tendency to the latter condition? Let any one who doubts carefully contemplate that now almost complete legal combination,—piece of machinery, so to speak,—compounded of the Nebraska doctrine and the Dred-Scott Decision. Let him consider, not only what work the machinery is adapted to do, and how well adapted, but also let him study the history of its construction, and trace, if he can, or rather fail, if he can, to trace, the evidences of design and concert of action among its chief master-workers from the beginning.
But so far Congress only had acted; and an indorsement by the people, real or apparent, was indispensable, to save the point already gained and give chance for more. The New Year of 1854 found slavery excluded from more than half the States by State constitutions, and from most of the national territory by congressional prohibition. Four days later commenced the struggle which ended in repealing that congressional prohibition. This opened all the national territory to slavery, and was the first point gained.
This necessity had not been overlooked, but had been provided for, as well as might be, in the notable argument of "squatter sovereignty" otherwise called "sacred right of self-government;" which latter phrase, though expressive of the only rightful basis of any government, was so perverted in this attempted use of it as to amount to just this: that, if any one man choose to enslave another, no third man shall be allowed to object. That argument was incorporated into the Nebraska Bill itself, in the language which follows: "It being the true intent and meaning of this act not to legislate slavery into any Territory or State, nor exclude it therefrom, but to leave the people thereof perfectly free to form and regulate their domestic institutions in their own way, subject only to the Constitution of the United States."
Then opened the roar of loose declamation in favor of "squatter sovereignty" and "sacred right of self-government."
"But," said opposition members, "let us be more specific,—let us amend the bill so as to expressly declare that the people of the Territory may exclude slavery."—"Not we," said the friends of the measure; and down they voted the amendment.
While the Nebraska Bill was passing through Congress, a law-case involving the question of a negro's freedom, by reason of his owner having voluntarily taken him first into a Free State, and then a Territory covered by the congressional prohibition, and held him as a slave,—for a long time in each,—was passing through the United-States Circuit Court for the District of Missouri; and both the Nebraska Bill and lawsuit were brought to a decision in the same month of May, 1854. The negro's name was Dred Scott, which name now designates the decision finally made in the case.
Before the then next Presidential election, the law-case came to, and was argued in, the Supreme Court of the United States; but the decision of it was deferred until after the election. Still, before the election, Senator Trumbull, on the floor of the Senate, requests the leading advocate of the Nebraska Bill to state his opinion whether a people of a Territory can constitutionally exclude slavery from their limits; and the latter answers, "That is a question for the Supreme Court."
The election came. Mr. Buchanan was elected, and the indorsement, such as it was, secured. That was the second point gained. The indorsement, however, fell short of a clear popular majority by nearly four hundred thousand votes; and so, perhaps, was not overwhelmingly reliable and satisfactory. The outgoing President, in his last annual Message, as impressively as possible echoed back upon the people the weight and authority of the indorsement.
The Supreme Court met again; did not announce their decision, but ordered a re-argument. The Presidential inauguration came, and still no decision of the court; but the incoming President, in his inaugural address, fervently exhorted the people to abide by the forthcoming decision, whatever it might he. Then, in a few days, came the decision.
This was the third point gained.
The reputed author of the Nebraska Bill finds an early occasion to make a speech at this Capitol indorsing the Dred-Scott Decision, and vehemently denouncing all opposition to it. The new President, too, seizes the early occasion of the Silliman letter to indorse and strongly construe that decision, and to express his astonishment that any different view had ever been entertained. At length a squabble springs up between the President and the author of the Nebraska Bill, on the mere question of fact whether the Lecompton Constitution was, or was not, in any just sense, made by the people of Kansas; and, in that squabble, the latter declares that all he wants is a fair vote for the people, and that he cares not whether slavery be voted down or voted up. I do not understand his declaration, that he cares not whether slavery be voted down or voted up, to be intended by him other than as an apt definition of the policy he would impress upon the public mind,—the principle for which he declares he has suffered much, and is ready to suffer to the end.
And well may he cling to that principle! If he has any parental feeling, well may he cling to it! That principle is the only shred left of his original Nebraska doctrine. Under the Dred-Scott Decision, squatter sovereignty squatted out of existence,—tumbled down like temporary scaffolding; like the mould at the foundery, served through one blast, and fell back into loose sand; helped to carry an election, and then was kicked to the winds. His late joint struggle with the Republicans against the Lecompton Constitution involves nothing of the original Nebraska doctrine. That struggle was made on a point—the right of a people to make their own constitution—upon which he and the Republicans have never differed.
The several points of the Dred-Scott Decision, in connection with Senator Douglas's "care-not" policy, constitute the piece of machinery in its present state of advancement. The working-points of that machinery are,—
First, That no negro slave, imported as such from Africa, and no descendant of such, can ever be a citizen of any State, in the sense of that term as used in the Constitution of the United States.
This point is made in order to deprive the negro, in every possible event, of the benefit of this provision of the United States Constitution, which declares that "The citizens of each State shall be entitled to all the privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States.
Secondly, That, "subject to the Constitution of the United States," neither Congress nor a Territorial Legislature can exclude slavery from any United States Territory.
This point is made in order that individual men may fill up the Territories with slaves, without danger of losing them as property, and thus to enhance the chances of permanency to the institution through all the future.
Thirdly, That whether the holding a negro in actual slavery in a Free State makes him free, as against the holder, the United States courts will not decide, but will leave it to be decided by the courts of any Slave State the negro may be forced into by the master.
This point is made, not to be pressed immediately; but if acquiesced in for a while, and apparently indorsed by the people at an election, then to sustain the logical conclusion, that, what Dred Scott's master might lawfully do with Dred Scott in the free State of Illinois, every other master may lawfully do with any other one or one thousand slaves in Illinois, or in any other Free State.
Auxiliary to all this, and working hand in hand with it, the Nebraska doctrine, or what is left of it, is to educate and mould public opinion, at least Northern public opinion, not to care whether slavery is voted down or voted up.
This shows exactly where we now are, and partially, also, whither we are tending.
It will throw additional light on the latter to go back and run the mind over the string of historical facts already stated. Several things will now appear less dark and mysterious than they did when they were transpiring.
The people were to be left "perfectly free," "subject only to the Constitution." What the Constitution had to do with it, outsiders could not then see. Plainly enough now, it was an exactly fitted niche for the Dred-Scott Decision afterward to come in, and declare that perfect freedom of the people to be just no freedom at all.
Why was the amendment expressly declaring the right of the people to exclude slavery voted down? Plainly enough now: the adoption of it would have spoiled the niche for the Dred-Scott Decision.
Why was the court decision held up? Why even a senator's individual opinion withheld till after the Presidential election? Plainly enough now: the speaking out then would have damaged the "perfectly free" argument upon which the election was to be carried.
Why the outgoing President's felicitation on the indorsement? Why the delay of a re-argument? Why the incoming President's advance exhortation in favor of the decision? These things look like the cautious patting and petting of a spirited horse preparatory to mounting him, when it is dreaded that he may give the rider a fall. And why the hasty after-indorsements of the decision by the President and others?
We cannot absolutely know that all these exact adaptations are the result of preconcert. But when we see a lot of framed timbers, different portions of which we know have been gotten out at different times and places, and by different workmen,—Stephen, Franklin, Roger, and James, for instance,—and when we see these timbers joined together, and see they exactly make the frame of a house or a mill, all the tenons and mortises, exactly fitting, and all the lengths and proportions of the different pieces exactly adapted to their respective places, and not a piece too many or too few,—not omitting even scaffolding—or, if a single piece be lacking, we can see the place in the frame exactly fitted and prepared to yet bring such piece in,—in such a case, we find it impossible not to believe that Stephen and Franklin and Roger and James all understood one another from the beginning, and all worked upon a common plan or draft drawn up before the first blow was struck.
It should not be overlooked, that, by the Nebraska Bill, the people of a State as well as Territory were to be left "perfectly free" "subject only to the Constitution." Why mention a State? They were legislating for Territories, and not for or about States. Certainly the people of a State are and ought to be subject to the Constitution of the United States; but why is mention of this lugged into this merely territorial law? Why are the people of a Territory and the people of a State therein lumped together, and their relation to the Constitution therein treated as being precisely the same?
While the opinion of the court by Chief-Justice Taney, in the Dred-Scott case, and the separate opinions of all the concurring judges, expressly declare that the Constitution of the United States neither permits Congress nor a Territorial Legislature to exclude slavery from any United States
Territory, they all omit to declare whether or not the same Constitution permits a State, or the people of a State, to exclude it. Possibly, this was a mere omission; but who can be quite sure, if McLean or Curtis had sought to get into the opinion a declaration of unlimited power in the people of a State to exclude slavery from their limits, just as Chase and Mace sought to get such declaration, in behalf of the people of a Territory, into the Nebraska Bill,—I ask, who can be quite sure that it would not have been voted down in the one case as it had been in the other?
The nearest approach to the point of declaring the power of a State over slavery is made by Judge Nelson. He approaches it more than once, using the precise idea, and almost the language too, of the Nebraska Act. On one occasion his exact language is, "Except in cases where the power is restrained by the Constitution of the United States, the law of the State is supreme over the subject of slavery within its jurisdiction."
In what cases the power of the State is so restrained by the United States Constitution is left an open question, precisely as the same question, as to the restraint on the power of the Territories, was left open in the Nebraska Act. Put that and that together, and we have another nice little niche, which we may ere long see filled with another Supreme Court decision, declaring that the Constitution of the United States does not permit a State to exclude slavery from its limits. And this may especially be expected if the doctrine of "care not whether slavery be voted down or voted up" shall gain upon the public mind sufficiently to give promise that such a decision can be maintained when made.
Such a decision is all that slavery now lacks of being alike lawful in all the States. Welcome or unwelcome, such decision is probably coming, and will soon be upon us, unless the power of the present political dynasty shall be met and overthrown. We shall lie down pleasantly dreaming that the people of Missouri are on the verge of making their State free; and we shall awake to the reality, instead, that the Supreme Court has made Illinois a Slave State.
To meet and overthrow the power of that dynasty is the work now before all those who would prevent that consummation. That is what we have to do. But how can we best do it?
There are those who denounce us openly to their own friends, and yet whisper softly, that Senator Douglas is the aptest instrument there is with which to effect that object. They do not tell us, nor has he told us, that he wishes any such object to be effected. They wish us to infer all, from the facts that he now has a little quarrel with the present head of the dynasty; and that he has regularly voted with us, on a single point, upon which he and we have never differed.
They remind us that he is a very great man, and that the largest of us are very small ones. Let this be granted. But "a living dog is better than a dead lion." Judge Douglas, if not a dead lion for this work, is at least a caged and toothless one. How can he oppose the advances of slavery? He don't care any thing about it. His avowed mission is impressing the "public heart" to care nothing about it.
A leading Douglas Democrat newspaper thinks Douglas's superior talent will be needed to resist the revival of the African slave-trade. Does Douglas believe an effort to revive that trade is approaching? He has not said so. Does he really think so? But, if it is, how can he resist it? For years he has labored to prove it a sacred right of white men to take negro slaves into the new Territories. Can he possibly show that it is less a sacred right to buy them where they can be bought cheapest? And unquestionably they can be bought cheaper in Africa than in Virginia.
He has done all in his power to reduce the whole question of slavery to one of a mere right of property; and as such, how can he oppose the foreign slave-trade,—how can he refuse that trade in that "property" shall be "perfectly free,"—unless he does it as a protection to the home production? And, as the home producers will probably not ask the protection, he will be wholly without a ground of opposition.
Senator Douglas holds, we know, that a man may rightfully be wiser to-day than he was yesterday; that he may rightfully change when he finds himself wrong. But can we for that reason run ahead, and infer that he will make any particular change, of which he himself has given no intimation? Can we safely base our action upon any such vague inferences?
Now, as ever, I wish not to misrepresent Judge Douglas's position, question his motives, or do aught that can be personally offensive to him. Whenever, if ever, he and we can come together on principle, so that our great cause may have assistance from his great ability, I hope to have interposed no adventitious obstacle.
But clearly he, is not now with us; he does not pretend to be; he does not promise ever to be. Our cause, then, must be intrusted to, and conducted by, its own undoubted friends,—those whose hands are free, whose hearts are in the work, who do care for the result.
Two years ago the Republicans of the nation mustered over thirteen hundred thousand strong. We did this under the single impulse of resistance to a common danger, with every external circumstance against us. Of strange, discordant, and even hostile elements, we gathered from the four winds, and formed and fought the battle through, under the constant hot fire of a disciplined, proud, and pampered enemy. Did we brave all then to falter now?—now, when that same enemy is wavering, dissevered, and belligerent?
The result is not doubtful. We shall not fail,—if we stand firm, we shall not fail. Wise counsels may accelerate or mistakes delay it; but, sooner or later, the victory is sure to come.
The speech produced a profound impression upon men of all parties: the Democrats rejoiced in it, and reprobated it; the conservative Republicans received it coldly, and saw in it the sign of certain defeat. In the eyes of the latter it was a disheartening mistake at the outset of a momentous campaign,—a fatal error, which no policy or exertion could retrieve. Alone of all those directly affected by it, the Abolitionists, the compatriots of Mr. Herndon, heard in it the voice of a fearless leader, who had the wisdom to comprehend an unwelcome fact, and the courage to proclaim it at the moment when the delusion of fancied security and peace was most generally and fondly entertained. It was the "irrepressible conflict" which Mr. Seward had been preaching, and to which the one party had given almost as little credit as the other. Except a few ultraists here and there, nobody as yet had actually prepared his armor for this imaginary conflict, to which the nation was so persistently summoned,—and, indeed, none but those few seriously believed in the possibility of its existence. The Republican party had heretofore disavowed the doctrine with a unanimity nearly as great as that exhibited by the little council of Mr. Lincoln's immediate friends. It was therefore to be expected, that, when a slow, cautious, moderate man like Mr. Lincoln came forward with it in this startling fashion, it would carry dismay to his followers, and a cheering assurance to his enemies. But Mr. Lincoln was looking farther than this campaign: he was quietly dreaming of the Presidency, and edging himself to a place in advance, where he thought the tide might take him up in 1860. He was sure that sectional animosities, far from subsiding, would grow deeper and stronger with time; and for that reason the next nominee of the exclusively Northern party must be a man of radical views. "I think," says Mr. Herndon, "the speech was intended to take the wind out of Seward's sails;" and Mr. Herndon is not alone in his opinion.
A day or two after Mr. Lincoln spoke, one Dr. Long came into his office, and delivered to him a foretaste of the remarks he was doomed to hear for several months. "Well, Lincoln," said he, "that foolish speech of yours will kill you,—will defeat you in this contest, and probably for all offices for all time to come. I am sorry, sorry,—very sorry: I wish it was wiped out of existence. Don't you wish it, now?" Mr. Lincoln had been writing during the doctor's lament; but at the end of it he laid down his pen, raised his head, lifted his spectacles, and, with a look half quizzical, half contemptuous, replied, "Well, doctor, if I had to draw a pen across, and erase my whole life from existence, and I had one poor gift or choice left, as to what I should save from the wreck, I should choose that speech, and leave it to the world unerased."
Leonard Swett, than whom there was no more gifted man, nor a better judge of political affairs, in Illinois, is convinced that "the first ten lines of that speech defeated him." "The sentiment of the 'house divided against itself' seemed wholly inappropriate," says Mr. Swett. "It was a speech made at the commencement of a campaign, and apparently made for the campaign. Viewing it in this light alone, nothing could have been more unfortunate or inappropriate. It was saying first the wrong thing; yet he saw that it was an abstract truth, and standing by the speech would ultimately find him in the right place. I was inclined at the time to believe these words were hastily and inconsiderately uttered; but subsequent facts have convinced me they were deliberate and had been matured.... In the summer of 1859, when he was dining with a party of his intimate friends at Bloomington, the subject of his Springfield speech was discussed. We all insisted that it was a great mistake; but he justified himself, and finally said, 'Well, gentlemen, you may think that speech was a mistake; but I never have believed it was, and you will see the day when you will consider it was the wisest thing I ever said.'"
John T. Stuart was a family connection of the Todds and Edwardses, and thus also of Lincoln. Mr. C. C. Brown married Mr. Stuart's daughter, and speaks of Mr. Lincoln as "our relative." This gentleman says, "The Todd-Stuart-Edwards family, with preacher and priest, dogs and servants, got mad at Mr. Lincoln because he made 'The House-divided-against-itself Speech.' He flinched, dodged, said he would explain, and did explain, in the Douglas debates."
But it was difficult to explain: explanations of the kind are generally more hurtful than the original offence. Accordingly, Mr. Herndon reports in his broad, blunt way, that "Mr. Lincoln met with many cold shoulders for some time,—nay, during the whole canvass with Douglas." At the great public meetings which characterized that campaign, "you could hear, from all quarters in the crowd, Republicans saying, 'Damn that fool speech! it will be the cause of the death of Lincoln and the Republican party. Such folly! such nonsense! Damn it!'"
Since 1840 Lincoln and Douglas had appeared before the people, almost as regularly as the elections came round, to discuss, the one against the other, the merits of parties, candidates, and principles. Thus far Mr. Lincoln had been in a certain sense the pursuer: he had lain in wait for Mr. Douglas; he had caught him at unexpected turns and upon sharp points; he had mercilessly improved the advantage of Mr. Douglas's long record in Congress to pick apart and to criticise, while his own was so much more humble and less extensive. But now at last they were abreast, candidates for the same office, with a fair field and equal opportunities. It was the great crisis in the lives of both. Let us see what they thought of each other; and, in the extracts which convey the information, we may also get a better idea of the character of each for candor, generosity, and truthfulness.
Dr. Holland quotes from one of Mr. Lincoln's unpublished manuscripts as follows:—
"Twenty-two years ago, Judge Douglas and I first became acquainted: we were both young then,—he a trifle younger than I. Even then we were both ambitious,—I, perhaps, quite as much so as he. With me the race of ambition has been a failure,—a flat failure; with him it has been one of splendid success. His name fills the nation, and is not unknown even in foreign lands. I affect no contempt for the high eminence he has reached,—so reached that the oppressed of my species might have shared with me in the elevation, I would rather stand on that eminence than wear the richest crown that ever pressed a monarch's brow."
Again, in the pending campaign, Mr. Lincoln said, "There is still another disadvantage under which we labor, and to which I will invite your attention. It arises out of the relative positions of the two persons who stand before the State as candidates for the Senate. Senator Douglas is of worldwide renown. All the anxious politicians of his party, or who had been of his party for years past, have been looking upon him as certainly, at no distant day, to be the President of the United States. They have seen, in his round, jolly, fruitful face, post-offices, land-offices, marshalships, and cabinet appointments, chargéships and foreign missions, bursting and sprouting out in wonderful exuberance, ready to be laid hold of by their greedy hands. And as they have been gazing upon this attractive picture so long, they cannot, in the little distraction that has taken place in the party, bring themselves to give up the charming hope; but, with greedier anxiety, they rush about him, sustain him, and give him marches, triumphal entries, and receptions, beyond what, even in the days of his highest prosperity, they could have brought about in his favor. On the contrary, nobody has ever expected me to be President. In my poor, lean, lank face, nobody has ever seen that any cabbages were sprouting out. These are disadvantages, all taken together, that the Republicans labor under. We have to fight this battle upon principle, and principle alone."
Now hear Mr. Douglas. In their first joint debate at Ottawa, he said, "In the remarks I have made on this platform, and the position of Mr. Lincoln upon it, I mean nothing personally disrespectful or unkind to that gentleman. I have known him for nearly twenty-five years. There were many points of sympathy between us when we first got acquainted. We were both comparatively boys, and both struggling with poverty in a strange land. I was a schoolteacher in the town of Winchester, and he a flourishing grocery-keeper in the town of Salem. He was more successful in his occupation than I was in mine, and hence more fortunate in this world's goods. Lincoln is one of those peculiar men who perform with admirable skill every thing which they undertake. I made as good a school-teacher as I could; and, when a cabinet-maker, I made a good bedstead and tables, although my old boss said I succeeded better with bureaus and secretaries than with any thing else; but I believe that Lincoln was always more successful in business than I, for his business enabled him to get into the Legislature. I met him there, however, and had a sympathy with him, because of the up-hill struggle we both had in life. He was then just as good at telling an anecdote as now. He could beat any of the boys wrestling, or running a foot-race, in pitching quoits, or tossing a copper; could ruin more liquor than all of the boys of the town together; and the dignity and impartiality with which he presided at a horse-race or fist-fight excited the admiration and won the praise of everybody that was present and participated. I sympathized with him because he was struggling with difficulties; and so was I. Mr. Lincoln served with me in the Legislature in 1836, when we both retired, and he subsided, or became submerged; and he was lost sight of as a public man for some years. In 1846, when Wilmot introduced his celebrated proviso, and the abolition tornado swept over the country, Lincoln again turned up as a member of Congress from the Sangamon district. I was then in the Senate of the United States, and was glad to welcome my old friend and companion. Whilst in Congress, he distinguished himself by his opposition to the Mexican War, taking the side of the common enemy against his own country; and, when he returned home, he found that the indignation of the people followed him everywhere, and he was again submerged, or obliged to retire into private life, forgotten by his former friends. He came up again in 1854, just in time to make this abolition or Black Republican platform, in company with Giddings, Lovejoy, Chase, and Fred. Douglas, for the Republican party to stand upon. Trumbull, too, was one of our own contemporaries."
Previous pages of this book present fully enough for our present purpose the issues upon which this canvass was made to turn. The principal speeches, the joint debates, with five separate and independent speeches by Mr. Lincoln, and three by Mr. Douglas, have been collected and published under Mr. Lincoln's supervision in a neat and accessible volume. It is, therefore, unnecessary, and would be unjust, to reprint them here. They obtained at the time a more extensive circulation than such productions usually have, and exerted an influence which is very surprising to the calm reader of the present day.
Mr. Douglas endeavored to prove, from Mr. Lincoln's Springfield speech, that he (Mr. Lincoln) was a self-declared Disunionist, in favor of reducing the institutions of all the States "to a dead uniformity," in favor of abolishing slavery everywhere,—an old-time abolitionist, a negropolist, an amalgamationist. This, with much vaunting of himself for his opposition to Lecompton, and a loud proclamation of "popular sovereignty," made the bulk of Mr. Douglas's speeches.
Mr. Lincoln denied these accusations; he had no "thought of bringing about civil war," nor yet uniformity of institutions: he would not interfere with slavery where it had a lawful existence, and was not in favor of negro equality or miscegenation. He did, however, believe that Congress had the right to exclude slavery from the Territories, and ought to exercise it. As to Mr. Douglas's doctrine of popular sovereignty, there could be no issue concerning it; for everybody agreed that the people of a Territory might, when they formed a State constitution, adopt or exclude slavery as they pleased. But that a Territorial Legislature possessed exclusive power, or any power at all, over the subject, even Mr Douglas could not assert, inasmuch as the Dred-Scott Decision was plain and explicit the other way; and Mr. Douglas boasted that decision as the rule of his political conduct, and sought to impose it upon all parties as a perfect definition of the rights and duties of government, local and general.
At Ottawa, Mr. Douglas put to Mr. Lincoln a series of questions, which, upon their next meeting (at Freeport), Mr. Lincoln answered as follows:—
I have supposed myself, since the organization of the Republican party at Bloomington, in May, 1856, bound as a party man by the platforms of the party, then and since. If, in any interrogatories which I shall answer, I go beyond the scope of what is within these platforms, it will be perceived that no one is responsible but myself.
Having said thus much, I will take up the judge's interrogatories as I find them printed in "The Chicago Times," and answer them seriatim. In order that there may be no mistake about it, I have copied the interrogatories in writing, and also my answers to them. The first one of these interrogatories is in these words:—
Question 1.—"I desire to know whether Lincoln to-day stands, as he did in 1854, in favor of the unconditional repeal of the Fugitive-Slave Law."
Answer.—I do not now, nor ever did, stand in favor of the unconditional repeal of the Fugitive-Slave Law.
Q. 2.—"I desire him to answer whether he stands pledged to-day, as he did in 1854, against the admission of any more Slave States into the Union, even if the people want them."
A.—I do not now, nor ever did, stand pledged against the admission of any more Slave States into the Union.
Q. 3.—"I want to know whether he stands pledged against the admission of a new State into the Union with such a constitution as the people of that State may see fit to make."
A.—I do not stand pledged against the admission of a new State into the Union, with such a constitution as the people of that State may see fit to make.
Q. 4.—"I want to know whether he stands to-day pledged to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia."
A.—I do not stand to-day pledged to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia.
Q. 5.—"I desire him to answer whether he stands pledged to the prohibition of the slave-trade between the different States."
A.—I do not stand pledged to the prohibition of the slave-trade between the different States.
Q. 6.—"I desire to know whether he stands pledged to prohibit slavery in all the Territories of the United States, north as well as south of the Missouri Compromise line."
A.—I am impliedly, if not expressly, pledged to a belief in the right and duty of Congress to prohibit slavery in all the United States Territories. [Great applause.]
Q 7.—"I desire him to answer whether he is opposed to the acquisition of any new territory unless slavery is first prohibited therein."
A.—I am not generally opposed to honest acquisition of territory; and, in any given case, I would or would not oppose such acquisition, accordingly as I might think such acquisition would or would not agitate the slavery question among ourselves.
Now, my friends, it will be perceived, upon an examination of these questions and answers, that so far I have only answered that I was not pledged to this, that, or the other. The judge has not framed his interrogatories to ask me any thing more than this, and I have answered in strict accordance with the interrogatories, and have answered truly that I am not pledged at all upon any of the points to which I have answered. But I am not disposed to hang upon the exact form of his interrogatory. I am rather disposed to take up at least some of these questions, and state what I really think upon them.
As to the first one, in regard to the Fugitive-Slave Law, I have never hesitated to say, and I do not now hesitate to say, that I think, under the Constitution of the United States, the people of the Southern States are entitled to a congressional slave law. Having said that, I have had nothing to say in regard to the existing Fugitive-Slave Law, further than that I think it should have been framed so as to be free from some of the objections that pertain to it, without lessening its efficiency. And inasmuch as we are not now in an agitation in regard to an alteration or modification of that law, I would not be the man to introduce it as a new subject of agitation upon the general question of slavery.
In regard to the other question, of whether I am pledged to the admission of any more Slave States into the Union, I state to you very frankly, that I would be exceedingly sorry ever to be put in a position of having to pass upon that question. I should be exceedingly glad to know that there would never be another Slave State admitted into the Union; but I must add, that, if slavery shall be kept out of the Territories during the Territorial existence of any one given Territory, and then the people shall, having a fair chance and a clear field, when they come to adopt the constitution, do such an extraordinary thing as to adopt a slave constitution, uninfluenced by the actual presence of the institution among them, I see no alternative, if we own the country, but to admit them into the Union. [Applause.]
The third interrogatory is answered by the answer to the second, it being, as I conceive, the same as the second.
The fourth one is in regard to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia. In relation to that, I have my mind very distinctly made up. I should be exceedingly glad to see slavery abolished in the District of Columbia. I believe that Congress possesses the constitutional power to abolish it. Yet, as a member of Congress, I should not, with my present views, be in favor of endeavoring to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, unless it would be upon these conditions: First, that the abolition should be gradual; Second, That it should be on a vote of the majority of qualified voters in the District; and Third, That compensation should be made to unwilling owners. With these three conditions, I confess I would be exceedingly glad to see Congress abolish slavery in the District of Columbia, and, in the language of Henry Clay, "sweep from our capital that foul blot upon our nation."
In regard to the fifth interrogatory, I must say here, that as to the question of the abolition of the slave-trade between the different States, I can truly answer, as I have, that I am pledged to nothing about it. It is a subject to which I have not given that mature consideration that would make me feel authorized to state a position so as to hold myself entirely bound by it. In other words, that question has never been prominently enough before me to induce me to investigate whether we really have the constitutional power to do it. I could investigate it if I had sufficient time to bring myself to a conclusion upon that subject; but I have not done so, and I say so frankly to you here and to Judge Douglas. I must say, however, that, if I should be of opinion that Congress does possess the constitutional power to abolish slave-trading among the different States, I should still not be in favor of the exercise of that power unless upon some conservative principle as I conceive it, akin to what I have said in relation to the abolition of slavery in the District of Columbia.
My answer as to whether I desire that slavery should be prohibited in all Territories of the United States is full and explicit within itself, and cannot be made clearer by any comments of mine. So I suppose, in regard to the question whether I am opposed to the acquisition of any more territory unless slavery is first prohibited therein, my answer is such that I could add nothing by way of illustration, or making myself better understood, than the answer which I have placed in writing.
Now, in all this the Judge has me, and he has me on the record. I suppose he had flattered himself that I was really entertaining one set of opinions for one place, and another set for another place,—that I was afraid to say at one place what I uttered at another. What I am saying here I suppose I say to a vast audience as strongly tending to abolitionism as any audience in the State of Illinois; and I believe I am saying that which, if it would be offensive to any persons, and render them enemies to myself, would be offensive to persons in this audience.
Mr. Douglas had presented his interrogatories on the 21st of August, and Mr. Lincoln did not answer them until the 27th. They had no meetings between those days; and Mr. Lincoln had ample time to ponder his replies, and consult his friends. But he did more: he improved the opportunity to prepare a series of insidious questions, which he felt sure Mr. Douglas could not possibly answer without utterly ruining his political prospects. Mr. Lincoln struggled for a great prize, unsuspected by the common mind, but the thought of which was ever present to his own. Mr. Douglas was a standing candidate for the Presidency; but as yet Mr. Lincoln was a very quiet one, nursing hopes which his modesty prevented him from obtruding upon others. He was wise enough to keep the fact of their existence to himself, and in the mean time to dig pitfalls and lay obstructions in the way of his most formidable competitors. His present purpose was not only to defeat Mr. Douglas for the Senate, but to "kill him,"—to get him out of the way finally and forever. If he could make him evade the Dred-Scott Decision, and deny the right of a Southern man to take his negroes into a Territory, and keep them there while it was a Territory, he would thereby sever him from the body of the Democratic party, and leave him the leader of merely a little half-hearted antislavery faction. Under such circumstances, Mr. Douglas could never be the candidate of the party at large; but he might serve a very useful purpose by running on a separate ticket, and dividing the great majority of conservative votes, which would inevitably elect a single nominee.
Mr. Lincoln went to Chicago, and there intimated to some of his friends what he proposed to do. They attempted to dissuade him, because, as they insisted, if Mr. Douglas should answer that the Dred-Scott Decision might be evaded by the people of a Territory, and slavery prohibited in the face of it, the answer would draw to him the sympathies of the antislavery voters, and probably, of itself, defeat Mr. Lincoln. But, so long as Mr. Douglas held to the decision in good faith, he had no hope of more aid from that quarter than he had already received. It was therefore the part of wisdom to let him alone as to that point. Mr. Lincoln, on the contrary, looked forward to 1860, and was determined that the South should understand the antagonism between Mr. Douglas's latest conception of "squatter sovereignty," on the one hand, and the Dred-Scott Decision, the Nebraska Bill, and all previous platforms of the party, on the other. Mr. Douglas taught strange doctrines and false ones; and Mr. Lincoln thought the faithful, far and near, should know it. If Mr. Douglas was a schismatic, there ought to be a schism, of which the Republicans would reap the benefit; and therefore he insisted upon his questions. "That is no business of yours," said his friends. "Attend exclusively to your senatorial race, and let the slaveholder and Douglas fight out that question among themselves and for themselves. If you put the question to him, he will answer that the Dred-Scott Decision is simply an abstract rule, having no practical application."—"If he answers that way, he's a dead cock in the pit," responded Mr. Lincoln. "But that," said they, "is none of your business: you are concerned only about the senator-ship."—"No," continued Mr. Lincoln, "not alone exactly: I am killing larger game. The great battle of 1860 is worth a thousand of this senatorial race."
He did accordingly propound the interrogatories as follows:—
1. If the people of Kansas shall, by means entirely unobjectionable in all other respects, adopt a State constitution, and ask admission into the Union under it, before they have the requisite number of inhabitants according to the English Bill,—some ninety-three thousand,—will you vote to admit them?
2. Can the people of a United States Territory, in any lawful way, against the wish of any citizen of the United States, exclude slavery from its limits?
3. If the Supreme Court of the United States shall decide that States cannot exclude slavery from their limits, are you in favor of acquiescing in, adopting, and following such decision as a rule of political action?
4. Are you in favor of acquiring additional territory, in disregard of how such acquisition may affect the nation on the slavery question?
The first and fourth questions Mr. Douglas answered substantially in the affirmative. To the third he replied, that no judge would ever be guilty of the "moral treason" of making such a decision. But to the second—the main question, to which all the others were riders and make-weights—he answered as he was expected to answer. "It matters not," said he, "what way the Supreme Court may hereafter decide as to the abstract question whether slavery may or may not go into a Territory under the Constitution: the people have the lawful means to introduce it or exclude it, as they please, for the reason that slavery cannot exist a day or an hour anywhere, unless it is supported by local police regulations. Those police regulations can only be established by the local Legislature; and, if the people are opposed to slavery, they will elect representatives to that body who will, by unfriendly legislation, effectually prevent the introduction of it into their midst."
The reply was more than enough for Mr. Lincoln's purpose. It cut Mr. Douglas off from his party, and put him in a state of perfect antagonism to it. He firmly denied the power of Congress to restrict slavery; and he admitted, that, under the Dred-Scott Decision, all Territories were open to its entrance. But he held, that, the moment the slaveholder passed the boundary of a Territory, he was at the mercy of the squatters, a dozen or two of whom might get together in a legislature, and rob him of the property which the Constitution, the Supreme Court, and Mr. Douglas himself said he had an indefeasible right to take there. Mr. Lincoln knew that the Southern people would feel infinitely safer in the hands of Congress than in the hands of the squatters. If they regarded the Republican mode of excluding slavery as a barefaced usurpation, they would consider Mr. Douglas's system of confiscation by "unfriendly legislation" mere plain stealing. The Republicans said to them, "We will regulate the whole subject by general laws, which you participate with us in passing;" but Mr. Douglas offered them, as sovereign judges and legislators, the territorial settlers themselves,—squatters they might be,—whom the aid societies rushed into the new Territories for the very purpose of keeping slavery away. The new doctrine was admirably calculated to alarm and incense the South; and, following so closely Mr. Douglas's conduct in the Lecompton affair, it was very natural that he should now be universally regarded by his late followers as a dangerous heretic and a faithless turncoat. The result justified Mr. Lincoln's anticipations. Mr. Douglas did not fully develop his new theory, nor personally promulgate it as the fixed tenet of his faction, until the next year, when he embodied it in the famous article contributed by him to "Harper's Magazine." But it did its work effectually; and, when parties began to marshal for the great struggle of 1860, Mr. Douglas was found to be, not precisely what he had promised,—a Republican, "fighting their battles,"—but an independent candidate, upon an independent platform, dividing the opposition.
Mr. Lincoln pointed out on the spot the wide difference between Mr. Douglas's present views and those he had previously maintained with such dogged and dogmatic persistence. "The new state of the case" had induced "the Judge to sheer away from his original ground." The new theory was false in law, and could have no practical application. The history of the country showed it to be a naked humbug, a demagogue's imposture. Slavery was established in all this country, without "local police regulations" to protect it. Dred Scott himself was held in a Territory, not only without "local police regulations" to favor his bondage, but in defiance of a general law which prohibited it. A man who believed that the Dred-Scott Decision was the true interpretation of the Constitution could not refuse to negro slavery whatever protection it needed in the Territories without incurring the guilt of perjury. To say that slave property might be constitutionally confiscated, destroyed, or driven away from a place where it was constitutionally protected, was such an absurdity as Mr. Douglas alone in this evil strait was equal to; the proposition meaning, as he said on a subsequent occasion, "no less than that a thing may lawfully be driven away from a place where it has a lawful right to be."
"Of that answer at Freeport," as Mr. Herndon has it, Douglas "instantly died. The red-gleaming Southern tomahawk flashed high and keen. Douglas was removed out of Lincoln's way. The wind was taken out of Seward's sails (by the House-divided Speech), and Lincoln stood out prominent."
The State election took place on the 2d of November, 1858. Mr. Lincoln had more than four thousand majority of the votes cast; but this was not enough to give him a majority in the Legislature. An old and inequitable apportionment law was still in operation; and a majority of the members chosen under it were, as it was intended by the law-makers they should be, Democrats. In the Senate were fourteen Democrats to eleven Republicans; and in the House, forty Democrats to thirty-five Republicans. Mr. Douglas was, of course, re-elected, and Mr. Lincoln bitterly disappointed. Some one asked Mr. Lincoln how he felt when the returns came in. He replied, "that he felt like the boy that stumped his toe,—'it hurt too bad to laugh, and he was too big to cry!'"
In this canvass Mr. Lincoln earned a reputation as a popular debater second to that of no man in America,—certainly not second to that of his famous antagonist. He kept his temper; he was not prone to personalities; he indulged in few anecdotes, and those of a decent character; he was fair, frank, and manly; and, if the contest had shown nothing else, it would have shown, at least, that "Old Abe" could behave like a well-bred gentleman under very trying circumstances. His marked success in these discussions was probably no surprise to the people of the Springfield District, who knew him as well as, or better than, they did Mr. Douglas. But in the greater part of the State, and throughout the Union the series of brilliant victories successively won by an obscure man over an orator of such wide experience and renown was received with exclamations of astonishment, alike by listeners and readers. It is true that many believed, or pretended to believe, that he was privately tutored and "crammed" by politicians of greater note than himself; and, when the speeches were at last collected and printed together, it was alleged that Mr. Lincoln's had been re-written or extensively revised by Mr. Judd, Judge Logan, Judge Davis, or some one else of great and conceded abilities.
IN the winter of 1858-9, Mr. Lincoln, having no political business on hand, appeared before the public in the character of lecturer, having prepared himself with much care. His lecture was, or might have been, styled, "All Creation is a mine, and every man a miner." He began with Adam and Eve, and the invention of the "fig-leaf apron," of which he gave a humorous description, and which he said was a "joint operation." The invention of letters, writing, printing, of the application of steam, of electricity, he classed under the comprehensive head of "inventions and discoveries," along with the discovery of America, the enactment of patent-laws, and the "invention of negroes, or the present mode of using them." Part of the lecture was humorous; a very small part of it actually witty; and the rest of it so commonplace that it was a genuine mortification to his friends. He delivered it at two or three points, and then declined all further invitations. To one of these he replied, in March, as follows: "Your note, inviting me to deliver a lecture in Gales-burgh, is received. I regret to say I cannot do so now: I must stick to the courts a while. I read a sort of a lecture to three different audiences during the last month and this; but I did so under circumstances which made it a waste of no time whatever."
From the Douglas discussion many of the leaders of the Republican party believed, and the reader will agree had some foundation for the belief, that Mr. Lincoln was one of the greatest and best men in the party. It was natural, therefore, that many eyes should be turned towards him for the coming Presidential nomination. He had all the requisites of an available candidate: he had not been sufficiently prominent in national politics to excite the jealousies of powerful rivals; he was true, manly, able; he was pre-eminently a man of the people; he had sprung from a low family in the lowest class of society; he had been a rail-splitter, a flat-boatman, a grocery-keeper,—every thing that could commend him to the "popular heart." His manners, his dress, his stories, and his popular name and style of "Honest Old Abe," pointed to him as a man beside whose "running qualities" those of Taylor and Harrison were of slight comparison. That he knew all this, and thought of it a great deal, no one can doubt; and in the late campaign he had most adroitly opened the way for the realization of his hopes. But he knew very well that a becoming modesty in a "new man" was about as needful as any thing else. Accordingly, when a Mr. Pickett wrote him on the subject in March, 1859, he replied as follows: "Yours of the 2d instant, inviting me to deliver my lecture on 'Inventions' in Rock Island, is at hand, and I regret to be unable from press of business to comply therewith. In regard to the other matter you speak of, I beg that you will not give it a further mention. I do not think I am fit for the Presidency."
But in April the project began to be agitated in his own town. On the 27th of that month, he was in the office of "The Central Illinois Gazette," when the editor suggested his name. Mr. Lincoln, "with characteristic modesty, declined." But the editor estimated his "No" at its proper value; and he "was brought out in the next issue, May 4." Thence the movement spread rapidly and strongly. Many Republicans welcomed it, and, appreciating the pre-eminent fitness of the nomination, saw in it the assurance of certain victory.
The West was rapidly filling with Germans and other inhabitants of foreign birth. Dr. Canisius, a German, foreseeing Mr. Lincoln's strength in the near future, wrote to inquire what he thought about the restrictions upon naturalization recently adopted in Massachusetts, and whether he favored the fusion of all the opposition elements in the next canvass. He replied, that, as to the restrictions, he was wholly and unalterably opposed to them; and as to fusion, he was ready for it upon "Republican grounds," but upon no other. He would not lower "the Republican standard even by a hair's breadth." The letter undoubtedly had a good effect, and brought him valuable support from the foreign population.
To a gentleman who desired his views about the tariff question, he replied cautiously and discreetly as follows:—
Dr. Edward Wallace.
My dear Sir,—I am here just now attending court. Yesterday, before I left Springfield, your brother, Dr. William S. Wallace, showed me a letter of yours, in which you kindly mention my name, inquire for my tariff-views, and suggest the propriety of my writing a letter upon the subject. I was an old Henry-Clay Tariff Whig. In old times I made more speeches on that subject than on any other.
I have not since changed my views. I believe yet, if we could have a moderate, carefully adjusted, protective tariff, so far acquiesced in as not to be a perpetual subject of political strife, squabbles, changes, and uncertain, ties, it would be better for us. Still, it is my opinion, that, just now, the revival of that question will not advance the cause itself, or the man who revives it.
I have not thought much on the subject recently; but my general impression is, that the necessity for a protective tariff will ere long force its old opponents to take it up; and then its old friends can join in and establish it on a more firm and durable basis. We, the old Whigs, have been entirely beaten out on the tariff question; and we shall not be able to re-establish the policy until the absence of it shall have demonstrated the necessity for it in the minds of men heretofore opposed to it. With this view, I should prefer to not now write a public letter upon the subject.
I therefore wish this to be considered confidential.
I shall be very glad to receive a letter from you.
In September Mr. Lincoln made a few masterly speeches in Ohio, where Mr. Douglas had preceded him on his new hobby of "squatter sovereignty," or "unfriendly legislation."
Clinton, Oct. 11,1859.
Yours truly,
A. Lincoln.
He spoke at Columbus, Cincinnati, and several other points, each time devoting the greater part of his address to Mr. Douglas and his theories, as if the habit of combating that illustrious chieftain was hard to break.
In December he went to Kansas, speaking at Elwood, Don-aphan, Troy, Atchison, and twice at Leavenworth. Wherever he went, he was met by vast assemblages of people. His speeches were principally repetitions of those previously made in Illinois; but they were very fresh and captivating to his new audiences. These journeys, which turned out to be continuous ovations, spread his name and fame far beyond the limits to which they had heretofore been restricted.
During the winter of 1859-60, he saw that his reputation had reached such a height, that he might honorably compete with such renowned men as Seward, Chase, and Bates, for the Presidential nomination. Mr. Jackson Grimshaw of Quincy urged him very strongly on the point. At length Mr. Lincoln consented to a conference with Grimshaw and some of his more prominent friends. It took place in a committee-room in the State House. Mr. Bushnell, Mr. Hatch (the Secretary of State), Mr. Judd (Chairman of the Republican State Central Committee), Mr. Peck, and Mr. Grimshaw were present,—all of them "intimate friends." They were unanimous in opinion as to the expediency and propriety of making him a candidate. But "Mr. Lincoln, with his characteristic modesty, doubted whether he could get the nomination, even if he wished it, and asked until the next morning to answer us.... The next day he authorized us to consider him, and work for him, if we pleased, as a candidate for the Presidency."
It was in October, 1859, that Mr. Lincoln received an invitation to speak in New York. It enchanted him: no event of his life had given him more heartfelt pleasure. He went straight to his office, and, Mr. Herndon says, "looked pleased, not to say tickled. He said to me, 'Billy, I am invited to deliver a lecture in New York. Shall I go?'—'By all means,' I replied; 'and it is a good opening too.'—'If you were in my fix, what subject would you choose?' said Lincoln. 'Why, a political one: that's your forte,' I answered." Mr. Herndon remembered his partner's previous "failure,—utter failure," as a lecturer, and, on this occasion, dreaded excessively his choice of a subject. "In the absence of a friend's advice, Lincoln would as soon take the Beautiful for a subject as any thing else, when he had absolutely no sense of it." He wrote in response to the invitation, that he would avail himself of it the coming February, provided he might be permitted to make a political speech, in case he found it inconvenient to get up one of another kind. He had purposely set the day far ahead, that he might thoroughly prepare himself; and it may safely be said, that no effort of his life cost him so much labor as this one. Some of the party managers who were afterwards put to work to verify its statements, and get it out as a campaign document, are alleged to have been three weeks in finding the historical records consulted by him.
On the 25th of February, 1860, he arrived in New York. It was Saturday, and he spent the whole day in revising and retouching his speech. The next day he heard Beecher preach, and on Monday wandered about the city to see the sights. When the committee under whose auspices he was to speak waited upon him, they found him dressed in a sleek and shining suit of new black, covered with very apparent creases and wrinkles, acquired by being packed too closely and too long in his little valise. He felt uneasy in his new clothes and a strange place. His confusion was increased when the reporters called to get the printed slips of his speech in advance of its delivery. Mr. Lincoln knew nothing of such a custom among the orators, and had no slips. He was, in fact, not quite sure that the press would desire to publish his speech. When he reached the Cooper Institute, and was ushered into the vast hall, he was surprised to see the most cultivated men of the city awaiting him on the stand, and an immense audience assembled to hear him. Mr. Bryant introduced him as "an eminent citizen of the West, hitherto known to you only by reputation." Mr. Lincoln then began, in low, monotonous tones, which gradually became louder and clearer, the following speech:—
Mr. President and Fellow-Citizens of New York,—The facts with which I shall deal this evening are mainly old and familiar; nor is there any thing new in the general use I shall make of them. If there shall be any novelty, it will be in the mode of presenting the facts, and the inferences and observations following that presentation.
In his speech last autumn, at Columbus, Ohio, as reported in "The New-York Times," Senator Douglas said,—"Our fathers, when they framed the government under which we live, understood this question just as well, and even better than we do now."
I fully indorse this, and I adopt it as a text for this discourse. I so adopt it, because it furnishes a precise and agreed starting-point for the discussion between Republicans and that wing of Democracy headed by Senator Douglas. It simply leaves the inquiry, "What was the understanding those fathers had of the questions mentioned?"
What is the frame of government under which we live?
The answer must be, "The Constitution of the United States." That Constitution consists of the original, framed in 1787 (and under which the present Government first went into operation), and twelve subsequently framed amendments, the first ten of which were framed in 1789.
Who were our fathers that framed the Constitution? I suppose the "thirty-nine" who signed the original instrument may be fairly called our fathers who framed that part of the present Government. It is almost exactly true to say they framed it; and it is altogether true to say they fairly represented the opinion and sentiment of the whole nation at that time. Their names, being familiar to nearly all, and accessible to quite all, need not now be repeated.
I take these "thirty-nine," for the present, as being "our fathers, who framed the Government under which we live."
What is the question which, according to the text, those fathers understood just as well, and even better than we do now?
It is this: Does the proper division of local from Federal authority, or any thing in the Constitution, forbid our Federal Government control as to slavery in our Federal Territories?
Upon this, Douglas holds the affirmative, and Republicans the negative. This affirmative and denial form an issue; and this issue, this question, is precisely what the text declares our fathers understood better than we.
Let us now inquire whether the "thirty-nine," or any of them, ever acted upon this question; and, if they did, how they acted upon it,—how they expressed that better understanding.
In 1784,—three years before the Constitution,—the United States then owning the North-western Territory, and no other, the Congress of the Confederation had before them the question of prohibiting slavery in that Territory; and four of the "thirty-nine" who afterward framed the Constitution were in that Congress, and voted on that question. Of these, Roger Sherman, Thomas Mifflin, and Hugh Williamson voted for the prohibition; thus showing, that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor any thing else, properly forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory. The other of the four, James McHenry, voted against the prohibition, showing that, for some cause, he thought it improper to vote for it.
In 1787—still before the Constitution, but while the Convention was in session framing it, and while the North-western Territory still was the only Territory owned by the United States—the same question of prohibiting slavery in the Territory again came before the Congress of the Confederation; and three more of the "thirty-nine" who afterward signed the Constitution were in that Congress, and voted on the question. They were William Blount, William Few, and Abraham Baldwin; and they all voted for the prohibition, thus showing that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor any thing else, properly forbids the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory. This time the prohibition became a law, being part of what is now well known as the Ordinance of '87.
The question of Federal control of slavery in the Territories seems not to have been directly before the convention which framed the original Constitution; and hence it is not recorded that the "thirty-nine," or any of them, while engaged on that instrument, expressed any opinion on that precise question.
In 1789, by the First Congress which sat under the Constitution, an act was passed to enforce the Ordinance of '87, including the prohibition of slavery in the North-western Territory. The bill for this act was reported by one of the "thirty-nine,"—Thomas Fitzsimmons, then a member of the House of Representatives from Pennsylvania. It went through all its stages without a word of opposition, and finally passed both branches without yeas and nays, which is equivalent to a unanimous passage. In this Congress there were sixteen of the "thirty-nine" fathers who framed the original Constitution. They were John Langdon, Nicholas Gilman, William S. Johnson, Roger Sherman, Robert Morris, Thomas Fitzsimmons, William Few, Abraham Baldwin, Rufus King, William Patterson, George Clymer, Richard Bassett, George Read, Pierce Butler, Daniel Carrol, James Madison.
This shows that, in their understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor any thing in the Constitution, properly forbade Congress to prohibit slavery in the Federal territory; else both their fidelity to correct principle, and their oath to support the Constitution, would have constrained them to oppose the prohibition.
Again, George Washington, another of the "thirty-nine," was then President of the United States, and, as such, approved and signed the bill, thus completing its validity as a law, and thus showing, that, in his understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor any thing in the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
No great while after the adoption of the original Constitution, North Carolina ceded to the Federal Government the country now constituting the State of Tennessee; and a few years later Georgia ceded that which now constitutes the States of Mississippi and Alabama. In both deeds of cession it was made a condition by the ceding States that the Federal Government should not prohibit slavery in the ceded country. Besides this, slavery was then actually in the ceded country. Under these circumstances, Congress, on taking charge of these countries, did not absolutely prohibit slavery within them. But they did interfere with it, take control of it, even there, to a certain extent. In 1798, Congress organized the Territory of Mississippi. In the act of organization they prohibited the bringing of slaves into the Territory, from any place without the United States, by fine, and giving freedom to slaves so brought. This act passed both branches of Congress without yeas and nays. In that Congress were three of the "thirty-nine" who framed the original Constitution: they were John Langdon, George Read, and Abraham Baldwin. They all, probably, voted for it. Certainly they would have placed their opposition to it upon record, if, in their understanding, any line dividing local from Federal authority, or any thing in the Constitution, properly forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
In 1803 the Federal Government purchased the Louisiana country. Our former territorial acquisitions came from certain of our own States; but this Louisiana country was acquired from a foreign nation. In 1804 Congress gave a territorial organization to that part of it which now constitutes the State of Louisiana. New Orleans, lying within that part, was an old and comparatively large city. There were other considerable towns and settlements, and slavery was extensively and thoroughly intermingled with the people. Congress did not, in the Territorial Act, prohibit slavery; but they did interfere with it, take control of it, in a more marked and extensive way than they did in the case of Mississippi. The substance of the provision therein made, in relation to slaves, was,—
First, That no slave should be imported into the Territory from foreign parts.
Second, That no slave should be carried into it who had been imported into the United States since the first day of May, 1798.
Third, That no slave should be carried into it, except by the owner, and for his own use as a settler; the penalty in all the cases being a fine upon the violator of the law, and freedom to the slave.
This act also was passed without yeas and nays. In the Congress which passed it there were two of the "thirty-nine:" they were Abraham Baldwin and Jonathan Dayton. As stated in the case of Mississippi, it is probable they both voted for it. They would not have allowed it to pass without recording their opposition to it, if, in their understanding, it violated either the line proper dividing local from Federal authority or any provision of the Constitution.
In 1819-20 came and passed the Missouri question. Many votes were taken by yeas and nays, in both branches of Congress, upon the various phases of the general question. Two of the "thirty-nine"—Rufus King and Charles Pinckney—were members of that Congress. Mr. King steadily voted for slavery prohibition and against all compromises; while Mr. Pinckney as steadily voted against slavery prohibition and against all compromises. By this Mr. King showed, that, in his understanding, no line dividing local from Federal authority, nor any thing in the Constitution, was violated by Congress prohibiting slavery in Federal territory; while Mr. Pinckney, by his votes, showed, that, in his understanding, there was some sufficient reason for opposing such prohibition in that case.
The cases I have mentioned are the only acts of the "thirty-nine," or of any of them, upon the direct issue, which I have been able to discover.
To enumerate the persons who thus acted as being four in 1784, three in 1787, seventeen in 1789, three in 1798, two in 1804, and two in 1819-20,—there would be thirty-one of them. But this would be counting John Lang-don, Roger Sherman, William Few, Rufus King, and George Read each twice, and Abraham Baldwin four times. The true number of those of the "thirty-nine" whom I have shown to have acted upon the question, which, by the text, they understood better than we, is twenty-three, leaving sixteen not shown to have acted upon it in any way.
Here, then, we have twenty-three out of our "thirty-nine" fathers, who framed the government under which we live, who have, upon their official responsibility and their corporal oaths, acted upon the very question which the text affirms they "understood just as well, and even better than we do now;" and twenty-one of them—a clear majority of the "thirty-nine"—so acting upon it as to make them guilty of gross political impropriety and wilful perjury if, in their understanding, any proper division between local and Federal authority, or any thing in the Constitution they had made themselves, and sworn to support, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. Thus the twenty-one acted; and, as actions speak louder than words, so actions under such responsibility speak still louder.
Two of the twenty-three voted against congressional prohibition of slavery in the Federal Territories in the instances in which they acted upon the question; but for what reasons they so voted is not known. They may have done so because they thought a proper division of local from Federal authority, or some provision or principle of the Constitution, stood in the way; or they may, without any such question, have voted against the prohibition, on what appeared to them to be sufficient grounds of expediency. No one who has sworn to support the Constitution can conscientiously vote for what he understands to be an unconstitutional measure, however expedient he may think it; but one may and ought to vote against a measure which he deems constitutional if, at the same time, he deems it inexpedient. It, therefore, would be unsafe to set down even the two who voted against the prohibition as having done so because, in their understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or any thing in the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in Federal territory.
The remaining sixteen of the "thirty-nine," so far as I have discovered, have left no record of their understanding upon the direct question of Federal control of slavery in the Federal Territories. But there is much reason to believe that their understanding upon that question would not have appeared different from that of their twenty-three compeers, had it been manifested at all.
For the purpose of adhering rigidly to the text, I have purposely omitted whatever understanding may have been manifested by any person, however distinguished, other than the "thirty-nine" fathers who framed the original Constitution; and, for the same reason, I have also omitted whatever understanding may have been manifested by any of the "thirty-nine" even, on any other phase of the general question of slavery. If we should look into their acts and declarations on those other phases, as the foreign slave-trade, and the morality and policy of slavery generally, it would appear to us, that, on the direct question of Federal control of slavery in Federal Territories, the sixteen, if they had acted at all, would probably have acted just as the twenty-three did. Among that sixteen were several of the most noted antislavery men of those times,—as Dr. Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and Gouverneur Morris; while there was not one now known to have been otherwise, unless it may be John Rutledge of South Carolina.
The sum of the whole is, that of our "thirty-nine" fathers who framed the original Constitution, twenty-one—a clear majority of the whole—certainly understood that no proper division of local from Federal authority, nor any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control slavery in the Federal Territories; while all the rest probably had the same understanding. Such, unquestionably, was the understanding of our fathers who framed the original Constitution; and the text affirms that they understood the question better than we.
But, so far, I have been considering the understanding of the question manifested by the framers of the original Constitution. In and by the original instrument, a mode was provided for amending it; and, as I have already stated, the present frame of government under which we live consists of that original, and twelve amendatory articles framed and adopted since. Those who now insist that Federal control of slavery in Federal Territories violates the Constitution point us to the provisions which they suppose it thus violates; and, as I understand, they all fix upon provisions in these amendatory articles, and not in the original instrument. The Supreme Court, in the Dred-Scott case, plant themselves upon the fifth amendment, which provides that "no person shall be deprived of property without due process of law;" while Senator Douglas and his peculiar adherents plant themselves upon the tenth amendment, providing that "the powers not granted by the Constitution are reserved to the States respectively and to the people."
Now, it so happens that these amendments were framed by the first Congress which sat under the Constitution,—the identical Congress which passed the act already mentioned, enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the North-western Territory. Not only was it the same Congress, but they were the identical, same individual men, who, at the same time within the session, had under consideration, and in progress toward maturity, these constitutional amendments, and this act prohibiting slavery in all the territory the nation then owned. The constitutional amendments were introduced before, and passed after, the act enforcing the Ordinance of '87; so that, during the whole pendency of the act to enforce the Ordinance, the constitutional amendments were also pending.
That Congress, consisting in all of seventy-six members, including sixteen of the framers of the original Constitution, as before stated, were preeminently our fathers who framed that part of the government under which we live, which is now claimed as forbidding the Federal Government to control slavery in the Federal Territories.
Is it not a little presumptuous in any one at this day to affirm that the two things which that Congress deliberately framed, and earned to maturity at the same time, are absolutely inconsistent with each other? And does not such affirmation become impudently absurd when coupled with the other affirmation, from the same mouth, that those who did the two things alleged to be inconsistent understood whether they were really inconsistent better than we,—better than he who affirms that they are inconsistent?
It is surely safe to assume that the "thirty-nine" framers of the original Constitution, and the seventy-six members of the Congress which framed the amendments thereto, taken together, do certainly include those who may be fairly called "our fathers who framed the government under which we live." And so assuming, I defy any man to show that any one of them ever, in his whole life, declared, that, in his understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. I go a step farther. I defy any one to show that any living man in the whole world ever did, prior to the beginning of the present century (and I might almost say prior to the beginning of the last half of the present century), declare, that, in his understanding, any proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbade the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories. To those who now so declare, I give, not only "our fathers, who framed the government under which we live," but with them all other living men within the century in which it was framed, among whom to search, and they shall not be able to find the evidence of a single man agreeing with them.
Now, and here, let me guard a little against being misunderstood. I do not mean to say we are bound to follow implicitly in whatever our fathers did. To do so would be to discard all the lights of current experience,—to reject all progress,—all improvement. What I do say is, that, if we would supplant the opinions and policy of our fathers in any case, we should do so upon evidence so conclusive, and argument so clear, that even their great authority, fairly considered and weighed, cannot stand; and most surely not in a case whereof we ourselves declare they understood the question better than we.
If any man, at this day, sincerely believes that a proper division of local from Federal authority, or any part of the Constitution, forbids the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories, he is right to say so, and to enforce his position by all truthful evidence and fair argument which he can. But he has no right to mislead others, who have less access to history and less leisure to study it, into the false belief that "our fathers, who framed the government under which we live," were of the same opinion, thus substituting falsehood and deception for truthful evidence and fair argument. If any man at this day sincerely believes "our fathers, who framed the government under which we live," used and applied principles, in other cases, which ought to have led them to understand that a proper division of local from Federal authority, or some part of the Constitution, forbids the Federal Government to control as to slavery in the Federal Territories, he is right to say so. But he should, at the same time, brave the responsibility of declaring, that, in his opinion, he understands their principles better than they did themselves; and especially should he not shirk that responsibility by asserting that they "understood the question just as well, and even better than we do now."
But enough. Let all who believe that "our fathers, who framed the government under which we live, understood this question just as well, and even better than we do now," speak as they spoke, and act as they acted upon it. This is all Republicans ask, all Republicans desire, in relation to slavery. As those fathers marked it, so let it be again marked, as an evil not to be extended, but to be tolerated and protected only because of and so far as its actual presence among us makes that toleration and protection a necessity. Let all the guaranties those fathers gave it be, not grudgingly, but fully and fairly maintained. For this Republicans contend, and with this, so far as I know or believe, they will be content.
And now, if they would listen,—as I suppose they will not,—I would address a few words to the Southern people.
I would say to them, You consider yourselves a reasonable and a just people; and I consider, that, in the general qualities of reason and justice, you are not inferior to any other people. Still, when you speak of us Republicans, you do so only to denounce us as reptiles, or, at the best, as no better than outlaws. You will grant a hearing to pirates or murderers, but nothing like it to "Black Republicans." In all your contentions with one another, each of you deems an unconditional condemnation of "Black Republicanism" as the first thing to be attended to. Indeed, such condemnation of us seems to be an indispensable prerequisite—license, so to speak—among you to be admitted or permitted to speak at all.
Now can you, or not, be prevailed upon to pause and to consider whether this is quite just to us, or even to yourselves?
Bring forward your charges and specifications, and then be patient long enough to hear us deny or justify.
You say we are sectional. We deny it. That makes an issue; and the burden of proof is upon you. You produce your proof; and what is it? Why, that our party has no existence in your section,—gets no votes in your section. The fact is substantially true; but does it prove the issue? If it does, then in case we should, without change of principle, begin to get votes in your section, we should thereby cease to be sectional. You cannot escape this conclusion; and yet are you willing to abide by it? If you are, you will probably soon find that we have ceased to be sectional, for we shall get votes in your section this very year. You will then begin to discover, as the truth plainly is, that your proof does not touch the issue. The fact that we get no votes in your section is a fact of your making, and not of ours. And if there be fault in that fact, that fault is primarily yours, and remains so until you show that we repel you by some wrong principle or practice. If we do repel you by any wrong principle or practice, the fault is ours; but this brings us to where you ought to have started,—to a discussion of the right or wrong of our principle. If our principle, put in practice, would wrong your section for the benefit of ours, or for any other object, then our principle, and we with it, are sectional, and are justly opposed and denounced as such. Meet us, then, on the question of whether our principle, put in practice, would wrong your section; and so meet it as if it were possible that something may be said on our side. Do you accept the challenge? No? Then you really believe that the principle which our fathers, who framed the government under which we live, thought so clearly right as to adopt it, and indorse it again and again upon their official oaths, is, in fact, so clearly wrong as to demand your condemnation without a moment's consideration.
Some of you delight to flaunt in our faces the warning against sectional parties given by Washington in his Farewell Address. Less than eight years before Washington gave that warning, he had, as President of the United States, approved and signed an act of Congress enforcing the prohibition of slavery in the North-western Territory, which act embodied the policy of the Government upon that subject up to and at the very moment he penned that warning; and about one year after he penned it he wrote Lafayette that he considered that prohibition a wise measure, expressing, in the same connection, his hope that we should some time have a confederacy of Free States.
Bearing this in mind, and seeing that sectionalism has since arisen upon this same subject, is that warning a weapon in your hands against us, or in our hands against you? Could Washington himself speak, would he cast the blame of that sectionalism upon us, who sustain his policy, or upon you, who repudiate it? We respect that warning of Washington; and we commend it to you, together with his example pointing to the right application of it.
But you say you are conservative,—eminently conservative; while we are revolutionary, destructive, or something of the sort. What is conservatism? Is it not adherence to the old and tried against the new and untried? We stick to, contend for, the identical old-policy on the point in controversy which was adopted by our fathers who framed the government under which we live; while you, with one accord, reject and scout and spit upon that old policy, and insist upon substituting something new. True, you disagree among yourselves as to what that substitute shall be. You have considerable variety of new propositions and plans; but you are unanimous in rejecting and denouncing the old policy of the fathers. Some of you are for reviving the foreign slave-trade; some for a Congressional Slave-code for the Territories; some for Congress forbidding the Territories to prohibit slavery within their limits; some for maintaining slavery in the Territories through the judiciary; some for the "gur-reat pur-rinciple" that, "if one man would enslave another, no third man should object," fantastically called "popular sovereignty;" but never a man among you in favor of Federal prohibition of slavery in Federal Territories, according to the practice of our fathers, who framed the government under which we live. Not one of all your various plans can show a precedent or an advocate in the century within which our Government originated. Consider, then, whether your claim of conservatism for yourselves, and your charge of destructiveness against us, are based on the most clear and stable foundations.
Again, you say we have made the slavery question more prominent than it formerly was. We deny it. We admit that it is more prominent, but we deny that we made it so. It was not we, but you, who discarded the old policy of the fathers. We resisted, and still resist, your innovation; and thence comes the greater prominence of the question. Would you have that question reduced to its former proportions? Go back to that old policy. What has been will be again, under the same conditions. If you would have the peace of the old times, re-adopt the precepts and policy of the old times.
You charge that we stir up insurrections among your slaves. We deny it. And what is your proof? Harper's Ferry! John Brown! John Brown was no Republican; and you have failed to implicate a single Republican in his Harper's Ferry enterprise. If any member of our party is guilty in that matter, you know it, or you do not know it. If you do know it, you are inexcusable to not designate the man, and prove the fact. If you do not know it, you are inexcusable to assert it, and especially to persist in the assertion after you have tried and failed to make the proof. You need not be told that persisting in a charge which one does not know to be true is simply malicious slander.
Some of you admit that no Republican designedly aided or encouraged the Harper's-Ferry affair, but still insist that our doctrines and declarations necessarily lead to such results. We do not believe it. We know we hold to no doctrine, and make no declarations, which were not held to and made by our fathers, who framed the government under which we live. You never deal fairly by us in relation to this affair. When it occurred, some important State elections were near at hand; and you were in evident glee with the belief, that, by charging the blame upon us, you could get an advantage of us in those elections. The elections came; and your expectations were not quite fulfilled. Every Republican man knew, that, as to himself at least, your charge was a slander, and he was not much inclined by it to cast his vote in your favor. Republican doctrines and declarations are accompanied with a continual protest against any interference whatever with your slaves, or with you about your slaves. Surely this does not encourage them to revolt. True, we do, in common with our fathers who framed the government under which we live, declare our belief that slavery is wrong; but the slaves do not hear us declare even this. For any thing we say or do, the slaves would scarcely know there is a Republican party. I believe they would not, in fact, generally know it but for your misrepresentations of us in their hearing. In your political contest among yourselves, each faction charges the other with sympathy with Black Republicanism; and then, to give point to the charge, defines Black Republicanism to simply be insurrection, blood, and thunder among the slaves.
Slave insurrections are no more common now than they were before the Republican party was organized. What induced the Southampton Insurrection, twenty-eight years ago, in which, at least, three times as many lives were lost as at Harper's Ferry? You can scarcely stretch your very elastic fancy to the conclusion that Southampton was got up by Black Republicanism. In the present state of things in the United States, I do not think a general, or even a very extensive slave insurrection, is possible. The indispensable concert of action cannot be attained. The slaves have no means of rapid communication; nor can incendiary free men, black or white, supply it. The explosive materials are everywhere in parcels; but there neither are, nor can be supplied, the indispensable connecting trains.
Much is said by Southern people about the affection of slaves for their masters and mistresses; and a part of it, at least, is true. A plot for an uprising could scarcely be devised and communicated to twenty individuals before some one of them, to save the life of a favorite master or mistress, would divulge it. This is the rule; and the slave revolution in Hayti was not an exception to it, but a case occurring under peculiar circumstances. The gunpowder plot of British history, though not connected with the slaves, was more in point. In that case, only about twenty were admitted to the secret; and yet one of them, in his anxiety to save a friend, betrayed the plot to that friend, and, by consequence, averted the calamity. Occasional poisoning from the kitchen, and open or stealthy assassinations in the field, and local revolts extending to a score or so, will continue to occur as the natural results of slavery; but no general insurrection of slaves, as I think, can happen in this country for a long time. Whoever much fears, or much hopes, for such an event will be alike disappointed.
In the language of Mr. Jefferson, uttered many years ago, "It is still in our power to direct the process of emancipation and deportation peaceably, and in such slow degrees, as that the evil will wear off insensibly; and their places be, pari passu, filled up by free white laborers. If, on the contrary, it is left to force itself on, human nature must shudder at the prospect held up."
Mr. Jefferson did not mean to say, nor do I, that the power of emancipation is in the Federal Government. He spoke of Virginia; and, as to the power of emancipation, I speak of the slaveholding States only.
The Federal Government, however, as we insist, has the power of restraining the extension of the institution,—the power to insure that a slave insurrection shall never occur on any American soil which is now free from slavery.
John Brown's effort was peculiar. It was not a slave insurrection. It was an attempt by white men to get up a revolt among slaves, in which the slaves refused to participate. In fact, it was so absurd that the slaves, with all their ignorance, saw plainly enough it could not succeed. 'That affair, in its philosophy, corresponds with the many attempts, related in history, at the assassination of kings and emperors. An enthusiast broods over the oppression of a people till he fancies himself commissioned by Heaven to liberate them. He ventures the attempt, which ends in little else than in his own execution. Orsini's attempt on Louis Napoleon, and John Brown's attempt at Harper's Ferry, were, in their philosophy, precisely the same. The eagerness to cast blame on old England in the one case, and on New England in the other, does not disprove the sameness of the two things.
And how much would it avail you, if you could, by the use of John Brown, Helper's book, and the like, break up the Republican organization? Human action can be modified to some extent; but human nature cannot be changed. There is a judgment and a feeling against slavery in this nation, which cast at least a million and a half of votes. You cannot destroy that judgment and feeling, that sentiment, by breaking up the political organization which rallies around it. You can scarcely scatter and disperse an army which has been formed into order in the face of your heaviest fire; but, if you could, how much would you gain by forcing the sentiment which created it out of the peaceful channel of the ballot-box, into some other channel? What would that other channel probably be? Would the number of John Browns be lessened or enlarged by the operation?
But you will break up the Union rather than submit to a denial of your constitutional rights.
That has a somewhat reckless sound; but it would be palliated, if not fully justified, were we proposing by the mere force of numbers to deprive you of some right plainly written down in the Constitution. But we are proposing no such thing.
When you make these declarations, you have a specific and well-under-stood allusion to an assumed constitutional right of yours to take slaves into the Federal Territories, and hold them there as property; but no such right is specifically written in the Constitution. That instrument is literally silent about any such right. We, on the contrary, deny that such a right has any existence in the Constitution, even by implication.
Your purpose then, plainly stated, is, that you will destroy the government, unless you be allowed to construe and enforce the Constitution as you please on all points in dispute between you and us. You will rule or ruin in all events.
This, plainly stated, is your language to us. Perhaps you will say the Supreme Court has decided the disputed constitutional question in your favor. Not quite so. But waiving the lawyer's distinction between dictum and decision, the courts have decided the question for you in a sort of way. The courts have substantially said, it is your constitutional right to take slaves into the Federal Territories, and to hold them there as property.
When I say the decision was made in a sort of way, I mean it was made in a divided court by a bare majority of the judges, and they not quite agreeing with one another in the reasons for making it; that it is so made as that its avowed supporters disagree with one another about its meaning, and that it was mainly based upon a mistaken statement of fact,—the statement in the opinion that "the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution."
An inspection of the Constitution will show that the right of property in a slave is not distinctly and expressly affirmed in it. Bear in mind, the judges do not pledge their judicial opinion that such right is impliedly affirmed in the Constitution; but they pledge their veracity that it is distinctly and expressly affirmed there,—"distinctly," that is, not mingled with any thing else; "expressly," that is, in words meaning just that, without the aid of any inference, and susceptible of no other meaning.
If they had only pledged their judicial opinion that such right is affirmed in the instrument by implication, it would be open to others to show that neither the word "slave" nor "slavery" is to be found in the Constitution, nor the word "property" even, in any connection with language alluding to the things slave or slavery, and that, wherever in that instrument the slave is alluded to, he is called a "person;" and wherever his master's legal right in relation to him is alluded to, it is spoken of as "service or labor due,"—as a "debt" payable in service or labor. Also it would be open to show, by contemporaneous history, that this mode of alluding to slaves and slavery, instead of speaking of them, was employed on purpose to exclude from the Constitution the idea that there could be property in man.
To show all this is easy and certain.
When this obvious mistake of the judges shall be brought to their notice, is it not reasonable to expect that they will withdraw the mistaken statement, and reconsider the conclusion based upon it?
And then it is to be remembered that "our fathers, who framed the government under which we live,"—the men who made the Constitution,—decided this same constitutional question in our favor long ago,—decided it without a division among themselves, when making the decision; without division among themselves about the meaning of it after it was made, and, so far as any evidence is left, without basing it upon any mistaken statement of facts.
Under all these circumstances, do you really feel yourselves justified to break up this Government, unless such a court decision as yours is shall be at once submitted to, as a conclusive and final rule of political action?
But you will not abide the election of a Republican President. In that supposed event, you say, you will destroy the Union; and then, you say, the great crime of having destroyed it will be upon us!
That is cool. A highwayman holds a pistol to my ear, and mutters through his teeth, "Stand and deliver, or I shall kill you; and then you will be a murderer!"
To be sure, what the robber demanded of me—my money—was my own; and I had a clear right to keep it; but it was no more my own than my vote is my own; and threat of death to me to extort my money, and threat of destruction to the Union to extort my vote, can scarcely be distinguished in principle.
A few words now to Republicans. It is exceedingly desirable that all parts of this great Confederacy shall be at peace, and in harmony, one with another. Let us Republicans do our part to have it so. Even though much provoked, let us do nothing through passion and ill-temper. Even though the Southern people will not so much as listen to us, let us calmly consider their demands, and yield to them if, in our deliberate view of our duty, we possibly can. Judging by all they say and do, and by the subject and nature of their controversy with us, let us determine, if we can, what will satisfy them.
Will they be satisfied if the Territories be unconditionally surrendered to them? We know they will not. In all their present complaints against us, the Territories are scarcely mentioned. Invasions and insurrections are the rage now. Will it satisfy them if, in the future, we have nothing to do with invasions and insurrections? We know it will not. We so know because we know we never had any thing to do with invasions and insurrections; and yet this total abstaining does not exempt us from the charge and the denunciation.
The question recurs, what will satisfy them? Simply this: We must not only let them alone, but we must, somehow, convince them that we do let them alone. This we know by experience is no easy task. We have been so trying to convince them from the very beginning of our organization, but with no success. In all our platforms and speeches we have constantly protested our purpose to let them alone; but this has had no tendency to convince them. Alike unavailing to convince them is the fact that they have never detected a man of us in any attempt to disturb them.
These natural, and apparently adequate means all failing, what will convince them? This, and this only: cease to call slavery wrong, and join them in calling it right. And this must be done thoroughly,—done in acts as well as in words. Silence will not be tolerated: we must place ourselves avowedly with them. Douglas's new sedition law must be enacted and enforced, suppressing all declarations that slavery is wrong, whether made in politics, in presses, in pulpits, or in private. We must arrest and return their fugitive slaves with greedy pleasure. We must pull down our Free-State Constitutions. The whole atmosphere must be disinfected from all taint of opposition to slavery, before they will cease to believe that all their troubles proceed from us.
I am quite aware they do not state their case precisely in this way. Most of them would probably say to us, "Let us alone, do nothing to us, and say what you please about slavery." But we do let them alone, have never disturbed them; so that, after all, it is what we say which dissatisfies them. They will continue to accuse us of doing until we cease saying.
I am also aware they have not as yet, in terms, demanded the overthrow of our Free-State constitutions. Yet those constitutions declare the wrong of slavery with more solemn emphasis than do all other sayings against it; and when all these other sayings shall have been silenced, the overthrow of these constitutions will be demanded, and nothing be left to resist the demand. It is nothing to the contrary, that they do not demand the whole of this just now. Demanding what they do, and for the reason they do, they can voluntarily stop nowhere short of this consummation. Holding, as they do, that slavery is morally right, and socially elevating, they cannot cease to demand a full national recognition of it, as a legal right and a social blessing.
Nor can we justifiably withhold this on any ground, save our conviction that slavery is wrong. If slavery is right, all words, acts, laws, and constitutions against it are themselves wrong, and should be silenced and swept away. If it is right, we cannot justly object to its nationality, its universality; if it is wrong, they cannot justly insist upon its extension, its enlargement. All they ask, we could readily grant, if we thought slavery right; all we ask, they could as readily grant, if they thought it wrong. Their thinking it right, and our thinking it wrong, is the precise fact upon which depends the whole controversy. Thinking it right, as they do, they are not to blame for desiring its full recognition, as being right; but thinking it wrong, as we do, can we yield to them? Can we cast our votes with their view, and against our own? In view of our moral, social, and political responsibilities, can we do this?
Wrong as we think slavery is, we can yet afford to let it alone where it is, because that much is due to the necessity arising from its actual presence in the nation; but can we, while our votes will prevent it, allow it to spread into the national Territories, and to overrun us here in these Free States?
If our sense of duty forbids this, then let us stand by our duty fearlessly and effectively. Let us be diverted by none of those sophistical contrivances wherewith we are so industriously plied and belabored,—contrivances such as groping for some middle ground between the right and the wrong, vain as the search for a man who should be neither a living man nor a dead man,—such as a policy of "don't care" on a question about which all true men do care,—such as Union appeals beseeching true Union men to yield to Dis-unionists, reversing the divine rule, and calling, not the sinners, but the righteous, to repentance,—such as invocations to Washington, imploring men to unsay what Washington said, and undo what Washington did.
Neither let us be slandered from our duty by false accusations against us, nor frightened from it by menaces of destruction to the Government, nor of dungeons to ourselves. Let us have faith that right makes might; and in that faith, let us, to the end, dare to do our duty as we understand it.
The next morning "The Tribune" presented a report of the speech, but, in doing so, said, "the tones, the gestures, the kindling eye, and the mirth-provoking look defy the reporter's skill.... No man ever before made such an impression on his first appeal to a New York audience." "The Evening Post" said, "We have made room for Mr. Lincoln's speech, notwithstanding the pressure of other matters; and our readers will see that it was well worthy of the deep attention with which it was heard." For the publication of such arguments the editor was "tempted to wish" that his columns "were indefinitely elastic." And these are but fair evidences of the general tone of the press.
Mr. Lincoln was much annoyed, after his return home, by the allegation that he had sold a "political speech," and had been generally governed by mercenary motives in his Eastern trip. Being asked to explain it, he answered as follows:—
Springfield, April 6, 1860.
C. F. McNeill, Esq.
Dear Sir,—Reaching home yesterday, I found yours of the 23d March, enclosing a slip from "The Middleport Press." It is not true that I ever charged any thing for a political speech in my life; but this much is true. Last October I was requested by letter to deliver some sort of speech in Mr. Beecher's church in Brooklyn,—$200 being offered in the first letter. I wrote that I could do it in February, provided they would take a political speech if I could find time to get up no other. They agreed; and subsequently I informed them the speech would have to be a political one. When I reached New York, I, for the first, learned that the place was changed to "Cooper Institute." I made the speech, and left for New Hampshire, where I have a son at school, neither asking for pay nor having any offered me. Three days after, a check for $200 was sent to me at N.H.; and I took it, and did not know it was wrong. My understanding now is, though I knew nothing of it at the time, that they did charge for admittance at the Cooper Institute, and that they took in more than twice $200.
I have made this explanation to you as a friend; but I wish no explanation made to our enemies. What they want is a squabble and a fuss: and that they can have if we explain; and they cannot have it if we don't.
When I returned through New York from New England, I was told by the gentlemen who sent me the check, that a drunken vagabond in the club, having learned something about the $200, made the exhibition out of which "The Herald" manufactured the article quoted by "The Press" of your town.
My judgment is, and therefore my request is, that you give no denial, and no explanations.
Thanking you for your kind interest in the matter, I remain
Yours truly,
A. Lincoln.
From New York Mr. Lincoln travelled into New England, to visit his son Robert, who was a student at Harvard; but he was overwhelmed with invitations to address Republican meetings. In Connecticut he spoke at Hartford, Norwich, New Haven, Meriden, and Bridgeport; in Rhode Island, at Woonsocket; in New Hampshire, at Concord and Manchester. Everywhere the people poured out in multitudes, and the press lavished encomiums. Upon his speech at Manchester, "The Mirror," a neutral paper, passed the following criticisms of his style of oratory,—criticisms familiar enough to the people of his own State: "He spoke an hour and a half with great fairness, great apparent candor, and with wonderful interest. He did not abuse the South, the administration, or the Democrats, or indulge in any personalities, with the exception of a few hits at Douglas's notions. He is far from prepossessing in personal appearance, and his voice is disagreeable; and yet he wins your attention and good-will from the start.... He indulges in no flowers of rhetoric, no eloquent passages. He is not a wit, a humorist, or a clown; yet so great a vein of pleasantry and good-nature pervades what he says, gilding over a deep current of practical argument, he keeps his hearers in a smiling mood, with their mouths open ready to swallow all he says. His sense of the ludicrous is very keen; and an exhibition of that is the clincher of all his arguments,—not the ludicrous acts of persons, but ludicrous ideas. Hence he is never offensive, and steals away willingly into his train of belief persons who were opposed to him. For the first half-hour his opponents would agree with every word he uttered; and from that point he began to lead them off little by little, until it seemed as if he had got them all into his fold. He displays more shrewdness, more knowledge of the masses of mankind, than any public speaker we have heard since Long Jim Wilson left for California."
On the morning after the Norwich speech, Mr. Lincoln was met, or is said to have been met, in the cars by a preacher, one Gulliver,—a name suggestive of fictions. Gulliver says he told Mr. Lincoln that he thought his speech "the most remarkable one he ever heard." Lincoln doubted his sincerity; but Gulliver persisted. "Indeed, sir," said he, "I learned more of the art of public speaking last evening than I could from a whole course of lectures on rhetoric." Lincoln found he had in hand a clerical sycophant, and a little politician at that,—a class of beings whom he most heartily despised. Whereupon he began to quiz the fellow, and told him, for a most "remarkable circumstance," that the professors of Yale College were running all around after him, taking notes of his speeches, and lecturing about him to the classes. "Now," continued he, "I should like very much to know what it was in my speech which you thought so remarkable, and which interested my friend the professor so much?" Gulliver was equal to the occasion, and answered with an opinion which Mr. Bunsby might have delivered, and died, leaving to the world a reputation perfected by that single saying. "The clearness of your statements," said Gulliver, "the unanswerable style of your reasoning, and especially your illustrations, which were romance and pathos, and fun and logic, all welded together." Gulliver closed the interview with the cant peculiar to his kind. "Mr. Lincoln," said he, "may I say one thing to you before we separate?"—"Certainly; any thing you please," replied the good-natured old Abe. "You have just spoken," preached Gulliver, "of the tendency of political life in Washington to debase the moral convictions of our representatives there by the admixture of mere political expediency. You have become, by the controversy with Mr. Douglas, one of our leaders in this great struggle with slavery, which is undoubtedly the struggle of the nation and the age. What I would like to say is this, and I say it with a full heart: Be true to your principles; and we will be true to you, and God will be true to us all." To which modest, pious, and original observation, Mr. Lincoln responded, "I say Amen to that! Amen to that!"
IT was not until May 9 and 10 that the Republican State Convention of Illinois met at Decatur. Mr. Lincoln was present, and is said to have been there as a mere "spectator." He had no special interest in the proceedings, and appears to have had no notion that any business relating to him was to be transacted that day. It was a very large and spirited body, comprising an immense number of delegates, among whom were the most brilliant, as well as the shrewdest men in the party. It was evident that something of more than usual importance was expected to transpire. A few moments after the convention organized, "Old Abe" was seen squatting, or sitting on his heels, just within the door of the Wigwam. Gov. Oglesby rose and said amid increasing silence, "I am informed that a distinguished citizen of Illinois, and one whom Illinois will ever delight to honor, is present; and I wish to move that this body invite him to a seat on the stand." Here the governor paused, as if to tease and dally, and work curiosity up to the highest point; but at length he shouted the magic name "Abraham Lincoln!" Not a shout, but a roar of applause, long and deep, shook every board and joist of the Wigwam. The motion was seconded and passed. A rush was made for the hero that sat on his heels. He was seized, and jerked to his feet. An effort was made to "jam him through the crowd" to his place of honor on the stage; but the crowd was too dense, and it failed. Then he was "troosted,"—lifted up bodily,—and lay for a few seconds sprawling and kicking upon the heads and shoulders of the great throng. In this manner he was gradually pushed toward the stand, and finally reached it, doubtless to his great relief, "in the arms of some half-dozen gentlemen," who set him down in full view of his clamorous admirers. "The cheering was like the roar of the sea. Hats were thrown up by the Chicago delegation, as if hats were no longer useful." Mr. Lincoln rose, bowed, smiled, blushed, and thanked the assembly as well as he could in the midst of such a tumult. A gentleman who saw it all says, "I then thought him one of the most diffident and worst-plagued men I ever saw."
At another stage of the proceedings, Gov. Oglesby rose again with another provoking and mysterious speech. "There was," he said, "an old Democrat outside who had something he wished to present to this Convention."—"Receive it!" "Receive it!" cried some. "What is it?" "What is it?" screamed some of the lower Egyptians, who had an idea the old Democrat might want to blow them up with an infernal machine. But the party for Oglesby and the old Democrat was the stronger, and carried the vote with a tremendous hurrah. The door of the Wigwam opened; and a fine, robust old fellow, with an open countenance and bronzed cheeks, marched into the midst of the assemblage, bearing on his shoulder "two small triangular heart rails," surmounted by a banner with this inscription:—
TWO RAILS,
FROM A LOT MADE BY ABRAHAM LINCOLN AND JOHN HANKS, IN THE SANGAMON BOTTOM, IN THE YEAR 1830.

The sturdy bearer was old John Hanks himself, enjoying the great field-day of his life. He was met with wild and tumultuous cheers, prolonged through several minutes; and it was observed that the Chicago and Central-Illinois men put up the loudest and longest. The whole scene was for a time simply tempestuous and bewildering. But it ended at last; and now the whole body, those in the secret and those out of it, clamored like men beside themselves for a speech from Mr. Lincoln, who in the mean time "blushed, but seemed to shake with inward laughter." In response to the repeated appeals he rose and said,—
"Gentlemen, I suppose you want to know something about those things" (pointing to old John and the rails). "Well, the truth is, John Hanks and I did make rails in the Sangamon Bottom. I don't know whether we made those rails or not; fact is, I don't think they are a credit to the makers" (laughing as he spoke). "But I do know this: I made rails then, and I think I could make better ones than these now."
By this time the innocent Egyptians began to open their eyes: they saw plainly enough now the admirable Presidential scheme unfolded to their view. The result of it all was a resolution declaring that "Abraham Lincoln is the first choice of the Republican party of Illinois for the Presidency, and instructing the delegates to the Chicago Convention to use all honorable means to secure his nomination, and to cast the vote of the State as a unit for him."
The crowd at Decatur, delegates and private citizens, who took part in these proceedings, was estimated at five thousand. Neither the numbers nor the enthusiasm was a pleasant sight to the divided and demoralized Democrats. They disliked to hear so much about "honest Old Abe," "the rail-splitter," "the flat-boatman," "the pioneer." These cries had an ominous sound in their ears. Leaving Decatur on the cars, an old man out of Egypt, devoted to the great principles of Democracy, and excessively annoyed by the demonstration in progress, approached Mr. Lincoln and said, "So you're Abe Lincoln?"—"That's my name, sir," answered Mr. Lincoln. "They say you're a self-made man," said the Democrat. "Well, yes," said Mr. Lincoln, "what there is of me is self-made."—"Well, all I've got to say," observed the old man, after a careful survey of the statesman before him, "is, that it was a d—n bad job."
In the mean time Mr. Lincoln's claims had been attractively presented to the politicians of other States. So early as 1858, Mr. Herndon had been to Boston partly, if not entirely, on this mission; and latterly Judge Davis, Leonard Swett, and others had visited Ohio, Indiana, Pennsylvania, and Maryland in his behalf. Illinois was, of course, overwhelmingly and vociferously for him.
On the 16th of May, the Republican Convention assembled at Chicago. The city was literally crammed with delegates, alternates, "outside workers," and spectators. No nominating convention had ever before attracted such multitudes to the scene of its deliberations.
The first and second days were spent in securing a permanent organization, and the adoption of a platform. The latter set out by reciting the Declaration of Independence as to the equality of all men, not forgetting the usual quotation about the right to "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness." The third resolution denounced disunion in any possible event; the fourth declared the right of each State to "order and control its own domestic institutions according to its own judgment exclusively;" the fifth denounced the administration and its treatment of Kansas, as well as its general support of the supposed rights of the South under the Constitution; the sixth favored "economy;" the seventh denied the "new dogma, that the Constitution, of its own force, carries slavery into any or all of the Territories of the United States;" the eighth denied the "authority of Congress, of a Territorial Legislature, or of any individuals, to give legal existence to slavery in any Territory of the United States;" the ninth called the African slave-trade a "burning shame;" the tenth denounced the governors of Kansas and Nebraska for vetoing certain antislavery bills; the eleventh favored the admission of Kansas; the twelfth was a high-tariff manifesto, and a general stump speech to the mechanics; the thirteenth lauded the Homestead policy; the fourteenth opposed any Federal or State legislation "by which the rights of citizenship, hitherto accorded to immigrants from foreign lands, shall be abridged or impaired," with some pretty words, intended as a further bid for the foreign vote; the fifteenth declared for "river and harbor improvements," and the sixteenth for a "Pacific Railroad." It was a very comprehensive "platform;" and, if all classes for whom planks were provided should be kind enough to stand upon them, there could be no failure in the election.
On the third day the balloting for a candidate was to begin. Up to the evening of the second day, Mr. Seward's prospects were far the best. It was certain that he would receive the largest vote on the first ballot; and outside of the body itself the "crowd" for him was more numerous and boisterous than for any other, except Mr. Lincoln. For Mr. Lincoln, however, the "pressure" from the multitude, in the Wigwam, in the streets, and in the hotels, was tremendous. It is sufficiently accounted for by the fact that the "spot" was Chicago, and the State Illinois. Besides the vast numbers who came there voluntarily to urge his claims, and to cheer for him, as the exigency demanded, his adherents had industriously "drummed up" their forces in the city and country, and were now able to make infinitely more noise than all the other parties put together. There was a large delegation of roughs there for Mr. Seward, headed by Tom Hyer, the pugilist. These, and others like them, filled the Wigwam toward the evening of the second day in expectation that the voting would begin. The Lincoln party found it out, and determined to call a check to that game. They spent the whole night in mustering and organizing their "loose fellows" from far and near, and at daylight the next morning "took charge" of the Wigwam, filling every available space, and much that they had no business to fill. As a result, the Seward men were unable to get in, and were forced to content themselves with curbstone enthusiasm.
Mr. Lincoln seemed to be very sure, all along, that the contest would be ultimately between him and Mr. Seward. The "Bates men" were supposed to be conservative, that is, not Abolitionists; and the object of the move in favor of Mr. Bates was to lower the fanatical tone of the party, and save the votes of certain "Union men" who might otherwise be against it. But a Seward man had telegraphed to St. Louis, to the friends of Mr. Bates, to say that Lincoln was as bad as Seward, and to urge them to go for Mr. Seward in case their own favorite should fail. The despatch was printed in "The Missouri Democrat," but was not brought to Mr. Lincoln's attention until the meeting of the Convention. He immediately caught up the paper, and "wrote on its broad margin," "Lincoln agrees with Seward in his irrepressible-conflict idea, and in negro equality; but he is opposed to Seward's Higher Law." With this he immediately despatched a friend to Chicago, who handed it to Judge Davis or Judge Logan.
Simon Cameron of Pennsylvania was nominally a candidate; but, in the language of Col. McClure, "it meant nothing:" it was a mere sham, got up to enable Cameron to make a bargain with some real candidate, and thus secure for himself and his friends the lion's share of the spoils in the event of a victory at the polls. The genuine sentiment of the Pennsylvania delegation was divided between Judge Bates and Judge McLean. But Cameron was in a fine position to trade, and his friends were anxious for business. On the evening of the second day, these gentlemen were gratified. A deputation of them—Casey, Sanderson, Reeder, and perhaps others—were invited to the Lincoln Head-quarters at the Tremont House, where they were met by Messrs. Davis, Swett, Logan, and Dole, on the part of Mr. Lincoln. An agreement was there made, that, if the Cameron men would go for Lincoln, and he should be nominated and elected, Cameron should have a seat in his Cabinet, provided the Pennsylvania delegation could be got to recommend him. The bargain was fulfilled, but not without difficulty. Cameron's strength was more apparent than real. There was, however, "a certain class of the delegates under his immediate influence;" and these, with the aid of Mr. Wilmot and his friends, who were honestly for Lincoln, managed to carry the delegation by a very small majority,—"about six."
About the same time a similar bargain was made with the friends of Caleb B. Smith of Indiana; and with these two contracts quietly ratified, the Lincoln men felt strong and confident on the morning of the third day.
While the candidates were being named, and when the ballotings began, every mention of Mr. Lincoln's name was received with thundering shouts by the vast mass of his adherents by whom the building had been packed. In the phrase of the day, the "outside pressure" was all in his favor. On the first ballot, Mr. Seward had 173 1/2 votes; Mr. Lincoln, 102; Mr. Cameron, 50 1/2; Mr. Chase, 49; Mr. Bates, 48; Mr. Dayton, 14; Mr. McLean, 12; Mr. Collamer, 10; and 6 were scattered. Mr. Cameron's name was withdrawn on the second ballot, according to the previous understanding; Mr. Seward had 184 1/2; Mr. Lincoln, 181; Mr. Chase, 42 1/2; Mr. Bates, 35; Mr. Dayton, 10; Mr. McLean, 8; and the rest scattered. It was clear that the nomination lay between Mr. Seward and Mr. Lincoln, and the latter was receiving great accessions of strength. The third ballot came, and Mr. Lincoln ran rapidly up to 231 1/2 votes; 233 being the number required to nominate. Hundreds of persons were keeping the count; and it was well known, without any announcement, that Mr. Lincoln lacked but a vote and a half to make him the nominee. At this juncture, Mr. Cartter of Ohio rose, and changed four votes from Mr. Chase to Mr. Lincoln. He was nominated. The Wigwam shook to its foundation with the roaring cheers. The multitude in the streets answered the multitude within, and in a moment more all the holiday artillery of Chicago helped to swell the grand acclamation. After a time, the business of the convention proceeded amid great excitement. All the votes that had heretofore been cast against Mr. Lincoln were cast for him before this ballot concluded; and, upon motion, the nomination was made unanimous. The convention then adjourned for dinner, and in the afternoon finished its work by the nomination of Hannibal Hamlin of Maine for Vice-President.
All that day and all the day previous Mr. Lincoln was in Springfield, trying to behave as usual, but watching the proceedings of the Convention, as they were reported by telegraph, with nervous anxiety. Mr. Baker, the friend who had taken "The Missouri Democrat" to Chicago with Mr. Lincoln's pregnant indorsement upon it, returned on the night of the 18th. Early in the morning, he and Mr. Lincoln went to the balll-alley to play at "fives;" but the alley was pre-engaged. They went to an "excellent and neat beer saloon" to play a game of billiards; but the table was occupied. In this strait they contented themselves with a glass of beer, and repaired to "The Journal" office for news.
C. P. Brown says that Lincoln played ball a great deal that day, notwithstanding the disappointment when he went with Baker; and Mr. Zane informs us that he was engaged in the same way the greater part of the day previous. It is probable that he took this physical mode of working off or keeping down the unnatural excitement that threatened to possess him.
About nine o'clock in the morning, Mr. Lincoln came to the office of Lincoln & Herndon. Mr. Zane was then conversing with a student, "Well, boys," said Mr. Lincoln, "what do you know?"—"Mr. Rosette," answered Zane, "who came from Chicago this morning, thinks your chances for the nomination are good." Mr. Lincoln wished to know what Mr. Rosette's opinion was founded upon; and, while Zane was explaining, Mr. Baker entered with a telegram, "which said the names of the candidates for nomination had been announced," and that Mr. Lincoln's had been received with more applause than any other. Mr. Lincoln lay down on a sofa to rest. Soon after, Mr. Brown entered; and Mr. Lincoln said to him, "Well, Brown, do you know any thing?" Brown did not know much; and so Mr. Lincoln, secretly nervous and impatient, rose and exclaimed, "Let's go to the telegraph-office." After waiting some time at the office, the result of the first ballot came over the wire. It was apparent to all present that Mr. Lincoln thought it very favorable. He believed that if Mr. Seward failed to get the nomination, or to "come very near it," on the first ballot, he would fail altogether. Presently the news of the second ballot arrived, and Mr. Lincoln showed by his manner that he considered the contest no longer doubtful. "I've got him," said he. He then went over to the office of "The Journal," where other friends were awaiting decisive intelligence. The local editor of that paper, Mr. Zane, and others, remained behind to receive the expected despatch. In due time it came: the operator was intensely excited; at first he threw down his pencil, but, seizing it again, wrote off the news that threw Springfield into a frenzy of delight. The local editor picked it up, and rushed to "The Journal" office. Upon entering the room, he called for three cheers for the next President. They were given, and then the despatch was read. Mr. Lincoln seemed to be calm, but a close observer could detect in his countenance the indications of deep emotion. In the mean time cheers for Lincoln swelled up from the streets, and began to be heard throughout the town. Some one remarked, "Mr. Lincoln, I suppose now we will soon have a book containing your life."—"There is not much," he replied, "in my past life about which to write a book, as it seems to me." Having received the hearty congratulations of the company in the office, he descended to the street, where he was immediately surrounded by "Irish and American citizens;" and, so long as he was willing to receive it, there was great handshaking and felicitating. "Gentlemen," said the great man with a happy twinkle in his eye, "you had better come up and shake my hand while you can: honors elevate some men, you know." But he soon bethought him of a person who was of more importance to him than all this crowd. Looking toward his house, he said, "Well, gentlemen, there is a little short woman at our house who is probably more interested in this despatch than I am; and, if you will excuse me, I will take it up and let her see it."
During the day a hundred guns were fired at Springfield; and in the evening a great mass meeting "ratified" the nomination, and, after doing so, adjourned to the house of the nominee. Mr. Lincoln appeared, made a "model" speech, and invited into his house everybody that could get in. To this the immense crowd responded that they would give him a larger house the next year, and in the mean time beset the one he had until after midnight.
On the following day the Committee of the Convention, with Mr. Ashmun, the president, at its head, arrived at Springfield to notify Mr. Lincoln of his nomination. Contrary to what might have been expected, he seemed sad and dejected. The re-action from excessive joy to deep despondency—a process peculiar to his constitution—had already set in. To the formal address of the Committee, he responded with admirable taste and feeling;—
"Mr. Chairman and Gentlemen of the Committee,—I tender to you, and through you to the Republican National Convention, and all the people represented in it, my profoundest thanks for the high honor done me, which you now formally announce. Deeply and even painfully sensible of the great responsibility which is inseparable from this high honor,—a responsibility which I could almost wish had fallen upon some one of the far more eminent men and experienced statesmen whose distinguished names were before the Convention, I shall, by your leave, consider more fully the resolutions of the Convention, denominated the platform, and, without unnecessary and unreasonable delay, respond to you, Mr. Chairman, in writing, not doubting that the platform will be found satisfactory, and the nomination gratefully accepted. And now I will not longer defer the pleasure of taking you, and each of you, by the hand."
The Committee handed him a letter containing the official notice, accompanied by the resolutions of the Convention; and to this he replied on the 23d as follows:—
Springfield, Ill, May 23,1860.
Hon. George Ashmun, President of the Republican National Convention.
Sir,—I accept the nomination tendered me by the Convention over which you presided, and of which I am formally apprised in the letter of yourself and others, acting as a Committee of the Convention for that purpose.
The declaration of principles and sentiments which accompanies your letter meets my approval; and it shall be my care not to violate or disregard it in any part.
Imploring the assistance of Divine Providence, and with due regard to the views and feelings of all who were represented in the Convention; to the rights of all the States and Territories, and people of the nation; to the inviolability of the Constitution, and the perpetual union, harmony, and prosperity of all,—I am most happy to co-operate for the practical success of the principles declared by the Convention.
Your obliged friend and fellow-citizen,
Abraham Lincoln.
In the mean time the National Democratic Convention had met at Charleston, S.C., and split in twain. The South utterly repudiated Mr. Douglas's new heresy; and Mr. Douglas insisted that the whole party ought to become heretics with him, and, turning their backs on the Dred-Scott Decision and the Cincinnati Platform, give up slavery in the Territories to the tender mercies of "squatter sovereignty" and "unfriendly legislation." Neither party to the controversy would be satisfied with a simple re-affirmation of the Cincinnati Platform; for under it Mr. Douglas could go to the North and say that it meant "squatter sovereignty," and Mr. Breckinridge could go to the South and say that it meant Congressional protection to slavery. In fact, it meant neither, and said neither, but declared, in plain English words, that Congress had no power to interfere with slavery in the Territories; and that, when the Territories were about to become States, they had all power to settle the question for themselves. Gen. B. F. Butler of Massachusetts proposed to heal the ominous divisions in the Convention by the re-adoption of that clear and emphatic provision; but his voice was soon drowned in the clamors of the fiercer disputants. The differences were irreconcilable. Mr. Douglas's friends had come there determined to nominate him at any cost; and, in order to nominate him, they dared not concede the platform to the South. A majority of the Committee on Resolutions reported the Cincinnati Platform, with the Southern interpretation of it; and the minority reported the same platform with a recitation concerning the "differences of opinion" "in the Democratic party," and a pledge to abide by the decision of the Supreme Court "on the questions of constitutional law,"—a pledge supposed to be of little value, since those who gave it were that moment in the very act of repudiating the only decision the Court had ever rendered. The minority report was adopted after a protracted and acrimonious debate, by a vote of one hundred and sixty-five to one hundred and thirty-eight. Thereupon the Southern delegates, most of them under instructions from their State conventions, withdrew, and organized themselves into a separate convention. The remaining delegates, called "the rump" by their Democratic adversaries, proceeded to ballot for a candidate for President, and voted fifty-seven times without effecting a nomination. Mr. Douglas, of course, received the highest number of votes; but, the old two-thirds rule being in force, he failed of a nomination. Mr. Guthrie of Kentucky was his principal competitor; but at one time and another Mr. Hunter of Virginia, Gen. Lane of Oregon, and Mr. Johnson of Tennessee, received flattering and creditable votes. After the fifty-seventh ballot, the Convention adjourned to meet at Baltimore on the 18th of June.
The seceders met in another hall, adopted the majority platform, as the adhering delegates had adopted the minority platform, and then adjourned to meet at Richmond on the second Monday in June. Faint hopes of accommodation were still entertained; and, when the seceders met at Richmond, they adjourned again to Baltimore, and the 28th of June.
The Douglas Convention, assuming to be the regular one, had invited the Southern States to fill up the vacant seats which belonged to them; but, when the new delegates appeared, they were met with the apprehension that their votes might not be perfectly secure for Mr. Douglas, and were therefore, in many instances, lawlessly excluded. This was the signal for another secession: the Border States withdrew; Mr. Butler and the Massachusetts delegation withdrew; Mr. Cushing deserted the chair, and took that of the rival Convention. The "regular" Convention, it was said, was now "the rump of a rump."
On the first ballot for a candidate, Mr. Douglas had 173 1/2 votes; Mr. Guthrie, 10; Mr. Breckinridge, 5; and 3 were scattered. On the second ballot, Mr. Douglas had 181 1/2; Mr. Breckinridge, 5; and Mr. Guthrie, 5 1/2. It was plain that under the two-thirds rule no nomination could be made here. Neither Mr. Douglas nor any one else could receive two-thirds of a full convention. It was therefore resolved that Mr. Douglas, "having received two-thirds of all the votes given in this Convention," should be declared the nominee. Mr. Fitzpatrick of Alabama was nominated for Vice-President, but declined to stand; and Mr. Johnson of Georgia was substituted for him by the Douglas "National Committee."
In the seceders' Convention, twenty-one States were represented more or less fully. It had no trouble in selecting a candidate. John C. Breckinridge of Kentucky and Joseph Lane of Oregon were unanimously nominated for the offices of President and Vice-President.
In the mean time another party—the "Constitutional Union party"—had met in Baltimore on the 19th of May, and nominated John Bell of Tennessee for President, and Edward Everett of Massachusetts for Vice-President. Its platform was, in brief, "The Constitution of the Country, the Union of the States, and the Enforcement of the Laws." This body was composed for the most part of impenitent Know-Nothings and respectable old-line Whigs.
The spring elections had given the democracy good reason to hope for success in the fall. The commercial classes, the shipping classes, and large numbers of the manufacturers, were thoroughly alarmed for the safety of the great trade dependent upon a political connection with the South. It seemed probable that a great re-action against antislavery agitations might take place. But the division at Charleston, the permanent organization of the two factions at Baltimore, and their mutual and rancorous hostility, completely reversed the delusive prospect. A majority of the whole people of the Union looked forward to a Republican victory with dread, and a large part with actual terror; and yet it was now clear that that majority was fatally bent upon wasting its power in the bitter struggles of the factions which composed it. Mr. Lincoln's election was assured; and for them there was nothing left but to put the house in order for the great convulsion which all our political fathers and prophets had predicted as the necessary consequence of such an event.
On the 6th of November, Abraham Lincoln was elected President of the United States. He received 1,857,610 votes; Mr. Douglas had 1,291,574; Mr. Breckinridge, 850,082; Mr. Bell, 646,124. Against Mr. Lincoln there was a majority of 980,170 of all the votes cast. Of the electoral votes, Mr. Lincoln had 180; Mr. Breckinridge, 72; Mr. Bell, 30; and Mr. Douglas, 12. It is more than likely that Mr. Lincoln owed this, his crowning triumph, to the skill and adroitness with which he questioned Mr. Douglas in the canvass of 1858, and drew out of him those fatal opinions about "squatter sovereignty" and "unfriendly legislation" in the Territories. But for Mr. Douglas's committal to those opinions, it is not likely that. Mr. Lincoln would ever have been President.
The election over, Mr. Lincoln was sorely beset by office-seekers. Individuals, deputations, "delegations," from all quarters, pressed in upon him in a manner that might have killed a man of less robust constitution. The hotels of Springfield were filled with gentlemen who came with, light baggage and heavy schemes. The party had never been in office: a "clean sweep" of the "ins" was expected; and all the "outs" were patriotically anxious to take the vacant places. It was a party that had never fed; and it was voraciously hungry. Mr. Lincoln and Artemus Ward saw a great deal of fun in it; and in all human probability it was the fun alone that enabled Mr. Lincoln to bear it.
Judge Davis says that Mr. Lincoln had determined to appoint "Democrats and Republicans alike to office." Many things confirm this statement. Mr. Lincoln felt deeply the responsibility of his great trust; and he felt still more keenly the supposed impossibility of administering the government for the sole benefit of an organization which had no existence in one-half of the Union. He was therefore willing, not only to appoint Democrats to office, but to appoint them to the very highest offices within his gift. At this time he thought very highly of Mr. Stephens of Georgia, and would gladly have taken him into his Cabinet but for the fear that Georgia might secede, and take Mr. Stephens along with her. He did actually authorize his friend, Mr. Speed, to offer the Treasury Department to Mr. Guthrie of Kentucky; and Mr. Guthrie, for good reasons of his own, declined it. The full significance of this act of courageous magnanimity cannot be understood without reference to the proceedings of the Charleston Convention, where Mr. Guthrie was one of the foremost candidates. He considered the names of various other gentlemen from the Border States, each of them with good proslavery antecedents. He commissioned Thurlow Weed to place a seat in the Cabinet at the disposal of Mr. Gilmore of North Carolina; but Mr. Gilmore, finding that his State was likely to secede, was reluctantly compelled to decline it. He was, in fact, sincerely and profoundly anxious that the South should be honestly represented in his councils by men who had an abiding-place in the hearts of her people. To accomplish that high purpose, he was forced to go beyond the ranks of his own party; and he had the manliness to do it. He felt that his strength lay in conciliation at the outset: that was his ruling conviction during all those months of preparation for the great task before him. It showed itself, not only in the appointments which he sought to make, but in those which he did make. Harboring no jealousies, entertaining no fears concerning his personal interests in the future, he called around him the most powerful of his late rivals,—Seward, Chase, Bates,—and unhesitatingly gave into their hands powers which most presidents would have shrunk from committing to their equals, and much more to their superiors in the conduct of public affairs.
The cases of Cameron and Smith, however, were very distressing. He had authorized no one to make such bargains for him as had been made with the friends of these men. He would gladly have repudiated the contracts, if it could have been done with honor and safety. For Smith he had great regard, and believed that he had rendered important services in the late elections. But his character was now grossly assailed; and it would have saved Mr. Lincoln serious embarrassments if he had been able to put him aside altogether, and select Mr. Lane or some other Indiana statesman in his place. He wavered long, but finally made up his mind to keep the pledge of his friends; and Smith was appointed.
In Cameron's case the contest was fierce and more protracted. At Chicago, Cameron's agents had demanded that he should have the Treasury Department; but that was too much; and the friends of Mr. Lincoln, tried, pushed, and anxious as they were, declined to consider it. They would say that he should be appointed to a Cabinet position, but no more; and to secure this, he must get a majority of the Pennsylvania delegation to recommend him. Mr. Cameron was disposed to exact the penalty of his bond, hard as compliance might be on the part of Mr. Lincoln. But Cameron had many and formidable enemies, who alleged that he was a man notorious for his evil deeds, shameless in his rapacity and corruption, and even more shameless in his mean ambition to occupy exalted stations, for which he was utterly and hopelessly incompetent; that he had never dared to offer himself as a candidate before the people of Pennsylvania, but had more than once gotten high offices from the Legislature by the worst means ever used by a politician; and that it would be a disgrace, a shame, a standing offence to the country, if Mr. Lincoln should consent to put him into his Cabinet. On the other hand, Mr. Cameron had no lack of devoted friends to deny these charges, and to say that his was as "white a soul" as ever yearned for political preferment: they came out to Springfield in numbers,—Edgar Cowan, J. K. Moorehead, Alexander Cummins, Mr. Sanderson, Mr. Casey, and many others, besides Gen. Cameron himself. On the ground, of course, were the powerful gentlemen who had made the original contract on the part of Mr. Lincoln, and who, from first to last, strenuously insisted upon its fulfilment. It required a hard struggle to overcome Mr. Lincoln's scruples; and the whole force was necessarily mustered in order to accomplish it. "All that I am in the world," said he,—"the Presidency and all else,—I owe to that opinion of me which the people express when they call me 'honest Old Abe.' Now, what will they think of their honest Abe, when he appoints Simon Cameron to be his familiar adviser?"
In Pennsylvania it was supposed for a while that Cameron's audacity had failed him, and that he would abandon the attempt. But about the 1st of January Mr. Swett, one of the contracting parties, appeared at Harrisburg, and immediately afterwards Cameron and some of his friends took flight to Springfield. This circumstance put the vigilant opposition on the alert, and aroused them to a clear sense of the impending calamity. The sequel is a painful story; and it is, perhaps, better to give it in the words of a distinguished actor,—Col. Alexander K. McClure. "I do not know," says he, "that any went there to oppose the appointment but myself. When I learned that Cameron had started to Springfield, and that his visit related to the Cabinet, I at once telegraphed Lincoln that such an appointment would be most unfortunate. Until that time, no one outside a small circle of Cameron's friends dreamed of Lincoln's calling him to the Cabinet. Lincoln's character for honesty was considered a complete guaranty against such a suicidal act. No efforts had therefore been made to guard against it.
"In reply to my telegram, Mr. Lincoln answered, requesting me to come to Springfield at once. I hastily got letters from Gov. Curtin, Secretary Slifer, Mr. Wilmot, Mr. Dayton, Mr. Stevens, and started. I took no affidavits with me, nor were any specific charges made against him by me, or by any of the letters I bore; but they all sustained me in the allegation, that the appointment would disgrace the administration and the country, because of the notorious incompetency and public and private villany of the candidate. I spent four hours with Mr. Lincoln alone; and the matter was discussed very fully and frankly. Although he had previously decided to appoint Cameron, he closed our interview by a reconsideration of his purpose, and the assurance that within twenty-four hours he would write me definitely on the subject. He wrote me, as he promised, and stated, that, if I would make specific charges against Mr. Cameron, and produce the proof, he would dismiss the subject. I answered, declining to do so for reasons I thought should be obvious to every one. I believe that affidavits were sent to him, but I had no hand in it.
"Subsequently Cameron regarded his appointment as impossible, and he proposed to Stevens to join in pressing him. Stevens wrote me of the fact; and I procured strong letters from the State administration in his favor. A few days after Stevens wrote me a most bitter letter, saying that Cameron had deceived him, and was then attempting to enforce his own appointment. The bond was demanded of Lincoln; and that decided the matter."1
1 As this was one of the few public acts which Mr. Lincoln performed with a bad conscience, the reader ought to know the consequences of it; and, because it may not be convenient to revert to them in detail at another place, we give them here, still retaining the language of the eye-witness, Col. McClure:—
"I saw Cameron the night of the day that Lincoln removed him. We met in the room of a mutual friend, and he was very violent against Lincoln for removing him without consultation or notice. His denunciation against the President was extremely bitter, for attempting, as he said, his 'personal as well as his political destruction.' He exhibited the letter, which was all in Mr. Lincoln's handwriting, and was literally as follows. I quote from carefully-treasured recollection:—
"'Hon. Simon Cameron, Secretary of War.
"Dear Sir,—I have this day nominated Hon. Edwin M. Stanton to be Secretary of War, and you to be Minister Plenipotentiary to Russia.
"I am sure there is no material error in my quotation of the letter.
"Cameron's chief complaint was, that he had no knowledge or intimation of the change until Chase delivered the letter. We were then, as ever before and since, and as we ever shall be, not in political sympathy, but our personal relations were ever kind. Had he been entirely collected, he would probably not have said and done what I heard and witnessed; but he wept like a child, and appealed to me to aid in protecting him against the President's attempt at personal degradation, assuring me that under like circumstances he would defend me. In my presence the proposition was made and determined upon to ask Lincoln to allow a letter of resignation to be antedated, and to write a kind acceptance of the same in reply. The effort was made, in which Mr. Chase joined, although perhaps ignorant of all the circumstances of the case; and it succeeded. The record shows that Mr. Cameron voluntarily resigned; while, in point of fact, he was summarily removed without notice.
"In many subsequent conversations with Mr. Lincoln, he did not attempt to conceal the great misfortune of Cameron's appointment and the painful necessity of his removal."
Very truly,
A. LINCOLN.'
As a slight relief to the miseries of his high position, and the doleful tales of the office-hunters, who assailed him morning, noon, and night, Mr. Lincoln ran off to Chicago, where he met with the same annoyances, and a splendid reception besides. Here, however, he enjoyed the great satisfaction of a long private conference with his old friend Speed; and it was then that he authorized him to invite Mr. Guthrie to the Cabinet.
And now he began to think very tenderly of his friends and relatives in Coles County, especially of his good stepmother and her daughters. By the first of February, he concluded that he could not leave his home to assume the vast responsibilities that awaited him without paying them a visit. Accordingly, he left Springfield on the first day of that month, and went straight to Charleston, where Col. Chapman and family resided. He was accompanied by Mr. Marshall, the State Senator from that district, and was entertained at his house. The people crowded by hundreds to see him; and he was serenaded by "both the string and brass bands of the town, but declined making a speech." Early the next morning, he repaired "to his cousin, Dennis Hanks;" and our Jolly old friend Dennis had the satisfaction of seeing a grand levee under his own roof. It was all very pleasant to Mr. Lincoln to see such multitudes of familiar faces smiling upon his wonderful successes. But the chief object of his solicitude was not here; Mrs. Lincoln lived in the southern part of the county, and he was all impatience to see her. As soon, therefore, as he had taken a frugal breakfast with Dennis, he and Col. Chapman started off in a "two-horse buggy" toward Farmington, where his step-mother was living with her daughter, Mrs. Moore. They had much difficulty in crossing "the Kickapoo" River, which was running full of ice; but they finally made the dangerous passage, and arrived at Farmington in safety. The meeting between him and the old lady was of a most affectionate and tender character. She fondled him as her own "Abe," and he her as his own mother. It was soon arranged that she should return with him to Charleston, so that they might enjoy by the way the unrestricted and uninterrupted intercourse which they both desired above all things, but which they were not likely to have where the people could get at him. Then Mr. Lincoln and Col. Chapman drove to the house of John Hall, who lived "on the old Lincoln farm," where Abe split the celebrated rails, and fenced in the little clearing in 1830. Thence they went to the spot where old Tom Lincoln was buried. The grave was unmarked and utterly neglected. Mr. Lincoln said he wanted to "have it enclosed, and a suitable tombstone erected." He told Col. Chapman to go to a "marble-dealer," ascertain the cost of the work proposed, and write him in full. He would then send Dennis Hanks the money, and an inscription for the stone; and Dennis would do the rest. (Col. Chapman performed his part of the business, but Mr. Lincoln noticed it no further; and the grave remains in the same condition to this day.)
"We then returned," says Col. Chapman, "to Farmington, where we found a large crowd of citizens—nearly all old acquaintances—waiting to see him. His reception was very enthusiastic, and appeared to gratify him very much. After taking dinner at his step-sister's (Mrs. Moore), we returned to Charleston, his step-mother coming with us.
"Our conversation during the trip was mostly concerning family affairs. Mr. Lincoln spoke to me on the way down to Farmington of his step-mother in the most affectionate manner; said she had been his best friend in the world, and that no son could love a mother more than he loved her. He also told me of the condition of his father's family at the time he married his step-mother, and of the change she made in the family, and of the encouragement he (Abe) received from her.... He spoke of his father, and related some amusing incidents of the old man; of the bull-dogs' biting the old man on his return from New Orleans; of the old man's escape, when a boy, from an Indian who was shot by his uncle Mordecai. He spoke of his uncle Mordecai as being a man of very great natural gifts, and spoke of his step-brother, John
D. Johnston, who had died a short time previous, in the most affectionate manner.
"Arriving at Charleston on our return from Farmington, we proceeded to my residence. Again the house was crowded by persons wishing to see him. The crowd finally became so great, that he authorized me to announce that he would hold a public reception at the Town Hall that evening at seven o'clock; but that, until then, he wished to be left with relations and friends. After supper he proceeded to the Town Hall, where large numbers from the town and surrounding country, irrespective of party, called to see him.
"He left this place Wednesday morning at four o'clock to return to Springfield.... Mr. Lincoln appeared to enjoy his visit here remarkably well. His reception by his old acquaintances appeared to be very gratifying to him. They all appeared so glad to see him, irrespective of party, and all appeared so anxious that his administration might be a success, and that he might have a pleasant and honorable career as President."
The parting between Mr. Lincoln and his mother was very touching. She embraced him with deep emotion, and said she was sure she would never behold him again, for she felt that his enemies would assassinate him. He replied, "No, no, mamma: they will not do that. Trust in the Lord, and all will be well: we will see each other again." Inexpressibly affected by this new evidence of her tender attachment and deep concern for his safety, he gradually and reluctantly withdrew himself from the arms of the only mother he had ever known, feeling still more oppressed by the heavy cares which time and events were rapidly augmenting.
The fear that Mr. Lincoln would be assassinated was not peculiar to his step-mother. It was shared by very many of his neighbors at Springfield; and the friendly warnings he received were as numerous as they were silly and gratuitous. Every conceivable precaution was suggested. Some thought the cars might be thrown from the track; some thought he would be surrounded and stabbed in some great crowd; others thought he might be shot from a house-top as he rode up Pennsylvania Avenue on inauguration day; while others still were sure he would be quietly poisoned long before the 4th of March. One gentleman insisted that he ought, in common prudence, to take his cook with him from Springfield,—one from "among his own female friends."
Mingled with the thousands who came to see him were many of his old New-Salem and Petersburg friends and constituents; and among these was Hannah Armstrong, the wife of Jack and the mother of William. Hannah had been to see him once or twice before, and had thought there was something mysterious in his conduct. He never invited her to his house, or introduced her to his wife; and this circumstance led Hannah to suspect that "there was something wrong between him and her." On one occasion she attempted a sort of surreptitious entrance to his house by the kitchen door; but it ended very ludicrously, and poor Hannah was very much discouraged. On this occasion she made no effort to get upon an intimate footing with his family, but went straight to the State House, where he received the common run of strangers. He talked to her as he would have done in the days when he ran for the Legislature, and Jack was an "influential citizen." Hannah was perfectly charmed, and nearly beside herself with pride and pleasure. She, too, was filled with the dread of some fatal termination to all his glory. "Well," says she, "I talked to him some time, and was about to bid him good-by; had told him that it was the last time I should ever see him: something told me that I should never see him; they would kill him. He smiled, and said jokingly, 'Hannah, if they do kill me, I shall never die another death.' I then bade him good-by."
IT was now but a few weeks until Mr. Lincoln was to become the constitutional ruler of one of the great nations of the earth, and to begin to expend appropriations, to wield armies, to apportion patronage, powers, offices, and honors, such as few sovereigns have ever had at command. The eyes of all mankind were bent upon him to see how he would solve a problem in statesmanship to which the philosophy of Burke and the magnanimity of Wellington might have been unequal. In the midst of a political canvass in his own State but a few years before, impressed with the gravity of the great issues which then loomed but just above the political horizon, he had been the first to announce, amid the objections and protestations of his friends and political associates, the great truth, that "a house divided against itself cannot stand;" that the perpetuity of the Union depended upon its becoming devoted either to the interests of freedom or slavery. And now, by a turn of fortune unparalleled in history, he had been chosen to preside over the interests of the nation; while, as yet unseen to him, the question that perplexed the founders of the government, which ever since had been a disturbing element in the national life, and had at last arrayed section against section, was destined to reach its final settlement through the fierce struggle of civil war. In many respects his situation was exceptionally trying. He was the first President of the United States elected by a strictly sectional vote. The party which elected him, and the parties which had been defeated, were inflamed by the heat of the canvass. The former, with faith in their principles, and a natural eagerness for the prizes now within their reach, were not disposed to compromise their first success by any lowering of their standard or any concession to the beaten; while many of the latter saw in the success of the triumphant party an attack on their most cherished rights, and refused in consequence to abide by the result of the contest. To meet so grave an exigency, Mr. Lincoln had neither precedents nor experience to guide him, nor could he turn elsewhere for greater wisdom than he possessed. The leaders of the new party were as yet untried in the great responsibilities which had fallen upon him and them. There were men among them who had earned great reputation as leaders of an opposition; but their eloquence had been expended upon a single subject of national concern. They knew how to depict the wrongs of a subject race, and also how to set forth the baleful effects of an institution like slavery on national character. But was it certain that they were equally able to govern with wisdom and prudence the mighty people whose affairs were now given to their keeping?
Until the day of his overthrow at Chicago, Mr. Seward had been the recognized chief of the party; had, like Mr. Lincoln, taught the existence of an irrepressible conflict between the North and the South, and had also inculcated the idea of a law higher than the Constitution, which was of more binding force than any human enactment, until many of his followers had come to regard the Constitution with little respect. It was this Constitution which Mr. Lincoln, having sworn to preserve, protect, and defend, was to attempt to administer to the satisfaction of the minority which had elected him, and which was alone expected to support him. To moderate the passions of his own partisans, to conciliate his opponents in the North, and divide and weaken his enemies in the South, was a task which no mere politician was likely to perform, yet one which none but the most expert of politicians and wisest of statesmen was fitted to undertake. It required moral as well as intellectual qualities of the highest order. William of Orange, with a like duty and similar difficulties, was ready at one time and another to give up the effort in despair, although aided by "the divinity that hedges round a king." Few men believed that Mr. Lincoln possessed a single qualification for his great office. His friends had indicated what they considered his chief merit, when they insisted that he was a very common, ordinary man, just like the rest of "the people,"—"Old Abe," a rail-splitter and a story-teller. They said he was good and honest and well-meaning; but they took care not to pretend that he was great. He was thoroughly convinced that there was too much truth in this view of his character. He felt deeply and keenly his lack of experience in the conduct of public affairs. He spoke then and afterwards about the duties of the Presidency with much diffidence, and said, with a story about a justice of the peace in Illinois, that they constituted his "great first case misunderstood." He had never been a ministerial or an executive officer. His most intimate friends feared that he possessed no administrative ability; and in this opinion he seems to have shared himself, at least in his calmer and more melancholy moments.
Having put his house in order, arranged all his private business, made over his interest in the practice of Lincoln & Herndon to Mr. Herndon, and requested "Billy," as a last favor, to leave his name on the old sign for four years at least, Mr. Lincoln was ready for the final departure from home and all familiar things. And this period of transition from private to public life—a period of waiting and preparing for the vast responsibilities that were to bow down his shoulders during the years to come—affords us a favorable opportunity to turn back and look at him again as his neighbors saw him from 1837 to 1861.
Mr. Lincoln was about six feet four inches high,—the length of his legs being out of all proportion to that of his body. When he sat down on a chair, he seemed no taller than an average man, measuring from the chair to the crown of his head; but his knees rose high in front, and a marble placed on the cap of one of them would roll down a steep descent to the hip. He weighed about a hundred and eighty pounds; but he was thin through the breast, narrow across the shoulders, and had the general appearance of a consumptive subject. Standing up, he stooped slightly forward; sitting down, he usually crossed his long legs, or threw them over the arms of the chair, as the most convenient mode of disposing of them. His "head was long, and tall from the base of the brain and the eyebrow;" his forehead high and narrow, but inclining backward as it rose. The diameter of his head from ear to ear was six and a half inches, and from front to back eight inches. The size of his hat was seven and an eighth. His ears were large, standing out almost at right-angles from his head; his cheek-bones high and prominent; his eyebrows heavy, and jutting forward over small, sunken blue eyes; his nose long, large, and blunt, the tip of it rather ruddy, and slightly awry toward the right-hand side; his chin, projecting far and sharp, curved upward to meet a thick, material, lower lip, which hung downward; his cheeks were flabby, and the loose skin fell in wrinkles, or folds; there was a large mole on his right cheek, and an uncommonly prominent Adam's apple on his throat; his hair was dark brown in color, stiff, unkempt, and as yet showing little or no sign of advancing age or trouble; his complexion was very dark, his skin yellow, shrivelled, and "leathery." In short, to use the language of Mr. Herndon, "he was a thin, tall, wiry, sinewy, grizzly, raw-boned man," "looking woe-struck." His countenance was haggard and careworn, exhibiting all the marks of deep and protracted suffering. Every feature of the man—the hollow eyes, with the dark rings beneath; the long, sallow, cadaverous face, intersected by those peculiar deep lines; his whole air; his walk; his long, silent reveries, broken at long intervals by sudden and startling exclamations, as if to confound an observer who might suspect the nature of his thoughts—showed he was a man of sorrows,—not sorrows of to-day or yesterday, but long-treasured and deep,—bearing with him a continual sense of weariness and pain.
He was a plain, homely, sad, weary-looking man, to whom one's heart warmed involuntarily, because he seemed at once miserable and kind.
On a winter's morning, this man could be seen wending his way to the market, with a basket on his arm, and a little boy at his side, whose small feet rattled and pattered over the ice-bound pavement, attempting to make up by the number of his short steps for the long strides of his father. The little fellow jerked at the bony hand which held his, and prattled and questioned, begged and grew petulant, in a vain effort to make his father talk to him. But the latter was probably unconscious of the other's existence, and stalked on, absorbed in his own reflections. He wore on such occasions an old gray shawl, rolled into a coil, and wrapped like a rope around his neck. The rest of his clothes were in keeping. "He did not walk cunningly,—Indian-like,—but cautiously and firmly." His tread was even and strong. He was a little pigeon-toed; and this, with another peculiarity, made his walk very singular. He set his whole foot flat on the ground, and in turn lifted it all at once,—not resting momentarily upon the toe as the foot rose, nor upon the heel as it fell. He never wore his shoes out at the heel and the toe more, as most men do, than at the middle of the sole; yet his gait was not altogether awkward, and there was manifest physical power in his step. As he moved along thus silent, abstracted, his thoughts dimly reflected in his sharp face, men turned to look after him as an object of sympathy as well as curiosity: "his melancholy," in the words of Mr. Herndon, "dripped from him as he walked." If, however, he met a friend in the street, and was roused by a loud, hearty "Good-morning, Lincoln!" he would grasp the friend's hand with one or both of his own, and, with his usual expression of "Howdy, howdy," would detain him to hear a story: something reminded him of it; it happened in Indiana, and it must be told, for it was wonderfully pertinent.
After his breakfast-hour, he would appear at his office, and go about the labors of the day with all his might, displaying prodigious industry and capacity for continuous application, although he never was a fast worker. Sometimes it happened that he came without his breakfast; and then he would have in his hands a piece of cheese, or Bologna sausage, and a few crackers, bought by the way. At such times he did not speak to his partner or his friends, if any happened to be present: the tears were, perhaps, struggling into his eyes, while his pride was struggling to keep them back. Mr. Herndon knew the whole story at a glance: there was no speech between them; but neither wished the visitors to the office to witness the scene; and, therefore, Mr. Lincoln retired to the back office, while Mr. Herndon locked the front one, and walked away with the key in his pocket. In an hour or more the latter would return, and perhaps find Mr. Lincoln calm and collected; otherwise he went out again, and waited until he was so. Then the office was opened, and every thing went on as usual.
When Mr. Lincoln had a speech to write, which happened very often, he would put down each thought, as it struck him, on a small strip of paper, and, having accumulated a number of these, generally carried them in his hat or his pockets until he had the whole speech composed in this odd way, when he would sit down at his table, connect the fragments, and then write out the whole speech on consecutive sheets in a plain, legible handwriting.
His house was an ordinary two-story frame-building, with a stable and a yard: it was a bare, cheerless sort of a place. He planted no fruit or shade trees, no shrubbery or flowers. He did on one occasion set out a few rose-bushes in front of his house; but they speedily perished, or became unsightly for want of attention. Mrs. Wallace, Mrs. Lincoln's sister, undertook "to hide the nakedness" of the place by planting some flowers; but they soon withered and died. He cultivated a small garden for a single year, working in it himself; but it did not seem to prosper, and that enterprise also was abandoned. He had a horse and a cow: the one was fed and curried, and the other fed and milked, by his own hand. When at home, he chopped and sawed all the wood that was used in his house. Late one night he returned home, after an absence of a week or so. His neighbor, Webber, was in bed; but, hearing an axe in use at that unusual hour, he rose to see what it meant. The moon was high; and by its light he looked down into Lincoln's yard, and there saw him in his shirt-sleeves "cutting wood to cook his supper with." Webber turned to his watch, and saw that it was one o'clock. Besides this house and lot, and a small sum of money, Mr. Lincoln had no property, except some wild land in Iowa, entered for him under warrants, received for his service in the Black Hawk War.
Mrs. Wallace thinks "Mr. Lincoln was a domestic man by nature." He was not fond of other people's children, but was extremely fond of his own: he was patient, indulgent, and generous with them to a fault. On Sundays he often took those that were large enough, and walked with them into the country, and, giving himself up entirely to them, rambled through the green fields or the cool woods, amusing and instructing them for a whole day at a time. His method of reading is thus quaintly described. "He would read, generally aloud (couldn't read otherwise),—would read with great warmth, all funny or humorous things; read Shakspeare that way. He was a sad man, an abstracted man. He would lean back, his head against the top of a rocking-chair; sit abstracted that way for minutes,—twenty, thirty minutes,—and all at once would burst out into a joke."
Mrs. Col. Chapman, daughter of Dennis Hanks, and therefore a relative of Mr. Lincoln, made him a long visit previous to her marriage. "You ask me," says she, "how Mr. Lincoln acted at home. I can say, and that truly, he was all that a husband, father, and neighbor should be,—kind and affectionate to his wife and child ('Bob' being the only one they had when I was with them), and very pleasant to all around him. Never did I hear him utter an unkind word. For instance: one day he undertook to correct his child, and his wife was determined that he should not, and attempted to take it from him; but in this she failed. She then tried tongue-lashing, but met with the same fate; for Mr. Lincoln corrected his child as a father ought to do, in the face of his wife's anger, and that, too, without even changing his countenance or making any reply to his wife.
"His favorite way of reading, when at home, was lying down on the floor. I fancy I see him now, lying full-length in the hall of his old house reading. When not engaged reading law-books, he would read literary works, and was very fond of reading poetry, and often, when he would be, or appear to be, in deep study, commence and repeat aloud some piece that he had taken a fancy to, such as the one you already have in print, and 'The Burial of Sir John Moore,' and so on. He often told laughable jokes and stories when he thought we were looking gloomy."

Mr. Lincoln was not supremely happy in his domestic relations: the circumstances of his courtship and marriage alone made that impossible. His engagement to Miss Todd was one of the great misfortunes of his life and of hers. He realized the mistake too late; and when he was brought face to face with the lie he was about to enact, and the wrong he was about to do, both to himself and an innocent woman, he recoiled with horror and remorse. For weeks together, he was sick, deranged, and on the verge of suicide,—a heavy care to his friends, and a source of bitter mortification to the unfortunate lady, whose good fame depended, in a great part, upon his constancy. The wedding garments and the marriage feast were prepared, the very hour had come when the solemn ceremony was to be performed; and the groom failed to appear! He was no longer a free agent: he was restrained, carefully guarded, and soon after removed to a distant place, where the exciting causes of his disease would be less constant and active in their operation. He recovered slowly, and at length returned to Springfield. He spoke out his feelings frankly and truly to the one person most interested in them. But he had been, from the beginning, except in the case of Ann Rutledge, singularly inconstant and unstable in his relations with the few refined and cultivated women who had been the objects of his attention. He loved Miss Rutledge passionately, and the next year importuned Miss Owens to be his wife. Failing in his suit, he wrote an unfeeling letter about her, apparently with no earthly object but to display his levity and make them both ridiculous. He courted Miss Todd, and at the moment of success fell in love with her relative, and, between the two, went crazy, and thought of ending all his woes with a razor or a pocket-knife. It is not impossible that the feelings of such a man might have undergone another and more sudden change. Perhaps they did. At all events, he was conscientious and honorable and just. There was but one way of repairing the injury he had done Miss Todd, and he adopted it. They were married; but they understood each other, and suffered the inevitable consequences, as other people do under similar circumstances. But such troubles seldom fail to find a tongue; and it is not strange, that, in this case, neighbors and friends, and ultimately the whole country, came to know the state of things in that house. Mr. Lincoln scarcely attempted to conceal it, but talked of it with little or no reserve to his wife's relatives, as well as his own friends. Yet the gentleness and patience with which he bore this affliction from day to day, and from year to year, was enough to move the shade of Socrates. It touched his acquaintances deeply, and they gave it the widest publicity. They made no pause to inquire, to investigate, and to apportion the blame between the parties, according to their deserts. Almost ever since Mr. Lincoln's death, a portion of the press has never tired of heaping brutal reproaches upon his wife and widow; whilst a certain class of his friends thought they were honoring his memory by multiplying outrages and indignities upon her, at the very moment when she was broken by want and sorrow, defamed, defenceless, in the hands of thieves, and at the mercy of spies. If ever a woman grievously expiated an offence not her own, this woman did. In the Herndon manuscripts, there is a mass of particulars under this head; but Mr. Herndon sums them all up in a single sentence, in a letter to one of Mr. Lincoln's biographers: "All that I know ennobles both."
It would be very difficult to recite all the causes of Mr. Lincoln's melancholy disposition. That it was partly owing to physical causes there can be no doubt. Mr. Stuart says, that in some respects he was totally unlike other people, and was, in fact, a "mystery." Blue-pills were the medicinal remedy which he affected most. But whatever the history or the cause,—whether physical reasons, the absence of domestic concord, a series of painful recollections of his mother, of his father and master, of early sorrows, blows, and hardships, of Ann Rutledge and fruitless hopes, or all these combined, Mr. Lincoln was the saddest and gloomiest man of his time. "I do not think that he knew what happiness was for twenty years," says Mr. Herndon. "Terrible" is the word which all his friends use to describe him in the black mood. "It was terrible! It was terrible!" says one and another.
His mind was filled with gloomy forebodings and strong apprehensions of impending evil, mingled with extravagant visions of personal grandeur and power. His imagination painted a scene just beyond the veil of the immediate future, gilded with glory yet tarnished with blood. It was his "destiny,"—splendid but dreadful, fascinating but terrible. His case bore little resemblance to those of religious enthusiasts like Bunyan, Cowper, and others. His was more like the delusion of the fatalist, conscious of his star. At all events, he never doubted for a moment but that he was formed for "some great or miserable end." He talked about it frequently and sometimes calmly. Mr. Herndon remembers many of these conversations in their office at Springfield, and in their rides around the circuit. Mr. Lincoln said the impression had grown in him "all his life;" but Mr. Herndon thinks it was about 1840 that it took the character of a "religious conviction." He had then suffered much, and, considering his opportunities, achieved great things. He was already a leader among men, and a most brilliant career had been promised him by the prophetic enthusiasm of many friends. Thus encouraged and stimulated, and feeling himself growing gradually stronger and stronger, in the estimation of "the plain people," whose voice was more potent than all the Warwicks, his ambition painted the rainbow of glory in the sky, while his morbid melancholy supplied the clouds that were to overcast and obliterate it with the wrath and ruin of the tempest. To him it was fate, and there was no escape or defence. The presentiment never deserted him: it was as clear, as perfect, as certain, as any image conveyed by the senses. He had now entertained it so long, that it was as much a part of his nature as the consciousness of identity. All doubts had faded away, and he submitted humbly to a power which he could neither comprehend nor resist. He was to fall,—fall from a lofty place, and in the performance of a great work. The star under which he was born was at once brilliant and malignant: the horoscope was cast, fixed, irreversible; and he had no more power to alter or defeat it in the minutest particular than he had to reverse the law of gravitation.
After the election, he conceived that he would not "last" through his term of office, but had at length reached the point where the sacrifice would take place. All precautions against assassination he considered worse than useless. "If they want to kill me," said he, "there is nothing to prevent." He complained to Mr. Gillespie of the small body-guard which his counsellors had forced upon him, insisting that they were a needless encumbrance. When Mr. Gillespie urged the ease and impunity with which he might be killed, and the value of his life to the country, he said, "What is the use of putting up the gap when the fence is down all around?"
"It was just after my election in 1860," said Mr. Lincoln to his secretary, John Hay, "when the news had been coming in thick and fast all day, and there had been a great 'hurrah boys!' so that I was well tired out, and went home to rest, throwing myself upon a lounge in my chamber.
"Opposite to where I lay was a bureau with a swinging glass upon it; and, in looking in that glass, I saw myself reflected nearly at full length; but my face, I noticed, had two separate and distinct images, the tip of the nose of one being about three inches from the tip of the other. I was a little bothered, perhaps startled, and got up and looked in the glass; but the illusion vanished. On lying down again, I saw it a second time,—plainer, if possible, than before; and then I noticed that one of the faces was a little paler—say five shades—than the other. I got up, and the thing melted away; and I went off, and in the excitement of the hour forgot all about it,—nearly, but not quite, for the thing would once in a while come up, and give me a little pang, as though something uncomfortable had happened. When I went home, I told my wife about it: and a few days after I tried the experiment again, when, sure enough, the thing came back again; but I never succeeded in bringing the ghost back after that, though I once tried very industriously to show it to my wife, who was worried about it somewhat. She thought it was 'a sign' that I was to be elected to a second term of office, and that the paleness of one of the faces was an omen that I should not see life through the last term."
In this morbid and dreamy state of mind, Mr. Lincoln passed the greater part of his life. But his "sadness, despair, gloom," Mr. Herndon says, "were not of the kind that leads a badly-balanced mind into misanthropy and universal hate and scorn. His humor would assert itself from the hell of misanthropy: it would assert its independence every third hour or day or week. His abstractedness, his continuity of thought, his despair, made him, twice in his life, for two weeks at a time, walk that narrow line that divides sanity from insanity.... This peculiarity of his nature, his humor, his wit, kept him alive in his mind.... It was those good sides of his nature that made, to him, his life bearable. Mr. Lincoln was a weak man and a strong man by turns."
Some of Mr. Lincoln's literary tastes indicated strongly his prevailing gloominess of mind. He read Byron extensively, especially "Childe Harold," "The Dream," and "Don Juan." Burns was one of his earliest favorites, although there is no evidence that he appreciated highly the best efforts of Burns. On the contrary, "Holy Willie's Prayer" was the only one of his poems which Mr. Lincoln took the trouble to memorize. He was fond of Shakspeare, especially "King Lear," and "The Merry Wives of Windsor." But whatever was suggestive of death, the grave, the sorrows of man's days on earth, charmed his disconsolate spirit, and captivated his sympathetic heart. Solemn-sounding rhymes, with no merit but the sad music of their numbers, were more enchanting to him than the loftiest songs of the masters. Of these were, "Why should the Spirit of Mortal be Proud?" and a pretty commonplace little piece, entitled "The Inquiry." One verse of Holmes's "Last Leaf" he thought was "inexpressibly touching." This verse we give the reader:—
"The mossy marbles rest On the lips that he has pressed In their bloom; And the names he loved to hear Have been carved for many a year On the tomb."
Mr. Lincoln frequently said that he lived by his humor, and would have died without it. His manner of telling a story was irresistibly comical, the fun of it dancing in his eyes and playing over every feature. His face changed in an instant: the hard lines faded out of it, and the mirth seemed to diffuse itself all over him, like a spontaneous tickle. You could see it coming long before he opened his mouth, and he began to enjoy the "point" before his eager auditors could catch the faintest glimpse of it. Telling and hearing ridiculous stories was one of his ruling passions. He would go a long way out of his road to tell a grave, sedate fellow a broad story, or to propound to him a conundrum that was not particularly remarkable for its delicacy. If he happened to hear of a man who was known to have something fresh in this line, he would hunt him up, and "swap jokes" with him. Nobody remembers the time when his fund of anecdotes was not apparently inexhaustible. It was so in Indiana; it was so in New Salem, in the Black-Hawk War, in the Legislature, in Congress, on the circuit, on the stump,—everywhere. The most trifling incident "reminded" him of a story, and that story reminded him of another, until everybody marvelled "that one small head could carry all he knew." The "good things" he said were repeated at second-hand, all over the counties through which he chanced to travel; and many, of a questionable flavor, were attributed to him, not because they were his in fact, but because they were like his. Judges, lawyers, jurors, and suitors carried home with them select budgets of his stories, to be retailed to itching ears as "Old Abe's last." When the court adjourned from village to village, the taverns and the groceries left behind were filled with the sorry echoes of his "best." He generally located his little narratives with great precision,—in Kentucky, Indiana, Illinois; and if he was not personally "knowing" to the facts himself, he was intimately acquainted with a gentleman who was.
Mr. Lincoln used his stories variously,—to illustrate or convey an argument; to make his opinions clear to another, or conceal them altogether; to cut off a disagreeable conversation, or to end an unprofitable discussion; to cheer his own heart, or simply to amuse his friends. But most frequently he had a practical object in view, and employed them simply "as labor-saving contrivances."
It was Judge Davis's opinion, that Mr. Lincoln's hilarity was mainly simulated, and that "his stories and jokes were intended to whistle off sadness." "The groundwork of his social nature was sad," says Judge Scott; "but for the fact that he studiously cultivated the humorous, it would have been very sad indeed. His mirth to me always seemed to be put on, and did not properly belong there. Like a plant produced in the hot-bed, it had an unnatural and luxuriant growth."
Although Mr. Lincoln's walk among men was remarkably pure, the same cannot be said of his conversation. He was endowed by nature with a keen sense of humor, and he found great delight in indulging it. But his humor was not of a delicate quality; it was chiefly exercised in hearing and telling stories of the grosser sort. In this tendency he was restrained by no presence and no occasion. It was his opinion that the finest wit and humor, the best jokes and anecdotes, emanated from the lower orders of the country people. It was from this source that he had acquired his peculiar tastes and his store of materials. The associations which began with the early days of Dennis Hanks continued through his life at New Salem and his career at the Illinois Bar, and did not desert him when, later in life, he arrived at the highest dignities.
Mr. Lincoln indulged in no sensual excesses: he ate moderately, and drank temperately when he drank at all. For many years he was an ardent agitator against the use of intoxicating beverages, and made speeches, far and near, in favor of total abstinence. Some of them were printed; and of one he was not a little proud. He abstained himself, not so much upon principle, as because of a total lack of appetite. He had no taste for spirituous liquors; and, when he took them, it was a punishment to him, not an indulgence. But he disliked sumptuary laws, and would not prescribe by statute what other men should eat or drink. When the temperance men ran to the Legislature to invoke the power of the State, his voice—the most eloquent among them—was silent. He did not oppose them, but quietly withdrew from the cause, and left others to manage it. In 1854 he was induced to join the order called Sons of Temperance, but never attended a single meeting after the one at which he was initiated.
Morbid, moody, meditative, thinking much of himself and the things pertaining to himself, regarding other men as instruments furnished to his hand for the accomplishment of views which he knew were important to him, and, therefore, considered important to the public, Mr. Lincoln was a man apart from the rest of his kind, unsocial, cold, impassive,—neither a "good hater" nor a fond friend. He unbent in the society of those who gave him new ideas, who listened to and admired him, whose attachment might be useful, or whose conversation amused him. He seemed to make boon-companions of the coarsest men on the list of his acquaintances,—"low, vulgar, unfortunate creatures;" but, as Judge Davis has it, "he used such men as tools,—things to satisfy him, to feed his desires." He felt sorry for them, enjoyed them, extracted from them whatever service they were capable of rendering, discarded and forgot them. If one of them, presuming upon the past, followed him to Washington with a view to personal profit, Mr. Lincoln would probably take him to his private room, lock the doors, revel in reminiscences of Illinois, new stories and old, through an entire evening, and then dismiss his enchanted crony with nothing more substantial than his blessing. It was said that "he had no heart;" that is, no personal attachments warm and strong enough to govern his actions. It was seldom that he praised anybody; and, when he did, it was not a rival or an equal in the struggle for popularity and power. His encomiums were more likely to be satirical than sincere, and sometimes were artfully contrived as mere stratagems to catch the applause he pretended to bestow, or at least to share it in equal parts. No one knew better how to "damn with faint praise," or to divide the glory of another by being the first and frankest to acknowledge it. Fully alive to the fact that no qualities of a public man are so charming to the people as simplicity and candor, he made simplicity and candor the mask of deep feelings carefully concealed, and subtle plans studiously veiled from all eyes but one. He had no reverence for great men, followed no leader with blind devotion, and yielded no opinion to mere authority. He felt that he was as great as anybody, and could do what another did. It was, however, the supreme desire of his heart to be right, and to do justice in all the relations of life. Although some of his strongest passions conflicted more or less directly with this desire, he was conscious of them, and strove to regulate them by self-imposed restraints. He was not avaricious, never appropriated a cent wrongfully, and did not think money for its own sake a fit object of any man's ambition. But he knew its value, its power, and liked to keep it when he had it. He gave occasionally to individual mendicants, or relieved a case of great destitution at his very door; but his alms-giving was neither profuse nor systematic. He never made donations to be distributed to the poor who were not of his acquaintance and very near at hand. There were few entertainments at his house. People were seldom asked to dine with him. To many he seemed inhospitable; and there was something about his house, an indescribable air of exclusiveness, which forbade the entering guest. It is not meant to be said that this came from mere economy. It was not at home that he wished to see company. He preferred to meet his friends abroad,—on a street-corner, in an office, at the Court House, or sitting on nail-kegs in a country store.
Mr. Lincoln took no part in the promotion of local enterprises, railroads, schools, churches, asylums. The benefits he proposed for his fellow-men were to be accomplished by political means alone. Politics were his world,—a world filled with hopeful enchantments. Ordinarily he disliked to discuss any other subject. "In his office," says Mr. Herndon, "he sat down, or spilt himself, on his lounge, read aloud, told stories, talked politics,—never science, art, literature, railroad gatherings, colleges, asylums, hospitals, commerce, education, progress, nothing that interested the world generally," except politics. He seldom took an active part in local or minor elections, or wasted his power to advance a friend. He did nothing out of mere gratitude, and forgot the devotion of his warmest partisans as soon as the occasion for their services had passed. What they did for him was quietly appropriated as the reward of superior merit, calling for no return in kind. He was always ready to do battle for a principle, after a discreet fashion, but never permitted himself to be strongly influenced by the claims of individual men. When he was a candidate himself, he thought the whole canvass and all the preliminaries ought to be conducted with reference to his success. He would say to a man, "Your continuance in the field injures me" and be quite sure that he had given a perfect reason for his withdrawal. He would have no "obstacles" in his way; coveted honors, was eager for power, and impatient of any interference that delayed or obstructed his progress. He worked hard enough at general elections, when he could make speeches, have them printed, and "fill the speaking trump of fame" with his achievements; but in the little affairs about home, where it was all work and no glory, his zeal was much less conspicuous. Intensely secretive and cautious, he shared his secrets with no man, and revealed just enough of his plans to allure support, and not enough to expose their personal application. After Speed left, he had no intimates to whom he opened his whole mind. This is the unanimous testimony of all who knew him. Feeling himself perfectly competent to manage his own affairs, he listened with deceptive patience to the views of others, and then dismissed the advice with the adviser. Judge Davis was supposed to have great influence over him; but he declares that he had literally none. "Once or twice," says he, "he asked my advice about the almighty dollar, but never about any thing else."
Notwithstanding his overweening ambition, and the breathless eagerness with which he pursued the objects of it, he had not a particle of sympathy with the great mass of his fellow-citizens who were engaged in similar scrambles for place. "If ever," said he, "American society and the United States Government are demoralized and overthrown, it will come from the voracious desire of office,—this wriggle to live without toil, work, and labor, from which I am not free myself." Mr. Lincoln was not a demagogue or a trimmer. He never deserted a party in disaster, or joined one in triumph. Nearly the whole of his public life was spent in the service of a party which struggled against hopeless odds, which met with many reverses and few victories. It is true, that about the time he began as a politician, the Whigs in his immediate locality, at first united with the moderate Democrats, and afterwards by themselves, were strong enough to help him to the Legislature as often as he chose to go. But, if the fact had been otherwise, it is not likely that he would have changed sides, or even altered his position in any essential particular, to catch the popular favor. Subsequently he suffered many defeats,—for Congress, for Commissioner of the Land Office, and twice for Senator; but on this account he never faltered in devotion to the general principles of the party, or sought to better his fortune by an alliance with the common enemy. It cannot be denied, that, when he was first a candidate for the Legislature, his views of public policy were a little cloudy, and that his addresses to the people were calculated to make fair weather with men of various opinions; nor that, when first a candidate for United States Senator, he was willing to make a secret bargain with the extreme Abolitionists, and, when last a candidate, to make some sacrifice of opinion to further his own aspirations for the Presidency. The pledge to Lovejoy and the "House-divided Speech" were made under the influence of personal considerations, without reference to the views or the success of those who had chosen and trusted him as a leader for a far different purpose. But this was merely steering between sections of his own party, where the differences were slight and easily reconciled,—manoeuvring for the strength of one faction today and another to-morrow, with intent to unite them and lead them to a victory, the benefits of which would inure to all. He was not one to be last in the fight and first at the feast, nor yet one to be first in the fight and last at the feast. He would do his whole duty in the field, but had not the slightest objection to sitting down at the head of the table,—an act which he would perform with a modest, homely air, that disarmed envy, and silenced the master when he would say, "Friend, go down lower." His "master" was the "plain people." To be popular was to him the greatest good in life. He had known what it was to be without popularity, and he had known what it was to enjoy it. To gain it or to keep it, he considered no labor too great, no artifice misused or misapplied. His ambition was strong; yet it existed in strict subordination to his sense of party fidelity, and could by no chance or possibility lure him into downright social or political treasons. His path may have been a little devious, winding hither and thither, in search of greater convenience of travel, or the security of a larger company; but it always went forward in the same general direction, and never ran off at right-angles toward a hostile camp. The great body of men who acted with him in the beginning acted with him at the last.
On the whole, he was an honest, although a shrewd, and by no means an unselfish politician. He
................."Foresaw Which way the world began to draw,"
and instinctively drew with it. He had convictions, but preferred to choose his time to speak. He was not so much of a Whig that he could not receive the support of the "nominal" Jackson men, until party lines were drawn so tight that he was compelled to be one thing or the other. He was not so much of a Whig that he could not make a small diversion for White in 1836, nor so much of a White man that he could not lead Harrison's friends in the Legislature during the same winter. He was a firm believer in the good policy of high "protective tariffs;" but, when importuned to say so in a public letter, he declined on the ground that it would do him no good. He detested Know-Nothingism with all his heart; but, when Know-Nothingism swept the country, he was so far from being obtrusive with his views, that many believed he belonged to the order. He was an anti-slavery man from the beginning of his service in the Legislature; but he was so cautious and moderate in the expression of his sentiments, that, when the anti-Nebraska party disintegrated, the ultra-Republicans were any thing but sure of his adherence; and even after the Bloomington Convention he continued to pick his way to the front with wary steps, and did not take his place among the boldest of the agitators until 1858, when he uttered the "House-divided Speech," just in time to take Mr. Seward's place on the Presidential ticket of 1860.
Any analysis of Mr. Lincoln's character would be defective that did not include his religious opinions. On such matters he thought deeply; and his opinions were positive. But perhaps no phase of his character has been more persistently misrepresented and variously misunderstood, than this of his religious belief. Not that the conclusive testimony of many of his intimate associates relative to his frequent expressions on such subjects has ever been wanting; but his great prominence in the world's history, and his identification with some of the great questions of our time, which, by their moral import, were held to be eminently religious in their character, have led many good people to trace in his motives and actions similar convictions to those held by themselves. His extremely general expressions of religious faith called forth by the grave exigencies of his public life, or indulged in on occasions of private condolence, have too often been distorted out of relation to their real significance or meaning to suit the opinions or tickle the fancies of individuals or parties.
Mr. Lincoln was never a member of any church, nor did he believe in the divinity of Christ, or the inspiration of the Scriptures in the sense understood by evangelical Christians. His theological opinions were substantially those expounded by Theodore Parker. Overwhelming testimony out of many mouths, and none stronger than that out of his own, place these facts beyond controversy.
When a boy, he showed no sign of that piety which his many biographers ascribe to his manhood. His stepmother—herself a Christian, and longing for the least sign of faith in him—could remember no circumstance that supported her hope. On the contrary, she recollected very well that he never went off into a corner, as has been said, to ponder the sacred writings, and to wet the page with his tears of penitence. He was fond of music; but Dennis Hanks is clear to the point that it was songs of a very questionable character that cheered his lonely pilgrimage through the woods of Indiana. When he went to church at all, he went to mock, and came away to mimic. Indeed, it is more than probable that the sort of "religion" which prevailed among the associates of his boyhood impressed him with a very poor opinion of the value of the article. On the whole, he thought, perhaps, a person had better be without it.
When he came to New Salem, he consorted with freethinkers, joined with them in deriding the gospel history of Jesus, read Volney and Paine, and then wrote a deliberate and labored essay, wherein he reached conclusions similar to theirs. The essay was burnt, but he never denied or regretted its composition. On the contrary, he made it the subject of free and frequent conversations with his friends at Springfield, and stated, with much particularity and precision, the origin, arguments, and objects of the work.
It was not until after Mr. Lincoln's death, that his alleged orthodoxy became the principal topic of his eulogists; but since then the effort on the part of some political writers and speakers to impress the public mind erroneously seems to have been general and systematic. It is important that the question should be finally determined; and, in order to do so, the names of some of his nearest friends are given below, followed by clear and decisive statements, for which they are separately responsible. Some of them are gentlemen of distinction, and all of them men of high character, who enjoyed the best opportunities to form correct opinions.
James H. Matheny says in a letter to Mr. Herndon:—
"I knew Mr. Lincoln as early as 1834-7; know he was an infidel. He and W. D. Herndon used to talk infidelity in the clerk's office in this city, about the years 1837-40. Lincoln attacked the Bible and the New Testament on two grounds: first, from the inherent or apparent contradictions under its lids; second, from the grounds of reason. Sometimes he ridiculed the Bible and New Testament, sometimes seemed to scoff it, though I shall not use that word in its full and literal sense. I never heard that Lincoln changed his views, though his personal and political friend from 1834 to 1860. Sometimes Lincoln bordered on atheism. He went far that way, and often shocked me. I was then a young man, and believed what my good mother told me. Stuart & Lincoln's office was in what was called Hoffman's Row, on North Fifth Street, near the public square. It was in the same building as the clerk's office, and on the same floor. Lincoln would come into the clerk's office, where I and some young men—Evan Butler, Newton Francis, and others—were writing or staying, and would bring the Bible with him; would read a chapter; argue against it. Lincoln then had a smattering of geology, if I recollect it. Lincoln often, if not wholly, was an atheist; at least, bordered on it. Lincoln was enthusiastic in his infidelity. As he grew older, he grew more discreet, didn't talk much before strangers about his religion; but to friends, close and bosom ones, he was always open and avowed, fair and honest; but to strangers, he held them off from policy. Lincoln used to quote Burns. Burns helped Lincoln to be an infidel, as I think; at least, he found in Burns a like thinker and feeler. Lincoln quoted 'Tam O'Skanter.' 'What! send one to heaven, and ten to hell!' &c.
"From what I know of Mr. Lincoln and his views of Christianity, and from what I know as honest and well-founded rumor; from what I have heard his best friends say and regret for years; from what he never denied when accused, and from what Lincoln has hinted and intimated, to say no more,—he did write a little book on infidelity at or near New Salem, in Menard County, about the year 1834 or 1835. I have, stated these things to you often. Judge Logan, John T. Stuart, yourself, know what I know, and some of you more.
"Mr. Herndon, you insist on knowing something which you know I possess, and got as a secret, and that is, about Lincoln's little book on infidelity. Mr. Lincoln did tell me that he did write a little book on infidelity. This statement I have avoided heretofore; but, as you strongly insist upon it,—probably to defend yourself against charges of misrepresentations,—I give it you as I got it from Lincoln's mouth."
From Hon. John T. Stuart:—
"I knew Mr. Lincoln when he first came here, and for years afterwards. He was an avowed and open infidel, sometimes bordered on atheism. I have often and often heard Lincoln and one W. D. Herndon, who was a freethinker, talk over this subject. Lincoln went further against Christian beliefs and doctrines and principles than any man I ever heard: he shocked me. I don't remember the exact line of his argument: suppose it was against the inherent defects, so called, of the Bible, and on grounds of reason. Lincoln always denied that Jesus was the Christ of God,—denied that Jesus was the Son of God, as understood and maintained by the Christian Church. The Rev. Dr. Smith, who wrote a letter, tried to convert Lincoln from infidelity so late as 1858, and couldn't do it."
William H. Herndon, Esq.:—
"As to Mr. Lincoln's religious views, he was, in short, an infidel,... a theist. He did not believe that Jesus was God, nor the Son of God,—was a fatalist, denied the freedom of the will. Mr. Lincoln told me a thousand times, that he did not believe the Bible was the revelation of God, as the Christian world contends. The points that Mr. Lincoln tried to demonstrate (in his book) were: First, That the Bible was not God's revelation; and, Second, That Jesus was not the Son of God. I assert this on my own knowledge, and on my veracity. Judge Logan, John T. Stuart, James H. Matheny, and others, will tell you the truth. I say they will confirm what I say, with this exception,—they all make it blacker than I remember it. Joshua F. Speed of Louisville, I think, will tell you the same thing."
Hon. David Davis:—
"I do not know any thing about Lincoln's religion, and do not think anybody knew. The idea that Lincoln talked to a stranger about his religion or religious views, or made such speeches, remarks, &c., about it as are published, is to me absurd. I knew the man so well: he was the most reticent, secretive man I ever saw, or expect to see. He had no faith, in the Christian sense of the term,—had faith in laws, principles, causes, and effects—philosophically: you [Herndon] know more about his religion than any man. You ought to know it, of course."
William H. Hannah, Esq.:—
"Since 1856 Mr. Lincoln told me that he was a kind of immortalist; that he never could bring himself to believe in eternal punishment; that man lived but a little while here; and that, if eternal punishment were man's doom, he should spend that little life in vigilant and ceaseless preparation by never-ending prayer."
Mrs. Lincoln:—
"Mr. Lincoln had no hope and no faith in the usual acceptance of those words."
Dr. C. H. Ray:—
"I do not know how I can aid you. You [Herndon] knew Mr. Lincoln far better than I did, though I knew him well; and you have served up his leading characteristics in a way that I should despair of doing, if I should try. I have only one thing to ask: that you do not give Calvinistic theology a chance to claim him as one of its saints and martyrs. He went to the Old-School Church; but, in spite of that outward assent to the horrible dogmas of the sect, I have reason from, himself to know that his 'vital purity' if that means belief in the impossible, was of a negative sort."
I. W. Keys, Esq.:—
"In my intercourse with Mr. Lincoln, I learned that he believed in a Creator of all things, who had neither beginning nor end, and possessing all power and wisdom, established a principle, in obedience to which worlds move, and are upheld, and animal and vegetable life come into existence. A reason he gave for his belief was, that, in view of the order and harmony of all nature which we behold, it would have been more miraculous to have come about by chance than to have been created and arranged by some great thinking power. As to the Christian theory, that Christ is God, or equal to the Creator, he said that it had better be taken for granted; for, by the test of reason, we might become infidels on that subject, for evidence of Christ's divinity came to us in a somewhat doubtful shape; but that the system of Christianity was an ingenious one at least, and perhaps was calculated to do good."
Mr. Jesse W. Fell of Illinois, who had the best opportunities of knowing Mr. Lincoln intimately, makes the following statement of his religious opinions, derived from repeated conversations with him on the subject:—
"Though every thing relating to the character and history of this extraordinary personage is of interest, and should be fairly stated to the world, I enter upon the performance of this duty—for so I regard it—with some reluctance, arising from the fact, that, in stating my convictions on the subject, I must necessarily place myself in opposition to quite a number who have written on this topic before me, and whose views largely pre-occupy the public mind. This latter fact, whilst contributing to my embarrassment on this subject, is, perhaps, the strongest reason, however, why the truth in this matter should be fully disclosed; and I therefore yield to your request. If there were any traits of character that stood out in bold relief in the person of Mr. Lincoln, they were those of truth and candor. He was utterly incapable of insincerity, or professing views on this or any other subject he did not entertain. Knowing such to be his true character, that insincerity, much more duplicity, were traits wholly foreign to his nature, many of his old friends were not a little surprised at finding, in some of the biographies of this great man, statements concerning his religious opinions so utterly at variance with his known sentiments. True, he may have changed or modified those sentiments after his removal from among us, though this is hardly reconcilable with the history of the man, and his entire devotion to public matters during his four years' residence at the national capital. It is possible, however, that this may be the proper solution of this conflict of opinions; or, it may be, that, with no intention on the part of any one to mislead the public mind, those who have represented him as believing in the popular theological views of the times may have misapprehended him, as experience shows to be quite common where no special effort has been made to attain critical accuracy on a subject of this nature. This is the more probable from the well-known fact, that Mr. Lincoln seldom communicated to any one his views on this subject. But, be this as it may, I have no hesitation whatever in saying, that, whilst he held many opinions in common with the great mass of Christian believers, he did not believe in what are regarded as the orthodox or evangelical views of Christianity.
"On the innate depravity of man, the character and office of the great Head of the Church, the atonement, the infallibility of the written revelation, the performance of miracles, the nature and design of present and future rewards and punishments (as they are popularly called), and many other subjects, he held opinions utterly at variance with what are usually taught in the Church. I should say that his expressed views on these and kindred topics were such as, in the estimation of most believers, would place him entirely outside the Christian pale. Yet, to my mind, such was not the true position, since his principles and practices and the spirit of his whole life were of the very kind we universally agree to call Christian; and I think this conclusion is in no wise affected by the circumstance that he never attached himself to any religious society whatever.
"His religious views were eminently practical, and are summed up, as I think, in these two propositions: 'the Fatherhood of God, and the brotherhood of man.' He fully believed in a superintending and overruling Providence, that guides and controls the operations of the world, but maintained that law and order, and not their violation or suspension, are the appointed means by which this providence is exercised.
"I will not attempt any specification of either his belief or disbelief on various religious topics, as derived from conversations with him at different times during a considerable period; but, as conveying a general view of his religious or theological opinions, will state the following facts. Some eight or ten years prior to his death, in conversing with him upon this subject, the writer took occasion to refer, in terms of approbation, to the sermons and writings generally of Dr. W. E. Channing; and, finding he was considerably interested in the statement I made of the opinions held by that author, I proposed to present him (Lincoln) a copy of Channing's entire works, which I soon after did. Subsequently, the contents of these volumes, together with the writings of Theodore Parker, furnished him, as he informed me, by his friend and law-partner, Mr. Herndon, became naturally the topics of conversation with us; and though far from believing there was an entire harmony of views on his part with either of those authors, yet they were generally much admired and approved by him.
"No religious views with him seemed to find any favor, except of the practical and rationalistic order; and if, from my recollections on this subject, I was called upon to designate an author whose views most nearly represented Mr. Lincoln's on this subject, I would say that author was Theodore Parker.
"As you have asked from me a candid statement of my recollections on this topic, I have thus briefly given them, with the hope that they may be of some service in rightly settling a question about which—as I have good reason to believe—the public mind has been greatly misled.
"Not doubting that they will accord, substantially, with your own recollections, and that of his other intimate and confidential friends, and with the popular verdict after this matter shall have been properly canvassed, I submit them."
John G. Nicolay, his private secretary at the White House:—
"Mr. Lincoln did not, to my knowledge, in any way change his religious views, opinions, or beliefs, from the time he left Springfield to the day of his death. I do not know just what they were, never having heard him explain them in detail; but I am very sure he gave no outward indication of his mind having undergone any change in that regard while here."
The following letter from Mr. Herndon was, about the time of its date, extensively published throughout the United States, and met with no contradiction from any responsible source.
Springfield, Feb. 18, 1870.
Mr. Abbott,—-Some time since I promised you that I would send a letter in relation to Mr. Lincoln's religion. I do so now. Before entering on that question, one or two preliminary remarks will help us to understand why he disagreed with the Christian world in its principles, as well as in its theology. In the first place, Mr. Lincoln's mind was a purely logical mind; secondly, Mr. Lincoln was purely a practical man. He had no fancy or imagination, and not much emotion. He was a realist as opposed to an idealist. As a general rule, it is true that a purely logical mind has not much hope, if it ever has faith in the unseen and unknown. Mr. Lincoln had not much hope and no faith in things that lie outside of the domain of demonstration: he was so constituted, so organized, that he could believe nothing unless his senses or logic could reach it. I have often read to him a law point, a decision, or something I fancied: he could not understand it until he took the book out of my hand, and read the thing for himself. He was terribly, vexatiously sceptical. He could scarcely understand any thing, unless he had time and place fixed in his mind.
I became acquainted with Mr. Lincoln in 1834, and I think I knew him well to the day of his death. His mind, when a boy in Kentucky, showed a certain gloom, an unsocial nature, a peculiar abstractedness, a bold and daring scepticism. In Indiana, from 1817 to 1830, it manifested the same qualities or attributes as in Kentucky: it only intensified, developed itself, along those lines, in Indiana. He came to Illinois in 1830, and, after some little roving, settled in New Salem, now in Menard County and State of Illinois. This village lies about twenty miles north-west of this city. It was here that Mr. Lincoln became acquainted with a class of men the world never saw the like of before or since. They were large men,—large in body and large in mind; hard to whip, and never to be fooled. They were a bold, daring, and reckless sort of men; they were men of their own minds,—believed what was demonstrable; were men of great common sense. With these men Mr. Lincoln was thrown; with them he lived, and with them he moved, and almost had his being. They were sceptics all,—scoffers some. These scoffers were good men, and their scoffs were protests against theology,—loud protests against the follies of Christianity: they had never heard of theism and the newer and better religious thoughts of this age. Hence, being natural sceptics, and being bold, brave men, they uttered their thoughts freely: they declared that Jesus was an illegitimate child.... They were on all occasions, when opportunity offered, debating the various questions of Christianity among themselves: they took their stand on common sense and on their own souls; and, though their arguments were rude and rough, no man could overthrow their homely logic. They riddled all divines, and not unfrequently made them sceptics,—disbelievers as bad as themselves. They were a jovial, healthful, generous, social, true, and manly set of people.
It was here, and among these people, that Mr. Lincoln was thrown. About the year 1834, he chanced to come across Volney's "Ruins," and some of Paine's theological works. He at once seized hold of them, and assimilated them into his own being. Volney and Paine became a part of Mr. Lincoln from 1834 to the end of his life. In 1835 he wrote out a small work on "Infidelity," and intended to have it published. The book was an attack upon the whole grounds of Christianity, and especially was it an attack upon the idea that Jesus was the Christ, the true and only-begotten Son of God, as the Christian world contends. Mr. Lincoln was at that time in New Salem, keeping store for Mr. Samuel Hill, a merchant and postmaster of that place. Lincoln and Hill were very friendly. Hill, I think, was a sceptic at that time. Lincoln, one day after the book was finished, read it to Mr. Hill, his good friend. Hill tried to persuade him not to make it public, not to publish it. Hill at that time saw in Mr. Lincoln a rising man, and wished him success. Lincoln refused to destroy it, said it should be published. Hill swore it should never see light of day. He had an eye, to Lincoln's popularity,—his present and future success; and believing, that if the book were published, it would kill Lincoln forever, he snatched it from Lincoln's hand, when Lincoln was not expecting it, and ran it into an old-fashioned tin-plate stove, heated as hot as a furnace; and so Lincoln's book went up to the clouds in smoke. It is confessed by all who heard parts of it, that it was at once able and eloquent; and, if I may judge of it from Mr. Lincoln's subsequent ideas and opinions, often expressed to me and to others in my presence, it was able, strong, plain, and fair. His argument was grounded on the internal mistakes of the Old and New Testaments, and on reason, and on the experiences and observations of men. The criticisms from internal defects were sharp, strong, and manly.
Mr. Lincoln moved to this city in 1837, and here became acquainted with various men of his own way of thinking. At that time they called themselves free-thinkers, or free-thinking men. I remember all these things distinctly; for I was with them, heard them, and was one of them. Mr. Lincoln here found other works,—Hume, Gibbon, and others,—and drank them in: he made no secret of his views, no concealment of his religion. He boldly avowed himself an infidel. When Mr. Lincoln was a candidate for our Legislature, he was accused of being an infidel, and of having said that Jesus Christ was an illegitimate child: he never denied his opinions, nor flinched from his religious views; he was a true man, and yet it may be truthfully said, that in 1837 his religion was low indeed. In his moments of gloom he would doubt, if he did not sometimes deny, God. He made me once erase the name of God from a speech which I was about to make in 1854; and he did this in the city of Washington to one of his friends. I cannot now name the man, nor the place he occupied in Washington: it will be known sometime. I have the evidence, and intend to keep it.
Mr. Lincoln ran for Congress, against the Rev. Peter Cartwright, in the year 1847 or 1848. In that contest he was accused of being an infidel, if not an atheist; he never denied the charge; would not; "would die first:" in the first place, because he knew it could and would be proved on him; and in the second place he was too true to his own convictions, to his own soul, to deny it. From what I know of Mr. Lincoln, and from what I have heard and verily believe, I can say, First, That he did not believe in a special creation, his idea being that all creation was an evolution under law; Secondly, That he did not believe that the Bible was a special revelation from God, as the Christian world contends; Thirdly, He did not believe in miracles, as understood by the Christian world; Fourthly, He believed in universal inspiration and miracles under law; Fifthly, He did not believe that Jesus was the Christ, the Son of God, as the Christian world contends; Sixthly, He believed that all things, both matter and mind, were governed by laws, universal, absolute, and eternal. All his speeches and remarks in Washington conclusively prove this. Law was to Lincoln every thing, and special interferences shams and delusions. I know whereof I speak. I used to loan him Theodore Parker's works: I loaned him Emerson sometimes, and other writers; and he would sometimes read, and sometimes would not, as I suppose,—nay, know.
When Mr. Lincoln left this city for Washington, I know he had undergone no change in his religious opinions or views. He held many of the Christian ideas in abhorrence, and among them there was this one; namely, that God would forgive the sinner for a violation of his laws. Lincoln maintained that God could not forgive; that punishment has to follow the sin; that Christianity was wrong in teaching forgiveness; that it tended to make man sin in the hope that God would excuse, and so forth. Lincoln contended that the minister should teach that God has affixed punishment to sin, and that no repentance could bribe him to remit it. In one sense of the word, Mr. Lincoln was a Universalist, and in another sense he was a Unitarian; but he was a theist, as we now understand that word: he was so fully, freely, unequivocally, boldly, and openly, when asked for his views. Mr. Lincoln was supposed, by many people in this city, to be an atheist; and some still believe it. I can put that supposition at rest forever. I hold a letter of Mr. Lincoln in my hand, addressed to his step-brother, John D. Johnston, and dated the twelfth day of January, 1851. He had heard from Johnston that his father, Thomas Lincoln, was sick, and that no hopes of his recovery were entertained. Mr. Lincoln wrote back to Mr. Johnston these words:—
"I sincerely hope that father may yet recover his health; but, at all events, tell him to remember to call upon and confide in One great and good and merciful Maker, who will not turn away from him in any extremity. He notes the fall of a sparrow, and numbers the hairs of our heads; and he will not forget the dying man who puts his trust in him. Say to him, that, if we could meet now, it is doubtful whether it would not be more painful than pleasant; but that, if it be his lot to go now, he will soon have a joyous meeting with many loved ones gone before, and where the rest of us, through the help of God, hope ere long to join them.
"A. Lincoln."
So it seems that Mr. Lincoln believed in God and immortality as well as heaven,—a place. He believed in no hell and no punishment in the future world. It has been said to me that Mr. Lincoln wrote the above letter to an old man simply to cheer him up in his last moments, and that the writer did not believe what he said. The question is, Was Mr. Lincoln an honest and truthful man? If he was, he wrote that letter honestly, believing it. It has to me the sound, the ring, of an honest utterance. I admit that Mr. Lincoln, in his moments of melancholy and terrible gloom, was living on the borderland between theism and atheism,—sometimes quite wholly dwelling in atheism. In his happier moments he would swing back to theism, and dwell lovingly there. It is possible that Mr. Lincoln was not always responsible for what he said or thought, so deep, so intense, so terrible, was his melancholy. I send you a lecture of mine which will help you to see what I mean. I maintain that Mr. Lincoln was a deeply-religious man at all times and places, in spite of his transient doubts.
Soon after Mr. Lincoln was assassinated, Mr. Holland came into my office, and made some inquiries about him, stating to me his purpose of writing his life. I freely told him what he asked, and much more. He then asked me what I thought about Mr. Lincoln's religion, meaning his views of Christianity. I replied, "The less said, the better." Mr. Holland has recorded my expression to him (see Holland's "Life of Lincoln," p. 241). I cannot say what Mr. Holland said to me, as that was private. It appears that he went and saw Mr. Newton Bateman, Superintendent of Public Instruction in this State. It appears that Mr. Bateman told Mr. Holland many things, if he is correctly represented in Holland's "Life of Lincoln" (pp. 236-241, inclusive). I doubt whether Mr. Bateman said in full what is recorded there: I doubt a great deal of it. I know the whole story is untrue,—untrue in substance, untrue in fact and spirit. As soon as the "Life of Lincoln" was out, on reading that part here referred to, I instantly sought Mr. Bateman, and found him in his office. I spoke to him politely and kindly, and he spoke to me in the same manner. I said substantially to him that Mr. Holland, in order to make Mr. Lincoln a technical Christian, made him a hypocrite; and so his "Life of Lincoln" quite plainly says. I loved Mr. Lincoln, and was mortified, if not angry, to see him made a hypocrite. I cannot now detail what Mr. Bateman said, as it was a private conversation, and I am forbidden to make use of it in public. If some good gentleman can only get the seal of secrecy removed, I can show what was said and done. On my word, the world may take it for granted that Holland is wrong, that he does not state Mr. Lincoln's views correctly. Mr. Bateman, if correctly represented in Holland's "Life of Lincoln," is the only man, the sole and only man, who dare say that Mr. Lincoln believed in Jesus as the Christ of God, as the Christian world represents. This is not a pleasant situation for Mr. Bateman. I have notes and dates of our conversation; and the world will sometime know who is truthful, and who is otherwise. I doubt whether Bateman is correctly represented by Holland. My notes bear date Dec. 3, 12, and 28, 1866. Some of our conversations were in the spring of 1866 and the fall of 1865.
I do not remember ever seeing the words Jesus or Christ in print, as uttered by Mr. Lincoln. If he has used these words, they can be found. He uses the word God but seldom. I never heard him use the name of Christ or Jesus but to confute the idea that he was the Christ, the only and truly begotten Son of God, as the Christian world understands it. The idea that Mr. Lincoln carried the New Testament or Bible in his bosom or boots, to draw on his opponent in debate, is ridiculous.
My dear sir, I now have given you my knowledge, speaking from my own experience, of Mr. Lincoln's religious views. I speak likewise from the evidences, carefully gathered, of his religious opinions. I likewise speak from the ears and mouths of many in this city; and, after all careful examination, I declare to your numerous readers, that Mr. Lincoln is correctly represented here, so far as I know what truth is, and how it should be investigated.
If ever there was a moment when Mr. Lincoln might have been expected to express his faith in the atonement, his trust in the merits of a living Redeemer, it was when he undertook to send a composing and comforting message to a dying man. He knew, moreover, that his father had been "converted" time and again, and that no exhortation would so effectually console his weak spirit in the hour of dismay and dissolution as one which depicted, in the strongest terms, the perfect sufficiency of Jesus to save the perishing soul. But he omitted it wholly: he did not even mention the name of Jesus, or intimate the most distant suspicion of the existence of a Christ. On the contrary, he is singularly careful to employ the word "One" to qualify the word "Maker." It is the Maker, and not the Saviour, to whom he directs the attention of a sinner in the agony of death.
While it is very clear that Mr. Lincoln was at all times an infidel in the orthodox meaning of the term, it is also very clear that he was not at all times equally willing that everybody should know it. He never offered to purge or recant; but he was a wily politician, and did not disdain to regulate his religious manifestations with some reference to his political interests. As he grew older, he grew more cautious; and as his New Salem associates, and the aggressive deists with whom he originally united at Springfield, gradually dispersed, or fell away from his side, he appreciated more and more keenly the violence and extent of the religious prejudices which freedom in discussion from his standpoint would be sure to arouse against him. He saw the immense and augmenting power of the churches, and in times past had practically felt it. The imputation of infidelity had seriously injured him in several of his earlier political contests; and, sobered by age and experience, he was resolved that that same imputation should injure him no more. Aspiring to lead religious communities, he foresaw that he must not appear as an enemy within their gates; aspiring to public honors under the auspices of a political party which persistently summoned religious people to assist in the extirpation of that which is denounced as the "nation's sin," he foresaw that he could not ask their suffrages whilst aspersing their faith. He perceived no reason for changing his convictions, but he did perceive many good and cogent reasons for not making them public.
Col. Matheny alleges, that, from 1854 to 1860, Mr. Lincoln "played a sharp game" upon the Christians of Springfield, "treading their toes," and saying, "Come and convert me." Mr. Herndon is inclined to coincide with Matheny; and both give the obvious explanation of such conduct; that is to say, his morbid ambition; coupled with a mortal fear that his popularity would suffer by an open avowal of his deistic convictions. At any rate, Mr. Lincoln permitted himself to be misunderstood and misrepresented by some enthusiastic ministers and exhorters with whom he came in contact. Among these was the Rev. Mr. Smith, then pastor of the First Presbyterian Church of Springfield, and afterwards Consul at Dundee, in Scotland, under Mr. Lincoln's appointment. The abilities of this gentleman to discuss such a topic to the edification of a man like Mr. Lincoln seem to have been rather slender; but the chance of converting so distinguished a person inspired him with a zeal which he might not have felt for the salvation of an obscurer soul. Mr. Lincoln listened to his exhortations in silence, apparently respectful, and occasionally sat out his sermons in church with as much patience as other people. Finding these oral appeals unavailing, Mr. Smith composed a heavy tract out of his own head to suit the particular case. "The preparation of that work," says he, "cost me long and arduous labor;" but it does not appear to have been read. Mr. Lincoln took the "work" to his office, laid it down without writing his name on it, and never took it up again to the knowledge of a man who inhabited that office with him, and who saw it lying on the same spot every day for months. Subsequently Mr. Smith drew from Mr. Lincoln an acknowledgment that his argument was unanswerable,—not a very high compliment under the circumstances, but one to which Mr. Smith often referred afterwards with great delight. He never asserted, as some have supposed, that Mr. Lincoln was converted from the error of his ways; that he abandoned his infidel opinions, or that he united himself with any Christian church. On the contrary, when specially interrogated on these points by Mr. Herndon, he refused to answer, on the ground that Mr. Herndon was not a proper person to receive such a communication from Mr. Newton Bateman is reported to have said that a few days before the Presidential election of 1860, Mr. Lincoln came into his office, closed the door against intrusion, and proposed to examine a book which had been furnished him, at his own request, "containing a careful canvass of the city of Springfield, showing the candidate for whom each citizen had declared his intention to vote at the approaching election. He ascertained that only three ministers of the gospel, out of twenty-three, would vote for him, and that, of the prominent church-members, a very large majority were against him." Mr. Bateman does not say so directly, but the inference is plain that Mr. Lincoln had not previously known what were the sentiments of the Christian people who lived with him in Springfield: he had never before taken the trouble to inquire whether they were for him or against him. At all events, when he made the discovery out of the book, he wept, and declared that he "did not understand it at all." He drew from his bosom a pocket New Testament, and, "with a trembling voice and his cheeks wet with tears," quoted it against his political opponents generally, and especially against Douglas. He professed to believe that the opinions adopted by him and his party were derived from the teachings of Christ; averred that Christ was God; and, speaking of the Testament which he carried in his bosom, called it "this rock, on which him I stand." When Mr. Bateman expressed surprise, and told him that his friends generally were ignorant that he entertained such sentiments, he gave this answer quickly: "I know they are: I am obliged to appear different to them." Mr. Bateman is a respectable citizen, whose general reputation for truth and veracity is not to be impeached; but his story, as reported in Holland's Life, is so inconsistent with Mr. Lincoln's whole character, that it must be rejected as altogether incredible. From the time of the Democratic split in the Baltimore Convention, Mr. Lincoln, as well as every other politician of the smallest sagacity, knew that his success was as certain as any future event could be. At the end of October, most of the States had clearly voted in a way which left no lingering doubts of the final result of November. If there ever was a time in his life when ambition charmed his whole heart,—if it could ever be said of him that "hope elevated and joy brightened his crest," it was on the eve of that election which he saw was to lift him at last to the high place for which he had sighed and struggled so long. It was not then that he would mourn and weep because he was in danger of not getting the votes of the ministers and members of the churches he had known during many years for his steadfast opponents: he did not need them, and had not expected them. Those who understood him best are very sure that he never, under any circumstances, could have fallen into such weakness—not even when his fortunes were at the lowest point of depression—as to play the part of a hypocrite for their support. Neither is it possible that he was at any loss about the reasons which religious men had for refusing him their support; and, if he said that he could not understand it at all, he must have spoken falsely. But the worst part of the tale is Mr. Lincoln's acknowledgment that his "friends generally were deceived concerning his religious sentiments, and that he was obliged to appear different to them."
According to this version, which has had considerable currency, he carried a Testament in his bosom, carefully hidden from his intimate associates: he believed that Christ was God; yet his friends understood him to deny the verity of the gospel: he based his political doctrines on the teachings of the Bible; yet before all men, except Mr. Bateman, he habitually acted the part of an unbeliever and reprobate, because he was "obliged to appear different to them." How obliged? What compulsion required him to deny that Christ was God if he really believed him to be divine? Or did he put his political necessities above the obligations of truth, and oppose Christianity against his convictions, that he might win the favor of its enemies? It may be that his mere silence was sometimes misunderstood; but he never made an express avowal of any religious opinion which he did not entertain. He did not "appear different" at one time from what he was at another, and certainly he never put on infidelity as a mere mask to conceal his Christian character from the world. There is no dealing with Mr. Bateman, except by a flat contradiction. Perhaps his memory was treacherous, or his imagination led him astray, or, peradventure, he thought a fraud no harm if it gratified the strong desire of the public for proofs of Mr. Lincoln's orthodoxy. It is nothing to the purpose that Mr. Lincoln said once or twice that he thought this or that portion of the Scripture was the product of divine inspiration; for he was one of the class who hold that all truth is inspired, and that every human being with a mind and a conscience is a prophet. He would have agreed much more readily with one who taught that Newton's discoveries, or Bacon's philosophy, or one of his own speeches, were the works of men divinely inspired above their fellows.1
1 "As we have bodily senses to lay hold on matter, and supply bodily wants, through which we obtain, naturally, all needed material things; so we have spiritual faculties to lay hold on God and supply spiritual wants: through them we obtain all needed spiritual things. As we observe the conditions of the body, we have nature on our side: as we observe the law of the soul, we have God on our side. He imparts truth to all men who observe these conditions: we have direct access to him through reason, conscience, and the religious faculty, just as we have direct access to nature through the eye, the ear, or the hand. Through these channels, and by means of a law, certain, regular, and universal as gravitation, God inspires men, makes revelation of truth; for is not truth as much a phenomenon of God as motion of matter? Therefore, if God be omnipresent and omniactive, this inspiration is no miracle, but a regular mode of God's action on conscious spirit, as gravitation on unconscious matter. It is not a rare condescension of God, but a universal uplifting of man. To obtain a knowledge of duty, a man is not sent away, outside of himself, to ancient documents: for the only rule of faith and practice, the Word, is very nigh him, even in his heart, and by this Word he is to try all documents whatsoever. Inspiration, like God's omnipresence, is not limited to the few writers claimed by the Jews, Christians, or Mohammedans, but is co- extensive with the race. As God fills all space, so all spirit; as he influences and constrains unconscious and necessitated matter, so he inspires and helps free, unconscious man. "This theory does not make God limited, partial, or capricious: it exalts man. While it honors the excellence of a religious genius of a Moses or a Jesus, it does not pronounce their character monstrous, as the supernatural, nor fanatical, as the rationalistic theory; but natural, human, and beautiful, revealing the possibility of mankind. Prayer—whether voluntative or spontaneous, a word or a feeling, felt in gratitude, or penitence, or joy, or resignation—is not a soliloquy of the man, not a physiological function, nor an address to a deceased man, but a sally into the infinite spiritual world, whence we bring back light and truth. There are windows towards God, as towards the world. There is no intercessor, angel, mediator, between man and God; for man can speak, and God hear, each for himself. He requires no advocate to plead for men, who need not pray by attorney. Each man stands close to the omnipresent God; may feel his beautiful presence, and have familiar access to the All-Father; get truth at first hand from its Author. Wisdom, righteousness, and love are the Spirit of God in the soul of man: wherever these are, and just in proportion to their power, there is inspiration from God. Thus God is not the author of confusion, but concord. Faith and knowledge and revelation and reason tell the same tale, and so legitimate and confirm each one another. "God's action on matter and on man is, perhaps, the same thing to him, though it appear differently modified to us. But it is plain, from the nature of things, that there can be but one kind of inspiration, as of truth, faith, or love: it is the direct and intuitive perception of some truth, either of thought or of sentiment. There can be but one mode of inspiration: it is the action of the Highest within the soul, the divine presence imparting light; this presence, as truth, justice, holiness, love, infusing itself into the soul, giving it new life; the breathing-in of the Deity; the in-come of God to the soul, in the form of truth through the reason, of right through the conscience, of love and faith through the affections and religious element. Is inspiration confined to theological matter alone? Most certainly not."— —Parker's Discourse pertaining to Religion.
But he never told any one that he accepted Jesus as the Christ, or performed a single one of the acts which necessarily follow upon such a conviction. At Springfield and at Washington he was beset on the one hand by political priests, and on the other by honest and prayerful Christians. He despised the former, respected the latter, and had use for both. He said with characteristic irreverence, that he would not undertake to "run the churches by military authority;" but he was, nevertheless, alive to the importance of letting the churches "run" themselves in the interest of his party. Indefinite expressions about "Divine Providence," the "justice of God," "the favor of the Most High," were easy, and not inconsistent with his religious notions. In this, accordingly, he indulged freely; but never in all that time did he let fall from his lips or his pen an expression which remotely implied the slightest faith in Jesus as the Son of God and the Saviour of men.
The effect of Mr. Lincoln's unbelief did not affect his constitutional love of justice. Though he rejected the New Testament as a book of divine authority, he accepted the practical part of its precepts as binding upon him by virtue of the natural law. The benevolence of his impulses served to keep him, for the most part, within the limits to which a Christian is confined by the fear of God. It is also true beyond doubt that he was greatly influenced by the reflected force of Christianity. If he did not believe it, the masses of the "plain people" did; and no one ever was more anxious to do "whatsoever was of good report among men." To qualify himself as a witness or an officer it was frequently necessary that he should take oaths; and he always appealed to the Christian's God either by laying his hand upon the Gospels, or by some other form of invocation common among believers. Of course the ceremony was superfluous, for it imposed no religious obligation upon him; but his strong innate sense of right was sufficient to make him truthful without that high and awful sanction which faith in divine revelation would have carried with it.
Mr. Lincoln was by no means free from a kind of belief in the supernatural. While he rejected the great facts of Christianity, as wanting the support of authentic evidence, his mind was readily impressed with the most absurd superstitions.1 He lived constantly in the serious conviction that he was himself the subject of a special decree, made by some unknown and mysterious power, for which he had no name. The birth and death of Christ, his wonderful works, and his resurrection as "the first-fruits of them that slept," Mr. Lincoln denied, because they seemed naturally improbable, or inconsistent with his "philosophy so called;" but his perverted credulity terrified him when he saw two images of himself in a mirror.
1 "He had great faith in the strong sense of country people; and he gave them credit for greater intelligence than most men do. If he found an idea prevailing generally amongst them, he believed there was something in it, although it might not harmonize with science. "He had great faith in the virtues of the 'mad-stone' although he could give no reason for it, and confessed that it looked like superstition. But, he said, he found the people in the neighborhood of these stones fully impressed with a belief in their virtues from actual experiment; and that was about as much as we could ever know of the properties of medicines."—Gillespie. "When his son 'Bob' was supposed to have been bitten by a rabid dog, Mr. Lincoln took him to Terre Haute, La., where there was a mad-stone, with the intention of having it applied, and, it is presumed, did so."—Mrs. Wallace.
It is very probable that much of Mr. Lincoln's unhappiness, the melancholy that "dripped from him as he walked," was due to his want of religious faith. When the black fit was on him, he suffered as much mental misery as Bunyan or Cowper in the deepest anguish of their conflicts with the evil one. But the unfortunate conviction fastened upon him by his early associations, that there was no truth in the Bible, made all consolation impossible, and penitence useless. To a man of his temperament, predisposed as it was to depression of spirits, there could be no chance of happiness, if doomed to live without hope and without God in the world. He might force himself to be merry with his chosen comrades; he might "banish sadness" in mirthful conversation, or find relief in a jest; gratified ambition might elevate his feelings, and give him ease for a time: but solid comfort and permanent peace could come to him only through "a correspondence fixed with heaven." The fatal misfortune of his life, looking at it only as it affected him in this world, was the influence at New Salem and Springfield which enlisted him on the side of unbelief. He paid the bitter penalty in a life of misery.
"It was a grievous sin in Cæsar; And grievously hath Cæsar answered it."
Very truly,
W. H. Herndon.
ON the 11th of February, 1861, the arrangements for Mr. Lincoln's departure from Springfield were completed. It was intended to occupy the time remaining between that date and the 4th of March with a grand tour from State to State and city to city. One Mr. Wood, "recommended by Senator Seward," was the chief manager. He provided special trains to be preceded by pilot engines all the way through.
It was a gloomy day: heavy clouds floated overhead, and a cold rain was falling. Long before eight o'clock, a great mass of people had collected at the station of the Great Western Railway to witness the event of the day. At precisely five minutes before eight, Mr. Lincoln, preceded by Mr. Wood, emerged from a private room in the dépôt building, and passed slowly to the car, the people falling back respectfully on either side, and as many as possible shaking his hands. Having finally reached the train, he ascended the rear platform, and, facing about to the throng which had closed around him, drew himself up to his full height, removed his hat, and stood for several seconds in profound silence. His eye roved sadly over that sea of upturned faces; and he thought he read in them again the sympathy and friendship which he had often tried, and which he never needed more than he did then. There was an unusual quiver in his lip, and a still more unusual tear on his shrivelled cheek. His solemn manner, his long silence, were as full of melancholy eloquence as any words he could have uttered. What did he think of? Of the mighty changes which had lifted him from the lowest to the highest estate on earth? Of the weary road which had brought him to this lofty summit? Of his poor mother lying beneath the tangled underbrush in a distant forest? Of that other grave in the quiet Concord cemetery? Whatever the particular character of his thoughts, it is evident that they were retrospective and painful. To those who were anxiously waiting to catch words upon which the fate of the nation might hang, it seemed long until he had mastered his feelings sufficiently to speak. At length he began in a husky tone of voice, and slowly and impressively delivered his farewell to his neighbors. Imitating his example, every man in the crowd stood with his head uncovered in the fast-falling rain.
"Friends,—No one who has never been placed in a like position can understand my feelings at this hour, nor the oppressive sadness I feel at this parting. For more than a quarter of a century I have lived among you, and during all that time I have received nothing but kindness at your hands. Here I have lived from my youth, until now I am an old man. Here the most sacred ties of earth were assumed. Here all my children were born; and here one of them lies buried. To you, dear friends, I owe all that I have, all that I am. All the strange, checkered past seems to crowd now upon my mind. To-day I leave you. I go to assume a task more difficult than that which devolved upon Washington. Unless the great God, who assisted him, shall be with and aid me, I must fail; but if the same omniscient mind and almighty arm that directed and protected him shall guide and support me, I shall not fail,—I shall succeed. Let us all pray that the God of our fathers may not forsake us now. To him I commend you all. Permit me to ask, that, with equal security and faith, you will invoke his wisdom and guidance for me. With these few words I must leave you: for how long I know not. Friends, one and all, I must now bid you an affectionate farewell."
"It was a most impressive scene," said the editor of "The Journal." "We have known Mr. Lincoln for many years; we have heard him speak upon a hundred different occasions; but we never saw him so profoundly affected, nor did he ever utter an address which seemed to us so full of simple and touching eloquence, so exactly adapted to the occasion, so worthy of the man and the hour."
At eight o'clock the train rolled out of Springfield amid the cheers of the populace. Four years later a funeral train, covered with the emblems of splendid mourning, rolled into the same city, bearing a discolored corpse, whose obsequies were being celebrated in every part of the civilized world.
Along with Mr. Lincoln's family in the special car were Gov. Yates, Ex-Gov. Moore, Dr. Wallace (Mr. Lincoln's brother-in-law), Mr. Judd, Mr. Browning, Judge Davis, Col. Ellsworth, Col. Lamon, and private secretaries Nicolay and Hay.
It has been asserted that an attempt was made to throw the train off the track between Springfield and Indianapolis, and also that a hand-grenade was found on board at Cincinnati, but no evidence of the fact is given in either case, and none of the Presidential party ever heard of these murderous doings until they read of them in some of the more imaginative reports of their trip.
Full accounts of this journey were spread broadcast over the country at the time, and have been collected and printed in various books. But, except for the speeches of the President elect, those accounts possess no particular interest at this day; and of the speeches we shall present here only such extracts as express his thoughts and feelings about the impending civil war.
In the heat of the late canvass, he had written the following private letter:—
Springfield, Ill., Aug. 15, 1860.
John B. Fry, Esq.
My dear Sir,—Yours of the 9th, enclosing the letter of Hon. John M. Botts, was duly received. The latter is herewith returned, according to your request. It contains one of the many assurances I receive from the South, that in no probable event will there be any very formidable effort to break up the Union. The people of the South have too much of good sense and good temper to attempt the ruin of the government, rather than see it administered as it was administered by the men who made it. At least, so I hope and believe.
I thank you both for your own letter and a sight of that of Mr. Botts.
Yours very truly,
A. Lincoln.
The opinion expressed in the letter as to the probability of war does not appear to have undergone any material change or modification during the eventful months which had intervened; for he expressed it in much stronger terms at almost every stage of his progress to Washington.
At Toledo he said,—
"I am leaving you on an errand of national importance, attended, as you are aware, with considerable difficulties. Let us believe, as some poet has expressed it, 'Behind the cloud the sun is shining still.'"
At Indianapolis:—
"I am here to thank you for this magnificent welcome, and still more for the very generous support given by your State to that political cause, which, I think, is the true and just cause of the whole country, and the whole world. Solomon says, 'There is a time to keep silence;' and when men wrangle by the mouth, with no certainty that they mean the same thing while using the same words, it perhaps were as well if they would keep silence.
"The words 'coercion' and 'invasion' are much used in these days, and often with some temper and hot blood. Let us make sure, if we can, that we do not misunderstand the meaning of those who use them. Let us get the exact definitions of these words, not from dictionaries, but from the men themselves, who certainly deprecate the things they would represent by the use of the words.
"What, then, is coercion? What is invasion? Would the marching of an army into South Carolina, without the consent of her people, and with hostile intent toward them, be invasion? I certainly think it would; and it would be coercion also, if the South Carolinians were forced to submit. But if the United States should merely hold and retake its own forts and other property, and collect the duties on foreign importations, or even withhold the mails from places where they were' habitually violated, would any or all of these things be invasion or coercion? Do our professed lovers of the Union, who spitefully resolve that they will resist coercion and invasion, understand that such things as these, on the part of the United States, would be coercion or invasion of a State? If so, their idea of means to preserve the object of their great affection would seem to be exceedingly thin and airy. If sick, the little pills of the homoeopathist would be much too large for them to swallow. In their view, the Union, as a family relation, would seem to be no regular marriage, but rather a sort of 'free-love' arrangement, to be maintained on passional attraction."
At Columbus:—
"Allusion has been made to the interest felt in relation to the policy of the new administration. In this, I have received from some a degree of credit for having kept silence, from others some depreciation. I still think I was right. In the varying and repeatedly-shifting scenes of the present, without a precedent which could enable me to judge for the past, it has seemed fitting, that, before speaking upon the difficulties of the country, I should have gained a view of the whole field. To be sure, after all, I would be at liberty to modify and change the course of policy as future events might make a change necessary.
"I have not maintained silence from any want of real anxiety. It is a good thing that there is no more than anxiety, for there is nothing going wrong. It is a consoling circumstance, that when we look out there is nothing that really hurts anybody. We entertain different views upon political questions; but nobody is suffering any thing. This is a most consoling circumstance, and from it I judge that all we want is time and patience, and a reliance on that God who has never forsaken this people."
At Pittsburg:—
"Notwithstanding the troubles across the river, there is really no crisis springing from any thing in the Government itself. In plain words, there is really no crisis, except an artificial one. What is there now to warrant the condition of affairs presented by our friends 'over the river'? Take even their own view of the questions involved, and there is nothing to justify the course which they are pursuing. I repeat it, then, there is no crisis, except such a one as may be gotten up at any time by turbulent men, aided by designing politicians. My advice, then, under such circumstances, is to keep cool. If the great American people will only keep their temper on both sides of the line, the trouble will come to an end, and the question which now distracts the country will be settled just as surely as all other difficulties of like character which have originated in this Government have been adjusted. Let the people on both sides keep their self-possession, and, just as other clouds have cleared away in due time, so will this; and this great nation shall continue to prosper as heretofore."
At Cleveland:—
"Frequent allusion is made to the excitement at present existing in our national politics, and it is as well that I should also allude to it here. I think that there is no occasion for any excitement. The crisis, as it is called, is altogether an artificial crisis.... As I said before, this crisis is all artificial! It has no foundation in fact. It was not 'argued up,' as the saying is, and cannot be argued down. Let it alone, and it will go down itself."
Before the Legislature of New York:—
"When the time comes, according to the custom of the Government, I shall speak, and speak as well as I am able for the good of the present and of the future of this country,—for the good of the North and of the South, for the good of one and of the other, and of all sections of it. In the mean time, if we have patience, if we maintain our equanimity, though some may allow themselves to run off in a burst of passion, I still have confidence that the Almighty Ruler of the Universe, through the instrumentality of this great and intelligent people, can and will bring us through this difficulty, as he has heretofore brought us through all preceding difficulties of the country. Relying upon this, and again thanking you, as I forever shall, in my heart, for this generous reception you have given me, I bid you farewell."
In response to the Mayor of New York City, who had said, "To you, therefore, chosen under the forms of the Constitution, as the head of the Confederacy, we look for a restoration of fraternal relations between the States,—only to be accomplished by peaceful and conciliatory means, aided by the wisdom of Almighty God," Mr. Lincoln said,—
"In regard to the difficulties that confront us at this time, and of which you have seen fit to speak so becomingly and so justly, I can only say that I agree with the sentiments expressed."
At Trenton:—
"I shall endeavor to take the ground I deem most just to the North, the East, the West, the South, and the whole country. I take it, I hope, in good temper,—certainly with no malice towards any section. I shall do all that may be in my power to promote a peaceful settlement of all our difficulties. The man does not live who is more devoted to peace than I am,—none who would do more to preserve it. But it maybe necessary to put the foot down firmly. And if I do my duty, and do right, you will sustain me: will you not? Received, as I am, by the members of a legislature, the majority of whom do not agree with me in political sentiments, I trust that I may have their assistance in piloting the Ship of State through this voyage, surrounded by perils as it is; for, if it should suffer shipwreck now, there will be no pilot ever needed for another voyage."
At Philadelphia:—
"It is true, as your worthy mayor has said, that there is anxiety among the citizens of the United States at this time. I deem it a happy circumstance that this dissatisfied portion of our fellow-citizens do not point us to any thing in which they are being injured, or are about to be injured; for which reason I have felt all the while justified in concluding that the crisis, the panic, the anxiety, of the country at this time is artificial. If there be those who differ with me upon this subject, they have not pointed out the substantial difficulty that exists. I do not mean to say that an artificial panic may not do considerable harm: that it has done such I do not deny. The hope that has been expressed by your mayor, that I may be able to restore peace, harmony, and prosperity to the country, is most worthy of him; and happy indeed will I be if I shall be able to verify and fulfil that hope. I promise you, in all sincerity, that I bring to the work a sincere heart. Whether I will bring a head equal to that heart, will be for future times to determine. It were useless for me to speak of details or plans now: I shall speak officially next Monday week, if ever. If I should not speak then, it were useless for me to do so now."
At Philadelphia again:—
"Now, in my view of the present aspect of affairs, there need be no bloodshed or war. There is no necessity for it. I am not in favor of such a course: and I may say, in advance, that there will be no blood shed unless it be forced upon the Government; and then it will be compelled to act in self-defence."
At Harrisburg:—
"I recur for a moment but to repeat some words uttered at the hotel in regard to what has been said about the military support which the General Government may expect from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in a proper emergency. To guard against any possible mistake, do I recur to this. It is not with any pleasure that I contemplate the possibility that a necessity may arise in this country for the use of the military arm. While I am exceedingly gratified to see the manifestation upon your streets of your military force here, and exceedingly gratified at your promise here to use that force upon a proper emergency; while I make these acknowledgments, I desire to repeat, in order to preclude any possible misconstruction, that I do most sincerely hope that we shall have no use for them; that it will never become their duty to shed Hood, and most especially never to shed fraternal blood. I promise that, so far as I have wisdom to direct, if so painful a result shall in any wise be brought about, it shall be through no fault of mine."
Whilst Mr. Lincoln, in the midst of his suite and attendants, was being borne in triumph through the streets of Philadelphia, and a countless multitude of people were shouting themselves hoarse, and jostling and crushing each other around his carriage-wheels, Mr. Felton, the President of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore Railway, was engaged with a private detective discussing the details of an alleged conspiracy to murder him at Baltimore. Some months before, Mr. Felton, apprehending danger to the bridges along his line, had taken this man into his pay, and sent him to Baltimore to spy out and report any plot that might be found for their destruction. Taking with him a couple of other men and a woman, the detective went about his business with the zeal which necessarily marks his peculiar profession. He set up as a stock-broker, under an assumed name, opened an office, and became a vehement Secessionist. His agents were instructed to act with the duplicity which such men generally use, to be rabid on the subject of "Southern rights," to suggest all manner of crimes in vindication of them; and if, by these arts, corresponding sentiments should be elicited from their victims, the "job" might be considered as prospering. Of course they readily found out what everybody else knew,—that Maryland was in a state of great alarm; that her people were forming military associations, and that Gov. Hicks was doing his utmost to furnish them with arms, on condition that the arms, in case of need, should be turned against the Federal Government. Whether they detected any plan to burn bridges or not, the chief detective does not relate; but it appears that he soon deserted that inquiry, and got, or pretended to get, upon a scent that promised a heavier reward. Being intensely ambitious to shine in the professional way, and something of a politician besides, it struck him that it would be a particularly fine thing to discover a dreadful plot to assassinate the President elect; and he discovered it accordingly. It was easy to get that far: to furnish tangible proofs of an imaginary conspiracy was a more difficult matter. But Baltimore was seething with political excitement; numerous strangers from the far South crowded its hotels and boarding-houses; great numbers of mechanics and laborers out of employment encumbered its streets; and everywhere politicians, merchants, mechanics, laborers, and loafers were engaged in heated discussions about the anticipated war, and the probability of Northern troops being marched through Maryland to slaughter and pillage beyond the Potomac. It would seem like an easy thing to beguile a few individuals of this angry and excited multitude into the expression of some criminal desire; and the opportunity was not wholly lost, although the limited success of the detective under such favorable circumstances is absolutely wonderful. He put his "shadows" upon several persons, whom it suited his pleasure to suspect; and the "shadows" pursued their work with the keen zest and the cool treachery of their kind. They reported daily to their chief in writing, as he reported in turn to his employer. These documents are neither edifying nor useful: they prove nothing but the baseness of the vocation which gave them existence. They were furnished to Mr. Herndon in full, under the impression that partisan feeling had extinguished in him the love of truth, and the obligations of candor, as it had in many writers who preceded him on the same subject-matter. They have been carefully and thoroughly read, analyzed, examined, and Compared, with an earnest and conscientious desire to discover the truth, if, perchance, any trace of truth might be in them. The process of investigation began with a strong bias in favor of the conclusion at which the detective had arrived. For ten years the author implicitly believed in the reality of the atrocious plot which these spies were supposed to have detected and thwarted; and for ten years he had pleased himself with the reflection that he also had done something to defeat the bloody purpose of the assassins. It was a conviction which could scarcely have been overthrown by evidence less powerful than the detective's weak and contradictory account of his own case. In that account there is literally nothing to sustain the accusation, and much to rebut it. It is perfectly manifest that there was no conspiracy,—no conspiracy of a hundred, of fifty, of twenty, of three; no definite purpose in the heart of even one man to murder Mr. Lincoln at Baltimore.
The reports are all in the form of personal narratives, and for the most relate when the spies went to bed, when they rose, where they ate, what saloons and brothels they visited, and what blackguards they met and "drinked" with. One of them "shadowed" a loud-mouthed, drinking fellow, named Luckett, and another, a poor scapegrace and braggart, named Hilliard. These wretches "drinked" and talked a great deal, hung about bars, haunted disreputable houses, were constantly half-drunk, and easily excited to use big and threatening words by the faithless protestations and cunning management of the spies. Thus Hilliard was made to say that he thought a man who should act the part of Brutus in these times would deserve well of his country; and Luckett was induced to declare that he knew a man who would kill Lincoln. At length the great arch-conspirator—the Brutus, the Orsini, of the New World, to whom Luckett and Hilliard, the "national volunteers," and all such, were as mere puppets—condescended to reveal himself in the most obliging and confiding manner. He made no mystery of his cruel and desperate scheme. He did not guard it as a dangerous secret, or choose his confidants with the circumspection which political criminals, and especially assassins, have generally thought proper to observe. Very many persons knew what he was about, and levied on their friends for small sums—five, ten, and twenty dollars—to further the "captain's" plan. Even Luckett was deep enough in the awful plot to raise money for it; and when he took one of the spies to a public bar-room, and introduced him to the "captain," the latter sat down and talked it all over without the slightest reserve. When was there ever before such a loud-mouthed conspirator, such a trustful and innocent assassin! His name was Ferrandina, his occupation that of a barber, his place of business beneath Barnum's Hotel, where the sign of the bloodthirsty villain still invites the unsuspecting public to come in for a shave.
"Mr. Luckett," so the spy relates, "said that he was not going home this evening; and if I would meet him at Barr's saloon, on South Street, he would introduce me to Ferrandina.
"This was unexpected to me; but I determined to take the chances, and agreed to meet Mr. Luckett at the place named at 7, p.m. Mr. Luckett left about 2.30, p.m.; and I went to dinner.
"I was at the office in the afternoon in hopes that Mr. Felton might call, but he did not; and at 6.15, p.m., I went to supper. After supper, I went to Barr's saloon, and found Mr. Luckett and several other gentlemen there. He asked me to drink, and introduced me to Capt. Ferrandina and Capt. Turner. He eulogized me very highly as a neighbor of his, and told Ferrandina that I was the gentleman who had given the twenty-five dollars he (Luckett) had given to Ferrandina.
"The conversation at once got into politics; and Ferrandina, who is a fine-looking, intelligent-appearing person, became very excited. He shows the Italian in, I think, a very marked degree; and, although excited, yet was cooler than what I had believed was the general characteristic of Italians. He has lived South for many years, and is thoroughly imbued with the idea that the South must rule; that they (Southerners) have been outraged in their rights by the election of Lincoln, and freely justified resorting to any means to prevent Lincoln from taking his seat; and, as he spoke, his eyes fairly glared and glistened, and his whole frame quivered, but he was fully conscious of all he was doing. He is a man well calculated for controlling and directing the ardent-minded: he is an enthusiast, and believes, that, to use his own words, 'murder of any kind is justifiable and right to save the rights of the Southern people.' In all his views he was ably seconded by Capt. Turner.
"Capt. Turner is an American; but although very much of a gentleman, and possessing warm Southern feelings, he is not by any means so dangerous a man as Ferrandina, as his ability for exciting others is less powerful; but that he is a bold and proud man there is no doubt, as also that he is entirely under the control of Ferrandina. In fact, it could not be otherwise: for even I myself felt the influence of this man's strange power; and, wrong though I knew him to be, I felt strangely unable to keep my mind balanced against him.
"Ferrandina said, 'Never, never, shall Lincoln be President. His life (Ferrandina's) was of no consequence: he was willing to give it up for Lincoln's; he would sell it for that Abolitionist's; and as Orsini had given his life for Italy, so was he (Ferrandina) ready to die for his country, and the rights of the South; and, said Ferrandina, turning to Capt. Turner, 'We shall all die together: we shall show the North that we fear them not. Every man, captain,' said he, 'will on that day prove himself a hero. The first shot fired, the main traitor (Lincoln) dead, and all Maryland will be with us, and the South shall be free; and the North must then be ours.'—'Mr. Hutchins,' said Ferrandina, 'if I alone must do it, I shall: Lincoln shall die in this city.'
"Whilst we were thus talking, we (Mr. Luckett, Turner, Ferrandina, and myself) were alone in one corner of the barroom; and, while talking, two strangers had got pretty near us. Mr. Luckett called Ferrandina's attention to this, and intimated that they were listening; and we went up to the bar, drinked again at my expense, and again retired to another part of the room, at Ferrandina's request, to see if the strangers would again follow us: whether by accident or design, they again got near us; but of course we were not talking of any matter of consequence. Ferrandina said he suspected they were spies, and suggested that he had to attend a secret meeting, and was apprehensive that the two strangers might follow him; and, at Mr. Luckett's request, I remained with him (Luckett) to watch the movements of the strangers. I assured Ferrandina, that, if they would attempt to follow him, that we would whip them.
"Ferrandina and Turner left to attend the meeting; and, anxious as I was to follow them myself, I was obliged to remain with Mr. Luckett to watch the strangers, which we did for about fifteen minutes, when Mr. Luckett said that he should go to a friend's to stay over night, and I left for my hotel, arriving there at about 9, p.m., and soon retired."
It is in a secret communication between hireling spies and paid informers that these ferocious sentiments are attributed to the poor knight of the soap-pot. No disinterested person would believe the story upon such evidence; and it will appear hereafter, that even the detective felt that it was too weak to mention among his strong points at that decisive moment, when he revealed all he knew to the President and his friends. It is probably a mere fiction. If it had had any foundation in fact, we are inclined to believe that the sprightly and eloquent barber would have dangled at a rope's end long since. He would hardly have been left to shave and plot in peace, while the members of the Legislature, the police-marshal, and numerous private gentlemen, were locked up in Federal prisons. When Mr. Lincoln was actually slain, four years later, and the cupidity of the detectives was excited by enormous rewards, Ferrandina was totally unmolested. But even if Ferrandina really said all that is here imputed to him, he did no more than many others around him were doing at the same time. He drank and talked, and made swelling speeches; but he never took, nor seriously thought of taking, the first step toward the frightful tragedy he is said to have contemplated.
The detectives are cautious not to include in the supposed plot to murder any person of eminence, power, or influence. Their game is all of the smaller sort, and, as they conceived, easily taken,—witless vagabonds like Hilliard and Luckett, and a barber, whose calling indicates his character and associations. They had no fault to find with the governor of the State: he was rather a lively trimmer, to be sure, and very anxious to turn up at last on the winning side; but it was manifestly impossible that one in such exalted station could meditate murder. Yet, if they had pushed their inquiries with an honest desire to get at the truth, they might have found much stronger evidence against the governor than that which they pretend to have found against the barber. In the governor's case the evidence is documentary, written, authentic,—over his own hand, clear and conclusive as pen and ink could make it. As early as the previous November, Gov. Hicks had written the following letter; and, notwithstanding its treasonable and murderous import, the writer became conspicuously loyal before spring, and lived to reap splendid rewards and high honors under the auspices of the Federal Government, as the most patriotic and devoted Union man in Maryland. The person to whom the letter was addressed was equally fortunate; and, instead of drawing out his comrades in the field to "kill Lincoln and his men," he was sent to Congress by power exerted from Washington at a time when the administration selected the representatives of Maryland, and performed all his duties right loyally and acceptably. Shall one be taken, and another left? Shall Hicks go to the Senate, and Webster to Congress, while the poor barber is held to the silly words which he is alleged to have sputtered out between drinks in a low groggery, under the blandishments and encouragements of an eager spy, itching for his reward?
State of Maryland, Executive Chamber, Annapolis, Nov. 9, 1860.
Hon. E. H. Webster.
My dear Sir,—I have pleasure in acknowledging receipt of your favor introducing a very clever gentleman to my acquaintance (though a Demo'). I regret to say that we have, at this time, no arms on hand to distribute, but assure you at the earliest possible moment your company shall have arms: they have complied with all required on their part. We have some delay, in consequence of contracts with Georgia and Alabama, ahead of us: we expect at an early day an additional supply, and of first received your people shall be furnished. Will they be good men to send out to kill Lincoln and his men? if not, suppose the arms would be better sent South.
How does late election sit with you? 'Tis too bad. Harford, nothing to reproach herself for.
Your obedient servant,
Thos. H. Hicks.
With the Presidential party was Hon. Norman B. Judd: he was supposed to exercise unbounded influence over the new President; and with him, therefore, the detective opened communications. At various places along the route, Mr. Judd was given vague hints of the impending danger, accompanied by the usual assurances of the skill and activity of the patriots who were perilling their lives in a rebel city to save that of the Chief Magistrate. When he reached New York, he was met by the woman who had originally gone with the other spies to Baltimore. She had urgent messages from her chief,—messages that disturbed Mr. Judd exceedingly. The detective was anxious to meet Mr. Judd and the President; and a meeting was accordingly arranged to take place at Philadelphia.
Mr. Lincoln reached Philadelphia on the afternoon of the 21st. The detective had arrived in the morning, and improved the interval to impress and enlist Mr. Felton. In the evening he got Mr. Judd and Mr. Felton into his room at the St. Louis Hotel, and told them all he had learned. He dwelt at large on the fierce temper of the Baltimore Secessionists; on the loose talk he had heard about "fire-balls or hand-grenades;" on a "privateer" said to be moored somewhere in the bay; on the organization called National Volunteers; on the fact, that, eaves-dropping at Barnum's Hotel, he had overheard Marshal Kane intimate that he would not supply a police-force on some undefined occasion, but what the occasion was he did not know. He made much of his miserable victim, Hilliard, whom he held up as a perfect type of the class from which danger was to be apprehended; but, concerning "Captain" Ferrandina and his threats, he said, according to his own account, not a single word. He had opened his case, his whole case, and stated it as strongly as he could. Mr. Judd was very much startled, and was sure that it would be extremely imprudent for Mr. Lincoln to pass through Baltimore in open daylight, according to the published programme. But he thought the detective ought to see the President himself; and, as it was wearing toward nine o'clock, there was no time to lose. It was agreed that the part taken by the detective and Mr. Felton should be kept secret from every one but the President. Mr. Sanford, President of the American Telegraph Company, had also been co-operating in the business; and the same stipulation was made with regard to him.
Mr. Judd went to his own room at the Continental, and the detective followed. The crowd in the hotel was very dense, and it took some time to get a message to Mr. Lincoln. But it finally reached him, and he responded in person. Mr. Judd introduced the detective; and the latter told his story over again, with a single variation: this time he mentioned the name of Ferrandina along with Hilliard's, but gave no more prominence to one than to the other.
Mr. Judd and the detective wanted Lincoln to leave for Washington that night. This he flatly refused to do. He had engagements with the people, he said,—to raise a flag over Independence Hall in the morning, and to exhibit himself at Harrisburg in the afternoon; and these engagements he would not break in any event. But he would raise the flag, go to Harrisburg, "get away quietly" in the evening, and permit himself to be carried to Washington in the way they thought best. Even this, however, he conceded with great reluctance. He condescended to cross-examine the detective on some parts of his narrative, but at no time did he seem in the least degree alarmed. He was earnestly requested not to communicate the change of plan to any member of his party, except Mr. Judd, nor permit even a suspicion of it to cross the mind of another. To this he replied, that he would be compelled to tell Mrs. Lincoln; "and he thought it likely that she would insist upon W. H. Lamon going with him; but, aside from that, no one should know."
In the mean time, Mr. Seward had also discovered the conspiracy. He despatched his son to Philadelphia to warn the President elect of the terrible plot into whose meshes he was about to run. Mr. Lincoln turned him over to Judd, and Judd told him they already knew all about it. He went away with just enough information to enable his father to anticipate the exact moment of Mr. Lincoln's surreptitious arrival in Washington.
Early on the morning of the 22d, Mr. Lincoln raised the flag over Independence Hall, and departed for Harrisburg. On the way, Mr. Judd "gave him a full and precise detail of the arrangements that had been made" the previous night. After the conference with the detective, Mr. Sanford, Col. Scott, Mr. Felton, railroad and telegraph officials, had been sent for, and came to Mr. Judd's room. They occupied nearly the whole of the night in perfecting the plan. It was finally understood that about six o'clock the next evening Mr. Lincoln should slip away from the Jones Hotel, at Harrisburg, in company with a single member of his party. A special car and engine would be provided for him on the track outside the dépôt. All other trains on the road would be "sidetracked" until this one had passed. Mr. Sanford would forward skilled "telegraph-climbers," and see that all the wires leading out of Harrisburg were cut at six o'clock, and kept down until it was known that Mr. Lincoln had reached Washington in safety. The detective would meet Mr. Lincoln at the West Philadelphia dépôt with a carriage, and conduct him by a circuitous route to the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore dépôt. Berths for four would be pre-engaged in the sleeping-car attached to the regular midnight train for Baltimore. This train Mr. Felton would cause to be detained until the conductor should receive a package, containing important "government despatches," addressed to "E. J. Allen, Willard's Hotel, Washington." This package was made up of old newspapers, carefully wrapped and sealed, and delivered to the detective to be used as soon as Mr. Lincoln was lodged in the car. Mr. Lincoln approved of the plan, and signified his readiness to acquiesce. Then Mr. Judd, forgetting the secrecy which the spy had so impressively enjoined, told Mr. Lincoln that the step he was about to take was one of such transcendent importance, that he thought "it should be communicated to the other gentlemen of the party." Mr. Lincoln said, "You can do as you like about that." Mr. Judd now changed his seat; and Mr. Nicolay, whose suspicions seem to have been aroused by this mysterious conference, sat down beside him, and said, "Judd, there is something up. What is it, if it is proper that I should know?"—"George," answered Judd, "there is no necessity for your knowing it. One man can keep a matter better than two."
Arrived at Harrisburg, and the public ceremonies and speech-making over, Mr. Lincoln retired to a private parlor in the Jones House; and Mr. Judd summoned to meet him Judge Davis, Col. Lamon, Col. Sumner, Major Hunter, and Capt. Pope. The three latter were officers of the regular army, and had joined the party after it had left Springfield. Judd began the conference by stating the alleged fact of the Baltimore conspiracy, how it was detected, and how it was proposed to thwart it by a midnight expedition to Washington by way of Philadelphia. It was a great surprise to most of those assembled. Col. Sumner was the first to break silence. "That proceeding," said he, "will be a damned piece of cowardice." Mr. Judd considered this a "pointed hit," but replied that "that view of the case had already been presented to Mr. Lincoln." Then there was a general interchange of opinions, which Sumner interrupted by saying, "I'll get a squad of cavalry, sir, and cut our way to Washington, sir!"—"Probably before that day comes," said Mr. Judd, "the inauguration day will have passed. It is important that Mr. Lincoln should be in Washington that day." Thus far Judge Davis had expressed no opinion, but "had put various questions to test the truthfulness of the story." He now turned to Mr. Lincoln, and said, "You personally heard the detective's story. You have heard this discussion. What is your judgment in the matter?"—"I have listened," answered Mr. Lincoln, "to this discussion with interest. I see no reason, no good reason, to change the programme; and I am for carrying it out as arranged by Judd." There was no longer any dissent as to the plan itself; but one question still remained to be disposed of. Who should accompany the President on his perilous ride? Mr. Judd again took the lead, declaring that he and Mr. Lincoln had previously determined that but one man ought to go, and that Col. Lamon had been selected as the proper person. To this Sumner violently demurred. "I have undertaken," he exclaimed, "to see Mr. Lincoln to Washington."
Mr. Lincoln was hastily dining when a close carriage was brought to the side-door of the hotel. He was called, hurried to his room, changed his coat and hat, and passed rapidly through the hall and out of the door. As he was stepping into the carriage, it became manifest that Sumner was determined to get in also. "Hurry with him," whispered Judd to Lamon, and at the same time, placing his hand on Sumner's shoulder, said aloud, "One moment, colonel!" Sumner turned around; and, in that moment, the carriage drove rapidly away. "A madder man," says Mr. Judd, "you never saw."
Mr. Lincoln and Col. Lamon got on board the car without discovery or mishap. Besides themselves, there was no one in or about the car but Mr. Lewis, general superintendent of the Pennsylvania Central Railroad, and Mr. Franciscus, superintendent of the division over which they were about to pass. As Mr. Lincoln's dress on this occasion has been much discussed, it may be as well to state that he wore a soft, light felt hat, drawn down over his face when it seemed necessary or convenient, and a shawl thrown over his shoulders, and pulled up to assist in disguising his features when passing to and from the carriage. This was all there was of the "Scotch cap and cloak," so widely celebrated in the political literature of the day.
At ten o'clock they reached Philadelphia, and were met by the detective, and one Mr. Kinney, an under-official of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore Railroad. Lewis and Franciscus bade Mr. Lincoln adieu. Mr. Lincoln, Col. Lamon, and the detective seated themselves in a carriage, which stood in waiting, and Mr. Kinney got upon the box with the driver. It was a full hour and a half before the Baltimore train was to start; and Mr. Kinney found it necessary "to consume the time by driving northward in search of some imaginary person."
On the way through Philadelphia, Mr. Lincoln told his companions about the message he had received from Mr. Seward. This new discovery was infinitely more appalling than the other. Mr. Seward had been informed "that about fifteen thousand men were organized to prevent his (Lincoln's) passage through Baltimore, and that arrangements were made by these parties to blow up the railroad track, fire the train." &c. In view of these unpleasant circumstances, Mr. Seward recommended a change of route. Here was a plot big enough to swallow up the little one, which we are to regard as the peculiar property of Mr. Felton's detective. Hilliard, Ferrandina, and Luckett disappear among the "fifteen thousand;" and their maudlin and impotent twaddle about the "abolition tyrant" looks very insignificant beside the bloody massacre, conflagration, and explosion now foreshadowed.
As the moment for the departure of the Baltimore train drew near, the carriage paused in the dark shadows of the dépôt building. It was not considered prudent to approach the entrance. The spy passed in first, and was followed by Mr. Lincoln and Col. Lamon. An agent of the former directed them to the sleeping-car, which they entered by the rear door. Mr. Kinney ran forward, and delivered to the conductor the "important package" prepared for the purpose; and in three minutes the train was in motion. The tickets for the whole party had been procured beforehand. Their berths were ready, but had only been preserved from invasion by the statement, that they were retained for a sick man and his attendants. The business had been managed very adroitly by the female spy, who had accompanied her employer from Baltimore to Philadelphia to assist him in this the most delicate and important affair of his life. Mr. Lincoln got into his bed immediately; and the curtains were drawn together. When the conductor came around, the detective handed him the "sick man's" ticket; and the rest of the party lay down also. None of "our party appeared to be sleepy," says the detective; "but we all lay quiet, and nothing of importance transpired." "Mr. Lincoln is very homely," said the woman in her "report," "and so very tall, that he could not lay straight in his berth." During the night Mr. Lincoln indulged in a joke or two, in an undertone; but, with that exception, the "two sections" occupied by them were perfectly silent. The detective said he had men stationed at various places along the road to let him know "if all was right;" and he rose and went to the platform occasionally to observe their signals, but returned each time with a favorable report.
At thirty minutes after three, the train reached Baltimore. One of the spy's assistants came on board, and informed him "in a whisper that all was right." The woman got out of the car. Mr. Lincoln lay close in his berth; and in a few moments the car was being slowly drawn through the quiet streets of the city toward the Washington dépôt. There again there was another pause, but no sound more alarming than the noise of shifting cars and engines. The passengers, tucked away on their narrow shelves, dozed on as peacefully as if Mr. Lincoln had never been born, until they were awakened by the loud strokes of a huge club against a night-watchman's box, which stood within the dépôt and close to the track. It was an Irishman, trying to arouse a sleepy ticket-agent, comfortably ensconced within. For twenty minutes the Irishman pounded the box with ever-increasing vigor, and, at each report of his blows, shouted at the top of his voice, "Captain! it's four o'clock! it's four o'clock!" The Irishman seemed to think that time had ceased to run at four o'clock, and, making no allowance for the period consumed by his futile exercises, repeated to the last his original statement that it was four o'clock. The passengers were intensely amused; and their jokes and laughter at the Irishman's expense were not lost upon the occupants of the "two sections" in the rear. "Mr. Lincoln," says the detective, appeared "to enjoy it very much, and made several witty remarks, showing that he was as full of fun as ever."
In due time the train sped out of the suburbs of Baltimore; and the apprehensions of the President and his friends diminished with each welcome revolution of the wheels. At six o'clock the dome of the Capitol came in sight; and a moment later they rolled into the long, unsightly building, which forms the Washington dépôt. They passed out of the car unobserved, and pushed along with the living stream of men and women toward the outer door. One man alone in the great crowd seemed to watch Mr. Lincoln with special attention. Standing a little on one side, he "looked very sharp at him," and, as he passed, seized hold of his hand, and said in a loud tone of voice, "Abe, you can't play that on me." The detective and Col. Lamon were instantly alarmed. One of them raised his fist to strike the stranger; but Mr. Lincoln caught his arm, and said, "Don't strike him! don't strike him! It is Washburne. Don't you know him?" Mr. Seward had given to Mr. Washburne a hint of the information received through his son; and Mr. Washburne knew its value as well as another. For the present, the detective admonished him to keep quiet; and they passed on together. Taking a hack, they drove towards Willard's Hotel. Mr. Lincoln, Mr. Washburne, and the detectives got out in the street, and approached the ladies' entrance; while Col. Lamon drove on to the main entrance, and sent the proprietor to meet his distinguished guest at the side door. A few minutes later Mr. Seward arrived, and was introduced to the company by Mr. Washburne. He spoke in very strong terms of the great danger which Mr. Lincoln had so narrowly escaped, and most heartily applauded the wisdom of the "secret passage." "I informed Gov. Seward of the nature of the information I had," says the detective, "and that I had no information of any large organization in Baltimore; but the Governor reiterated that he had conclusive evidence of this."
It soon became apparent that Mr. Lincoln wished to be left alone. He said he was "rather tired;" and, upon this intimation, the party separated. The detective went to the telegraph-office, and loaded the wires with despatches, containing the pleasing intelligence that "Plums" had brought "Nuts" through in safety. In the spy's cipher the President elect was reduced to the undignified title of "Nuts."
That same day Mr. Lincoln's family and suite passed through Baltimore on the special train intended for him. They saw no sign of any disposition to burn them alive, or to blow them up with gunpowder, but went their way unmolested and very happy.
Mr. Lincoln soon learned to regret the midnight ride. His friends reproached him, his enemies taunted him. He was convinced that he had committed a grave mistake in yielding to the solicitations of a professional spy and of friends too easily alarmed. He saw that he had fled from a danger purely imaginary, and felt the shame and mortification natural to a brave man under such circumstances. But he was not disposed to take all the responsibility to himself, and frequently upbraided the writer for having aided and assisted him to demean himself at the very moment in all his life when his behavior should have exhibited the utmost dignity and composure.
The news of his surreptitious entry into Washington occasioned much and varied comment throughout the country; but important events followed it in such rapid succession, that its real significance was soon lost sight of. Enough that Mr. Lincoln was safely at the capital, and in a few days would in all probability assume the power confided to his hands.
If before leaving Springfield he had become weary of the pressure upon him for office, he found no respite on his arrival at the focus of political intrigue and corruption. The intervening days before his inauguration were principally occupied in arranging the construction of his Cabinet. He was pretty well determined on this subject before he reached Washington; but in the minds of the public, beyond the generally accepted fact, that Mr. Seward was to be the Premier of the new administration, all was speculation and conjecture. From the circumstances of the case, he was compelled to give patient ear to the representations which were made him in favor of or against various persons or parties, and to hold his final decisions till the last moment, in order that he might decide with a full view of the requirements of public policy and party fealty.
The close of this volume is not the place to enter into a detailed history of the circumstances which attended the inauguration of Mr. Lincoln's administration, nor of the events which signalized the close of Mr. Buchanan's. The history of the former cannot be understood without tracing its relation to that of the latter, and both demand more impartial consideration than either has yet received.
The 4th of March, 1861, at last arrived; and at noon on that day the administration of James Buchanan was to come to a close, and that of Abraham Lincoln was to take its place. Mr. Lincoln's feelings, as the hour approached which was to invest him with greater responsibilities than had fallen upon any of his predecessors, may readily be imagined by the readers of the foregoing pages. If he saw in his elevation another step towards the fulfilment of that destiny which at times he believed awaited him, the thought served but to tinge with a peculiar, almost poetic sadness, the manner in which he addressed himself to the solemn duties of the hour.

The morning opened pleasantly. At an early hour he gave his inaugural address its final revision. Extensive preparations had been made to render the occasion as impressive as possible. By nine o'clock the procession had begun to form, and at eleven o'clock it commenced to move toward Willard's Hotel. Mr. Buchanan was still at the Capitol, signing bills till the official term of his office expired. At half-past twelve he called for Mr. Lincoln; and, after a delay of a few moments, both descended, and entered the open barouche in waiting for them. Shortly after, the procession took up its line of march for the Capitol.
Apprehensions existed, that possibly some attempt might be made to assassinate Mr. Lincoln; and accordingly his carriage was carefully surrounded by the military and the Committee of Arrangements. By order of Gen. Scott, troops were placed at various points about the city, as well as on the tops of some of the houses along the route of the procession.
The Senate remained in session till twelve o'clock, when Mr. Breckinridge, in a few well-chosen words, bade the senators farewell, and then conducted his successor, Mr. Hamlin, to the chair. At this moment, members and members elect of the House of Representatives, and the Diplomatic Corps, entered the chamber. At thirteen minutes to one, the Judges of the Supreme Court were announced; and on their entrance, headed by the venerable Chief-Justice Taney, all on the floor arose, while they moved slowly to the seats assigned them at the right of the Vice-President, bowing to that officer as they passed. At fifteen minutes past one, the Marshal-in-Chief entered the chamber ushering in the President and President elect. Mr. Lincoln looked pale, and wan, and anxious. In a few moments, the Marshal led the way to the platform at the eastern portico of the Capitol, where preparations had been made for the inauguration ceremony; and he was followed by the Judges of the Supreme Court, Sergeant-at-Arms of the Senate, the Committee of Arrangements, the President and President elect, Vice-President, Secretary of the Senate, Senators, Diplomatic Corps, Heads of Departments, and others in the chamber.
On arriving at the platform, Mr. Lincoln was introduced to the assembly, by the Hon. E. D. Baker, United States Senator from Oregon. Stepping forward, in a manner deliberate and impressive, he read in a clear, penetrating voice, the following
INAUGURAL ADDRESS.
Fellow-Citizens of the United States:—
In compliance with a custom as old as the Government itself, I appear before you to address you briefly, and to take, in your presence, the oath prescribed by the Constitution of the United States to be taken by the President before he enters on the execution of his office.
I do not consider it necessary, at present, for me to discuss those matters of administration about which there is no special anxiety or excitement. Apprehension seems to exist among the people of the Southern States, that, by the accession of a Republican administration, their property and their peace and personal security are to be endangered. There has never been any reasonable cause for such apprehension. Indeed, the most ample evidence to the contrary has all the while existed, and been open to their inspection. It is found in nearly all the published speeches of him who now addresses you. I do but quote from one of those speeches, when I declare, that "I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists." I believe I have no lawful right to do so; and I have no inclination to do so. Those who nominated and elected me did so with the full knowledge that I had made this and many similar declarations, and had never recanted them. And, more than this, they placed in the platform, for my acceptance, and as a law to themselves and to me, the clear and emphatic resolution which I now read:—
"Resolved, That the maintenance inviolate of the rights of the States, and especially the right of each State to order and control its own domestic institutions according to its own judgment exclusively, is essential to that balance of power on which the perfection and endurance of our political fabric depend; and we denounce the lawless invasion by armed force of the soil of any State or Territory, no matter under what pretext, as among the gravest of crimes."
I now reiterate these sentiments; and, in doing so, I only press upon the public attention the most conclusive evidence of which the case is susceptible, that the property, peace, and security of no section are to be in any wise endangered by the now incoming administration.
I add, too, that all the protection which, consistently with the Constitution and the laws, can be given, will be cheerfully given to all the States, when lawfully demanded, for whatever cause, as cheerfully to one section as to another.
There is much controversy about the delivering up of fugitives from service or labor. The clause I now read is as plainly written in the Constitution as any other of its provisions:—
"No person held to service or labor in one State under the laws thereof, escaping into another, shall, in consequence of any law or regulation therein, be discharged from such service or labor, but shall be delivered up on claim of the party to whom such service or labor may be due."
It is scarcely questioned that this provision was intended by those who made it for the reclaiming of what we call fugitive slaves; and the intention of the lawgiver is the law.
All members of Congress swear their support to the whole Constitution,—to this provision as well as any other. To the proposition, then, that slaves whose cases come within the terms of this clause "shall be delivered up," their oaths are unanimous. Now, if they would make the effort in good temper, could they not, with nearly equal unanimity, frame and pass a law by means of which to keep good that unanimous oath?
There is some difference of opinion whether this clause should be enforced by national or by State authority; but surely that difference is not a very material one. If the slave is to be surrendered, it can be of but little consequence to him or to others by which authority it is done; and should any one in any case be content that this oath shall go unkept on a merely unsubstantial controversy as to how it shall be kept?
Again, in any law upon this subject, ought not all the safeguards of liberty known in civilized and humane jurisprudence to be introduced, so that a free man be not, in any case, surrendered as a slave? And might it not be well at the same time to provide by law for the enforcement of that clause in the Constitution which guarantees that "the citizens of each State shall be entitled to all the privileges and immunities of citizens in the several States"?
I take the official oath to-day with no mental reservations, and with no purpose to construe the Constitution or laws by any hypercritical rules; and, while I do not choose now to specify particular acts of Congress as proper to be enforced, I do suggest, that it will be much safer for all, both in official and private stations, to conform to and abide by all those acts which stand unrepealed, than to violate any of them, trusting to find impunity in having them held to be unconstitutional.
It is seventy-two years since the first inauguration of a President under our national Constitution. During that period, fifteen different and very distinguished citizens have in succession administered the executive branch of the government. They have conducted it through many perils, and generally with great success. Yet, with all this scope for precedent, I now enter upon the same task, for the brief constitutional term of four years, under great and peculiar difficulties.
A disruption of the Federal Union, heretofore only menaced, is now formidably attempted. I hold, that, in the contemplation of universal law and of the Constitution, the Union of these States is perpetual. Perpetuity is implied, if not expressed, in the fundamental law of all national governments. It is safe to assert that no government proper ever had a provision in its organic law for its own termination. Continue to execute all the express provisions of our national Constitution, and the Union will endure forever; it being impossible to destroy it, except by some action not provided for in the instrument itself.
Again, if the United States be not a government proper, but an association of States in the nature of a contract merely, can it, as a contract, be peaceably unmade by less than all the parties who made it? One party to a contract may violate it,—break it, so to speak; but does it not require all to lawfully rescind it? Descending from these general principles, we find the proposition that in legal contemplation the Union is perpetual confirmed by the history of the Union itself.
The Union is much older than the Constitution. It was formed, in fact, by the Articles of Association in 1774. It was matured and continued in the Declaration of Independence in 1776. It was further matured, and the faith of all the then thirteen States expressly plighted and engaged that it should be perpetual, by the Articles of Confederation, in 1778; and, finally, in 1787, one of the declared objects for ordaining and establishing the Constitution was to form a more perfect Union. But, if the destruction of the Union by one or by a part only of the States be lawfully possible, the Union is less than before, the Constitution having lost the vital element of perpetuity.
It follows from these views that no State, upon its own mere motion, can lawfully get out of the Union; that resolves and ordinances to that effect are legally void; and that acts of violence within any State or States against the authority of the United States, are insurrectionary or revolutionary according to circumstances.
I therefore consider, that, in view of the Constitution and the laws, the Union is unbroken; and, to the extent of my ability, I shall take care, as the Constitution itself expressly enjoins upon me, that the laws of the Union shall be faithfully executed in all the States. Doing this, which I deem to be only a simple duty on my part, I shall perfectly perform it, so far as is practicable, unless my rightful masters, the American people, shall withhold the requisite power, or in some authoritative manner direct the contrary.
I trust this will not be regarded as a menace, but only as the declared purpose of the Union that it will constitutionally defend and maintain itself.
In doing this, there need be no bloodshed or violence; and there shall be none unless it is forced upon the national authority.
The power confided to me will be used to hold, occupy, and possess the property and places belonging to the government, and collect the duties and imposts; but, beyond what may be necessary for these objects, there will be no invasion, no using of force against or among the people anywhere.
Where hostility to the United States shall be so great and so universal as to prevent competent resident citizens from holding the Federal offices, there will be no attempt to force obnoxious strangers among the people for that object. While the strict legal right may exist of the Government to enforce the exercise of these offices, the attempt to do so would be so irritating, and so nearly impracticable withal, that I deem it better to forego for the time the uses of such offices.
The mails, unless repelled, will continue to be furnished in all parts of the Union.
So far as possible, the people everywhere shall have that sense of perfect security which is most favorable to calm thought and reflection.
The course here indicated will be followed, unless current events and experience shall show a modification or change to be proper; and in every case and exigency my best discretion will be exercised according to the circumstances actually existing, and with a view and hope of a peaceful solution of the national troubles, and the restoration of fraternal sympathies and affections.
That there are persons, in one section or another, who seek to destroy the Union at all events, and are glad of any pretext to do it, I will neither affirm nor deny. But, if there be such, I need address no word to them.
To those, however, who really love the Union, may I not speak? Before entering upon so grave a matter as the destruction of our national fabric, with all its benefits, its memories, and its hopes, would it not be well to ascertain why we do it? Will you hazard so desperate a step, while any portion of the ills you fly from have no real existence? Will you, while the certain ills you fly to are greater than all the real ones you fly from? Will you risk the commission of so fearful a mistake? All profess to be content in the Union if all constitutional rights can be maintained. Is it true, then, that any right, plainly written in the Constitution, has been denied? I think not. Happily the human mind is so constituted, that no party can reach to the audacity of doing this.
Think, if you can, of a single instance in which a plainly written provision of the Constitution has ever been denied. If, by the mere force of numbers, a majority should deprive a minority of any clearly written constitutional right, it might, in a moral point of view, justify revolution: it certainly would, if such right were a vital one. But such is not our case.
All the vital rights of minorities and of individuals are so plainly assured to them by affirmations and negations, guaranties and prohibitions, in the Constitution, that controversies never arise concerning them. But no organic law can ever be framed with a provision specifically applicable to every question which may occur in practical administration. No foresight can anticipate, nor any document of reasonable length contain, express provisions for all possible questions. Shall fugitives from labor be surrendered by National or by State authority? The Constitution does not expressly say. Must Congress protect slavery in the Territories? The Constitution does not expressly say. From questions of this class spring all our constitutional controversies, and we divide upon them into majorities and minorities.
If the minority will not acquiesce, the majority must, or the government must cease. There is no alternative for continuing the government but acquiescence on the one side or the other. If a minority, in such a case, will secede rather than acquiesce, they make a precedent which in turn will ruin and divide them; for a minority of their own will secede from them, whenever a majority refuses to be controlled by such a minority. For instance, why not any portion of a new confederacy, a year or two hence, arbitrarily secede again, precisely as portions of the present Union now claim to secede from it? All who cherish disunion sentiments are now being educated to the exact temper of doing this. Is there such perfect identity of interests among the States to compose a new Union as to produce harmony only, and prevent renewed secession? Plainly, the central idea of secession is the essence of anarchy.
A majority held in restraint by constitutional check and limitation, and always changing easily with deliberate changes of popular opinions and sentiments, is the only true sovereign of a free people. Whoever rejects it does, of necessity, fly to anarchy or to despotism. Unanimity is impossible: the rule of a minority, as a permanent arrangement, is wholly inadmissible; so that, rejecting the majority principle, anarchy or despotism in some form is all that is left.
I do not forget the position assumed by some, that constitutional questions are to be decided by the Supreme Court, nor do I deny that such decisions must be binding in any case upon the parties to a suit, as to the object of that suit; while they are also entitled to very high respect and consideration in all parallel cases by all other departments of the government; and, while it is obviously possible that such decision may be erroneous in any given case, still, the evil effect following it, being limited to that particular case, with the chance that it may be overruled and never become a precedent for other cases, can better be borne than could the evils of a different practice.
At the same time, the candid citizen must confess, that, if the policy of the government upon the vital questions affecting the whole people is to be irrevocably fixed by the decisions of the Supreme Court the instant they are made, as in ordinary litigation between parties in personal actions, the people will have ceased to be their own masters, having to that extent practically resigned their government into the hands of that eminent tribunal.
Nor is there in this view any assault upon the court or the judges. It is a duty from which they may not shrink, to decide cases properly brought before them; and it is no fault of theirs if others seek to turn their decisions to political purposes. One section of our country believes slavery is right and ought to be extended, while the other believes it is wrong and ought not to be extended; and this is the only substantial dispute: and the fugitive-slave clause of the Constitution, and the law for the suppression of the foreign slave-trade, are each as well enforced, perhaps, as any law can ever be in a community where the moral sense of the people imperfectly supports the law itself. The great body of the people abide by the dry, legal obligation in both cases, and a few break over in each. This, I think, cannot be perfectly cured; and it would be worse in both cases after the separation of the sections than before. The foreign slave-trade, now imperfectly suppressed, would be ultimately revived, without restriction, in one section; while fugitive slaves, now only partially surrendered, would not be surrendered at all by the other.
Physically speaking, we cannot separate: we cannot remove our respective sections from each other, nor build an impassable wall between them. A husband and wife may be divorced, and go out of the presence and beyond the reach of each other; but the different parts of our country cannot do this. They cannot but remain face to face; and intercourse, either amicable or hostile, must continue between them. Is it possible, then, to make that intercourse more advantageous or more satisfactory after separation than before? Can aliens make treaties easier than friends can make laws? Can treaties be more faithfully enforced between aliens than laws can among friends? Suppose you go to war, you cannot fight always; and when, after much loss on both sides, and no gain on either, you cease fighting, the identical questions as to terms of intercourse are again upon you.
This country, with its institutions, belongs to the people who inhabit it. Whenever they shall grow weary of the existing government, they can exercise their constitutional right of amending, or their revolutionary right to dismember or overthrow it. I cannot be ignorant of the fact, that many worthy and patriotic citizens are desirous of having the national Constitution amended. While I make no recommendation of amendment, I fully recognize the full authority of the people over the whole subject, to be exercised in either of the modes prescribed in the instrument itself; and I should, under existing circumstances, favor rather than oppose a fair opportunity being afforded the people to act upon it.
I will venture to add, that to me the convention mode seems preferable, in that it allows amendments to originate with the people themselves, instead of only permitting them to take or reject propositions originated by others not especially chosen for the purpose, and which might not be precisely such as they would wish either to accept or refuse. I understand that a proposed amendment to the Constitution (which amendment, however, I have not seen) has passed Congress, to the effect that the Federal Government shall never interfere with the domestic institutions of States, including that of persons held to service. To avoid misconstruction of what I have said, I depart from my purpose not to speak of particular amendments so far as to say, that, holding such a provision to now be implied constitutional law, I have no objection to its being made express and irrevocable.
The chief magistrate derives all his authority from the people, and they have conferred none upon him to fix the terms for the separation of the States. The people themselves, also, can do this if they choose; but the Executive, as such, has nothing to do with it. His duty is to administer the present government as it came to his hands, and to transmit it unimpaired by him to his successor. Why should there not be a patient confidence in the ultimate justice of the people? Is there any better or equal hope in the world? In our present differences, is either party without faith of being in the right? If the Almighty Ruler of nations, with his eternal truth and justice, be on your side of the North, or on yours of the South, that truth and that justice will surely prevail by the judgment of this great tribunal,—the American people. By the frame of the government under which we live, this same people have wisely given their public servants but little power for mischief, and have with equal wisdom provided for the return of that little to their own hands at very short intervals. While the people retain their virtue and vigilance, no administration, by any extreme wickedness or folly, can very seriously injure the Government in the short space of four years.
My countrymen, one and all, think calmly and well upon this whole subject. Nothing valuable can be lost by taking time.
If there be an object to hurry any of you, in hot haste, to a step which you would never take deliberately, that object will be frustrated by taking time; but no good object can be frustrated by it.
Such of you as are now dissatisfied still have the old Constitution unimpaired, and, on the sensitive point, the laws of your own framing under it; while the new administration will have no immediate power, if it would, to change either.
If it were admitted that you who are dissatisfied hold the right side in the dispute, there is still no single reason for precipitate action. Intelligence, patriotism, Christianity, and a firm reliance on Him who has never yet forsaken this favored land, are still competent to adjust, in the best way, all our present difficulties.
In your hands, my dissatisfied fellow-countrymen, and not in mine, is the momentous issue of civil war. The Government will not assail you.
You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors. You can have no oath registered in heaven to destroy the Government; while I shall have the most solemn one to "preserve, protect, and defend" it.
I am loah to close. We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies. Though passion may have strained, it must not break our bonds of affection.
The mystic chords of memory, stretching from every battle-field and patriot grave to every living heart and hearthstone all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union, when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature.
This address, so characteristic of its author, and so full of the best qualities of Mr. Lincoln's nature, was well received by the large audience which heard it. Having finished, Mr. Lincoln turned to Chief-Justice Taney, who, with much apparent agitation and emotion, administered to him the following oath:—
"I, Abraham Lincoln, do solemnly swear that I will faithfully execute the office of President of the United States, and will, to the best of my ability, preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution of the United States."
The ceremony concluded, Mr. Lincoln, as President of the United States, in charge of the Committee of Arrangements, was accompanied by Mr. Buchanan back to the Senate- Chamber, and from there to the Executive Mansion. Here Mr. Buchanan took leave of him, invoking upon his administration a peaceful and happy result; and here for the present we leave him. In another volume we shall endeavor to trace his career as the nation's Chief Magistrate during the ensuing four years.



THE circumstances under which the original of the accompanying facsimile was written are explained in the following letter:—
National Hotel, Washington, D.C., Feb. 19, 1872. Colonel Ward H. Lamon.
Dear Sir,—In compliance with your request, I place in your hands a copy of a manuscript in my possession written by Abraham Lincoln, giving a brief account of his early history, and the commencement of that political career which terminated in his election to the Presidency.
It may not be inappropriate to say, that some time preceding the writing of the enclosed, finding, in Pennsylvania and elsewhere, a laudable curiosity in the public mind to know more about the early history of Mr. Lincoln, and looking, too, to the possibilities of his being an available candidate for the Presidency in 1860, I had on several occasions requested of him this information, and that it was not without some hesitation he placed in my hands even this very modest account of himself, which he did in the month of December, 1859.
To this were added, by myself, other facts bearing upon his legislative and political history, and the whole forwarded to a friend residing in my native county (Chester, Pa.),—the Hon. Joseph J. Lewis, former Commissioner of Internal Revenue,—who made them the basis of an ably-written and somewhat elaborate memoir of the late President, which appeared in the Pennsylvania and other papers of the country in January, 1860, and which contributed to prepare the way for the subsequent nomination at Chicago the following June.
Believing this brief and unpretending narrative, written by himself in his own peculiar vein,—and injustice to him I should add, without the remotest expectation of its ever appearing in public,—with the attending circumstances, may be of interest to the numerous admirers of that historic and truly great man, I place it at your disposal.
I am truly yours,
Jesse W. Fell.
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you will have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this eBook.