
The Project Gutenberg EBook of John Hus, by William Dallmann
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: John Hus
A brief story of the life of a martyr
Author: William Dallmann
Release Date: July 25, 2008 [EBook #26129]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK JOHN HUS ***
Produced by Juliet Sutherland, D Alexander and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at https://www.pgdp.net

by

 JOHN HUS
JOHN HUS
| PAGE | ||
| 1. | The Youth of Hus | 1 |
| 2. | Wiclif's Influence on Hus | 5 |
| 3. | Hus is Opposed | 6 |
| 4. | Hus Offends the Clergy | 6 |
| 5. | Hus Again Rector | 8 |
| 6. | Hus is Accused to the Pope | 10 |
| 7. | Hus Opposes the Pope | 15 |
| 8. | Hus is Excommunicated | 17 |
| 9. | Hus in Exile | 18 |
| 10. | The Council of Constance is Called to Convene | 20 |
| 11. | Hus Arrives at Constance | 22 |
| 12. | Hus in Prison | 28 |
| 13. | Hus Before the Council | 35 |
| 14. | Hus Again Before the Council | 38 |
| 15. | Hus Once More Before the Council | 40 |
| 16. | Hus Prepares for Death | 45 |
| 17. | Hus Condemned | 48 |
| 18. | Hus Degraded | 51 |
| 19. | Hus Made Over to the Emperor | 55 |
| 20. | Hus Burned | 55 |

In a humble hamlet in the southern section of beautiful Bohemia near the Bavarian border of poor peasant parents was born a boy and called Jan—Hus was added from Husinec, his birthplace; some say he saw the light of day on July 6, 1373, but that is not certain.
When about sixteen Hus went to the University of Prag, the first one founded in the German empire by Charles IV in 1348. Here he sang for bread in the streets, like Luther after him, and often had to go to sleep hungry on the bare ground.
 WHERE HUS WAS BORN
WHERE HUS WAS BORN
Though many of the thousands of students from all parts of Europe were rowdies and immoral, the behavior of Hus was excellent and his diligence great. He took part in the rough sports; sometimes he played chess and even won money prizes.[Pg 3] To the day of his death none of his many bitter enemies even so much as breathed a suspicion on his pure life. When pardons for sins were publicly sold during a jubilee in 1393, the devout young student gave up his last four pennies to secure this heavenly favor from the Pope.
Jerome of Prag was a fellow student.
In 1393, at a very early age, Hus was made a Bachelor of Arts; in 1394, a Bachelor of Theology; in 1396, a Master of Arts; like Melanchthon, he never took his degree as Doctor of Theology. In 1400, Hus was ordained a priest; in 1401, appointed Dean of the Philosophical Faculty; in 1402, chosen Rector of the University—at an unusually early age. In the same year he became preacher at the important Bethlehem chapel, seating about 1,000 worshipers, founded by John of Milheim in 1391, that the people might hear the Word of God in their own language.
From the very first the powerful preacher made his pulpit potent and popular, even among the nobility; Queen Sophia was a frequent worshiper, made him her confessor, and had him appointed court chaplain.
 BETHLEHEM CHAPEL
BETHLEHEM CHAPEL
When Anne, the daughter of Emperor Charles IV, and sister of King Wenzel of Bohemia and of King Sigismund of Hungary, was married to King Richard II of England in 1382, there was much travel between Bohemia and England, and Jerome of Prag brought the writings of Wiclif from Oxford. They spread like wild fire, deeply impressed Hus, and made him an apt pupil and loyal follower of the great "Evangelical Doctor." He saw the dangers ahead and said in a sermon: "O Wiclif, Wiclif, you will trouble the heads of many!"
Converted by missionaries from Greece, the Bohemians never felt quite so dependent on Rome. They had the Bible translated in their own language; Queen Anne took with her the Gospels in Latin and German and Bohemian. In addition Milic of Kremsier and Matthias of Janov had but recently fiercely denounced the wicked lives of popes and prelates and priests. So it came that the teaching of Wiclif and the preaching of Hus fell upon the Bohemian soul as upon a prepared soil.
On May 28, 1403, Master John Huebner in the Church of the Black Rose called attention to certain condemned statements of Wiclif—many of which had been forged. Hus cried out the falsifiers ought to be executed the same as recently the two adulterators of food. After a stormy debate in the great hall of the Carolinum, a majority of the professors forbade the public and private teaching of these articles, forty-five in all.
The decree produced no effect, and the opponents of Hus got Pope Innocent VII to order the Archbishop to root out the heresy of Wiclif, in 1405.
In 1405, Archbishop Sbynko appointed Hus the Synodal preacher, and he often with fierce and fiery fervor severely scored the avarice and immorality of the clergy. He held sin no more permitted to a clergyman than to a layman, and indeed more blameworthy—a most astonishing novelty, [Pg 7]especially to the priesthood. They honored him with their undying hatred.
About this time two followers of Wiclif, James and Conrad of Canterbury, came to Prag and in their house outside the city painted a cartoon contrasting the lowly Christ and the proud pope. Crowds went to view it, and Hus recommended it from the pulpit as a true representation of the opposition between Christ and Antichrist. Later Luther edited similar cartoons—"Passional of Christ and Antichrist."
When amid the wreckage of a church at Wilsnack in Brandenburg a red wafer was found, it was proclaimed the blood of Christ, preserved through thirteen centuries or sent direct from heaven, had baptized and reddened the white wafer, or host. The miracle drew many pilgrims from even distant countries to be cured of their incurable diseases; of course, they left much money to the pious priests. Hus condemned this coarse fraud, and Archbishop Zbynek, or Sbynko, forbade the pilgrimages from his diocese.
In order to justify his step, Hus wrote a book asserting a Christian need not seek for [Pg 8]signs and miracles but need only hold by the Holy Scriptures.
Hurt in pride and pocket, the enraged clergy lodged complaints against Hus as a pestiferous heretic, who had to be suppressed; he lost his position as the Synodal preacher in 1408.
Since 1378, there were two sets of rival popes most lustily pelting one another with papal curses. The Council of Pisa in 1409 deposed popes Benedict XIII and Gregory XII as heretics and schismatics and then elected Alexander V, who died on May 11, 1410, most probably poisoned by "Diavolo Cardinale" Cossa, who then became Pope John XXIII. Now there were three popes and a three-cornered fight. To make the good old times still more interesting, three rivals struggled for the crown of the Holy Roman Empire.
 POPE ALEXANDER V
POPE ALEXANDER V
Though King Wenzel demanded strict neutrality, Archbishop Sbynko sided with Gregory XII, and at the University the Bohemian "nation" under the lead of Hus was the only one to remain neutral. Wenzel[Pg 10] was bitter and on Jan. 18, 1409, decreed the Bohemian "nation" three votes and the three German "nations" one vote in all University affairs.
Aeneas Sylvius, later Pope Pius II, estimates that 200 German professors and students on May 16, 1409, left Prag and founded the University of Leipzig and spread the news of the Bohemian heresies and hatred of Hus.
At Prag Hus was now at the height of his influence, enjoying the favor of the Court; he was again elected Rector of the University.
Now Archbishop Sbynko went over to the rival pope, Alexander V, and convinced him that all the troubles in Bohemia were due to the teachings of Wiclif spread by Hus. These teachings, he said, made the clergy disobedient and led them to ignore the authority of the Roman Church, made the laity think it was for them to lead the clergy, encouraged the King to lay hands on the property of the Church.
 KING WENZEL OF BOHEMIA
KING WENZEL OF BOHEMIA
As a result Alexander V sent a bull on[Pg 12] Dec. 20, 1409, ordering the Archbishop to suppress all books of Wiclif and all preaching except at the usual places; this last was to silence Hus in Bethlehem Chapel.
On July 16, 1410, the Archbishop burned two hundred manuscripts of Wiclif, many of them in costly binding; two days later he excommunicated Hus and his followers.
 POPE JOHN XXIII
POPE JOHN XXIII
This caused an indescribable sensation all over, in some places serious riots resulted. The publishers of the excommunication were in danger of their lives. The King compelled the Archbishop to pay damages to those whose manuscripts had been burned. Hus defended the writings of Wiclif in public debates. The Wiclifites in England were delighted. Hus wrote them: "The whole Bohemian people thirst for the truth, it will have nothing but the Gospel and the Epistles, and wherever in a city or village or castle a preacher of the holy truth appears, the people stream together in great crowds. Our king, all his court, the barons, and the plain people favor the word of Christ." Hus continued to preach in the Bethlehem Chapel in ever bolder tones. He said: "We must obey God rather than men in things which are necessary for salvation."[Pg 14] Against the authority of the Church Hus placed the individual conscience. The decisive step of a breach with the Papal system had been taken.
Hus, the King, and the Queen repeatedly appealed to the new Pope, but John XXIII twice confirmed the sentence of Pope Alexander V; Hus was declared a heretic and Prag placed under interdict. This was done on the advice of Cardinal Otto Colonna, later Pope Martin V. Hus was summoned to appear before the Pope. Hus did not appear; he was pronounced excommunicated in February 1411, published in Prag on March 15, 1411.
The bold preacher said: "I avow it to be my purpose to defend the truth which God has enabled me to know, and especially the truth of the Holy Scriptures, even to death, since I know that the truth stands and is forever mighty and abides eternally; and with Him there is no respect of persons. And if the fear of death should terrify me, still I hope in my God and in the assistance of the Holy Spirit that the Lord will give me firmness. And if I have found favor in His sight He will crown me with martyrdom."
In June the King's commission requested the removal of the interdict. On September 28, the Archbishop died; they say he poisoned himself. In the attempt to sacrifice Hus, he sacrificed himself.
On Dec. 2, 1411, Pope John XXIII decreed a crusade against King Ladislas of Naples, who favored the rival Pope Gregory XII, "the heretic, blasphemer, schismatic," as John called him, and offered a plenary indulgence, or forgiveness of sins, to all who would give money for the war.
Tiem, the papal pedler, like Tetzel a century later, caused trouble. He came to Prag and with beating of drums ordered the people into the churches, where contribution boxes had been placed; even the confessional was abused to extort money from the people.
In the University and in the Church Hus protested against this shameless business. On June 7, 1412, there was a great disputation on the subject in the large hall of the Carolinum. Hus held no pope or bishop had the right to draw the sword in the name [Pg 16]of the Church, he must pray for his enemies and bless them that curse him. Man gets forgiveness of sins through real sorrow and repentance, not through money. Unless one be of the elect, the indulgence will do him no good. If the Pope's bulls are against the Bible, they are to be resisted.
Jerome also made a stormy speech, and the younger scholars escorted him home in triumph.
On June 24, there was an uproarious procession, and a crowd burned the Pope's bull.
The King threatened death for speaking against the indulgence.
On Sunday, July 10, three young men in church called the indulgence a lie. Hus and thousands of students pleaded for them. The magistrates made fair promises, but on Monday the three young men were executed. They were buried in Bethlehem Chapel, which the people now called the "Church of the Three Saints." The Reformation had won its first martyrs.
King Wenzel now forbade the preaching of Wiclif's teaching. Hus demanded it be proven against the Bible, and proceeded to prove it in accordance with the Bible.
The riots at Prag caused a disagreeable sensation in all Bohemia, but all efforts for peace were vain.
Pope John XXIII turned the case of Hus over to Cardinal Annibaldi, who promptly pronounced the greater excommunication against Hus: if within twenty days he did not submit to the Church, none were to speak to him or receive him into their houses; all church services were to cease when he was present, and the sentence was to be read in all churches in all Bohemia on all Sundays. A second decree ordered all the faithful to seize Hus and deliver him to be burned; Bethlehem Chapel was to be leveled with the ground.
As Bishop Robert Grosseteste of Lincoln before him, Hus now appealed from the Pope to Jesus Christ, the Supreme Head of the Church.
The excitement grew greater. Bloody conflicts loomed ahead. On the royal request Hus left Prag in the autumn of 1412.
As later Luther in the Wartburg, so Hus now found shelter in the castle of the Lord of Usti, and later with Henry of Lazan in his castle of Cracowec.
Hus had a rare gift of persuasion, and wherever he preached, in city or country, everybody became his follower; he was the pastor of his people; his immense popularity clings to his memory to the present day.
Besides much preaching, the exile did much writing. He revised a Bohemian translation of the Bible of the fourteenth century and thereby greatly improved the popular language, much like Luther with his German Bible. He guarded the purity of his Bohemian language against the foreign, disfiguring influences. He labored to establish fixed rules of grammar and invented a new system of spelling, which is in general use today! He wrote letters, tracts, poems, and hymns. His chief work was "On the Church," based on Wiclif, often to the word and letter.
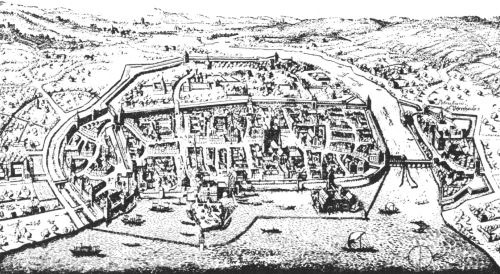 CONSTANCE ON THE RHINE
CONSTANCE ON THE RHINE
The excitement in Prag continued. The King convened the Estates of the realm for[Pg 20] Christmas, 1412. These called for a Synod, which met Feb. 2, in the Archbishop's palace at Prag; it was a failure. The King had a Commission continue the work of peace in April, 1414. The papists held the Pope the Head of the Church, the Cardinals the body of the Church, and all commands of this Church are to be obeyed. Of course, Hus and his followers could not accept such monstrously wicked teaching. On the contrary, Hus held it the duty of kings to restrain the wickedness of the clergy and root out simony.
King Sigismund and Pope John XXIII, the two vilest men then living on the face of the earth, were the rulers of the Christian world, and they agreed to call a General Council at Constance, in Baden, near Switzerland, for Nov. 1, 1414, in order to end the Schism, to begin the sorely needed reform of the Church, and to settle the heresies of Wiclif and Hus.
 THE EMPEROR SIGISMUND
THE EMPEROR SIGISMUND
Heir to his childless brother Wenzel's Bohemian crown, King Sigismund of Hungary[Pg 22] was naturally anxious to have the stain of heresy removed from the fair land that was now the talk of the world, and he ordered three Bohemian noblemen to protect Hus on his way to Constance, during his stay at the Council, and on his return to Bohemia.
Even Divucek, one of Sigismund's envoys, warned Hus, "Master, be sure that thou wilt be condemned."
Thinking he was going to his death, Hus put his house in order, got a certificate of orthodoxy from his bishop, and bade farewell to his people—"Beloved, if my death ought to contribute to the Master's glory, pray that it may come quickly and that He may enable me to support all my calamities with constancy. You will probably nevermore behold my face at Prag."
He set out on Oct. 11, as boldly as later Luther to Worms.
On his journey Hus was everywhere welcomed heartily and at Biberach even triumphantly. He reached Constance, a beautiful city of fifty thousand inhabitants,[Pg 24] on Nov. 3, and found lodgings with Fida, "a second widow of Sarepta," in St. Paul St.,—now Hus St.—near the Schnetz Gate, not far from the abode of Pope John XXIII. On the same day came the historic and notorious safe-conduct of Sigismund—"The honorable Master John Hus we have taken under the protection and guardianship of ourselves and of the Holy Empire. We enjoin upon you to allow him to pass, to stop, to remain and to return, freely and without any hindrance whatever; and you will, as in duty bound, provide for him and for his, whenever it shall be needed, secure and safe conduct, to the honor and dignity of our Majesty." Dated at Speyer, October 18, 1414.
 HOUSE WITH TABLET WHERE HUS LODGED AND THE SCHNETZ GATE.
HOUSE WITH TABLET WHERE HUS LODGED AND THE SCHNETZ GATE.
John XXIII with piratical pomposity promised the papal protection: "Even if Hus had killed my own brother, he shall be safe in Constance."
With the Emperor Sigismund came twenty princes and one hundred and forty counts. The Pope had been a pirate; at Bologna he had plundered and oppressed his people and sold licenses to usurers, gamblers, and prostitutes; his cruelty thinned the population; in the first year as [Pg 25]legate at Bologna he outraged two hundred maidens, wives, or widows, and a multitude of nuns; at least so Catholic historians say.
With this holy father there came to the Council twenty-nine cardinals, seven patriarchs, over three hundred bishops and archbishops, four thousand priests, two hundred and fifty university professors, besides Greeks and Turks, Armenians and Russians, Africans and Ethiopians, in all from sixty to a hundred thousand strangers, and thirty thousand horses.
In order to amuse these godly fathers amid their grave labors there came seventeen hundred artists, dancers, actors, jugglers, musicians and—prostitutes, seven hundred public ones, not counting the private ones.
Hus wrote: "Would that you could see this Council, which is called most holy and infallible; truly you would see great wickedness, so that I have been told by Suabians that Constance could not in thirty years be purged of the sins which the Council has committed in the city."
These men of sin, who kissed the toe of Pope John XXIII, a man of sin, burned the saintly Hus; no wonder he likened them to [Pg 26]the scarlet whore of the Revelation. At one stage of the holy and infallible Council these learned fathers used arguments that strike us as rather striking: a cardinal assaulted an archbishop; a patriarch hit a protonotary; a Spanish prelate hurled an Englishman into the mud; the English were caught in arms to assault Pierre d'Ailly, the Cardinal of Cambray. As members of the Church militant they were certainly fighting a good fight.
Sigismund burnt Hus as a Wiclifite, the next year the Council called the Emperor a Wiclifite and Hussite and heretic. Pope John XXIII condemned Hus as a heretic, soon after he was a prisoner in the same prison with Hus. Dramatic!
 PIERRE D'AILLY
PIERRE D'AILLY
John Gerson, the celebrated Chancellor of the great University of Paris and "Doctor Christianissimus," and Pierre d'Ailly, the great Cardinal of Cambray, accused Hus of heresy; later on themselves were accused of heresy by the same Council. Gerson declared Hus had never been sentenced had not an attorney been denied him, and himself would rather be tried by Jews and infidels than before the commission. Such [Pg 28]were the men that were to try a man such as Hus.
As Paul preached in his own hired house under the very palace of Nero, so Hus preached Christ to all who came to his humble house and with a few friends maintained daily worship, close to the Pope's palace. Greater than emperors and popes, princes and prelates from all Europe that crowded Constance, was the humble Bohemian Hus; they are seen today mainly in the light shed from his shining name.
Despite the royal safe-conduct and the promised papal protection, Hus was flung into prison in a prelate's palace on Nov. 28.
John of Chlum forced his way into the papal apartments and charged the holy ex-pirate Pope John XXIII to his infallible face with having broken his sacred papal promise, and then fixed on the doors of the Cathedral a solemn protest against the papal perfidy and the shameless violation of the royal safe-conduct.
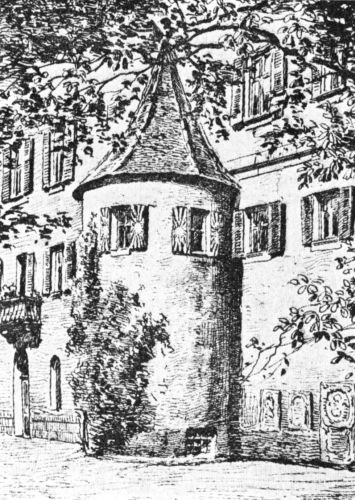 HUS TOWER
HUS TOWER
On Dec. 6, Hus was dragged to the Dominican[Pg 30] convent on an island in Lake Constance, and stuck into a dark hole at the opening of a sewer, where he was struck down by a violent fever, so that his life was despaired of, and the Pope sent his own physician.
Crowned in Aachen on Nov. 8, as Emperor of Germany, Sigismund arrived in Constance on Christmas and seated himself in his imperial robes on his throne in the cathedral during the imposing religious service.
The Emperor read the Gospel for the day from Luke 2: 1—"There went out a decree from Caesar Augustus." The Pope trembled as he saw before him the successor to the throne and power of Caesar.
Near the Emperor sat the Empress; beside him stood the Markgraf of Brandenburg with the scepter; the Duke of Saxony, as marshal of the realm, held aloft a drawn sword; between the Pope and the Emperor stood his father-in-law, Count Cilley, holding the golden globe; the Pope handed the Emperor a sword with the charge to use it in defence of the Church, which Sigismund promised to do.
When the Emperor heard his safe-conduct [Pg 31]had been disgracefully broken, he blustered. The Pope insisted the Emperor had no right to interfere in the treatment of a pestilent heretic. The Emperor broke his sacred word and sacrificed Hus to his enemies.
This treachery cost him the kingdom of Bohemia. The Holy Synod defended Sigismund, declaring "no faith whatever, either by natural, human or divine right, ought to be observed toward a heretic."
On the same day, New Year, 1415, the Emperor also sacrificed the Holy Father, John XXIII.
About the first of March Hus was taken to the Franciscan convent near the Pope's dwelling and fed from the Pope's kitchen, that is, he was almost starved; on March 20, the Pope fled, and Hus had to go without food for three days.
 CASTLE OF GOTTLIEBEN ON THE RHINE
CASTLE OF GOTTLIEBEN ON THE RHINE
Did the Emperor release Hus, now that the Pope was fled? On March 25, the Emperor turned Hus over to the Bishop of Constance, who imprisoned him in his Castle of Gottlieben in a chamber so low Hus could not stand upright. He was handcuffed by day and chained to the wall by night, poorly fed, and separated from his [Pg 33]friends; and this went on for seventy-three days!
"The holy and infallible Council," as the Pope called it, brought against the infallible Pope seventy-two charges—the murder of Pope Alexander V, rape, adultery, sodomy, incest, simony, corruption, poisoning, denying the resurrection and eternal life, etc., etc.
Though hostile to the Pope personally, the Patriarch of Antioch quoted Gratian that if a Pope, by his misconduct and negligence, should lead crowds of men into hell, no one but God would be entitled to find fault with him.
The Pope promised to resign, and the Emperor joyfully kissed the toe of John XXIII and thanked him in the name of the Council.
 MONUMENT TO POPE JOHN XXIII
MONUMENT TO POPE JOHN XXIII
The Council considered the charges proved and on May 25, 1415, deposed him as "the supporter of iniquity, the defender of simonists, the enemy of all virtue, the slave of lasciviousness, a devil incarnate." The Bishop of Salisbury thought he ought to be burnt at the stake. And yet this precious prelate was made a cardinal and after his death at Florence on Nov.[Pg 35] 23, 1419, an exquisite monument by Donatello was erected in 1427 to his saintly memory.
When the Council deposed John XXIII, Hus wrote: "Courage, friends! You can now give answer to those who declare that the Pope is God on earth; that he is the head and heart of the Church; that he is the fountain from which all virtue and excellence issue; that he is the sun, the sure asylum where all Christians ought to find refuge. Behold this earthly god bound in chains!"
On June 3, Pope John XXIII was a prisoner in the same prison with Hus!
On May 4, Wiclif's writings were ordered to be burnt as heretical; his memory was condemned, and it was decreed to dig out his bones and cast them out of consecrated ground. It does not need a prophet to foretell the end of Hus. It needed only to show Hus was a follower of Wiclif, and he would be burned also.
Though the Bohemians and Moravians earnestly protested against the harsh [Pg 37] treatment of Hus and demanded his release, he was not released. On June 5, he was brought to the Franciscan cloister, between the Cathedral and St. Stephen's Church, where he spent his last days on earth.
 CATHEDRAL OF CONSTANCE
CATHEDRAL OF CONSTANCE
In the afternoon, bearing his chains, he was brought before the Council. He admitted the authorship of his books and declared himself ready to retract every expression that could be proved wrong.
The first article was then read. When Hus tried to reply, he was bellowed into silence. When he was silent, they said, Silence gives consent.
Socrates was allowed to make a long defence before his heathen judges; Hus was overwhelmed with angry outcries by the representatives of all Christendom!
Luther commented: "All worked themselves into a rage like wild boars. The bristles of their backs stood on end; they bent their brows and gnashed their teeth against John Hus."
Hus protested: "I supposed that there would have been more fairness, kindness, and order in the Council." Hus asked wherein he had erred. "Recant first, and [Pg 38]then you will be informed!" Thus ended the first hearing.
When a synod would condemn Wiclif's writings in May, 1382, an earthquake delayed the decision, and when the Council on June 7, 1415, would condemn Hus, a total eclipse of the sun delayed the proceeding. At one o'clock the sky was clear and Hus was again brought in, again in chains, and under guard. He was accused of denying the presence of Christ's body in the sacrament. Hus repelled the charge and stuck to it against the famous Pierre d'Ailly of Cambray and many other French and Italian prelates, and he did it so stoutly that the British objected: "This man, so far as we see, has right views as to the sacrament of the altar." Violent disputes arose. As the Roman captain had to interfere when Paul stood before the factions of the Jewish Sanhedrin, so the Emperor Sigismund had now to exercise his authority and command and compel order in the grave and reverend holy Council. Hus could not with a good conscience condemn[Pg 40] all of Wiclif's writings until they were proven against Holy Scriptures, and such was his admiration of the stainless life of the man, that he wished his soul might be where Wiclif's was.
 THE INTERIOR OF THE CATHEDRAL
THE INTERIOR OF THE CATHEDRAL
Renewed jeers and derision. Pierre d'Ailly advised Hus to submit to the Council; the Emperor likewise, since he would not protect a heretic; rather would he with his own hands fire the stake.
"I call God to witness ... that I came here of my own accord with this intent—that if any one could give me better instruction I would unhesitatingly change my views."
In the final hearing, on June 8, thirty-nine articles from his books were brought against Hus, twenty-six of them from his "On the Church." He was charged with teaching that only the electing grace of God made one a true member of the Church, not any outward sign or high office. This God's truth was condemned as false by the Council.
Hus held the Pope a vicar of Christ only [Pg 41]as he imitates Christ in his living; if he lives wickedly, he is the agent of Antichrist.
The prelates looked at one another, shook their heads and laughed. If Hus was to be burned for only saying that, what did they deserve for actually imprisoning the Pope?
Hus held the Pope's temporal power came from the (forged) donation of the Emperor Constantine, not from Christ, and stoutly stuck to it against the great Cardinal of Cambray.
Hus had spoken and written plainly against the wicked lives of prelates and popes, and for this he was to be burned, although d'Ailly and Gerson also had done so, and this very Council had deposed a vile wretch, Pope John XXIII.
Another heresy of Hus was this: "A heretic ought to be first instructed kindly, justly, and humbly from the Sacred Scriptures," then he may be burned.
"All those who give up to the civil sword any innocent man, as the scribes and Pharisees did Christ," are like the Pharisees.
 HUS BEFORE THE COUNCIL, BY BROZIK
HUS BEFORE THE COUNCIL, BY BROZIK
The Prelates felt the thrust. "You mean[Pg 43] to condemn the dignitaries of the Church!" For this they would burn Hus.
Hus said an evil nature cannot do good. In a state of grace, however, the man, whether he eat or drink or sleep, does everything to the glory of God. This plain truth of God was damned as heresy!
Hus was charged with calling an unjust excommunication a benediction. "In truth, I say the same thing now, according to that Scripture, 'They shall curse, but Thou shalt bless'."
Another heresy ran thus: "If pope, bishop or prelate be in mortal sin, then is he no longer pope, bishop or prelate." Hus defended it by asking pointedly: "If John XXIII was a true pope, why did you depose him from his office?"
Hus said the Church did not need an earthly head, a pope; Christ, the true head, can rule His church better without the popes, who were often monsters of iniquity. Shouts of derision!
Hus calmly added the telling point: "Surely the Church in the times of the Apostles was infinitely better ruled than now. At present we have no such head at all."
He could not be answered, and so he was derided.
An Englishman correctly pointed out that this was the teaching of Wiclif. That was ample to damn Hus as a heretic.
Pierre d'Ailly said to the Emperor Sigismund: "Almost all the articles are based on Wiclif, so that the Englishman John Stokes was right in saying Hus had no right to boast of these teachings as his property, since they all demonstrably belonged to Wiclif."
In order to embitter the Emperor against Hus, they tried to show his teachings to be dangerous to the civil government. Finally d'Ailly advised Hus to submit to the Council. Hus again said he was open to conviction. He only asked for a hearing to explain and prove his doctrines. If his reasons and Bible proofs were not sufficient, he would be ready to be taught better.
The Cardinal said: "You have only to perform the three conditions required of you—to confess your errors, to promise not to teach them hereafter, and to renounce all the articles charged against you."
Sigismund also again urged Hus to submit, [Pg 45]and said, in effect: "Recant now, or die."
Hus humbly but firmly refused to do anything against his conscience; he asked for proof from God's word, then he would submit.
"I stand before the judgment of God; He will judge me and you in righteousness, as we deserve it."
As Hus was led back to prison, John of Chlum, a Bohemian nobleman, shook hands with him, just as Frundsberg comforted Luther at Worms.
Sigismund hounded on the prelates to make an end of Hus, even if he recanted. This lost him the Bohemian crown for ever.
Hus had about a month after the trial to await the end. He remembered his and his friends' forebodings, and wrote bitterly: "Put not your trust in princes. I thought the Emperor had some regard for law and truth; now I perceive that these weigh little with him. Truly did they say that Sigismund would deliver me up to my adversaries: he has condemned [Pg 46]me before they did. Would that he could have shown me as much moderation as the heathen Pilate."
He wrote a touching farewell letter to his beloved flock in the Bethlehem Chapel and another to the University at Prag.
After Hus had left Prag, Jacobellus of Mies began to give the cup as well as the bread to the lay communicants. The General Council on June 15, admitted Christ had instituted the Lord's Supper in the two species of bread and wine, yet it decreed to burn as heretics all who did as Christ commanded.
Hus on June 21, writes to Gallus (Havlik), preacher at the Bethlehem Chapel: "What wickedness! Behold, they condemn Christ's institutions as heresy!"
Till the end of June they made many efforts to get Hus to recant; he firmly refused: "I cannot recant; in the first place, I would thereby recant many truths, and in the second place, I would commit perjury and give offence to pious souls. I stand at the judgment-seat of Christ, to whom I have appealed, knowing that He will judge every man, not according to false witness, but according to the truth and each one's [Pg 47]deserts." Against the authority of men Hus asserted the authority of his conscience enlightened by the Holy Scriptures.
On July 1, Hus was brought out again to recant his heresies. He replied in writing: "I, John Hus, fearing to sin against God, and fearing to commit perjury, am not willing to abjure ... any of them."
On July 5, a deputation of some of the most eminent members of the Council made a final effort to get Hus to recant. Wenzel of Duba said: "Behold Master John, I am a layman and cannot give advice. Consider then if thou feelest thyself guilty of any of the things of which thou art accused. If so, do not hesitate to accept instruction and recant. But if thou dost not feel guilty of these things that are brought forward against thee, be guided by thy conscience, do nothing against thy conscience, nor lie before the face of God; rather hold unto death to the truth as thou hast understood it."
Hus answered in tears: "Be it known to you that if I knew I had written or preached anything against the law and holy Mother Church, I would humbly recant; may God be my witness to this; but I always desired [Pg 48]that they should show me doctrines better and more credible than those I have written and taught. If such be shown me, I will gladly recant."
A bishop sneered: "Wilt thou then be wiser than the whole Council?"
Master Hus replied: "I do not claim to be wiser than the whole Council, but, I beg you, give me the least man at the Council that he may instruct me out of the word of God, and I am ready to recant at once."
"Behold, how obstinate he is in his heresy!"
On Saturday, July 6, the Council had great scruples in condemning the Duke of Burgundy, a self-confessed would-be assassin, but it had absolutely no scruples in condemning the blameless patriot reformer of Bohemia.
"Dressed in black with a handsome silver girdle, and wore his robes as a Magister"—Hus was led after Mass before the whole Council in the cathedral. He kneeled and prayed fervently for several minutes. James Arigoni, Bishop of Lodi, preached from [Pg 49]Rom. 6:6—"That the body of sin might be destroyed." Henry de Piro proposed that Hus be delivered to the civil power for burning.
Sixteen charges from Wiclif's writings were read. When Hus tried to explain, he was brutally refused. Thirty articles from Hus' own works were then read. He attempted to speak, but was stopped by loud cries, despite the admonition of the Bishop of Constance.
Hus knelt down and cried: "I beg you, in the name of God, to grant me a hearing, that those who are present may not think I am a heretic. After that deal with me as you see fit."
They threatened to silence him forcibly by the soldiers. He continued to kneel and pray with uplifted face to God, the just Judge.
Hus was next charged with saying, "that he was and would be a Fourth Person in the Trinity."
Even the Roman Catholic Hefele admits the absolute falsehood of this infamous accusation.
When his appeal to Christ was condemned as a damnable heresy, Hus cried out: "O [Pg 50]God and Lord, now the Council condemns even Thine own act and Thy law as heresy, for Thou Thyself didst commend Thy case into the hands of Thy Father as the righteous judge."
Charged with treating the papal excommunication with contempt, Hus replied he had three times sent representatives to the papal court and had never had a hearing. "For this reason I came freely to this Council, relying upon the public faith of the Emperor, who is here present, assuring me that I should be safe from all violence, so that I might attest my innocence and give a reason of my faith to the whole Council."
As he spoke of the safe-conduct, the prisoner looked straight at the Emperor; the Emperor blushed. That blush was never forgotten. Urged to betray Luther at Worms, the Emperor Charles V said: "I should not like to blush like Sigismund."
"A bald and old Italian priest" then read the two decrees of the Council that all the writings of Hus, both Latin and Bohemian, should be destroyed, and that Hus as a true and manifest heretic was to be burned.
Hus loudly protested: "Up to now you [Pg 51]have not proved that my books contain any heresies. As to my Bohemian writings, which you have never seen, why do you condemn them?"
Hus again knelt and prayed with a loud voice: "Lord Jesus Christ, forgive all my enemies, I entreat Thee, because of Thy great mercy. Thou knowest that they have falsely accused me, brought forth false witnesses against me, devised false articles against me. Forgive them because of Thy boundless mercy."
This touching prayer was greeted with derisive laughter by the foremost ecclesiastical dignitaries.
The priestly robes were now put on Hus, and the sacramental cup into his hands. When the white robe, the alb, was put on, Hus said: "My Master Christ, when He was sent away by Herod to Pilate, was clothed in a white robe."
 HUS DEGRADED, BY MARTERSTEIG
HUS DEGRADED, BY MARTERSTEIG
He was once more urged to swear off his errors. Turning to the people with tears in his eyes and emotion in his trembling[Pg 53] voice—"How could I thus sin against my conscience and divine truth alike?"
As they took off his priestly robes, the Archbishop of Milan said: "O cursed Judas, who hast left the realms of peace and allied thyself with the Jews, we today take from thee the chalice of salvation."
"I hope to drink of the chalice in the heavenly kingdom this day."
The holy fathers of the General Council of all Christendom then gravely and learnedly debated whether to use shears or a razor to remove the tonsure. Finally they decided for the shears, and his hair was cut to leave bare the form of a cross. Next his head was washed, to remove the oil of anointing, by which he had been consecrated to the priesthood.
A paper cap, two feet high, painted with three ghastly devils tormenting a soul, and with the words, "This is a heretic," was placed on his head; Hus remarked: "My Lord Jesus Christ wore for me a crown of thorns; why should I not for His sake wear this easier though shameful badge?"
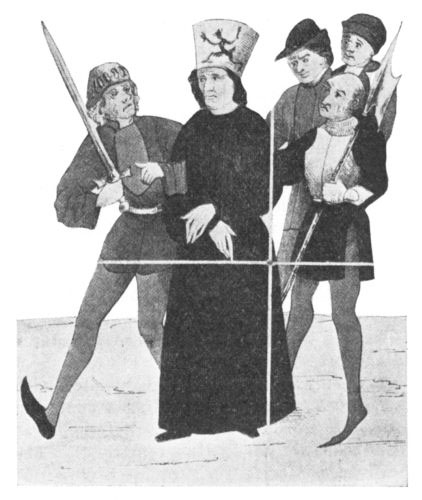 HUS WITH THE HERETIC'S CAP
HUS WITH THE HERETIC'S CAP
Doomed by the Church, Hus was now made over to the Emperor, with the usual hypocritical prayer that he might not be put to death.
Sigismund said: "Sweet Cousin, Duke Louis, Elector of the Holy Roman Empire and our High Steward, since I bear the temporal sword, take thou this man in my stead and treat him as a heretic."
The "sweet cousin" called the warden of Constance: "Warden, take this man, because of the judgment against him, and burn him as a heretic." Others added: "And we give thy soul over to the devil."
"And I commit my soul to the Lord Jesus Christ."
The Warden made him over to the executioner, who led Hus out under a strong guard, escorted by eight hundred armed men, followed by an immense multitude of people curious to see the final scene.
In the church-yard they were just burning the books of Hus; he smiled sadly.[Pg 57] With a firm step, singing and praying, Hus went to the "Bruehl," a quarter of a mile north of the Schnetz gate. There he knelt, spread out his hands, lifted up his face, and prayed with a loud voice: "Into Thy hands I commit my spirit."
 HUS LED TO DEATH, BY HELLQUIST
HUS LED TO DEATH, BY HELLQUIST
The paper cap, "the crown of blasphemy," as it was called, fell to the ground, and Hus noticed the three painted devils; smiling sadly, he said: "Lord Jesus Christ, I will bear patiently and humbly this horrible and shameful and cruel death for the sake of Thy Gospel and the preaching of Thy word."
He was stripped of his clothes, his hands roped behind his back, his neck chained to the stake, wood and straw were piled around him neck-high. They say as an old woman brought her few fagots to the funeral pile, Hus cried out: "O sancta simplicitas!"—O holy simplicity. Another story goes Hus said: "Today you are burning a goose (hus in Bohemian); in a hundred years will come a swan you will not burn." This came true in Luther.
In the last moment the Marshal of the realm, Pappenheim, called on Hus to recant and save his life. "God is my witness [Pg 58]that I never taught of what false witnesses accuse me. In the truth of the Gospel, that I have written, taught, and preached, I will today joyfully die."
The fagots were lighted. With raised voice Hus sang: "O Christ, Thou Son of the living God, have mercy on me." When he sang that and continued, "Thou that art born of the Virgin Mary," the wind drove the flames into his face; his lips and head still moved; then he choked without a sound.
As the flames flickered down, the executioners knocked over the stake with the charred body still dangling by the neck, heaped on more wood, poked up the bones with sticks, broke in the skull, ran a sharp stake through the heart, and set the whole ablaze again. The jumbled embers were thrown into a wheelbarrow and tipped into the Rhine.
Like Luther later, Hus placed his conscience above the mighty Emperor, the infallible Pope, and the learning of the world; he would rather die than lie.
 JEROME OF PRAG
JEROME OF PRAG
Even Aeneas Sylvius, later Pope Pius II, afterwards said with admiration: "No one[Pg 60] of the ancient Stoics ever met his death more bravely."
A year later, on May 30, on the same spot in the same clover field they burned Jerome of Prag. He went to his death with a smiling face. "You condemn me, though innocent. But after my death I will leave a sting in you. I call on you to answer me before Almighty God within a hundred years."
When the fagots were lighted, he sang the Easter hymn, "Hail, Festal Day," and protested his innocence to the bystanders. His last words were in Bohemian, "God Father, forgive me my sins."
A great stone marks the spot where the two Bohemian saints ascended to heaven in chariots of fire.
The words of Erasmus might well have been his epitaph—"John Hus, burned, not convicted." Lechler says: "To inflict defeat by meeting defeat, that was his lot."
Wiclif and Hus are the constellation "Gemini," or Twins, shining in the papal night till their dim twinkling is swallowed up in the glorious sun bursting from Wittenberg in Luther.
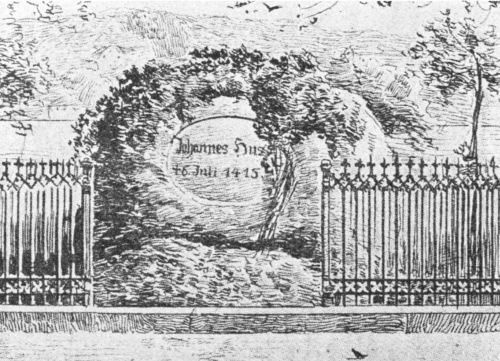 THE BRUEHL, PLACE OF BURNING
THE BRUEHL, PLACE OF BURNING
The Synod of Pisa tried to reform the[Pg 62] Church and failed. The Synod of Constance tried it and failed. The Synod of Basel and Ferrara tried it and failed. The Fifth General Lateran Synod from 1512-1517 tried it and failed. The great Roman Catholic scholar Von Doellinger says: "The last hope of a reformation of the Church was carried to the grave."
What could not be done by all Europe was done by Luther.
Luther's reformation brought liberty for Church and State, and to him we owe it that men like Hus can no longer be burned.

JESUS—His Words and His Works, 20 Art Plates in Colors after Dudley, 195 Half-tones, and 2 maps of Palestine. IX and 481 pages. Size 7-¾ x 10. Beautifully bound. Gilt top. $3.00.
THE TEN COMMANDMENTS Third Edition. 335 Pages. $1.00.
FOLLOW JESUS 300 Pages. Cloth, $1.00.
THE LORD'S PRAYER 271 Pages, $1.00.
PORTRAITS OF JESUS Cloth, 227 Pages. $1.00.
| Christian Science Unchristian. 5th Ed. | 05c | |
| Mission Work. 4th Edition | 05c | |
| What is Christianity? 3d Edition | 05c | |
| Temperance. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Why Lutheran, not 7 Day Advent. 2d | ||
| Edition | 05c | |
| Why the Name "Lutheran." 2d Ed. | 05c | |
| Infant Baptism. 6th Edition | 05c | |
| Christian Giving No. 2. 3d Thousand | 10c | |
| Why I Believe the Bible. 2d Edition | 15c | |
| The Real Presence. | 10c | |
| The Dance. 5th Edition | 05c | |
| The Theater. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Opinions on Secret Societies. 2d Ed. | 05c | |
| Freemasonry. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Oddfellowship. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Churchgoing. 3d Edition | 05c | |
| What Think Ye of Christ? 2d Ed. | 05c | |
| Wm. Tyndale, Translator Eng. Bible. | 10c | |
| Patrick Hamilton, Scotch Martyr. | 10c | |
| The Pope in Politics. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Church and State. 2d Edition | 05c | |
| Carlyle's Luther. | leather | 20c |
| paper | 10c | |
| Why Protestant, not Roman Catholic | 05c | |
| Principles of Protestantism. | 02c | |
| Why I am a Lutheran. 5th Edition | 05c | |
| Luther's Catechism. 8th Edition | 10c | |
| The Congregational Meeting. | 05c | |
| Luther and our Fourth of July. | 05c |
Minor changes have been made to correct typesetters' errors; every effort has been made, otherwise, to remain true to the author's words and intent.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of John Hus, by William Dallmann
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK JOHN HUS ***
***** This file should be named 26129-h.htm or 26129-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
https://www.gutenberg.org/2/6/1/2/26129/
Produced by Juliet Sutherland, D Alexander and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at https://www.pgdp.net
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
https://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at https://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
https://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at https://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit https://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: https://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
https://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.