
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: The Brownings
Their Life and Art
Author: Lilian Whiting
Release Date: December 14, 2009 [eBook #30671]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
***START OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BROWNINGS***
| Note: | Images of the original pages are available through Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries. See http://www.archive.org/details/browningstheirli00whituoft |

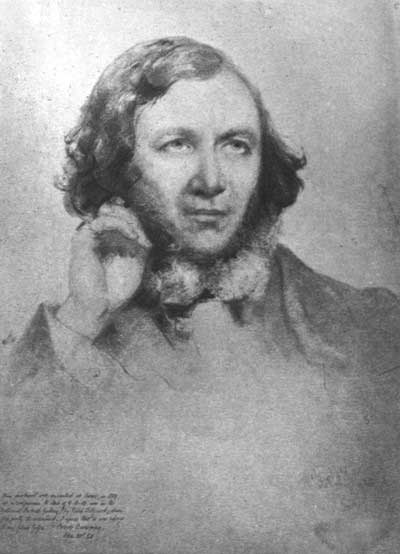
ROBERT BROWNING
From a drawing made by Field Talfourd, in Rome, 1855
Copyright, 1911,
By Little, Brown, and Company.
All rights reserved
Published, October, 1911
Printers
S. J. Parkhill & Co., Boston, U.S.A.
INSCRIBED TO
ROBERT BARRETT BROWNING
(CAVALIERE DELLA CORONA D’ITALIA)
PAINTER, SCULPTOR, CONNOISSEUR IN ART
WITH ENCHANTING REMEMBRANCES OF HOURS IN “LA TORRE
ALL’ ANTELLA” AND THE FAITHFUL REGARDS OF
LILIAN WHITING
Florence, Italy,
June, 1911
The present volume was initiated in Florence, and, from its first inception, invested with the cordial assent and the sympathetic encouragement of Robert Barrett Browning. One never-to-be-forgotten day, all ethereal light and loveliness, has left its picture in memory, when, in company with Mr. Browning and his life-long friend, the Marchesa Peruzzi di’ Medici (náta Story), the writer of this biography strolled with them under the host’s orange trees and among the riotous roses of his Florentine villa, “La Torre All’ Antella,” listening to their sparkling conversation, replete with fascinating reminiscences. To Mr. Browning the tribute of thanks, whose full scope is known to the Recording Angel alone, is here offered; and there is the blending of both privilege and duty in grateful acknowledgements to Messrs. Smith, Elder, & Company for their courtesy in permitting the somewhat liberal drawing on their published Letters of both the Brownings, on which reliance had to be based in any effort to
“Call up the buried Past again,”
and construct the story, from season to season, so far as might be, of that wonderful interlude of the wedded life of the poets.
Yet any formality of thanks to this house is almost lost sight of in the rush of memories of that long and mutually-trusting friendship between the late George Murray Smith,[Pg viii] the former head of this firm, and Robert Browning, a friendship which was one of the choicest treasures in both their lives.
To The Macmillan Company, the publishers for both the first and the present Lord Tennyson; To Houghton Mifflin Company; to Messrs. Dodd, Mead, & Company; to The Cornhill Magazine (to which the writer is indebted for some data regarding Browning and Professor Masson); to each and all, acknowledgments are offered for their courtesy which has invested with added charm a work than which none was ever more completely a labor of love.
To Edith, Contessa Rucellai (náta Bronson), whose characteristically lovely kindness placed at the disposal of this volume a number of letters written by Robert Browning to her mother, Mrs. Arthur Bronson, special gratitude is offered.
“Poetry,” said Mrs. Browning, “is its own exceeding great reward.” Any effort, however remote its results from the ideal that haunted the writer, to interpret the lives of such transcendent genius and nobleness as those of Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning, must also be its own exceeding reward in leading to a passion of pursuit of all that is highest and holiest in the life that now is, and in that which is to come.
LILIAN WHITING
The Brunswick, Boston
Midsummer Days, 1911
| Page | |
| CHAPTER I | |
| 1812-1833 | |
| The Most Exquisite Romance of Modern Life—Ancestry and Youth of Robert Browning—Love of Music—Formative Influences—The Fascination of Byron—A Home “Crammed with Books”—The Spell of Shelley—“Incondita”—Poetic Vocation Definitely Chosen—“Pauline” | 1 |
| CHAPTER II | |
| 1806-1832 | |
| Childhood and Early Youth of Elizabeth Barrett—Hope End—“Summer Snow of Apple-Blossoms”—Her Bower of White Roses—“Living with Visions”—The Malvern Hills—Hugh Stuart Boyd—Love of Learning—“Juvenilia”—Impassioned Devotion to Poetry | 16 |
| CHAPTER III | |
| 1833-1841 | |
| Browning Visits Russia—“Paracelsus”—Recognition of Wordsworth and Landor—“Strafford”—First Visit to Italy—Mrs. Carlyle’s Baffled Reading of “Sordello”—Lofty Motif of the Poem—The Universal Problem of Life—Enthusiasm for Italy—The Sibylline Leaves Yet to Unfold | 26 |
| [Pg x] | |
| CHAPTER IV | |
| 1833-1841 | |
| Elizabeth Barrett’s Love for the Greek Poets—Lyrical Work—Serious Entrance on Professional Literature—Noble Ideal of Poetry—London Life—Kenyon—First Knowledge of Robert Browning | 44 |
| CHAPTER V | |
| 1841-1846 | |
| “Bells and Pomegranates”—Arnould and Domett—“A Blot in the ’Scutcheon”—Macready—Second Visit to Italy—Miss Barrett’s Poetic Work—“Colombe’s Birthday”—“Lady Geraldine’s Courtship”—“Romances and Lyrics”—Browning’s First Letter to MissBarrett—The Poets Meet—Letters of Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett—“Loves of the Poets”—Vita Nuova | 67 |
| CHAPTER VI | |
| 1846-1850 | |
| Marriage and Italy—“In That New World”—The Haunts of Petrarca—The Magic Land—In Pisa—Vallombrosa—“Un Bel Giro”—Guercino’s Angel—Casa Guidi—Birth of Robert Barrett Browning—Bagni di Lucca—“Sonnets from the Portuguese”—The Enchantment of Italy | 92 |
| CHAPTER VII | |
| 1850-1855 | |
| “Casa Guidi Windows”—Society in Florence—Marchesa d’Ossoli—Browning’s Poetic Creed—Villeggiatura in Siena—Venice—Brilliant Life in London—Paris[Pg xi] and Milsand—Browning on Shelley—In Florence—Idyllic Days in Bagni di Lucca—Mrs. Browning’s Spiritual Outlook—Delightful Winter in Rome—A Poetic Pilgrimage—Harriet Hosmer—Characteristics of Mrs. Browning | 115 |
| CHAPTER VIII | |
| 1855-1861 | |
| London Life—An Interlude in Paris—“Aurora Leigh”—Florentine Days—“Men and Women”—The Hawthornes—“The Old Yellow Book”—A Summer in Normandy—The Eternal City—The Storys and Other Friends—Lilies of Florence—“It Is Beautiful!” | 163 |
| CHAPTER IX | |
| 1861-1869 | |
| The Completed Cycle—Letters to Friends—Browning’s Devotion to His Son—Warwick Crescent—“Dramatis Personæ”—London Life—Death of the Poet’s Father—Sarianna Browning—Oxford Honors the Poet—Death of Arabel Barrett—Audierne—“The Ring and the Book” | 199 |
| CHAPTER X | |
| 1869-1880 | |
| In Scotland with the Storys—Browning’s Conversation—An Amusing Incident—With Milsand at St. Aubin’s—“The Red Cotton Night-cap Country”—Robert Barrett Browning’s Gift for Art—Alfred Domett (“Waring”)—“Balaustion’s Adventure”—Browning and Tennyson—“Pacchiarotto”—Visits Jowett at Oxford—Declines Lord Rectorship of St. Andrews—“La Saisiaz”—Italy Revisited—The Dream of Asolo—“Ivanovitch”—Pride in His Son’s Success—“Dramatic Idylls” | 221 |
| [Pg xii] | |
| CHAPTER XI | |
| 1880-1888 | |
| “Les Charmettes”—Venetian Days—Dr. Hiram Corson—The Browning Society—Oxford Honors Browning—Katherine DeKay Bronson—Honors from Edinburgh—Visit to Professor Masson—Italian Recognition—Nancioni—The Goldoni Sonnet—At St. Moritz—In Palazzo Giustiniani—“Ferishtah’s Fancies”—Companionship with His Son—Death of Milsand—Letters to Mrs. Bronson—DeVere Gardens—Palazzo Rezzonico—Sunsets from the Lido—Robert Barrett Browning’s Gift in Portraiture | 238 |
| CHAPTER XII | |
| 1888-1889 | |
| “Asolando”—Last Days in DeVere Gardens—Letters of Browning and Tennyson—Venetian Lingerings and Friends—Mrs. Bronson’s Choice Circle—Browning’s Letters to Mrs. Bronson—Asolo—“In Ruby, Emerald, Chrysopras”—Last Meeting of Browning and Story—In Palazzo Rezzonico—Last Meeting with Dr. Corson—Honored by Westminster Abbey—A Cross of Violets—Choral Music to Mrs. Browning’s Poem, “The Sleep”—“And with God Be the Rest!” | 269 |
| Index | 297 |
| In Photogravure | |
| Robert Browning From a drawing by Field Talfourd, Rome, 1855 | Frontispiece |
| Page | |
| Elizabeth Barrett Browning From a drawing by Field Talfourd, Rome, 1855 | 39 |
| Engravings | |
| Busts of Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning | 2 |
| Monument to Michael Angelo, by Vasari Church of Santa Croce, Florence | 80 |
| Old Monastery at Vallombrosa | 98 |
| The Guardian Angel, Guercino Church of San Agostino, Fano | 103 |
| Monument to Dante, by Stefano Ricci Piazza di Santa Croce, Florence | 108 |
| Palazzo Vecchio, Florence | 113 |
| Statue of Savonarola, by E. Pazzi Sala dei Cinquecento, Palazzo Vecchio, Florence | 116 |
| Fresco of Dante, by Giotto The Bargello, Florence | 121 |
| Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore, Florence (known as the Duomo) | 126 |
| The Ponte Vecchio and the Arno, Florence | 142 |
| Casa Guidi | 146 |
| The Clasped Hands of the Brownings Cast in bronze from the model taken by Harriet Hosmer in Rome, 1853 | 153 |
| [Pg xiv]The Campagna and Ruins of the Claudian Aqueducts, Rome | 156 |
| The Coronation of the Virgin, by Filippo Lippi Accademia di Belle Arti, Florence | 166 |
| Andrea del Sarto. Portrait of the Artist and his Wife Pitti Gallery, Florence | 170 |
| Equestrian Statue of Ferdinando de’ Medici, by Giovanni da Bologna Piazza dell’ Annunziata, Florence | 174 |
| Villa Petraja, near Florence | 178 |
| Church of San Miniato, near Florence | 182 |
| The Palazzo Barberini, Via Quattro Fontane, Rome | 188 |
| The English Cemetery, Florence | 197 |
| Tomb of Elizabeth Barrett Browning | 200 |
| Kate Field From the portrait by Elihu Vedder, Florence, 1860 | 208 |
| The Pallazzo Riccardi, Florence | 214 |
| Bust of Robert Browning, by his Son | 226 |
| Portrait of Robert Browning in 1882, by his Son | 242 |
| Church of San Lorenzo, Florence | 246 |
| Portrait of Robert Barrett Browning, as a Child, 1859 | 263 |
| Portrait of Robert Browning, by George Frederick Watts, R.A. | 270 |
| Mrs. Arthur Bronson, by Ellen Montalba, in Asolo | 274 |
| Miss Edith Bronson, (Comtessa Rucellai) | 280 |
| Portrait of Professor Hiram Corson, by J. Colin Forbes, R.A. | 290 |
| Palazzo Rezzonico, Venice | 294 |
| Engraved Facsimile of a letter from Robert Browning to Professor Hiram Corson | 260 |
| “Allons! after the Great Companions! and to belong to them!” “To know the universe itself as a road—as many roads—as roads for travelling souls.” |
The Most Exquisite Romance of Modern Life—Ancestry and Youth of Robert Browning—Love of Music—Formative Influences—The Fascination of Byron—A Home “Crammed with Books”—The Spell of Shelley—“Incondita”—Poetic Vocation Definitely Chosen—“Pauline.”
Such a very page de Contes is the life of the wedded poets, Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning, that it is difficult to realize that this immortal idyl of Poetry, Genius, and Love was less than fifteen years in duration, out of his seventy-seven, and her fifty-five years of life. It is a story that has touched the entire world
“... with mystic gleams,
Like fragments of forgotten dreams,”
this story of beautiful associations and friendships, of artistic creation, and of the entrance on a wonderful realm of inspiration and loveliness. At the time of their marriage he was in his thirty-fifth, and she in her forty-first year,[Pg 2] although she is described as looking so youthful that she was like a girl, in her slender, flower-like grace; and he lived on for twenty-eight years after
“Clouds and darkness
Fell upon Camelot,”
with the death of his “Lyric Love.” The story of the most beautiful romance that the world has ever known thus falls into three distinctive periods,—that of the separate life of each up to the time of their marriage; their married life, with its scenic setting in the enchantment of Italy; and his life after her withdrawal from earthly scenes. The story is also of duplex texture; for the outer life, rich in associations, travel, impressions, is but the visible side of the life of great creative art. A delightful journey is made, but its record is not limited to the enjoyment of friends and place; a poem is written whose charm and power persist through all the years.
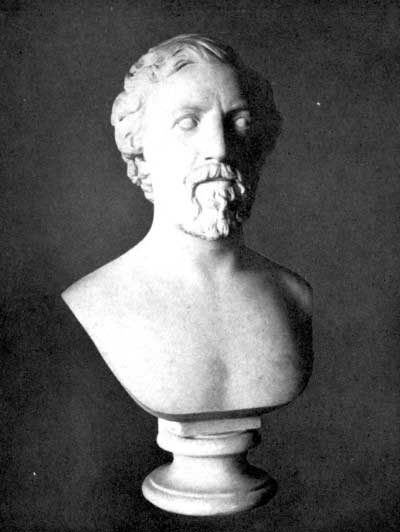 |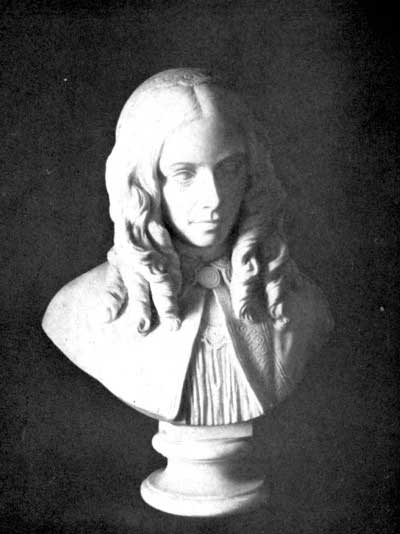  |
Busts of Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning
Made in 1861 by William Wetmore Story
No adequate word could be written of the Brownings that did not take account of this twofold life of the poets. It is almost unprecedented that the power and resplendence and beauty of the life of art should find, in the temporal environment, so eminent a correspondence of beauty as it did with Robert and Elizabeth Browning. Not that they were in any wise exempt from sorrow and pain; the poet, least of all, would choose to be translated, even if he might, to some enchanted region remote from all the mingled experiences of humanity; it is the common lot of destiny, with its prismatic blending of failure and success, of purpose and achievement, of hope and defeat, of love and sorrow, out of which the poet draws his song. He would not choose
“That jar of violet wine set in the air,
That palest rose sweet in the night of life,”
to the exclusion of the common experiences of the day.
[Pg 3]
“Who never ate his bread in sorrow,
Who never spent the darksome hours
Weeping, and watching for the morrow,
He knows you not, ye unseen Powers.”
But to those who, poets or otherwise, see life somewhat in the true proportion of its lasting relations, events are largely transmuted into experiences, and are realized in their extended relations. The destiny of the Brownings led them into constantly picturesque surroundings; and the force and manliness of his nature, the tender sweetness and playful loveliness of hers, combined with their vast intellectual range, their mutual genius for friendships, their devotion to each other and to their son, their reverence for their art, and their lofty and noble spirituality of nature,—all united to produce this exquisite and unrivaled romance of life,—
“A Beauty passing the earth’s store.”
The rapture of the poet’s dream pervaded every experience.
“O Life, O Poetry,
Which means life in life.”
The transmutation of each into the other, both Life and Poetry, as revealed in their lives, is something as exceptional as it is beautiful in the world’s history.
It is only to those who live for something higher than merely personal ends, that the highest happiness can come; and the aim of these wedded poets may well be read in the lines from “Aurora Leigh”:
“... Beloved, let us love so well,
Our work shall still be better for our love,
And still our love be sweeter for our work,
And both commended, for the sake of each,
By all true workers and true lovers born.”
[Pg 4]In the ancestry of Robert Browning there was nothing especially distinctive, although it is representative of the best order of people; of eminently reputable life, of moderate means, of culture, and of assured intelligence. It is to the Brownings of Dorsetshire, who were large manor-owners in the time of Henry VII, that the poet’s family is traced. Robert Browning, the grandfather of the poet, was a clerk in the Bank of England, a position he obtained through the influence of the Earl of Shaftesbury. Entering on this work at the age of twenty, he served honorably for fifty years, and was promoted to the position of the Bank Stock office, a highly responsible place, that brought him in constant contact with the leading financiers of the day. Born in 1749, he had married, in 1778, Margaret Tittle, the inheritor of some property in the West Indies, where she was born of English parentage. The second Robert, the father of the poet, was the son of this union. In his early youth he was sent out to take charge of his mother’s property, and his grandson, Robert Barrett Browning, relates with pardonable pride how he resigned the post, which was a lucrative one, because he could not tolerate the system of slave labor prevailing there. By this act he forfeited all the estate designed for him, and returned to England to face privation and to make his own way. He, too, became a clerk in the Bank of England, and in 1811, at the age of thirty, married Sarah Anna Wiedemann, the daughter of a ship-owner in Dundee. Mr. Wiedemann was a German of Hamburg, who had married a Scotch lady; and thus, on his maternal side, the poet had mingled Scotch and German ancestry. The new household established itself in Southampton Street, Camberwell, and there were born their two children, Robert, on May 7, 1812, and on January 7, 1814, Sarah Anna, who came to be known as Sarianna through all her later life.
The poet’s father was not only an efficient financier, but[Pg 5] he was also a man of scholarly culture and literary tastes. He was a lover of the classics, and was said to have known by heart the first book of the Iliad, and the Odes of Horace. There is a legend that he often soothed his little son to sleep by humming to him an ode of Anacreon. He wrote verse, he was a very clever draughtsman, and he was a collector of rare books and prints. Mr. W. J. Stillman, in his “Autobiography of a Journalist,” refers to the elder Browning, whom he knew in his later years, as “a serene, untroubled soul,... as gentle as a gentle woman, a man to whom, it seemed to me, no moral conflict could ever have arisen to cloud his frank acceptance of life as he found it come to him.... His unworldliness had not a flaw.” In Browning’s poem entitled “Development” (in “Asolando”) he gives this picture of his father and of his own childhood:
“My Father was a scholar and knew Greek.
When I was five years old, I asked him once
‘What do you read about?’
‘The siege of Troy.’
‘What is a siege, and what is Troy?’
Whereat
He piled up chairs and tables for a town,
Set me a-top for Priam, called our cat
—Helen, enticed away from home (he said)
By wicked Paris, who couched somewhere close
Under the footstool....
········
This taught me who was who and what was what;
So far I rightly understood the case
At five years old; a huge delight it proved
And still proves—thanks to that instructor sage
My Father....”
The poet’s mother was a true gentlewoman, characterized by fervent religious feeling, delicacy of perception, and a great love for music. She was reared in the Scottish[Pg 6] kirk, and her husband in the Church of England, but they both connected themselves after their marriage with an “Independent” body that held their meetings in York Street, where the Robert Browning Hall now stands. They were, however, greatly attached to the Rev. Henry Melvill (later Canon at St. Paul’s), whose evening service they habitually attended. While the poet’s mother had little training in music, she was a natural musician, and was blessed with that keen, tremulous susceptibility to musical influence that was so marked a trait in her son. William Sharp pictures a late afternoon, when, playing softly to herself in the twilight, she was startled to hear a sound in the room. “Glancing around, she beheld a little white figure distinctly outlined against an oak bookcase, and could just discern two large wistful eyes looking earnestly at her. The next moment the child had sprung into her arms, sobbing passionately at he knew not what, but, as his paroxysm of emotion subsided, whispering over and over,‘Play! Play!’”
The elder Browning was an impassioned lover of medieval legend and story. He was deeply familiar with Paracelsus, with Faust, and with many of the Talmudic tales. His library was large and richly stored,—the house, indeed, “crammed with books,” in which the boy browsed about at his own will. It was the best of all possible educations, this atmosphere of books. And the wealth of old engravings and prints fascinated the child. He would sit among these before a glowing fire, while from the adjoining room floated strains “of a wild Gaelic lament, with its insistent falling cadences.” It is recorded as his mother’s chief happiness,—“her hour of darkness and solitude and music.” Of such fabric are poetic impressions woven. The atmosphere was what Emerson called the “immortal ichor.” The boy was companioned by the “liberating gods.” Something mystic and beautiful beckoned to him, and [Pg 7]incantations, unheard by the outer sense, thronged about him, pervading the air. The lad began to recast in English verse the Odes of Horace. From his school, on holiday afternoons, he sought a lonely spot, elm-shaded, where he could dimly discern London in the distance, with the gleam of sunshine on the golden cross of St. Paul’s,—lying for hours on the grass whence, perchance, he
“Saw distant gates of Eden gleam
And did not dream it was a dream.”
Meantime the boy read Junius, Voltaire, Walpole’s Letters, the “Emblems” of Quarles (a book that remained as a haunting influence all his life), and Mandeville’s “Fable of the Bees.” The first book of his own purchase was a copy of Ossian’s poems, and his initial effort in literary creation was in likeness of the picturesque imaginations that appealed with peculiar fascination to his mind.
“The world of books is still the world,” wrote Mrs. Browning in “Aurora Leigh,” and this was the world of Robert Browning’s early life. The genesis of many of his greatest poems can be traced directly to this atmosphere of books, and their constant use and reference in his childhood. Literature and life, are, indeed, so absolutely interpenetrated and so interdependent that they can almost invariably be contemplated as cause and effect, each reacting upon the other in determining sequences. By the magic of some spiritual alchemy, reading is transmuted into the qualities that build up character, and these qualities, in turn, determine the continued choice of books, so that selection and result perpetuate themselves, forming an unceasing contribution to the nature of life. If with these qualities is united the kindling imagination, the gift that makes its possessor the creative artist, the environment of books and perpetual reference to them act as a torch that ignites the divine fire. Browning’s early stimulus owes much, not[Pg 8] only to the book-loving father, but to his father’s brother, his uncle Reuben Browning, who was a classical scholar and who took great interest in the boy. Preserved to the end of the poet’s life was a copy of the Odes of Horace, in translation, given to him as a lad of twelve, with his uncle’s autograph inscription on the fly-leaf. This was the translation made by Christopher Smart, whose “Song of David” soon became one of the boy’s favorites, and it is curious to trace how, more than sixty years later, Browning embodied Smart in his “Parleyings with Certain People of Importance in their Day,” as one with whom
“... truth found vent
In words for once with you....”
Browning, with the poet’s instant insight, read the essential story of his boyhood into the lines:
“... Dreaming, blindfold led
By visionary hand, did soul’s advance
Precede my body’s, gain inheritance
Of fact by fancy...?”
No transcription of the poet’s childhood could even suggest the fortunate influences surrounding him that did not emphasize the rare culture and original power of his father. The elder Browning was familiar with old French and with both Spanish and Italian literature. “His wonderful store of information might really be compared to an inexhaustible mine,” said one who knew him well.
It is easy to see how out of such an atmosphere the future poet drew unconsciously the power to weave his “magic web” of such poems as the “Parleyings,” “Abt Vogler,” “Ferishtah’s Fancies,” and was lured on into that realm of marvelous creation out of which sprang his transcendent masterpiece, “The Ring and the Book.”
The elder Browning’s impassioned love of books was [Pg 9]instanced by the curious fact that he could go in the dark to his library, and out of many hundreds of volumes select some particular one to which conversational reference had incidentally been made regarding some point which he wished to verify. He haunted all the old book-stalls in London, and knew their contents better than did their owners.
Books are so intimately associated with the very springs of both character and achievement that no adequate idea of the formative influences of the life and poetry of Robert Browning could be gained without familiarity with this most determining and conspicuous influence of his boyhood. The book with which a man has lived becomes an essential factor in his growth. “None of us yet know,” said Ruskin, “for none of us have yet been taught in early youth, what fairy palaces we may build of beautiful thought, proof against all adversity, bright fancies, satisfied memories, noble histories, faithful sayings, treasure-houses of precious and restful thoughts,... houses built without hands for our souls to live in.” These houses for the soul, built in thought, will be transposed into outer form and semblance.
There is a nebulous but none the less pernicious tradition that great literature is formidable, and presents itself as a task rather than as a privilege to the reader. Devotion to the best books has been regarded as something of a test of mental endurance, for which the recompense, if not the antidote, must be sought in periods of indulgence in the frivolous and the sensational. Never was there a more fatal misconception. It is the inconsequential, the crude, the obtuse, that are dull in literature, as in life; and stupidity in various languages might well be entitled to rank among the Seven Deadly Sins of Dante. Even in the greatest literature there is much that the child may easily learn to appreciate and to love.
[Pg 10]
“Great the Master
And sweet the Magic”
that opens the golden door of literary stimulus. Books are to the mind as is food to the body. Emerson declares that the poet is the only teller of news, and Mrs. Browning pronounced poets as
“The only truth-tellers now left to God.”
Familiarity with noble thought and beautiful expression influences the subconscious nature to an incalculable degree, and leads “the spirit finely touched” on “to all fine issues.”
Browning lived in this stimulating atmosphere. He warmed his hands at the divine fire; and the fact that all this richness of resource stimulated rather than stifled him is greatly to the credit of his real power. Favorable surroundings and circumstances did not serve him as a cushion on which to go to sleep, but rather as the pedestal on which he might climb to loftier altitudes. It was no lotus-eating experience into which the lad was lulled, but the vital activity of the life of creative thought. The Heavenly Powers are not invariably, even if frequently, sought in sorrow only, and in the mournful midnight hours. There are natures that grow by affluence as well as by privation, and that develop their best powers in sunshine.
“Even in a palace life can be well lived,” said Marcus Aurelius. The spirit formed to dwell in the starry spaces is not allured to the mere enjoyment of the senses, even when material comfort and intellectual luxuries may abound. Not that the modest abundance of the elder Browning’s books and pictures could take rank as intellectual luxury. It was stimulus, not satiety, that these suggested.
[Pg 11]Pictures and painters had their part, too, in the unconscious culture that surrounded the future poet. London in that day afforded little of what would be called art; the National Gallery was not opened until Browning was in his young manhood; the Tate and other modern galleries were then undreamed of. But, to the appropriating temperament, one picture may do more than a city full of galleries might for another, and to the small collection of some three or four hundred paintings in the Dulwich Gallery, Browning was indebted for great enjoyment, and for the art that fostered his sympathetic appreciation. In after years he referred to his gratitude for being allowed its privileges when under the age (fourteen) at which these were supposed to be granted. Small as was the collection, it was representative of the Italian and Spanish, the French and the Dutch schools, as well as of the English, and the boy would fix on some one picture and sit before it for an hour, lost in its suggestion. It was the more imaginative art that enchained him. In later years, speaking of these experiences in a letter to Miss Barrett, he wrote of his ecstatic contemplation of “those two Guidos, the wonderful Rembrandt’s ‘Jacob’s Vision,’ such a Watteau....” An old engraving from Correggio, in his father’s home, was one of the sources of inspiration of Browning’s boyhood. The story fascinated him; he never tired of asking his father to repeat it, and something of its truth so penetrated into his consciousness that in later years he had the old print hung in his room that it might be before him as he wrote. It became to him, perhaps, one of
“the unshaped images that lie
Within my mind’s cave.”
The profound significance of the picture evidently haunted him, as is made evident by a passage in “Pauline” that opens:
[Pg 12]
“But I must never grieve whom wing can waft
Far from such thoughts—as now. Andromeda!
And she is with me; years roll, I shall change,
But change can touch her not—so beautiful
With her fixed eyes....”
Is there gained another glimpse of Browning’s boyhood in those lines in “Pauline”?:
“I am made up of an intensest life,
Of a most clear idea of consciousness
Of self, distinct from all its qualities,
From all affections, passions, feelings, powers.”
The various and complex impressions, influences, and shaping factors of destiny that any biographer discerns in the formative years of his subject are as indecipherable as a palimpsest, and as little to be classified as the contents of Pandora’s box; nor is it on record that the man himself can look into his own history and rightly appraise the relative values of these. Nothing, certainly, could be more remote from the truth than the reading of autobiographic significance into any stray line a poet may write; for imagination is frequently more real than reality. Yet many of the creations of after life may trace their germination to some incident or impression. William Sharp offers a beautiful and interesting instance of one of these when he ascribes the entrancing fantasy of “The Flight of the Duchess” to a suggestion made on the poet’s mind as a child on a Guy Fawkes day, when he followed across the fields a woman singing a strange song, whose refrain was: “Following the Queen of the Gypsies, O!” The haunting line took root in his memory and found its inflorescence in that memorable poem.
It was not conducive to poetic fancy when the lad was placed in the school of a Mr. Ready, at Peckham, where he solaced himself for the rules and regulations which he [Pg 13]abhorred by writing little plays, and persuading his school-fellows to act in them with him.
Browning’s first excursion into Shelley’s poems, brought home to him one night as a gift from his mother, was in one of the enchanting evenings of May; where, at the open window by which he sat, there floated in the melody of two nightingales, one in a laburnum, “heavy with its weight of gold,” and the other in a copper-beech, at the opposite side of the garden. Such an hour mirrors itself unconsciously in a poet’s memory, and affords, in future years, “such stuff as dreams are made of.”
Byron, who, as Mazzini says, “led the genius of Britain on a pilgrimage throughout all Europe,” stamped an impress upon the youthful Browning that may be traced throughout his entire life. There was something in the genius of Byron that acted as an enormous force on the nature in response to it, that transformed nebulous and floating ideals and imaginings into hope and resolution, that burned away barriers and revealed truth. By its very nature influence is determined as much by the receiver as by the inspirer, and if a light is applied to a torch, the torch, too, must be prepared to ignite, or there will be no blaze.
“A deft musician does the breeze become
Whenever an Æolian harp it finds;
Hornpipe and hurdygurdy both are dumb
Unto the most musicianly of winds.”
The fire of Byron, the spirituality of Shelley, illuminated that world of drift and dream in which Robert Browning dwelt; and while Shelley, with his finer spirit, his glorious, impassioned imagination,
“A creature of impetuous breath,”
incited poetic ardors and unmeasured rapture of vision, Byron penetrated his soul with a certain effective energy that awakened in him creative power. The spell of[Pg 14] Shelley’s poetry acted upon Browning as a vision revealed of beauty and radiance. For Shelley himself, who, as Tennyson said, “did yet give the world another heart and new pulses,” Browning’s feeling was even more intense.
In the analysis of Shelley’s poetic nature Browning offers the critical reader a key to his own. He asserts that it is the presence of the highest faculty, even though less developed, that gives rank to nature, rather than a lower faculty more developed. Although it was in later years that the impression Shelley made upon his boyhood found adequate expression in his noted essay, the spell reflected itself in “Pauline,” and is to be distinctly traced in many of his poems throughout his entire life. He was aware from the first of that peculiarly kindling quality in Shelley, the flash of life in his work:
“He spurreth men, he quickeneth
To splendid strife.”
Under the title of “Incondita” was collected a group of the juvenile verses of Robert Browning, whose special claim to interest is in the revelation of the impress made upon the youth by Byron and Shelley.
Among the early friends of the youthful poet were Alfred Domett (the “Waring” of his future poem), and Joseph Arnould, who became a celebrated judge in India.
With Browning there was never any question about his definite vocation as a poet. “Pauline” was published in 1833, before he had reached his twenty-first birthday. Rejected by publishers, it was brought out at the expense of his aunt, Mrs. Silverthorne; and his father paid for the publication of “Paracelsus,” “Sordello,” and for the first eight parts of “Bells and Pomegranates.” On the appearance of “Pauline,” it was reviewed by Rev. William Johnson Fox, as the “work of a poet and a genius.” Allan Cunningham and other reviewers gave encouraging expressions.[Pg 15] The design of “Pauline” is that spiritual drama to which Browning was always temperamentally drawn. It is supposed to be the confessions and reminiscences of a dying man, and while it is easy to discern its crudeness and inconsistencies, there are in it, too, many detached passages of absolute and permanent value. As this:
“Sun-treader, life and light be thine for ever!
Thou art gone from us; years go by and spring
Gladdens, and the young earth is beautiful,
Yet thy songs come not....”
Mr. Browning certainly gave hostages to poetic art when he produced “Pauline,” in which may be traced the same conceptions of life as those more fully and clearly presented in “Paracelsus” and “Sordello.” It embodies the conviction which is the very essence and vital center of all Browning’s work—that ultimate success is attained through partial failures. From first to last Browning regards life as an adventure of the soul, which sinks, falls, rises, recovers itself, relapses into faithlessness to its higher powers, yet sees the wrong and aims to retrieve it; gropes through darkness to light; and though “tried, troubled, tempted,” never yields to alien forces and ignominious failure. The soul, being divine, must achieve divinity at last. That is the crystallization of the message of Browning.
The poem “Pauline,” lightly as Mr. Browning himself seemed in after life to regard it, becomes of tremendous importance in the right approach to the comprehension of his future work. It reveals to us in what manner the youthful poet discerned “the Gleam.” Like Tennyson, he felt “the magic of Merlin,”—of that spirit of the poetic ideal that bade him follow.
“The Master whisper’d
‘Follow The Gleam.’”
And what unguessed sweetness and beauty of life and love awaited the poet in the unfolding years!
| “Here’s the garden she walked across. ······ Roses ranged in a valiant row, I will never think she passed you by!” |
Childhood and Early Youth of Elizabeth Barrett—Hope End—“Summer Snow of Apple-blossoms”—Her Bower of White Roses—“Living with Visions”—The Malvern Hills—Hugh Stuart Boyd—Love of Learning—“Juvenilia”—Impassioned Devotion To Poetry.
The literature of childhood presents nothing more beautiful than the records of the early years of Elizabeth Barrett. Fragmentary though they be, yet, gathered here and there, they fall into a certain consecutive unity, from which one may construct a mosaic-like picture of the daily life of the little girl who was born on March 6, 1806, in Coxhoe Hall, Durham, whence the family soon removed to Hope End, a home of stately beauty and modest luxury. There were brothers to the number of eight; and two sisters, Henrietta and Arabel, all younger than herself. Edward, the eldest son, especially cared for Elizabeth, holding her in tender and almost reverential love, and divining, almost from his infancy, her exquisite gifts. Apparently, the eldest sister was also greatly beloved by the whole troop of the younger brothers,—Charles, Samuel, George, Henry, Alfred, and the two younger, who were named Septimus and Octavius.
With three daughters and eight sons, the household did not lack in merriment and overflowing life; and while the[Pg 17] little Elizabeth was born to love books and dreams, and assimilated learning as naturally as she played with her dolls, she was no prodigy, set apart because of fantastic qualities, but an eager, earnest little maid, who, although she read Homer at eight years of age, yet read him with her doll clasped closely in one hand, and who wrote her childish rhymes as unconsciously as a bird sings. It is a curious coincidence that this love of the Greeks, as to history, literature, and mythology, characterized the earliest childhood of both Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett. Pope’s Homer was the childish favorite of each. “The Greeks were my demigods,” she herself said, in later life, of her early years, “and haunted me out of Pope’s Homer, until I dreamt more of Agamemnon than of Moses the black pony.”
The house at Hope End has been described by Lady Carmichael as “a luxurious home standing in a lovely park, among trees and sloping hills,” and the earliest account that has been preserved of the little girl reveals her sitting on a hassock, propped against the wall, in a lofty room called “Elizabeth’s chamber,” with a stained glass oriel window through which golden gleams of light fell, lingering on the long curls that drooped over her face as she sat absorbed in a book. She was also an eager worker in her garden, the children all being given a plot to cultivate for themselves, and Elizabeth won special fame for her bower of white roses.
There are few data about the parents of Elizabeth Barrett, and the legal name, Moulton-Barrett, by which she signed her marriage register and by which her father is commonly known, has been a source of some confused statements. Her father, Edward Barrett Moulton, came into an inheritance of property by which he was required to add the name of Barrett again, hyphenating it, and was thus known as Edward Barrett Moulton-Barrett. He[Pg 18] married Mary Graham Clarke, a native of Newcastle-on-the-Tyne, a woman of gentle loveliness, who died on October 1, 1828. Mr. Moulton-Barrett lived until 1860, his death occurring only a year before that of his famous daughter, who was christened Elizabeth Barrett Moulton, and who thus became, after her father’s added name, Elizabeth Barrett Moulton-Barrett, although, except when a legal signature was necessary, she signed her name as Elizabeth Barrett. The family are still known by the hyphenated name; and Mrs. Browning’s namesake niece, a very scholarly and charming young woman, now living in Rome, is known as Elizabeth Moulton-Barrett. She is the daughter of Mrs. Browning’s youngest brother, Alfred, and her mother, who is still living, is the original of Mrs. Browning’s poem, “A Portrait.” While Miss Moulton-Barrett never saw her aunt (having been born after her death), she is said to resemble Mrs. Browning both in temperament and character. By a curious coincidence the Barrett family, like the Brownings, had been for generations the owners of estates in the West Indies, and it is said that Elizabeth Barrett was the first child of their family to be born in England for more than a hundred years.
Her father, though born in Jamaica, was brought to England as a young child, and he was the ward of Chief Baron Lord Abinger. He was sent to Harrow, and afterwards to Cambridge, but he did not wait to finish his university course, and married when young. One of his sisters was painted by Sir Thomas Lawrence, and this portrait is now in the possession of Octavius Moulton-Barrett, Esq., of the Isle of Wight.
Elizabeth’s brother Edward was but two years her junior. It was he who was drowned at Torquay, almost before her eyes, and who is commemorated in her “De Profundis.” Of the other brothers only three lived to manhood. When Elizabeth was three years of age, the family[Pg 19] removed to Hope End in Herefordshire, a spacious and stately house with domes and minarets embowered in a grove of ancient oaks. It was a place calculated to appeal to the imagination of a child, and in later years she wrote of it:
“Green the land is where my daily
Steps in jocund childhood played,
Dimpled close with hill and valley,
Dappled very close with shade,—
Summer-snow of apple-blossoms,
Running up from glade to glade.”
Here all her girlhood was passed, and it was in the garden of Hope End that she stood, holding up an apron filled with flowers, when that lovely picture was painted representing her as a little girl of nine or ten years of age. Much of rather apochryphal myth and error has grown up about Mrs. Browning’s early life. However gifted, she was in no wise abnormal, and she galloped on Moses, her black pony, through the Herefordshire lanes, and offered pagan sacrifices to some imaginary Athene, “with a bundle of sticks from the kitchen fire and a match begged from an indulgent housemaid.” In a letter to Richard Hengist Home, under date of October 5, 1843, in reply to a request of his for data for a biographical sketch of her for “The New Spirit of the Age,” she wrote:
“... And then as to stories, mine amounts to the knife-grinder’s, with nothing at all for a catastrophe. A bird in a cage would have as good a story. Most of my events, and nearly all my intense pleasures, have passed in my thoughts. I wrote verses—as I dare say many have done who never wrote any poems—very early, at eight years of age, and earlier. But, what is less common, the early fancy turned into a will, and remained with me, and from that day to this, poetry has been a distinct object with me,—an object to read, think, and live for.”
[Pg 20]When she was eleven or twelve, she amused herself by writing a great epic in four books, called “The Battle of Marathon,” which possessed her fancy. Her father took great pride in this, and, “bent upon spoiling me,” she laughingly said in later years, had fifty copies of this childish achievement printed, and there is one in the British Museum library to-day. No creator of prose romance could invent more curious coincidences than those of the similar trend of fancy that is seen between the childhood of Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett. Her “Battle of Marathon” revealed how the Greek stories enchanted her fancy, and how sensitive was her ear in the imitation of the rhythm caught from Pope. This led her to the delighted study of Greek, that she might read its records at first hand; and Greek drew her into Latin, and from this atmosphere of classic lore, which, after all, is just as interesting to the average child as is the (too usual) juvenile pabulum, she drew her interest in thought and dream. The idyllic solitude in which she lived fostered all these mental excursions. “I had my fits of Pope and Byron and Coleridge,” she has related, “and read Greek as hard under the trees as some of your Oxonians in the Bodleian; gathered visions from Plato and the dramatists, and ate and drank Greek.... Do you know the Malvern Hills? The Hills of Piers Plowman’s Visions? They seem to me my native hills. Beautiful, beautiful they were, and I lived among them till I had passed twenty by several years.”
Mr. Moulton-Barrett was one of the earliest of social reformers. So much has been said, and, alas! with too much justice, it must be conceded, of his eccentric tyranny, his monomania,—for it amounted to that, in relation to the marriage of any of his children regarding which his refusal was insanely irrational,—that it is pleasant to study him for a moment in his more normal life. In Ledbury, the nearest village, he would hold meetings for the untaught people,[Pg 21] read and pray with them, and this at a period when for a man of wealth to concern himself in social betterment was almost unknown. He was truly “the friend of the unfriended poor,” and by his side, with wondering, upturned, childish eyes, was the little Elizabeth, an ardent and sympathetic companion. Until quite recently there were still living those who remembered Mr. Barrett as this intelligent and active helper; and in the parish church is a monument to him, by the side of a gloriously decorated tomb of the fourteenth century, with an inscription to his memory that vividly recalls the work of one who strove to revive the simple faith in God that has always, in all nations and in all centuries, met every real need of life.
Mrs. Barrett, a sweet and gentle woman, without special force of character, died when Elizabeth was but twenty years of age; and it was some five years before her mother’s death that Elizabeth met with the accident, from the fall from her saddle when trying to mount her pony, that caused her life-long delicacy of health. Her natural buoyancy of spirits, however, never failed, and she was endowed with a certain resistless energy which is quite at variance with the legendary traditions that she was a nervous invalid.
Hardly less than Browning in his earliest youth, was Elizabeth Barrett “full of an intensest life.” Her Italian master one day told her that there was an unpronounceable English word that expressed her exactly, but which, as he could not give in English, he would express in his own tongue,—testa lunga. Relating this to Mr. Browning in one of her letters, she says: “Of course the signor meant headlong!—and now I have had enough to tame me, and might be expected to stand still in my stall. But you see I do not. Headlong I was at first, and headlong I continue,—precipitately rushing forward through all manner of nettles and briers instead of keeping the path; guessing at[Pg 22] the meaning of unknown words instead of looking into the dictionary,—tearing open letters, and never untying a string,—and expecting everything to be done in a minute, and the thunder to be as quick as the lightning.”
Impetuous, vivacious, with an inimitable sense of humor, full of impassioned vitality,—this was the real Elizabeth Barrett, whose characteristics were in no wise changed during her entire life. Always was she
“A creature of impetuous breath,”
full of vivacious surprises, and witty repartee.
Hope End was in the near vicinity of Eastnor Castle, a country seat of the Somersets; it is to-day one of the present homes of Lady Henry Somerset, and there are family records of long, sunny days that the young girl-poet passed at the castle, walking on the terraces that lead down to the still water, or lying idly in the boat as the ripples of the little lake lapped against the reeds and rushes that grew on the banks. In the castle library is preserved to-day an autograph copy of the first volume of Elizabeth Barrett’s poems, published when she was twenty, and containing that didactic “Essay on Mind” written when she was but seventeen, and of which she afterward said that it had “a pertness and a pedantry which did not even then belong to the character of the author,” and which she regretted, she went on to say, “even more than the literary defectiveness.” This volume was presented by her to a member of the Somerset family whose name is inscribed over that of her own signature.
During these years Hugh Stuart Boyd, the blind scholar, was living in Great Malvern, and one of Miss Barrett’s greatest pleasures was to visit and read Greek with him. He was never her “tutor,” in the literal sense, as has so widely been asserted, for her study of Greek was made with her brother Edward, under his tutor, a Mr. [Pg 23]MacSweeney; but she read and talked of Greek literature (especially of the Christian poets) with him, and she loved to record her indebtedness to him “for many happy hours.” She wrote of him as one “enthusiastic for the good and the beautiful, and one of the most simple and upright of human beings.” The memory of her discussions with him is embalmed in her poem, “Wine of Cyprus,” which was addressed to him:
“And I think of those long mornings
Which my thought goes far to seek,
When, betwixt the folio’s turnings,
Solemn flowed the rhythmic Greek.”
Elizabeth Barrett was more than a student, however scholarly, of Greek. She had a temperamental affinity for the Greek poets, and such translations as hers of “Prometheus Bound” and Bion’s “Lament for Adonis,” identify her with the very life itself of Æschylus and Bion. In her essay on “The Greek Christian Poets” we find her saying: “We want the touch of Christ’s hand upon our literature, as it touched other dead things ... Something of a yearning after this may be seen among the Greek Christian poets,... religious poets of whom the universal church and the world’s literature would gladly embrace more names than can be counted to either.”
All her work of these early years is in that same delicate microscopic handwriting of her later life. She laughingly professed a theory that “an immense amount of physical energy must go to the making of those immense, sweeping hand-writings achieved by some persons.” She instanced that of Landor, “who writes as if he had the sky for a copy-book and dotted his i’s in proportion.”
Poetry as a serious art was the most earnest object in the life of Elizabeth Barrett. To her poetry meant “life in life.”
“Art’s a service,—mark.”
[Pg 24]The poetic vocation could hardly be said to be so much a conscious and definite choice with her as a predetermined destiny, and still it was both. The possibility of not being a poet could never have occurred to her. There could have been as little question of Beethoven’s being other than a musician or of Raphael as being other than a painter. In poetry Elizabeth Barrett recognized the most potent form of service; and she held that poetic art existed for the sake of human co-operation with the Divine purposes.
The opening chapters of her life in the lovely seclusion of Hope End closed in 1832 with the removal of the family to Sidmouth in Devonshire. Here they were bestowed in a house which had been occupied by the Grand Duchess Helena. It commanded a splendid sea view, on which four drawing-room windows looked out, and there were green hills and trees behind. They met a few friends,—Sir John Kean, the Herrings,—and the town abounded in green lanes, “some of them quite black with foliage, where it is twilight in the middle of the day, and others letting in beautiful glimpses of the hills and the sunny sea.” Henrietta Barrett took long walks, Elizabeth accompanying her sister, mounted on her donkey. The brothers and sisters were all fond of boating and passed much time on the water. They would row as far as Dawlish, ten miles distant, and back; and after the five o’clock dinner there were not infrequently moonlight excursions on the sea. During these first months at Sidmouth Miss Barrett read Bulwer’s novels, which she asserts “quite delighted” her; as she found in them “all the dramatic talent which Scott has, and all the passion which he has not.” Bulwer seemed to her, also, “a far more profound discriminator of character” than Scott. She read Mrs. Trollope, “that maker of books,” whose work she characterized as not novels but “libels.” She found in Mrs. Trollope “neither the delicacy nor the candor which constitute true nobility of mind,” and thought that her[Pg 25] talent formed but “a scanty veil to shadow her other defects.”
Miss Barrett grew to love Sidmouth, with its walks on the seashore; and letters, reading, poetic production, and family interests filled the time. Here, too, she found time to enter on a task dear to her, the translation of the “Prometheus Bound” of Æschylus.
Some years later, however, she entirely revised this early translation, of which she wrote to Hugh Stuart Boyd that it was “as cold as Caucasus, and flat as the neighboring plain,” and that “a palinodia, a recantation,” was necessary to her. In her preface to the later translation she begged that her reader would forgive her English for not being Greek, and herself for not being Æschylus.
| “... I press God’s lamp Close to my breast; its splendor, soon or late, Will pierce the gloom; I shall emerge one day.” |
Browning Visits Russia—“Paracelsus”—Recognition of Wordsworth and Landor—“Strafford”—First Visit to Italy—Mrs. Carlyle’s Baffled Reading of “Sordello”—Lofty Motif of the Poem—The Universal Problem of Life—Enthusiasm for Italy—The Sibylline Leaves Yet To Unfold.
From Camberwell to St. Petersburg was somewhat of a transition. This was Mr. Browning’s initial excursion into a wider world of realities, as distinguished from that mirage which rises in the world of dreams and mental nebulæ. “To know the universe itself as a road,—as many roads,” is the way in which the beckoning future prefigures itself to the artist temperament.
“All around him Patmos lies
Who hath spirit-gifted eyes.”
The eyes thus touched with the chrism of poetic art see the invisible which is peopled with forms unseen to others, and which offers a panorama of living drama. It is the poet who overhears the “talk of the gods,” and when he shall report
“Some random word they say,”
he becomes
“... the fated man of men
Whom the ages must obey.”
[Pg 27]This was the undreamed destiny hovering over the young poet, luring him on like a guiding cloud which became a pillar of fire by night.
Among his London friends was the Chevalier George de Benkhausen, the Russian Consul-General, who, being suddenly summoned to Russia on some secret mission of state, invited Browning to accompany him. Browning went “nominally in the character of secretary,” Mrs. Orr says, and they fared forth on March 1, by steamer to Rotterdam, and then journeyed more than fifteen hundred miles by diligence, drawn by relays of galloping horses. The expedition was to Browning a rich mine of poetic material. The experience sank into the subconsciousness as seed to await fruition. In his “Ivan Ivanovitch,” where is seen
“This highway broad and straight e’en from the Neva’s mouth
To Moscow’s gates of gold,”
and in which the unending pine forests rising from the snow-covered ground are so vividly pictured; and in “Colombe’s Birthday,” where is seen the region of the heroine,—
“Castle Ravestein—
That sleeps out trustfully its extreme age
On the Meuse’ quiet bank, where she lived queen
Over the water-buds,...”
and the place
“... when he hid his child
Among the river-flowers at Ravestein,”
it can be seen how all this country impressed his imagination. Professor Hall Griffin finds in the fifth book of “Sordello” an unmistakable description of the most famous and oldest portrait of Charlemagne, which hangs in the Council Hall of the Rath-haus, in Aix, which Mr. Browning saw on this trip. During these three months he saw something of[Pg 28] Russian society, and on the breaking up of the ice in the Neva in spring, witnessed the annual ceremony of the Czar’s drinking the first glass of water from it. Much of the gorgeous, barbaric splendor of Russian fairs and booths, “with droshkies and fish-pies” on the one hand, and stately palaces on the other, haunted him, and reflected themselves in several of his poems. Especially did the Russian music and strains of folk-song linger in his memory for all the after years.
On his return from Russia Browning had some fancy for entering on a diplomatic career, and was momentarily disappointed at not receiving an appointment to Persia, which he had in mind; fortunately for him and for the world he was held to the orbit of his poetic gift. Diplomacy has an abundance of recruits without devastating poetic genius to furnish them. The winter of 1834 found him deeply absorbed in “Paracelsus.” This poem is dedicated to the Marquis Amédée de Ripert-Monclar, who was a great friend of Browning at this time. The Marquis was four years his senior; he was in England as a private agent for the Duchesse de Berri and the Royalist party in France to the English government. The subject of the poem is said to have been suggested by the Marquis, although the fact that all this medieval lore had been familiar to Browning from his earliest childhood must be accounted the pre-determining factor in its creation. William Sharp quotes Browning as having once said of his father: “The old gentleman’s brain was a storehouse of literary and philosophical antiquities. He was completely versed in medieval legend, and seemed to have known Paracelsus, Faustus, and even Talmudic personages, personally,” and his son assimilated unconsciously this entire atmosphere.
Both “Paracelsus” and “Sordello” seem to spring, as by natural poetic evolution, from “Pauline”; all three of these poems are, in varying degree, a drama of the soul’s[Pg 29] progress. They all suggest, and “Paracelsus,” especially, in a great degree embodies, the Hegelian philosophy; yet Mr. Barrett Browning expresses his rather positive conviction that his father never read Hegel at any period of his life. Dr. Corson regarded these early poems of Browning as of peculiar value in showing his attitude toward things. “We see in what direction the poet has set his face,” said Dr. Corson, “what his philosophy of life is, what soul-life means with him, what regeneration means, what edification means in its deepest sense of building up within us the spiritual temple.” Dr. Corson further illuminated this attitude of the poet by pointing out that he emphasized the approach to perfection as something that cannot be brought out through what is born and resides in the brain; but it must be by “the attracting power of magnetic personalities, the ultimate, absolute personality being the God-man, Christ. The human soul is regarded in Browning’s poetry,” continued Dr. Corson, “as a complexly organized, individualized, divine force, destined to gravitate toward the Infinite. How is this force with its numberless checks and counter-checks, its centripetal and centrifugal tendencies, best determined in its necessarily oblique way? How much earthly ballast must it carry to keep it sufficiently steady, and how little, that it may not be weighed down with materialistic heaviness?” Incredibly enough, in the revelations of the retrospective view, “Paracelsus” made little impression on the literary critics of the day; the Athenæum devoting to it less space even than to “the anonymous Pauline,” while the “Philip van Artevelde” of Henry Taylor (now hardly remembered) received fifteen columns of tribute, in which the critic confided to the public his enthusiastic estimate of that production. Neither Blackwood’s, the Quarterly, nor the Edinburgh even mentioned “Paracelsus”; the Athenæum admitted that it had talent, but admonished the poet that “Writers would[Pg 30] do well to remember that though it is not difficult to imitate the mysticism and vagueness of Shelley, we love him—not because of these characteristics, but in spite of them.” The one gleam of consolation to the young poet in all this general neglect or unfavorable comment was that of a three-column article from the pen of John Forster in the Examiner, then conducted by Leigh Hunt, and on whose staff were Sergeant Talfourd and Proctor (Barry Cornwall) beside Forster, who was then a rising young journalist of twenty-three, only one month the senior of Browning. But Forster spoke with no uncertain note; rather, with authority, and in this critique he said:
“Since the publication of ‘Philip van Artevelde’ we have met with no such evidences of poetical genius ... and we may safely predict for its author a brilliant career, if he continues true to the present promise of his genius.”
The immediate effect of the publication of “Paracelsus” was of a social rather than of a literary character, for something in it seemed magnetic to the life of the day, and the young poet found himself welcomed by a brilliant literary circle. He met Wordsworth and Walter Savage Landor, Dickens, Monckton Milnes (later Lord Houghton), Proctor (Barry Cornwall), Horne, Sergeant Talfourd, Leigh Hunt, and others. Hunt was then domiciled in Cheyne Row, in close proximity to the Carlyles, with whom Browning had already formed a friendship.
Rev. William Johnson Fox, one of Browning’s earliest friends, was at this time living at Craven Hill, Bayswater, and on an evening when Macready had dined with him, Browning came in. This evening (November 27, 1835) is noted in Macready’s diary, and after speaking of Mr. Fox as an “original and profound thinker,” he adds:
“Mr. Robert Browning, the author of ‘Paracelsus,’ came in after dinner; I was very much pleased to meet him. His face[Pg 31] is full of intelligence.... I took Mr. Browning on, and requested to be allowed to improve my acquaintance with him. He expressed himself warmly, as gratified by the proposal, wished to send me his book. We exchanged cards, and parted.”
Later (under date of December 7), Mr. Macready records:
“Read ‘Paracelsus,’ a work of great daring, starred with poetry of thought, feeling, diction, but occasionally obscure. The writer can scarcely fail to be a leading spirit of the time.”
On New Year’s Eve Mr. Macready invited a little house party, among whom were Forster and Browning. “Mr. Browning was very popular with the whole party,” writes Mr. Macready in his journal; “his simple and enthusiastic manner engaged attention and won golden opinions from all present; he looks and speaks more like a youthful poet than any man I ever saw.”
Browning’s personal appearance, “slim, and dark, and very handsome,” as Mary Cowden Clarke said, is pictured by many of his friends of that time. “As a young man,” writes William Sharp, “he seems to have had a certain ivory delicacy of coloring ... and he appeared taller than he really was, partly because of his rare grace of movement, and partly from a characteristic high poise of the head when listening intently to music or conversation.... His hair was so beautiful in its heavy sculpturesque waves as to attract frequent notice. Another, and more subtle personal charm, was his voice, then with a rare, flute-like tone, clear, sweet, and resonant.”
Macready was not only a notable figure on the stage at this period, but he was also (what every great actor must be) a man of thought, intense sensibility, and wide culture. Soon after Macready had appeared in Talfourd’s “Ion”[Pg 32] (the première being on the playwright’s birthday), Talfourd gave a supper at his house, at which Browning for the first time met Wordsworth and Landor. Macready himself sat between these two illustrious poets, with Browning opposite to him. The guests included Ellen Tree, Miss Mitford, and Forster. Macready, recording this night in his diary, writes of “Wordsworth who pinned me.” Landor, it seems, talked of constructing drama, and said he “had not the faculty,” that he “could only set persons to talking; all the rest was chance.” But an ever remembered moment came for the young poet when the host proposed a toast to the author of “Paracelsus,” and Wordsworth, rising, said: “I am proud to drink to your health, Mr. Browning,” and Landor bowed with his inimitable, courteous grace, raising his glass to his lips. For some years, whenever Wordsworth visited London, Forster invited Browning to meet him. The younger poet was never an enthusiast in his mild friendship for the elder, although in after years (1875) he replied to a question by Rev. A. B. Grosart, the editor of Wordsworth’s works, that while in hasty youth he did “presume to use the great and venerated personality of Wordsworth as a sort of painter’s model,” he intended in “The Lost Leader” no portrait of the entire man. While Wordsworth’s political attitude did not please the young disciple of Shelley, for Landor he conceived the most profound admiration and sympathetic affection. It was a striking sequel to this youthful attraction that in Landor’s desolate old age it should be Browning who tenderly cared for him, and surrounded his last days with unfailing comfort and solicitude.
At this memorable supper, just as Browning was about to take his leave, Macready laid his hand on the young man’s shoulder, saying earnestly: “Write a play for me, and keep me from going to America.” The thought appealed to the poet, who replied: “Shall it be historical and[Pg 33] English? What do you say to ‘Strafford’ for a subject?” Forster was then bringing out his biography of Strafford, on which Browning had assisted, so that the theme had already engaged his imagination. A few days after the supper Macready records in his diary receiving a note from Browning and adds: “What can I say upon it? It was a tribute which remunerated me for the annoyances and cares of years; it was one of the very highest, may I not say the highest, honor I have through life received.”
A certain temperamental sympathy between the two men is evident, though Macready sounded no such fathomless depths as lay, however unsuspected, in Browning; but Macready gives many indications of poetic sympathies, as, for instance, when he records in his diary how he had been looking through Coleridge’s translation of Wallenstein, “abounding with noble passages and beautiful scenes,” to see if it would lend itself to stage representation.
On November 19 of this autumn Macready notes in his journal that Browning came that night to bring his tragedy of “Strafford,” of which the fourth act was incomplete. “I requested him to write in the plot of what was deficient,” says Macready, and drove to the Garrick Club while Browning wrote out this story. Later, there was a morning call from Browning, who gave him an interesting old print of Richard, from some tapestry, and they talked of “La Vallière.” All the time we get glimpses of an interesting circle: Bulwer and Forster call, and they discuss Cromwell; Bulwer’s play of “Virginius” is in rehearsal; Macready acts Cardinal Wolsey; there is a dinner at Lady Blessington’s, where are met Lord Canterbury, Count D’Orsay, Bulwer, Trelawney, and Proctor; there is a call on Miss Martineau, and meetings with Thackeray and Dickens; Kenyon appears in the intersecting circles; Marston (the father of the blind poet) writes his play, “The Patrician’s Daughter”; Mr. Longfellow, “a Professor[Pg 34] at one of the U. S. Universities,” appears on the scene, and there is a dinner at which “Mr. and Mrs. N. P. Willis sat next to Longfellow.” On a night when Browning came with some alterations for “Strafford,” a stranger called, “saying he was a Greek, a great lover of the drama; I introduced Browning to him as a great tragic poet,” records Macready, “and the youth wrote down his name, telling us he was setting off for Athens directly.”
The rehearsals of “Strafford” came on, but Macready seems already to have had misgivings. “In Shakespeare,” he writes, “the great poet has only introduced such events as act on the individuals concerned; but in Browning’s play we have a long scene of passion—upon what? A plan destroyed, a parliament dissolved....” It is easy to see how Browningesque this was; for to the poet no events of the objective life were so real and significant as those of the purely mental drama of thought, feeling, and purpose. The rehearsals were, however, gratifying to the author, it seems, for Macready records in his diary (that recurs like the chorus in a Greek tragedy) that he was happy “with the extreme delight Browning testified at the rehearsal of my part, which he said to him was a full recompense for having written the play, as he had seen his utmost hopes of character perfectly embodied.” The play was performed at the Covent Garden Theater on the night of May 3, 1837.
Both Edmund Gosse and William Sharp deny that Browning’s plays failed on the stage; at all events, with each attempt there were untoward circumstances which alone would have contributed to or even doomed a play to a short tenure.
In 1886 “Strafford” was produced in London under the auspices of the Browning Society, and the real power of the play surprised as well as deeply impressed the audiences who saw it. But “Pauline,” “Paracelsus,” and “Strafford” all have a peculiar element of reminiscent importance,[Pg 35] if it may be so termed, in that they were the forerunners, the indications of the great work to come.
There is no dramatic poem of Browning’s that has not passages of superb acting effects, as well as psychological fascinations for the thinker; and the future years were to touch him with new power to produce work whose dramatic power lives in imperishable significance. “Strafford” had a run of only five nights at this first time of its production; Macready received and accepted an offer to go to America, and other things happened. Browning became absorbed in his “Sordello,” and suddenly, on Good Friday of 1838, he sailed for Venice, “intending to finish my poem among the scenes it describes,” he wrote to John Robertson, who had been introduced to Browning by Miss Martineau. On a sailing ship, bound for Trieste, the poet found himself the only passenger. It was on this voyage, while between Gibraltar and Naples, that he wrote “How They Brought the Good News from Ghent to Aix.” It was written on deck, penciled on the fly-leaf of Bartoli’s De’ Simboli trasportati al Morale. When Dr. Corson first visited Browning in 1881, in his London home in Warwick Crescent, Browning showed his guest this identical copy of the book, with the penciled poem on the fly-leaves, of which Dr. Corson said, in a private letter to a friend:
“One book in the library I was particularly interested in,—Bartoli’s Simboli, or, rather, in what the poet had written in pencil on its fly-leaves, front and back, namely, ‘How they brought the good news from Ghent to Aix.’”
Dr. Corson added that he had been so often asked as to what this “good news” was, that he put the question to Mr. Browning, who replied:
“‘I don’t remember whether I had in my mind any in particular, when I wrote the poem’; and then, after a pause,” continued Dr. Corson, “he said, with a dash of expression[Pg 36] characteristic of him, ‘Of course, very important news were carried between those two cities during that period.’”
In Mrs. Orr’s biography of Browning she quotes a long letter written by him to Miss Haworth, in the late summer of 1838, after his return from this Italian trip, in which he says:
“You will see ‘Sordello’ in a trice, if the fagging fit holds. I did not write six lines while absent (except a scene in a play, jotted down as we sailed through the straits of Gibraltar), but I did hammer out some four, two of which are addressed to you,... I saw the most gorgeous and lavish sunset in the world.... I went to Trieste, then to Venice, then through Treviso, and Bassano to the mountains, delicious Asolo, all my places and castles you will see. Then to Vicenza, Padua, and Venice again. Then to Verona, Trent, Innspruck (the Tyrol), Munich, Salzburg, Frankfort and Mayence; down the Rhine to Cologne, then to Aix-le-Chapelle, Liège, and Antwerp; then home.... I saw very few Italians, ‘to know,’ that is. Those I did see I liked....”
It is related that the captain of the ship became so much attached to Browning that he offered him a free passage to Constantinople; and that his friendly attraction to his youthful passenger was such that on returning to England he brought to the poet’s sister a gift of six bottles of attar of roses. The poems of “Pippa Passes” and “In a Gondola” may be directly traced to this visit, and Browning seemed so invigorated by it that his imagination was aflame with a multitude of ideas at once.
Meanwhile “Paracelsus” was winning increasing appreciation. The poet did not escape the usual sweeping conclusion generally put forth regarding any unusual work, that the author has made extensive studies for it,—as if ideas and imagination drew their inspiration from the outer world, and were solely to be appraised, as to their[Pg 37] results, by the capacity for cramming. So much cramming, so much genius! He who thus mistakes inspiration for industry certainly proves how very remote is his mind from the former. With this marvelous work by a young man of twenty-three the usual literary legends were set afloat, like thistledown in the air, which seem to have floated and alighted everywhere, and which now, more than seventy-five years later, are apparently still floating and alighting on the pens of various writers, to the effect that “Paracelsus” is the result of “vast research among contemporary records,” till the poem added another to the Seven Labors of Hercules. As a matter of fact, and as has already been noted, Browning had merely browsed about his father’s library.
Dr. Berdoe points out that the real “Paracelsus” cannot be understood without considerable excursions into the occult sciences, and he is quite right as to the illumination these provide, in proportionate degree as they are acquired by the reader; as a matter of course they enlarge his horizon, and offer him clues to unsuspected labyrinths; and so fine and complete is Dr. Berdoe’s own commentary on “Paracelsus” that it might not unduly be held as supplementary to the reader’s entire enjoyment of the poem. Dr. Berdoe notes that the Bishop of Spanheim, who was the instructor of Paracelsus, defined “divine magic,” as another name for alchemy, “and lays down the great doctrine of all medieval occultism, as of all modern theosophy,—of a soul-power equally operative in the material and the immaterial, in nature and in the consciousness of man.” The sympathetic reader of Browning’s “Paracelsus” will realize, however, that the drama he presents is spiritual, rather than occult. It is not the search for the possible mysteries, or achievements of the crucible. It is the adventure of the soul, not the penetration into the secrets of unknown elementals.
In the autumn of 1835 the Browning family removed[Pg 38] from Camberwell to Hatcham. They bestowed themselves in a spacious, delightful old house, with “long, low rooms,” wherein the household gods, inclusive of the six thousand books of the elder Browning’s treasured library, found abundant accommodation; and the outlook on the Surrey hills gratified them all. During these years we catch a few glimpses of the poet’s only sister, Sarianna, who was two years younger than her brother, and quite as fond of listening to the conversation of an uncle, William Shergold Browning, who had removed to Paris. Here he was connected with the Rothschild banking house, and had achieved some distinction as the author of a “History of the Huguenots.” He also wrote two historical novels, entitled “Hoel Mar en Morven” and “Provost of Paris,” and compiled one of those harmless volumes entitled “Leisure Hours.” It was this uncle who had brought about the introduction of his nephew and Marquis Amédée de Ripert-Monclar, whose uncle, the Marquis de Fortia, a member of the Institut, was a special friend of William Shergold Browning. In later years a grandson of the Paris Browning, after graduating at Lincoln College, became Crown prosecutor in New South Wales. He is known as Robert Jardine Browning, and he was on terms of intimacy with his cousins, Robert and Sarianna, whom he often visited.
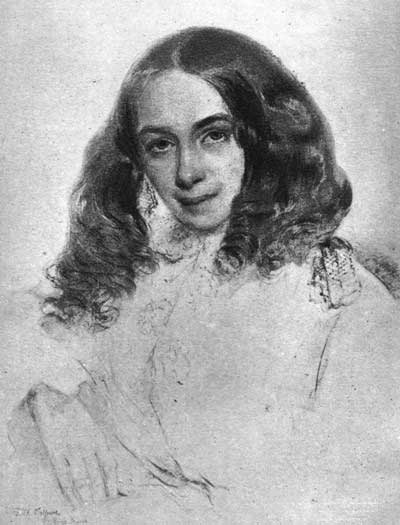

ELIZABETH BARRETT BROWNING
From a drawing made by Field Talfourd, in Rome, 1855
The family friendship with Carlyle was a source of great pleasure to Mrs. Browning, the poet’s mother, and there is on record a night when Carlyle and his brother dined with the Brownings at Hatcham. Another family friend and habitué was the Rev. Archer Gurney, who at a later time became Chaplain to the British Embassy in Paris. Mr. Gurney was a writer of poems and plays, lyrics and dramatic verse, and a volume of his work entitled “Fra Cipollo and Other Poems” was published, from which Browning drew his motto for “Colombe’s Birthday.” Mr.[Pg 39] Gurney was deeply interested in young Browning’s poetry, and there is a nebulous trace of his having something to do with the publication of “Bells and Pomegranates.” Another friend of the poet was Christopher Dowson, who married the sister of Alfred Domett; at their homes, Albion Terrace, and their summer cottage in Epping Forest, Browning was a frequent visitor. Dowson died early; but Field Talfourd (a brother of the author of “Ion” and the artist who made those crayon portraits of Browning and his wife, in the winter of 1859, in Rome), Joseph Arnould, and Alfred Domett, with one or two other young men, comprised the poet’s more intimate circle at this time. Arnould and Domett were both studying for the Bar; Arnould had gained the Newdigate in 1834, and had won great applause by his recital (in the Sheldonian Theater) of his “Hospice of St. Bernard.” Later he was offered the editorship of the Daily News, founded by Forster and Dickens, but he kept true to his legal studies and in time became the Judge of the High Court at Bombay, and was knighted by the Crown.
There was a dinner given by Macready at which Browning, Carlyle, and Miss Martineau were guests, and later a dinner at the Carlyles’ where Browning met a son of Burns “who sang some of his father’s songs.” To a friend Browning wrote: “I dined with dear Carlyle and his wife (catch me calling people ‘dear’ in a hurry) yesterday. I don’t know any people like them.”
Browning passed a day with Miss Martineau at Ascot, and again visited her in Elstree, where she was staying with the Macreadys. She greatly admired “Paracelsus,” and spoke of her first acquaintance with his poetry as a “wonderful event.” He dined with her at her home in Westminster, and there met John Robertson, the assistant editor of the Westminster Review, to which Miss Martineau was a valued contributor. Henry Chorley, a musical critic of the day, was another guest that night, and soon after[Pg 40] Browning dined with him “in his bachellor abode,” the other guests being Arnould, Domett, and Bryan Proctor; later, at a musicale given by Chorley, Browning met Charlotte Cushman and Adelaide Kemble. Chorley drew around him the best musicians of the time: Mendelssohn, Moscheles, Liszt, David, and other great composers were often rendered in his chambers. Proctor was then living in Harley Street, and his house was a center for the literary folk of the day.
George Eliot speaks of the indifference with which we gaze at our unintroduced neighbor, “while Destiny stands by, sarcastic, with our dramatis personæ folded in her hands.” It was such an hour of destiny as this when, at a dinner given by Sergeant Talfourd, at his home (No. 56) in Russell Square, Browning first met John Kenyon. Our great events mostly come to us like gods in disguise, and this evening was no exception. Unknown and undreamed of, the young poet had come to one of those partings of the ways which are only recognized in the perspective of time. Browning’s life had been curiously free from any romance beyond that with the muses. The one woman with whom he had seemed most intimate, Miss Fanny Haworth, was eleven years his senior, and their intercourse, both conversationally and in letters, had been as impersonal as literature itself. She was a writer of stories and verse, and had celebrated her young friend in two sonnets. This friendship was one of literary attractions alone, and the poet had apparently devoted all his romance to poetry rather than demanded it in life. But now, golden doors were to open.
At this dinner at Mr. Talfourd’s, John Kenyon came over to the poet, after they had left the dining-room, and inquired if he were not the son of his old school-fellow, Robert Browning. Finding this surmise to be true, he became greatly attached to him. Mr. Kenyon had lost his wife[Pg 41] some time previously; he had no children, and he was a prominent and favorite figure in London society. Southey said of Kenyon that he was “one of the best and pleasantest of men, whom every one likes better the longer he is known,” and Kenyon, declaring that Browning “deserved to be a poet, being one in heart and life,” offered to him his “best and most precious gift,”—that of an introduction to his second cousin, Elizabeth Barrett.
This was the first intimation of Destiny, but the meeting was still to remain in the future. “Sordello” was published in 1840,—“a colossal derelict on the ocean of poetry,” as William Sharp terms it. The impenetrable nature of the intricacies of the work has been the theme of many anecdotes. Tennyson declared that there were only two lines in it—the opening and the closing ones—which he understood, and “they are both lies,” he feelingly added. Douglas Jerrold tackled it when he was just recovering from an illness, and despairingly set down his inability to comprehend it to the probability that his mind was impaired by disease; and thrusting the book into the hands of his wife he entreated her to read it at once. He watched her breathlessly, and when she exclaimed, “I don’t know what this means; it is gibberish,” Jerrold exclaimed, “Thank God, I am not an idiot.”
Still another edifying testimony to the general inability to understand “Sordello” is given by a French critic, Odysse Barot, who quotes a passage where the poet says, “God gave man two faculties,” and adds, “I wish while He was about it (pendant qu’il était en train) God had supplied another—namely, the power of understanding Mr. Browning.”
Mrs. Carlyle declared that she read “Sordello” attentively twice, but was unable to discover whether the title referred to “a man, a city, or a tree”; yet most readers of this poem will be able to recognize that Sordello was a[Pg 42] singer of the thirteenth century, whose fame suddenly lures him from the safety of solitude to the perils of society in Mantua, after which “immersion in worldliness” he again seeks seclusion, and partially recovers himself. The motif of the poem recalls the truth expressed in the lines:
“Who loves the music of the spheres
And lives on earth, must close his ears
To many voices that he hears.”
Suddenly a dazzling political career opens before Sordello; he is discovered to be—not a nameless minstrel, but the son of the great Ghibelline chief, Salinguerra; more marvelous still, he is loved by Palma, in her youthful beauty and fascination; and the crucial question comes, as in some form it must come to every life, whether he shall choose all the kingdoms of power and glory, or that kingdom which is not of earth, and cometh not with observation.
It is easy to realize how such a problem would appeal to Robert Browning. Notwithstanding the traditional “obscurity” of “Sordello,” it offers to the thoughtful reader a field of richest and most entrancing suggestion.
To Alfred Domett, under date of May 22, 1842, Browning writes:[1]
“... I cannot well say nothing of my constant thoughts of you, most pleasant remembrances of you, earnest desires for you. I have a notion you will come back some bright morning a dozen years hence and find me just gone—to heaven, or Timbuctoo! I give way to this fancy, for it lets me write what, I dare say, I have written niggardly enough, of my real love for you, better love than I had supposed I was fit for.... I have read your poems; you can do anything, and I should think would do much. I will if I live. At present, if I stand on head or heels I don’t know; what men require I know as little; and of what they are in possession I know not.... With this[Pg 43] I send you your ‘Sordello.’ I suppose, I am sure, indeed, that the translation from Dante, on the fly-leaf, is your own....”
In another letter to Alfred Domett, Browning thus refers to Tennyson:
“... But how good when good he is! That noble ‘Locksley Hall!’”
Browning had already become enamored of Italy; and Mrs. Bridell-Fox, writing to William Sharp, speaks of meeting the poet after his return, and thus describes the impression he made upon her:[2]
“I remember him as looking in often in the evenings, having just returned from his first visit to Venice. I cannot tell the date for certain. He was full of enthusiasm for that Queen of Cities. He used to illustrate his glowing descriptions of its beauties, the palaces, the sunsets, the moonrises, by a most original kind of etching. Taking up a bit of stray notepaper, he would hold it over a lighted candle, moving the paper about gently till it was cloudily smoked over, and then utilizing the darker smears for clouds, shadows, water, or what not, would etch with a dry pen the forms of lights on cloud and palace, on bridge or gondola, on the vague and dreamy surface he had produced. My own passionate longing to see Venice dates from those delightful, well-remembered evenings of my childhood.”
This visit of the young poet to Italy forged the link of that golden chain which was to unite all his future with that land of art and song which held for him such wonderful Sibylline leaves of the yet undreamed-of chapters of his life.
| “O Life, O Beyond, Art thou fair, art thou sweet?” “How the world is made for each of us! How all we perceive and know in it Tends to some moment’s product thus, When a soul declares itself—to wit, By its fruit, the thing it does!” |
Elizabeth Barrett’s Love for the Greek Poets—Lyrical Work—Serious Entrance on Professional Literature—Noble Ideal of Poetry—London Life—Kenyon—First Knowledge of Robert Browning.
Elizabeth Barrett was but twelve days in translating the “Prometheus Bound” of Æschylus, and of the result of this swift achievement she herself declared, when laughingly discussing this work with Home in later years, that it ought to have been “thrown in the fire immediately afterward as the only means of giving it a little warmth.” Combined with a few of her other poems, however, it was published (anonymously) in 1832, and received from the Athenæum the edifying verdict that “those who adventure in the hazardous lists of poetic translation should touch any one rather than Æschylus, and they may take warning from the writer before us.”
The quiet life at Sidmouth goes on,—goes on, in fact, for three years,—and the life is not an unmixed joy to Miss Barrett. “I like the greenness and the tranquillity and the[Pg 45] sea,” she writes to a friend. “Sidmouth is a nest among elms; and the lulling of the sea and the shadow of the hills make it a peaceful one; but there are no majestic features in the country. The grandeur is concentrated upon the ocean without deigning to have anything to do with the earth....”
In the summer of 1835 the Barretts left Sidmouth for London, locating at first in Gloucester Place (No. 74) where they remained for three years. Hugh Stuart Boyd had, in the meantime, removed to St. John’s Wood; Mr. Kenyon and Miss Mitford became frequent visitors. Miss Barrett’s literary activity was stimulated by London life, and she began contributing to a number of periodicals, and her letter-writing grew more and more voluminous. To Mr. Boyd she wrote soon after their arrival in London:
“As George is going to do what I am afraid I shall not be able to do to-day,—to visit you,—he must take with him a few lines from me, to say how glad I am to feel myself again only at a short distance from you; and gladder I shall be when the same room holds both of us. But I cannot open the window and fly.... How much you will have to say to me about the Greeks, unless you begin first to abuse me about the Romans. If you begin that, the peroration will be a very pathetic one, in my being turned out of your doors. Such is my prophecy.
“Papa has been telling me of your abusing my stanzas on Mrs. Hemans’s death. I had a presentiment that you would....”
If the classic lore and ponderous scholarship unfitted Mr. Boyd to feel the loveliness of this lyric, those who enter into its pathos may find some compensation for not being great classicists. It is in this poem that the lines occur,—
“Nor mourn, O living One, because her part in life was mourning:
Would she have lost the poet’s fire, for anguish of the burning?
··········
Albeit softly in our ears her silver song was ringing,
The foot-fall of her parting soul is softer than her singing.”
[Pg 46]Miss Barrett’s fugitive poems of this time tell much of the story of her days. She sees Haydon’s portrait of Wordsworth, and it suggests the sonnet beginning:
“Wordsworth upon Helvellyn!...”
The poems written previously to “A Drama of Exile” do not at all indicate the power and beauty and the depth of significance for which all her subsequent work is so remarkable. “The Seraphim,” “Isobel’s Child,” “The Virgin Mary to the Child Jesus,” however much they may contain occasional glimpses of poetic fire, would never have established her rank. Yet “The Sleep” belongs to this period, and that poem of exquisite pathos, “Cowper’s Grave.” Anticipating a little, there came that poem which awakened England and the modern world, indeed, to a sense of the suffering of children in factory life, “The Cry of the Children,” which appeared almost simultaneously with Lord Shaftesbury’s great speech in Parliament on child labor. The poem and the statesman and philanthropist together aroused England.
A poem called “Confessions” is full of a mysterious power that haunts the reader in a series of pictures:
“Face to face in my chamber, my silent chamber, I saw her:
God and she and I only, there I sate down to draw her
Soul through the clefts of confession—‘Speak, I am holding thee fast,
As the angel of resurrection shall do at the last.’”
And what touching significance is in these lines:
“The least touch of their hands in the morning, I keep it by day and by night;
Their least step on the stair, at the door, still throbs through me, if ever so light.”
There were the “Crowned and Wedded” that celebrated the marriage of England’s beloved queen; “Bertha in the[Pg 47] Lane,” which has been one of the most universal favorites of any of her lyrics; still later, “The Dead Pan,” which essentially embodies her highest convictions regarding the poetic art: that Poetry must be real, and, above all, true.
“O brave poets, keep back nothing,
Nor mix falsehood with the whole!
······
Hold, in high poetic duty,
Truest Truth the fairest Beauty!”
In such lines as these she expressed her deepest feeling.
Then appeared “Comfort,” “Futurity,” and “An Apprehension”; the dainty little picture of her childish days in “Hector in the Garden”; the sonnets to George Sand, on which the French biographer[3] of Mrs. Browning, in recent years, has commented, translating the first line,—
“Vrai genie, mais vraie femme!”
and adding that these words, addressed to George Sand, are illustrated by her own life.
The sonnet “Insufficiency,” of this period, closes with the lines,
“And what we best conceive we fail to speak.
Wait, soul, until thine ashen garments fall,
And then resume thy broken strains, and seek
Fit peroration without let or thrall.”
In all this work that deep religious note, that exaltation of spirituality which so completely characterized Elizabeth Barrett Browning, is felt by the reader. Religion was always to her a life, not a litany. The Divine Love was as the breath of life to her, wherein she lived and moved, and on which she relied for her very being.
The poem called “A Rhapsody of Life’s Progress,” though [Pg 48]not often noted by the critical writers on Mrs. Browning, is one full of impressive lines, with that haunting refrain of every stanza,—
“O Life, O Beyond,
Thou art strange, thou art sweet!”
Albeit, a candid view must also recognize that this poem reveals those early faults, the redundancy, the almost recklessness of color and rhythm, that are much less frequently encountered in the poems of Mrs. Browning than they were in those of Miss Barrett. For poetic work is an art as well as a gift, and while “Poets are born, not made,” yet, being born, the poet must proceed also to make himself. In this “Rhapsody” occur the lines that are said to have thrown cultured Bostonians into a bewilderment exceptional; a baffled and despairing state not to be duplicated in all history, unless by that of the Greeks before the Eleusinian mysteries; the lines running,—
“Let us sit on the thrones
In a purple sublimity,
And grind down men’s bones
To a pale unanimity.”
Polite circles in Boston pondered unavailingly upon this medley, and were apparently reduced to the same mental condition as was Mrs. Carlyle when she read “Sordello.” Unfortunately for Jane Carlyle there were in her day no Browning societies, with their all-embracing knowledge, to which Browning himself conveniently referred all persons who questioned him as to the meaning of certain passages. One Boston woman, not unknown to fame, recalls even now that she walked the Common, revolving these cryptic lines in her mind, and meeting Dr. Holmes, asked if he understood them, to which the Autocrat replied, “God forbid!”
[Pg 49]This very affluence of feeling, however, or even recklessness of imagery, was not without its place as a chastened and subdued factor in the power of Miss Barrett later on. From her earliest childhood she had the scholar’s instinct and love of learning; she read fluently French, German, and Italian; she was well grounded in Latin, and for the Greek she had that impassioned love that made its literature to her an assimilation rather than an acquirement. Its rich intellectual treasure entered into her inmost life. She also read Hebrew, and all her life kept with her a little Hebrew Bible, as well as a Greek Testament, the margins of both of which are filled with her notes and commentaries in her clear, microscopic handwriting. Miss Barrett’s earliest work, published anonymously, at her father’s expense, rather to gratify himself and a few friends than to make any appeal to the public, had no special claim to literary immortality, whatever its promise; but once in London, something in the very atmosphere seemed to act as a solvent to precipitate her nebulous dreams and crystallize them into definite and earnest aims. Poetry had always been to her “its own exceeding great reward,” but she was now conscious of a desire to enter into the stress and storm of the professional writer, who must sink or swim, accept the verdict of success or failure, and launch forth on that career whose very hardships and uncertainties are a part of its fascination. To Elizabeth Barrett, secure in her father’s home, there was little possibility of the hardships and privations on the material side not unfrequently incidental to the pursuit of letters, but to every serious worker life prefigures itself as something not unlike the Norse heaven with its seven floors, each of which must be conquered.
“Here a star, and there a star,
Some lose their way,—
Here a mist, and there a mist,
Afterwards ... day!”
[Pg 50]Miss Barrett finds London “wrapped up like a mummy, in a yellow mist,” but she tries to like it, and “looks forward to seeing those here whom we might see nowhere else.” Her brother George, who had recently graduated from the University of Glasgow, was now a barrister student at the Inner Temple. Henrietta and Arabel, the two sisters, found interest and delight in the new surroundings.
Retrospectively viewed, Mrs. Browning’s life falls easily into three periods, which seem to name themselves as a prelude, an interlude, and a realization. She was just past her twenty-ninth birthday when the family came up to London, and up to that time she had, indeed, lived with dreams and visions for her company. These years were but the prelude, the preparatory period. She then entered on the experimental phase, the testing of her powers, the interlude that lay between early promise and later fulfillment. In her forty-first year came her marriage to Robert Browning and the beginning of those nearly fifteen years of marvelous achievement, during which the incomparable “Sonnets from the Portuguese” and “Aurora Leigh” were written,—the period of realization.
Before the beginning of the London period Miss Barrett’s literary work had been largely that of the amateur, though in the true meaning of that somewhat misused term, as the lover, rather than as merely the more or less crude experimenter. For Poetry to Elizabeth Barrett was a divine commission no less than an inborn gift. Under any circumstances, she would have poured her life “with passion into music,” and with the utmost sincerity could she have said, with George Eliot’s “Armgart,”
“I am not glad with that mean vanity
Which knows no good beyond its appetite
Full feasting upon praise! I am only glad,
Being praised for what I know is worth the praise;
Glad of the proof that I myself have part
In what I worship!”
[Pg 51]As is revealed and attested in many expressions of her maturer years, Poetry was to her the most serious, as well as the most enthralling, of pursuits, while she was also a very accomplished scholar. A special gift, and a facility for the acquirement of scholarly knowledge in the academic sense, do not invariably go together; often is the young artist so bewitched with his gift, so entranced with the glory and the splendor of a dream, that the text-book, by contrast, is a dull page, to which he cannot persuade himself to turn. To him the air is peopled with visions and voices that fascinate his attention. In the college days of James Russell Lowell is seen an illustration of this truth, the young student being temporarily suspended, and sent—not to Coventry, but to Concord. Perhaps the banishment of a Harvard student for the high crime and misdemeanor of being addicted to rhyme rather than mathematics, and his penalty in the form of exile to Concord, the haunt of Emerson and the Muses, may have made Pan laugh. But, at all events, Miss Barrett was as naturally a scholar, in the fullest significance of the term, as she was a poet. This splendid equipment was a tremendous factor in that splendor of achievement, and in that universally recognized success, that has made the name of Elizabeth Barrett Browning immortal in all ages, as the greatest woman poet the world has ever known.
The professional literary life is a drama in itself,—comedy, or tragedy, as may be, and usually a mixture of both. It ranges over wide areas of experience, from that of the author of “Richard Feverel,” who is said to have written that novel on a diet of oatmeal and cold water, to that of the luxurious author whose séances with the Muses are decorously conducted in irreproachable interiors, with much garnishing, old rose and ivory, ebony carvings, and inlaid desks, at which the marvelous being who now and then condescends to “dictate” a “best seller,” is apt to[Pg 52] be surprised by a local photographer. But as a noted educator defined a University as “a log,—with Mark Hopkins sitting on the other end,” so the “real thing” in a literary career may not inaptly be typified by Louisa Alcott sitting on the back stairs, writing on an old atlas; and it was into actualities somewhat like these that Elizabeth Barrett desired to plunge. The question that she voiced in later years, in “Aurora Leigh,”—
“My own best poets, am I one with you,
That thus I love you,—or but one through love?
Does all this smell of thyme about my feet
Conclude my visit to your holy hill
In personal presence, or but testify
The rustling of your vesture through my dreams
With influent odours?”—
this question, in substance, stirred now in her life, and insisted upon reply. She must, like all real poets, proceed to “hang her verses in the wind,” and watch if perchance there are
“... the five
Which five hundred will survive.”
Elizabeth Barrett was of a simplicity that had no affinities with the poseur in any respect, and she had an inimitable sense of humor that pervaded all her days. Wit and pathos are, indeed, so closely allied that it would be hardly possible that the author of the “De Profundis,” a poem that sounds the profoundest depths of the human soul, should not have the corresponding quality of the swiftest perception of the humorous. It was somewhere about this time that Poe sent to her a volume of his poems with an inscription on the fly-leaf that declared her to be “the noblest of her sex.”
“And what could I say in reply,” she laughingly [Pg 53]remarked, “but ‘Sir, you are the most discerning of yours!’”
The first poem of hers that was offered in a purely professional way was “The Romaunt of Margret.” It appeared in the New Monthly Magazine, then edited by Bulwer, who was afterward known as the first Lord Lytton. At this time Richard Hengist Horne was basking in the fame of his “Orion,” and to him Miss Barrett applied, through a mutual friend, as to whether her enclosed poem had any title to that name, or whether it was mere verse. “As there could be no doubt in the mind of the recipient on that point,” said Mr. Horne, “the poem was forwarded to Bulwer, and duly appeared. The next one sent,” continues Mr. Horne, “started the poetess at once on her bright and noble career.” This “next one” appears to have been “The Poet’s Vow,” and a confirmation of this supposition is seen in a letter of hers at this date to Mr. Boyd, in which she explains her not having at hand a copy of the Athenæum that he had wished to see, and adds:
“I can give you, from memory, the Athenæum’s review in that number. The critic says ‘It is rich in poetry ... including a fine, although too dreamy, ballad, The Poet’s Vow. We are almost tempted to pause and criticise the work of an artist of so much inspiration and promise as the author of this poem, and to exhort him to a greater clearness of expression, and less quaintness in the choice of his phraseology, but this is not the time or place for digression.’
“You see my critic has condemned me with a very gracious countenance. Do put on yours.”
Again, under date of October, 1836, she writes to Mr. Boyd:
“... But what will you say to me when I confess that in the face of all your kind encouragement, my Drama of the[Pg 54] Angels (The Seraphim) has not been touched until the last three days? It was not out of pure idleness on my part, nor of disregard to your admonition; but when my thoughts were distracted with other things, books just began enclosing me all around, a whole load of books upon my conscience, and I could not possibly rise to the gate of heaven and write about my angels. You know one can’t sometimes sit down to the sublunary occupation of even reading Greek, unless one feels free to it. And writing poetry requires a double liberty, and an inclination which comes only of itself....
“... I have had another note from the editor—very flattering, and praying for farther supplies. The ‘Angels’ were not ready, and I was obliged to send something else.”
A discussion arises in the family regarding the taking of a house in Wimpole Street, and Elizabeth remarks that for her part she would rather go on inhabiting castles in the air than to live in that particular house, “whose walls look so much like Newgate’s turned inside out.” She continues, however, that if it is decided upon, she has little doubt she will wake and sleep very much as she would anywhere else. With a strong will, and an intense, resistless kind of energy in holding any conviction, and an independence of character only equalled by its preeminent justice and generous magnanimity, she was singularly free from any tenacious insistence upon the matters of external life. She had her preferences; but she always accommodated herself to the decision or the necessity of the hour, and there was an end of it. She had that rare power of instantaneous mental adjustment; and if a given thing were right and best, or if it were not best but was still inevitable, she accepted it and did not make life a burden to every one concerned by endless discussion.
London itself did not captivate her fancy. “Did Dr. Johnson in his paradise in Fleet Street love the pavements and the walls?” she questioned. “I doubt that,”[Pg 55] she added; “the place, the privileges, don’t mix in one’s love as is done by the hills and the seaside.”
The privileges, however, became more and more interesting to her. One of these was when she met Wordsworth, whom she describes as being “very kind,” and that he “let her hear his conversation.”
This conversation she did not find “prominent,” for she saw at the same time Landor, “the brilliant Landor,” she notes, and felt the difference “between great genius and eminent talent.” But there was a day on which she went to Chiswick with Wordsworth and Miss Mitford, and all the way she thought she must be dreaming. It was Landor, though, who captivated her fancy at once, as he already had that of her future poet-lover and husband, who was yet unrevealed to her. Landor, “in whose hands the ashes of antiquity burn again,” she writes, gave her two Greek epigrams he had recently written. All this time she is reading everything,—Sheridan Knowles’s play of “The Wreckers,” which Forrest had rejected, “rather for its unfitness to his own personal talent than for its abstract demerit,” she concludes; and “Ion,” which she finds beautiful morally rather than intellectually, and thinks that, as dramatic poetry, it lacks power, passion, and condensation. Reading Combe’s “Phrenology,” she refers to his theory that slowness of the pulse is a sign of the poetical impulse. If this be true, she fears she has no hope of being a poet, “for my pulse is in a continual flutter,” she notes; and she explains to Mr. Boyd that the line
“One making one in strong compass”
in “The Poet’s Vow,” which he found incomprehensible, really means that “the oneness of God, ‘in Whom are all things,’ produces a oneness, or sympathy, with all things. The unity of God preserves a unity in man.”
All in all, Miss Barrett is coming to enjoy her London[Pg 56] life. There was the Royal Academy, “and real live poets, with their heads full of the trees and birds, and sunshine of Paradise”; and she has “stood face to face with Wordsworth and Landor”; Miss Mitford has become a dear friend, but she visits London only at intervals, as she lives—shades of benighted days!—thirty miles from London. A twentieth century residence across the continent could hardly seem more remote.
The removal to Wimpole Street was decided upon, and to that house (No. 50), gloomy or the reverse, the Barretts migrated. Miss Barrett’s new book, under the title of “The Seraphim and Other Poems,” was published, marking her first professional appearance before the public over her own name. “I feel very nervous about it,” she said; “far more than I did when my ‘Prometheus’ crept out of the Greek.”
Mr. Kenyon was about to go to Rydal Mount on a visit to Wordsworth, and Miss Barrett begs him to ask, as for himself, two garden cuttings of myrtle or geranium, and send to her—two, that she may be sure of saving one.
Autographs had value in those days, and in a note to Mr. Bray Miss Barrett alludes to one of Shakespeare’s that had been sold for a hundred pounds and asks if he feels sure of the authenticity of his own Shakespearean autograph.
A new poetic era had dawned about the time that “The Seraphim” appeared. Tennyson had written “Audley Court,” and was beginning to be known in America, owing this first introduction to Emerson, who visited Landor in Florence and made some sojourn afterward in England. The Boston publishing house of C. C. Little and Company (now Little, Brown, and Company) had written to Tennyson (under date of April 27, 1838) regarding a republishing of his volume, as the future laureate was already recognized for the musical quality and perfection of art in his[Pg 57] work. Browning had published only “Pauline,” “Paracelsus,” and “Strafford.” Shelley and Keats were dead, their mortal remains reposing in the beautiful English cemetery in Rome, under the shadow of the tall cypresses, by the colossal pyramid of Caius Cestus. Byron and Scott and Coleridge had also died. There were Landor and Southey, Rogers and Campbell; but with Miss Barrett there came upon the scene a new minstrelsy that compelled its own recognition. Some of her shorter poems had caught the popular ear; notably, her “Cowper’s Grave,” which remains, to-day, one of her most appealing and exquisite lyrics.
“It is a place where poets crowned may feel the heart’s decaying;
It is a place where happy saints may weep amid their praying.”
The touching pathos of the line,
“O Christians, at your cross of hope a hopeless hand was clinging!”
moves every reader. And what music and touching appeal in the succeeding stanza:
“And now, what time ye all may read through dimming tears his story,
How discord on the music fell and darkness on the glory,
And how when, one by one, sweet sounds and wandering lights departed,
He wore no less a loving face because so broken-hearted.”
In seeing, “on Cowper’s grave,... his rapture in a vision,” Miss Barrett pictured his strength—
“... to sanctify the poet’s high vocation.”
Her reverence for poetic art finds expression in almost every poem that she has written.
Among other shorter poems included with “The Seraphim” were “The Poet’s Vow,” “Isobel’s Child,” and[Pg 58] others, including, also, “The Romaunt of Margret.” The Athenæum pronounced the collection an “extraordinary volume,—especially welcome as an evidence of female genius and accomplishment,—but hardly less disappointing than extraordinary. Miss Barrett’s genius is of a high order,” the critic conceded; but he found her language “wanting in simplicity.” One reviewer castigated her for presuming to take such a theme as “The Seraphim” “from which Milton would have shrank!” All the critics agree in giving her credit for genius of no ordinary quality; but the general consensus of opinion was that this genius manifested itself unevenly, that she was sometimes led into errors of taste. That she was ever intentionally obscure, she denied. “Unfortunately obscure” she admitted that she might be, but “willingly so,—never.”
Of the personal friends of Elizabeth Barrett one of the nearest was Mary Russell Mitford, who was nineteen years her senior. Miss Mitford describes her at the time of their meeting as having “such a look of youthfulness that she had some difficulty in persuading a friend that Miss Barrett was old enough to be introduced into society.” Miss Mitford added that she was “certainly one of the most interesting persons” she had ever seen; “of a slight, delicate figure,... large, tender eyes, and a smile like a sunbeam.”
Mr. Kenyon brought Andrew Crosse, a noted electrician of the day, to see Miss Barrett; and in some reminiscences[4] written by Mrs. Andrew Crosse there is a chapter on “John Kenyon and his Friends” that offers the best comprehension, perhaps, of this man who was so charming and beloved a figure in London society,—a universal favorite. Born in 1784 in Jamaica, the son of a wealthy land-owner, he was sent to England as a lad, educated there, and in 1815 he set out for a tour of the continent. In 1817, in [Pg 59]Paris, he met and became intimate with Professor George Ticknor of Harvard University, the Spanish historian; and through this friendship Mr. Kenyon came to know many of the distinguished Americans of the day, including Emerson, Longfellow, and Willis. Coleridge, Southey, Wordsworth, and Landor were among Kenyon’s most intimate circle; and there is a record of one of his dinners at which the guests were Daniel Webster, Professor and Mrs. Ticknor, Dickens, Montalembert, and Lady Mary Shepherd. In 1823 Kenyon married Miss Curteis, and they lived for some years in Devonshire Place, with frequent interludes of travel on the continent. Mrs. Kenyon died in 1835, but when the Barretts came up to London Kenyon had resumed his delightful hospitalities, of which he made fairly a fine art. Professor Ticknor has left an allusion to another dinner at Kenyon’s where he met Miss Barrett. In the autumn of 1839 Miss Barrett, accompanied by her brother Edward, went to Torquay, for the warmer climate, and Mr. Kenyon also had gone there for the winter. Around him were gathered a group of notable friends, with whom Miss Barrett, his cousin (with one remove), was constantly associated,—Landor, Andrew Crosse, Theodosia Garrow (afterwards the wife of Thomas Adolphus Trollope), and Bezzi, an accomplished Italian, who was afterward associated with Seymour Kirkup in discovering Dante’s portrait concealed under the whitewash applied to the walls of the Bargello in Florence. Miss Barrett was at this time entering into that notable correspondence with Richard Hengist Horne, many of these letters containing passages of interest. For instance, of poetry we find her saying:
“If poetry under any form be exhaustible, Nature is; and if Nature is, we are near a blasphemy, and I, for one, could not believe in the immortality of the soul.
‘Si l’âme est immortelle,
L’amour ne l’est-il-pas?’
[Pg 60]Extending l’amour into all love of the ideal, and attendant power of idealizing.... I don’t believe in mute, inglorious Miltons, and far less in mute, inglorious Shakespeares.”
Referring to some correspondence with Miss Martineau, Miss Barrett characterizes her as “the noblest female intelligence between the seas,” and of Tennyson, in relation to some mention of him, she wrote that “if anything were to happen to Tennyson, the whole world should go into mourning.”
A project (said to have originated with Wordsworth) was launched to “modernize” Chaucer, in which Miss Barrett, Leigh Hunt, Monckton Milnes, Mr. Horne, and one or two others enthusiastically united, the only dissenter being Landor, who characteristically observed that any one who was fit to read Chaucer at all could read him in the original. Later on the co-operation of Browning, Tennyson, Talfourd, Bulwer, Mary Howitt, and the Cowden Clarkes was solicited and in part obtained. But Landor held firm, and of his beloved Chaucer he said: “I will have no hand in breaking his dun, but rich-painted glass, to put in thinner (if clearer) panes.” A great deal of correspondence ensued in connection with this Herculean labor, most of which is of less interest to the general reader than it might well be to the literary antiquarian.
The next special literary enthusiasm of Mr. Horne and Miss Barrett was the projection of a work of criticism, to be issued anonymously, and entitled “The New Spirit of the Age.” They collaborated on the critique on Wordsworth and Leigh Hunt, and for the one on Landor Miss Barrett was mainly responsible, in which she says he “writes poetry for poets, and criticism for critics;... and as if poetry were not, in English, a sufficiently unpopular dead language, he has had recourse to writing poetry in Latin.” She speaks of his “Pericles and Aspasia” and his “Pentameron” as “books for the world and for all time, complete[Pg 61] in beauty of sentiment and subtlety of criticism.” Two of Landor’s works, very little known, the “Poems from the Arabic and Persian” and “A Satire upon Satirists,” are here noted. “It will be delightful to me to praise Tennyson,—although, by Saint Eloy, I never imitated him,” she writes to Mr. Horne; “and I take that oath because the Quarterly was sure that if it had not been for him I should have hung a lady’s hair ‘blackly’ instead of ‘very blackly.’” Miss Mitford was somewhat concerned with this hazardous venture, but she had no desire to discuss Dickens, as she “could not admire his love of low life!” Miss Barrett’s appreciation of Tennyson is much on record. She finds him “a divine poet.” Monckton Milnes, whose first work she liked extremely, seemed to her in his later poems as wanting in fire and imagination, and as being too didactic. Barry Cornwall’s lyrics impressed her “like embodied music.” Mr. Horne finally wrote the critique on Dickens, and of it Miss Barrett said: “I think the only omission of importance in your admirable essay is the omission of the influence of the French school of imaginative literature upon the mind of Dickens, which is manifest and undeniable.... Did you ever read the powerful Trois Jours d’un Condamné, and will you confront that with the tragic saliences of ‘Oliver Twist’?... We have no such romance writer as Victor Hugo ... George Sand is the greatest female genius of the world, at least since Sappho.” (At this time George Eliot had not appeared.) Miss Barrett appreciatively alludes to Sir Henry Taylor (the author of “Philip van Artevelde”) as “an infidel in poetry,” and to the author of “Festus” as “a man of great thoughts.” She finds part of the poem “weak,” but, “when all is said,” she continues, “what poet-stuff remains! what power! what fire of imagination, worth the stealing of Prometheus!”
In relation to some strictures on Carlyle, Miss Barrett[Pg 62] vivaciously replies that his object is to discover the sun, not to specify the landscape, and that it would be a strange reproach to bring against the morning star that it does not shine in the evening.
The idea of a lyrical drama, “Psyche Apocalypte,” was entertained by Mr. Horne and Miss Barrett, but, fortunately, no fragment of it was materialized into public light. There was a voluminous correspondence between them concerning this possible venture. Meanwhile Miss Barrett’s poems won success past her “expectation or hope. Blackwood’s high help was much,” she writes, “and I continue to have the kindest letters from unknown readers.... The American publisher has printed fifteen hundred copies. If I am a means of ultimate loss to him, I shall sit in sackcloth.”
In another of her letters to Mr. Horne we read that Wordsworth is in a fever because of a projected railroad through the Lake Country, and that Carlyle calls Harriet Martineau “quite mad,” because of her belief in Mesmerism. “For my own part,” adds Miss Barrett, “I am not afraid to say that I almost believe in Mesmerism, and quite believe in Harriet Martineau.” She is delighted that Horne’s “Orion” is to be published in New York. “I love the Americans,” she asserts, “a noble and cordial people.”
Miss Barrett remained for three years in Torquay, the climate being regarded as better for her health. But the tragedy of her life took place there in the drowning of her brother Edward, who went out one day with two friends in a boat and never returned. Three days later the boat was found floating, overturned, and the bodies of the three young men were recovered. This sad event occurred in the August of 1840, and it was more than a year before she was able to resume her literary work and her correspondence. In the September of 1841 she returned to[Pg 63] London, and in a letter to Mr. Boyd soon after she replied to his references to Gregory as a poet, saying she has not much admiration even for his grand De Virginitate, and chiefly regards him as one who is only poetical in prose.
Miss Barrett’s delicacy of health through all these years has been so universally recorded (and, according to her own words, so exaggerated) that it needs no more than passing allusion here. So far as possible she herself ignored it, and while it was always a factor to be reckoned with, yet her boundless mental energy tided her over illness and weakness to a far greater degree than has usually been realized. “My time goes to the best music when I read or write,” she says, “and whatever money I can spend upon my own pleasures flows away in books.”
Elizabeth Barrett was the most sympathetic and affectionate of friends, and her devotion to literature resulted in no mere academic and abnormal life. Her letters are filled with all the little inquiries and interests of household affection and sweetness of sympathy with the personal matters of relatives and friends, and if those are not here represented, it is simply that they are in their nature colloquial, and to be taken for granted rather than repeated for reading, when so long separated by time from the conditions and circumstances that called them forth. She was glad to return from Torquay to her family again. “Papa’s domestic comfort is broken up by the separation,” she said, “and the associations of Torquay lie upon me, struggle against them as I may, like a nightmare.... Part of me is worn out; but the poetical part—that is, the love of poetry—is growing in me as freshly every day. Did anybody ever love poetry and stop in the middle? I wonder if any one ever could?... besides, I am becoming better. Dear Mr. Boyd,” she entreats, “do not write another word about my illness either to me or to others. I am sure you would not willingly disturb me. I can’t let ... prescribe[Pg 64] anything for me except her own affection.” These words illustrate the spirit in which Miss Barrett referred to her own health. No one could be more remote from a morbid invalidism too often associated with her.
One of her first efforts after her return from Torquay was to send to the Athenæum some Greek translations, which, to her surprise, were accepted, and she writes to Mr. Boyd that she would enclose to him the editor’s letter “if it were legible to anybody except people used to learn reading from the Pyramids.” It must have been due to a suggestion from the editor of the Athenæum at this time that she wrote her noble and affluent essay on “The Greek Christian Poets,” which is perhaps her finest work in prose. Something in the courteous editorial note suggested this to her, and she discusses the idea with Mr. Boyd.
Mr. Dilke was then the editor of the Athenæum. He quite entered into the idea of this essay, only begging Miss Barrett to keep away from theology. Mr. Dilke also suggests that she write a review of English poetical literature, from Chaucer to contemporary times, and this initiated her essay called “The Book of the Poets.” For her Greek review she desired a copy of the Poetæ Christiani, but found the price (fourteen guineas) ruinous. But whether she had all the needful data or not, the first paper was a signal success, and she fancied that some bona avis, as good as a nightingale, had shaken its wings over her. Of the three Greek tragedians, Æschylus, Euripides, and Sophocles, Elizabeth Barrett had read every line. Plato she loved and read exhaustively; of Aristotle at this time she had read his Ethics, Poetics, and his work on Rhetoric, and of Aristophanes a few, only, of his plays. But Miss Barrett was also a great novel-reader, keeping her “pillows stuffed with novels,” as she playfully declared. Her room, in the upper part of the house, revealed the haunt of the scholar. Upon a bracket the bust of Homer looked[Pg 65] down; her bookcase showed one entire shelf occupied by the Greek poets; another relegated wholly to the English poets; and philosophy, ethics, science, and criticism were liberally represented. A bust of Chaucer companioned that of Homer. By her sofa nestled Flush, her dog, Miss Mitford’s gift.
It was in this year of 1841 that there penetrated into her atmosphere and consciousness the first intimation of Robert Browning. “Pippa Passes” had just been published, and John Kenyon, ever alert to bring any happiness into the lives of his friends (Kenyon, “the joy-giver,” as he was well termed), suggested introducing the young poet to her, but on the plea of her ill-health she declined. A little later, in a letter to Mr. Boyd, she mentions one or two comments made on her essay, “The Greek Christian Poets,”—that Mr. Horne, and also “Mr. Browning, the poet,” had both, as she was told, expressed approval. “Mr. Browning is said to be learned in Greek,” she adds, “especially the dramatists.” So already the air begins to stir and tremble with the coming of him of whom in later days she wrote:
“I yield the grave for thy sake, and resign
My near sweet view of heaven for earth with thee.”
The entrancing thrill of that wonderful Wagner music that ushers in the first appearance of the knight in the music-drama of “Lohengrin” is typical of the vibrations that thrill the air in some etherial announcement of experiences that are on the very threshold, and which are recognized by a nature as sensitive and impressionable as was that of Elizabeth Barrett. A new element with its transfiguring power awaited her, and some undefined prescience of that
“... most gracious singer of high poems”
whose music was to fall at her door
“... in folds of golden fulness”
haunted her like “an odor from Dreamland sent.”[Pg 66]
She pondered on
“... how Theocritus had sung
Of the sweet years, the dear and wished-for years,”
but she dared not dream that the “mystic Shape” that drew her backward, and whose voice spoke “in mastery,” had come to lead her,—not to Death, but Love.
| “... If a man could feel, Not one day in the artist’s ecstasy, But every day,—feast, fast, or working-day, The spiritual significance burn through The hieroglyphic of material shows, Henceforward he would paint the globe with wings.” |
“Bells and Pomegranates”—Arnould and Domett—“A Blot in the ’Scutcheon”—Macready—Second Visit To Italy—Miss Barrett’s Poetic Work—“Colombe’s Birthday”—“Lady Geraldine’s Courtship”—“Romances And Lyrics”—Browning’s First Letter To Miss Barrett—The Poets Meet—Letters of Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett—“Loves of the Poets”—Vita Nuova.
The appearance of “Bells and Pomegranates” made a deep impression on Elizabeth Barrett, as the numbers, opening with “Pippa Passes,” successively appeared between 1841 and 1846. Of “Pippa” she said she could find it in her heart to covet the authorship, and she felt all the combinations of effect to be particularly “striking and noble.” In a paper that Miss Barrett wrote in these days for the Athenæum, critically surveying the poetic outlook of the time, she referred to Browning and Tennyson as “among those high and gifted spirits who would still work and wait.” When this London journal reviewed (not too favorably) Browning’s “Romances and Lyrics,” Miss Barrett took greatly to heart the injustice that she felt was done him, and reverted to it in a number of personal[Pg 68] letters, expressing her conviction that “it would be easier to find a more faultless writer than a poet of equal genius.” An edition of Tennyson, in two volumes, came out, including the “Ulysses,” “Morte d’Arthur,” “Locksley Hall,” and “Œnone,” of which she says no one quite appeals to her as does “Œnone,” and she expresses her belief that philosophic thinking, like music, is always involved in high ideality of any kind. Wordsworth she insisted upon estimating from his best, not from his poorest work, and his “Ode” was to her so grand as to atone for a multitude of poetic sins. “I confess,” she wrote to Boyd, “that he is not unfrequently heavy and dull, and that Coleridge has an intenser genius.” To her cousin, Kenyon, Miss Barrett sent the manuscript of her poem, “The Dead Pan,” which he showed to Browning, who wrote of it to Kenyon with ardent admiration. This note was sent to Miss Barrett, who displayed it to Horne that he might see the opinion of the poet whom they both admired. Still later, Horne published in his “New Spirit of the Age” sketches of several writers with their portraits; and those of Carlyle, Miss Martineau, Wordsworth, Tennyson, and Browning, Miss Barrett had framed for her own room. She asked Kenyon if that of Browning were a good one. “Rather like,” he replied. So here and there the Fates were invisibly at work, forging the subtle threads that were drawing the poets unconsciously nearer.
It was the suggestion of Browning’s publisher, Moxon, that “Bells and Pomegranates” might be issued in pamphlet form, appearing at intervals, as this plastic method would be comparatively inexpensive, and would also permit the series to be stopped at any time if its success was not of a degree to warrant continuance. The poet found his title, as he afterward explained in a letter to Miss Barrett, in Exodus, “... upon the hem of the robe thou shalt make pomegranates of blue and of purple, and of[Pg 69] scarlet, and bells of gold between them round about.” After “Pippa Passes” there followed “King Victor and King Charles,” a number of Lyrics, “The Return of the Druses,” “A Blot in the ’Scutcheon,” “Luria,” and “A Soul’s Tragedy.” On each of the title-pages the author was named as the writer of “Paracelsus,” “Sordello” being ignored. Among the dedications of these several numbers those so honored included John Kenyon, Proctor, and Talfourd.
Browning offered “A Blot in the ’Scutcheon” to Macready (whose stage fortunes at this period were not brilliant), with the remark that “The luck of the third venture is proverbial.” The actor consulted Forster, who passed the play on to Dickens, to whom it deeply appealed. Under date of November 25, 1842, Dickens wrote of it to Forster in the most enthusiastic words, saying the reading of it had thrown him “into a perfect passion of sorrow,” and that it was “full of genius, natural, and great thoughts,... and I swear it is a tragedy that must be played, and played by Macready,” continued the novelist. “And tell Browning that I believe from my soul there is no man living (and not many dead) who could produce such a work.” Forster did not, however, administer this consolation to the young author, who was only to learn of Dickens’s admiration thirty years later, when Forster’s biography of him appeared. The story of the production of the play is told in a letter from Joseph Arnould to Alfred Domett (then in New Zealand), written under date of May, 1843, dated from Arnould’s home in Victoria Square, Pimlico:
“As one must begin somewhere, suppose we take Browning.... In February his play, ‘A Blot in the ’Scutcheon,’ was announced as forthcoming at Drury Lane.... Meantime, judicious friends had a habit of asking when the play was coming out....”[5]
[Pg 70]A long chapter of vexations is humorously described by Domett, who concludes his letter with this tribute to the play.
“... With some of the finest situations and grandest passages you can conceive, it does undoubtedly want a sustained interest to the end of the third act; in fact the whole of that act on the stage is a falling off from the second, which I need not tell you is, for purposes of performance, the most unpardonable fault. Still, it will no doubt—nay, it must—have done this, viz., produced a higher opinion than ever of Browning’s genius and the great things he is yet to do, in the minds not only of a clique, but of the general world of readers. This man will go far yet....”
While this vexation cancelled the friendly relations that had existed between Browning and Macready, it fostered the friendship between the poet and Helen Faucit (later Lady Martin), who remembered Browning’s attitude “as full of generous sympathy” for the actors of the cast; while he recalled Miss Faucit’s “perfect behavior as a woman, and her admirable playing, as the one gratifying factor” in the affair. But Browning was too noble by nature for any lasting resentment, and meeting Macready soon after the death of both his own wife, in Italy, and of Mrs. Macready, he could only grasp his old friend’s hand and exclaim with emotion, “Oh, Macready!”
In the autumn of 1844 Browning set forth for Italy on his second visit. Two years before his friend Domett had left England for New Zealand, commemorated by the poet in the lines,—
“How, forsooth, was I to know it
If Waring meant to glide away
Like a ghost at break of day.”
Browning landed at Naples, and there, according to Mrs. Orr, he became acquainted with a young Neapolitan,[Pg 71] Signor Scotti, who took the bargaining of their tour upon himself, after they had agreed to travel together, “and now as I write,” said Mr. Browning in a letter from his Naples hotel to his sister Sarianna, “I hear him disputing our bill. He does not see why we should pay for six wax candles when we have used only two.” The pair wandered over the enchanting shores of all the Naples region, lingered in Sorrento, drove over the picturesque road to Amalfi, and listened to the song of the sirens along the shore. Their arrival in Rome was Browning’s first sight of the Eternal City. Here Mr. Browning found an old friend, the Contessa Carducci, with whom the two passed most of their evenings. He made his poetic pilgrimage to the graves of Shelley and Keats, as do all later pilgrims, and he visited the grotto of Egeria in memory of Byron. He loitered in the old chiesa near Santa Maria Maggiore, where the sixteenth century Bishop “ordered his tomb,” and he visited Trelawney in Leghorn. There exists little record of this trip save in the poem “The Englishman in Italy,” and his return to England through Germany is alike unrecorded.
Six years had passed since the publication of “The Seraphim and Other Poems,” and on Mr. Browning’s arrival at home again, he found two new volumes of Miss Barrett’s, entitled simply “Poems,” in which were “A Drama of Exile,” “Bertha in the Lane,” “Catarina to Camoens,” “A Vision of Poets,” nearly all of the sonnets that she ever wrote save that immortal sequence, “Sonnets from the Portuguese,” and “Lady Geraldine’s Courtship.” These volumes absolutely established her poetic rank with that of Tennyson and Browning. She “heard the nations praising her far off.” While she had many expressions of grateful gladness for all this chorus of praise with hardly a dissenting voice, the verdict did not affect her own high standards. “I have written these poems as well as I could,” she says, “and I hope to write others better. I have not[Pg 72] reached my own ideal ... but I love poetry more than I love my own successes in it.”
Her love of absolute truth, and the absence of any petty self-love in her character, stand out in any study of her life. “Why, if you had told me that my books were without any value in your eyes, do you imagine that I should not have valued you, reverenced you ever after for your truth, so sacred a thing in friendship?” she writes to a friend.
The reviews are eminently appreciative and satisfying. Blackwood’s gave a long critique in a special article, frankly pointing out faults, but asserting that her merits far outweighed her defects, and that her genius “was profound, unsullied, and without a flaw.” The long poem, “A Drama of Exile” was pronounced the least successful of all, and the prime favorite was “Lady Geraldine’s Courtship.” Of this poem of ninety-two stanzas, with eleven more in its “Conclusion,” thirty-five of the stanzas, or one hundred and forty-four lines, were written in one day.
Though lack of health largely restricted Miss Barrett to her room, her sympathies and interests were world-wide. She read the reviews of the biography of Dr. Arnold, a work she desired to read, entire, and records that “Dr. Arnold must have been a man in the largest and noblest sense.” She rejoices in the refutation of Puseyism that is offered in the Edinburgh Review; she reads “an admirable paper by Macaulay” in the same number; she comments on the news that Newman has united himself with the Catholic Church; and in one letter she writes that Mr. Horne has not returned to England and adds: “Mr. Browning is not in England, either, so that whatever you send for him must await his return from the east, or west, or south, wherever he is; Dickens is in Italy; even Miss Mitford talks of going to France, and the ‘New Spirit of the Age’ is a wandering spirit.”
[Pg 73]In her “Lady Geraldine’s Courtship” had occurred the lines:
“Or from Browning some ‘Pomegranate,’ which, if cut deep down the middle,
Shows a heart within blood-tinctured, of a veined humanity.”
A certain consciousness of each other already stirred in the air for Browning and Miss Barrett, and still closer were the Fates drawing the subtle threads of destiny.
It was in this November that Mrs. Jameson first came into Miss Barrett’s life, coming to the door with a note, and “overcoming by kindness was let in.” This initiated a friendship that was destined in the near future to play its salient part in the life of Elizabeth Barrett. In what orderly sequence the links of life appear, viewed retrospectively!
She “gently wrangles” with Mr. Boyd for addressing her as “Miss Barrett,” deprecating such cold formality, and offering him his choice of her little pet name “Ba” or of Elizabeth.
She reads Hans Christian Andersen’s “Improvisatore,” and in reply to some expressed wonder at her reading so many novels she avows herself “the most complete and unscrupulous romance reader” possible; and adds that her love of fiction began with her breath, and will end with it; “and it goes on increasing. On my tombstone may be written,” she continued, “‘Ci gît the greatest novel reader in the world,’ and nobody will forbid the inscription.”
And so the prelude of her life draws to a close, and the future is to be no more the mere living “with visions for her company,” for now, in this January of 1845, she has a letter from Browning, and she writes: “I had a letter from Browning, the poet, last night, which threw me into ecstasies,—Browning, the author of ‘Paracelsus,’ and king of the mystics.” Not long after she writes that she is getting[Pg 74] deeper and deeper into correspondence with Robert Browning, and that they are growing to be the truest of friends. Lowell writes to Miss Barrett regarding her poems, though the letter does not seem to be anywhere on record, and she writes to Mr. Westwood that in her view Mr. Browning’s power is of a very high order, and that he must read “Paracelsus.” In its author she finds one who “speaks true oracles.” She finds “Colombe’s Birthday” exquisite, and “Pippa Passes” she “kneels to, with deepest reverence.”
The first letter of Browning to Miss Barrett was written on January 10 of this year (1845), and he began with the words: “I love your verses with all my heart, dear Miss Barrett.” He enters into the “fresh strange music, the exquisite pathos, and true, brave thought” of her work; and reminds her that Kenyon once asked him if he would like to see Miss Barrett, but that she did not feel able, and he felt as if close to some world’s wonder, but the half-opened door shut. Her reply, which is dated the next day, thanks him for his sympathy and offers him her gratitude, “agreeing that of all the commerce from Tyre to Carthage, the exchange of sympathy for gratitude is the most princely thing.” And she craves a lasting obligation in that he shall suggest her master-faults in poetry. She does not pretend to any extraordinary meekness under criticism, and possibly might not be at all obedient to it, but she has such high respect for his power in Art, and his experience as an artist. She refers to Mr. Kenyon as her friend and helper, and her books’ friend and helper, “critic and sympathizer, true friend at all hours!” and she adds that “while I live to follow this divine art of poetry ... I must be a devout student and admirer of your works.”
Browning is made very happy by her words, and he feels that his poor praise “was nearly as felicitously brought out as a certain tribute to Tasso, which amused me in Rome[Pg 75] some weeks ago,” he says. “In a neat penciling on the wall by his tomb at Sant’ Onofrio—‘Alla cara memoria—di—Torquato Tasso—il Dottore Bernardini—offriva—il sequente Carme—tu’—and no more; the good man, it would seem, breaking down with the over-load of love here! But my ‘O tu’ was breathed out most sincerely, and now you have taken it in gracious part, the rest will come after.” And then he must repeat (to himself) that her poetry must be infinitely more to him than his could be to her, “for you do what I have only hoped to do.” And he hopes she will nevermore talk of “the honor” of his acquaintance, but he will joyfully wait for the delight of her friendship. And to his fear that she may hate letter-writing she replies suggesting that nobody likes writing to everybody, but it would be strange and contradictory if she were not always delighted to hear from and to write to him; and she can read any manuscript except the writing on the pyramids, and if he will only treat her en bon camarade “without reference to the conventionalities of ‘ladies and gentlemen’”; taking no thought for his sentences (or hers), “nor for your badd speling nor for mine,” she is ready to sign and seal the contract of correspondence. And while she throws off the ceremony, she holds faster to the kindness. She is overjoyed with this cordial sympathy. “Is it true,” she asks, “that I know so little of you? And is it true that the productions of an artist do not partake of his real nature? It is not true to my mind,—and therefore it is not true that I know little of you, except in so far as it is true that your greatest works are to come.... I think—if I may dare name myself with you in the poetic relation—that we both have high views of the Art we follow and steadfast purpose in the pursuit of it.... And that neither of us would be likely to be thrown from the course by the casting of any Atalanta ball of speedy popularity.
[Pg 76]“And after all that has been said and mused upon the anxiety experienced by the true artist,—is not the good immeasurably greater than the evil? For my part I sometimes wonder how, without such an object and purpose of life, people contrive to live at all.”
And her idea of happiness “lies deep in poetry and its associations.” And he replies that what he has printed “gives no knowledge of me,” and that he has never begun what he hopes he was born to begin and end—“R. B. a poem.”
“Do you know Tennyson?” she asks, “that is, with a face to face knowledge? I have great admiration for him,” she continues. “In execution he is exquisite,—and in music a most subtle weigher out to the ear of fine airs.” And she asks if he knows what it is to covet his neighbor’s poetry,—not his fame, but his poetry. It delights her to hear of his garden full of roses and his soul full of comforts. She finds the conception of his Pippa “most exquisite, and altogether original.”
In one of Miss Barrett’s letters a few weeks later there seems discernible a forecast of “Aurora Leigh,” when she writes that her chief intention is the writing “of a sort of novel-poem,” and one “as completely modern as ‘Geraldine’s Courtship,’ running into the midst of our conventions, and rushing into drawing-rooms and the like ‘where angels fear to tread’; and so meeting face to face and without mask the Humanity of the age, and speaking the truth, as I conceive of it, out plainly.” She is waiting for a story; she will not take one, because she likes to make her own. Here is without doubt the first conception of “Aurora Leigh.”
Touching on Life in another letter, she records her feeling that “the brightest place in the house is the leaning out of the window.”
Browning replies: “And pray you not to lean out of the window when my own foot is only on the stair.”...
[Pg 77]“But I did not mean to strike a tragic chord,” she replies; “indeed I did not. As to ‘escaping with my life,’ it was just a phrase ... for the rest I am essentially better ... and feel as if it were intended for me to live and not to die.” And referring to a passage relating to Prometheus she asks: “And tell me, if Æschylus is not the divinest of all the divine Greek souls?” She continues:
“But to go back to the view of Life with the blind Hopes; you are not to think—whatever I may have written or implied—that I lean either to the philosophy or affectation which beholds the world through darkness instead of light ... and after a course of bitter mental discipline and long bodily seclusion I come out with two lessons learned—the wisdom of cheerfulness and the duty of social intercourse. Anguish has instructed me in joy, and solitude in society.... What we call life is a condition of the soul, and the soul must improve in happiness and wisdom, except by its own fault.... And I do like to hear testimonies like yours, to happiness, and I feel it to be a testimony of a higher sort than the obvious one.... Remember, that as you owe your unscathed joy to God, you should pay it back to His world. I thank you for some of it already.”
And she feels how kind he is,—how gently and kindly he speaks to her. In his next letter he alludes with much feeling to her idea of the poem-novel:
“The Poem you propose to make; the fresh, fearless, living work you describe, is the only Poem to be undertaken now by you or any one who is a poet at all; the only reality, only effective piece of service to be rendered God or man; it is what I have been all my life intending to do, and now shall be much nearer doing since you will be along with me. And you can do it, I know and am sure,—so sure that I could find it in my heart to be jealous of your stopping on the way even to translate the Prometheus....”
[Pg 78]The lovers, for such they already are, however unconsciously to both, fall into a long discussion of Prometheus, and the Greek drama in general, and in another letter, with allusion to his begging her to take her own good time in writing, she half playfully proffers that it is her own bad time to which she must submit. “This implacable weather!” she writes; “this east wind that seems to blow through the sun and the moon!... There will be a May and June if we live to see such things,” and then she speaks of seeing him besides, and while she recognizes it is morbid to shrink and grow pale in the spirit, yet not all her fine philosophy about social duties quite carries her through. But “if he thinks she shall not like to see him, he is wrong, for all his learning.” What pathos of revelation of this brave, celestial spirit, tenanting the most fragile of bodies, is read in the ensuing passage:
“What you say of society draws me on to many comparative thoughts of your life and mine. You seem to have drunken of the cup of life full with the sun shining on it. I have lived only inwardly, or with sorrow for a strong emotion. Before this seclusion of my illness I was secluded still, and there are few of the youngest women in the world who have not seen more, known more, of society, than I, who am hardly to be called young now. I grew up in the country, had no social opportunities, had my heart in books and poetry, and my experience in reveries.... Books and dreams were what I lived in—and domestic life seemed to buzz gently around, like the bees about the grass.... Why, if I live on and escape this seclusion, do you not perceive that I labor under signal disadvantages, that I am, in a manner, a blind poet?... I have had much of the inner life ... but how willingly would I exchange some of this ponderous, helpless knowledge of books for some experience of life.... But grumbling is a vile thing, and we should all thank God for our measures of life, and think them enough.... Like to write? Of course, of course I do. I seem to live while I write—it is life for me. Why, what is it to live? Not to eat[Pg 79] and drink and breathe,—but to feel the life in you down all the fibers of being, passionately and joyfully....
“Ah, you tempt me with a grand vision of Prometheus!... I am inclined to think that we want new forms.... The old gods are dethroned. Why should we go back to the antique moulds? If it is a necessity of Art to do this, then those critics are right who hold that Art is exhausted.... I do not believe this; and I believe the so-called necessity of Art to be the mere feebleness of the artist. Let us all aspire rather to Life.... For there is poetry everywhere....”
Miss Barrett writes to him, continuing the discussion of poetry as an Art, that she does not want “material as material, but that every life requires a full experience,” and she has a profound conviction that a poet is at a lamentable disadvantage if he has been shut from most of the outer aspects of life. And he, replying, deprecates a little the outward life for a poet, with amusing references to a novel of D’Israeli’s, where, “lo, dinner is done, and Vivian Grey is here, and Violet Fane there, and a detachment of the party is drafted off to catch butterflies.” But still he partly agrees, and feels that her Danish novel (“The Improvisatore”) must be full of truth and beauty, and “that a Dane should write so, confirms me in a belief that Italy is stuff for the use of the North and no more—pure Poetry there is none, as near as possible none, in Dante, even;... and Alfieri,... with a life of travel, writes you some fifteen tragedies as colorless as salad grown under a garden glass....” But she—if she asks questions about novels it is because she wants to see him by the refracted lights, as well as by the direct ones; and Dante’s poetry—“only material for northern rhymers?” She must think of that before she agrees with him.
As for Browning, he bids her remember that he writes letters to no one but her; but there is never enough of telling her.... And she, noting his sitting up in the morning[Pg 80] till six, and sleeping only till nine, wants to know “how ‘Lurias’ can be made out of such ungodly imprudences? And what is the reasonableness of it,” she questions, “when we all know that thinking, dreaming, creative people, like yourself, have two lives to bear instead of one, and therefore ought to sleep more than others”; and he is anticipating the day when he shall see her with his own eyes, and now a day is named on which he will call, and he begs her not to mind his coming in the least, for if she does not feel able to see him he will come again, and again, as his time is of no importance.
It was on the afternoon of May 20 (1845) that Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett first met, and of them it could almost have been said, in words ascribed to Michael Angelo for Vittoria Colonna,—
“We are the only two, that, face to face,
Do know each other, as God doth know us both.”
It is said that the first letter of Browning’s to her after this meeting is the only one destroyed of all this wonderful correspondence; and this was such a letter as could only be interpreted into a desire for marriage, which she, all tender thoughtfulness always for others, characteristically felt would be fatal to his happiness because of her invalid state. He begged her to return the letter, and he then destroyed it; and again pleaded that their friendship and intellectual comradeship should continue. “Your friendship and sympathy will be dear and precious to me all my life, if you indeed leave them with me so long, or so little,” she writes; and she utterly forbids any further expression or she must do this “to be in my own eyes and before God a little more worthy, or a little less unworthy, of a generosity....” And he discreetly veils his ardors for the time, and the wonderful letters run on.
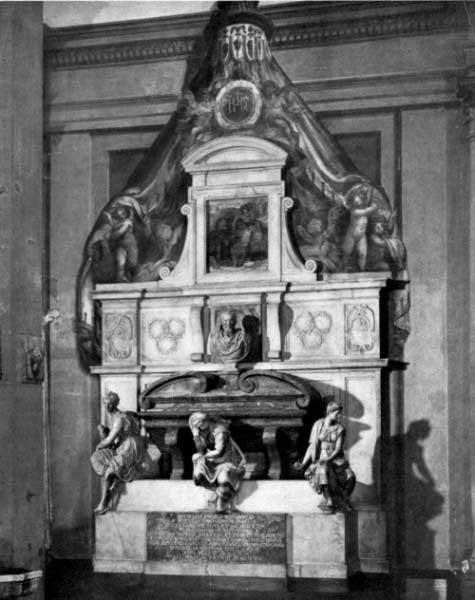

Monument to Michael Angelo, by Vasari
church of santa croce.
| “They are safe in heaven.... The Michaels and Rafaels....” |
| Old Pictures in Florence. |
He is writing “The Flight of the Duchess,” and sending[Pg 81] it to her by installments; she finds it “past speaking of,” and she also refers to “exquisite pages” of Landor’s in the “Pentameron.” And poems which he has left with her,—she must have her own gladness from them in her own way. And did he go to Chelsea, and hear the divine philosophy?
Apparently he did, for he writes:
“Yes, I went to Chelsea and found dear Carlyle alone—his wife is in the country where he will join her as soon as the book’s last proof sheets are corrected.... He was all kindness, and talked like his own self while he made me tea—and would walk as far as Vauxhall Bridge with me on my way home.”
She writes:
“I had a letter yesterday from Charles Hemans, the son of Felicia, ... who says his mother’s memory is surrounded to him ‘with almost a divine lustre,’... and is not that better than your tradition about Shelley’s son? and is it not pleasant to know that the noble, pure-hearted woman, the Vittoria Colonna of our country, should be so loved and comprehended by one, at least, of her own house?”
Under date of August 25, Miss Barrett has been moved to write out the pathetic story of her brother Edward’s death. He had accompanied her to Torquay,—he, “the kindest, the noblest, the dearest, and when the time came for him to return I, weakened by illness, could not master my spirits or drive back my tears,” and he then decided not to leave her. “And ten days from that day,” she continued, “the boat left the shore which never returned—and he had left me! For three days we waited,—oh, that awful agony of three days!... Do not notice what I have written to you, my dearest friend. I have never said so much to a living being—I never could speak or write of it....”
But he writes her that “better than being happy in her[Pg 82] happiness, is it to participate in her sorrow.” And the very last day of that August he writes that he has had such power over himself as to keep silent ... but “Let me say now—this only once,—that I loved you from my soul, and gave you my life, as much of it as you would take, and all that ... is independent of any return on your part.” She assures him that he has followed the most generous of impulses toward her, “yet I cannot help adding that, of us two, yours has not been quite the hardest part.” She confesses how deeply she is affected by his words, “but what could I speak,” she questions, “that would not be unjust to you?... Your life! if you gave it to me and I put my whole heart into it, what should I put in but anxiety, and more sadness than you were born to? What could I give you which it would not be ungenerous to give?”
There was a partial plan that Miss Barrett should pass that next winter in Pisa, but owing to the strange and incalculable disposition of her father, who, while he loved her, was singularly autocratic in his treatment, the plan was abandoned. All this sorrow may have contributed to her confession to Browning that no man had ever been to her feelings what he was; and that if she were different in some respects she would accept the great trust of his happiness.... “But we may be friends always,” she continues, “and cannot be so separated that the knowledge of your happiness will not increase mine.... Worldly thoughts these are not at all, there need be no soiling of the heart with any such;... you cannot despise the gold and gauds of the world more than I do,... and even if I wished to be very poor, in the world’s sense of poverty, I could not, with three or four hundred a year, of which no living will can dispossess me. And is not the chief good of money, the being free from the need of thinking of it?” But he, perfect in his beautiful trust and tenderness, was “joyfully confident” that the way would open, and he[Pg 83] thanks God that, to the utmost of his power, he has not been unworthy of having been introduced to her. He is “no longer in the first freshness of his life” and had for years felt it impossible that he should ever love any woman. But he will wait. That she “cannot dance like Cerito” does not materially disarrange his plan! And by the last of those September days she confesses that she is his “for everything but to do him harm,” he has touched her so profoundly, and now “none, except God and your own will, shall interpose between you and me.” And he answered her in such words as these:
“When I come back from seeing you and think over it all, there is never a least word of yours I could not occupy myself with....”
In a subsequent letter Elizabeth Barrett questions: “Could it be that heart and life were devastated to make room for you? if so it was well done.” And she sends thanks to Browning’s sister, Sarianna, for a copy of Landor’s verses.
And with all these gracious and tenderly exquisite personal matters, the letters are yet brilliant in literary allusion and criticism.
During these three years from 1844 to 1847 were written the greater number of Miss Barrett’s finest lyrics. Those two remarkable poems, “A Rhapsody of Life’s Progress” and “Confessions”; “Loved Once”; “The Sleep” (the poem which was read at her burial in the lovely, cypress-crowned cemetery in Florence, and whose stanzas, set to music, were chanted by the choir in Westminster Abbey when the body of her husband was laid in the “Poets’ Corner”), “The Dead Pan,” and that most exquisite lyric of all, “Catarina to Camoens,” were all written during this period.
The title of the latter was but a transparent veil for her own feelings toward Robert Browning, and had she[Pg 84] died in his absence, as Catarina did in that of Camoens, the words would have expressed her own feeling. What profound pathos is in the line,
“Death is near me,—and not you,”
and how her own infinite sweetness of spirit is mirrored in the stanza,
“I will look out to his future;
I will bless it till it shine,
Should he ever be a suitor
Unto sweeter eyes than mine.”
And read her own self-revelation again in “A Denial,”
“We have met late—it is too late to meet,
O friend, not more than friend!”
But the denial breaks down, and the last lines tell the story:
“Here’s no more courage in my soul to say
‘Look in my face and see.’”
And in that last line of “Insufficiency,”
“I love thee so, Dear, that I only can leave thee.”
In “Question and Answer,” in “Proof and Disproof,” “A Valediction,” “Loved Once,” and “Inclusions,” he who reads between the lines and has the magic of divination may read the story of her inner life.
In the poem “Confessions” is touched a note of mystical, spiritual romance, spiritual tragedy, wholly of the inner life, that entirely differentiates from any other poetic expression of Mrs. Browning. In one stanza occur these lines:
“The least touch of their hands in the morning, I keep it by day and by night;
Their least step on the stair, at the door, still throbs through me, if ever so light.”
[Pg 85]Even with all allowance for the imagination of the poet, these lines reveal such feeling, such tremulous susceptibility, that with less intellectual balance than was hers, combined with such lack of physical vigor, would almost inevitably have resulted in failure of poise. The current of spiritual energy was so strong with Elizabeth Barrett as to largely take the place of greater physical strength. That she never relapsed into the conditions of morbid invalidism is a marvel, and it is also an impressive testimony to the power of spiritual energy to control and determine physical conditions.
All through that summer the letters run on, daily, semi-daily. Of his work Browning writes that he shall be “prouder to begin one day,—may it be soon!—with your hand in mine from the beginning.” Miss Barrett, referring to the Earl of Compton, who is reported from Rome as having achieved some prominence as a painter, proceeds to say:
“People in general would rather be Marquises than Roman artists, consulting their own wishes and inclination. I, for my part, ever since I could speak my mind and knew it, always openly and inwardly preferred the glory of those who live by their heads, to the opposite glory of those who carry other people’s arms. So much for glory. Happiness goes the same way to my fancy. There is something fascinating to me in that Bohemian way of living.... All the conventions of society cut so close and thin, that the soul can see through.... Beyond, above. It is real life as you say ... whether at Rome or elsewhere. I am very glad that you like simplicity in habits of life—it has both reasonableness and sanctity.... I am glad that you—who have had temptation enough, more than enough, I am sure, in every form—have lived in the midst of this London of ours, close to the great social vortex, yet have kept so safe, and free, and calm, and pure from the besetting sins of our society.”
[Pg 86]Browning, in one letter, alluding to the prevailing stupidity of the idea that genius and domestic happiness are incompatible, says: “We will live the real answer, will we not?... A man of genius mistreats his wife; well, take away the genius,—does he so instantly improve?”
Of the attitude of his family toward their marriage he writes:
“My family all love you, dearest,—you cannot conceive my father’s and mother’s childlike faith in goodness—and my sister is very high-spirited, and quick of apprehension—so as to seize the true point of the case at once.... Last night I asked my father, who was absorbed over some old book, if he should not be glad to see his new daughter?—to which he, starting, replied, ‘Indeed I shall’; with such a fervor as to make my mother laugh,—not abated by his adding: ‘And how I should be glad of her seeing Sarianna!’”
And she writes:
“Shall we go to Greece, then, Robert? Let us, if you like it. When we have used a little the charm of your Italy,... I should like to see Athens with my living eyes.... Athens was in all the dreams I dreamed, before I knew you. Why should we not see Athens, and Egypt, too, and float down the mystical Nile, and stand in the shadow of the Pyramids? All of it is more possible now, than walking up the street seemed to me last year.”
And he writes that he always felt her “Wine of Cyprus” poem to fill his heart “with unutterable desires.”
To book-lovers the question as to how many books may be taken on a journey, or what volumes, indeed, may be left behind, is a vital one. The reader will smile sympathetically at Miss Barrett’s consultation with Browning as to whether, if they do “achieve the peculiar madness of going to Italy,” they could take any books? And whether it would be well to so arrange that they should not take[Pg 87] duplicates? He advises the narrowest compass for luggage. “We can return for what we want, or procure it abroad,” he says, made wise by his two Italian journeys; and he adds:
“I think the fewer books we take the better; they take up room,—and the wise way always seemed to me to read at home, and open one’s eyes and see abroad. A critic somewhere mentioned that as my characteristic—there were two other poets he named placed in novel circumstances ... in a great wood, for instance, Mr. Trench would begin opening books to see how woods were treated ... the other man would set to writing poetry forthwith,—and R. B. would sit still and learn how to write after! A pretty compliment, I thought that. But, seriously, there must be a great library at Pisa (with that University) and abroad they are delighted to facilitate such matters.... I have read in a chamber of the Doges’ palace at Venice painted all over by Tintoretto, walls and ceiling, and at Rome there is a library with a learned priest always kept ready ‘to solve any doubts that may arise.’”
Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett were married on September 12, 1846, in the church of St. Pancras, Marylebone, the only witnesses being his cousin, James Silverthorne, and her maid, Wilson. To have taken her sisters into her confidence would have been to expose them to the fairly insane wrath of her father. “I hate and loathe everything which is clandestine—we both do, Robert and I,” said Mrs. Browning later; but this was the only possible way. Had Mr. Browning spoken to her father in the usual manner, “he would have been forbidden the house without a moment’s scruple,” she explained to a friend; “and I should have been incapacitated from any after exertion by the horrible scenes to which, as a thing of course, I should have been exposed.... I cannot bear some words. In my actual state of physical weakness, it would have been the sacrifice of my whole life—of my convictions, of my[Pg 88] affections, and, above all, of what the person dearest to me persisted in calling his life, and the good of it—if I had observed that ‘form.’ Therefore I determined not to observe it, and I consider that in not doing so, I sinned against no duty. That I was constrained to act clandestinely, and did not choose to do so, God is my witness. Also, up to the very last, we stood in the light of day for the whole world, if it please, to judge us. I never saw him out of the Wimpole Street house. He came twice a week to see me, openly in the sight of all.”
In no act of her life did Mrs. Browning more impressively reveal her good sense than in this of her marriage. “I had long believed such an act,” she said, “the most strictly personal of one’s life,—to be within the rights of every person of mature age, man or woman, and I had resolved to exercise that right in my own case by a resolution which had slowly ripened. All the other doors of life were shut to me, and shut me as in a prison, and only before this door stood one whom I loved best and who loved me best, and who invited me out through it for the good’s sake he thought I could do him.”... To a friend she explained her long refusal to consent to the marriage, fearing that her delicate health would make it “ungenerous” in her to yield to his entreaty; but he replied that
“he would not tease me, he would wait twenty years if I pleased, and then, if life lasted so long for both of us, then, when it was ending, perhaps, I might understand him and feel that I might have trusted him.... He preferred, he said, of free and deliberate choice, to be allowed to sit only an hour a day by my side, to the fulfillment of the brightest dream which should exclude me, in any possible world.”
She continues:
“I tell you so much that you may see the manner of man I had to do with, and the sort of attachment which for nearly two[Pg 89] years has been drawing and winning me. I know better than any in the world, indeed, what Mr. Kenyon once unconsciously said before me, that ‘Robert Browning is great in every thing.’... Now may I not tell you that his genius, and all but miraculous attainments, are the least things in him, the moral nature being of the very noblest, as all who ever knew him admit.”
After the marriage ceremony Mrs. Browning drove with her maid to the home of Mr. Boyd, resting there, as if making a morning call on a familiar friend, until joined by her sisters, who took her for a little drive on Hampstead Heath. For five days she remained in her father’s house, and during this time Browning could not bring himself to call and ask for his wife as “Miss Barrett,” so they arranged all the details of their journey by letter. On September 19 they left for Paris, and the last one of these immortal letters, written the evening before their departure, from Mrs. Browning to her husband, contains these words:
“By to-morrow at this time I shall have you, only, to love me, my beloved! You, only! As if one said, God, only! And we shall have Him beside, I pray of Him!”
With her maid, Mrs. Browning walked out of her father’s house the next day, meeting her husband at a bookseller’s around the corner of the street, and they drove to the station, leaving for Southampton to catch the night boat to Havre.
Never could the world have understood the ineffable love and beauty and nobleness of the characters of both Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning, had these letters been withheld from the public. Quite aside from the deeper interest of their personal revelation,—the revelation of such nobleness and such perfect mutual comprehension and tenderness of sympathy as are here revealed,—the pages are full of interesting literary allusion and comment, of wit, repartee, and of charm that defies analysis. It was a wise[Pg 90] and generous gift when the son of the poets, Robert Barrett Browning, gave these wonderful letters to the reading public. The supreme test of literature is that which contributes to the spiritual wealth of the world. Measured by this standard, these are of the highest literary order. No one can fail to realize how all that is noblest in manhood, all that is holiest in womanhood, is revealed in this correspondence.
Edmund Clarence Stedman, after reading these letters, said: “It would have been almost a crime to have permitted this wonderful, exceptional interchange of soul and mind, between these two strong, ‘excepted’ beings, to leave no trace forever.”
Robert Barrett Browning, in referring to his publication of this correspondence in a conversation with the writer of this volume, remarked that he really had no choice in the matter, as the Apochryphal legends and myths and improvisations that had even then begun to weave themselves about the remarkable and unusual story of the acquaintance, courtship, and marriage of his parents, could only be dissipated by the simple truth, as revealed in their own letters.
Their love took its place in the spiritual order; it was a bond that made itself the mystic force in their mutual development and achievement; and of which the woman, whose reverence for the Divine Life was the strongest element in her nature, could yet say,—
“And I, who looked for only God, found thee!”
Life, as well as Literature, would have been the poorer had not Mr. Barrett Browning so wisely and generously enriched both by the publication of this correspondence.
Not the least among the beautiful expressions that have been made by those spirits so touched to fine issues as to enter into the spiritual loveliness of these letters of Robert[Pg 91] Browning and Elizabeth Barrett, is a sonnet by a New England poet, Rev. William Brunton,—a poet who “died too soon,” but whose love for the poetry of the Brownings was as ardent as it was finely appreciative:
“Oh! dear departed saints of highest song,
Behind the screen of time your love lay hid,
Its fair unfoldment was in life forbid—
As doing such divine affection wrong,
But now we read with interest deep and strong,
And lift from off the magic jar the lid,
And lo! your spirit stands the clouds amid
And speaks to us in some superior tongue!
“Devotion such as yours is heavenly-wise,
And yet the possible of earth ye show;
Ye dwellers in the blue of summer skies,
Through you a finer love of love we know;
It is as if the angels moved with men,
And key of Paradise were found again!”
| “And on her lover’s arm she leant And round her waist she felt it fold, And far across the hills they went To that new world which is the old. Across the hills, and far away, Beyond their utmost purple rim, Beyond the night, beyond the day, Through all the world she followed him.” |
Marriage and Italy—“In that New World”—The Haunts of Petrarca—The Magic Land—In Pisa—Vallombrosa—“Un Bel Giro”—Guercino’s Angel—Casa Guidi—Birth of Robert Barrett Browning—Bagni di Lucca—“Sonnets from the Portuguese”—The Enchantment of Italy.
Paris, “and such a strange week it was,” wrote Mrs. Browning to Miss Mitford; “whether in the body, or out of the body, I can scarcely tell. Our Balzac should be flattered beyond measure by my even thinking of him at all.” The journey from London to Paris was not then quite the swift and easy affair it now is, the railroad between Paris and Havre not being then completed beyond Rouen; still, such an elixir of life is happiness that Mrs. Browning arrived in the French Capital feeling much better than when she left London. Mrs. Jameson had only recently taken leave of Miss Barrett on her sofa, and sympathetically offered to take her to Italy herself for the winter with her niece; Miss Barrett had replied: “Not only am I grateful to you, but happy to be grateful to you,” but she had given no hint of the impending marriage.[Pg 93] Mrs. Jameson’s surprise, on receiving a note from Mrs. Browning, saying she was in Paris, was so great that her niece, Geraldine Bate (afterward Mrs. MacPherson of Rome), asserted that her aunt’s amazement was “almost comical.” Mrs. Jameson lost no time in persuading the Brownings to join her and her niece at their quiet pension in the Rue Ville l’Eveque, where they remained for a week,—this “strange week” to Mrs. Browning.
In Paris they visited the galleries of the Louvre, but did little sight-seeing beyond, “being satisfied with the idea of Paris,” she said.
To a friend Mrs. Jameson wrote:
“I have also here a poet and a poetess—two celebrities who have run away and married under circumstances peculiarly interesting, and such as render imprudence the height of prudence. Both excellent; but God help them! for I know not how the two poet heads and poet hearts will get on through this prosaic world.”
As for ways and means, however, the Brownings were sufficiently provided. He had a modest independence, and she also had in her own right a little fortune of some forty thousand pounds, yielding three or four hundred pounds a year; but in the July preceding their marriage Browning, with his sensitive honor, insisted upon her making a will bequeathing this capital to her own family. In a letter to him dated July 27 of that summer the story of his insistence on this is revealed in her own words: “I will write the paper as you bid me.... You are noble in all things ... but I will not discuss it so as to tease you.... I send you the paper therefore, to that end, and only to that end....” The “document,” by Browning’s insistence, gave her property to her two sisters, in equal division, or, in case of their death, to the surviving brothers. Nothing less than this would satisfy Robert Browning.
[Pg 94]Meantime, there was the natural London comment. Wordsworth observed: “So Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett have gone off together! It is to be hoped they can understand each other, for no one else can.”
Mr. Kenyon wrote “the kindest letter” to them both, and pronounced them “justified to the uttermost,” and to Mrs. Browning he said: “I considered that you had imperiled your life upon this undertaking and I still thought you had done wisely!” But by that magic alchemy of love and happiness Mrs. Browning only gained constantly in strength, and Mrs. Jameson pronounced them “wise people, whether wild poets or not.”
Among the interesting comments on the marriage was Joseph Arnould’s letter to Alfred Domett, under date of November of that year. He wrote:
“... I think the last piece of news I told you of was Browning’s marriage to Miss Barrett. She is, you know, our present greatest living English poetess: ... she has been in the most absolute and enforced seclusion from society; cultivating her mind to a wonderful amount of accomplishment, instructing herself in all languages, reading Chrysostom in the original Greek, and publishing the best metrical translation that has yet appeared of the ‘Prometheus Bound’—having also found time to write three volumes of poetry, the last of which raised her name to a place second only to that of Browning and Tennyson, amongst all those who are not repelled by eccentricities of external form from penetrating into the soul and quintessential spirit of poetry that quickens the mould into which the poet has cast it. Well, this lady, so gifted, so secluded, so tyrannized over, fell in love with Browning in the spirit before ever she saw him in the flesh—in plain English, loved the writer, before she knew the man. Imagine, you who know him, the effect which his graceful bearing, high demeanor, and noble speech must have had on such a mind when first she saw the man of her visions in the twilight of her darkened room. She was at once in love as a poet-soul only can be; and Browning, as[Pg 95] by contagion or electricity, was no less from the first interview wholly in love with her.... He is a glorious fellow! Oh, I forgot to say that the soi-disante invalid, once emancipated from the paternal despotism, has had a wondrous revival, or rather, a complete metamorphosis; walks, rides, eats, and drinks like a young and healthy woman,—in fact, is a healthy woman of, I believe, some five and thirty. But one word covers all; they are in Love, who lends his own youth to everything.”
The journey from Paris to Italy, if less comfortable and expeditious than now, was certainly more romantic, and the Brownings, in company with Mrs. Jameson and her niece, fared forth to Orleans, and thence to Avignon, where they rested for two days, making a poetic pilgrimage to Vaucluse, where Petrarca had sought solitude. “There at the very source of the ‘chiare, fresche e dolci acque,’” records Mrs. MacPherson in her biography of Mrs. Jameson, “Mr. Browning took his wife up in his arms, and carrying her across through the shallow, curling waters, seated her on a rock that rose throne-like in the middle of the stream. Thus Love and Poetry took a new possession of the spot immortalized by Petrarca’s fancy.”
From Marseilles they sailed to Livorno (Leghorn), the port only a few miles from Pisa. The voyage was a delight to Mrs. Browning. She was enchanted with the beautiful panorama of the Riviera as they sailed down the coast, where the terraces of mountains rise, with old castles and ruins often crowning their summits, and the white gleam of the hill-towns against a background of blue sky. All the Spezzia region was haunted by memories of Shelley; Lerici, where last he had lived, was plainly in view, and they gazed sadly at Viareggio, encircled by pine woods and mountains, where the body of the poet had been found. In Pisa they took rooms in the Collegio Fernandino, in the Piazza del Duomo, in that corner of Pisa wherein are grouped the Cathedral, the Baptistery, the Leaning Tower,[Pg 96] and the Campo Santo, all in this consummate beauty of silence and seclusion,—a splendor of abandoned glory. All the stir of life (if, indeed, one may dream of life in Pisa) is far away on the other side of the city; to this corner is left the wraith-like haunted atmosphere, where only shadows flit over the grass, and the sunset reflections linger on the Tower. A statue of Cosimo di Medici was near; the Lanfranchi palace, where Byron had lived, was not far away, on the banks of the Arno. They quite preferred the Duomo and the Campo Santo to social festivities, and Professor Ferrucci offered them all the hospitalities of the University library. They had an apartment of four rooms, “matted and carpeted,” coffee and rolls in the morning, dinner at the Trattoria, “thrushes and chianti with a marvelous cheapness, no trouble, no cook, no kitchen; the prophet Elijah, or the lilies of the field, took as little thought for their dining,” writes Mrs. Browning, “and it exactly suits us. At nine we have our supper of roast chestnuts and grapes.... My head goes round sometimes. I was never happy before in my life.... And when I am so good as to let myself be carried up-stairs, and so angelical as to sit still on the sofa, and so considerate as not to put my foot into a puddle, why, my duty is considered done to a perfection worthy all adoration.... Mrs. Jameson and Geraldine are staying in the hotel, and we manage to see them every day; so good and true and affectionate she is, and so much we shall miss her when she goes.... Our present residence we have taken for six months, but we have dreams, and we discuss them like soothsayers over the evening grapes and chestnuts.”
That in London Mrs. Jameson, on her first call on Miss Barrett, should have so winningly insisted on being admitted to her room as to be successful, almost to Miss Barrett’s own surprise, seems, when seen in connection with the way in which Fate was to throw them together[Pg 97] afterward, in Italy, to have been one of those “foreordained” happenings of life.
They heard a musical mass for the dead in the Campo Santo; they walked under orange trees with golden fruit hanging above their heads; they took drives to the foot of the mountains, and watched the reflections in the little lake of Ascuno. Mrs. Browning, from her windows, could see the cathedral summit glitter whitely, between the blue sky and its own yellow marble walls. Beautiful and tender letters came to them both from Mr. Kenyon, and they heard that Carlyle had said that he hoped more from Robert Browning, for the people of England, than from any other living English writer. All of these things entered into the very fiber of their Pisan days. Pisa seemed to her a beautiful town,—it could not be less, she felt, with Arno and its palaces, and it was to her full of repose, but not desolate. Meantime, Mr. Browning was preparing for a new edition of his collected poems.
Curiously, all the biographers of Robert Browning have recorded that it was during this sojourn in Pisa that the “Sonnets from the Portuguese” were first made known to him. Dr. Dowden quotes the story as given by Mr. Edmund Gosse, and Mr. Gosse cites Browning himself as his authority. Yet there was some mistake, as the Sonnets were not seen by Mr. Browning till some time later.
Robert Barrett Browning, in Florence, in the spring of 1910, in reply to a question asked by the writer of this book in regard to the accuracy of this impression, replied that both Mr. Gosse and Dr. Dowden were mistaken; as his mother did not show these “Sonnets” to his father until the summer of 1849, when they were at Bagni di Lucca. Mr. Gosse must in some way have mistaken Mr. Browning’s words, and the error has perpetuated itself through every successive biography of the poet.
The first home of the Brownings in Florence was in an[Pg 98] apartment near Santa Maria Novella, where the Italian sunshine burned fiercely, and where Mrs. Browning exclaimed that she began to comprehend the possibility of St. Lawrence’s ecstasies on the gridiron. “Yet there have been cool intermissions,” she wrote, “and as we have spacious and airy rooms, and as we can step out of the window on a balcony terrace which is quite private, and swims over with moonlight in the evenings, and as we live upon watermelons, and iced water, and figs, and all manner of fruit, we bear the heat with angelic patience.”
There was a five days’ interlude at Vallombrosa, which the poets vainly entreated the monks to prolong to two months, but the brethren would have none of the presence of two women,—Mrs. Browning and her maid, Wilson. So they perforce left these fascinating hills, “a sea of hills looking alive among the clouds.” Still further up above the monastery was the old Hermitage now transformed into a hotel. It was here that Migliorotti passed many years, asserting that he could only think of it as Paradise, and thus it came to be known as Paradisino, the name it still bears. Far below in a dim distance lies Florence, with her domes and towers on which the sunshine glitters, or the white moonlight of the Val d’Arno shines; and on every hand are the deep valleys and crevasses, the Val di Sieve, the Val di Casentino, and the height of San Miniato in Alpe. Castles and convents, or their ruins, abound; and here Dante passed, and there St. Benedict, and again is the path still holy with the footsteps of St. Francis. The murmuring springs that feed the Arno are heard in the hills; and the vast solitudes of the wood, with their ruined chapels and shrines, made this sojourn to the Brownings something to be treasured in memory forever. They even wandered to that beautiful old fifteenth-century church, Santa Maria delle Grazie Vallombrosella, “a daughter of the monastery of Vallombrosa,” where were works of Robbia, and saw [Pg 99]the blue hills rise out of the green forests in their infinite expanse.

Old Monastery at Vallombrosa
| “And Vallombrosa we two went to see Last June beloved companion...” |
| Casa Guidi Windows. |
When they fared forth for Vallombrosa, it was at four o’clock in the morning, Mrs. Browning being all eagerness and enthusiasm for this matutinal pilgrimage. Reaching Pelago, their route wound for five miles along a “via non rotabile,” through the most enchanting scenery, to Pontassieve.
“Oh! such mountains,” wrote Mrs. Browning of this never-to-be-forgotten journey, “as if the whole world were alive with mountains—such ravines—black in spite of flashing waters in them—such woods and rocks—traveled in basket sledges drawn by four white oxen—Wilson and I and the luggage—and Robert riding step by step. We were four hours doing the five miles, so you may fancy what rough work it was. Whether I was most tired or charmed was a tug between body and soul.
“The worst was that,” she continued, “there being a new abbot at the monastery—an austere man, jealous of his sanctity and the approach of women—our letter, and Robert’s eloquence to boot, did nothing for us, and we were ingloriously and ignominiously expelled at the end of five days.”
While the Brownings were in Vallombrosa Arnould wrote to Alfred Domett:
“Browning is spending a luxurious year in Italy—is, at this present writing, with his poetess bride dwelling in some hermit hut in Vallombrosa, where the Etruscan shades high overarched embower. He never fails to ask pressingly about you, and I give him all your messages. I would to God he would purge his style of obscurities,—that the wide world would, and the gay world and even the less illuminated part of the thinking world, know his greatness even as we do. I find myself reading ‘Paracelsus’ and the ‘Dramatic Lyrics’ more often than anything else in verse.”
They descended, perforce, into Florence again, burning sunshine and all, the abbot of the monastery having someway[Pg 100] confounded their pleadings with the temptation of St. Anthony, as something to be as heroically resisted. They set up their household gods in the shades of the Via delle Belle Donne, near the Duomo, where dinners, “unordered,” Mrs. Browning said, “come through the streets, and spread themselves on our table, as hot as if we had smelt cutlets hours before.” She found Florence “unspeakably beautiful,” both by grace of nature and of art, but they planned to go to Rome in the early autumn, taking an apartment “over the Tarpeian rock.” Later this plan was relinquished, and with an apartment on their hands for six months they yet abandoned it, for want of sunshine, and removed to Casa Guidi.
“Think what we have done,” wrote Mrs. Browning to Miss Mitford; “taken two houses, that is, two apartments, each for six months, pre-signing the contract. You will set it down to excellent poet’s work in the way of domestic economy, but the fault was altogether mine, for my husband, to please me, took rooms with which I was not pleased for three days, through the absence of sunshine. The consequence was that we had to pay heaps of guineas away, for leave to go, ourselves, but you can scarcely fancy the wonderful difference which the sun makes in Italy. So away we came into the blaze of him into the Piazza Pitti; precisely opposite the Grand Duke’s palace; I with my remorse, and poor Robert without a single reproach. Any other man, a little lower than the angels, would have stamped and sworn a little for the mere relief of the thing,—but as for his being angry with me for any cause except not eating enough dinner, the said sun would turn the wrong way first.”
Mrs. Browning’s dog, Flush, was a member of the household not to be ignored, and her one source of consolation, in being turned away from the Vallombrosa summer, lay in the fact that “Flush hated it,” and was frightened by the vast and somber pine forests. “Flush likes civilized life,”[Pg 101] said Mrs. Browning laughingly, “and the society of little dogs with turned-up tails, such as abound in Florence.”
So now they bestowed themselves in “rooms yellow with sunshine from morning till night,” in Casa Guidi, where, “for good omen,” they looked down on the old gray church of San Felice. There was a large, square anteroom, where the piano was placed, with one large picture, picked up in an obscure street in Florence; and a little dining-room, whose walls were covered with tapestry, and where hung medallions of Tennyson, Carlyle, and of Robert Browning; a long, narrow room, wraith-like with plaster casts and busts, was Mr. Browning’s study, while she had her place in the large drawing-room, looking out upon the ancient church. Its old pictures of saints, gazing sadly from their sepulchral frames of black wood, with here and there a tapestry, and with the lofty, massive bookcases of Florentine carving, all gave the room a medieval look. Almost could one fancy that it enthroned the “fairy lady of Shalott,” who might weave
“... from day to day,
A magic web of colors gay.”
Dante’s grave profile, a cast of the face of Keats taken after death, and a few portraits of friends, added their interest to the atmosphere of a salon that seemed made for poets’ uses. There were vast expanses of mirrors in the old carved Florentine frames, a colossal green velvet sofa, suggesting a catafalque, and a supernaturally deep easy-chair, in the same green velvet, which was Mrs. Browning’s favorite seat when she donned her singing robes. Near this low arm-chair was always her little table, strewn with writing materials, books, and newspapers. Other tables in the salotto bore gayly bound volumes, the gifts of brother authors. On the floor of a bedroom were the arms (in scabola), of the last count who had lived in this apartment, and there was a picturesque oil-jar, to hold rain-water, which[Pg 102] Mrs. Browning declared would just hold the Captain of the Forty Thieves. All in all, the poets vowed they would not change homes with the Grand Duke himself, who was their neighbor in the Palazzo Pitti at the distance of a stone’s throw. In the late afternoons they would wander out to the Loggia dei Lanzi, where Mrs. Browning greatly admired Cellini’s Perseus with the Head of Medusa, and they watched “the divine sunsets on the Arno, turning it to pure gold under the bridges.” Sometimes they were joined by Hiram Powers, who was one of their earliest friends in Florence, “our chief friend and favorite,” Mrs. Browning said of him, and she found him a “simple, straightforward, genial American, as simple as the man of genius he has proved himself need be.” Another friend of these early days was Miss Boyle, a niece of the Earl of Cork, somewhat a poet, withal, who, with her mother, was domiciled in the Villa Careggi, in which Lorenzo il Magnifico died, and which was loaned to the Boyles by Lord Holland. Miss Boyle frequently dropped in on them in the evening, “to catch us at hot chestnuts and mulled wine,” said Mrs. Browning, “and a good deal of laughing she and Robert make between them.” On the terrace of Casa Guidi orange trees and camellias bloomed, and the salons with their “rococo chairs, spring sofas, carved bookcases, and satin from Cardinals’ beds,” were a picturesque haunt. The ideal and poetic life of Mrs. Browning, so far from isolating her from the ordinary day and daylight duties, invested these, instead, with glow and charm and playful repartee; and, indeed, her never-failing sense of humor transformed any inconvenience or inadvertence into amusement. She, who is conceded to have written the finest sonnets since Shakespeare, could also mend a coat for her husband with a smile and a Greek epigram.

The Guardian Angel.
guercino. church of san agostino, fano, italy
| “Guercino drew this angel I saw teach (Alfred, dear friend!) that little child to pray.” |
| The Guardian Angel; A Picture at Fano. |
[Pg 103]Joseph Arnould again wrote to their mutual friend, Domett:
“Browning and his wife are still in Florence; both ravished with Italy and Italian life; so much so, that I think for some years they will make it the Paradise of their poetical exile. I hold fast to my faith in ‘Paracelsus.’ Browning and Carlyle are my two crowning men amongst the highest English minds of the day. Third comes Alfred Tennyson.... By-the-bye, did you ever happen upon Browning’s ‘Pauline’? a strange, wild (in parts singularly magnificent) poet-biography; his own early life as it presented itself to his own soul viewed poetically; in fact, psychologically speaking, his ‘Sartor Resartus’; it was written and published three years before ‘Paracelsus,’ when Shelley was his God.”
A little later Arnould wrote again:
“Browning and his wife are still in Florence, and stay there till the summer; he is bringing out another edition of his poems (except ‘Sordello’), Chapman and Hall being his publishers, Moxon having declined. He writes always most affectionately, and never forgets kind inquiries about and kind messages to you.”
Allured by resplendent tales of Fano, the Brownings made a trip to that seaside hamlet, but found it uninhabitable in the late summer heat. A statue in the Piazza commemorated the ancient Fanum Fortunæ of tradition, and in the cathedral of San Fortunato were frescoes by Domenichino, and in the chiesa of Sant’ Agostino was the celebrated painting of Sant’ Angelo Custode, by Guercino, which suggested to Browning his poem “The Guardian Angel.” The tender constancy of Browning’s friendship for Alfred Domett is in evidence in this poem, and the beauty of his reference to his wife,—
“My angel with me, too,...”
lingers with the reader.
In no poem of his entire work has Browning given so complete a revelation of his own inner life as in this memorable[Pg 104] lyric. The picture, dim as is the light in which it is seen, is one of the most impressive of all Guercino’s works. In the little church of San Paterniano is a “Marriage of the Virgin,” by Guercino, and in the Palazzo del Municipio of Fano is Guercino’s “Betrothal of the Virgin,” and the “David” of Domenichino.
The Brownings while in Fano made the excursion to the summit of Monte Giove, an hour’s drive from the Piazza, where was the old monastery and a wonderful view of the Adriatic, and of the panorama of the Apennines. “We fled from Fano after three days,” wrote Mrs. Browning, “and finding ourselves cheated out of our dream of summer coolness, we resolved on substituting for it what the Italians call ‘un bel giro.’ So we went to Ancona ... where we stayed a week, living on fish and cold water.” They found Ancona “a straggling sea city, holding up against the brown rocks, and elbowing out the purple tides,” and Mrs. Browning felt an inclination to visit it again when they might find a little air and shadow. They went on to Loreto, and then to Ravenna, where in the early dawn of a summer morning they stood by the tomb of Dante, deeply touched by the inscription. All through this journey they had “wonderful visions of beauty and glory.” Returning to Florence, to their terraces, orange trees, and divine sunsets, one of their earliest visitors in Casa Guidi was Father Prout, who had chanced to be standing on the dock at Livorno when they first landed in Italy, from the journey from France, and who now appeared in Florence on his way to Rome. Mr. Browning had fallen ill after their trip to Fano, and Father Prout prescribed for him “port wine and eggs,” which régime, combined with the racy conversation of the genial priest, seemed efficacious.
In the meantime Mrs. Browning stood with her husband by the tomb of Michael Angelo in Santa Croce; she saw the Venus, the “divine Raphaels.” The Peruzzi chapel[Pg 105] had then recently been restored—some exquisite frescoes by Giotto being among the successful restorations. The “mountainous marble masses” of the Duomo, “tessellated marbles climbing into the sky, self-crowned with that prodigy of marble domes,” struck Mrs. Browning as the wonder of all architecture.
The political conditions of Italy began to enlist her interest. In June of 1846 Pio Nono had ascended the Papal throne, preceded by a reputation for a liberal policy, and it was even hoped that he would not oppose the formation of a United Italy. The papal and the temporal government was still one, but Pius IX was a statesman as well as a churchman. England had especially commissioned Lord Minto to advocate reform, and the enthusiasts for Italian liberty received him with acclaim. The disasters of 1848 were still in the unrevealed future, and a new spirit was stirring all over the Italian kingdom. Piedmont was looked to with hope; and the Grand Duke of Tuscany had instituted a National Guard, as the first step toward popular government. The great topic of the day was the new hope of Italy. In Florence the streets and piazzas were vocal with praises of the Grand Duke. On one night that Browning went to the opera the tumult grew intense, and the Duke was escorted back to Palazzo Pitti with thousands of wax torchlights and a blaze of glory and cries of “Eviva! Eviva!” Browning, however, distrusted Pio Nono, thinking him weak, and events proved that his opinion was justified.
The winter of 1847-1848 was passed by the Brownings in Casa Guidi. “I wish you could see what rooms we have,” wrote Mrs. Browning to her husband’s sister, Sarianna: “what ceilings, what height and breadth, what a double terrace for orange trees; how cool, how likely to be warm, how perfect every way!”
The poets were constantly engaged in their work. Mrs.[Pg 106] Browning began her long poem, “Casa Guidi Windows,” and many of Browning’s lyrics that appeared in the collection called “Men and Women” were written at this period. They passed much time in the galleries and churches. They drove in the beautiful environs of Florence. The pictures, history, and legends entered into their lives to serve in later days as poetic material. In the brief twilight of winter days they often strolled into the old gray church of San Felice, on which their windows looked out, where Browning would gratify his passion for music by evolving from the throbbing keys of the organ some faint Toccata of Galuppi’s, while his wife smiled and listened, and the tide of Florentine life flowed by in the streets outside. Casa Guidi is almost opposite the Palazzo Pitti, so that Mrs. Browning had easy access to her beloved Madonnas in the Pitti gallery, which to her husband, also, was so unfailing a resource.
One of Mrs. Browning’s American admirers, and one of the reviewers of her poems, George Stillman Hillard, visited Florence that winter, and passed more than one evening in Casa Guidi with the Brownings. Of Mrs. Browning he wrote:
“Mrs. Browning is in many respects the correlative of her husband.... I have never seen a human frame which seemed so nearly a transparent veil for a celestial and immortal spirit. She is a soul of fire enclosed in a shell of pearl.... Nor is she more remarkable for genius and learning than for sweetness of temper, tenderness of heart, depth of feeling, and purity of spirit.... A union so complete as theirs—in which the mind has nothing to crave, nor the heart to sigh for—is cordial to behold and cheering to remember.”
Of all Italy Mr. Hillard perhaps best loved Florence, finding there an indescribable charm, “a blending of present beauty and traditional interest; but then Florence is alive,” he added, “and not enslaved.” It was probably[Pg 107] Hillard who suggested to William Wetmore Story that he should meet Browning. At all events this meeting took place, initiating the friendship that endured “forty years, without a break,” and that was one of the choicest social companionships.
The spring of 1849 brought new joy to Casa Guidi, for on March 9 was born their son, who was christened Robert Wiedemann Barrett, the middle name (which in his manhood he dropped) being the maiden name of the poet’s mother. The passion of both husband and wife for poetry was now quite equaled by that for parental duties, which they “caught up,” said Mrs. Browning, “with a kind of rapture.” Mr. Browning would walk the terraces where orange trees and oleanders blossomed, with the infant in his arms, and in the summer, when they visited Spezzia, and the haunt of Shelley at Lurici, they wandered five miles into the mountains, the baby with them, on horseback and donkey-back. The child grew rounder and rosier; and Mrs. Browning was able to climb hills and help her husband to lose himself in the forests.
The death of Browning’s mother immediately after the birth of his son was a great sadness to the poet, and one fully shared by his wife, who wrote to Miss Browning: “I grieve with you, as well as for you; for though I never saw her face, I loved that pure and tender spirit.... Robert and I dwell on the hope that you and your father will come to us at once.... If Florence is too far off, is there any other place where we could meet and arrange for the future?”
The Brownings went for the summer to Bagni di Lucca, after the little détour on the Mediterranean coast, where they lingered in the white marble mountains of Carrara. In Lucca they passed long summer hours in the beautiful Duomo, which had been consecrated by Pope Alexander II in the eleventh century. The beauty and the solitude[Pg 108] charmed the poets; the little Penini was the “most popular of babies,” and when Wilson carried the child out in the sunshine the Italians would crowd around him and exclaim, “Che bel bambino!” They had given him the pet Italian name “Penini,” which always persisted. The Austrians had then taken possession of Florence, and Leopoldo, “L’intrepido,” as the Italians asserted, remained quietly in the Palazzo Pitti. Browning, writing to Mrs. Jameson, says there is little for his wife to tell, “for she is not likely to encroach upon my story which I could tell of her entirely angel nature, as divine a heart as God ever made.” The poet with his wife and Wilson and the baby made almost daily excursions into the forests and mountains, up precipitous fays and over headlong ravines; dining “with the goats,” while the baby “lay on a shawl, rolling and laughing.” The contrast of this mountain-climbing Mrs. Browning, with her husband and child, and the Miss Barrett of three or four years before, lying on a sofa in a darkened room, is rather impressive. The picture of one day is suggested by Mrs. Browning’s description in a letter to Miss Mitford, where she writes:
“... I have performed a great exploit, ridden on a donkey five miles deep into the mountains, to an almost inaccessible volcanic ground not far from the stars. Robert on horseback, Wilson and the nurse with baby, on other donkeys; guides, of course. We set off at eight in the morning and returned at six p. m., after dining on the mountain pinnacle.... The scenery, sublime and wonderful,... innumerable mountains bound faintly with the gray sea, and not a human habitation.”

Monument To Dante, in the Piazza di Santa Croce.
Stefano Ricci.
| “....The architect and hewer Did pile the empty marbles as thy tomb.” |
| Casa Guidi Windows. |
[Pg 110]It was during this villeggiatura that Mrs. Browning, one morning after their breakfast, with shy sweetness, tucked the pages of the “Sonnets” into her husband’s pocket and swiftly vanished. Robert Barrett Browning, who, as already noted, gave the history of this poetic interlude viva voce, has also recorded it in writing, as follows:
What earthly vocabulary can offer fit words in which to speak of celestial beauty? How these exquisite “Sonnets” tell the story of that romance of Genius and Love,—from the woman’s first thrill of interest in the poetry of an unknown poet, to the hour when he, “the princely giver,” brought to her “the gold and purple” of his heart
“For such as I to take or leave withal,”
and she questions
“Can it be right to give what I can give?”
with the fear that her delicacy of health should make such gifts
“Be counted with the ungenerous.”
But she thinks of how he “was in the world a year ago,” and thus she drinks
“Of life’s great cup of wonder! Wonderful,
Never to feel thee thrill the day or night
With personal act or speech,—
······
... Atheists are as dull,
Who cannot guess God’s presence out of sight.”
And the questioning,—
“How do I love thee? Let me count the ways.
I love thee to the depth and breadth and height
My soul can reach,...
... I love thee with the breath,
Smiles, tears, of all my life!—and, if God choose,
I shall but love thee better after death.”
Returning to Florence in October, Browning soon began the preparation for his poem, “Christmas Eve and Easter Day,” and Mrs. Browning arranged for a new one-volume edition of her poems, to include “The Seraphim,” and the poems that had appeared in the same volume, and also the poems appearing in 1844, many of them revised.
[Pg 111]Marchesa d’Ossoli, whom the Brownings had heretofore known as Margaret Fuller, surprised them by appearing in Florence with her husband and child, the private marriage having taken place some two years before. The Greenoughs, the Storys, and Mr. and Mrs. Christopher Pearse Cranch were all in Florence, and were all habitués of Casa Guidi. Mr. Cranch, poet, painter, and musician, was the kindly friend of Longfellow and of Lowell in their Cambridge homes, and the Greenoughs and Storys were also of the Cambridge circle. To friends at home the Marchesa wrote of going to the opera with the Greenoughs, and that she saw the Brownings often, “and I love and admire them more and more,” she continued. “Mr. Browning enriches every hour passed with him, and he is a most true, cordial, and noble man.”
The Florentine days have left their picturings: Mr. Story opens a studio, and while he is modeling, Mrs. Story reads to him from Monckton Milnes’s Life of Keats, which Mr. Browning loaned them. Mrs. Story drives to Casa Guidi to carry Mrs. Browning her copy of “Jane Eyre,” and Mrs. Greenough takes both Mrs. Story and Mrs. Browning to drive in the Cascine. Two American painters, Frank Boott and Frank Heath, are in Florence, and are more or less caught up in the Casa Guidi life; and the coterie all go to Mrs. Trollope’s to see fancy costumes arranged for a ball to be given at Sir George Hamilton’s. In one of the three villas on Bellosguardo Miss Isa Blagden was now domiciled. For more than a quarter of a century Miss Blagden was a central figure in English society in Florence. She became Mrs. Browning’s nearest and most intimate friend, and she was the ardently prized friend of the Trollopes also, and of Miss Frances Power Cobbe, who shared her villa during one spring when Florence was in her most radiant beauty. “Isa was a very bright, warm-hearted, clever little woman,” said Thomas Adolphus Trollope[Pg 112] of her; “who knew everybody, and was, I think, more universally beloved among us than any other individual.” Miss Blagden had written one or two novels, of little claim, however, and after her death a small volume of her poems was published, but all these had no more than the mere succès d’estime, as apparently the pen was with her, as with Margaret Fuller, a non-conductor; but as a choice spirit, of the most beautiful and engaging qualities of companionship, “Isa,” as she was always caressingly called, is still held in memory. Madame Pasquale Villari, the wife of the great historian and the biographer of Machiavelli and of Savonarola, well remembers Miss Blagden, who died, indeed, in her arms in the summer of 1872.
The intimate friendship between Mrs. Browning and Miss Blagden was initiated in the early months of the residence of the Brownings in Florence; but it was in this winter of 1849-1850 that they began to see each other so constantly. The poems of Matthew Arnold were published that winter, among which Mrs. Browning especially liked “The Deserted Merman” and “The Sick King of Bokkara,” and about this time the authorship of “Jane Eyre” was revealed, and Charlotte Brontë discovered under the nom-de-plume of Currer Bell.
During the time that Mrs. Browning had passed at Torquay, before her marriage, she had met Theodosia Garrow, whose family were on intimate terms with Mr. Kenyon. Miss Barrett and Miss Garrow became friends, and when they met again it was in Florence, Miss Garrow having become the wife of Thomas Adolphus Trollope. Hiram Powers in these days was domiciled in the Via dei Serragli, in close proximity to Casa Guidi, and he frequently dropped in to have his morning coffee with the Brownings.

The Palazzo Vecchio, Florence.
Landor had been for some years in his villa on the Fiesolean slope, not far from Maiano, where Leigh Hunt had wandered, dreaming of Boccaccio. Two scenes of the [Pg 113]“Decameron” were laid in this region, and the deep ravine at the foot of one of the neighboring hills was the original of the “Valley of the Ladies.” Not far away had been the house of Machiavelli; and nestling among the blue hills was the little white village of Settignano, where Michael Angelo was born. Leigh Hunt had been on terms of the most cordial intimacy with Landor, whom he described as “living among his paintings and hospitalities”; and Landor had also been visited by Emerson, and by Lord and Lady Blessington, by Nathaniel Parker Willis (introduced by Lady Blessington), by Greenough, Francis and Julius Hare, and by that universal friend of every one, Mr. Kenyon, all before the arrival of the Brownings in Florence. Landor had, however, been again in England for several years, where Browning and Miss Barrett had both met and admired him, as has been recorded.
The Florence on which the Brownings had entered differed little from the Florence of to-day. The Palazzo Pitti, within a stone’s throw of Casa Guidi, stood in the same cyclopean massiveness as now; the piazza and church of San Miniato, cypress-shaded, rose from the sweep of the hills, and the miraculous crucifix of San Giovanni Gualberto was then, as now, an object of pilgrimage. The wonder of the Italian sunsets, that “perished silently of their own glory,” burned away over the far hills, and the strange, lofty tower of the Palazzo Vecchio caught the lingering rays. Beyond the Porta Romana, not far from Casa Guidi, was the road to the Val d’Emo, where the Certosa crowns an eminence. The stroll along the Arno at sunset was a favorite one with the poets, and in late afternoons they often climbed the slope to the Boboli Gardens for the view over Florence and the Val d’Arno. Nor did they ever tire of lingering in the Piazza della Signoria, before the marvelous palace with its medieval tower, and standing before the colossal fountain of Neptune, just behind the spot that is[Pg 114] commemorated by a tablet in the pavement marking the martyrdom of Savonarola. The great equestrian statue of Cosimo I always engaged their attention in this historic piazza, which for four centuries had been the center of the political life of the Florentines. All these places, the churches, monuments, palaces, and the art of Florence, were fairly mirrored in the minds of the wedded poets, impressing their imagination with the fidelity of an image falling on a sensitized plate. To them, as to all who love and enter into the ineffable beauty of the City of Lilies, it was an atmosphere of enchantment.
| “I heard last night a little child go singing ’Neath Casa Guidi windows, by the church, O bella libertà, O bella!...” “But Easter-Day breaks! But Christ rises! Mercy every way Is infinite,—and who can say?” |
“Casa Guidi Windows”—Society in Florence—Marchesa d’Ossoli—Browning’s Poetic Creed—Villeggiatura in Siena—Venice—Brilliant Life in London—Paris and Milsand—Browning on Shelley—In Florence—Idyllic Days in Bagni Di Lucca—Mrs. Browning’s Spiritual Outlook—Delightful Winter in Rome—A Poetic Pilgrimage—Harriet Hosmer—Characteristics of Mrs. Browning.
The Brownings were never for a moment caught up in the wave of popular enthusiasm for Pio Nono that swept over Italy. Yet Mrs. Browning confessed herself as having been fairly “taken in” by the Grand Duke of Tuscany. Had Blackwood’s Magazine published Part I of her “Casa Guidi Windows” at the time that she sent it to this periodical, the poem would have been its own proof of her distrust of the Pope, but it would also have offered the same proof of her ill-founded trust in the Grand Duke; so that, on the whole, she was well content to fail in having achieved the distinction of a prophet regarding Pio Nono, as no Cassandra can afford to be convicted of delusion in some portion of the[Pg 116] details of her prophecy. To achieve lasting reputation as a soothsayer, the prophecy must be accurate throughout. The fact that there was an interval of three years between the first and the second parts of this poem accounts for the discrepancy between them. In her own words she confessed:
“I wrote a meditation and a dream,
Hearing a little child sing in the street:
I leant upon his music as a theme,
Till it gave way beneath my heart’s full beat
Which tried at an exultant prophecy,
But dropped before the measure was complete—
Alas for songs and hearts! O Tuscany,
O Dante’s Florence, is the type too plain?”
The flashing lightnings of a betrayed people gleam like an unsheathed sword in another canto beginning:
“From Casa Guidi windows I looked forth,
And saw ten thousand eyes of Florentines
Flash back the triumph of the Lombard north.”
These ardent lines explain how she had been misled, for who could dream at the time that Leopoldo (“l’Intrepido,” as a poet of Viareggio called him in a truly Italian fervor of enthusiasm) could have proved himself a traitor to these trusting people,—these tender-hearted, gentle, courteous, refined Italians? All these attributes pre-eminently characterize the people; but also Mrs. Browning’s insight that “the patriots are not instructed, and the instructed are not patriots,” was too true. The adherents of the papal power were strong and influential, and the personal character, whatever might be said of his political principles,—the personal character of Pio Nono was singularly winning, and this was by no means a negligible factor in the great problem then before Italy.
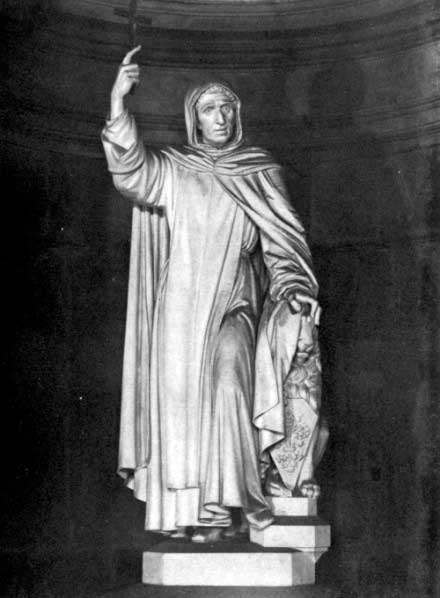

Statue of Savonarola, by E. Pazzi,
in the sala dei cinquecento, palazzo vecchio.
Mrs. Browning very wisely decided to let “Casa Guidi Windows” stand as written, with all the inconsistency[Pg 117] between its first and second parts, as each reflected what she believed true at the time of writing; and it thus presents a most interesting and suggestive commentary on Italian politics between 1850 and 1853. Its discrepancies are such “as we are called upon to accept at every hour by the conditions of our nature,” she herself said of it, “implying the interval between aspiration and performance, between faith and disillusion, between hope and fact.” This discrepancy was more painful to her than it can be even to the most critical reader; but the very nature of the poem, its very fidelity to the conditions and impressions of the moment, give it great value, though these impressions were to be modified or canceled by those of a later time; it should stand as it is, if given to the world at all. And the courage to avow one’s self mistaken is not the least of the forms that moral courage may assume.
Regarding Pio Nono, Mrs. Browning is justified by history, notwithstanding the many amiable and beautiful qualities of the Pontiff which forever assure him a place in affection, if not in political confidence. Even his most disastrous errors were the errors of judgment rather than those of conscious intention. Pio Nono had the defects of his qualities, but loving and reverent pilgrimages are constantly made to that little chapel behind the iron railing in the old church of San Lorenzo Fuori le Mura in Rome (occupying the site of the church founded by Constantine), where his body is entombed in a marble sarcophagus of the plainest design according to his own instructions; but the interior of the vestibule is richly decorated with mosaic paintings, the tribute of those who loved him.
Leopoldo was so kindly a man, so sincere in his work for the liberty of the press and for other important reforms, that it is no marvel that Mrs. Browning invested him with resplendence of gifts he did not actually possess, but which it was only logical to feel that such a man must have. [Pg 118]Sometimes a too complete reliance on the ex pede Herculem method of judgment is misleading.
While the cause of Italian liberty had the entire sympathy of Robert Browning, he was yet little moved to use it as a poetic motive. Professor Hall Griffin suggests that it is possible that Browning deliberately chose not to enter a field which his wife so particularly made her own; but that is the less tenable as they never discussed their poetic work with each other, and as a rule rarely showed to each other a single poem until it was completed.
The foreign society in Florence at this time included some delightful American sojourners, for, beside the Storys and Hiram Powers (an especial friend of the Brownings), there were George S. Hillard, George William Curtis, and the Marchesa d’Ossoli with her husband,—all of whom were welcomed at Casa Guidi. The English society then in Florence was, as Mrs. Browning wrote to Miss Mitford, “kept up much after the old English models, with a proper disdain for continental simplicities of expense; and neither my health nor our pecuniary circumstances,” she says, “would admit of our entering it. The fact is, we are not like our child, who kisses everybody who smiles on him! You can scarcely imagine to yourself how we have retreated from the kind advances of the English here, and struggled with hands and feet to keep out of this gay society.” But it is alluring to imagine the charm of their chosen circle, the Storys always first and nearest, and these other gifted and interesting friends.
Mr. Story is so universally thought of as a sculptor that it is not always realized how eminent he was in the world of letters as well. Two volumes of his poems contain many of value, and a few, as the “Cleopatra,” “An Estrangement,” and the immortal “Io Victis,” that the world would not willingly let die; his “Roba di Roma” is one of those absolutely indispensable works regarding the Eternal City;[Pg 119] and several other books of his, in sketch and criticism, enrich literature. A man of the most courtly and distinguished manner, of flawless courtesy, an artist of affluent expressions, it is not difficult to realize how congenial and delightful was his companionship, as well as that of his accomplished wife, to the Brownings. Indeed, no biographical record could be made of either household, with any completeness, that did not largely include the other. In all the lovely chronicles of literature and life there is no more beautiful instance of an almost lifelong friendship than that between Robert Browning and William Wetmore Story.
In this spring of 1850 Browning was at work on his “Christmas Eve and Easter Day,” and Casa Guidi preserved a liberal margin of quiet and seclusion. “You can scarcely imagine,” wrote Mrs. Browning, “the retired life we live.... We drive day by day through the lovely Cascine, only sweeping through the city. Just such a window where Bianca Capello looked out to see the Duke go by,—and just such a door where Tasso stood, and where Dante drew his chair out to sit.”
When Curtis visited Florence he wrote to Browning begging to be permitted to call, and he was one of the welcomed visitors in Casa Guidi. Browning took him on many of those romantic excursions with which the environs of Florence abound,—to Settignano, where Michael Angelo was born; to the old Roman amphitheater in Fiesole; to that somber, haunted summit of San Miniato, and to Vallombrosa, where he played to Curtis some of the old Gregorian chants on an organ in the monastery. Afterward, in a conversation with Longfellow, Mr. Curtis recalled a hymn by Pergolese that Browning had played for him.
Tennyson’s poem, “The Princess,” went into the third edition that winter, and Mrs. Browning observed that she knew of no poet, having claim solely through poetry, who had attained so certain a success with so little delay.[Pg 120] Hearing that Tennyson had remarked that the public “hated poetry,” Mrs. Browning commented that, “divine poet as he was, and no laurel being too leafy for him,” he must yet be unreasonable if he were not gratified with “so immediate and so conspicuous a success.”
Browning’s “imprisoned splendor” found expression that winter in several lyrics, which were included in the new (two volume) edition of his poems.
Among these were the “Meeting at Night,” “Parting at Morning,” “A Woman’s Last Word,” and “Evelyn Hope.” “Love among the Ruins,” “Old Pictures in Florence,” “Saul,” and his “A Toccata of Galuppi’s,” all belong to this group. In that ardent love poem, “A Woman’s Last Word,” occur the lines:
“Teach me, only teach, Love!
As I ought
I will speak thy speech, Love,
Think thy thought—
“Meet, if thou require it,
Both demands,
Laying flesh and spirit
In thy hands.”
No lyric that Robert Browning ever wrote is more haunting in its power and sweetness, or more rich in significance, than “Evelyn Hope,” with “that piece of geranium flower” in the glass beside her beginning to die. The whole scene is suggested by this one detail, and in characterization of the young girl are these inimitable lines,—
“The good stars met in your horoscope,
Made you of spirit, fire, and dew—
······
Yet one thing, one, in my soul’s full scope,
Either I missed or itself missed me;
······
[Pg 121]So, hush,—I will give you this leaf to keep;
See, I shut it inside the sweet cold hand!
There, that is our secret: go to sleep!
You will wake, and remember, and understand.”

Fresco of Dante, by Giotto, in the Bargello, Florence.
| “.... With a softer brow Than Giotto drew upon the wall.” |
Casa Guidi Windows.
Mrs. Browning’s touching lyric, “A Child’s Grave at Florence,” was published in the Athenæum that winter; and in this occur the simple but appealing stanzas,—
“Oh, my own baby on my knees,
My leaping, dimpled treasure,
······
But God gives patience, Love learns strength,
And Faith remembers promise;
······
Still mine! maternal rights serene
Not given to another!
The crystal bars shine faint between
The souls of child and mother.”
To this day, that little grave in the English cemetery in Florence, with its “A. A. E. C.” is sought out by the visitor. To Mrs. Browning the love for her own child taught her the love of all mothers. In “Only a Curl” are the lines:
“O children! I never lost one,—
But my arm’s round my own little son,
And Love knows the secret of Grief.”
Florence “bristled with cannon” that winter, but nothing decisive occurred. The faith of the Italian people in Pio Nono, however, grew less. Mr. Kirkup, the antiquarian, still carried on his controversy with Bezzi as to which of them were the more entitled to the glory of discovering the Dante portrait, and in the spring there occurred the long-deferred marriage of Mrs. Browning’s sister Henrietta to Captain Surtees Cook, the attitude of Mr. Barrett being precisely the same as on the marriage of his daughter Elizabeth to Robert Browning. The death of Wordsworth was another of the events of this spring, leaving vacant the Laureateship. The Athenæum at once advocated the [Pg 122]appointment of Mrs. Browning, as one “eminently suitable under a female sovereign.” Other literary authorities coincided with this view, it seeming a sort of poetic justice that a woman poet should be Laureate to a Queen. The Athenæum asserted that “there is no living poet of either sex who can prefer a higher claim than Elizabeth Barrett Browning,” but the honor was finally conferred upon Tennyson, with the ardent approbation of the Brownings, who felt that his claim was rightly paramount.
In the early summer the Marchese and Marchesa d’Ossoli, with their child, sailed on that ill-starred voyage whose tragic ending startled the literary world of that day. Their last evening in Florence was passed with the Brownings. The Marchesa expressed a fear of the voyage that, after its fatal termination, was recalled by her friends as being almost prophetic. Curiously she gave a little Bible to the infant son of the poets as a presentation from her own little child; and Robert Barrett Browning still treasures, as a strange relic, the book on whose fly-leaf is written “In memory of Angelino d’Ossoli.” Mrs. Browning had a true regard for the Marchesa, of whom she spoke as “a very interesting person, thoughtful, spiritual, in her habitual mode of mind.”
In his poetic creed, Browning deprecated nothing more entirely (to use a mild term where a stronger would not be inappropriate) than that the poet should reveal his personal feeling in his poem; and to the dramatic character of his own work he held tenaciously. He rebuked the idea that Shakespeare “unlocked his heart” to his readers, and he warns them off from the use of any fancied latch-key to his own inner citadel.
“Which of you did I enable
Once to slip inside my breast,
There to catalogue and label
What I like least, what love best?”
[Pg 123]And in another poem the reader will recall how fervently he thanks God that “even the meanest of His creatures”
“Boasts two soul-sides, one to face the world with,
One to show a woman when he loves her!”
It was the knowledge of this intense and pervading conviction of her husband’s that kept Mrs. Browning so long from showing to him her exquisitely tender and sacred self-revelation in the “Sonnets from the Portuguese.” Yet it was in that very “One Word More” where Browning thanks God for the “two soul-sides,” that he most simply reveals himself, and also in “Prospice” and in this “Christmas Eve and Easter Day.” This poem, with its splendor of vision, was published in 1850, with an immediate sale of two hundred copies, after which for the time the demand ceased. William Sharp well designates it as a “remarkable Apologia for Christianity,” for it can be almost thought of in connection with Newman’s “Apologia pro vita sua,” and as not remote from the train of speculative thought which Matthew Arnold wrought into his “Literature and Dogma.” It is very impressive to see how the very content of Hegelian Dialectic is the key-note of Browning’s art. “The concrete and material content of a life of perfected knowledge and volition means one thing, only, love,” teaches Hegelian philosophy. This, too, is the entire message of Browning’s poetry. Man must love God in the imperfect manifestation which is all he can offer of God. He must relate the imperfect expression to the perfect aspiration.
“All I aspired to be
And was not—comforts me.”
In the unfaltering search for the Divine Ideal is the true reward.
“One great aim, like a guiding star, above—
Which tasks strength, wisdom, stateliness, to lift
His manhood to the height that takes the prize.”
[Pg 124]Browning conceived and presented the organic idea and ideal of life, in its fullness, its intensity, as perhaps few poets have ever done. He would almost place a positive sin above a negative virtue. To live intensely, even if it be sinfully, was to Browning’s vision to be on the upward way, rather than to be in a state of negative good. The spirit of man is its own witness of the presence of God. Life cannot be truly lived in any fantastic isolation.
“Just when we’re safest, there’s a sunset touch,
A fancy from a flower-bell, some one’s death,
A chorus ending from Euripides.”
With Browning, as with Spinoza, there is an impatience, too, with the perpetual references to death, and they both constantly turn to the everlasting truth of life. “It is this harping on death that I despise so much,” exclaimed Browning, in the later years of his life, in a conversation with a friend. “In fiction, in poetry, in art, in literature this shadow of death, call it what you will,—despair, negation, indifference,—is upon us. But what fools who talk thus!... Why, death is life, just as our daily momentarily dying body is none the less alive, and ever recruiting new forces of existence. Without death, which is our word for change, for growth, there could be no prolongation of that which we call life.”
After the completion of “Christmas Eve and Easter Day,” Mrs. Browning questioned her husband about the apparent asceticism of the second part of the poem, and he replied that he meant it to show only one side of the matter. “Don’t think,” she wrote to a friend, “that Robert has taken to the cilix,—indeed he has not, but it is his way to see things as passionately as other people feel them.”
Browning teaches in this poem that faith is an adventure of the spirit, the aspiration felt, even if unnamed. But as to renunciation,—
[Pg 125]“‘Renounce the world!’—Ah, were it done
By merely cutting one by one
Your limbs off, with your wise head last,
How easy were it!”
The renunciation that the poet sees is not so simple. It is not to put aside all the allurements of life, but to use them nobly; to persist in the life of the spirit, to offer love for hatred, truth for falsehood, generous self-sacrifice rather than to grasp advantages,—to live, not to forsake the common daily lot. It is, indeed, the philosophy amplified that is found in the words of Jesus, “I pray not that Thou shouldest take them out of the world, but that thou shouldest keep them from the evil.”
The Brownings remained till late in the summer in their Casa Guidi home, detained at first by the illness of Mrs. Browning, after which they decided to postpone going to England until another year. In the late summer they went for a few weeks to Siena, where, two miles outside the walls, they found a seven-roomed villa with a garden and vineyard and olive orchard, and “a magnificent view of a noble sweep of country, undulating hills and verdure, and on one side the great Maremma extending to the foot of the Roman mountains.” They were located on a little hill called Poggia dei venti, with all the winds of the heavens, indeed, blowing about them, and with overflowing quantities of milk and bread and wine, and a loggia at the top of the villa. Mrs. Browning found herself rapidly recovering strength, and their comfort was further extended by finding a library in Siena, where, for three francs a month, they had access to the limited store of books which seem so luxurious in Italy. The boy Browning was delighted with his new surroundings, his sole infelicity being his inability to reach the grapes clustering over the trellises; he missed the Austrian band that made music (or noise) for his delectation in Florence, although to compensate for this privation[Pg 126] he himself sang louder than ever. In after years Mr. Browning laughingly related this anecdote of his son’s childhood: “I was one day playing a delicate piece of Chopin’s on the piano, and hearing a loud noise outside, hastily stopped playing when my little boy ran in, and my wife exclaimed: ‘How could you leave off playing when Penini brought three drums to accompany you?’”
For all this bloom and beauty in Siena they paid a little less than fifteen francs a week. Soon after their arrival they learned of the shipwreck in which the Marchese and Marchesa d’Ossoli and the little Angelino all perished, and the tragedy deeply impressed Mrs. Browning. “The work that the Marchesa was preparing upon Italy would have been more equal to her faculties than anything she has ever produced,” said Mrs. Browning, “her other writings being curiously inferior to the impression made by her conversation.”
Before returning to Florence the Brownings passed a week in the town of Siena to visit the pictures and churches, but they found it pathetic to leave the villa, and especially harrowing to their sensibilities to part with the pig. There is consolation, however, for most mortal sorrows, and the Brownings found it in their intense interest in Sienese art. The wonderful pulpit of the Duomo, the work of Niccola Pisano; the font of San Giovanni; the Sodomas, and the Libreria (the work of Pius III, which he built when he was Cardinal, and in which, at the end of the aisle, is a picture of his own elevation to the Papal throne, painted after his death) fascinated their attention. The Brownings found it dazzling to enter this interior, all gold and color, with the most resplendent decorative effects. They followed in the footsteps of Saint Catherine, as do all pilgrims to Siena, and climbed the hill to the Oratorio di Santa Caterina in Fontebranda, and read that inscription: “Here she stood and touched that precious vessel and gift [Pg 127]of God, blessed Catherine, who in her life did so many miracles.” They lingered, too, in the Cappella Santa Caterina in San Domenico, where Catherine habitually prayed, where she beheld visions and received her mystic revelations. They loitered in the piazza, watching the stars hang over that aerial tower, “Il Mangia,” and drove to San Gimignano, with its picturesque medieval atmosphere.

Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore, Florence,
known as the Duomo.
| “The most to praise and the best to see Was the startling bell-tower Giotto raised.” |
| Old Pictures in Florence. |
It was in the autumn of 1850 that Tennyson’s “In Memoriam,” first privately and then anonymously printed, was acknowledged by the poet. The Brownings read extracts from it in the Examiner, and they were deeply moved by it. “Oh, there’s a poet!” wrote Mrs. Browning. At last, “by a sort of miracle,” they obtained a copy, and Mrs. Browning was carried away with its exquisite touch, its truth and earnestness. “The book has gone to my heart and soul,” she says, “I think it full of deep pathos and beauty.”
An interesting visitor dropped in at Casa Guidi in the person of a grandson of Goethe; and his mission to Florence, to meet the author of “Paracelsus” and discuss with him the character of the poem, was a tribute to its power. Mrs. Browning, whose poetic ideals were so high, writing to a friend of their guest, rambled on into some allusions to poetic art, and expressed her opinion that all poets should take care to teach the world that poetry is a divine thing. “Rather perish every verse I ever wrote, for one,” she said, “than help to drag down an inch that standard of poetry which, for the sake of humanity as well as literature, should be kept high.”
In “Aurora Leigh” she expresses the same sentiment in the lines:
“I, who love my art,
Would never wish it lower to suit my stature.”
Full of affection and interest are Mrs. Browning’s letters to her husband’s sister, Sarianna, who, with her father, is[Pg 128] now living in Hatcham, near London. In the spring of 1852, after passing the winter in Florence, the Brownings set out for England; the plan at first being to go south to Naples, pause at Rome, and then go northward; but this was finally abandoned, and they proceeded directly to Venice, where Mrs. Browning was enchanted with life set in a scenic loveliness of “music and stars.”
“I have been between heaven and earth since our arrival in Venice,” she writes. “The heaven of it is ineffable. Never have I touched the skirts of so celestial a place. The beauty of the architecture, the silver trails of water between all that gorgeous color and carving, the enchanting silence, the moonlight, the music, the gondolas,—I mix it all up together....”
In the divine beauty of Venetian evenings they sat in the white moonlight in the piazza of San Marco, taking their coffee and the French papers together. Or they would go to the opera, where for a ridiculously small sum they had an entire box to themselves. But while Mrs. Browning longed “to live and die in Venice, and never go away,” the climate did not agree with Mr. Browning, and they journeyed on toward Paris, stopping one night at Padua and driving out to Arqua for Petrarca’s sake. In Milan Mrs. Browning climbed the three hundred and fifty steps, to the topmost pinnacle of the glorious cathedral. At Como they abandoned the diligence for the boat, sailing through that lovely chain of lakes to Flüelen, and thence to Lucerne, the scenery everywhere impressing Mrs. Browning as being so sublime that she “felt as if standing in the presence of God.” From Lucerne they made a détour through Germany, pausing at Strasburg, and arriving in Paris in July. This journey initiated an absence of almost a year and a half from Italy. They had let their apartment, so they were quite free to wander, and they were even considering the possibility of remaining permanently in Paris, whose[Pg 129] brilliant intellectual life appealed to them both. After a brief sojourn in the French capital, they went on to England, and they had rather an embarrassment of riches in the number of houses proffered them, for Tennyson begged them to accept the loan of his house and servants at Twickenham, and Joseph Arnould was equally urgent that they should occupy his town house. But they took lodgings, instead, locating in Devonshire Street, and London life proceeds to swallow them up after its own absorbing fashion. They breakfast with Rogers, and pass an evening with the Carlyles; Forster gives a “magnificent dinner” for them; Mrs. Fanny Kemble calls, and sends them tickets for her reading of “Hamlet”; and the Proctors, Mrs. Jameson, and other friends abound. They go to New Cross, Hatcham, to visit Mr. Browning’s father and sister, where the little Penini “is taken into adoration” by his grandfather. Mrs. Browning’s sisters show her every affection, and her brothers come; but her father, in reply to her own and her husband’s letter, simply sends back to her, with their seals unbroken, all the letters she had written to him from Italy. “So there’s the end,” she says; “I cannot, of course, write again. God takes it all into His own hands, and I wait.” The warm affection of her sisters cheered her, Mrs. Surtees Cook (Henrietta Barrett) coming up from Somersetshire for a week’s visit, and her sister Arabel being invited with her. It was during this sojourn in London that Bayard Taylor, poet and critic, and afterward American Minister Plenipotentiary to Germany, called upon the Brownings, bringing a letter of introduction from Hillard.
The poet’s wife impressed Taylor as almost a spirit figure, with her pallor and slender grace, and the little Penini, “a blue-eyed, golden-haired boy, babbling his little sentences in Italian,” strayed in like a sunbeam. While Taylor was with them, Mr. Kenyon called, and[Pg 130] after his departure Browning remarked to his guest: “There goes one of the most splendid men living,—a man so noble in his friendship, so lavish in his hospitality, so large-hearted and benevolent, that he deserves to be known all over the world as Kenyon the Magnificent.”
The poets were overwhelmed with London hospitalities, and as Mrs. Browning gave her maid, Wilson, leave of absence to visit her own family, the care of little Pen fell upon her. He was in a state of “deplorable grief” for his nurse, “and after all,” laughed Mrs. Browning, “the place of nursery maid is more suitable to me than that of poetess (or even poet’s wife) in this obstreperous London.”
In the late September the Brownings crossed to Paris, Carlyle being their traveling companion, and after an effort to secure an apartment near the Madeleine, they finally established themselves in the Avenue des Champs Élysées (No. 128), where they had pretty, sunny rooms, tastefully furnished, with the usual French lavishness in mirrors and clocks,—all for two hundred francs a month, which was hardly more than they had paid for the dreary Grosvenor Street lodgings in London. Mrs. Browning was very responsive to that indefinable exhilaration of atmosphere that pervades the French capital, and the little Penini was charmed with the gayety and brightness. Mrs. Browning enjoyed the restaurant dining, à la carte, “and mixing up one’s dinner with heaps of newspapers, and the ‘solution’ by Émile de Girardin,” who suggested, it seems, “that the next President of France should be a tailor.” Meantime she writes to a friend that “the ‘elf’ is flourishing in all good fairyhood, with a scarlet rose leaf on each cheek.” They found themselves near neighbors of Béranger, and frequently saw him promenading the avenue in a white hat, and they learned that he lived very quietly and “kept out of scrapes, poetical and political.” Mrs. Browning notes that they would like to know Béranger,[Pg 131] were the stars propitious, and that no accredited letter of introduction to him would have been refused, but that they could not make up their minds to go to his door and introduce themselves as vagrant minstrels. To George Sand they brought a letter from Mazzini, and although they heard she “had taken vows against seeing strangers,” Mrs. Browning declared she would not die, if she could help it, without meeting the novelist who had so captivated her. Mazzini’s letter, with one from themselves, was sent to George Sand through mutual friends, and the following reply came:
Madame, j’aurai l’honneur de vous recevoir Dimanche prochain, rue Racine, 3. C’est le seul jour que je puisse passer chez moi; et encore je n’en suis pas absolument certaine—mais je ferai tellement mon possible, que ma bonne étoile m’y aidera peut-être un peu. Agréez mille remerciments de cœur ainsi que Monsieur Browning, que j’espère voir avec vous, pour la sympathie que vous m’accordez.
George Sand.
Paris, 12 fevrier, 1852.
The visit must have been mutually satisfactory, for it was repeated two or three times, and they found her simple, “without a shade of affectation or consciousness.” Another pleasure they had was in meeting Lamartine, who took the initiative in asking to be allowed to call on them. After their arrival in Paris Carlyle passed several evenings with them, and Mrs. Browning felt, with her husband, that he was one of the most interesting of men, “highly picturesque” in conversation. Her sympathetic insight gave her always the key and the clue to character, and perhaps no one ever read Carlyle more truly than she, when she interpreted his bitterness only as melancholy, and his scorn as sensibility.
The Brownings had not been long in Paris before they were invited to a reception at Lady Elgin’s, where they met[Pg 132] Madame Mohl, who at once cordially urged their coming to her “evenings,” to meet her French celebrities. Lady Elgin was domiciled in the old Faubourg Saint Germain, and received every Monday evening from eight to twelve, sans façon, people being in morning dress, and being served with simple refreshment of tea and cakes. Lady Elgin expressed the hope that the Brownings would come to her on every one of these evenings, Mrs. Browning said that she had expected “to see Balzac’s duchesses and hommes de lettres on all sides,” but she found it less notable, though very agreeable. The elder Browning and his daughter pay a visit to them, greatly to Mrs. Browning’s enjoyment. At this time they half contemplated living permanently in Paris, if it seemed that Mrs. Browning could endure the climate, and she records, during the visit of her husband’s father and sister, that if they do remain in Paris they hope to induce these beloved members of the family to also establish themselves there. As it turned out, the Brownings passed only this one winter in the French capital, but the next spring Mr. Browning (père) and his daughter Sarianna took up their residence in Paris, where they remained during the remainder of his life. Mrs. Browning was always deeply attached to her husband’s sister. “Sarianna is full of accomplishment and admirable sense,” she wrote of her, and the visit of both gave her great pleasure. The coup d’état took place early in December, but they felt no alarm. Mrs. Browning expressed her great faith in the French people, and declared the talk about “military despotism” to be all nonsense. The defect she saw in M. Thiers was “a lack of breadth of view, which helped to bring the situation to a dead lock, on which the French had no choice than to sweep the board clean and begin again.”
It was during this early winter, with French politics and French society and occasional spectacles and processions extending from the Carrousel to the Arc de l’Étoile, that[Pg 133] Browning wrote that essay on Shelley, which his publisher of that time, Mr. Moxon, had requested to accompany a series of Shelley letters which had been discovered, but which were afterward found to be fraudulent. The edition was at once suppressed; but a few copies had already gone out, and, as Professor Dowden says, “The essay is interesting as Browning’s only considerable piece of prose;... for him the poet of ‘Prometheus Unbound’ was not that beautiful and ineffectual angel of Matthew Arnold’s fancy, beating in the void his luminous wings. A great moral purpose looked forth from Shelley’s work, as it does from all lofty works of art.” It was “the dream of boyhood,” Browning tells us, to render justice to Shelley; and he availed himself of this opportunity with alluring eagerness. His interpretation of Shelley is singularly noble and in accord with all the great spiritual teachings of his own poetic work. Browning’s plea that there is no basis for any adequate estimate of Shelley, who “died before his youth was ended,” cannot but commend its justice; and he urges that in any measurement of Shelley as a man he must be contemplated “at his ultimate spiritual stature” and not judged by the mistakes of ten years before when in his entire immaturity of character.
How all that infinite greatness of spirit and almost divine breadth of comprehension that characterize Robert Browning reveal themselves in this estimate of Shelley. It is seeing human errors and mistakes as God sees them,—the temporary faults, defects, imperfections of the soul on its onward way to perfection. This was the attitude of Browning’s profoundest convictions regarding human life.
“Eternal process moving on;
From state to state the spirit walks.”
This achievement of the divine ideal for man is not within the possibilities of the brief sojourn on earth,[Pg 134] but what does the transition called death do for man but to
“Interpose at the difficult moment, snatch Saul, the mistake,
Saul, the failure, the ruin he seems now,—and bid him awake
From the dream, the probation, the prelude, to find himself set
Clear and safe in new light and new life,—a new harmony yet
To be run, and continued, and ended—who knows?—or endure!
The man taught enough by life’s dream, of the rest to make sure.”
Browning’s message in its completeness was invariably that which is imaged, too, in these lines from Mrs. Browning’s “Aurora Leigh”:
“And take for a worthier stage the soul itself,
Its shifting fancies and celestial lights.”
For it is only in this drama of the infinite life that the spiritual man can be tested. It was from the standpoint of an actor on this celestial stage that Browning considered Shelley. In the entire range of Browning’s art the spiritual man is imaged as a complex and individualized spark of the divine force. He is seen for a flitting moment on his way toward a divine destiny.
Professor Hall Griffin states as his belief that Browning’s paper was to some degree inspired by that of Joseph Milsand on himself, which appeared in August, 1851, in the Revue des Deux Mondes in which Milsand commended Browning’s work “as pervaded by an intense belief in the importance of the individual soul.”
To Browning this winter was enchanted by the initiation of his friendship with Milsand, the distinguished French scholar and critic, who had already made a name as a philosophic thinker and had published a book on Ruskin (L’Esthétique Anglaise), and who was a discerner of spirits in poetic art as well. About the time that “Paracelsus” appeared, Milsand had seen an extract from the poem that captivated him, and he at once sent for the[Pg 135] volume. He had also read, with the deepest interest, Browning’s “Christmas Eve and Easter Day.” He was contributing to the Revue des Deux Mondes two papers on La Poésie Anglaise depuis Byron, the first of which, on Tennyson, had appeared the previous August. Milsand was about completing the second paper of this series (on Browning), and it happened just at this time that Miss Mitford’s “Recollections of a Literary Life” was published, in which, writing of the Brownings, she had told the story of that tragic death of Mrs. Browning’s brother Edward, who had been drowned at Torquay. In these days, when, as Emerson rhymes the fact,
“Every thought is public,
Every nook is wide,
The gossips spread each whisper
And the gods from side to side,”
it is a little difficult to quite comprehend, even in comprehending Mrs. Browning’s intense sensitiveness and the infinite sacredness of this grief, why she should have been so grieved at Miss Mitford’s tender allusion to an accident that was, by its very nature, public, and which must have been reported in the newspapers of the day. Mrs. Browning was always singularly free from any morbid states, from any tendency to the idée fixe, to which a semi-invalid condition is peculiarly and pardonably liable; but she said, in an affectionate letter to Miss Mitford:
“I have lived heart to heart (for instance) with my husband these five years: I have never yet spoken out, in a whisper even, what is in me; never yet could find heart or breath; never yet could bear to hear a word of reference from his lips.”
It is said there are no secrets in heaven, and in that respect, at least, the twentieth century is not unlike the celestial state; and it is almost as hard a task for the imagination to comprehend the reserve in all personal matters that[Pg 136] characterized the mid-nineteenth century as it would be to enter into absolute comprehension of the medieval mind; but Mrs. Browning’s own pathetic deprecation of her feelings regarding this is its own passport to the sympathy of the reader. To Miss Mitford’s reply, full of sympathetic comprehension and regret, Mrs. Browning replied that she understood, “and I thank you,” she added, “and love you, which is better. Now, let us talk of reasonable things.” For Mrs. Browning had that rare gift and grace of instantly closing the chapter, and turning the page, and ceasing from all allusion to any subject of regret, after the inevitable reference of the moment had been made. She had the mental energy and the moral buoyancy to drop the matter, and this characteristic reveals how normal she was, and how far from any morbidness.
Milsand, with a delicacy that Robert Browning never forgot, came to him to ask his counsel regarding the inclusion of this tragic accident that had left such traces on his wife’s genius and character (traces that are revealed in immortal expression in her poem, “De Profundis,” written some years later), and Browning was profoundly touched by his consideration. Grasping both Milsand’s hands, he exclaimed, “Only a Frenchman could have done this!” A friendship initiated under circumstances so unusual, and with such reverent intuition of Mrs. Browning’s feelings, could not but hold its place apart to them both.
The Brownings found Paris almost as ineffable in beauty in the early spring as was their Florence. “It’s rather dangerous to let the charm of Paris work,” laughed Mrs. Browning; “the honey will be clogging our feet soon, and we shall find it difficult to go away.”
They had a delightful winter socially, as well; they went to Ary Scheffer’s and heard Madame Viardot, then in the height of her artistic fame; George Sand sent them tickets for the première of “Les Vacances de Pandolphe”; they[Pg 137] went to the Vaudeville to see the “Dame aux Camellias,” of which Mrs. Browning said that she did not agree with the common cry about its immorality. To her it was both moral and human, “but I never will go to see it again,” she says, “for it almost broke my heart. The exquisite acting, the too literal truth to nature....” They met Paul de Musset, but missed his brother Alfred that winter, whose poems they both cared for.
The elder Browning retained through his life that singular talent for caricature drawing that had amused and fascinated his son in the poet’s childhood; and during his visit to the Brownings in Paris he had produced many of these drawings which became the delight of his grandson as well. The Paris streets furnished him with some inimitable suggestions, and Robert Barrett Browning, to this day, preserves many of these keen and humorous and extremely clever drawings of his grandfather. Thierry, the historian, who was suffering from blindness, sent to the Brownings a request that they would call on him, with which they immediately complied, and they were much interested in his views on France. The one disappointment of that season was in not meeting Victor Hugo, whose fiery hostility to the new régime caused it to be more expedient for him to reside quite beyond possible sight of the gilded dome of the Invalides.
In June the Brownings returned to London, where they domiciled themselves in Welbeck Street (No. 58), Mrs. Browning’s sisters both being near, Mrs. Surtees Cook having established herself only twenty doors away, and Miss Arabel Barrett being in close proximity in Wimpole Street. They were invited to Kenyon’s house at Wimbledon, where Landor was a guest, whom Mrs. Browning found “looking as young as ever, and full of passionate energy,” and who talked with characteristic exaggeration of Louis Napoleon and of the President of the French[Pg 138] nation. Landor “detested” the one and “loathed” the other; and as he did not accept Talleyrand’s ideal of the use of language, he by no means concealed these sentiments. Mazzini immediately sought the Brownings, his “pale, spiritual face” shining, and his “intense eyes full of melancholy illusions.” He brought Mrs. Carlyle with him, Mrs. Browning finding her “full of thought, and feeling, and character.” Miss Mulock, who had then written “The Ogilvies,” and had also read her title clear to some poetic recognition, was in evidence that season, as were Mr. and Mrs. Monckton Milnes, and Fanny Kemble was also a brilliant figure in the social life. Nor was the London of that day apparently without a taste for the sorceress and the soothsayer, for no less a personage than Lord Stanhope was, it seems, showing to the elect the “spirits of the sun” in a crystal ball, which Lady Blessington had bought from an Egyptian magician and had sold again. Lady Blessington declared she had no understanding of the use of it, but it was on record that the initiated could therein behold Oremus, Spirit of the Sun. Both the crystal ball and the seers were immensely sought, notwithstanding the indignation expressed by Mr. Chorley, who regarded the combination of social festivities and crystal gazing as eminently scandalous. Which element he considered the more dangerous is not on the palimpsest that records the story of these days. Lord Stanhope invited the Brownings to these occult occasions of intermingled attractions, and Mrs. Browning writes: “For my part, I endured both luncheon and spiritual phenomena with great equanimity.” An optician of London took advantage of the popular demand and offered a fine assortment of crystal ball spheres, at prices which quite restricted their sale to the possessors of comfortable rent-rolls, and Lord Stanhope asserted that a great number of persons resorted to these balls to divine the future, without the courage to[Pg 139] confess it. One wonders as to whom “the American Corinna, in yellow silk,” in London, that season, could have been?
The Brownings were invited to a country house in Farnham, to meet Charles Kingsley, who impressed them with his genial and tender kindness, and while they thought some of his social views wild and theoretical, they loved his earnestness and originality, and believed he could not be “otherwise than good and noble.” It was during this summer (according to William Michael Rossetti) that Browning and Dante Gabriel Rossetti first met, Rossetti coming to call on them in company with William Allingham. On August 30, from Chapel House, Twickenham, Tennyson wrote to Mrs. Browning of the birth of his son, Hallam, to which she replied:
“Thank you and congratulate you from my heart. May God bless you all three.... Will you say to dear Mrs. Tennyson how deeply I sympathize in her happiness....”
To this letter Browning added a postscript saying:
“How happy I am in your happiness, and in the assurance that it is greater than even you can quite know yet. God bless, dear Tennyson, you and all yours.”
Tennyson wrote again to Mrs. Browning, saying, “... How very grateful your little note and Browning’s epilogue made me.” And he signs himself “Ever yours and your husband’s.” There was a brilliant christening luncheon at the home of Monckton Milnes, “and his baby,” notes Mrs. Browning, “was made to sweep, in India muslin and Brussels lace, among a very large circle of admiring guests.” The Brownings were especially invited to bring their little Penini with them, “and he behaved like an angel, everybody said,” continued his mother, “and looked very pretty, I said myself; only he disgraced us all at[Pg 140] last by refusing to kiss the baby on the ground of its being ‘troppo grande.’”
To Mrs. Tennyson’s note of invitation to the Brownings to attend the christening of their child, Mrs. Browning replied that they had planned to leave England before that date; “but you offer us an irresistible motive for staying, in spite of fogs and cold,” she continued, “and we would not miss the christening for the world.” At the last, however, Mrs. Browning was unable to go, so that the poet went alone. After the little ceremony Browning took the boy in his arms and tossed him, while Tennyson, looking on, exclaimed: “Ah, that is as good as a glass of champagne for him.”
Florence Nightingale was a not infrequent visitor of the Brownings that summer, and she always followed her calls by a gift of masses of flowers. While “Morte d’Arthur” had been written more than ten years previously, Tennyson was now evolving the entire plan of the “Idylls of the King.” Coventry Patmore, who brought the manuscript copy of his own poems, published later, for Mr. Browning to read, mentioned to the poets that Tennyson was writing a collection of poems on Arthur, which were to be united by their subject, after the manner of “In Memoriam,” which project interested Mrs. Browning greatly. “The work will be full of beauty, I don’t doubt,” she said.
Ruskin invited the Brownings to Denmark Hill to see his Turners, and they found the pictures “divine.” They liked Ruskin very much, finding him “gentle, yet earnest.”
During this London sojourn Mr. Browning’s old friend, William Johnson Fox, who had first encouraged the young poet by praising “not a little, which praise comforted me not a little,” the verses of his “Incondita”; who had written a favorable review of “Pauline”; who had found a publisher for “Paracelsus,” and had introduced the poet to Macready, again appears, and writes to his daughter that he has had[Pg 141] “a charming hour” with the Brownings, and that he is more fascinated than ever with Mrs. Browning. “She talked lots of George Sand, and so beautifully, and she silver-electroplated Louis Napoleon!” Mr. Fox adds:[6] “They came in to their lodgings late at night, and R. B. says that in the morning twilight he saw three pictures on the bedroom wall, and speculated as to whom they might be. Light gradually showed the first to be Beatrice Cenci. ‘Good,’ said he; ‘in a poetic region.’ More light; the second, Lord Byron! Who can the third be? And what think you it was? Your (Fox’s) sketch (engraved chalk portrait) of me?’ He made quite a poem and picture of the affair. She seems much better; and the young Florentine was gracious.”
In November the Brownings again left London for Florence, pausing a week in Paris on the way, where they witnessed the picturesque pomp of the reception of Louis Napoleon, the day being brilliant with sunshine, and the hero of the hour producing an impression by riding entirely alone, with at least ten paces between himself and the nearest of his escort, till even Charlotte Cushman, sitting at the side of Mrs. Browning, watching the spectacle, declared this to be “fine.” The “young Florentine” was in a state of ecstasy, which he expressed in mingled French and Italian.
They journeyed to Florence by the Mont Cenis, stopping a week in Genoa, where Mrs. Browning lay ill on her sofa; but the warmth of the Italian sunshine soon restored her, and for two days before they left, she was able to walk all about the beautiful old city. They visited together the Andrea Doria palace, and enjoyed sauntering in a sunshine that was like that of June days dropped into the heart [Pg 142]of November. They were delighted to hear the sound of their “dear Italian” again, and proceeded by diligence to Florence, where they took possession of their Casa Guidi home, which looked, wrote Mrs. Browning to her sister-in-law, as if they had only left it yesterday. The little Penini was “in a state of complete agitation” on entering Florence, through having heard so much talk of it, and expressed his emotion by repeated caresses and embraces. Mrs. Browning shared the same amazement at the contrast of climate between Turin and Genoa that twentieth-century travelers experience; Turin having been so cold that they were even obliged to have a fire all night, while at Genoa they were “gasping for breath, with all the windows and doors open, blue skies burning overhead, and no air stirring.” But this very heat was life-giving to Mrs. Browning as they lingered on the terraces, gazing on the beautiful bay encircled by its sweep of old marble palaces. She even climbed half-way up the lighthouse for the view, resting there while Browning climbed to the top, for that incomparable outlook which every visitor endeavors to enjoy. In Florence there were the “divine sunsets” over the Arno, and Penini’s Italian nurse rushing in to greet the child, exclaiming, “Dio mio, come e bellino!” They “caught up their ancient traditions” just where they left them, Mrs. Browning observes, though Mr. Browning, “demoralized by the boulevards,” missed the stir and intensity of Parisian life. They found Powers, the sculptor, changing his location, and Mr. Lytton (the future Earl), who was an attaché at the English Embassy, became a frequent and a welcome visitor. In a letter to Mr. Kenyon Mrs. Browning mentions that Mr. Lytton is interested in manifestations of spiritualism, and had informed her that, to his father’s great satisfaction (his father being Sir E. Bulwer Lytton), these manifestations had occurred at Knebworth, the Lytton home in England. Tennyson’s brother, who had [Pg 143]married an Italian lady, was in Florence, and the American Minister, Mr. Marsh. With young Lytton at this time, Poetry was an article of faith, and nothing would have seemed to him more improbable, even had any of his clairvoyants foretold it, than his future splendid career as Viceroy of India.
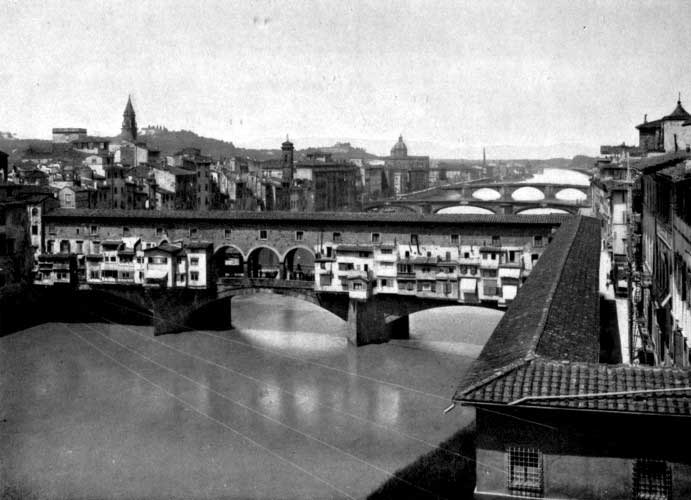

The Ponte Vecchio and the Arno, Florence.
Mrs. Browning was reading Prudhon that winter, and also Swedenborg, Lamartine, and other of the French writers. Browning was writing from time to time many of the lyrics that appear in the Collection entitled “Men and Women,” while on Mrs. Browning had already dawned the plan of “Aurora Leigh.” They read the novel of Dumas, Diane de Lys, Browning’s verdict on it being that it was clever, but outrageous as to the morals; and Mrs. Browning rejoiced greatly in Mrs. Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Uncle Tom’s Cabin,” saying of Mrs. Stowe, “No woman ever had such a success, such a fame.” All in all, this winter of 1852-1853 was a very happy one to the poets, what with their work, their friends, playing with the little Wiedemann (Penini), the names seeming interchangeably used, and their reading, which included everything from poetry and romance to German mysticism, social economics, and French criticism. Mrs. Browning found one of the best apologies for Louis Napoleon in Lamartine’s work on the Revolution of ’48; and she read, with equal interest, that of Louis Blanc on the same period. In April “Colombe’s Birthday” was produced at the Haymarket Theater in London, the role of the heroine being taken by Miss Helen Faucit, afterward Lady Martin. The author had no financial interest in this production, which ran for two weeks, and was spoken of by London critics as holding the house in fascinated attention, with other appreciative phrases.
Mrs. Browning watches the drama of Italian politics, and while she regarded Mazzini as noble, she also felt him to be unwise, a verdict that time has since justified. “We see[Pg 144] a great deal of Frederick Tennyson,” she writes; “Robert is very fond of him, and so am I. He too writes poems, and prints them, though not for the public.” Their mutual love of music was a strong bond between Browning and Mr. Tennyson, who had a villa on the Fiesolean slope, with a large hall in which he was reported to “sit in the midst of his forty fiddlers.”
For the coming summer they had planned a retreat into Giotto’s country, the Casentino, but they finally decided on Bagni di Lucca again, where they remained from July till October, Mr. Browning writing “In a Balcony” during this villeggiatura. Before leaving Florence they enjoyed an idyllic day at Pratolina with Mrs. Kinney, the wife of the American Minister to the Court of Turin, and the mother of Edmund Clarence Stedman. The royal residences of the old Dukes of Tuscany were numerous, but among them all, that at Pratolina, so associated with Francesco Primo and Bianca Capella, is perhaps the most interesting, and here Mrs. Kinney drove her guests, where they picnicked on a hillside which their hostess called the Mount of Vision because Mrs. Browning stood on it; Mr. Browning spoke of the genius of his wife, “losing himself in her glory,” said Mrs. Kinney afterward, while Mrs. Browning lay on the grass and slept. The American Minister and Mrs. Kinney were favorite guests in Casa Guidi, where they passed with the Brownings the last evening before the poets set out for their summer retreat. Mrs. Browning delighted in Mr. Kinney’s views of Italy, and his belief in its progress and its comprehension of liberty. The youthful Florentine, Penini, was delighted at the thought of the change, and his devotion to his mother was instanced one night when Browning playfully refused to give his wife a letter, and Pen, taking the byplay seriously, fairly smothered her in his clinging embrace, exclaiming, “Never mind, mine darling Ba!” He had caught up his mother’s pet name, “Ba,”[Pg 145] and often used it. It was this name to which she refers in the poem beginning,
“I have a name, a little name,
Uncadenced for the ear.”
Beside the Pratolina excursion, Mr. Lytton gave a little reception for them before the Florentine circle dissolved for the summer, asking a few friends to meet the Brownings at his villa on Bellosguardo, where they all sat out on the terrace, and Mrs. Browning made the tea, and they feasted on nectar and ambrosia in the guise of cream and strawberries.
“Such a view!” said Mrs. Browning of that evening. “Florence dissolving in the purple of the hills, and the stars looking on.” Mrs. Browning’s love for Florence grew stronger with every year. That it was her son’s native city was to her a deeply significant fact, for playfully as they called him the “young Florentine,” there was behind the light jest a profound recognition of the child’s claim to his native country. Still, with all this response to the enchantment of Florence, they were planning to live in Paris, after another winter (which they wished to pass in Rome), as the elder Browning and his daughter Sarianna were now to live in the French capital, and Robert Browning was enamored of the brilliant, abounding life, and the art, and splendor of privilege, and opportunity in Paris. “I think it too probable that I may not be able to bear two successive winters in the North,” said Mrs. Browning, “but in that case it will be easy to take a flight for a few winter months into Italy, and we shall regard Paris, where Robert’s father and sister are waiting for us, as our fixed place of residence.” This plan, however, was never carried out, as Italy came to lay over them a still deeper spell, which it was impossible to break. Mr. Lytton, with whom Mrs. Browning talked of all these plans and dreams that[Pg 146] evening on his terrace, had just privately printed his drama, “Clytemnestra,” which Mrs. Browning found “full of promise,” although “too ambitious” because after Æschylus. But this young poet, afterward to be so widely known in the realm of poetry as “Owen Meredith,” and as Lord Lytton in the realm of diplomacy and statesmanship, impressed her at the time as possessing an incontestable “faculty” in poetry, that made her expect a great deal from him in the future. She invited him to visit them in their sylvan retreat that summer at Bagni di Lucca, an invitation that he joyously accepted. Some great savant, who was “strong in veritable Chinese,” found his way to Casa Guidi, as most of the wandering minstrels of the time did, and “nearly assassinated” the mistress of the ménage with an interminable analysis of a Japanese novel. Mr. Lytton, who was present, declared she grew paler and paler every moment, which she afterward asserted was not because of sympathy with the heroine of this complex tale! But this formidable scholar had a passport to Mrs. Browning’s consideration by bringing her a little black profile of her beloved Isa, which gave “the air of her head,” and then, said Mrs. Browning, laughingly, “how could I complain of a man who rather flattered me than otherwise, and compared me to Isaiah?”
But at last, after the middle of July, what with poets, and sunsets from terraces, and savants, and stars, they really left their Florence “dissolving in her purple hills” behind them, and bestowed themselves in Casa Tolomei, at the Baths, where a row of plane trees stood before the door, in which the cicale sang all day, and solemn, mysterious mountains kept watch all day and night. There was a garden, lighted by the fireflies at night, and Penini mistook the place for Eden. His happiness overflowed in his prayers, and he thriftily united the petition that God would “mate him dood” with the supplication that God would also “tate [Pg 147]him on a dontey,” thus uniting all possible spiritual and temporal aspirations. The little fellow was wild with happiness in this enchanted glade, where the poets were “safe among mountains, shut in with a row of seven plane-trees joined at top.” Mr. Browning was still working on his lyrics, of which his wife had seen very few. “We neither of us show our work to the other till it is finished,” she said. She recognized that an artist must work in solitude until the actual result is achieved.
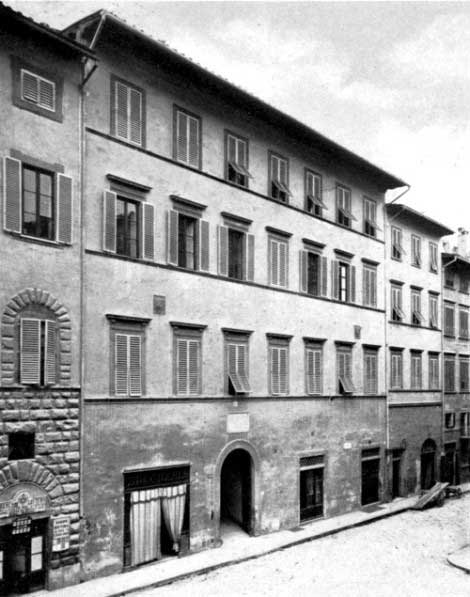

Casa Guidi
| “I heard last night a little child go singing ’Neath Casa Guidi windows, by the church.” |
| Casa Guidi Windows. |
It seems that Mr. Chorley in London had fallen into depressed spirits that summer, indulging in the melancholy meditations that none of his friends loved him, beyond seeing in him a “creature to be eaten,” and that, having furnished them with a banquet, their attentions to him were over (a most regrettable state of mind, one may observe, en passant, and one of those spiritual pitfalls which not only Mr. Chorley in particular, but all of us in general would do particularly well to avoid). The letter that Mrs. Browning wrote to him wonderfully reveals her all-comprehending sympathy and her spiritual buoyancy and intellectual poise. “You are very wrong,” she says to him, “and I am very right to upbraid you. I take the pen from Robert—he would take it if I did not. We scramble a little for the pen which is to tell you this, and be dull in the reiteration, rather than not to instruct you properly.... I quite understand how a whole life may seem rumpled and creased—torn for the moment; only you will live it smooth again, dear Mr. Chorley, take courage. You have time and strength and good aims; and human beings have been happy with much less.... I think we belied ourselves to you in England. If you knew how, at that time, Robert was vexed and worn! why, he was not the same, even to me!... But then and now believe that he loved and loves you. Set him down as a friend, as somebody to rest on, after all; and don’t fancy that because we are away here[Pg 148] in the wilderness (which blossoms as the rose, to one of us, at least) we may not be full of affectionate thoughts and feelings toward you in your different sort of life in London.” The lovely spirit goes on to remind Mr. Chorley that they have a spare bedroom “which opens of itself at the thought of you,” and that if he can trust himself so far from home, she begs him to try it for their sakes. “Come and look in our faces, and learn us more by heart, and see whether we are not two friends?”
Surely, that life was rich, whatever else it might be denied, that had Elizabeth Browning for a friend. Her genius for friendship was not less marvelous, nor less to be considered, than her genius as a poet. Indeed, truly speaking, the one, in its ideal fullness and completeness, comprehends the other.
The summer days among the beautiful hills, and by the green, rushing river, were made aboundingly happy to the Brownings by the presence of their friends, the Storys, who shared these vast solitudes. The Storys had a villa perched on the top of the hill, just above the Brownings’, the terrace shaded with vines, and the great mountains towering all around them, while a swift mountain brook swept by under an arched bridge, its force turning picturesque mills far down the valley. Under the shadow of the chestnut trees fringing its banks, Shelley had once pushed his boat. “Of society,” wrote Story to Lowell, “there is none we care to meet but the Brownings, and with them we have constant and delightful intercourse, interchanging long evenings, two or three times a week, and driving and walking whenever we meet. They are so simple, unaffected, and sympathetic. Both are busily engaged in writing, he on a volume of lyrics, and she on a tale or novel in verse.”
This “tale” must have been “Aurora Leigh.” The wives of the poet and the sculptor held hilarious intercourse while going back and forth between each other’s houses on[Pg 149] donkey-back, with an enjoyment hardly eclipsed by that of Penini himself, whose prayer that God would let him ride on “dontey-back” was so aboundingly granted that the child might well believe in the lavishness of divine mercies. Browning and Story walked beside and obediently held the reins of their wives’ steeds, that no mishap might occur. How the picture of these Arcadian days, in those vast leafy solitudes, peopled only by gods and muses, the attendant “elementals” of these choice spirits, flashes out through more than the half century that has passed since those days of their joyous intercourse. There was a night when Story went alone to take tea with the Brownings, staying till nearly midnight, and Browning accompanied him home in the mystic moonlight. Mrs. Browning, who apparently shared her little son’s predilections for the donkey as a means of transportation, would go for a morning ride, Browning walking beside her as slowly as possible, to keep pace with the donkey’s degree of speed.
Into this Arcady came, by some untraced dispensation of the gods, a French master of recitations, who had taught Rachel, and had otherwise allied himself with the great. M. Alexandre brought his welcome with him, in his delightful recitations from the poets. Mr. Lytton, having accepted Mrs. Browning’s invitation given to him on his Bellosguardo terrace, now appeared; and the Storys and the Brownings organized a festa, in true Italian spirit, in an excursion they should all make to Prato Fiortito.
Prato Fiortito is six miles from Bagni di Lucca, perpendicularly up and down, “but such a vision of divine scenery,” said Mrs. Browning. High among the mountains, Bagni di Lucca is yet surrounded by higher peaks of the Apennines. The journey to Prato Fiortito is like going up and down a wall, the only path for the donkeys being in the beds of the torrents that cut their way down in the spring.
Here, after “glorious climbing,” in which Mrs. Browning[Pg 150] distinguished herself no less than the others, they arrived at the little old church, set amid majestic limestone mountains and embowered in purple shade. Here they feasted, Penini overcome with delight, and on shawls spread under the great chestnut trees Mrs. Browning and Mrs. Story were made luxuriously comfortable, while they all talked and read, M. Alexandre reciting from the French dramatists, and Lytton reading from his “Clytemnestra.” The luncheon was adorned by a mass of wild strawberries, picked on the spot, by Browning, Story, Lytton, and Alexandre, while the ladies co-operated in the industry at this honestly earned feast by assisting to hull the berries. The bottle of cream and package of sugar tucked away in the picnic basket added all that heart could desire to this ambrosial luncheon. Mrs. Story, whom Mrs. Browning described as “a sympathetic, graceful woman, fresh and innocent in face and thought,” was a most agreeable companion; and she and Mrs. Browning frequently exchanged feminine gossip over basins of strawberries and milk in each other’s houses, for strawberries abounded in these hills. “If a tree is felled in the forests,” said Mrs. Browning, “strawberries spring up just as mushrooms might, and the peasants sell them for just nothing.”
One night when the Brownings were having tea with the Storys, the talk turned on Hawthorne. Story, of course, knew the great romancer, whom the Brownings had not then met and about whom they were curious. “Hawthorne is a man who talks with a pen,” said Story; “he does not open socially to his intimate friends any more than he does to strangers. It isn’t his way to converse.” Mrs. Browning had then just been reading the “Blithedale Romance,” in which she had sought unavailingly, it seems, for some more personal clue to the inner life of its author.
On a brilliant August day the Brownings and the Storys fared forth on a grand excursion on donkey-back, to[Pg 151] Benabbia, a hilltown, perched on one of the peaks. Above it on the rocks is a colossal cross, traced by some thunder-bolt of the gods, cut in the solid stone. From this excursion they all returned after dark, in terror of their lives lest the donkeys slip down the sheer precipices; but the scenery was “exquisite, past all beauty.” Mrs. Browning was spell-bound with its marvelous sublimity, as they looked around “on the world of innumerable mountains bound faintly with the gray sea, and not a human habitation.”
Mrs. Browning was then reading the poems of Coventry Patmore, just published, of which Browning had read the manuscript in London in the previous year. The poems of Alexander Smith had also appeared at this time, and in him Mrs. Browning found “an opulence of imagery,” but a defect as to the intellectual part of poetry. With her characteristic tolerance, she instanced his youth in plea of this defect, and said that his images were “flowers thrown to him by the gods, gods beautiful and fragrant, but having no root either in Etna or Olympus.” Enamored, as ever, of novels, she was also reading “Vilette,” which she thought a strong story, though lacking charm, and Mrs. Gaskell’s “Ruth,” which pleased her greatly.
With no dread of death, Mrs. Browning had a horror of the “rust of age,” the touch of age “which is the thickening of the mortal mask between souls. Why talk of age,” she would say, “when we are all young in soul and heart?... Be sure that it’s highly moral to be young as long as possible. Women who dress ‘suitably to their years’ (that is, as hideously as possible) are a disgrace to their sex, aren’t they now?” she would laughingly declare.
This summer in the Apennines at Bagni di Lucca had been a fruitful one to Browning in his poetic work. It became one of constant development, and, as Edmund Gosse points out, “of clarification and increasing selection.” He had already written many of his finest lyrics, “Any[Pg 152] Wife to Any Husband,” “The Guardian Angel,” and “Saul”; and in these and succeeding months he produced that miracle of beauty, the poem called “The Flight of the Duchess”; and “A Grammarian’s Funeral,” “The Statue and the Bust,” “Childe Roland to the Dark Tower Came,” “Fra Lippo Lippi,” and “Andrea del Sarto.” To Milsand, Browning wrote that he was at work on lyrics “with more music and painting than before.”
The idyllic summer among the grand chestnut trees came to an end, as summers always do, and October found the Brownings again in Casa Guidi, though preparing to pass the winter in Rome. Verdi had just completed his opera of “Trovatore,” which was performed at the Pergola in Florence, and the poets found it “very passionate and dramatic.”
In November they fared forth for Rome, “an exquisite journey of eight days,” chronicled Mrs. Browning, “seeing the great monastery and triple church of Assisi, and that wonderful passion of waters at Terni.”
It was the picturesque Rome of the popes that still remained in that winter, and the Eternal City was aglow with splendid festivals and processions and with artistic interest. The Brownings caught something of its spirit, even as they came within view of the colossal dome of St. Peter’s, and they entered the city in the highest spirits, “Robert and Penini singing,” related Mrs. Browning, “actually, for the child was radiant and flushed with the continual change of air and scene.” The Storys had engaged an apartment for them, and they found “lighted fires and lamps,” and all comfort.
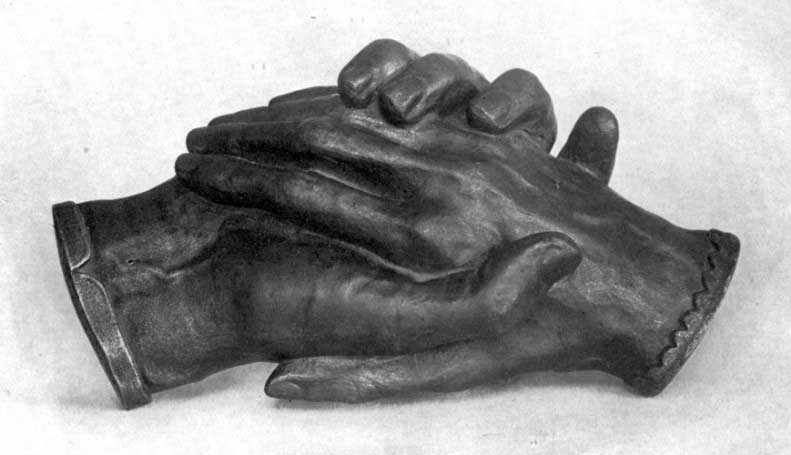
The Clasped Hands of Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning
Cast in bronze from the model taken by Harriet Hosmer in Rome, 1853.
The original is in the possession of the author.
That winter of 1853-1854 still stands out in the Roman panorama as one of exceptional brilliancy. There was a galaxy of artists,—Story, who had already won fame on two continents; William Page, who believed he had discovered the secret of Titian’s coloring; Crawford, and [Pg 153]“young Leighton,” as Mrs. Browning called the future president of the Royal Academy; Gibson, and his brilliant pupil, Harriet Hosmer; Fisher, who painted a portrait of Browning, and also of Penini, for his own use to exhibit in London. It was during this winter that Miss Hosmer took the cast of the “Clasped Hands” of the Brownings, which was put into bronze, and which must always remain a work of the most tender interest. Mrs. Browning was very fond of “Hatty,” as she called her, and in a letter to her Isa she described a pretty scene when Lady Marian Alford, the daughter of the Duke of Northampton, knelt before the girl sculptor and placed on her finger a ring of diamonds surrounding a ruby. Browning’s early friend, M. de Ripert-Monclar, to whom he had dedicated his “Paracelsus,” and Lockhart, were also in Rome; and Leighton was completing his great canvas of Cimabue’s Madonna carried in procession through the streets of Florence.
The Brownings were domiciled in the Bocca di Leone, while the Storys were in the Piazza di Spagna; Thackeray and his two daughters were close at hand, in and out at the Brownings’, with his “talk of glittering dust swept out of salons.” There were Hans Christian Andersen, and Fanny Kemble, with her sister, Mrs. Sartoris, and Lady Oswald, a sister of Lord Elgin. Thackeray’s daughter, Miss Anne Thackeray (now Lady Ritchie), still finds vivid her girlish memory of Mrs. Browning,—“a slight figure in a thin black gown and the unpretentious implements of her magic,” by her sofa, on a little table. Lady Ritchie turns back to her diary of that winter to find in it another of her early impressions of Mrs. Browning, “in soft, falling flounces of black silk, with her heavy curls drooping, and a thin gold chain around her neck.” This chain held a tiny locket of crystal set in coils of gold, which she had worn from childhood, not at all as an ornament, but as a little souvenir. On her death Mr. Browning put into it some[Pg 154] of her hair, and gave the treasured relic to Kate Field, from whom it came later into the possession of the writer of this book. Lady Ritchie recalls one memorable evening that season in the salon of Mrs. Sartoris, when the guests assembled in the lofty Roman drawing-room, full of “flowers and light, of comfort and color.” She recalls how the swinging lamps were lighted, shedding a soft glow; how the grand piano stood open, and there was music, and “tables piled with books,” and flowers everywhere. The hostess was in a pearl satin gown with flowing train, and sat by a round table reading aloud from poems of Mr. Browning, when the poet himself was announced, “and as she read, in her wonderful muse-like way, he walked in.” All the lively company were half laughing and half protesting, and Mrs. Kemble, with her regal air, called him to her side, to submit to him some disputed point, which he evaded. Mrs. Sartoris had a story, with which she amused her guests, of a luncheon with the Brownings, somewhere in Italy, where, when she rose to go, and remarked how delightful it had been, and the other guests joined in their expressions of enjoyment, Mr. Browning impulsively exclaimed: “Come back and sup with us, do!” And Mrs. Browning, with the dismay of the housewife, cried: “Oh, Robert, there is no supper, nothing but the remains of the pie.” To which the poet rejoined: “Then come back and finish the pie.”
Mrs. Browning was deeply attached to Fanny Kemble. She describes her, at this time, as “looking magnificent, with her black hair and radiant smile. A very noble creature, indeed,” added Mrs. Browning; “somewhat unelastic, attached to the old modes of thought and convention, but noble in qualities and defects.... Mrs. Sartoris is genial and generous ... and her house has the best society in Rome, and exquisite music, of course.”
Mrs. Browning often joined her husband in excursions to[Pg 155] galleries, villas, and ruins; and when in the Sistine Chapel, on a memorable festival, they heard “the wrong Miserere,” she yet found it “very fine, right or wrong, and overcoming in its pathos.” M. Goltz, the Austrian Minister, was an acquaintance whom the Brownings found “witty and agreeable,” and Mrs. Browning called the city “a palimpsest Rome,” with its records written all over the antique.
The sorrow of the Storys over the death of a little son shadowed Mrs. Browning, and she feared for her own Penini, but as the winter went on she joyfully wrote of him that he “had not dropped a single rose-leaf from his cheeks,” and with her sweet tenderness of motherly love she adds that he is “a poetical child, really, and in the best sense. He is full of sweetness and vivacity together, of imagination and grace,” and she pictures his “blue, far-reaching eyes, and the innocent face framed in golden ringlets.” Mrs. Kemble came to them two or three times a week, and they had long talks, “we three together,” records Mrs. Browning. Mr. Page occupied the apartment just over that of the Brownings, and they saw much of him. “His portrait of Miss Cushman is a miracle,” exclaimed Mrs. Browning. Page begged to paint a portrait of the poet, of which Mrs. Browning said that he “painted a picture of Robert like an Italian, and then presented it to me like a prince.” The coloring was Venetian, and the picture was at first considered remarkable, but its color has entirely vanished now, so that it seems its painter was not successful in surprising the secret of Titian. In the spring of 1910 Mr. Barrett Browning showed this picture to some friends in his villa near Florence, and its thick, opaque surface hardly retained even a suggestion of color.
Not the least of Mrs. Browning’s enjoyment of that winter was the pleasure that Rome gave to her little son. “Penini is overwhelmed with attentions and gifts of all kinds,” she wrote, and she described a children’s party[Pg 156] given for him by Mrs. Page, who decorated the table with a huge cake, bearing “Penini” in sugar letters, where he sat at the head and did the honors. Browning all this time was writing, although the social allurements made sad havoc on his time. They wandered under the great ilex trees of the Pincio, and gazed at the Monte Mario pine. Then, as now, every one drove in that circular route on the Pincian hill, where carriages meet each other in passing every five minutes. With the Storys and other friends they often went for long drives and frequent picnics on the wonderful Campagna, that vast green sea that surrounds Rome, the Campagna Mystica. On one day Mr. Browning met “Hatty” Hosmer on the Spanish Steps, and said to her: “Next Saturday Ba and I are going to Albano on a picnic till Monday, and you and Leighton are to go with us.” “Why this extravagance?” laughingly questioned Miss Hosmer. “On account of a cheque, a buona grazia, that Ticknor and Fields of Boston have sent—one they were not in the least obliged to send,” replied the poet.
In those days there was no international copyright, but Mr. Browning’s Boston publishers needed no legal constraint to act with ideal honor. So on the appointed morning, a partie carré of artists—two poets, one sculptor, one painter—drove gayly through the Porta San Giovanni, on that road to Albano, with its wonderful views of the Claudian aqueducts in the distance, through whose arches the blue sky is bluer, and beyond which are the violet-hued Alban hills. Then, as now, the road led by the Casa dei Spirite, with its haunting associations, and its strange mural decorations of specters and wraiths. Past that overhanging cliff, with its tragic legend, they drove, encountering the long procession of wine carts, with their tinkling bells, and the dogs guarding the sleeping padrones. Passing the night in Albano, the next day they mounted donkeys for their excursion into the Alban hills, past lonely [Pg 157]monasteries, up the heights of Rocca di Papa, where the traveler comes on the ancient camping-ground of Hannibal, and where they see the padres and acolytes sunning themselves on the slopes of Monte Cavo; on again, to the rocky terraces from which one looks down on Alba Longa and the depths of Lago di Nemi, beneath whose waters is still supposed to be the barque of Caligula, and across the expanse of the green Campagna to where Æneas landed.
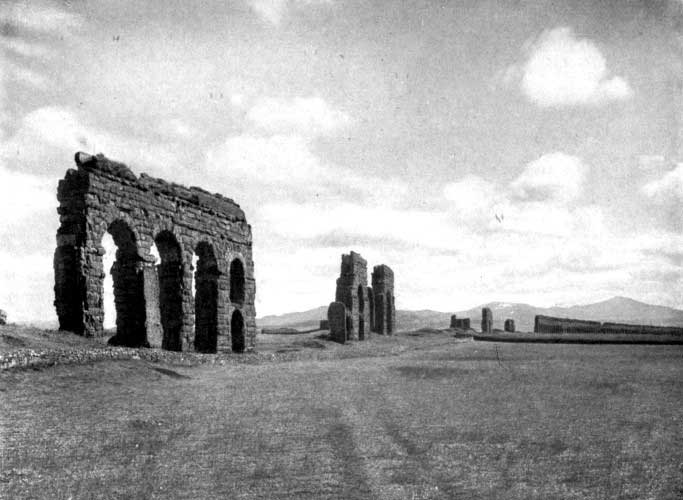

The Campagna and Ruins of the Claudian Aqueducts, Rome.
| “There, branching from the brickwork’s cleft, Some old tomb’s ruin....” |
| Two in the Campagna. |
Miss Hosmer is the authority on this poetic pilgrimage, and she related that they all talked of art, of the difficulties of art,—those encountered by the poet, the sculptor, and the painter,—each regarding his own medium of expression as the most difficult. Mrs. Browning’s “Hatty” had bestowed in her bag a volume of Mr. Browning’s, and on the homeward journey from Albano to Rome he read aloud to them his “Saul.” At the half-way house on the Campagna, the Torre di Mezza, they paused, to gaze at the “weird watcher of the Roman Campagna,” the monument to Apuleia, whose ruins are said to have assumed her features.
Nothing in all the classic atmosphere of Rome, filled with the most impressive associations of its mighty past, appealed more strongly to the Brownings than the glorious Campagna, with its apparently infinite open space, brilliant with myriads of flowers, and the vast billowing slopes that break like green waves against the purple hills, in their changeful panorama of clouds and mists and snow-crowned heights dazzling under a glowing sun.
Fascinating as this winter in Rome had been to them, rich in friendships and in art, the Brownings were yet glad to return to their Florence with the May days, to give diligence and devotion to their poetic work, which nowhere proceeded so felicitously as in Casa Guidi.
Browning was now definitely engaged on the poems that were to make up the “Men and Women.” Mrs. Browning[Pg 158] was equally absorbed in “Aurora Leigh.” Each morning after their Arcadian repast of coffee and fruit, he went to his study, and she to the salotto, whose windows opened on the terrace looking out on old gray San Felice where she always wrote, to devote themselves to serious work. “Aurora Leigh” proceeded rapidly some mornings, and again its progress would remind her of the web of Penelope. During this summer Browning completed “In a Balcony,” and wrote the “Holy Cross Day,” the “Epistle of Karnish,” and “Ben Karshook’s Wisdom.” Like his wife, Browning held poetry to be above all other earthly interests; he was a poet by nature and by grace, and his vast range of scholarship, his “British-Museum-Library memory,” and his artistic feeling and taste, all conserved to this one end. But poetry to him was not outside, but inclusive of the very fullest human life. Mrs. Browning’s lines,
“... No perfect artist is developed here
From any imperfect woman,...”
embodied his convictions as well, for man and woman alike. He had that royal gift of life in its fullness, an almost boundless capacity of enjoyment, and to him life meant the completest development and exercise of all its powers.
The Brownings found their Florentine circle all in evidence. Mr. Lytton, a favorite and familiar visitor at Casa Guidi; Frederick Tennyson (and perhaps his “forty fiddlers” as well), and the Trollopes, Isa Blagden, and various wandering minstrels. They passed evenings with Mr. Lytton in his villa, and would walk home “to the song of nightingales by starlight and firefly light.” To Mrs. Browning Florence looked more beautiful than ever after Rome. “I love the very stones of it,” she said. Limitations of finance kept them in Florence all that summer. “A ship was to have brought us in something, and[Pg 159] brought us in nothing,” she explained to a friend in England, “and the nothing had a discount, beside.” But she took comfort in the fact that Penini was quite as well and almost as rosy as ever, despite the intense heat; and the starlight and the song of the nightingales were not without consolation. A letter from Milsand (“one of the noblest and most intellectual men,” says Mrs. Browning of him) came, and they were interested in his arraignment of the paralysis of imagination in literature. In September she hears from Miss Mitford of her failing health, and tenderly writes: “May the divine love in the face of our Lord Jesus Christ shine upon you day and night, with His ineffable tenderness.” Mrs. Browning’s religious feeling was always of that perfect reliance on the Divine Love that is the practical support of life. “For my own part,” she continues, “I have been long convinced that what we call death is a mere incident in life.... I believe that the body of flesh is a mere husk that drops off at death, while the spiritual body emerges in glorious resurrection at once. Swedenborg says some people do not immediately realize that they have passed death, which seems to me highly probable. It is curious that Frederick Denison Maurice takes this precise view of the resurrection, with apparent unconsciousness of what Swedenborg has stated, and that I, too, long before I had ever read Swedenborg, or had even heard the name of Maurice, came to the same conclusion.... I believe in an active, human life, beyond death, as before it, an uninterrupted life.” Mrs. Browning would have found herself in harmony with that spiritual genius, Dr. William James, who said: “And if our needs outrun the visible universe, why may not that be a sign that the invisible universe is there? Often our faith in an uncertified result is the only thing that makes the result come true.” Faith is the divine vision, and no one ever more absolutely realized this truth than Elizabeth Browning.
[Pg 160]“Ah, blessed vision! blood of God!
My spirit beats her mortal bars,
As down dark tides the glory slides,
And star-like mingles with the stars.”
At another time Mrs. Browning remarked that she should fear for a revealed religion incapable of expansion, according to the needs of man; while Dr. James has said, “Believe what is in the line of your needs.” Many similarities of expression reveal to how wonderful a degree Mrs. Browning had intuitively grasped phases of truth that became the recognized philosophy of a succeeding generation, and which were stamped by the brilliant and profound genius of William James, the greatest psychologist of the nineteenth century. “What comes from God has life in it,” said Mrs. Browning, “and certainly from the growth of all living things, spiritual growth cannot be excepted.”
The summer passed “among our own nightingales and fireflies,” playfully said Mrs. Browning, and in the autumn Mrs. Sartoris stopped to see them, on her way to Rome, “singing passionately and talking eloquently.”
Notwithstanding some illness, Mrs. Browning completed four thousand lines of “Aurora Leigh” before the new year of 1855, in which were expressed all her largest philosophic thought, and her deepest insight into the problems of life. Fogazzaro, whose recent death has deprived Italy of her greatest literary inspirer since Carducci, said of “Aurora Leigh” that he wished the youth of Italy might study this great poem,—“those who desire poetic fame that they might gain a high conception of poetry; the weak, in that they might find stimulus for strength; the sad and discouraged, in that they might find comfort and encouragement.” It was this eminent Italian novelist and Senator (the King of Italy naming a man as Senator, not in the least because of any political reasons, but to confer on him the honor of recognition of his genius in Literature, Science,[Pg 161] or Art, and a very inconvenient, however highly prized, honor he often finds it),—Senator Antonio Fogazzaro, who contributed, to an Italian biography[7] of the Brownings by Fanny Zampini, Contessa Salazar, an “Introduction” which is a notable piece of critical appreciation of the wedded poets from the Italian standpoint. The Senator records himself as believing that few poets can be read “with so much intellectual pleasure and spiritual good; for if the works of Robert and Elizabeth Browning surprise us by the vigorous originality of their thought,” he continues, “they also show us a rare and salutary spectacle,—two souls as great in their moral character as in their poetic imagination. ‘Aurora Leigh’ I esteem Mrs. Browning’s masterpiece.... The ideal poet is a prophet, inspired by God to proclaim eternal truth....”
The student of Italian literature will find a number of critical appreciations of the Brownings, written within the past forty or fifty years, some of which offer no little interest. “Every man has two countries, his own and Italy,” and the land they had made their own in love and devotion returned this devotion in measure overflowing.
Robert and Elizabeth Browning would have been great,—even immortally great, as man and woman, if they had not been great poets. They both lived, in a simple, natural way, the essential life of the spirit, the life of scholarship and noble culture, of the profound significance of thought, of creative energy, of wide interest in all the important movements of the day, and of beautiful and sincere friendships.
“O life, O poetry,
Which means life in life,”
wrote Mrs. Browning.
The character of Mrs. Browning has been so often portrayed as that of some abnormal being, half-nervous invalid,[Pg 162] half-angel, as if she were a special creation of nature with no particular relation to the great active world of men and women, that it is quite time to do away with the category of nonsense and literary hallucination. One does not become less than woman by being more. Mrs. Browning fulfilled every sweetest relation in life as daughter, sister, friend, wife, and mother; and her life was not the less normal in that it was one of exceptional power and exaltation. She saw in Art the most potent factor for high service, and she held that it existed for Love’s sake, for the sake of human co-operation with the purposes of God.
| “Inward evermore To outward,—so in life, and so in art Which still is life.” “... I love thee with the breath, Smiles, tears, of all my life!—and, if God choose, I shall but love thee better after death.” |
London Life—An Interlude in Paris—“Aurora Leigh”—Florentine Days—“Men and Women”—The Hawthornes—“The Old Yellow Book”—A Summer in Normandy—The Eternal City—The Storys and Other Friends—Lilies of Florence—“It is Beautiful!”
The Florentine winter is by no means an uninterrupted dream of sunshine and roses; the tramontana sweeps down from the encircling Apennines, with its peculiarly piercing cold that penetrates the entire system with the unerring precision of the Röentgen ray; torrents of icy rains fall; and the purple hills, on whose crest St. Domenico met St. Benedict, are shrouded in clouds and mist. All the loveliness of Florence seems to be utterly effaced, till one questions if it existed except as a mirage; but when the storm ceases, and the sun shines again, there is an instantaneous transformation. In a moment, in the twinkling of an eye, the spell of enchantment resumes its sway over the Flower Town, and all is forgiven and forgotten.
The winter of 1855 was bitterly cold, and by January the Brownings fairly barricaded themselves in two rooms which could best be heated, and in these fires were kept[Pg 164] up by day as well as night. In April, however, the divine days came again, and the green hillslope from the Palazzo Pitti to the Boboli Gardens was gay with flowers. Mr. Browning gave four hours every day to dictating his poems to a friend who was transcribing them for him. Mrs. Browning had completed some seven thousand lines of “Aurora Leigh,” but not one of these had yet been copied for publication. Various hindrances beset them, but finally in June they left for England, their most important impedimenta being sixteen thousand lines of poetry, almost equally divided between them, comprising his manuscript for “Men and Women,” and hers for “Aurora Leigh,” complete, save for the last three books. The change was by no means unalloyed joy. To give up, even temporarily, their “dream-life of Florence,” leaving the old tapestries and pre-Giotto pictures, for London lodgings, was not exhilarating; but after a week in Paris they found themselves in an apartment in No. 13 Dorset Street, Manchester Square, where they remained until October, every hour filled with engagements or work. Proof-sheets were coming in at all hours; likewise friends, with the usual contingent of the “devastators of a day,” and all that fatigue and interruption and turmoil that lies in wait for the pilgrim returning to his former home, beset and entangled them. Mrs. Browning’s youngest brother, Alfred Barrett, was married that summer to his cousin Lizzie, the “pretty cousin” to whom allusion has already been made as the original of Mrs. Browning’s poem, “A Portrait.” They were married in Paris at the English Embassy, and passed the summer on the Continent. Mrs. Browning’s sister Henrietta (Mrs. Surtees Cook) was unable to come up to London, so that the hoped-for pleasure of seeing this brother and sister was denied her; but Miss Arabel Barrett was close at hand in the Wimpole Street home, and the sisters were much together. Mr. Barrett had never changed his mental attitude[Pg 165] regarding the marriage of his daughter Elizabeth, nor that of any of his children, and while this was a constant and never-forgotten grief with Mrs. Browning, there seems no necessity for prolonged allusion to it. The matter can only be relegated to the realms of non-comprehension as the idiosyncrasy of an otherwise good man, of intelligence and much nobility of nature.
The Brownings were invited to Knebworth, to visit Lord Lytton, but they were unable to avail themselves of the pleasure because of proof-sheets and contingent demands which only writers with books in press can understand. Proof-sheets are unquestionably endowed with some super-human power of volition, and invariably arrive at the psychological moment when, if their author were being married or buried, the ceremony would have to be postponed until they were corrected. But the poets were not without pleasant interludes, either; as when Tennyson came from the Isle of Wight to London for three or four days, two of which he passed with the Brownings. He “dined, smoked, and opened his heart” to them; and concluded this memorable visit at the witching hour of half-past two in the morning, after reading “Maud” aloud the evening before from the proof-sheets. The date of this event is established by an inscription affixed to the back of a pen-and-ink sketch of Tennyson, made on that night by Dante Gabriel Rossetti, and which is now in the possession of Robert Barrett Browning. This inscription, written by Robert Browning, reads: “Tennyson read his poem ‘Maud’ to E. B. B., R. B., Arabel, and Rossetti, on the evening of Sept. 27th, 1855, at 13, Dorset Street. Rossetti made this sketch of Tennyson, as he sat, reading, on one end of the sofa, E. B. B. being on the other end.” And this is signed, “R. B. March 6th, 1874 ... 19, Warwick Crescent.” As the date is Mrs. Browning’s birthday, it is easy to realize how, in that March of 1874, he was recalling[Pg 166] tender and beloved memories. On the drawing itself Mrs. Browning had, at the time of the reading, copied the first two lines of “Maud.” Tennyson replied to a question from William Sharp, who in 1882 wrote to the Laureate to ask about this night, that he had “not the slightest recollection” of Rossetti’s presence; but the inscription on the picture establishes the fact. William Michael Rossetti was also one of the group, and a record that he made quite supports the fact of Tennyson’s unconsciousness of his brother’s presence, for he says: “So far as I remember the Poet-Laureate neither saw what my brother was doing nor knew of it afterward.” And as if every one of this gifted group present that night left on record some impression, Dante Gabriel Rossetti has noted that, after Tennyson’s reading, Browning read his “Fra Lippo Lippi,” and “with as much sprightly variation as there was in Tennyson of sustained continuity.” In a letter to Allingham, Rossetti also alluded to this night, and infused a mild reproach to Mrs. Browning in that her attention was diverted by “two not very exciting ladies”; and in a letter to Mrs. Tennyson, Mrs. Browning speaks of being “interrupted by some women friends whom I loved, but yet could not help wishing a little further just then, that I might sit in the smoke, and listen to the talk,” after the reading. So, from putting together, mosaic fashion, all the allusions made by the cloud of witnesses, the reader constructs a rather accurate picture of that night of the gods. Mrs. Browning, who “was born to poet-uses,” like the suitor of her own “Lady Geraldine,” was in a rapture of pleasure that evening, and of “Maud” she wrote: “The close is magnificent, full of power, and there are beautiful, thrilling lines all through. If I had a heart to spare, the Laureate would have won mine.” Tennyson’s voice she found “like an organ, music rather than speech,” and she was “captivated” by his naïveté, as he stopped every now [Pg 167]and then to say, “There’s a wonderful touch!” Mrs. Browning writes to Mrs. Tennyson of “the deep pleasure we had in Mr. Tennyson’s visit to us.” She adds:
“He didn’t come back, as he said he would, to teach me the ‘Brook’ (which I persist, nevertheless, in fancying I understand a little), but he did so much and left such a voice (both him ‘and a voice!’) crying out ‘Maud’ to us, and helping the effect of the poem by the personality, that it’s an increase of joy and life to us ever.”
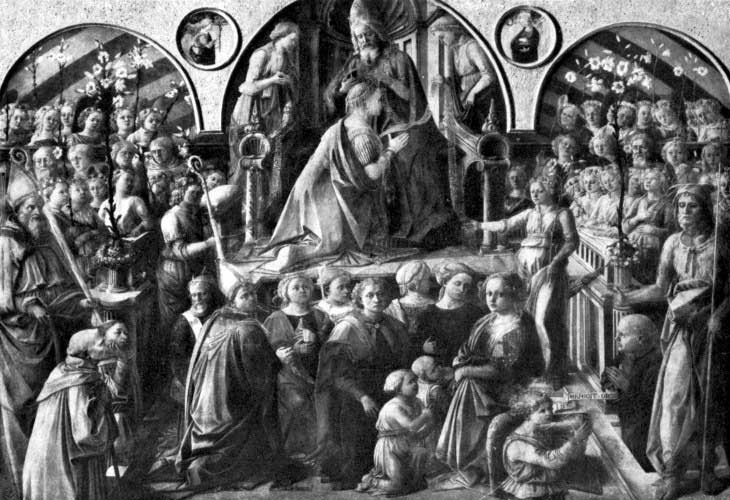

The Coronation of the Virgin, Filippo Lippi.
in the accademia di belle arti, florence.
| “Ringed by a bowery, flowery angel-brood, Lilies and vestments and white faces....” |
| Fra Lippo Lippi |
Deciding to pass the ensuing winter in Paris, the Brownings found themselves anxious to make the change, that they might feel settled for the time, as she needed entire freedom from demands that she might proceed with her “Aurora Leigh.” He had conceived the idea of revising and recasting “Sordello.” They passed an evening with Ruskin, however, and presented “young Leighton” to him. They met Carlyle at Forster’s, finding him “in great force”—of denunciations. They met Kinglake, and were at the Proctors, and of the young poet, Anne Adelaide Proctor, Mrs. Browning says, “How I like Adelaide’s face!” Mrs. Sartoris and Mrs. Kemble were briefly in London, and Kenyon, the beloved friend, vanished to the Isle of Wight. To Penini’s great delight, Wilson, the maid, married a Florentine, one Ferdinando Romagnoli, who captivated the boy by his talk of Florence, and Penini caught up his pretty Italian enthusiasms, and discoursed of Florentine skies, and the glories of the Cascine, to any one whom he could waylay.
In Paris they first established themselves in the Rue de Grenelle, in the old Faubourg San Germain, a location they soon exchanged for a more comfortable apartment in the Rue de Colisée, just off the Champs Élysées. Here they renewed their intercourse with Lady Elgin (now an invalid) and with her daughter, Lady Augusta Bruce, Madame Mohl, and with other friends. Mrs. Browning was absorbed[Pg 168] in her great poem, which she was able to complete, however, only after their return to London the next June, and never did an important literary work proceed with less visible craft. She lay on her sofa, half supported by cushions, writing with pencil on little scraps of paper, which she would slip under the pillows if any chance visitor came in. “Elizabeth is lying on the sofa, writing like a spirit,” Browning wrote to Harriet Hosmer. To Mrs. Browning Ruskin wrote, praising her husband’s poems, which gratified her deeply, and she replied, in part, that when he wrote to praise her poems, of course she had to bear it. “I couldn’t turn around and say, ‘Well, and why don’t you praise him, who is worth twenty of me?’ One’s forced,” she continued, “to be rather decent and modest for one’s husband as well as for one’s self, even if it’s harder. I couldn’t pull at your coat to read ‘Pippa Passes,’ for instance.... But you have put him on your shelf, so we have both taken courage to send you his new volumes, ‘Men and Women,’... that you may accept them as a sign of the esteem and admiration of both of us.” Mrs. Browning considered these poems beyond any of his previous work, save “Paracelsus,” but there is no visible record left of what she must have felt regarding that tender and exquisite dedication to her, that “One Word More ... To E. B. B.,” which must have been to her
“The heart’s sweet Scripture to be read at night.”
These lines are, indeed, a fitting companion-piece to her “Sonnets from the Portuguese.” For all these poems, his “fifty men and women,” were for her,—his “moon of poets.”
“There they are, my fifty men and women
Naming me the fifty poems finished!
Take them, Love, the book and me together;
Where the heart lies, let the brain lie also.
······
[Pg 169]
I shall never, in the years remaining,
Paint you pictures, no, nor carve you statues,
Make you music that should all-express me;
······
Verse and nothing else have I to give you.
Other heights in other lives, God willing;
All the gifts from all the heights, your own, Love!”
So he wrote to his “one angel,—borne, see, on my bosom!” For her alone were the
“Silent, silver lights and darks undreamed of,”
and while there was one side to face the world with, he thanked God that there was another,—
“One to show a woman when he loves her!”
It was Rossetti, however, who was the true interpreter of Browning to Ruskin,—for if it requires a god to recognize a god, so likewise in poetic recognitions. To Rossetti the poems comprised in “Men and Women” were the “elixir of life.” The moving drama of Browning’s poetry fascinated him. Some years before he had chanced upon “Pauline” in the British Museum, and being unable to procure the book, had copied every line of it. The “high seriousness” which Aristotle claims to be one of the high virtues of poetry, impressed Rossetti in Browning. What a drama of the soul universal was revealed in that “fifty men and women”! What art, what music, coming down the ages, from Italy, from Germany, and what pictures from dim frescoes, and long-forgotten paintings hid in niche and cloister, were interpreted in these poems! How one follows “poor brother Lippo” in his escapade:
“... I could not paint all night—
Ouf! I leaned out of window for fresh air.
There came a hurry of feet and little feet,
A sweep of lute-strings, laughs, and whifts of song,—
[Pg 170]Flower o’ the broom,
Take away love, and our earth is a tomb!
Flower o’ the quince,
I let Lisa go, and what good in life since?”
And in “Andrea del Sarto” what passionate pathos of an ideal missed!
“But all the play, the insight and the stretch—
Out of me, out of me! And wherefore out?
Had you enjoined them on me, given me soul,
We might have risen to Rafael, I and you!
······
Had you ... but brought a mind!
Some women do so. Had the mouth there urged
‘God and the glory! never care for gain.
The present by the future, what is that?
Live for fame, side by side with Agnolo!
Rafael is waiting; up to God, all three!’
I might have done it for you....”
And that exquisite idyl of “the love of wedded souls” in “By the Fire-side.” It requires no diviner to discover from whose image he drew the line,
“My perfect wife, my Leonor.”
How Browning’s art fused poetic truth and poetic beauty in all these poems, vital with keen and shrewd observation, deep with significance, and pervaded by the perpetual recognition of a higher range of achievements than are realized on earth.
“A man’s grasp should exceed his reach,
Or what’s a heaven for?”
In all these poems can be traced the magic of Italy and happiness. (Are the two more than half synonymous?) The perfect sympathy, the delicate divination and intuitive comprehension with which Browning was surrounded by [Pg 171]his wife, were the supreme source of the stimulus and development of his powers as a poet.
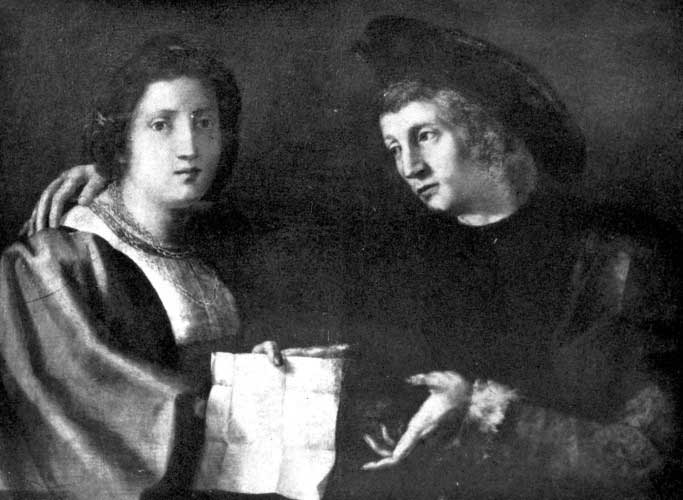

Andrea del Sarto. Portrait of the Artist and His Wife.
in the Pitti Gallery, Florence.
| “You turn your face, but does it bring your heart?” |
| Andrea del Sarto. |
The Parisian winter was full of movement and interest. No twentieth-century prophet had then arisen to instruct the populace how to live on twenty-four hours a day, but the Brownings captured what time they could rescue from the devouring elements, rose early, breakfasted at nine, and gave the next hour and a half to Penini’s lessons,—“the darling, idle, distracted child,” who was “blossoming like a rose” all this time; who “learned everything by magnetism,” and, however “idle,” was still able in seven weeks to read French “quite surprisingly.” Mrs. Browning had already finished and transcribed some six thousand lines (making five books) of “Aurora Leigh ”; but she planned at least two more books to complete the poem, which must needs be ready by June; and when, by the author’s calendar, it is February, by some necromancy June is apt to come in the next morning. The Brownings made it an invariable rule to receive no visitors till after four, but the days had still a trick of vanishing like the fleet angel who departs before he leaves his blessing. At all events, the last days of May came before “Aurora Leigh” was completed, and its author half despairingly realized that two weeks more were needed for the transcription of her little slips to the pages ready for the press.
Meantime Browning had occupied himself for a time in an attempt to revise “Sordello,” an effort soon abandoned, as he saw that, for good or ill, the work must stand as first written.
Madame Mohl’s “evenings” continued to attract Browning, where he met a most congenial and brilliant circle, and while his wife was unable to accompany him to these mild festivities, she insisted that he should avail himself of these opportunities for intercourse with French society. With Lady Monson he went to see Ristori in “Medea,” finding[Pg 172] her great, but not, in his impression, surpassing Rachel. Monckton Milnes comes over to Paris, and a Frenchman of letters gives a dinner for him, at which Browning meets George Sand and Cavour.
The success of “Men and Women” was by this time assured. Browning stood in the full light of recognition on both sides the ocean. For America—or rather, perhaps, one should say, Boston, for American recognition focused in Boston (which was then, at all events, incontestably the center of all “sweetness and light”)—discerned the greatness of Robert Browning as swiftly as any transatlantic dwellers on the watch-tower.
Rossetti, who from the days that he copied “Pauline” in the British Museum Library, not knowing the author, was an ardent admirer of Browning, found himself in Paris, and he and Browning passed long mornings in the Louvre. The painter declared that Browning’s knowledge of early Italian art was beyond that of any one whom he had met, Ruskin not excepted.
Ruskin was a standard of artistic measurement in those days to a degree hardly conceivable now; not that much of his judgment does not stand the test of time, but that authoritative criticism has so many embodiments. Mrs. Browning, to whom Ruskin was one of the nearest of her circle, considered him a critic who was half a poet as well, and her clear insight discerned what is now universally recognized, that he was “encumbered by a burning imagination.” She told him that he was apt to light up any object he looked upon, “just as we, when we carried torches into the Vatican, were not clear as to how much we brought to that wonderful Demosthenes, folding the marble round him in its thousand folds,” and questioned as to where was the dividing line between the sculptor and the torch-bearer. This fairly clairvoyant insight of Mrs. Browning into character, the ability to discern defects as[Pg 173] well as virtues where she loved, and to love where she discerned defects, is still further illustrated by a letter of hers to Ruskin on the death of Miss Mitford. “But no, her ‘judgment’ was not ‘unerring,’” wrote Mrs. Browning. “She was too intensely sympathetic not to err often ... if she loved a person it was enough.... And yet ... her judgment could be fine and discriminating, especially upon subjects connected with life and society and manners.”
Again, to a friend who had met a great bereavement she also wrote in these Paris days:
“We get knowledge in losing what we hoped for, and liberty by losing what we love. This world is a fragment, or, rather, a segment, and it will be rounded presently. Not to doubt that is the greatest blessing it gives now. The common impression of death is as false as it is absurd. A mere change of circumstances,—what more? And how near these spirits are, how conscious of us, how full of active energy, of tender reminiscence and interest in us? Who shall dare to doubt? For myself, I do not doubt at all.”
In that latest collection of Browning’s poems, no one excited more discussion at the time than “The Statue and the Bust.” There being then no Browning Societies to authoritatively decide the poet’s real meaning on any disputed point, the controversy assumed formidable proportions. Did Browning mean this poem to be an apologia for illegal love? was asked with bated breath.
The statue of Fernandino di Medici, in the Piazza dell’ Annunziata, in Florence,—that magnificent equestrian group by Giovanni da Bologna,—is one of the first monuments that the visitor who has a fancy for tracing out poetic legends fares forth to see. As an example of plastic art, alone, it is well worth a pilgrimage; but as touched by the magic of the poet’s art, it is magnetic with life. Dating back to 1608, it was left for Robert Browning to invest it with immortality.
[Pg 174]
“There’s a palace in Florence, the world knows well
And a statue watches it from the square.”
In the poem Mr. Browning alludes to the cornice, “where now is the empty shrine”; but his son believes that there never was any bust in this niche, the bust being simply the poet’s creation. The statue of the Grand Duke is remarkable enough to inspire any story; and the Florentine noble may well take pride in the manner that “John of Douay” has presented him, if he still “contrives” to see it, and still “laughs in his tomb” at the perpetual pilgrimage that is made to the scene of the legend, as well as to the royal Villa Petraja, also immortalized in Browning’s poem.
June came, the closing books of “Aurora Leigh” had been written, and under the roof of her dear friend and cousin, Kenyon, who had begged the Brownings to accept the loan of his house in Devonshire Place, the last pages were transcribed, and the dedication made to the generous friend who was the appointed good angel of their lives. They were saddened by Kenyon’s illness, which imprisoned him for that summer on the Isle of Wight, and after seeing “Aurora Leigh” through the press, they passed a little time with him at Cowes, and also visited Mrs. Browning’s sister Henrietta (Mrs. Surtees Cook), before setting out for Italy. No one in London missed them more than Dante Gabriel Rossetti. “With them has gone one of my delights,” he said; “an evening resort where I never felt unhappy.”
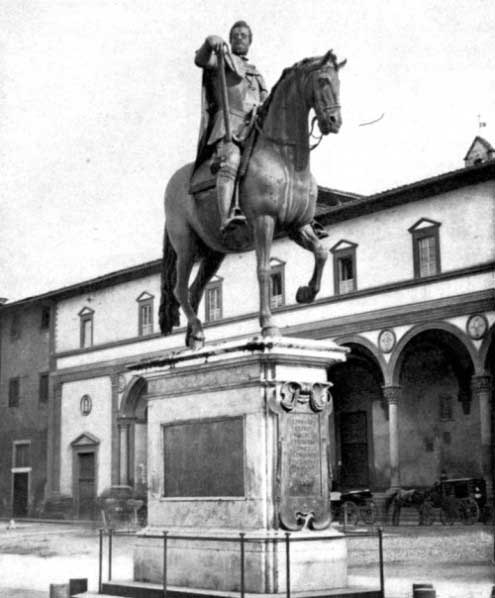

Equestrian Statue of Ferdinando de’ medici,
by Giovanni da Bologna.
in the piazza dell’ annunziata, florence.
| “There’s a palace in Florence the world knows well, And a statue watches it from the square.” |
| The Ring and the Book. |
The success of “Aurora Leigh” was immediate, a second edition being called for within a fortnight, and edition after edition followed. This work, of which, twelve years before, she had a dim foreshadowing, as of a novel in verse, has the twofold interest of a great dramatic poem and of a philosophic commentary on art and life. To estimate it only as a social treatise is to recognize but one element in its kaleidoscopic interest. Yet the narrative, it must be confessed, [Pg 175]is fantastic and unreal. When the conception of the work first dawned upon her, she said she preferred making her story to choosing that of any legend, for the theme; but the plot is its one defect, and is only saved from being a serious defect by the richness and splendor of thought with which it is invested. The poem is to some degree a spiritual autobiography; its narrative part having no foundation in reality, but on this foundation she has recorded her highest convictions on the philosophy of life. Love, Art, Ethics, the Christianity of Christ,—all are here, in this almost inexhaustible mine of intellectual and spiritual wealth. It is a poem peculiarly calculated to kindle and inspire. What a passage is this:
“... I can live
At least my soul’s life, without alms from men,
And if it be in heaven instead of earth,
Let heaven look to it,—I am not afraid.”
A profound occult truth is embodied in the following:
“Whate’er our state we must have made it first;
And though the thing displease us,—aye, perhaps,
Displease us warrantably, never doubt
That other states, though possible once, and then
Rejected by the instinct of our lives,
If then adopted had displeased us more.
······
What we choose may not be good;
But that we choose it, proves it good for us.”
No Oriental savant could more forcibly present his doctrine of karma than has Mrs. Browning in these lines. Her recognition of the power of poetry is here expressed:
“And plant a poet’s word even deep enough
In any man’s breast, looking presently
For offshoots, you have done more for the man
Than if you dressed him in a broadcloth coat,
And warmed his Sunday pottage at your fire.”
[Pg 176]Poetry was to her as serious a thing as life itself. “There has been no playing at skittles for me in either poetry, or life,” she said; “I never mistook pleasure for the final cause of poetry; nor leisure, for the hour of the poet.”
In the success of “Aurora Leigh” she was herself surprised. Private letters from strangers filled with the warmest, even if sometimes indiscriminate, praises, rained down upon her, and she found the press “astonishing in its good will.” That her “golden-hearted Robert” was “in ecstasies about it, far more than as if it had been a book of his own,” was apparently her most precious reward. Milsand, who she had fancied would hardly like this poem, wrote a critique of it for the Revue which touched her with its “extraordinary kindness.” He asked and obtained permission to translate it into French, and in a letter to Miss Sarianna Browning she speaks of her happiness that he should thus distinguish the poem.
Soon after their arrival in Florence came the saddest of news, that of the death of John Kenyon, their beloved friend, whose last thoughtful kindness was to endow them with a legacy insuring to them that freedom from material care which is so indispensable to the best achievements in art. During his life he had given to them one hundred pounds a year, and in his will he left them ten thousand guineas,—the largest of the many legacies that his generous will contained.
The carnival, always gay in Florence, was exceedingly so that year, and Penini, whose ardor for a blue domino was gratified, and who thought of nothing else for the time being, seemed to communicate his raptures, so that Browning proposed taking a box at the opera ball, and entertaining some invited friends with gallantina and champagne. Suddenly the air grew very mild, and he decided that his wife might and must go; she sent out hastily to buy a mask and domino (he had already a beautiful black[Pg 177] silk one, which she later transmuted into a black silk gown for herself), and while her endurance and amusement kept her till two o’clock in the morning, the poet and his friends remained till after four. The Italian carnival, however wild and free it may be (and is), yet never degenerates into rudeness. The inborn delicacy and gentle refinement of the people render this impossible. Yet for the time being there is perfect social equality, and at this ball the Grand Duke and Wilson’s husband, Ferdinando, were on terms of fellowship.
In the early April of that spring the summer suddenly dawned upon lovely Florence like a transformation scene on a stage. The trees in the Cascine were all a “green mist.” Everywhere was that ethereal enchantment of the Flower City, with her gleaming towers and domes, her encircling purple hills and picturesque streets. And how, indeed, could any one who has watched the loveliness of a Florentine springtime ever escape its haunting spell? The dweller in Italy may see a thousand things to desire,—better public privileges, more facilities for comfort, but the day comes when, if he has learned to love the Italian atmosphere so intensely that all the glories of earth could not begin to compensate for it, he would give every conceivable achievement of modern art and progress for one hour among those purple hills, for one hour with the sunset splendors over the towers, and the olive-crowned heights of Fiesole and Bellosguardo; or to hear again the impassioned strains of street singers ring out in pathetic intensity in the bewildering moonlight. La Bella Firenze, lying dream-enchanted among her amethyst hills, would draw her lover from the wilds of Siberia, for even one of those etherial evenings, when the stars blaze in a splendor over San Miniato, or one rose-crowned morning, when the golden sunshine gilds the tower of the old cathedral on Fiesole.
In that spring Mrs. Stowe visited Florence, and the[Pg 178] Brownings liked her and rejoiced that she had moved the world for good. To Mrs. Jameson Mrs. Browning wrote that “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” was a “sign of the times.” She read Victor Hugo’s “Contemplations,” finding some of the personal poems “overcoming in their pathos”; they went to tea on the terrace at Bellosguardo, in April evenings, gazing over Florence veiled in transparent blue haze in the valley below.
In this April Mrs. Browning’s father died; she had never ceased to hope for reconciliation, and her sorrow was great, but, as usual, she was gently serene, “not despondingly calm,” she said. Mrs. Jameson again came to Florence, and there were more teas on overhanging terraces, and enjoyments of the divine sunsets.
In August they went with Miss Blagden, Mr. Lytton, and one or two others to again make villeggiatura at Bagni di Lucca, where Mrs. Browning rose every morning at six to bathe in the rapid little mountain stream,—finding herself strengthened by this heroic practice,—and Penini flourished “like a rose possessed by a fairy.”
The succeeding winter was passed in Florence, Mrs. Browning instructing her little son in German, and herself reveled in French and German romances. Her rest was always gained in lying on the sofa and reading novels; Browning, who cared little for fiction, found his relaxation in drawing. He taught Penini on the piano, and the boy read French, German, and Italian every day, and played in the open air under the very shadow of the Palazzo Pitti.

Villa Petraja, near Florence.
| “... Try if Petraja, cool and green. Cure last night’s fault with this morning’s flowers.” |
| The Statue and the Bust. |
The Hawthornes, who had met the Brownings in London at a breakfast given by Lord Houghton, came up from Rome, and Mrs. Hawthorne declared that the grasp of Browning’s hand “gives a new value to life.” They passed an evening at Casa Guidi, and Mrs. Hawthorne recorded that in the corridor, as they entered, was a little boy who answered in the affirmative as to whether he were “Penini,” [Pg 179]and who “looked like a waif of poetry, lovelier still in the bright light of the drawing-room.” Mr. Browning instantly appeared with his cordial welcome, leading them into the salon that looked out on the terrace, filled with growing plants. From San Felice there came the chanting of music, and the flowers, the melody, the stars hanging low in the sky, all ablaze over San Miniato, with the poet and his child, all conspired to entrance the sensitive and poetic Mrs. Hawthorne. Then Mrs. Browning came in, “delicate, like a spirit, the ethereal poet-wife, with a cloud of curls half concealing her face, and with the fairy fingers that gave a warm, human pressure,—a very embodiment of heart and intellect.” Mrs. Hawthorne had brought her a branch of pink roses, which Mrs. Browning pinned on her black velvet gown.
They were taken into the drawing-room, a lofty, spacious apartment where Gobelin tapestries, richly carved furniture, pictures, and vertu all enchanted Mrs. Hawthorne, and they talked “on no very noteworthy topics,” Hawthorne afterward recorded, though he added that he wondered that the conversation of Browning should be so clear and so much to the purpose, considering that in his poetry one ran “into the high grass of obscure allusion.” The poet Bryant and his daughter were present that evening, a little to the regret of Mrs. Hawthorne, and there were tea and strawberries, Mrs. Browning presiding at the tray, and Penini, “graceful as Ganymede,” passing the cake.
The Brownings left Florence soon after this evening. The summer of 1858 was passed in Normandy, in company with Mr. Browning’s father and his sister Sarianna, all of them occupying together a house on the shore of the Channel, near Havre. They confessed themselves in a heavenly state of mind, equally appreciative of the French people,—manners, cooking, cutlets, and costumes, all regarded with perpetual admiration. Penini, too, was by no[Pg 180] means behind in his pretty, childish enthusiasms. He was now nine years of age, reading easily French and German, as well as the two languages, English and Italian—each of which was as much his native tongue as the other—and with much proficiency at the piano. Browning already played duets with his little son, while the happy mother looked smilingly on. Mrs. Browning was one who lived daily her real life. For there is much truth in the Oriental truism that our real life is that which we do not live,—in our present environment, at least. She always gave of her best because she herself dwelt in the perpetual atmosphere of high thought. Full of glancing humor and playfulness of expression, never scorning homely conditions, she yet lived constantly in the realm of nobleness.
“Poets become such
By scorning nothing,”
she has said.
The following winter found them again in Rome, where Mrs. Browning was much occupied with Italian politics. Her two deepest convictions were faith in the honest purposes of Louis Napoleon, and her enthusiasm for Italian liberty and unity. In her poem, “A Tale of Villafranca,” she expressed her convictions and feelings. One of their nearer friends in Rome was Massimo d’Azeglio, the Prime Minister of Piedmont from 1849 to 1852, one of the purest of Italian patriots, who was full of hope for Italy. The English Minister Plenipotentiary to Rome at that time was Lord Odo Russell, and when the Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII) arrived in Rome, the Minister (later Lord Ampthill) invited (through Colonel Bruce) several gentlemen to meet him, Colonel Bruce said to Browning that he knew it “would gratify the Queen that the Prince should make the acquaintance of Mr. Browning.” Mrs. Browning spoke of “the little prince” in one of her[Pg 181] letters to Isa Blagden as “a gentle, refined boy,” and she notes how Massimo d’Azeglio came to see them, and talked nobly, and confesses herself more proud of his visit “than of another personal distinction, though I don’t pretend to have been insensible to that,” she adds, evidently referring to the meeting with the young prince.
Mrs. Browning’s love for novels seemed to have been inherited by her son, for this winter he was reading an Italian translation of “Monte Cristo” with such enthusiasm as to resolve to devote his life to fiction. “Dear Mama,” he gravely remarked, “for the future I mean to read novels. I shall read all Dumas’s to begin.”
On their return to Florence in the spring, Mrs. Browning gives William Page a letter of introduction to Ruskin, commending Mr. Page “as a man earnest, simple and noble, who “has not been successful in life, and when I say life I include art, which is life to him. You will recognize in this name Page,” she continues, “the painter of Robert’s portrait which you praised for its Venetian color, and criticised in other respects,” she concluded. And she desires Ruskin to know the “wonder and light and color and space and air” that Page had put into his “Venus Rising from the Sea,” which the Paris salon of that summer had refused on the ground of its nudity,—a scruple that certainly widely differentiates the Salon of 1858 from that of 1911.
Salvini, even then already recognized as a great artist, was playing in a theater in Florence that spring, and the Brownings saw with great enjoyment and admiration his impersonations of Hamlet and Othello.
On a glowing June morning Browning was crossing the Piazza San Lorenzo, when the market-folk had all their curious wares of odds and ends spread about on tables. At one of these he chanced on “the square old yellow book” which held the story of the Franceschini tragedy, which[Pg 182] the poet’s art transmuted into his greatest poem, “The Ring and the Book.” No other single work of Browning’s can rival this in scope and power. It would seem as if he had, at the moment, almost a prescience of the incalculable value of this crumpled and dilapidated volume; as if he intuitively recognized what he afterward referred to as “the predestination.” On his way homeward he opened the book;
“... through street and street,
At the Strozzi, at the Pillar, at the Bridge;
Till, by the time I stood at home again
In Casa Guidi by Felice Church,
······
I had mastered the contents, knew the whole truth.”
In this brief time he had comprehended the entire story of the trial and execution of Count Guido Franceschino, Nobleman of Arezzo, for the murder of his wife, Pompilia, and apparently much of the conception of his great work of future years, “The Ring and the Book,” took possession of him at once. But it was like the seed that must germinate and grow. Little indeed did he dream that in this chance purchase he had been led to the material for the supreme achievement of his art.
One evening before leaving Florence for Siena, where the Brownings had taken the Villa Alberti for the summer, they had Walter Savage Landor to tea, and also Miss Blagden and Kate Field, then a young girl, studying music in Florence, who was under Miss Blagden’s charge. Just as the tea was placed on the table, Browning turned to his honored guest, and thanked him for his defense of old songs; and opening Landor’s latest book, “Last Fruit,” he read in a clear, vibrant voice from the “Idylls of Theocritus.” The chivalrous deference touched the aged poet. “Ah, you are kind,” said he; “you always find out the best bits in my books.”
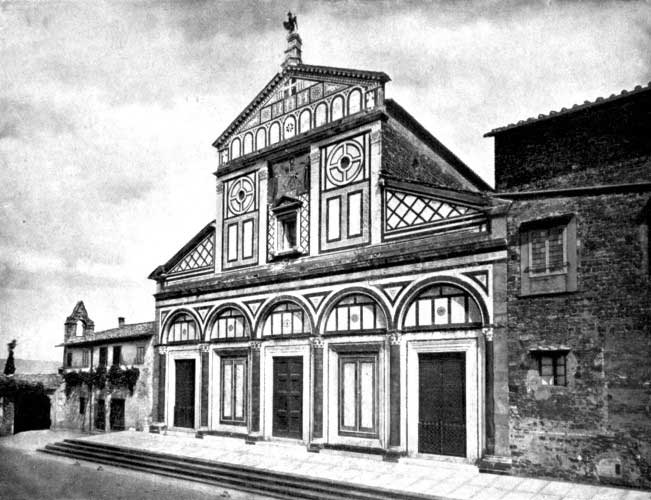

Church Of San Miniato, near Florence.
| “Came she, our new crescent of a hair’s breadth. Full she flared it, lamping Samminiato.” |
| One Word More. |
[Pg 183]The loyal homage rendered by the younger poet, in all the glow of his power, to the “old master,” was lovely to see. As will be recalled, Landor had been one of the first to recognize the genius of Browning when his youthful poem, “Paracelsus,” appeared. Landor had then written to Southey: “God grant that Robert Browning live to be much greater, high as he now stands among most of the living.”
It was one noon soon after this evening that Landor came to Casa Guidi, desolate and distraught, declaring he had left his villa on the Fiesolean slope never to return, because of his domestic difficulties. The Brownings were about leaving for Siena and Mr. Browning decided to engage an apartment for the venerable poet, when the Storys, who were making villeggiatura in the strange old medieval city, invited Landor to be their guest. The villa where the Storys were domiciled was near the Brownings, and Landor was much in both households. “He made us a long visit,” wrote Mrs. Story, “and was our honored and cherished guest. His courtesy and high breeding never failed him.” Landor would often be seen astir in the early dawn, sitting under the olive trees in the garden, writing Latin verses. To Kate Field, who had become a great favorite with the Brownings, Mr. Browning wrote with some bit of verse of Landor’s:
Siena, Villa Alberti, July 18.
Dear Miss Field:—I have only a minute to say that Mr. Landor wrote these really pretty lines in your honor the other day,—you remember on what circumstances they turn. I know somebody who is ready to versify to double the extent at the same cost to you, and do his best, too, and you also know.
Yours Affectionately Ever,
R. B.
The servant waits for this and stops the expansion of soul!
P. S. ... What do you mean by pretending that we are not the obliged, the grateful people? Your stay had made us[Pg 184] so happy, come and make us happy again, says (or would say were she not asleep) my wife, and yours also,—
R. B.
Of Landor, while they were in Siena, Mrs. Browning wrote to a friend that Robert always said he owed more to him than any other contemporary, and that Landor’s genius insured him the gratitude of all artists. In these idyllic days Mr. Story’s young daughter, Edith, (now the Marchesa Peruzzi di Medici, of Florence,) had a birthday, which the poetic group all united to celebrate. In honor of the occasion Landor not only wrote a Latin poem for the charming girl, but he appeared in a wonderful flowered waistcoat, one that dated back to the days of Lady Blessington, to the amusement of all the group. From Isa Blagden, who remained in her villa on Bellosguardo, came almost daily letters to Mrs. Browning, who constantly gained strength in the life-giving air of Siena, where they looked afar over a panorama of purple hills, with scarlet sunsets flaming in the west, the wind blowing nearly every day, as now. The Cave of the Winds, as celebrated by Virgil, might well have been located in Siena.
Mrs. Browning and Mrs. Story would go back and forth to visit each other, mounted on donkeys, their husbands walking beside, as they had done in the Arcadian days at Bagni di Lucca. Odo Russell passed two days with the Brownings on his way from Rome to London, to their great enjoyment. Landor’s health and peace of mind became so far restored that he was able to “write awful Latin alcaics.” Penini, happy in his great friends, the Story children, Julian, Waldo, and Edith, and hardly less so with the contadini, whom he helped to herd the sheep and drive in the grape-carts, galloped through lanes on his own pony, insisted on reading to his contadini from the poems of Dall’ Ongaro, and grew apace in happiness and stature. For[Pg 185] two hours every day his father taught him music, and the lad already played Beethoven sonatas, and music of difficult execution from German composers.
The Brownings and the Storys passed many evenings together, “sitting on the lawn under the ilexes and the cypresses, with tea and talk, until the moon had made the circuit of the quarter of the sky.” Mrs. Browning’s health grew better, and Story writes to Charles Eliot Norton that “Browning is in good spirits about her, and Pen is well, and as I write,” he continues, “I hear him laughing and playing with my boys and Edith on the terrace below.”
It was late in October before they returned to Florence, and then only for a sojourn of six weeks before going to Rome for the winter. The Siena summer had been a period of unalloyed delight to Mrs. Browning, whose health was much improved, and not the least of the happiness of both had been due to the congenial companionship of the Storys, and to their delicate courtesies, which Mrs. Browning wrote to Mrs. Jameson that she could never forget. Browning wrote to Mrs. Story saying to her that she surely did not need to be told how entirely they owed “the delightful summer” to her own and Mr. Story’s kindness. “Ba is hardly so well,” he adds, “as when she was let thrive in that dear old villa and the pleasant country it hardly shut out.”
Mrs. Browning’s small book, the “Poems before Congress,” only eight in all, was published in this early spring of 1860, and met with no cheering reception. She felt this keenly, but said, “If I were ambitious of any thing it would be to be wronged where, for instance, Cavour is wronged.” With Mrs. Browning a political question was equally a moral question. Her devotion to Italy, and faith in the regeneration of the country, were vital matters to her. She was deeply touched by the American attitude toward her[Pg 186] poem, “A Curse for a Nation,” for the Americans, she noted, rendered thanks to the reprover of ill deeds, “understanding the pure love of the motive.” These very “Poems before Congress” brought to her praises, and the offer of high prices as well, and of this nation she said it was generous.
A letter from Robert Browning written to Kate Field, who was then in Florence with Miss Blagden, and which has never before been published, is as follows:
Rome, Via del Tritone, 28,
March 29th, 1860.
Dear Miss Field,—Do you really care to have the little photograph? Here it is with all my heart. I wonder I dare be so frank this morning, however, for a note just rec’d from Isa mentions an instance of your acuteness, that strikes me with a certain awe. “Kate,” she says, “persists that the ‘Curse for a Nation’ is for America, and not England.” You persist, do you? No doubt against the combined intelligence of our friends who show such hunger and thirst for a new poem of Ba’s—and, when they get it, digest the same as you see. “Write a nation’s curse for me,” quoth the antislavery society five years ago, “and send it over the Western sea.” “Not so,” replied poor little Ba, “for my heart is sore for my own lands’ sins, which are thus and thus,—what curse assign to another land when heavy for the sins of mine?” “Write it for that very reason,” rejoined Ba’s cheerer, “because thou hast strength to see and hate a foul thing done within thy gate,” and so, after a little more dallying, she wrote and sent over the Western seas what all may read, but it appears only Kate Field, out of all Florence, can understand. It seems incredible. How did you find out, beside, the meaning of all these puzzling passages which I quote in the exact words of the poem? In short, you are not only the delightful Kate Field which I always knew you to be, but the sole understander of Ba in all Florence. I can’t get over it....
Browning, the husband, means to try increasingly and somewhat intelligibly to explain to all his intimates at Florence,[Pg 187] with the sole exception of Kate Field; to whose comprehension he will rather endeavor to rise, than to stoop, henceforth. And so, with true love from Ba to Kate Field, and our united explanation to all other friends, that the subject matter of the present letter is by no means the annexation of Savoy and Nice, she will believe me,
Hers very faithfully
Robert Browning.
To Kate Field Mrs. Browning wrote, the letter undated, but evidently about this time, apparently in reply to some request of Miss Field’s to be permitted to write about them for publication:
My Dear Kate,—I can’t put a seal on your lips when I know them to be so brave and true. Take out your license, then, to name me as you please, only remembering, dear, that even kind words are not always best spoken. Here is the permission, then, to say nothing about your friends except that they are your friends, which they will always be glad to have said and believed. I had a letter from America to-day, from somebody who, hearing I was in ill health, desired to inform me that he wouldn’t weep for me, were it not for Robert Browning and Penini! No, don’t repeat that. It was kindly meant, and you are better, my dear Kate, and happier, and we are all thanking God for Italy. Love us here a little, and believe that we all love and think of you.
Yours ever affectionately,
E. B. B.
The American appreciation of Mrs. Browning constantly increased, and editors offered her an hundred dollars each for any poem, long or short, that might pass through their publications on its way to final destiny.
Theodore Parker had passed that winter in Rome, and Mrs. Browning felt that he was “high and noble.” Early in May he left for Florence, where his death occurred before the return of the Brownings.
[Pg 188]The education of Penini during these months was conducted by an old Abbé, who was also the instructor of Mr. Story’s only daughter, Edith, and the two often shared their lessons, the lad going to Palazzo Barberini to join Miss Edith in this pursuit of knowledge. Certain traditions of the venerable Abbé have drifted down the years, indicating that his breviary and meditations on ecclesiastical problems did not exclusively occupy his mind, for the present Marchesa Peruzzi has more than one laughing reminiscence of this saintly father, who at one time challenged his pupil to hop around the large table on one foot. The hilarity of the festivity was not lessened when the Reverendo himself joined in the frolic, his robes flapping around him, as they all contributed to the merriment. The Marchesa has many a dainty note written to her by Penini’s mother. Once it is as Pen’s amanuensis that she serves, praying the loan of a “‘Family Robinson,’ by Mayne Reid,” to solace the boy in some indisposition. “I doubt the connection between Mayne Reid and Robinson,” says Mrs. Browning, “but speak as I am bidden.” And another note was to tell “Dearest Edith” that Pen’s papa wanted him for his music, and that there were lessons, beside; and “thank dear Edith for her goodness,” and “another day, with less obstacles.” The intercourse between the Brownings and the Storys was always so full of mutual comprehension and perfect sympathy and delicate, lovely recognition on both sides, that no life of either the sculptor or the wedded poets could be presented that did not include these constant amenities of familiar, affectionate intercourse.
Many English friends of the Brownings came and went that winter, and among others was Lady Annabella Nöel, a granddaughter of Lord Byron, and a great admirer of Mr. Browning. A new acquaintance of the Brownings was Lady Marion Alford, a daughter of the Earl of [Pg 189]Northampton, “very eager about literature, and art, and Robert,” laughed Mrs. Browning, and Lady Marion and “Hatty” (Miss Hosmer) were, it seems, mutually captivated.

The Palazzo Barberini, via Quattro Fontane, Rome.
The home of William Wetmore Story and his family for nearly forty years.
Some of the English artists came to Rome, Burne-Jones and Val Prinsep among them, and they with Browning wandered about the classic byways of the city and drove to see the Coliseum by moonlight.
In June the Brownings left Rome, by way of Orvieto and Chiusi. They crossed that dead, mystic Campagna that flows, like a sea, all around Rome—a sea of silence and mystery; with its splendid ruins of the old aqueducts and tombs, its vast stretches of space that were all aglow, in those June days, with scarlet poppies. They stopped one night at Viterbo, the little city made famous since those days by Richard Bagot’s tragic novel, “Temptation,” and where the convent is interesting from its associations with Vittoria Colonna, who in 1541 made here a retreat for meditation and prayer.
In Orvieto they rested for a day and night, and Mrs. Browning was able to go with her husband into the marvelous cathedral, with its “jeweled and golden façade” and its aerial Gothic construction. Mr. Browning, with his little son, drove over to the wild, curious town of Bagnorgio, which, though near Orvieto, is very little known. But this was the birthplace of Giovanni da Fidenza, the “Seraphic Doctor,” who was canonized as St. Buonaventura, from the exclamation of San Francesco, who, on awakening from a dream communion with Giovanni da Fidenza, exclaimed, “O buona ventura!” Dante introduces this saint into the Divina Commedia, as chanting the praises of San Domenico in Paradise:
“Io san vita di Bonaventura
Du Bagnorgio, che ne grandi uffici,
Sempre posposi la sinistra cura.”
[Pg 190]Bagnorgio is, indeed, the heart of poetic legend and sacred story, but it is so inaccessible, perched on its high hill, with deep chasms, evidently the work of earthquakes, separating it from the route of travel, that from a distance it seems impossible that any conveyance save an airship could ever reach the town.
By either route, through the Umbrian region, by way of Assisi and Perugia, or by way of Orvieto and Siena, the journey between Rome and Florence is as beautiful as a dream. The Brownings paused for one night’s rest at Lake Thrasymene, the scenes of the battlefield of Hannibal and Flaminius, with the town on a height overlooking the lake. “Beautiful scenery, interesting pictures and tombs,” said Mrs. Browning of this journey, “but a fatiguing experience.” She confessed to not feeling as strong as she had the previous summer, but still they were planning their villeggiatura in Siena, taking the same villa they had occupied the previous season, where Penini should keep tryst with the old Abbé, who was to come with the Storys and with his Latin.
They found Landor well and fairly amenable to the new conditions of his life. Domiciled with Isa Blagden was Miss Frances Power Cobbe, who was drawn to Florence that spring largely to meet Theodore Parker, with whom she had long corresponded. Mr. and Mrs. Lewes (George Eliot) were in Florence that spring of 1860, the great novelist making her studies for “Romola.” They were the guests of the Thomas Adolphus Trollopes.
Landor, too, came frequently to take tea with Miss Blagden and Miss Cobbe on their terrace, and discuss art with Browning. Dall’ Ongaro and Thomas Adolphus Trollope were frequently among the little coterie. His visits to Casa Guidi and his talks with Mrs. Browning were among the most treasured experiences of Mr. Trollope. “I was conscious, even then,” he afterward wrote in his[Pg 191] reminiscences of this lovely Florentine life, “of coming away from Casa Guidi a better man, with higher views and aims. The effect was not produced by any talk of the nature of preaching, but simply by the perception and appreciation of what Elizabeth Browning was: of the purity of the spiritual atmosphere in which she habitually dwelt.”
Miss Hosmer came, too, that spring, as the guest of Miss Blagden, and she often walked down the hill to breakfast with her friends in Casa Guidi. Browning, who was fond of an early walk, sometimes went out to meet her, and on one occasion they had an escapade which “Hatty” related afterward with great glee. It was on one of these morning encounters that Miss Hosmer confessed to the poet that the one longing of her soul was to ride behind Caretta, the donkey, and Browning replied that nothing could be easier, as Girolamo, Caretta’s owner, was the purveyor of vegetables to Casa Guidi, and that they would appropriate his cart for a turn up Poggia Imperiale. “Di gustibus non,” began Browning. “Better let go Latin and hold on to the cart,” sagely advised the young sculptor. In the midst of their disasters from the surprising actions of Caretta, they met her owner. “Dio mio” exclaimed Girolamo, “it is Signor Browning. San Antonio!” Girolamo launched forth into an enumeration of all the diabolical powers possessed by Caretta, and called on all the saints to witness that she was a disgrace to nature. Meantime the poet, the sculptor, the vegetables, and the donkey were largely combined into one hopeless mass, and Browning’s narration and re-enactment of the tragedy, after they reached Casa Guidi, threw Mrs. Browning into peals of laughter.
Again the Brownings sought their favorite Siena, where Miss Blagden joined them, finding a rude stone villino, of two or three rooms only, the home of some contadini, within fifteen minutes’ walk of Mrs. Browning, and taking it to be near her friend. But for the serious illness of Mrs.[Pg 192] Browning’s sister Henrietta (Mrs. Surtees Cook) the summer would have been all balm and sunshine. The Storys were very near, and Mr. Landor had been comfortably housed not far from his friends, who gave the aged scholar the companionship he best loved. Browning took long rides on horseback, exploring all the romantic regions around Siena, such rides that he might almost have exclaimed with his own hero, the Grand Duke Ferdinand,—
“For I ride—what should I do but ride?”
Penini, too, galloped through the lanes on his pony, his curls flying in the wind, and read Latin with the old Abbé. The lessons under this genial tutor were again shared with Miss Edith Story, one of whose earliest childish recollections is of sitting on a low hassock, leaning against Mrs. Browning, while Penini sat on the other side, and his mother talked with both the children. Mr. Story’s two sons, the future painter and sculptor respectively, were less interested at this time in canvas and clay than they were in their pranks and sports. The Storys and Brownings, Miss Blagden and Landor, all loaned each other their books and newspapers, and discussed the news and literature of the day. The poet was much occupied in modeling, and passed long mornings in Mr. Story’s improvised studio, where he copied two busts, the “Young Augustus” and the “Psyche,” with notable success.
In the October of that year both the Brownings and the Storys returned to Rome, the poets finding a new apartment in the Via Felice. Mrs. Browning’s sister Henrietta died that autumn, and in her grief she said that one of the first things that did her good was a letter from Mrs. Stowe. She notes her feeling that “how mere a line it is to overstep between the living and the dead.” Her spiritual insight never failed her, and of herself she said: “I wish to live just so long, and no longer, than to grow in the spirit.”
[Pg 193]In the days of inevitable sadness after her sister’s death, whatever the consolations and reassurances of faith and philosophy, Mrs. Browning wrote to a friend of the tender way in which her husband shielded her, and “for the rest,” she said, “I ought to have comfort, for I believe that love, in its most human relations, is an eternal thing.” She added: “One must live; and the only way is to look away from one’s self into the larger and higher circle of life in which the merely personal grief or joy forgets itself.”
Penini and his friend, Miss Edith, continued their studies under the old Abbé; his mother heard him read a little German daily, and his father “sees to his music, and the getting up of arithmetic,” noted Mrs. Browning. The lad rode on his pony over Monte Pincio, and occasionally cantered out on the Campagna with his father. But Mrs. Browning had come to know that her stay on earth was to be very brief, and to her dear Isa she wrote that for the first time she had pain in looking into her little son’s face—“which you will understand,” she adds, but to her husband she did not speak of this premonition. She urged him to go out into the great world, for Rome was socially resplendent that winter. Among other notable festivities there was a great ball given by Mrs. Hooker, where princes and cardinals were present, and where the old Roman custom of attending the princes of the church up and down the grand staircase with flaming torches was observed. The beautiful Princess Rospoli was a guest that night, appearing in the tri-color. Commenting on the Civil War that was threatening America, Mrs. Browning said she “believed the unity of the country should be asserted with a strong hand.”
Val Prinsep, in Rome that winter, was impressed by Mr. Browning into the long walks in which they both delighted, and they traversed Rome on both sides the Tiber. The poet was not writing regularly in those days, though his[Pg 194] wife “gently wrangled” with him to give more attention to his art, and held before him the alluring example of the Laureate who shut himself up daily for prescribed work. Browning had “an enormous superfluity of vital energy,” which he had to work off in long walks, in modeling, and in conversations. “I wanted his poems done this winter very much,” said Mrs. Browning; “and here was a bright room with three windows consecrated to use.... There has been little poetry done since last winter.” But in later years Browning became one of the most regular of workers, and considered that day lost on which he had not written at least some lines of poetry. At this time the poet was fascinated by his modeling. “Nothing but clay does he care for, poor, lost soul,” laughed Mrs. Browning. Her “Hatty” ran in one day with a sketch of a charming design for a fountain for Lady Marion Alford. “The imagination is unfolding its wings in Hatty,” said Mrs. Browning.
In days when Mrs. Browning felt able to receive visitors, there were many to avail themselves of the privilege. On one day came Lady Juliana Knox, bringing Miss Sewell (Amy Herbert); and M. Carl Grun, a friend of the poet, Dall’ Ongaro, came with a letter from the latter, who wished to translate into Italian some of the poems of Mrs. Browning. Lady Juliana had that day been presented to the Holy Father, and she related to Mrs. Browning how deeply touched she had been by his adding to the benediction he gave her, “Priez pour le pape.”
Penini had a choice diversion in that the Duchesse de Grammont, of the French Embassy, gave a “matinée d’enfants,” to which he received a card, and went, resplendent in a crimson velvet blouse, and was presented to small Italian princes of the Colonna, the Doria, Piombiono, and others, and played leap-frog with his titled companions.
Mrs. Browning reads with eager interest a long speech[Pg 195] of their dear friend, Milsand, which filled seventeen columns of the Moniteur, a copy of which his French friend sent to Browning.
The Brownings had planned to join the poet’s father and sister in Paris that summer, but a severe attack of illness in which for a few days her life was despaired of made Mrs. Browning fear that she would be unable to take the journey. Characteristically, her only thought was for the others, never for herself, and she writes to Miss Browning how sad she is in the thought of her husband’s not seeing his father, and “If it were possible for Robert to go with Pen,” she continues, “he should, but he wouldn’t go without me.”
When she had sufficiently recovered to start for Florence, they set out on June 4, resting each night on the way, and reaching Siena four days later, where they lingered. From there Mr. Browning wrote to the Storys that they had traveled through exquisite scenery, and that Ba had borne the journey fairly well. But on arriving in Florence and opening their apartment again in Casa Guidi, it was apparent that the poet had decided rightly that there was to be no attempt made to visit Paris. During these closing days of Mrs. Browning’s stay on earth, her constant aim was “to keep quiet, and try not to give cause for trouble on my account, to be patient and live on God’s daily bread from day to day.”
“O beauty of holiness,
Of self-forgetfulness, of lowliness!”
It is difficult to read unmoved her last words written to Miss Sarianna Browning. “Don’t fancy, dear,” she said, “that this is the fault of my will,” and she adds:
“Robert always a little exaggerates the difficulties of traveling, and there’s no denying that I have less strength than is usual to me.... What does vex me is that the dearest nonno[Pg 196] should not see his Peni this year, and that you, dear, should be disappointed, on my account again. That’s hard on us all. We came home into a cloud here. I can scarcely command voice or hand to name Cavour. That great soul, which meditated and made Italy, has gone to the diviner country. If tears or blood could have saved him to us, he should have had mine. I feel yet as if I could scarcely comprehend the greatness of the vacancy.”
For a week previous to her transition to that diviner world in which she always dwelt, even on earth, she was unable to leave her couch; but she smilingly assured them each day that she was better, and in the last afternoon she received a visit from her beloved Isa, to whom she spoke with somewhat of her old fire of generous enthusiasm of the new Premier, who was devoted to the ideals of Cavour, and in whose influence she saw renewed hope for Italy. The Storys were then at Leghorn, having left Rome soon after the departure of the Brownings, and they were hesitating between Switzerland for the summer, or going again to Siena, where they and the Brownings might be together. The poet had been intending to meet the Storys at Leghorn that night, but he felt that he could not leave his wife, though with no prescience of the impending change. She was weak, but they talked over their summer plans, decided they would soon go to Siena, and agreed that they would give up Casa Guidi that year, and take a villa in Florence, instead. They were endeavoring to secure an apartment in Palazzo Barberini for the winter, the Storys being most anxious that they should be thus near together, and Mrs. Browning discussed with him the furnishing of the rooms in case they decided upon the Palazzo. Only that morning Mr. Lytton had called, and while Mrs. Browning did not see him, her husband talked with him nearly all the morning. Late in the evening she seemed a little wandering, but soon she slept, waking again about [Pg 197]four, when they talked together, and she seemed to almost pass into a state of ecstasy, expressing to him in the most ardent and tender words her love and her happiness. The glow of the luminous Florentine dawn brightened in the room, and with the words “It is beautiful!” she passed into that realm of life and light and loveliness in which she had always seemed to dwell.
“And half we deemed she needed not
The changing of her sphere,
To give to heaven a Shining One,
Who walked an angel here.”
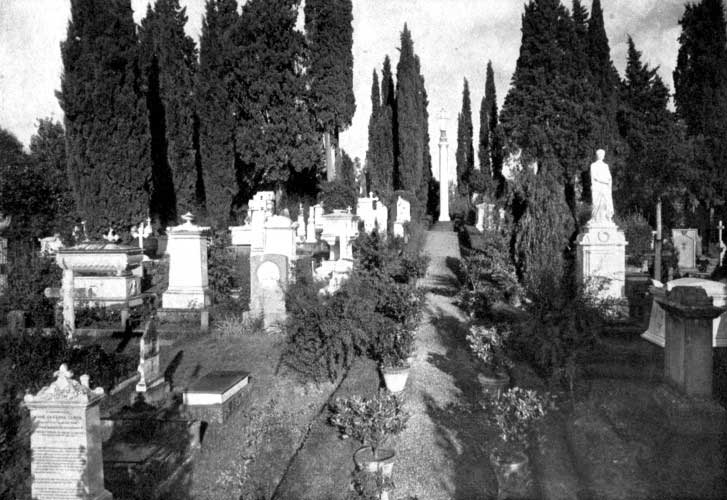

The English Cemetery, Florence, in which Mrs. Browning is Buried.
Curiously, Miss Blagden had not slept at all that night. After her return from her visit to Mrs. Browning the previous afternoon, “every trace of fatigue vanished,” she wrote to a friend, “and all my faculties seemed singularly alert. I was unable to sleep, and sat writing letters till dawn, when a cabman came to tell me ‘La Signora della Casa Guidi e morte!’”
The Storys came immediately from Leghorn, and Miss Blagden took Edith Story and Penini to her villa. It was touching to see his little friend’s endeavor to comfort the motherless boy. Mr. and Mrs. Story stayed with Browning in the rooms where everything spoke of her presence: the table, strewn with her letters and books; her little chair, a deep armchair of dark green velvet, which her son now holds sacred among his treasures, was drawn by the table just as she had left it, and in her portfolio was a half-finished letter to Madame Mario, speaking of Cavour, and her noble aspirations for Italy.
In the late afternoon of July 1, 1861, a group of English and American, with many Italian friends gathered about the little casket in the lovely cypress-shaded English cemetery of Florence, and as the sun was sinking below the purple hills it was tenderly laid away, while the amethyst mountains hid their faces in a misty veil.
[Pg 198]
“What would we give to our beloved?
The hero’s heart to be unmoved,
The poet’s star-tuned harp to sweep.
······
God strikes a silence through you all,
And giveth His beloved, sleep.”
Almost could the friends gathered there hear her poet-voice saying:
“And friends, dear friends, when it shall be
That this low breath is gone from me,
And round my bier ye come to weep,
Let One, most loving of you all,
Say ‘Not a tear must o’er her fall!
He giveth His beloved, sleep.’”
| “Think, when our one soul understands The great Word which makes all things new, When earth breaks up and heaven expands, How will the change strike me and you In the house not made with hands? “Oh, I must feel your brain prompt mine, Your heart anticipate my heart, You must be just before, in fine, See and make me see, for your part, New depths of the divine!” |
The Completed Cycle—Letters to Friends—Browning’s Devotion to his Son—Warwick Crescent—“Dramatis Personæ”—London Life—death of the Poet’s Father—Sarianna Browning—Oxford Honors the Poet—Death of Arabel Barrett—Audierne—“The Ring and the Book.”
“The cycle is complete,” said Browning to the Storys, as they all stood in those desolate rooms and gazed about. The salon was just as she had left it; the table covered with books and magazines, her little chair drawn up to it, the long windows open to the terrace, and the faint chant of nuns, “made for midsummer nights,” in San Felice, on the air. “Here we came fifteen years ago,” continued Mr. Browning; “here Ba wrote her poems for Italy; here Pen was born; here we used to walk up and down this terrace on summer evenings.” The poet lingered over many tender reminiscences, and after the Storys had taken leave,[Pg 200] he and his son yielded to the entreaties of Isa Blagden to stay with her in her villa on Bellosguardo during the time that he was preparing to leave Florence, which he never looked upon again.
When all matters of detail were concluded, Miss Blagden, “perfect in all kindness,” accompanied them to Paris, continuing her own journey to England, while Browning with his son, his father, and sister, proceeded to St. Enogat, near St. Malo, on the Normandy coast. Before Mrs. Browning’s illness there had been a plan that all the Brownings and Mr. and Mrs. W. J. Stillman should pass the summer together at Fontainebleau.
There was something about St. Enogat singularly restful to Browning, the sea, the solitude, the “unspoiled, fresh, and picturesque place,” as he described it in a letter to Madame Du Quaire. The mystic enchantment of it wrought its spell, and Penini had his pony and was well and cheerful, and Browning realized too well that the change called death is but the passing through “the gates of new life,” to be despairing in his sorrow. The spirit of one
“... who never turned his back, but marched breast forward,”
breathes through all the letters that he wrote at this time to friends. “Don’t fancy I am prostrated,” he wrote to Leighton; “I have enough to do for myself and the boy, in carrying out her wishes.” Somewhat later he expressed his wish that Mr. (later Sir Frederick) Leighton should design the memorial tomb, in that little Florence cemetery, for his wife; and the marble with only “E. B. B.” inscribed on it, visited constantly by all travelers in Florence and rarely found without flowers, is the one Sir Frederick designed.
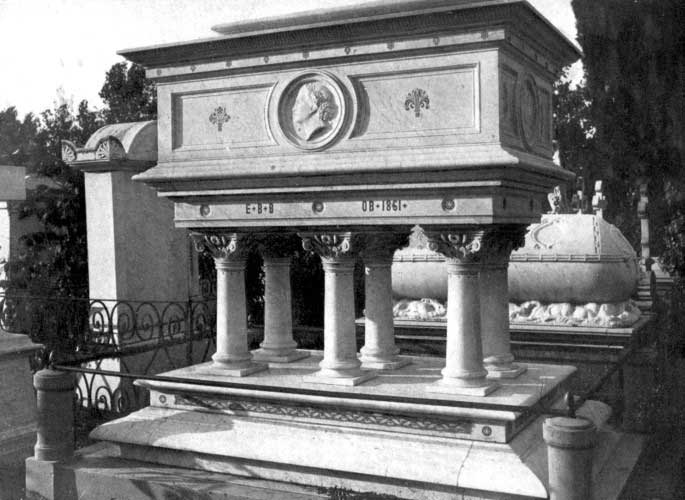

Tomb of Elizabeth Barrett Browning in the English Cemetery, Florence
Designed by Sir Frederick Leighton, R.A.
In a letter to his boyhood’s friend, Miss Haworth, Browning alluded to the future, when Penini would so need the help of “the wisdom, the genius, the piety” of [Pg 201]his mother; and the poet adds: “I have had everything, and shall not forget.” In reply to a letter of sympathy from Kate Field, he wrote:
“Dear Friend,—God bless you for all your kindness which I shall never forget. I cannot write now except to say this, and beside, that I have had great comfort from the beginning.”
In the early autumn Browning took his son to London. The parting of the ways had come, and already he dimly perceived that the future would not copy fair the past. There are “reincarnations,” in all practical effect, that are realized in this life as well as, speculatively, hereafter; and his days of Italian terraces and oleander blooms, of enchanting hours on Bellosguardo, and lingerings in old palaces and galleries, and saunterings down narrow streets crowded with contadini,—these days were as entirely past as if he had been transported to another planet.
“Not death; we do not call it so,
Yet scarcely more with dying breath
Do we forego;
We pass an unseen line,
And lo! another zone.”
The sea and the sands and the sky prefigured themselves in those days to Browning as all indistinguishably blended in an unreal world, from which the past had receded and on which the Future had not yet dawned.
“Gray rocks and grayer sea,
And surf along the shore;
And in my heart a name
My lips shall speak no more.”
To Story he wrote with assurances of affection, but saying, “I can’t speak about anything. I could, perhaps, if we were together, but to write freezes me.” Miss Blagden, in London, had taken rooms in Upper Westbourne[Pg 202] Terrace, and when in the late autumn Browning and his son went on to England, he took an apartment in Chichester Road, almost opposite the house where Miss Blagden was staying. But she had lived too long in enchanted Florence to be content elsewhere, and she soon returned to her villa on the heights of Bellosguardo, from which the view is one of the most beautiful in all Europe. Browning soon took the house, No. 19 Warwick Crescent, which for nearly all the rest of his life continued to be his home. Here he was near Mrs. Browning’s sister, Arabel Barrett, of whom he was very fond, and whose love for her sister’s little son was most grateful to them both. Mr. Browning had his old tapestries, pictures, and furniture of old Florentine carving, some of it black with age, sent on from Casa Guidi, and he proceeded to transform a prim London house into an interior of singular charm. He lined the staircase with Italian pictures; books overflowed in all the rooms, and the glimpse of water in the canal near reflected the green trees of the Crescent, giving the place a hint of sylvan Arcadias. There was the grand piano on which Penini practiced, and a tutor was engaged to prepare the lad for the university. The poet felt that this was the critical time to give his son “the English stamp,” in “whatever it is good for,” he added. But as a matter of fact the young Florentine had little affinity with English ways. He was the child of poets; a linguist from his infancy, an omnivorous reader, and with marked talent for art, distinguishing himself later in both painting and sculpture, but he had little inclination for the exact sciences.
In his London home Browning was soon again launched on a tide of work,—the dearest of which was in preparing the “Last Poems” of his wife for publication. He gave it a dedication to “Grateful Florence, and Tommaseo, her spokesman.” He was also preparing a new edition of his own works to be issued in three volumes. The tutor he[Pg 203] had secured for his son was considered skillful in “grammatical niceties,” which, he said, “was much more to my mind than to Pen’s.” But he, as well as the boy, was homesick for Italy, and he wrote to Story that his particular reward would be “just to go back to Italy, to Rome”; and he adds:
“Why should I not trust to you what I know you will keep to yourselves, but which will certainly amuse you as nothing else I could write is like to do? What good in our loving each other unless I do such a thing? So, O Story, O Emelyn, (dare I say, for the solemnity’s sake?) and O Edie, the editorship has, under the circumstances, been offered to me: me! I really take it as a compliment because I am, by your indulgence, a bit of a poet, if you like, but a man of the world and able editor hardly!”[8]
The editorship in question was that of Cornhill, left vacant by the death of Thackeray.
Browning was too great of spirit to sink into the recluse, and first beguiled into Rossetti’s studio, he soon met Millais, and by degrees he responded again to friends and friendships, and life called to him with many voices. In the late summer of 1862 the poet and his son were at “green, pleasant little Cambo,” and then at Biarritz. He was absorbed in Euripides; and the supreme work of his life, “The Ring and the Book,” the Roman murder story, as he then called it, was constantly in his thought and beginning to take shape. The sudden and intense impression that the Franceschini tragedy had made on him, on first reading it, rushed back and held him as under a spell. But the “Dramatis Personæ” and “In a Balcony” were to be completed before the inauguration of this great work.
For more than four years the thrilling tragedy had lain [Pg 204]in his mind, impressing that subconscious realm of mental action where all great work in art acquires its creative vitality. It is said that episodes of crime had a great fascination for Browning, père, who would write out long imaginary conversations regarding the facts, representing various persons in discussion, the individual views of each being brought out. The analogy of this to the treatment of the Franceschini tragedy in his son’s great poem is rather interesting to contemplate. With the poet it was less dramatic interest in the crime, per se, than it was that the complexities of crime afforded the basis from which to work out his central and controlling purpose, his abiding and profound conviction that life here is simply the experimental and preparatory stage for the life to come; that all its events, even its lapses from the right, its fall into terrible evil, are—
“Machinery just meant
To give thy soul its bent,”
a part of the mechanism to “try the soul’s stuff on”; that man lives in an environment of spiritual influences which act upon him in just that degree to which he can recognize and respond to them; and that he must sometimes learn the ineffable blessedness of the right through tragic experiences of the wrong. In the very realities of man’s imperfection Browning sees his possibilities of
“Progress, man’s distinctive work alone.”
When Browning asks:
“And what is our failure here but a triumph’s evidence
For the fullness of the days?...”
he condenses in these lines his philosophy of life.
Many of the poems appearing in the “Dramatis Personæ” had already been written: “Gold Hair” and “James Lee’s Wife” at Pornic, and others at green Cambo. In[Pg 205] the splendor and power of “Abt Vogler,” “Rabbi Ben Ezra,” and “A Death in the Desert,” the poet expressed a philosophy that again suggests his intuitive agreement with the Hegelian. “Rabbi Ben Ezra” holds in absolute solution the Vedanta philosophy. To the question as to what all this enigma of life means, the poet answers:
“Thence shall I pass, approved
A man, for aye removed
From the developed brute; a god though in the germ.
······
He fixed thee ’mid this dance
Of plastic circumstance,
This Present, thou, forsooth, would fain arrest.”
How keen the sense of humor and of the sharp contrasts of life in “Fra Lippo Lippi,” and what power of character analysis. The intellectual vigor and the keen insight into the play of mental action in “Bishop Blougram’s Apology”—a poem that occasioned great discussion on its appearance (from a real or fancied resemblance of the “Bishop” to Cardinal Wiseman)—are almost unsurpassed in poetic literature. Many of the poems in the “Dramatis Personæ” are aglow with the romance of life, as in the “Eurydice to Orpheus,” and “A Face,” which refers to Emily Patmore. There are studio traces as well in these, and in the “Deaf and Dumb,” suggested by a group of Woolner. The crowning power of all is revealed in the noble faith and the exquisite tenderness of “Prospice,” especially in those closing lines when all of fear and pain and darkness and cold,—
“Shall change, shall become first a peace out of pain,
Then a light, then thy breast,
O thou soul of my soul! I shall clasp thee again,
And with God be the rest!”
The references to his wife in this poem, in the enthralling “One Word More,” and in the dedication to “The Ring[Pg 206] and the Book,” as well as those to be divined in his character drawing of “Pompilia,” are incomparable in their impressiveness and beauty, and must live so long as poetry is enshrined in life. The vital drama, the splendor of movement, the color, the impassioned exaltation of feeling, the pictorial vividness that are in these poems grouped under “Dramatic Romances” and “Dramatis Personæ,” give them claim to the first rank in the poet’s creations. Curiously, during this period, the change in Browning’s habits of work, which his wife used to urge upon him, seemed to gradually take possession of him, so that he came to count that day lost in which he had not written some lines of poetry. Did he, perchance in dreams, catch something of “the rustling of her vesture” that influenced his mind to the change? To Elizabeth Browning poetry was not only a serious calling, but its “own exceeding great reward,” always.
Another change came to Browning, which redeemed him from the growing tendency to become a recluse, and made him a familiar figure in the great world. He seemed to become aware that there was something morbid and unworthy in the avoidance of the world of men and women. Browning’s divinely commissioned work had to do with life, in its most absolute actualities as well as its great spiritual realities, because the life eternal in its nature was the theme on which he played his poetic variations, and no revelation of human nature came amiss to him.
He had already supervised the publication of Mrs. Browning’s essay on “The Greek Christian Poets” and “The Book of the Poets,” and “nothing,” he said, “that ought to be published, shall be kept back.” He had also lent Story considerable assistance in arranging with Blackwood for the serial publication of “Roba di Roma.”
For two or three summers Browning with his father, his sister, and his son, passed the summers at St. Marie, near[Pg 207] Pornic, from where in the August of 1863 he wrote to Leighton that he was living on fruit and milk, and that each day he completed some work, read a little with Pen, and somewhat more by himself. St. Marie was a “wild little place” in Brittany, on the very edge of the sea, a hamlet of hardly more than a dozen houses, of which the Brownings had the privilege of occupying that of the mayor, whose chief attraction, apparently, was that, though bare, it was clean. The poet liked it all, and it was there that he wrote “In the Doorway” in “James Lee’s Wife,” with the sea, the field, and the fig-tree visible from his window.
In the late summer the Brownings are all again at St. Marie in Brittany, and the poet writes to Isa Blagden that he supposes what she “calls fame within these four years” has come somewhat from his going about and showing himself alive, “but,” he adds, “I was in London from the time that I published ‘Paracelsus’ till I ended the writing of plays with ‘Luria,’—and I used to go out then, and see far more of merely literary people, critics, etc., than I do now,—but what came of it?” If in the lines following there is a hint of sadness, who can blame him?
During this summer he revised “Sordello” for re-publication, not, however, as he had once contemplated, making in it any significant changes. In the dedication to his friend Milsand, he incorporated so clear an exposition of his idea in the poem that this dedication will always be read with special interest. In London again the next winter, Browning wrote to Isa Blagden that he “felt comfort in doing the best he could with the object of his life,—poetry. I hope to do much more yet,” he continued; “and that the flower of it will be put into Her hand somehow.”
The London spring found the poet much engaged, taking his son to studios, and to the Royal Academy, to concerts, and for long walks, and in a letter to Kate Field not heretofore published is indicated something of the general trend of the days:
[Pg 208]
London, 19, Warwick Crescent,
Upper Westbourne Terrace, May 5th, 1864.
Dear Kate Field, (so let me call you, please, in regard to old times when I might have done it, and did not,) I know well enough that there is great stupidity in this way of mine, this putting off a thing because I hope to compass some other thing, as here, for had you not asked for some photographs which I supposed I could soon find time and inclination to get, I should have thanked you at once; as I do now, indeed, and with all my heart, but the review article is wavering and indistinct in my mind now, and though it is inside a drawer of this table where I write, I cannot bring myself to look at it again,—not from a motive which is disparaging to you, as I am sure you understand; the general impression is enough for me, also, if you care in the least how I feel toward you. The boy has certainly the likeness to which you refer, and an absolute sameness, almost, in feature as well as in look, with certain old portraits of hers,—here, older and younger; there is not a trace of me in him, thank God! I know that dear, teasing Isa, and how she won’t answer your questions, but sometimes, for compensation, she tells you what you never asked for, and though I always, or very often, ask about you, yet I think it may have been in reply to curiosity about the price of Italian stock, that she lately described to me a photograph of you, yourself, and how you were: what? even that’s over. And moreover, how you were your old self with additions, which, to be sure, I don’t require.
Give my true regard to your mother, and thank her for her goodness in understanding me. But I write only to have a pleasant chat with you, in a balcony, looking for fire-flies in the garden, wider between us than the slanting Pitti façade, now that it’s warm and Maylike in Florence.
Always yours,
Robert Browning.
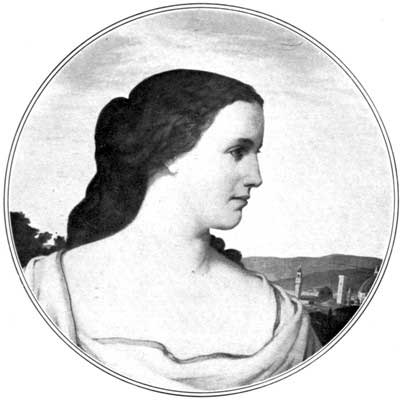

Kate Field
From a portrait painted by Elihu Vedder, Florence, 1860.
Mr. Browning had now begun to think of placing his son, who had passed his sixteenth birthday, in Oxford. In quest of this desire the poet sought the acquaintance of [Pg 209]Dr. Jowett, afterward Master of Balliol College. This initiated a friendship between Browning and Jowett that lasted all the poet’s life, and that has insured to Balliol many priceless treasures of association with both Robert and Elizabeth Browning. Up to that time Jowett had not been an admirer of Browning’s poetry. But his keen interest in the theme then engaging Browning was aroused, and he wrote to a friend:
“I thought I was getting too old to make new friends, but I believe that I have made one,—Mr. Browning, the poet, who has been staying with me during the past few days. It is impossible to speak without enthusiasm of his open, generous nature, and his great ability and knowledge. I had no idea that there was a perfectly sensible poet in the world, entirely free from vanity, jealousy, or any other littleness, and thinking no more of himself than if he were an ordinary man. His great energy is very remarkable, as is his determination to make the most of the remainder of life. Of personal objects he seems to have none, except the education of his son, in which I hope in some degree to help him.”[9]
After returning to London, Browning writes to Tennyson, in thanks for a book received from the Laureate:[10]
19, Warwick Crescent, W., Oct. 10, 1865.
My Dear Tennyson,—When I came back last year from my holiday I found a gift from you, a book; this time I find only the blue and gold thing which, such as it is, I send you, you are to take from me. I could not even put in what I pleased but I have said all about it in the word or two of preface, as also that I beg leave to stick the bunch in your buttonhole. May I beg that Mrs. Tennyson will kindly remember me?
Ever Affectionately Yours,
Robert Browning.
Tennyson wrote in reply that the nosegay was very welcome. “I stick it in my buttonhole ... and feel ——’s cork heels added to my boots,” he added.
Volumes of selections from the poems of both Browning and his wife were now being demanded for the “Golden Treasury”; and to Miss Blagden Browning says further that he will certainly do the utmost to make the most of himself before he dies, “for one reason that I may help Pen the better.”
Browning complies with his publisher’s request to prepare a new selection of his wife’s poems. “How I have done it, I can hardly say,” he noted, “but it is one dear delight that the work of her goes on more effectually than ever—her books are more and more read,”—and a new edition of her “Aurora Leigh” was exhausted within a few months.
The winter was a very full and engaging one. On one evening he dined at the deanery of St. Paul’s, Sir John Lubbock and Tennyson being also guests, but the Stanleys, who were invited, were not present. At another dinner the poets met, Tennyson recording: “Mr. Browning gave me an affectionate greeting after all these years,” and Browning writing to a friend: “... I have enjoyed nothing so much as a dinner last week with Tennyson, who with his wife and one son is staying in town for a few weeks, and she is just what she was and always will be, very sweet and dear: he seems to me better than ever. I met him at a large party ... also at Carlyle’s....”
In May of 1866 Browning’s father was in poor health, and on June 14 he died, at his home in Paris, his son having arrived three days before. Although nearly eighty-five years of age, the elder Browning had retained all his clearness of mind, and only just before he passed away he had responded to some question of his son regarding[Pg 211] a disputed point in medieval history with “a regular book-full of notes and extracts.” His son speaks of the aged man’s “strange sweetness of soul,” apparently a transmitted trait, for the poet shared it, and has left it in liberal heritage to his son, Robert Barrett Browning, the “Pen” of all these pages. Of his father the poet said:
“He was worthy of being Ba’s father,—out of the whole world, only he, so far as my experience goes. She loved him, and he said very recently, while gazing at her portrait, that only that picture had put into his head that there might be such a thing as the worship of the images of saints.”
Miss Browning came henceforth to live with her brother, and for the remainder of his life she was his constant companion. She was a woman of delightful qualities,—of poise, cheerfulness, of great intelligence and of liberal culture. She was a very discriminating reader, and was peculiarly gifted with that sympathetic comprehension that makes an ideal companionship. Her presence now transformed the London house into a home.
The next summer they passed at Le Croisic, where Browning wrote “Hervé Riel,” in “the most delicious and peculiar old house,” and he and his sister, both very fond of the open air, walked once to Guerande, the old capital of Bretagne, some nine miles from their house.
Browning had received his first academic honors that summer, Oxford having conferred on him her degree of M.A. The next October Browning was made Honorary Fellow of Balliol College, a distinction that he greatly prized.
During this summer Rev. Dr. Phillips Brooks (later Bishop of Massachusetts) was in London, and visited Browning once or twice. To a Boston friend who asked for his impressions of the great poet, Dr. Brooks wrote:[11]
[Pg 212]“... I can’t say anything now except that he is one of the nicest people to pass an evening with in London. He is a clear-headed and particularly clear-eyed man of the world, devoted to society, one of the greatest diners-out in London, cordial and hearty, shakes your hand as if he were really glad to see you.... As to his talk it wasn’t ‘Sordello,’ and it wasn’t as fine as ‘Paracelsus,’ but nobody ever talked more nobly, truly, and cheerily than he. I went home and slept after hearing him as one does after a fresh starlight walk with a good cool breeze on his face.”
In 1863, on July 19, a little more than two years after the death of Mrs. Browning, Arabel Barrett had a dream, in which she was speaking with her sister Elizabeth, and asked, “When shall I be with you?” “Dearest, in five years,” was the reply. She told this dream to Mr. Browning, who recorded it at the time. In June of 1868 Miss Barrett died, the time lacking one month only of being the five years. “Only a coincidence, but noticeable,” Mr. Browning wrote to Isa Blagden. But in the larger knowledge that we now have of the nature of life and the phenomena of sleep, that the ethereal body is temporarily released from the physical (sleep being the same as death, save that in the latter the magnetic cord is severed, and the separation is final)—in the light of this larger knowledge it is easy to realize that the two sisters actually met in the ethereal realm, and that the question was asked and answered according to Miss Barrett’s impression. The event was sudden, its immediate cause being rheumatic affection of the heart, and she died in Browning’s arms, as did his wife. Her companionship had been a great comfort to him, and Mr. Gosse notes that for many years after her death he could not bear to pass Delamere Terrace.
The late summer of that year was devoted to traveling from Cannes about the coast, and they finally decided[Pg 213] on Audierne for a sojourn. “Sarianna and I have just returned from a four hours’ walk,” he writes to a friend from this place; but here, as everywhere, he was haunted by Florentine memories, and by intense longings for his vanished paradise. To Isa Blagden he wrote:
“I feel as if I should immensely like to glide along for a summer day through the streets and between the old stone walls, unseen come and unheard go,—perhaps by some miracle I shall do so ... Oh, me! to find myself some late sunshiny afternoon with my face turned toward Florence....”
While at Audierne, Browning put the final touches to the new six-volume edition of his works that was about to appear from the house of Smith, Elder, and Company, on the title-page of which he signs himself as M.A., Honorary Fellow of Balliol College. Mr. Nettleship’s volume of essays on Browning’s poems was published that season, indicating a strong interest in the poet; and another very gratifying experience to him was the interest in his work manifested by the undergraduates of both Oxford and Cambridge. Undoubtedly the pleasant glow of this appreciation stimulated his energy in the great poem on which he was now definitely at work, “The Ring and the Book.” Publishers were making him offers for its publication, “the R. B. who for six months once did not sell a single copy of his poems,” he exclaimed in a letter to a friend, to whom he announced that he should “ask two hundred pounds for the sheets to America, and get it!” with an evident conviction that this was a high price for his work. The increasing recognition of the poet was further indicated by a request from Tauchnitz for the volumes of selections which Browning dedicated to the Laureate in these graceful words: “To Alfred Tennyson. In Poetry—illustrious and consummate; In Friendship—noble and sincere.”
[Pg 214]The publication of “The Ring and the Book” was the great literary event of 1869. Two numbers had appeared in the previous autumn, but when offered in its completeness the poem was found to embody the most remarkable interpretation of transfigured human life to be found in all the literature of poetry. The fame of the poet rose to splendor. This work was the inauguration of an epoch, of a period from which his work was to be read, studied, discussed, to a degree that would have been incredible to him, had any Cassandra of previous years lifted the veil of the future. The great reviews united in a very choral pean of praise; the Fortnightly, the Quarterly, the Edinburgh Review, the Revue des Deux Mondes, and others were practically unanimous in their recognition of a work which was at once felt to be the very epitome of the art and life of Robert Browning. The poem is, indeed, a vast treasure into which the poet poured all his searching, relentless analysis of character, and grasp of motive; all his compassion, his sensitive susceptibility to human emotion; all his gift of brilliant movement; all his heroic enthusiasms, and his power of luminous perception. But all this wealth of feeling and thought had been passed through the crucible of his critical creation; it had been fused and recast by the alchemy of genius. He transmuted fact into truth.
“Do you see this Ring?
’T is Rome-work made to match
(By Castellani’s imitative craft)
Etrurian circlets....
······
I fused my live soul and that inert stuff,
Before attempting smithcraft....”
The “square old yellow book” which Browning had chanced upon in the market-place of San Lorenzo, in that June of 1860, was not a volume, but a “lawyer’s file of [Pg 215]documents and pamphlets.” In relating how he found the book Browning says, in the poem:
“... I found this book,
Gave a lira for it, eightpence English just,
(Mark the predestination!) when a Hand,
Always above my shoulder, pushed me once,
······
Across a Square in Florence, crammed with booths.”
He stepped out on the narrow terrace, built
“Over the street and opposite the church,
······
Whence came the clear voice of the cloistered ones
Chanting a chant made for midsummer nights—”
and making his own the story.

The Palazzo Riccardi, Florence.
erected by Michelozzo about 1435.
| “....Riccardi where they lived His race........” |
| The Ring and the Book. |
In 1908 Dr. Charles W. Hodell was enabled by the courtesy of Balliol College, to whom Browning left the “Old Yellow Book,” to make a photographic reproduction of the original documents, to which Dr. Hodell added a complete and masterly translation, and a noble essay entitled “On the Making of a Great Poem,” the most marvelous analysis and commentary on “The Ring and the Book” that has ever been produced. The photographed pages of the original documents, the translation, and this essay were published by the Carnegie Institution, in a large volume entitled “The Old Yellow Book.” In his preface Professor Hodell records that he was drawn to the special study of this poem by Professor Hiram Corson, Litt.D., LL.D., to whom he reverently refers as “my Master.” Of “The Ring and the Book” Dr. Hodell says:
“In the wide range of the work of Robert Browning no single poem can rival ‘The Ring and the Book,’ in scope and manifold power. The subject had fallen to his hands at the very fulness of his maturity, by ‘predestination,’ as it seemed to him. [Pg 216]In the poem, as he planned his treatment, there was opportunity for every phase of his peculiar genius.... so that the completed masterpiece becomes the macrocosm of his work.... Without doubt it may be held to be the greatest poetic work, in a long poem, of the nineteenth century. It is a drama of profound spiritual realities.
‘So write a book shall mean beyond the facts,
Suffice the eye, and save the soul beside.’
Browning was the only important poet of the Victorian age who did not draw upon the Morte d’Arthur legends; and the rich mythology of the Greeks tempted him as little. The motive that always appealed to him most was that of the activity of the human spirit, its power to dominate all material barriers to transcend every temporary limit, by the very power of its own energy.”
In his historic researches Professor Hodell found reason to believe that the Pope, in “The Ring and the Book,” was Stephen VI, and not VII; and writing to Robert Barrett Browning to inquire regarding this point, he received from the poet’s son the following interesting letter, which, by Dr. Hodell’s generous courtesy, is permitted to appear in this book.
La Torre all’ Antella, Florence, Jan. 6, 1904.
My Dear Sir,—I wish I were able to give you the information you ask me for, but my father’s books are in Venice, and I have not any here touching on the matter to refer to.
If Pope Stephen was, as you say, the Sixth and not the Seventh, of course the mistake is obvious and perhaps attributable to an unconscious slip of the memory, which with my father was not at its best in dates and figures. It is not likely that such an error should have appeared in any old work, such as he would have consulted; and certainly it was not caused by carelessness, for he was painstaking to a degree, and had a proper horror of blundering, which is the word he would have used. I can only account for such a mistake as this—which [Pg 217]he would have been the first to pronounce unpardonable—by his absent-mindedness, his attention being at the moment absorbed by something else. Absent-mindedness was one of his characteristics, over instances of which he used to laugh most heartily. My father’s intention, I know, was to be scrupulously accurate about the facts in this poem. I may tell you as an instance that, wishing to be sure that there was moonlight on a particular night, he got a distinguished mathematician to make the necessary calculation. The description of the finding of the book is without doubt true in every detail. Indeed, to this day the market at San Lorenzo is very much what it was then and as I can remember it. Not long ago, I myself bought an old volume there off a barrow.
The “Yellow Book” was probably picked up in June of 1860 before going to Rome for the winter—the last my father passed in Italy. As it had always been understood that the Book should be presented to Balliol, I went soon after my father’s death to stay a few days with Jowett, and gave it to him.
In the portrait that hangs in Balliol Hall I painted my father as he sat to me with the Book in his hands.
Nothing would have gratified him more than what you tell me about the interest with which his works are studied in America, and I need not say how much pleasure this gives me.
Believe me with many thanks for your kind letter,
Yours Very Sincerely,
R. Barrett Browning.
A very curious discovery was made in Rome, in the winter of 1900, by Signer Giorgi, the Librarian of the Royal Casanatense Library, in an ancient manuscript account of curious legal trials, among which were those of Beatrice Cenci, of Miguel de Molinos (in 1686), and of the trial and sentence of Guido Franceschini. The fact that taxes credulity in regard to this manuscript, of whose existence, even, no one in modern times had ever dreamed, is that the three points of view, as presented by Browning in the[Pg 218] “Half Rome,” “The Other Half Rome,” and “Tertium Quid,” are in accord with those given in this strange document, which for more than a century had lain undisturbed in the archives.
In a little explanation regarding the significance of the closing lines of “The Ring and the Book,” also kindly given by Robert Barrett Browning, it seems that his mother habitually wore a ring of Etruscan gold, wrought by Castellani, with the letters “A. E. I.” on it; and that after her death the poet always wore it on his watch-chain, as does now his son. In the tablet placed on Casa Guidi to the memory of Mrs. Browning (the inscription of which was written by the Italian poet, Tommaseo) the source of the other allusion, of the linking Italy and England, is found. As the reader will recall, the lines run:
“And save the soul! If this intent save mine,—
If the rough ore be rounded to a ring,
Render all duty which good ring should do,
And, failing grace, succeed in guardianship,—
Might mine but lie outside thine, Lyric Love,
Thy rare gold ring of verse (the poet praised)
Linking our England to his Italy!”
Dr. Corson especially notes Browning’s opening invocation to his wife, praying her aid and benediction in the work he has undertaken. “This passage,” says Dr. Corson, “has a remarkable movement, the unobtrusive but distinctly felt alliteration contributing to the effect.”
“O lyric Love, half angel and half bird
And all a wonder and a wild desire,—
Boldest of hearts that ever braved the sun,
Took sanctuary within the holier blue.”
That Browning could never have created the character of Pompilia, save for that all-enfolding influence of the[Pg 219] character of his wife, all the greater critics of “The Ring and the Book” agree. To Dr. Corson, Browning said of her:
“I am not sorry, now, to have lived so long after she went away, but I confess to you that all my types of women were beautiful and blessed by my perfect knowledge of one woman’s pure soul. Had I never known Elizabeth, I never could have written ‘The Ring and the Book.’”
Of Pompilia Dr. Hodell also says:
“... But there is another influence in the creation of this ideal character beside that of the Madonna, it was the Madonna of his home, the mother of his own child, whose spiritual nature was as noteworthy as her intellect. And before this spiritual nature the poet bowed in humble reverence.”
Mrs. Orr, too, has written:
“Mrs. Browning’s spiritual presence was more than a presiding memory in the heart. I am convinced that it entered largely into the conception of Pompilia.
“It takes, however, both the throbbing humanity of Balaustion and the saintly glory of Pompilia to express fully the nature of Elizabeth Barrett Browning as she appeared to her husband.”
Dr. Dowden, Brooke, Corson, Herford, Hodell, Chesterton, and other authoritative critics allude to their recognition of Mrs. Browning in the character of Pompilia; and no reader of this immortal masterpiece of poetic art can ever fail to find his pulses thrilling with those incomparable lines, spoken in her last hour on earth by Pompilia:
“O lover of my life, O soldier-saint,
No work begun shall ever pause for death!
Love will be helpful to me more and more
I’ the coming course, the new path I must tread—
······
[Pg 220]
Tell him that if I seem without him now,
That’s the world’s insight! Oh, he understands!
······
So let him wait God’s instant men call years;
Meantime hold hard by truth and his great soul,
Do out the duty!...”
In the entire range of Browning’s heroines Pompilia is the most exalted and beautiful character.
| “I am strong in the spirit, deep-thoughted, clear-eyed; I could walk, step for step, with an angel beside, On the heaven-heights of truth. Oh, the soul keeps its youth ······ “’Twixt the heavens and the earth can a poet despond? O Life, O Beyond, Thou art strange, thou art sweet!” |
In Scotland with the Storys—Browning’s Conversation—An Amusing Incident—With Milsand at St. Aubin’s—“Red Cotton Night-cap Country”—Robert Barrett Browning’s Gift for Art—Alfred Domett (“Waring”)—“Balaustion’s Adventure”—Browning and Tennyson—“Pacchiarotto”—Visits Jowett at Oxford—Declines Lord Rectorship of St. Andrews—“La Saisiaz”—Italy Revisited—The Dream of Asolo—“Ivanovitch”—Pride in His Son’s Success—“Dramatic Idylls.”
In the summer of 1869 the Storys, with their daughter, came from Rome and joined Browning with his sister and his son, for a holiday in Scotland. They passed some time at a little inn on Loch Achnault, where Lady Marian Alford also came, and there are still vivid reminiscences of picnic lunches on the heather, and of readings by the poet from “The Ring and the Book.” Chapters from “Rob Roy” also contributed to the enjoyment of evenings when the three ladies of the party—Mrs. Story, Lady Marian, and the lovely young girl, Miss Edith Story—were glad to draw a little nearer to the blazing fire which, even in[Pg 222] August, is not infrequently to be desired in Scotland. Lord Dufferin was also a friend of those days, and for the tower he had built at Clandeboye in the memory of his mother, Helen, Countess of Gifford, Browning wrote, soon after, his poem entitled “Helen’s Tower.” Mrs. Orr speaks of this poem as little known, and not included in his published works; but it is now to be found in all the complete editions of Browning. After this Arcadian sojourn Browning and his son, with Miss Browning, were the guests of Lady Ashburton at Loch Luichart Lodge.
For two or three years after the publication of “The Ring and the Book,” Browning wrote little. The demands of friends and of an always enormous correspondence occupied much time; his son was growing into young manhood, and already manifesting his intense love of art, and his gifts as both painter and sculptor.
Browning’s conversation was always fascinating. It was full of glancing allusion, wit, sparkle, and with that constant undertone of significance that may be serious or gay, but which always lingers with a certain impressiveness to haunt the mind of the listener. Dr. Hiram Corson, who may perhaps be regarded as Browning’s greatest interpreter, speaks of one of his visits to the poet, in London, where the conversation turned from Shelley to Shakespeare. “He spoke with regret of the strangely limited reading of the Plays, even by those who believe themselves habitual and devoted readers,” says Dr. Corson.
“At luncheon,” continues Dr. Corson, “his talk was, as usual with him, rapid and off-hand. He gave but a coup d’œil to every subject that came up. In all subsequent talks with him, I never got the slightest impression from him of pride of intellect, though his was certainly one of the subtlest and most comprehensive intellects of his time. He was absolutely free from it; was saved from it by his spiritual vitality. His intellectual and his spiritual nature jointly operated. Nor did he ever show[Pg 223] to me any pride of authorship; never made any independent allusion to his poetry. One might have supposed that his poetry, great and extensive as it was, was a πάρεργον, a by-work, with him.
“I have no recollection of any saying of his, such as might be recorded for its wisdom or profundity. Never a brilliant thought crystallized in a single sentence. His talk was especially characterized by its cordiality and rapid flow. The ‘member of society’ and the poet seemed to be quite distinct.
“One day when Mrs. Corson and I were lunching with him in Warwick Crescent,” said Dr. Corson, “he told us a most amusing incident. On that morning Browning was particularly ‘an embodied joy.’ He told several good stories, one of which showed that the enigmatical character attributed to his poetry by some of his critics was to him a good joke. I have no doubt he must have enjoyed the Douglas Jerrold story, that Jerrold, in endeavoring to read ‘Sordello,’ thought he had lost his mind.
“But to Browning’s story. He said, ‘I was visited by the Chinese minister and his attachés, without having been previously informed of their coming. Before they entered, I had noticed from my window a crowd in the street, which had been attracted by the celestials in their national rigs, who were just then getting out of their carriages, I not knowing then what manner of visitors I was to have. Soon the interpreter announced at the drawing-room door, “His Excellency, the Chinese Minister and his attachés.” As they entered, the interpreter presented them, individually, first, of course, his Excellency, the Minister, and then the rest in order of rank. It was quite an impressive occasion. Recovering myself, I said to the interpreter: “To what am I indebted for this great honor?” He replied: “You are a distinguished poet in your country, and so is his Excellency in his.” We did obeisance to each other. I then asked the character of his Excellency’s poetry. The interpreter replied, “Chiefly poetical enigmas.” Grasping his Excellency’s hand, I said, “I salute you as a brother.”’
“Browning told this story while walking up and down the room. When he said, ‘I salute you as a brother,’ he made the motion of a most hearty hand-shake.”
[Pg 224]Mrs. Arthur Bronson, than whom Mr. Browning never had a more sympathetic and all-comprehending friend, said that if she tried to recall Robert Browning’s words it was as though she had talked to a being apart from other men. “My feeling may seem exaggerated,” she smiled, “but it was only natural, when considering my vivid sense of his moral and intellectual greatness. His talk was not abstruse and intricate, like some of his writings. Far from it. As a rule he seemed rather to avoid deep and serious subjects. There was no loss, for everything he chose to say was well said. A familiar story, grave or gay, when clothed with his words, and accentuated by his expressive gestures and the mobility of his countenance, had all the charm of novelty; while a comic anecdote from his lips sparkled with wit, born of his own keen sense of humor. I found in him that most rare combination of a powerful personality united to a nature tenderly sympathetic.”
Another who knew him well perpetrated the mot that “Tennyson hides behind his laurels, and Browning behind the man of the world.” Henry James, whose gift of subtle analysis was never more felicitously revealed than in his expressions about Browning, declared that the poet had two personalities: one, the man of the world, who walked abroad, talked, did his duty; the other, the Poet,—“an inscrutable personage,—who sat at home and knew, as well he might, in what quarters of that sphere to look for suitable company. The poet and the man of the world were disassociated in him as they can rarely elsewhere have been.”
For three or four summers after this sojourn in Scotland the Brownings were at St. Aubin, in Brittany, where they had a cottage “not two steps away” from that of his friend Milsand. In the early mornings Browning would be seen pacing the sands, reading from his little Greek copy of Homer; and in the late afternoons the two friends would[Pg 225] stroll on the Normandy beach with their arms around each other’s shoulders. They are described as very different in appearance,—Browning vigorous and buoyant, Milsand nervous, thin, reserved,—but akin in a certain delicate sensitiveness, a swift susceptibility to impressions. Of Browning Milsand said that what he really valued most was his kindness, his simple, open, radiant goodness. “All the chords of sympathy vibrated in his strong voice,” added Milsand. The French critic was very fond of the poet’s son, and in reference to him he once said: “The father has reason to be happy that in walking before he has opened a path for his son, instead of making him stumble.” As has been seen, in Mrs. Browning’s letters, she always shared her husband’s enthusiasm for Milsand, and the latter had said that he felt in her “that shining superiority always concealing itself under her unconscious goodness and lovely simplicity.”
On Sundays at St. Aubin’s, Browning frequently accompanied Milsand to the little chapel of Château-Blagny, for Protestant worshipers. From his cottage Browning could gaze across the bay to the lighthouse at Havre, and he “saw with a thrill” the spot where he once passed a summer with his wife.
Italian recollections sometimes rose before his inner vision. To Isa Blagden, who had gone to Siena, he wrote that he could “see the fig-tree under which Ba sat, reading and writing, poor old Landor’s oak opposite.”
Of Milsand he wrote to a friend: “I never knew or shall know his like among men,” and to Milsand, who had assisted him in some proof-reading, he wrote acknowledging his “invaluable assistance,” and said:
“The fact is, in the case of a writer with my peculiarities and habits, somebody quite ignorant of what I may have meant to write, and only occupied with what is really written, ought to supervise the thing produced. I won’t attempt to thank[Pg 226] you, dearest friend.... The poem will reach you in about a fortnight. I look forward with all confidence and such delight to finding us all together again in the autumn. All love to your wife and daughter. R. B.”
Milsand, writing of Browning in the Revue, revealed his high appreciation of the poet when he said: “Browning suggests a power even greater than his achievement. He speaks like a spirit who is able to do that which to past centuries has been almost impossible.”
It was St. Aubin that furnished Browning with material for his poem, “Red Cotton Night-cap Country,” the title of which was suggested by Miss Thackeray (now Lady Ritchie) who had a cottage there one summer, near those of Browning and Milsand. Browning and his sister occupied one of the most primitive of cottages, but the location was beautiful, perched on the cliff of St. Aubin, and commanded a changeful panorama of sea and sky. “The sitting-room door opened to the garden and the sea beyond—a fresh-swept bare floor, a table, three straw chairs, one book upon the table,—the only book he had with him. The bedrooms were as bare as the sitting-room, but there was a little dumb piano standing in a corner, on which he used to practice in the early morning. Mr. Browning declared they were perfectly satisfied with their little house; that his brains, squeezed as dry as a sponge, were only ready for fresh air.”[12] As all Browning readers will remember, “Red Cotton Night-cap Country” is dedicated to Miss Thackeray.
In the succeeding autumn Browning passed some weeks at Fontainebleau, where he was absorbed in reading Æschylus, and in making an especial study of the great dramatist. It was perhaps at this time that he conceived the idea of translating the Agamemnon, which, he says in his preface, [Pg 227]“was commanded of me by my venerated friend Thomas Carlyle, and rewarded it will be if I am permitted to dignify it by the prefatory insertion of his dear and noble name.”

Bust of Robert Browning, by his Son,
Robert Barrett Browning.
In the possession of the sculptor at his villa near Florence.
Before the close of this year Browning had also complied with a request from Tauchnitz to prepare for publication a selection from the poems of Mrs. Browning. This Tauchnitz Edition of Mrs. Browning will always retain its interest as representing her husband’s favorites among her poems. “The Rhyme of the Duchess May,” with its artistic symmetry and exquisite execution, was of course included. This poem may be said to exhibit all Mrs. Browning’s poetic characteristics.
Encouraged by Millais, Robert Barrett Browning had seriously entered on the study of painting, his first master being M. Heyermans in Antwerp. In 1875 Frederick Lehmann had expressed high appreciation of a work of the young artist, the study of a monk absorbed in reading a book,—a picture that he liked so well as subsequently to purchase it. Another picture by Barrett Browning was entitled “The Armorer,” and found a place in the Royal Academy of that year, and was purchased by a Member of Parliament who was also something of a connoisseur in art. In this season was inaugurated the annual “private view” of the paintings of the poet’s son, which were exhibited in a house in Queen’s Gate Gardens and attracted much attention. In his son’s success Browning took great pride and pleasure. On the sale of the picture to the M. P., Browning wrote to Millais:
19, Warwick Crescent, May 10, 1878.
My Beloved Millais,—You will be gladdened in the kind heart of you to learn that Pen’s picture has been bought by Mr. Fielder, a perfect stranger to both of us. You know what your share has been in his success, and it cannot but do a world[Pg 228] of good to a young fellow whose fault was never that of being insensible to an obligation.
Ever Affectionately Yours,
Robert Browning.[13]
In 1871 Browning had been appointed Life Governor of the University of London, an honor that he particularly appreciated as indicating the interest of students in his poetry. In the late winter of 1872, after an absence of thirty years, Alfred Domett again appeared. He had vanished
“like a ghost at break of day,”
and like a ghost he returned, calling at once on his friend in Warwick Crescent. A letter from Miss Browning to Domett explains itself:
19, Warwick Crescent,
Upper Westbourne Terrace, Feb. 1872.
My Dear Mr. Domett,—My brother was so sorry to miss you yesterday; he is a man of many engagements, and unfortunately is engaged every evening next week, or I would ask you to join our family dinner as soon as possible—but meanwhile, as he is impatient to see you, will you be very kind and come to lunch with us on Monday at one o’clock? We shall be delighted to meet you. If you cannot come on Monday, name some other morning.
Always Yours Truly,
Sarianna Browning.
The old friendship between Browning and Domett was renewed with constant intercourse and interchange of delightful letters. Milsand was in the habit of passing a part of every spring with Browning in his home in Warwick Crescent, and with the arrival of Domett a warm and sincere friendship united all three.
[Pg 229]Once, in Scotland, as the guest of Ernest Benzon, when Browning missed part of a visit from Milsand, the poet said: “No words can express the love I have for Milsand, increasingly precious as he is.” The Benzons were at that time in the hills above Loch Tummel, where Jowett was staying, Swinburne also with the Master of Balliol. Had there been a phonograph to register the conversation of such a trio as Jowett, Browning, and Swinburne, its records would be eagerly sought.
A fragmentary record, indeed, remains in a note made by Edwin Harrison, who was with Jowett at this time. In his diary Mr. Harrison recorded:
“R. B. was in the neighborhood, staying at Little Milton, above Loch Tummel, where he was perpetrating ‘Prince Hohenstiel-Schwangau’ at the rate of so many lines a day, neither more nor less. He walked over to see Jowett one afternoon, very keen about a fanciful rendering he had imagined for lines in the Alcestis. A few evenings later we met him and his son at dinner at Altaine House, by the foot of the loch. You may be sure that where Jowett and Browning were, the conversation was animated and interesting.”
In “Balaustion’s Adventure” the poet seemed to take captive the popular appreciation of the day, for more than three thousand copies had been sold within the first six months, and his sister told Domett that she regarded it as the most swiftly appreciated poem of all her brother’s works. Certainly it is one of the most alluring of Browning’s works,—this delightful treatment of the interwoven life of mortals and of the immortal gods.
The June of 1872 brought to Browning the sad news of the death of his wife’s dearest friend, Isa Blagden. “A little volume of Isabella Blagden’s poems was published after her death,” writes Thomas Adolphus Trollope. “They are not such as would take the world by storm, but it is impossible to read them without perceiving how choice[Pg 230] a spirit their author must have been, and understanding how she was especially honored with the friendship of Mrs. Browning.”[14]
On the publication of “Red Cotton Night-cap Country,” Browning sent a first copy to Tennyson, and the Laureate’s son says of it: “Among the lines which my father liked were
‘Palatial, gloomy chambers for parade,
And passage lengths of lost significance’;
and he praised the simile about the man with his dead comrade in the lighthouse. He wrote to Mr. Browning: ‘My wife has just cut the leaves. I have yet again to thank you, and feel rather ashamed that I have nothing of my own to send you back.’”
An entry in Tennyson’s diary in the following December notes: “Mr. Browning dined with us. He was very affectionate and delightful. It was a great pleasure to hear his words,—that he had not had so happy a time for a long while as since we have been in town.”
Tennyson’s “Queen Mary” was published in 1875, and on receiving a copy from the author Browning wrote expressing thanks for the gift, and even more for “Queen Mary the poem.” He found it “astonishingly fine”; and he adds: “What a joy that such a poem should be, and be yours.” The relations between the two great poets of the Victorian age were always ideally beautiful, in their cordial friendship and their warm mutual appreciation.
In a note dated in the Christmas days of 1876 Browning writes:
My Dear Tennyson,—True thanks again, this time for the best of Christmas presents, another great work, wise, good, and beautiful. The scene where Harold is overborne to take the[Pg 231] oath is perfect, for one instance. What a fine new ray of light you are entwining with your many-colored wreath!...
All happiness befall you and yours this good season and ever.[15]
The present Lord Tennyson, in his biography of his father, makes many interesting allusions to the friendship and the pleasant intercourse between the poets. “Browning frequently dined with us,” he says, “and the tête-à-tête conversations between him and my father on every imaginable topic were the best talk I have ever heard, so full of repartee, epigram, anecdote, depth, and wisdom, too brilliant to be possible to reproduce. These brother poets were two of the most widely read men of their time, absolutely without a touch of jealousy, and reveling, as it were, in each other’s power.... Browning had a faculty for absurd and abstruse rhymes, and I recall a dinner where Jebb, Miss Thackeray, and Browning were all present, and Browning said he could make a rhyme for every word in the language. We proposed rhinoceros, and without pause he said,
‘O, if you should see a rhinoceros
And a tree be in sight,
Climb quick, for his might
Is a match for the gods,—he can toss Eros.’”
A London friend relates that on one occasion Browning chanced upon a literal translation some one had made from the Norwegian:
“The soul where love abideth not resembles
A house by night, without a fire or torch,”
and remarked how easy it would be to put this into rhyme; and immediately transmuted it into the couplet,
[Pg 232]
“What seems the soul when love’s outside the porch?
A house by night, without a fire or torch.”
When Browning’s “Inn Album” appeared, and he sent a copy to Tennyson, the Laureate responded:
“My Dear Browning,—You are the most brotherly of poets, and your brother in the muses thanks you with the affection of a brother. She would thank you too, if she could put hand to pen.”
Tennyson once remarked to his son, Hallam, that he wished he had written Browning’s lines:
“The little more, and how much it is,
The little less, and what worlds away.”
There was an interval of twelve years between the appearance of the “Dramatis Personæ” (in 1864) and the publication of “Pacchiarotto.” In this collection Browning’s amusing play of rhyme is much in evidence. Among Mr. Browning’s most enjoyable experiences were his frequent visits to Oxford and Cambridge, in both of which he was an honored guest. In the spring of 1877 he had an especially delightful stay at Oxford, the pleasure even beginning on the train, “full of men, all my friends,” he wrote of it; and continued: “I was welcomed on arrival by a Fellow who installed me in my rooms—then came the pleasant meeting with Jowett, who at once took me to tea with his other guests, the Archbishop of Canterbury, the Bishop of London, the Dean of Westminster, Lord Airlie, and others.”
There was a banquet and much postprandial eloquence that night, and Browning mentions among the speakers Lord Coleridge, Professor Smith, Mr. Green (on science and literature with a most complimentary appreciation of Browning), and “a more rightly-directed one,” says the poet, “on Arnold, Swinburne, and the old pride of Balliol,[Pg 233] Clough, which was cleverly and almost touchingly answered by dear Matthew Arnold.” The Dean of Westminster responded to the toast of “The Fellows and the Scholars,” and the entire affair lasted over six hours. “But the whole thing,” said Browning, “was brilliant, genial, and there was a warmth, earnestness, and refinement about it which I never experienced in any previous public dinner.”
The profound impression that Browning made both by his personality and his poetic work is further attested by his being again chosen Lord Rector of the University of Glasgow. Dr. William Knight, the Professor of Moral Philosophy at St. Andrews, urges Browning’s acceptance of this office, and begs the poet to realize “how the thoughtful youth of Scotland” estimate his work. Professor Knight closes by saying that his own obligations to Browning, “and to the author of ‘Aurora Leigh’ are such that of them silence is golden.” While Mr. Browning was deeply touched by this testimonial of esteem, he still, for the second time, declined the honor.
Many readers and lovers of Robert Browning’s poem “La Saisiaz” little dream of the singular story connected with it. “La Saisiaz” is a chalet above Geneva, high up in the Savoyard mountains, looking down on Geneva and Lake Leman. It is a tall, white house, with a red roof that attracted the lovers of beauty, solitude, and seclusion. Among the few habitués for many years were Robert Browning and his sister, Sarianna, and their friend, Miss Egerton-Smith. It was the bond of music that especially united Browning and this lady, and in London they were apt to frequent concerts together. “La Saisiaz” is surrounded by tall poplar trees, but the balcony from a third-floor window, which was Browning’s room, looked through a space in the trees out on the blue lake, and on this balcony he would draw out his chair and writing desk. Back of the[Pg 234] chalet a steep path ran up the mountains, where the three friends often climbed, to enjoy a gorgeous and unrivaled sunset spectacle.
In 1877 they were all there as usual in August, and one evening had planned that the next day they would start early in the morning and pass the day on the mountain, going by carriage, a servant accompanying them carrying the basket of luncheon. In the early evening Browning and Miss Egerton-Smith were out, pacing up and down the “grass-grown path,” and talking of the infinite life which includes death and that which is beyond death. The next morning she did not appear, and Browning and his sister waited for her. They sat out on the terrace after having morning coffee, expecting to see the “tall white figure,” and finally Miss Browning went to her room to ask if she were ill, and she lay dead on the floor. Miss Egerton-Smith was buried in the neighboring cemetery of Collonge, where her grave, over which a wonderful willow tree bends, is still seen—a place of frequent pilgrimage to visitors in this region. Five days after her death Browning made the excursion up the mountain alone,
“But a bitter touched its sweetness, for the thought stung ‘Even so
Both of us had loved and wondered just the same, five days ago!’”
La Salève, the mountain overlooking the Arve and the Rhone Valley, is one of the most wildly picturesque points in all the Alpine region. The chalet of “La Saisiaz” was perched on this mountain spur, about half-way up the mountain, on a shelving terrace, with vast and threatening rocks rising behind. The poem called “La Saisiaz” is one of Browning’s greatest. It is full of mystical questioning and of his positive and radiant assertions of faith; it abounds in vivid and exquisite scenic effects, and it has the personal touches of tenderness. The morning after her death is thus pictured:
[Pg 235]
“No, the terrace showed no figure, tall, white, leaning through the wreaths,
Tangle-twine of leaf and bloom that intercept the air one breathes.”
Browning and Miss Egerton-Smith had first met in Florence. She was an English lady of means (being part proprietor of the Liverpool Mercury) and of a reserve of temperament which kept her aloof from people in general. With the poet and his sister she was seen in all that cordial sweetness of her nature which her sensitive reserve veiled from strangers.
Italy again! A sapphire sky bending over hills and peaks and terraces swimming in violet shadows; villas, and sudden views, and arching pianterreni, and winding roads between low stone walls hidden in their riotous overgrowth of roses! And the soft air, the tall black cypresses against the sky, the sunsets and the stars, and golden lights, and dear Italian phrases! The trailing ivy vines all in a tangle; the wayside shrine, the vast white monastery perched on an isolated mountain top; the flaming scarlet of the poppies in the grass, the castles and battlements dimly caught on the far horizon,—the poetry, the loveliness, the ineffable beauty of Italy! Seventeen years had passed since that midsummer day when the dear form of his “Lyric Love” had been laid under the Florentine lilies, when Browning, in the spring of 1878, returned to his Italy. What dreams and associations thronged upon him!
“Places are too much,
Or else too little for immortal man,—
······
... thinking how two hands before
Had held up what is left to only one.”
Seventeen years had passed, but Venice, the ethereal city, the mystic dream of sea and sky, was unchanged, and, however unconsciously, the poet was now to initiate another era, another new “state” in his life. He never[Pg 236] again went farther south than Venice; he could never see Florence or Rome again, where she had lived beside him; but the dream city now became for him a second and dearer home. With his sister Sarianna, he broke the journey by lingering in a hotel on the summit of the Splügen, where he indulged himself in those long walks which he loved, Miss Browning often accompanying him down the Via Cala Mala, or to the summit where they could look down into Lombardy. Browning was at work on his “Dramatic Idyls,” and not only “Ivan Ivanovitch,” but several others were written on the Splügen. Pausing at Lago di Como, and a day in Verona, they made their way to Asolo, “my very own of all Italian cities,” the poet would say of it. Asolo, which from its rocky hilltop, has an outlook over all Veneto,—over all Italy, it would almost seem, for the towers and domes of Venice are visible on a clear day,—gave its full measure of joy to Browning, and when they descended into Venice they were domiciled in the Palazzo Brandolin-Rota, on the Grand Canal, near the Accademia. In Venice he met a Russian lady whom he consulted about some of the names he was giving to the characters in his “Ivan Ivanovitch.”
The success of his son in the Paris Salon and other exhibitions was a continual happiness to Mr. Browning. Both in Paris and in London the pictures of Barrett Browning were accorded an honorable place “on the line”; he received a medal from the Salon, and there was not wanting, either, that commercial side of success that sustains its theory. The young artist had now seriously entered on sculpture, under Rodin, with much prestige and promise.
The first series of “Dramatic Idyls” was published in the autumn of 1872, closely following “La Saisiaz” and the “Two Poets of Croisic.” The devoted student of Browning could hardly fail to be impressed by one feature of his poetry which, though a prominent one, has received[Pg 237] little attention from the critics. This feature is his doctrine of the sub-self, as the source of man’s highest spiritual knowledge. He has given his fullest expression of this belief in his “Paracelsus,” and it appears in “Sordello” (especially in the fifth book), in “A Death in the Desert,” in “Fifine,” and in “Christopher Smart,” and is largely developed in “The Ring and the Book.” Again, in “Beatrice Signorini,” contained in “Asolando,” published only on the day of his death, this theory is again apparent, and these instances are only partial out of the many in which the doctrine is touched or elaborated, showing how vital it was with him from the earliest to the latest period of his work. Another striking quality in Browning is that of the homogeneous spirit of his entire poetic expression. It is the great unity in an equally great variety. It is always clear as to the direction in which Browning is moving, and as to the supreme message of his philosophy of life.
| “Moreover something is or seems, That touches me with mystic gleams, Like shadows of forgotten dreams.” “Alas! our memories may retrace Each circumstance of time and place, Season and change come back again, And outward things unchanged remain; The rest we cannot re-instate; Ourselves we cannot re-create; Nor set our souls to the same key Of the remembered harmony!” |
“Les Charmettes”—Venetian Days—Dr. Hiram Corson—The Browning Society—Oxford Honors Browning—Katherine DeKay Bronson—Honors from Edinburgh—Visit to Professor Masson—Italian Recognition—Nancioni—The Goldoni Sonnet—At St. Moritz—In Palazzo Giustiniani—“Ferishtah’s Fancies”—Companionship with his Son—Death of Milsand—Letters to Mrs. Bronson—DeVere Gardens—Palazzo Rezzonico—Sunsets from the Lido—Robert Barrett Browning’s Gift in Portraiture.
Twenty-five years after Robert Browning had visited the famous haunts of Rousseau with his wife, he again made a little sojourn with his sister in lovely Chambéry, making various excursions in all the picturesque region about, and again visiting “Les Charmettes,” which Miss Browning had not before seen; as before, Browning sat down to the old harpsichord, attempting to play “Rousseau’s Dream,” but only two notes of the antique instrument responded[Pg 239] to his touch. Through all the wonderful scenery of the Mont Cenis pass they proceeded to Turin and thence to Venice, where they arrived in the midst of the festivities of the Congress Carnival in September of 1881. The Storys, whom Browning had anticipated meeting in Venice, had gone to Vallombrosa, where their daughter (the Marchesa Peruzzi di’ Medici) had a villa, to which the family retired in summer from their stately old palace in Florence. Mr. Story’s two sons, the painter and the sculptor, both had studios in Venice at this time, and Mr. Browning often strolled into these. Among other friends Browning and his sister visited the Countess Mocenigo, who was ensconced in the same palace that Byron had occupied. She showed her guests through all the rooms with their classic associations, and Browning sat down to the desk at which Byron had written the last canto of “Childe Harold.” To the satisfaction of the Brownings, Venice soon regained her usual quiet,—that wonderful silence broken only by the plash of water against marble steps, and the cries of the gondoliers,—and he resumed his long walks, often accompanied by Miss Browning, exploring every curious haunt and lingering in shops and squares. The poet familiarized himself with the enchanting dream city, as no tours in gondolas alone could ever do. To him Venice came to be dear beyond words, and soon after he made all arrangements to purchase the Palazzo Manzoni, an ancient Venetian palace of the fifteenth century, whose façade was a faint glow of color from its medallions of colored marbles, and whose balconies and arched windows seemed especially designed for a poet’s habitation. But the ancient structure was found to be in a too perilous condition, and Browning, with never-failing regret, resigned the prospect; nor was he ever consoled, it is said, until, some years later, his son became the owner of the noble Palazzo Rezzonico.
[Pg 240]Every day the poet saw Venice transformed into new splendor. “To see these divine sunsets is the joy of life,” he would say, as a city, flushed with rose, reflected itself in pale green waters, and the golden sunset filled with liquid light every narrow street and passage, contrasting sharply with the dense black shadows. Browning had a love of the sky that made its glorious panorama one of the delights of his life.
One of the crowning honors of the poet’s life invested these days for him with renewed vitality of interest,—that of the formation of the Browning Society in London for the study and promulgation of his poetic work. This was, indeed, a contrast to the public attitude of thirty years before. Once, in a letter to Mrs. Millais (dated January 7, 1867) he had described himself to her as “the most unpopular poet that ever was.” The Browning Society was due, in its first inception, to Dr. Furnivall and to Miss Emily Hickey, and its founding was entirely without Browning’s knowledge. Although the poet avowed himself as “quite other than a Browningite,” he could not fail to be touched and gratified by such a mark of interest and appreciation.
Dr. Hiram Corson, Professor of Literature at Cornell University, had, however, formed a Browning Club, composed of professors and their wives and many eminent scholars, some four or five years before the formation of the Browning Society in London, and the notable Browning readings which Professor Corson had given continually in many of the large cities and before universities, had been of incalculable aid in making Robert Browning’s poetry known and understood in the United States. As an interpreter of Browning, Dr. Corson stood unrivaled. His aim was to give to his audience the spiritual meaning of the poem read. His rich voice had the choral intonation without which no poem can be vocally interpreted. His[Pg 241] reading gave not only the articulated thought, but the spiritual message of the poet. It is hardly too much to say that no one has ever fully realized the dramatic power of Browning who has not listened to the interpretation of Dr. Corson. Of his own part in the creation of the Browning Society in London, Dr. Corson kindly contributed this record:
“I was stopping with my wife at the Inns of Court Hotel, on High Holborn. A day or two before receiving Mr. Browning’s invitation, Dr. Frederick James Furnivall dined with us, and after dinner we went over to the Inns of Court Gardens, just back of the hotel. There we walked about during the long evening twilight, and talked over the founding of a Society which Dr. Furnivall and Miss Emily Henriette Hickey, the poetess, had been contemplating, for the study of Browning’s poetry. I told him of what I had done at Cornell University, the previous four or five years, in a Browning Club composed of Professors and their wives, and in my University classes. It was decided that the London Browning Society should be organized in October; and I engaged to go over to England the following June, and read a paper before the Society; which I did at its eighth meeting, on the 23d of June, the subject of the paper being ‘The Idea of Personality as embodied in Robert Browning’s Poetry, and of Art as an intermediate Agency of Personality.’”
Another source of joy to Browning, and one that far exceeded that of any recognition of himself, was the increasing recognition of his son’s achievements in art. Barrett Browning was at this time a pupil of Rodin in Paris, devoting himself to sculpture with the same ardor that he gave to his painting. As to which expression in art was the more his métier, chi lo sa? The young man was the child of the muses, and all forms of art were to him a temperamental inheritance.
Oxford again honored Browning, this time in the June[Pg 242] of 1882, with the degree of D.C.L. “I never saw my father happier than on this occasion,” Mr. Barrett Browning said to the writer of this volume when questioned regarding it; and another observer who was present speaks of Browning’s distinction in his red Oxford gown, his shoulders thrown back, and his swift, light step. One of the humors of the occasion was the dangling of a red cotton night-cap over his head by one of the undergraduates, who was in danger of a not ill-merited rebuke, but Browning interceded with the Vice-Chancellor not to be too hard “on the harmless drolleries of the young man.” It was in this Oxford gown, holding in his hand “the square old yellow book,” that Robert Barrett Browning painted the portrait of his father, which he presented to Oxford, and which now hangs, a treasured possession, in Balliol Hall, to which portrait some allusion has already been made.

Portrait of Robert Browning, by his Son.
Painted in 1882, and presented to Oxford University by the artist.
One of the most beautiful of the friendships of the last decade of the poet’s life was that with Mrs. Arthur Bronson, a very cultivated and charming American woman who for more than twenty years made her home in Venice. Casa Alvisi, on the Grand Canal, opposite Santa Maria della Salute, came to be such a delightful center of social life for the choice circle that Mrs. Bronson gathered around her, that its records fairly enter into the modern history of Venice. Adjoining Casa Alvisi was the old Giustiniani Palace, in which Mrs. Bronson had taken a suite of rooms that she might use them in dispensing her hospitalities. No one who has been the privileged guest of Mrs. Bronson can ever lose the grateful appreciation of her genius as a hostess. Her lovely hospitality was dispensed with the quality that entitled it to be considered as absolutely a special gift of the gods, and when she invited Browning and his sister to occupy these rooms in the Palazzo Giustiniani Recanti, it was with a grace that forestalled any refusal. At first Miss Browning did a little housekeeping [Pg 243]on their own account, except that they dined and passed the evening with Mrs. Bronson; later on, for several seasons, they were her house-guests in Casa Alvisi,—that unique and dream-enchanted interior crowded with lovely Venetian things, and bibelots and bric-à-brac picked up the world over. But the brother and sister always occupied the rooms in the palace. It was after the first one of this series of annual visits that Browning wrote to Mrs. Bronson the following letter after his return to London:
19, Warwick Crescent, W.
Nov. 18, ’81.
I would not write at first arriving, Dear Friend, because I fancied that I might say too much all at once, and afterward be afraid of beginning again till some interval; this fortnight since I saw you, however, must pass for a very long interval indeed, I will try to tell you as quietly as possible that I never shall feel your kindness,—such kindness!—one whit less than I do now; perhaps I feel it “now” even more deeply than I could, at all events, realize that I was feeling.
You have given Venice an appreciation that will live in my mind with every delight of that dearest place in the world. But all the same you remain for me a dearest of friends, whether I see you framed by your Venice, or brightening up our bleak London, should you come there. In Venice, however, should I live and you be there next autumn, it will go hard with me if I do not meet you again.
What a book of memories, and instigations to get still more memories, does your most beautiful and precious book prove to me! I never supposed that photographers would have the good sense to use their art on so many out-of-the-way scenes and sights, just those I love most....
You—you have lost Lowell, and Field, and the rest of the good fellowship, but you will be sure of a succession of the sort.
On the poet’s seventieth birthday he received, from the Browning Societies of Oxford, Cambridge, Cornell [Pg 244]University, and others, a gift of a complete set of his own works, bound in olive green morocco, in a beautifully carved oak case, with this inscription:
“To Robert Browning on his seventieth birthday, May 7th, 1882, from some members of the Browning Societies. These members having ascertained that the works of a Great Modern Poet are never in Robert Browning’s house, beg him to accept a set of these works which they assure him will be found worthy of his most serious attention.”
Dr. Corson has related that when he visited the poet at one time Browning showed him this case, placed against the wall of the drawing-room, with an almost boyish delight.
In August of 1882, on their leisurely way to Venice, Browning and his sister lingered at Saint-Pierre la Chartreuse and at Gressoney Saint-Jean, where his enchanting outlook upon Monte Rosa was a continual joy, Mr. Browning spent one night in the monastery of the Grand Chartreuse, in order to hear the midnight mass; while Miss Browning, denied hospitality in the monastery, received that of the convent near at hand, where she was cordially entertained by the Mother Superior.
The Prologue of “Ferishtah’s Fancies,” published the next year, is dated from Gressoney, Val d’Aosta, and the lines,
“A fancy-freak by contrast born of thee,
Delightful Gressoney!”
will recall themselves to the memory. Miss Browning was an ideal companion in these mountain wanderings. She was equal to endless walks, and she had the accomplishment of being able to ride a mule or a donkey as one to the manor born. From Gressoney they looked up to the glaciers of Monte Rosa, almost overhanging, and from Saint-Pierre Browning wrote to a friend that they were in[Pg 245] the roughest and most primitive inn, “but my sister bears it bravely.”
Italian recognition of Browning was stimulated and extended, if not primarily inspired, by Il Signor Dottore Nancioni, who had the Chair of Literature in the University of Florence, and whom the Brownings had first met in the old Siena days. As Milsand first made Browning known in France, through his critical papers in the Revue, so Nancioni published, in the Nuova Antologia, and in the Fanfulla della Domenica of Rome, several papers devoted to serious and critical study and interpretation of Browning’s work; and he made the journey from Rome to Venice to meet the poet again. The recital of poetry was by no means ended in Italy in the days of the Improvvisatori, and Professor Nanciani frequently gave readings from Browning before cultivated Italian audiences.
When Venice honored Goldoni with a statue, Browning was invited to contribute to that wonderful “Album” of letters, with which Italy characteristically commemorates all scholarly events, with contributions from literary men. The sonnet so pleased the Venetians that they gave it the place of honor in the album.
The London seasons during all these years were of unrivaled brilliancy. Browning was seen in all the great houses, and often for two weeks he would dine out every consecutive night. Dr. Corson, whose first visit to Browning was made in the early eighties, gave to a friend in a personal letter this little transcription of his first meeting with the poet, with whom he had long been in correspondence:
“He received me in the drawing-room, on the second floor. After a few minutes’ conversation, he showed me various interesting things, in the drawing-room, busts and portraits and mementoes of Mrs. Browning, keeping up a rapid and meandering current of talk. Something was said, I forget what, which[Pg 246] caused me to allude to ‘the Book,’ the ‘square old yellow book,’ with ‘crumpled vellum covers,’ which he picked out of the market-day trumpery in the Piazza San Lorenzo, in Florence, and which led to the composition of his masterpiece, ‘The Ring and the Book,’ ‘I’ll take you down in a few minutes,’ he said, ‘to the library, and show it to you.’ When we left the drawing-room and were at the top of the stairway, he, with an apparent unconsciousness, and as if I were a younger brother, put his arm over my off shoulder, and so descended with me, talking all the while at his usual rapid rate. I tell this little incident, as I observed later, on several occasions, such an expression of unconscious cordiality and good fellowship was a characteristic of him.
“Beside his chair, at the writing table, stood Mrs. Browning’s low-seated, high and straight-backed, black haircloth covered chair, on which were piled books almost to the top of the back, which most effectually excluded any one from the honor of sitting in it.
“When showing me ‘The Book,’ he called my attention to passages in the Latin portion of it—the arguments of the two lawyers, Bottinius and Hyacinthus de Archangelis, and I was struck with the way in which he translated them, the rapid and close recasting of the thought in English, a rare gift even with the best Latin scholars. I had occasions to discover, in subsequent visits, that he read the Greek in a genial way and with less grammatical consciousness than do many Greek professors. His scholarship was extensive and, I would add, vital, it not having been imposed upon him at a public school and a university, and he having had what must have been Shakespeare’s power of acquiring and absorbing knowledge of all kinds. On some subsequent visit, I don’t remember what we had been talking about that led to the remark, he said to me, in his rapid mode of speech, ‘I never could have done much at a public school,’ meaning, of course, an endowed foundation school, such as Eton and others, in which there is a special preparation for the Universities. After a pause, he added, ‘no, nor at a university either. Italy was my university.’ In his ‘De Gustibus——’ he says:
[Pg 247]‘Open my heart and you will see
Graved inside of it, Italy.’
“While he was showing me ‘The Book,’ I asked him about a passage in ‘The Ring and the Book.’ He replied, ‘I don’t remember the passage. It has been some time since I read the poem, and I haven’t a copy of it in my house!’
“He showed me many of Mrs. Browning’s books—nearly all of them 24mo editions—said she couldn’t hold big books—English, French, Italian, Latin, and Greek books; a Hebrew Bible which had belonged to a distinguished English bishop, whose name I’ve forgotten. ‘Did Mrs. Browning read Hebrew?’ I asked. ‘Oh, yes,’ he replied, and added with a sigh, ‘she was a wonderful woman.’”
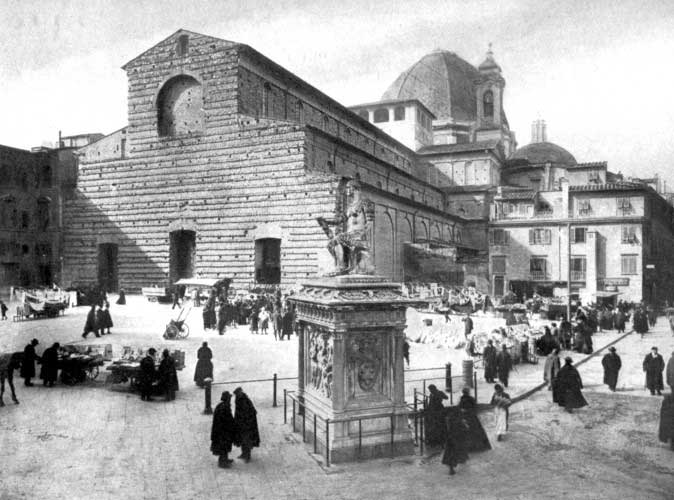

Church of San Lorenzo, Florence
| “June was the month, Lorenzo named the Square.” |
| The Ring and the Book. |
The succeeding summer found the Corsons again in London, and the following invitation from Browning particularly pleased them in its assurance that “nobody else” would be present.
Dear Professor Corson,—Could Mrs. Corson and yourself do my sister and me the great pleasure of taking luncheon with us—and nobody else—next Tuesday (27th) at one o’clock?
Believe me, dear Professor Corson,
Yours Truly Ever,—
Robert Browning.
On Browning’s return to England in 1861, after his wife’s death, he had entered into a most brilliant and congenial social life. Thackeray died soon after his return; but there were Carlyle, Ruskin, Jowett, Millais, Rossetti, Proctor, Matthew Arnold, Woolner, Leighton, Tennyson (whose companionship, as we have seen, was one of his keenest enjoyments), and his publisher, George Murray Smith, of the head of the house of Smith, Elder, and Company, who was one of his chosen friends. Carlyle died in 1881, but many of this group well outlived Browning.[Pg 248] On New Year’s Day of 1884 Miss Browning wrote to Mrs. Bronson:
The very first word I write this year is to you, dearest friend, wishing you every good gift the earth below, and Heaven above, can offer. If Robert does not write his own share in these kind feelings, it is only because we have mutually agreed that we shall come more constantly before you if we keep our letters apart.
... You cannot think how incessantly we dwell on the memories of the pleasant past. We are in Casa Alvisi in spirit daily, and I picture to myself all that is going on in the well-loved rooms. I hope Edith works at her guitar. She will find that it will repay the trouble.
Give our kindest love to her, and take yourself our loving hearts.
God bless you this year.
Ever Yours Affectionately,
Sarianna Browning.
In a letter to Mrs. Bronson Browning alludes to the purchase of the new house in DeVere Gardens:
“... I am really in treaty—not too deeply in it for extrication at need—with the land-owner who proposes to build me the house I want,—freehold, if you please! so that it can be Pen’s after me; my notion is to contract just what Sarianna and I require now, leaving it in the said Pen’s power to add and alter according to future advisability.”
Portions of other letters from Browning to Mrs. Bronson are as follows. The first refers to the little daughter of Princess Mélanie Metternich.
“First and worst of all, dear friend, how truly grieved I am to hear of the sad end of the poor little girl I remember so well. Do you remember how she, with her sister, walked before us on our way homeward from the Piazza on nearly our last evening? And how prettily she asked me at her own house to write in[Pg 249] her Birthday Book! All this sudden extinction of light in the gay Ca’ Bembo, where I saw the silks bespread before your knowledge and my ignorance!
“It is needless to say how much I pity the Princess, and her kindly husband, too, and I am sorry, very sorry, for you also, Dear Friend of mine, well knowing how you must have suffered in degree.”
Mrs. Bronson had a talent for the writing of drawing-room comedies, and to one of these the poet alludes:
“Dear Friend,—I kept your Comedietta by me a whole week that I might taste of it again and again; how clever it is, who can know better than I, who furnished the bare framework which your Virginia creeper has over-flourished so charmingly? It is all capitally done; quite as much elaborated as the little conception was worth; but its great value to me is the proof it really gives what really good work you might do on a larger scale....
“... I dined last evening at John Murray’s, in the room where used to meet Byron, Scott, Moore, all those famous men of old, whose portraits still adorn the walls. Murray told me he well remembered Byron and his ways; could still in fancy see him and Scott, and also hear them, as they stamped heavily (lame as both were) down the somewhat narrow stairs. Sociability may well come to the relief of people who cannot amuse themselves at home, for the weather, mild, and too mild, is gray, sunless and spiritless, altogether. To-day it rains, a rare occurrence....”
One of the very pleasant interludes in Mr. Browning’s life came about this time in the receipt of a letter from Professor Masson of the University of Edinburgh, inviting the poet to be his guest the week of the coming Tercentenary celebration of the University. It had been decided to confer on Mr. Browning an Honorary Degree, but by some misadventure the official letter announcing this had not reached him, and in reply to Professor Masson[Pg 250] he wrote that he had not received “the invitation to Edinburgh which occasions this particularly kind one,” which he thankfully acknowledged, “but I should find it difficult if not impossible to leave London in April,” he continues, “as my son will then be with me; but had I seen my way in so doing it would delight me, indeed, could I spend the days in question with you and Mrs. Masson.” He added that if ever he was privileged “to see the as famous as beautiful City again,” he should call on the Massons the first thing of all, and he desired thanks to Mrs. Masson “for associating her goodness with yours.”
Apparently another letter appears from Professor Masson, but still Browning does not receive the official invitation of the University. “Should it follow,” he writes, “I will acknowledge the distinction as gratefully as I have done already when it was conferred by Oxford and Cambridge.” The Massons also invited Mr. Browning to bring his son with him, and he responded:
“... So, my dear Professor Masson, I provisionally accept your hospitality with thankfulness, and that of Mrs. Masson. For my son, who is away, I can only say that he shall be informed of your goodness, and I fully believe will be delighted to avail himself of it.... As to the ‘vagueness or intelligibility’ of your note, I can assure you that one thing was intelligible enough,—that you wished to help me most kindly and pleasantly to witness an extremely interesting ceremony, and I have written to my son and his answer you shall hear as soon as possible.... By the way, ought I to attend in the Oxford D.C.L. gown,—at any preliminary entertainment, for instance.”
The next letter tells its own story.
19, Warwick Crescent, W.
March 25th, 1884.
My Dear Professor Masson,—Nothing can be kinder than all your proposed arrangements. My son arrived two days[Pg 251] ago, and, unfortunately, is obliged to return to Paris next week in order to finish work begun there—and he will be detained too long to allow of the visit which he would otherwise delight in paying you and for the invitation to which he desires me to offer you and Mrs. Masson his grateful acknowledgments, being well aware of what a privilege he is forced to deprive himself.... I shall bring the Oxford D.C.L. gown and provide myself with a Hood in Edinburgh.
So, with repeated thanks for all your goodness, and looking forward with much pleasure to the approaching festivities, and even more in the opportunity to converse, believe me, my dear Professor Masson,
Yours Very Sincerely,
Robert Browning.
Miss Rosaline Masson, the Professor’s daughter, has described how Browning sat before the fire the evening of his arrival, in an armchair, his hands resting on it, while he spoke with sympathetic pride of his son’s work, and told how the son, who had studied so much abroad, had once announced to Millais his intention of going to Egypt to paint, and that Millais had replied that he would not give up his months in the highlands of Scotland for any years in Egypt.
The Massons had as their guests for this great commemoration the Count and Countess Aurelio Saffi, the Count bringing with him his gorgeous Bologna gown, in which he had the resplendence of a figure in a stained glass window.
The week was a most enjoyable one to Mr. Browning. Receptions and dinners made up a round of festivity, and when he was asked by his hostess if he objected to all the adulation he received, he replied: “Object to it? No; I have waited forty years for it and now—I like it.”
After his return to London he sent to Mrs. Masson two manuscripts of Mrs. Browning’s, her translations of “Psyche and Pan” and of “Psyche Propitiating Ceres,”[Pg 252] and to Professor Masson a letter from Leigh Hunt to himself, which the Professor had wished to copy,—the original which he sent being written on sheets of different colors held together with colored embroidery.
Browning wrote to his host that he had read with delight his two lectures on Carlyle, and that “the goodness of that memorable week” was never long out of his mind.
The letters written to Mrs. Bronson offer almost a panoramic picture of his life over all these closing years. Alluding to a studio that he had taken for the temporary accommodation of his son’s pictures and busts, Mr. Browning resumes:
... Pen’s statues and busts are in bronze now, and his large “Idyl,” three landscapes, and whatsoever else, to arrive soon. Were you only here to see! Well, you can bear with the talking about them you shall undergo, for we two understand each other, don’t we? I know I am ever yours and your own Edith’s affectionately,
Robert Browning.
In the late summer Browning and his sister were the guests of Mrs. Bloomfield Moore, in her villa at St. Moritz, from which Mr. Browning thus writes to Mrs. Bronson:
Villa Berry, St. Moritz, Ober Engadine.
Sept. 6, ’84.
Yes, dearest friend, your pretty wreath came this morning, and opposite this table shall it hang till I leave the house, be it withered or no, and at present it is fresh. Now, thank you for what? For everything, your love, and thoughts, and regrets, too. Do not we, too, regret that Italy is closed to us; but the comfort out of the vexation is that you will, will you not, cross to London from Paris, and so we shall see you for all the multiplied hindrances. Now how do you suppose it is faring with us? We are alone. Our hostess was summoned to America last week, to her extreme regret, and after a hot business of tele[Pg 253]graphing and being telegraphed to, left last Wednesday. She had taken this comfortable villa till the middle of December, and would not hear of our quitting it, and, all things considered, we had little inclination to do so, for you were from home, and what would be the good of lingering out this month elsewhere, the air and influences happening to suit us extremely. So our plan is to stay out Sept. here, and be content with at most two months’ absence, instead of the four we utterly enjoyed last year. Mrs. Moore was altogether as kind and considerate as possible, and has made every possible provision for our comfort after her departure. We are quite alone. Friends are in the place, but we only get glimpses of them. The place is emptying fast, the pensions shut up, the walks on the mountain-side are wholly our own. Two days ago the snow fell thickly, and what a sight were the mountains next morning in a glowing sun! These changes I expect will diversify the whole month, and inside this warm, pleasant room Sarianna and I read, and don’t require “the devil to find some missing ill for idle hands to do.” You have much more to enjoy with all that good music thrown in, and I am glad for you. We get books and papers enough, and I am correcting proofs of the poem I was too negligent about in London. Many distractions stood in the way of that. After all, we have attained the main object of our journey, the complete re-establishment of Sarianna’s health, who walks twice a day, just as of old. I am cheered, too, by letters from Robert, the last of which comes just now.
He was anxious that his statue of “Dryope” should be seen at the Brussels exhibition, a triennial one, and important from the concurrence of the best foreign artists; but the “Grosvenor,” where it was shown, did not close till the first week in August, while the Brussels Gallery was closed to (entrance of) works on the 25th of July. Robert sent his photographs with a petition for a “delai,” only exceptionally granted; the committee conceded it unanimously, and have given it a place where it stands by itself, and is capitally seen. He went to see it, and so did the King and Queen, to whom he would have been presented, had he not been in morning dress. (The father of Robert to the mother of Edith.) You know very well how [Pg 254]interested and delighted I shall be to read your German translations if you send them; do!
Again, from this invigorating mountain village Browning writes to his Venetian friend and hostess in Casa Alvisi:
Villa Berry, St. Moritz, Engadine, S.
Sept. 23, ’84.
For first thing, dearest friend, I am glad to know that my letter with the poems reached you before your departure. I had some fear that you might miss it. It is like your goodness to care so much about what amounts to so little. I did what I could to be of use by amending; I could have done more to the purpose if the poems were original; but I know your translations were faithful, as they should be. When you write out of your own dear head let me see, and try hard to improve it, never so little. I well remember the whole book of verses you let me read at Venice; I could not well have helped you there. And now for a sorrow after the gladness; we do not pass through Paris this time, but take the direct and more convenient route by Amiens and Calais. Last year we wanted, or needed, to see Pen, who was at his Paris studio; but now he is still in Dinard. I do not know when he means to leave; if he finds you at Paris it will be a delight for him to see you....
Well, yes, the king’s behavior has been admirable; what a chance the poor Pope has thrown away in not preceding him! If the “Prisoner of the Vatican” had quietly walked out of his confinement, with a Cross before him, and an attendant on each side, and passed on to Naples and the hospitals “braving all danger in imitation of his Master,” I verily believe there might have happened a revolution. Such events from much less causes being frequent enough. Where is the “wisdom of the serpent”?
Dearest friend, my sister writes, all love to Edith, all love to you, from your ever affectionate
Robert Browning.
On their return to London the letters to Mrs. Bronson again resume the story of this interesting life:
[Pg 255]“... I have got rid of my last proof-sheets, and all of a sudden it occurs to me to ask—now that alteration is impossible, I suppose—whether I have offended in just dating the last poem from the place where I wrote it—the Giustiniani? The first poem was dated at the inn, and the last seemed to belong to the beloved place where it was penned, as I wanted to remember, or be remembered, rather. Have I done wrong? (I hear at this moment my sister actually singing in the next room,—so completely is she re-established in health.) By letters we find that the admirable weather at St. Moritz was continued up to the end of the last week; here the weather is fine, and finer than usual, but the sparkle is off the wine, the wonderful freshness of St. Moritz does not incline one to dance rather than walk.
“I am in absolute peace and quietude, and so thoroughly prepared to enjoy your coming,—if that may be....”
The next letter speaks of American friends:
19, Warwick Crescent, W.
Oct. 14, ’84.
Dearest Friend,—I waited a little before replying to your letter, wanting to be sure when I could say that Pen would be in Paris; he proposed to go there yesterday, and you will certainly have a visit from him as soon as he can manage to do what I know he desires very much.
Here are your verses which I try to be as severe about as possible, with no success, at all, worth speaking of! You will take my corrections (infinitesimal, this time) for what they are worth, and continue to send me what you write, will you not?
I was surprised two days ago by a note from Mr. Lowell, inviting me and my sister to meet the Storys at dinner to-morrow, they being his guests during a short stay in London; and yesterday afternoon they called on my sister, both the Storys and Mr. Lowell; the former are flourishing, and go in a few days to Rome. Where they have passed the summer, we were not told. Last evening at a dinner given by Sidney Colvin, I met Mr. James, who showed great interest in hearing how you were, and how much nearer you were likely to be. On the other hand,[Pg 256] there will be a sad visitor to Venice presently, Professor Huxley, in a deplorable state of health, from over-work. I hate to speak of what is only too present with me,—your own health,—I trust you have got rid of that cough, (all dreadful things go with a cough in my memory.)...
... My book, which you kindly inquire about, is out of my hands and in print, but the publishing, the when and how, concerns the publisher. I do not expect to see the completed thing for another month.
Yes, I felt so lovingly to the Giustinian-Reconnati that I could not bear cutting the link allowed by the Place and Date that were appended to the Ms., and you permit, so all is well, if you remember me as ever affectionately yours,
Robert Browning.
Under date of October 23, 1884, Browning says in one letter:
“I saw Huxley’s brother-in-law, Sir Robert Collier, last evening, at Dr. Granville’s, and inquired about the stay in Venice. It will be a very short one as he has to return almost immediately for the marriage of his daughter Rachel; I can hardly think he will re-return, the ceremony at an end, yet he may; and in that case he shall be informed of your goodness to himward, in apostolically appropriate language. He is a thoroughly admirable person in all but his inconsiderateness in this waste of a precious life. I duly told the Storys how much you wanted to see them, and they probably have seen you by this time. Mrs. Story meant to rest at Paris, and forego the Amiens route. She has been unwell, but I thought her appearance very satisfactory. I dined with them last week at Mr. Lowell’s, and called there on Sunday. I met Henry James the other day, and surprised as well as inspirited him by the news that you were so near, and, as I believed, so soon to be nearer. Now write to me, tell me all you are about to do; how is dear Edith?...
O, no, Pen is none of mine to outward view, but wholly his mother’s—in some respects, at least. At the same age there was small difference between Pen’s face and that of the brother she lost,—to judge by a drawing I possess....”
[Pg 257]To the Marchesa Peruzzi di’ Medici who sent to him a translation she had made of the “Ricordo Autobiografici” of Giovanni Duprè, Browning thus writes:[16]
“It is not so very ‘little’ an affair, and in the fear that when my sister has finished it, I may have to begin my own reading, and end it so late as to lead you to suppose that either book or letter has gone wrong, on this account I write at once to thank you most heartily. My sister says the Autobiography is fascinating; I can well believe it, for I never knew such a work to be without interest, and this of Duprè must abound in precisely the matters that interest me most.... When I have thoroughly gone through the book I will write you again, if you permit me, as I know your old memories will be indulgent in the case. We may be in Italy this autumn, and if you are within reach you will be certain to see the old friend who always rejoices when he hears of your well-being, and trusts it may continue.... Pen is very well; at Dinard just now, painting landscape in the open air. I have told him already of the book which he will take delight in reading. I am occupied this very day in sending his statue of ‘Dryope’ to Brussels, where the Exhibition will give it a chance of being judged by better knowledge than is found here.”
The following letter indicates, in Browning’s own charming way, the warm attachment that both he and his sister had for Mrs. Bronson:
19, Warwick Crescent, W.
Feb. 15, ’85.
Dearest Mrs. Bronson,—This dull morning grew to near blackness itself, when, at breakfast, my sister said once again, “No news of her from Venice,”—and I once again calculated and found by this time it was a month and a full half since we heard from you. Why should this be? If I had simply and rationally written a line, instead of thinking a thought, I should have known, as your dear goodness will let me know, as soon as you receive this, how you are, how Edith is, now that the winter[Pg 258] is over and gone with the incentives to that cough which was still vexatious when we had your last letter.
Do not let us mind high-days and holidays: be sure of this, that every day will be truly festal that brings us a word from you, for other clouds than the material ones make us melancholy just now; and how this turbid element about us contrasts with the golden hours near the beloved friends,—perhaps more vivid,—certainly more realized as valuable, than ever! I do not mean to write much because what I want to impress on your generosity is that just a half sheet, with mere intelligence about you, will be a true comfort and sustainment to me and to my sister,—the barest account of yourself, and what we appreciate with you; and, for our part, you shall hear, at least, that we are well, or ailing, stationary, or about to move.
In the early spring Browning again writes to Mrs. Bronson:
19, Warwick Crescent, W.
April 8, ’85.
Dearest Friend,—This is not a letter, for I have this minute returned from a funeral, in pitiful weather, and am unable either in body or soul to write one, much as I hope to do, with something of my warm self in it. But I find Burne Jones’s pretty and touching letter, and want this leaf to serve as an envelope to what may please you, who deserve so thoroughly that it should. I will write in a day or two. I heard from Pen this morning, who is at Dinard, being too ill to remain in Paris, but finds himself already better. He told me and re-told me how good you had been to him. How I trust all is going well with you,—certainly you need no assurance of,—enough that I love you with all my heart. Bless you and your Edith. It is an Edith,—Proctor’s (Barry Cornwall’s) daughter, whom I have been following to her grave. Some fifty years ago her father said to me while caressing her, “Ah, Browning, this is the Poetry.” “I know it.” “No, you know nothing about it.” Well, if I was ignorant then, I am instructed now. So, dear Two Poems, long may I have you to read and to enjoy!
Yours affectionately Ever,
Robert Browning.
[Pg 259]In the following autumn Mr. Barrett Browning, who had not seen Venice since his infancy, joined his father, and was “simply infatuated” with the dream city. It was for his sake that Browning had wished to purchase the Manzoni Palace, “to secure for him a perfect domicile, every facility for his painting and sculpture.”
The autumn of 1886 brought to Browning a great sadness in the death of Milsand, and Miss Browning being out of health, and unequal to a continental journey, they both passed a part of the autumn at Llangollen, where Sir Theodore and Lady Martin (Helen Faucit) were their near neighbors, with whom they had tea every Sunday, and renewed one of the most delightful friendships.
On the publication of Dr. Corson’s “Introduction to the Poetry of Browning,” he sent a copy to the poet who thus replied:
19. Warwick Crescent.
W.
Dec. 28. ’86.
My dear Dr Corson,
I waited some days after the arrival of your Book and Letter thinking I might be able to say more of my sense of your goodness: but I can do no more now than a week ago. You “hope I shall not find too much to disapprove of”: what I ought to protest against, is “a load to sink a navy—too much honor”: how can I put aside your generosity, as if cold justice—however befitting myself,—would be in better agreement with your nature? Let it remain as an assurance to younger poets that, after fifty years’ work unattended by any conspicuous recognition, an over-payment may be made, if there be such another munificent appreciator as I have been privileged to find—in which case let them, even if more deserving, be equally grateful.
I have not observed anything in need of correction in the notes. The “little tablet” was a famous “Last Supper,” mentioned by Varwn, (page. 232) and gone astray long ago from the Church of S. Spirito: it turned up, according to report, in[Pg 260] some obscure corner, while I was in Florence, and was at once acquired by a stranger. I saw it,—genuine or no, a work of great beauty. (Page 156.) A “canon,” in music, is a piece wherein the subject is repeated—in various keys—and being strictly obeyed in the repetition, becomes the “Canon”—the imperative law—to what follows. Fifty of such parts would be indeed a notable peal: to manage three is enough of an achievement for a good musician.
And now,—here is Christmas: all my best wishes go to you and Mrs. Corson—those of my sister also. She was indeed suffering from grave indisposition in the summer, but is happily recovered. I could not venture, under the circumstances, to expose her convalescence to the accidents of foreign travel—hence our contenting ourselves with Wales rather than Italy. Shall you be again induced to visit us? Present or absent, you will remember me always, I trust, as
Yours most affectionately
Robert Browning.
The year of 1887 was an eventful one in that the “Parleyings” were published in the early spring; that Browning removed from Warwick Crescent to 29 DeVere Gardens; and that the marriage of his son to Miss Coddington of New York was celebrated on October 4 of that year, an event that gave the poet added happiness. To a stranger who had asked permission to call upon him Browning wrote about this time:
“... My son returns the day after to-morrow with his wife, from their honeymoon at Venice, to stay with me till to-morrow week only, when they leave for Liverpool and America—there to pass the winter. During their short stay, I am bound to consult their convenience, and they will be engaged in visiting, or being visited by friends, so as to preclude me from any chance of an hour at my own disposal. If you please—or, rather, if circumstances permit you to give me the pleasure of seeing you at twelve on Saturday morning, the first day when I shall be at liberty, I shall be happy to receive you.”




[Pg 261]The stranger did so arrange that his visit should extend itself over the magic date of “November 5th,” and on that day he stood at the portal to DeVere Gardens house.
“I was taken up to the poet’s study,” he writes. “There had been that day a memorial meeting for Matthew Arnold, to which Browning had been, and he spoke with reminiscent sadness of Arnold’s life.
“‘I have been thinking all the way home of his hardships,’ said Mr. Browning. ‘He once told me, when I asked why he had not recently written any poetry, that he could not afford to, but that when he had saved enough, he intended to give up all other work, and devote himself to poetry. I wonder if he has turned to it now?’ Browning added musingly.”
One interesting incident related by this caller is that, having just been reading and being greatly impressed by Mr. Nettleship’s analysis and interpretation of “Childe Roland,” he asked the author if he accepted it. “Oh, no,” replied Mr. Browning; “not at all. Understand, I don’t repudiate it, either; I only mean that I was conscious of no allegorical intention in writing it. ’Twas like this; one year in Florence I had been rather lazy; I resolved that I would write something every day. Well, the first day I wrote about some roses, suggested by a magnificent basket that some one had sent my wife. The next day ‘Childe Roland’ came upon me as a kind of dream. I had to write it, then and there, and I finished it the same day, I believe. But it was simply that I had to do it. I did not know then what I meant beyond that, and I’m sure I don’t know now. But I am very fond of it.”
This interesting confession emboldened the visitor to ask if the poet considered ‘James Lee’s wife’ quite guiltless in her husband’s estrangement. “Well, I’m not sure,” replied Mr. Browning; “I was always very fond of her, but I fancy she had not much tact, and did not quite know how to treat her husband. I think she worried him a little.[Pg 262] But if you want to know any more,” he continued, with a twinkle in his eye, “you had better ask the Browning Society,—you have heard of it, perhaps?”
When Robert Barrett Browning purchased the Palazzo Rezzonico, the acquirement was a delight to his father, not unmixed with a trace of consternation, for it is one of the grandest and most imposing palaces in Italy. Up to 1758 it was occupied by Cardinal Rezzonico himself, when, at that date, he became Pope under the title of Clement XIII. This palace, built in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, commands an unparalleled situation on the Grand Canal, and the majestic structure of white marble, with its rich carvings, the baroque ornaments of its key-stones, its classic cornices and tripartite loggias, its columns and grand architectural lines, is remarked, even in Venice, the city of palaces, for its sumptuous magnificence. As Mr. Browning had before remarked to Mrs. Bronson, “Pen” was infatuated with Venice. It is equally true that much of the infatuation of the ethereal city for subsequent visitors was due in no small measure to the beautiful and reverent manner in which Robert Barrett Browning made this palace a very Valhalla of the wedded poets, Robert and Elizabeth Barrett Browning. Here the son gathered every exquisite treasure associated with his mother, and when, three years later, his father breathed his last within this noble palace, the younger Browning added to the associations of his mother those, also, of his father’s books, art, and intimate possessions. With his characteristic courtesy and generous consideration Mr. Barrett Browning permitted visitors, for many years, through his entire ownership of the palace, to visit and enjoy the significant collections, treasures which his taste and his love had there gathered.

Portrait of Robert Barrett Browning
(“Penini”), as a Child.
Painted at Siena, by Hamilton Wild, 1859.
On the façade of the palace two stately entrances open upon the broad flight of marble steps that lead down [Pg 263]to the water, and on the architraves are carved river-gods. In the spacious court was placed his own statue of “Dryope.” Ascending one marble flight of the grand escalier, one entered a lofty apartment whose noble proportions and richness of effect were most impressive. The floor, of red marble, in its rich, Byzantine hue, harmonized with a richly painted ceiling, which was one celebrated in Venetian art. From this vast salon opened, through richly carved doors, a series of rooms, each made vital with the portraits, sketches, busts, and other memorials of the poets. There were Story’s busts of Browning and of his wife; there was Robert Barrett Browning’s bust of his father,—one of the most remarkable among portrait busts in contemporary art; the portraits of Robert and Elizabeth Browning painted by Gordigiani of Rome, about 1855; a lovely pastel of Mrs. Browning when she was a child, representing her as standing in a garden, holding up her apron filled with flowers; there was her little writing-desk, and other intimate personal mementoes about. The immense array of presentation copies from other authors to the poets made an interesting library of themselves, as did the various translations of their own poems into many languages. There was a portrait of Browning painted when a young man, with a troubadour cloak falling over his shoulders; and a most interesting portrait of Milsand, painted by Barrett Browning, as a gift to his father.
There was also a picture of himself as a lad, the “Penini” of Siena days, mounted on his pony, and painted by Hamilton Wild (a Boston artist), in that most picturesque of hill-towns, during one of those summers that the Brownings and the Storys had passed in the haunts of Santa Caterina.
By Mrs. Browning’s little writing tablet was placed the last manuscript she had ever written; and on a table lay a[Pg 264] German translation of “Aurora Leigh,” with an inscription of presentation to Browning.
From one of these salons, looking out on the Grand Canal, is an alcove, formerly used as the private chapel of the Rezzonico. It was all white and gold, with a Venetian window draped in the palest green plush, while on either side were placed tall vases encrusted with green. In this alcove Mr. Barrett Browning had caused to be inscribed, in golden letters, surrounded with traceries and arabesques in gold, a copy of the inscription that was composed by the poet, Tommaseo, and placed by the city of Florence on the wall of Casa Guidi, near the grand portal:
qui scrisse e mori
ELISABETTA BARRETT BROWNING
che in cuore di donna conciliava
scienza di dotto e spirito di poeta
e fece del suo verso aureo anello
fra italia e inghilterra
pone questo memoria
firenze grata
1861.
On the first floor was the room in which the poet wrote when the guest of his son in the palace; a sala empaneled with the most exquisite decorated alabaster, panels of which also formed the doors, and opening from this was his sleeping-room, also beautifully decorated.
In one splendid sala, with rich mural decorations, and floor of black Italian marble, were many choice works of art, rare souvenirs, pictures of special claim to interest, wonderful tapestries, and almost, indeed, an embarras de richesse of beauty.
In 1906 Robert Barrett Browning sold the Rezzonico; and now, beside his casa and studios in Asolo, he has one of the old Medici villas, near Florence,—“La Torre[Pg 265] all’ Antella,” with a lofty tower, from which the view is one of the most commanding and fascinating in all Tuscany. The panorama includes all Florence, with her domes and campanile and towers; and the Fiesolean hills, with the old town picturesquely revealed among the trees and against the background of sky, and with numerous other villages and hamlets, and a mountain panorama of changing color always before the eye. Mr. Browning is one of the choicest of spirits, with all that culture and beauty of spiritual life that characterized his parents. He is a great linguist, and is one of the most interesting of men. No one knew his father, in that wonderful inner way, as did his son. He was twelve years old at the time of his mother’s death, and from that period he was the almost constant companion of his father, until Browning’s death, twenty-eight years later. Robert Barrett Browning has also purchased the massive Casa Guidi, thus fitly becoming the owner of the palace in which he was born, and that is forever enshrined in literary history and poetic romance. It is, also, one of those poetic sequences of life, that Casa Guidi and Palazzo Peruzzi, near each other, in the Via Maggiore in Florence, are respectively owned by Mr. Browning and the Marchesa Peruzzi di’ Medici, under which stately title Mr. Story’s daughter Edith, the childhood friend and companion of “Penini,” is now known.
After the return to London of Browning and his sister Sarianna, from St. Moritz, his constant letters to Mrs. Bronson again take up the story of a poet’s days.
In the early winter he thus writes to his cherished friend—the date being December 4, 1887:
“Now let us shut the gondola glasses (I forget the technical word) and Talk, dear Friend! Here are your dear labors of love,—the letters and enclosures, and here is my first day of leisure this long fortnight, for, would you believe it? I have been silly enough to sit every morning for three hours to one painter,[Pg 266] who took an additional two hours yesterday, in order to get done; before which exercise of patience I had to sit to another gentleman, who will summon me again in due time,—all this since my return from Venice and the youthful five! However, when, two days ago, there was yet another application to sit, the bear within the ‘lion’ came out, and I declined, as little gruffly as I was able. And so the end is I can talk and enjoy myself—even at a distance—with a friend as suddenly dear as all hands from the clouds must needs be. I will not try and thank you for what you know I so gratefully have accepted,—and shall keep forever, I trust.
“Well, here is the Duke’s letter; he is a man of few words, and less protestation; but feels, as he should, your kindness, and will gladly acknowledge it, should you come to England, and it seems that you may. But what will Venice be without you next year, if we return there as we hope to do?
“... Mrs. Bloomfield Moore passed through London some three weeks ago, and at once wrote to me about what pictures of Robert’s might be visible? She at once bought the huge ‘Delivery to the Secular Arm,’ for the Philadelphia Academy of Fine Arts, and the ‘Dinard Market Woman’ for herself, and this so spontaneously, and I did hear in a day or two that she was convinced I had not asked half enough for the pictures! She had inquired at the Gallery where the larger one was exhibited, and they estimated its value at so much. I told her their estimate was not mine, and that Robert was thoroughly remunerated—to say nothing of what he would think of all this graciousness; and since her departure I have had an extremely gratifying letter full of satisfaction at her purchases,...”
On the death of Lord Houghton, Mr. Browning had been prevailed upon to accept the office of Foreign Correspondent to the Royal Academy; he was much beloved by the Academicians, many of whom were among his familiar friends, and that his son was an artist endeared to him all art.
To Mrs. Bronson Browning once remarked: “Do you know, dear friend, if the thing were possible, I would [Pg 267]renounce all personal ambition and would destroy every line I ever wrote, if by so doing I could see fame and honors heaped on my Robert’s head.” Mrs. Bronson’s comment on this was that in his son he saw the image of his wife, whom he adored,—“literally adored,” she added.
At the Academy banquets Browning was always an honored guest, and his nomination by the President to the post of Foreign Correspondent was promptly ratified by the Council.
On the removal to DeVere Gardens, Mr. Browning took great pleasure in the arrangement of his home. His father’s library of six thousand books was now unpacked, and, for the first time, he had space for them; many of the beautiful old carvings, chests, cabinets, bookcases, that he had brought from Florence, could in the new home be placed to advantage. The visitor, to-day, to Mr. Barrett Browning’s Florentine villa will see many of these rich and elaborate furnishings, and the younger Browning will point out an immense sofa (that resembles a catafalque), with amused recollection of having once seen his father and Ruskin sitting side by side on it, “their feet dangling.” From Venice the poet had brought home, first and last, many curious and beautiful things,—a silver lamp, old sconces from churches, and many things of which he speaks in his letters to Mrs. Bronson.
The initial poem in “Asolando,” entitled “Rosny,” was written at the opening of the year 1888, and it was soon followed by “Beatrice Signorini” and “Flute-Music.” In February he writes to George Murray Smith, his publisher, of his impulse to revise “Pauline,” which had lain untouched for fifty years,—an impulse to “correct the most obvious faults ... letting the thoughts, such as they are, remain exactly as at first.” It seems that the portrait, too, that is to accompany the volume does not quite please him, and he suggests slight changes. “Were Pen here,” he says, “he could manage it all in a moment.”
[Pg 268]This confidence was not undeserved. Richly gifted in many directions, a true child of the gods, Robert Barrett Browning has an almost marvelous gift in portraiture. He seems to be the diviner, the seer, as well as the artist, when transferring to canvas a face that interests him. The portrait of Milsand, to which allusion has before been made, and that of his father, painted in his Oxford robes, with “the old yellow book in his hand,” which is in Balliol, are signal illustrations of his power in portraying almost the very mental processes of thought and feeling and kindling imagination,—all that goes to make up the creative life of art.
He is fairly a connoisseur in literature, as well as in his own specialties of painting and sculpture; and the poetry of the elder Browning has no more critically appreciative reader than his son. Some volume of his father’s is always at hand in his traveling; and he, like all Browning-lovers, can never open any volume of Robert Browning’s without finding revealed to him new vistas of thought, renewed aspiration and resolve for all noble living, and infinite suggestiveness of spiritual achievement.
| “On the earth the broken arcs; in the heaven, a perfect round.” “O thou soul of my soul! I shall clasp thee again, And with God be the rest!” |
“Asolando”—Last Days in DeVere Gardens—Letters of Browning and Tennyson—Venetian Lingerings and Friends—Mrs. Bronson’s Choice Circle—Browning’s Letters to Mrs. Bronson—Asolo—“In Ruby, Emerald, Chrysopras”—Last Meeting of Browning and Story—In Palazzo Rezzonico—Last Meeting with Dr. Corson—Honored by Westminster Abbey—a Cross of Violets—Choral Music to Mrs. Browning’s Poem, “The Sleep”—“And With God be the Rest.”
In the winter of 1887-1888 Mr. Browning wrote “Rosny,” which follows the “Prologue” in “Asolando,” and soon after the “Beatrice Signorini” and “Flute Music.” He also completely revised his poems for the new edition which his publishers were issuing in monthly volumes, the works completed in July. “Parleyings,” which had appeared in 1887, had, gloriously or perilously as may be, apparently taken all the provinces of learning, if not all the kingdoms of earth, for its own; for its themes ranged over Philosophy, Politics, Love, and Art, as well as Alchemy, and one knows not what; but its power and vigor reveal that there had been no fading of the divine fire. The poet made a few minor changes in “The Inn Album,” but with that exception he agreed with his friend and publisher, that no further alterations of any importance[Pg 270] were required. Mr. Browning’s relations with his publishers were always harmonious and mutually gratifying. Such a relation is, to any author, certainly not the least among the factors of his happiness or of his power of work, and to Browning, George Murray Smith was his highly prized friend and counselor, as well as publisher, whose generous courtesies and admirable judgment had more than once even served him in ways quite outside those of literature.
In the late summer of 1888 Browning and his sister fared forth for Primiero, to join the Barrett Brownings, with whom the poet concurred in regarding this little hill-town as one of the most beautiful of places, his favorite Asolo always excepted. “Primiero is far more beautiful than Gressoney, far more than Saint-Pierre de Chartreuse,” he wrote to a friend: “with the magnificence of the mountains that, morning and evening, are literally transmuted to gold.” In letters or conversation, as well as in his verse, Browning’s love of color was always in evidence. “He dazzles us with scarlet, and crimson, and rubies, and the poppy’s ‘red effrontery,’” said an English critic; “with topaz, amethyst, and the glory of gold, and makes the sonnet ache with the luster of blue.” When, in the haunting imagery of memory pictures, after leaving Florence, he reverted to the gardens of Isa Blagden, on Bellosguardo, the vision before him was of “the herbs in red flower, and the butterflies on the wall under the olive trees.” For Browning was the poet of every thrill and intensity of life—the poet and prophet of the dawn, not of the dark; the herald who announced the force of the positive truth and ultimate greatness; never the interpreter of the mere negations of life. The splendor of color particularly appealed to him, thrilling every nerve; and when driving with Mrs. Bronson in Asolo he would beg that the coachman would hasten, if there were fear of missing the sunset pageant from the loggia of “La Mura.” [Pg 271]In “Pippa Passes,” how he painted the splendor of sunrise pouring into her chamber, and in numberless other of his poems is this fascination of color for him revealed.
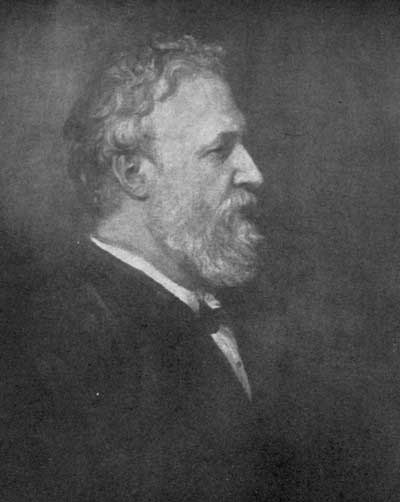

Portrait of Robert Browning in 1865.
Painted by George Frederick Watts, R.A.
In the possession of the National Portrait Gallery, London.
Under the date of August, 1888, the poet writes to Mrs. Bronson:
Dearest,—We have at last, only yesterday, fully determined on joining the couple at Primiero, and, when the heats abate, going on to Venice for a short stay. May the stay be with you as heretofore? I don’t feel as if I could go elsewhere, or do otherwise, although in case of any arrangements having been made that stand in the way, there is the obvious Hôtel Suisse. I suppose at need there could be found a messenger to poor Guiseppina, whose misfortunes I commiserate. You know exactly how much and how little we want. But if I am to get any good out of my visit I must lead the quietest of lives....
We propose setting out next Monday, the 13th,—Basle, Milan, Padua, Treviso, Primiero, by the week’s end.
I have been nearly eleven weeks in town, with an exceptional four days’ visit to Oxford; and hard social work all the time, indeed, up to the latest, when, three weeks ago, I found it impossible to keep going. Don’t think that the kindness which sometimes oppresses me while in town, forgets me afterward; I have pouring invitations to the most attractive places in England, Ireland, Scotland,—but “c’est admirable, mais ce n’est pas la paix.” May I count on the “paix” where I so much enjoyed it? I hear with delight that Edith will be with you again,—that completes the otherwise incompleteness. Yes, the Rezzonico is what you Americans call a “big thing.”... But the interest I take in its acquisition is different altogether from what accompanied the earlier attempt. At most, I look on approvingly, as by all accounts I am warranted in doing, but there an end....
... So, dearest friend, “a rivederci!” Give my love to Edith and tell her I hope in her keeping her kindness for me, spite of the claims on it of all the others. And my sister, not one word of her? Somehow you must know her more thoroughly than poor, battered me, tugged at and torn to pieces, metaphorically,[Pg 272] by so many sympathizers, real or pretended. She wants change, probably more than I do. And, but for her, I believe I should continue here, with the gardens for my place of healing. How she will enjoy the sight of you, if it may be! Tell me what is to be hoped, or feared, or despaired of, at Pen’s address, whatever it may be. And remember me as ever most affectionately yours,
Robert Browning.
The succeeding letter, written from Albergo Gille, Primiero, tells the story of a rather trying journey, what with the heat and his indisposition, but on finding himself bestowed at Primiero he is “absolutely well again,” and anticipating his Venice: “what a Venice it would be,” he says, “if I went elsewhere than to the beloved friend who calls me so kindly!” And he adds:
“My stay will be short, but sweet in every sense of the word if I find her in good health, and in all other respects just as I left her; ‘no change’ meaning what it does to me who remember her goodness so well. It will be delightful to meet Edith again, if only it may be that she arrives while we are yet with you, even before, perhaps.
“Can I tell you anything about my journey except that it was so agreeable an one? On the first evening as I stepped outside our carriage for a moment, I caught sight of a well-known face. ‘Dr. Butler, surely.’ You have heard of his marriage the other day to a learnedest of young ladies, who beat all the men last year at Greek. He insisted on introducing me to her; I had seen her once before without undergoing that formality and willingly I shook hands with a sprightly young person ... pretty, and grand-daughterly, she is, however, only twenty-six years his junior. Then, this happened; the little train from Montebelluna to Feltre was crowded—we could find no room except in a smoking carriage—wherein I observed a good-natured, elderly gentleman, an Italian, I took for granted. Presently he said, ‘Can I offer you an English paper?’ ‘What, are you English?’ ‘Oh, yes, and I know you,—who are going[Pg 273] to see your son at Primiero.’ ‘Why, who can you be?’ ‘One who has seen you often.’ ‘Not surely, Mr. Malcolm?’ ‘Well, nobody else.’ So ensued an affectionate greeting, he having been the guardian angel of Pen in all his chafferings about the purchase of the palazzo. He gave me abundance of information, and satisfied me on many points. I had been anxious to write and thank him as he deserved, but this provided an earlier and more graceful way, for a beginning at least.
“Pen is at work on a pretty picture, a peasant girl whom he picked up in the neighborhood, and his literal treatment stands him in good stead; he is reproducing her cleverly, at any rate, he takes pains enough.”
Towards the end of September they joined in Venice the “beloved friend,” whose genius for friendship only made each sojourn with her more beautiful than the preceding, if that which was perfect could receive an added degree. “It was curious to see,” wrote Mrs. Bronson, “how on each of his arrivals in Venice he took up his life precisely as he had left it.” Browning and his sister frequently went on Sundays to the Waldensian chapel, where in this autumn there was a preacher of great eloquence. Every morning, after their early coffee, the poet was off for a brisk walk, and after returning he busied himself with his letters and newspapers, his mail always containing more or less letters from strangers and admirers, some of whom solicited autographs, which, so far as possible, he always granted. Mrs. Bronson has somewhere noted that when asked, viva voce, for an autograph, he would look puzzled, and say “I don’t like to always write the same verse, but I can only remember one,” and he would then proceed to copy “All that I know of a certain star,” which, however it “dartles red and blue,” he knew nothing of save that it had “opened its soul” to him. Arthur Rogers, delivering the Bohlen lectures for 1909, compared Browning with Isaiah, in his lecture on “Poetry and Prophecy,”[Pg 274] and he instanced this “star” which “opened its soul” to the poet, as attesting that Browning, like Isaiah, could do no more than search depths of life.
The Palazzo Giustiniani-Recanti was a fitting haunt for a poet. Casa Alvisi, adjoining, in which Mrs. Bronson lived, looked out, as has been noted, on Santa Maria della Salute, which was on the opposite side of the Grand Canal; but the Giustiniani palace, dating to the fifteenth century, had its outlook through Gothic windows to the south, on a court and garden of romantic loveliness. The perfect tact of their hostess left the poet and his sister entirely free to come and go as they pleased, and at midday they took their déjeuner together, ordering by preference Italian dishes, as rissotto, macaroni, and fruits, especially figs and grapes. They enjoyed these tête-à-tête repasts, talking and laughing all the while, and then, about three every afternoon they joined Mrs. Bronson and her daughter for the gondola trip. The hostess records that the poet’s invariable response to the question as to where they should go would be: “Anywhere, all is beautiful, only let it be toward the Lido.” While both the poet and his sister were scrupulously prompt in returning all calls of ceremony, they were glad to evade formal visits so far as possible; and the absolute freedom with which their hostess surrounded them was grateful beyond words. “The thought deeply impressed me,” said Mrs. Bronson, “that one who had lifted so many souls above the mere necessity for living in a troublesome world deserved from those permitted to approach him their best efforts to brighten his personal life.... The little studies for his comfort, the small cares entailed upon me during the too brief days and weeks when his precious life was partly entrusted to my care, might seem to count for little in an existence far removed from that of an ordinary man; yet, as a fact, he was glad and grateful for the smallest attention. He [Pg 275]was appreciative of all things. He never regarded gratitude as a burden, as less generous minds are apt to do,” continued Mrs. Bronson.

Mrs. Arthur Bronson
From a painting by Ellen Montalba, in Asolo
In the possession of Edittá, Contessa Rucellai (née Bronson),
Palazzo Rucellai, Florence.
One of his greatest enjoyments in Venice was to wander with Edith Bronson through the Venetian calli. “Edith is the best cicerone in the world,” he would remark; “she knows everything and teaches me all she knows. There never was such a guide.” The young girl indeed knew her Venice as a devotee knows his illuminated missal, and her lovely vivacity and sweetness must have invested her presence with the same charm that is felt to-day in the Contessa Rucellai, in her Florentine palace, for Miss Bronson, it may be said en passant, became the wife of one of the most eminent Italian nobles, the Rucellai holding peculiar claim to distinction even among the princely houses of Florence.
From these gondola excursions they always returned about five, and sometimes the poet would join the group around Mrs. Bronson’s tea-table, conversing with equal facility in French, German, or Italian, and to their delight would say, “Edith, dear, you may give me a cup of tea.” But as a rule he considered this beverage as too unhygienic at that hour, and whenever with an “Excuse me, please,” he sought his own apartments, he was never questioned for his reasons. “It was enough that he wished it,” said his hostess. He and Miss Browning always appeared promptly for dinner, which was at half-past seven in Casa Alvisi. The poet was scrupulous about his evening dress; and Miss Browning, Mrs. Bronson relates, was habitually clad “in rich gowns of a somber tint, with quaint, antique jewels, and each day with a different French cap of daintiest make.”
The evenings seem to have been idyllic. Browning would often read aloud, and he loved to improvise on an old spinnet standing in a dim recess in one of the salons. The great Venetian families were usually in villeggiatura at the time[Pg 276] when Browning was in Venice, so that he met comparatively few of them; it was this freedom from social obligations that contributed so much to the restful character of his sojourns, and enabled him to give himself up to that ineffable enchantment of Venice. He made a few friends, however, among Mrs. Bronson’s brilliant circle, and one of the notable figures among these was the old Russian noble and diplomat, Prince Gagarin, who, born in Rome, had been educated in his own country, and had represented Russia at the courts of Athens, Constantinople, and Turin. Mrs. Bronson has told the story of one evening when the poet and the old diplomat indulged in a mutual tournament of music; “first one would sing, and then the other,” Browning recalling folk-songs of Russia which he had caught up in his visit to that country fifty years before.
Another of Mrs. Bronson’s inner circle, which included the Principessa Montenegro, the mother of Queen Elena, and other notable figures, was the Contessa Marcello, whom both the poet and his sister greatly liked; and one radiant day they all accepted an invitation to visit the Contessa at her villa at Mogliano, a short railway trip from Venice. The poet seemed to much enjoy the brief journey, and at the station was the Contessa with her landau, in which Mrs. Bronson, the poet, and his sister were seated, while Miss Bronson rode one of the ponies on which some of the young people had come down to greet the guests. After luncheon the Contessa, with her young daughter, the Contessina, led their guests out in the grounds to a pergola where coffee was served, and which commanded a vista of a magnificent avenue of copper beeches, whose great branches met and interlaced overhead. The Contessa was the favorite lady of honor at the court of Queen Margherita, and she interested Mr. Browning very much by speaking of her beloved royal mistress, and showing him some of the handwriting of the Queen, which he thought characteristically[Pg 277] graceful and forcible. The Contessina and Miss Bronson, with others of the younger people, seated themselves in rustic chairs to listen to every word from the poet; and a Venetian sculptor, who was there, concealed himself in the shrubbery and made a sketch of Browning. The Contessina, who, like all the young Italian girls of high breeding and culture, kept an album of foreign poetry, brought hers, and pleadingly asked Mr. Browning if he would write in it for her. As usual, for the reasons already given, he (perforce) wrote “My Star,” and when the girl looked at it she exclaimed that it was one of her old favorites, and showed him where she had already copied it into the book.
At the station, when they drove down again to take the returning train, one of the young literati of Italy was there, and the Contessa introduced him to Browning, saying that the young man had already achieved distinction in letters. Mr. Browning talked with him most cordially, and after they were on their way he said that the young writer “seemed to be a youth of promise, and that he hoped he should meet him again.” But when they did hear of him again it was as the lecturer of a series of talks on Zola, “which, as may be supposed,” notes Mrs. Bronson, “the poet expressed no desire to attend.” The marvelous days of that unearthly loveliness of Venice in the early autumn flew by, and Mrs. Bronson’s guest returned to DeVere Gardens. To his hostess the poet wrote, under date of DeVere Gardens, December 15, 1888:
Dearest Friend,—I may just say that and no more; for what can I say? I shall never have your kindness out of my thoughts,—and you never will forget me, I know. We shall please you by telling you our journey was quite prosperous, and wonderfully fine weather, till it ended in grim London, and its fog and cold. (At Basle there was cold, but the sun made up for everything.) We altered our plans so far as to sleep and to stay through a long day at Basle, visiting the museum, cathedral,[Pg 278] etc., and went on by night train in a sleeping-car, of which we were the sole occupants, to Calais, directly. At Dover the officials were prepared for us, would not look at the luggage, and were very helpful as well as courteous; and at London orders had been given to treat us with all possible good nature. They wouldn’t let us open any box but that where the lamp was packed; offered to take our word for its weight, and finally asked me, “since there were the three portions, would I accept the weight of the little vessel at bottom as that of the other two?” “Rather,” as Pen says, so they declined to weigh the whole lamp, charging less than a quarter of what it does weigh, and even then requiring assurance that I was “quite satisfied.” We were to be looked after first of all the passengers, and so got away early enough to find things at home in excellent order.... I send a hasty line to try to express the impossible,—how much I love you, and how deeply I feel all your great kindness. Every hour of the day I miss you, and wish I were with you and dear Edith again, in beloved Casa Alvisi.
These letters to Mrs. Bronson reveal Browning the man as do no other records in literature. The consciousness of being perfectly understood, and the realization of the delicacy and beauty of the character of Mrs. Bronson made this choice companionship one of the greatest joys in Browning’s life. It may, perhaps, as well be interpolated here that a large package of the fascinating letters from Robert Browning to Mrs. Bronson, from which these extracts are made, were placed at the disposal of the writer of this volume by the generous kindness of Mrs. Bronson’s daughter, the Contessa Rucellai, and with the slight exception of a few paragraphs used by Mrs. Bronson herself (in two charming papers that she wrote on Browning), they have never before been drawn upon for publication.
Under the date of January 4, 1889, the poet writes to Mrs. Bronson:
No, dearest friend, I can well believe you think of me sometimes, even oft-times, for in what place, or hour, or hour of the[Pg 279] day, can you fail to be reminded of some piece of kindness done by you and received by me during those memorable three months when you cared for me and my sister constantly, and were so successful in your endeavor to make us perfectly happy. Depend on it, neither I nor she move about this house (which has got to be less familiar to us through our intimate acquaintance with yours),—neither of us forget you for a moment, nor are we without your name on our lips much longer, when we sit quietly down at home of an evening, and talk over the pleasantest of pleasant days....
The sole invitation I can but accept this morning is to the Farewell dinner about to be given by the Lord Mayor to Mr. Phelps; that I am bound to attend. I have not seen him or Mrs. Phelps yet; but they receive this afternoon, and if I am able I shall go. You will wish to know that all our articles have arrived safely, and more expeditiously than we had expected. The tables, lanterns, etc., are very decidedly approved of, and fit into the proper corners very comfortably; so that everywhere will be an object reminding us, however unnecessarily, of Venice. Your ink-stand brightens the table by my hand; the lamp will probably stand beside it; while Tassini tempts me to dip into him every time I pass the book-case. I may never see the loved city again, but where in the house will not some little incident of the then unparalleled months, wake up memories of the gondola, and the stopping, here and there, and the fun at Morchio’s; the festive return home, behind broad-backed Luigi; then the tea, and the dinner, and Gargarin’s crusty old port flavor, and the Dyers, and Ralph Curtis, and O, the delightful times! Of Edith I say nothing because she has herself, the darling! written to me, the surprise and joy of that! And I mean to have a talk with her on paper, alas! my very self, and induce her not to let me have the last word. Oh, my two beloveds I must see Venice again; it would be heart-breaking to believe otherwise. Of course I entered into all your doings, the pretty things you got, and prettier, I am sure, you gave. And I was sorry, so sorry, to hear that naughty Edith, no darling, for half a second, now I think of it,—did not figure in the tableaux. I hope and believe, however, she did dance in the New Year. Bid her[Pg 280] avoid this cold-catching and consequent headache. Do write, dearest friend, keep me au courant of everything. No minutest of your doings but is full of interest to me and Sarianna. But I am at the paper’s extreme edge. Were it elephant folio (is there such a size?) it would not hold all I have in my heart, and head, too, of love for you and “our Edie;” so, simply, God bless you, my beloveds!
Robert Browning.
Princess Montenegro sent me by way of a New Year’s card,—what do you think? A pretty photograph of the Rezzonico. The young lady was equally mindful of Sarianna.
R. B.
To Miss Edith Bronson the poet wrote, as follows:
Dearest Edie,—I did not reply to your letter at once for this reason; an immediate answer might seem to imply I expected such a delightful surprise every day, or week, or even month; and it was wise economy to let you know that I can go on without a second piece of kindness till you again have such a good impulse and yield to it—by no means binding yourself to give me regularly such a pleasure. You shall owe me nothing, but be as generous as is consistent with justice to other people.... I did not go out except to the complimentary farewell dinner our Lord Mayor gave to Mr. Phelps which nobody could be excused from attending. We all grieved at the loss, especially of Mrs. Phelps, who endeared herself to everybody. Both of them were sorry to go from us....
The next letter reveals anew Browning’s always thoughtful courtesy in bespeaking kindness for mutual friends, as he writes:
“There is arranged to be a sort of expedition [to Venice] of young Toynbee Hall men, headed by Alberto Ball, the son of our common friend, for the purpose of studying, not merely amusing, themselves with,—the beloved city. Well as the Balls are entitled to say that they know you, still, the young and clever Ball chooses to wish me to beg your kind notice; and I suppose[Pg 281] that his companions are to be noticed also,—of what really appears to be a praiseworthy effort after self-instruction. Will you smile on him when he calls on you? for his father’s sake, who is anxious about the scheme’s success? I have bespoken Pen’s assistance, and he will do the honors of the Rezzonico with alacrity, I have no doubt.”
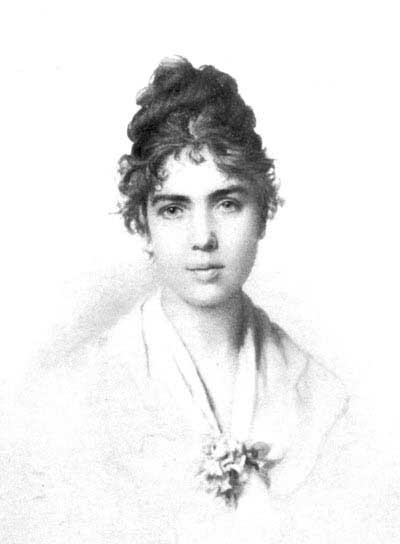

Miss Edith Bronson,
(now Contessa Rucellai)
From a Water-Color by Passini, Venice, 1883.
In almost every life that is strongly individualized those who look back after it has passed from visible sight cannot but recognize how rhythmic are the sequences that have characterized its last months on earth. If the person in question had actually known the day on which he should be called away, he would hardly have done other than he did. It is as if the spirit had some prescience, not realized by the ordinary consciousness, but still controlling its conduct of the last time allotted here. With this last year of Robert Browning’s life, this unseen leading is especially obvious. In the spring he had revised his poetic work; he had passed Commemoration week at Oxford, as he loved to do; he had passed much of the time with his friend, the Master of Balliol, and among his last expressions on leaving Oxford was “Jowett knows how I love him.” He was also in Cambridge, and Edmund Gosse has charmingly recalled the way in which he dwelt, retrospectively, on his old Italian days.
In June, also, he paid his usual visit to Lord Albemarle (the last survivor of those who fought at Waterloo), and in that month he wrote to Professor Knight, who was about to exchange the Chair of Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for that of Literature at St. Andrews, saying: “It is the right order; Philosophy first, and Poetry, which is its highest outcome, afterward, and much harm has been done by reversing the usual process.”
The letters to Mrs. Bronson tell much of the story of these days. In one, dated June 10, 1899, he gives this reminiscence of Asolo:
[Pg 282]Dearest Friend,—It was indeed a joy to get your letter. I know that a change of place would be desirable for you, darling Edie told me so, but I fancied you would not leave Venice so soon....
... One thing is certain, that if I do go to Venice, and abide at the Rezzonico, every day during the visit I shall pass over to the beloved Alvisi and entirely beloved friends there, who are to me in Venice what San Marco is to the Piazza. Enough of this now, and something about Asolo.
When I first found out Asolo, I lodged at the main hotel in the Square,—an old, large inn of the most primitive kind. The ceiling of my bed-room was traversed by a huge crack, or rather cleft, caused by the earthquake last year; the sky was as blue as blue could be, and we were all praying in the fields, expecting the town to tumble in. On the morning after my arrival, I walked up to the Rocca; and on returning to breakfast I mentioned it to the land-lady, wherein a respectable middle-aged man, sitting by, said: “You have done what I, born here, never thought of doing.” I took long walks every day, and carried away a lively recollection of the general beauty, but I did not write a word of ‘Pippa Passes’—that idea struck me when walking in an English wood, and I made use of Italian memories.
I used to dream of seeing Asolo in the distance and making vain attempts to reach it—repeatedly dreamed this for many a year. And when I found myself once more in Italy, with Sarianna, I went there straight from Venice. We found the old inn lying in ruins, a new one (being) built, to take its place,—I suppose that which you see now. We went to a much inferior albergo, the best then existing, and were roughly, but pleasantly, entertained for a week, as I say. People told me the number of inhabitants had greatly increased, and things seemed generally more ordinary and life-like. I am happy that you like it so much. When I got my impression, Italy was new to me....
... I shall go to Oxford for Commemoration, and stay a week for another affair,—a “gaudy” dinner given to the magnates of Eton.
[Pg 283]To the forthcoming collection, entitled “Asolando,” the group of poems dedicated to Mrs. Bronson, the poet alludes as follows:
... By the way the new little book of poems that was to associate your name with mine, remains unprinted. For why? The publishers think its announcement might panic-strike the purchasers of the new edition, who have nearly enough of me for some time to come! Never mind. We shall have our innings.
Bless you ever and your Edith; keep me in mind as your very own always affectionate
R. B.
The poet’s love for Asolo is revealed in the following letter to Mrs. Bronson:
29, DeVere Gardens, W.
July 17,’89.
Dearest Friend,—I shall delight in fancying your life at Asolo, my very own of all Italian towns; your house built into the wall, and the neighboring castle ruins, and the wonderful outlook; on a clear day you can see much further than Venice. I mentioned some of the dear spots pointed out to my faith as ruins, while what wants no faith at all,—the green hills surrounding you, Posagno close by,—how you will enjoy it! And do go there and get all the good out of the beautiful place I used to dream about so often in old days, till at last I saw it again, and the dreams stopped,—to begin, again, I trust, with a figure there never associated with Asolo before. Shall I ever see you there in no dream? I cannot say; I feel inclined to leave England this next autumn that is so soon to overtake us....
Pen stays a few days longer in Paris to complete his picture. He had declined to compete at the Exposition, but has been awarded a Medal (3rd), which, however, enables him to dispense with the permission of the Salon that his works shall be received. Julian Story gets also a medal of the same class. Pen reports stupendously of the Paris show....
... Well, you know we have been entertaining and enter[Pg 284]tained by the Shah. I met him at Lord Roseberry’s, and before dinner was presented to him, when he asked me in French: “Êtes-vous poëte?” “On s’est permis de le dire quelquefois.” “Et vous avez fait des livres?” “Plusieurs livres?” “Trop de livres.” “Voulez-vous m’en faire le cadeau d’un de vos livres afin que je puisse me ressouvenir de vous?” “Avec plaisir.” Accordingly I went next day to a shop where they keep them ready bound, and chose a brightly covered “selection.”...
All the outing I have accomplished was a week at Oxford, which was a quiet one,—Jowett’s health, I fear, not allowing the usual invitation of guests to Balliol. I had all the more of him, to my great satisfaction.
Sarianna is quite in her ordinary health, but tired as we cannot but be. She is away from the house, but I know how much she would have me put in of love in what I would say for her.... Did you get a little book by Michael Field? “Long Ago,” a number of poems written to innestare what fragmentary lines and words we have left of Sappho’s poetry. I want to know particularly how they strike you.
To Tennyson for his eightieth birthday Mr. Browning writes:
To-morrow is your birthday, indeed a memorable one. Let me say I associate myself with the universal pride of our country in your glory, and in its hope that for many and many a year we may have your very self among us; secure that your poetry will be a wonder and delight to all those appointed to come after; and for my own part let me further say, I have loved you dearly. May God bless you and yours! I have had disastrous experience.... Admiringly and Affectionately yours,
Robert Browning.[17]
To this letter Lord Tennyson replied:
Aldworth, August, 1889.
My Dear Browning,—I thank you with my whole heart and being for your noble and affectionate letter, and with my [Pg 285]whole heart and being I return your friendship. To be loved and appreciated by so great and powerful a nature as yours will be a solace to me, and lighten my dark hours during the short time of life that is left to us.
Ever Yours,
A. Tennyson.
The poet found himself again longing for his Italy. To Mrs. Bronson, under date of August 8, he wrote, referring to a letter of hers received two days before, crowned with “the magical stamp of Asolo”:
“... So a fancy springs up which shall have utterance as just a fancy. The time has come for determining on some change of place, if change is ever to be, and, I repeat, just a fancy, if I were inclined to join you at Asolo, say a fortnight hence, could good rooms be procurable for Sarianna and myself? Now as you value—I won’t say my love, but my respect and esteem—understand me literally, and give me only the precise information I want—not one half-syllable about accommodation in your house!
“I ask because when I and Sarianna went there years ago, the old Locanda on the Square lay in ruins, and we put up at a rougher inn in the town’s self. I dare say the principal hotel is rebuilt by this time, or rather has grown somewhat old. Probably you are there indeed. Just tell us exactly. Pen is trying his best to entice us his way, which means to Primiero and Venice; but the laziness of age is subduing me, and how I shrink from the ‘middle passage,’—all that day and night whirling from London to Basle, with the eleven or twelve hours to Milan. Milan opens on Paradise, but the getting to Milan! Perhaps I shall turn northward and go to Scotland after all. Still, dear and good one, tell me what I ask. After the requisite information you will please tell me accurately how you are, how that wicked gad-a-bout, Edith, is, and where; and what else you can generously afford of news,—news Venetian, I mean....”
Later the poet writes:
[Pg 286]“... I trust that as few clouds as may be may trouble the blue of our month at Asolo; I shall bring your book full of verses for a final overhauling on the spot where, when I first saw it, inspiration seemed to steam up from the very ground.
“And so Edith is (I conjecture, I hope, rightly) to be with you; won’t I show her the little ridge in the ruin where one talks to the echo to greatest advantage.”
From Milan Browning wrote to Mrs. Bronson:
Dearest Friend,—It is indeed a delight to expect a meeting so soon. Be good and mindful of how simple our tastes and wants are, and how they have been far more than satisfied by the half of what you provided to content them. I shall have nothing to do but to enjoy your company, not even the little business of improving my health since that seems perfect. I hear you do not walk as in the old days. I count upon setting that right again. O Venezia, benedetta!
It was with greater enjoyment, apparently, than ever before even, that Mr. Browning turned to the Asolo of his “Pippa Passes” and “Sordello.” Mrs. Bronson, in her brilliant and sympathetic picturing of the poet, speaks of his project “to raise a tower like Pippa’s near a certain property in Asolo, where he and Miss Browning might pass at least a part of every year.” The “certain property,” to which Mrs. Bronson so modestly alludes, was her own place, “La Mura.” The tower has since been erected by the poet’s son, and the dream is thus fulfilled, though the elder Browning did not live to see it. Mrs. Bronson describes his enjoyment of nature in this lovely little hill-town,—“the ever-changing cloud shadows on the plain, the ranges of many-tinted mountains in the distance, and the fairy-like outline of the blue Euganean Hills, which form in part the southern boundary of the vast Campagna.” Browning would speak of the associations which these hills bear with the names of Shelley and Byron.
[Pg 287]Across the deep ravine from La Mura a ruined tower was all that remained of the villa of Queen Catarina Cornaro, who, when she lost Cyprus, retired to Asolo; and in Browning’s dedication to Mrs. Bronson of his “Asolando,” he ascribes the title to Cardinal Bembo, the secretary of Queen Catarina. Mr. Browning loved to recall the traditions of that poetic little court, which for two decades was held within those walls, whose decay was fairly hidden by the wealth of flowers that embowered them. Of his own project he would talk, declaring that he would call it “Pippa’s Tower,” and that it should be so built that from it he could see Venice every day. He playfully described the flag-signals that should aid communication between “Pippa’s Tower” and Casa Alvisi. “A telephone is too modern,” he said; and explained that when he asked his friend to dine the flag should be blue,—her favorite color; and if her answer was yes, her flag should be the same color; or if no, her flag should be red. This last visit of the poet to his city of dream and vision seemed to Mrs. Bronson one of unalloyed pleasure. “To think that I should be here again!” he more than once exclaimed, as if with an unconscious recognition that these weeks were to complete the cycle of his life on earth. Asolo is thirty-four miles from Venice, and it is within easy driving distance of Possagno, the native place of Canova, in whose memory the town has a museum filled with his works and casts. “Pen must see this,” remarked Mr. Browning, as he lingered over the statues and groups and tombs. Mrs. Bronson records that one day on returning from a drive to Bassano the poet was strangely silent, and no one spoke; finally he announced that he had written a poem since they left Bassano. In response to an exclamation of surprise he said: “Oh, it’s all in my head, but I shall write it out presently.” His hostess asked if he would not even say what inspired it, to which he returned:
[Pg 288]“Well, the birds twittering in the trees suggested it. You know I don’t like women to wear those things in their bonnets.” The poem in question proved to be “The Lady and the Painter.”
Mr. Browning took the greatest enjoyment in the view from Mrs. Bronson’s loggia. “Here,” he would say, “we can enjoy beauty without fatigue, and be protected from sun, wind, and rain.” His hostess has related that its charm made him often break his abstemious habit of refusing the usual five o’clock refreshment, and that he “loved to hear the hissing urn,” and when occasionally accepting a cup of tea and a biscuit would say, “I think I am the better for this delicious tea, after all.”
Every afternoon at three they all went to drive, exploring the region in all directions. The driving in Asolo seemed to charm him as did the gondola excursions in Venice. “He observed everything,” said Mrs. Bronson, “hedges, trees, the fascination of the little river Musone, the great carri piled high with white and purple grapes. He removed his hat in returning the salutation of a priest, and touched his hat in returning the salutation of the poorest peasant, who, after the manner of the country, lifted his own to greet the passing stranger. ‘I always salute the church,’ Mr. Browning would say; ‘I respect it.’”
All his life Browning was an early riser. In Asolo, as elsewhere, he began his day with a cold bath at seven, and at eight he and his sister sat down to their simple breakfast, their hostess keeping no such heroic hours. Mrs. Bronson had adopted the foreign fashion of having her light breakfast served in her room, and her mornings were given to her wide correspondence and her own reading and study. She was a most accomplished and scholarly woman, whose goodness of heart and charm of manner were paralleled by her range of intellectual interests and her grasp of affairs.
[Pg 289]After breakfasting Browning and his sister, inseparable companions always, would start off on their wanderings over the hills. The poet was keenly interested in searching out the points of interest of his early years in Asolo; the “echo,” the remembered views, the vista whose fascination still remained for him. From the ruined rocca that crowned the hill, the view comprised all the violet-hued plain, stretching away to Padua, Vicenzo, Bassano; the entire atmosphere filled with historic and poetic associations. How the poet mirrored the panorama in his stanzas:
“How many a year, my Asolo,
Since—one step just from sea to land—
I found you, loved yet feared you so—
For natural objects seemed to stand
Palpably fire-clothed! No—”
The “lambent flame,” and “Italia’s rare, o’er-running beauty,” enchanted his vision.
Returning from their saunterings, the brother and sister took up their morning reading of English and French newspapers, Italian books, with the poet’s interludes always of his beloved Greek dramatists.
In these October days the Storys arrived to visit Mrs. Bronson in her picturesque abode. An ancient wall, mostly in ruins, with eighteen towers, still surrounds Asolo, and partly in one of these towers, and partly in the arch of the old portal, “La Mura” was half discovered and half constructed. Its loggia had one wall composed entirely of sliding glass, which could be a shelter from the storm with no obstruction of the view, or be thrown open to all the bloom and beauty of the radiant summer. Just across the street was the apartment in which Mrs. Bronson bestowed her guests.
That Browning and Story should thus be brought together again for their last meeting on earth, however undreamed of to them, prefigures itself now as another[Pg 290] of those mosaic-like events that combined in beauty and loveliness to make all his last months on earth a poetic sequence. The Storys afterward spoke of Mr. Browning as being “well, and in such force, brilliant, and delightful as ever”; and the last words that passed between the poet and the sculptor were these of Browning’s: “We have been friends for forty years, forty years without a break!”
On the first day of November this perfect and final visit to Asolo ended, and yielding to the entreaties of his son, Browning and his sister bade farewell to Mrs. Bronson and her daughter, who were soon to follow them to Venice, where the poet and Miss Browning were to be the guests of the Barrett Brownings in Palazzo Rezzonico.
The events of all these weeks seem divinely appointed to complete with stately symmetry this noble life. As one of them he found in Venice his old friend, and (as has before been said) the greatest interpreter of his poetry, Dr. Hiram Corson. The Cornell professor was taking his University Sabbatical year, and with Mrs. Corson had arrived in Venice just before the poet came down from Asolo. “I called on him the next day,” Dr. Corson said of this meeting. “He seemed in his usual vigor, and expressed great pleasure in the restorations his son was making in the palace. ‘It’s a grand edifice,’ he said, ‘but too vast.’”
Dr. Corson continued:
“He was then engaged in reading the proofs of his ‘Asolando.’ He usually walked two hours every day; went frequently in his gondola with his sister to his beloved Lido, and one day when I walked with him
‘Where St. Mark’s is, where the Doges used to wed the sea with rings,’
I had to quicken my steps to keep pace with him. He called my attention to an interesting feature of this world-renowned place, and told me much of their strange history. He knew the city literally par cœur.”

Professor Hiram Corson
From a painting by J. Colin Forbes, R.A., in the possession of Eugene Rollin Corson.
[Pg 291]Mr. Browning passed with Dr. and Mrs. Corson the last morning they were in Venice. Of the parting Dr. Corson has since written in a personal letter to a friend:
“He told us much about himself; about Asolo, which he had first visited more than fifty years before, during his visit to Italy in 1838, when, as he says in the Prologue to ‘Asolando,’ alluding to ‘the burning bush,’
‘Natural objects seemed to stand
Palpably fire-clothed.’
“A servant announcing that the gondola had come to take us to the railway station, he rose from his chair, and said, ‘Now be sure to visit me next May, in London. You’ll remember where my little house is in De Vere Gardens’; and bidding us a cordial good-bye, with a ‘God bless you both,’ he hastened away. We little thought, full of life as he then was, that we should see him no more in this world.”
To a letter from Miss Browning to their hostess, Browning added:
Dearest Mrs. Bronson,—I am away from you in one sense, never to be away from the thought of you, and your inexpressible kindness. I trust you will see your way to returning soon. Venice is not herself without you, in my eyes—I dare say this is a customary phrase, but you well know what reason I have to use it, with a freshness as if it were inspired for the first time. Come, bringing news of Edith, and the doings in the house, and above all of your own health and spirits and so rejoice
Ever your affectionate
Robert Browning.
With another letter of his sister’s to their beloved friend and hostess, Mr. Browning sent the following note,—perhaps the last lines that he ever wrote to Mrs. Bronson, as she returned almost immediately to Casa Alvisi, and[Pg 292] the daily personal intercourse renewed itself to be broken only by his illness and death. The poet wrote:
Palazzo Rezzonico, Nov. 5th, 1889.
Dearest Friend,—A word to slip into the letter of Sarianna, which I cannot see go without a scrap of mine. (Come and see Pen and you will easily concert things with him.) I have all confidence in his knowledge and power.
I delight in hearing how comfortably all is proceeding with you at La Mura. I want to say that having finished the first two volumes of Gozzi, I brought the third with me to finish at my leisure and return to you; and particularly I may mention that the edition is very rare and valuable. It appears that Symmonds has just thought it worth while to translate the work, and he was six months finding a copy to translate from!
... I have got—since three or four days—the whole of my new volume in type, and expect to send it back, corrected, by to-morrow at latest. But I must continue at my work lest interruptions occur, so, bless you and good-bye in the truest sense, dear one!
Ever Your Affectionately
Robert Browning.
The “new volume in type” to which he referred was his collection entitled “Asolando,” all of which, with the exception of one poem, had been written within the last two years of his life.
Mr. Barrett Browning relates that while his father was reading aloud these last proofs to himself and his wife, the poet paused over the “Epilogue,” at the stanza—
“One who never turned his back but marched breast forward,
Never doubted clouds would break,
Never dreamed, though right were worsted, wrong would triumph,
Held we fall to rise, are baffled to fight better,
Sleep to wake.”
and remarked: “It almost seems like praising myself to say this, and yet it is true, the simple truth, and so I shall not cancel it.”
[Pg 293]November, often lovely in Venice, was singularly summer-like that year. On one day Mr. Browning found the heat on the Lido “scarcely endurable,” indeed, but “snow-tipped Alps” revealed themselves in the distance, offering a strange contrast to the brilliant sunshine and the soft blue skies. Still November is not June, after all, however perfect the imitation of some of its days. One day there was a heavy fog on his favorite Lido, and the poet, who refused to be deprived of his walk, became thoroughly chilled and illness followed. The following note from Mr. Barrett Browning to Mrs. Bronson indicates the anxiety that prevailed in Palazzo Rezzonico, where the tenderest care of his son and daughter-in-law ministered to the poet. The note is undated, save by the day of the week.
Palazzo Rezzonico,
9 o’clock, Monday Evening.
Dearest Mrs. Bronson,—The improvement of last night is scarcely maintained this morning,—the action of the heart being weaker at moments. He is quite clear-headed, and is never tired of saving he feels better, “immensely better,—I don’t suppose I could get up and walk about, in fact I know I could not, but I have no aches or pains,—quite comfortable, could not be more so,”—this is what he said a moment ago.
I will let you know if there is any change as the day goes on.
My love to you.
Yours, Pen.
The delightful relations that had always prevailed between the poet and his publishers were touchingly completed when, just before he breathed his last, came a telegram from George Murray Smith with its tidings of the interest with which “Asolando” was being received in England. And then this little note written on that memorable date of December 12, 1889, from Barrett Browning to Mrs. Bronson, tells the story of the poet’s entrance on the new life.
[Pg 294]Palazzo Rezzonico,
10.30 p.m.
Dearest Friend,—Our Beloved breathed his last as San Marco’s clock struck ten,—without pain—unconsciously.
I was able to make him happy a little before he became unconscious by a telegram from Smith saying, “Reviews in all this day’s papers most favorable, edition nearly exhausted.”
He just murmured, “How gratifying.”
Those were his last intelligible words.
Yours, Pen.
In that hour how could the son and the daughter who so loved him remember aught save the exquisite lines with which the poet had anticipated the reunion with his “Lyric Love”:
“Then a light, then thy breast,
O thou soul of my soul! I shall clasp thee again,
And with God be the rest!”
In the grand sala with its floor of black Italian marble and its lofty ceiling with exquisite fresco decoration, the simple and impressive service was held in Palazzo Rezzonico, and a fleet of gondolas, filled with friends and accompanied by the entire Venetian Syndic, bore the casket to its temporary resting-place in the chapel of San Michele, in the campo santo. The gondola that carried the casket had an angel, carved in wood, at the prow, and a lion at the stern. Dean Bradley, on behalf of Westminster Abbey, had telegraphed to Robert Barrett Browning, asking that the body of the poet might be laid within those honored walls; and as the cemetery in Florence wherein is Mrs. Browning’s tomb had long been closed, this honor from England was accepted. The same honor of a final resting-place in Westminster Abbey was also extended for the removal of the body of Mrs. Browning, but their son rightly felt that he must yield to the wishes of Florence [Pg 295]that her tomb be undisturbed, and it is fitting that it should remain in the Italy she so loved.

Palazzo Rezzonico, Venice
Owned by Robert Browning from 1888 to 1906. In the upper room, at the left-hand corner, the poet died.
So associated with her brother’s life was Miss Sarianna Browning that the story would be incomplete not to add that she survived him many years,—a gracious and beloved presence. In the January following the poet’s death, she said in a letter to Mrs. Bronson:
“I have already let a day pass without thanking you for the most beautiful locket, which I love even more for your sake than his. I shall always think of you, so good, so near, and so dearly loved by him. All your watchfulness over our smallest comfort,—how he felt it!... Bless you forever for all the joy you gave him at Asolo,—how happy he was! And how you were entwined in all our plans for the happy future we were to enjoy there! Think of him when you go back, as loving the whole place, and yourself, the embodiment of its sweetness.”
Miss Browning died in her nephew’s home, La Torre All’ Antella, near Florence, in the spring of 1903, in her ninetieth year.
On the façade of the Palazzo Rezzonico the City of Venice placed this inscription to the memory of the poet:
a
ROBERTO BROWNING
morto in questo palazzo
il 12 Dicembre, 1889
venezia
pose
“Open my heart and you will see
Graved inside of it,—‘Italy’”
It was on the last day of 1889 that the impressive rites were held in Westminster Abbey for Robert Browning. The Archbishop of Canterbury, the Dean of Windsor, an aid-de-camp representing Queen Victoria, Dean Bradley, the sub-dean, and many eminent canons, and Sir Frederick[Pg 296] Bridge, of the Abbey choir, all were present among the officiating clergy. The casket under its purple pall, with a massive cross of violets, and wreaths of lilies-of-the valley, and white roses (Mrs. Browning’s favorite flower), was followed by the honorary pall-bearers including Hallam Tennyson, representing the Poet Laureate (whose health did not permit him to be present), Archdeacon Farrar, the Master of Balliol (representing Oxford), the Master of Trinity (representing Cambridge), Professor Masson (representing the University of Edinburgh), and George Murray Smith. The committal service was entirely choral, and Mrs. Browning’s poem with its touching refrain,
“He giveth His beloved sleep!”
was chanted by the full vested choir of the Abbey, to music composed for the occasion by Sir Frederick Bridge. Preceding the Benediction, the entire vast concourse of people united in singing the hymn,
“O God, our help in ages past!”
As that great assemblage turned away from the last rites in commemoration of the poet who produced the largest body of poetry, and the most valuable as a spiritual message, of any English poet, was there not wafted in the air the choral strains from some unseen angelic choir, that thrilled the venerable Abbey with celestial triumph:
“‘Glory to God—to God!’ he saith:
Knowledge by suffering entereth,
And Life is perfected by Death.”
Abinger, Lord, 18
“Abt Vogler,” 205
“Andrea del Sarto,” 152, 170
“Any Wife to Any Husband,” 152
“Apprehension, An,” 47
Arnold, Matthew, 112
Arnould, Joseph, friendship for Browning, 14, 39, 40, 129;
letters to Domett, 69, 94, 99, 103
Ashburton, Lady Louisa, 222
“Asolando,” 5, 282, 292
“Aurora Leigh,” 50, 52, 76, 127, 134, 143, 148, 158, 160, 164, 167, 171, 174-176, 210
“Balaustion’s Adventure,” 229
Barrett, Alfred, 16, 164
——, Arabel, 16, 50, 129, 137, 164, 202, 212
——, Edward (brother), 16, 22, 59;
death of, 18, 62, 135
——, Edward (father) legal name, 17;
marriage, 18;
character, 20, 21, 121, 164;
death, 178
——, Elizabeth. See Moulton-Barrett, Elizabeth
——, George, 16, 50
——, Henrietta (Mrs. Surtees Cook), 16, 50;
marriage, 121;
affection for sister, 129;
137, 164, 192
——, Mrs. (mother), 18, 21
“Battle of Marathon,” 20
“Beatrice Signorini,” 237, 267
“Bells and Pomegranates,” 14, 39, 67, 68
“Ben Karshook’s Wisdom,” 158
Berdoe, Dr., commentary on "Paracelsus," 37
“Bertha in the Lane,” 46, 71
“Bishop Blougram’s Apology,” 205
Blagden, Isabella, friendship with Brownings, 111, 112, 178, 182, 184, 190, 191, 197, 200, 201, 207, 225;
death, 229
Blessington, Lady, 33, 113, 138
“Blot in the ’Scutcheon, A,” 69
“Book of the Poets, The,” 64, 206
Boyd, Hugh Stuart, tutor, 22;
letters from Elizabeth Barrett, 25, 45, 53, 55, 63, 64, 68, 73, 89
Bronson, Mrs. Arthur (Katherine DeKay), friendship with Browning, 242, 273;
letters from Browning, 243, 248, 249, 252-260, 265, 271, 272, 277-286, 291, 292;
hospitality, 242, 274-276;
entertains Browning in Asolo, 286, 287, 290;
letters from Robert Barrett Browning, 293-294;
letter from Sarianna Browning, 295
Bronson, Edith (Contessa Rucellai), 275, 280
Brooks, Rev. Dr. Phillips, 211, 212
Browning, Mrs. (mother), 4-6, 38
——, Elizabeth Barrett, birth, 16;
childhood, 17, 19;
ancestry, 17, 18;
first literary work, 20;
accident to, 21;
studies, 22;
tastes, 23, 24;
removal to Sidmouth, 24;
translation of "Prometheus Bound," 44;
removal to London, 45;
[Pg 298]fugitive poems, 46-48, 53;
Hebrew Bible, 49;
definite periods in her life, 50;
change of residence, 54, 56;
notable friends, 58, 59;
publication of "The Seraphim," 56;
literary criticisms, 60, 61, 67, 68;
goes to Torquay, 59;
personal appearance, 58;
death of brother, 62;
returns to England, 63;
translations from Greek, 64;
description of her room, 65;
refusal to meet Browning, 65;
publication of two volumes of poems, 71;
literary reputation established, 71, 72;
first letter from Browning, 73, 74;
correspondence of poets, 74-89;
meets Browning, 80;
lyrics, 83, 84;
marriage, 87, 89;
will, 93;
lyrics, 100, 101;
mentioned for Laureateship, 121, 122;
books read by, 143;
genius for friendship, 148;
comment on dress, 151;
description of, 153, 179;
souvenir locket, 153;
views on life, 159;
appreciation of Tennyson, 166;
success of "Aurora Leigh," 174-176;
American appreciation, 187;
ill health, 193, 195;
closing days, 196;
last words, 197;
burial, 197;
tomb, 200;
tablet on Casa Guidi to her memory, 218, 264;
Tauchnitz edition of poems, 227
Browning, Reuben (uncle), 8
——, Robert (father), character and qualities, 4-6;
removal to Paris, 132;
talent for caricature, 137;
death, 210
——, Robert (grandfather), 4
——, Robert, ancestry of, 4-6;
birth, 4;
childhood and early tastes, 6-8;
first literary work, 7;
home atmosphere, 10, 11;
school, 12;
influenced by Byron and Shelley, 13, 14;
juvenile verses, 14;
publication of "Pauline," 14;
visit to Russia, 27, 28;
meets Wordsworth, Landor, Dickens, and Leigh Hunt, 30, 32;
personal appearance, 31;
writes play for Macready, 33;
visit to Venice, 35, 36;
removal to Hatcham, 38;
English friends and social life, 38-41;
hears of Elizabeth Barrett, 41;
visit to Italy, 70, 71;
return to England, 71;
correspondence of the poets, 74-89;
first meeting with Miss Barrett, 80;
marriage, 87, 89;
sees "Sonnets from the Portuguese," 109;
lyrics, 120, 121, 152;
keynote of his art, 122-125;
interpretation of Shelley, 133, 134;
Fisher’s portrait of, 153;
Page’s portrait of, 155;
literary standing, 172;
finds "Old Yellow Book," 181;
homage to Landor, 183;
leaves Florence forever, 200;
returns to London, 200;
takes London house, 202;
literary work, 203-207;
extension of social activities, 206, 207;
friendship with Jowett, 209;
meeting with Tennyson, 210;
death of father, 210;
Oxford conferred degree of M.A., 211;
made Honorary Fellow of Balliol College, 211;
new six-volume edition of poems, 213;
dedication to Tennyson, 213;
success of "The Ring and the Book," 214-215;
comparison of character of Pompilia to that of his wife, 219;
visits Scotland with the Storys, 221-222;
conversation and personal charm, 222-224;
with Milsand in "Red Cotton Night-cap Country," 224-226;
prepares Tauchnitz edition of Mrs. Browning’s poems, 227;
friendship with Domett, 228;
relations with Tennyson, 230-232;
[Pg 299]facility for rhyming, 231;
visit to Oxford and Cambridge, 232;
sojourn at "La Saisiaz," 233-234;
revisits Italy, 235, 239-240;
doctrine of life, 237;
Oxford conferred degree of D.C.L., 241;
son’s portrait of, 242;
friendship with Mrs. Bronson, 242;
gift from Browning Societies, 243;
letters to Mrs. Bronson, 243, 248, 249, 252-260, 265, 271, 272, 277-286, 291;
Italian recognition, 245;
honored at Edinburgh, 249;
letters to Professor Masson, 249, 250;
removal to DeVere Gardens, 260;
Foreign Correspondent to Royal Academy, 266;
poet of intensity, 270;
last year in London, 281;
return to Asolo, 287-288;
last meeting with the Storys and Dr. Corson, 289-290;
death, 294;
memorial inscription, 295;
burial, 295
Browning, Robert Barrett ("Penini"), birth, 107;
anecdotes of, 126, 139, 144, 146, 147, 155;
studies of, 171, 178, 180, 185, 188, 192, 193;
love of novels, 181;
enjoyment of Siena, 184;
children’s party at French Embassy, 194;
preparation for University, 202;
characteristics, 202, 265;
explanation of "The Ring and the Book," 218;
begins study of painting, 227;
picture in Royal Academy, 227;
success in art, 236, 241;
marriage to Miss Coddington, 260;
purchase of Palazzo Rezzonico, 262;
portrait of father, 217, 242;
portrait of Milsand, 263;
purchase of Casa Guidi, 265;
Florentine villa, 264-265, 267
——, Robert Jardine, 38
——, Sarianna, 4, 38;
letter from Browning, 71;
letters from Mrs. Browning, 195;
goes to live with brother, 211;
letter to Domett, 228;
travels with brother, 236;
letters to Mrs. Bronson, 248, 293;
death, 295
Brownings, The, life in Paris, 92, 93;
finances, 93;
journey to Italy, 95;
winter in Pisa, 95, 97;
home in Florence, 97;
visit to Vallombrosa, 98, 99;
apartments in Casa Guidi, 100, 101;
trip to Fano, 103, 104;
literary work, 106;
meet Story, 107;
summer at Bagni di Lucca, 107;
Florentine friends and life, 111-113, 118, 119;
visit to Siena, 125;
return to England, 129;
life and friends in Paris, 130-137;
return to England, 137;
social life in London, 137-141;
return to Casa Guidi, 142;
summer at Bagni di Lucca, 144-151;
winter in Rome, 152-157;
“Clasped Hands,” 153;
pilgrimage to Albano, 156;
return to Florence, 157;
poetic work, 158;
Italian appreciation, 161;
return to London, 164;
Tennyson reads "Maud" to them, 165;
winter and social life in Paris, 167-172;
return to Florence, 176;
Florentine gayety, 176, 178;
summer in Normandy, 179;
another winter in Rome, 180;
return to Florence, 181;
summer in Siena, 184-185;
in Florence again, 185;
Roman winter, 185, 188-189;
journey to Florence, 189-190;
last summer in Siena, 191-192;
last winter in Rome, 192-193;
return to Casa Guidi, 195;
memorials in Palazzo Rezzonico, 262
“Browning Society, The,” 240
Browning, William Shergold, 38
Brunton, Rev. Wm., poem, 91
“By the Fire-side,” 170
[Pg 300]
Carducci, Contessa, 71
Carlyle, Thomas and Jane, 30, 38, 39, 41, 61, 68, 97, 129, 130, 131
Casa Alvisi, 242, 243, 274
“Casa Guidi Windows,” 106, 115, 116
“Catarina to Camoens,” 71, 83
Chaucer, project to modernize, 60
“Childe Roland to the Dark Tower Came,” 152, 261
“Child’s Grave at Florence, A,” 121
Chorley, Henry, 39, 40, 147
“Christmas Eve and Easter Day,” 110, 119, 123, 124, 125
“Christopher Smart,” 237
Clarke, Mary Graham. See Barrett, Mrs.
“Clasped Hands, The,” 153
Coddington, Fanny, 260
“Colombe’s Birthday,” 27, 38, 143
“Comfort,” 47
“Conclusion,” 72
“Confessions,” 46, 83, 84
Cook, Mrs. Surtees. See Barrett, Henrietta
Corson, Dr. Hiram, criticism of Browning’s poetry, 29, 218;
visit to Browning, 35, 222, 244, 245-247, 290-291;
founder of Browning Society, 240-241;
letters from Browning, 247, 259;
215
Cosimo I, statue of, 114
“Cowper’s Grave,” 46, 57
Coxhoe Hall, 16
Cranch, Christopher Pearse, 111
Crosse, Andrew, 58, 59
“Crowned and Wedded,” 46
“Cry of the Children, The,” 46
“Curse for a Nation, A,” 186
Curtis, George William, 118, 119
Cushman, Charlotte, 40, 141
“Dead Pan, The,” 47, 68, 83
“Deaf and Dumb,” 205
“Death in the Desert, A,” 205, 237
“Denial, A,” 84
“De Profundis,” 18, 52, 136
“Development,” 5
Dickens, Charles, 30, 33, 59, 61, 69
Dilke, Mr., 64
Domett, Alfred, friendship for Browning, 14, 39, 228;
Browning’s letters to, 42, 43;
Arnould’s letters to, 69, 94, 99, 103
Dowden, Dr. Edward, 97, 133
Dowson, Christopher, 39
“Drama of Exile, A,” 46, 71-72
“Dramatic Idyls,” 236
“Dramatis Personæ,” 203-205
“Dryope,” statue of, 263
Dulwich Gallery, 11
Eastnor Castle, 22
Egerton-Smith, Miss, 233-234
Elgin, Lady, 131, 132, 167
Eliot, George, 190
“Englishman in Italy, The,” 71
“Epistle of Karnish,” 158
“Essay on Mind,” 22
“Eurydice to Orpheus,” 265
“Evelyn Hope,” 120
“Face, A,” 205
Faucit, Helen (Lady Martin), 70, 143
“Ferishtah’s Fancies,” 244
Field, Kate, Browning gives locket, 154;
visit to the Brownings, 182;
Browning’s letters to, 183, 186, 208;
Mrs. Browning’s letter to, 187
“Fifine,” 237
“Flight of the Duchess, The,” 80, 152
“Flute-Music,” 267
Forster, John, criticism of “Paracelsus,” 30;
friendship for Browning, 31, 32, 129;
33, 39, 69
Fox, Rev. William Johnson, 30, 140, 141
“Fra Lippo Lippi,” 152, 169-170
[Pg 301]
Franceschini, tragedy of, 181
Fuller, Margaret. See D’Ossoli, Marchesa
Furnivall, Dr., 240
“Futurity,” 47
Garrow, Theodosia. See Trollope
Giorgi, Signor, 217
“Gold Hair,” 204
Gosse, Edmund, 97, 281
“Grammarian’s Burial, A,” 152
“Greek Christian Poets, The,” 23, 65, 206
Griffin, Professor Hall, 27, 118, 134
“Guardian Angel, The,” 103, 152
Gurney, Rev. Archer, 38
“Half Rome,” 218
Haworth, Fanny, letter from Browning, 36;
40
Hawthorne, Nathaniel, 150, 178-179
“Hector in the Garden,” 47
“Helen’s Tower,” 222
“Hervé Riel,” 211
Hillard, George Stillman, 106, 118
Hodell, Dr. Charles W., 215-216
Holmes, Dr. Oliver Wendell, 48
“Holy Cross Day,” 158
Hope End, 16, 19, 22, 24
Horne, Richard Hengist, letter from Elizabeth Barrett, 19, 59;
friendship with Miss Barrett, 30, 53, 60, 61, 62, 65, 68
Hosmer, Harriet, takes cast of “Clasped Hands,” 153;
excursion with Brownings, 156, 157;
letter from Browning, 168;
visits poets, 191, 194
“How They Brought the Good News from Ghent to Aix,” 35
“In a Balcony,” 144, 158, 203
“In a Gondola,” 36
“Inclusions,” 84
“Incondita,” 14, 140
“Inn Album,” 232, 269
“Insufficiency,” 47, 84
“In the Doorway,” 207
“Isabel’s Child,” 46, 57
Italy, political conditions of, 105, 108, 115, 117, 121, 143, 180
“Ivan Ivanovitch,” 27, 236
James, Henry, characterization of Browning, 224
“James Lee’s Wife,” 204, 261
Jameson, Mrs., friendship with Miss Barrett, 73, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 129;
letter from Browning, 108
Jerrold, Douglas, 41
Jowett, Dr., 209, 229, 281
Kemble, Mrs. Fanny, 129, 138, 153, 154, 155
Kenyon, John, 33;
meets Browning, 40;
offers an introduction to Miss Barrett, 41;
45;
visit to Rydal Mount, 56;
account of, 58, 59;
termed the “joy-giver,” 65;
shows manuscript of “Dead Pan” to Browning, 68;
dedication of "Paracelsus" to, 69;
appreciation of, 74;
letters to the Brownings, 74, 97;
friendship, 112, 113, 129, 137;
dedication of “Aurora Leigh” to, 174;
death and legacy to Brownings, 176
Kingsley, Charles, 139
King Victor and King Charles, 69
Kinney, Mrs., 144, 145
“Lady and the Painter, The,” 288
“Lady Geraldine’s Courtship,” 71, 72, 73
“Lament for Adonis,” 23
Landor, Walter Savage, chirography of, 23;
meets Browning, 30;
courtesy of, 32;
[Pg 302]meets Miss Barrett, 55, 59, 137;
quoted, 60;
intimacy with Leigh Hunt, 112, 113;
opinions, 138;
guest of Brownings, 182;
homage from Browning, 183;
guest of Storys, 183, 184, 190, 192
“La Saisiaz,” 233-234
“Last Poems,” 202
“La Torre all’ Antella,” 264, 295
“La Vallière,” 33
Leighton, Sir Frederic, 200
“Les Charmettes,” 238
“Lost Leader, The,” 32
“Loved Once,” 83, 84
Lowell, James Russell, 51, 74
“Luria,” 69
Lytton, Bulwer, 33, 53, 60
——, Lord (Owen Meredith), 142;
entertains Mrs. Browning, 145-146;
visits the Brownings, 149, 150, 158
Macready, William, meeting with Browning, 30, 31;
suggests playwriting to Browning, 32;
sees “Strafford,” 33;
produces “Strafford,” 34;
dinner to Browning, 39;
produces “A Blot in the ’Scutcheon,” 69, 70
Marcello, Contessa, 276
Martineau, Harriet, friendship with Brownings, 33, 35, 39, 60, 62, 68
Masson, Professor, Browning entertained by, 249-251
Mazzini, 13, 143
Medici, Marchesa Peruzzi di, birthday fête, 184;
reminiscences of, 188, 193;
visit to Scotland, 221;
villa of, 239;
translation of Duprè’s Autobiography, 257;
Browning’s letter to, 257;
Florentine palace of, 265
Medici, statue of Fernandino di, 173
“Meeting at Night,” 120
“Men and Women,” 106, 157, 164, 169, 172
Millais, Lady, 240
——, Sir John Everett, Browning’s letter to, 227-228;
251
Milnes, Monckton (Lord Houghton), 30, 60, 61, 138;
christening party, 139
Milsand, Joseph, meeting with Browning, 134;
paper on Browning, 135;
letter from Browning, 152, 225;
friendship with Brownings, 159, 224, 225, 226;
criticism of "Aurora Leigh," 176;
death, 259;
portrait, 263
Mitford, Mary Russell, 32;
association with the Brownings, 32, 45, 55, 56, 58, 61, 65, 72;
letter from Mrs. Browning, 108, 118, 135, 136, 159;
death, 173
Mohl, Mme., 132, 167, 171
Moore, Mrs. Bloomfield, 252
Moulton-Barrett, Elizabeth (niece), 18
——. See Barrett, explanation of name, 17
Nancioni, il Signor Dottore, 245
Nettleship, Mr., essays on Browning, 213
“New Spirit of the Age, The,” 60, 68
Nightingale, Florence, 140
“Old Yellow Book, The,” 215
“One Word More,” 123, 168-169, 205
Ongaro, Dall’, 194
“Only a Cure,” 121
Ossoli, Marchesa d’ (Margaret Fuller), 111, 112;
visits the Brownings, 118;
death, 112, 126
“Other Half Rome, The,” 218
“Pacchiarotto,” 232
Page, William, 152, 155, 181
[Pg 303]
Palazzo Giustiniani, 242
—— Peruzzi, 265
—— Pitti, 102, 105, 106
—— Rezzonico, 262-264, 290, 293, 295
“Paracelsus,” 14, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 34, 36, 37, 39, 57, 69, 168, 237
“Parleyings,” 269
“Parting at Morning,” 120
Patmore, Coventry, 140
“Pauline,” 12, 14, 15, 28, 34, 57, 169, 172, 267
“Penini.” See Browning, Robert Barrett
“Pippa Passes,” 36, 65, 67, 69, 271, 286-287
Pius IX (Pio Nono), 105, 115, 117, 118, 121
Poe, Edgar Allan, 52
“Poems before Congress,” 185
“Poet’s Vow, The,” 53, 55, 57
“Pompilia,” 206, 218, 219
“Portrait, A,” 18, 164
Powers, Hiram, 102, 112, 118, 142
Prince of Wales (Edward VII), 180-181
Proctor (“Barry Cornwall”), 30, 33, 40, 61, 69, 129
“Prometheus Bound,” 23, 25, 44
“Proof and Disproof,” 84
“Prospice,” 123, 205
“Question and Answer,” 84
“Rabbi Ben Ezra,” 205
“Recollections of a Literary Life,” 135
“Red Cotton Night-cap Country,” 226, 230
“Return of the Druses, The,” 69
“Rhapsody of Life’s Progress, A,” 47, 48, 83
“Rhyme of the Duchess May, The,” 227
“Ring and the Book, The,” 182, 203 205, 214-220
Ripert-Monclar, Marquis Amédée de, 28, 38, 153
Ritchie, Lady, 153, 154, 226
Robertson, John, 35, 39
Rogers, Arthur, 273
“Romances and Lyrics,” 67
“Romaunt of Margret, The,” 53, 58
“Rosny,” 267
Rossetti, Dante Gabriel, 139, 165, 166, 169, 174
Sand, George, 131, 136
“Saul,” 120, 157
Scotti, Signor, 71
“Seraphim, The,” 46, 56, 58, 110
Sharp, William, quoted, 6;
suggested origin of “Flight of the Duchess,” 12;
quoted, 28;
description of Browning, 31;
43
Shelley, Percy Bysshe, 13, 133, 134
Silverthorne, Mrs., 14
“Sleep, The,” 46, 83
Smith, Alexander, 151
Smith, George Murray, 247, 270, 296
“Sonnets from the Portuguese,” 50, 71, 97, 108, 109, 110, 123, 168
“Sordello,” 14, 27, 28, 35, 41-42, 69, 171, 207, 237
“Soul’s Tragedy, A,” 69
“Statue and the Bust, The,” 152, 173
Stedman, Edmund Clarence, 90
Story, Edith. See Medici, Marchessa Peruzzi di
——, William Wetmore and Emeline, Browning’s first meeting, 107, 111;
characteristics, 118, 119;
associations with the Brownings, 148-152, 155, 184, 185, 192, 196, 197, 199, 221, 239;
entertain Landor, 183;
characterization of Hawthorne, 150;
last meeting with Browning, 289-290
“Strafford,” 33, 34, 35, 57
[Pg 304]
Talfourd, Field, 39
Talfourd, Sergeant, 30, 32, 40, 60, 69
Taylor, Bayard, 129
Tennyson, Alfred, 15;
comment on “Sordello,” 41;
60;
works, 56, 68;
Miss Barrett’s comments on, 61, 67, 120;
becomes Laureate, 122;
letter to Mrs. Browning, 139, 140;
reads “Maud” to the poets, 165;
letters from Browning, 209, 230, 284;
friendship with Browning, 231;
dedication, 213;
regarding Browning’s lines, 232
——, Frederick, 144, 158
——, Hallam, 296
“Tertium Quid,” 218
Thackeray, Anne. See Ritchie, Lady
Ticknor and Fields, 156
Tittle, Margaret, 4
“Toccata of Galuppi’s, A,” 120
Trollope, Thomas Adolphus and Theodosia, 59, 111, 112, 190, 229
“Two Poets of Croisic,” 236
“Valediction, A,” 84
Vallombrosa, 98, 99
Villari, Mme. Pasquale, 112
“Virgin Mary to the Child Jesus, The,” 46
“Vision of Poets, A,” 71
Wiedemann, Sarah Anna, 4-6
“Wine of Cyprus,” 23, 86
“Woman’s Last Word, A,” 120
Wordsworth, William, 30, 32, 55, 56, 59, 68, 94
Zampini, Fanny (Contessa Salazar), 161
[1] Letters of Robert Browning and Alfred Domett. New York: Dodd, Mead and Co.
[2] Life of Robert Browning. London: Walter Scott, Limited.
[3] La Vie et l’œuvre de Elizabeth Browning, par Germaine-Marie Merlette; Licencie des lettres; Docteur de l’Université de Paris.
[4] Red Letter Days of my Life. London: Richard Bentley and Son.
[5] “Letters of Robert Browning and Alfred Domett.” New York: Dodd, Mead, and Company.
[6] Robert Browning: Life and Letters. Boston: Houghton, Mifflin, and Company.
[7] “La Vita e le Opere di Roberto et Elisabetta Barrett Browning. Rome: Societa Typografico-Editrice Nazionale.”
[8] William Wetmore Story and his Friends. Boston: The Houghton-Mifflin Co.
[9] Life and Letters of Benjamin Jowett. London: John Murray.
[10] Alfred Lord Tennyson. London and New York: The Macmillan Co.
[11] Life of Phillips Brooks. New York: E. P. Dutton and Co.
[12] Records of Tennyson, Ruskin, and Browning. London: The Macmillan Company.
[13] Life and Letters of Sir John Millais. London: Methuen and Co.
[14] What I Remember. New York: Harper and Brothers.
[15] Alfred Lord Tennyson. London and New York: The Macmillan Company.
[16] William Wetmore Story. Boston: The Houghton-Mifflin Company.
[17] Alfred Lord Tennyson. London and New York: The Macmillan Co.
Transcriber’s note:
Images have been moved from the middle of a paragraph to the closest paragraph break.
Additional spacing after some of the quotes is intentional to indicate both the end of a quotation and the beginning of a new paragraph as presented in the original text.
Some quotes are opened with marks but are not closed. Obvious errors have been silently closed, while those requiring interpretation have been left open.
Other than the corrections noted by hover information, printer's inconsistencies in spelling and hyphenation usage have been retained.
***END OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BROWNINGS***
******* This file should be named 30671-h.txt or 30671-h.zip *******
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/3/0/6/7/30671
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is subject to the trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://www.gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS,' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.gutenberg.org/fundraising/pglaf.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://www.gutenberg.org/about/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://www.gutenberg.org/fundraising/pglaf
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://www.gutenberg.org/fundraising/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Each eBook is in a subdirectory of the same number as the eBook's
eBook number, often in several formats including plain vanilla ASCII,
compressed (zipped), HTML and others.
Corrected EDITIONS of our eBooks replace the old file and take over
the old filename and etext number. The replaced older file is renamed.
VERSIONS based on separate sources are treated as new eBooks receiving
new filenames and etext numbers.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.
EBooks posted prior to November 2003, with eBook numbers BELOW #10000,
are filed in directories based on their release date. If you want to
download any of these eBooks directly, rather than using the regular
search system you may utilize the following addresses and just
download by the etext year.
http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/etext06/
(Or /etext 05, 04, 03, 02, 01, 00, 99,
98, 97, 96, 95, 94, 93, 92, 92, 91 or 90)
EBooks posted since November 2003, with etext numbers OVER #10000, are
filed in a different way. The year of a release date is no longer part
of the directory path. The path is based on the etext number (which is
identical to the filename). The path to the file is made up of single
digits corresponding to all but the last digit in the filename. For
example an eBook of filename 10234 would be found at:
http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/1/0/2/3/10234
or filename 24689 would be found at:
http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/2/4/6/8/24689
An alternative method of locating eBooks:
http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/GUTINDEX.ALL
*** END: FULL LICENSE ***